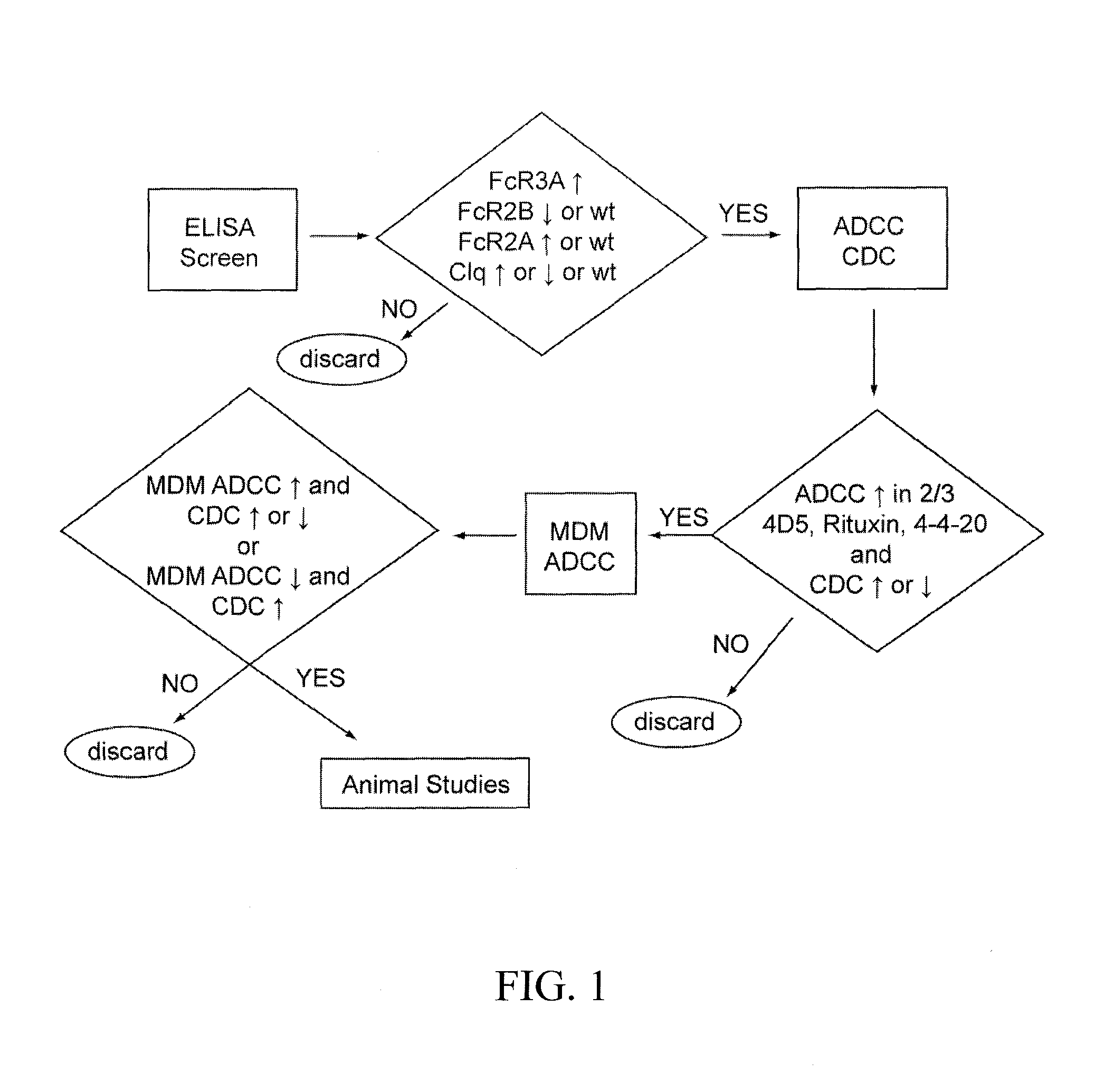
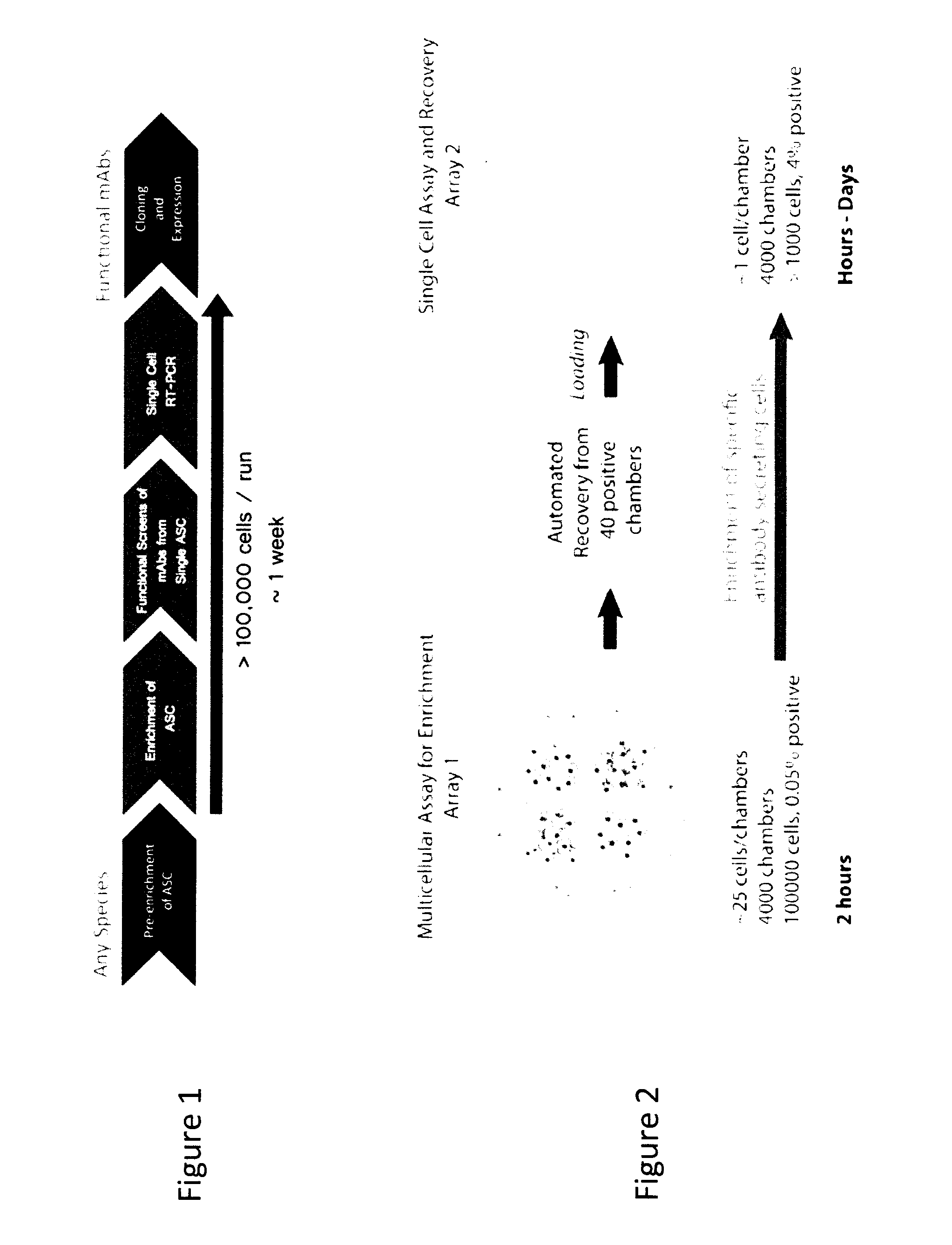
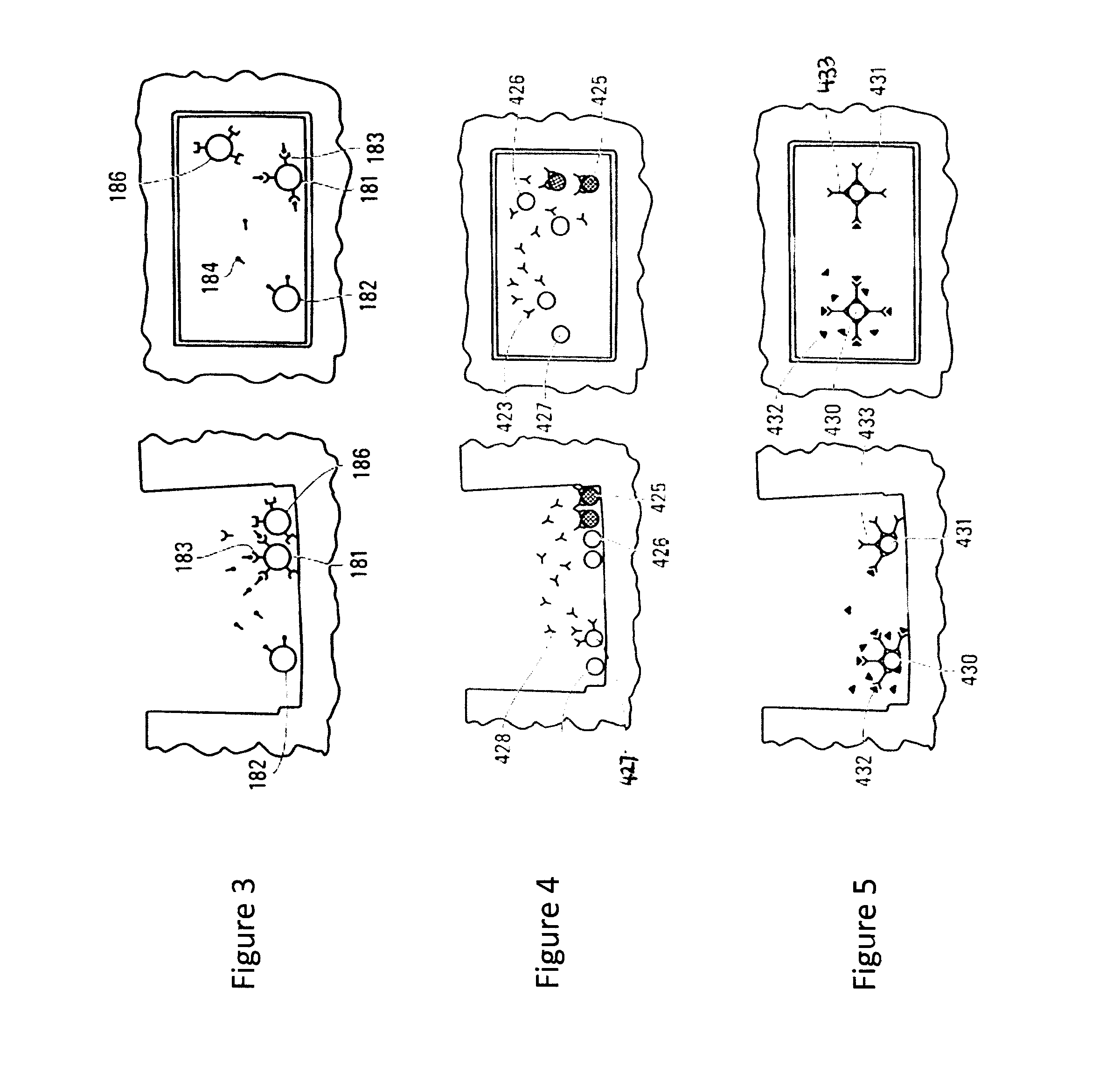
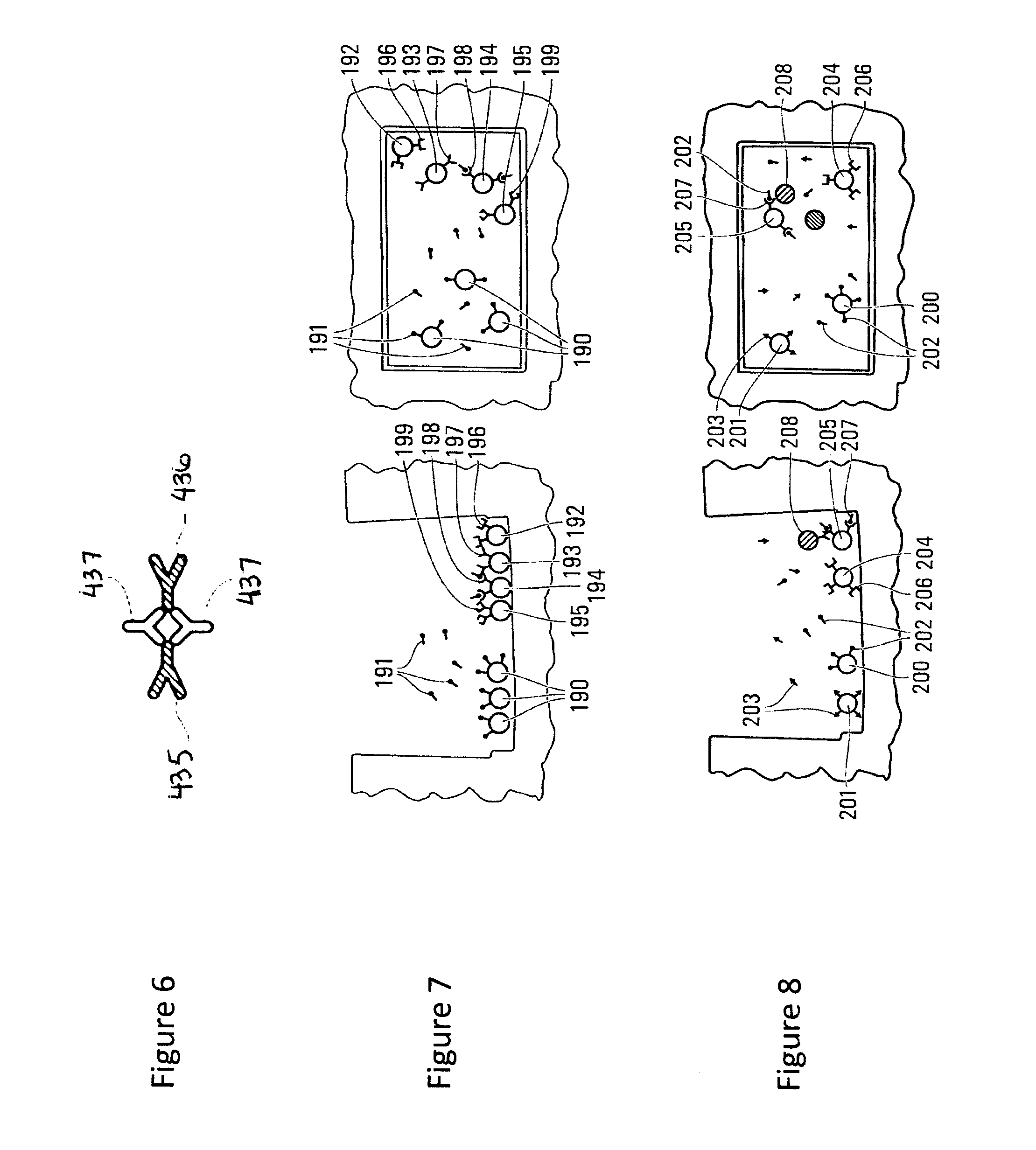
Patents
Literature
478 results about "Effector cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An effector cell is any of various types of cell that actively responds to a stimulus and effects some change (brings it about).
