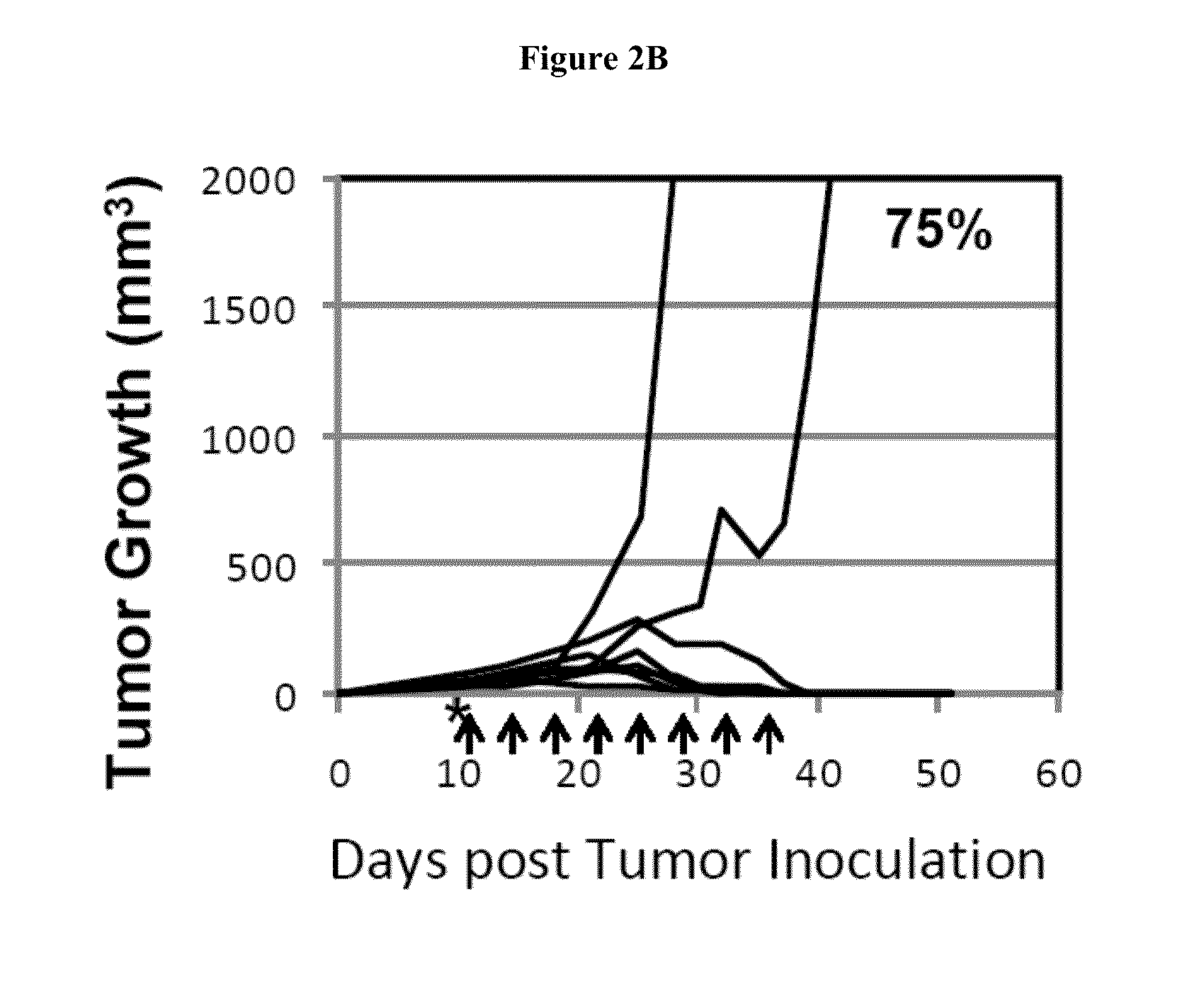
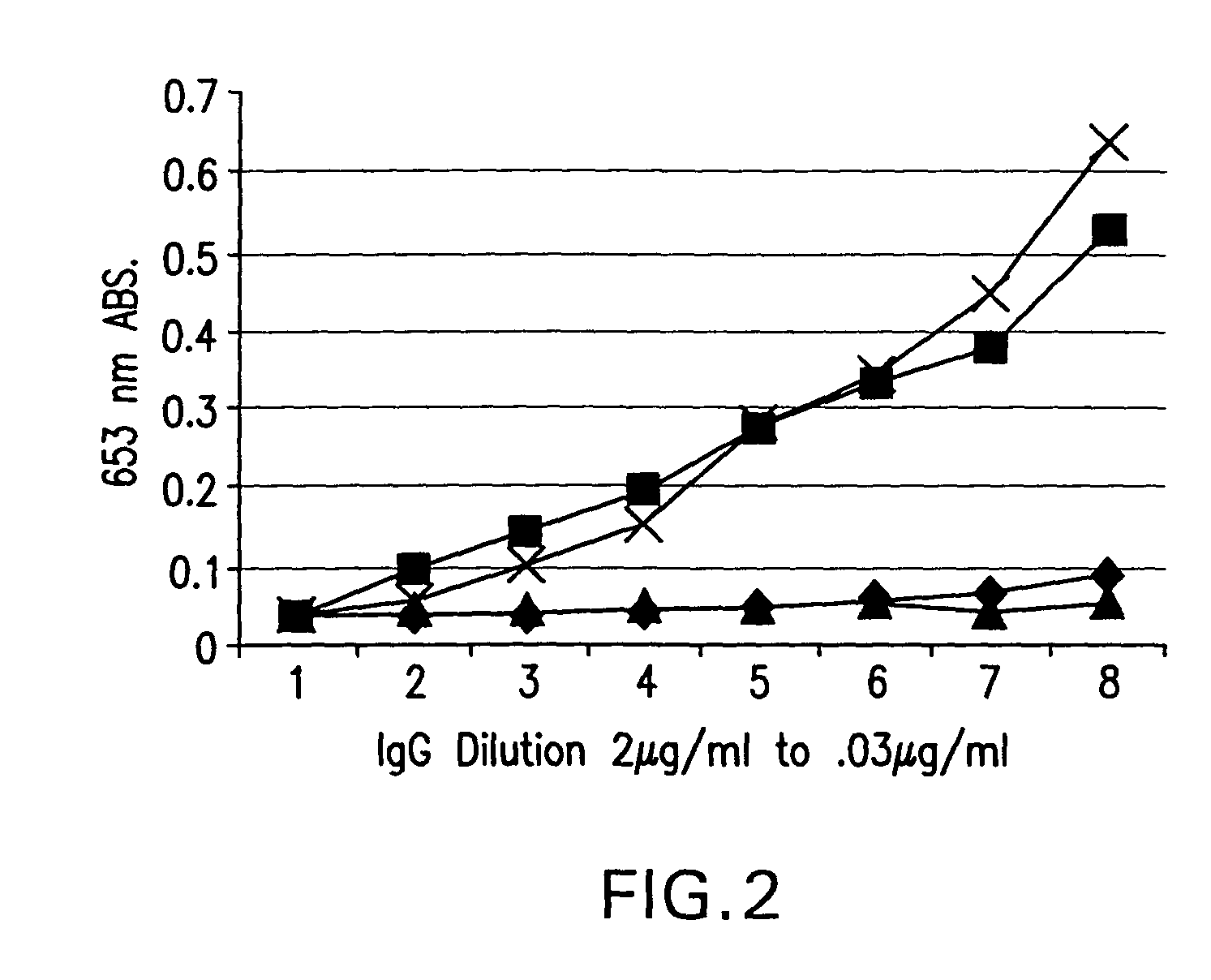
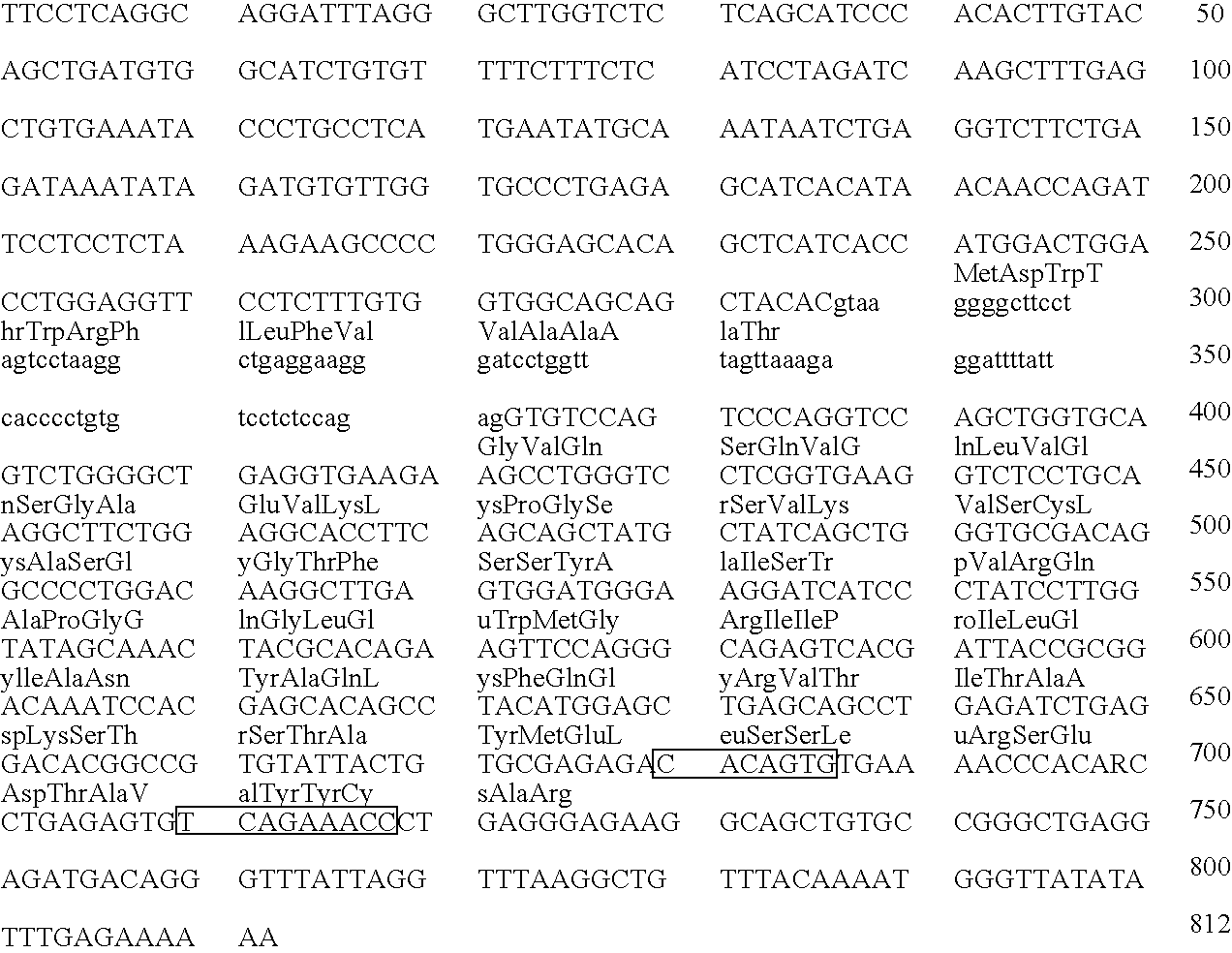
Patents
Literature
217 results about "Affinity binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Binding affinity is the strength of the binding interaction between a single biomolecule (e.g. protein or DNA) to its ligand/binding partner (e.g. drug or inhibitor).
