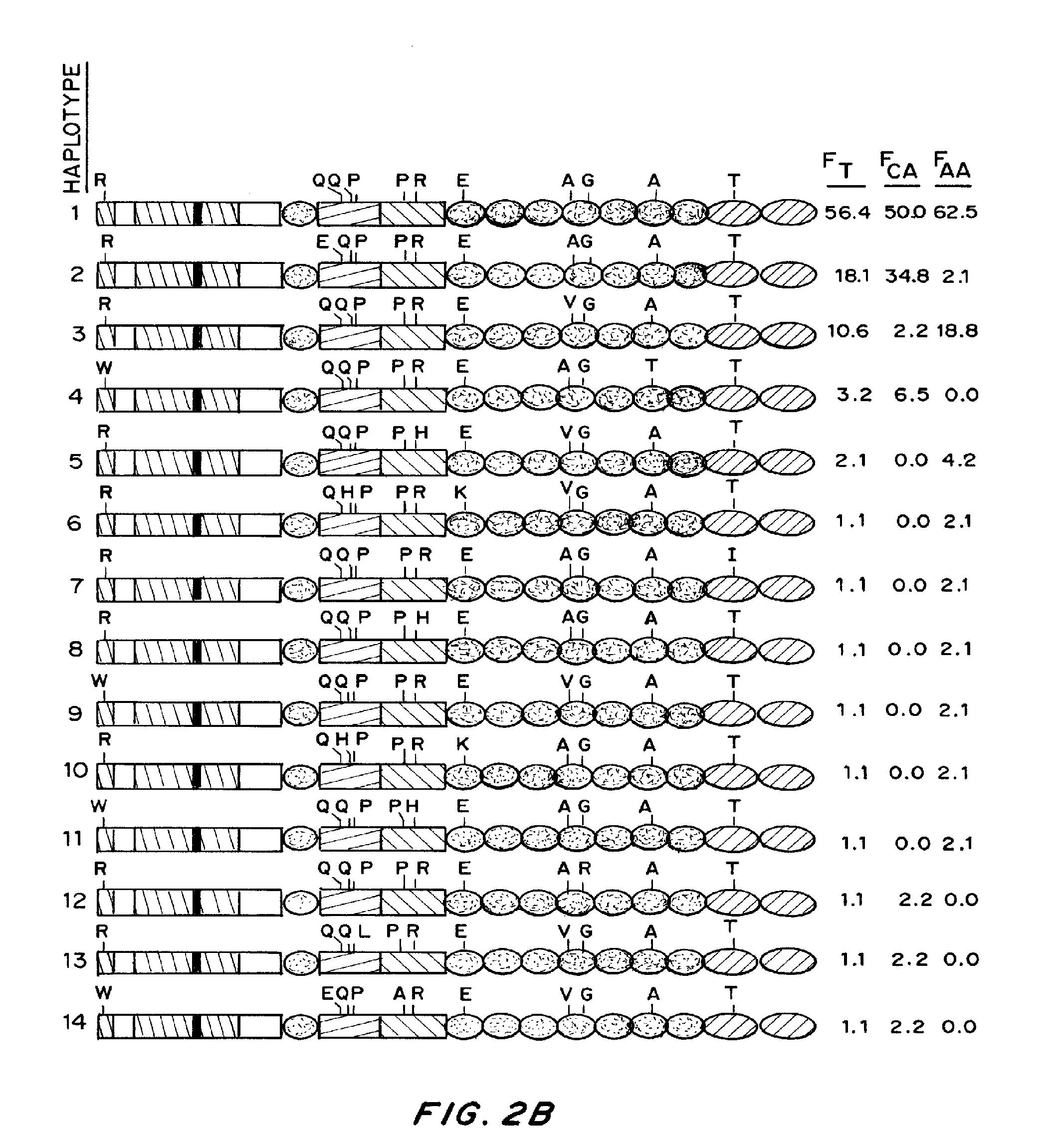
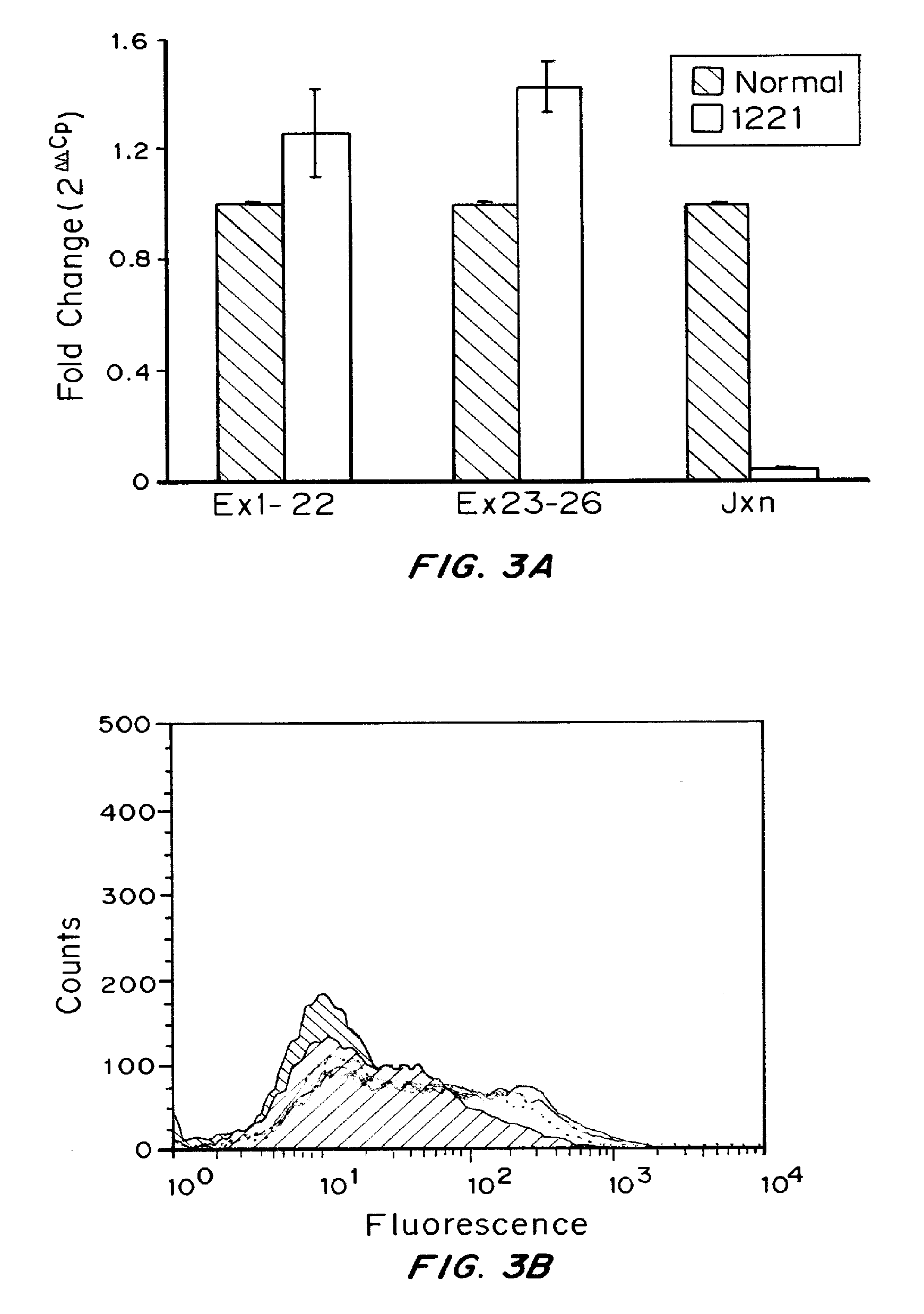
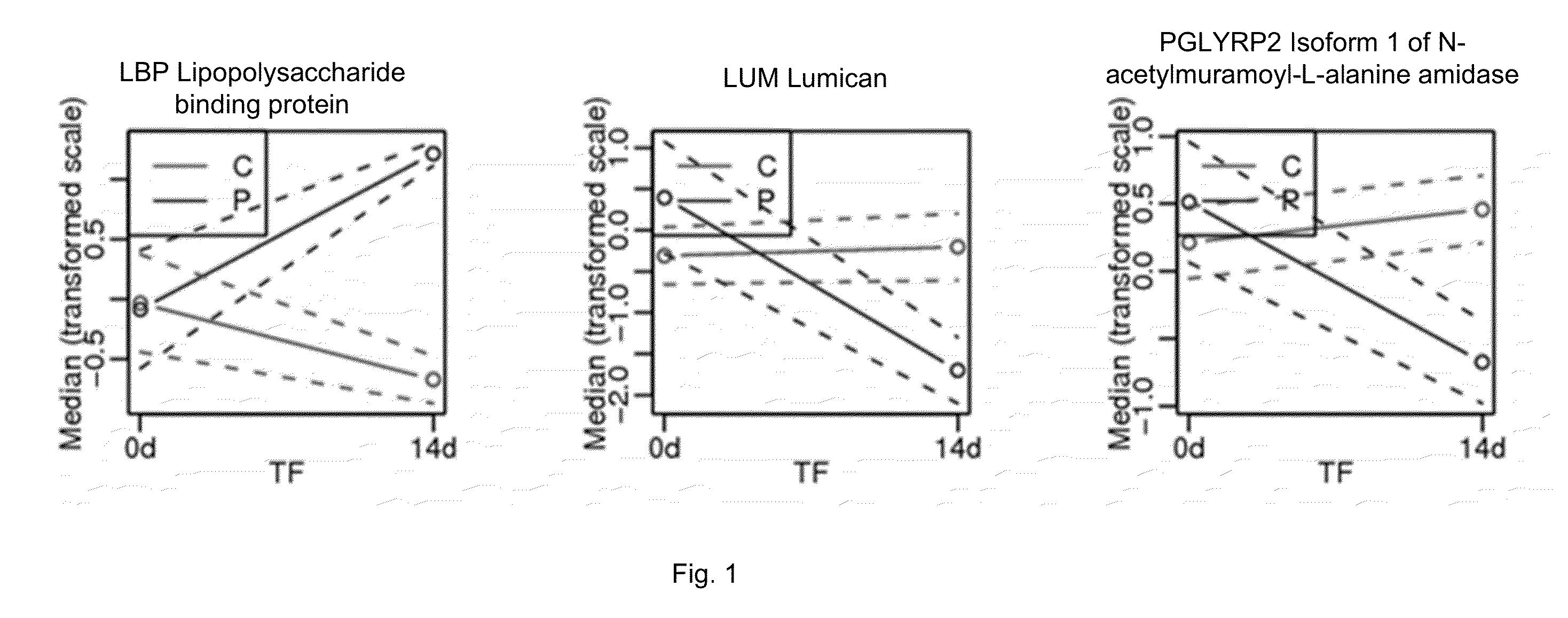
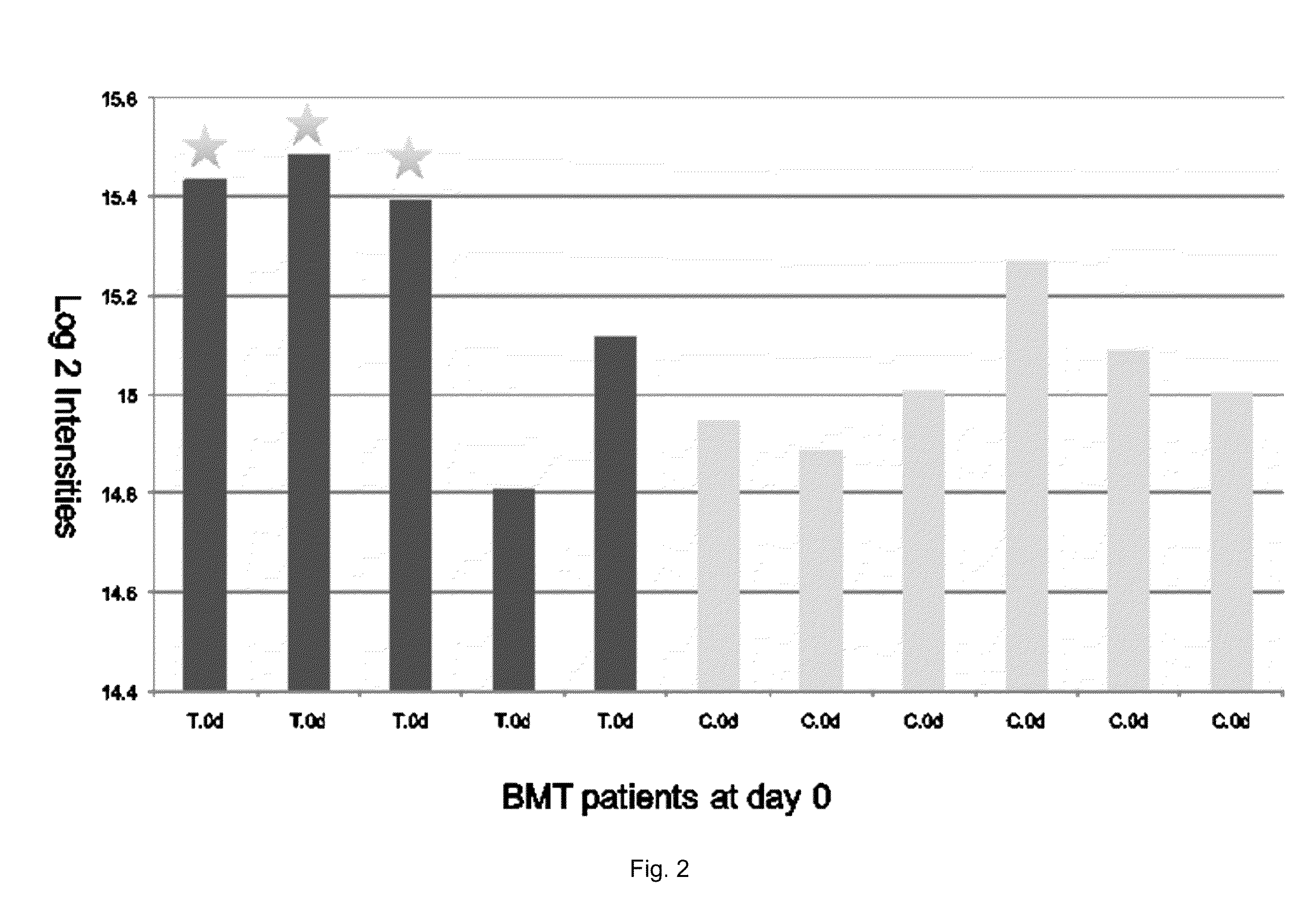
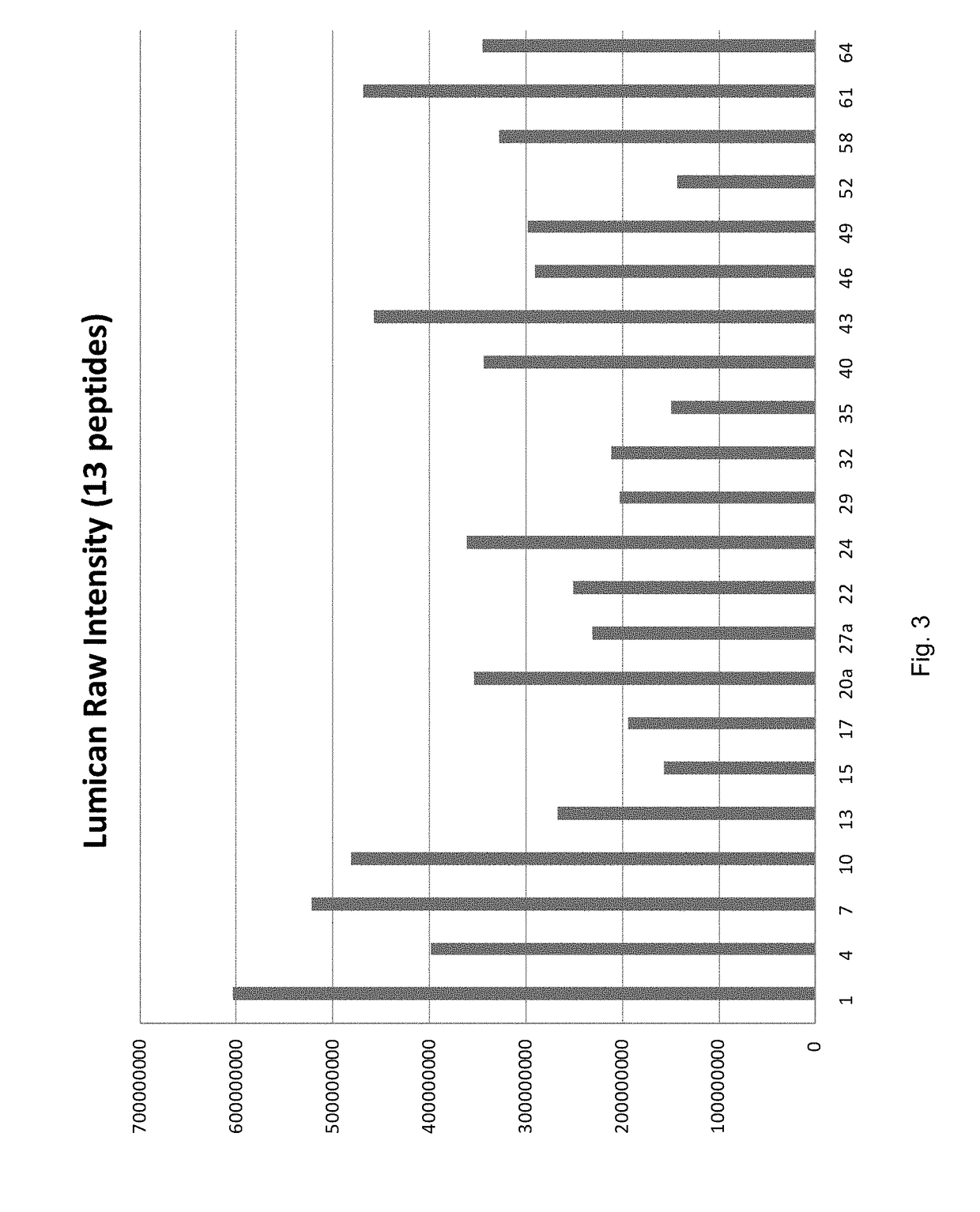
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Alloimmunity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alloimmunity (sometimes called isoimmunity) is an immune response to nonself antigens from members of the same species, which are called alloantigens or isoantigens. Two major types of alloantigens are blood group antigens and histocompatibility antigens. In alloimmunity, the body creates antibodies against the alloantigens, attacking transfused blood, allotransplanted tissue, and even the fetus in some cases. Alloimmune (isoimmune) response results in graft rejection, which is manifested as deterioration or complete loss of graft function. In contrast, autoimmunity is an immune response to the self's own antigens. (The allo- prefix means "other", whereas the auto- prefix means "self".) Alloimmunization (isoimmunization) is the process of becoming alloimmune, that is, developing the relevant antibodies for the first time.
