Pic1 variants with improved solubility and methods of using the same
A technology of complement and donor, applied in the field of PIC1 variant with improved solubility and its use, can solve the problem of DHTR not being recognized
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Example 1: Peptide Solubility
[0097]To assess the effect of sarcosine residues on the solubility and biological function of the base peptide IALILEPICCQERAA(PA), peptides were synthesized with sarcosine residue substitutions at all 15 positions. Also included are peptides in which adjacent cysteines at positions 9 and 10 (C9, C10) are replaced by a single sarcosine residue. The peptides are shown in Table 2. Water solubility assays were performed for each peptide and the results are shown in Table 3. Substitution of sarcosines at positions A2, L3, I4, L5, I8, C9 and C9,10 resulted in peptides soluble in water. Due to their enhanced solubility in the absence of PEGylation, these peptides were selected for further evaluation of various biological activities.
[0098] Table 3. Results of Peptide Aqueous Solubility Assays
[0099]
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: Complement Inhibition Assay of Peptide Variants
[0101] An assessment of the extent to which the peptide variants inhibit antibody-initiated complement activation was performed. The peptide variants were tested in two hemolytic assays: (i) ABO incompatibility ex vivo assay, and (ii) classical pathway CH50 type assay in factor B deprived serum.
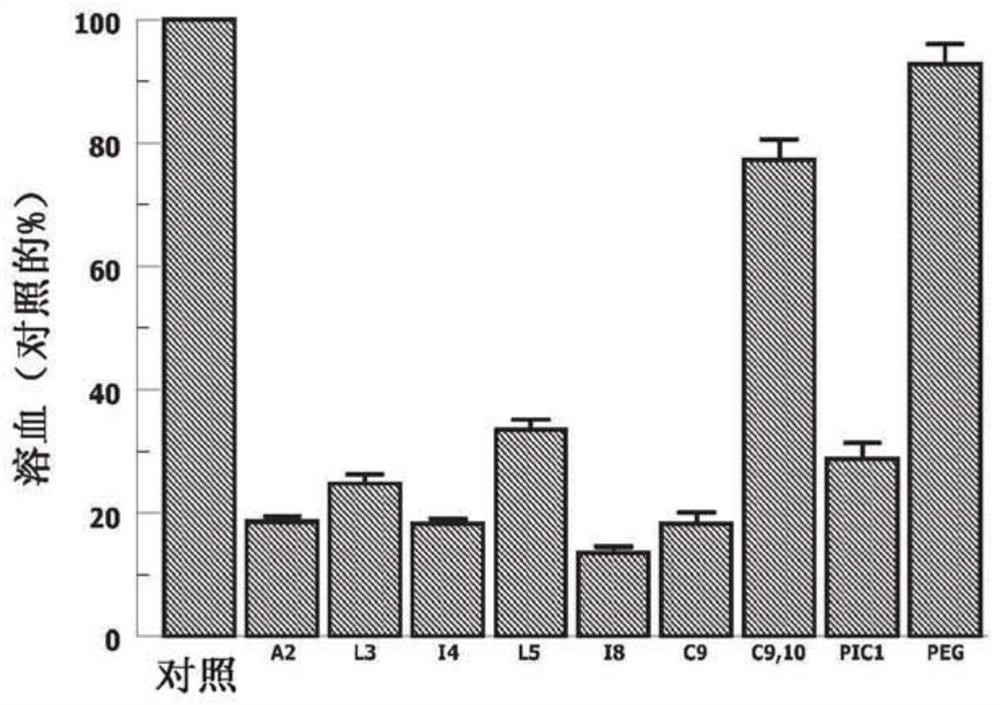
[0102] In the ABO incompatibility hemolysis assay, purified erythrocytes from "AB+ type" donors are incubated with serum from "O" subjects containing anti-A and anti-B antibodies; the peptides tested is 1.8mM. The data is shown in Figure 1A middle. On an equimolar basis, variants A2, I4, I8 and C9 each inhibited ABO incompatibility hemolysis to a greater extent than the PA-dPEG24(PIC1) parent compound (P<0.015). The 18 variant reduced ABO hemolysis by 53% more than PA-dPEG24 (P<0.002). However, the C9,10 variant showed very low inhibition of ABO hemolysis.