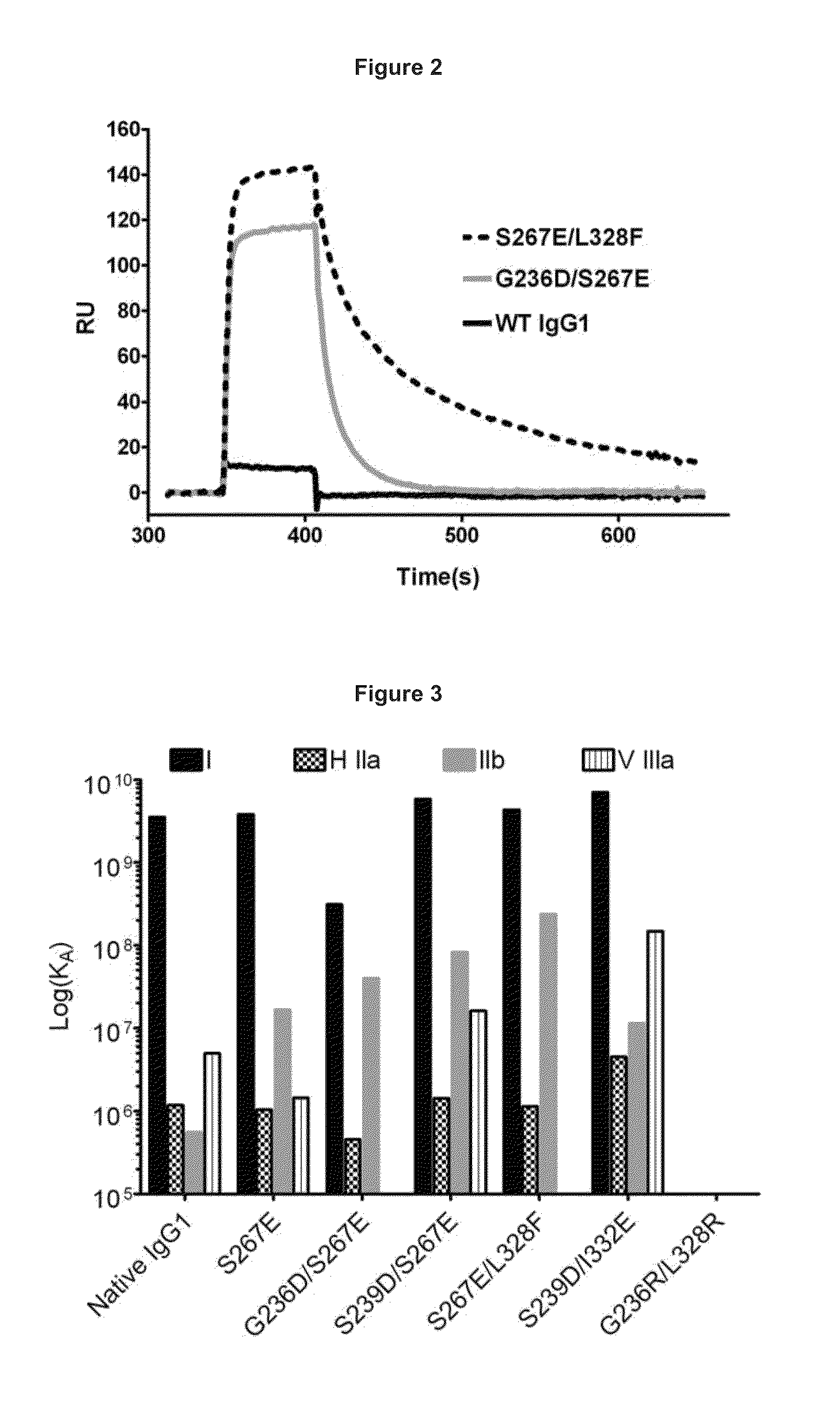
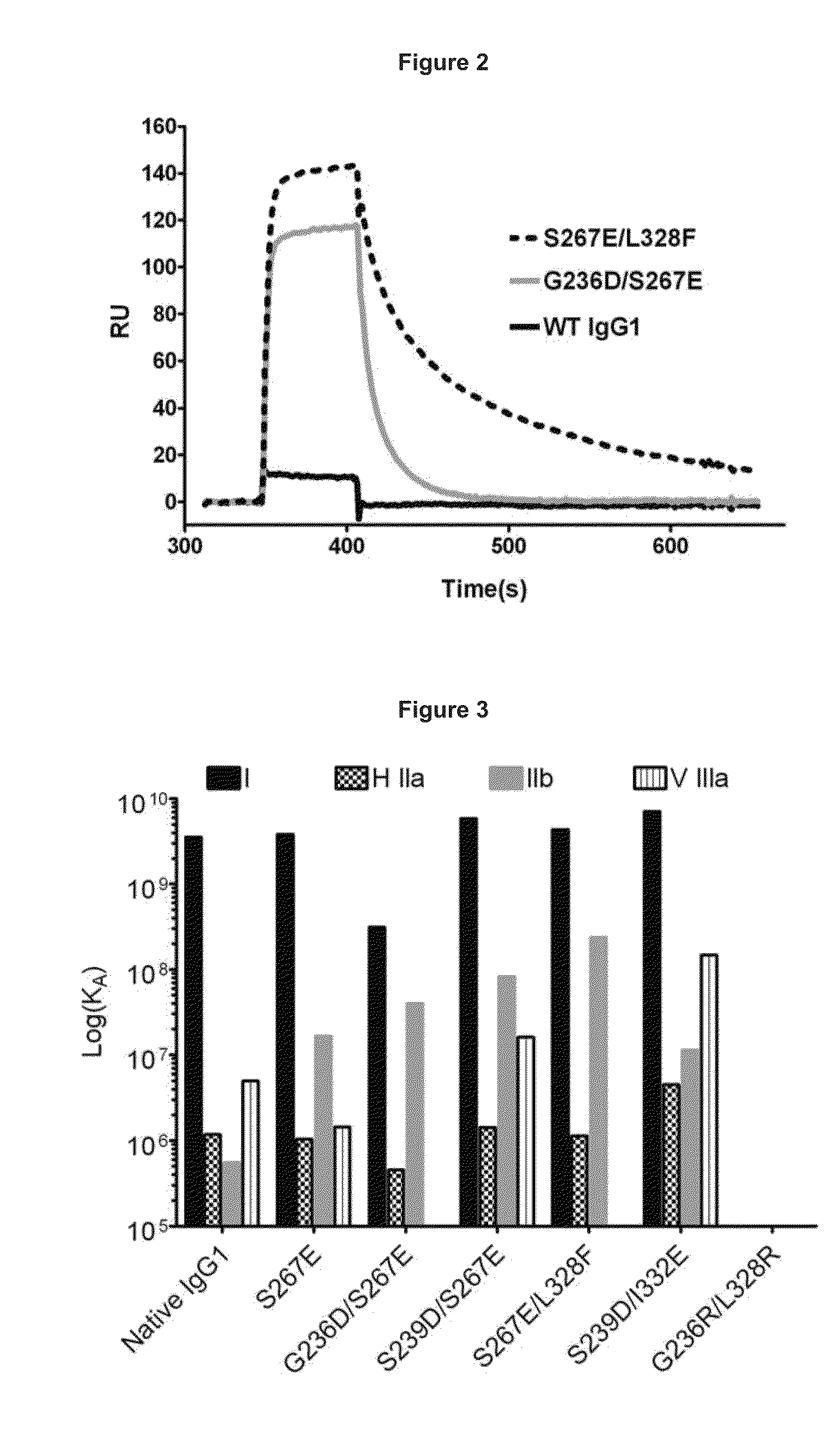
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050037000A1High affinityAltered affinityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderTherapeutic antibodyWild type
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcgammaRIIA and / or FcgammaRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcgammaR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MARCOGENICS INC +1
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS7355008B2Function increaseGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderTherapeutic antibodyEffector cell
Owner:MARCOGENICS INC +1
Transgenic non-human animals for producing chimeric antibodies
InactiveUS20060015957A1Inhibit expressionEasy to switchImmunoglobulinsGenetic engineeringAntigenHuman animal
The invention relates to transgenic non-human animals capable of producing heterologous antibodies and methods for producing human sequence antibodies which bind to human antigens with substantial affinity.
Owner:GENPHARM INT INC
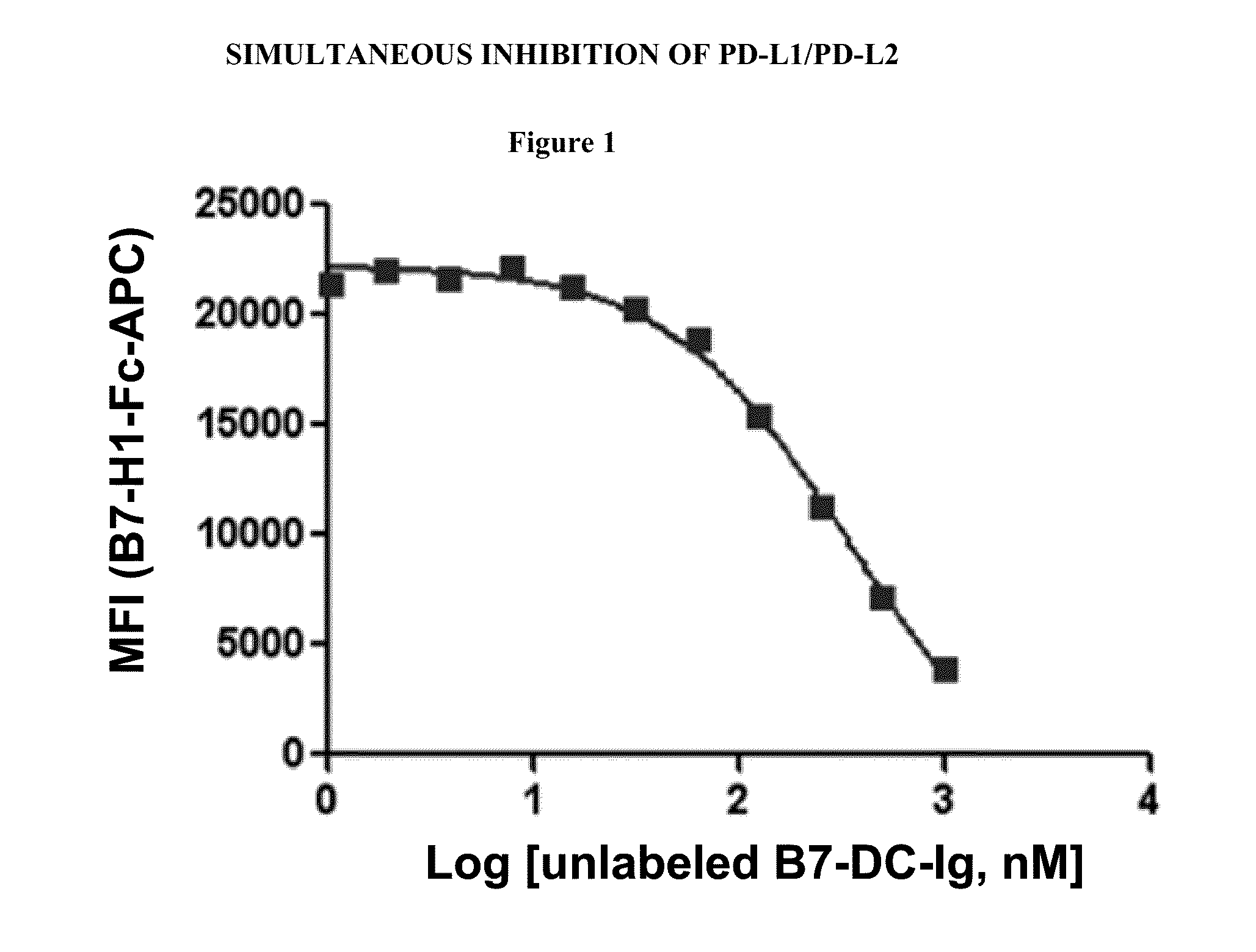
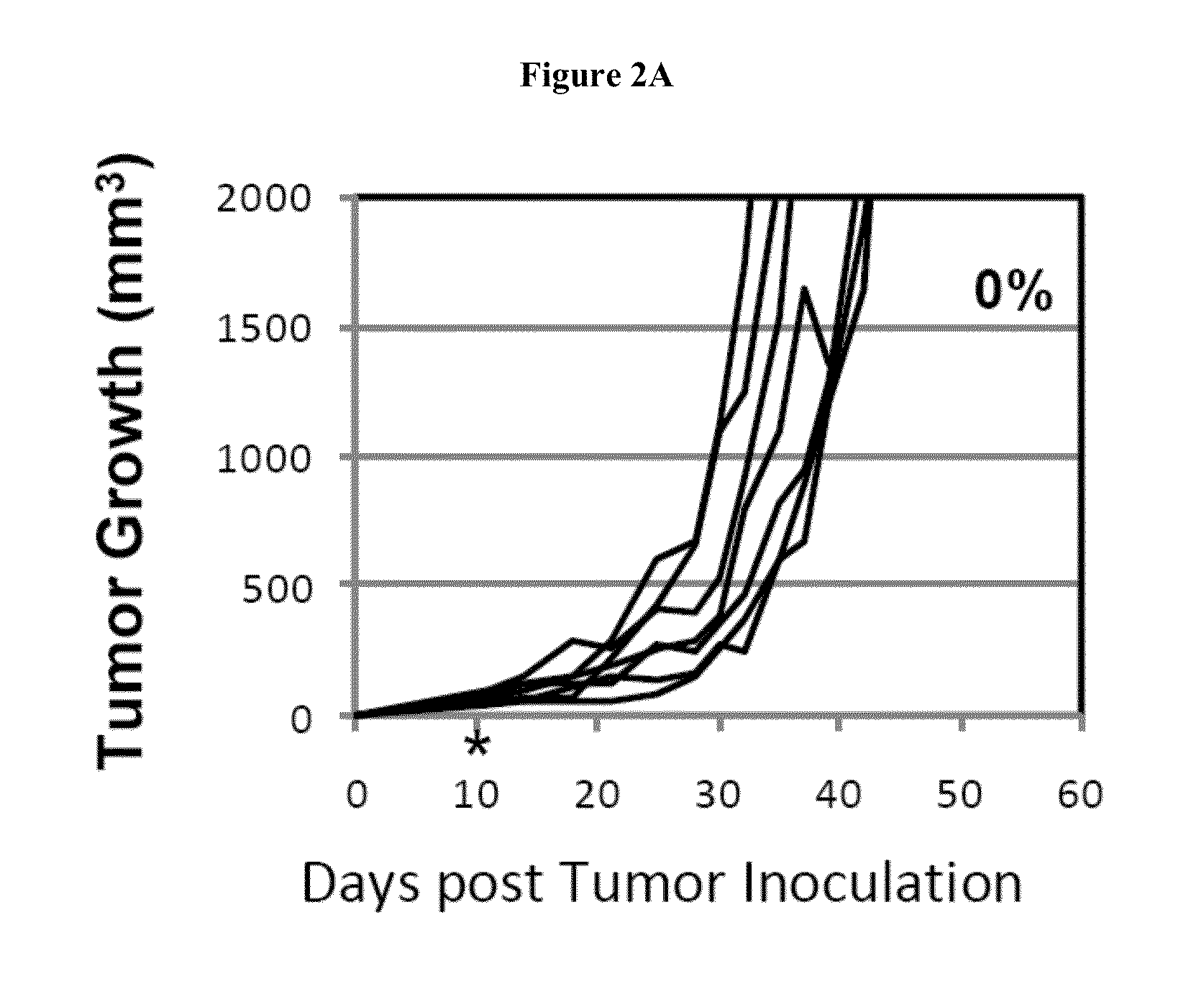
Simultaneous inhibition of pd-l1/pd-l2
InactiveUS20130017199A1Increase frequencyIncrease percentageAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseDendritic cell
Methods and compositions for treating an infection or disease that results from (1) failure to elicit rapid T cell mediated responses, (2) induction of T cell exhaustion, T cell anergy or both, or (3) failure to activate monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and / or other APCs, for example, as required to kill intracellular pathogens. The method and compositions solve the problem of undesired T cell inhibition by simultaneously inhibiting the PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. The immune response can be modulated by providing antagonists which bind with different affinity, by varying the dosage of agent which is administered, by intermittent dosing over a regime, and combinations thereof, that provides for dissociation of agent from the molecule to which it is bound prior to being administered again. In some cases it may be particularly desirable to stimulate the immune system, then remove the stimulation.