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
Antibodies to heavy chain of human FcRn are provided which function as non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal, monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, or antigen binding fragments thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Novel chimeric proteins and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20030216546A1Compounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein insertion
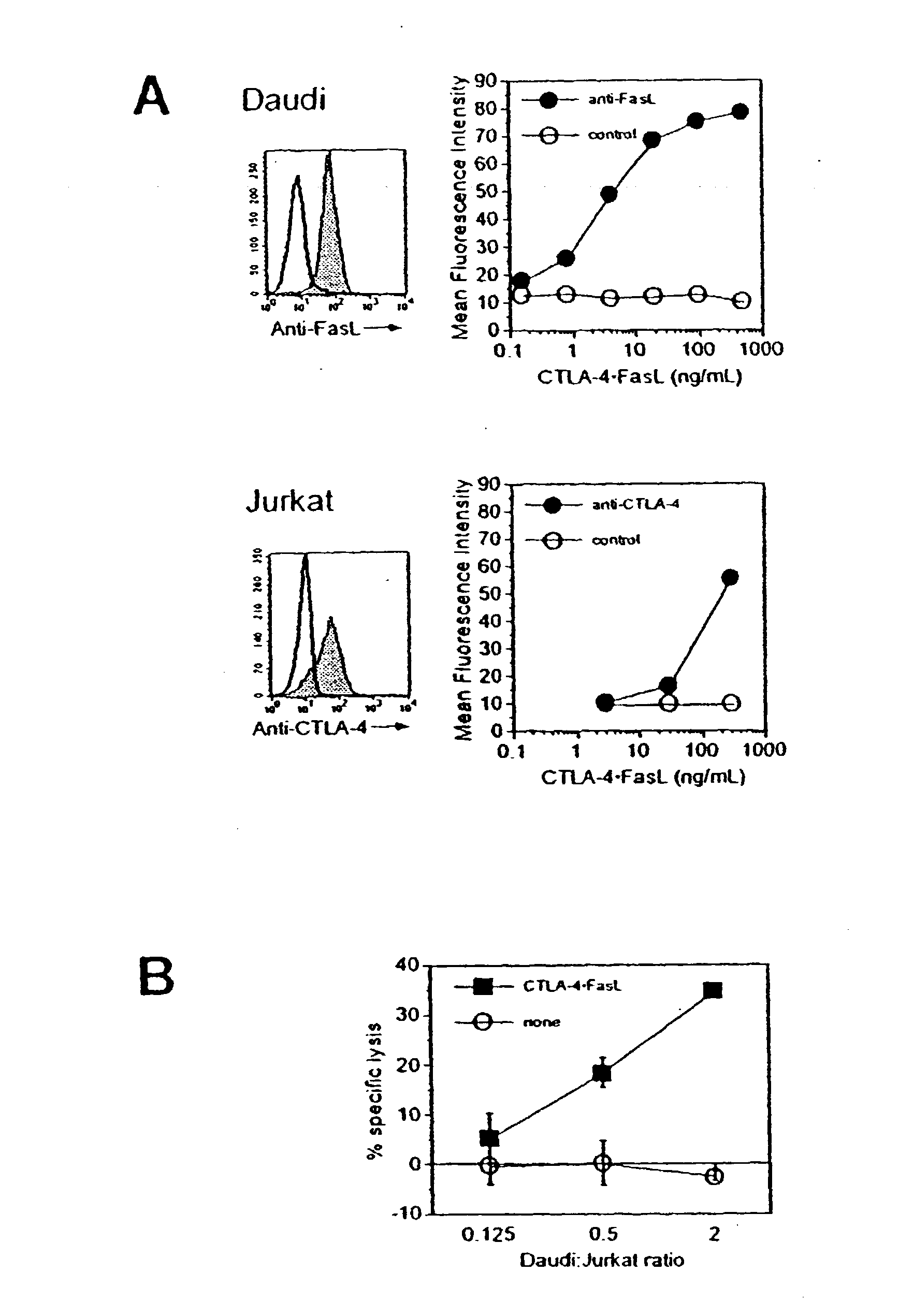
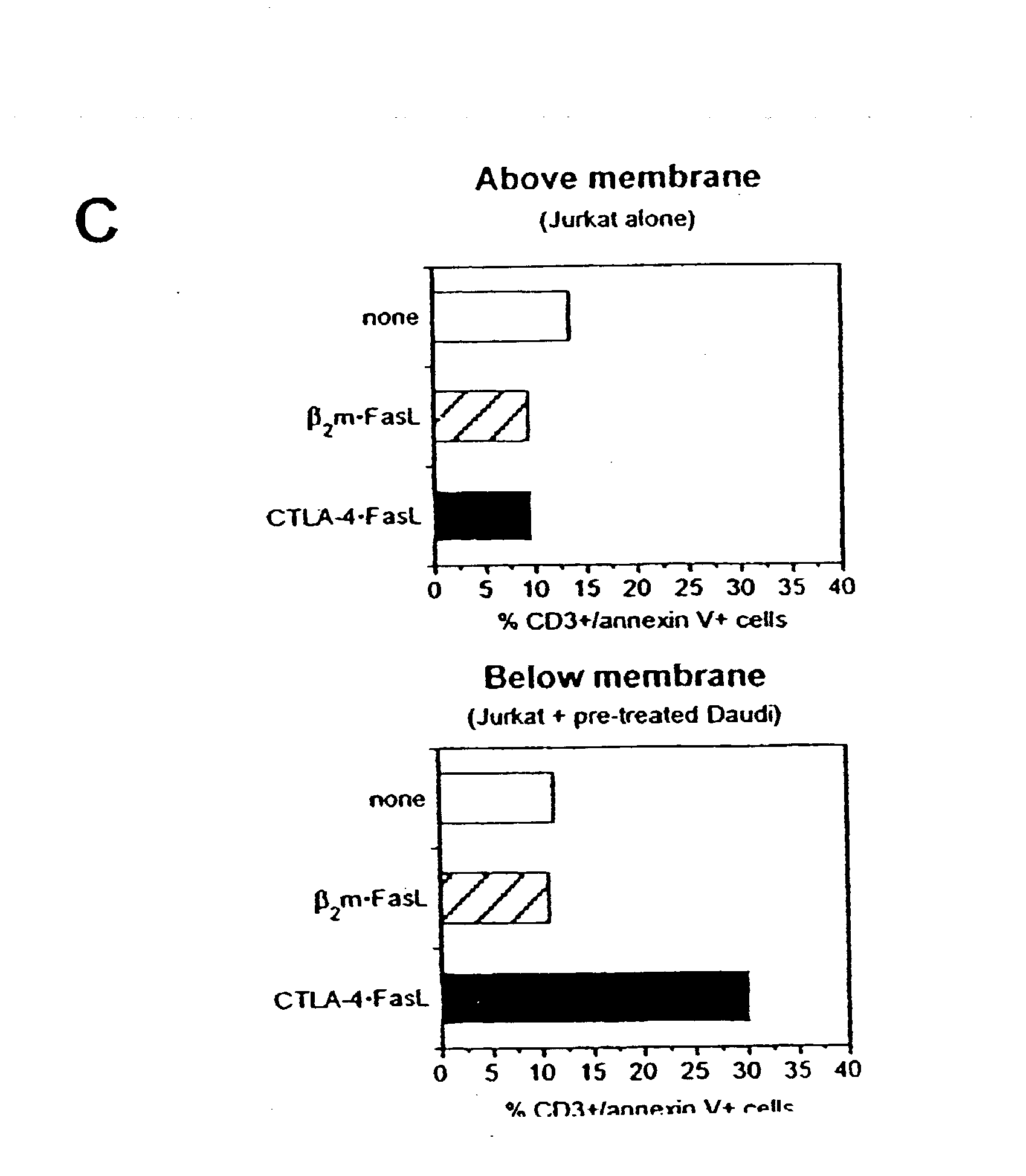
Novel chimeric proteins are disclosed. The proteins comprise at least two portions. The first portion binds to a first cell and decreases the cell's ability to send a trans signal to a second cell; the second portion sends its own trans signal to the second cell. Methods for making and using these proteins in the treatment of cancer, viral infections, autoimmune and alloimmune diseases are also disclosed, as are pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel chimeric proteins and genes. Either the proteins themselves or a genetic sequence encoding the protein can be administered. Other methods are also disclosed in which two molecular components result in decrement of a first trans signal from a first cell and the conferring of a second trans signal to a second cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Blood Group and Platelet Antigen Genotypes
InactiveUS20080261205A1Reduce in quantityMeet demandSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood collectionRed blood cell
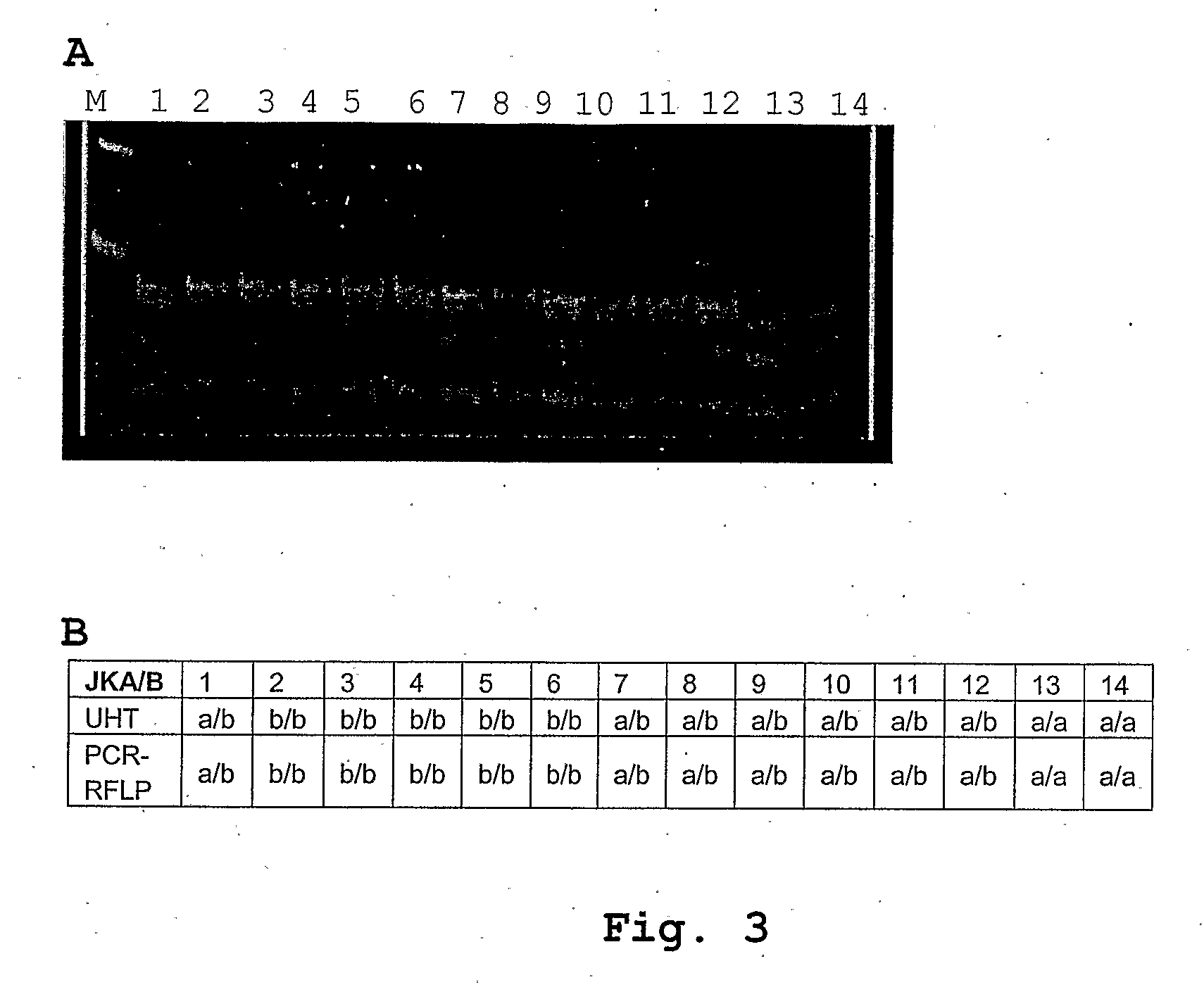
RBC and platelet (Plt) alloimmunization requires antigen-matched blood to avoid adverse transfusion reactions. Some blood collection facilities use unregulated Abs to reduce the cost of mass screening, and later confirm the phenotype with government approved reagents. Alternatively, RBC and Plt antigens can be screened by virtue of their associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). We developed a multiplex PCR-oligonucleotide extension assay using the GenomeLab SNPStream platform to genotype blood for a plurality of blood group antigen-associated SNPs, including but not limited to: RhD (2), RhC / c, RhE / e, S / s, K / k, Kpa / b, Fya / b, FYO, Jka / b, Dia / b, and HPA-1a / b.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
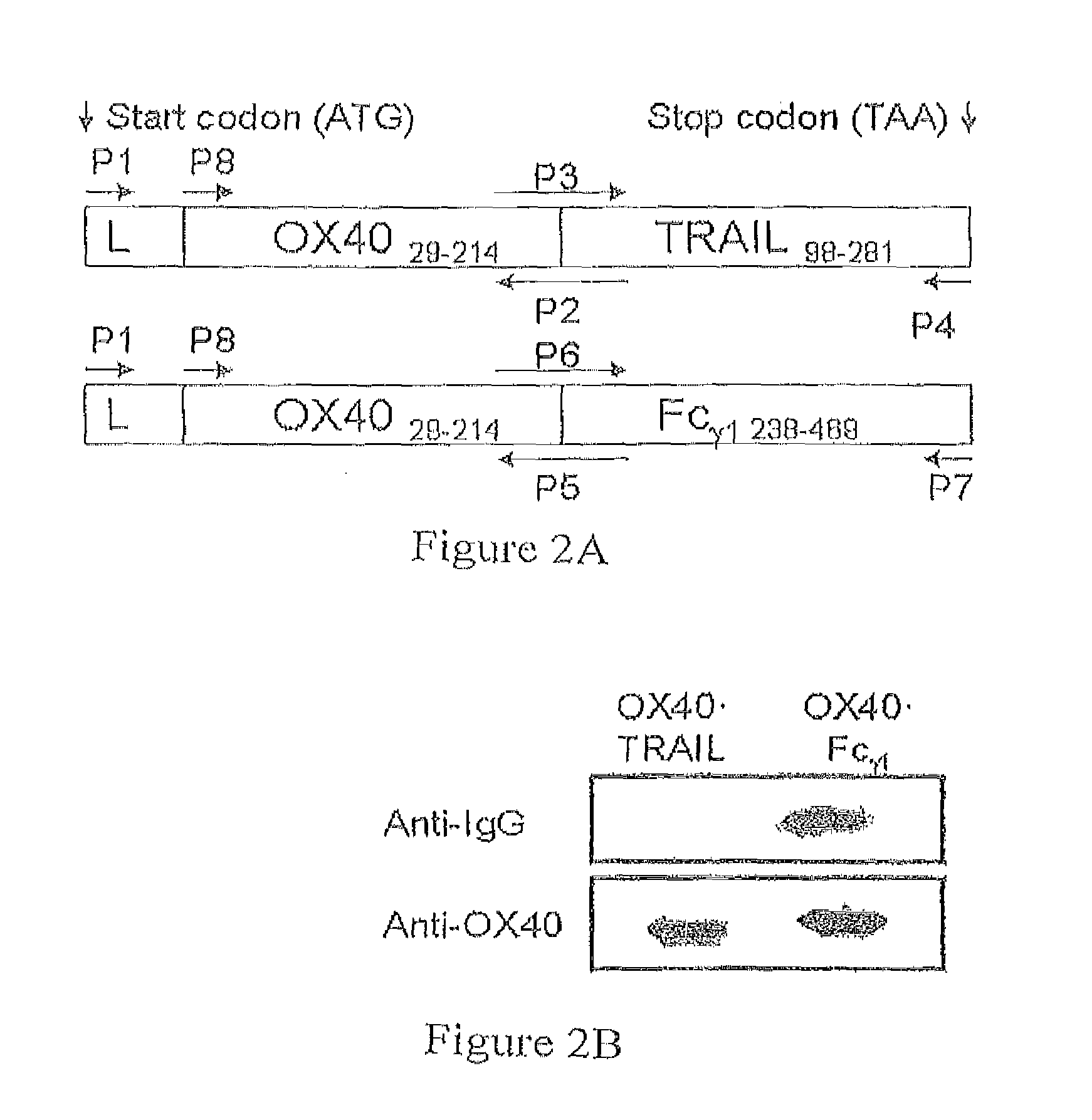
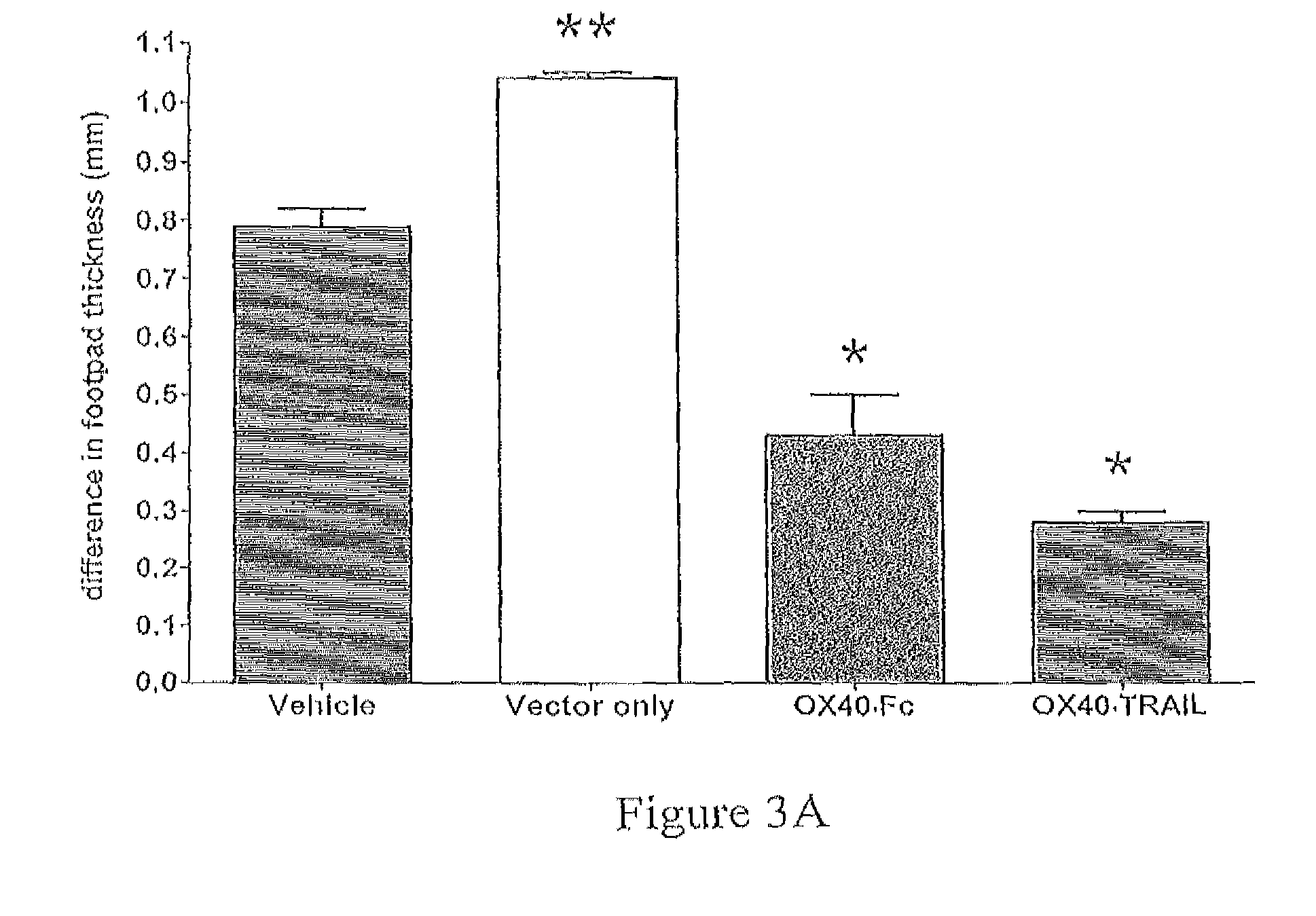
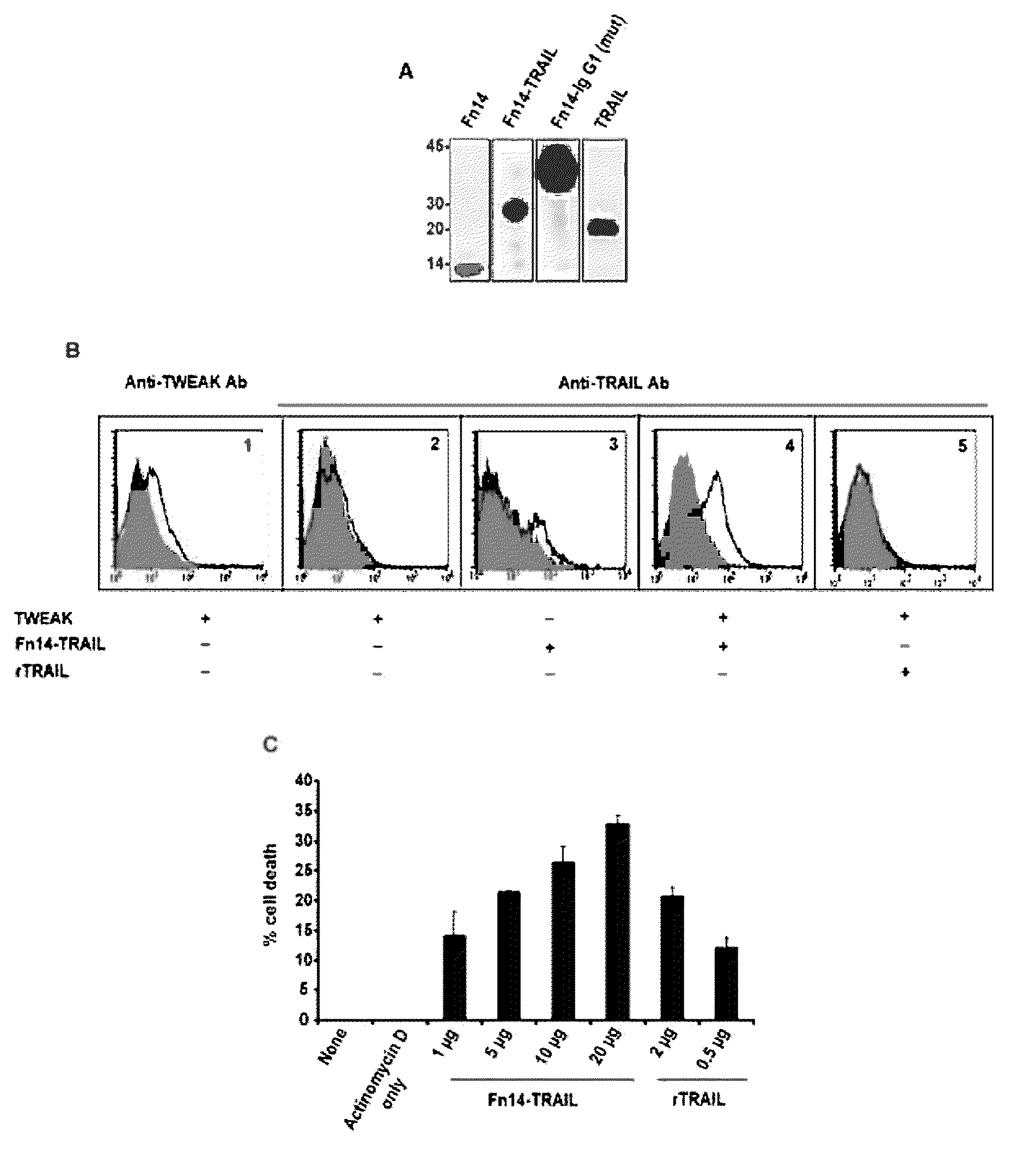
OX40/TRAIL fusion proteins
Fusion proteins which act on the OX40 / TRAIL signaling axes are provided. The proteins are useful in the treatment or amelioration of autoimmune diseases, particularly multiple sclerosis, and alloimmune diseases, as well as cancer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Novel chimeric proteins
InactiveUS20110041190A1Extended half-lifeEnhanced advantageCompounds screening/testingBiocideTrans signalingDisease
Novel chimeric proteins are disclosed. The proteins comprise at least two portions. The first portion binds to a first cell and decreases the cell's ability to send a trans signal to a second cell; the second portion sends its own trans signal to the second cell. Methods for making and using these proteins in the treatment of cancer, viral infections, autoimmune and alloimmune diseases are also disclosed, as are pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel chimeric proteins and genes. Either the proteins themselves or a genetic sequence encoding the protein can be administered. Other methods are also disclosed in which two molecular components result in decrement of a first trans signal from a first cell and the conferring of a second trans signal to a second cell.
