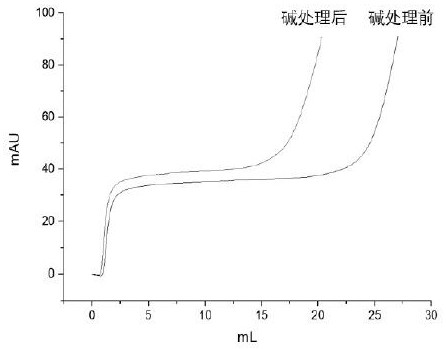
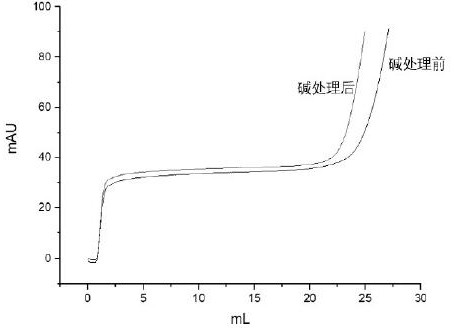
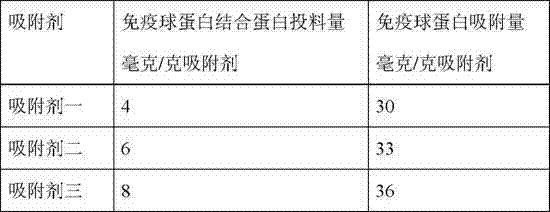
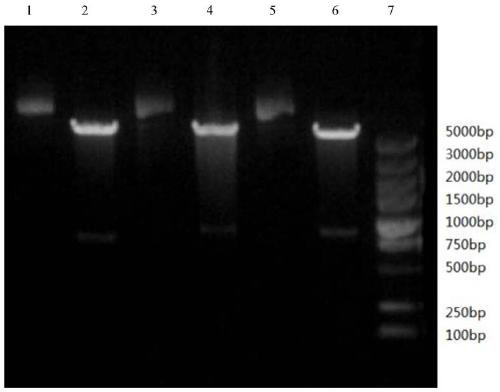
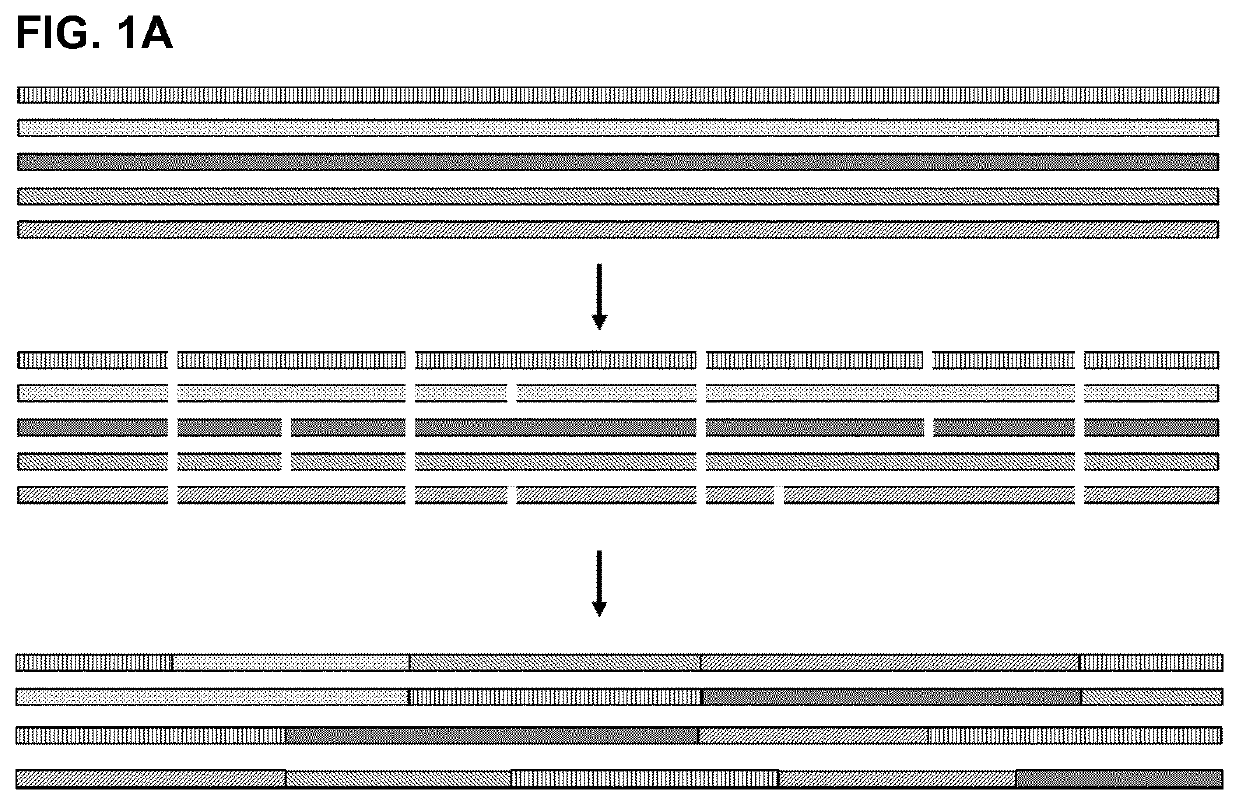
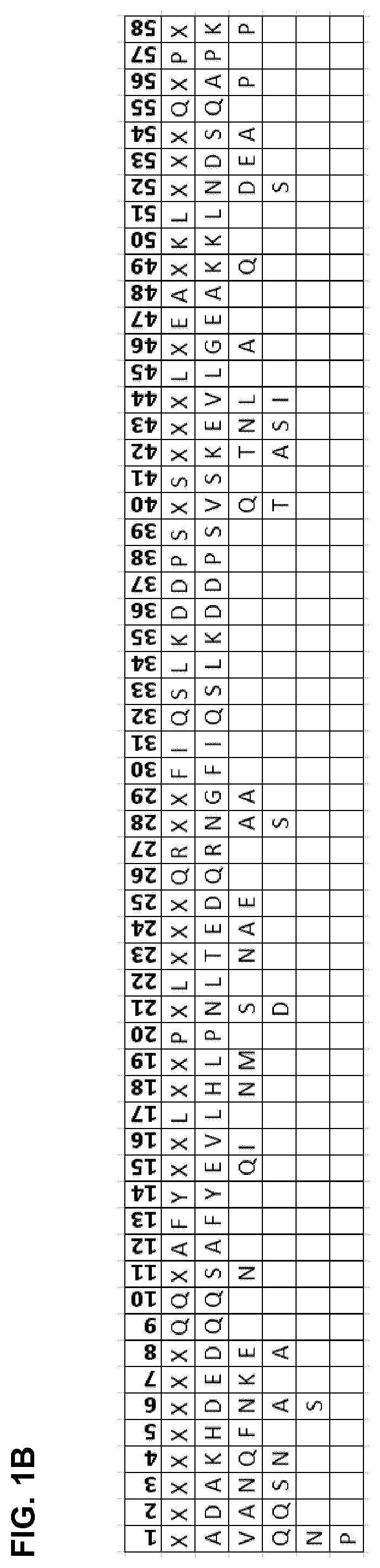
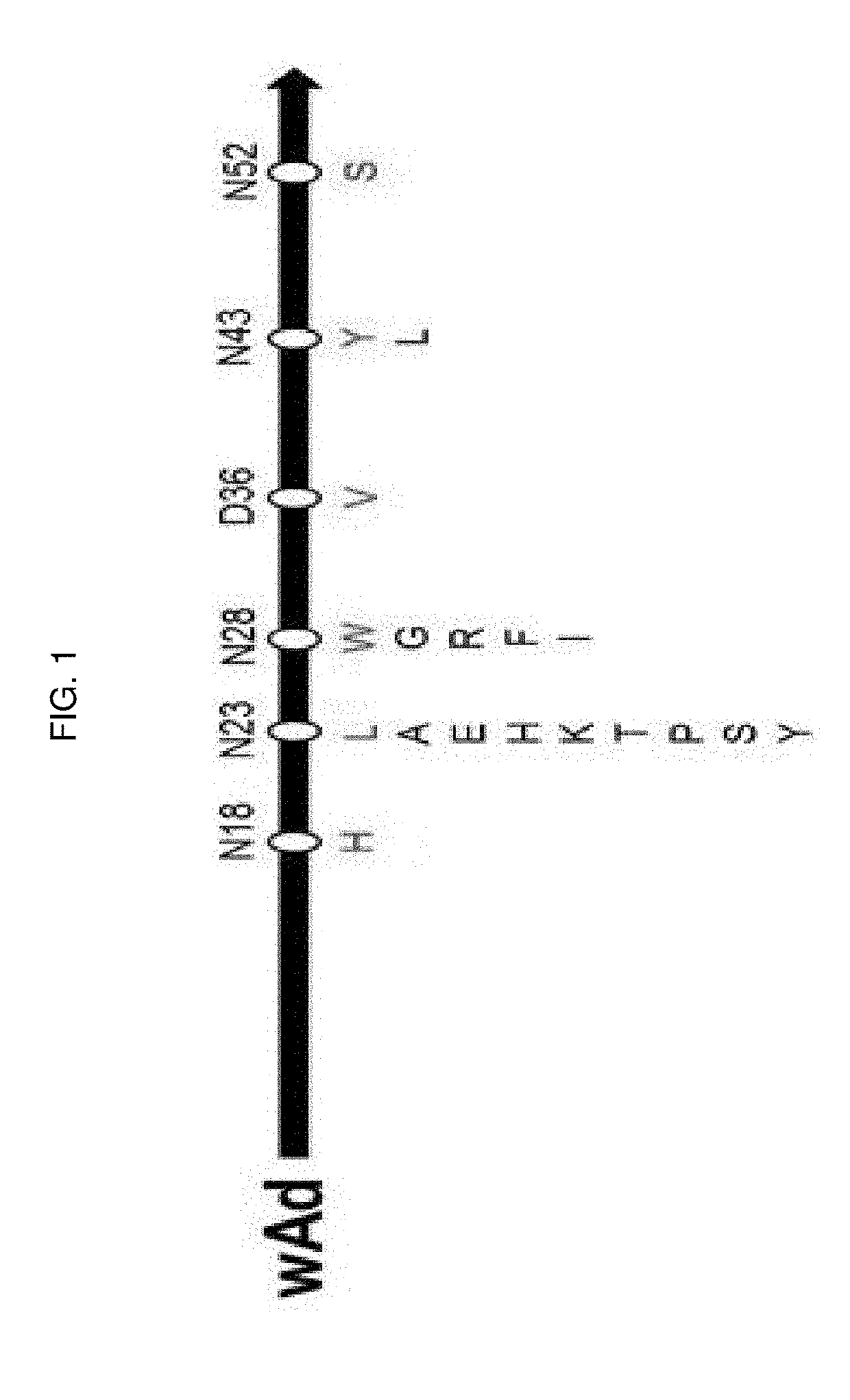
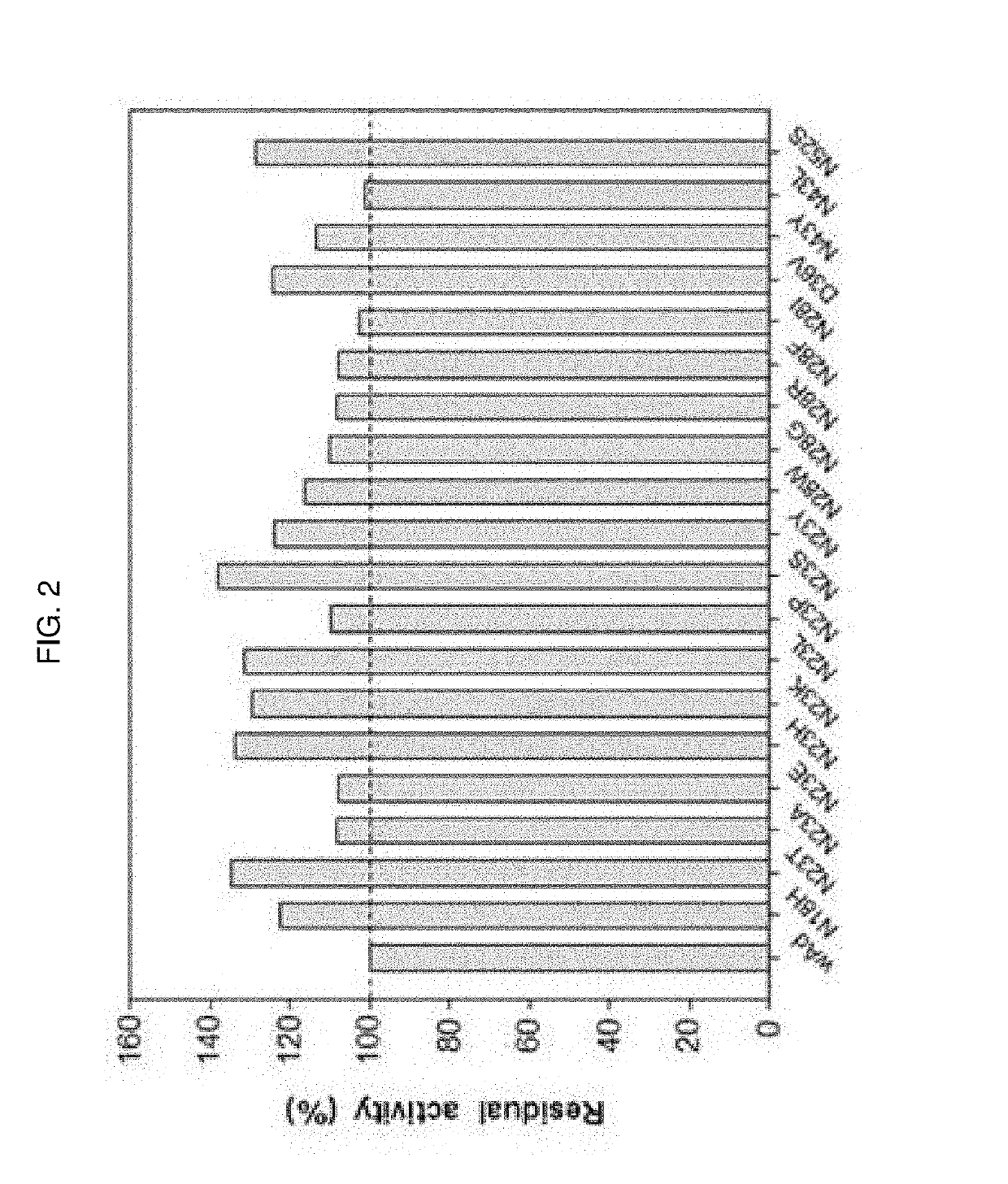
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Immunoglobulin-binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
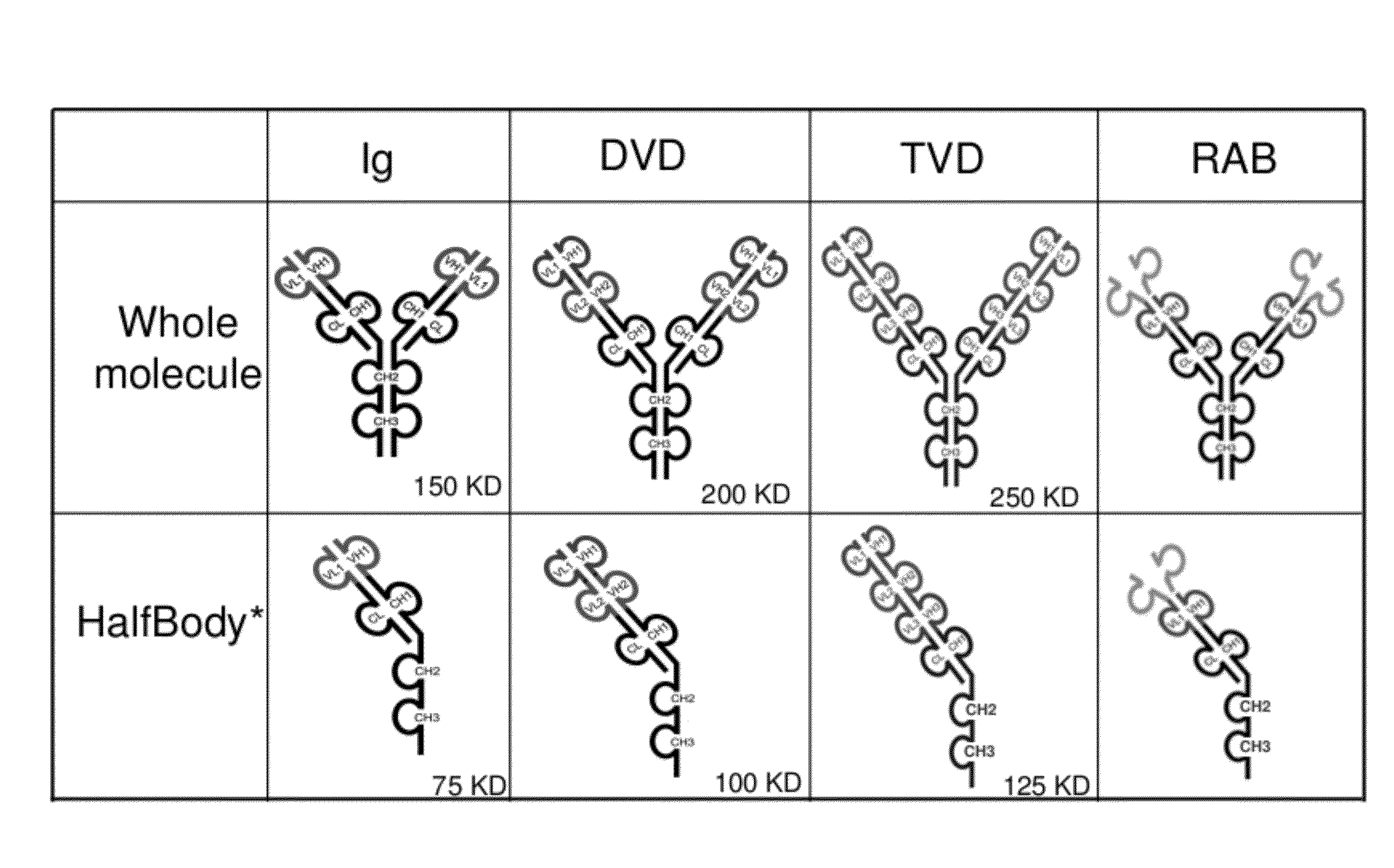
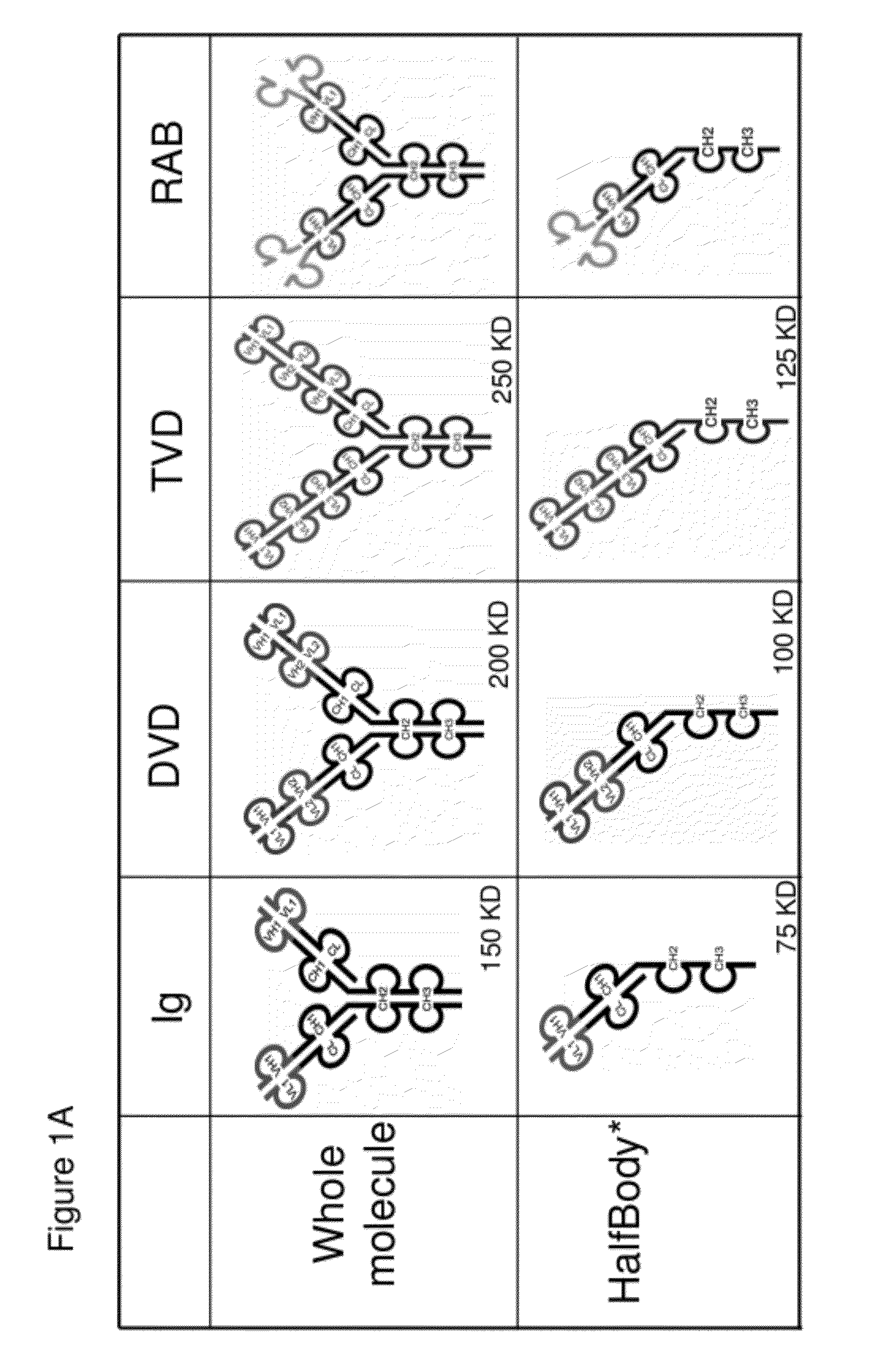
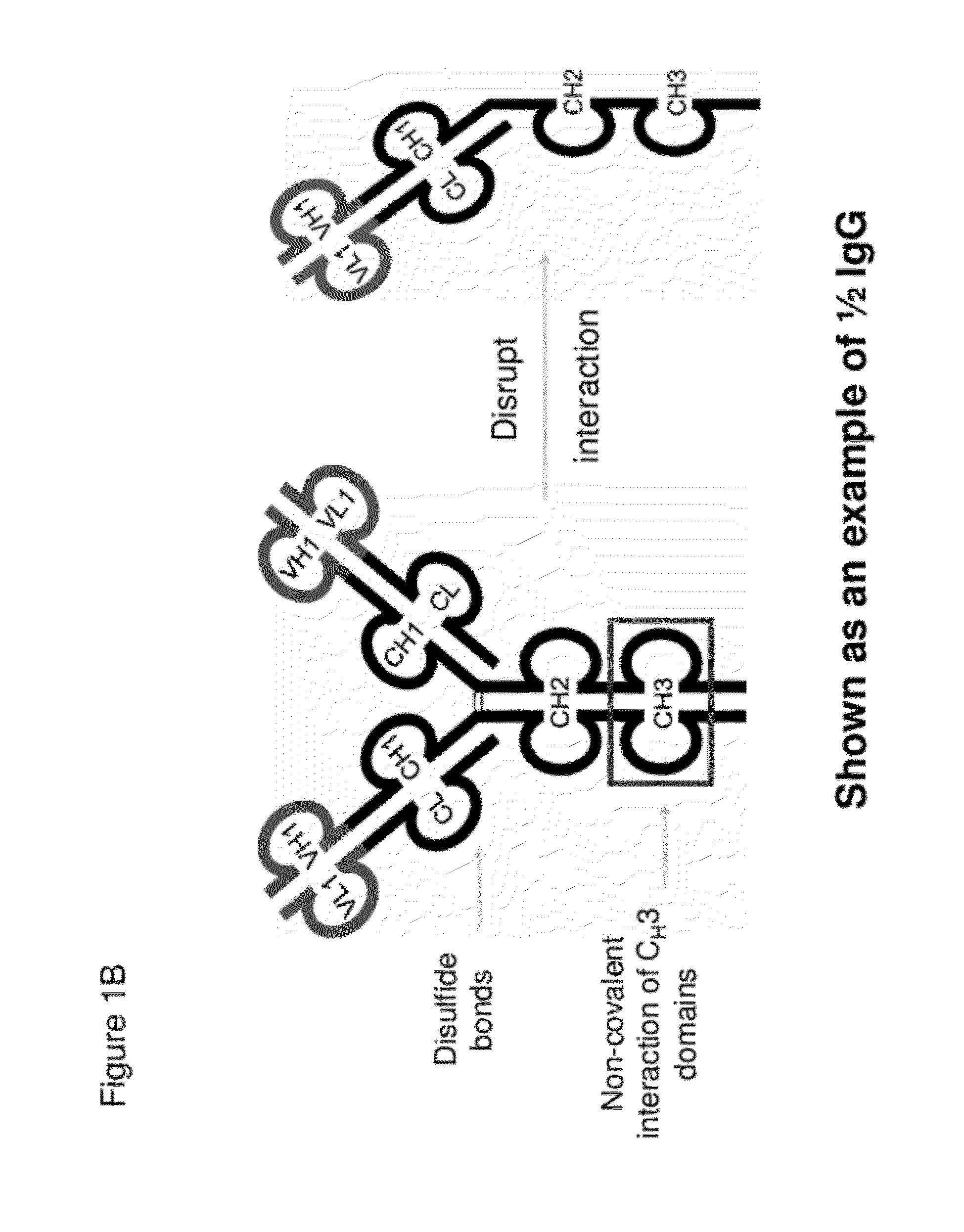
Half immunoglobulin binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120201746A1Altered pharmacokineticAltered pharmacodynamic propertyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody Binding SiteBinding site
The invention provides compositions, methods, and kits related to half-Ig binding proteins that include a functional antibody binding site and a CH3 domain wherein the CH3 domain includes at least one mutation to inhibit CH3-CH3 dimerization.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Mutant protein
InactiveUS20060194950A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesBacteriaSerum immunoglobulinsMutated proteinComplementarity determining region
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding protein
ActiveUS20050143566A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesSerum immunoglobulinsComponent separationComplementarity determining regionChemical stability
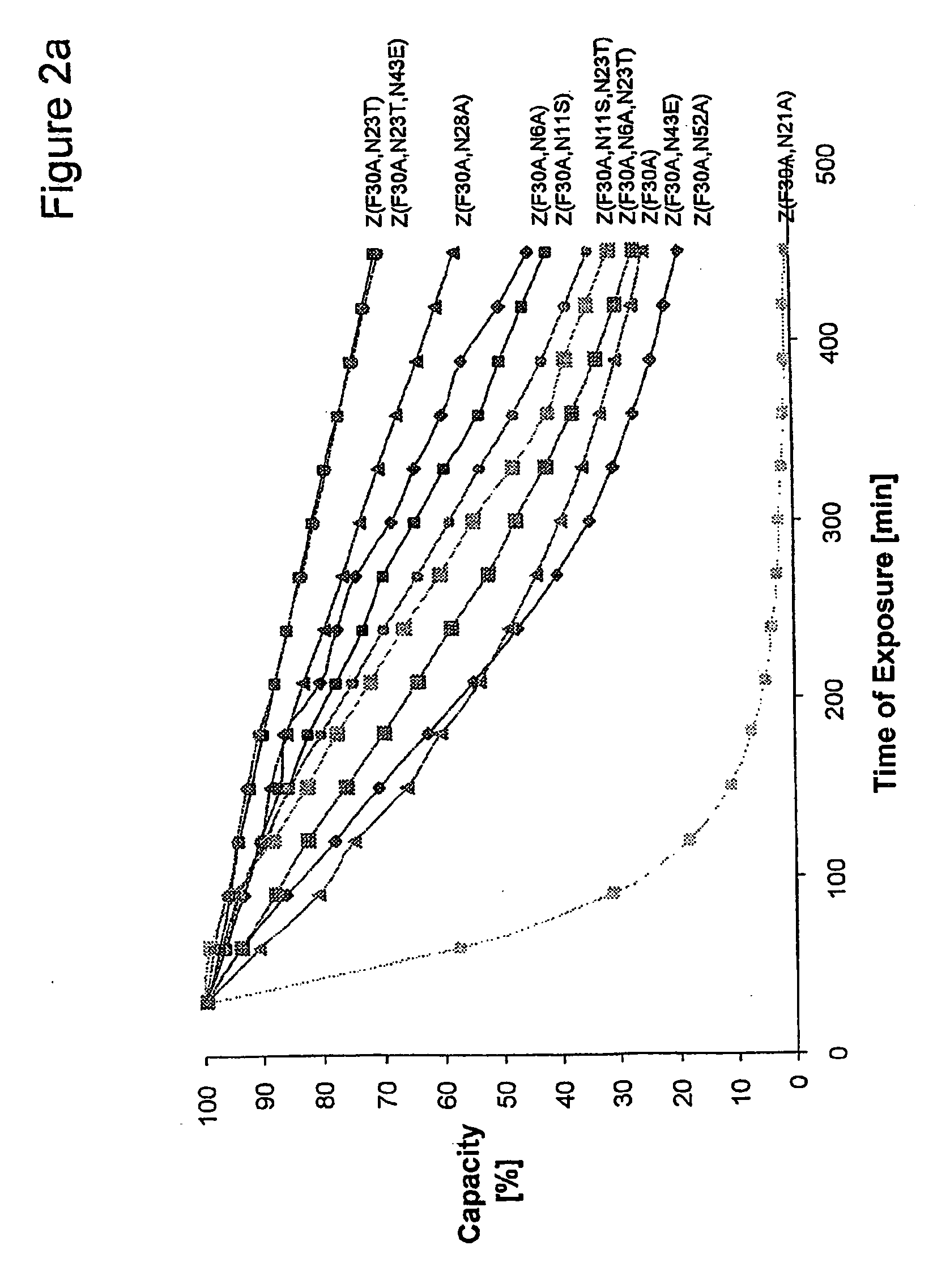
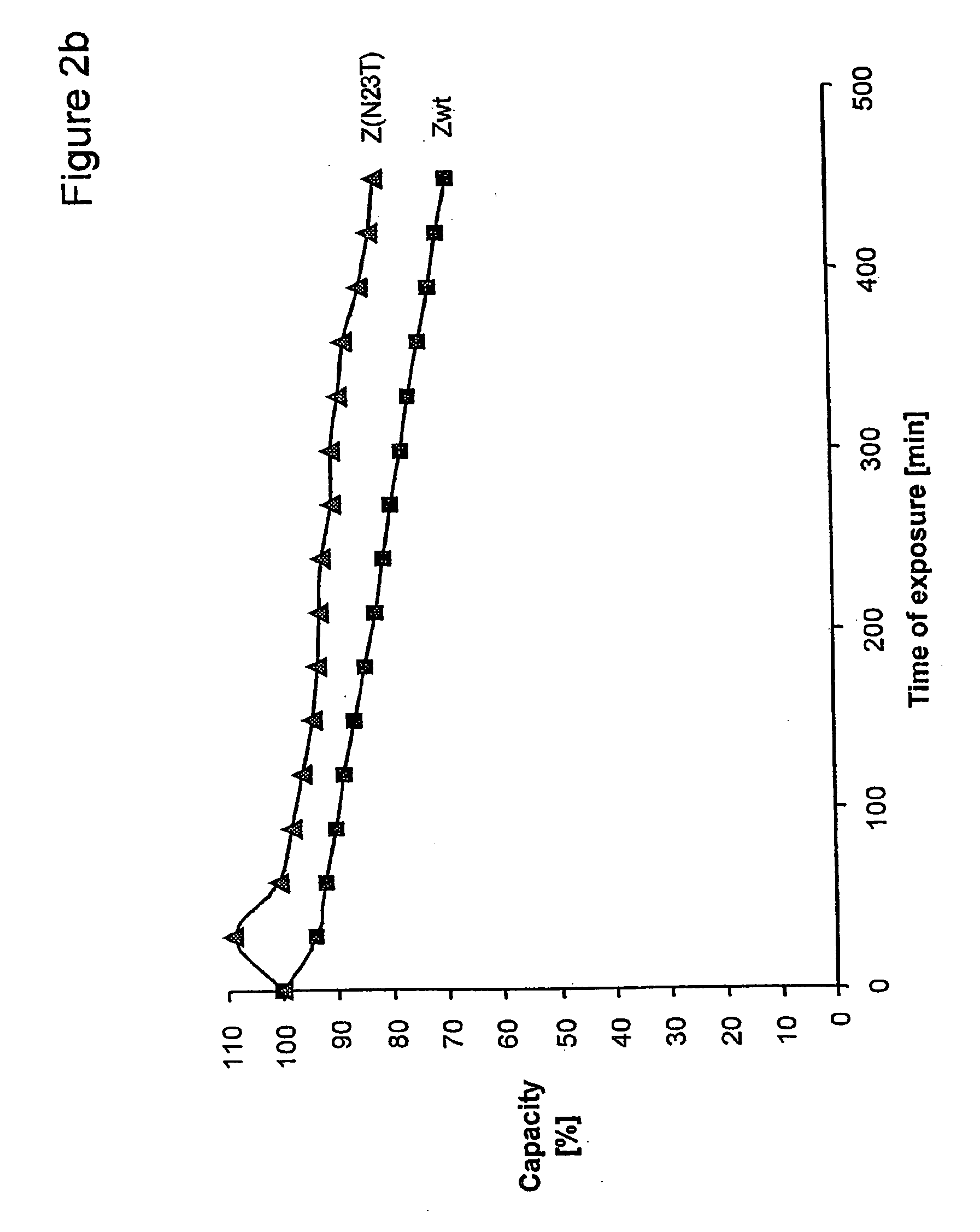
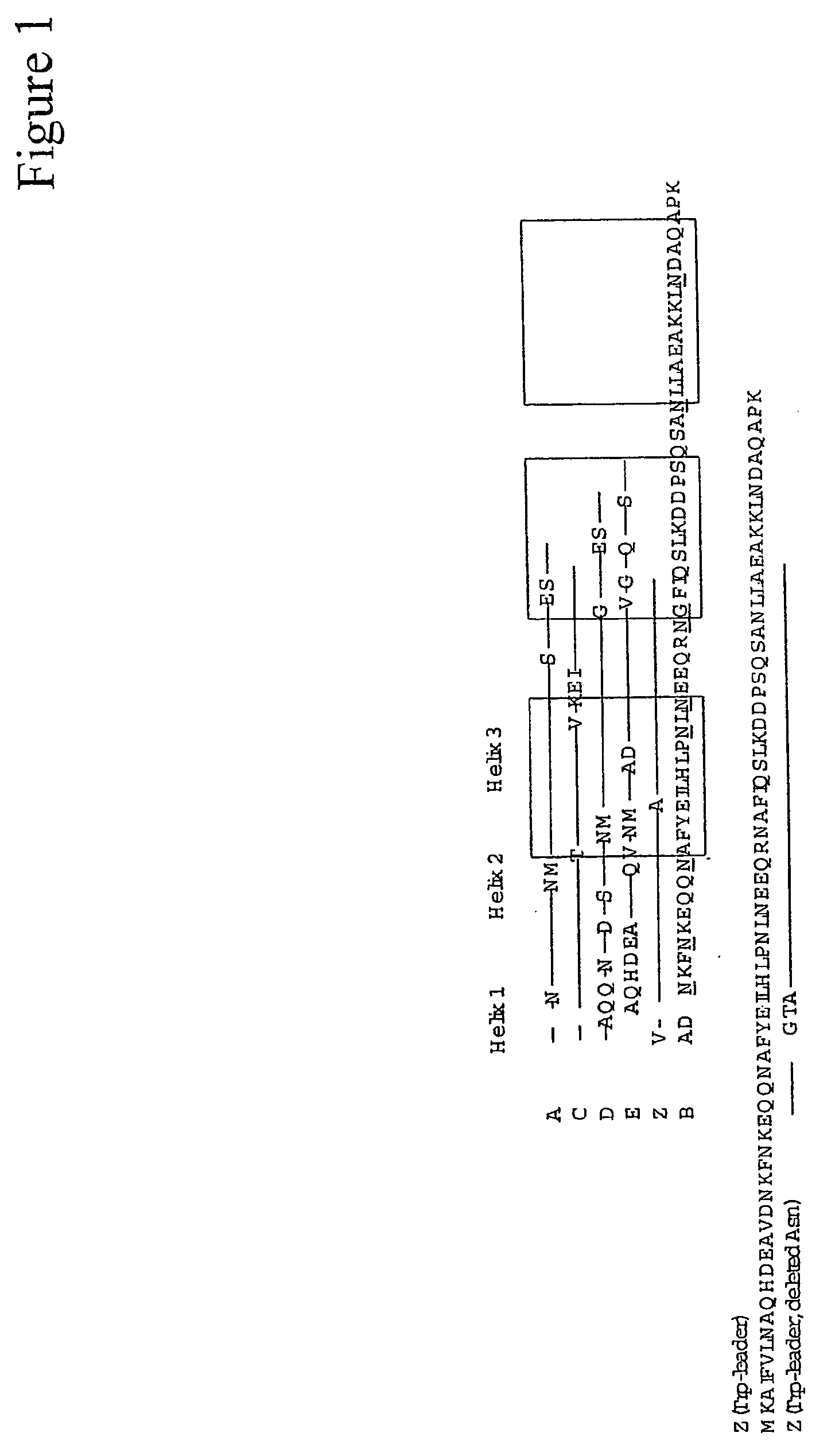
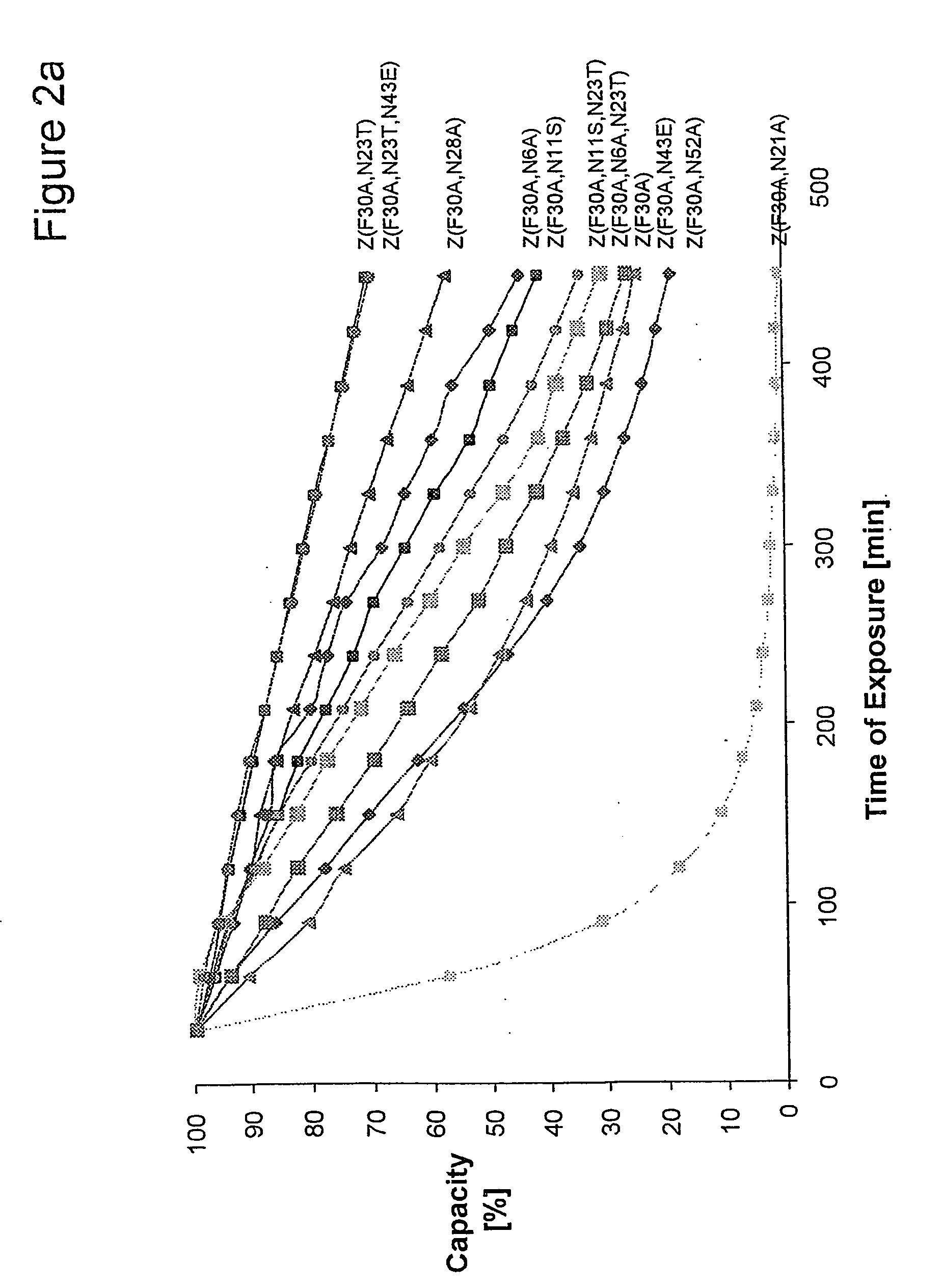