Owner:AMPLIMMUNE
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS20070036799A1Good curative effectEnhanced ADCC activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTherapeutic antibodyWild type
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
InactiveUS7960512B2High affinityLow affinityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
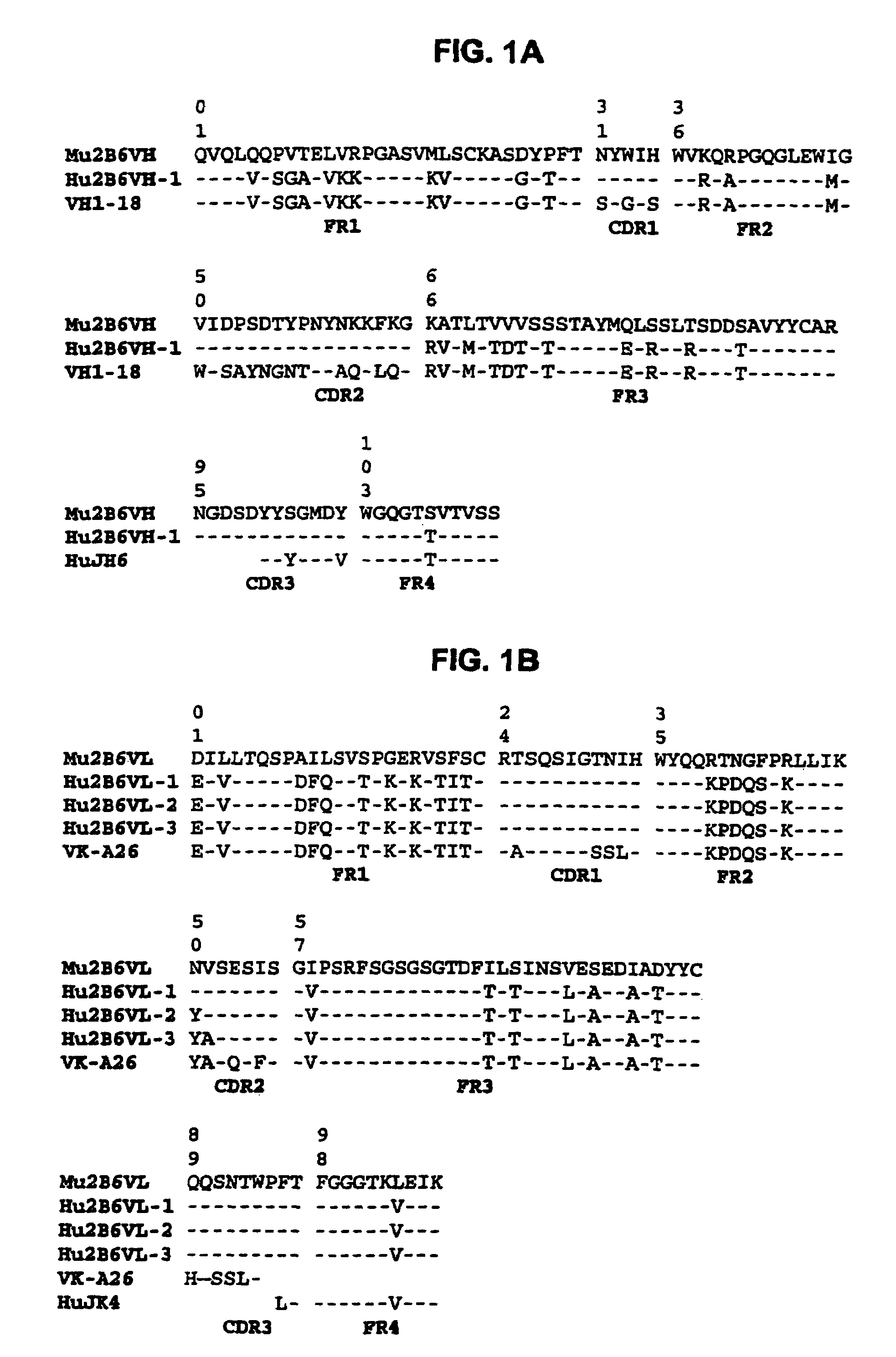
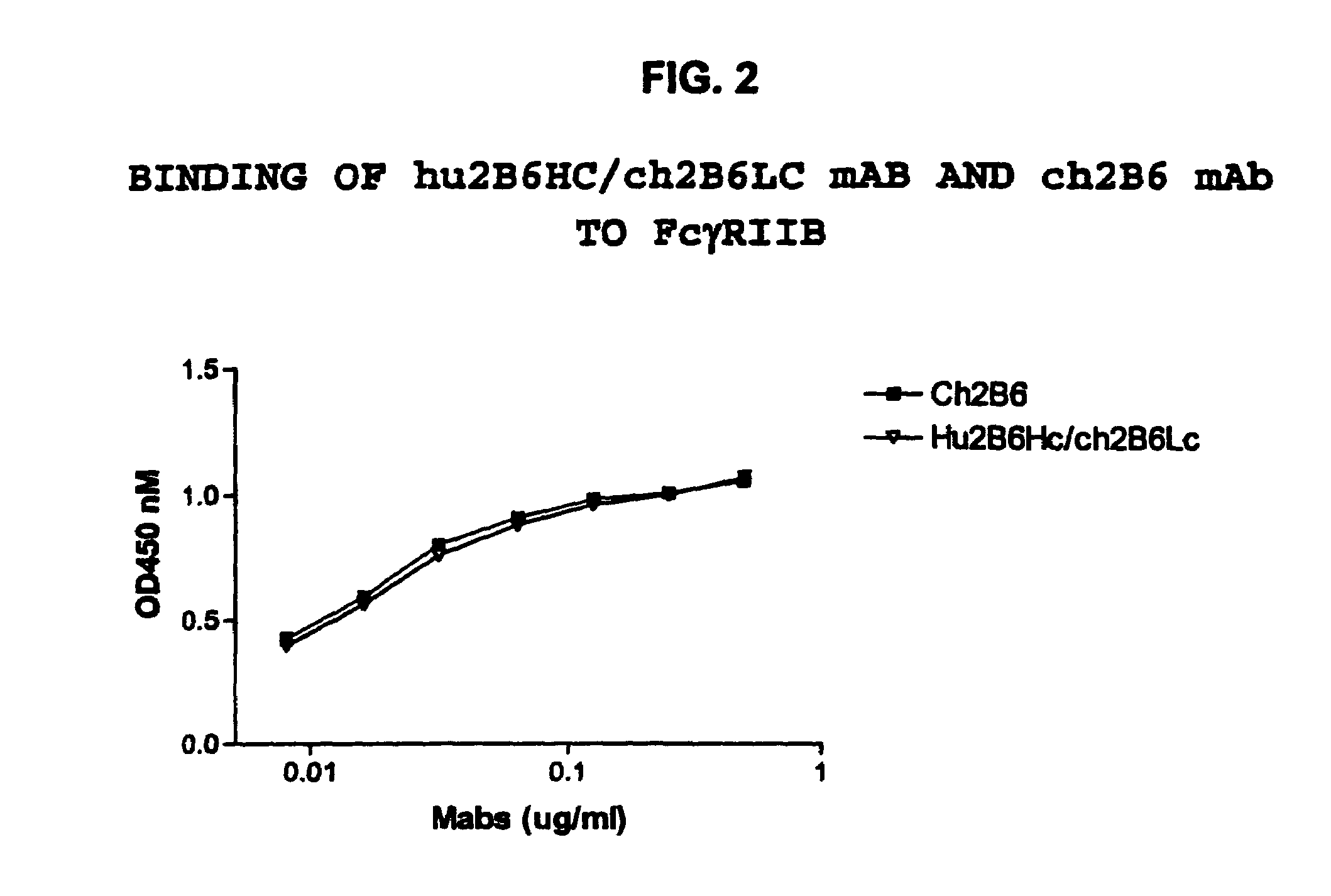
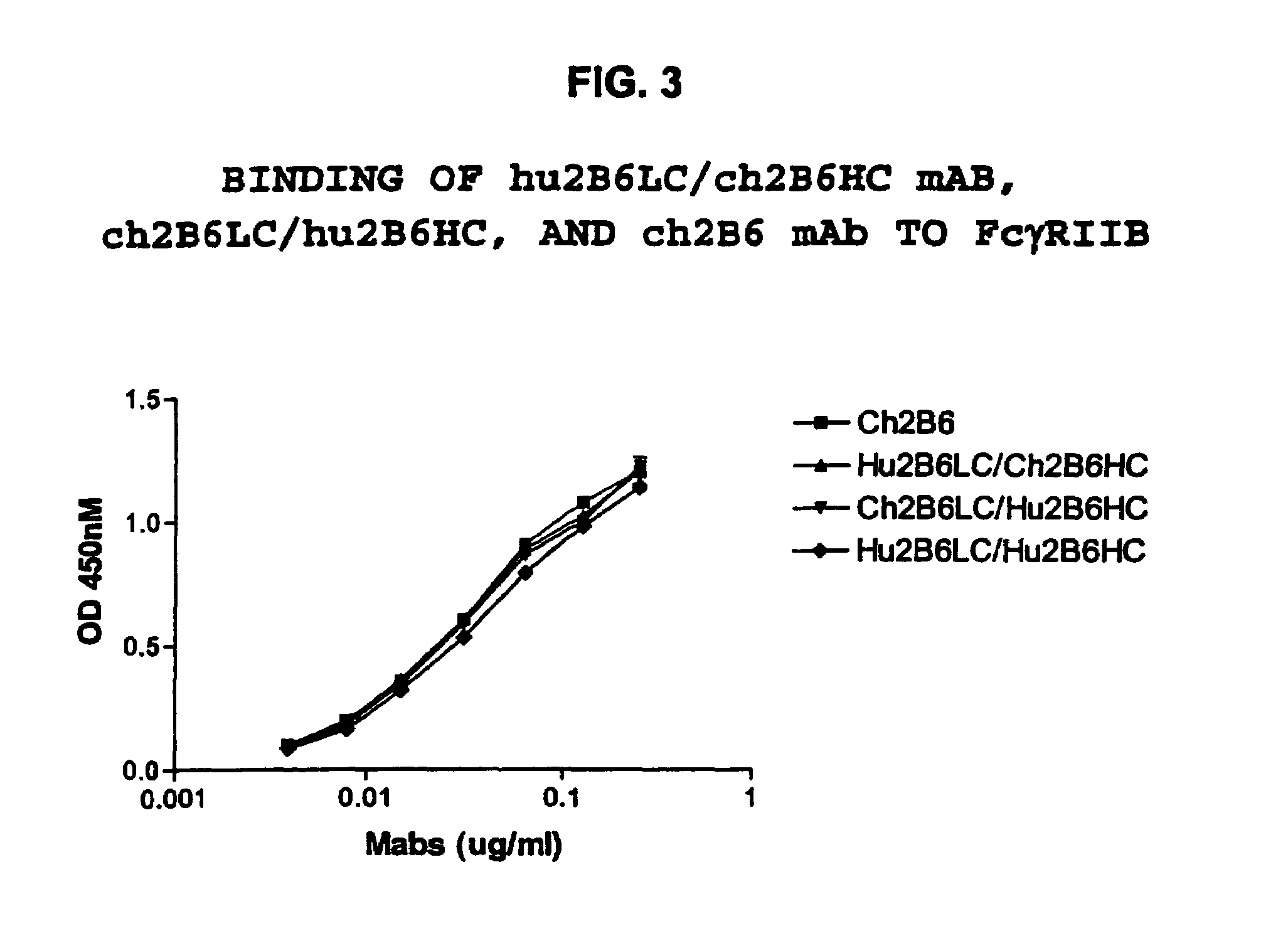
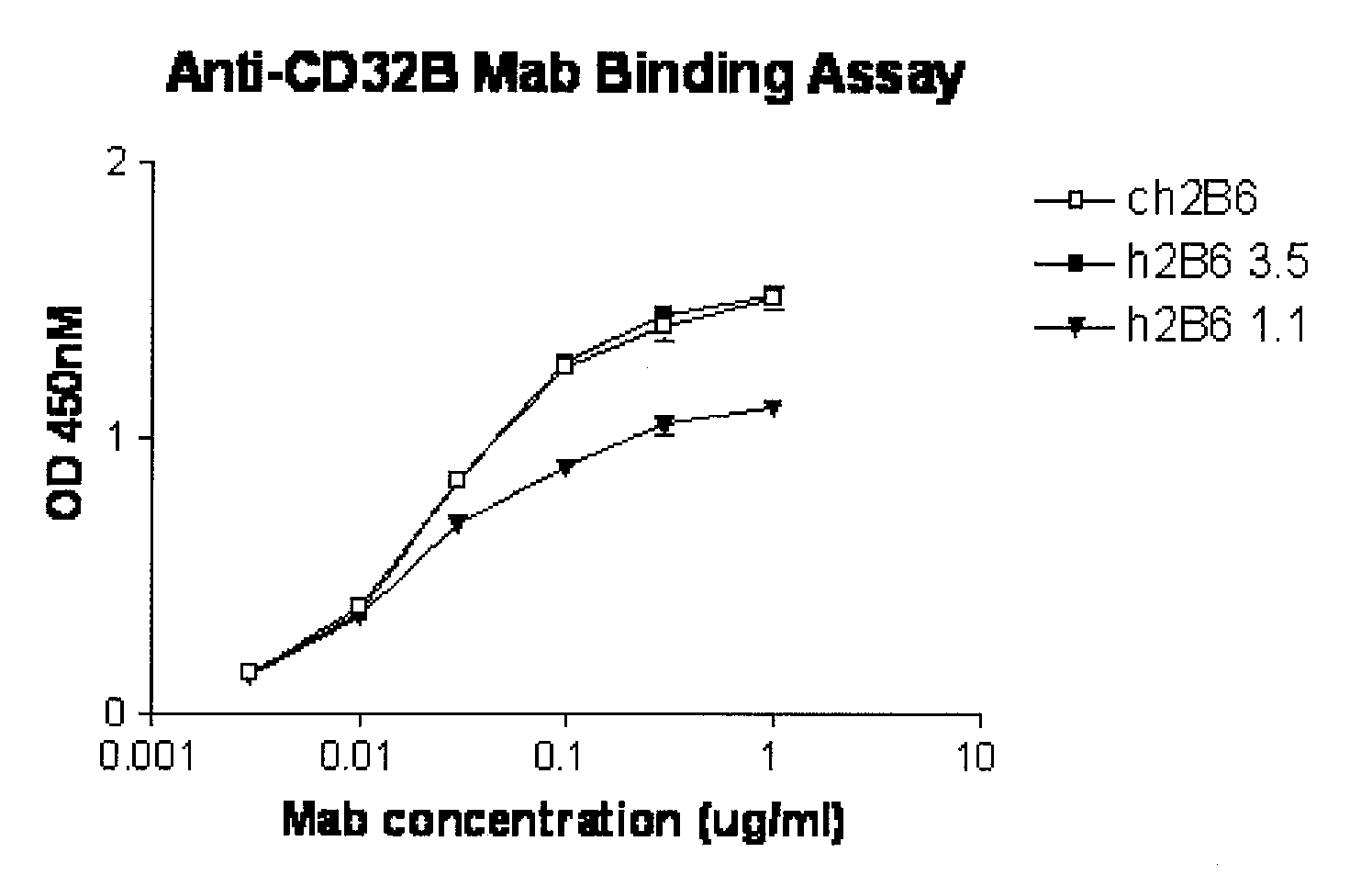
Humanized FcgammaRIIB-specific antibodies and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20060013810A1Good curative effectConvenient treatmentSenses disorderNervous disorderFc(alpha) receptorDisease
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Humanized FcgammaRIIB-specific antibodies and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7521542B2Immune responseAvoid immune responseSenses disorderNervous disorderFc(alpha) receptorTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Transgenic non-human animals capable of producing heterologous antibodies
The invention relates to transgenic non-human animals capable of producing heterologous antibodies and methods for producing human sequence antibodies which bind to human antigens with substantial affinity.
