Application of JQ1 in preparing organ transplantation immunological rejection inhibiting medicines
A technology of immune rejection and immune exclusion, applied in the field of medical bioengineering, which can solve problems such as suppressing immune responses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
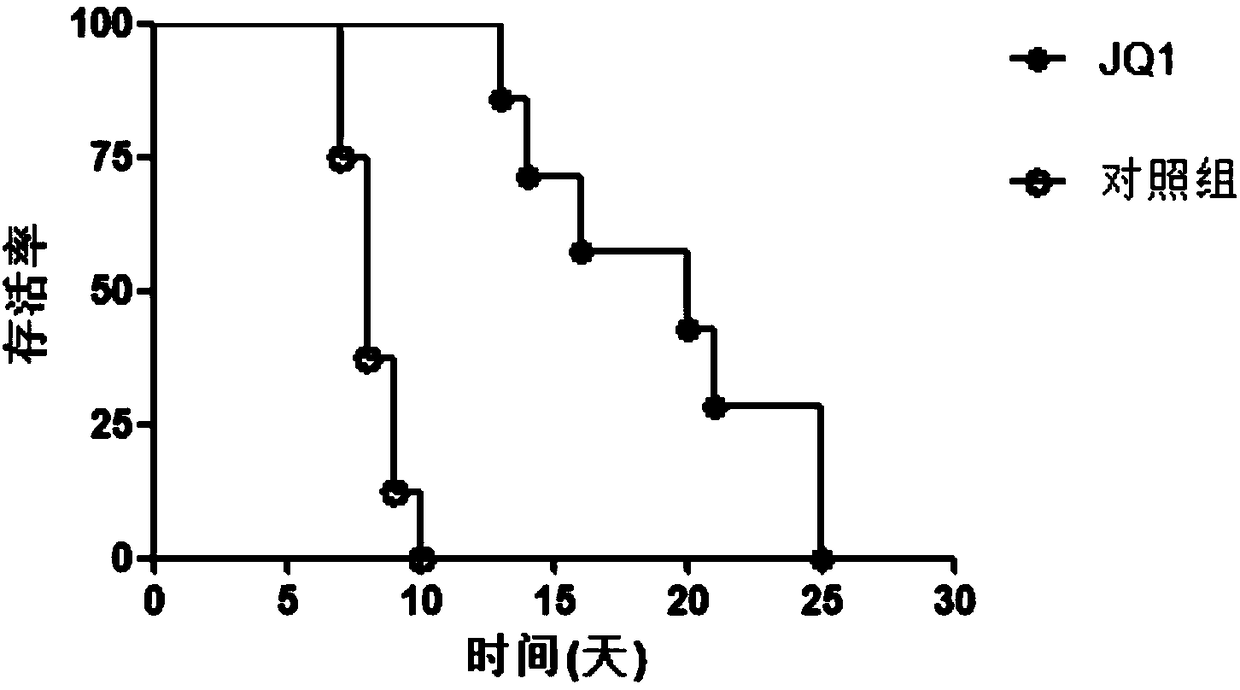
[0013] Example 1: The influence of JQ1 on the survival time of the transplanted heart was detected by constructing a mouse neck heterotopic heart transplantation model.
[0014] 1. Construction of mouse heterotopic heart transplantation model
[0015] 1.1 Experimental animals and main materials: The donor is a male pure-line C57 mouse, weighing 20-25g, purchased from Shanghai SLEC; the recipient is a male pure-line BALB / c mouse, weighing 20-25g, purchased from Shanghai Lecco Company. The arterial cannula is 26.
[0016] 1.2 Recipient preparation: The operation was performed under clean and non-sterile conditions, and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg / kg of 1% pentobarbital sodium. After success, the mice were fixed in a supine position, and an oblique incision was made from the bottom of the right mandibular angle to the top of the midpoint of the right clavicle, and the right submandibular gland and right sternocleidomastoid muscle were removed layer by lay...