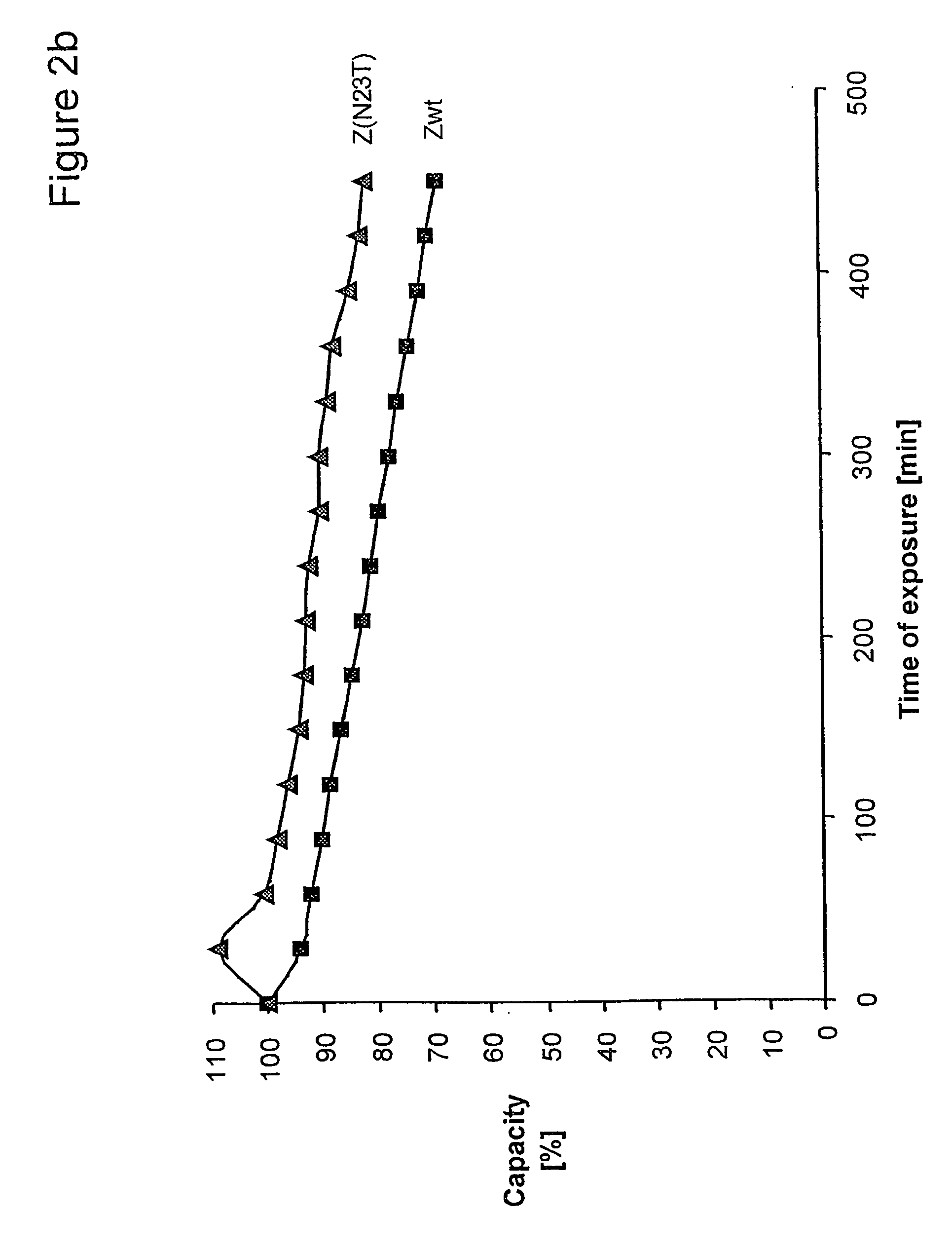
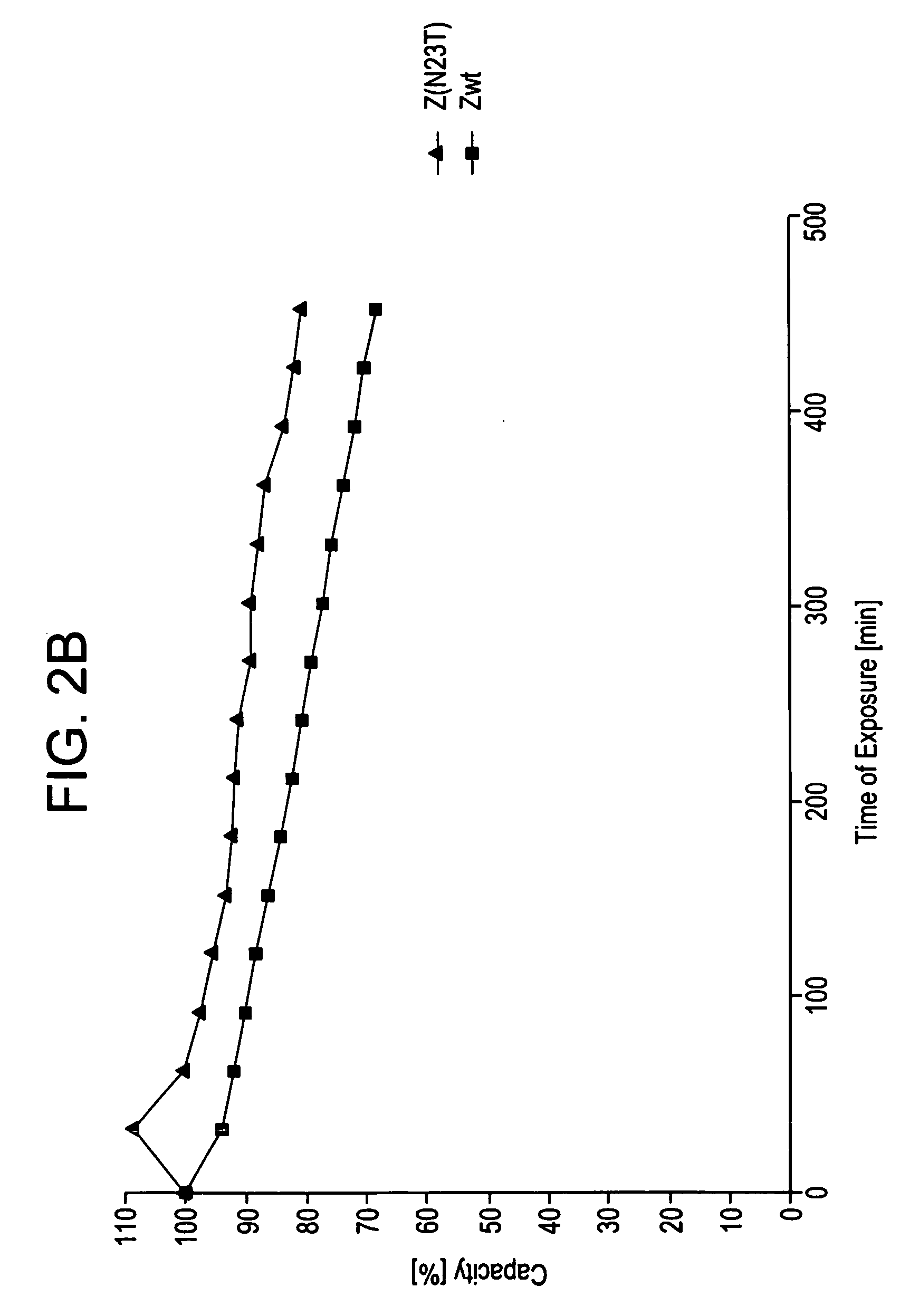
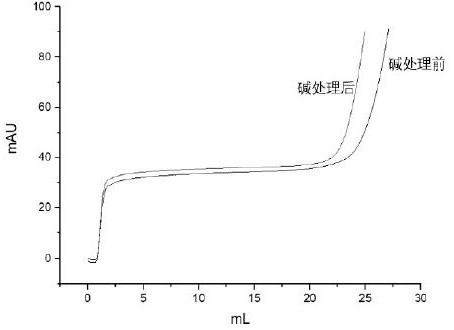
The present invention relates to an immunoglobulin-binding protein, wherein at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine or aspartic acid, which mutation confers an increased chemical stability at pH-values of up to about 13-14 compared to the parental molecule. The protein can for example be derived from a protein capable of binding to other regions of the immunoglobulin molecule than the complementarity determining regions (CDR), such as protein A, and preferably the B-domain of Staphylococcal protein A. The invention also relates to a matrix for affinity separation, which comprises an immunoglobulin-binding protein as ligand coupled to a solid support, in which protein ligand at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Protein ligands
ActiveUS20060194955A1Retention characteristicReduce leakageImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingComplementarity determining regionStaphylococcus
The present invention relates to the use of an alkali-stable protein, wherein at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine or aspartic acid, which mutation confers an increased chemical stability at pH-values of up to about 13-14 compared to the parental molecule. The protein can for example be derived from a protein capable of binding to other regions of the immunoglobulin molecule than the complementarity determining regions (CDR), such as protein A, and preferably the B-domain of Staphylococcal protein A. The invention also relates to a matrix for affinity