Owner:GENPHARM INT INC
Transgenic non-human animals for producing heterologous and chimeric antibodies
The invention relates to transgenic non-human animals capable of producing heterologous antibodies and methods for producing human sequence antibodies which bind to human antigens with substantial affinity.
Owner:GENPHARM INT INC
Sensor arrangement with electrically controllable arrays
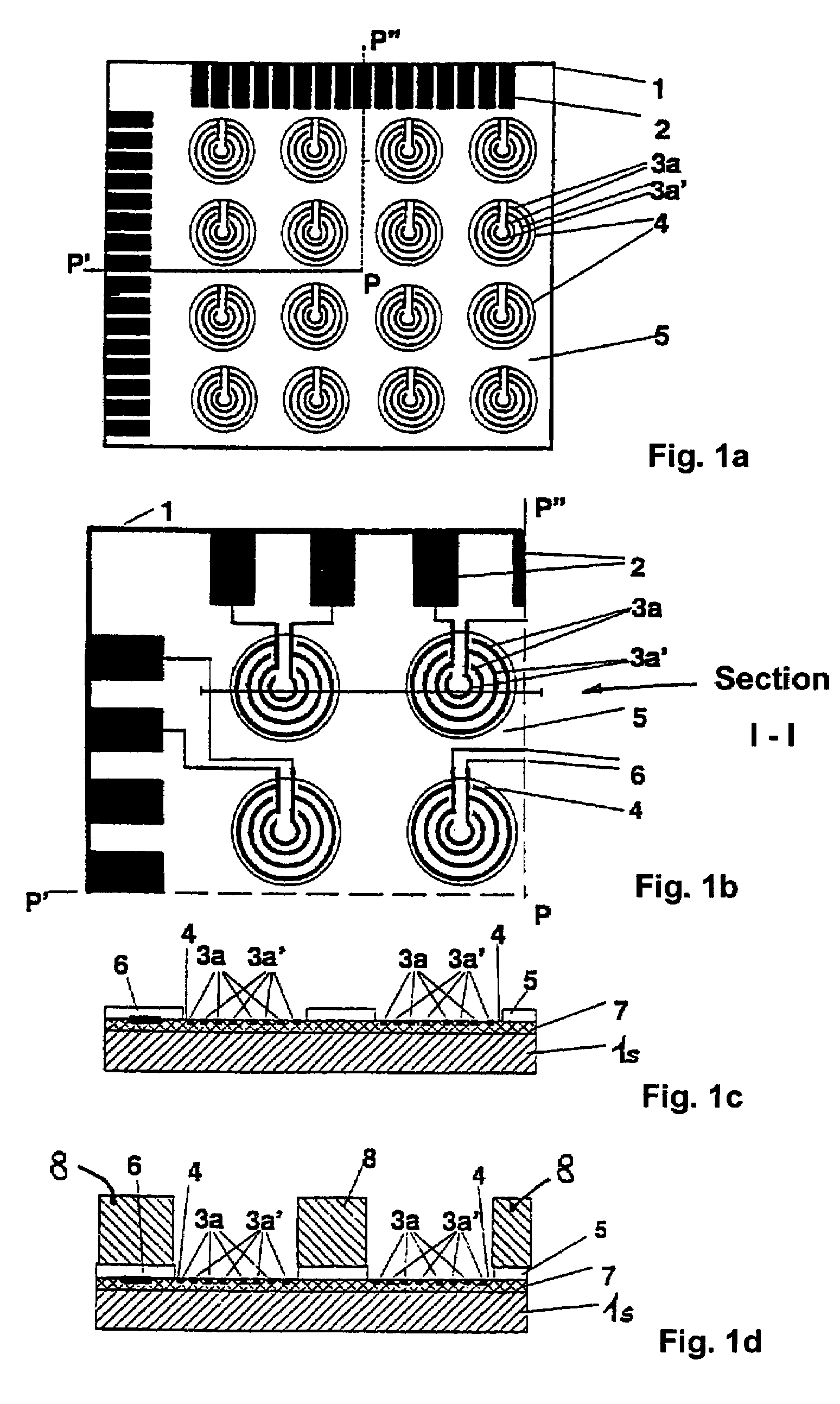
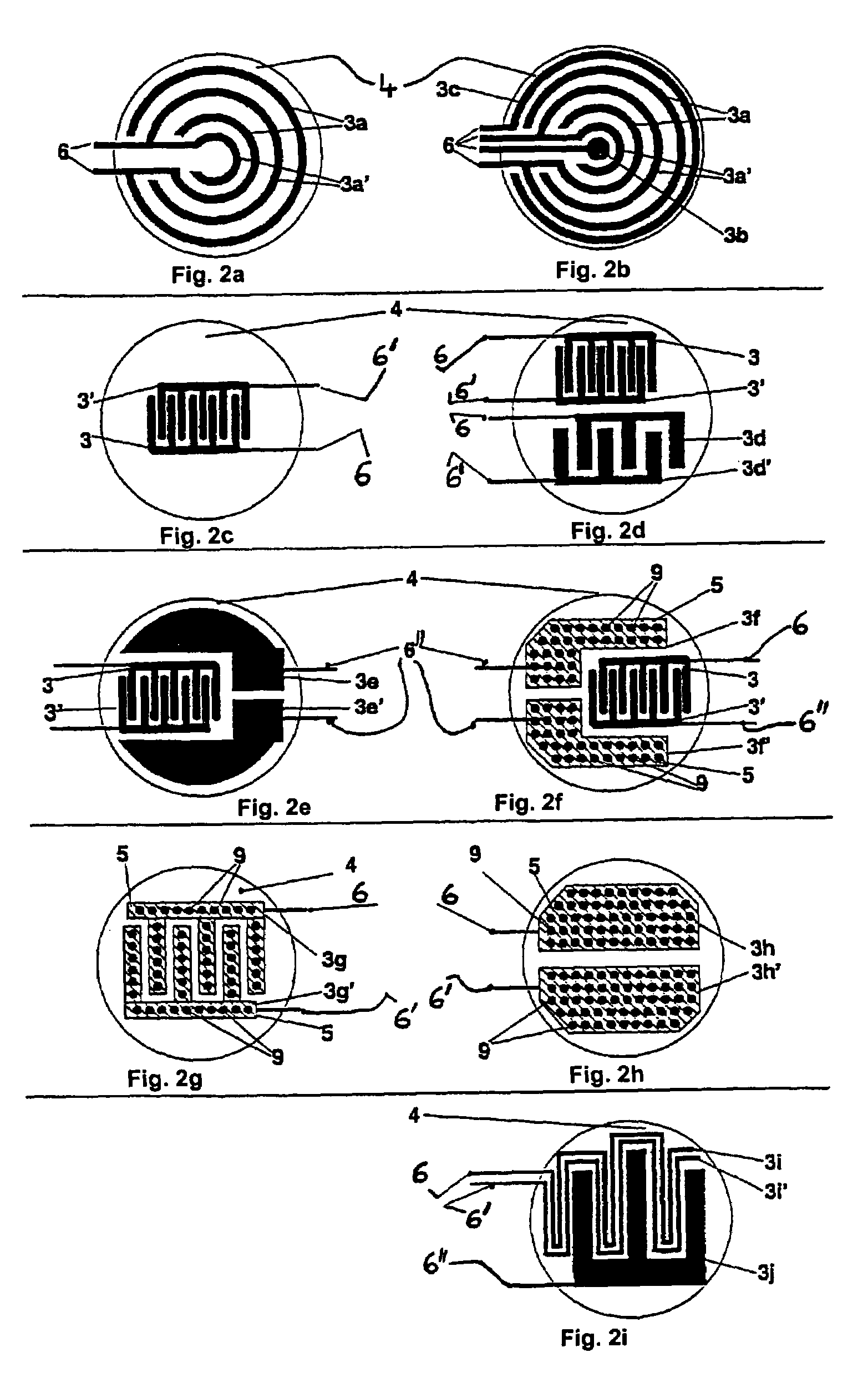
InactiveUS7208077B1Eliminating undesired binding eventAvoid polarizationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSensor arrayMicroelectrode
An electric sensor array which is provided with several sensor positions that each have at least two microelectrodes. Molecular substances can be detected electrochemically and charged molecules can be transported or handled using the array. Measuring procedures can be effected, especially using two addressing procedures, in which sensor positions can be individually addressed and electrochemically or electrically controlled by pairing or in groups for voltage or impedance measurements. For biomolecular assays, affinity-binding molecules can be immobilized at the sensor positions, between the microelectrodes, or on auxiliary surfaces.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Identification and engineering of antibodies with variant Fc regions and methods of using same
ActiveUS8217147B2High affinityLow affinityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsDiseaseTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Humanized Fc.gamma.RIIB-Specific Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080044417A1Good curative effectEnhanced effector functionDisease diagnosisTissue cultureFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Method of and system for multiplexed analysis by spectral imaging
A method of detecting the presence, absence and / or level of a plurality of analytes-of-interest in a sample, the method comprisES: (a) providing a plurality of objects, each of the plurality of objects having a predetermined, measurable and different imagery characteristic, and further having a predetermined and specific affinity to one analyte of the plurality of analytes-of-interest, each the imagery characteristic corresponding to one the predetermined specific affinity, hence each the imagery characteristic corresponds to one analyte of the plurality of analytes-of interest; (b) providing at least one affinity moiety having a predetermined and specific affinity or predetermined and specific affinities to the plurality of analytes-of-interest, each the affinity moiety having a predetermined, measurable response to light; (c) combining the objects, the at least one affinity moiety and the sample under conditions for affinity binding; and (d) simultaneously determining, for each object of the plurality of objects an imagery characteristic, and for at least a portion of the at least one affinity moiety a response to light, thereby detecting the presence, absence and / or level of the plurality of analytes-of-interest in the sample.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Human antibodies specific to KDR and uses thereof
The invention provides an antibodies that bind to KDR with an affinity comparable to or higher than human VEGF, and that neutralizes activation of KDR. Antibodies include whole immunoglobulins, monovalent Fabs and single chain antibodies, multivalent single chain antibodies, diabodies, triabodies, and single domain antibodies. The invention further provides nucleic acids and host cells that encode and express these antibodies. The invention further provides a method of neutralizing the activation of KDR, a method of inhibiting angiogenesis in a mammal and a method of inhibiting tumor growth in a mammal.
Owner:IMCLONE SYSTEMS
Antibodies specific to KDR and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050214860A1Inhibit tumor growthCompound screeningVirusesSingle-Chain AntibodiesAngiogenesis growth factor
The invention provides an immunoglobulin molecule which binds KDR with an affinity comparable to human VEGF, and that neutralizes activation of KDR. Immunoglobulin molecules include monovalent single chain antibodies, multivalent single chain antibodies, diabodies, triabodies, antibodies, humanized antibodies and chimerized antibodies. The invention further provides nucleic acid molecules that encode these immunoglobulin molecules. The invention also provides a method of making the immunoglobulin molecules mentioned above. The invention further provides a method of neutralizing the activation of KDR, a method of inhibiting angiogenesis in a mammal and a method of inhibiting tumor growth in a mammal with such immunoglobulin molecules.
