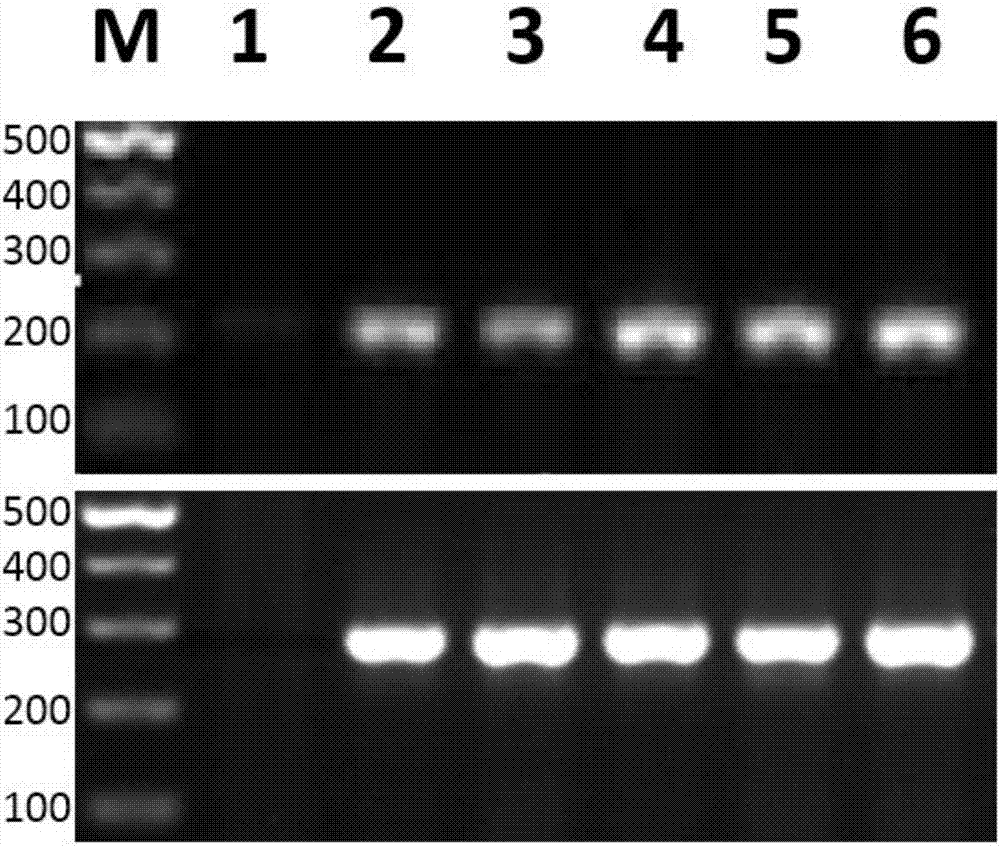
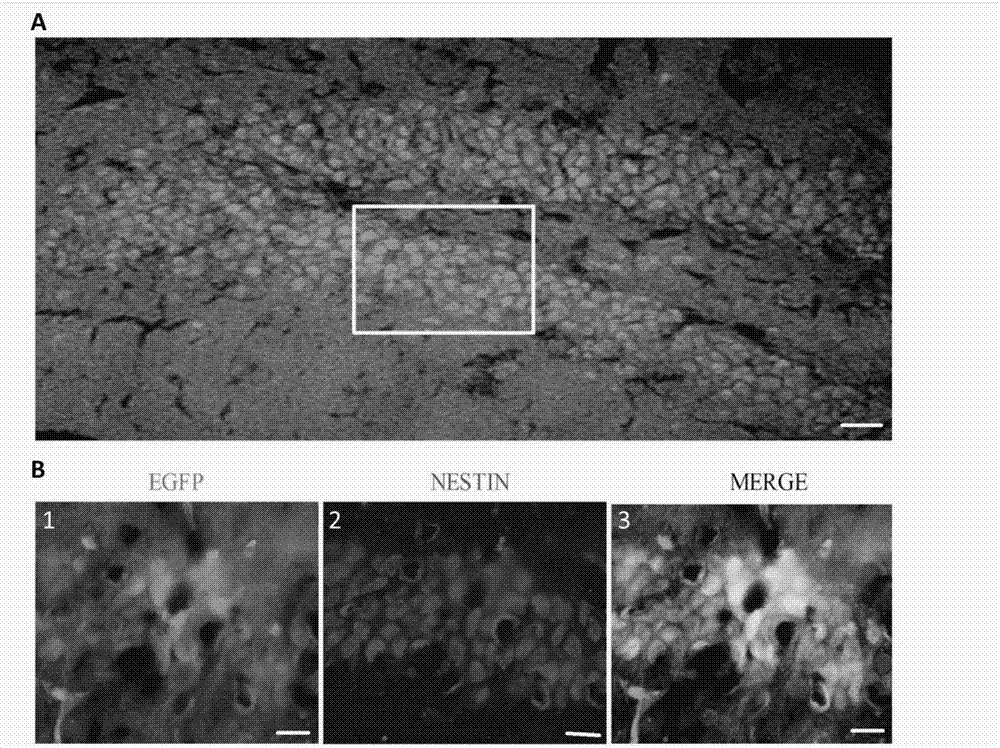
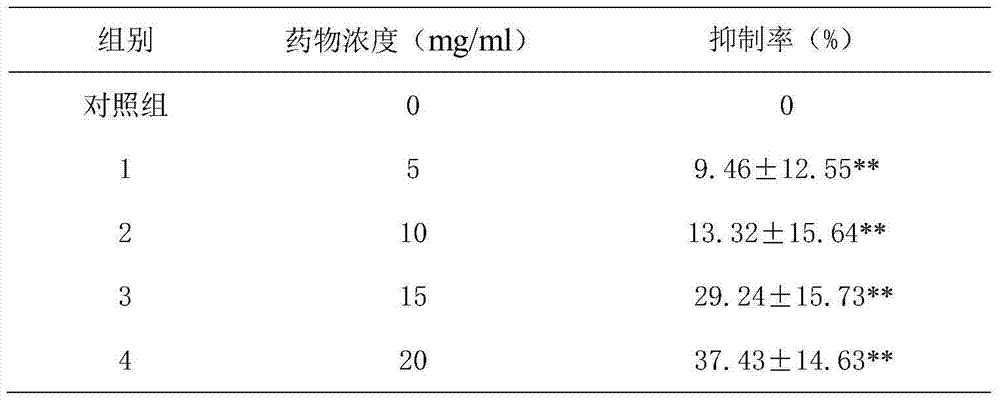
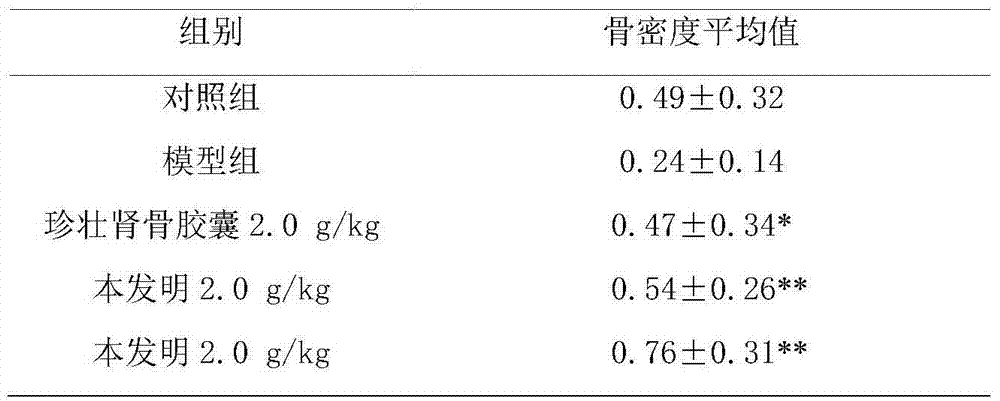
Patents
Literature
145 results about "C57BL/6" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
C57BL/6, often referred to as "C57 black 6", "C57" or "black 6", is a common inbred strain of laboratory mouse. It is the most widely used "genetic background" for genetically modified mice for use as models of human disease. They are the most widely used and best-selling mouse strain, due to the availability of congenic strains, easy breeding, and robustness.
Mango aglycone, preparation purification process and uses thereof
InactiveCN101367787AGood reproducibilityHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPurification methodsCarbon–carbon bond
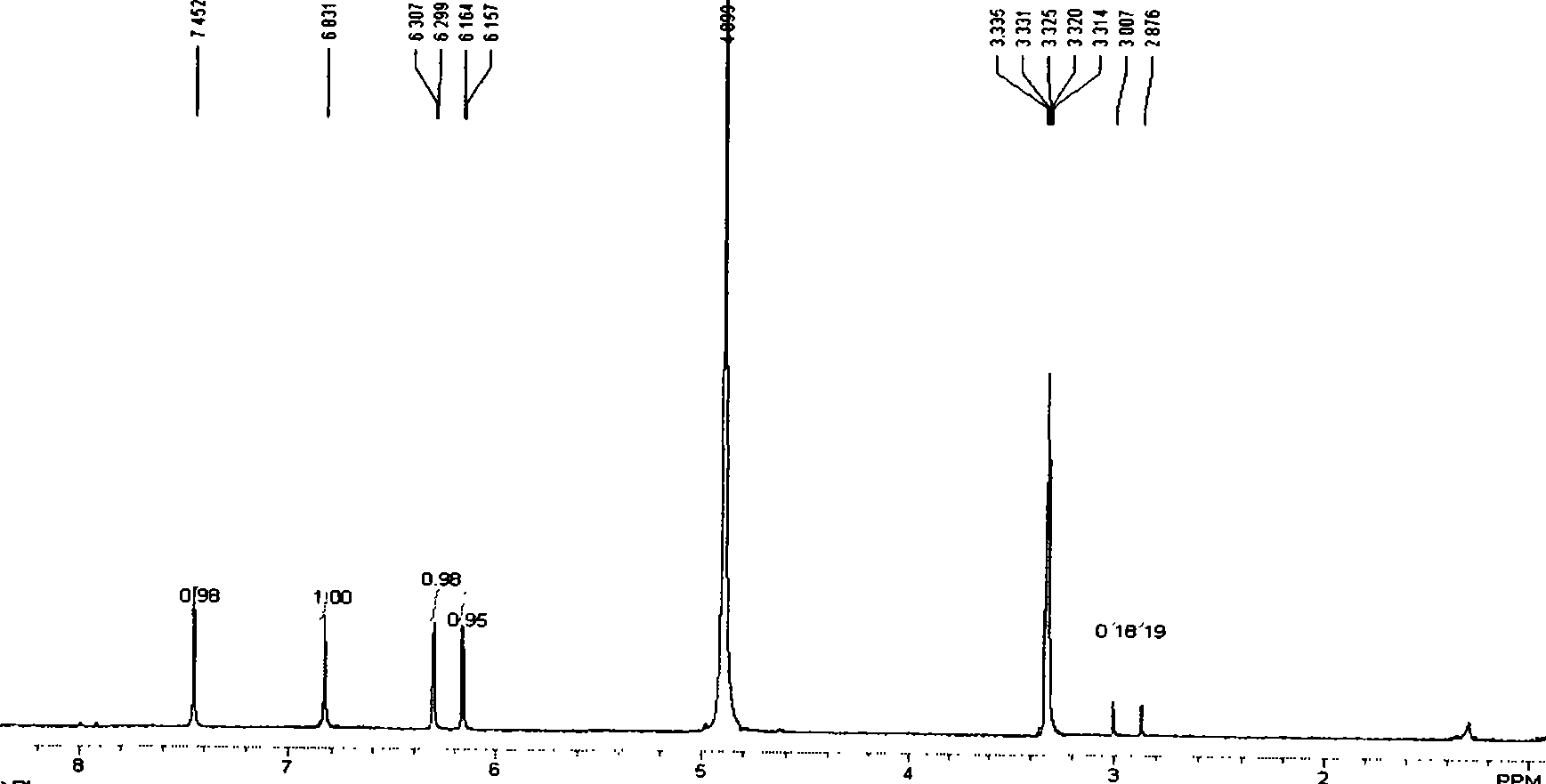
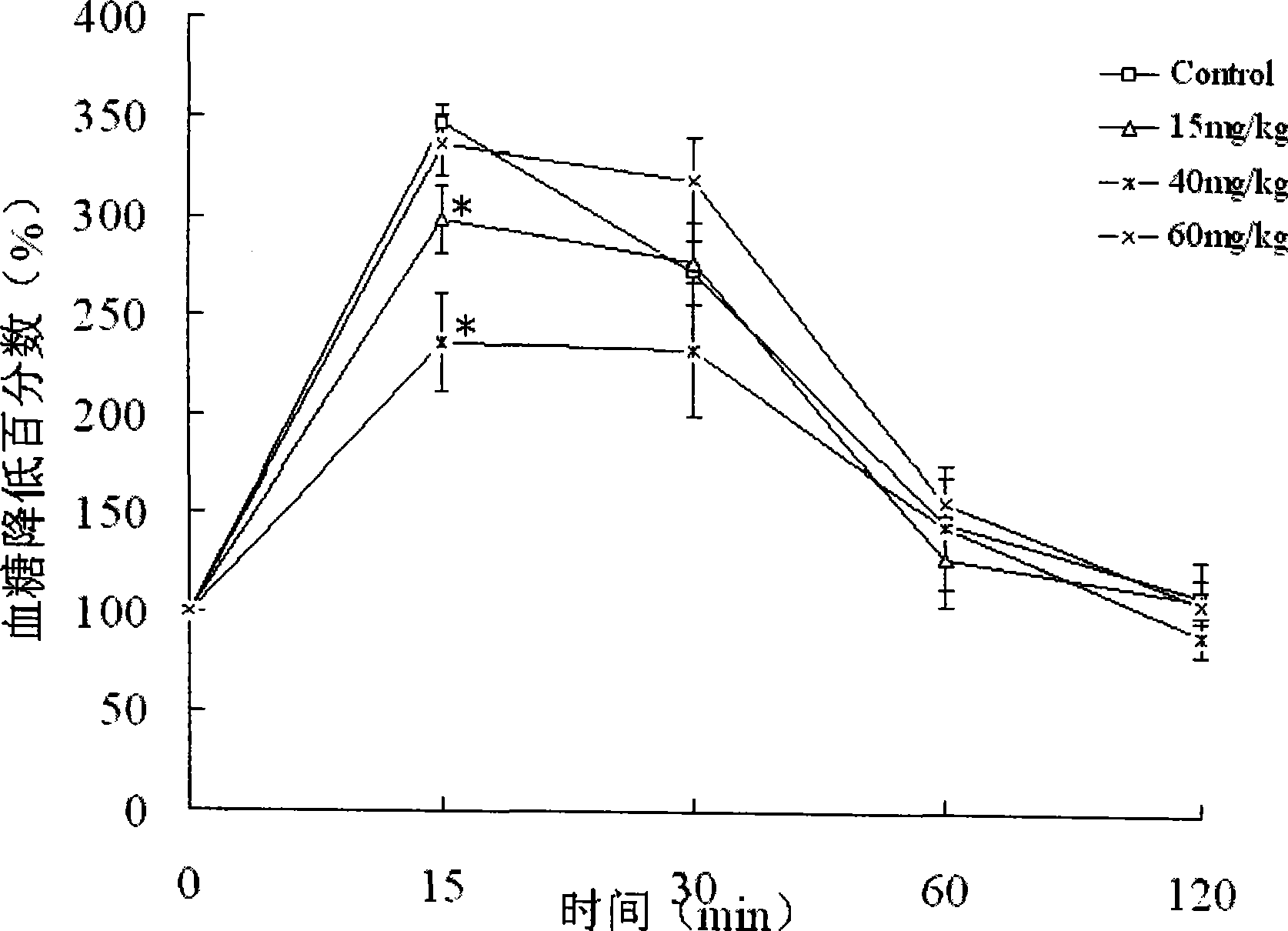
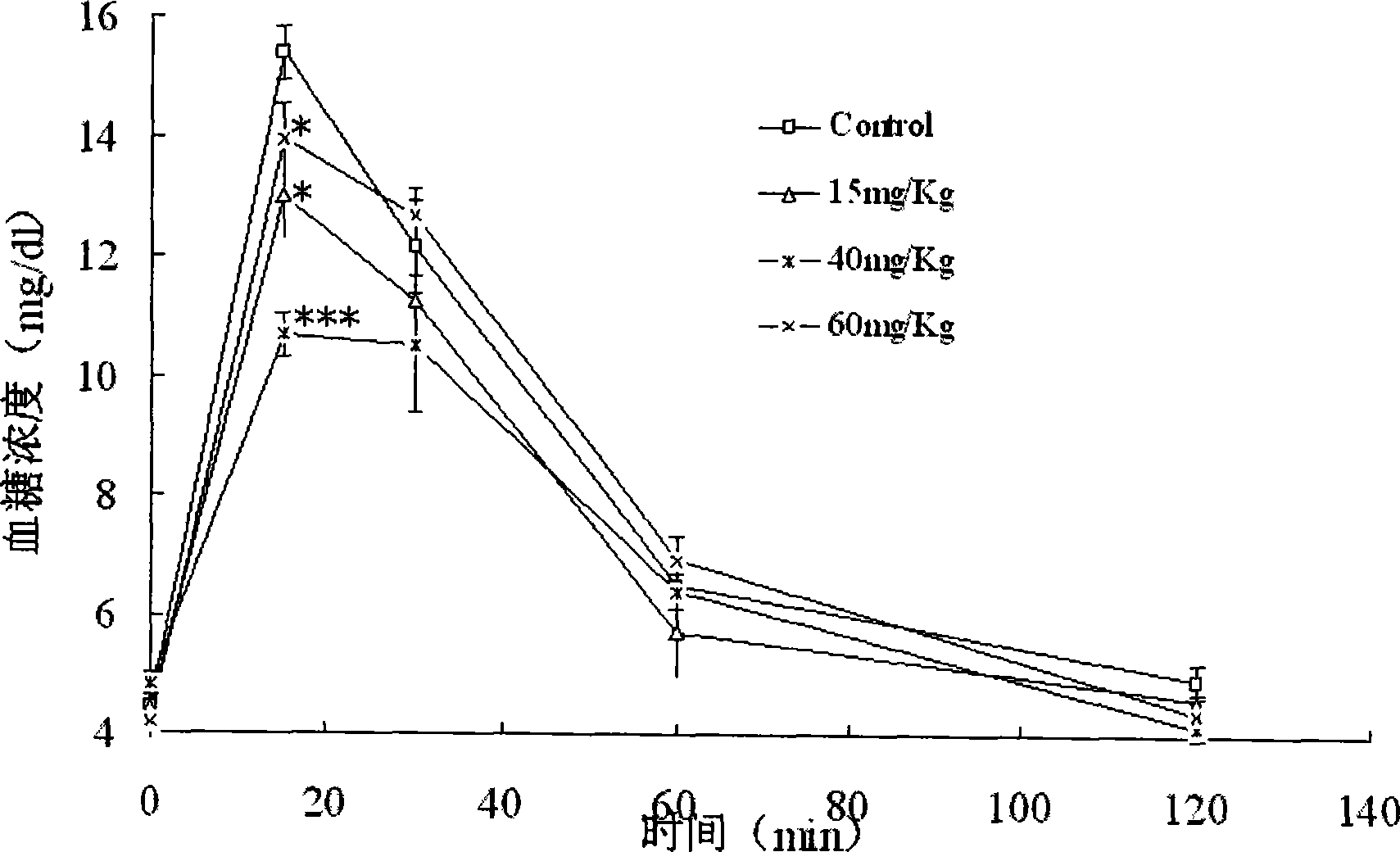
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy, and in particular relates to a preparation and purification method of tetra-hydroxyl xanthone mango aglycone (norathyriol), and an application thereof in hypoglycemic medicine. Based on biological experiments, mango glycoside is used as raw material; under the condition with phenol and hydroiodic acid, carbon-carbon bonds are broken to produce the crude product of mango aglycone; the crude product is separated and purified through silica gel column chromatography so that the mango aglycone is separated; the yield rate reaches 12 percent, the purity is higher than 