separation, which comprises an immunoglobulin-binding protein as ligand coupled to a solid support, in which protein ligand at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Chromatography matrices including novel staphylococcus aureus protein a based ligands
ActiveUS20130046056A1Reduce lossesLarge degree of fragmentationSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus protein A
The present invention relates to chromatography matrices including ligands based on one or more domains of immunoglobulin-binding proteins such as, Staphylococcus aureus Protein A (SpA), as well as methods of using the same.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Protein ligands
ActiveUS7709209B2Retention characteristicReduce leakageImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingComplementarity determining regionChemical stability
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Synthetic method used for preparing adsorbent for clearing pathogenic antibody by oxidizing periodate
ActiveCN102000550ASimple methodEase of mass productionOther chemical processesAntibody adsorptionOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a synthetic method used for preparing an adsorbent for clearing a pathogenic antibody by oxidizing periodate, and discloses a method for preparing a protein immunoadsorption material by oxidizing the periodate by taking agarose gel as a carrier. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing aldehyde group-containing agarose gel by oxidizing the agarose gel by using the periodate; coupling the aldehyde group-containing agarose gel and immunoglobulin binding protein; and blocking a material and reducing or reducing directly without blocking to obtain the immunoadsorption blood purification material. The method has the characteristics of simple process, environmental friendliness, low cost and the like; and simultaneously the product has high specificity, adsorptive property, regenerability and the like, and can be used for clinical immunoadsorption treatment practically.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KONCEN BIOSCI
Chromatography matrices including novel Staphylococcus aureus protein A based ligands
ActiveUS8754196B2Reduce lossesLarge degree of fragmentationPeptide/protein ingredientsSolid sorbent liquid separationStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus bacteria
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS20150080554A1Optimize purification stepsInhibition formationOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationThreonineHistidine
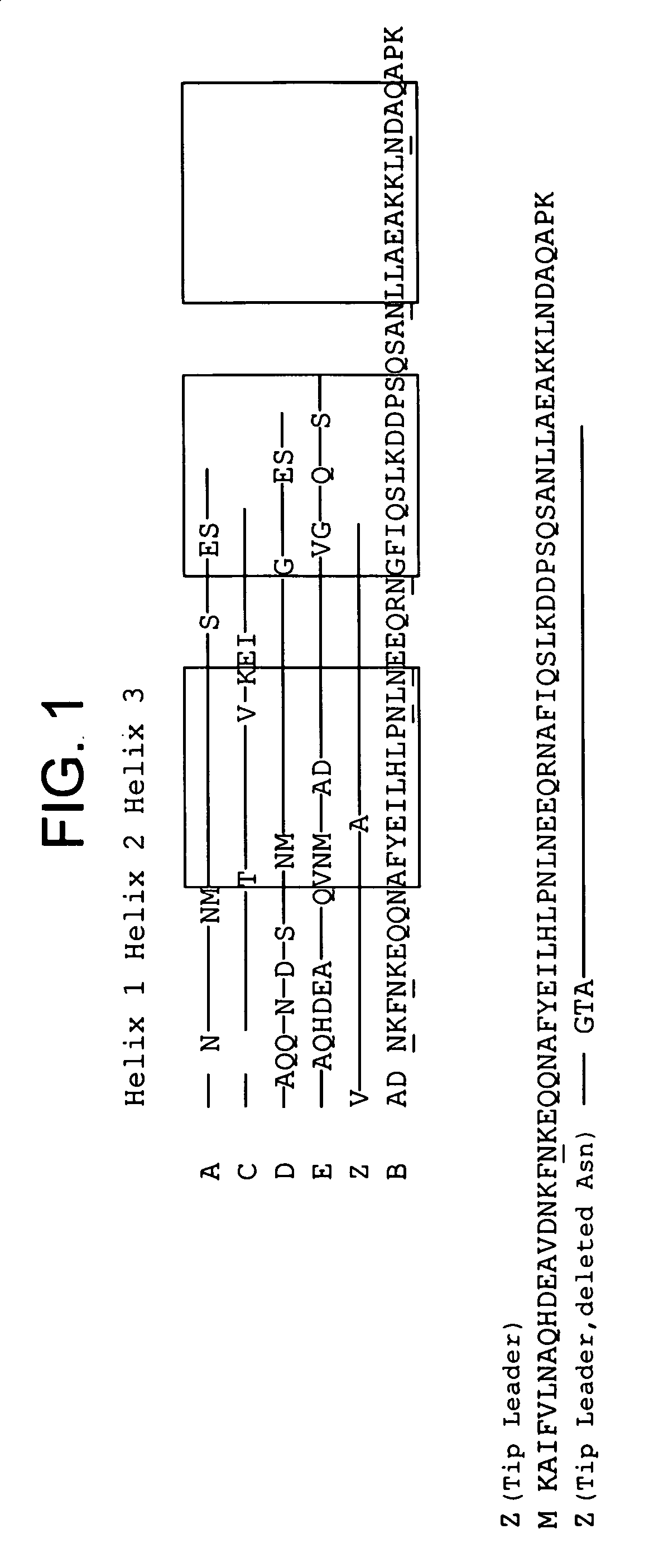
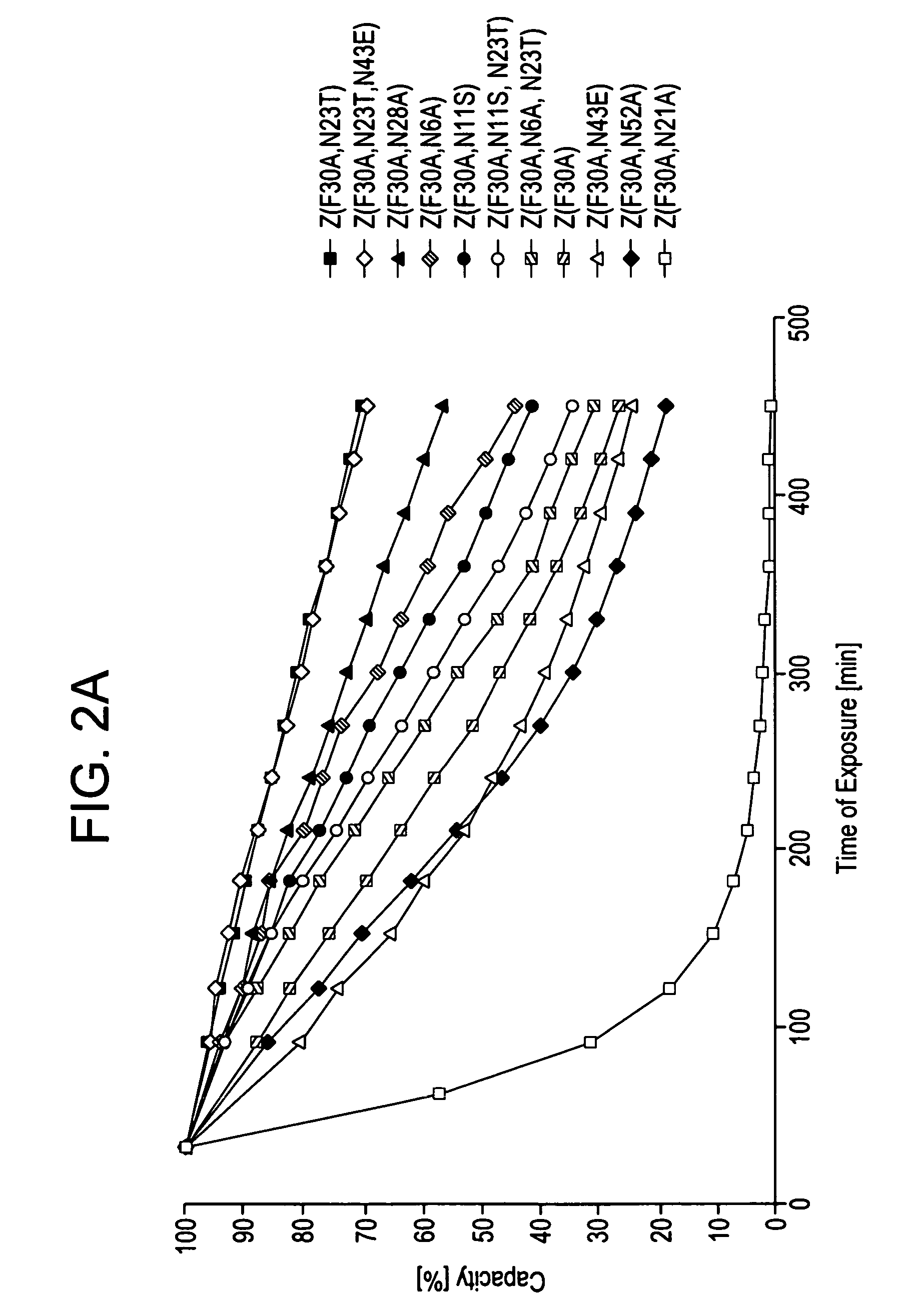
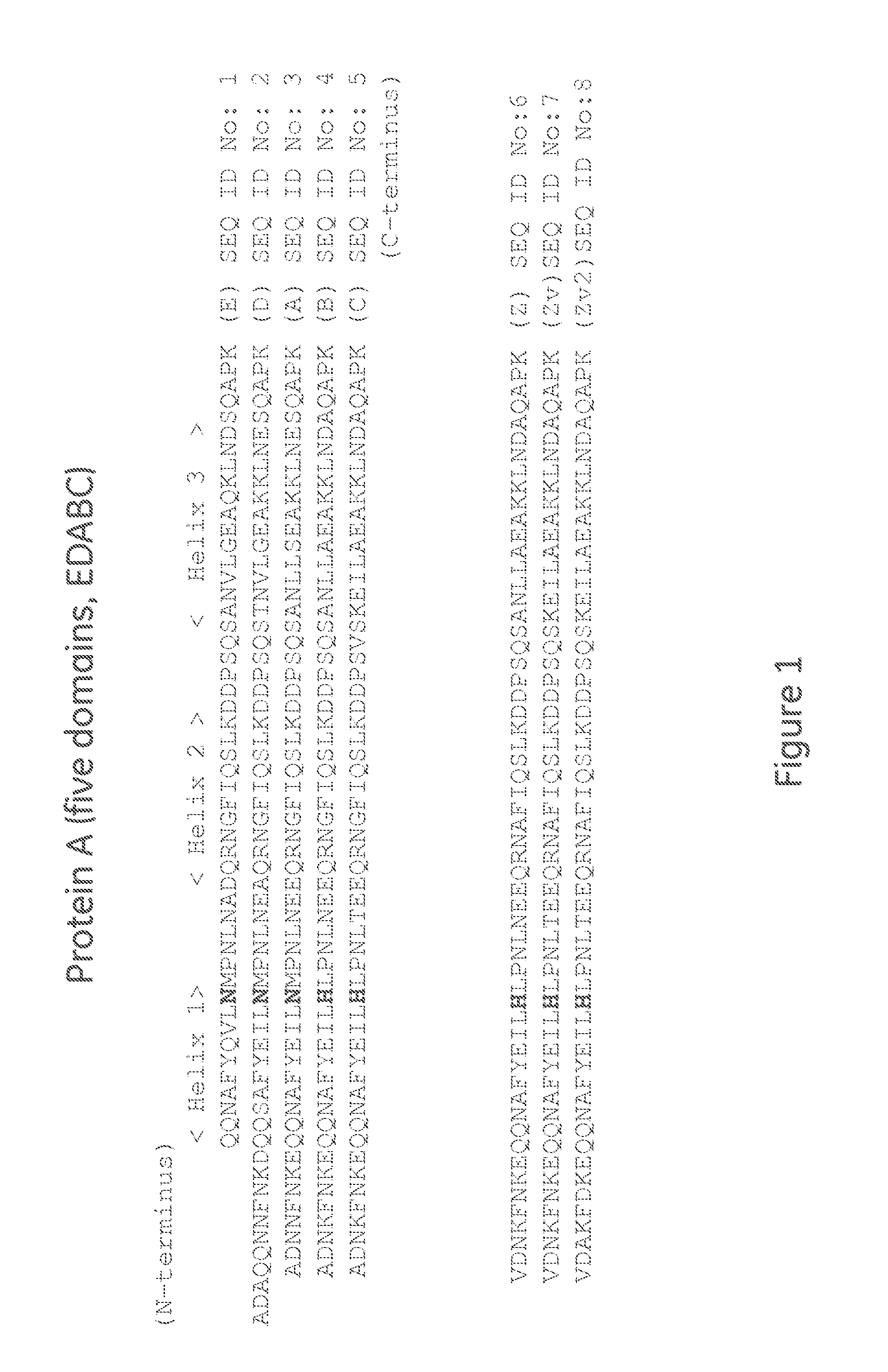
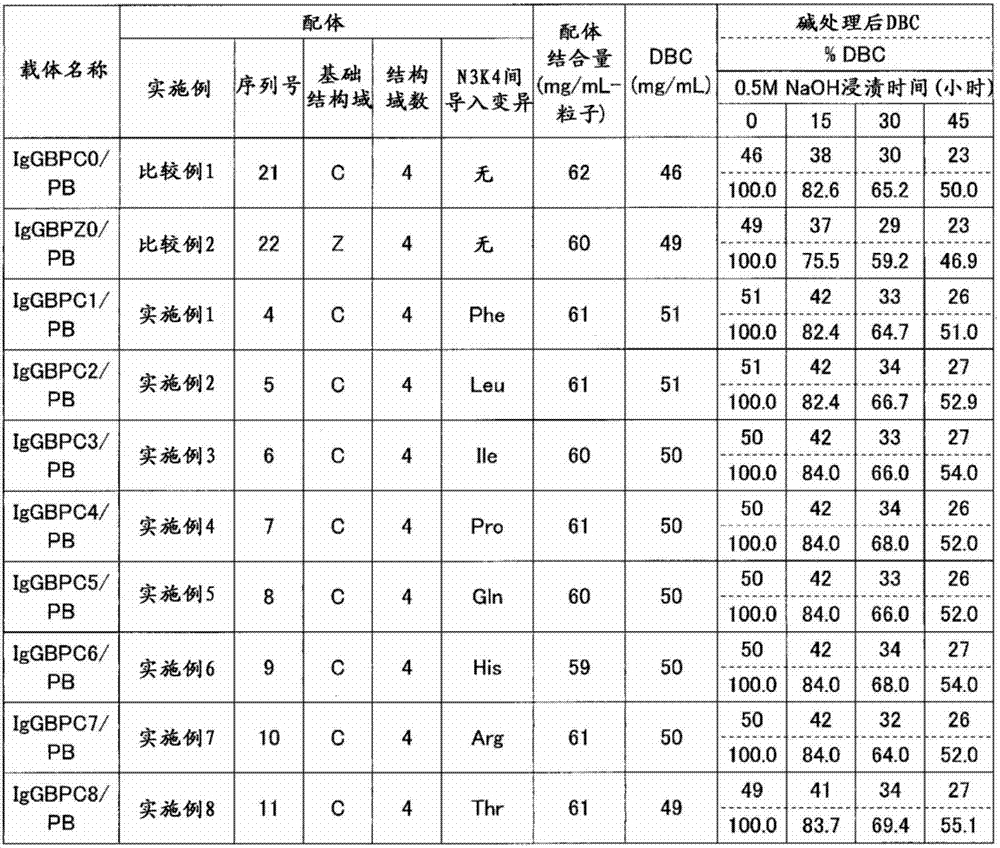
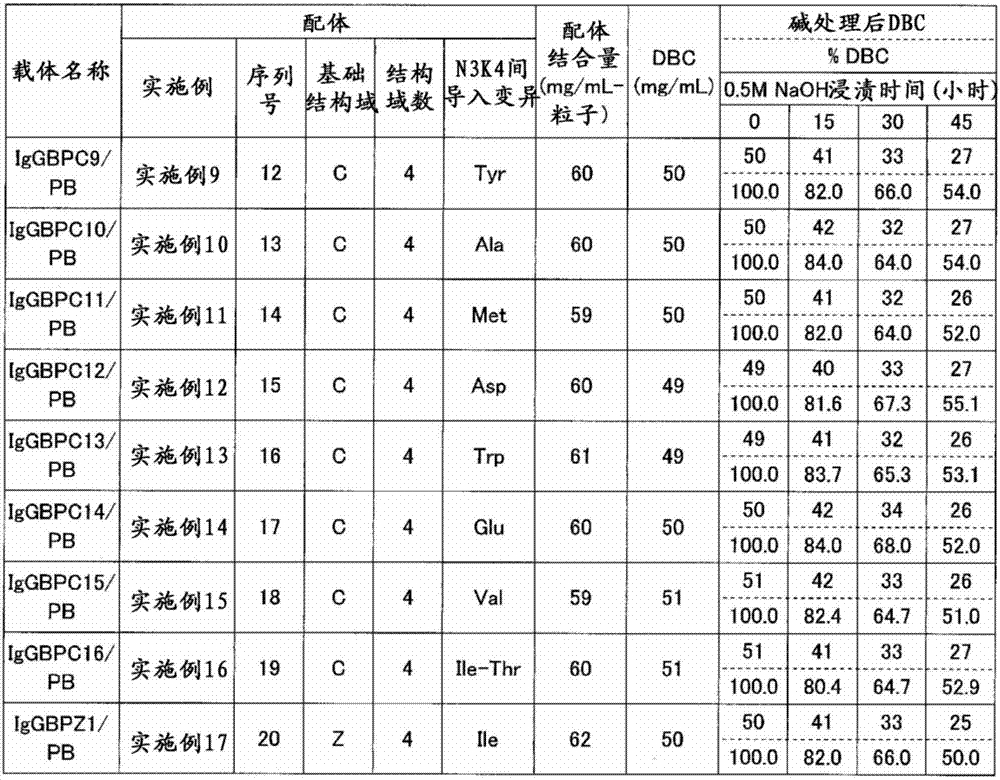
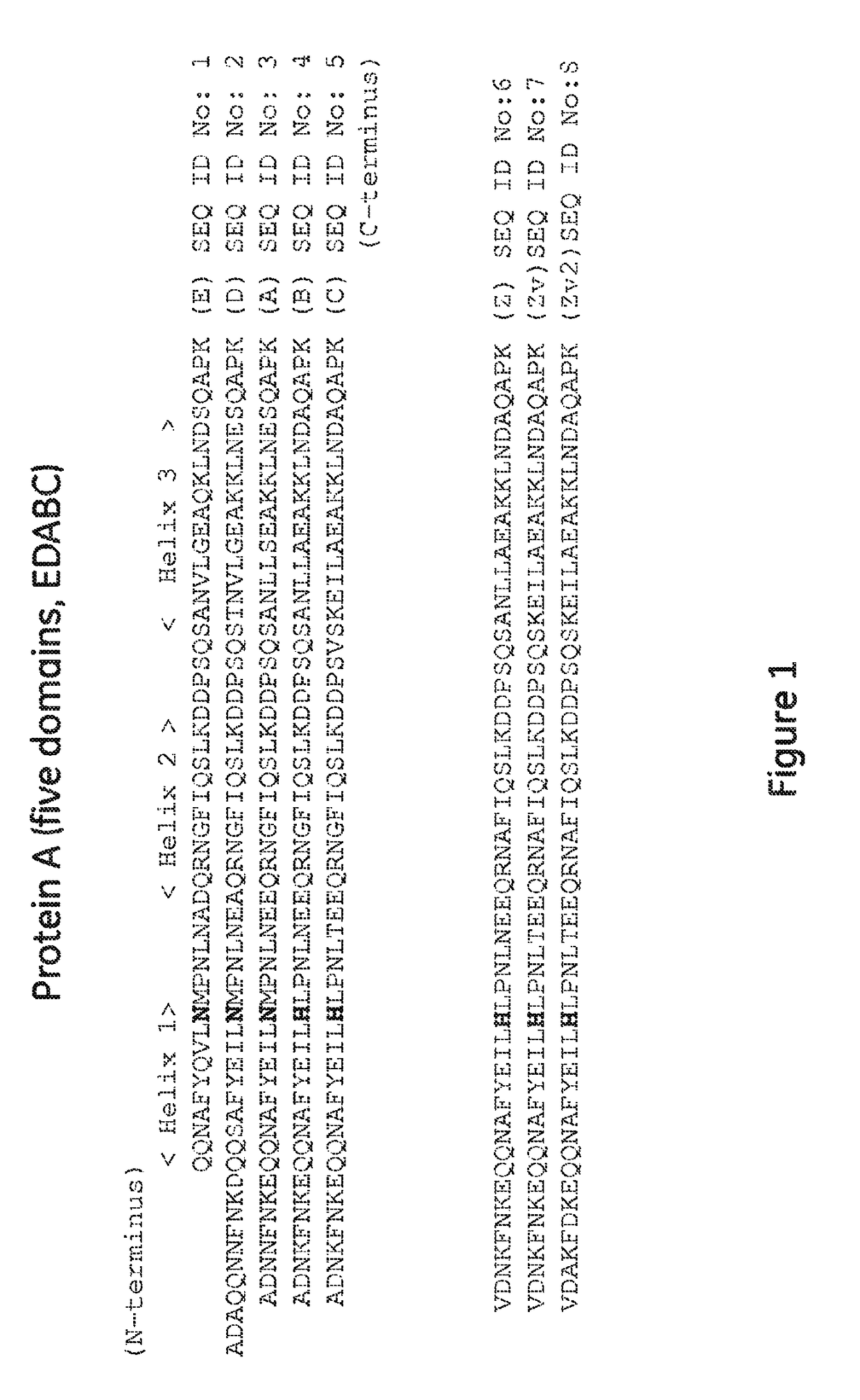
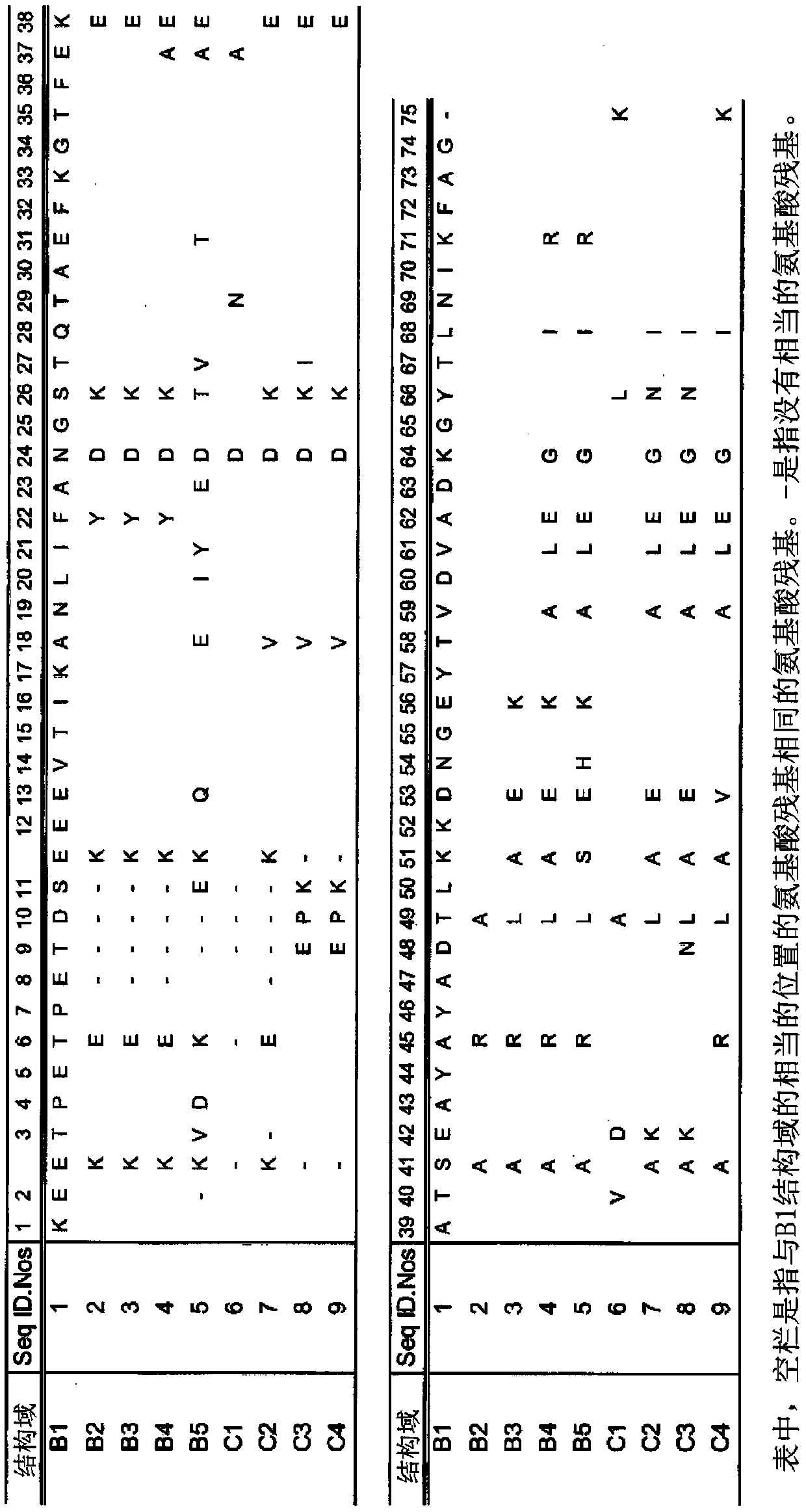
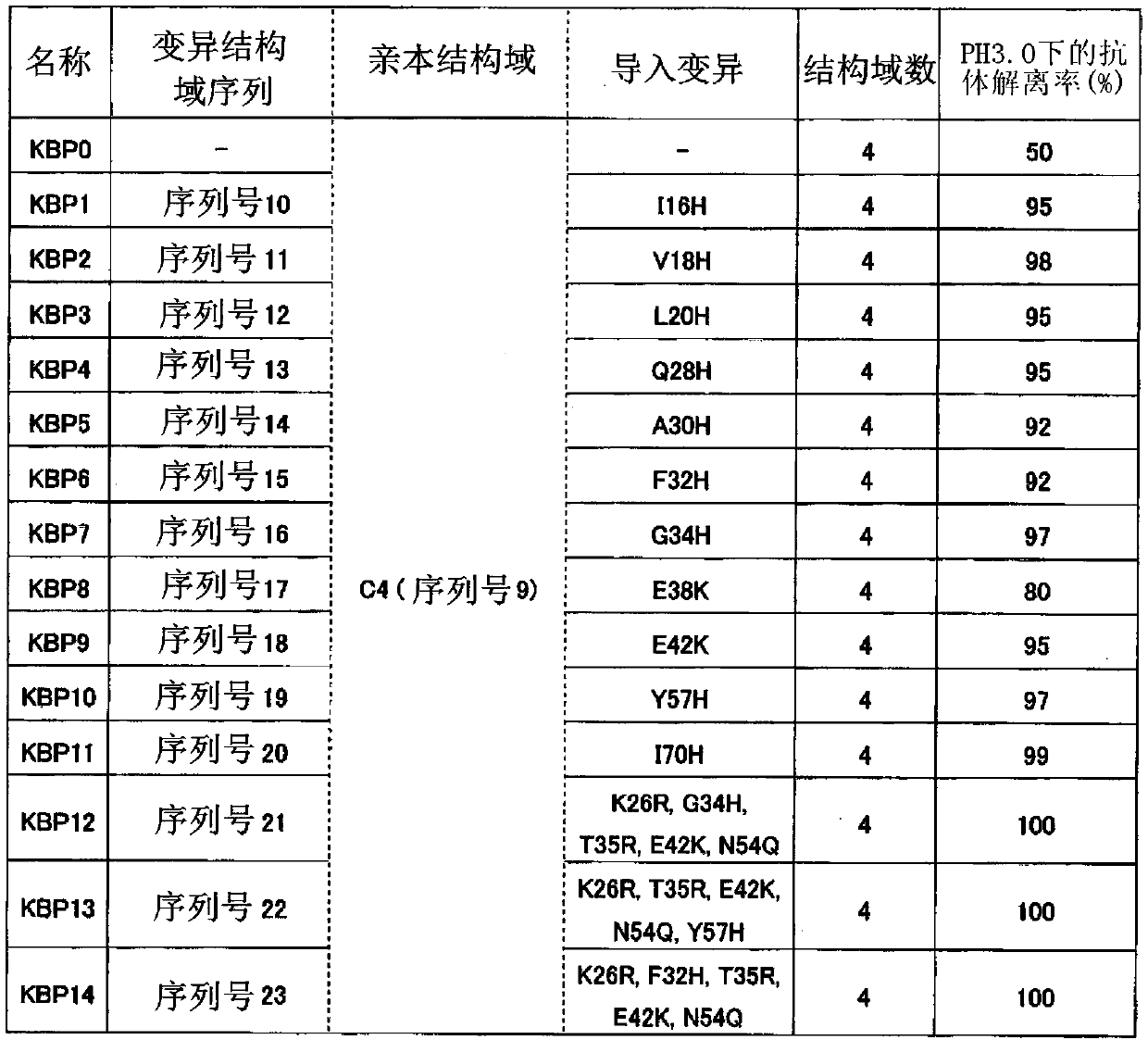
The invention discloses an immunoglobulin-binding protein comprising one or more mutated immunoglobulin-binding domains (monomers) of staphylococcal Protein A (E, D, A, B, C) or protein Z or a functional variant thereof, wherein in at least one of the one or more mutated monomers, the asparagine or histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of Protein A or of Protein Z has been deleted or substituted