Owner:ZHU ZHENPING +1
Microfluidic device and surface decoration process for solid phase affinity binding assays
InactiveUS7258837B2Easy to storeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteConcentration gradient
This invention provides a microfluidic device for use in the detection of one or more analytes in a fluid using solid-phase affinity binding assays. The device offers a practical, easy-to-use, portable, inexpensive, robust analytical system for the parallel and quantitative detection of multiple analytes. In addition, this invention provides methods and devices for the formation of concentration gradients of capture molecules immobilized on a solid phase.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Human anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody
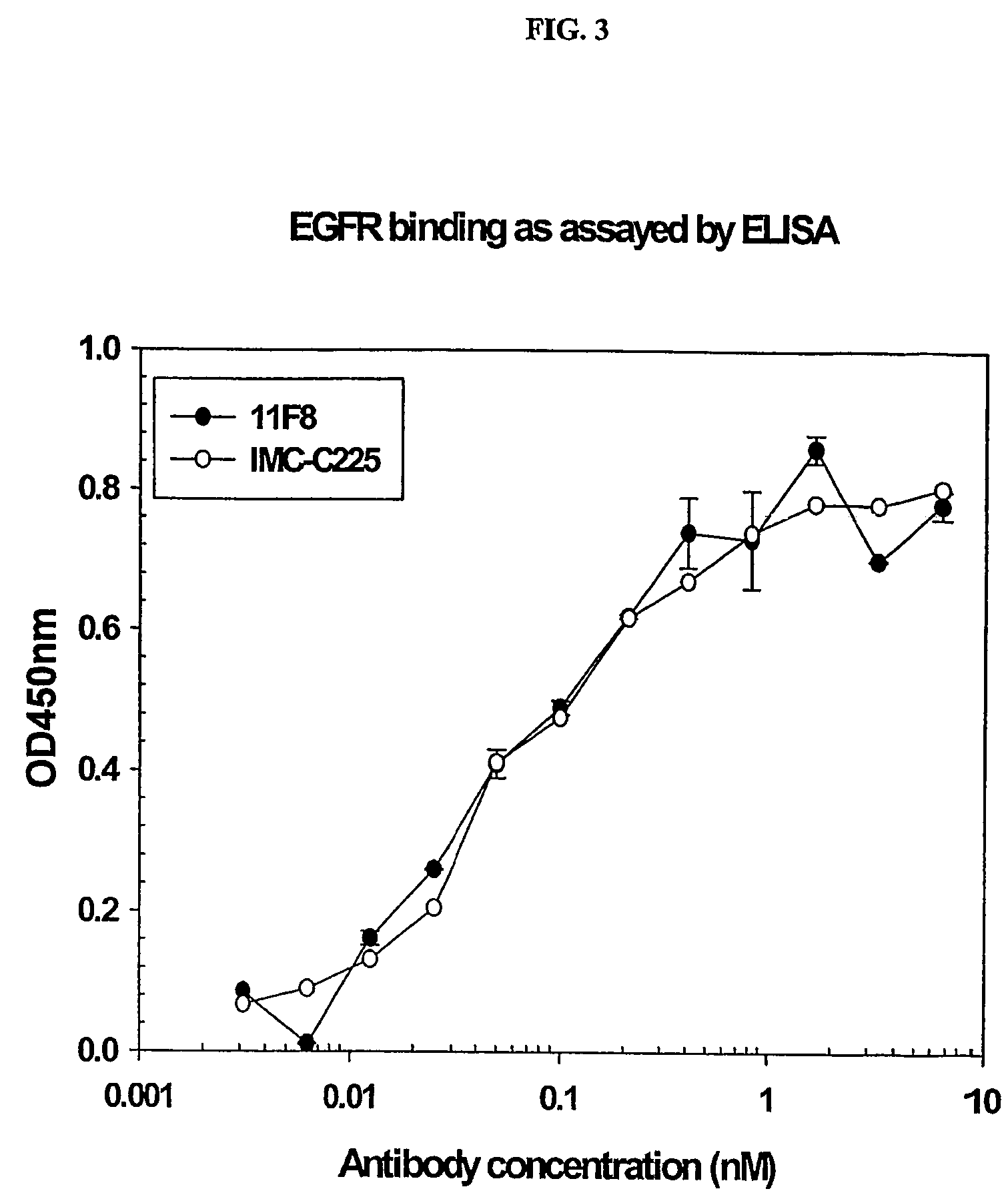
ActiveUS7598350B2Neutralize EGFRInhibit bindingSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSingle-Chain AntibodiesHuman epidermal growth factor receptor
Owner:IMCLONE SYSTEMS
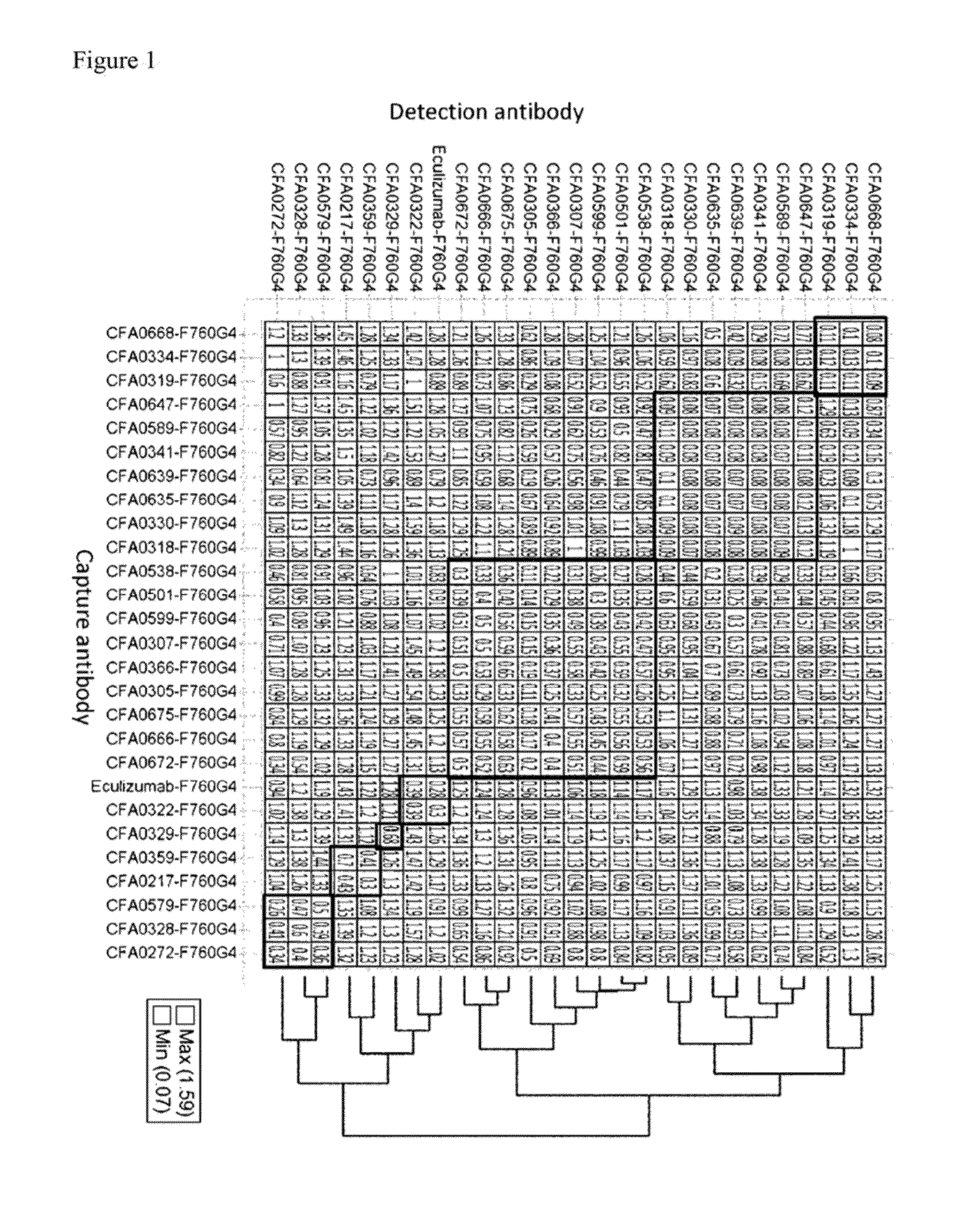
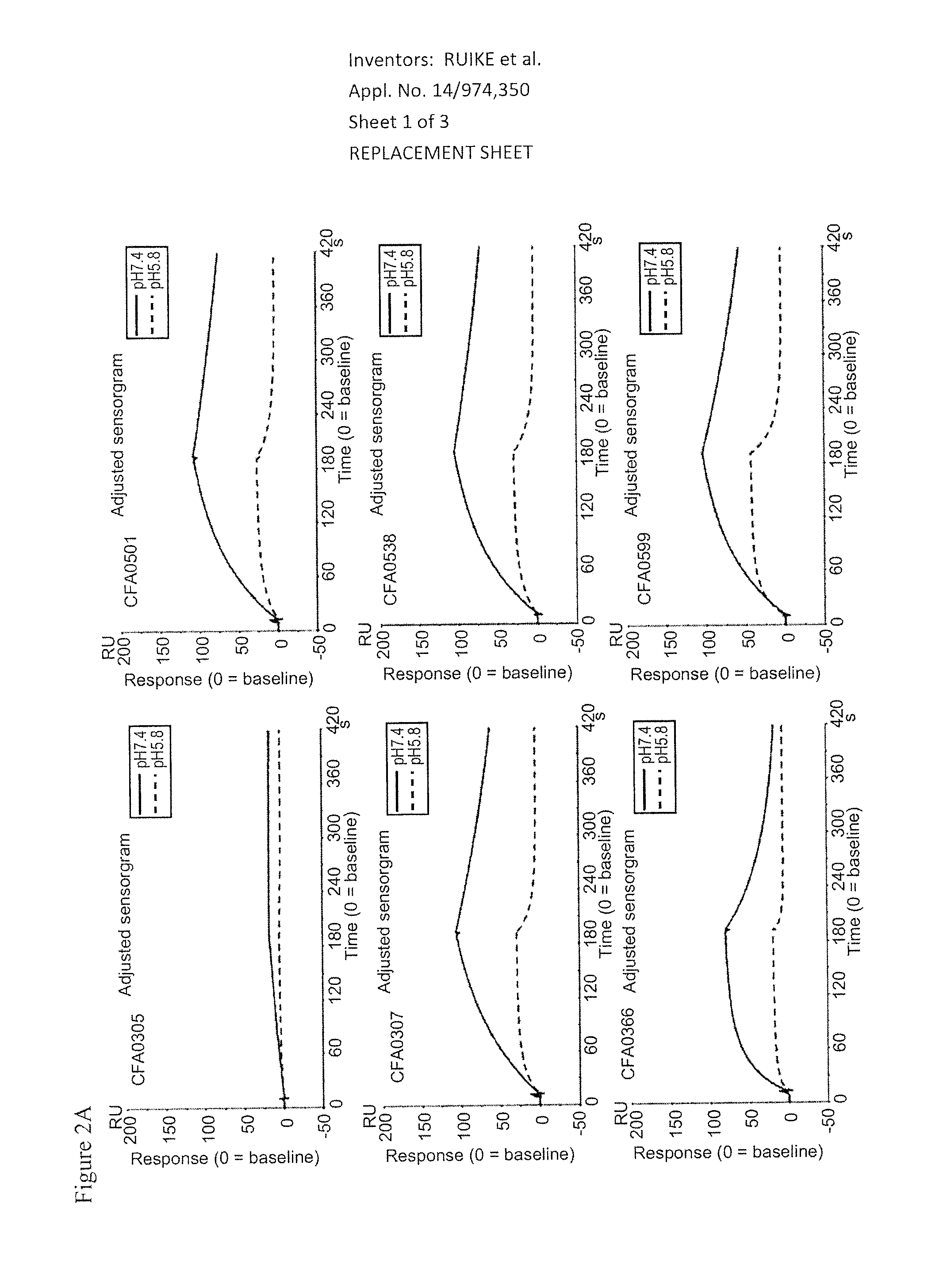
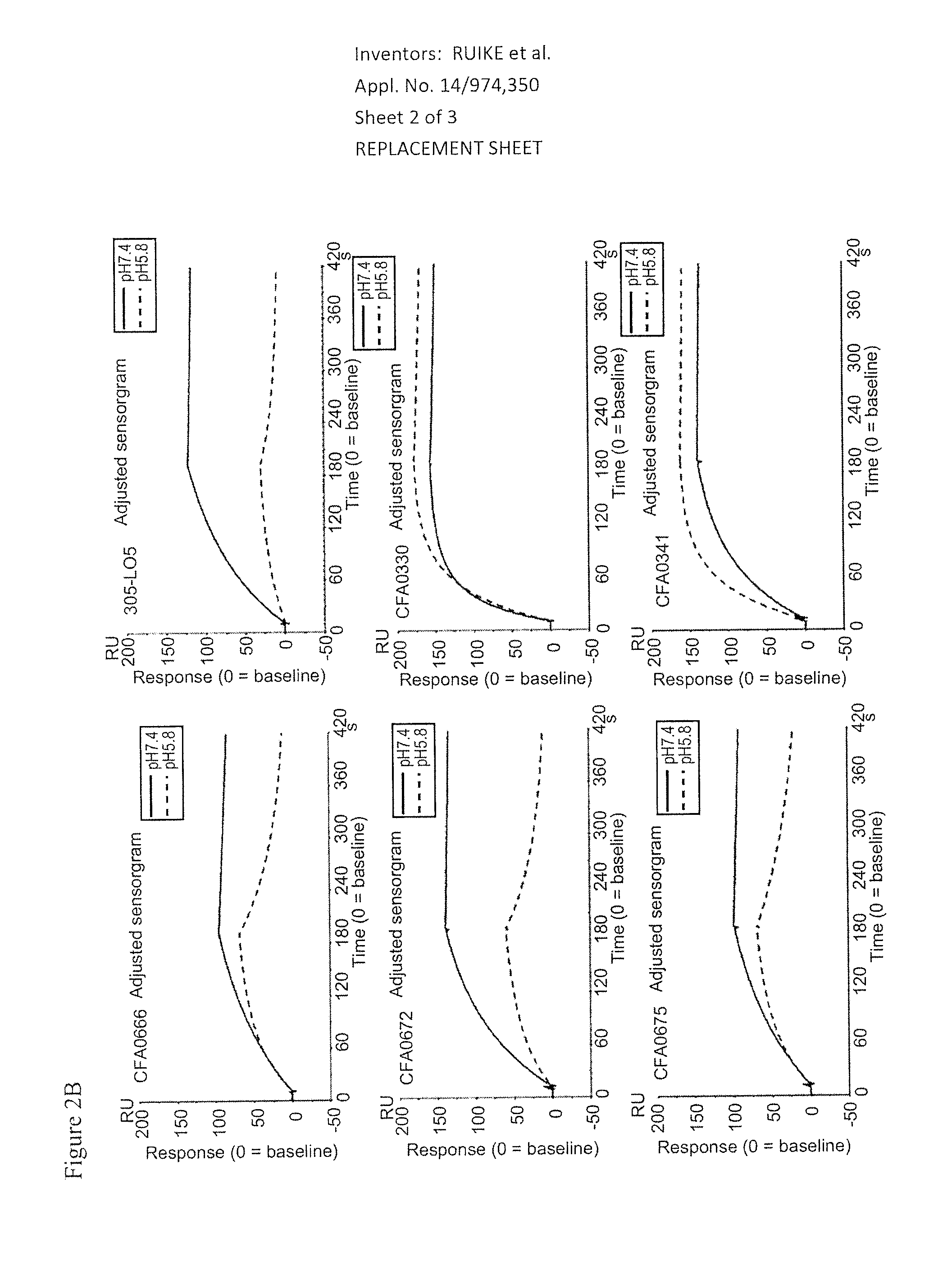
Anti-C5 Antibodies and Methods of Use
An objective of the invention is to provide anti-C5 antibodies and methods of using the same. The invention provides anti-C5 antibodies and methods of using the same. In some embodiments, an isolated anti-C5 antibody of the present invention binds to an epitope within the β chain of C5 with a higher affinity at neutral pH than at acidic pH. The invention also provides isolated nucleic acids encoding an anti-C5 antibody of the present invention. The invention also provides host cells comprising a nucleic acid of the present invention. The invention also provides a method of producing an antibody comprising culturing a host cell of the present invention so that the antibody is produced. The invention further provides a method of producing an anti-C5 antibody comprising immunizing an animal against a polypeptide which comprises the MG1-MG2 domain of the β chain of C5. Anti-C5 antibodies of the present invention may be for use as a medicament. Anti-C5 antibodies of the present invention may be for use in treating a complement-mediated disease or condition which involves excessive or uncontrolled activation of C5. Anti-C5 antibodies of the present invention may be for use in enhancing the clearance of C5 from plasma.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
