Antibody directed against immunoglobulin-binding proteins of S. Aureus
A technology for staphylococcus and staphylococcus infection, which is applied in the field of monoclonal antibodies and can solve the problems of low correlation of SpA-E domains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
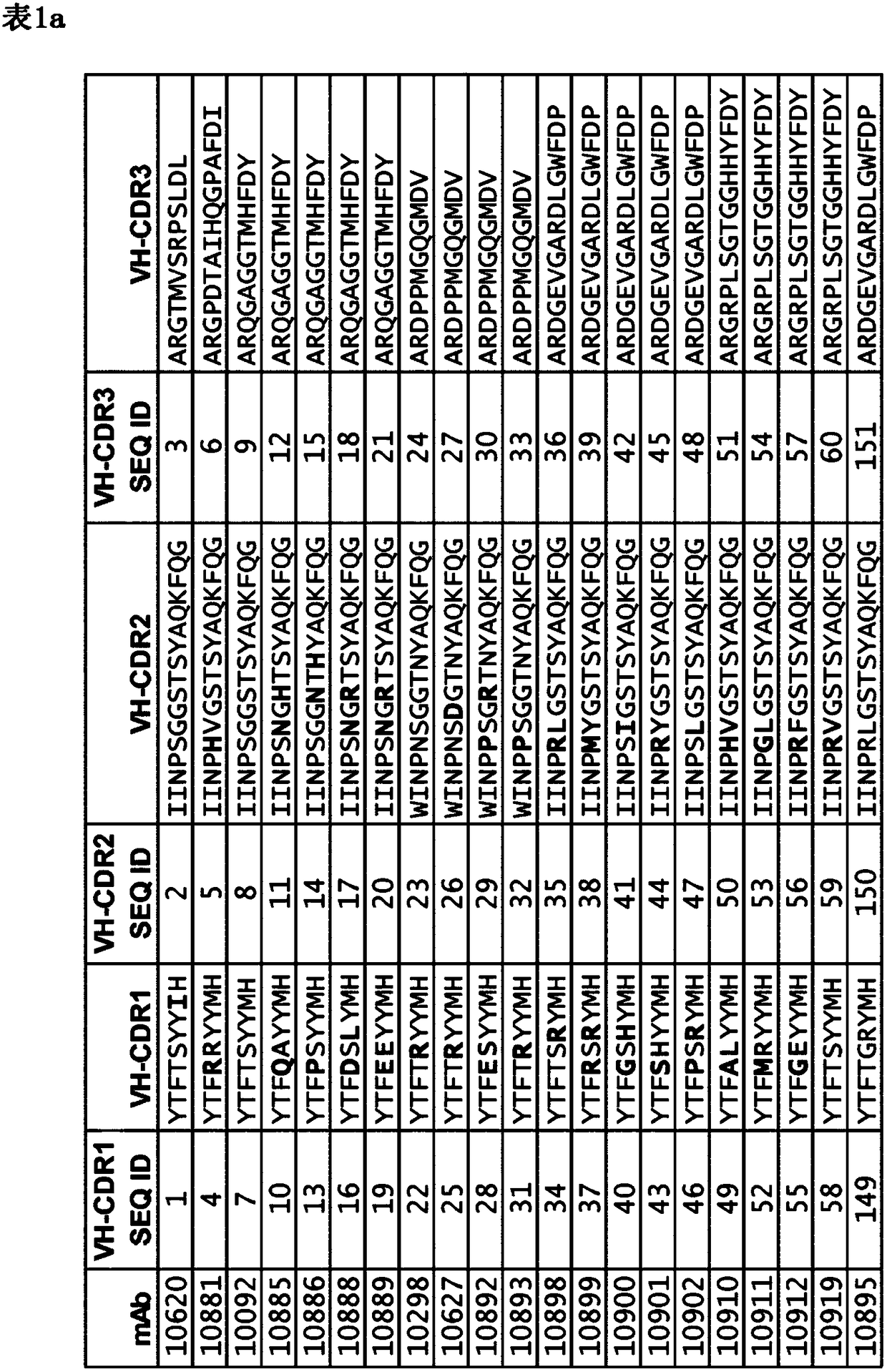
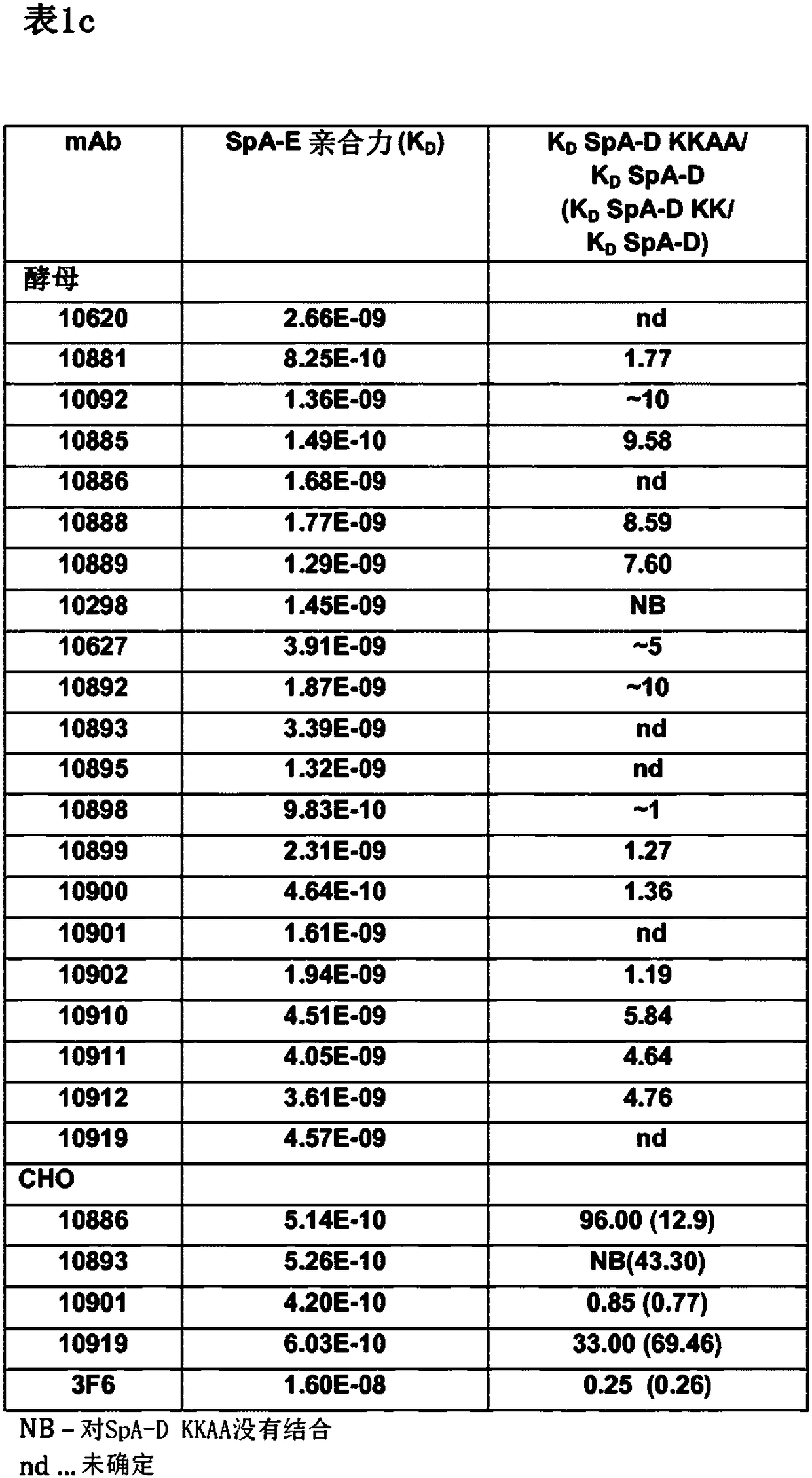
[0484] 1. A monoclonal antibody that resists or neutralizes Staphylococcus aureus by specifically binding to the wild-type immunoglobulin binding protein (IGBP) of Staphylococcus aureus, comprising a cross-specific recognition of at least three IGBP domains CDR binding site, the IGBP domain is selected from protein A (SpA) domain and immunoglobulin binding protein (Sbi) domain SpA-A, SpA-B, SpA-C, SpA-D, SpA-E, The panel consisting of Sbi-I and Sbi-II, wherein the antibody binding to SpA-E has a K as determined by standard optical interferometry on F(ab)2 fragments D less than 5×10 -9 M affinity.
[0485] 2. The antibody according to definition 1, which recognizes at least three IGBP domains, preferably at least four, five or six IGBP domains.
[0486] 3. The antibody according to definition 1 or 2, which recognizes at least three IGBP domains, each K D less than 5×10 - 9 M, preferably identifying at least four or five IGBPs, each with less than 5 x 10 -9 M of K D .
...
Embodiment 1
[0624] Example 1: Generation of protein baits representing the IgG binding domains of SpA and Sbi.