Owner:TYKOCINSKI MARK L +1
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
ActiveUS7662928B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainAntigen Binding Fragment
Antibodies to heavy chain of human FcRn are provided which function as non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal, monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, or antigen binding fragments thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Novel Chimeric Proteins and Methods for Using The Same
InactiveUS20130243697A1Enhanced advantageImprove propertiesCompounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsTrans signalingDisease
Novel chimeric proteins are disclosed. The proteins comprise at least two portions. The first portion binds to a first cell and decreases the cell's ability to send a trans signal to a second cell; the second portion sends its own trans signal to the second cell. Methods for making and using these proteins in the treatment of cancer, viral infections, autoimmune and alloimmune diseases are also disclosed, as are pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel chimeric proteins and genes. Either the proteins themselves or a genetic sequence encoding the protein can be administered. Other methods are also disclosed in which two molecular components result in decrement of a first trans signal from a first cell and the conferring of a second trans signal to a second cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
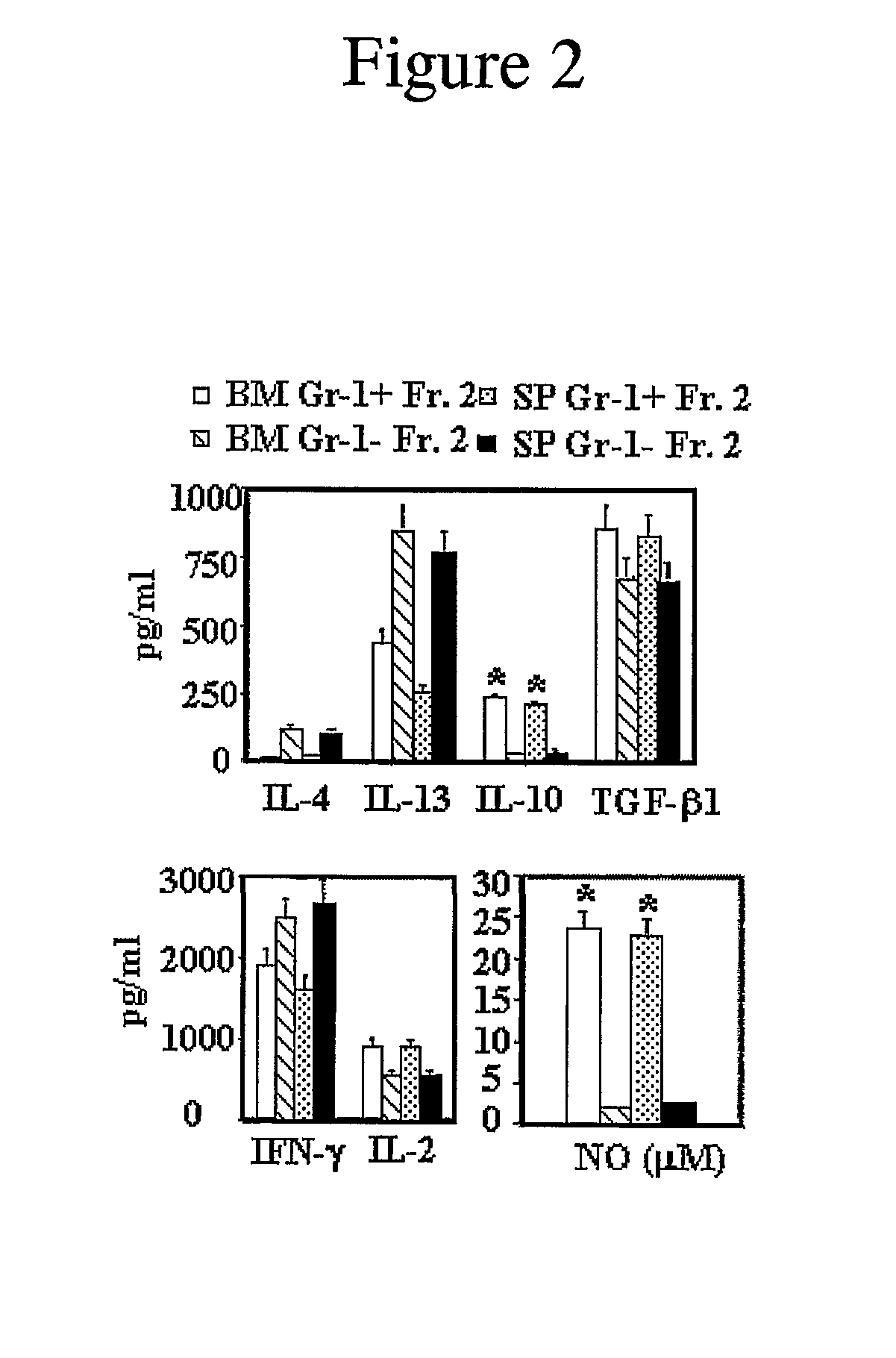
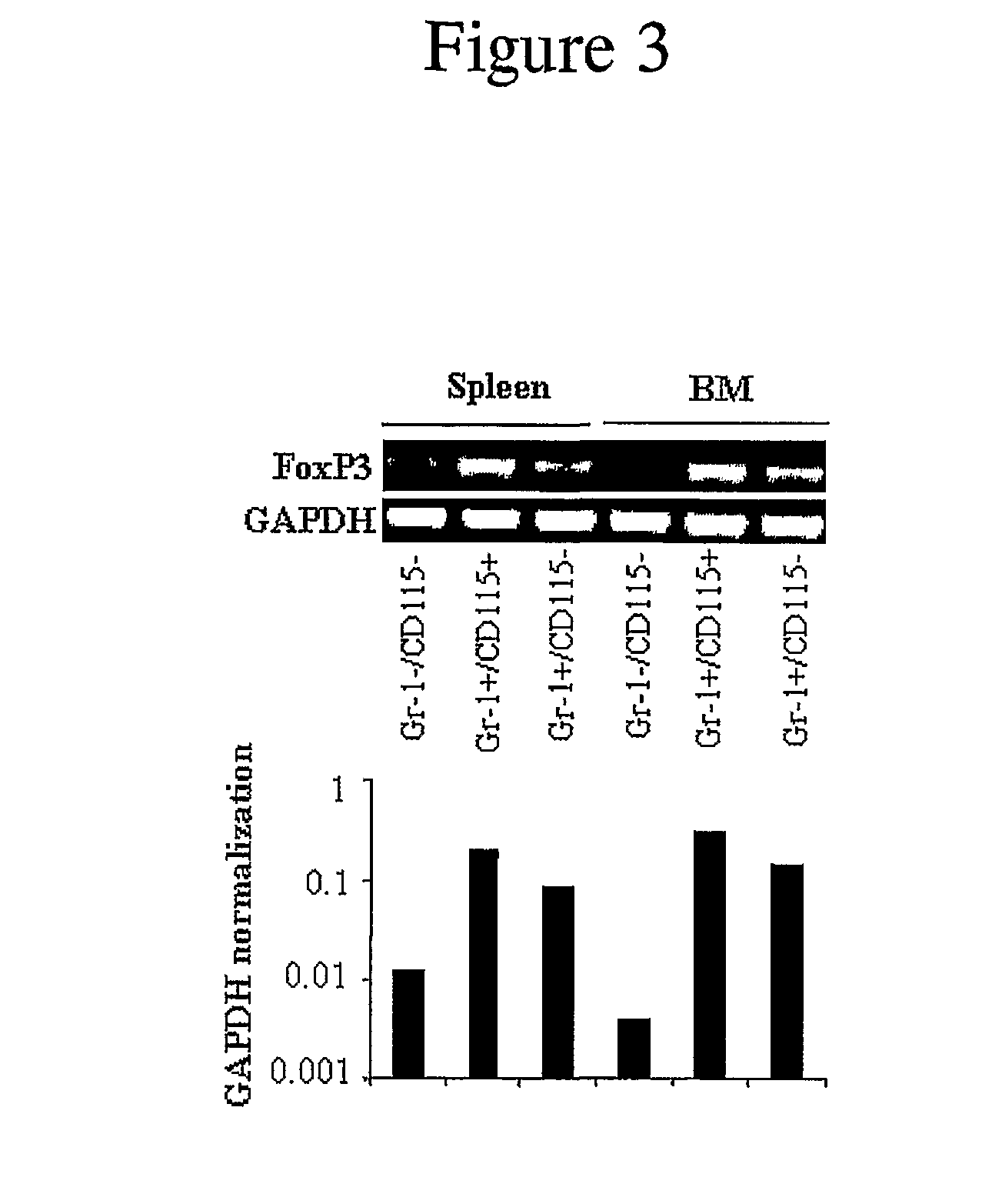
Myeloid Suppressor Cells, Methods For Preparing Them, and Methods For Using Them For Treating Autoimmunity
The present invention relates to novel myeloid suppressor cells (MSCs) and to methods of isolating these MSCs are also included. The MSCs of the present invention can be used to treat or prevent autoimmune diseases or alloimmune responses. The MSCs of the present invention may also be used to reduce a T cell response, induce T regulatory cells, and produce T cell tolerance.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
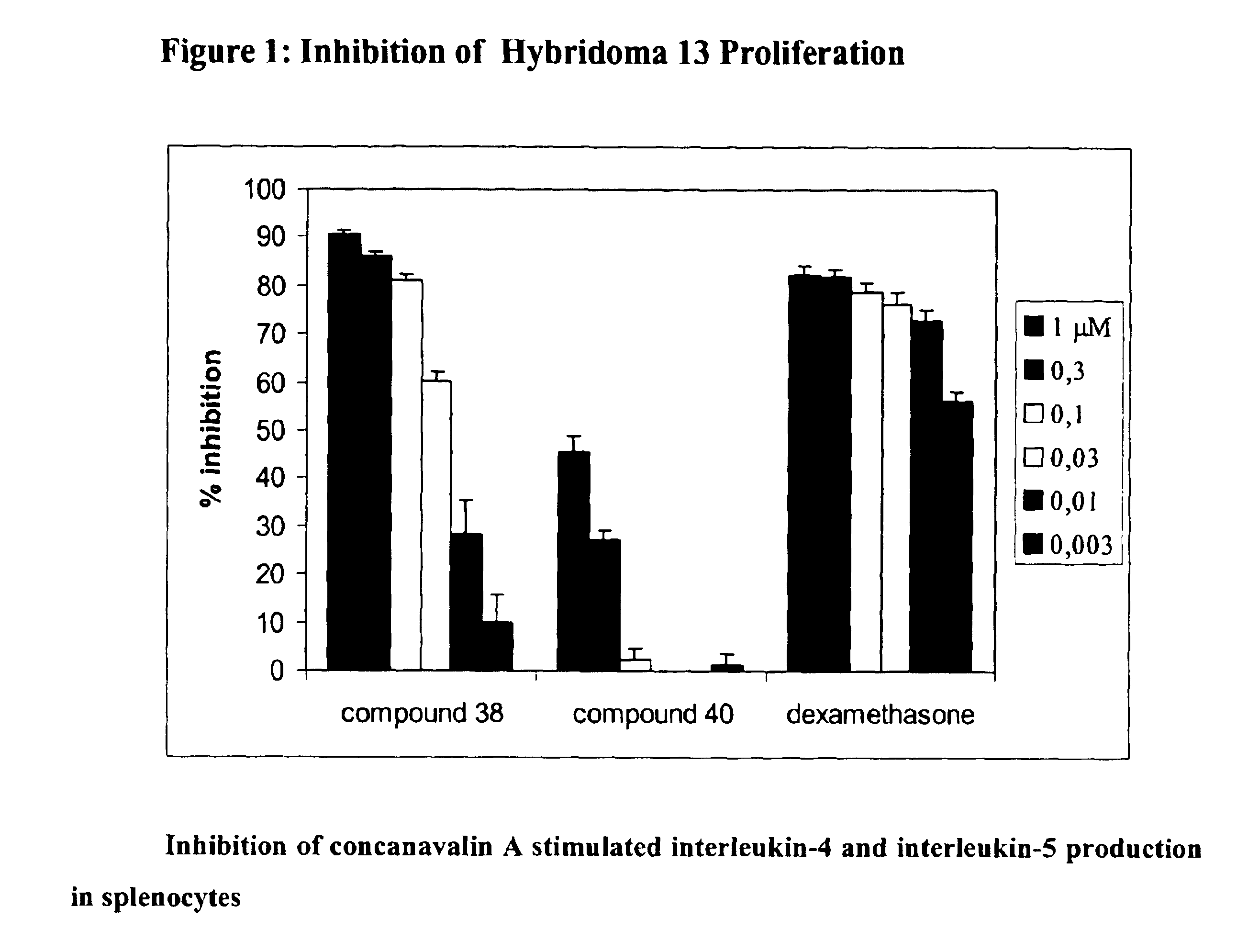
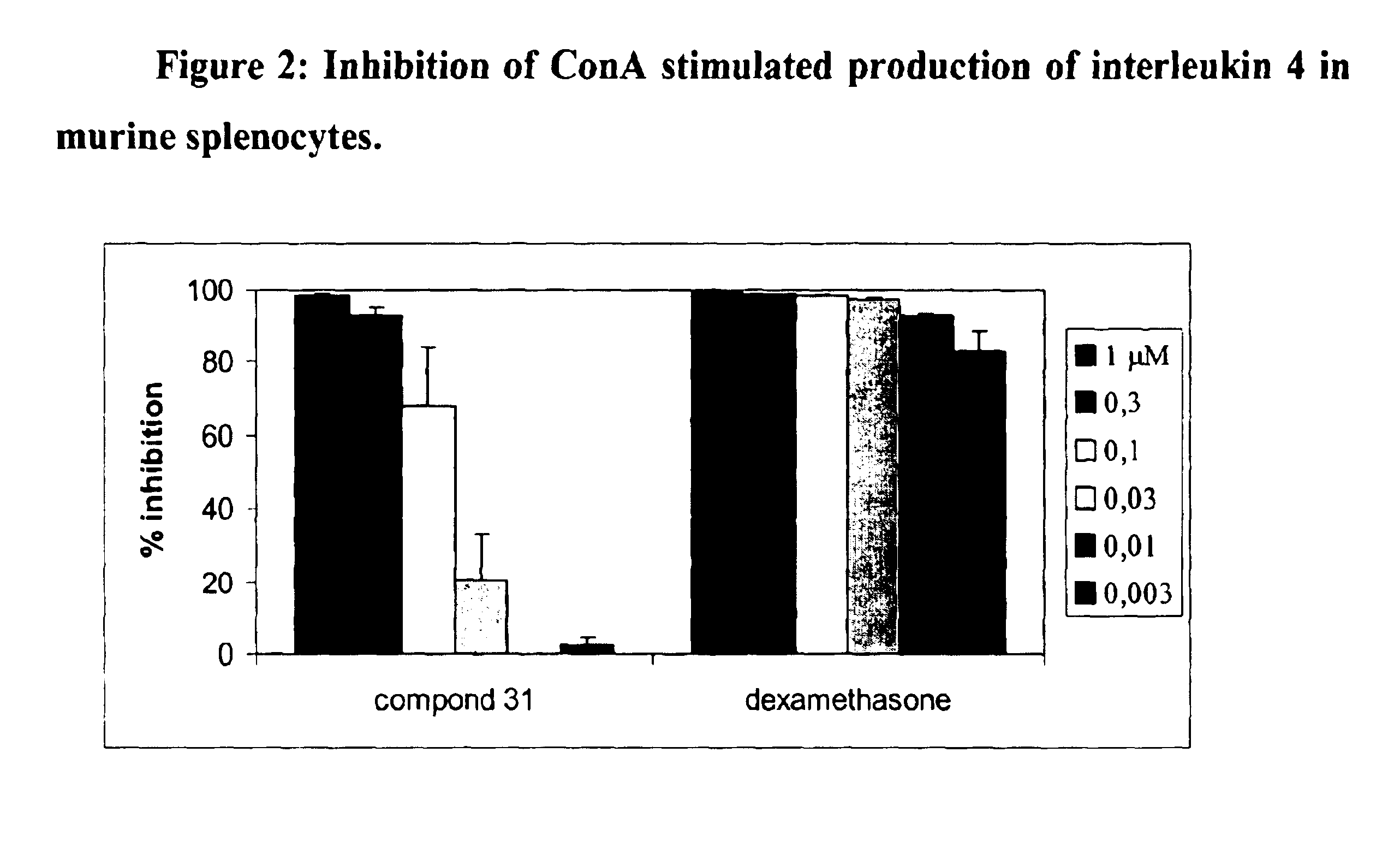
Compounds, compositions and methods for treatment of inflammatory diseases and conditions
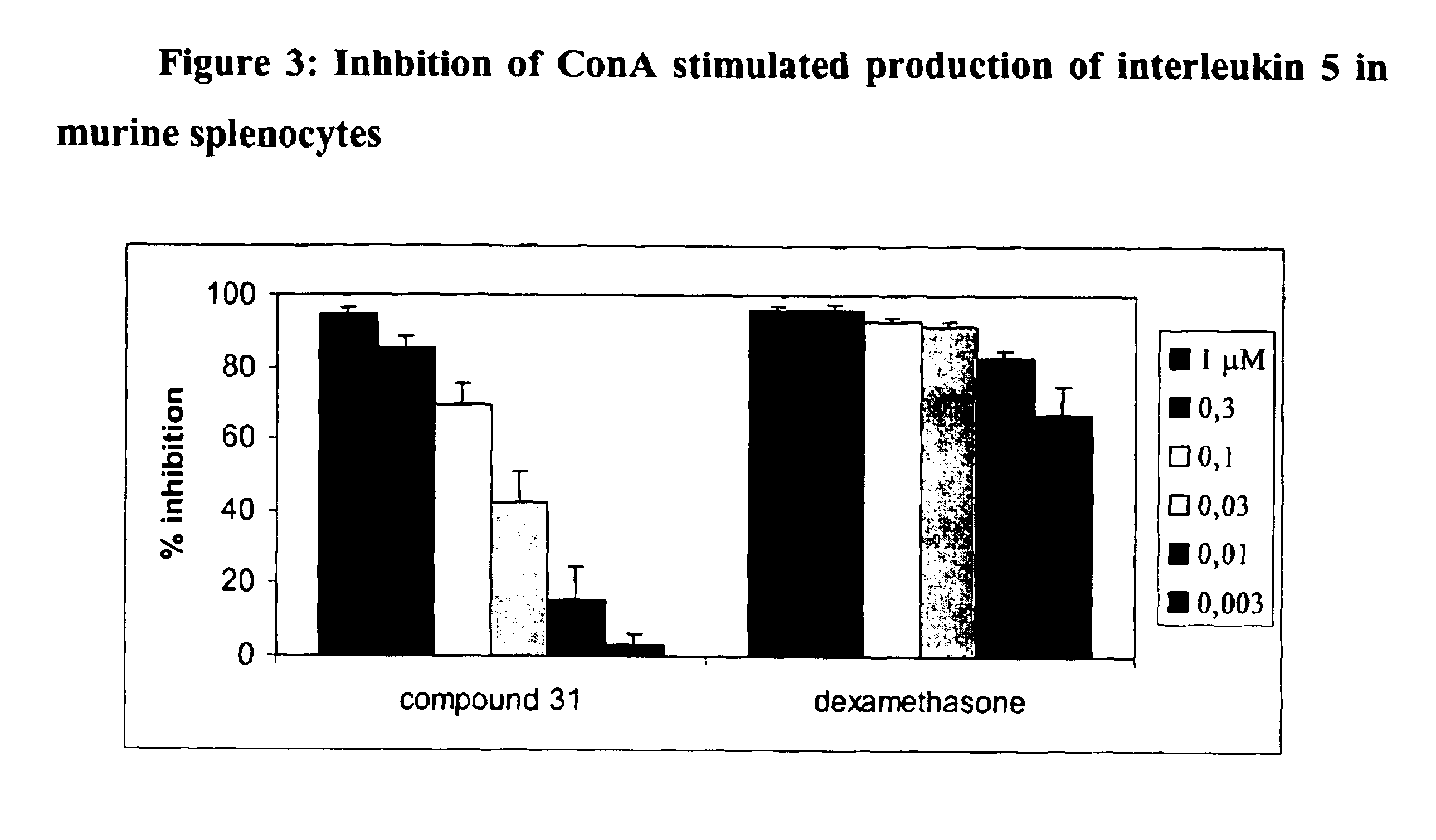
The present invention relates (a) to new compounds represented by Formula I: wherein M represents a macrolide subunit (macrolide moiety) derived from macrolide possessing the property of accumulation in inflammatory cells, S represents a steroid subunit (steroid moiety) derived from steroid drug with anti-inflammatory activity and L represents a linker molecule linking M and S, (b) to their pharmacologically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates, (c) to