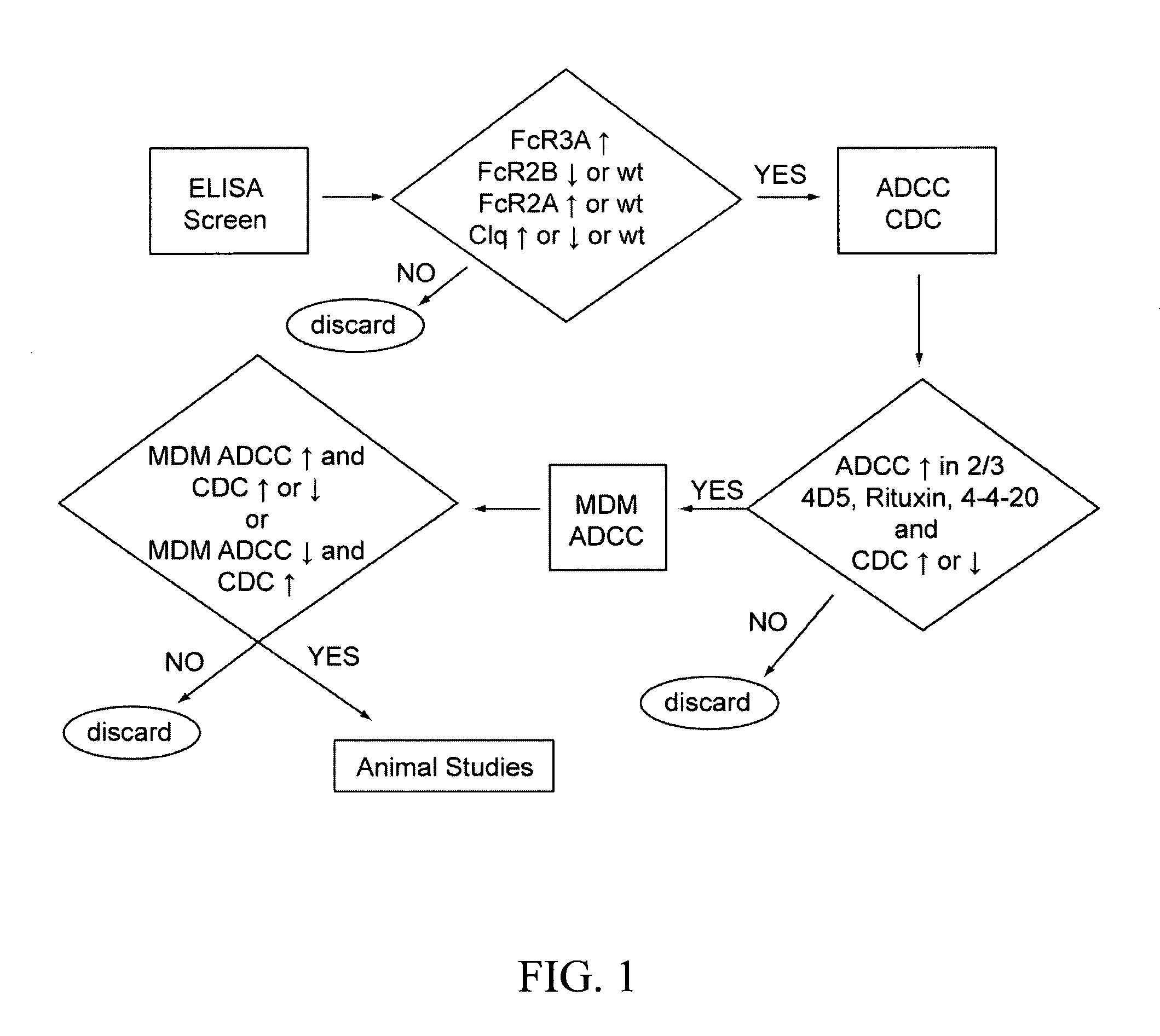
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050037000A1High affinityAltered affinityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderTherapeutic antibodyWild type
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcgammaRIIA and / or FcgammaRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcgammaR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MARCOGENICS INC +1
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS7355008B2Function increaseGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderTherapeutic antibodyEffector cell
Owner:MARCOGENICS INC +1
Recombinant anti-CD30 antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040018194A1Nervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseChemotherapeutic drugs
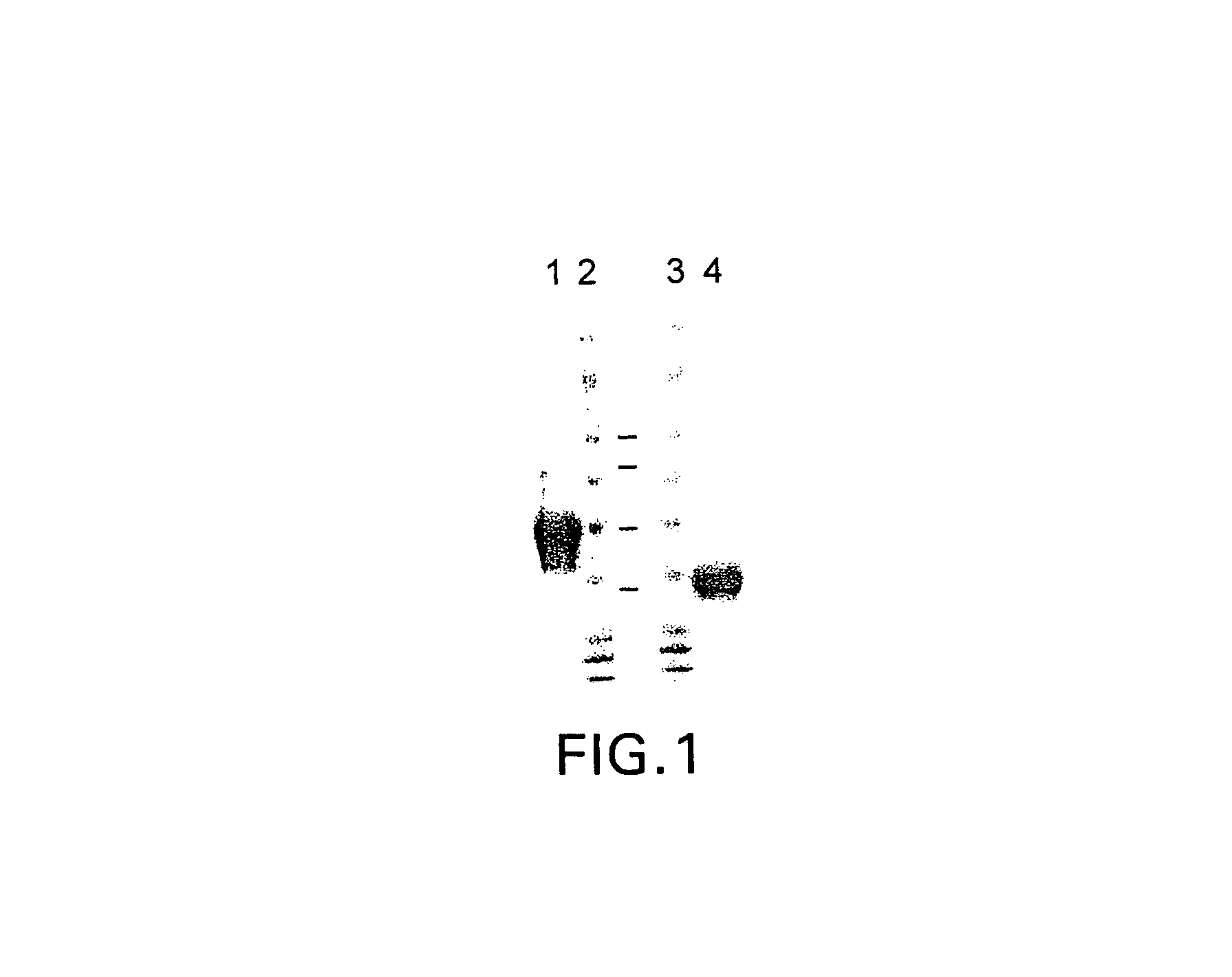
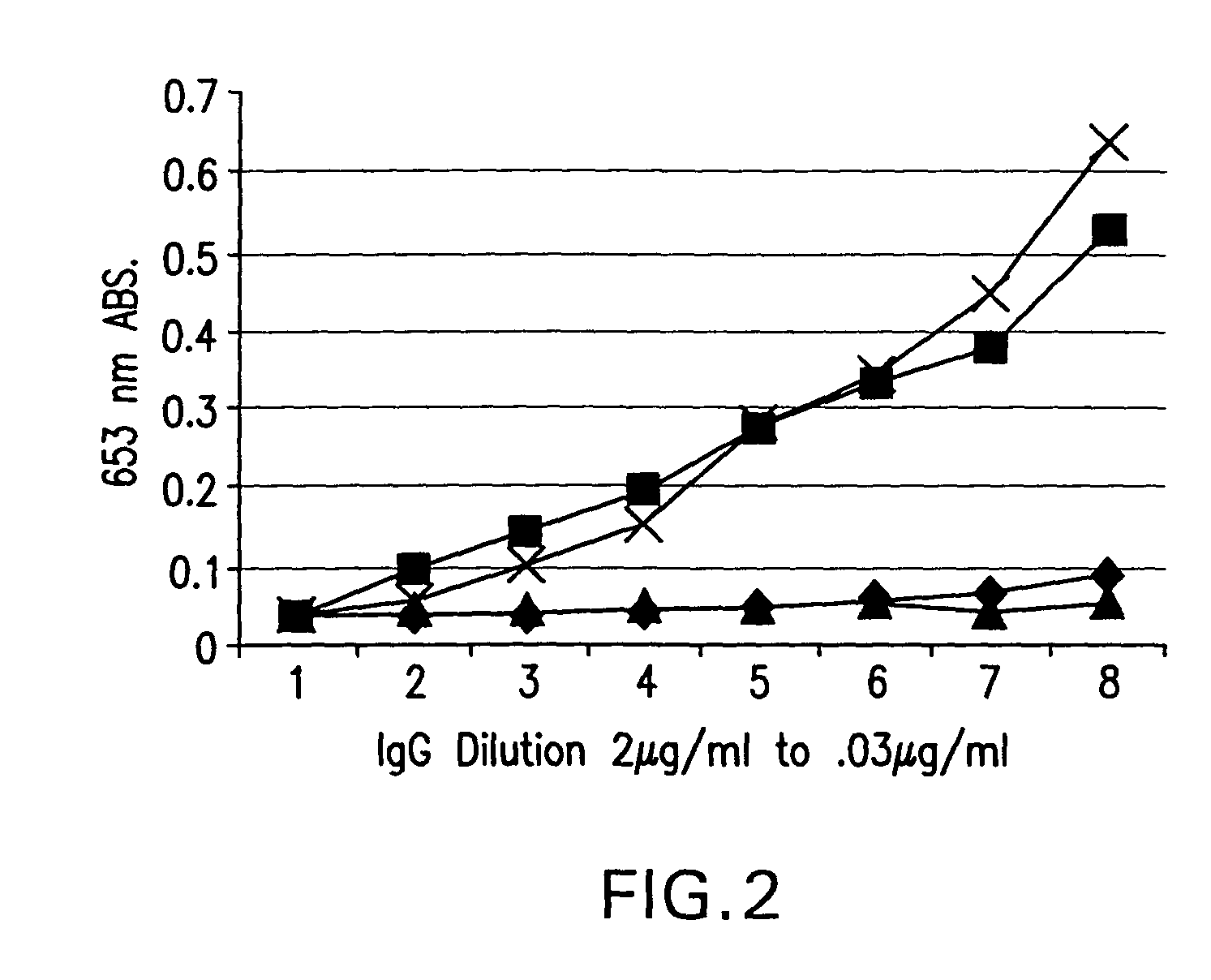
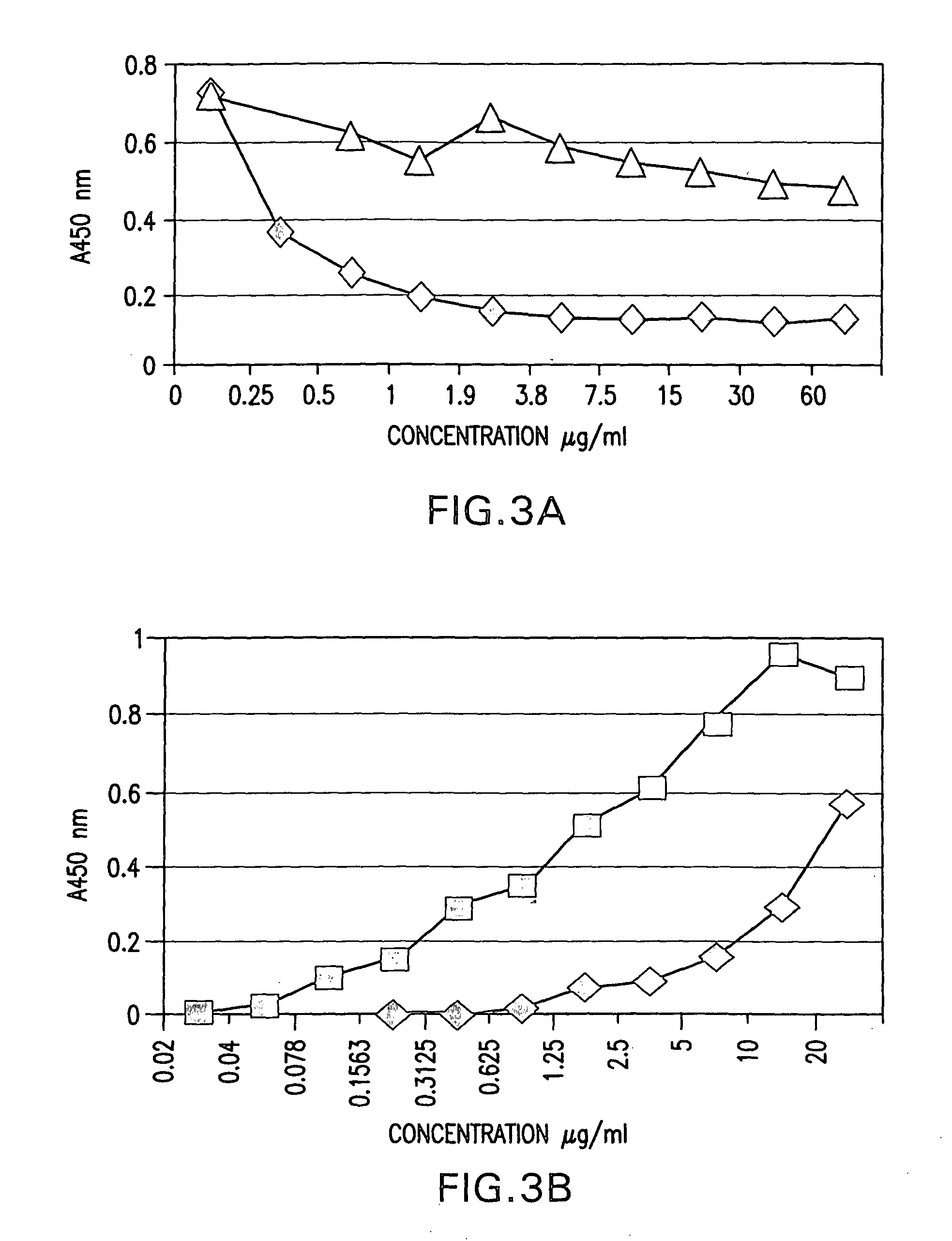
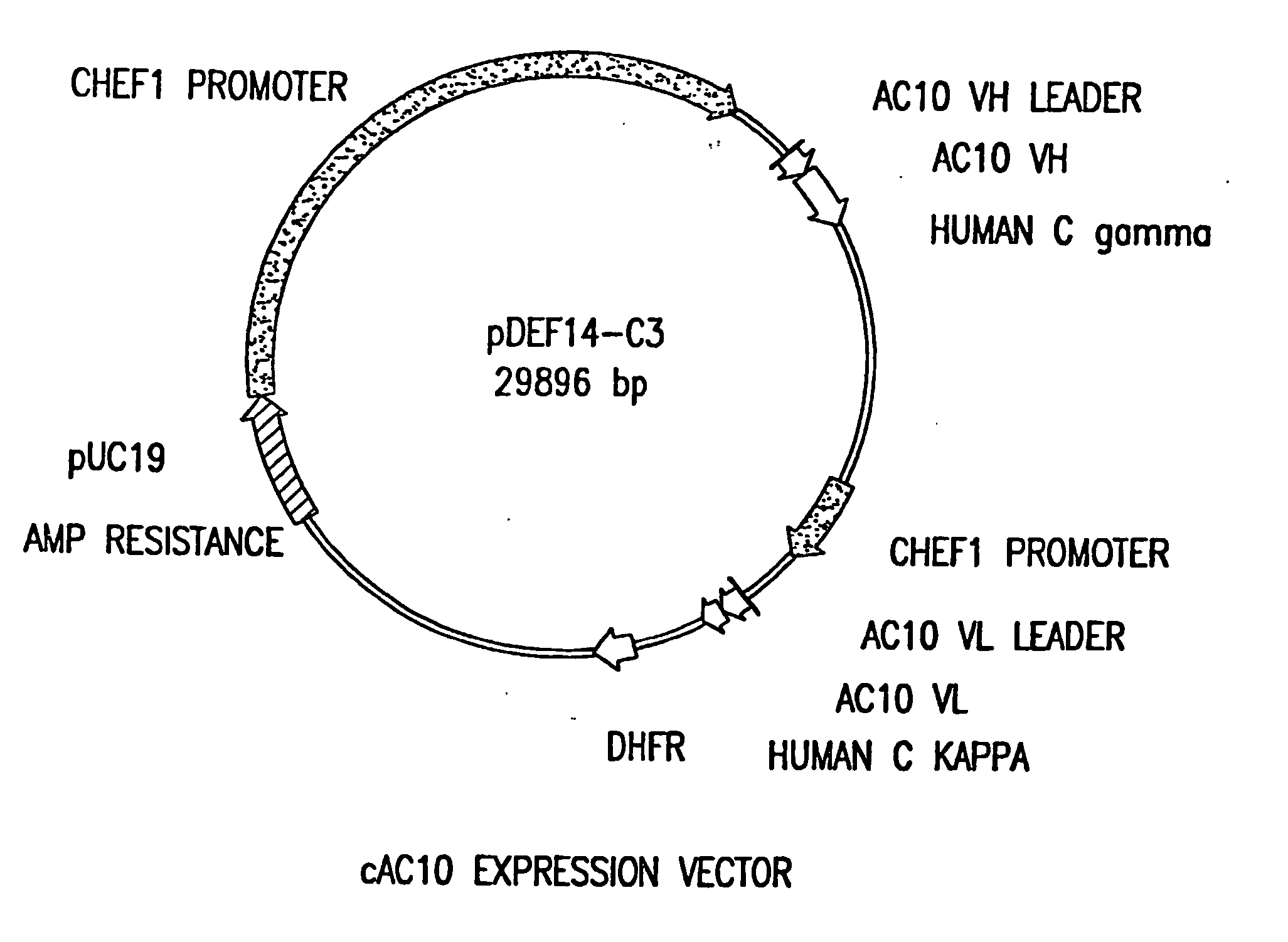
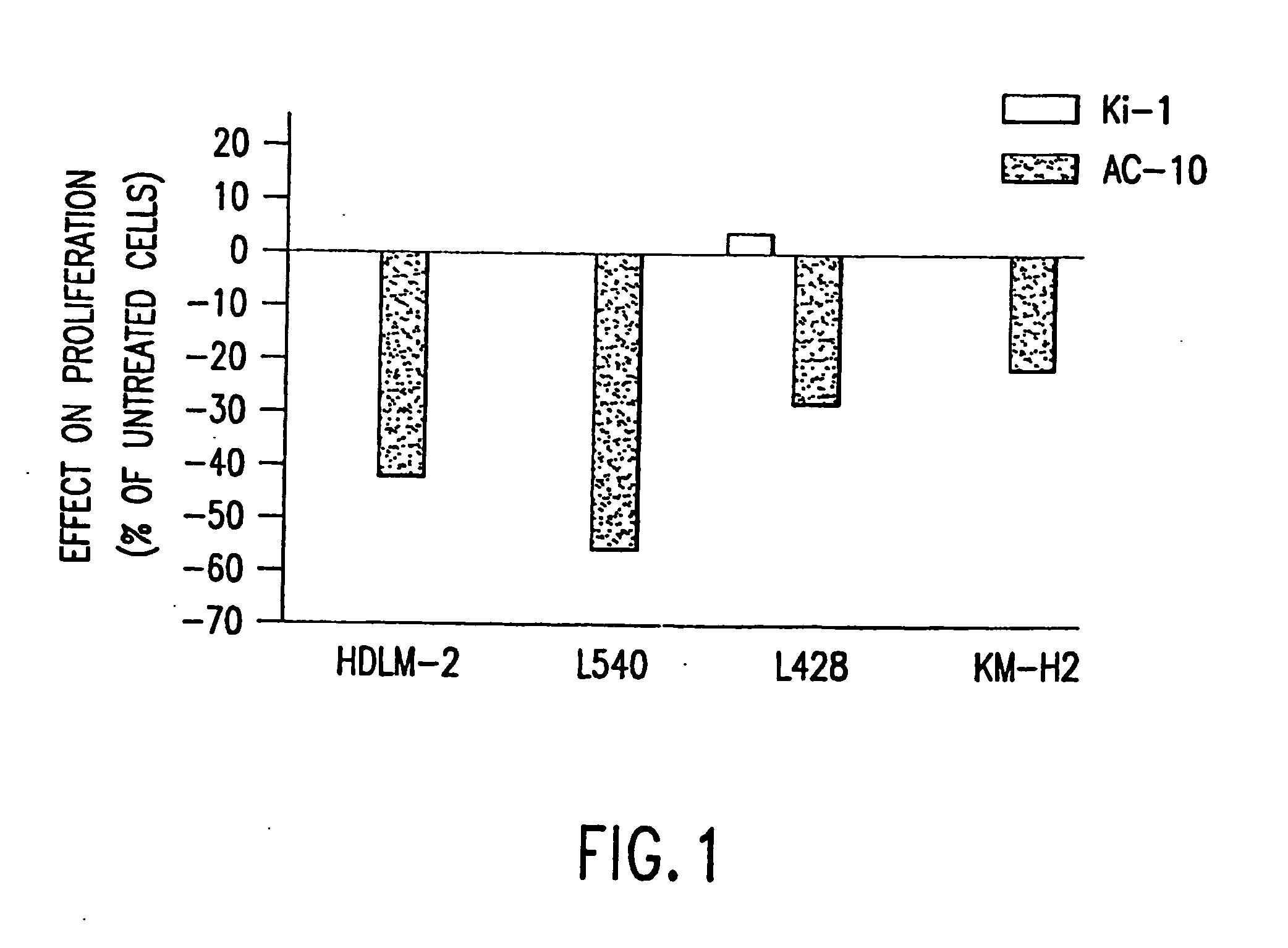
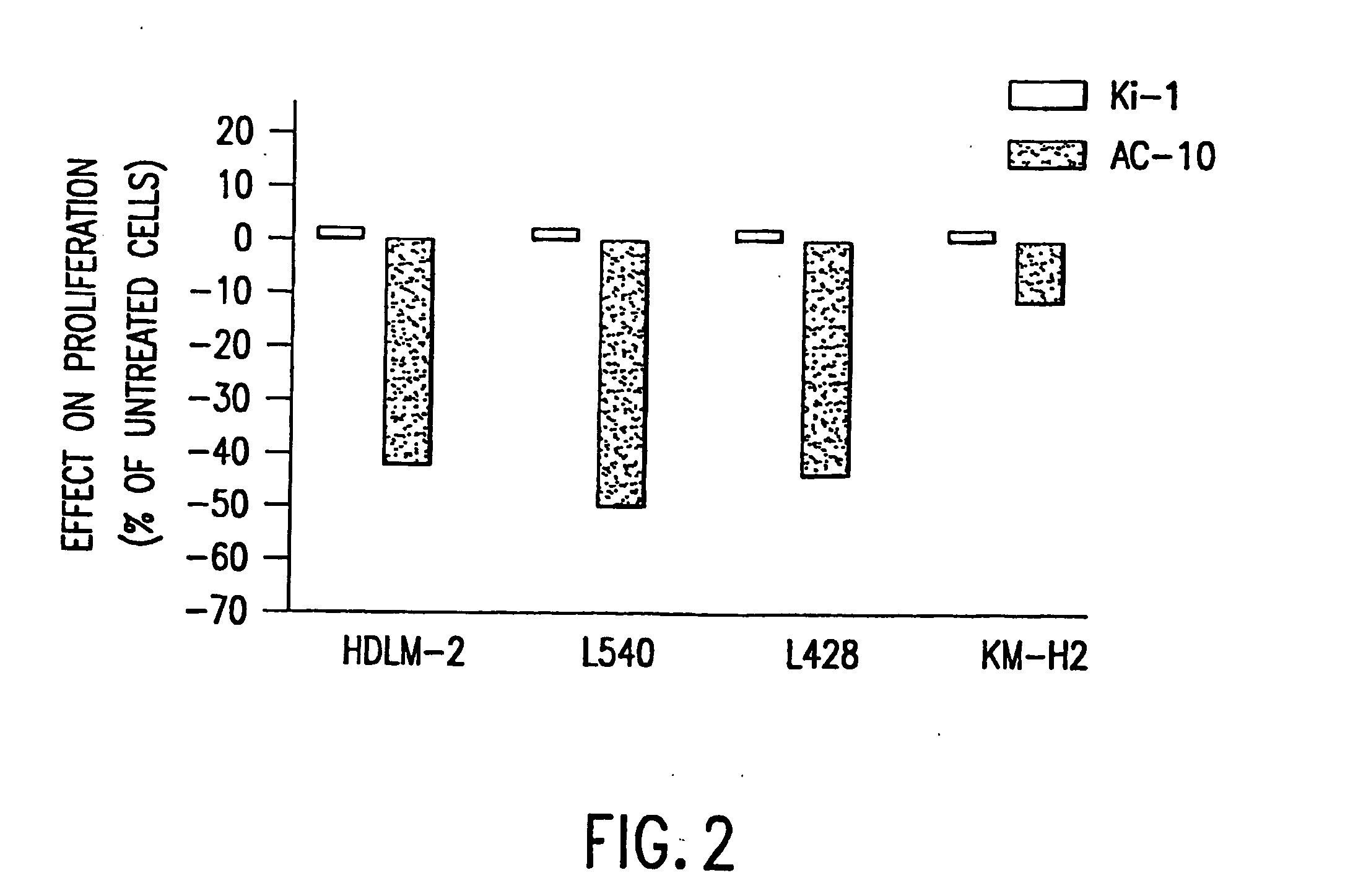
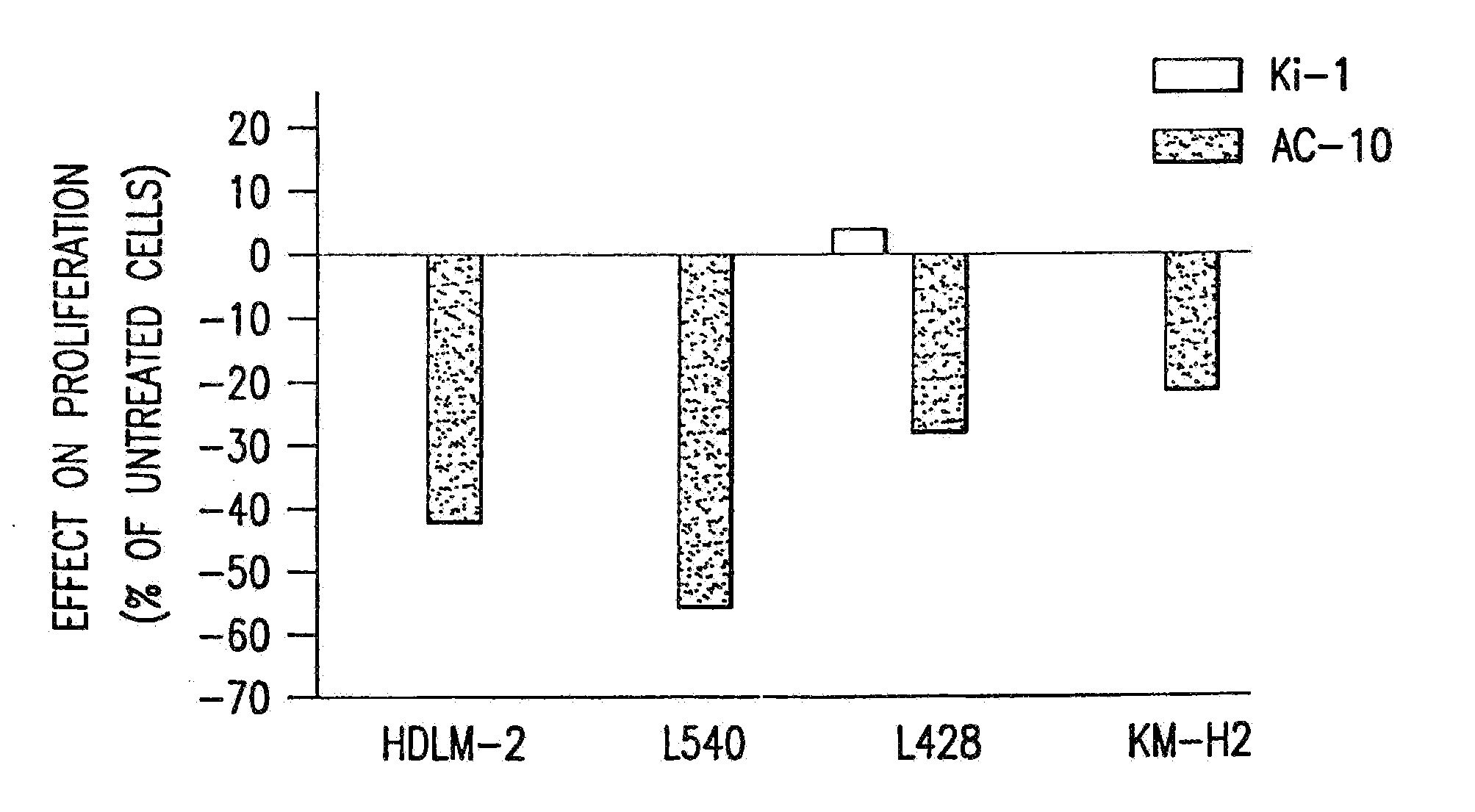
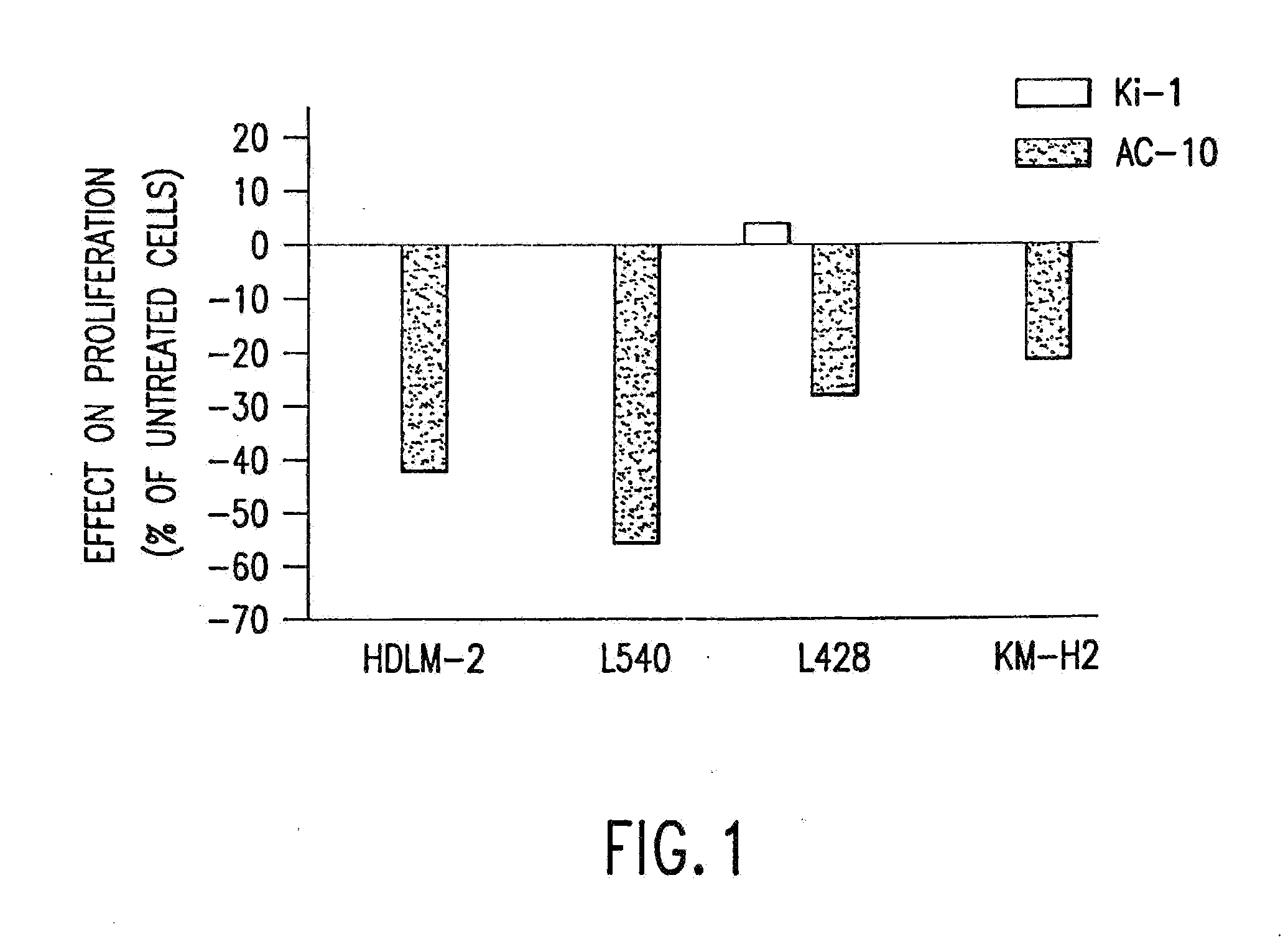
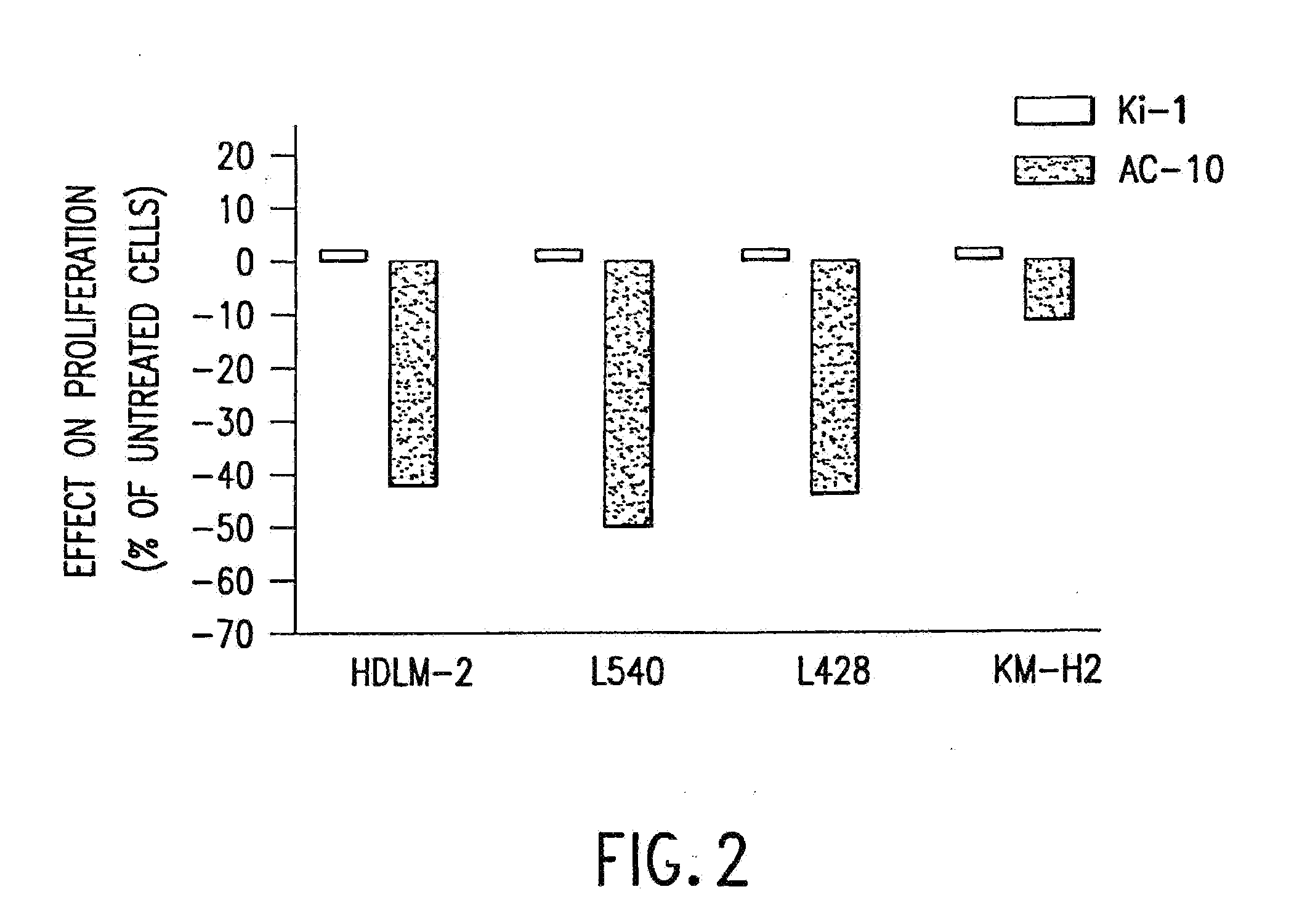
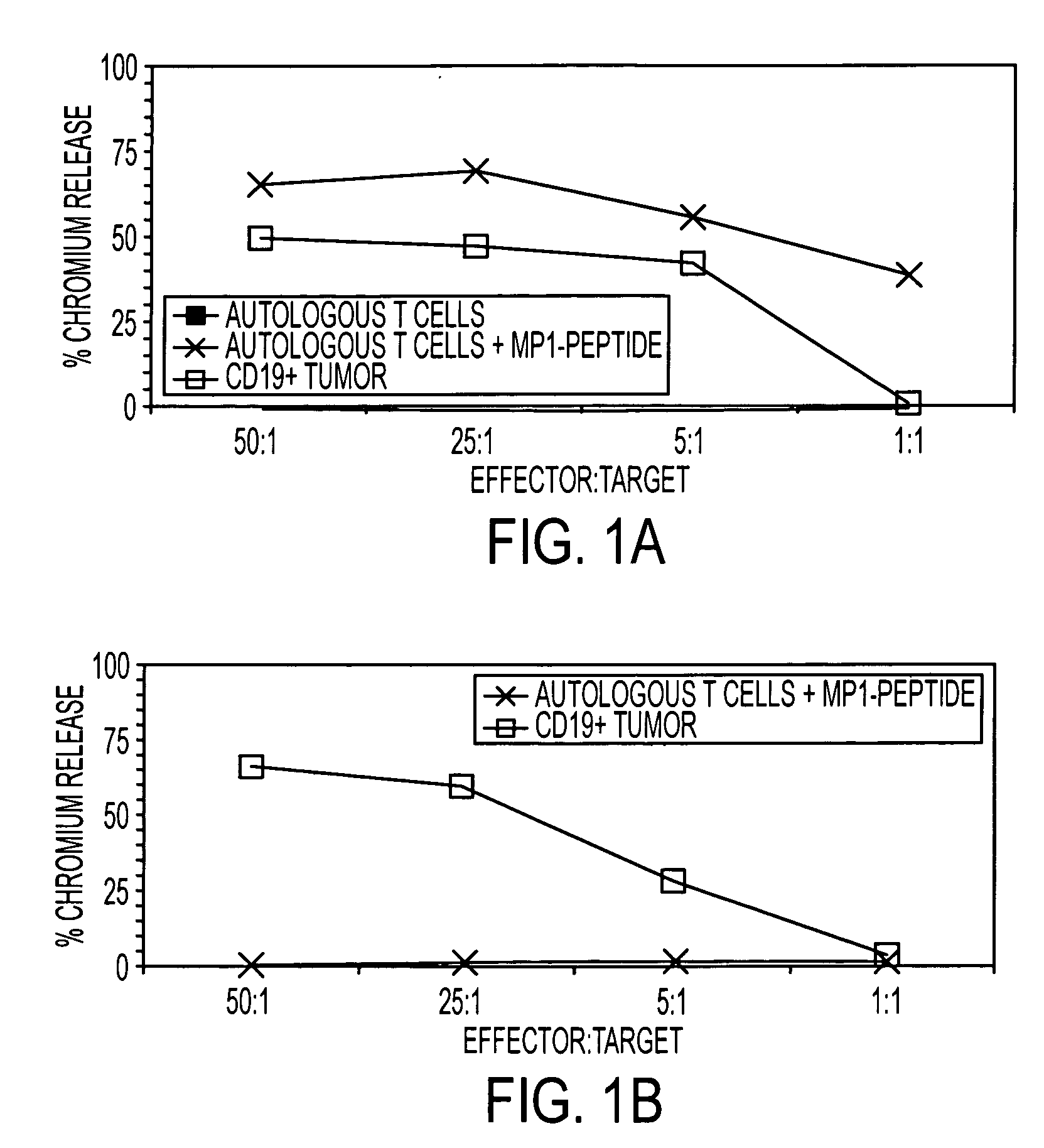
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of Hodgkin's Disease, comprising administering proteins characterized by their ability to bind to CD30, or compete with monoclonal antibodies AC10 or HeFi-1 for binding to CD30, and exert a cytostatic or cytotoxic effect on Hodgkin's disease cells in the absence of effector cells or complement. Such proteins include derivatives of monoclonal antibodies AC10 and HeFi-1. The proteins of the invention can be human, humanized, or chimeric antibodies; further, they can be conjugated to cytotoxic agents such as chemotherapeutic drugs. The invention further relates to nucleic acids encoding the proteins of the invention. The invention yet further relates to a method for identifying an anti-CD30 antibody useful for the treatment or prevention of Hodgkin's Disease.