Auto/allo-immune defense receptors for the selective targeting of activated pathogenic t cells and nk cells
a technology of auto-immune defense and alloimmune defense, which is applied in the field of immunology, cell biology, molecular biology, medicine, can solve the problems of limiting the therapeutic benefit, and achieve the effect of avoiding allo-immune reactions and convenient us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Auto / Allo-Immune Defense Receptors for the Selective Targeting of Pathogenic T Cells
[0140]Disclosed herein is a novel approach to specifically target pathogenic T cells using auto / allo-immune defense receptors (ADRs) expressed on normal T cells. ADR-expressing T cells find and eliminate only activated T cells and spare resting non-pathogenic naïve and memory T cells, which constitute the majority of circulating lymphocytes
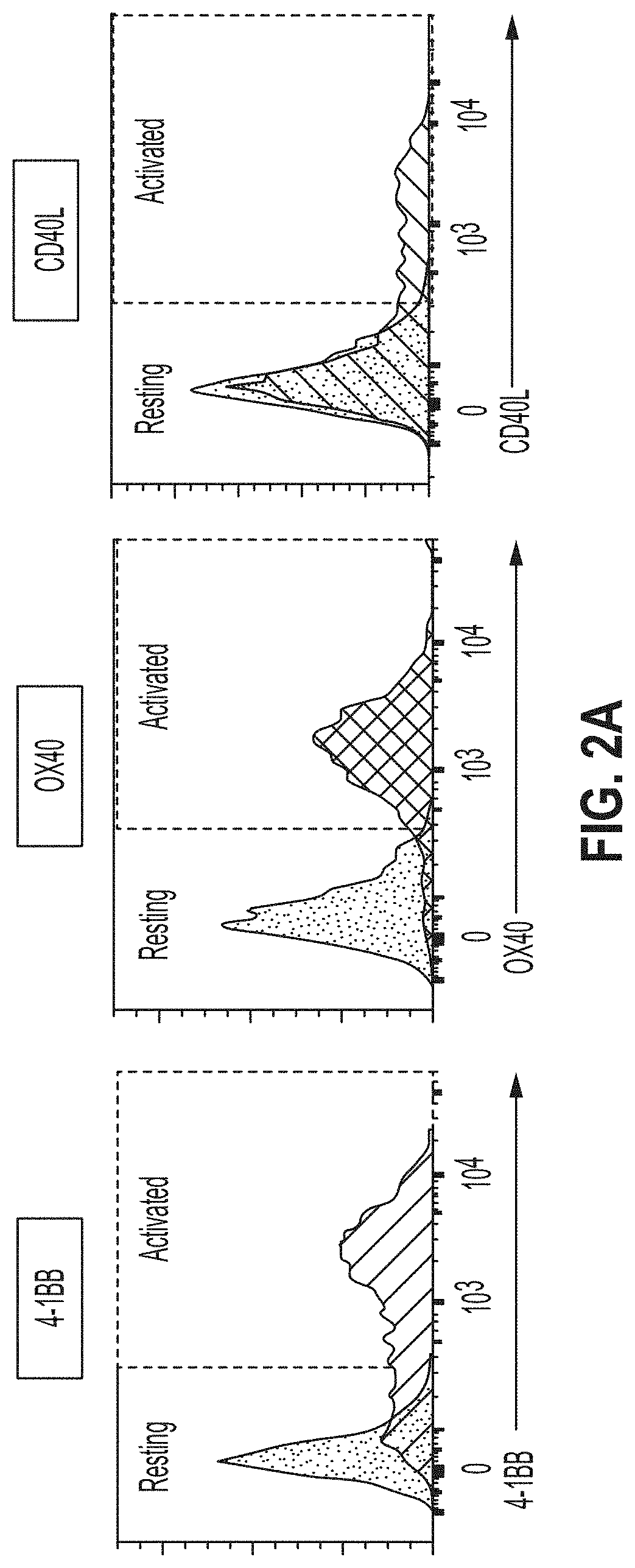
[0141]The concept of the ADR-mediated targeting is based on the observation that within 24 h of activation, T cells transiently upregulate costimulatory genes 4-1BB, OX40, and / or CD40L on their cell surface. The expression of 4-1BB, OX40, and / or CD40L is only maintained when the T-cells are actively cytotoxic and is gradually downregulated within 4-5 days, when TCR signaling has stopped. Notably, activated CD8+ T cells showed higher magnitude of 4-1BB expression whereas CD4+ T cells preferentially expressed OX40 and / or CD40L. Apart from activated T cells, ADR ligan...
example 2
Auto / Allo-Immune Defense Receptors for the Selective Targeting of NK Cells
[0146]The ADRs demonstrate a specific cytotoxic activity against NK cells, a key cell population mediating rapid rejection of HLAlow or HLA-mismatched cells.
