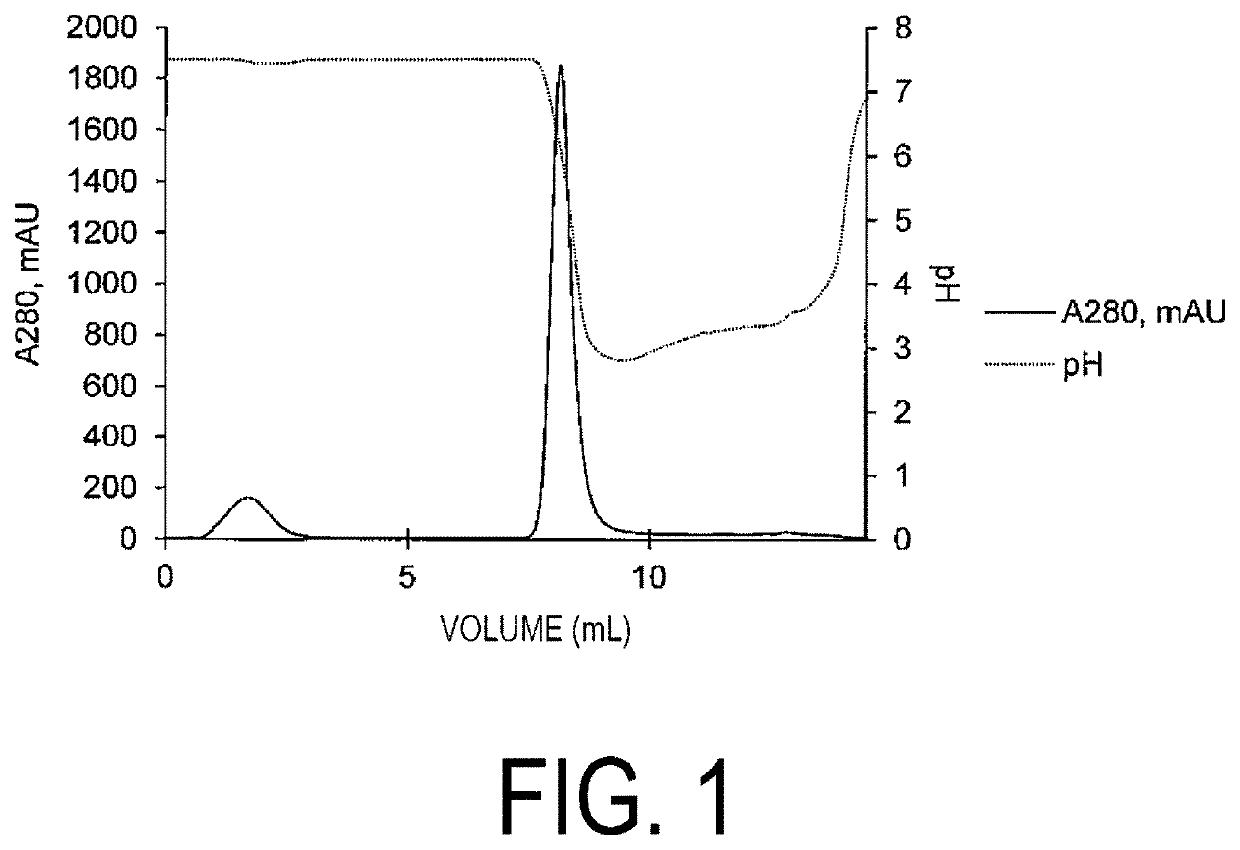
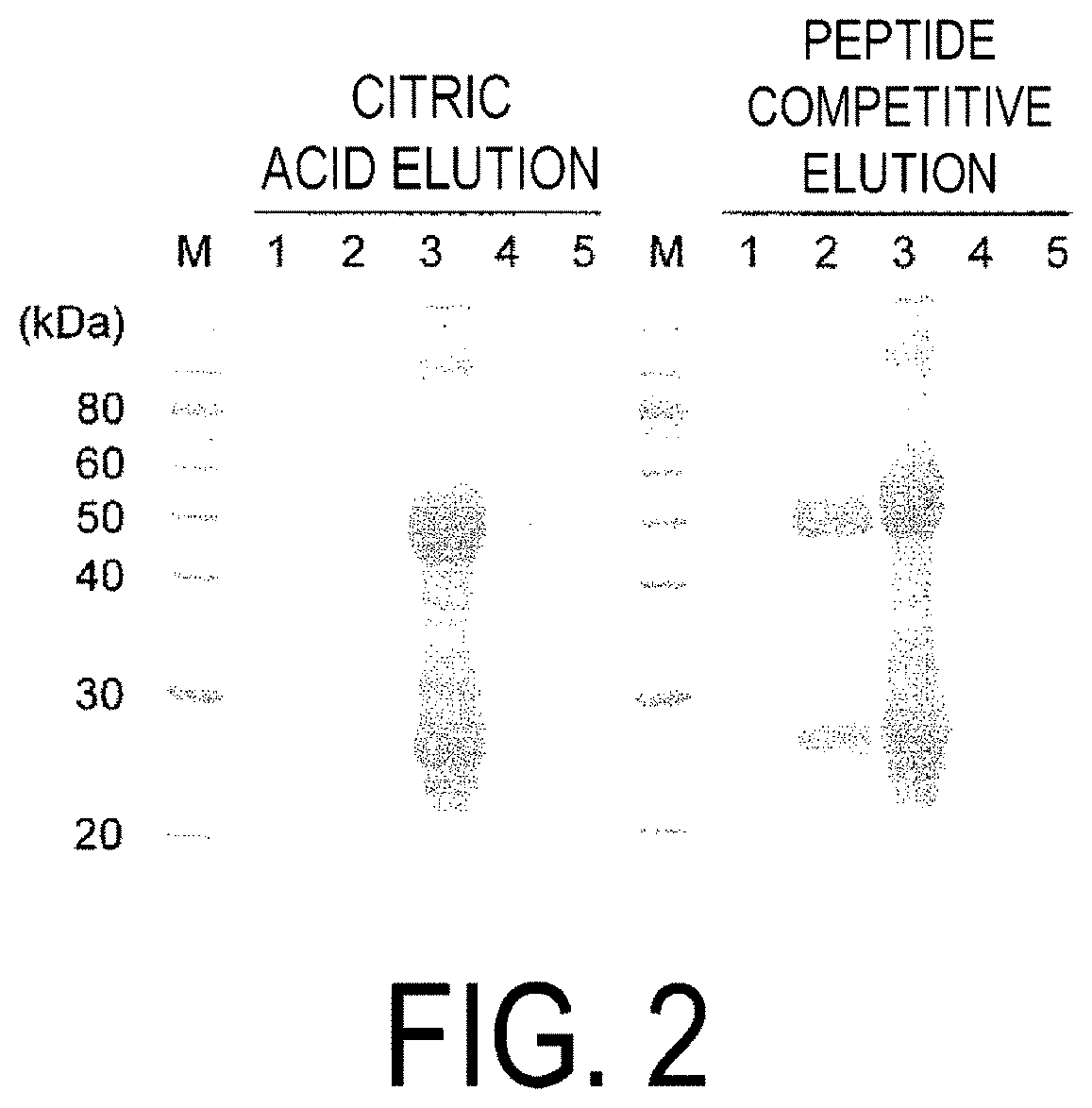
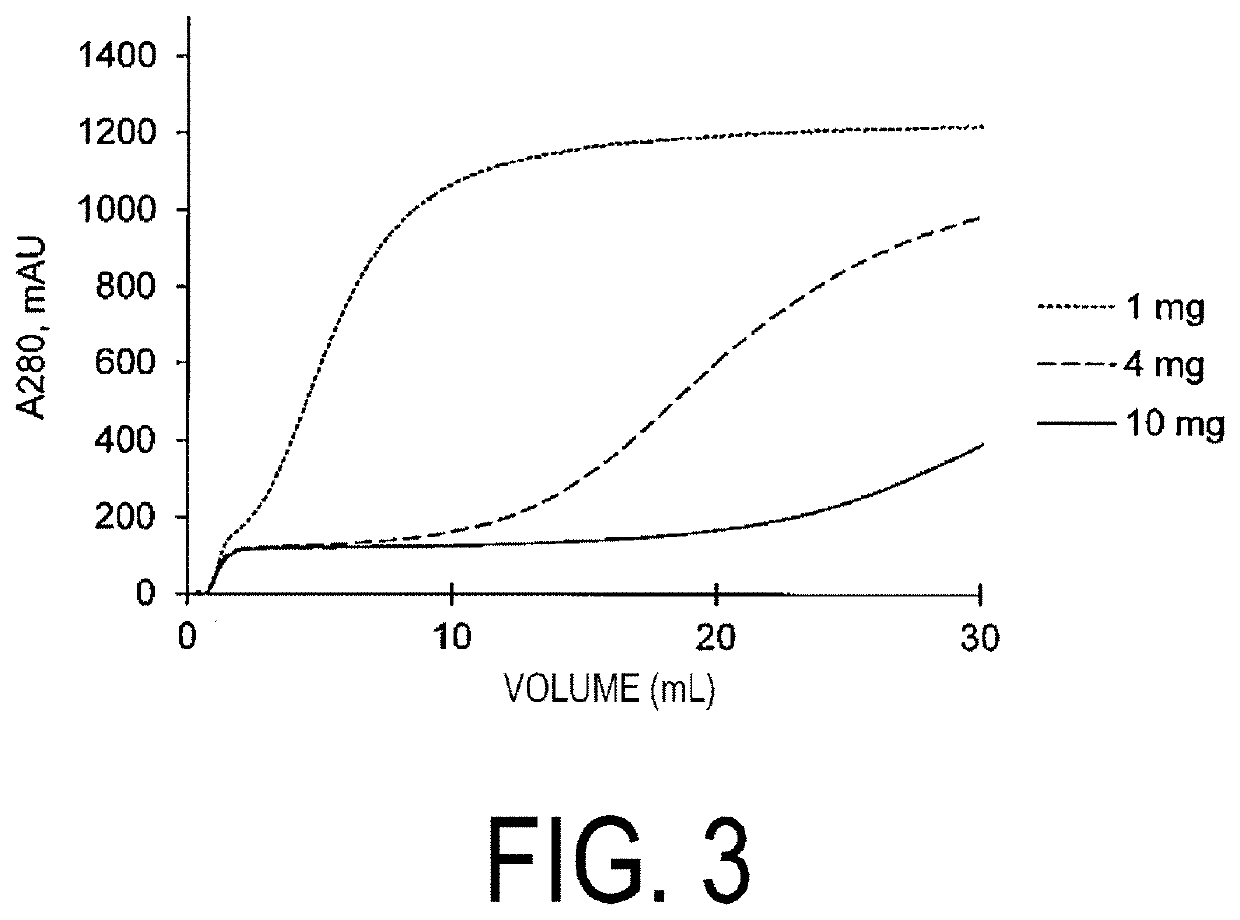
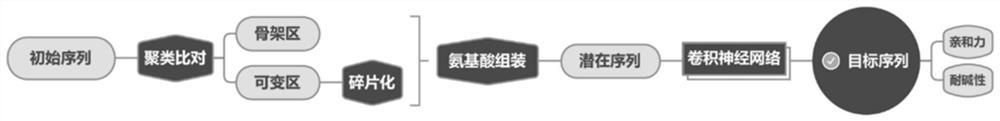
Patents
Literature
44 results about "IgG binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an immunoglobulin of an IgG isotype. [GOC:add, ISBN:0781735149]
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
Antibodies to heavy chain of human FcRn are provided which function as non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal, monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, or antigen binding fragments thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
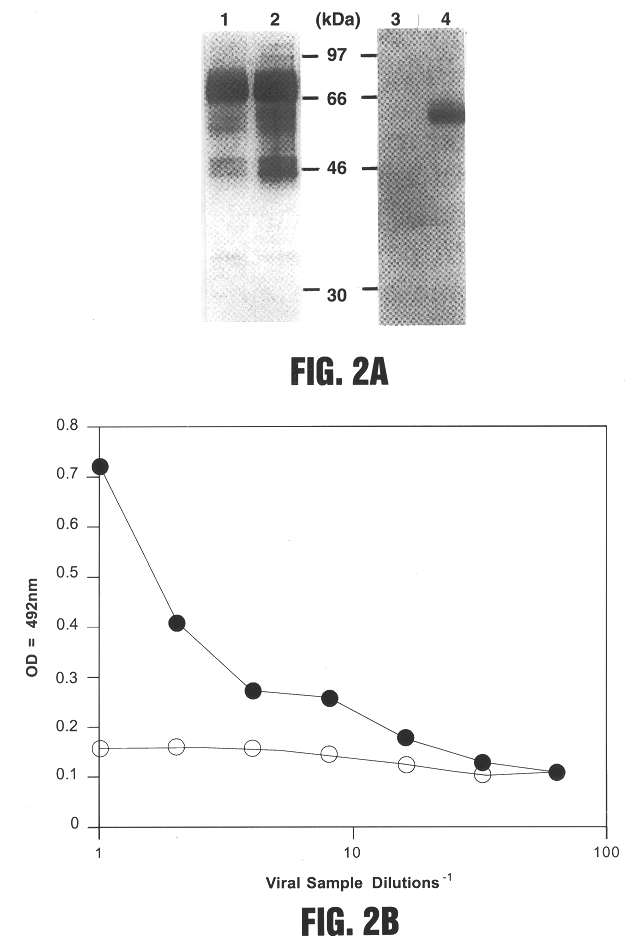
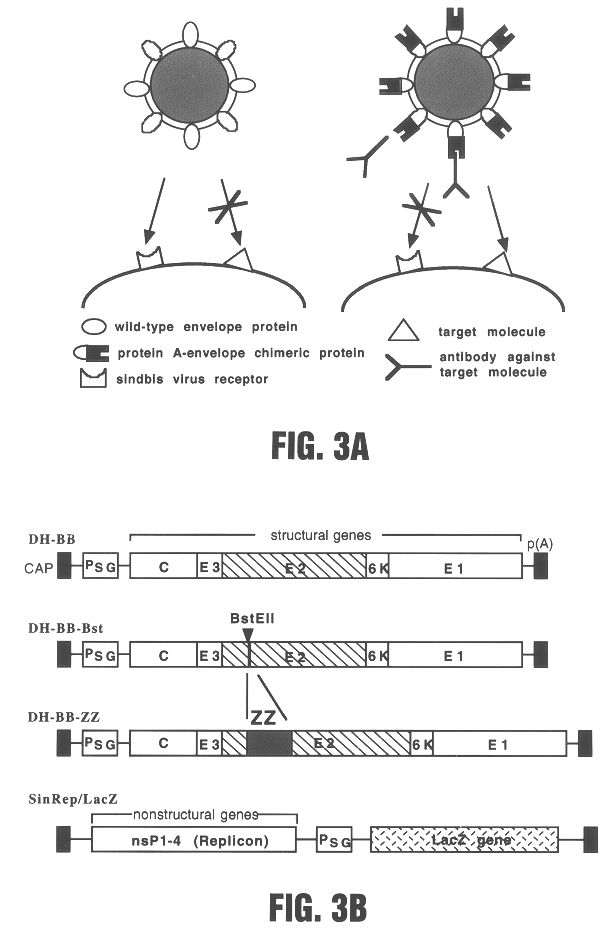
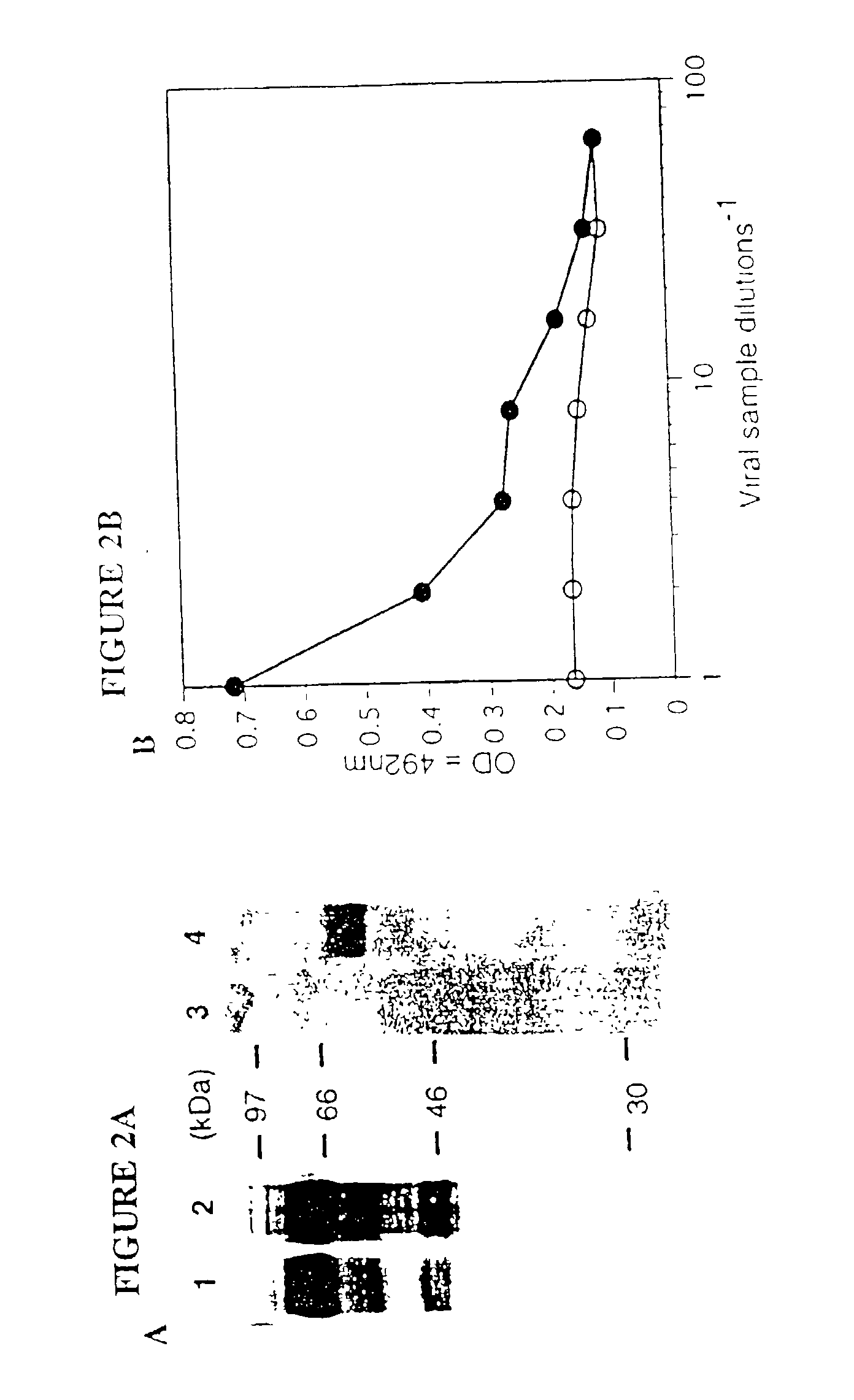
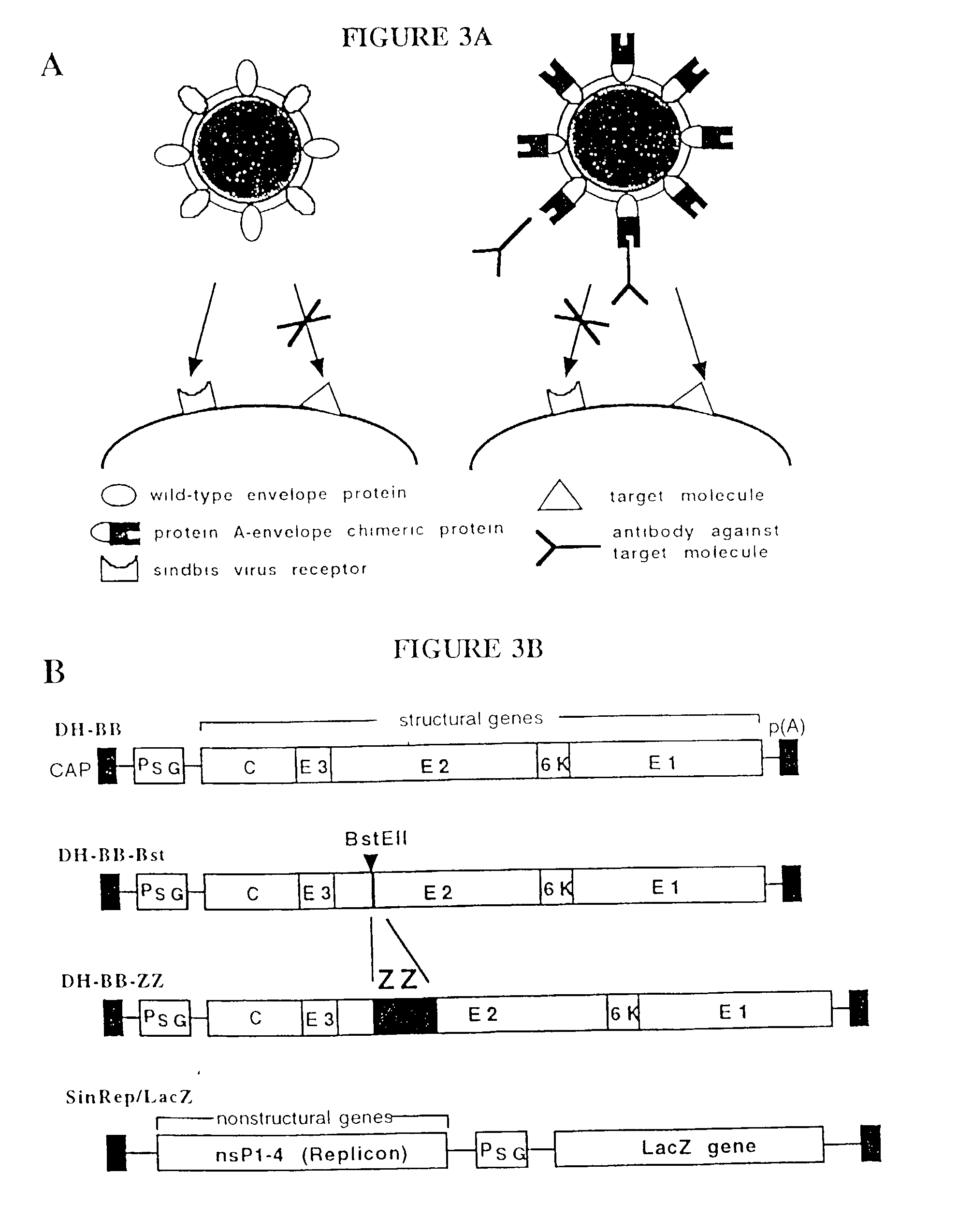
Viral vectors having chimeric envelope proteins containing the IgG-binding domain of protein A
InactiveUS6432699B1SsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsGenetic MaterialsHuman cell
The invention involves viral vectors that can be used to transduce a target cell, i.e., to introduce genetic material into the cell. The targets of interest are eukaryotic cells and particularly human cells. The transduction can be done in vivo or in vitro. More particularly the invention concerns viral vectors that have chimeric envelope proteins and contain the IgG-binding domain of protein A. These vectors when used in conjunction with antibodies targeting a particular cell are particularly useful for gene therapy.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
ActiveUS7662928B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainAntigen Binding Fragment
Antibodies to heavy chain of human FcRn are provided which function as non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal, monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, or antigen binding fragments thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for the removal/purification of serum albumins and means for use in the method
InactiveUS6613884B1Simple methodHigh selectivityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSerum albuminSerum protein albuminAqueous medium