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050064514A1Enhanced antibody effector functionGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderEffector cellChemistry
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcgammaRIIIA and / or FcgammaRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcgammaR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS20070036799A1Good curative effectEnhanced ADCC activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTherapeutic antibodyWild type
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
InactiveUS7960512B2High affinityLow affinityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Recombinant Anti-Cd30 Antibodies and Uses Thereof
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of Hodgkin's Disease, comprising administering proteins characterized by their ability to bind to CD30, or compete with monoclonal antibodies AC10 or HeFi-1 for binding to CD30, and exert a cytostatic or cytotoxic effect on Hodgkin's disease cells in the absence of effector cells or complement. Such proteins include derivatives of monoclonal antibodies AC10 and HeFi-1. The proteins of the invention can be human, humanized, or chimeric antibodies; further, they can be conjugated to cytotoxic agents such as chemotherapeutic drugs. The invention further relates to nucleic acids encoding the proteins of the invention. The invention yet further relates to a method for identifying an anti-CD30 antibody useful for the treatment or prevention of Hodgkin's Disease.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
Identification and Engineering of Antibodies with Variant Fc Regions and Methods of Using Same
InactiveUS20080112961A1Enhanced antibody effector functionGood curative effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesTherapeutic antibodyCancer prevention
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing cancer and other diseases using molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The methods of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease. The methods of the invention are also of use in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Recombinant Anti-cd30 antibodies and uses thereof
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of Hodgkin's Disease, comprising administering proteins characterized by their ability to bind to CD30, or compete with monoclonal antibodies AC10 or HeFi-1 for binding to CD30, and exert a cytostatic or cytotoxic effect on Hodgkin's disease cells in the absence of effector cells or complement. Such proteins include derivatives of monoclonal antibodies AC10 and HeFi-1. The proteins of the invention can be human, humanized, or chimeric antibodies; further, they can be conjugated to cytotoxic agents such as chemotherapeutic drugs. The invention further relates to nucleic acids encoding the proteins of the invention. The invention yet further relates to a method for identifying an anti-CD30 antibody useful for the treatment or prevention of Hodgkin's Disease.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS8217147B2High affinityLow affinityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsDiseaseTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
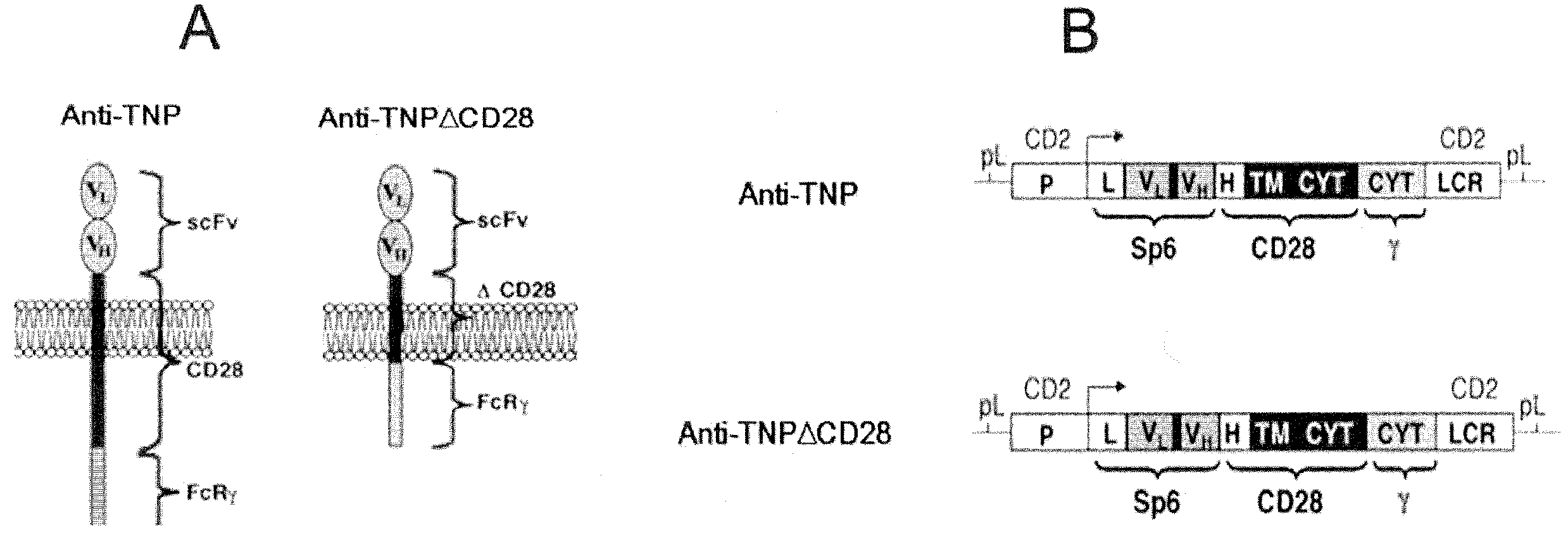
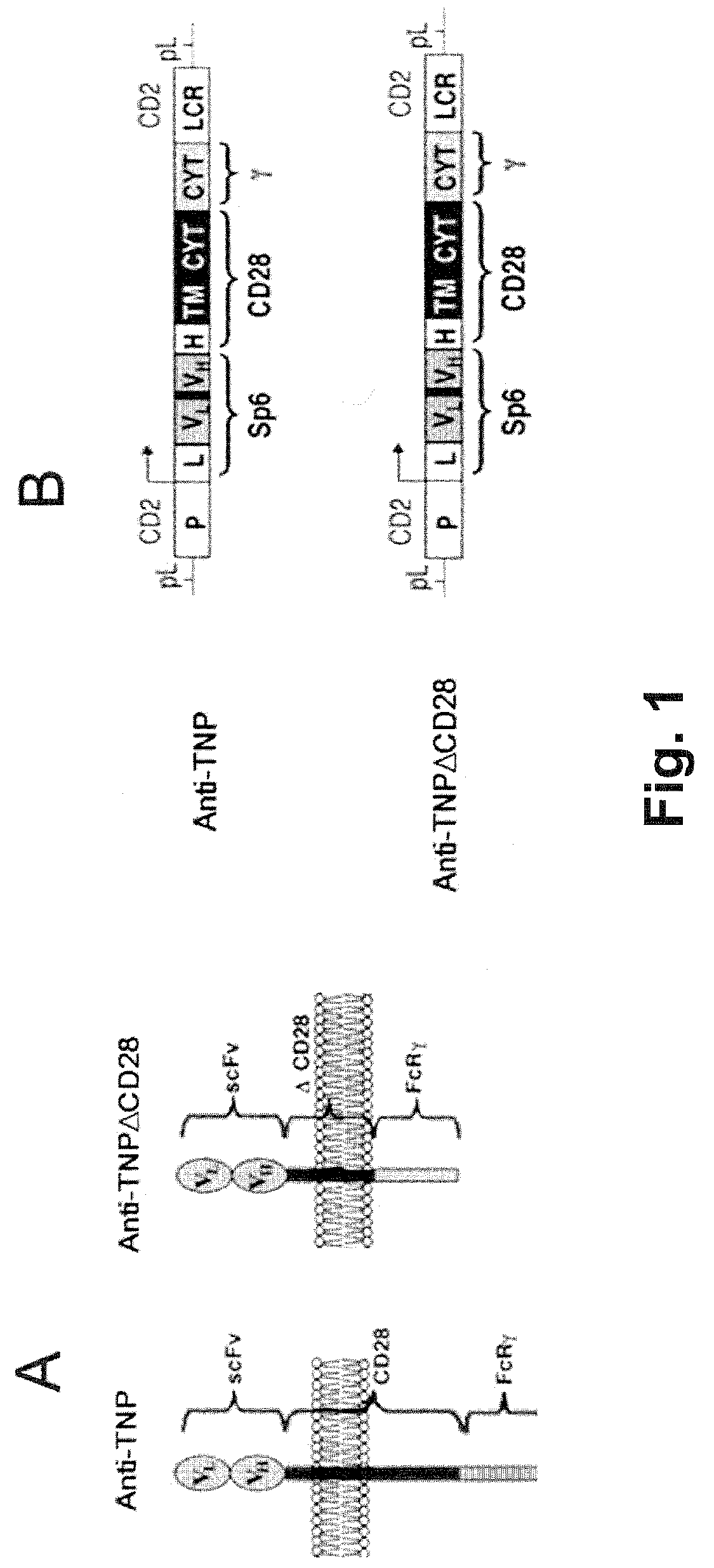
Mammalian antigen-presenting T cells and bi-specific T cells
InactiveUS20050129671A1Guaranteed functionImproving in vivo survivalBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAutoimmune condition