Embodiment 2
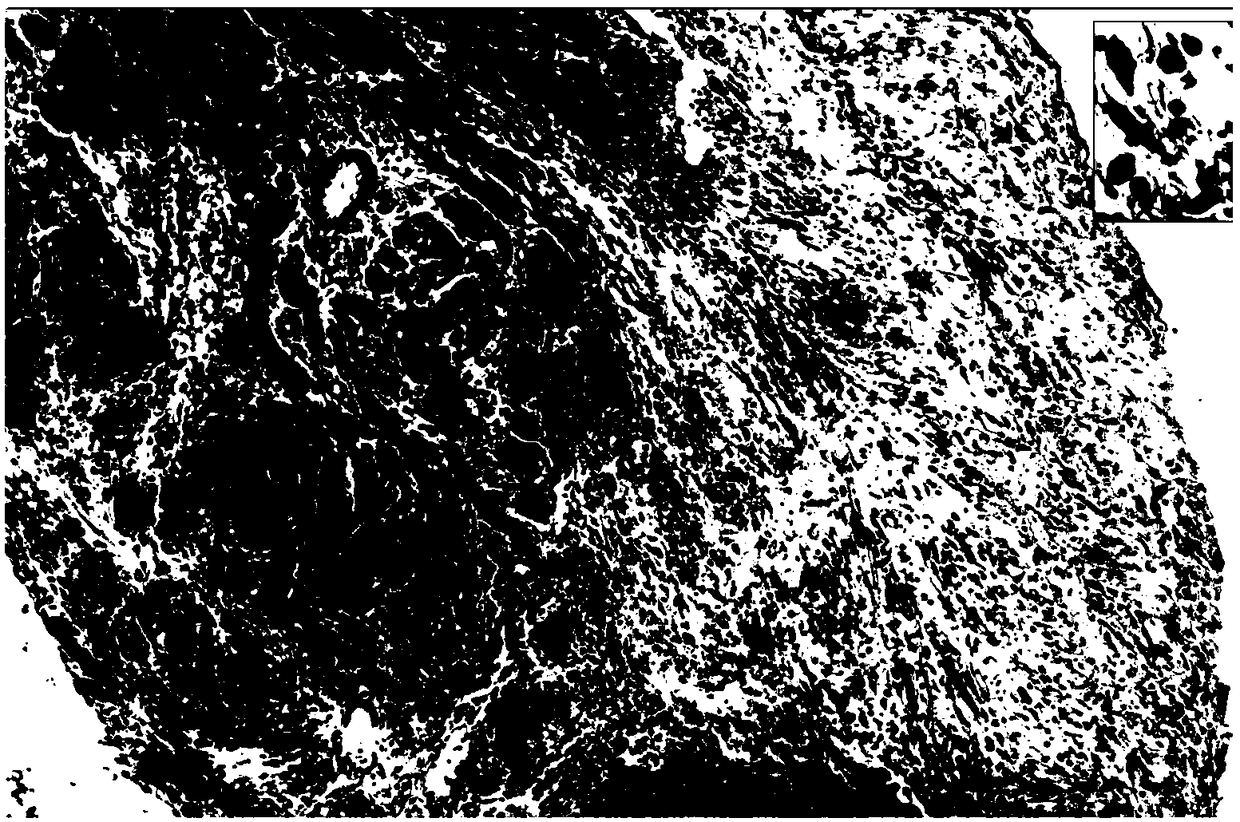
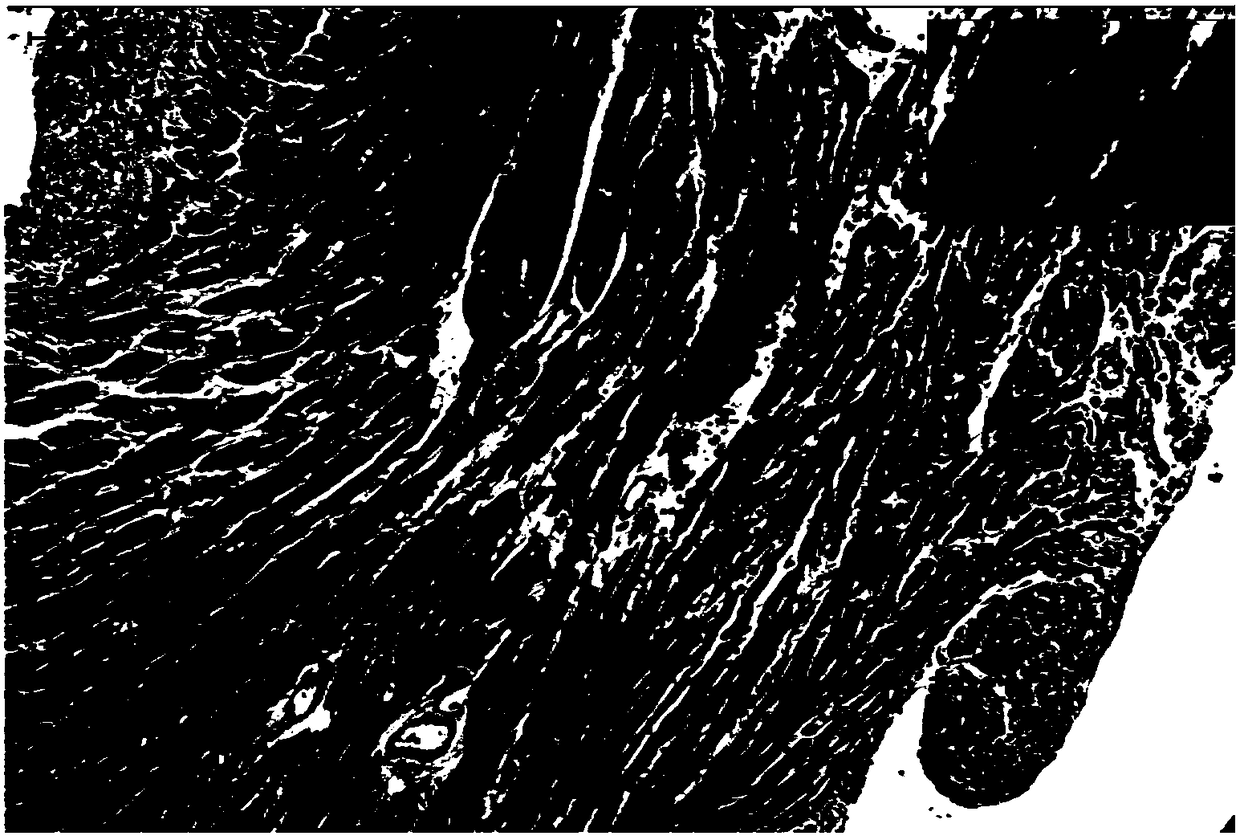
[0025] Example 2: Observation of pathological changes of heart grafts by HE staining.
[0026] 1. Experimental method: 1) On the 7th day after the transplantation, each 3 recipient mice in the control group and the experimental group were killed to obtain transplanted heart tissue pieces, which were fixed with 10% neutral formalin, Routinely embedded in paraffin, sliced at 4 μm with a Leica microtome. 2) Sections were dewaxed with xylene and washed with various levels of ethanol to water. The dewaxing steps are: xylene (I) 5 min→xylene (II) 5 min→100% ethanol for 2 min→95% ethanol for 1 min→80% ethanol for 1 min→75% ethanol for 1 min→distilled water washing for 2 min. 3) Harris hematoxylin semen was stained for 5 minutes, and washed with tap water for 1 minute. 4) Differentiate in hydrochloric acid ethanol solution for 30s. 5) Soak in tap water for 15 minutes or warm water (about 50°C) for 5 minutes. 6) Place the eosin aqueous solution for 2 minutes. 7) Routine dehydrat...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: Detection of the expression changes of related inflammatory factors in the heart of mouse recipients by means of fluorescent quantitative PCR.
[0029] 1. Obtaining Heart Graft Specimens
[0030] Seven days after the transplantation, six mice in each of the control group and the experimental group were sacrificed, and the heart grafts were taken out, marked and stored at -80°C.
[0031] 2. Total RNA extraction (pipe tips and centrifuge tubes are sterilized by moist heat, no RNase)
[0032] 1) Take a homogenizer, add 1ml of Trizol Reagent, and pre-cool on ice.
[0033] 2) Take 100 mg of tissue and add it to a homogenizer.
[0034] 3) Grind thoroughly until no tissue pieces are visible.
[0035] 4) Centrifuge at 13000 g for 10 min to take the supernatant.
[0036] 5) Add 250 μl of chloroform, invert the centrifuge tube for 15 seconds, mix well, and let stand for 3 minutes.
[0037] 6) Centrifuge at 13000 g for 8 min at 4°C.
[0038] 7) Transfer the supernat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com