A method for removing a serum albumin from a mixture of other compounds by contacting said mixture with a ligand a) having affinity for and enabling selective binding of the serum albumin and b) being attached to a base matrix insoluble in the aqueous media used or being possible to attach to such a matrix after having become bound to the serum albumin, characterized in that said ligand is derived from an albumin binding bacterial cell surface receptor and that the ligand lacks the IgG-binding and / or alpha2-macroglobulin-binding ability found in native forms of these type of bacterial receptors. An albumin-binding ligand derived from a cell surface bacterial receptor and attached covalently to a carrier matrix, characterized in that the ligand is monovalent with respect to ability to bind a serum albumin. A method for removal of serum albumin from a sample that is to be assayed for non-serum albumin components. The characteristic feature is to subject the sample to affinity adsorption by an albumin-binding ligand derived from an albumin-binding receptor.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Igg-binding peptide and method for detecting and purifying igg using same
ActiveCN103890174AHigh selectivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComponent separationCysteine thiolateArginine
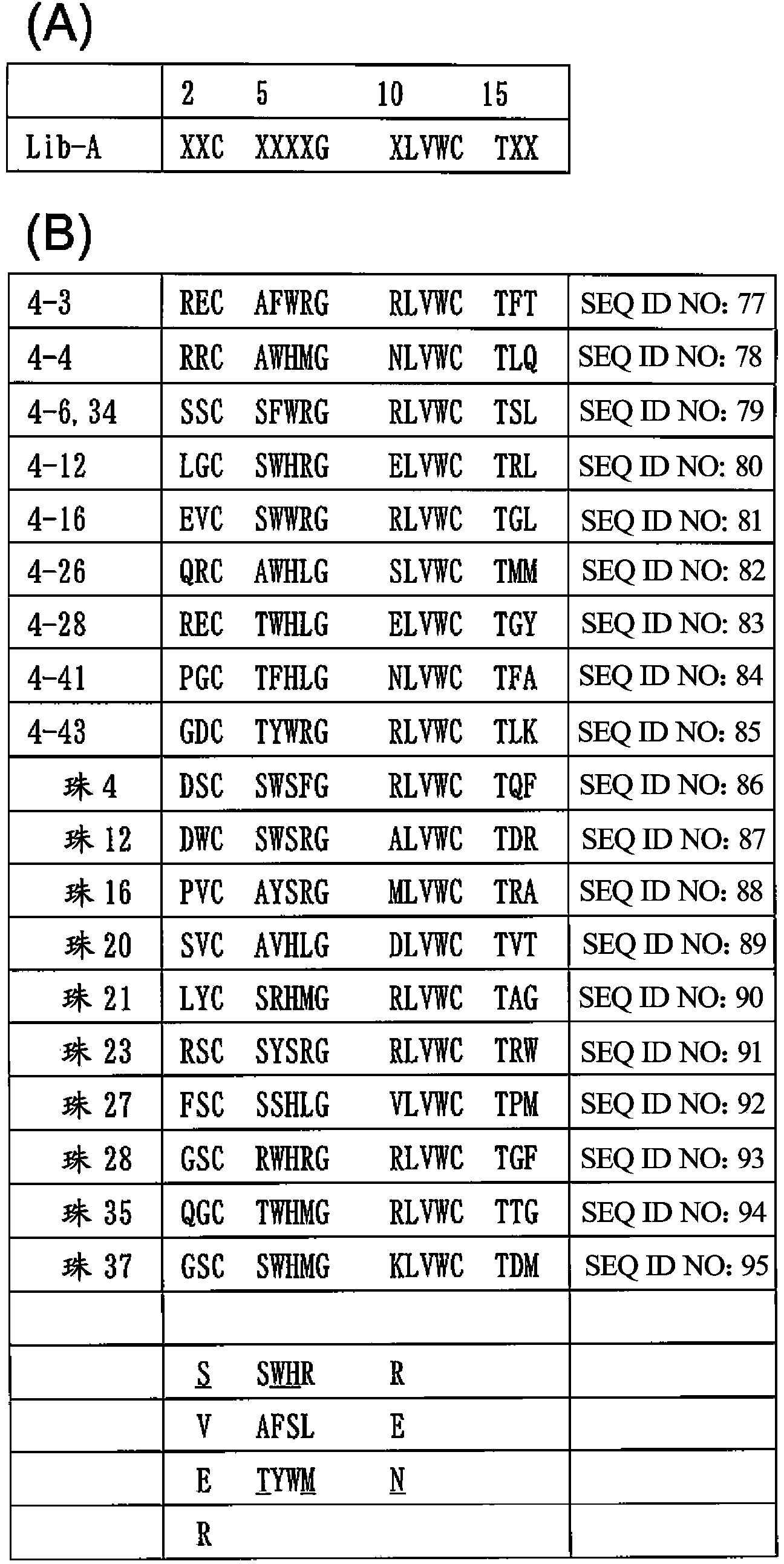
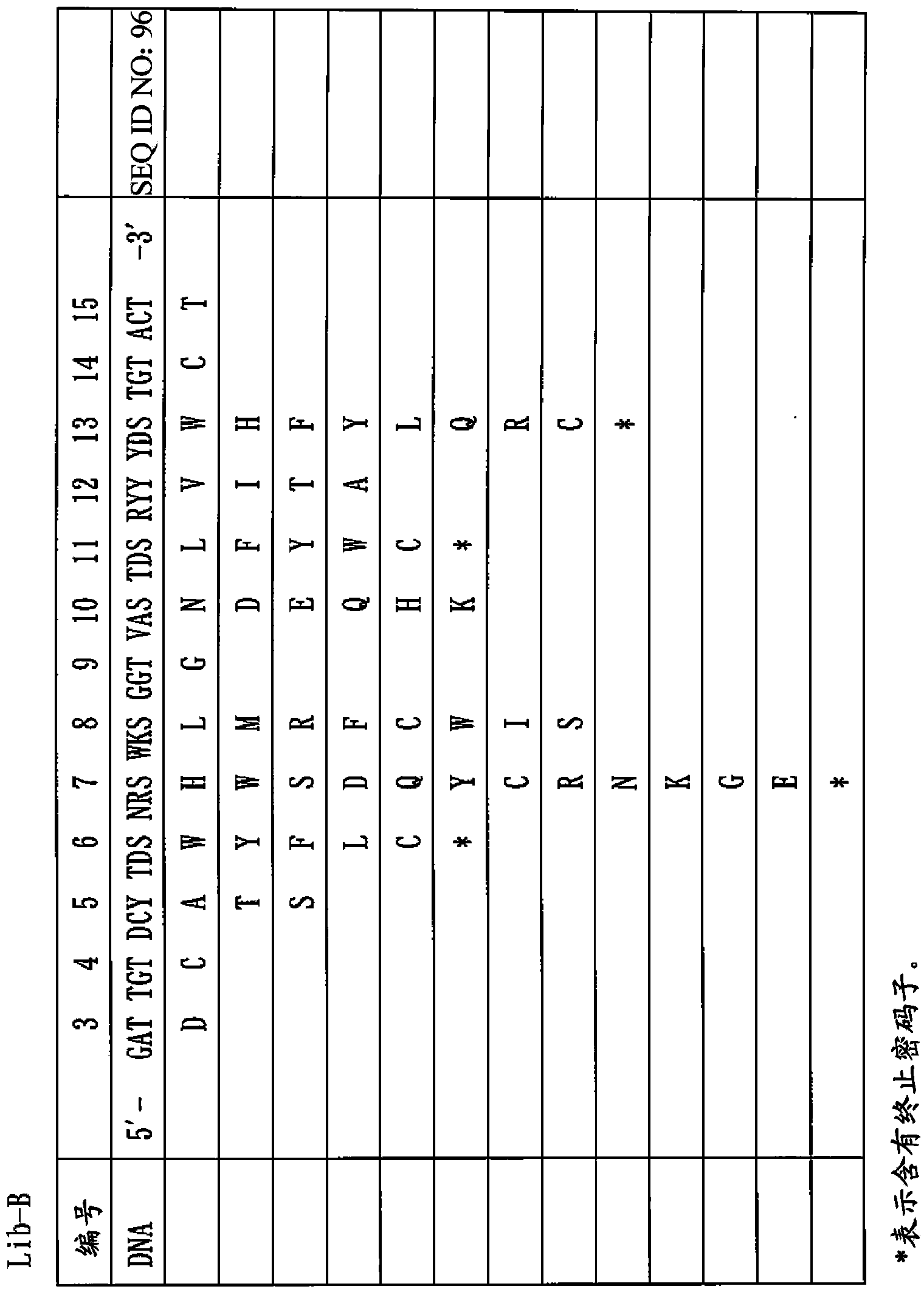
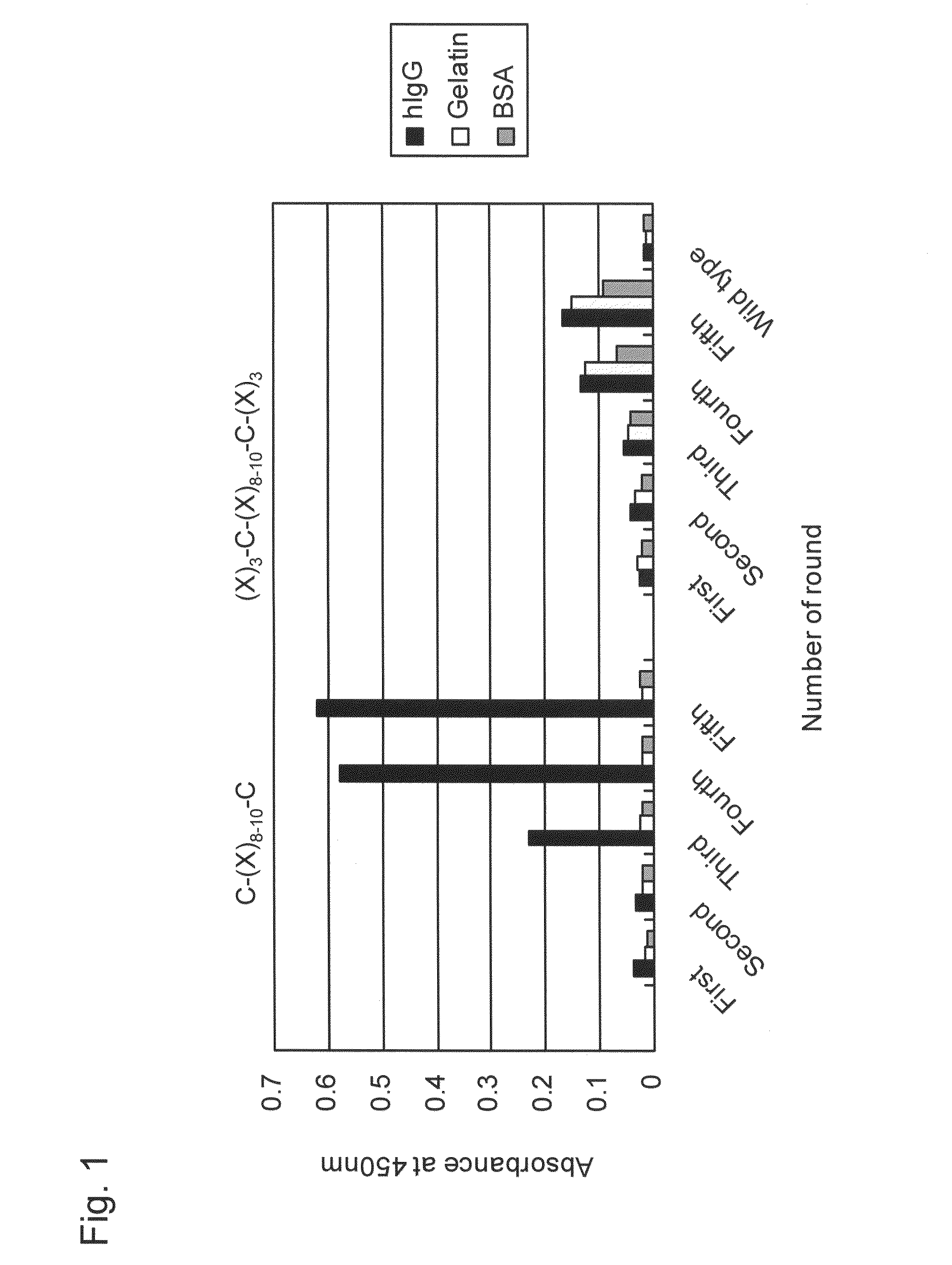
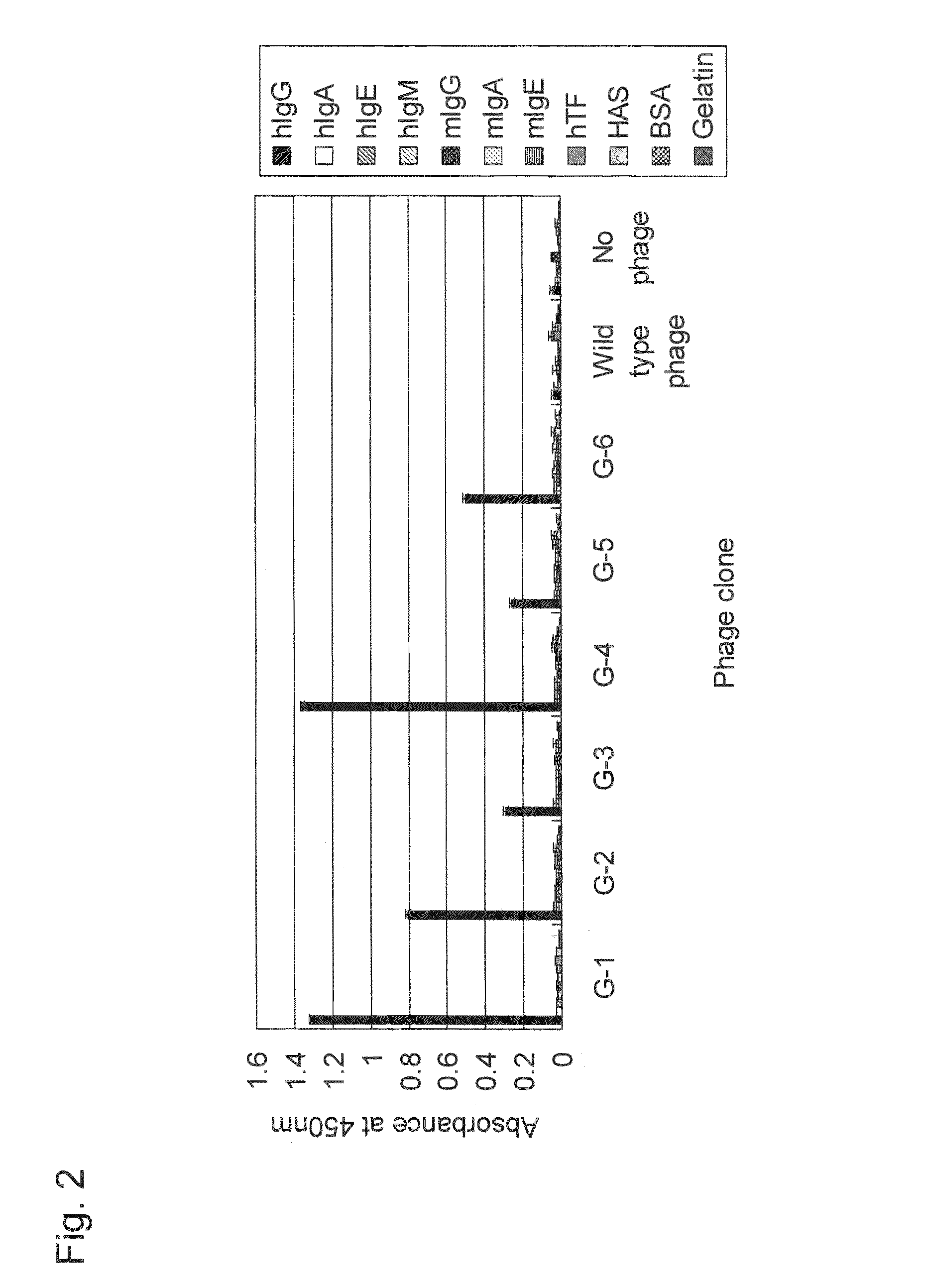
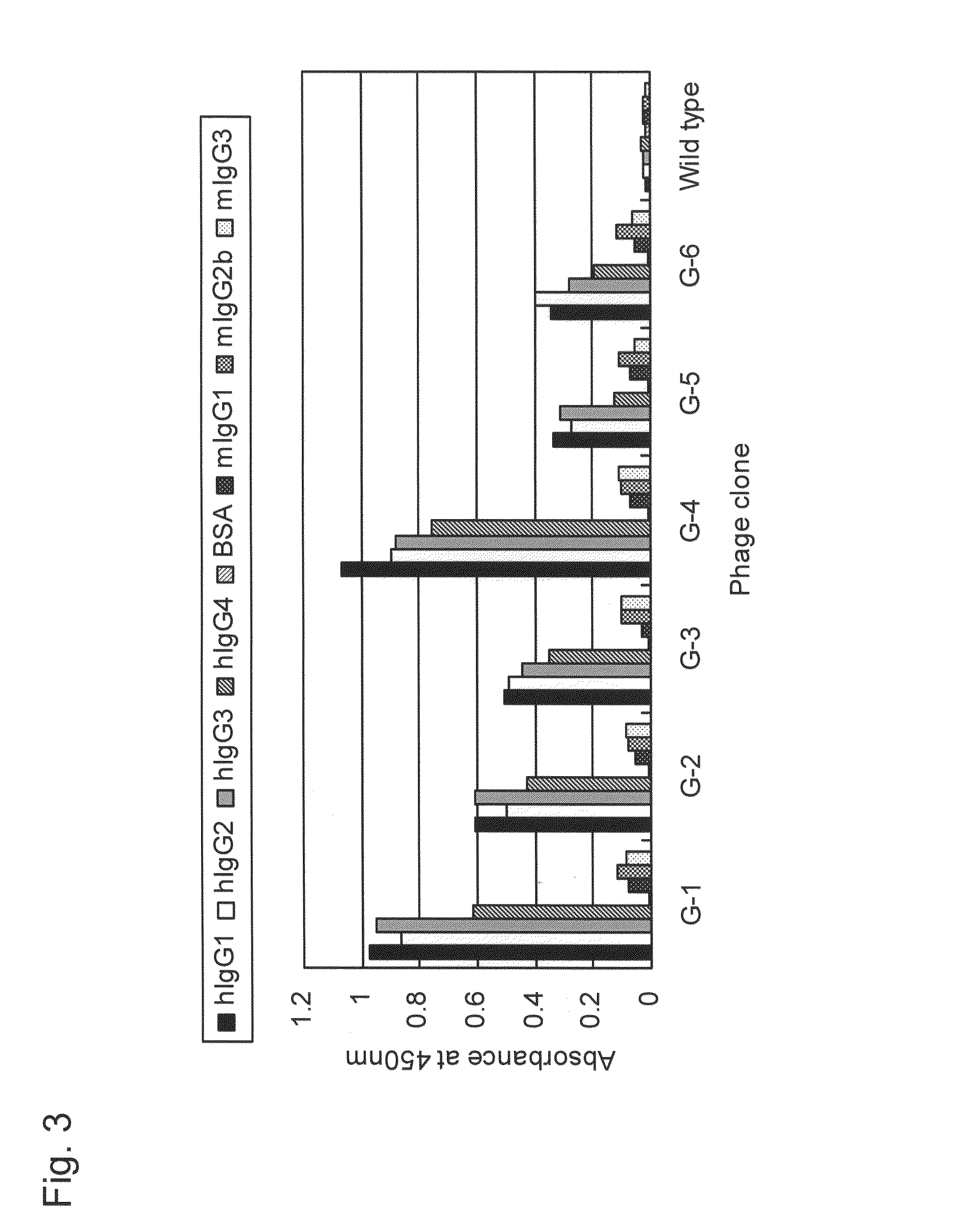
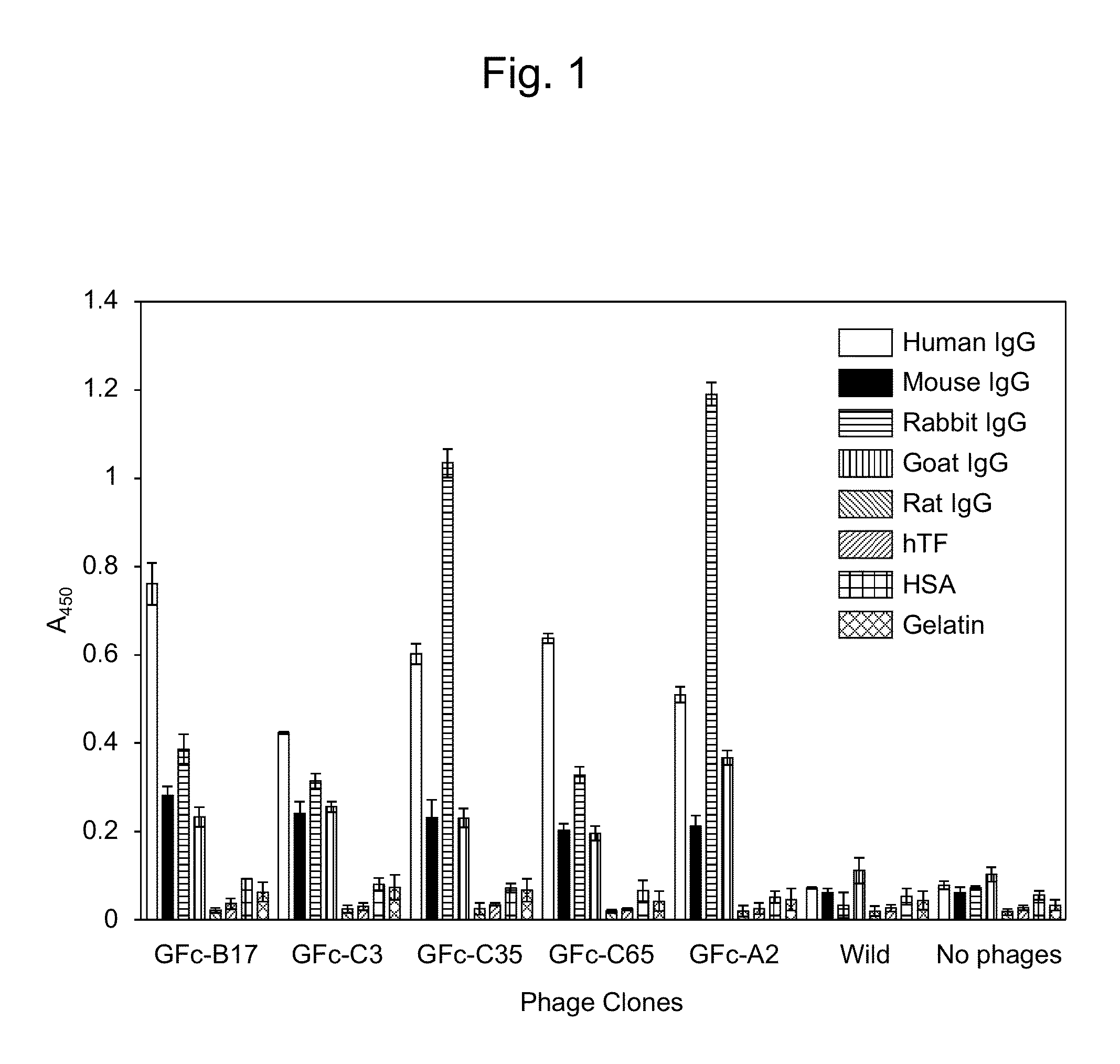
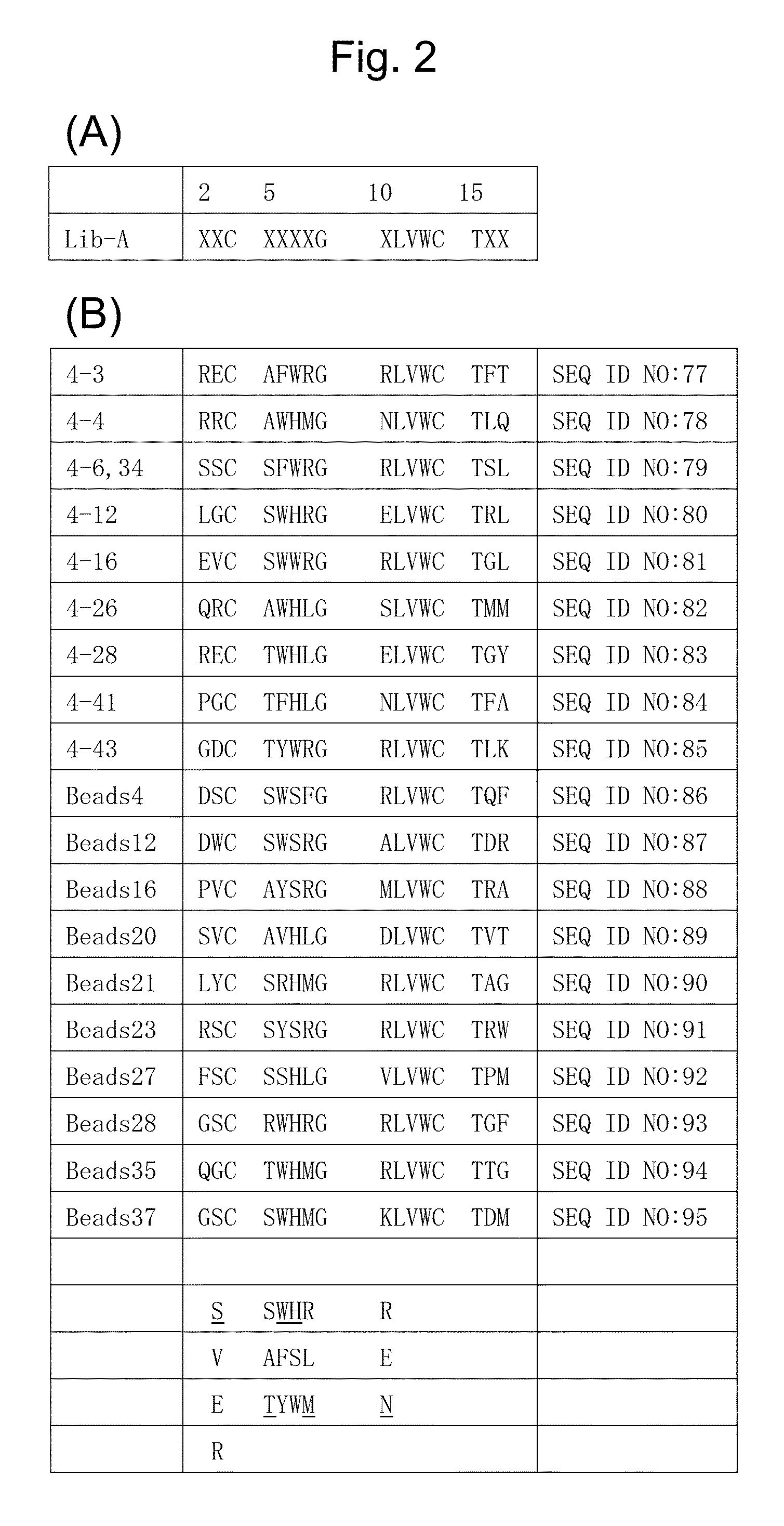
Provided is a peptide capable of binding to human IgG specifically or selectively. A peptide characterized by comprising an amino acid sequence represented by formula (I): (X1-3)-C-(X2)-H-R-G-(Xaa1)-L-V-W-C-(X1-3) (wherein Xs independently represent an arbitrary amino acid residue other than a cysteine residue; C represents a cysteine residue; H represents a histidine residue; R represents an arginine residue; G represents a glycine residue; Xaa1 represents a glutamic acid residue or an asparagine residue; L represents a leucine residue; V represents a valine residue; and W represents a tryptophan residue) and composed of 13-17 amino acid residues, and also characterized by being capable of binding to human IgG.