processes and intermediates for their preparation, and (d) to their use in the treatment of inflammatory diseases and conditions in humans and animals. Such compounds inhibit many cytokines and immune mediators involved in immune responses which cause inflammation, allergy, or alloimmunity, including without limitation IL-1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, GMCSF, ICAM, and TNF-α. Importantly, anti-inflammatory steroids exert a direct anti-inflammatory effect through binding to the glucocorticosteroid receptor.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE ISTRAZIVACKI CENTAR ZAGREB D O O
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
InactiveUS20050079169A1Increase the gapInhibit bindingMuscular disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
Antibodies to FcRn are provided which are non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal or monoclonal or antigen binding fragment thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
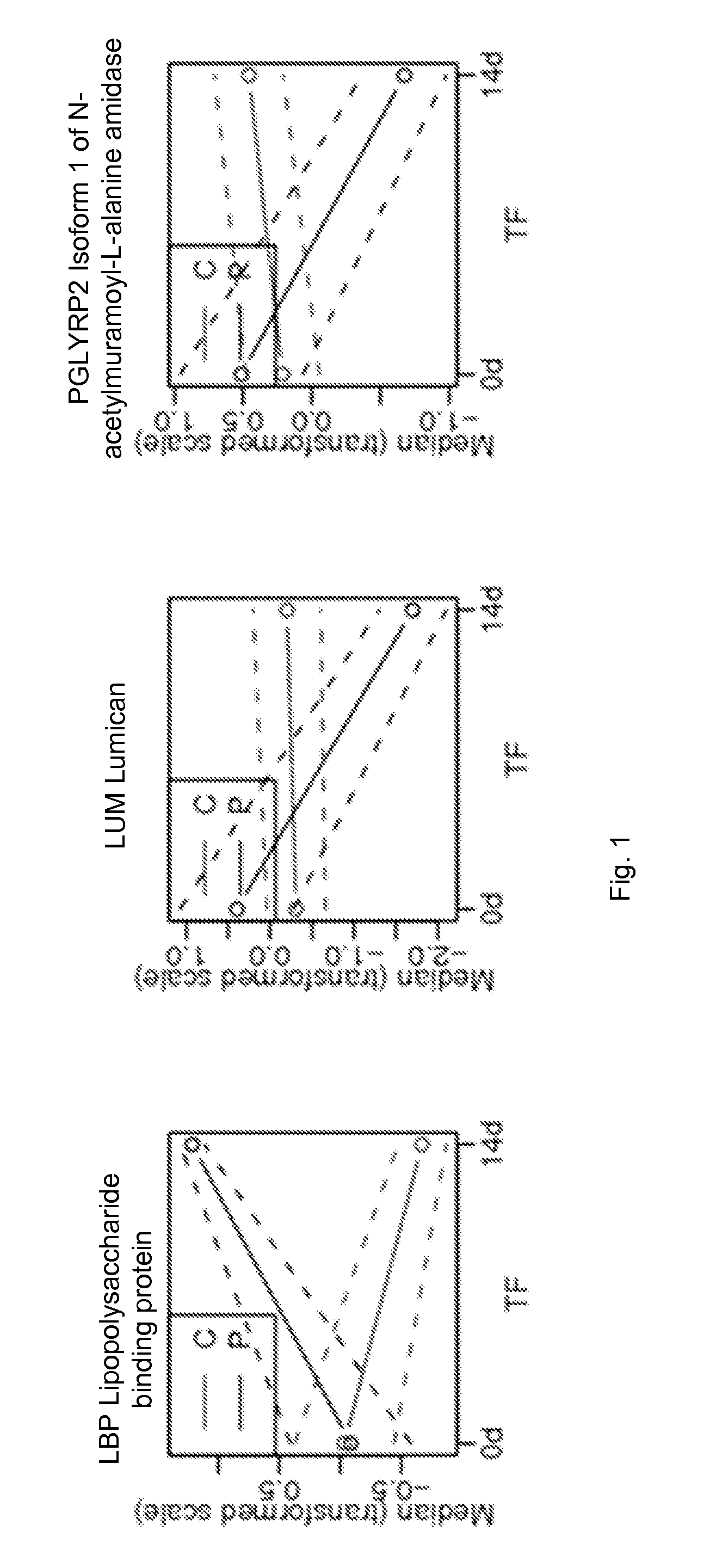
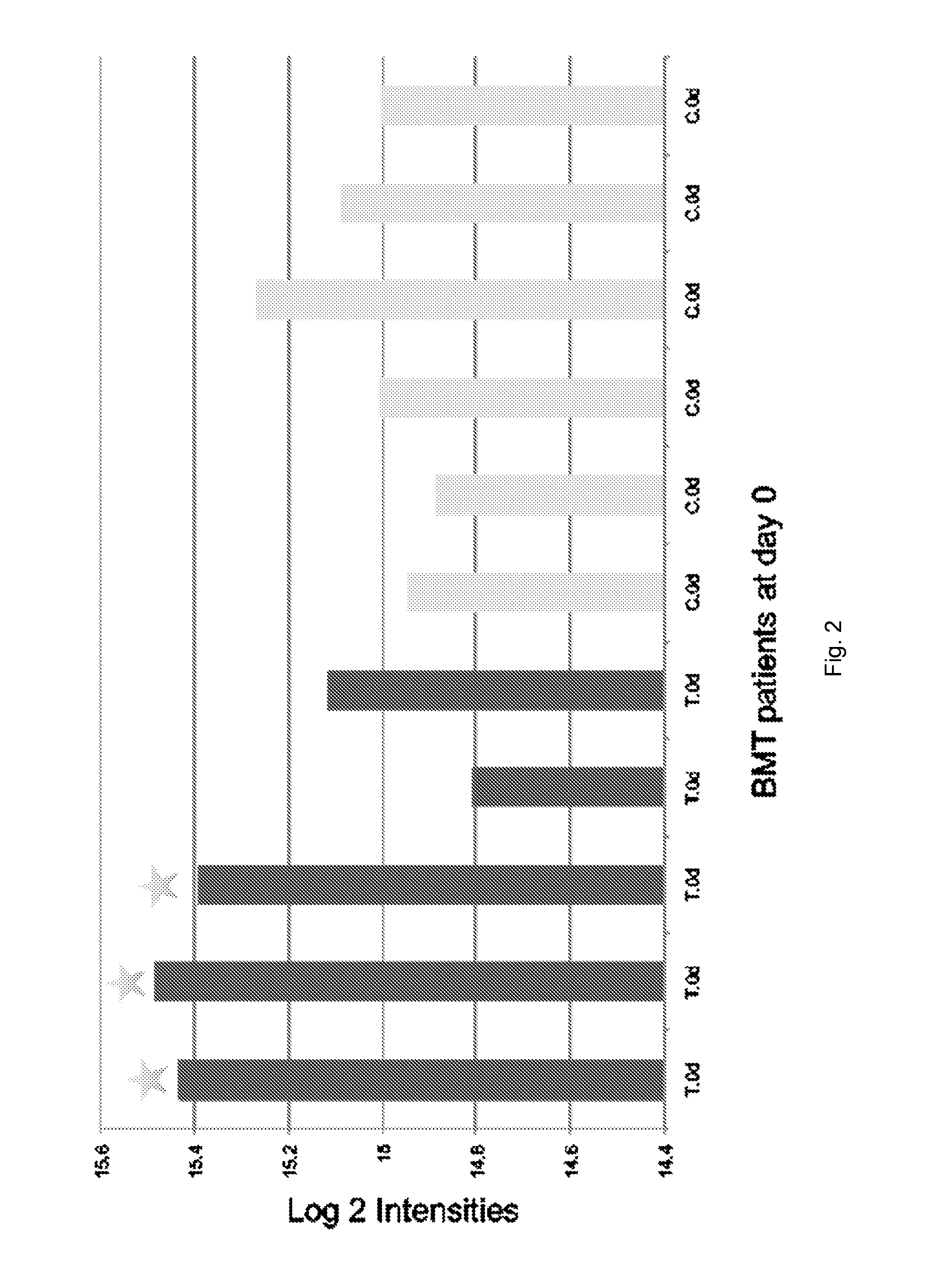
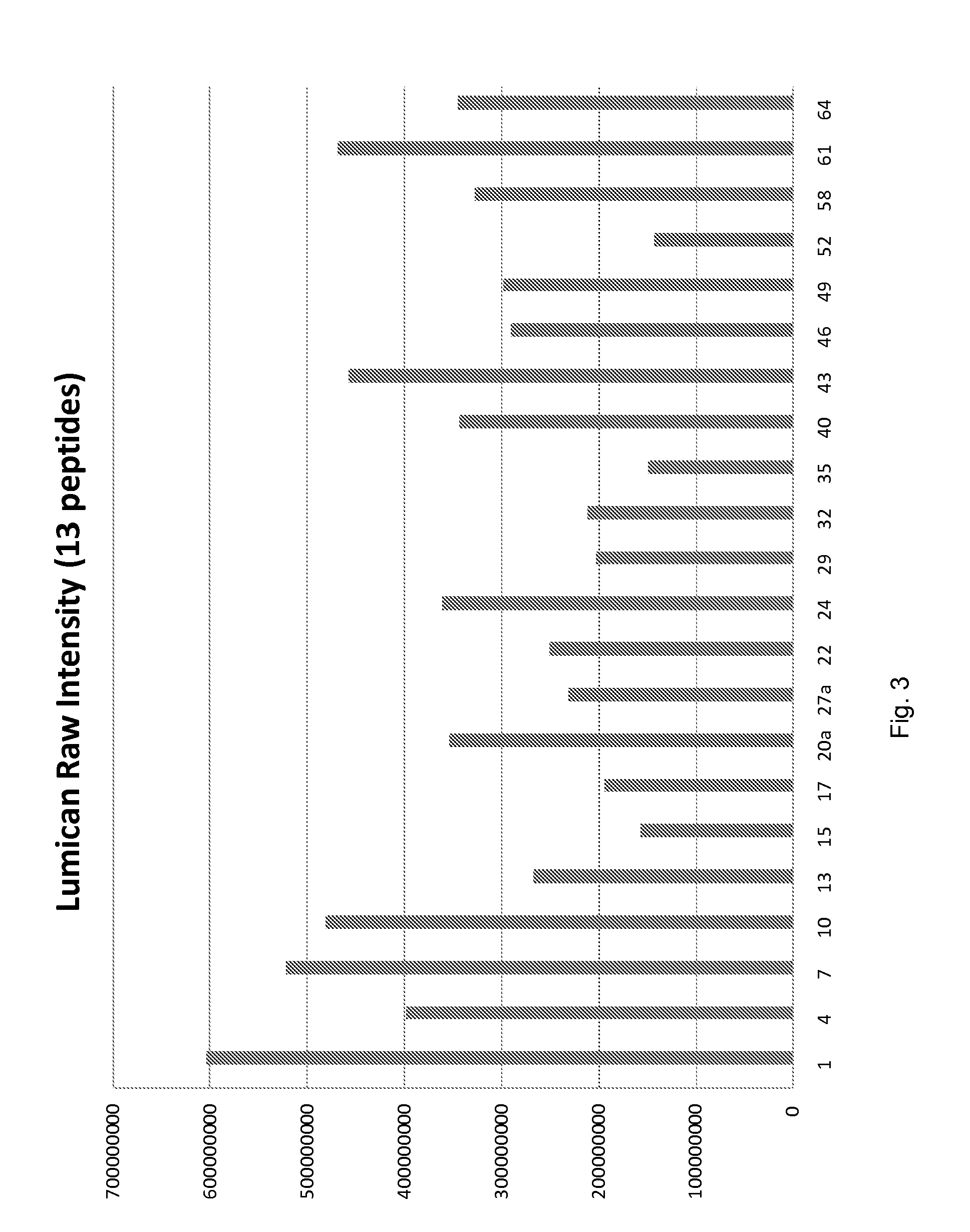
Protein biomarkers and therapeutic targets for autoimmune and alloimmune diseaes
ActiveUS20120077209A1Solid foundationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAutoimmune diseaseTissue transplant
A method for characterizing the risk a subject will develop an autoimmune and / or alloimmune disease following tissue transplant includes obtaining a biological sample from the subject, wherein the subject has received the tissue transplant determining in the biological sample a level of at least one protein selected from Tables 1-4, comparing the measured level of the at least one protein to a control value, and characterizing a subject as at greater risk of developing an autoimmune disease and / or alloimmune disease if the level of at least one protein determined is increased or decreased compared to the control value.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
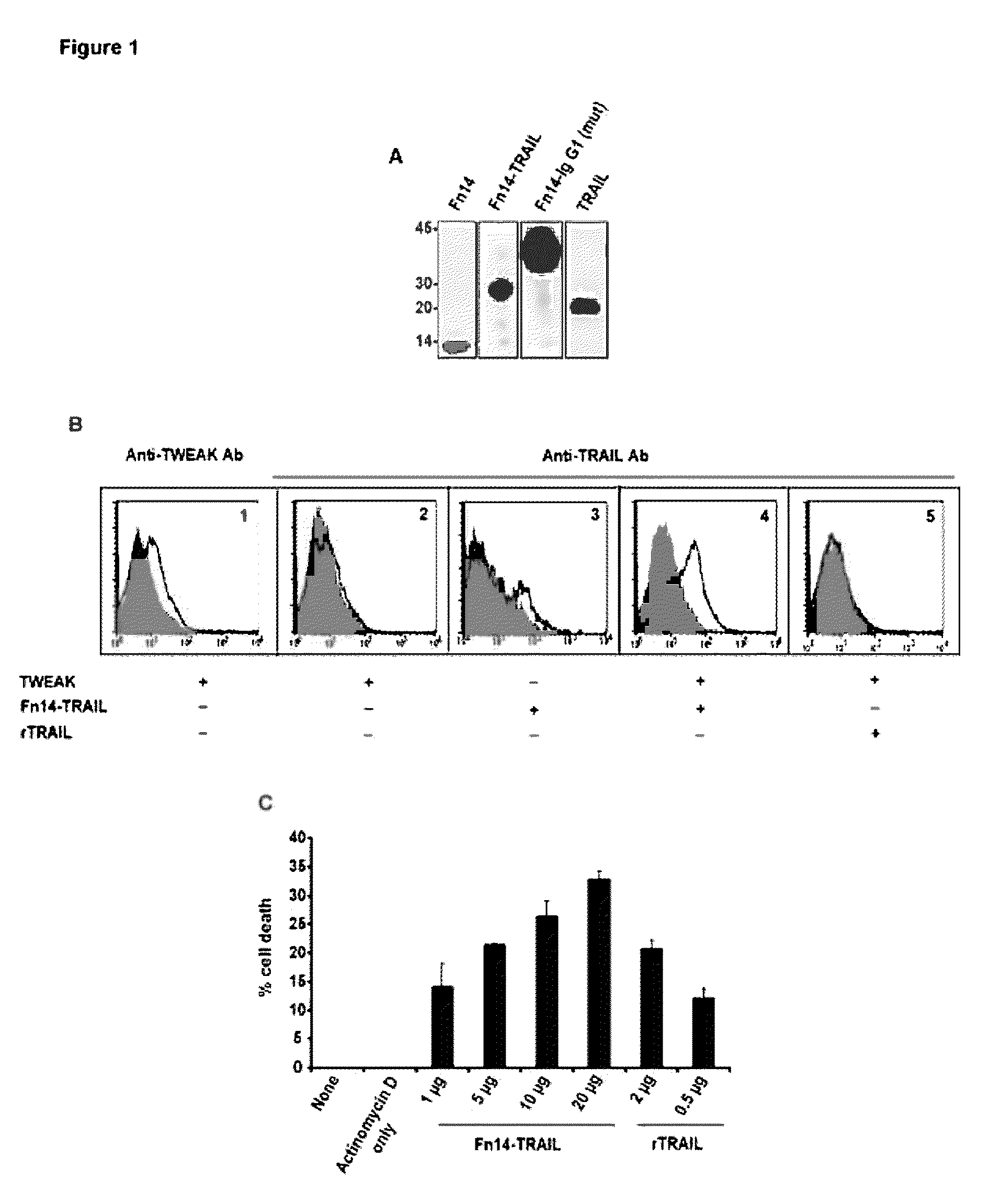
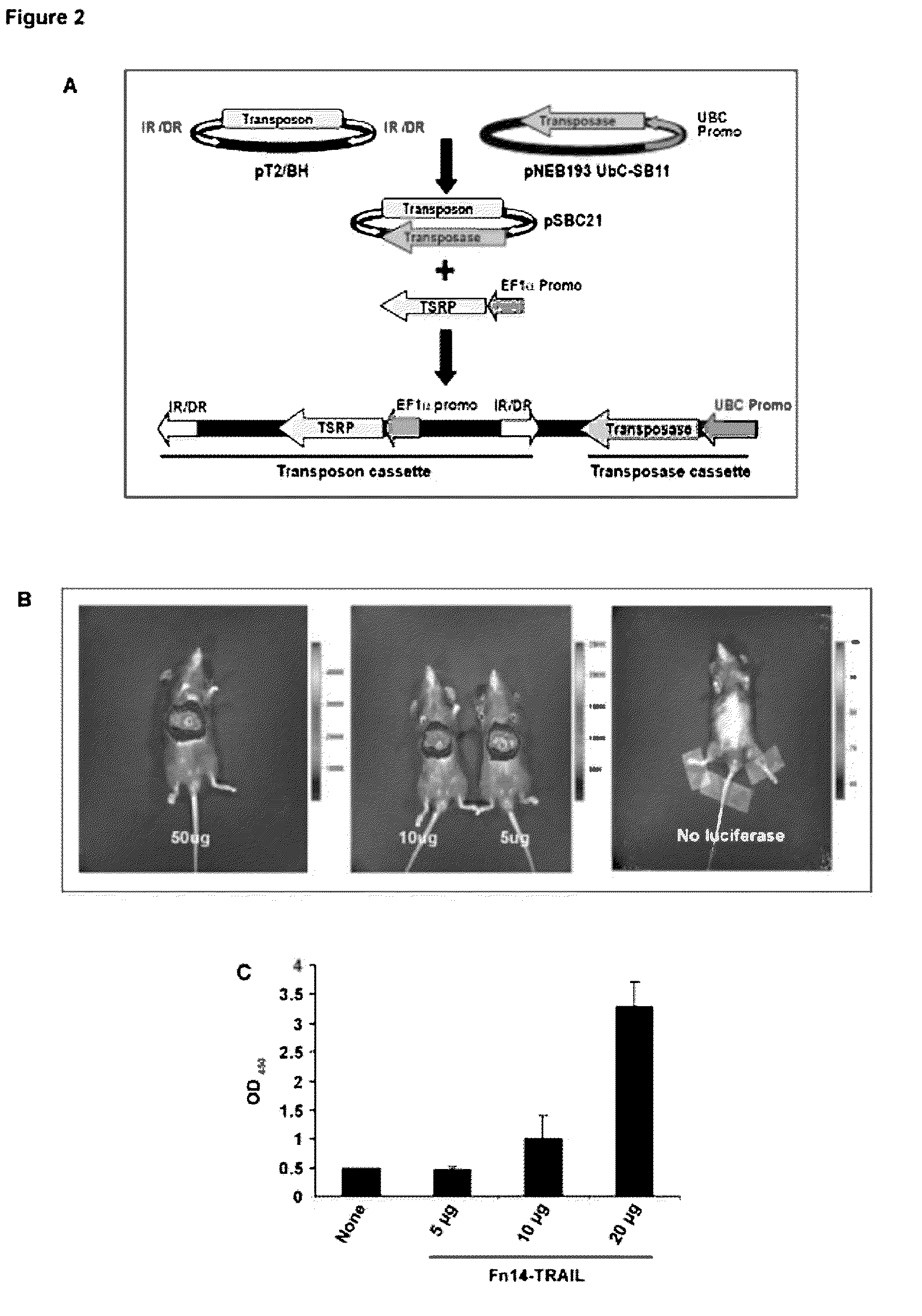
Fn14/trail fusion proteins
Fusion proteins which act on the TWEAK and TRAIL signaling axes are provided. The proteins are useful in the treatment or amelioration of autoimmune diseases, particularly multiple sclerosis, as well as other diseases such as alloimmune diseases and cancer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
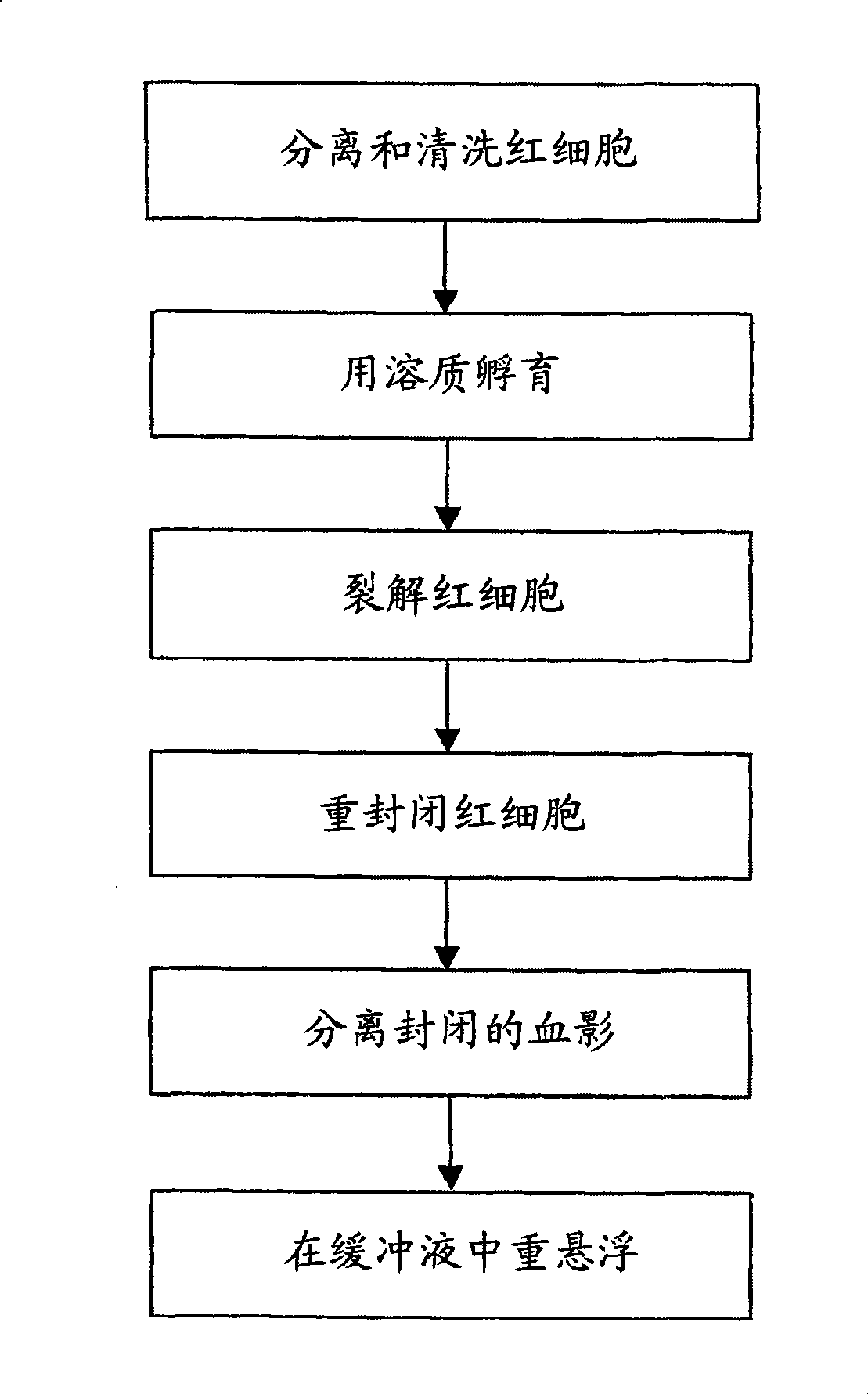
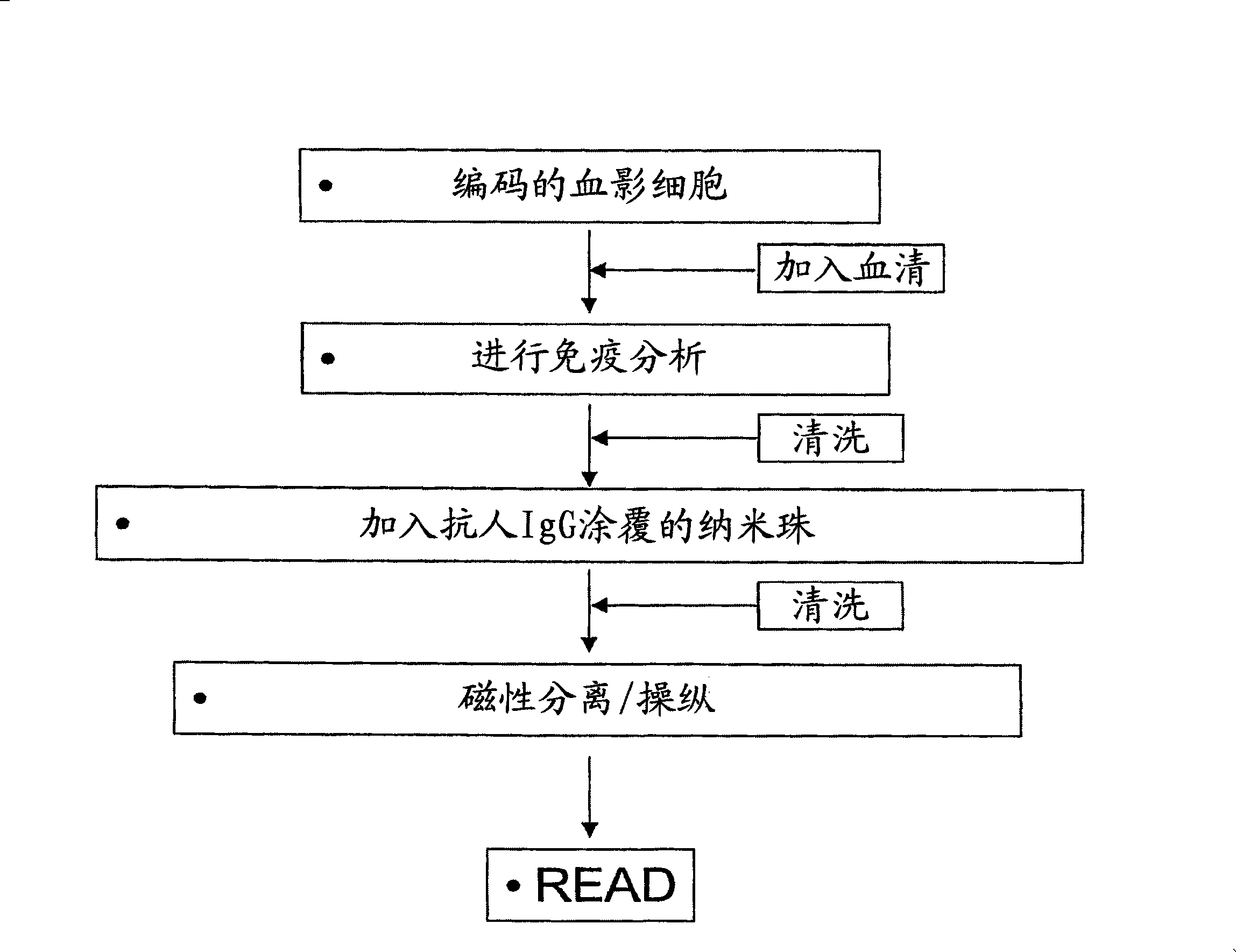
Multiplexed detection of anti-red cell alloantibodies