95 percent, and the reproduction performance is good; the IGTT of C57BL / 6 normal mice is effectively improved with the norathyriol; and simultaneously the quantity of insulin secretion induced by glucose in vivo for the C57BL / 6 normal mice can be improved with the norathyriol. Therefore, the mango aglycone can be applied for preparation of hypoglycemic medicine.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Suppressive activity of mango aglycone on PTP1B and application thereof
InactiveCN101669934AHigh activityIncreased sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseDiabetes model
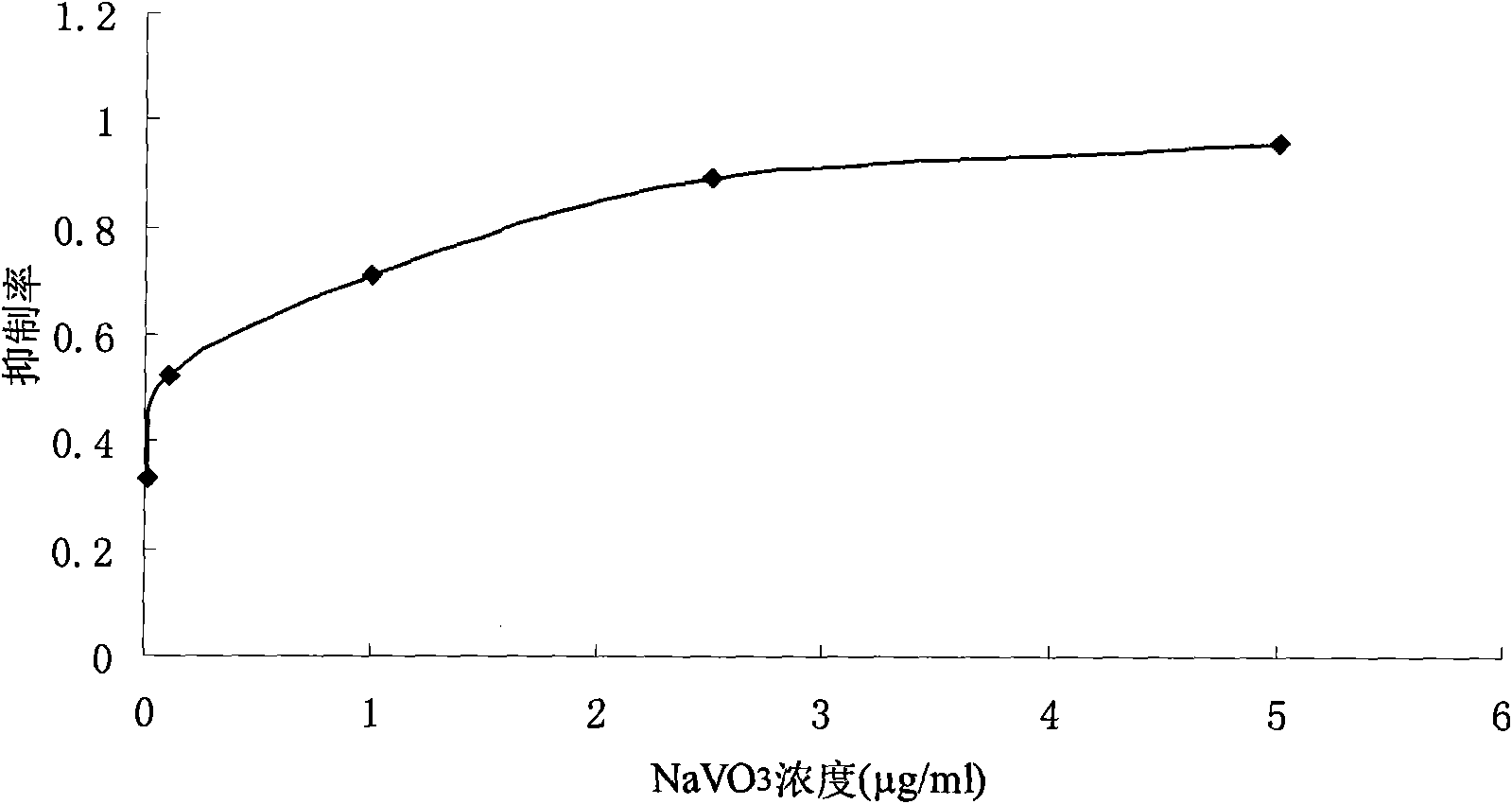
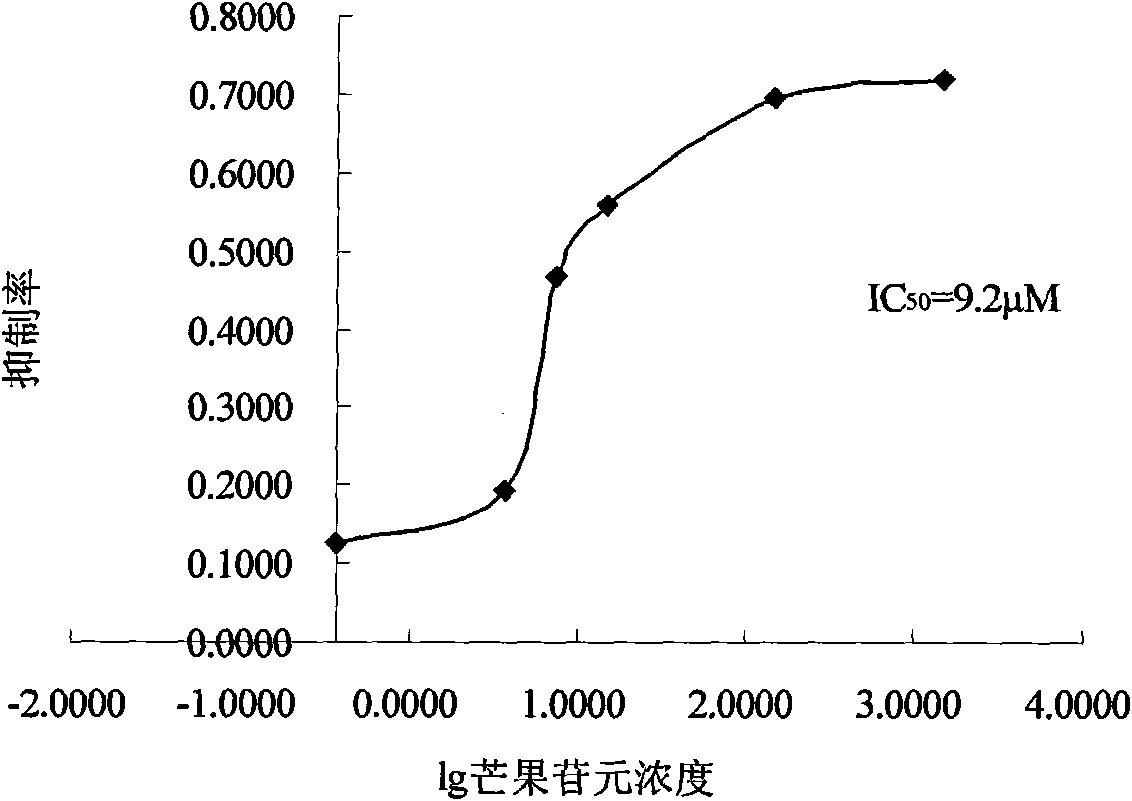
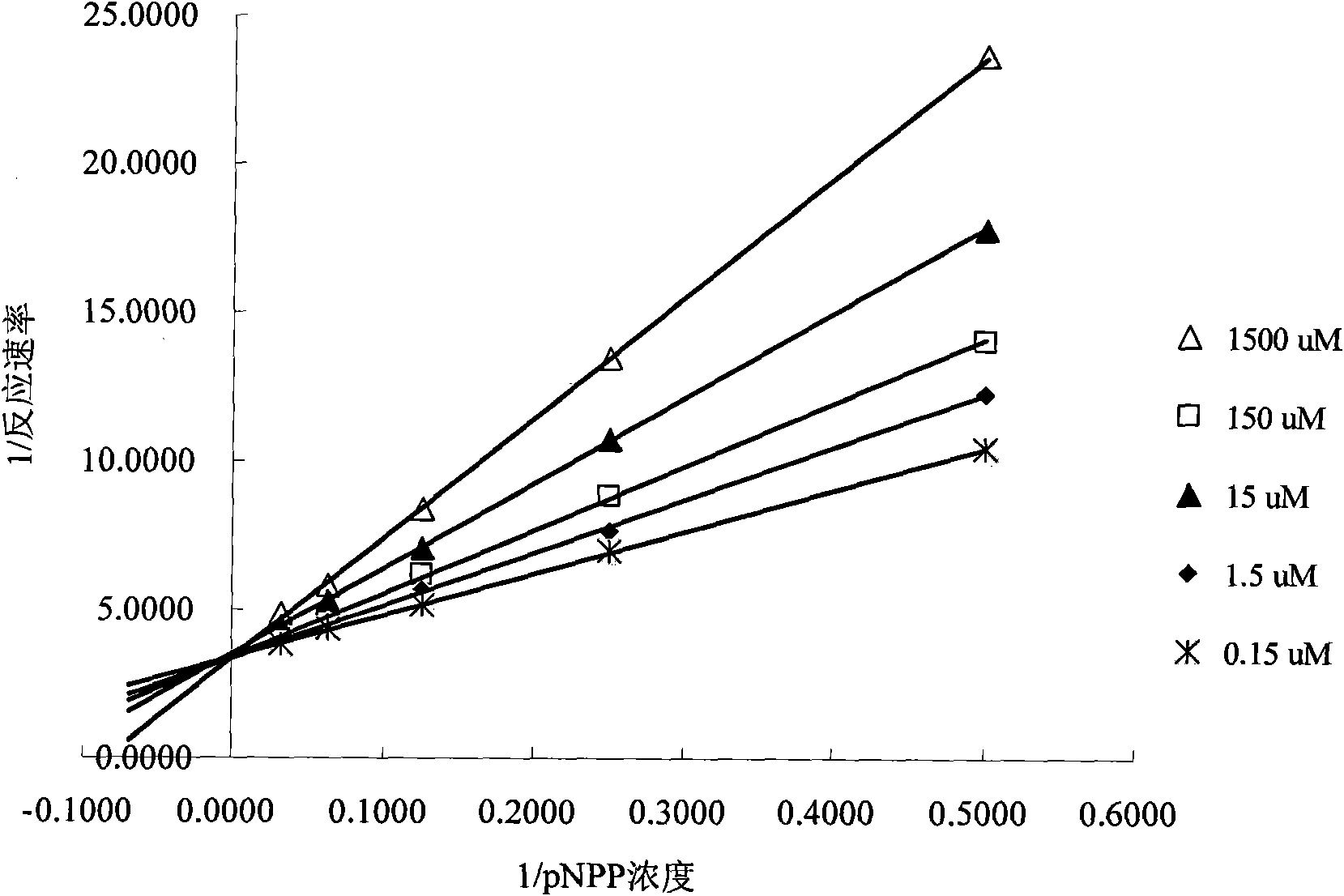
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy, and in particular relates to suppressive activity detection of tetrahydroxy norathyriol on protein-tyrosine-phosphatase (PTP) 1B, improvement of resistance function of insulin and accpication in medicament for PTP1B related diseases. Proved by in vitro enzyme suppression experiments, the invention testifies that mango aglycone is the competitive suppressant of restructuring humanized PTP1B with IC50 value being 9.2 mu m; mango aglycone can ensure the sensitivity of C57BL / 6 normal mouse and ob / ob diabetes model mouse on insulin to be obviously improved, and reduce blood sugar of experimental animals, which suggests that mango aglycone is a novel suppressant of PTP1B, and can be taken as potential lead compound to be applied in preparing medicament for curing insulin resistance related diabetes, obesity and other metabolic syndrome, tumor and other PTP1B related diseases.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast