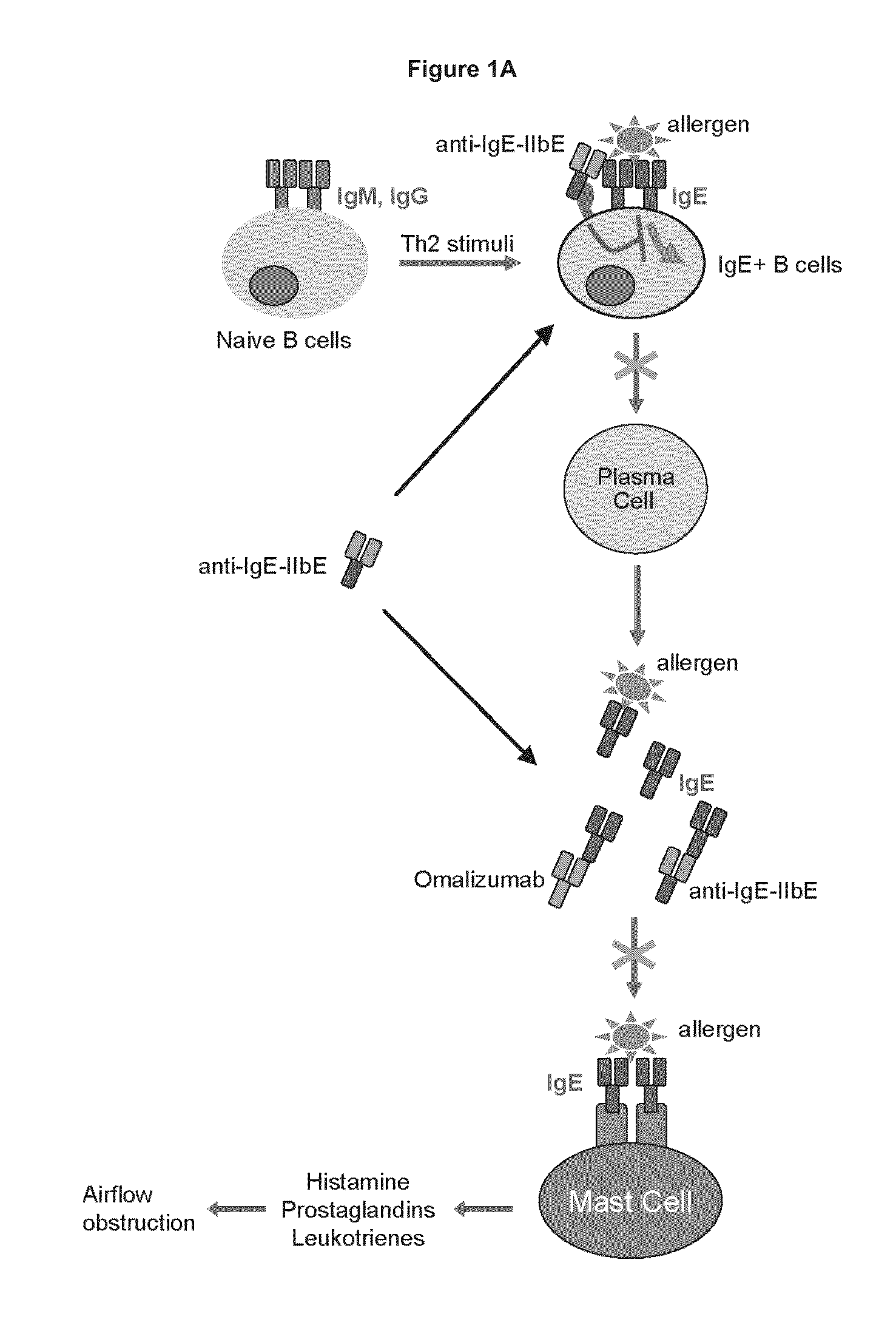
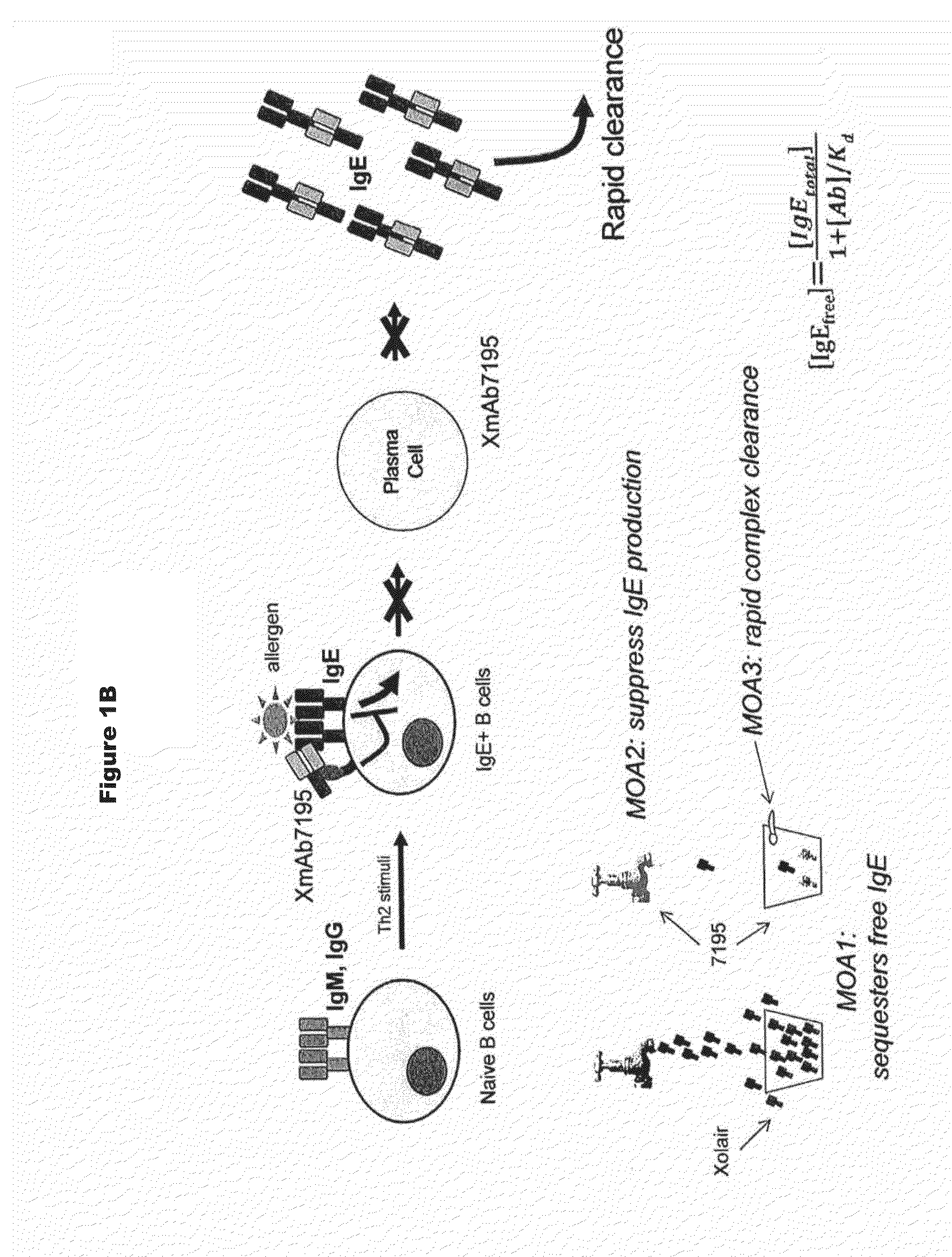
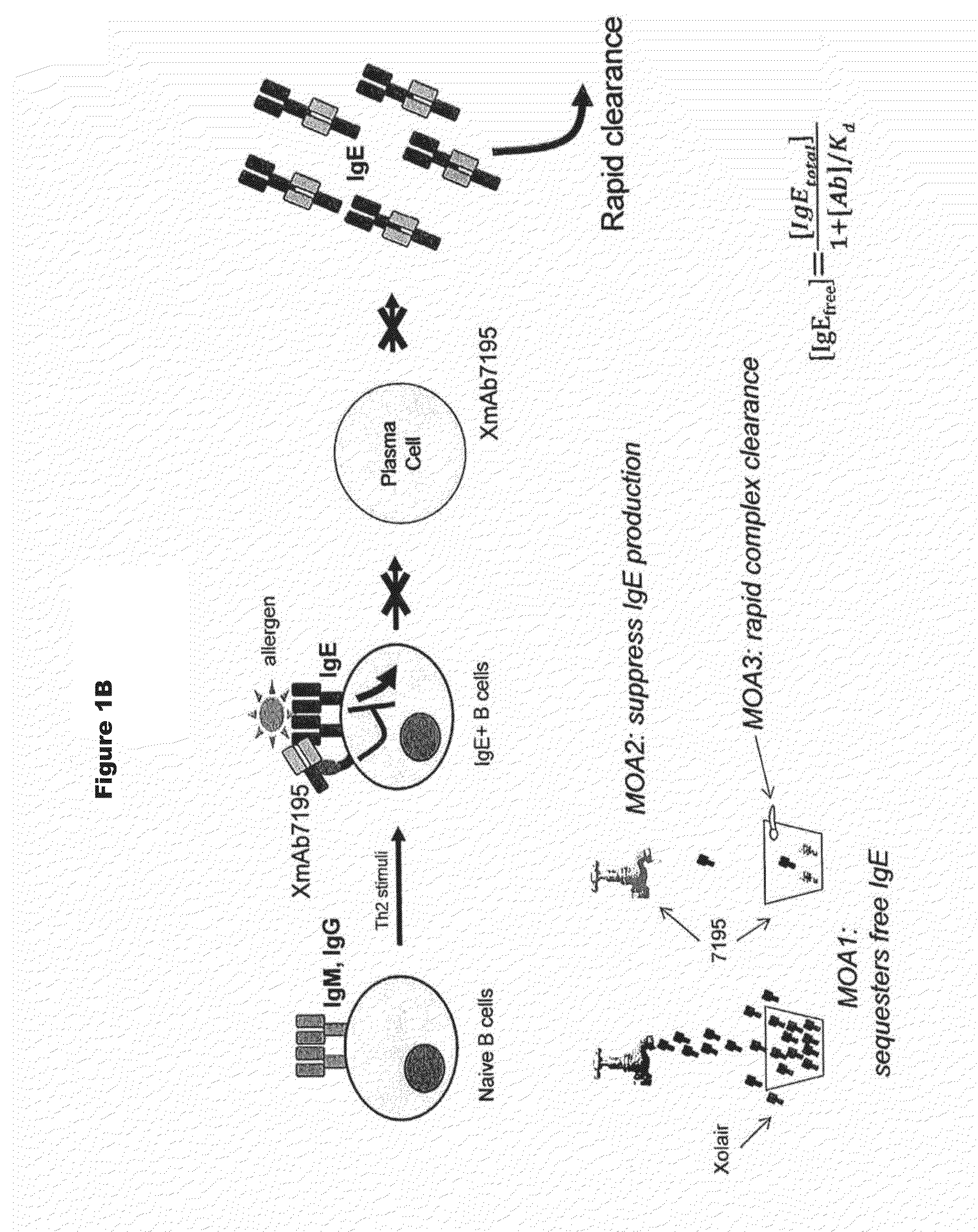
Rapid clearance of antigen complexes using novel antibodies
ActiveUS20140212436A1Reduce serum concentrationHigh affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsVirologyDisease cause
Owner:XENCOR
Apparatus and method for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20030127396A1Simple construction operationMaximizes mixing efficiencyElectrostatic separationWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetic gradientMagnetic source
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
Humanized FcγRIIB-specific antibodies and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7786270B2Immune responseAvoid immune responseDisease diagnosisTissue cultureFc(alpha) receptorCancer cell
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Rapid clearance of antigen complexes using novel antibodies
InactiveUS20160060360A1Reduce serum concentrationHigh affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseVirology
Owner:XENCOR
Identification and Engineering of Antibodies with Variant Fc Regions and Methods of Using Same
InactiveUS20110243941A1High affinityLow affinitySenses disorderNervous disorderTherapeutic antibodyInfectious Disorder
The present invention relates to molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds FcγRIIIA and / or FcγRIIA with a greater affinity, relative to a comparable molecule comprising the wild-type Fc region. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection. The molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment or prevention of a disease or disorder where an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function (e.g., ADCC) mediated by FcγR is desired, e.g., cancer, infectious disease, and in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic antibodies the effect of which is mediated by ADCC.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
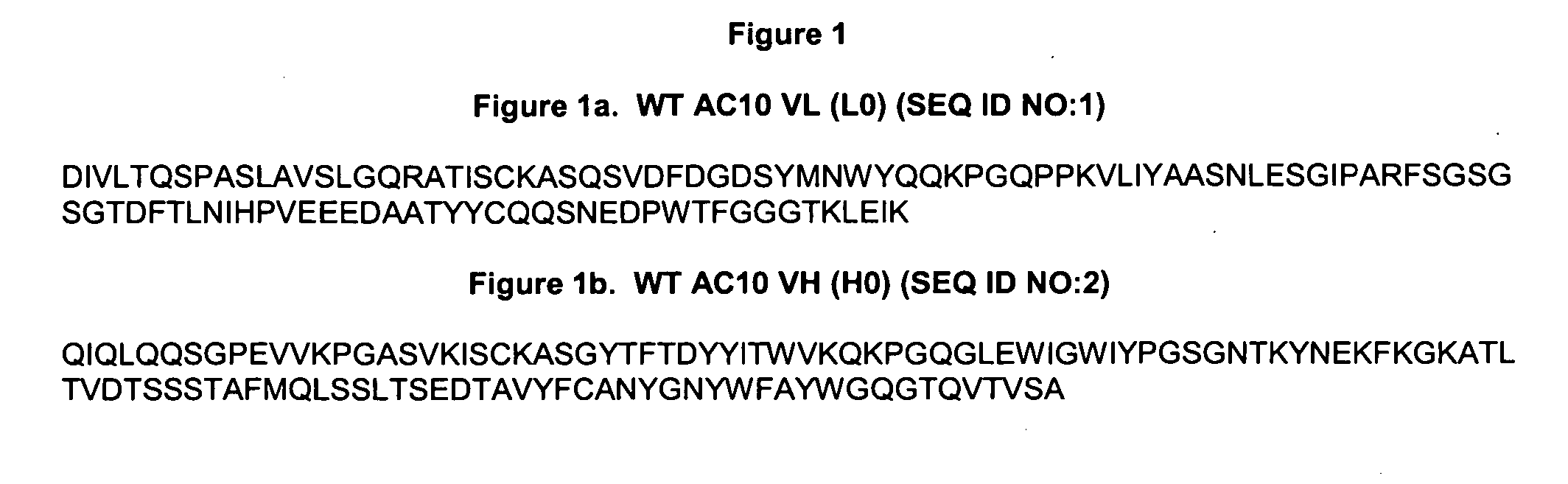
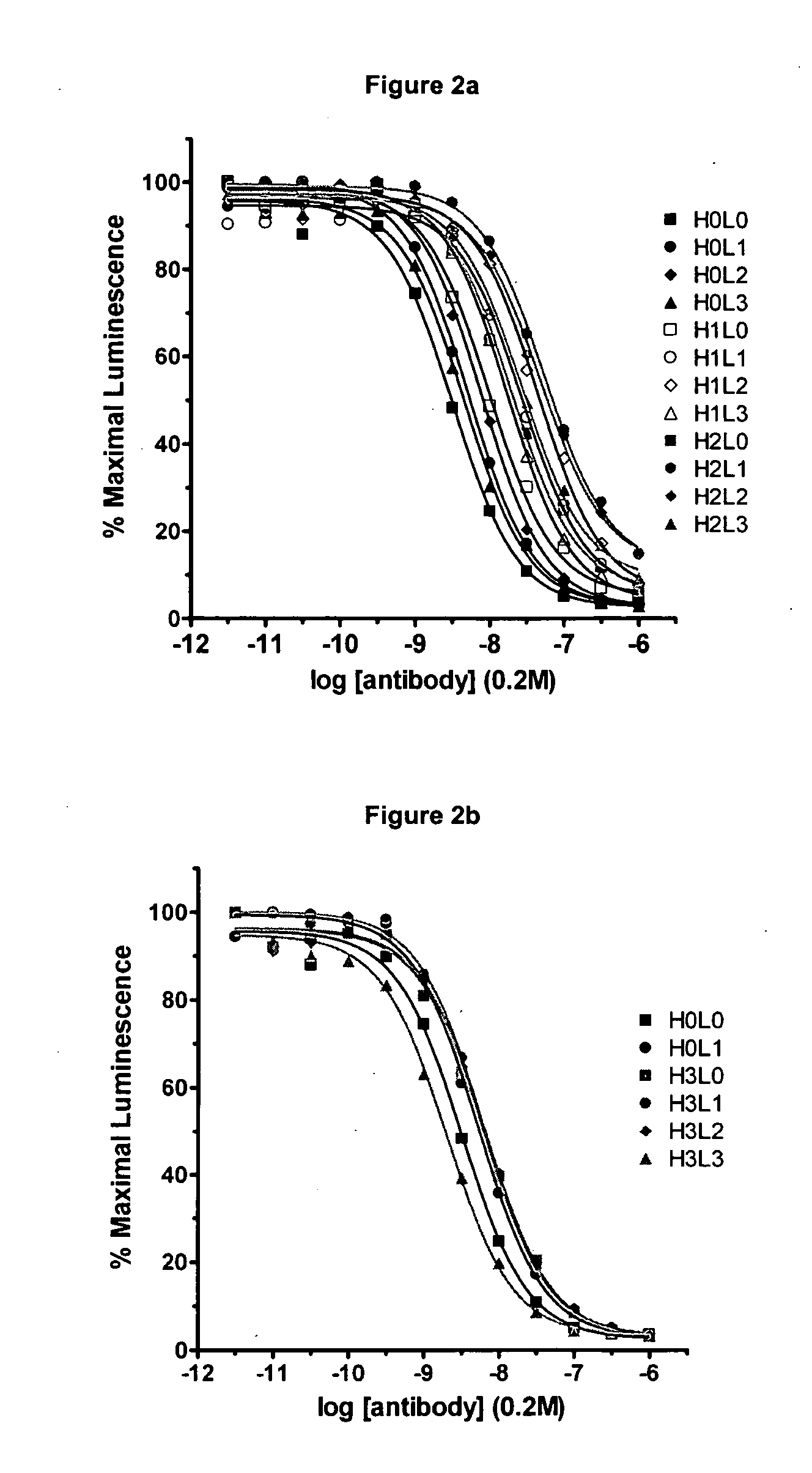
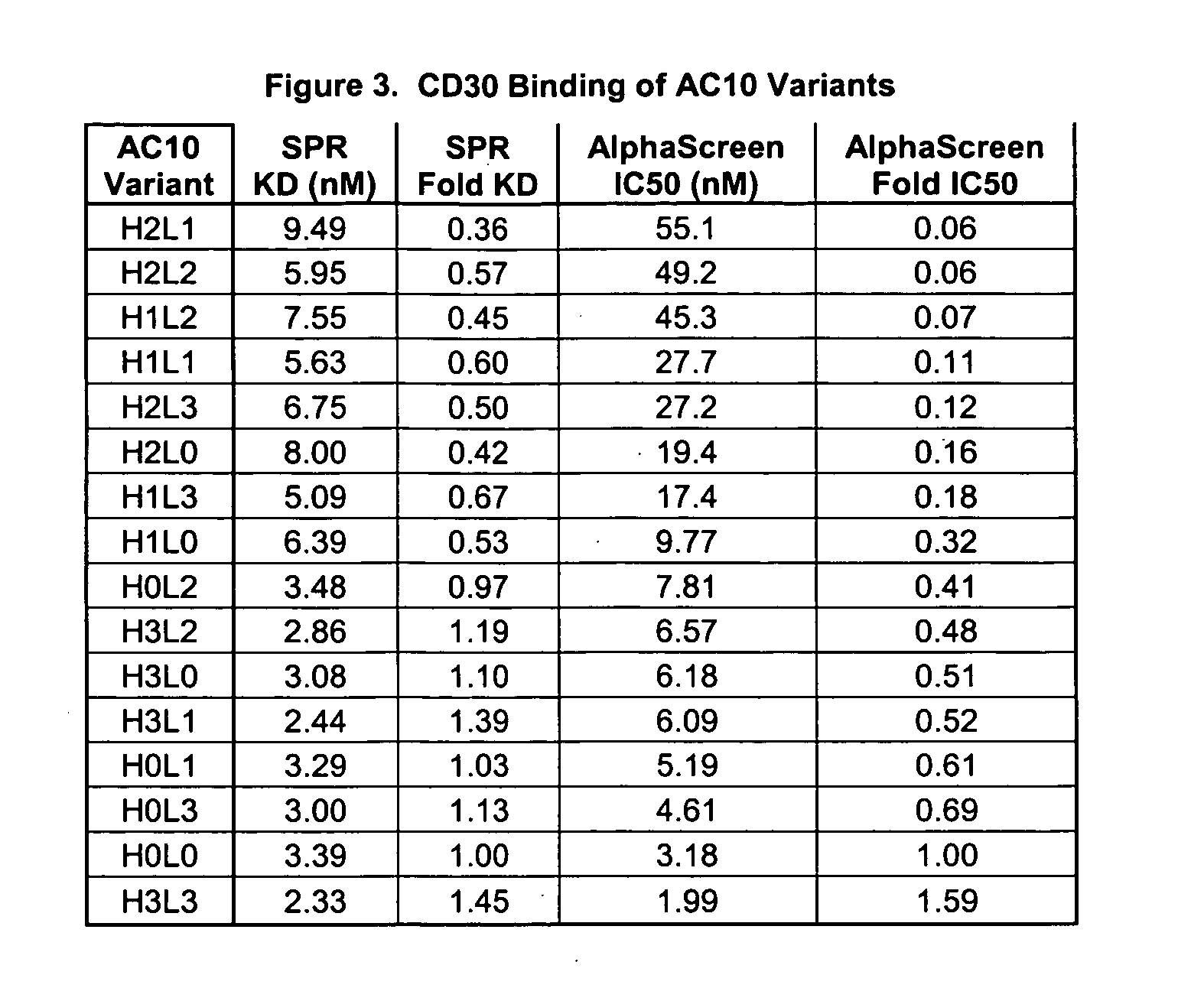