The present invention is directed to mammalian bi-specific T cells and methods for using these bi-specific T cells. More specifically, the invention relates to viral specific T cells that express chimeric anti-tumor receptors. These bi-specific T cell clones are a source of effector cells that persist in vivo in response to stimulation with viral antigen, leading to long-term function after their transfer to patients with cancer and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Humanized antibodies against CD3
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Method for assaying for natural killer, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and neutrophil-mediated killing of target cells using real-time microelectronic cell sensing technology
ActiveUS7468255B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEffector cellNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention includes a method of measuring cytolytic activity including providing a device capable of monitoring cell-substrate impedance operably connected to an impedance analyzer, adding target cells to at least one well of the device, adding effector cells to the at least one well, monitoring impedance of the at least one well and optionally determining a cell index from the impedance, wherein monitoring impedance includes measuring impedance during at least one time point before and at least one time point after adding effector cells, and determining viability of said target cells after adding effector cells by comparing the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point after adding effector cells to the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point before adding effector cells.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
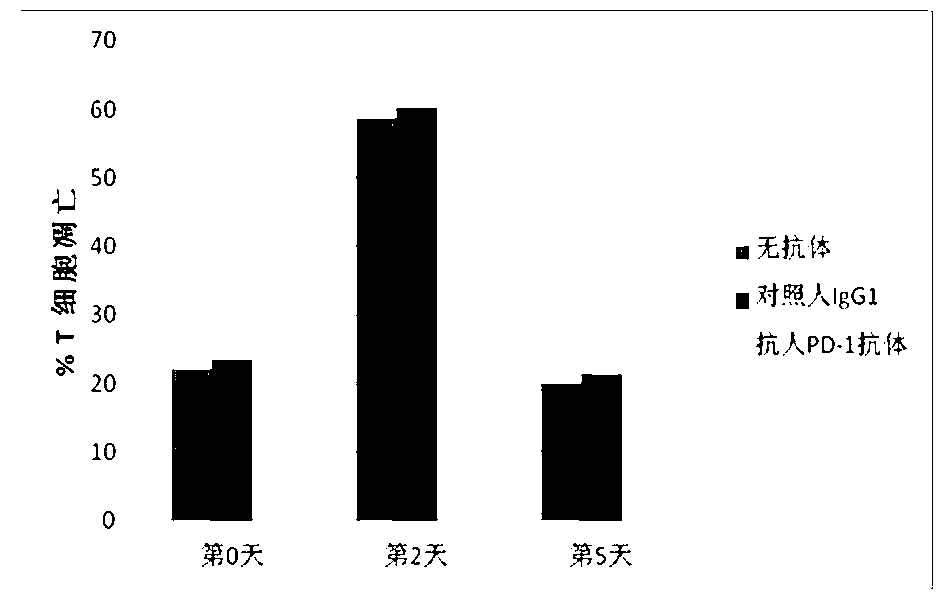
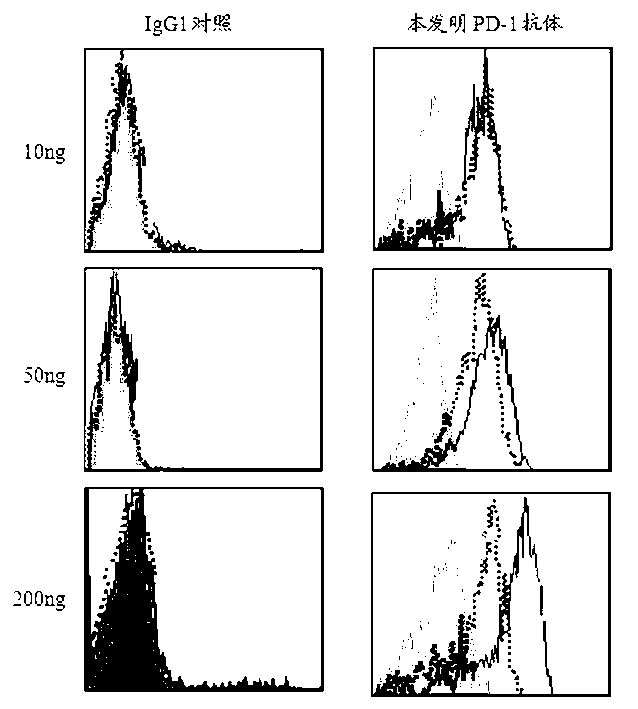