Owner:OTSUKA CHEM CO LTD +1
Nucleic acids encoding ara h 3 polypeptides
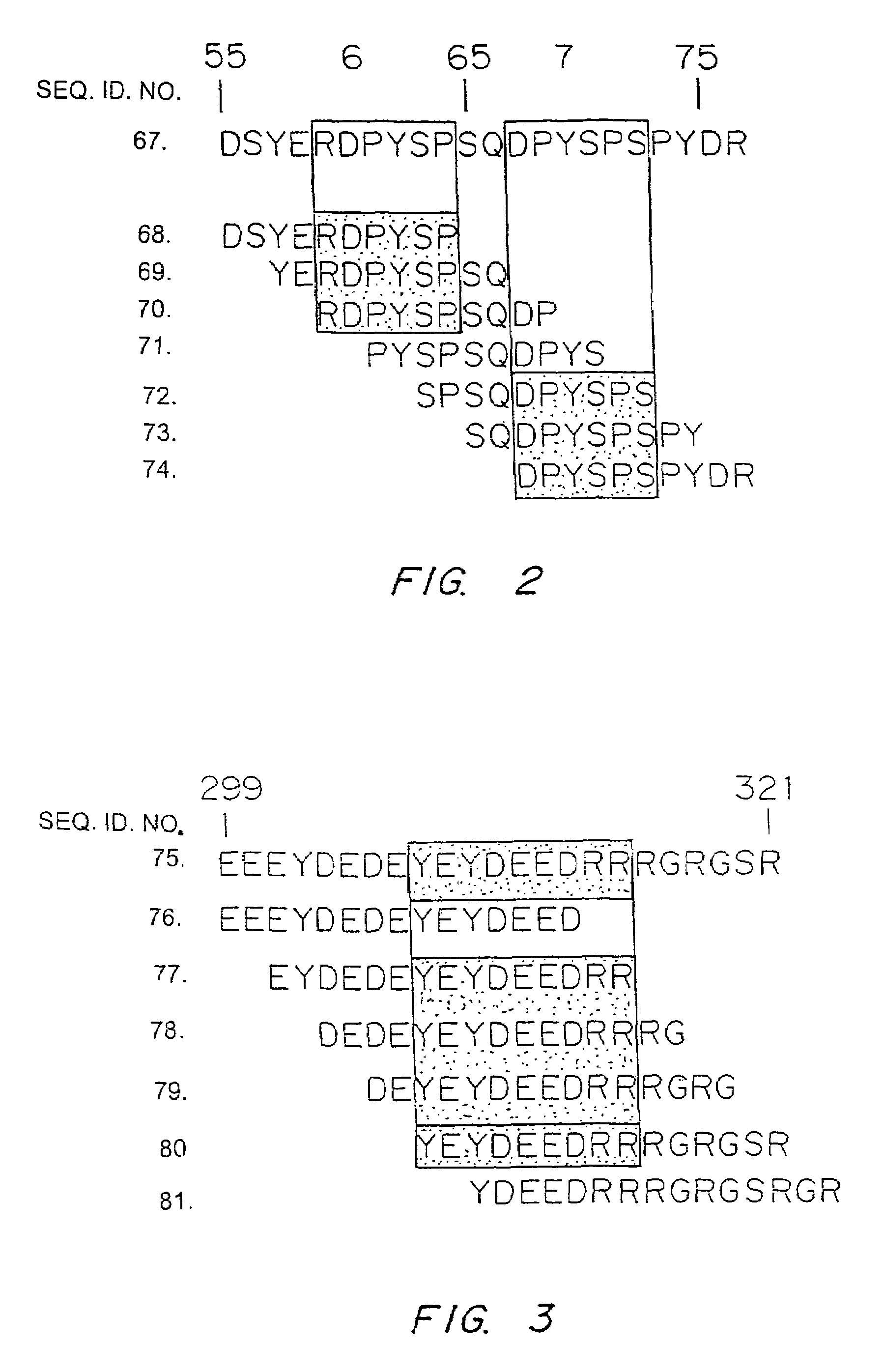
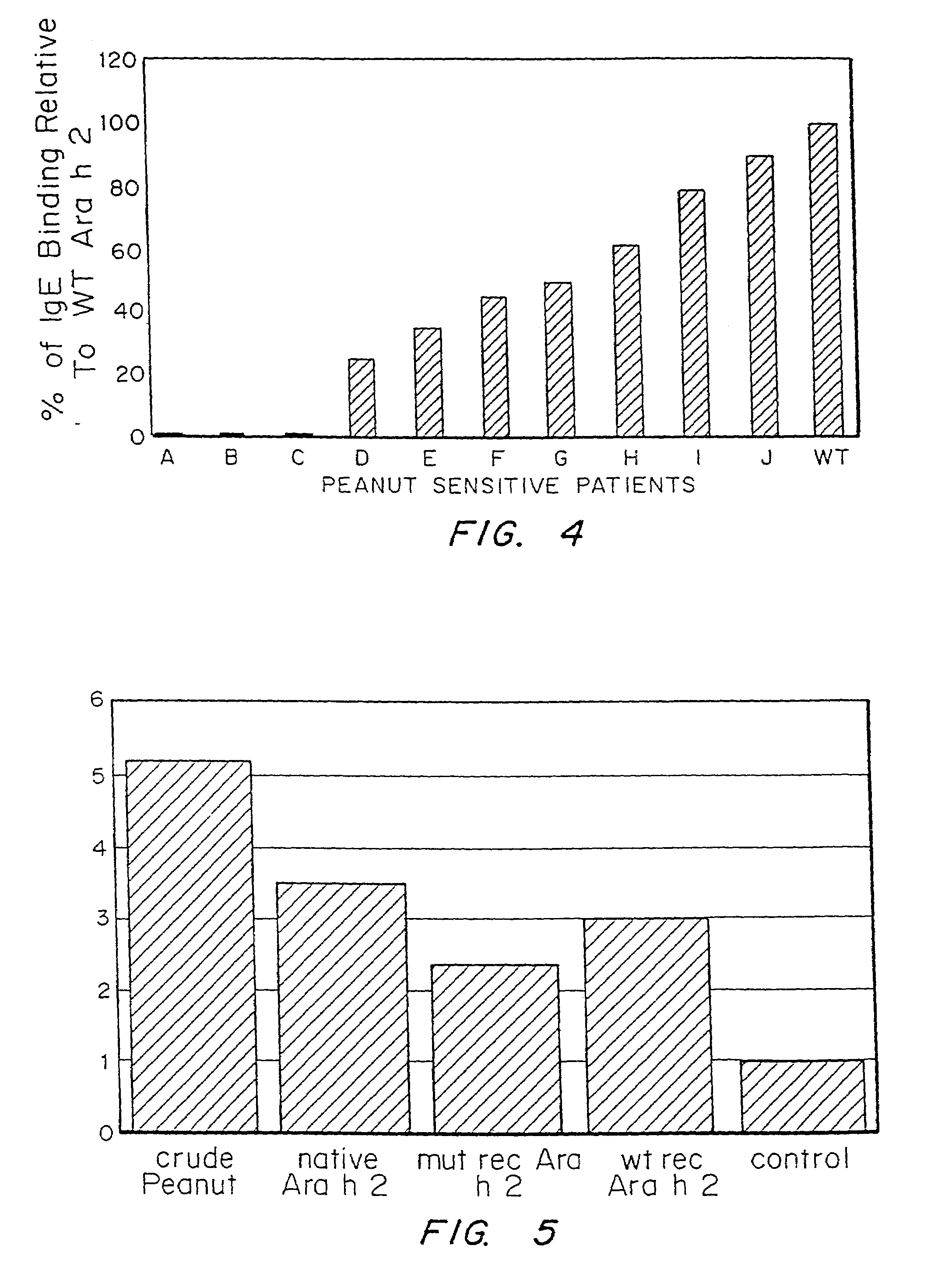
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity. The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
InactiveUS20050079169A1Increase the gapInhibit bindingMuscular disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
Antibodies to FcRn are provided which are non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal or monoclonal or antigen binding fragment thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Specific modification of antibody by IgG-binding peptide
ActiveCN107614514AReduce functionEasy to retouchTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding peptideAntibody
The present invention pertains to an IgG-binding peptide, an IgG-binding peptide modified with a cross-linking agent, a complex of IgG and said IgG-binding peptide modified with a cross-linking agent,and a method for preparing said complex.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS20070213507A1Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsFungi peptidesBinding siteT cell
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method for labeling of compounds
ActiveUS20130184442A1Maximize antigen bindingImmunoglobulinsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesAntigen bindingHelix structure
The present invention relates to site-specific labeling of antibodies or fragments thereof with one or more reporter group(s) in a way that does not affect antigen binding. The method for labeling antibodies and / or fragments thereof, comprises the following steps a) providing an IgG binding protein, which comprises α-helix structures, with a photoactivatable group and at least one label; b) forming a mixture of said IgG binding protein and the antibodies and / or fragments to be labeled; and c) UV illuminating said mixture for site-specific labeling of said antibodies and / or fragments thereof. The IgG binding protein is preferably the Z domain of Protein A.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Site-specific radioisotope-labeled antibody using IgG-binding peptide