Disclosed are methods for detecting antibody in a sample, where the antibody targets an antigen expressed by red blood cells or red blood cell ghosts. Rather than detecting the binding events between a particular antigen antibody pair (as in traditional agglutination based assays) the methods herein allow for multiplexed detection of clinically important allo-immune antibodies to blood group antigens. Specifically the method involves generating fluorescently encoded red blood cells or red blood cell ghosts with known antigen presentation and using them to detect the presence of antibody in serum / plasma with a fluorescent sandwich type immunoassay. The assay results can be read using flow cytometric or fluorescent microscope based imaging techniques.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
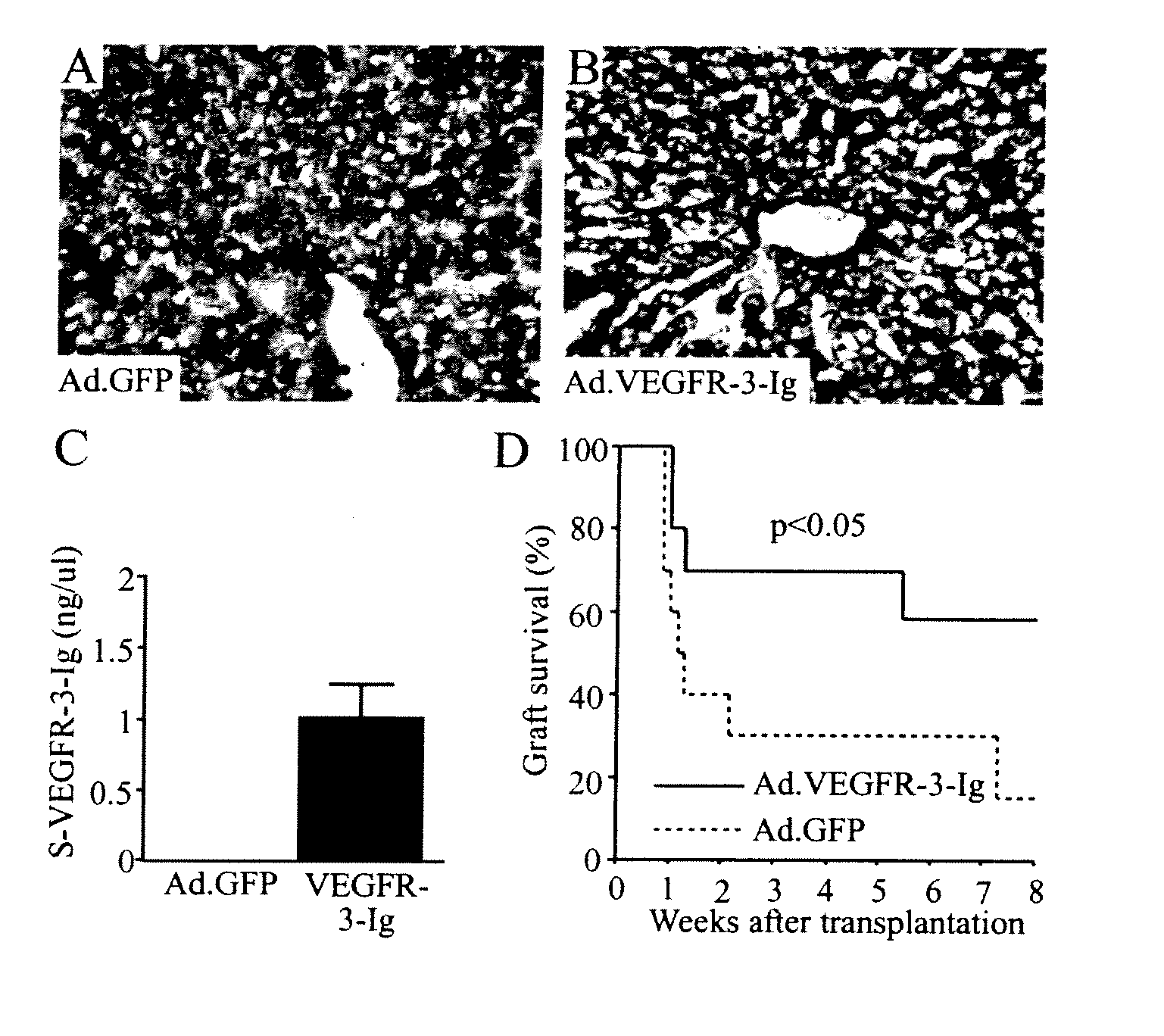
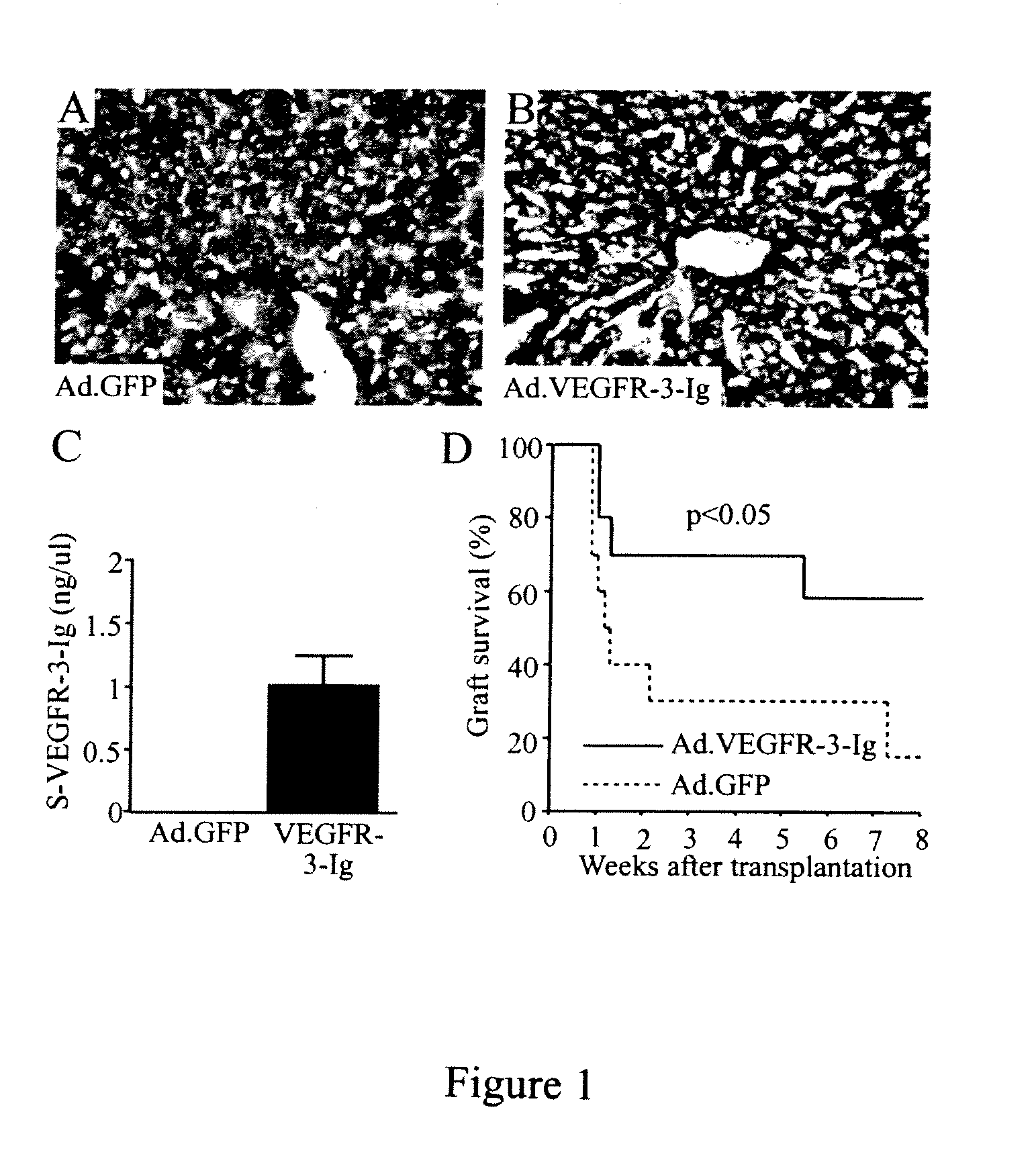
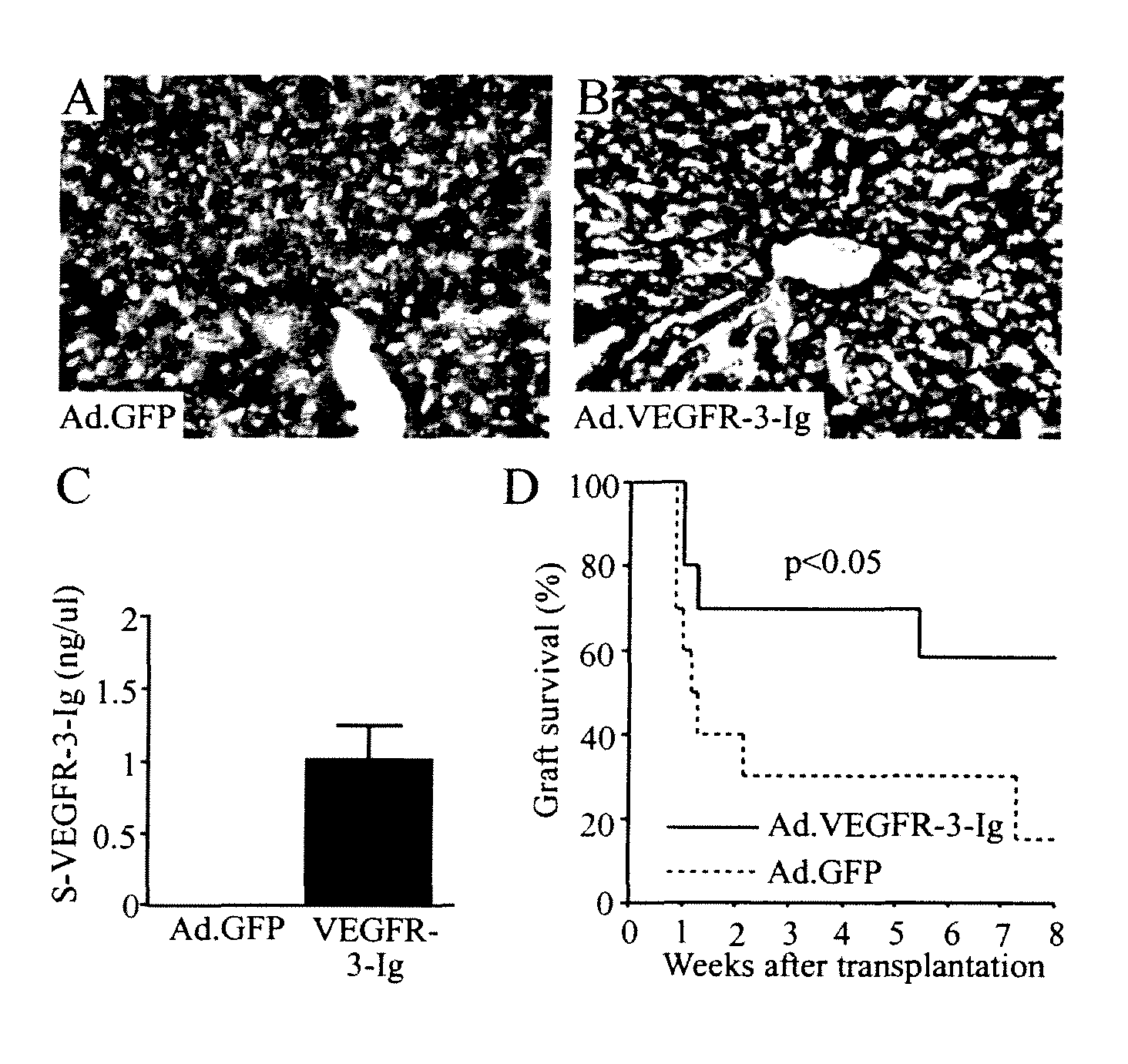
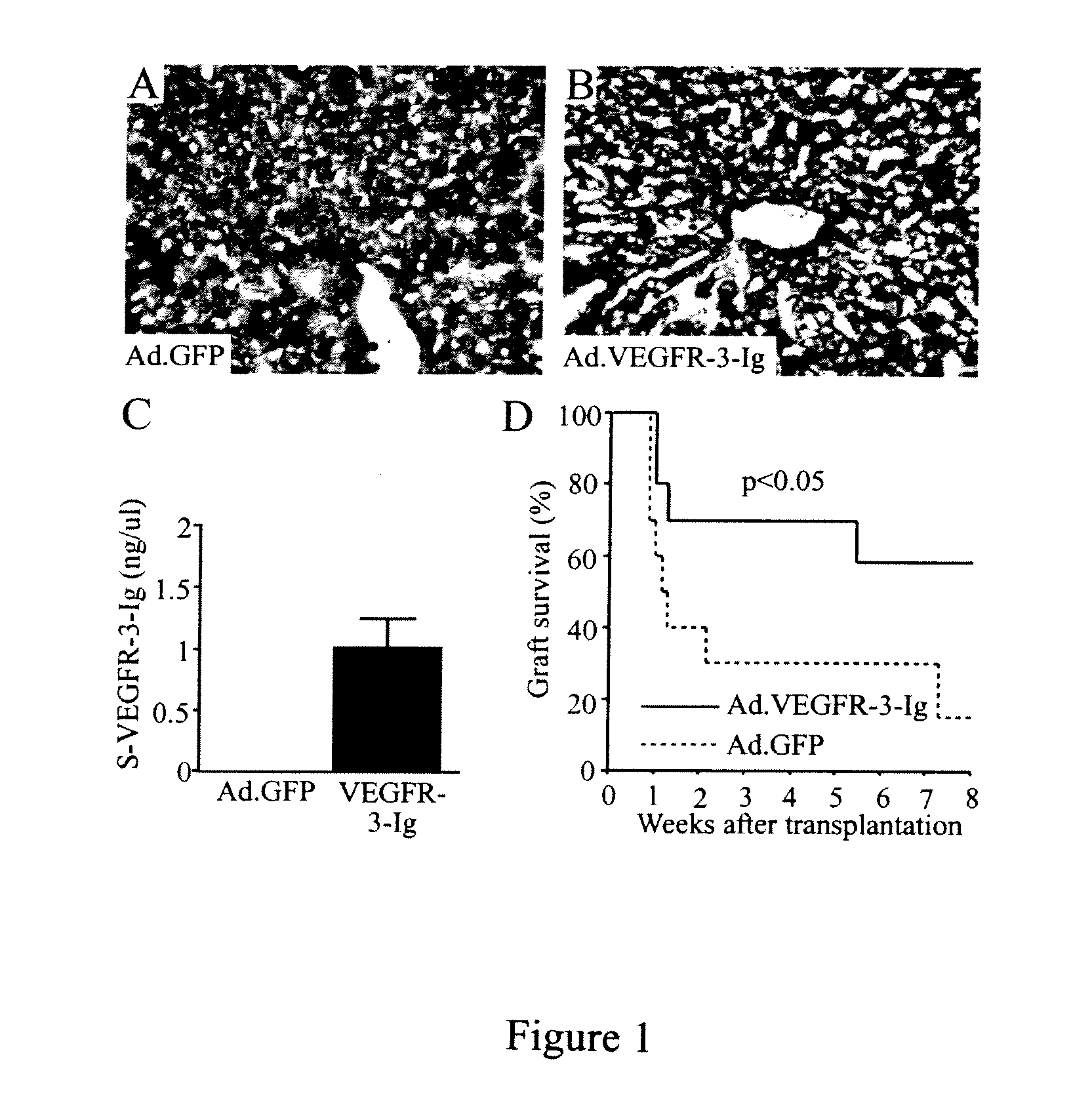
Growth factor antagonists for organ transplant alloimmunity and arteriosclerosis
ActiveUS20080267956A1Promote resultsReduced immune reactionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological bodyProviding material
The present invention provides materials and methods for antagonizing the function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, platelet derived growth factor receptors and other receptors, to prevent, inhibit, or ameliorate allograft rejection or arteriosclerosis in organisms that receive an organ transplant.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
Protein biomarkers and therapeutic targets for autoimmune and alloimmune diseases
ActiveUS20150099664A1Solid foundationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAutoimmune responsesAutoimmune disease
A method for characterizing the risk a subject will develop an autoimmune and / or alloimmune disease following tissue transplant includes obtaining a biological sample from the subject, wherein the subject has received the tissue transplant determining in the biological sample a level of at least one protein selected from Tables 1-4, comparing the measured level of the at least one protein to a control value, and characterizing a subject as at greater risk of developing an autoimmune disease and / or alloimmune disease if the level of at least one protein determined is increased or decreased compared to the control value.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Growth factor antagonists for organ transplant alloimmunity and arteriosclerosis
ActiveUS9073997B2Reduce dependenceReduce needPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProviding materialAllograft rejection
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
Nitrophenyls and related compounds and thimerosal for the inhibition of immune related cell or tissue destruction
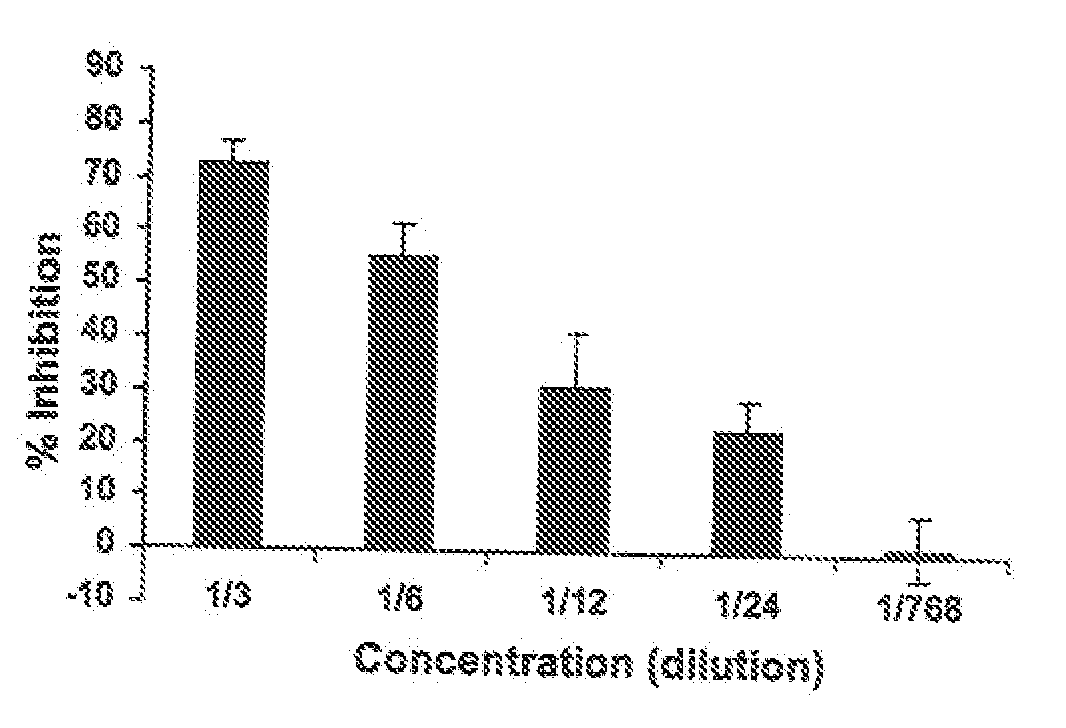
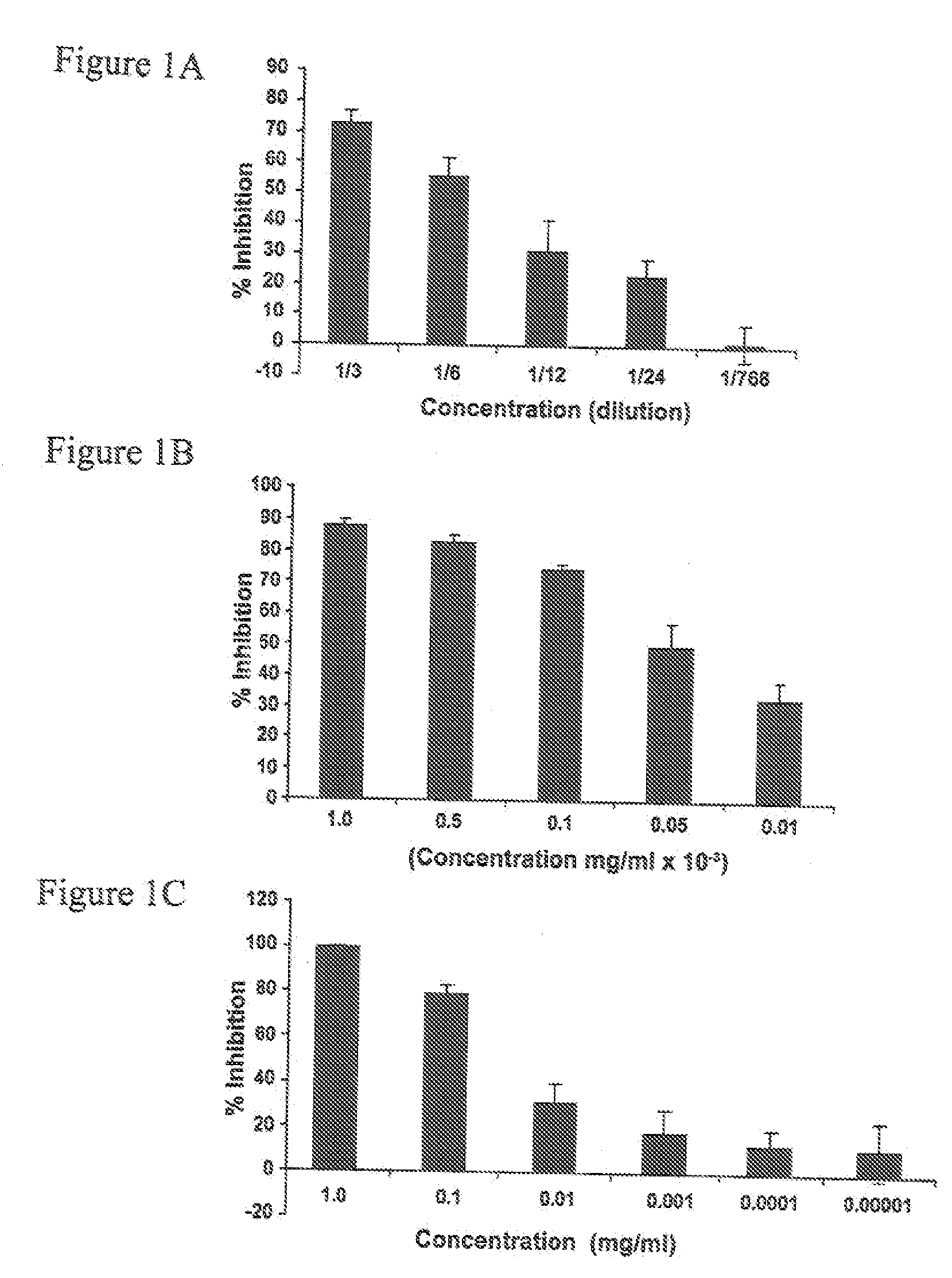