Full-humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103242448AHigh affinityImproving immunogenicityAntiviralsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune diseaseFactor ii
The invention discloses a full-humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody having a heavy-chain amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 7 in a sequence table and a light-chain amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 8 in the sequence table. The full-humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody has the advantages that the antibody has high appetency and low immunogenicity on PD-1, is efficiently expressed in animal cells, and can be used for industrial production. An experiment proves that the full-humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody specifically blocks a PD-1 / PD-L inhibiting signal, so that a disabled effector cell in an organism restores a biological function; activation proliferation of a tumor and a virus specificity CD8+T cell and secretion of a cell factor are facilitated; the killability of lymphocyte on tumor antigen, an exotic invasive virus and the like is enhanced; the immunity of the organism is improved; and the tumor cell and the virus are timely cleared. Therefore, the antibody disclosed by the invention has a wide application prospect on treatment of tumors, infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
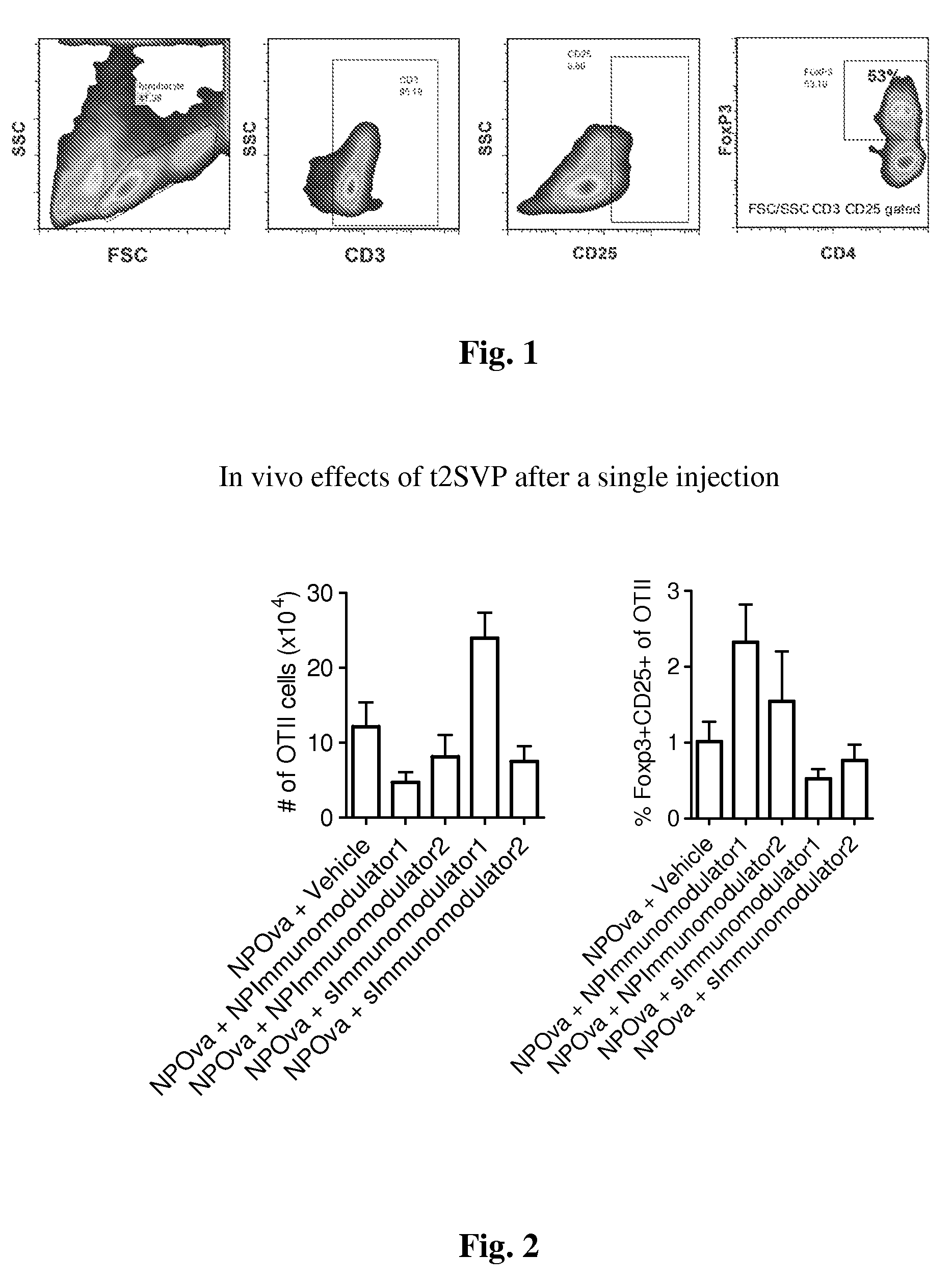
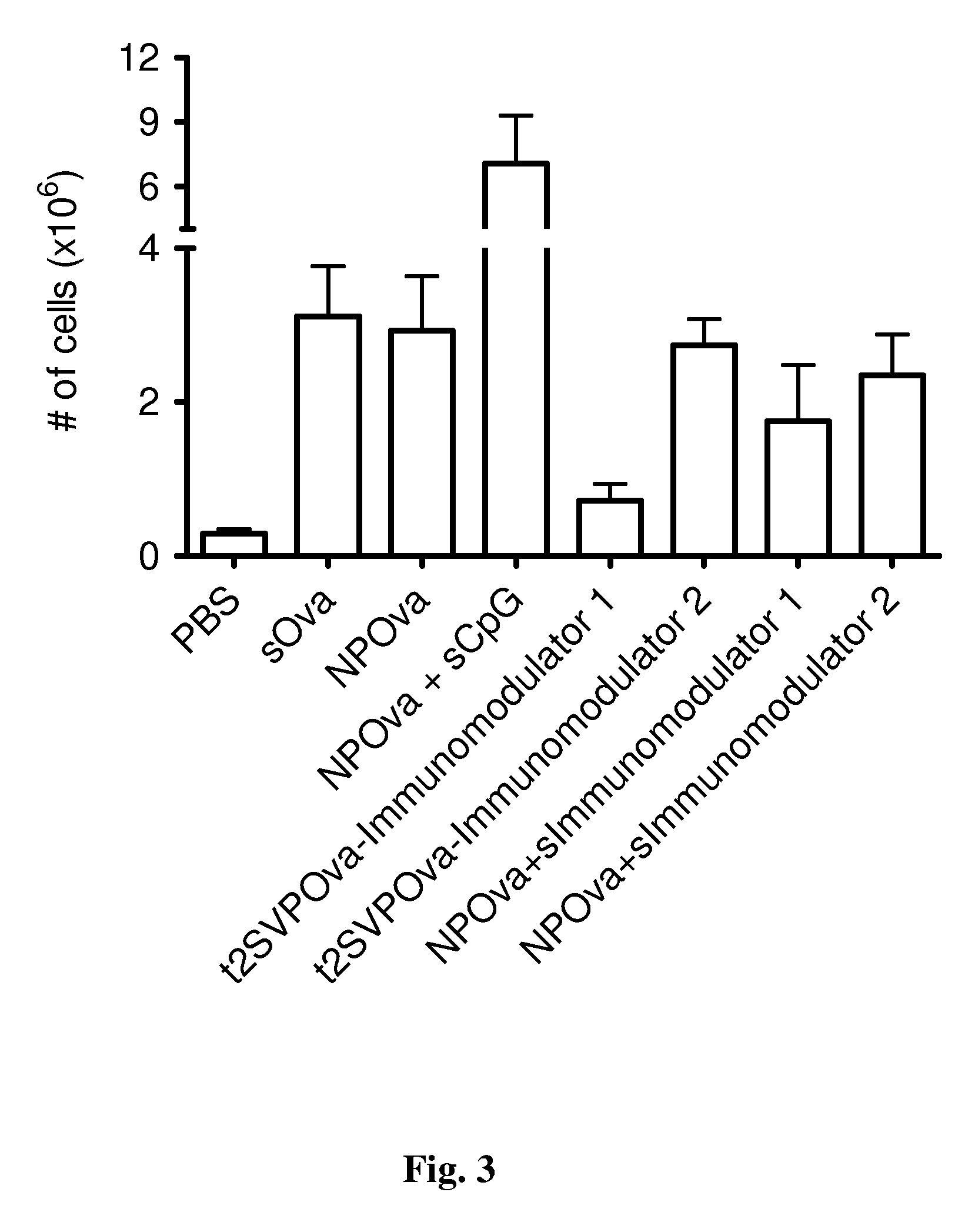
Tolerogenic synthetic nanocarriers for antigen-specific deletion of t effector cells
Disclosed are synthetic nanocarrier methods, and related compositions, comprising administering immunosuppressants and MHC Class I-restricted and / or MHC Class II-restricted epitopes that can generate tolerogenic immune responses (e.g., antigen-specific T effector cell deletion).