PendingCN109071606AImprove bindingNo functional degradationIn-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulinsDiagnostic agentBinding peptide
The present invention pertains to: an IgG-binding peptide containing a ligand which can be bound to a radioactive metal nuclide; an IgG-binding peptide labeled with a radioactive metal nuclide; a complex of the IgG-binding peptide with IgG; and a nuclear medical imaging diagnostic agent or a cancer diagnostic agent, etc., containing the IgG-binding peptide or the complex.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV +1
Viral vectors having chimeric envelope proteins containing the IgG-binding domain of protein A
InactiveUS20030049845A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsGenetic MaterialsHuman cell
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS7879977B2Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from yeastsBinding siteADAMTS Proteins
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Supramolecular high affinity protein-binding system for purification of biomacromolecules
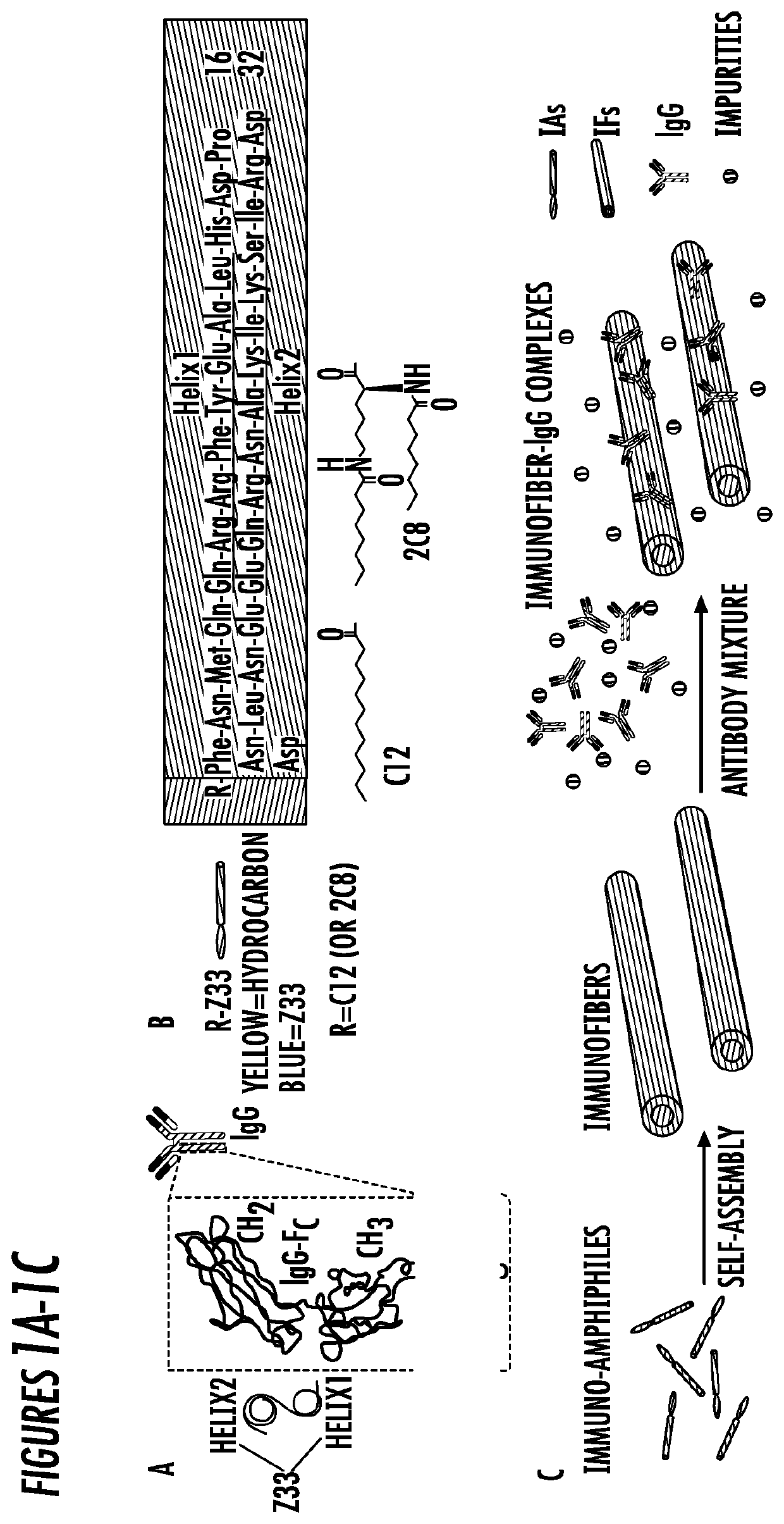
In certain embodiments, the present invention provides novel antibody purification methods and systems using a potentially simple and cost-efficient means. In some embodiments, customized Z-33 derived from Staphylococcus aureus Protein A is used to construct immuno-amphiphile molecules which can assemble into immunofibers in aqueous solution with bioactive epitopes on the surface and have IgG binding ability.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO +1
IgG binding peptide
ActiveUS8372950B2High binding activitySlow dissociation ratePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCrystallographyBinding peptide
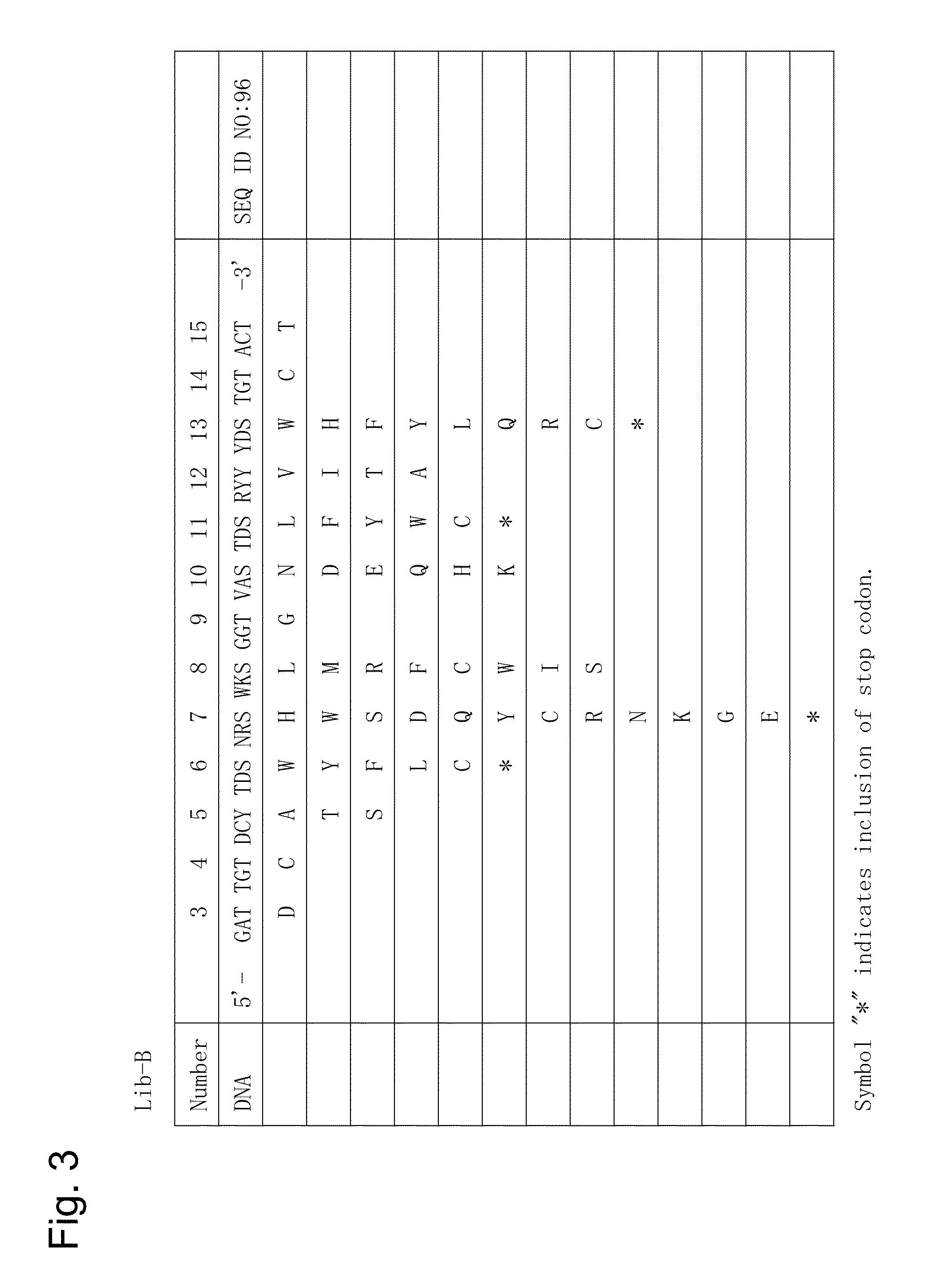