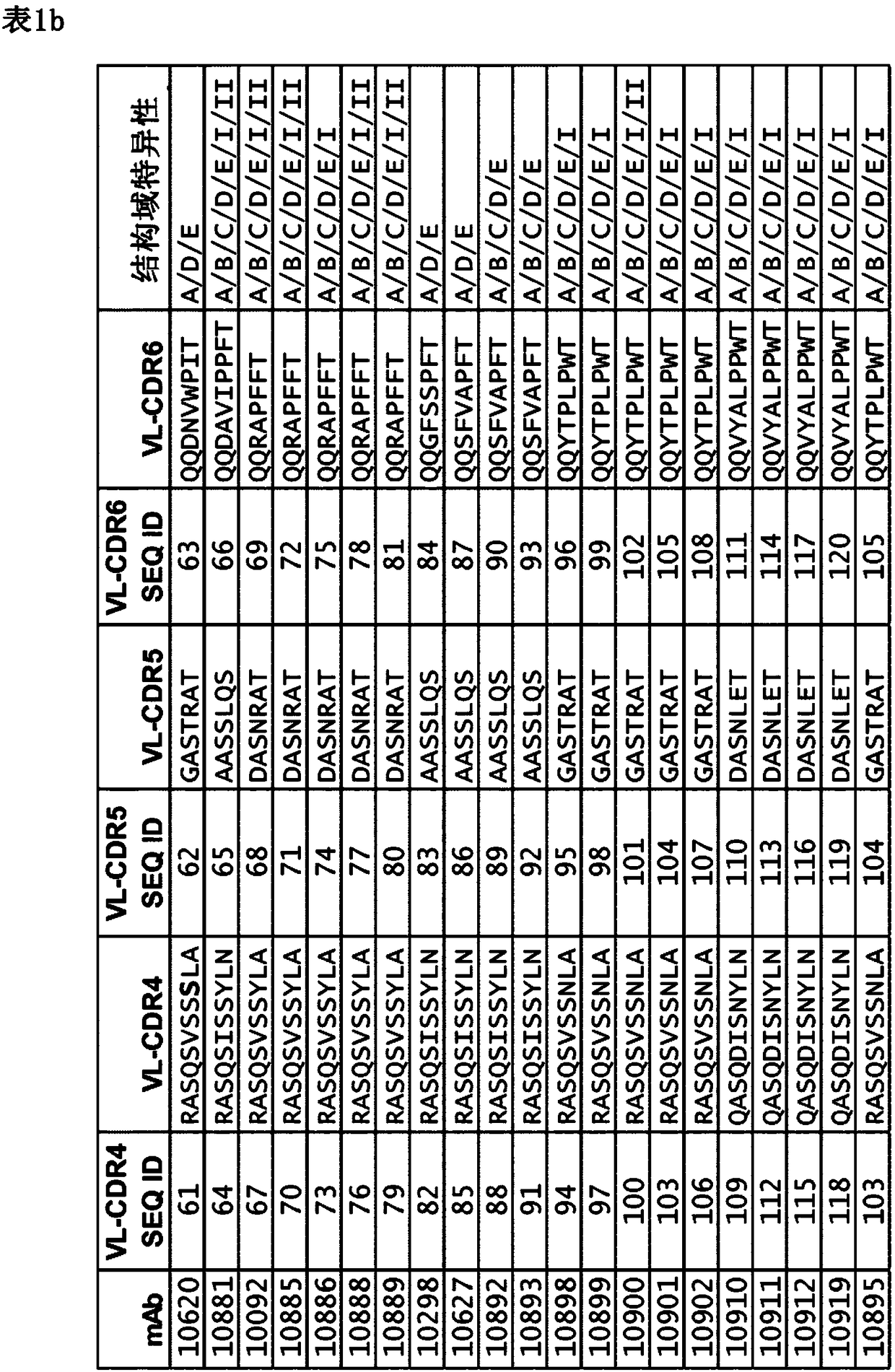
[0625] The two IgG-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus, SpA and Sbi, are multidomain proteins and contain five and two IgG-binding domains, respectively ( image 3 ). The SpA domains A-E share 63-91% amino acid sequence identity, and the two Sbi domains share much less homology (27-32%) with each other or with the SpA domain ( Figure 4 A, B). These domains are highly conserved among different S. aureus strains, with SpA showing sequence variation in the C-terminus beyond the five IgG binding domains (SEQ ID: 121-134). To support the selection and characterization of monoclonal antibodies that bind to S. aureus IgG-binding proteins, the five IgG-binding domains of protein A (SpA) and the two domains of Sbi were recombinantly produced in E. coli Tuner DE3 cells. The DNA sequence of the seven domains was derived from the published genome sequence of S. aureus strain USA...
Embodiment 2
[0626] Example 2: Development of a human IqG library using yeast-expressed human IqG and an SpA IgG binding domain with wild-type sequence Human Monoclonal Antibody
[0627] SpA and Sbi binding monoclonal antibodies were selected from yeast based antibody presentation libraries developed according to WO2009 / 036379A2, WO2010105256 and WO2012009568.
[0628] Engineered to express full-length human IgG1 antibodies (with approximately 10 9 Diversity) yeast cell library, incubated with different concentrations of native full-length SpA (purified from Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 8325, purchased from Sigma, cat#P6031) or recombinant Spa-D domain, the former using the amino reactive reagent Sulfo - NHS-LC (Thermo Scientific) biotinylation and latter as described above. To avoid non-specific binding by the Fab domain, all VH3 germline sequences were excluded from the library for selection. Yeast cells expressing antibodies with the ability to bind these baits were isolated in seve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com