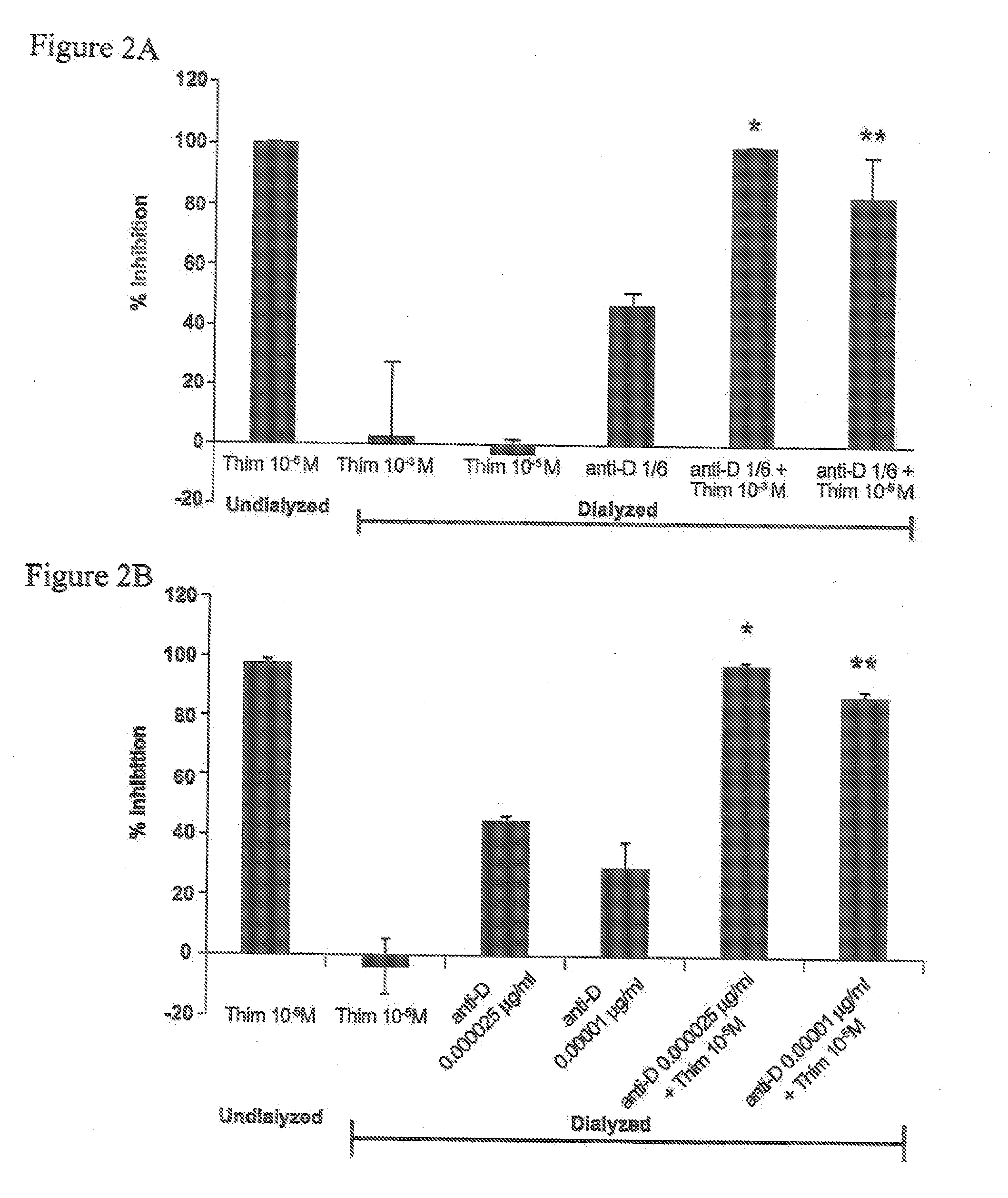
A method and composition for inhibiting phagocytosis of blood cells. The method involves providing a nitrophenyl compound or thimerosal with administration of the compound to a host having an auto or alloimmune disease to inhibit phagocytosis of blood cells.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
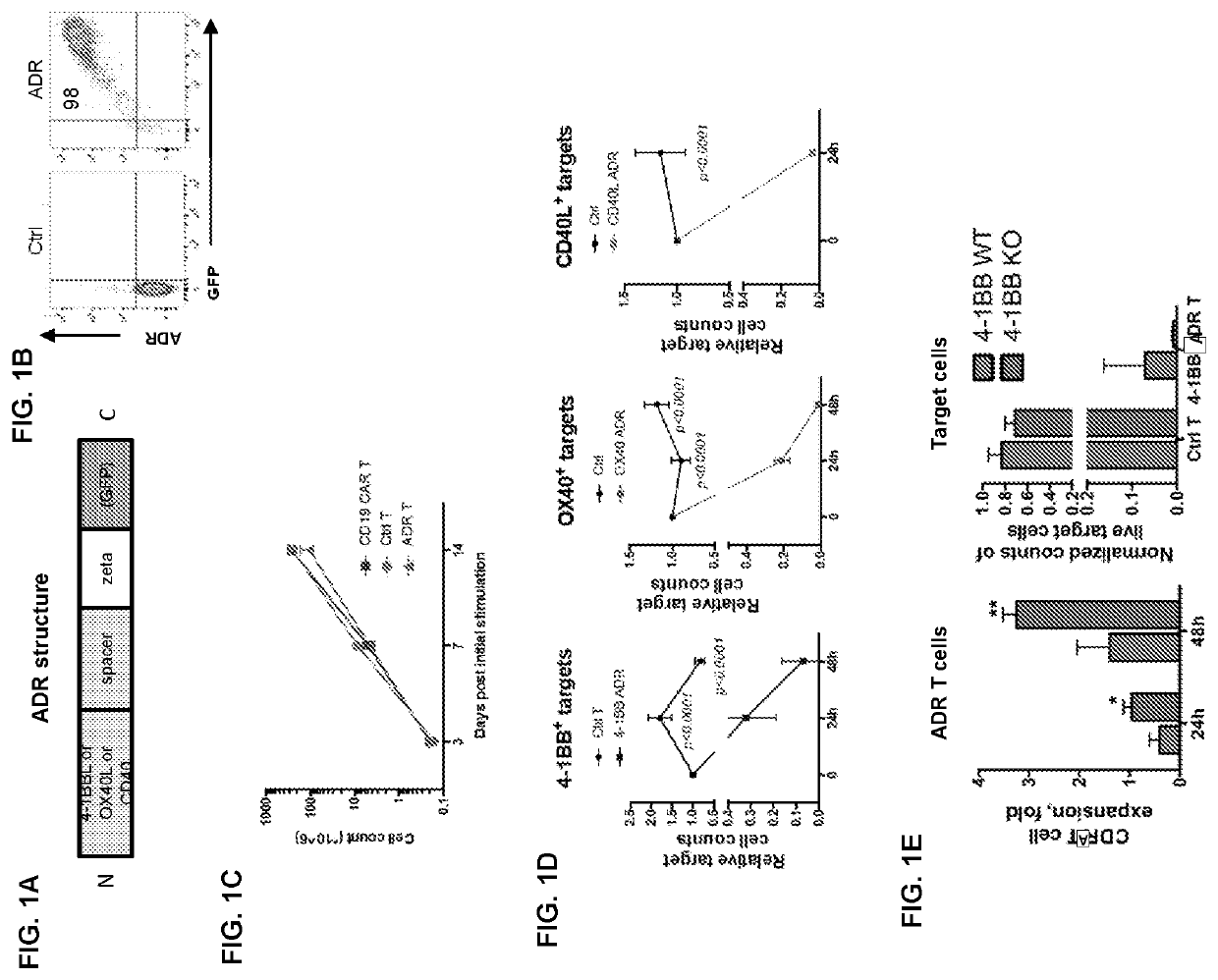
Auto/allo-immune defense receptors for the selective targeting of activated pathogenic t cells and nk cells
PendingUS20210077530A1Easy to usePrevent rejectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsReceptor
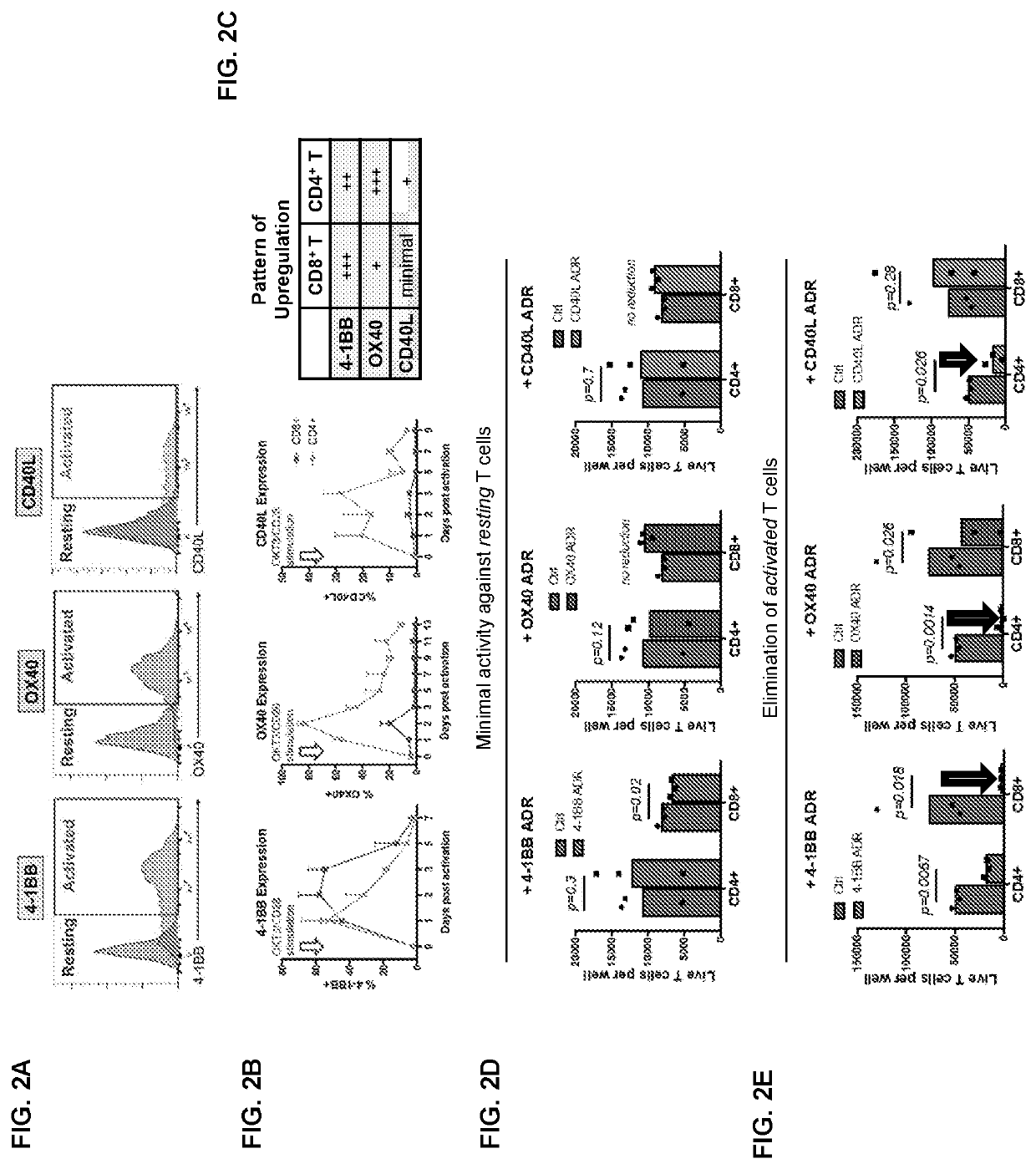
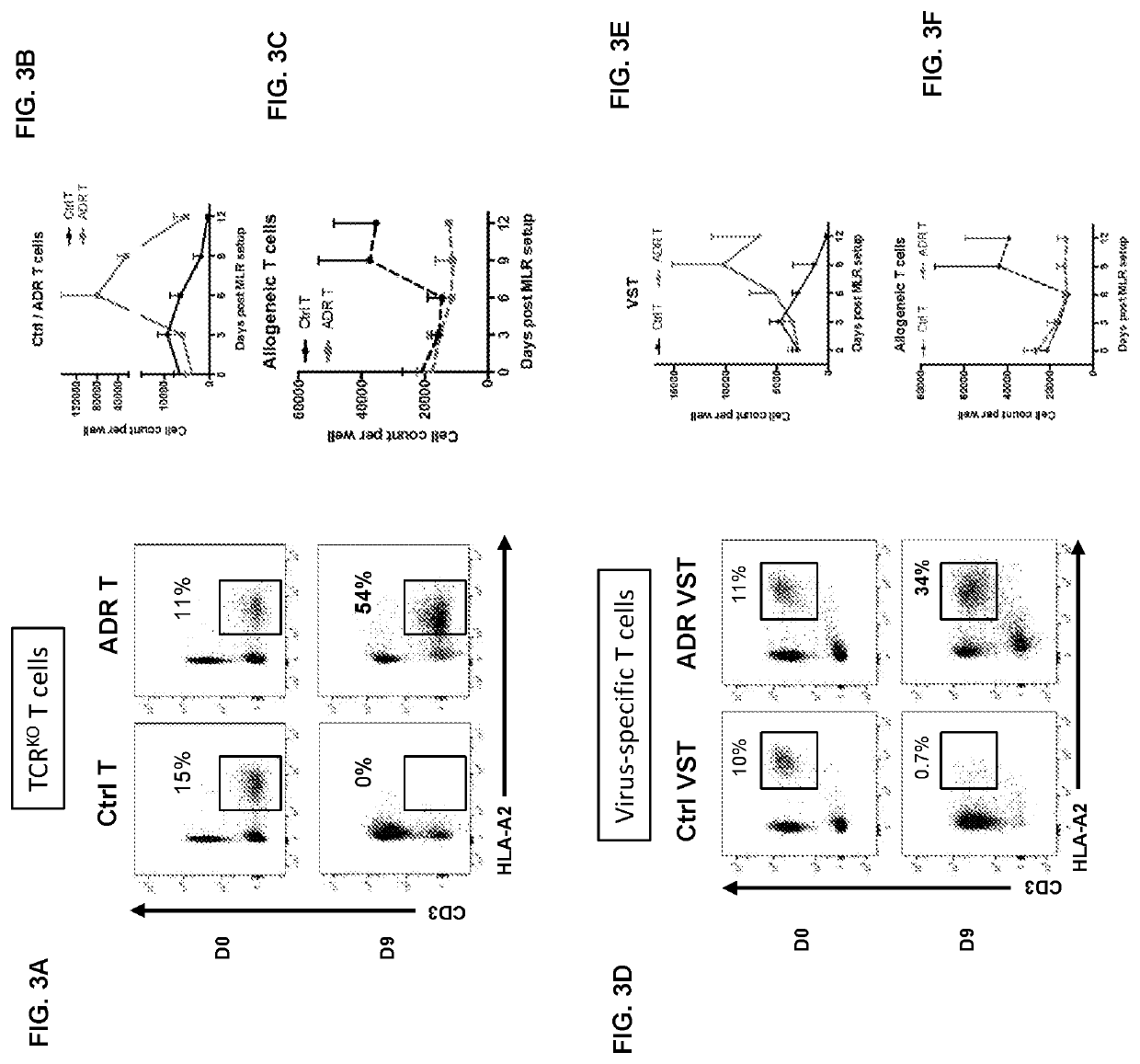
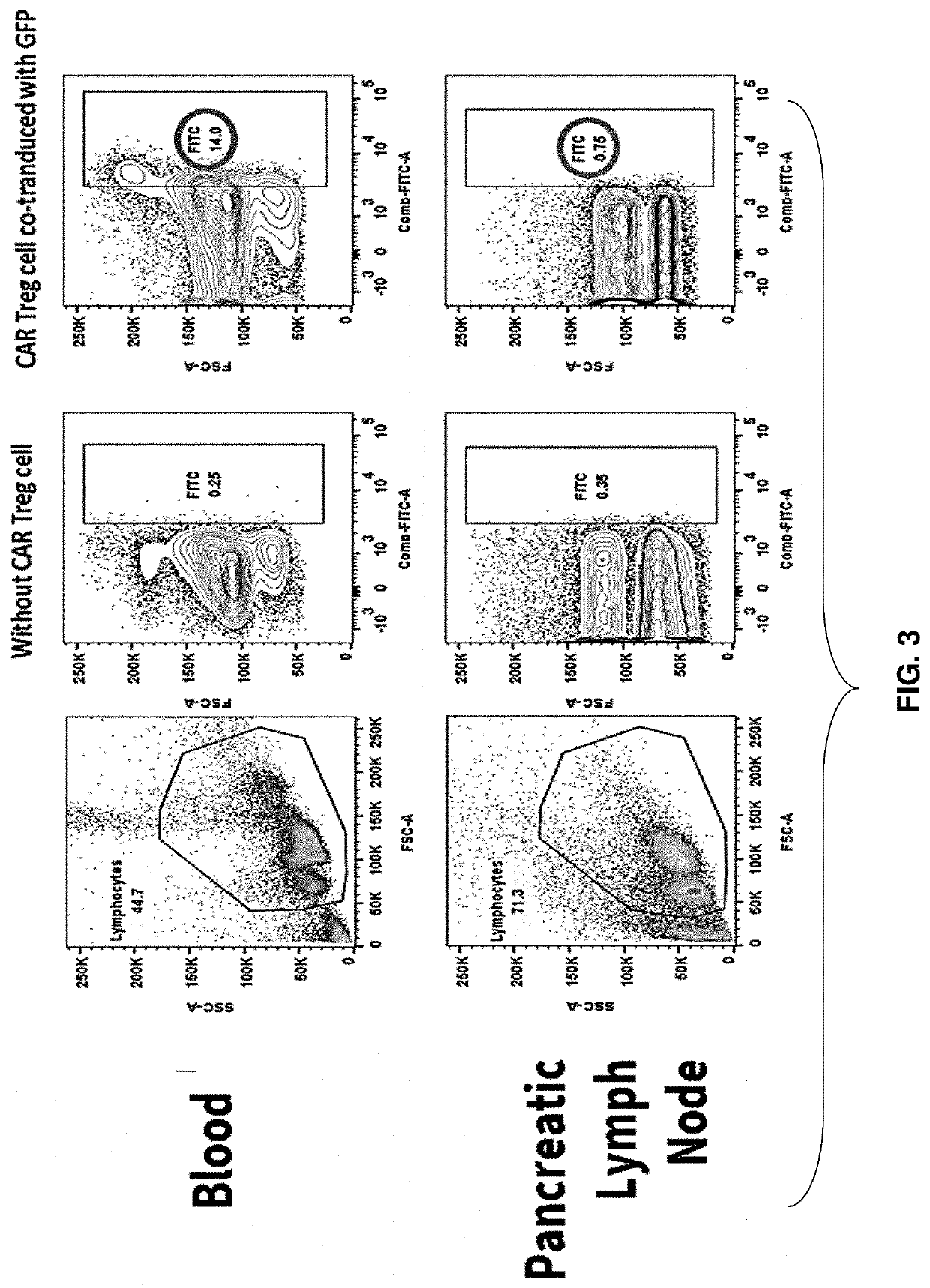
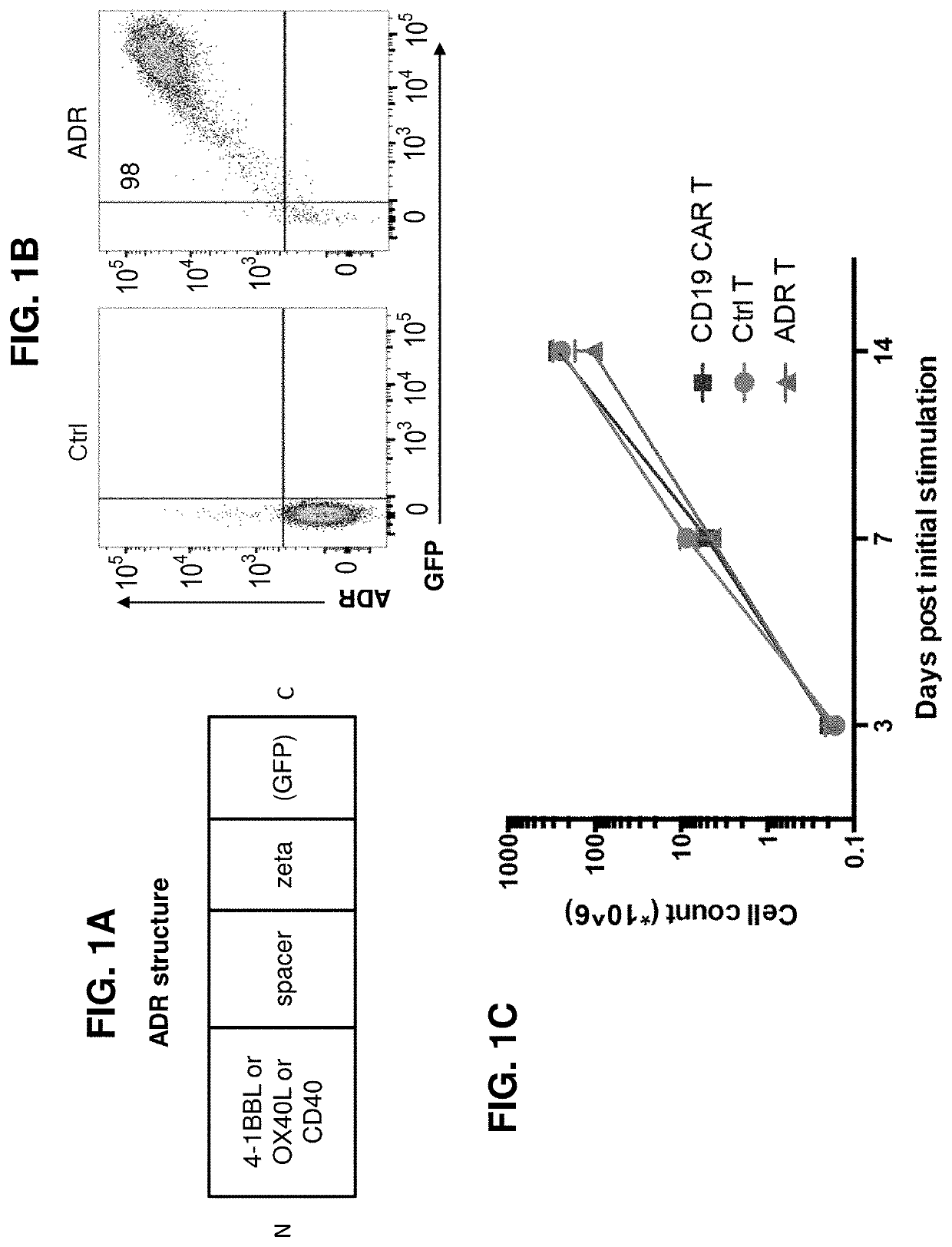
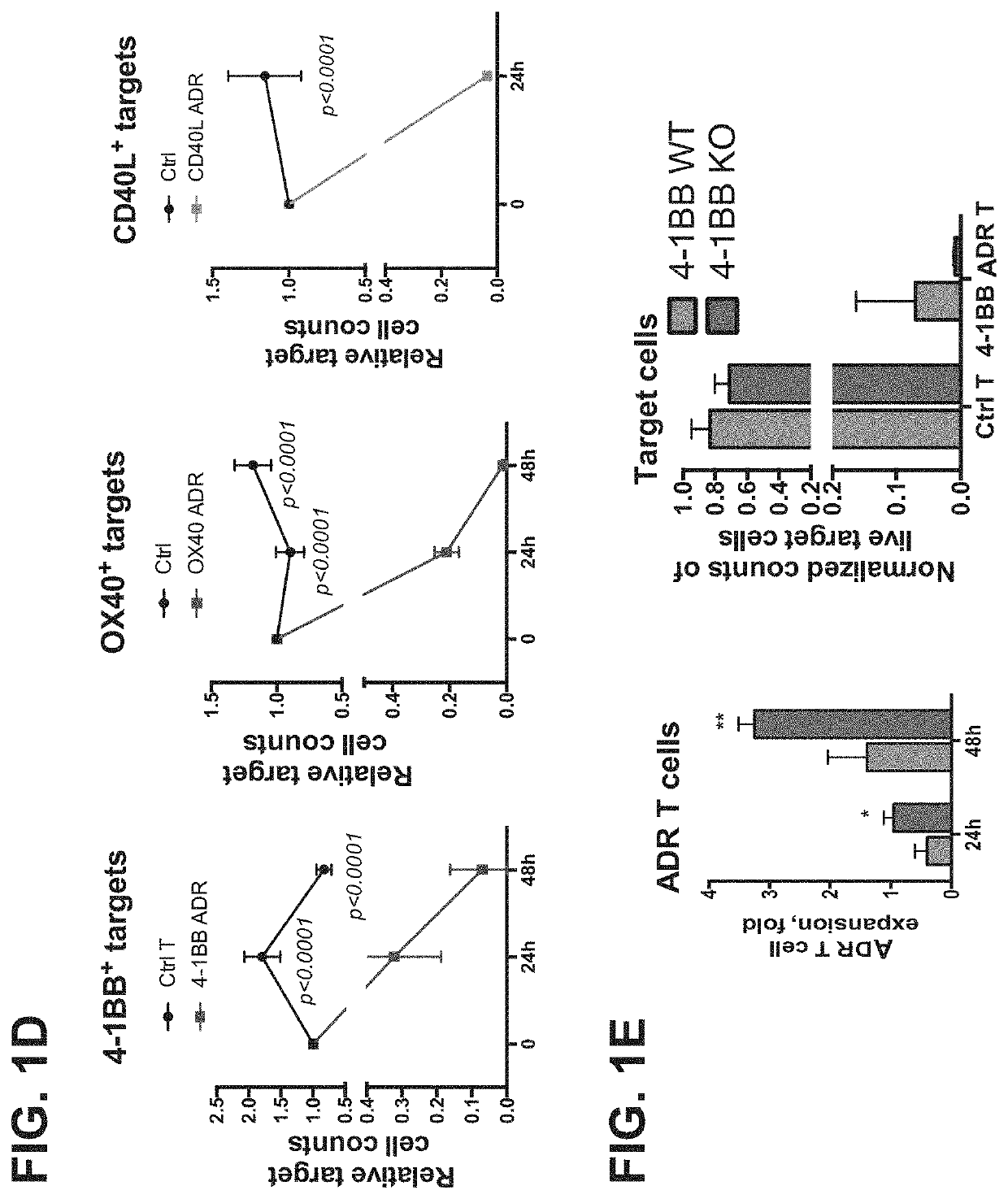
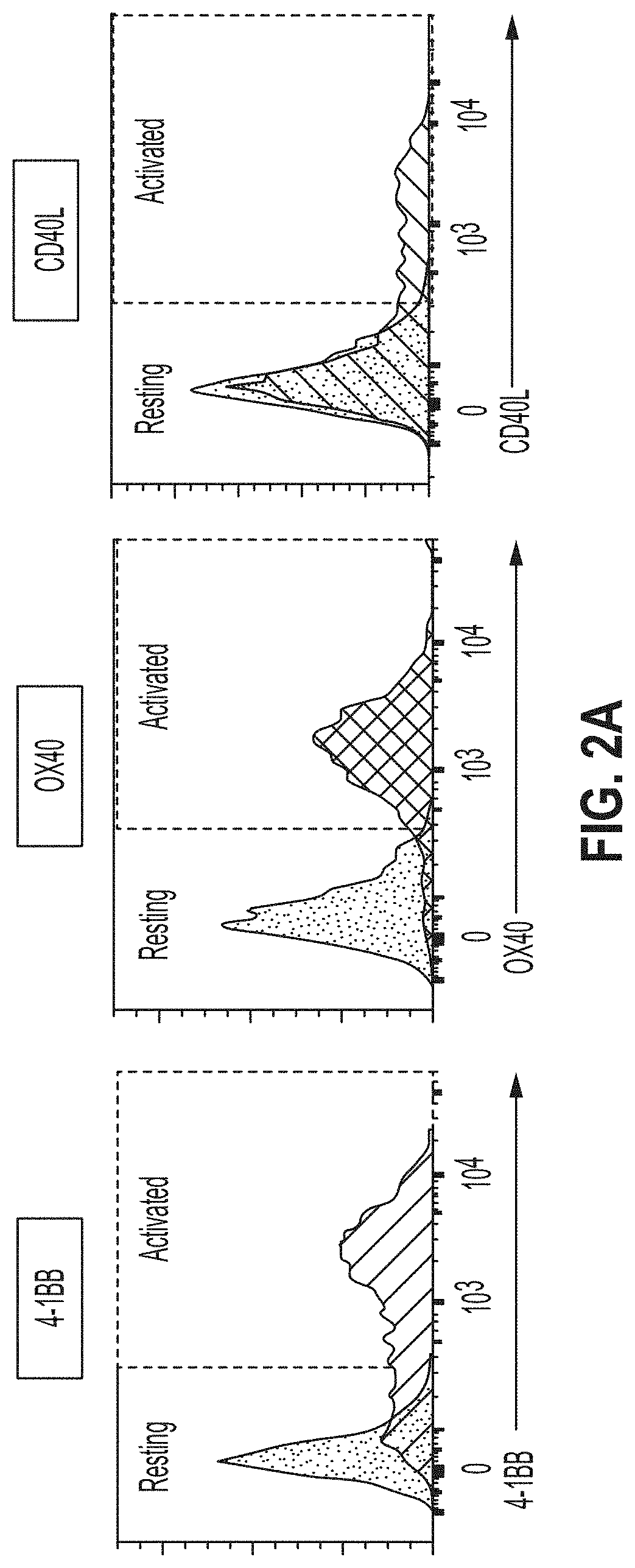
Embodiments of the disclosure concern engineered auto / allo-immune defense receptor (ADR)-expressing T cells that selectively target activated T cells, including pathogenic T cells, to incapacitate them. The chimeric receptors comprise moieties for targeting 4-1BB, 0X40, and CD40L, for example, whose expression is indicative of activated T cells. In particular embodiments, there are methods of preventing or treating conditions associated with activated T cells using adoptive T-cell transfer of cells encoding the ADRs.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Growth factor antagonists for organ transplant alloimmunity and arteriosclerosis
ActiveUS20150218249A1Reduce dependenceReduce needAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsProviding materialAllograft rejection
The present invention provides materials and methods for antagonizing the function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, platelet derived growth factor receptors and other receptors, to prevent, inhibit, or ameliorate allograft rejection or arteriosclerosis in organisms that receive an organ transplant.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
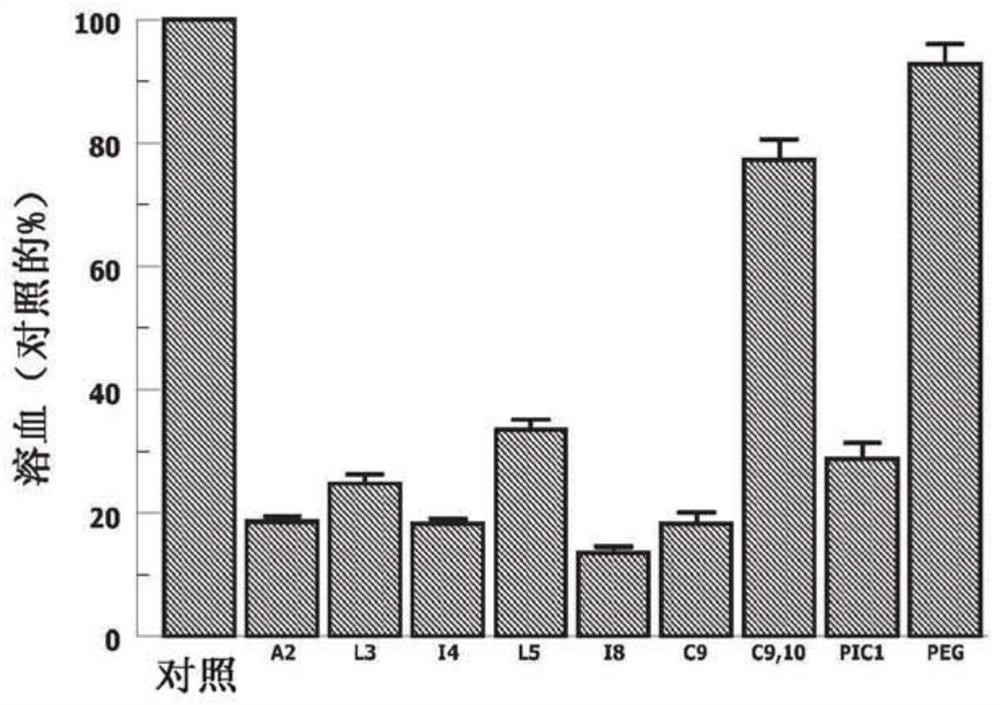
Pic1 variants with improved solubility and methods of using the same
PendingCN113474050APeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPlateletImproved solubility
A method of improving the lifespan of transfused platelets is described. The method may be useful for patients with alloimmunozation who are refractory to transfused platelets. A method of treating delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction is also described. Also described are PIC1 peptide variants with improved solubility and activity.
Owner:瑞尔塔控股有限公司
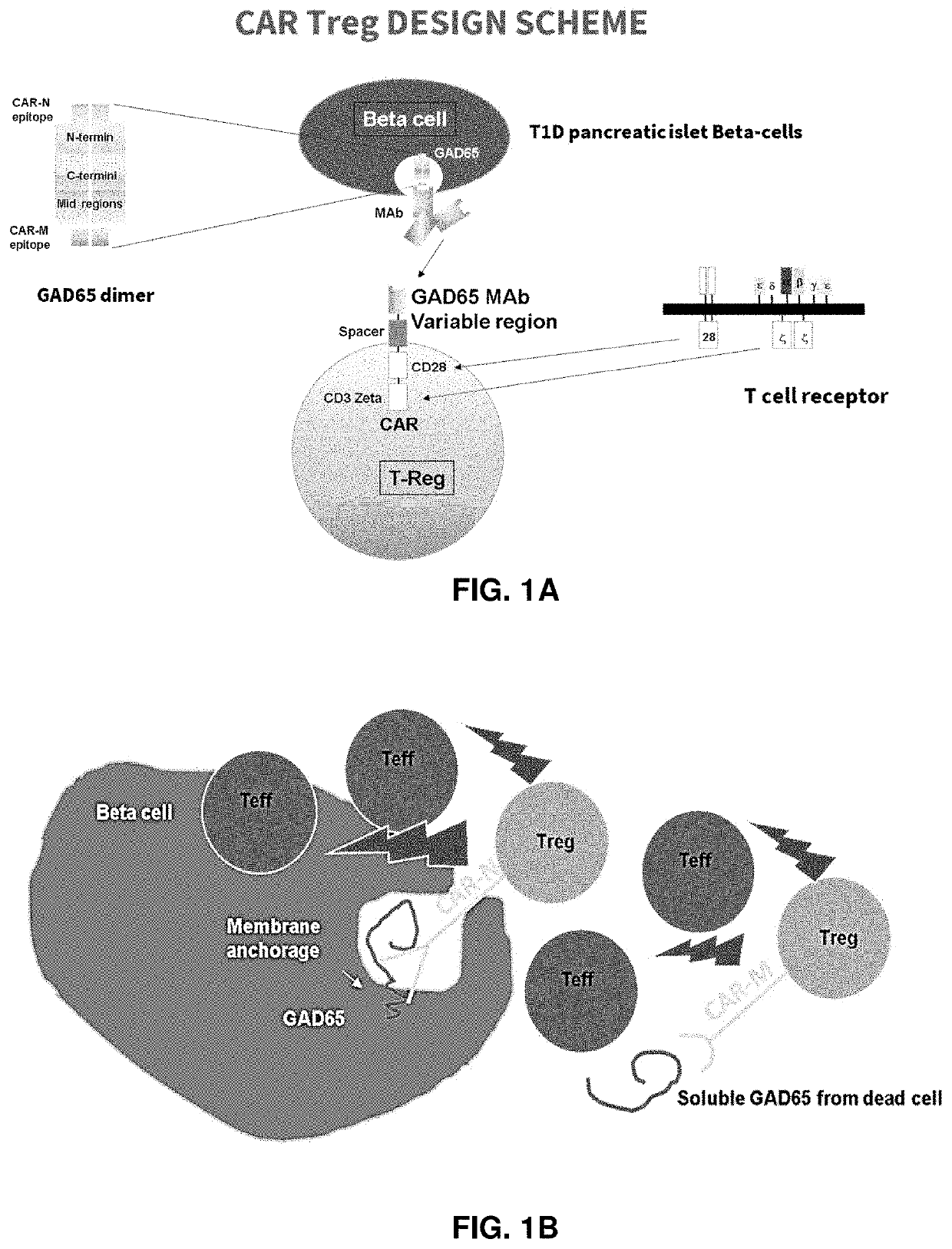
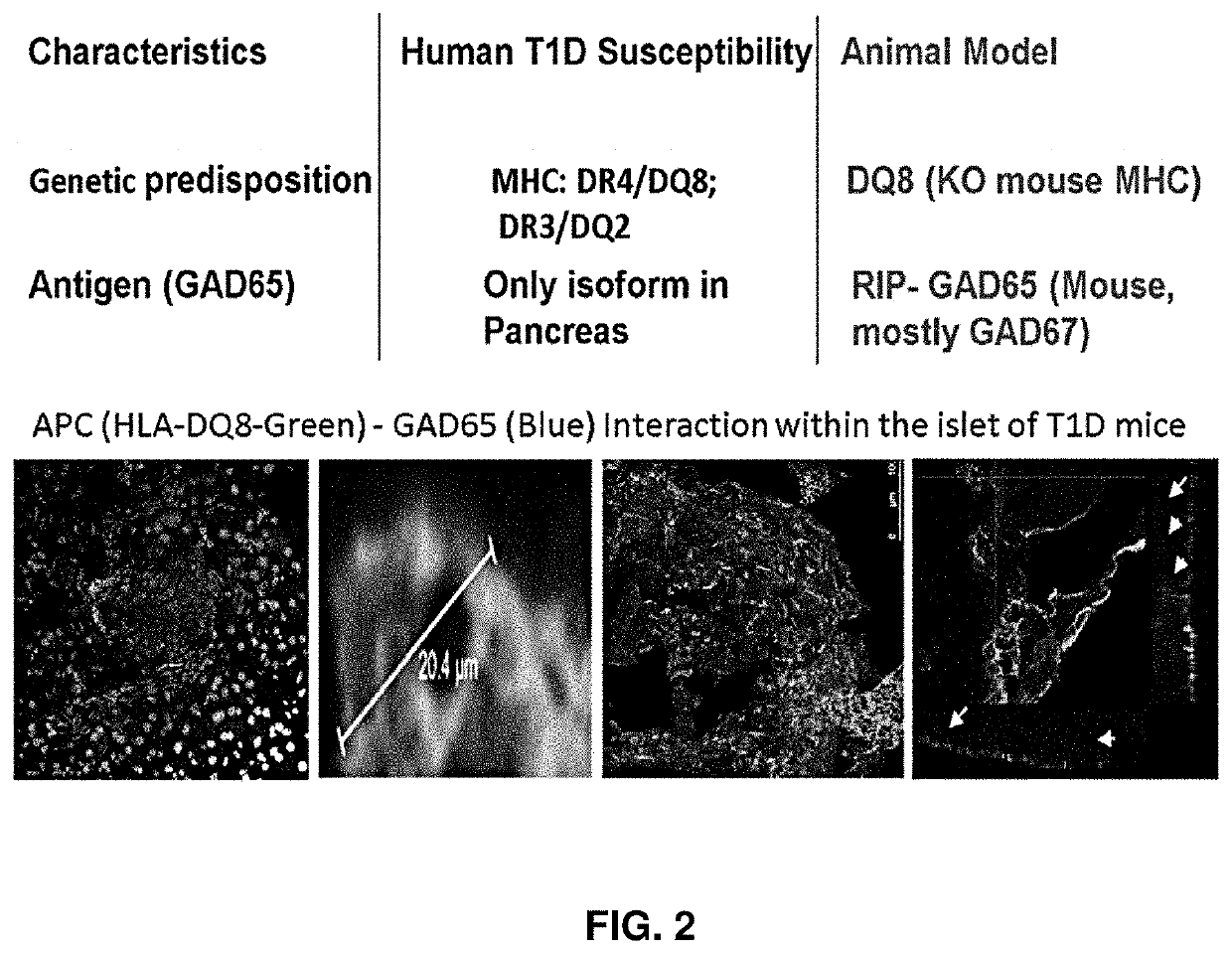
Immunosuppressive antigen-specific chimeric antigen receptor treg cells for prevention and/or treatment of autoimmune and alloimmune disorders