The present invention provides a peptide capable of specifically binding to human IgG. In particular, the present invention relates to a human IgG binding peptide tag of 11 to 16 amino acids in length, comprising at least an amino acid sequence of the formula I:C-(X)n-W-X-X-X-W-(X)m-C(I)(SEQ ID NO: 17)wherein n and m are each an integer of 1 or more and the sum n+m is 4 or 5, wherein X-X-X in the formula I contains no cysteine residue, andwherein said amino acid sequence satisfies either or both of a) and b):a) (X)n-W in the formula I denotes Za-G-Y-W (SEQ ID NO: 18); andb) W-(X)m in the formula I denotes W-G-L-Zb (SEQ ID NO: 19)wherein Za and Zb are each 0, 1, or more amino acid residues.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
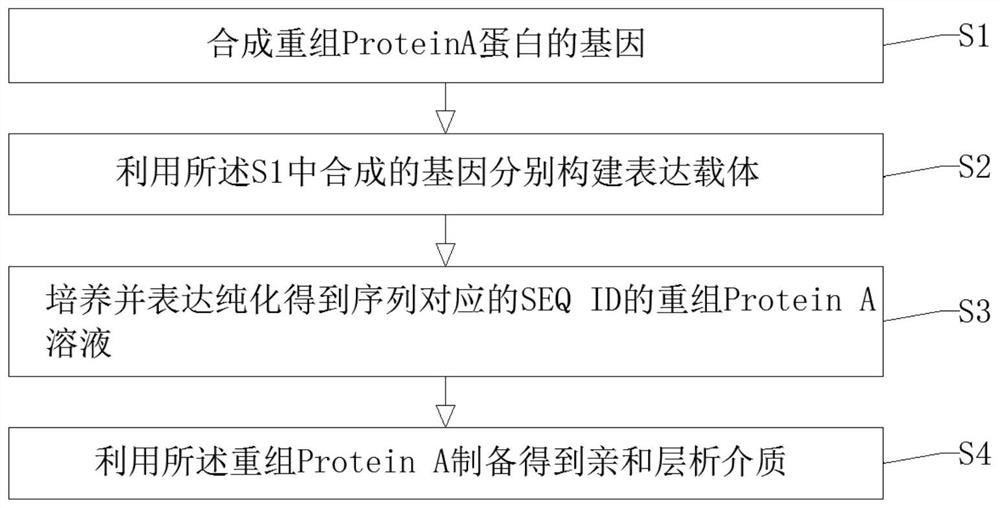
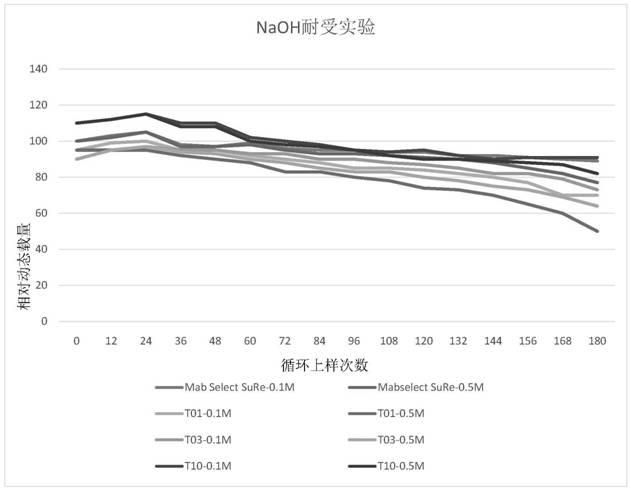
Recombinant Protein A protein and preparation method of affinity chromatography medium
ActiveCN113278052AGood chemical stabilityHigh binding capacityOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsMutantChemical stability
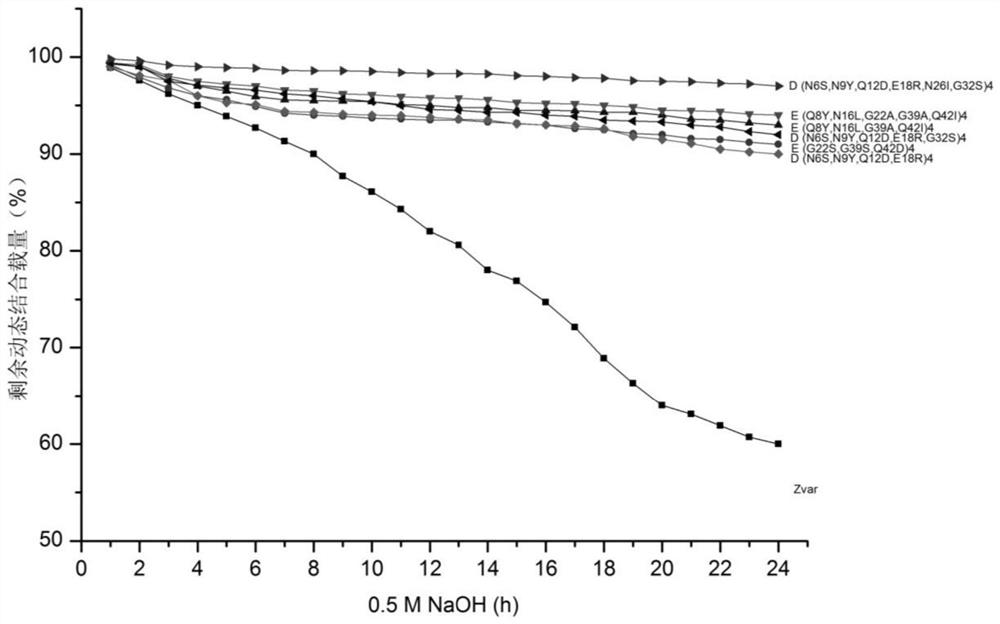
The invention discloses a recombinant Protein A protein and a preparation method of an affinity chromatography medium. The protein is a mutant of parent immune globulin-binding protein as defined by SEQ ID No 1 and SEQ ID No 2; and the preparation method of the affinity chromatography medium comprises the following steps: S1, synthesizing genes of the recombinant Protein A protein, S2, respectively constructing expression vectors by using the genes synthesized in the S1, S3, culturing, expressing and purifying to obtain a recombinant Protein A solution with a corresponding sequence of SEQ ID, and S4, preparing the affinity chromatography medium by using the recombinant Protein A. The preparation method has the advantages that the chemical stability of the Protein A in alkali liquor is greatly improved by redesigning an amino acid sequence, so that the Protein A with a specific binding effect on an antibody is provided, the Protein A has good chemical stability under an alkaline condition, the binding load of the recombinant Protein A and affinity chromatography medium is remarkably improved, in-place cleaning under 0.5-1.0 M NaOH can be tolerated, and the IgG binding load is 60-90 mg / ml.