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant heavy chains and methods of using same
InactiveUS20090098124A1Optimize therapeutic antibody functionalityAltered affinitySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTherapeutic antibodyHeavy chain
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant heavy chain, which variant heavy chain comprises constant domains from more than one IgG isotype. The variant heavy chain of the invention may further comprise at least one amino acid modification relative to the parental heavy chain, such that the Fc region of said variant heavy chain binds an FcγR with an altered affinity relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type heavy cahin. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Fc Region-Containing Polypeptides That Exhibit Improved Effector Function Due To Alterations Of The Extent Of Fucosylation, And Methods For Their Use
ActiveUS20120219551A1Enhanced antibody effector functionGood curative effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsEffector cellEffector functions
The present invention relates to Fc region-containing polypeptides that exhibit improved effector function due to alterations of the extent of fucosylation, and to methods of using such polypeptides for treating or preventing cancer and other diseases. The Fc region-containing polypeptides of the present invention are preferably immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), in which the Fc region comprises at least one amino acid substitution relative to the corresponding amino acid sequence of a wild type Fc region, and which is sufficient to attenuate post-translational fucosylation and mediate improved binding to an activating Fc receptor and reduced binding to an inhibitory Fc receptor. The methods of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection where either an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., cancer, infectious disease) or an inhibited effector cell response mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., inflammation, autoimmune disease).
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Methods for the treatment of disease using immunoglobulins having Fc regions with altered affinities for FcgammaRactivating and FcgammaRinhibiting
ActiveUS8652466B2Enhanced antibody effector functionGood curative effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunologic disordersCancer prevention
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing cancer and other diseases using molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds an FcγR that activates a cellular effector (“FcγRActivating,” such as FcγRIIA or FcγRIIIA) and an FcγR that inhibits a cellular effector (“FcγRInhibiting,” such as FcγRIIA) with an altered Ratio of Affinities relative to the respective binding affinities of such FcγR for the Fc region of the wild-type immunoglobulin. The methods of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection where either an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., cancer, infectious disease) or an inhibited effector cell response mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., inflammation, autoimmune disease).
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Microfluidic Devices and Methods for Use Thereof in Multicellular Assays of Secretion
ActiveUS20160252495A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresMicroreactorEffector cell
Methods and devices are provided herein for identifying a cell population comprising an effector cell that exerts an extracellular effect. In one embodiment the method comprises retaining in a microreactor a cell population comprising one or more effector cells, wherein the contents of the microreactor further comprise a readout particle population comprising one or more readout particles, incubating the cell population and the readout particle population within the microreactor, assaying the cell population for the presence of the extracellular effect, wherein the readout particle population or subpopulation thereof provides a direct or indirect readout of the extracellular effect, and determining, based on the results of the assaying step, whether one or more effector cells within the cell population exerts the extracellular effect on the readout particle. If an extracellular effect is measured, the cell population is recovered for further analysis to determine the cell or cells responsible for the effect.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
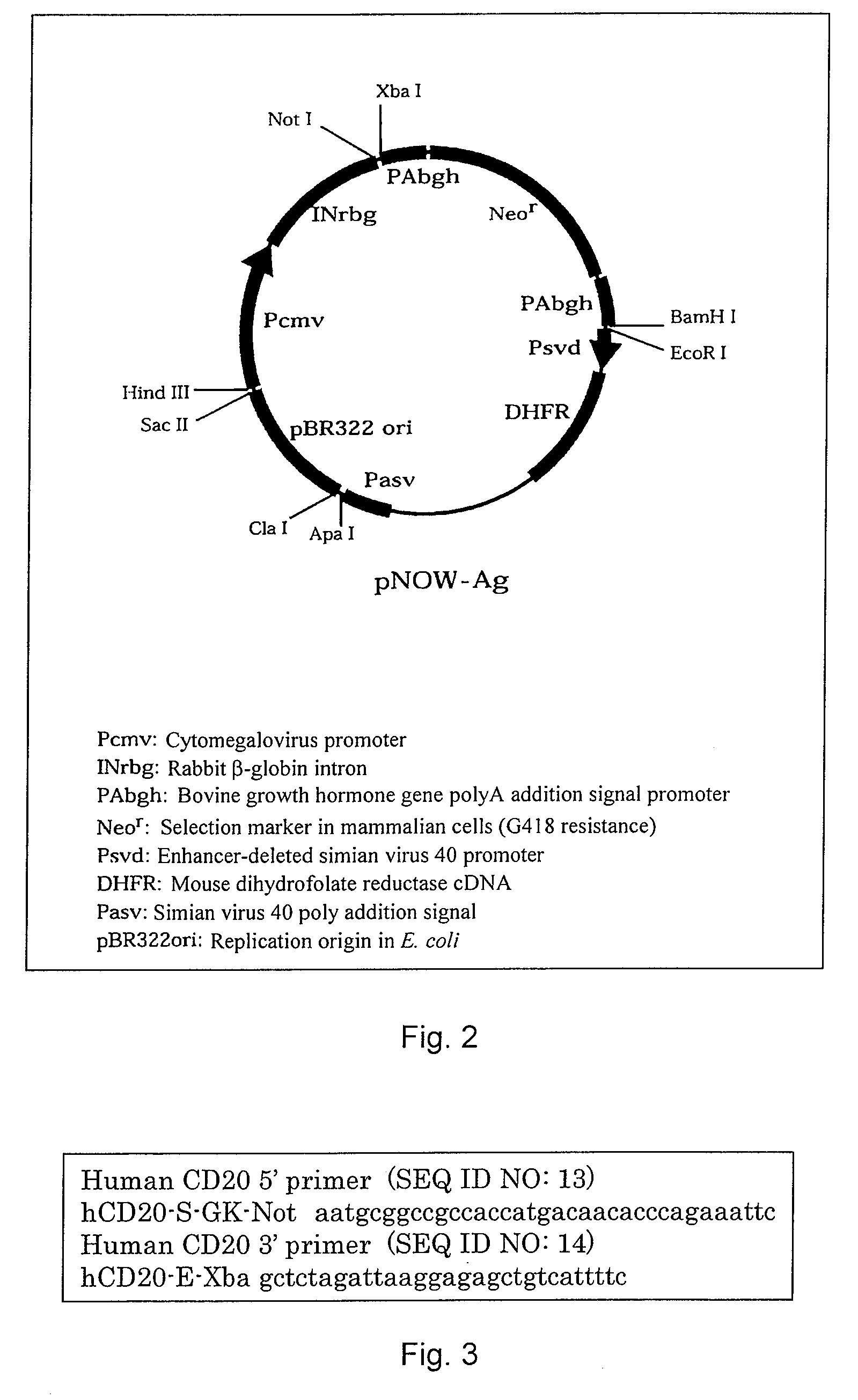
Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody
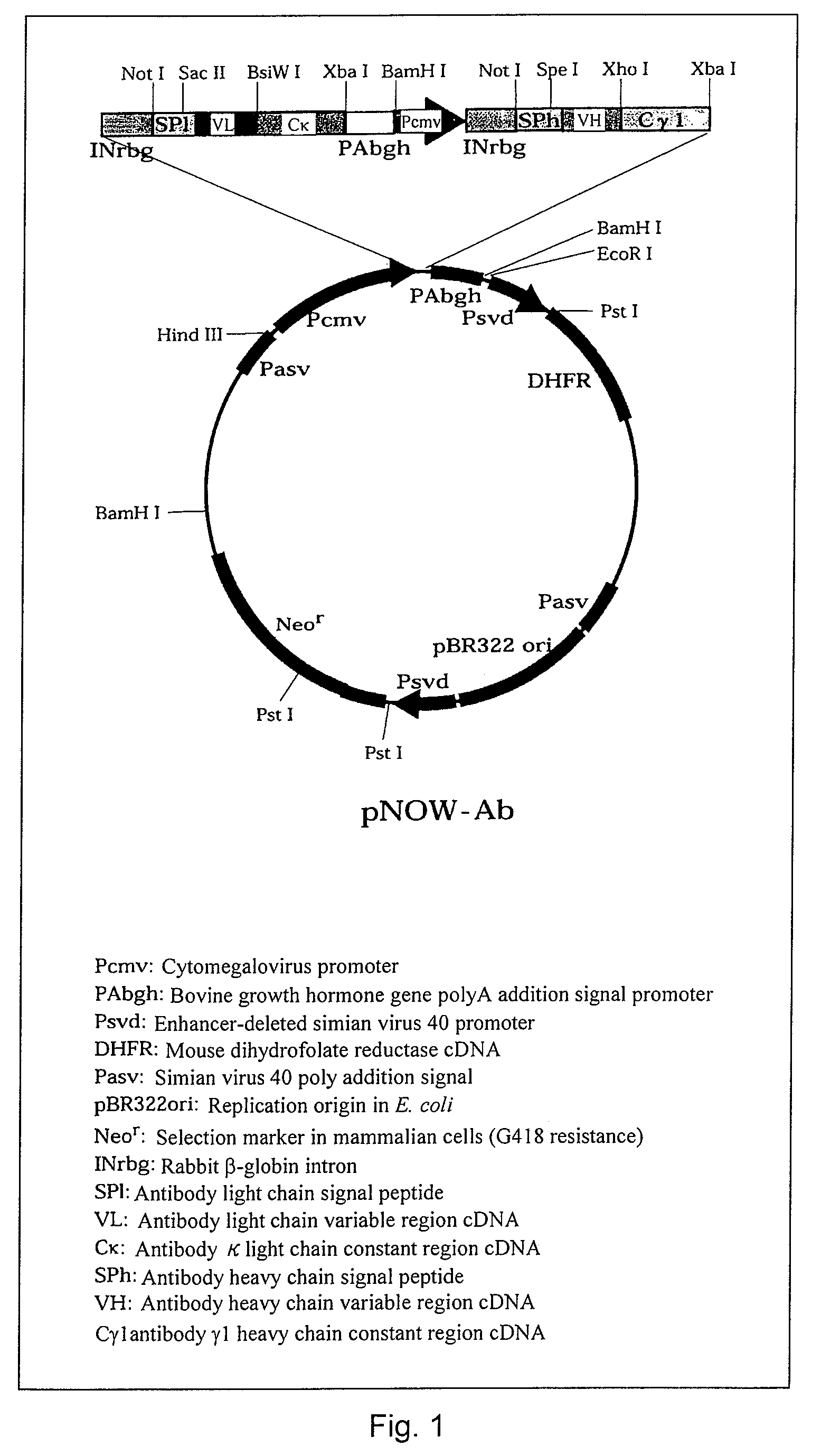
A murine anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody having cell growth inhibitory activities is disclosed. Cell growth inhibitory activities include apoptosis against human CD20 antigen expressing cells in culture of the CD20 antigen expressing cells without effector cells. The anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody is incorporated into chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in which the amino acid sequences of the variable regions of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and the amino acid sequences of the constant regions of human immunoglobulin are fused. Also a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody is described which includes all of the variable region CDRs of the H chain of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and all of the variable region CDRs of the L chain of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and an amino acid sequence of human immunoglobulin. A nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence of the chimeric or humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody can be expressed in mammalian cells.