PendingUS20220008522A1Improve survivalEnhance immune responsePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
Described herein are immunoresponsive cells which are useful for their preventive and therapeutic potential against autoimmune diseases and rejections of solid organ transplants.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Auto/allo-immune defense receptors for the selective targeting of activated pathogenic t cells and nk cells
PendingUS20220000920A1Easy to usePrevent rejectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsReceptor
Embodiments of the disclosure concern engineered auto / allo-immune defense receptor (ADR)-expressing T cells that selectively target activated T cells, including pathogenic T cells, to incapacitate them. The chimeric receptors comprise moieties for targeting 4-1BB, OX40, and CD40L, for example, whose expression is indicative of activated T cells. In particular embodiments, there are methods of preventing or treating conditions associated with activated T cells using adoptive T-cell transfer of cells encoding the ADRs.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Methods of preventing platelet alloimmunization and alloimmune platelet refractoriness and induction of tolerance in transfused recipients
InactiveUS20200138950A1Prevent alloimmune platelet refractorinessReduce Alloimmunization To PlateletsOther blood circulation devicesEnergy modified materialsPre transfusionPlatelet refractoriness
Methods and compositions for the prevention or reduction of platelet transfusion associated complications are provided. The subject methods include modifying donor whole blood or platelets prior to transfusion to prevent or reduce alloimmune platelet refractoriness.
Owner:BLOODWORKS
Use of telmisartan to prevent and treat graft versus host disease and other alloimmune and autoimmune diseases
ActiveUS9937154B2Improve survivalPreserve alloreactivityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune conditionAngiotensin Receptor Blockers
The described invention relates to methods for preventing or treating graft-versus-host disease while preserving a graft-versus-tumor effect, increasing survival of, preserving alloreactivity, or a combination thereof in a patient with a tumor receiving a transplant. The described methods comprise administering to the patient a therapeutic amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a Rho kinase inhibitor compound, e.g., telmisartan or related angiotensin receptor blockers, and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The therapeutic amount may be effective to attenuate graft-versus-host disease and to preserve the graft-versus-tumor effect of the transplant.