Owner:PINGHU YOUPU BIOTECH CO LTD
Specific modification of antibody with IgG-binding peptide
ActiveUS10227383B2Less side effectsReduce functionTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding peptideAntibody
This invention relates to an IgG-binding peptide, an IgG-binding peptide modified with a cross-linking agent, a conjugate of the IgG-binding peptide modified with a cross-linking agent and IgG, and a method for producing the conjugate, etc.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
Diagnosis and therapy of antibody-mediated inflammatory auto-immune disorders
InactiveUS7998681B2Reduced activityAlleviating antibody-mediated auto-immune diseasesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsVertebrate cellsBiochemical mechanismT cell
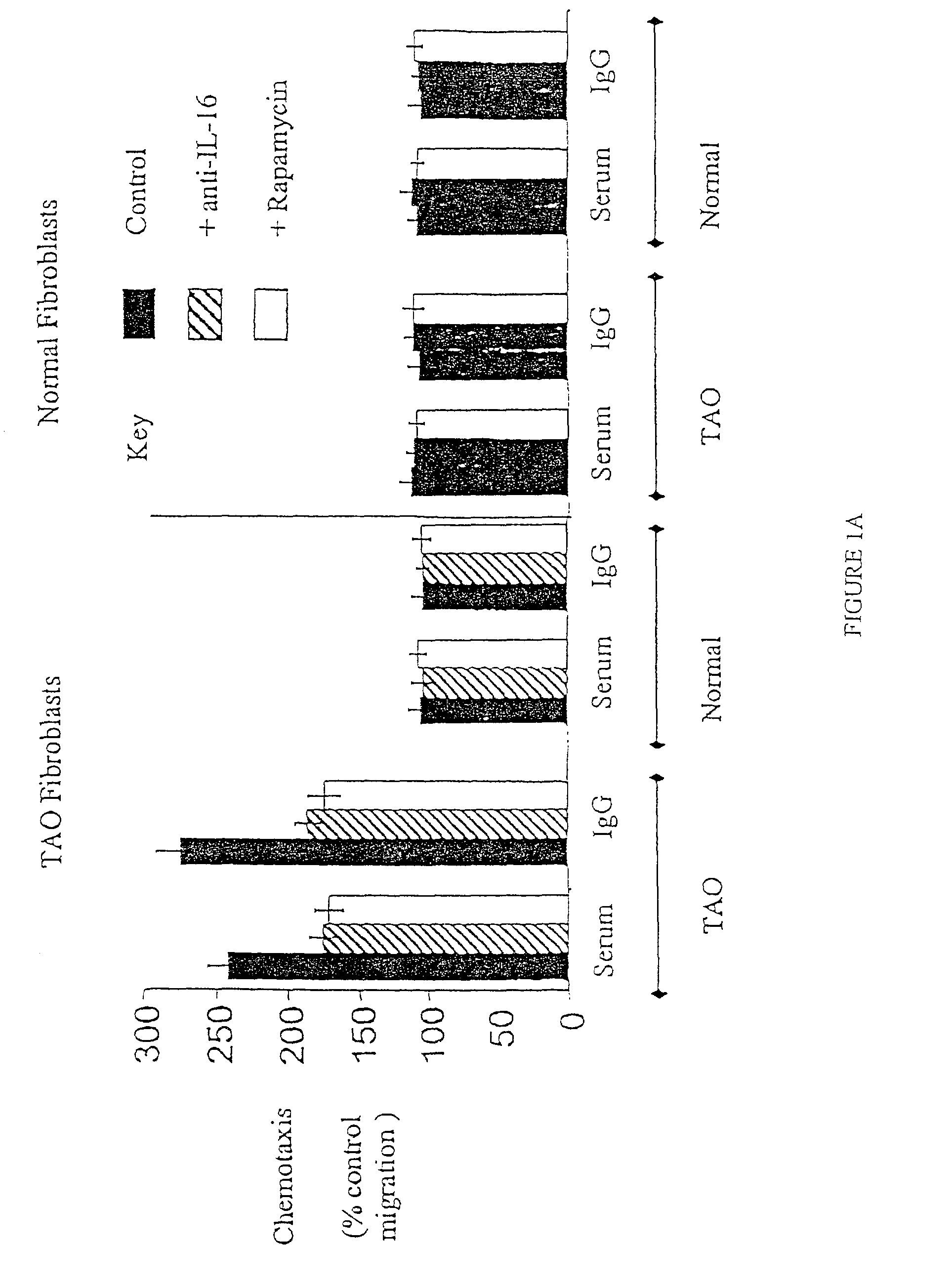
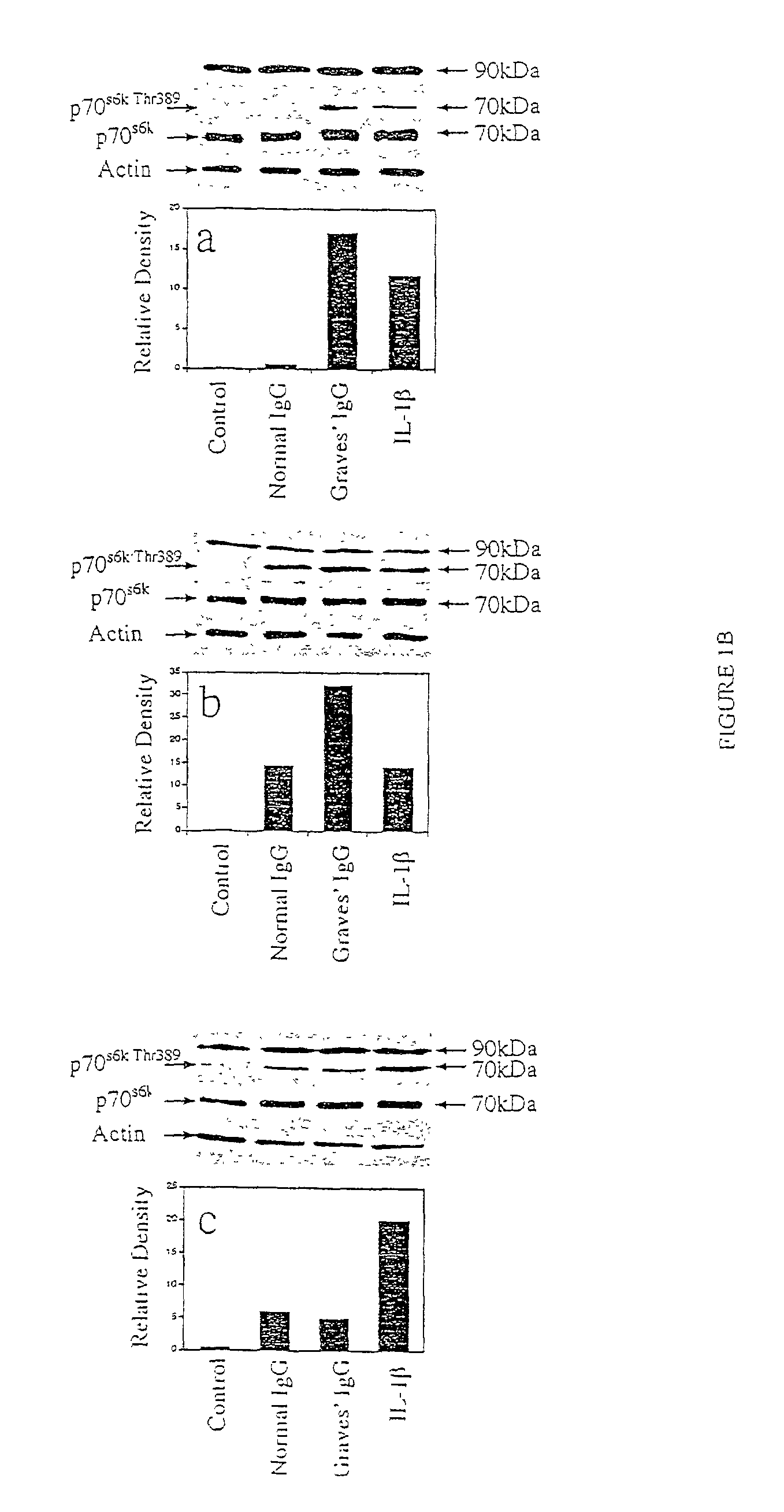
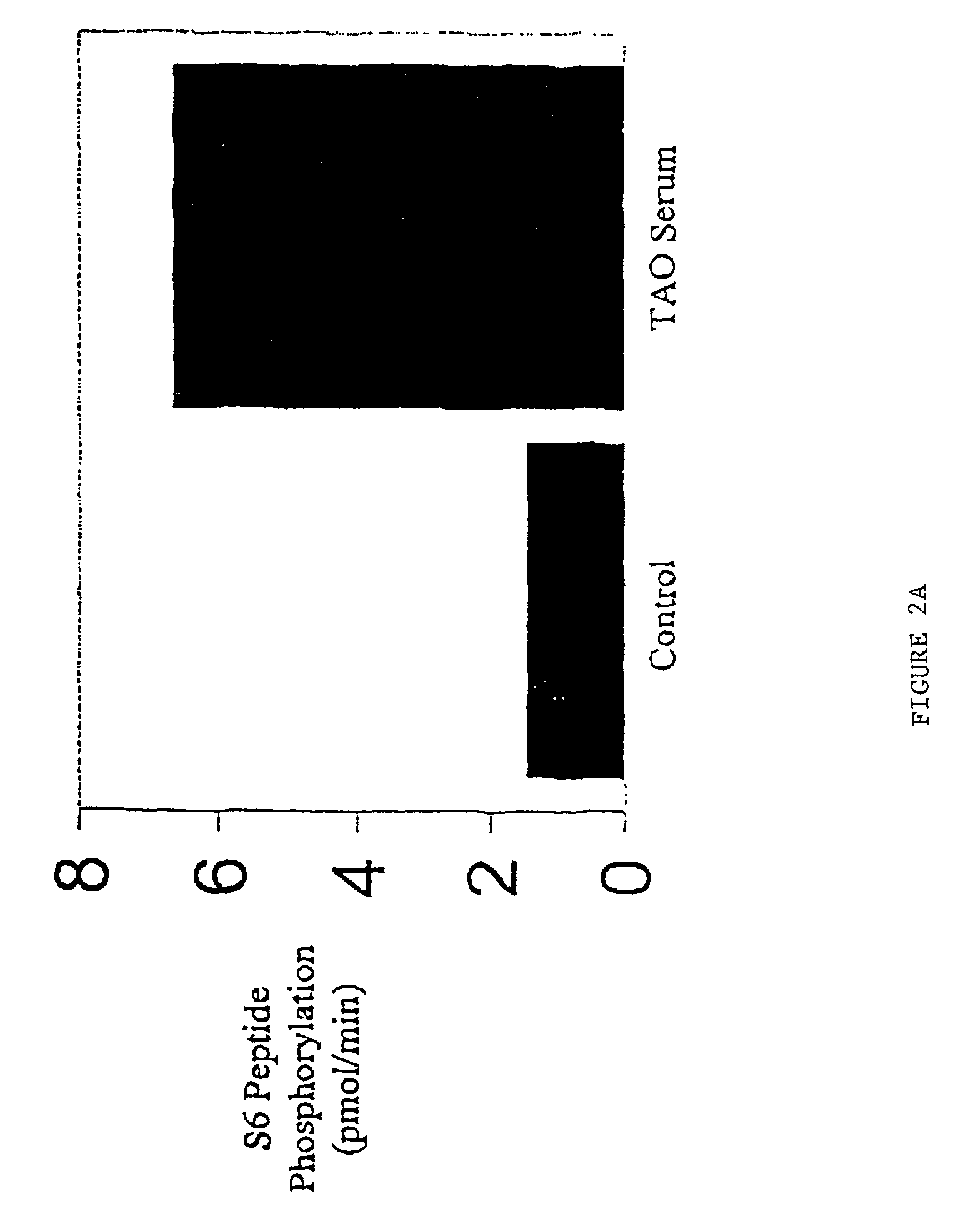
The present invention describes diagnosis and treatment of antibody-mediated inflammatory auto-immune diseases. The biochemical mechanisms underlying such disorders are described as characteristic molecular markers and antibody-mediated ligand-receptor interactions. Specifically, the activation of T-cells by disease specific IgG binding to the IGF-1 receptor is shown to underlie thyroid associated ophthalmopathy associated with Graves' disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Diagnostics for detection of disease are provided, as are therapeutics based on the determination of the mechanisms underlying a particular pathology.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT +2
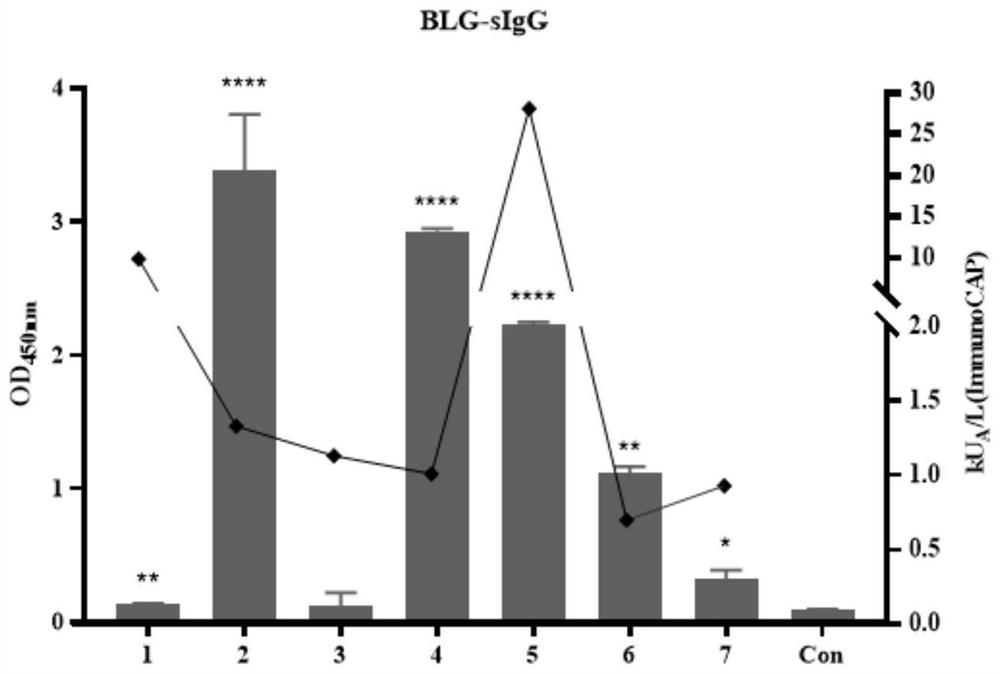
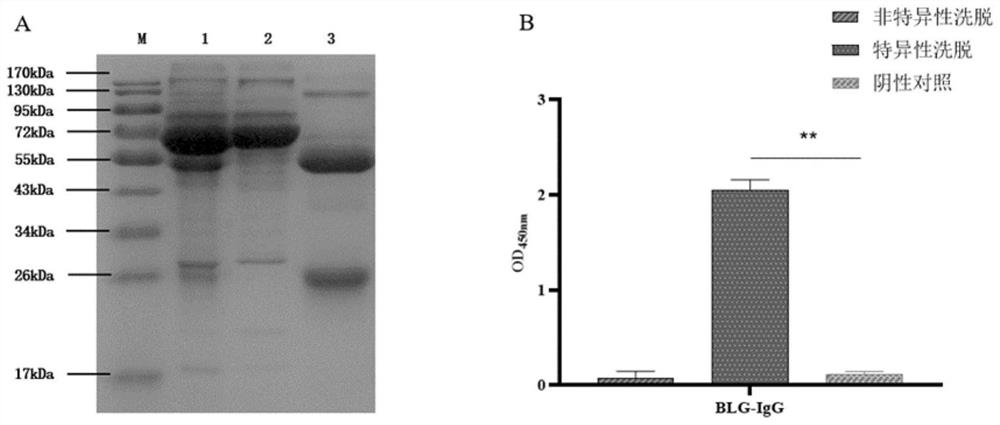
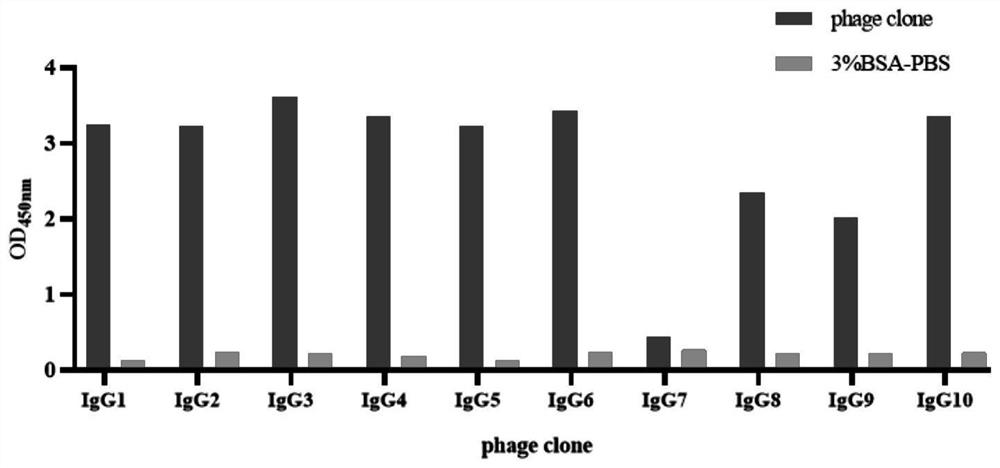
IgG epitope peptide of whey allergen beta-lactoglobulin
PendingCN114874310AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisCow milkingMilk Serum
Owner:AUSNUTRIA DAIRY CHINA
Use of urea variants as affinity ligands
ActiveUS20060014735A1Avoid disadvantagesAdvantageous chemical propertyBiocideUrea derivatives preparationBinding siteAntibody Affinity Chromatography
The present invention relates to an IgG-binding compound, which more specifically has affinity for human IgGs of κ-type and functional derivatives thereof. More specifically, the compound according to the invention comprises an N,N-alkylated urea moiety located between an aromatic part and another part, which is a linear or cyclic substituted or unsubstituted aliphatic group. The compound binds to a pocket-shaped binding site present on all human IgG κ-Fabs, which site is located between the two domains (CH1 and CL) of its constant part. Accordingly, the compound according to the invention is a ligand for human IgGs of κ-type, and consequently, the invention also relates to a separation matrix for affinity chromatography, which matrix comprises said compound, as well as to other uses of the compound.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Method for labeling of compounds
ActiveUS8916689B2Maximize antigen bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAntigen bindingHelix structure
The present invention relates to site-specific labeling of antibodies or fragments thereof with one or more reporter group(s) in a way that does not affect antigen binding. The method for labeling antibodies and / or fragments thereof, comprises the following steps a) providing an IgG binding protein, which comprises α-helix structures, with a photoactivatable group and at least one label; b) forming a mixture of said IgG binding protein and the antibodies and / or fragments to be labeled; and c) UV illuminating said mixture for site-specific labeling of said antibodies and / or fragments thereof. The IgG binding protein is preferably the Z domain of Protein A.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Solid-Phase Support Comprising IgG-Binding Peptide, and Method for Separating IgG