Optimized Anti-CD30 antibodies
InactiveUS20070166309A1Reduced fucosylationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD30Antiantibody
Owner:XENCOR INC
FcGammaRIIB Specific Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090202537A1Balanced functionImmune responseSenses disorderNervous disorderFc(alpha) receptorImmunologic disorders
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer (preferably a B-cell malignancy, particularly, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma), autoimmune disease, inflammatory disease or IgE-mediated allergic disorder. The present invention also encompasses the use of a humanized FcγRIIB antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, in combination with other cancer therapies. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention with a vaccine composition.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
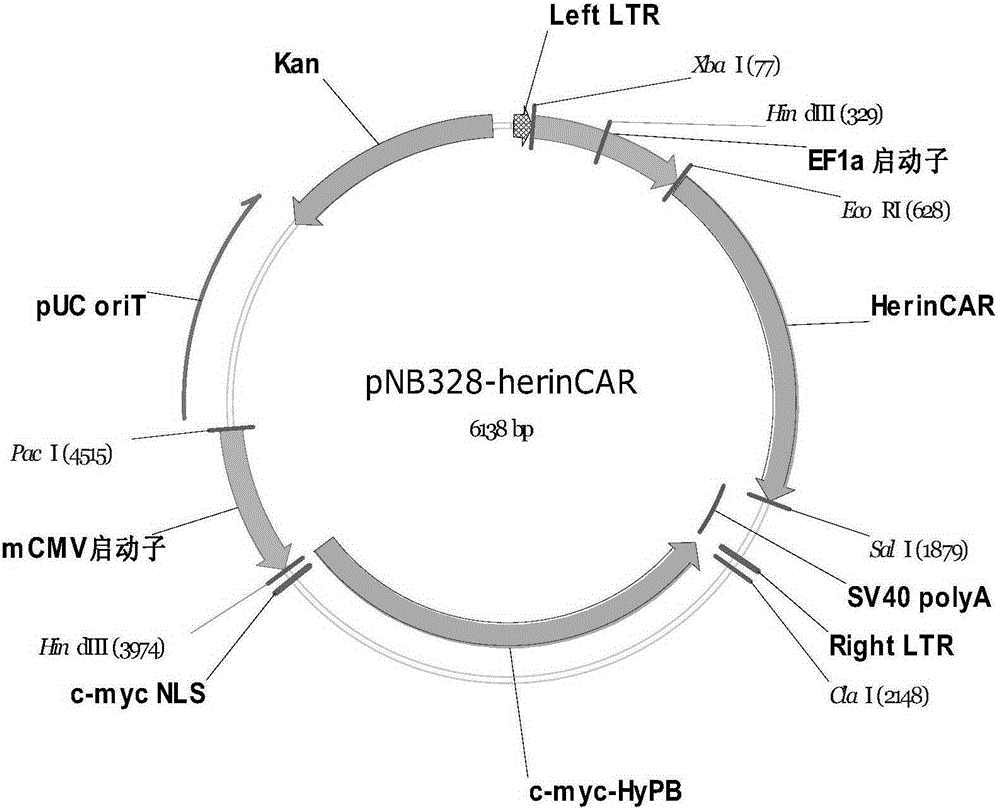
Tumor precision T cell containing efficient killing starting mechanism and application of tumor precision T cell
ActiveCN105331586AActivate proliferationActivate growthImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigen receptorsT lymphocyte
The invention belongs to the fields of immunology and cell biology, and relates to a tumor precision T cell containing an efficient killing starting mechanism and an application of the tumor precision T cell, in particular to a CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) having moderate-affinity binding characteristic with a broad-spectrum expression membrane antigen on the tumor cell surface as well as a new-generation tumor precision T cell, namely, Baize T. T cell activation is started rapidly under the action of the CAR having the moderate-affinity binding characteristic, an activation signal of the CAR is superposed with a TCR (T cell receptor) signal with tumor antigen natural recognition capacity in a CTL (tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte), the CTL is activated to proliferate and grow in a tumor microenvironment, and a tumor cell is killed preciously by the tumor-antigen-specific TCR. The tumor precision T cell has broad anti-tumor application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +2
Optimized anti-CD30 antibodies