Owner:HACKENSACK UNIVERSTIY MEDICAL CENT
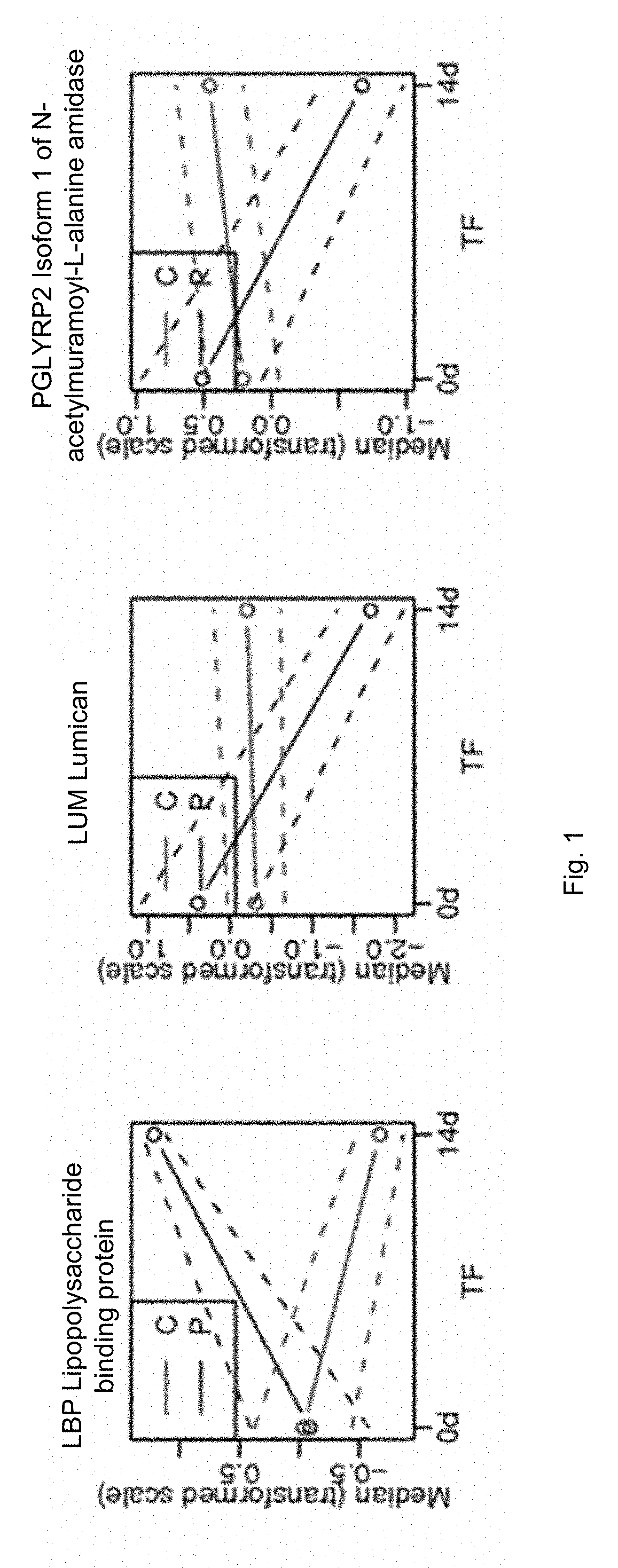
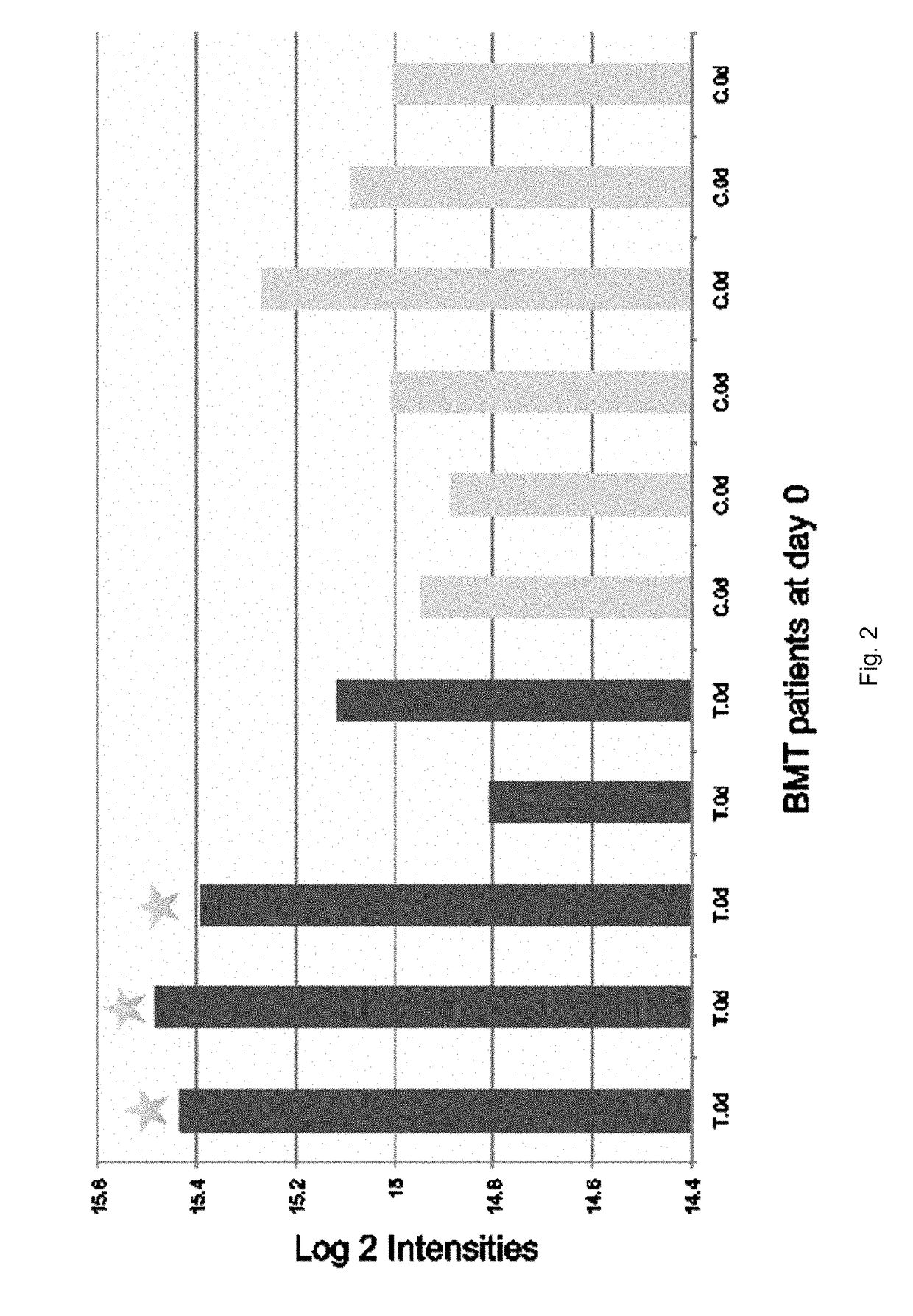
PGLYRP2 biomarker in idiopathic pneumonia syndrome
ActiveUS9810696B2Solid foundationDisease diagnosisBiological testingAutoimmune thyroid diseaseAutoimmune disease
A method for characterizing the risk a subject will develop an autoimmune and / or alloimmune disease following tissue transplant includes obtaining a biological sample from the subject, wherein the subject has received the tissue transplant determining in the biological sample a level of at least one protein selected from Tables 1-4, comparing the measured level of the at least one protein to a control value, and characterizing a subject as at greater risk of developing an autoimmune disease and / or alloimmune disease if the level of at least one protein determined is increased or decreased compared to the control value.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
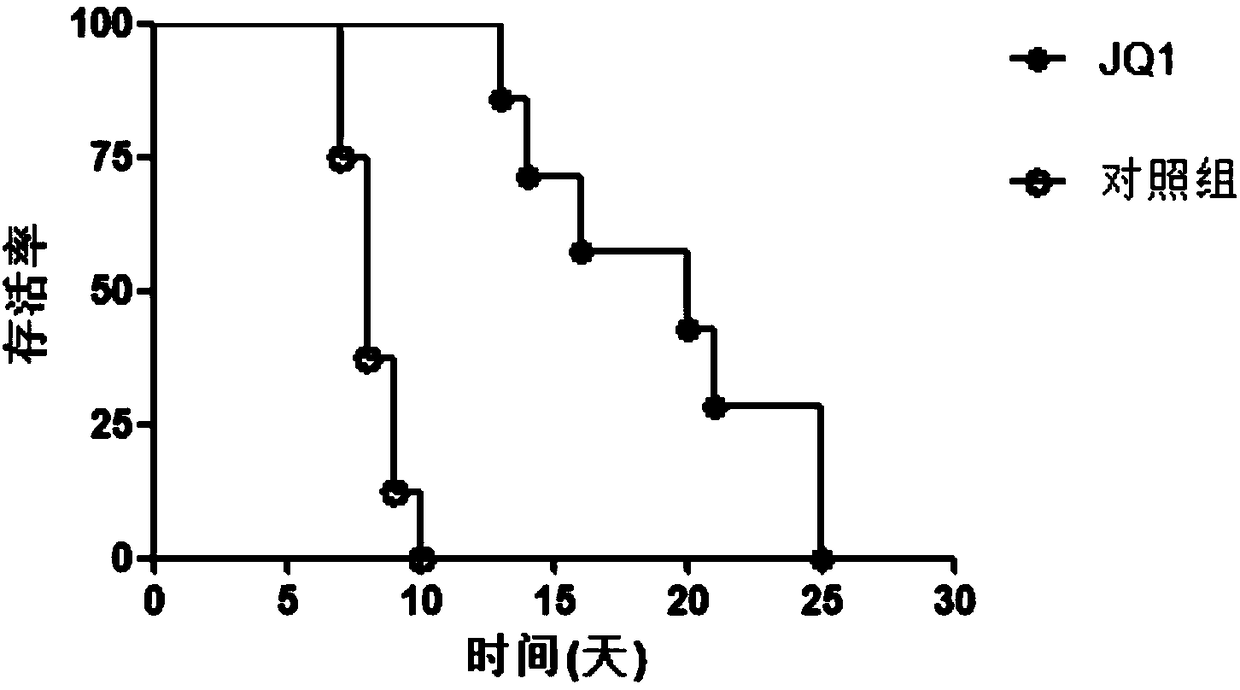
Application of JQ1 in preparing organ transplantation immunological rejection inhibiting medicines
ActiveCN108096252AConducive to survivalLower immune responseOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersBALB/cHeart transplantation
The invention provides an application of JQ1 in preparing organ transplantation immunological rejection inhibiting medicines, in particular an application in preparing medicines for preventing and treating cardiac transplantation immunological rejection. Based upon experiments, it is proved that the survival time of transplanted hearts of an allogeneic mice (C57BL / 6 to BALB / c) in a control group is 7-10 days, while the survival time of transplanted hearts of mice applied with the JQ1 can reach 25 days to the greatest extent, indicating that the JQ1 provided by the invention is beneficial for reducing an alloimmunity reaction and prolonging the survival of transplants. The JQ1, as a novel small-molecule inhibitor, can solve the problem that transplanted organs are low in survival rate for along time due to rejection, and the JQ1 can offer a basis for preparing organ transplantation immunological rejection inhibiting preparations; therefore, an effective approach is provided for treating such chronic end-stage diseases such as liver diseases, renal diseases, cardiac diseases and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Immunosuppressive composition for use in treating immunological disorders
ActiveUS20190262424A1Reduce concentrationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoimmune conditionStromal cell
The present disclosure describes a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one antibody and at least one mesenchymal stromal cell-derived protein. Disclosed herein is also the use of said pharmaceutical composition for treating immunological diseases, for example alloimmune and autoimmune diseases. Further disclosed herein is the use of the pharmaceutical composition for immunomodulation.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE
Therapeutic substances, their preparation and diagnostic procedure
PendingUS20210177905A1Suppressing expansion/infiltrationEffective treatmentMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAutoimmune conditionTissue repair
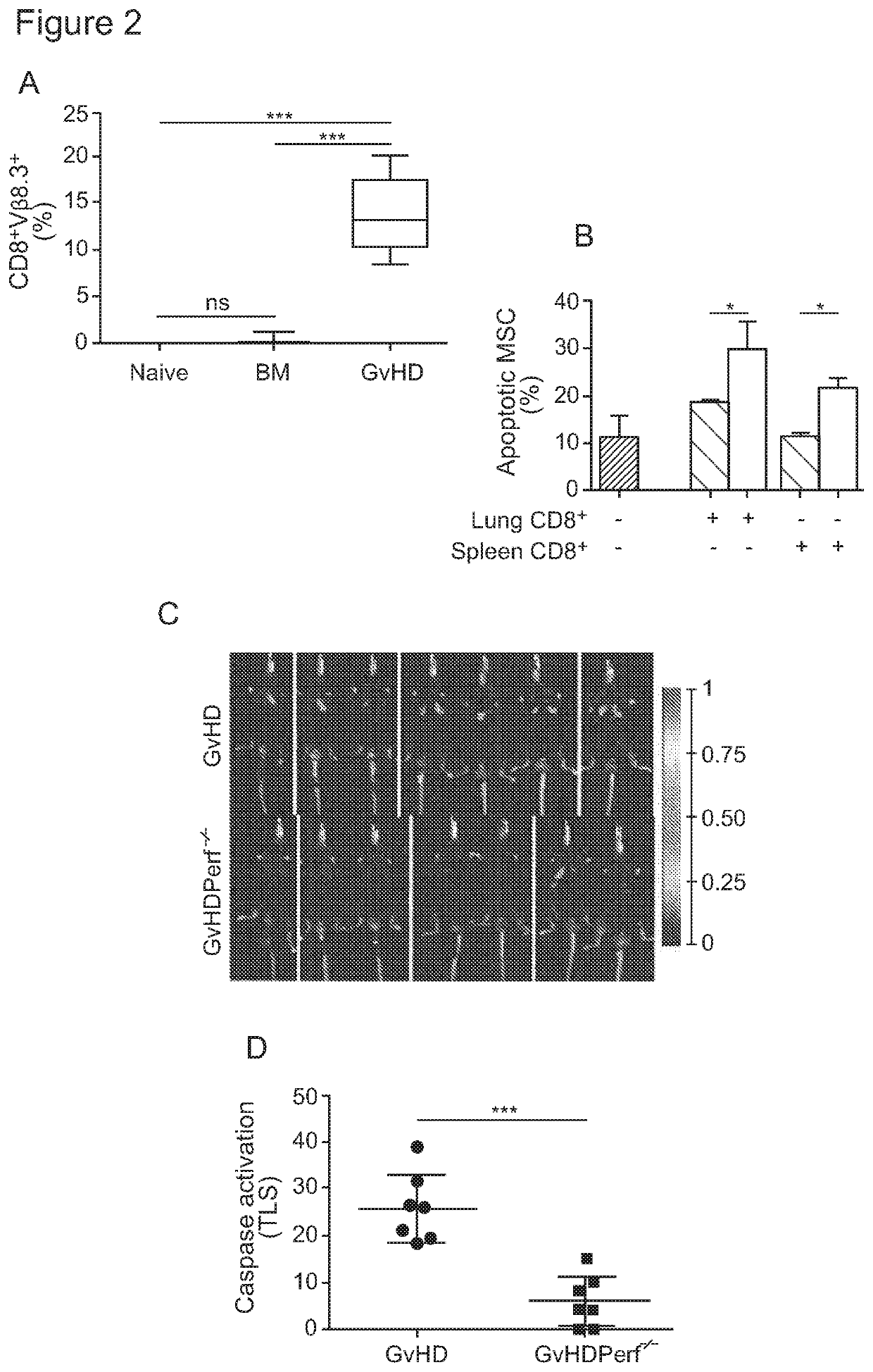
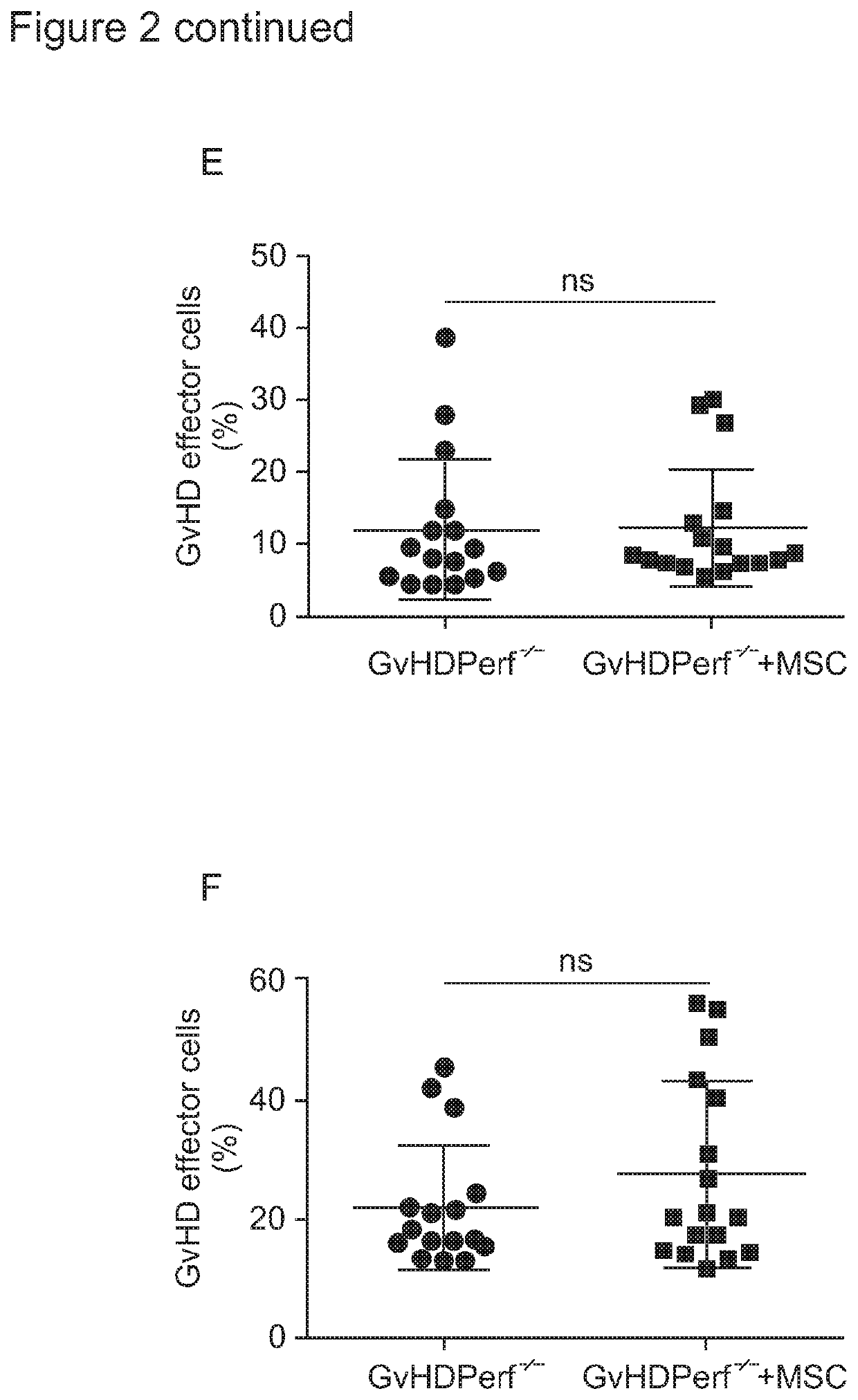
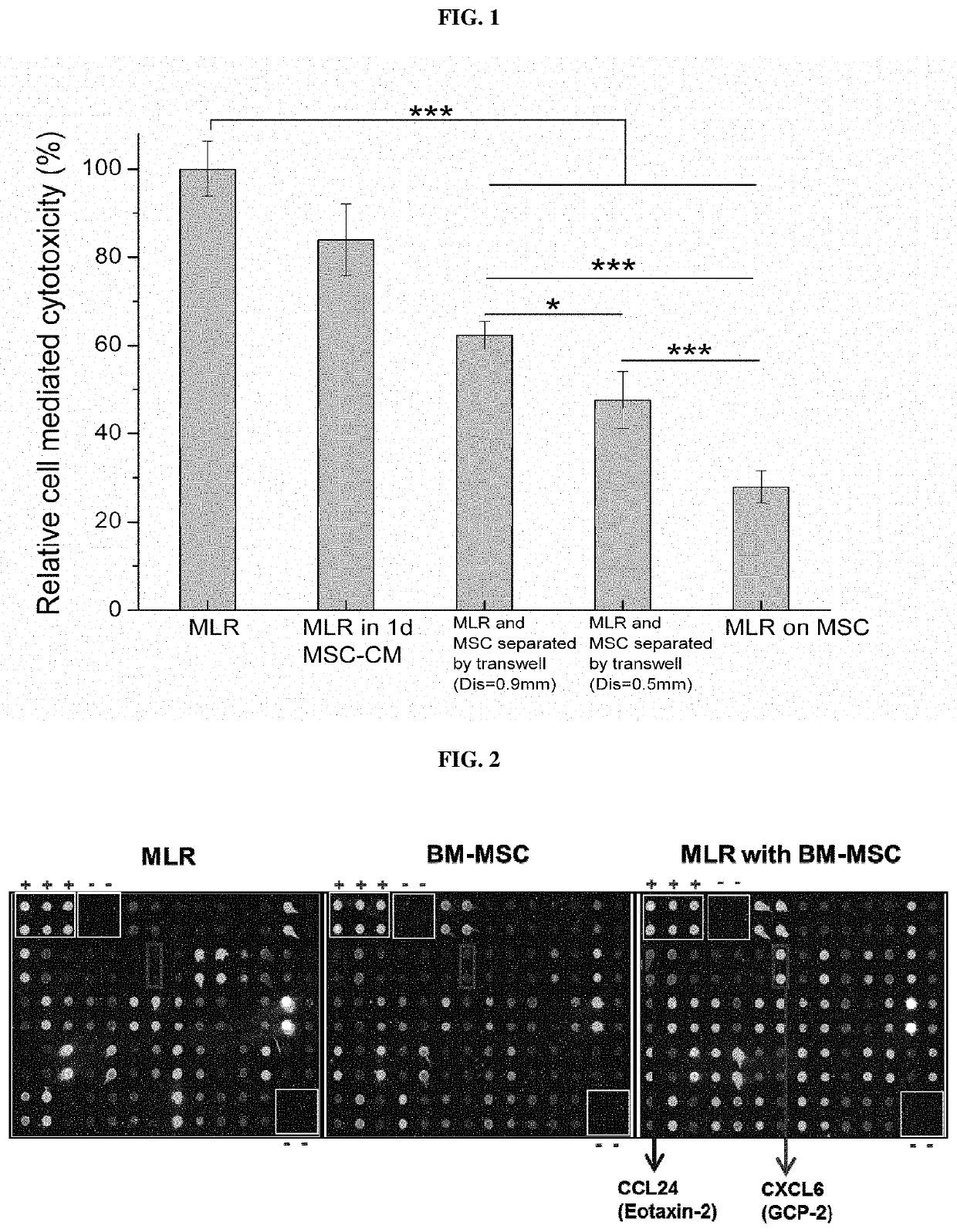
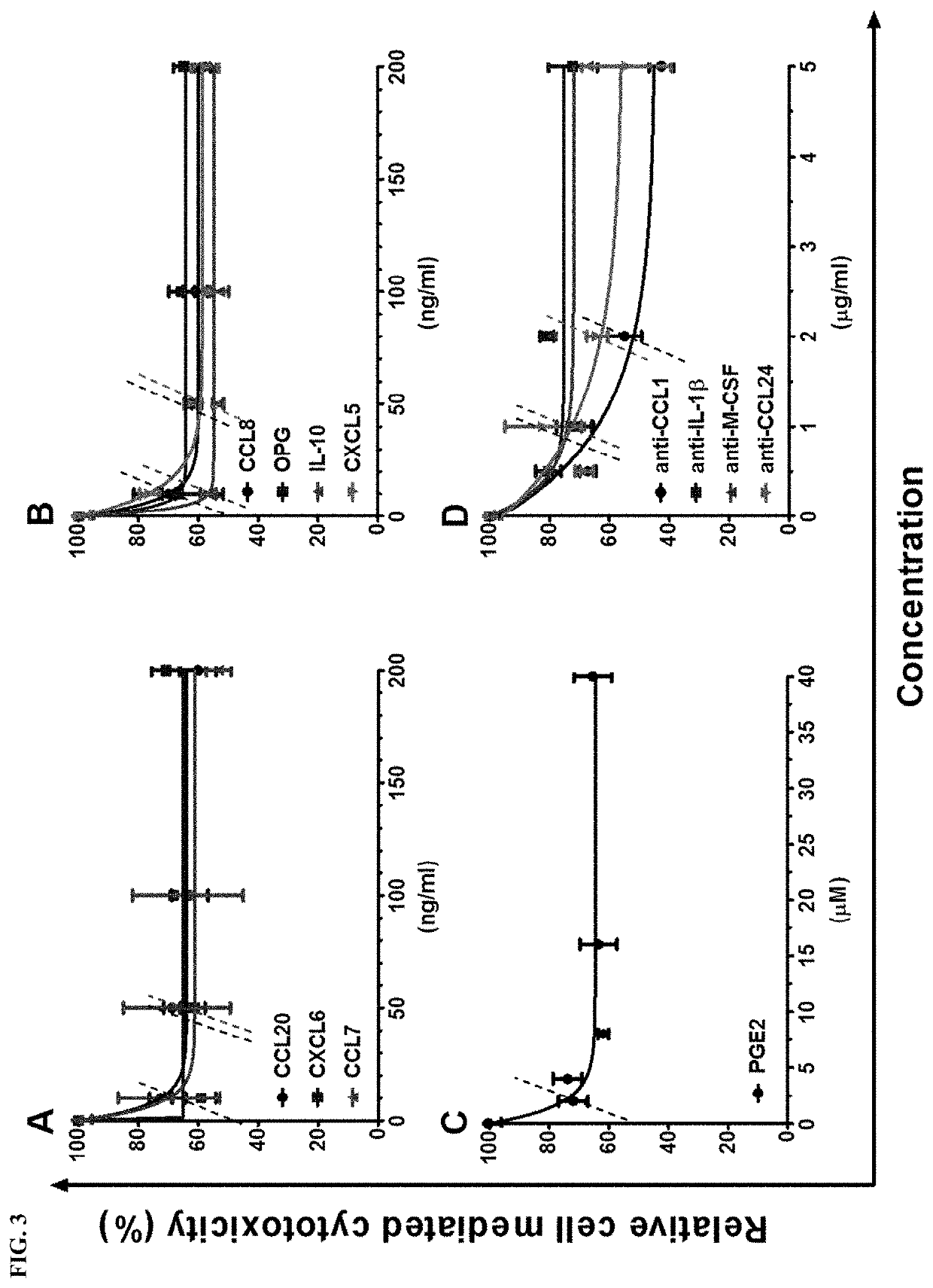
A method is described for using live mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) in a way which allows for identification of patients likely to respond to immunosuppressive treatment using MSCs. The method involves contacting a sample from said patient with live MSCs in vitro, and determining whether the sample is able to induce at least some apoptosis to occur in live MSCs in vitro, or detection of elevated levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The ability of the sample to induce said apoptosis and / or elevated levels of PGE2 is indicative of responsiveness of said patient to said immunosuppressive treatment and / or indicative of fitness to recover. Also provided are apoptotic MSCs for use in the treatment of immune-mediated disease or conditions, such as allo-immune or autoimmune disease, or for the prevention or treatment of rejection of a transplanted organ; or in regenerative medicine to stimulate tissue repair. Methods for preparing pharmaceutical compositions comprising the apoptotic MSCs are also described and claimed.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON
Immunosuppressive composition for use in treating immunological disorders
ActiveUS20210252140A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAntiendomysial antibodies
The present disclosure describes a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one antibody and at least one mesenchymal stromal cell-derived protein. Disclosed herein is also the use of said pharmaceutical composition for treating immunological diseases, for example alloimmune and autoimmune diseases. Further disclosed herein is the use of the pharmaceutical composition for immunomodulation.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com