ActiveUS20190367560A1Improve stabilityEfficient purificationSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsBinding peptideCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention provides an IgG-binding peptide which can be used for the purification of IgG and has excellent stability, e.g., alkali stability. The present invention also provides a method for purifying IgG using the IgG-binding peptide. Specifically, the present invention relates to a solid-phase support including an IgG-binding peptide, an IgG separation column including the solid-phase support, a kit including the solid-phase support or the column, and a method for purifying IgG using the solid-phase support or the column.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV +1
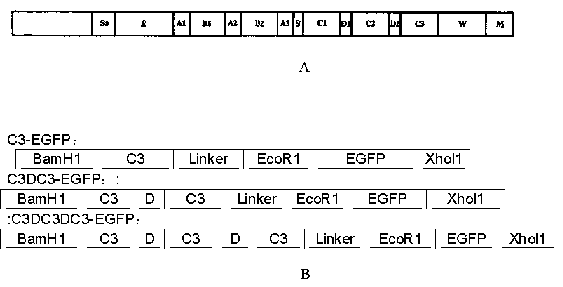
Multispecies universal detection protein with green fluorescence activity and application of universal detection protein
InactiveCN110615844AFluorescently activeEfficient captureMicroorganism based processesHybrid peptidesGlobin bindingFluorescence
The invention provides a multispecies universal detection protein with green fluorescence activity and application of the universal detection protein. The universal detection protein is characterizedin that the detection protein comprises a streptococcus protein G (SPG) segment and a fluorescent protein; and an IgG binding segment of an SPG gene is reconstructed, only a C3 region where the protein G can be specifically bound with the Fc terminal of an antibody IgG is retained, the C3 region is divided into three groups of C3, C3-D-C3 and C3-D-C3-D-C3, all the groups are connected to EGFP, anda prepared recombinant protein has the fluorescence activity and dual activity of binding to antibodies of different species. Disclosed evolutionary immunoglobulin binding molecules can widely bind to total IgG and IgG of different subclasses in humans and many animals in a wide spectrum mode, and compared with immunoglobulin binding molecules in the prior art, the binding force of the evolutionary immunoglobulin binding molecules is also higher than that of the existing immunoglobulin binding molecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel coronavirus antibody detection kit as well as preparation method and application thereof
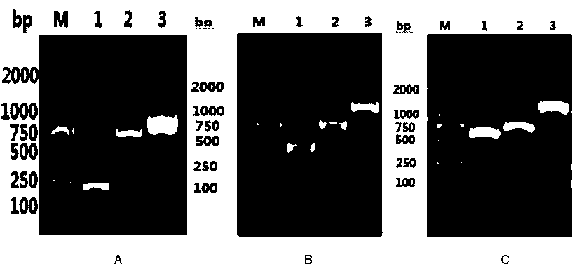
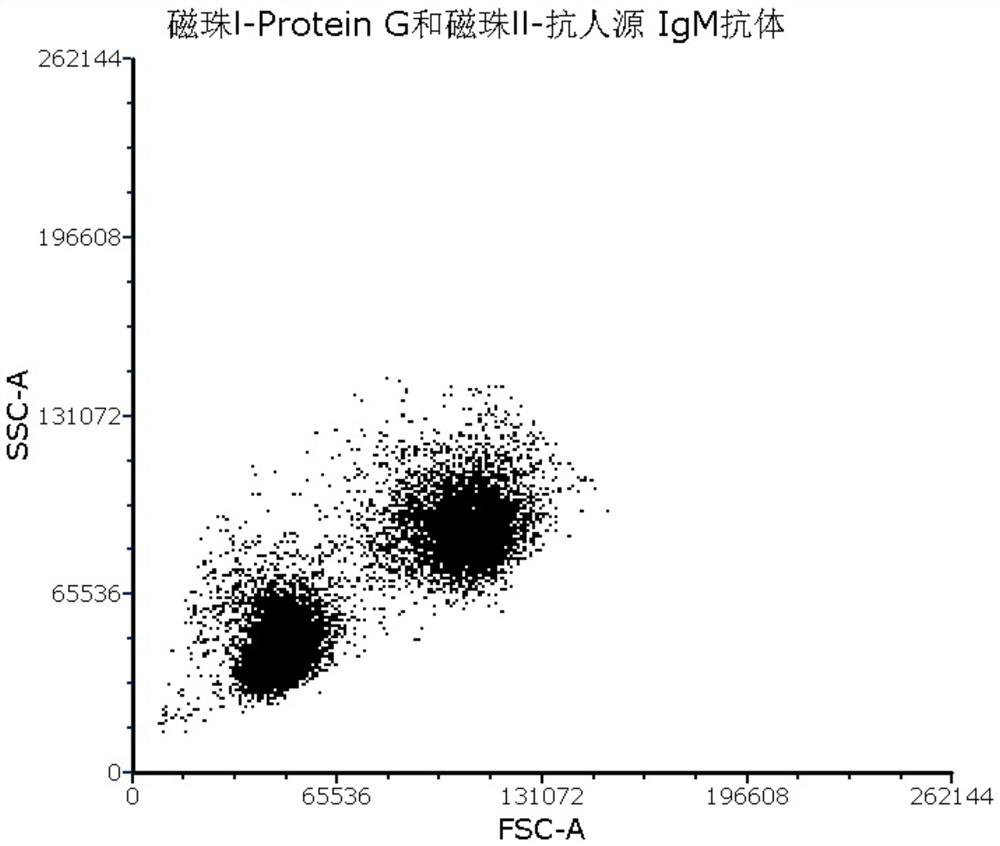
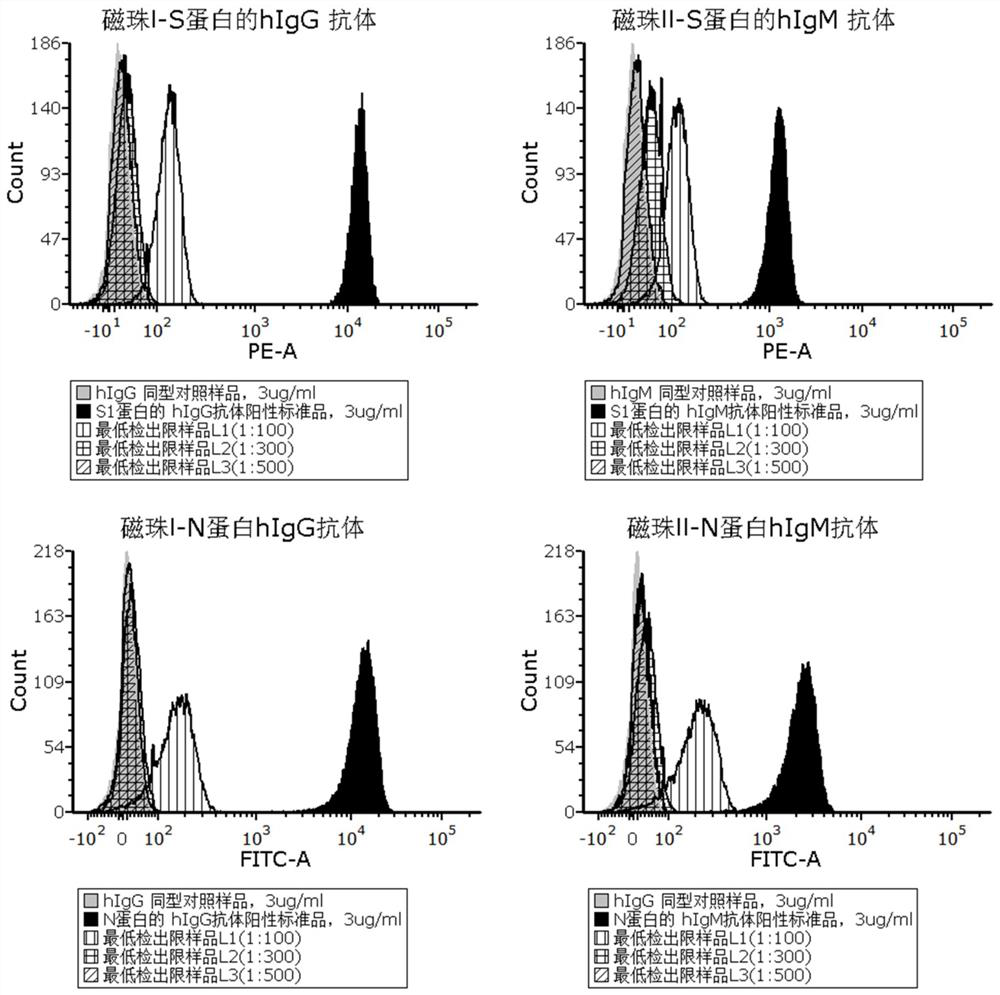
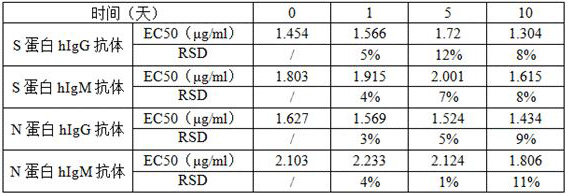
ActiveCN112379090AReduce dosageImprove detection efficiencyIndividual particle analysisBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesCoronavirus antibody
The invention provides a novel coronavirus antibody detection kit as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The kit comprises an IgG binding molecule, an anti-IgM antibody, fluorescently-labeled novel coronavirus S1 protein, fluorescently-labeled novel coronavirus N protein, an hIgG antibody positive standard substance of the S1 protein, an hIgG antibody positive standard substanceof the N protein, an hIgM antibody positive standard substance of the S1 protein, an hIgM antibody positive standard substance of the N protein, a negative control hIgG antibody sample and a negativecontrol hIgM antibody sample, wherein the IgG binding molecule and the anti-IgM antibody are loaded on nanoparticles with different particle sizes. The kit disclosed by the invention is used for detecting novel coronavirus antibodies, can be used for quickly detecting novel coronavirus neutralizing antibodies in serum within 12 h, and has the advantages of small dosage of a to-be-detected sample,good specificity, high sensitivity, good repeatability, simplicity in operation, low laboratory requirement and high safety.
Owner:ACROBIOSYSTEMS INC
IgG-binding peptide and method for detecting and purifying IgG using same
ActiveUS9365619B2Selectively separateComponent separationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsArginineTryptophan
Provided is a peptide that specifically or selectively binds to human IgG. This peptide comprises an amino acid sequence consisting of 13 to 17 amino acid residues and is capable of binding to human IgG, wherein the amino acid sequence is represented by formula I: (X1-3)-C-(X2)-H-R-G-(Xaa1)-L-V-W-C-(X1-3), wherein, X each independently represents any amino acid residue except cysteine, C represents a cysteine residue, H represents a histidine residue, R represents an arginine residue, G represents a glycine residue, Xaa1 represents a glutamic acid residue or an asparagine residue, L represents a leucine residue, V represents a valine residue, and W represents a tryptophan residue.