[0147]NK cells are capable of recognizing HLA-mismatched cells or cells with low HLA expression, as a part of the anti-tumor and anti-viral immune surveillance. Adoptive transfer of allogeneic cells into immunoreplete patients would thus result in NK-cell activation and rejection of the HLA-mismatched cells. Here, it is shown that co-culture of T cells expressing 4-1BB- and OX40-specific auto / allo-immune defense receptors (ADRs) leads to elimination of NK cells and thus would offset the NK cell-mediated host rejection of ADR-armed allogeneic T cells. Therefore, ADRs do not only inhibit the alloreactive T-cell response but also suppress NK cell mediated rejection, further supporting the application of ADRs to enhance the persistence and activity of “off-the...
example 3
ADR-Expressing T Cells Eliminate Target Cells
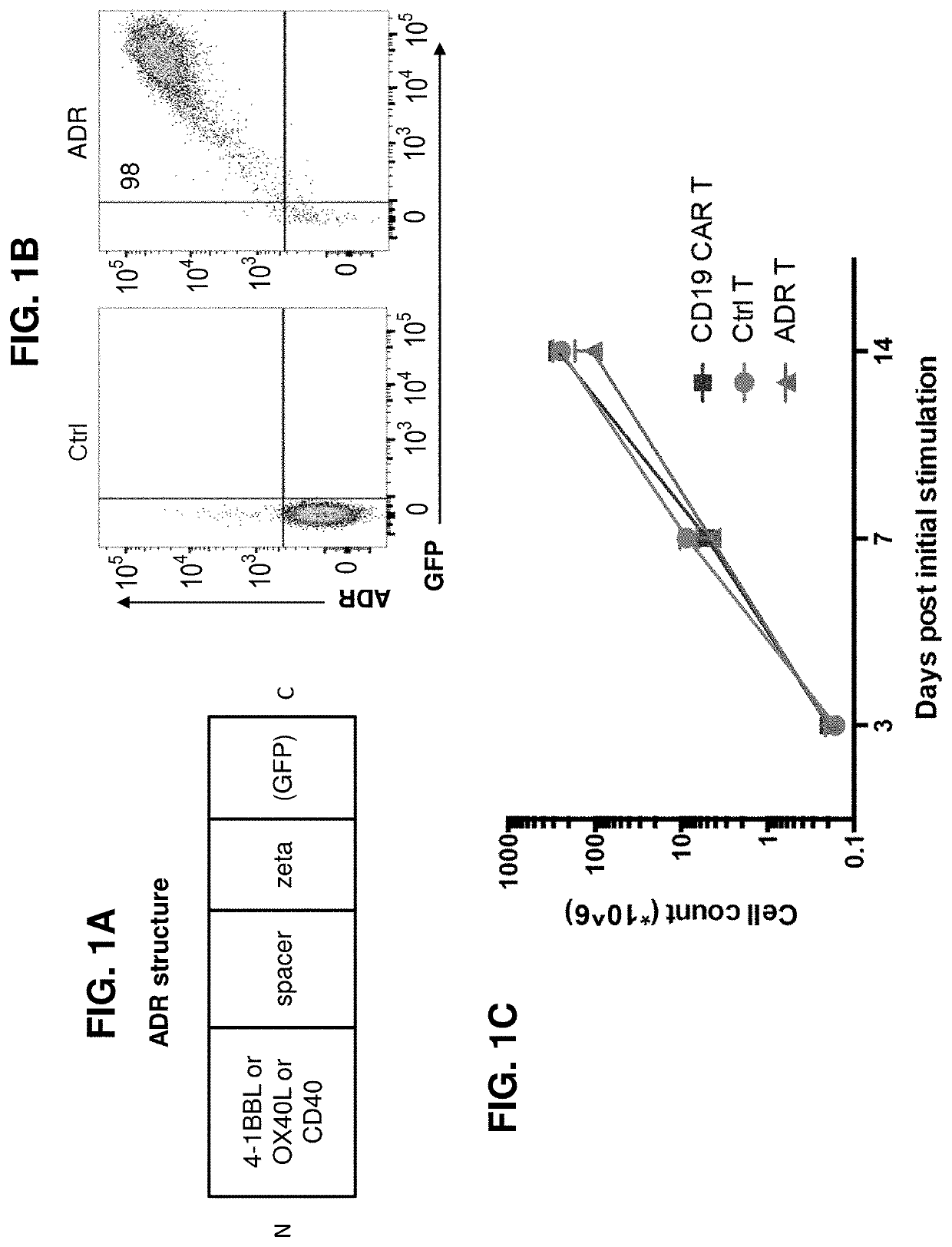
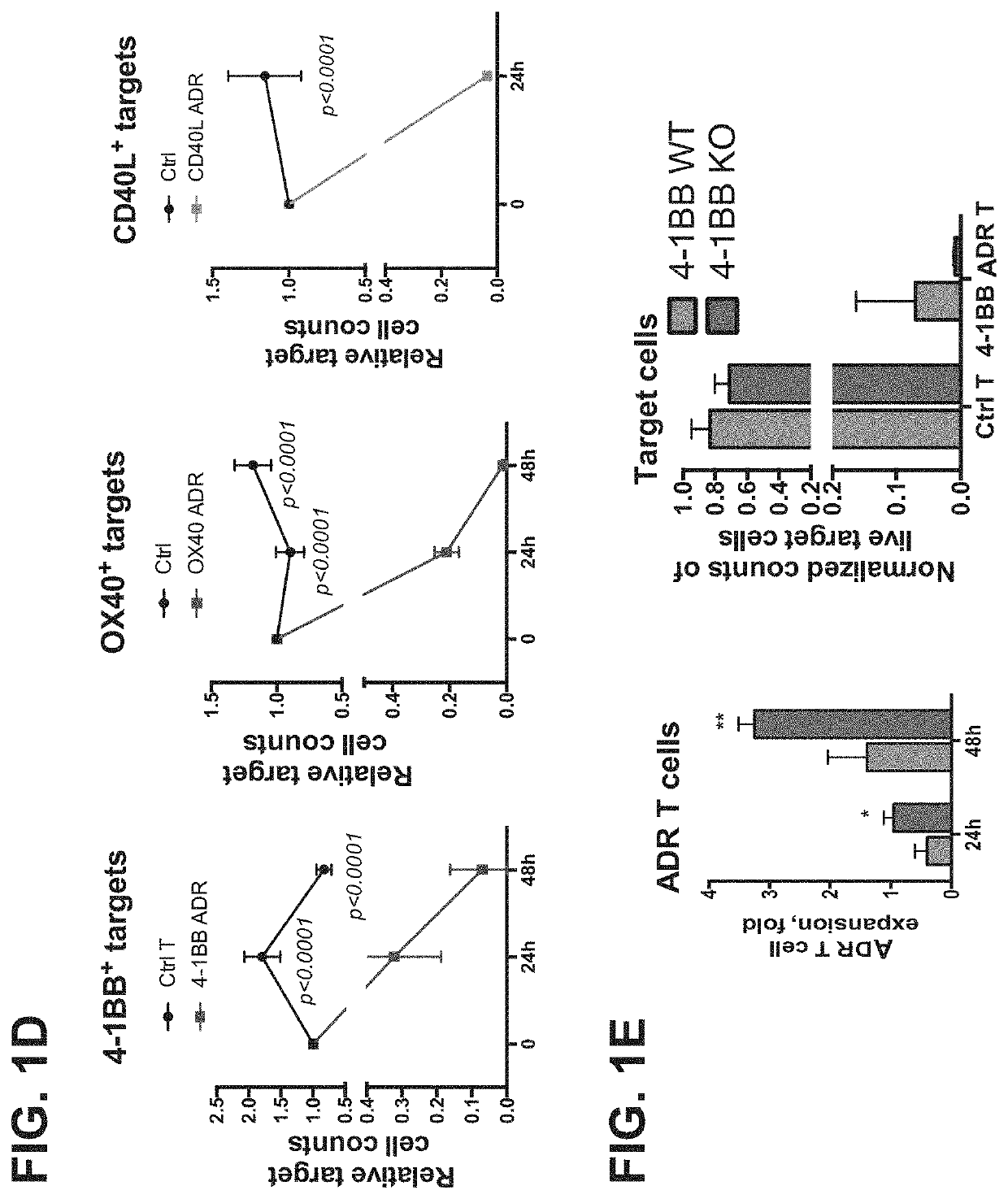
[0148]ADRs can be expressed on cell surface of immune cells and promote cytotoxicity against respective targets. FIG. 1A illustrates one example of a schematic of ADR (a label such as GFP is optional). The expression of ADR on the surface of T cells was confirmed (FIG. 1B) and the cells were expanded commensurate with controls (FIG. 1C). (FIG. 1D) The ADR-expressing T cells were cytotoxicity against target cells expressing corresponding ADR ligands (FIG. 1D). FIG. 1E demonstrates expansion of wild-type vs 4-1BB KO T cells expressing 4-1BB ADR and their cytotoxicity against 4-1BB+ targets. Knocking out the ADR ligand on T cells can further enhance expansion and cytotoxicity, and co-expression of ADR and its ligand on T cells is not required for ADR-T cell expansion or function (FIG. 1E).
[0149]Selective expression of ADR ligands on activated T cells enables their selective elimination by ADR T cells. Expression of ADR ligands on resting vs ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compositions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com