InactiveCN104651302AStable traitsLower requirementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteocyteCellular density
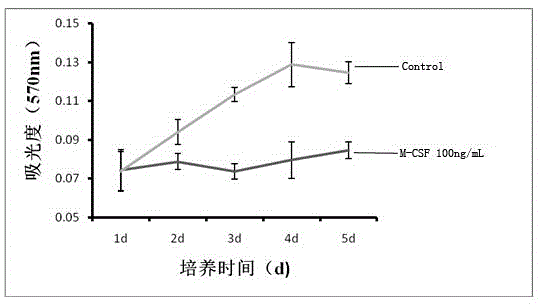
The invention belongs to the field of cell extraction and differentiation authentication, and discloses a method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast. The method comprises the following steps: (A) performing sterile myelomonocyte separation, culturing in a complete medium of 20-100ng / mLM-CSF, replacing the complete medium every other day, and observing the morphological characteristics of monocyte; (B) when the density of monocyte is 80-90%, taking out a part of the cells for surface antigen authentication; (C) drawing a growth curve of other cells and performing differentiation induction for osteoclast on other cells. The method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast is simple, convenient and reliable, low in requested condition requirements, low in cost and short in time, the extracted monocyte is stable in property, and C57BL / 6 mice myelomonocyte which is reliable and stable in resource can be provided for medical basis, clinical research, tissue engineering study, and the like.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
Composition comprising an extract of combined herb or the processed extract thereof and used for preventing hair loss and treating hair loss, and the use thereof.