InactiveUS20070148171A1Reduced fucosylationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD30Antiantibody
Owner:XENCOR
Affinity based system for detecting particulates in a fluid
InactiveUS20060194264A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusParticulatesMicroparticle
This invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting and quantifying particulate matter suspended in a fluid. Specifically, the invention provides an integrated, affinity-binding based, analytical system comprising a platform for performing an affinity-binding based assay for specifically binding particulates including microbial cells, and a detection means for detecting the particulates specifically bound to a defined surface or chamber comprising the platform. Methods for using the analytical systems of the invention are also provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Methods for discovering molecules that bind to proteins
InactiveUS20130053541A1Inhibit functionPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein targetPeptide ligand
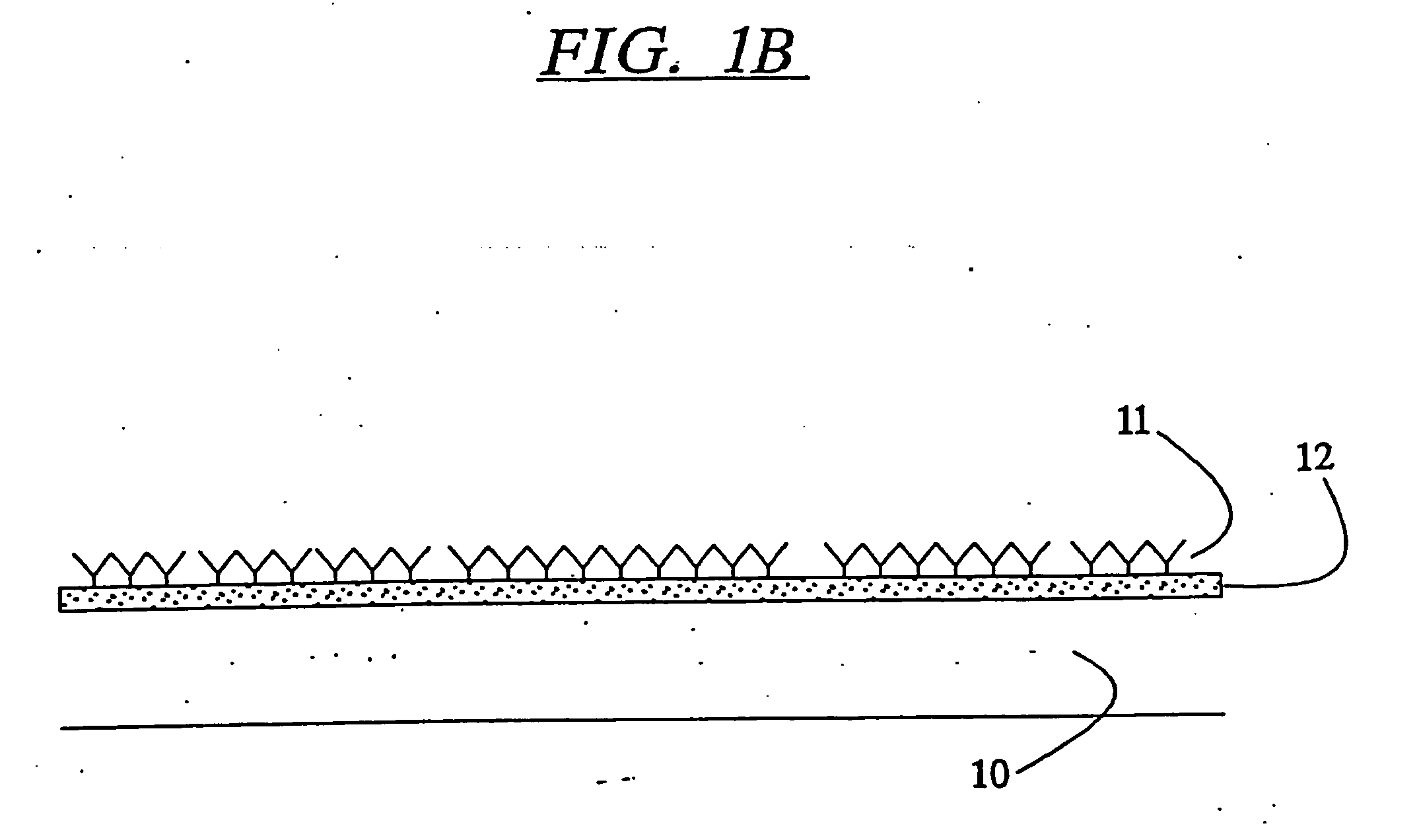
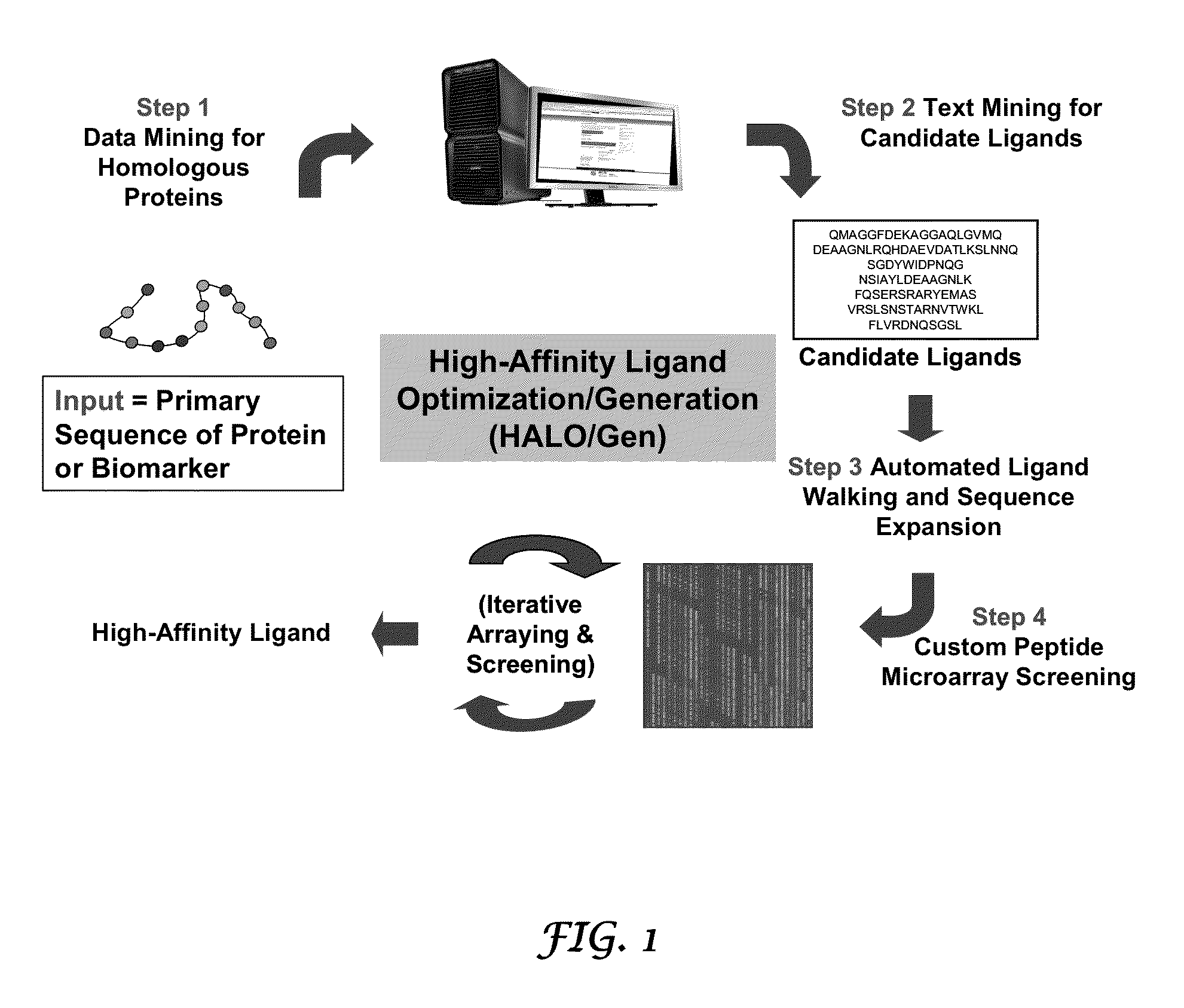
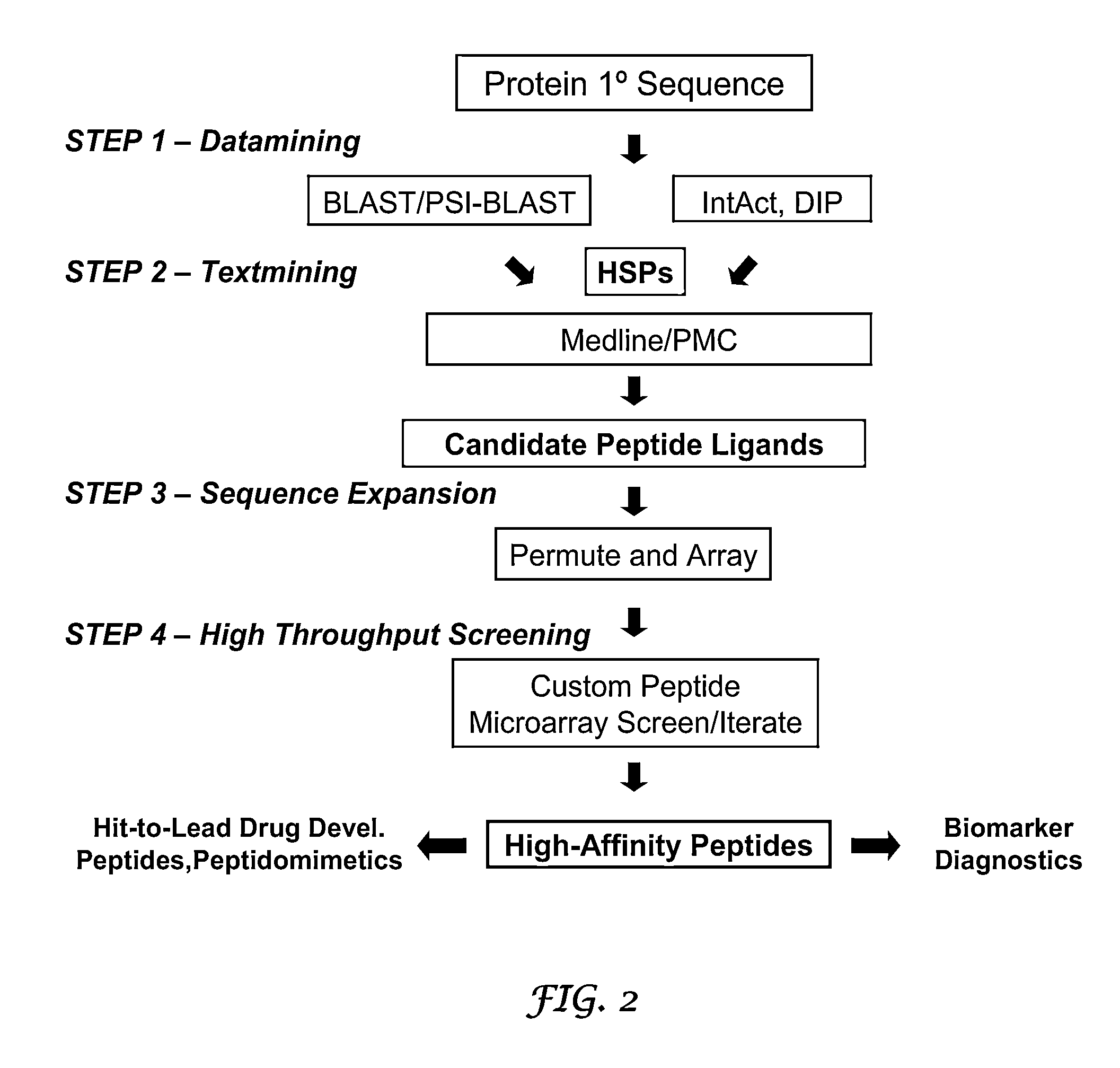
Methods and systems for the discovery of high-affinity peptide ligands and the resulting compositions are described herein. The amino acid sequence of a target protein is used to identify one or more homologous proteins of the target protein. Publications and databases are textmined to retrieve the sequences of peptide ligands that bind to the homologues or the target protein. Complementary proteins, which are proteins that bind to the target or homologous proteins or to DNA, and their target protein- or DNA-binding regions may also be identified. These candidate ligands are predicted to have a high probability of binding to the target protein or the DNA. The library of candidate peptide ligands is modulated by substituting native amino acid residues with suitable amino acids, thus increasing the explored protein space in a knowledge-based manner. Peptides designed in the modulation step are experimentally screened to identify high-affinity binding ligands, and further optimized through iterative application of the modulation and screening steps.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com