Owner:INST OF IMMUNOLOGY
Redirected, genetically-engineered t regulatory cells and their use in suppression of autoimmune and inflammatory disease
InactiveUS20100135974A1Effective quantityOvercome scarcityBiocideAntipyreticIntracellular signallingInflammatory Bowel Diseases
A redirected Treg cell is endowed with specificity toward a selected target antigen or ligand. The cell contains a chimeric receptor polypeptide that is expressed in a single, continuous chain, with an extracellular recognition region displayed on the surface of the cell, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signaling region. The extracellular recognition region is specific for the selected target antigen or ligand. The intracellular signaling region includes a combination of T-cell signaling polypeptide moieties, which combination, upon binding of the extracellular recognition region to the selected target antigen or ligand, triggers activation of the redirected Treg cells to cause suppression of T-cell mediated immunity. Such redirected Treg cells may be used to suppress undesired activity of T effector cells thereby mediating an immune or inflammatory response. They are particularly useful in treating T effector cell-mediated diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, transplant rejection and GVH disease.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Identification and Engineering of Antibodies with Variant Fc Regions and Methods of Using Same
InactiveUS20110243941A1High affinityLow affinitySenses disorderNervous disorderTherapeutic antibodyInfectious Disorder
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Antibodies as chimeric effector cell receptors against tumor antigens
InactiveUS20070031438A1Improve the level ofAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthProstate specific membrane
This invention relates to specific antibodies against ganglioside GD3 called MB3.6 and against protein prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) called 3D8, 4D4 and 3E11 when prepared as chimeric molecules with signaling molecules of T cells and other effector cells, and the use thereof in the treatment of cancers expressing these antigens.
Owner:JUNGHANS RICHARD P
Molecules preferentially associated with effector T cells or regulatory T cells and methods of their use
The present invention is based, at least in part, on the finding that certain molecules are preferentially associated with effector T cells or regulatory T cells. Accordingly, immune responses by one or the other subset of cells can be preferentially modulated. The invention pertains, e.g., to methods of modulating (e.g., up- or down-modulating), the balance between the activation of regulatory T cells and effector T cells leading to modulation of immune responses and to compositions useful in modulating those responses. The invention also pertains to methods useful in diagnosing, treating, or preventing conditions that would benefit from modulating effector T cell function relative to regulatory T cell function or from modulating regulatory T cell function relative to effector T cell function in a subject. The subject methods and compositions are especially useful in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of conditions characterized by a too-vigorous effector T cell response to antigens associated with the condition, in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of conditions characterized by a weak effector T cell response, in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of conditions characterized by a too-vigorous regulatory T cell response, or in the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of conditions characterized by a weak regulatory T cell response.
Owner:TOLERX INC
Use of heat shock proteins to enhance efficacy of antibody therapeutics
InactiveUS20060093612A1Good effectReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderStress ProteinsNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention relates to methods and pharmaceutical compositions useful for the prevention and treatment of any disease wherein the treatment of such disease would be improved by an enhanced immune response, such as infectious diseases, primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases (i.e., cancer), or neurodegenerative or amyloid diseases. In particular, the contemplated invention is directed to method comprising the administration of heat shock / stress proteins (HSPs) or HSP complexes alone or in combination with each other, in combination with the administration of an immunoreactive reagent. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more HSPs or HSP complexes in combination with an immunoreactive reagent. Additionally, the invention contemplates the use of the methods and compositions of the invention to enhance or improve passive immunotherapy and effector cell function.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT HEALTH CENT
Autologous immune cell therapy: cell compositions, methods and applications to treatment of human disease
InactiveUS20020182730A1Promote cell-mediated inflammatory reactionActivation functionDead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsAutologous immune enhancement therapyEffector cell
Compositions containing clinically relevant numbers of immune cells that have been isolated from a patient differentiated and / or expanded ex vivo. Methods for treating or preventing disease or otherwise altering the immune status of the patient by reinfusing such cells into the donor are also provided. Methods for expanding and / or immune cells, including effector cells, in the absence of exogenous IL-2, and for administering the cells in the absence of co-infused IL-2 are also provided.
Owner:VALEOCYTE THERAPIES
Autologous immune cell therapy: cell compositions, methods and applications to treatment of human disease
InactiveUS20010031253A1Promote cell-mediated inflammatory reactionActivation functionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsEffector cellCell therapy
Compositions containing clinically relevant numbers of immune cells that have been isolated from a patient differentiated and / or expanded ex vivo. Methods for treating or preventing disease or otherwise altering the immune status of the patient by reinfusing such cells into the donor are also provided. Methods for expanding and / or immune cells, including effector cells, in the absence of exogenous IL-2, and for administering the cells in the absence of co-infused IL-2 are also provided.
Owner:VALEOCYTE THERAPIES
Methods for the Treatment of Disease Using Immunoglobulins Having Fc Regions with Altered Affinities for FcgammaRactivating and FcgammaRinhibiting
ActiveUS20140134162A1Additive and synergistic and novel propertyImproved phenotypeSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunglobulin eWild type
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing cancer and other diseases using molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds an FcγR that activates a cellular effector (“FcγRActivating,” such as FcγRIIA or FcγRIIIA) and an FcγR that inhibits a cellular effector (“FcγRInhibiting,” such as FcγRIIA) with an altered Ratio of Affinities relative to the respective binding affinities of such FcγR for the Fc region of the wild-type immunoglobulin. The methods of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection where either an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., cancer, infectious disease) or an inhibited effector cell response mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., inflammation, autoimmunde disease).
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
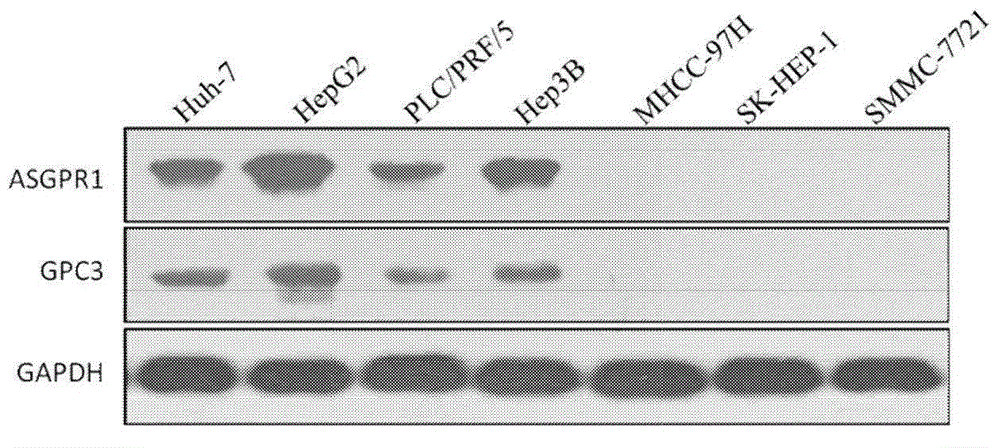
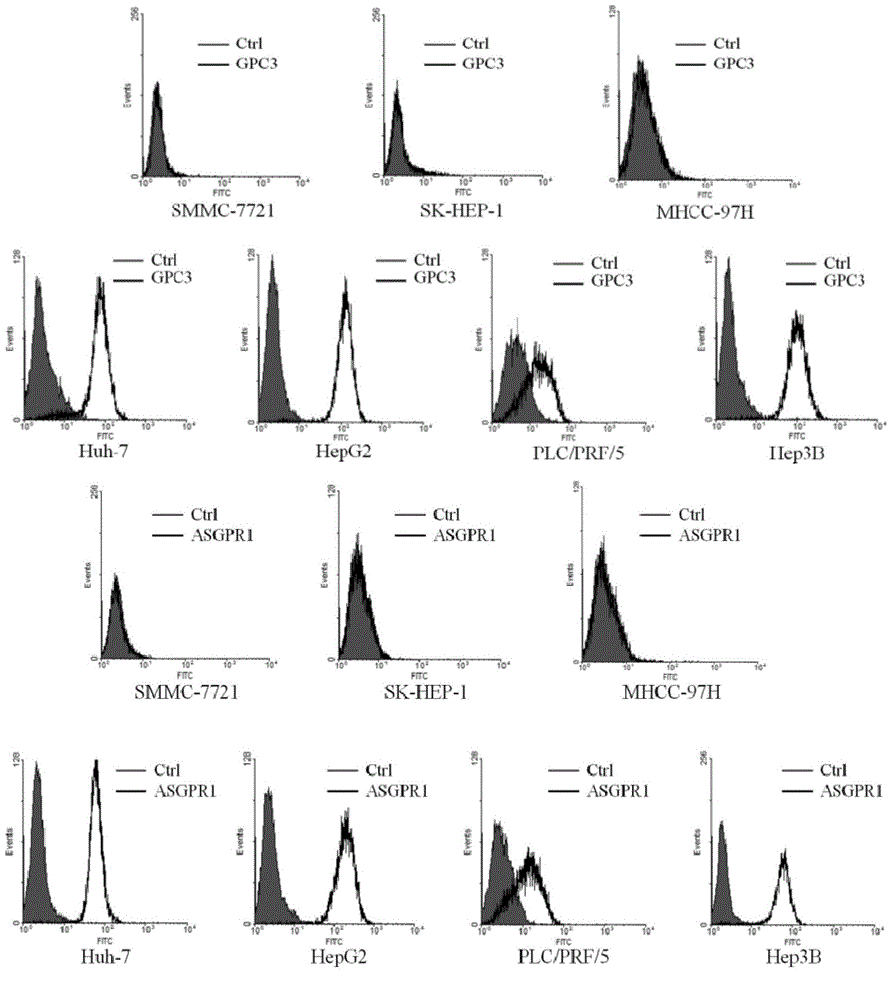
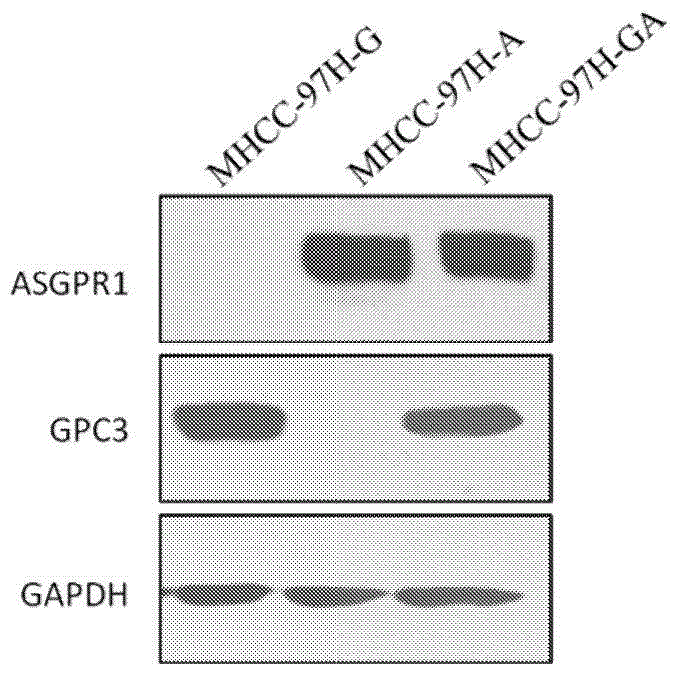
Dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (Glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell
ActiveCN105713881APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmune effector cellEffector cell
The invention relates to a dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of the dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell. The invention discloses the gene-modified immunologic effector cell capable of simultaneously identifying GPC3 and ASGPR1 for the first time, and the gene-modified immunologic effector cell can be used for the treatment of the GPC3 and ASGPR1 double-positive tumor, such as liver cancer.
Owner:CARSGEN THERAPEUTICS
Modified hematopoietic stem/progenitor and non-t effector cells, and uses thereof
Hematopoeitic stem / progenitor cells (HSPC) and / or non-T effector cells are genetically modified to express (i) an extracellular component including a ligand binding domain that binds a cellular marker preferentially expressed on an unwanted cell; and (ii) an intracellular component comprising an effector domain. Among other uses, the modified cells can be administered to patients to target unwanted cancer cells without the need for immunological matching before administration.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com