InactiveCN105963426AGrowth stimulating activityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsMedicineHair growth
Owner:GINSENG SCI
Escherichia coli anti-tumor targeted engineering strain, and building method and application thereof
ActiveCN107574138AGood antitumor effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliTumor target
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Process for preparing non-alcohol fatty liver mouse model
InactiveCN101011585AGood model stabilityComplete disease spectrumIn-vivo testing preparationsAnimal husbandryFatty liverAlcohol
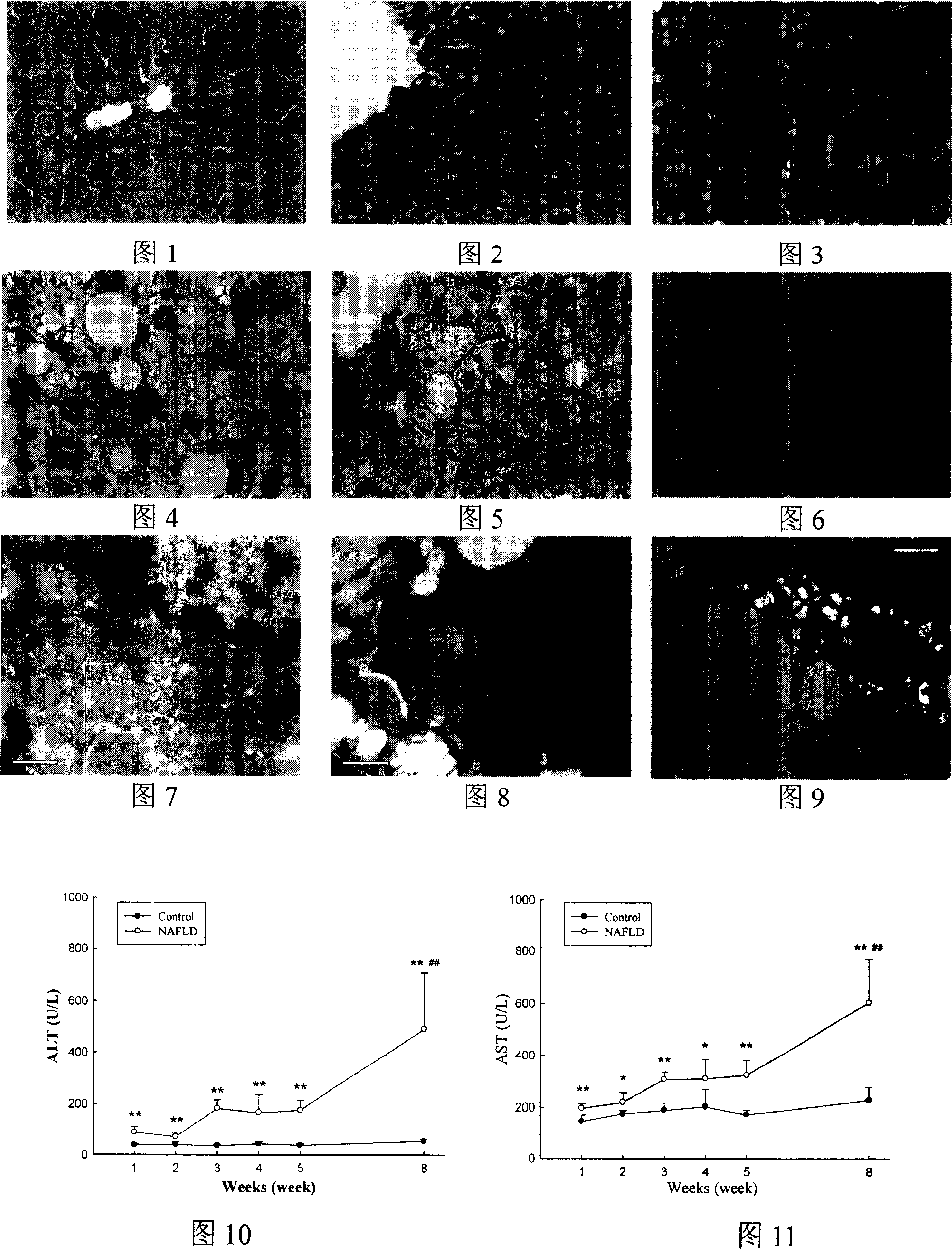
The invention relates to a method for preparing non-alcohol fatty hepatic disease mouse model, which comprises that randomly distributing the SPF male C57BL / 6 mouse at 18-25g into model group and normal contrast group, while each group has 36 mouse; two groups can be divided into six groups via different feeding times, as 1 week, 2, weeks, 3 weeks, 4 weeks, 5 weeks, and 8 weeks, while each time point has six mouse; all mouse are fed via normal contrast forage, then to be fed via bursine-acimetion lack forage, while the contrast group is fed via normal contrast forage; weighting them in each week, killing at first, second, third, fourth, fifth, and eighth week, to evaluate the model condition. The inventive model has high stability, integral disease spectrum, and high speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Modeling method of Sjogren syndrome mouse model
InactiveCN106110315ALow physiological stateLow mental stateAntibody medical ingredientsMulti siteSjögren syndrome
The invention discloses a modeling method of an Sjogren syndrome mouse model. The modeling method comprises the following steps: killing mice, taking out bilateral salivary glands and peeling off capsules and connective tissues; washing with PBS (Poly Butylenes Succinate); adding the PBS according to the amount of adding 0.5ml of the PBS into each salivary gland; shearing the salivary glands into pieces, and uniformly homogenizing and centrifuging in an ice bath; then taking supernatant and quantifying salivary gland antigens by adopting a BCA (Bicinchoninic Acid) protein quantifying method; adjusting the concentration of the salivary gland antigens to be 4mg / ml by utilizing the PBS; adding equal quantity of an FCA (Freund Complete Adjuvant) or an FIA (Freund Incomplete Adjuvant) and diluting the concentration to be 2mg / ml; repeatedly blowing and beating until two liquid phases are dissolved mutually to form an ivory color; randomly grouping C57BL / 6 mice and shaving off furs on the backs of the mice; carrying out intradermal multi-site injection of 2mg / ml mouse salivary gland antigens prepared by the FCA on the back and tails of the mice on the current day and the 7th day, wherein the injection amount is 0.1ml per mouse; injecting equal quantity of the salivary gland antigens prepared by the FIA on the 14th day through the same method; after modeling for about 6 weeks, detecting indexes and screening the successfully modeled mice. The modeling method disclosed by the invention is high in modeling efficiency and short in modeling time.
Owner:魏伟
Method for establishing green fluorescence BALB/c nude mouse model and model application
InactiveCN107439489AConvenience for tracer studiesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryBALB/cMating
The invention discloses a method for establishing a green fluorescence BALB / c nude mouse model. The method includes: selecting female C57BL / 6-Tg (CAG-EGFP) mice and male Foxn1nu mice to perform hybrid to acquire F1 child generation hairy fluorescence mice, selecting the female mice, selecting the female mice having sexual maturation and the parental generation male Foxn1nu mice to perform mating (backcross) to acquire an F2 child generation; generating segregation of characters of the F2 child generation, selecting female hairy fluorescence mice and the parental generation male Foxn1nu mice to perform backcross, and completing a backcross cycle; performing the backcross cycle for ten times to acquire an F10 child generation, and establishing the green fluorescence BALB / c nude mouse model. The invention also discloses application of an animal model established by the method to a brain tumor transplanting model. The method uses a homogenous introduction method to establish the new strain model mice which can stably express EGFP, and can lay a firm foundation for human glioma orthotopic transplantation tracking and research on glioma and a micro environment thereof.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Extracting method and application of seabuckthorn flavone