Owner:OTSUKA CHEM CO LTD +1
A Class of Small Proteins and Their Applications
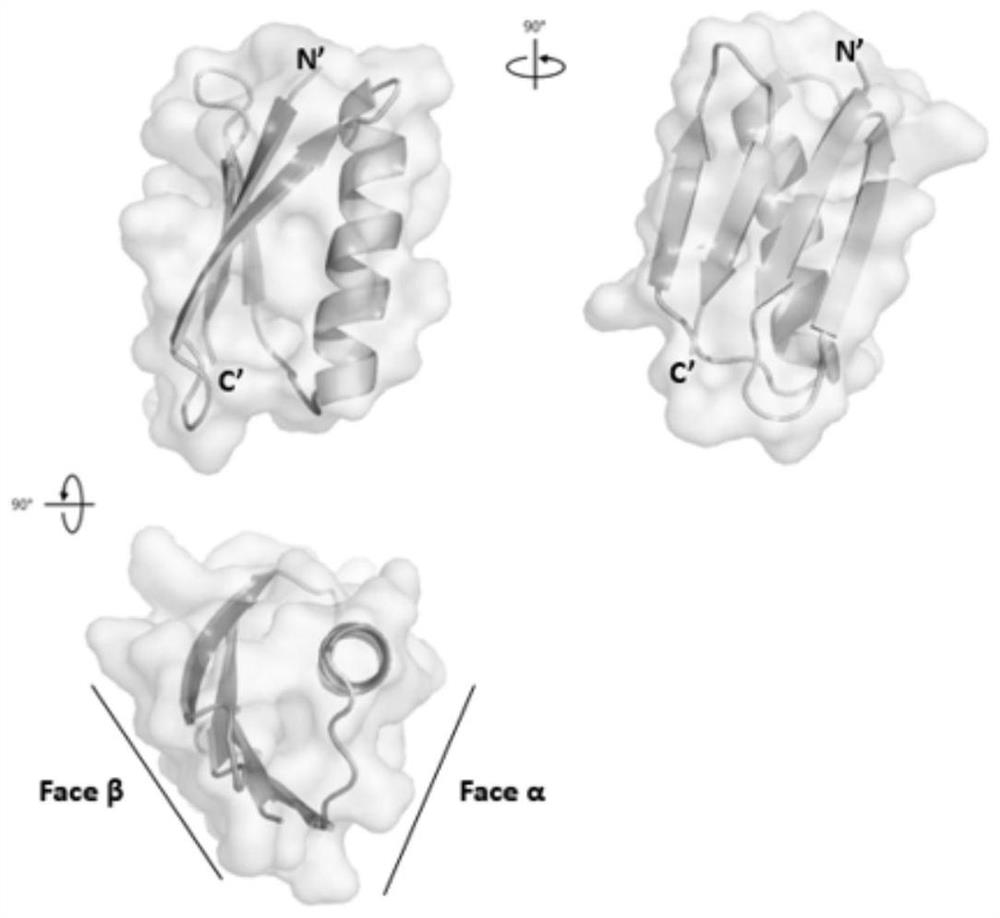
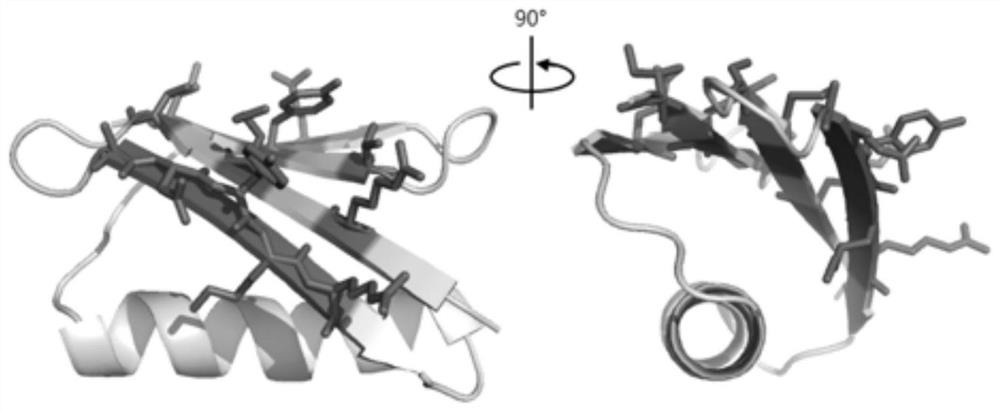
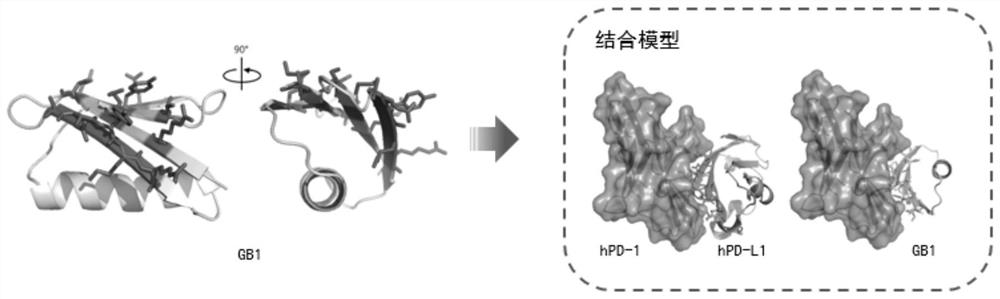
ActiveCN110305200BImprove structural stabilityHigh structural similarityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAlpha helixProtein G
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
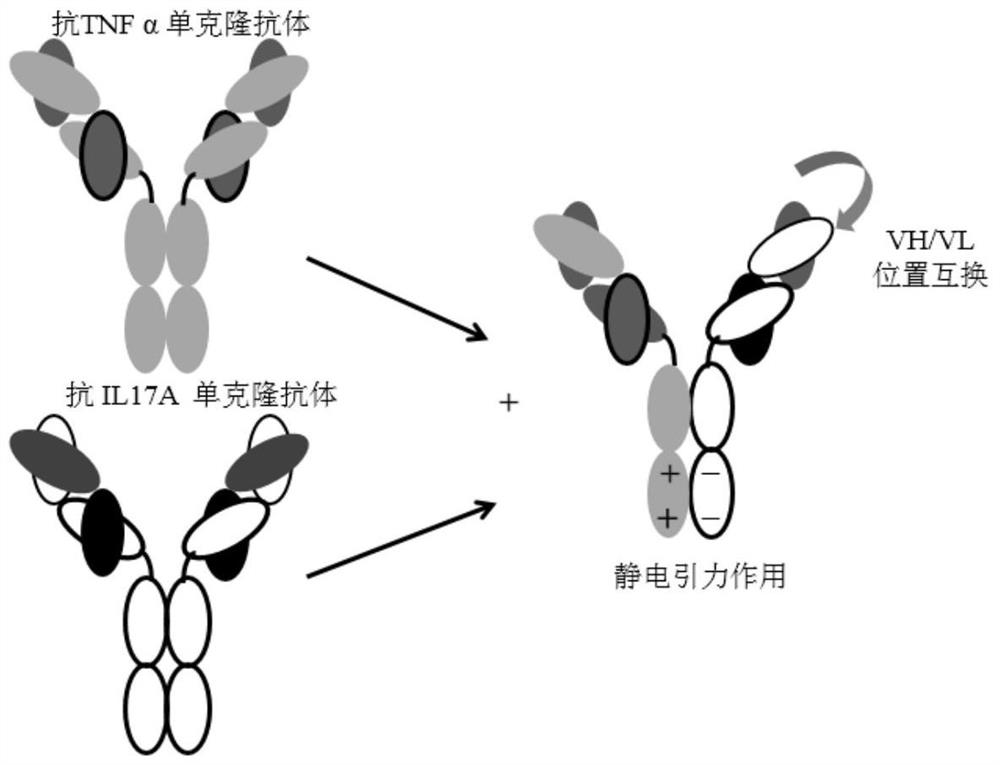
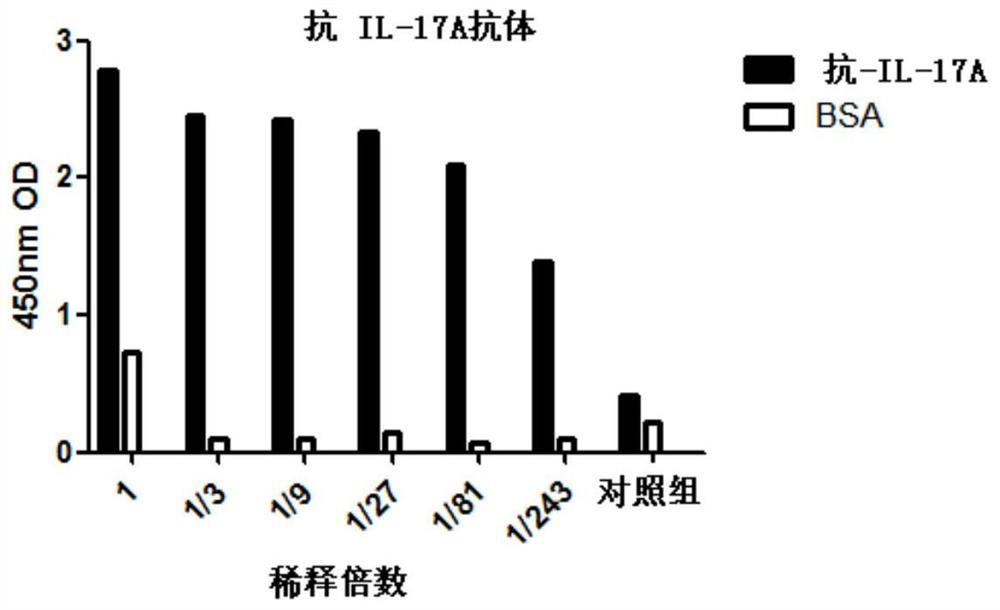
IgG heterozygous anti-TNFα and IL-17A bispecific antibody
ActiveCN106661117BImprove stabilityStrong specificityAntipyreticAnalgesicsAntiendomysial antibodiesBispecific antibody
The present invention provides an IgG hybrid bispecific antibody against TNFα and IL-17A. The hybrid antibody comprises a first heavy chain and a first light chain from a human IgG binding specifically to TNFα, and a second heavy chain and a second light chain of a human IgG binding specifically to IL-17A. A variable region of the second heavy chain is exchanged with a variable region of the second light chain, and / or a variable region of the first heavy chain is exchanged with a variable region of the first light chain; and constant regions of the first heavy chain and the second heavy chain interact with each other via enhanced electrostatic interaction or hydrophobic interaction.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
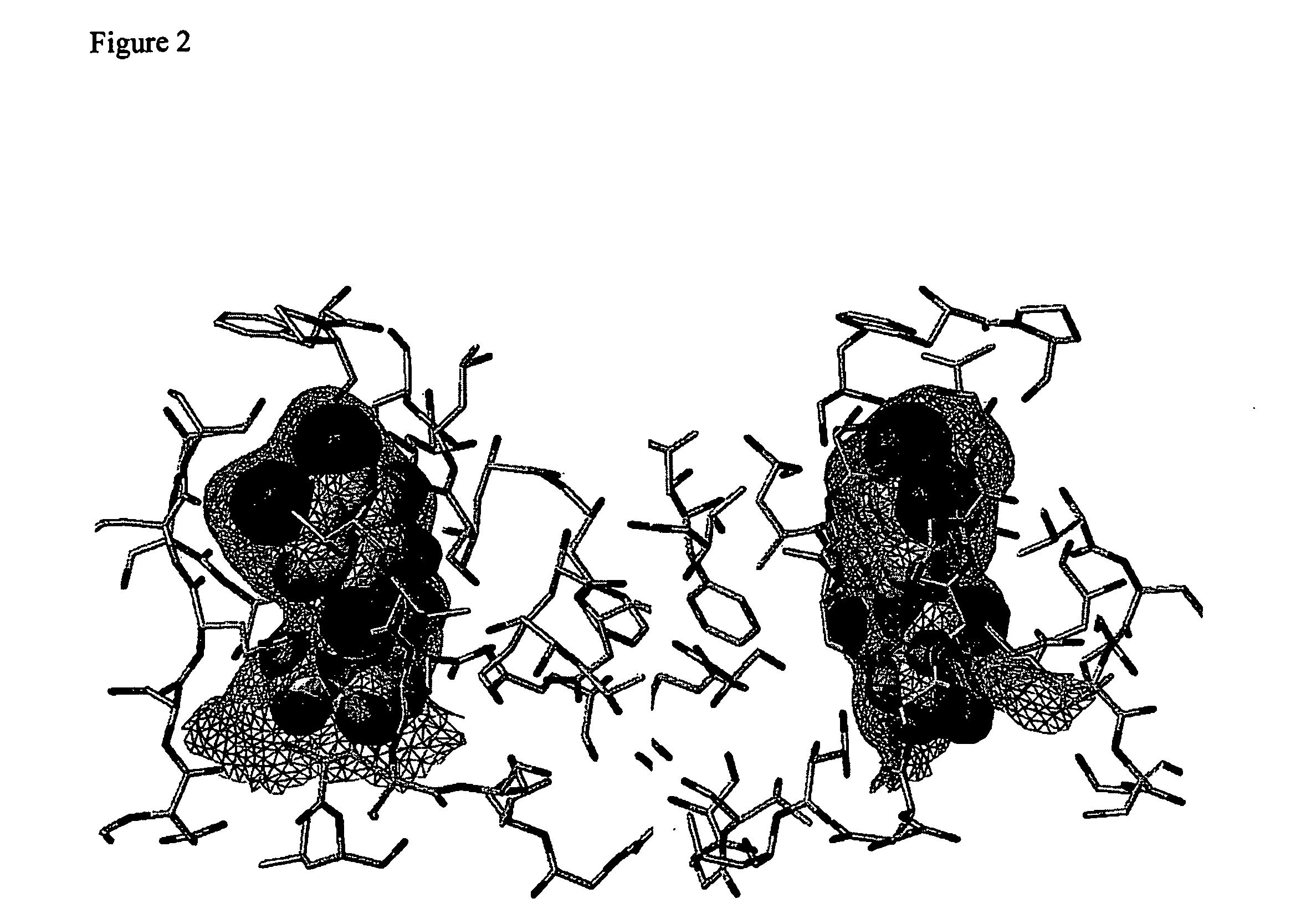
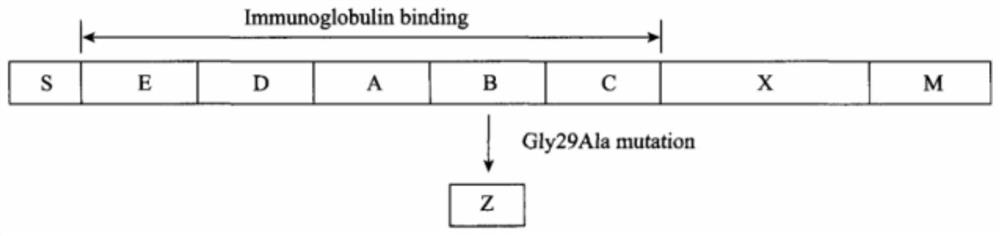
Immunoglobulin g binding pocket
InactiveUS20090138208A1Easy to implementOrganic chemistryBiological testingIgG.heavy chainHeavy chain
The present invention relates to a human IgG binding pocket comprised of a first interacting surface, which originates from an IgG κ light chain, and a second interacting surface, which originates from an IgG heavy chain, which amino acids are strictly conserved between human IgGs of κ-type. The invention also embraces an isolated and purified polypeptide, which comprises said binding pocket. Further, the invention relates to various methods of using the novel binding pocket, such as in screening for identification of chemical entities capable of selective binding thereof, and in other experimental and / or virtual methods for design and / or identification of chemical entities capable of selective binding thereof.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Alkali-resistant protein A variants and uses thereof
The invention discloses a protein A variant, and particularly relates to a protein A variant with high alkali resistance and high IgG binding affinity. The invention also discloses application of the protein A variant.
Owner:百林科(兰州)新材料有限公司 +1
IgG binding epitopes of main soybean allergen Gly m Bd 28K
The invention relates to three IgG binding epitopes of a main soybean allergen Gly m Bd 28K. Amino acid sequences of the three IgG binding epitopes are 28H-Gly-Asp-Lys-Lys-Ser-Pro-Lys-Ser-Leu-Phe-Leu-Met-Ser-Asn-Ser-OH42, 56H-Leu-Lys-Ser-His-Gly-Gly-Arg-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Arg-His-Met-His-Ile-OH70 and 154H-Glu-Thr-Phe-Gln-Ser-Phe-Tyr-Ile-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ala-Asn-Ser-His-OH168 respectively. According to the IgG binding epitopes, suppression of the binding of a Gly m Bd 28K natural protein and a Gly m Bd 28K monoclonal antibody (mAb3F5) by the chemically synthesized polypeptide 56H-Leu-Lys-Ser-His-Gly-Gly-Arg-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Arg-His-Met-His-Ile-OH70 shows that the linear epitope polypeptide has a good suppression effect on affiliation of the Gly m Bd 28K natural protein and the Gly m Bd 28K monoclonal antibody (mAb3F5). The IgG binding epitopes are significant for proving a molecular mechanism produced by food allergy, understanding the effect of the allergen in food allergy, developing researches on non-allergic and hypoallergenic food and researching the occurrence of allergic diseases.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com