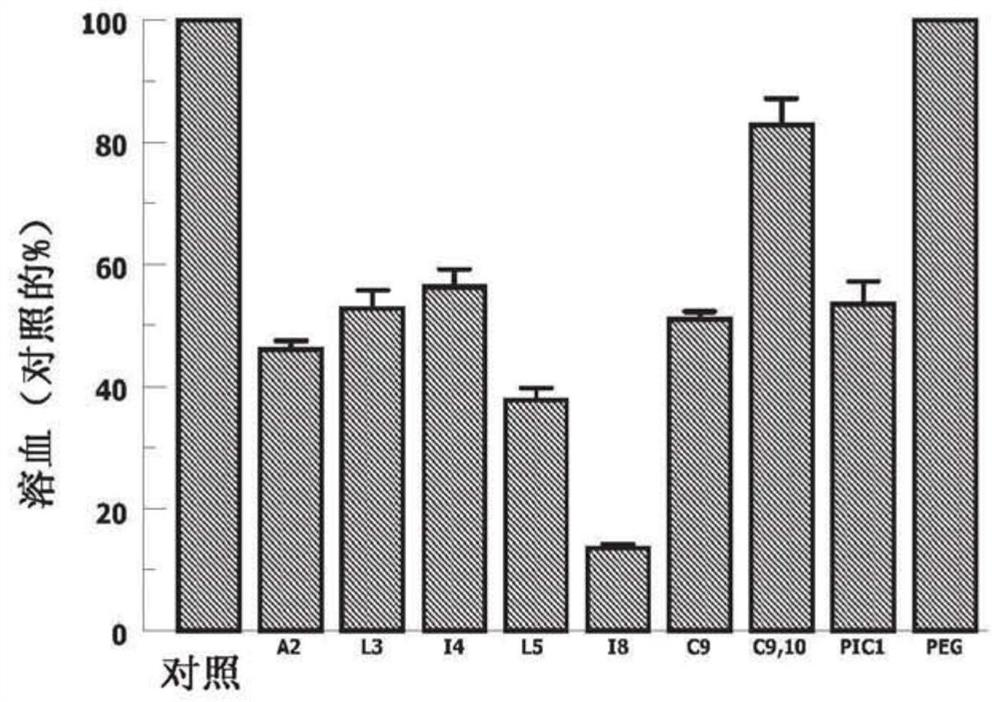
[0103] A CH50-type hemolytic assay was then performe...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Myeloperoxidase Inhibition and Binding
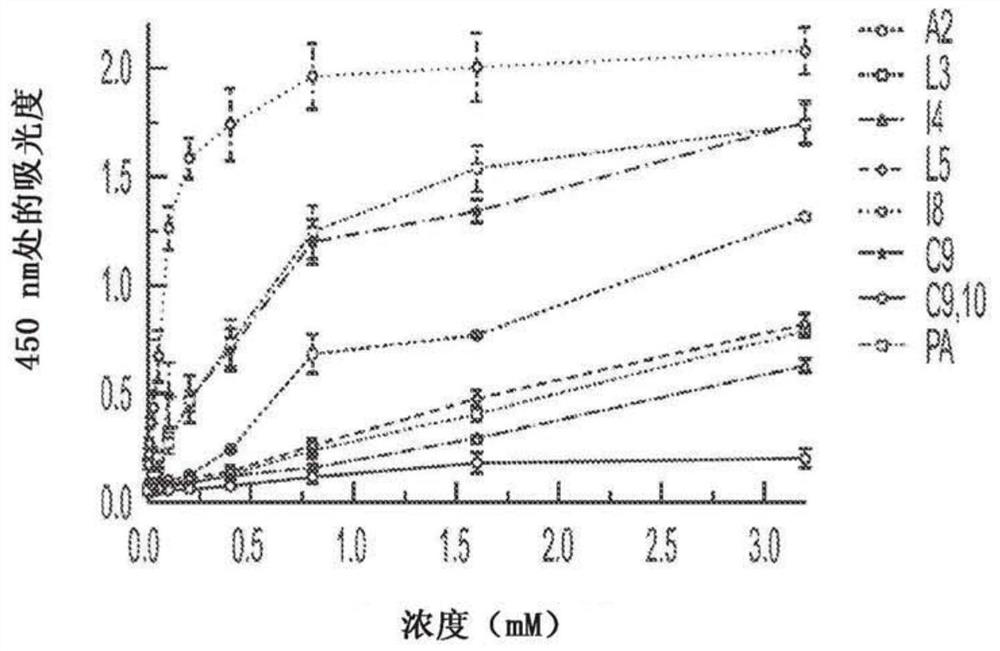
[0106] Inhibition of myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was then tested in a TMB-based in vitro assay as previously described for PA-dPEG24 [7]. In this assay, the variants were tested for MPO inhibition over a range of concentrations. The data is shown in Figure 2A middle. Strong MPO inhibition was found for all variants with the exception of cysteine-free variants (C9,10). The half-maximal inhibition values for each variant were calculated from the dose-response curves, and the data are shown in Figure 2B middle. There was a measurable difference in MPO inhibition, with variant 18 again showing the greatest efficacy among the different variants.
[0107] A plate-based assay was performed to test the binding of the peptide variants to immobilized MPO. Binding curves are shown in Figure 2C middle. MPO binding was identified for all variants except C9,10. Since the I8 and PA curves overlap almost completely, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com