InactiveCN103494848AIncrease contentHigh yieldSkeletal disorderAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical drugIncreased Bone Density
The invention provides an extracting method of seabuckthorn flavone which is prepared by adopting supercritical extraction and microwave extraction, so that content is greatly improved. The invention further provides application of the seabuckthorn flavone in preparation of a drug for restraining cell proliferation of C57BL / 6 mouse fibrosarcoma cells S180 and application of the seabuckthorn flavone in preparation of a drug for increasing bone density.
Owner:NANJING ZHENGLIANG MEDICAL TECH
Experimental animal model with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis transforming into hepatic carcinoma
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology and in particular to a construction method of an experimental animal model, specifically a mouse model, with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) transforming into hepatic carcinoma (HCC), and use thereof. The present invention provides a construction method of a mouse model with NASH and chronic steatohepatitis developing into chronic hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis and HCC. The construction method comprises the following steps: newborn C57BL / 6 mice (including male and female newborn mice) are subjected to subcutaneous single injection of streptozotocin (STZ) (100-400 [mu]g / newborn mouse) and the mice begin to be fed with experiment use high-fat feed after the completion of female mouse breastfeeding to construct the NASH mouse model with hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis and HCC. The provided mouse model is relatively simple in construction process, relatively simple in technical means, and low in construction cost, has an extremely high value as the needed animal model in scientific research and drug research and development, and belongs to a domestic initiative.
Owner:凯斯艾生物科技(苏州)有限公司
Method for constructing tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with gastric cancer based on organ-like method, and application thereof
InactiveCN109182271AConvenient researchNormal food intakeTumor/cancer cellsGeneral culture methodsWilms' tumorStomach cancer
The invention discloses a method for constructing a tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with gastric cancer based on an organ-like method, and an application thereof. The invention relates to a medical tumor animal model, based on an organ-like method. For the first time, the present invention employs a quasi-organ technique, that is, using a microcarrier as substrate. The composite human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901 / MKN-45 is transplanted subcutaneously into C57BL / 6 mice to establish a tumor model of human gastric cancer with normal immune function. The tumor model constructed by this method has good tumorigenicity, and the tumorigenicity rate is up to 75%. The HE staining and the immunohistochemistry of the transplanted tumor accord with the characteristics of human gastric cancer. Compared with the existing immunodeficient mice transplanted tumor model, the model can better study and further clarify the mechanism of tumor occurrence and development in the normal immune system, and also provides a more valuable new animal model for the research and development of anticancer drugs. The invention is applied to the tumor model field.
Owner:上海美峰生物技术有限公司
Establishment of C578L/6 mouse animal model of transbuman senile dementia APP gene and use
InactiveCN1686567AHave a behavioral disorderIn-vivo testing preparationsMicroorganismMale pronucleus
A mouse animal model C57BL / 6 for the APP gene of human presenile dementia (AD) is disclosed, which can be used to research the AD, develop its medicine and screen its vaccine. Its configuring process includes using PDGF promoter to regulate APP and configure its transgene, injecting it in the male pronucleus of fertilized ovum of mouse, PCR, southern discrimination to obtain transgenic male animal, cesarean section, and DNA recombination-inbred-line passage for configuring its line.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