with a first amino acid residue which is not proline or asparagine and wherein, if the amino acid residue at position 57 is proline and the amino acid residue at position 28 is asparagine, then the amino acid residue at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of protein A or of protein Z is not serine, threonine or lysine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Immunoglobulin-binding protein and affinity carrier using same
PendingCN107429244AImprove bindingReduced dynamic binding capacityFungiBacteria1-aminohydantoinStaphylococcus aureus protein A
Provided is an affinity chromatography carrier in which high immunoglobulin-binding capacity and alkali resistance are maintained. Provided is an immunoglobulin-binding protein, wherein: the immunoglobulin-binding protein contains at least one modified immunoglobulin-binding domain; and the modified immunoglobulin-binding domain is a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence having at least one amino acid residue inserted between positions corresponding to 3 and 4 of the amino acid sequence of the B domain, Z domain, or C domain in an amino acid sequence of an immunoglobulin-binding domain selected from the group consisting of the B domain, Z domain, C domain, and variants thereof of Staphylococcus aureus protein A.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
Novel alkaline stable immunoglobulin-binding proteins
ActiveUS20190177376A1Serum immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationBinding domainAffinity matrix
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Multimeric immunoglobulin-binding domain
ActiveUS20160215027A1Prevent inhibiting immunoglobulin activityLow costImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPeptide preparation methodsGlobin bindingAntibody Affinity Chromatography
A multimeric immunoglobulin-binding protein having improved properties as an affinity ligand for affinity chromatography, and an insoluble support inmmobilizing such a multimer. The immunoglobulin-binding protein is represented by the formula: (R1)n-(R2)m, or (R2)m-(R1)n. R2 is an immunoglobulin-binding domain including an amino acid residue that covalently bonds to an insoluble support upon immobilization reaction with the insoluble support, and R1 is an immunoglobulin-binding domain without containing an amino acid residue the presence of which in the sequence compared to when it is absent in the sequence reduces the immunoglobulin-binding activity of the support yielded by the immobilization reaction. The immunoglobulin-binding protein satisfies: (1) n is an integer of 5 to 9; (2) m is an integer of 1 or 2; (3) the n (R1) domains may or may not have the same sequence; and (4) the total number of domains (n+m) is 6 to 10.
Owner:PROTENOVA
Immunoglobin conjugated protein and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of separation and purification of immunoglobin, and relates to an immunoglobin conjugated protein and an application thereof. The immunoglobin conjugated protein is obtained by splicing E, C and Z-domain of staphylococcus protein A, improvement of antibody capacity and alkali proof characteristics are accidently obtained, and further, the immunoglobin conjugated protein can be used for affinity chromatography of the immunoglobin.