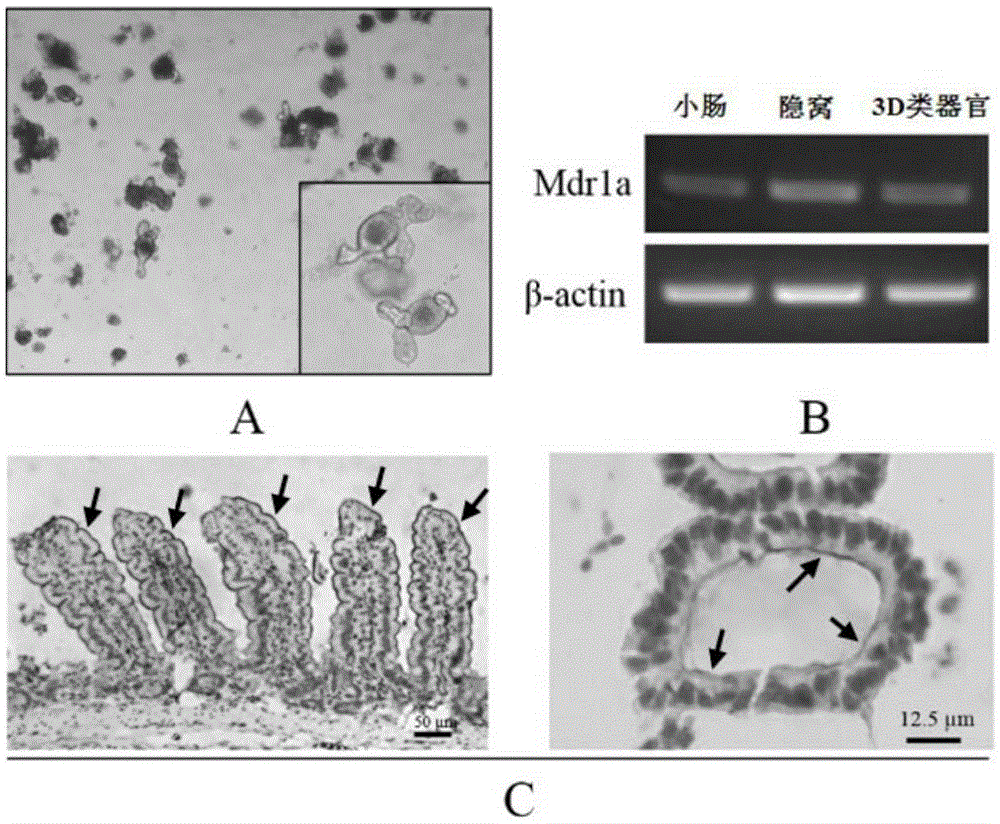
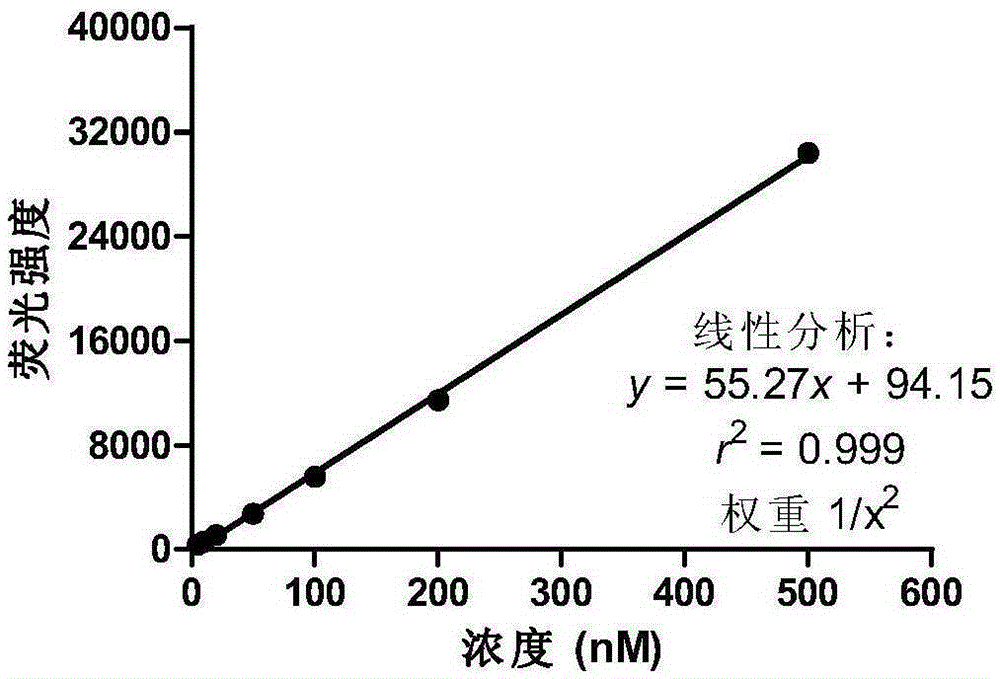
Method for detection of P-gp mediated Rh123 transport in 3D type organ and application thereof
ActiveCN105334196AFully lysedAvoid interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPetri dishOrgan Model
The invention relates to a method for detection of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated rhodamine 123 (Rh123) transport in a 3D type organ and an application thereof in screening of P-gp inhibitors. The method comprises the steps: firstly, sorting small intestinal crypts of C57BL / 6 mice, inoculating a petri dish containing a matrix gel, culturing in an Advanced DMEM / F12 culture medium, and forming the 3D type organ; and then carrying out qualitative and quantitative detection of P-gp mediated Rh123 transport and influence of the P-gp inhibitor verapamil on Rh123 transport by using the 3D type organ model. The method particularly comprises the steps of respectively co-incubating the 3D type organ with (1) the P-gp substrate Rh123 and with (2) the Rh123 and the verapamil, releasing the Rh123 in the 3D type organ by using an ultrasonic crushing method, and finally detecting the concentration of the Rh123 on a multifunctional microplate reader. The method has the advantages of being simple, rapid, and high in sensitivity, can be combined with the 3D type organ model for carrying out research of the P-gp mediated drug transport, and also can perform research of in-vitro screening of the P-gp inhibitors.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Separation and culture method of testicular mesenchymal stem cells for expressing nidogen and application of testicular mesenchymal stem cells
The invention discloses a separation and culture method of testicular mesenchymal stem cells for expressing nidogen and an application of the testicular mesenchymal stem cells. The separation and culture method comprises the following steps: providing a nidogen-green fluorescent protein transgenic mice model adopting C57BL / 6 as the genetic background; raising the mice for one or more than one week, separating the testis, removing envelopes and blood vessels, exposing the seminiferous tubule, then digesting by using collagenase IV, and filtering digested cell suspension; and sorting by a flow cytometer to obtain single cells and collecting the cells for expressing green fluorescent protein with the fluorescence intensity being 10 times or more than 10 times of the fluorescence intensity of negative control cells so as to separate the testicular mesenchymal stem cells for expressing the nidogen. The invention provides testicular mesenchymal stem / progenitor cells separated according to the preparation and culture method and self-renewed and proliferated cells obtained by culture in a culture medium and provides the application of the cells in preparing a composition for treating related diseases with low testosterone level.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Use of fly-maggot powder in anti-fatigue, anti-senescence and anti-adiposity health care function aspects
InactiveCN101292998AGood anti-fatigue effectImprove anti-aging effectAnthropod material medical ingredientsMetabolism disorderHigh fatRat model
The invention discloses an application of a fly maggot powder for the health-care functions of anti-fatigue, anti-aging and anti-obesity. The fly maggot powder is used for producing health care products of anti-fatigue, anti-aging and anti-obesity. Five percent of fly maggot powder is added into the feed for feeding the strain of D-galactose-induced aging C57BL / 6 rat to test and find that the fly maggot powder has remarkable effect in anti-fatigue; in a rat model induced by combined biological rhythm disorder and the D-galactose, the fly maggot powder can effectively prevent the reduction of liver weight, the descending of the activity and the corresponding gene expression of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, catalase and other antioxidases, and the increase of the content of MDA of the products of lipid peroxidation caused by aging. The fly maggot powder has remarkable efficacy of anti-aging; 5 percent of the fly maggot powder is added in the high-fat feed, which can effectively prevent the rapid growth of Wistar rats as a result of high-fat diet and can suggests that the fly maggot powder has remarkable effect of anti-obesity.