Owner:SUZHOU NANOMICRO TECH CO LTD
Synthetic method used for preparing adsorbent for clearing pathogenic antibody by oxidizing periodate
ActiveCN102000550BSimple methodEase of mass productionOther chemical processesAntibody adsorptionOrganic chemistry
Owner:GUANGZHOU KONCEN BIOSCI
Immunoglobulin binding protein, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111057153AQuality improvementGuaranteed purityPeptide/protein ingredientsOther chemical processesProtein LProtein
An immunoglobulin binding protein provided by the invention comprises variants of the B structural domain of a protein A, the C2 structural domain of a protein G and the B3 structural domain of a protein L or a combination of any one to three of the variants. The protein A, the protein G and the protein L have different binding characteristics and certain complementarity, so the immunoglobulin binding protein is an alkali-resistant multifunctional IBP molecule with wide reactivity and high affinity. The protein is purified by a three-step chromatography method, so that the protein quality canbe stabilized, the protein purity is more than 97%, the endotoxin level is lower than 1 Eu / mg, and the requirement of clinical protein is met. The stability of an immunoadsorption filler synthesized from the purified immunoglobulin binding protein is improved, so the use frequency of the filler can be effectively increased, and the service life of the filler is prolonged.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KONCEN BIOSCI
Novel immunoglobulin-binding proteins and their use in affinity purification
ActiveUS20180305463A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide preparation methodsBinding domainOrganic chemistry
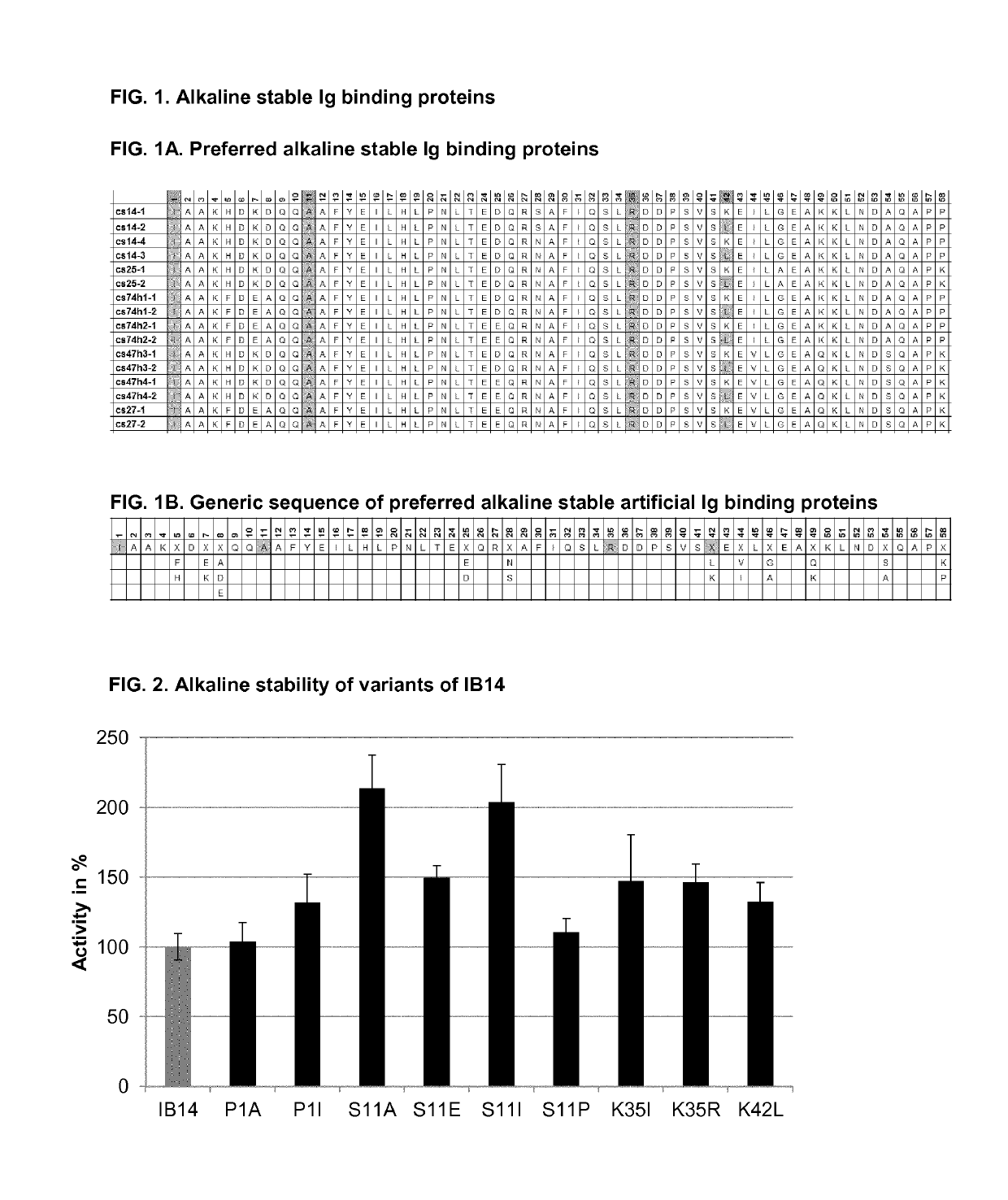
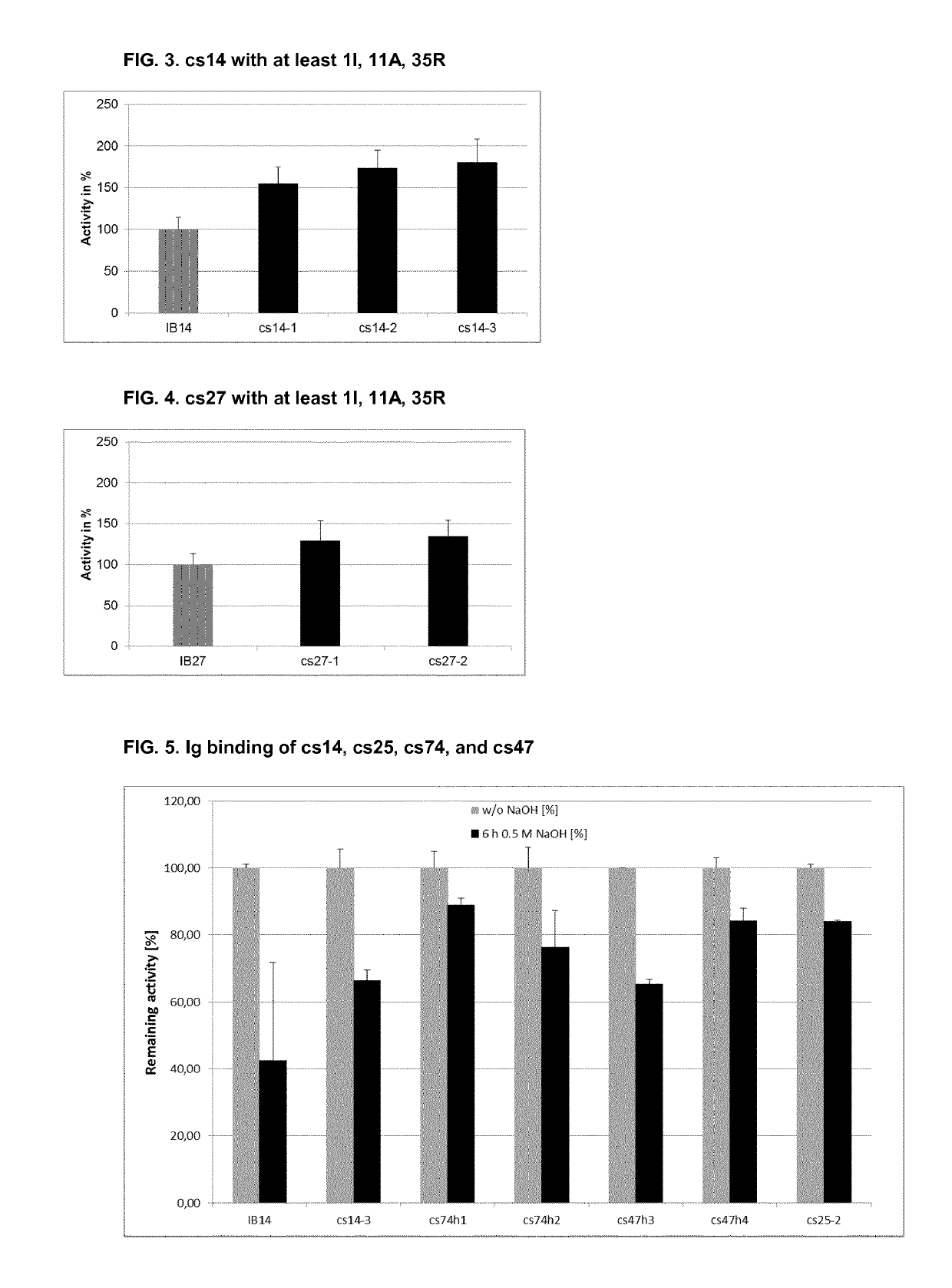
The present disclosure relates to non-natural binding proteins comprising one or more non-natural immunoglobulin (Ig) binding domains wherein at least one non-natural lg-binding domain comprises the amino acid sequence X1 X2X3XiXsX5X7 XsQQX11AFYX1sX15LX1 sX19PX21 LX23X24X2sQRX28X2gf IQSLKDDPSXio SXi2Xi3Xi4LXi5EAXigKLXs2Xs3Xs4QXs5PX. The disclosure also relates to compositions such as affinity matrices comprising the non-natural Ig-binding proteins of the invention. Use of these Ig-binding proteins or of the compositions for affinity purification of immunoglobulins and to methods of affinity purification.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Caustic stable chromatography ligands
ActiveUS10072050B2Cost-effectiveComponent separationOther chemical processesChromatography columnImmunoglobulin binding
The present invention relates to chromatography ligands having improved caustic stability, e.g., ligands based on immunoglobulin-binding proteins such as, Staphylococcal protein A, as well as methods of making and using such ligands.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Immunoglobulin-binding proteins and their use in affinity purification
ActiveUS10808042B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBinding domainOrganic chemistry
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Mutated Immunoglobulin-Binding Protein Having Increased Alkaline Tolerance
ActiveUS20190202871A1Improved alkali toleranceImprove stabilitySolid sorbent liquid separationDepsipeptidesGlobin bindingA domain
The present invention relates to a mutated immunoglobulin-binding protein having increased alkaline tolerance and, more specifically, to an immunoglobulin-binding protein in which, with respect to the A-domain of Staphylococcal protein A, or a functional variant thereof, an amino acid at a specific site is mutated and thereby exhibits an increased chemical stability at an alkaline pH value in comparison to a parental molecule. The present invention can provide an antibody-purifying immunoglobulin-binding protein ligand and matrix which have enhanced alkaline tolerance and accordingly enhanced stability in multiple times of alkaline cleaning.
Owner:AMICOGEN INC
Immunoglobulin-binding protein, and affinity carrier using same
Provided is an affinity carrier having improved alkali resistance. This immunoglobulin-binding protein contains a mutant polypeptide chain. This affinity carrier includes a solid-phase carrier to which the immunoglobulin-binding protein is bound. The mutant polypeptide chain has an amino acid sequence having at least 85% identity to an amino acid sequence indicated by any of SEQ ID NO: 1-6 and 57-62 and having a predetermined mutation, and has immunoglobulin-binding activity.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +2
Immunoglobulin binding protein andapplication thereof
ActiveCN113999294AHigh alkali resistanceOther chemical processesDepsipeptidesStaphylococcal proteinGlobulin
The invention relates to the technical field of immunoglobulin separation and purification, in particular to an immunoglobulin binding protein and application thereof. The immunoglobulin binding protein is obtained by splicing partial fragments of D, C and Z-domain of staphylococcus protein A, and the binding protein with improved alkali-resistant characteristic is accidentally obtained, so that the immunoglobulin binding protein can be used for affinity chromatography of immunoglobulin.
Owner:SUZHOU NANOMICRO TECH CO LTD +1
Immunoglobulin binding protein and its application
ActiveCN111732642BSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsStaphylococcusIntravenous gammaglobulin
The invention relates to the technical field of immunoglobulin separation and purification, in particular to an immunoglobulin binding protein and its application. The immunoglobulin binding protein is obtained by splicing the E, C and Z-domains of staphylococcal protein A, and unexpectedly obtains an increase in antibody loading and alkali resistance properties, and can be used for affinity chromatography of immunoglobulins.
Owner:SUZHOU NANOMICRO TECH CO LTD
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS10189891B2Optimize purification stepsInhibition formationOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationThreonineHistidine
The invention discloses an immunoglobulin-binding protein comprising one or more mutated immunoglobulin-binding domains (monomers) of staphylococcal Protein A (E, D, A, B, C) or protein Z or a functional variant thereof, wherein in at least one of the one or more mutated monomers, the asparagine or histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of Protein A or of Protein Z has been deleted or substituted with a first amino acid residue which is not proline or asparagine and wherein, if the amino acid residue at position 57 is proline and the amino acid residue at position 28 is asparagine, then the amino acid residue at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of protein A or of protein Z is not serine, threonine or lysine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Immunoglobulin binding protein, and affinity support using same
A protein L-derived immunoglobulin binding protein with an improved antibody dissociation rate under acidic conditions, and an affinity support using the same are provided. This immunoglobulin bindingprotein contains at least one mutant of an immunoglobulin binding domain, and this affinity support includes a solid-phase support to which said immunoglobulin binding protein is bonded. The mutant of the immunoglobulin binding domain is formed from an amino acid sequence which is at least 85% identical with an amino acid sequence represented in any of sequence numbers 1-9 and which has a given mutation, and said mutant has immunoglobulin k-chain binding activity.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +3
A kind of immunoglobulin binding protein and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111057153BQuality improvementGuaranteed purityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein LProtein
An immunoglobulin binding protein provided by the present invention includes the B domain of protein A, the C2 domain of protein G, the variant of the B3 domain of protein L or any combination of 1-3 variants thereof, through protein A The different binding properties of protein G and protein L have certain complementarity, and they are alkali-resistant multifunctional IBP molecules with wider reactivity and higher affinity. In the present invention, the three-step chromatography is used to purify the protein, which can stabilize the protein quality, ensure the protein purity is greater than 97%, and the endotoxin level is lower than 1Eu / mg, meeting the requirements of clinical protein. The stability of the immunoadsorption filler synthesized by the purified immunoglobulin binding protein is increased, which can effectively increase the use times of the filler and prolong the service life of the filler.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KONCEN BIOSCI
Cleavage of bip by subtilase cytotoxin
InactiveUS20100104550A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseVascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor
Cleavage of BIP (Immunoglobulin binding protein) by subtilase toxin and its application to inhibiting growth of or killing of cells. This has application to treatment of cancers and to conformational diseases and in particular to conformational diseases involving BiP that are influenced by cleavage by the subtilase cytotoxin. The invention also relates to subtilase toxin molecules specifically targeting proliferating cells, in particular tumor cells, or cells expressing a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Owner:ADELAIDE RES & INNOVATION PTY LTD +1
Immunoglobulin binding protein and its application
ActiveCN113999294BHigh alkali resistanceOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsIntravenous gammaglobulinStaphylococcal protein
Owner:SUZHOU NANOMICRO TECH CO LTD +1
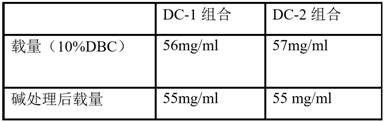
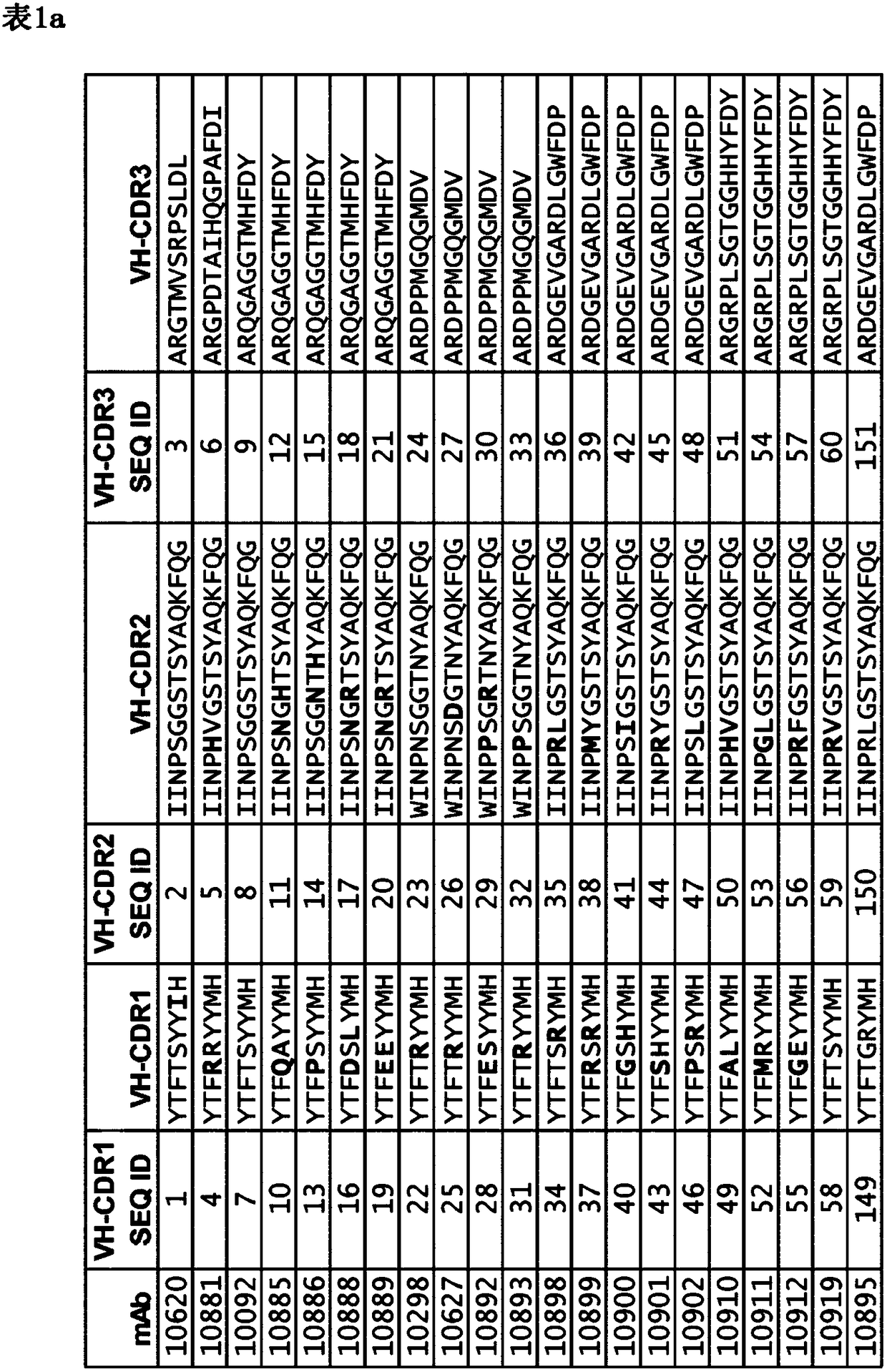
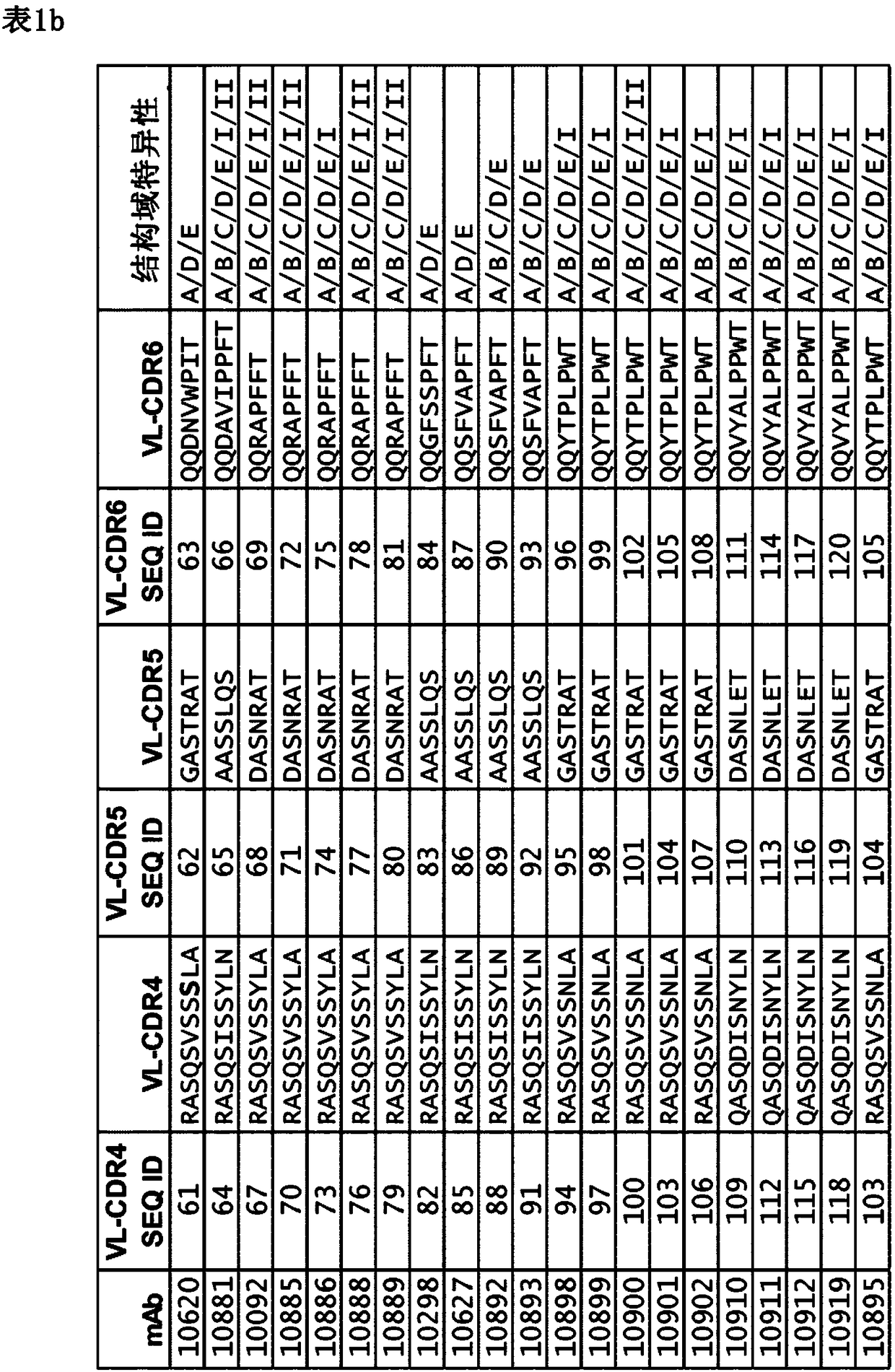
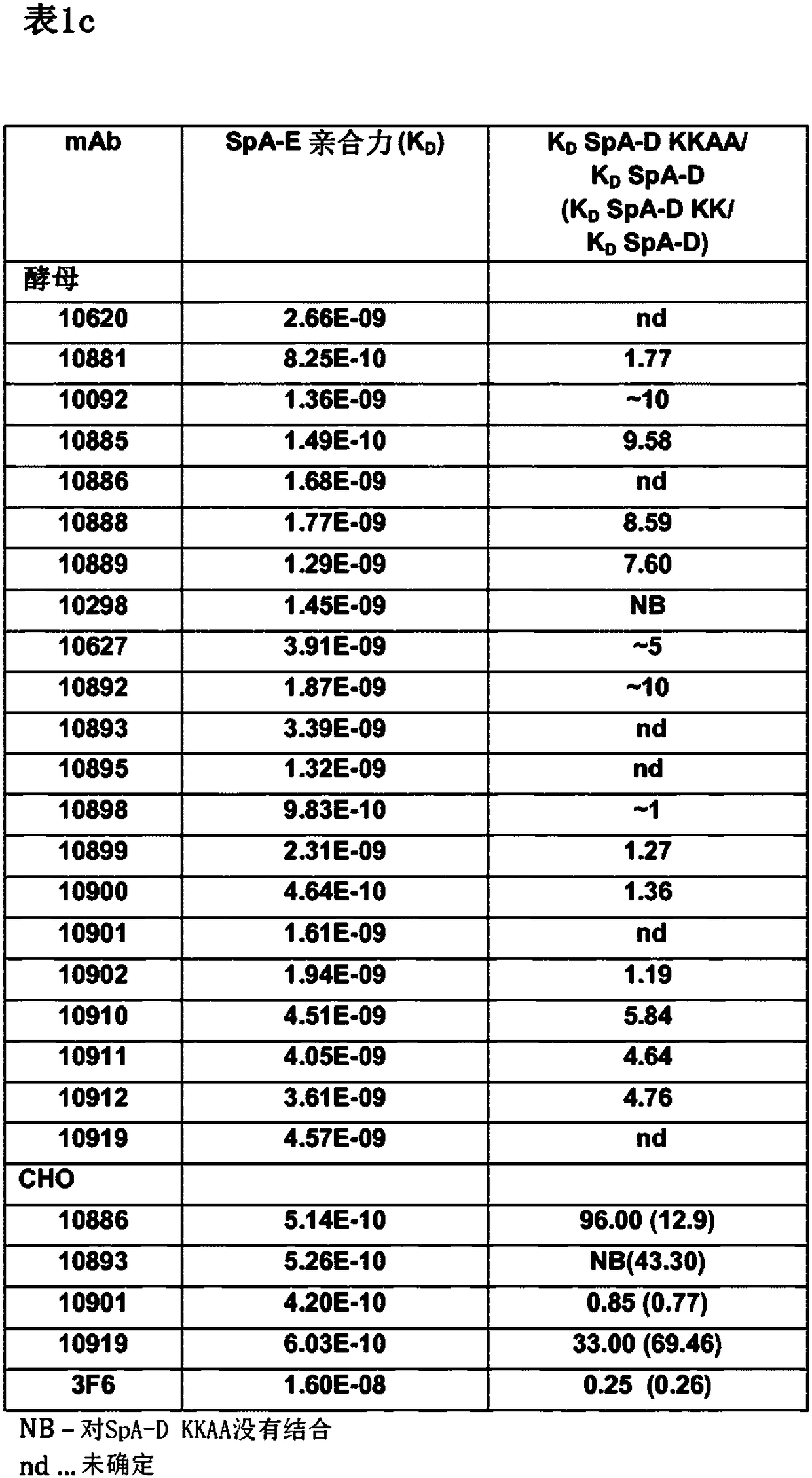
Antibody directed against immunoglobulin-binding proteins of S. Aureus
InactiveCN108064241AImprove manufacturabilityImprove toleranceAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderBinding siteWild type
A monoclonal antibody that counteracts Staphylococcus aureus by specifically binding to wild-type immunoglobulin-binding proteins (IGBP) of S. aureus comprising a cross-specific CDR binding site recognizing at least three of the IGBP domains selected from the group consisting of Protein A (SpA) domains and immunoglobulin-binding protein (Sbi) domains SpA-A, SpA-B, SpA-C, SpA-D, SpA-E, Sbi-I, and Sbi-ll, wherein the antibody has an affinity to bind SpA-E with a KD of less than 5x10-9M as determined by a standard optical interferometry method for a F(ab)2 fragment, and preferably binds to wt SpAequally or better compared to mutant SpA-KKAA that lacks binding to IgG Fc or VH3.
Owner:ARSANIS BIOSCI
Immunoglobulin-binding protein and affinity support using same
PendingUS20220242975A1High immunoglobulin-binding activityImproved immunoglobulin-binding capacitySerum immunoglobulinsOther chemical processesProtein targetGlobin binding
An affinity support having improved binding capacity for target proteins. An immunoglobulin-binding protein including a mutant immunoglobulin-binding domain, an affinity support including a solid-phase support and the immunoglobulin-binding protein immobilized thereto. The mutant immunoglobulin-binding domain consists of an amino acid sequence having at least 85% identity with an amino acid sequence of any of SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 12.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +2
Method and device for developing disease marker by using immunoglobulin-associated proteome
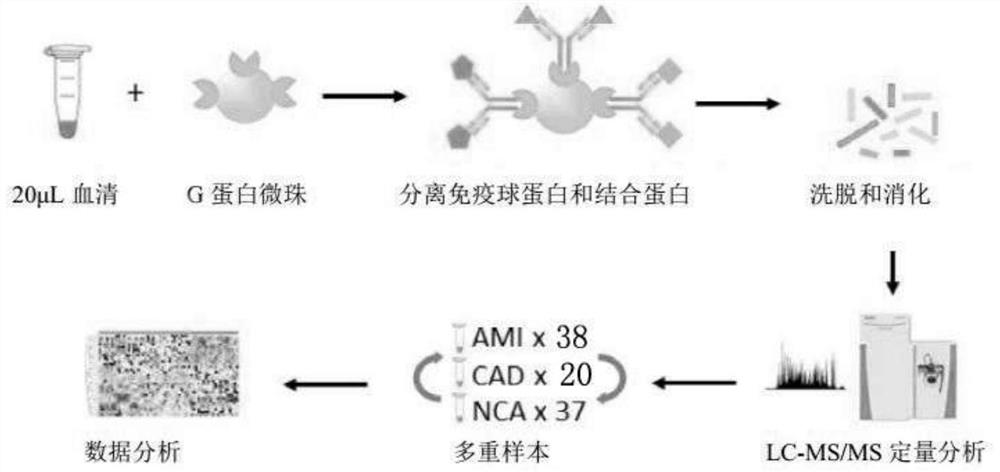
PendingCN114113624AReduce complexityComponent separationDisease diagnosisDiseaseIntravenous gammaglobulin
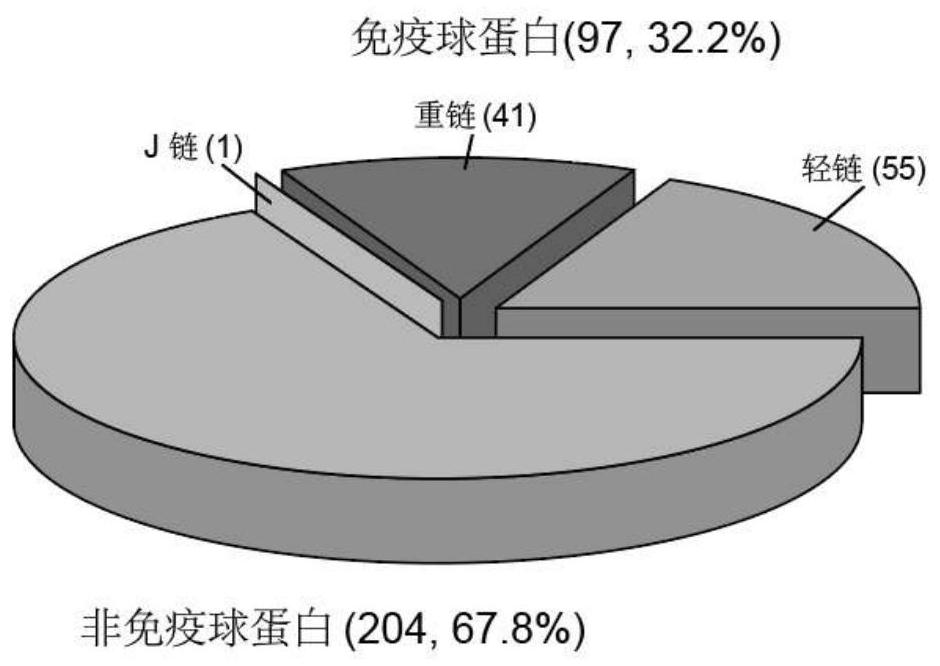
The invention provides a method and a device for developing a disease marker by using an immunoglobulin-associated proteome. The invention provides a method for screening a disease marker. The method comprises a process of identifying the disease marker by using an immunoglobulin associated proteome. The method specifically comprises the following steps: separating immune globulin and binding protein in a sample by adopting a G protein cross-linked agarose bead technology; the separated protein is eluted from the magnetic beads; then carrying out trypsin digestion and desalination on the eluted protein; the desalted peptide sample is subjected to LC-MS / MS analysis by a label-free quantitative workflow. Hundreds of immunoglobulin binding proteins are quantitatively evaluated from a serum sample, a series of IgAP proteins are detected, and individuals in different health states can be classified.
Owner:香港城市大学深圳研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com