Owner:沈荣法 +1
Compositions and methods for protecting the kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury
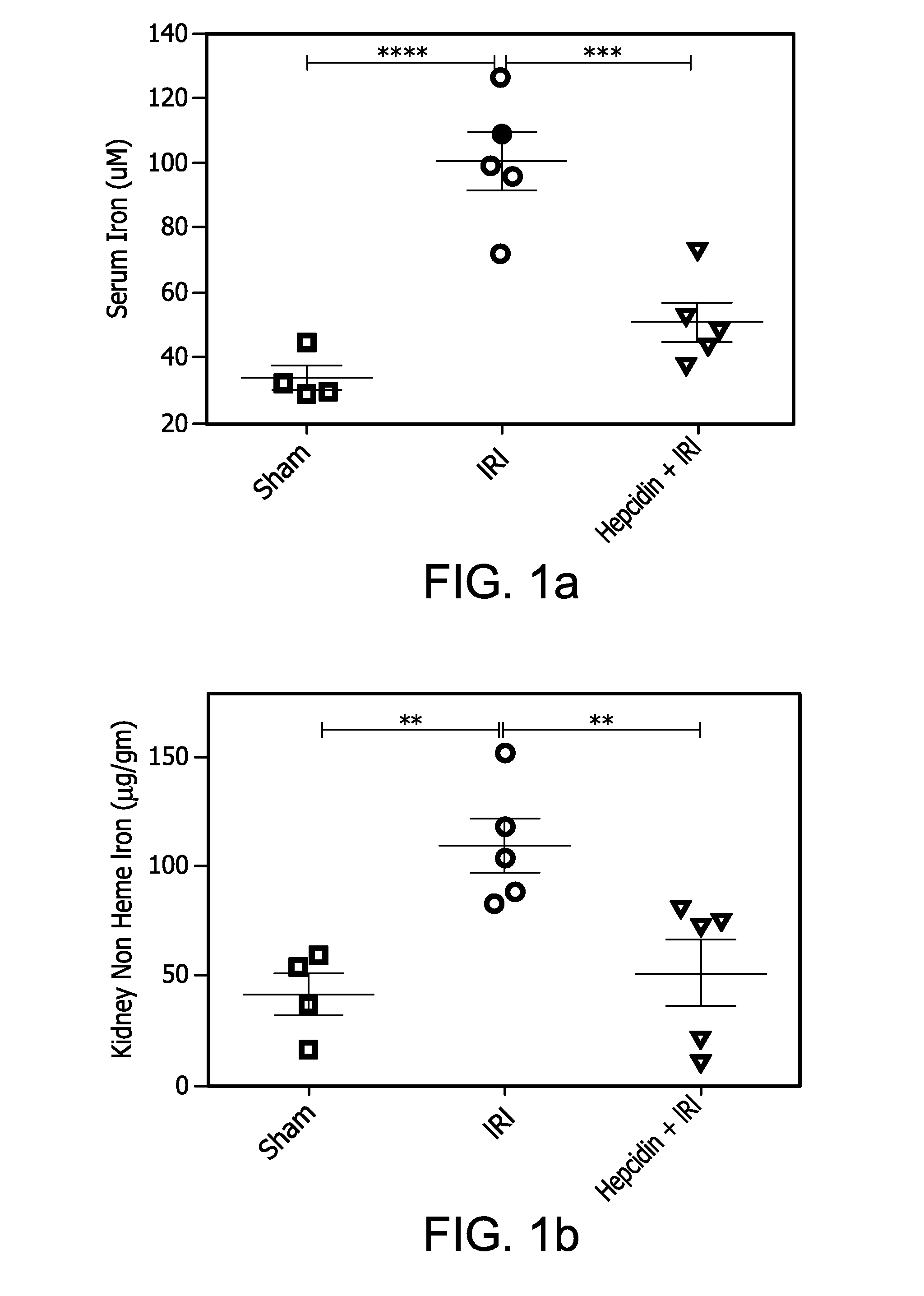
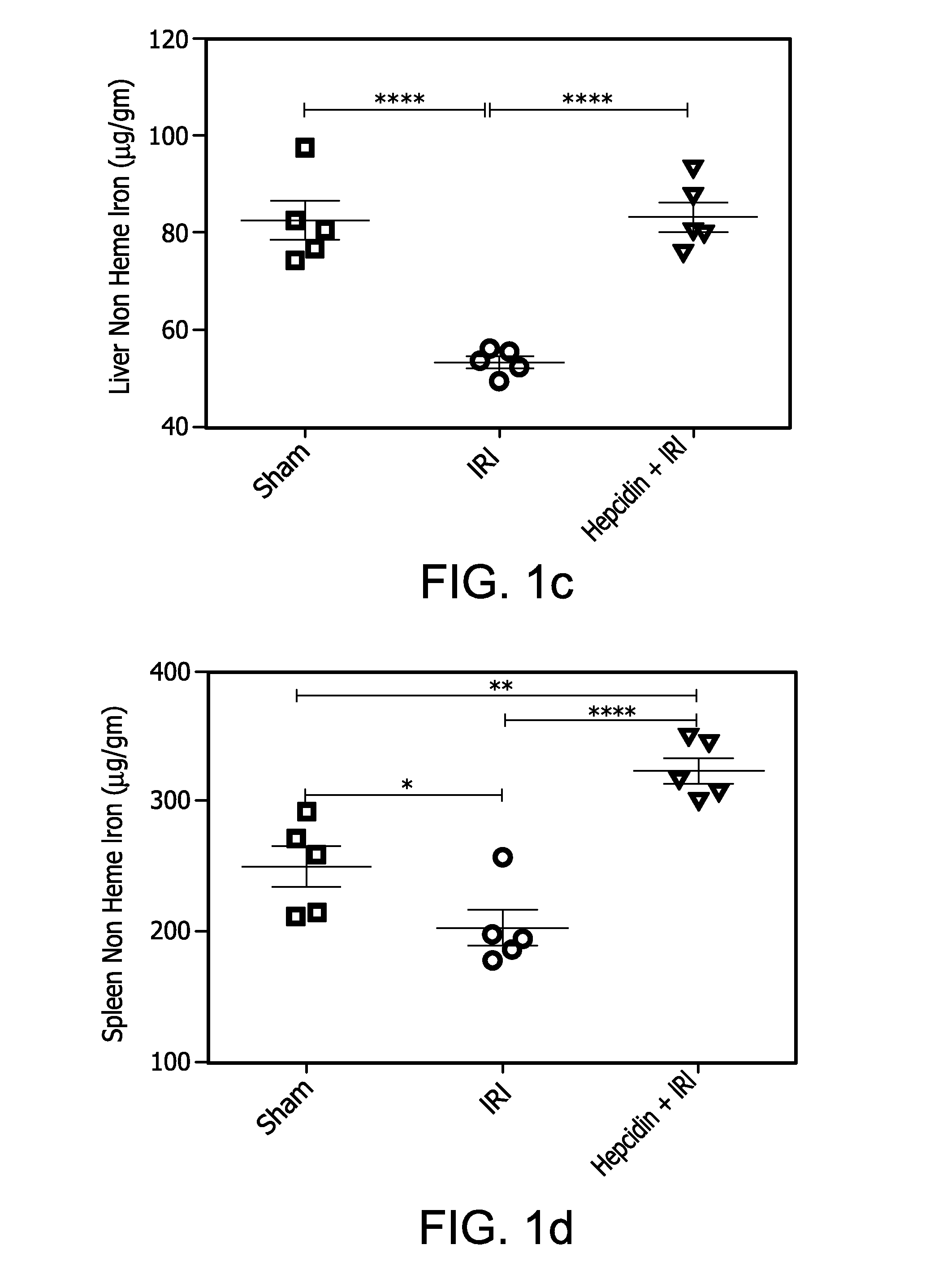
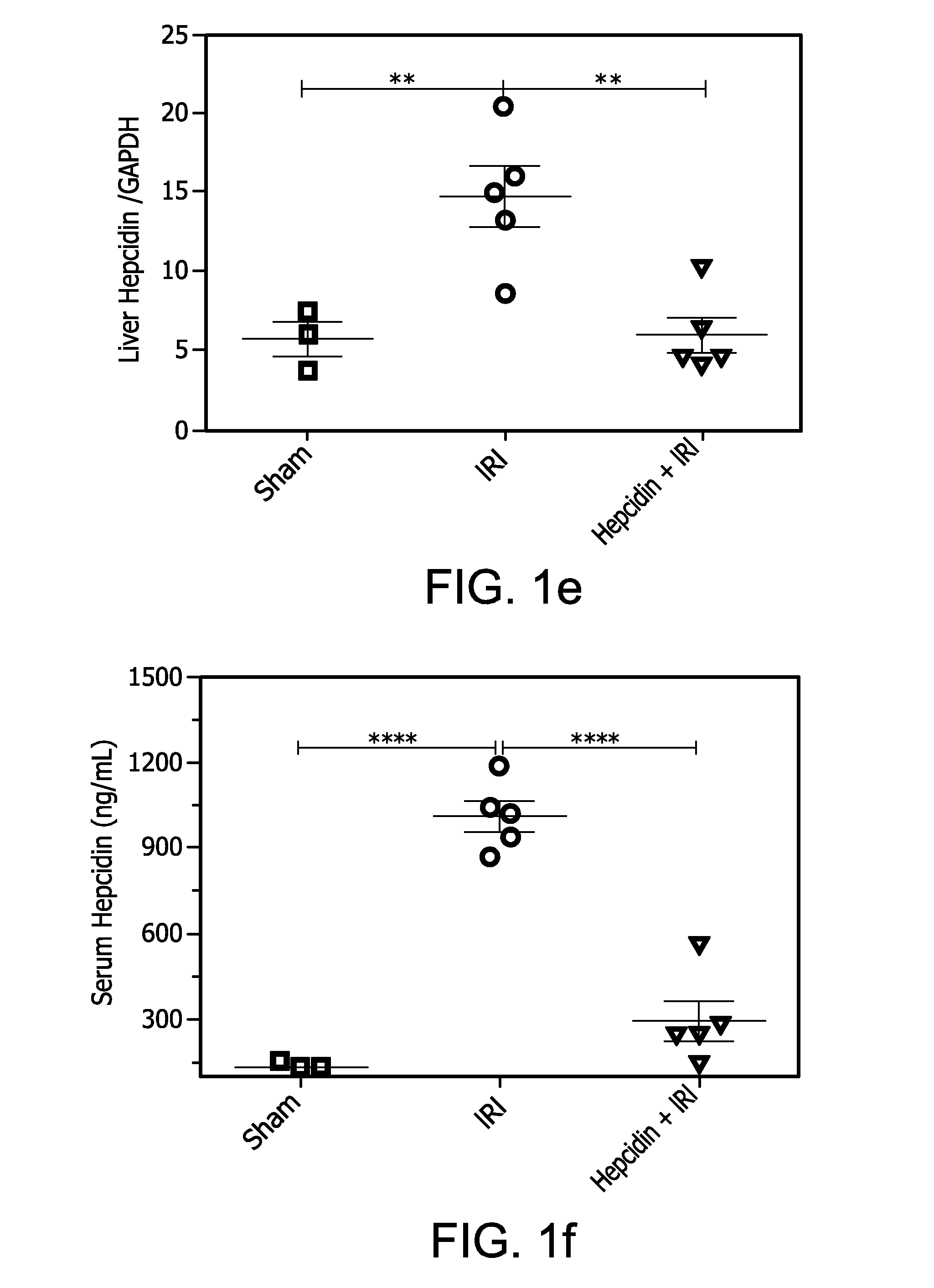
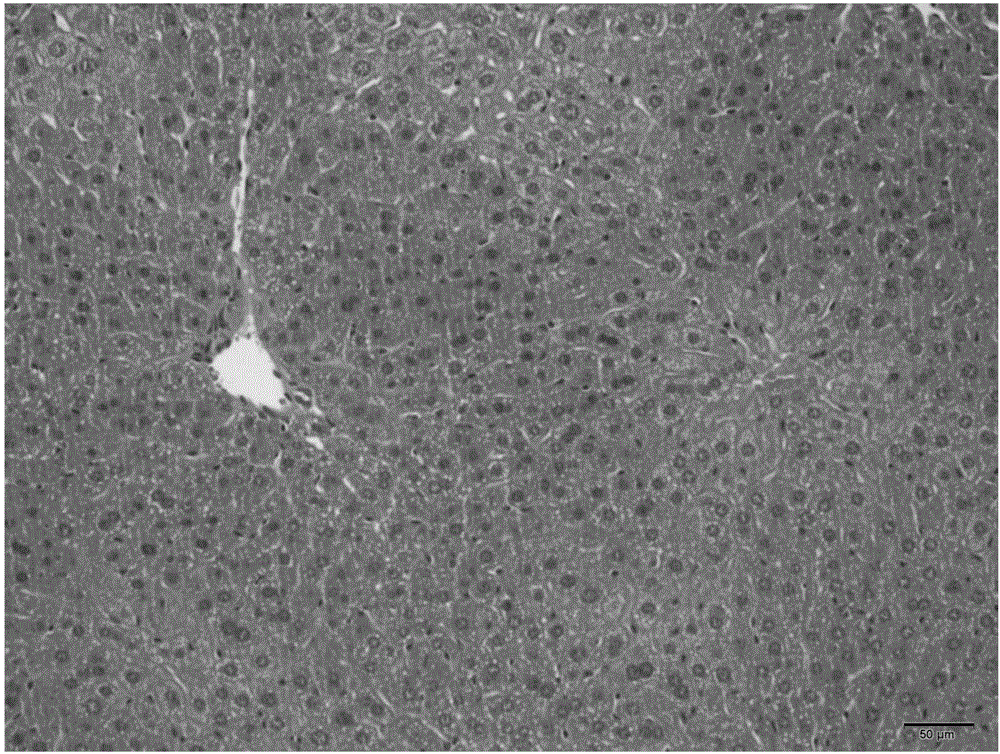
ActiveUS20160263195A1Severe renal injuryMitigates renal IRIHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsReperfusion injuryRenal Tubular Epithelial Cells
The effects of hepcidin treatment on mitigating IRI and acute kidney injury by decreasing iron availability and ROS-mediated cell death were tested. C57Bl / 6 (WT) and hepcidin knock out (Hamp− / −) mice were treated with saline or 50 μg of hepcidin i.p. prior to bilateral renal IRI. Renal function, injury markers, histopathology, and inflammation were examined after 24 hours of reperfusion. In WT mice, IRI induced increases in serum and kidney non-heme iron levels, but hepcidin treatment induced sequestration of iron in the spleen and liver and prevented IRI-associated increases in serum and kidney non-heme iron. Kidney function was significantly better in hepcidin-treated mice, accompanied by less acute tubular necrosis and reduced infiltration of immune cells. Hepcidin treatment decreased kidney ferroportin expression and induced the expression of cytoprotectant, H-Ferritin, and was associated with less ROS and tubular epithelial apoptosis. These results demonstrate a protective role of hepcidin in IRI and AKI.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation
ActiveCN106727470AGood treatment effectGood effectOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsTreatment effect
The invention relates to application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine. According to the application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation, a treating effect of the benserazide hydrochloride on acute inflammation is researched through animal experiments, and experiment results show that the benserazide hydrochloride has an inhibiting effect on inflammatory factors generated by mouse acute inflammation caused by lipopolysaccharide. Specifically, a C57BL / 6 mouse acute inflammation model is induced to be constructed through the lipopolysaccharide, different concentrations of benserazide hydrochloride is utilized to treat the mouse, results show that the benserazide hydrochloride can reduce inflammatory factor level generated by C57BL / 6 mouse acute inflammation and pathological change degree of hepatic tissues, and the low dosage benserazide hydrochloride has the optimal effect. The benserazide hydrochloride is prepared into varieties of preparation required by clinic by adding carriers accepted by pharmacy, and the application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation has the beneficial effect of providing a novel path for preparing acute inflammation medicine.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
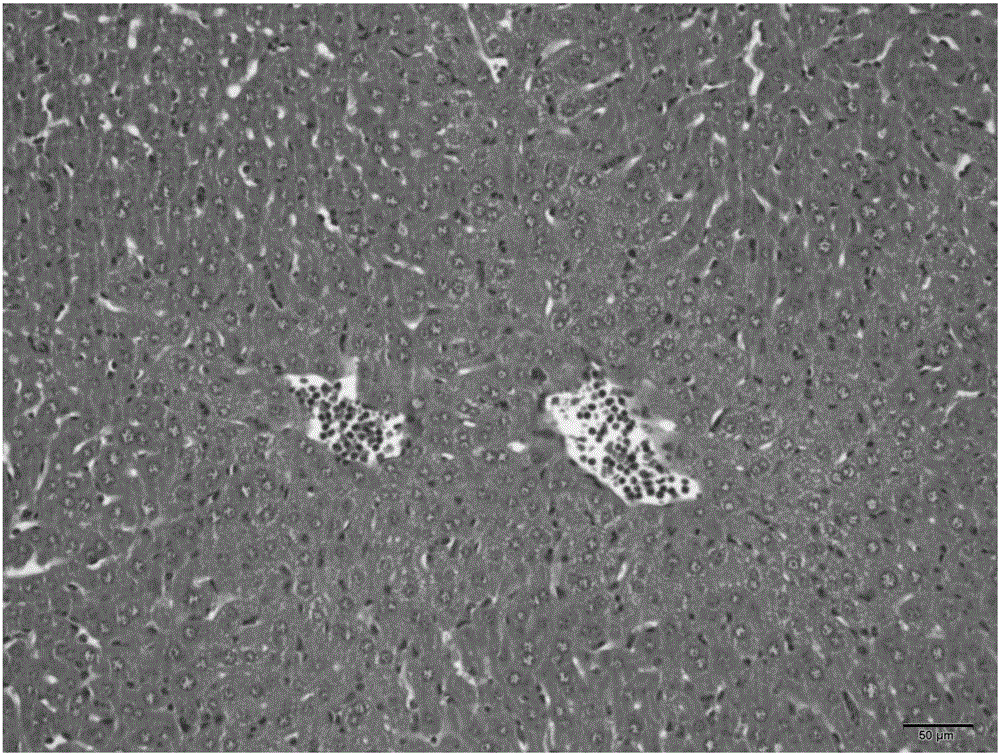
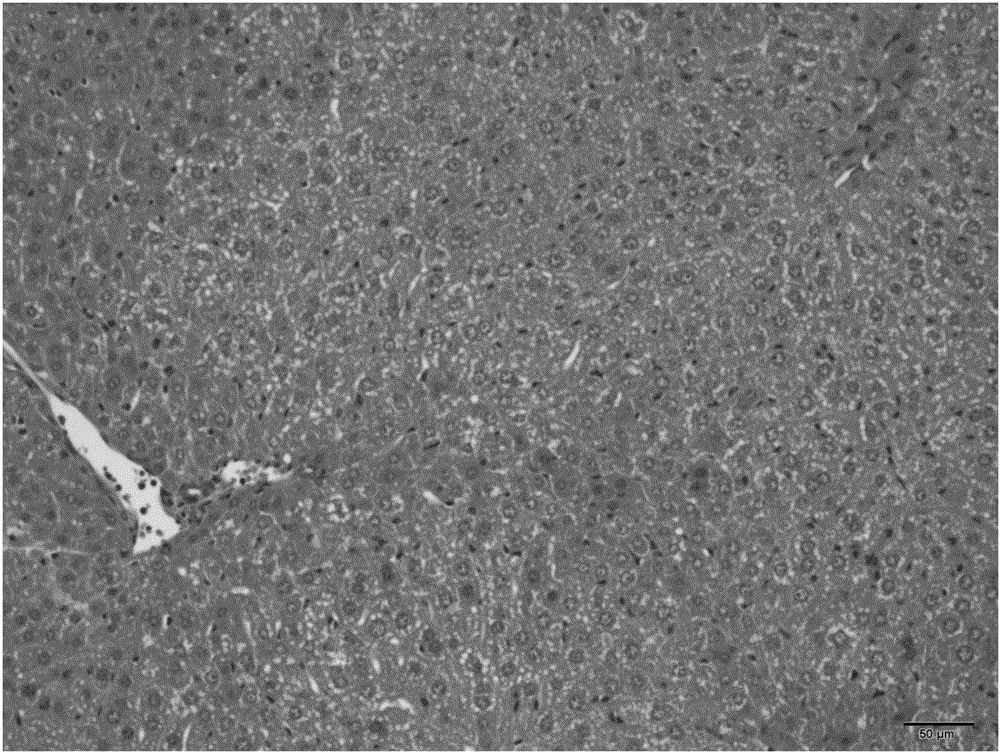
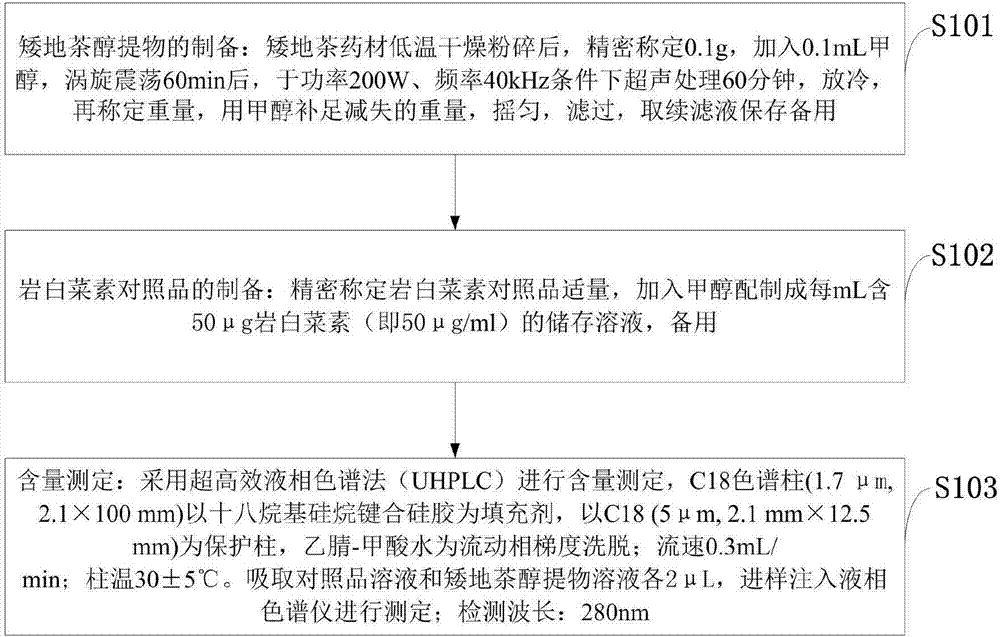
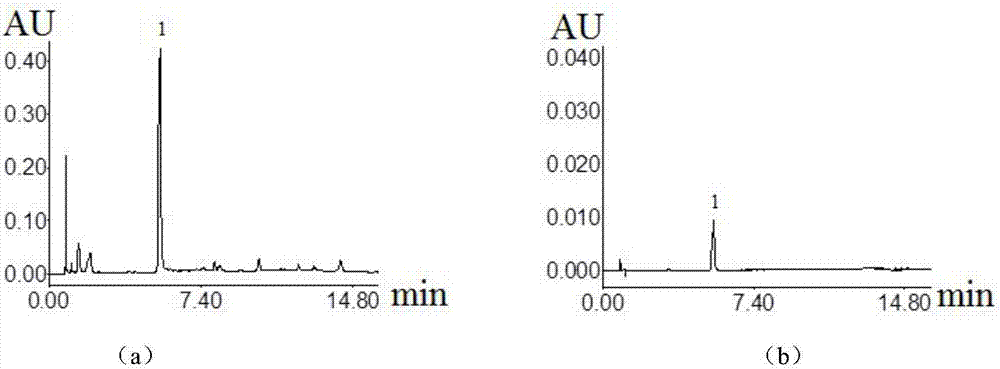
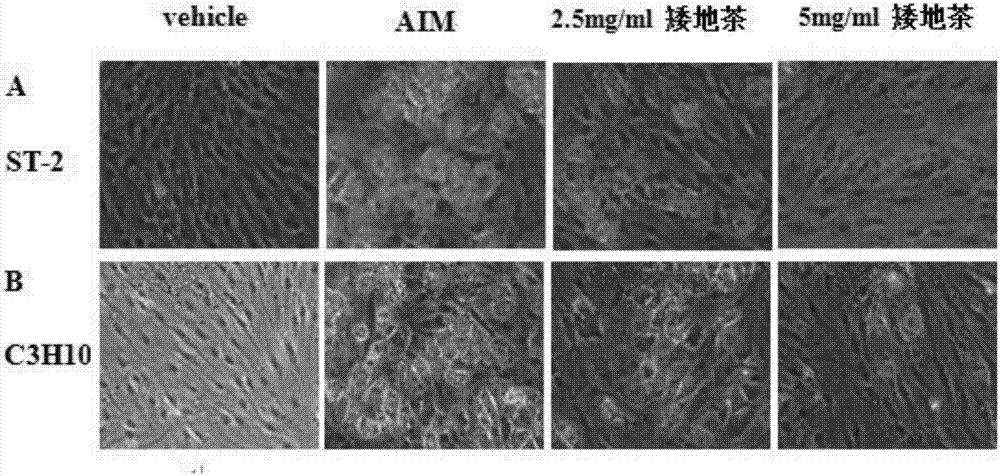
Preparation method and application of herba ardisiae japonicae alcohol extract
InactiveCN107184623ARaise quality standardsLipid droplet increaseMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicinal herbsLipid formation
The invention belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines, and discloses a preparation method and application of a herba ardisiae japonicae alcohol extract. The preparation method comprises the following steps: after drying and crushing a herba ardisiae japonicae medicinal material at low temperature, weighing 0.1g of the crushed herba ardisiae japonicae medicinal material, and adding 0.1mL of methanol; after carrying out vortex oscillation, carrying out ultrasonic treatment and cooling; then weighing the weight, and supplementing the reduced weight with the methanol; uniformly shaking and filtering; taking subsequent filtrate and preserving for later use; weighing a bergenin reference substance, and adding the methanol to prepare a solution; determining the content of bergenin in the herba ardisiae japonicae alcohol extract by adopting an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography. According to the preparation method and the application of the herba ardisiae japonicae alcohol extract, the content of the bergenin in the herba ardisiae japonicae alcohol extract is 9.88mg / g and accords with quality standards; herba ardisiae japonicae can be used for reducing the quantity of lipid droplets in ST-2 and C3H10 cells which are obtained by inducing adipogenesis differentiation, and for inhibiting mRNA expression of adipogenesis differentiation characterization genes PPARgamma, C / EBPalpha and aP2; interventional treatment of the herba ardisiae japonicae can be used for effectively reducing the weight of C57BL / 6 mice fed by high fat diet.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
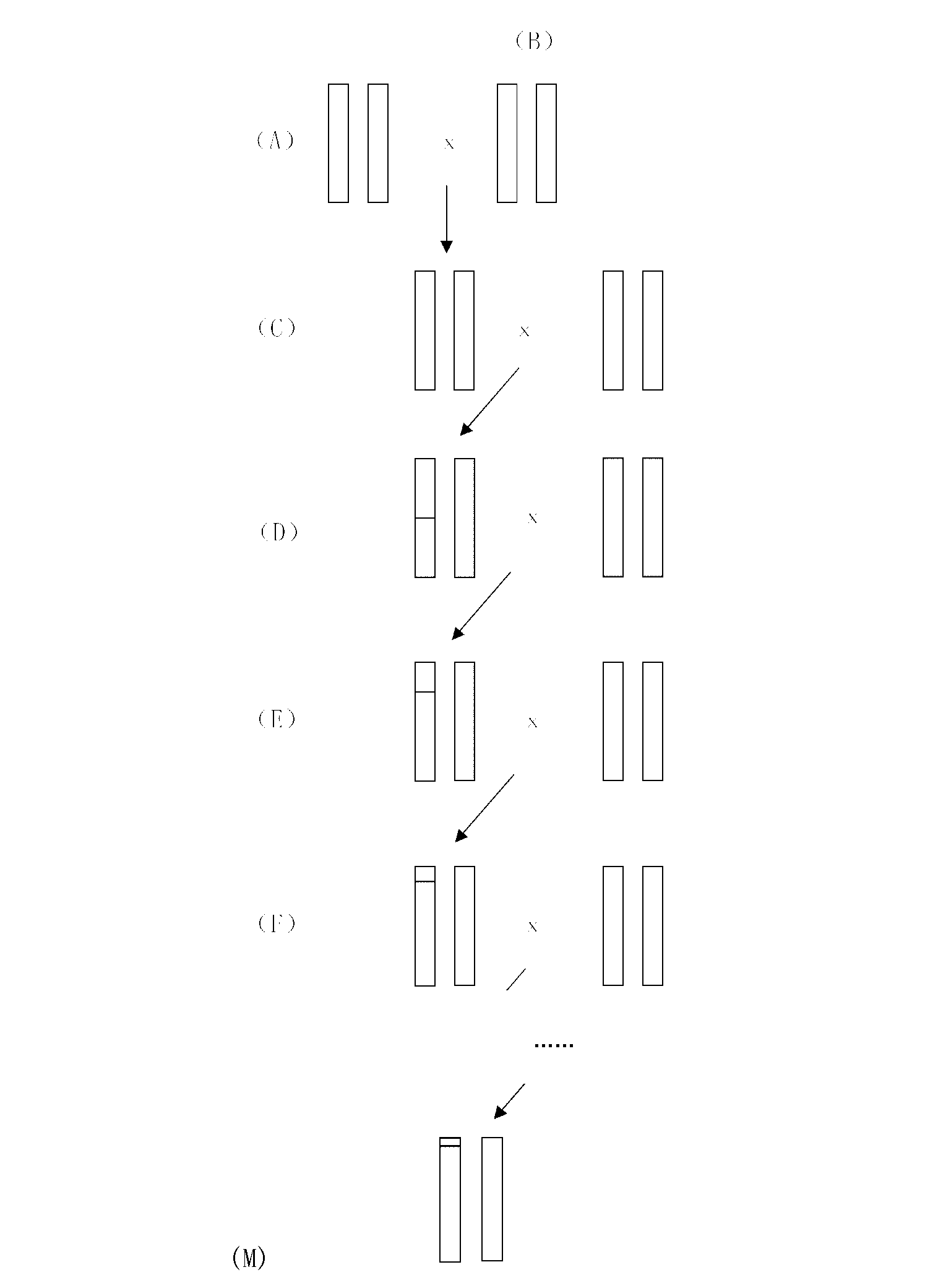
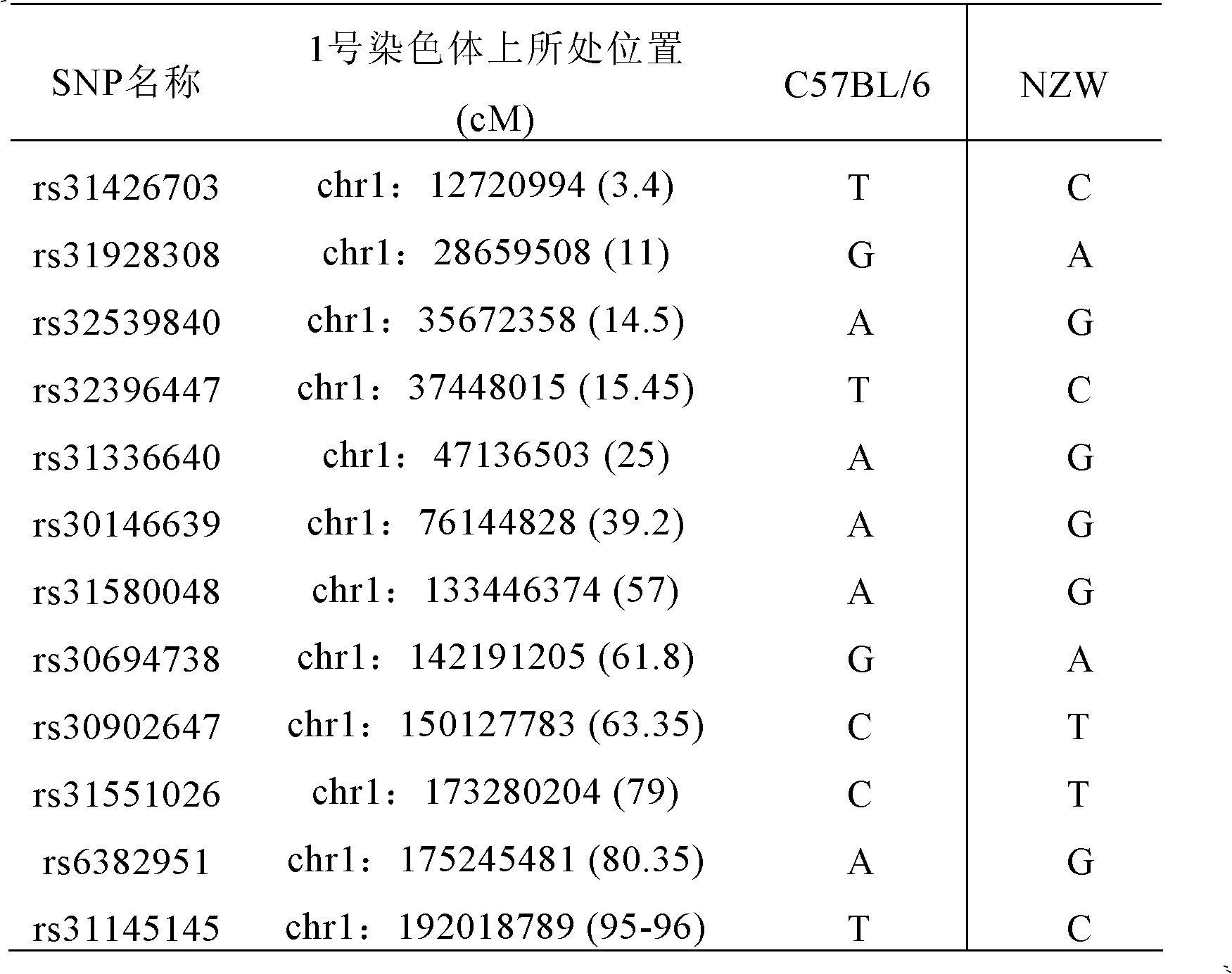
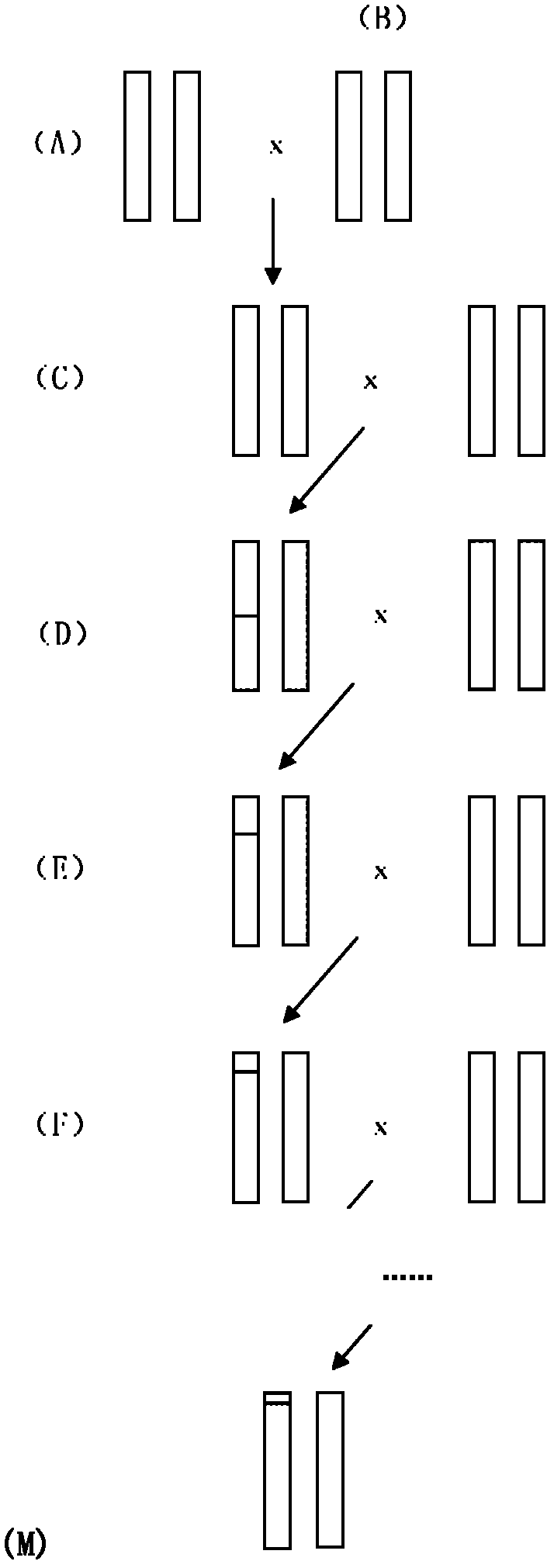
Construction for number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL/6-Chr1NZW
The invention relates to construction for a number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1NZW. According to the construction for the number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1NZW, a new chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain is constructed. A genetic background of the chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain is based on a C57BL / 6 mouse, while wherein a number 1 chromosome is from an NZW mouse. According to the construction for the number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1NZW, the chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain can be used for research of character differences brought by different number 1 chromosome genomes under the same genome background, and can be a useful tool for research of the chromosome genome functions by adoption of a genetic method.
Owner:上海西普尔-必凯实验动物有限公司 +1
Recombinant protein-based method for the delivery of silencer RNA to target the brain
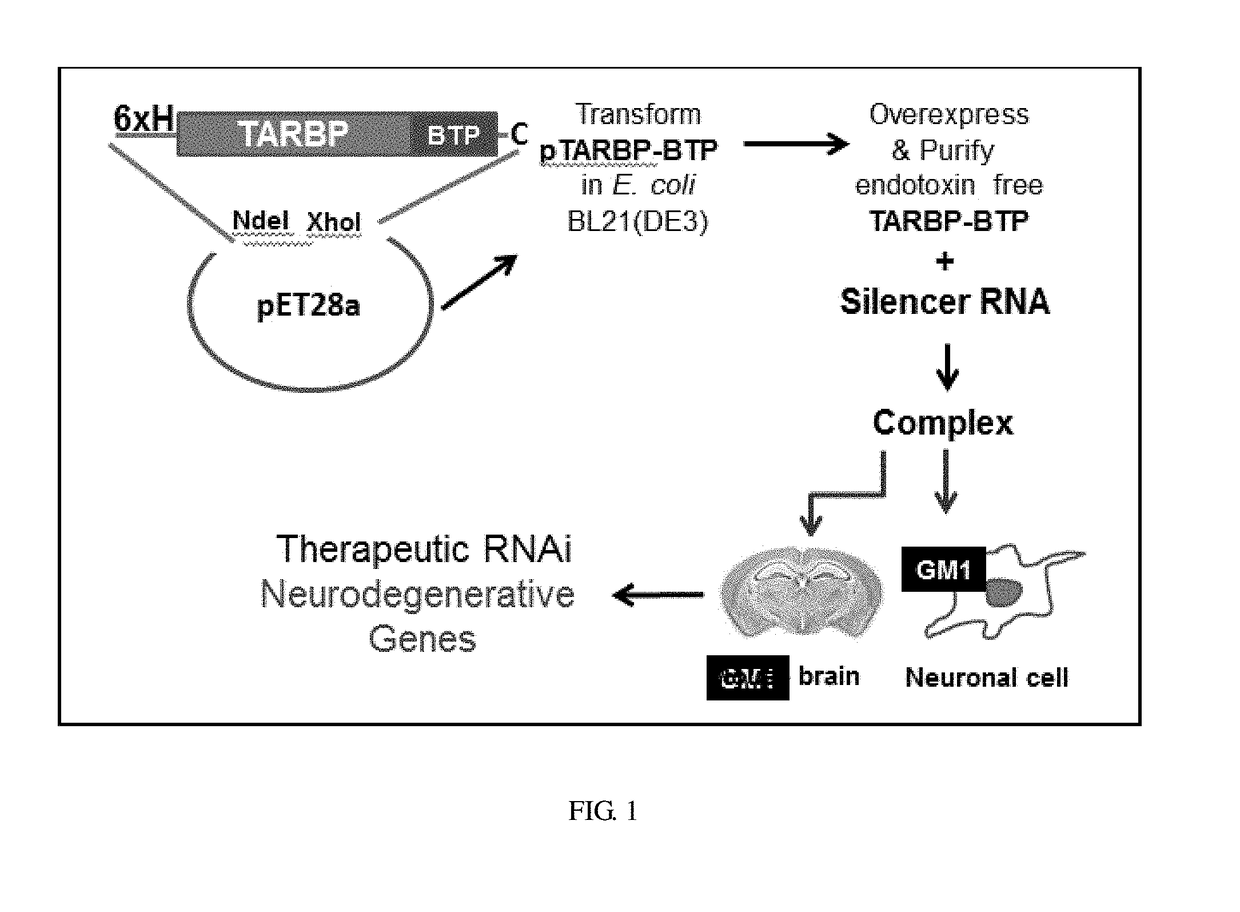
ActiveUS20180073021A1Well formedOrganic active ingredientsFusion with RNA-binding domainNeural cellCerebral hemisphere
The present invention relates to the design and development of recombinant protein for the delivery of silencer RNA complex to mediate RNA interference since it represents a novel therapeutic approach to modulate several neurodegenerative disease-related genes across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To overcome challenges due to this barrier for biologics and other biological complex, the present invention describes a method wherein peptide having sequence GGGGHLNILSTLWKYRC represented by SEQ ID NO. 9 known to target specific gangliosides was linked to a double-stranded RNA binding protein to bind and deliver silencer RNA to the brain parenchyma. The designed fusion protein comprising a double-stranded RNA-binding domain (dsRBD) of human Trans Activation response element (TAR) RNA Binding Protein (TARBP2) and a brain targeting peptide sequence that binds GM1. Conformation-specific binding of TARBP2 domain to silencer RNA results in the formation of homogenous serum-stable complex with GM1 targeting potential. Uptake of the complex in neural cells reveals selective requirement of GM1 for entry. Remarkably, the invention pertains to the systemic delivery of the complex comprising TARBP-BTP and silencer RNA in AβPP-PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD) led to distinctive localization primarily in the cerebral hemisphere in the hippocampus and brain cortex and in principle can work across other mammalian CNS targets. Further, the delivery of silencer-RNA mediated by brain targeting peptide fusion led to significant knockdown of BACE1, a therapeutic protease target in both AβPP-PS1 and wild type C57BL / 6 mice. The invention establishes the emergent importance of fusion proteins in delivering therapeutic siRNA as a simple complex to brain tissues to treat neurodegenerative diseases besides Alzheimer's disease (AD). The complex is also useful to study gene function of hitherto unidentified genes / interplay of genes in mammalian systems and central nervous system.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Chronic food-borne Parkinson's disease mouse model and building method and application thereof
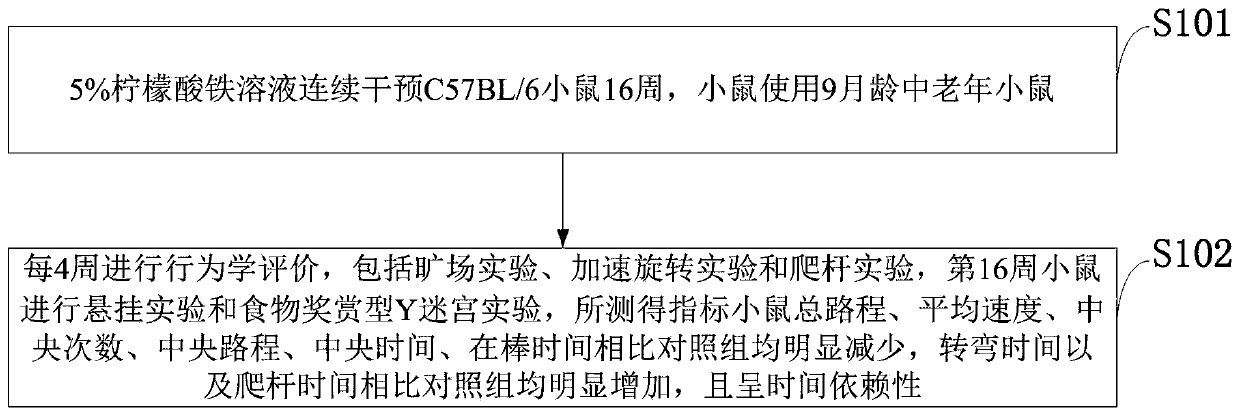
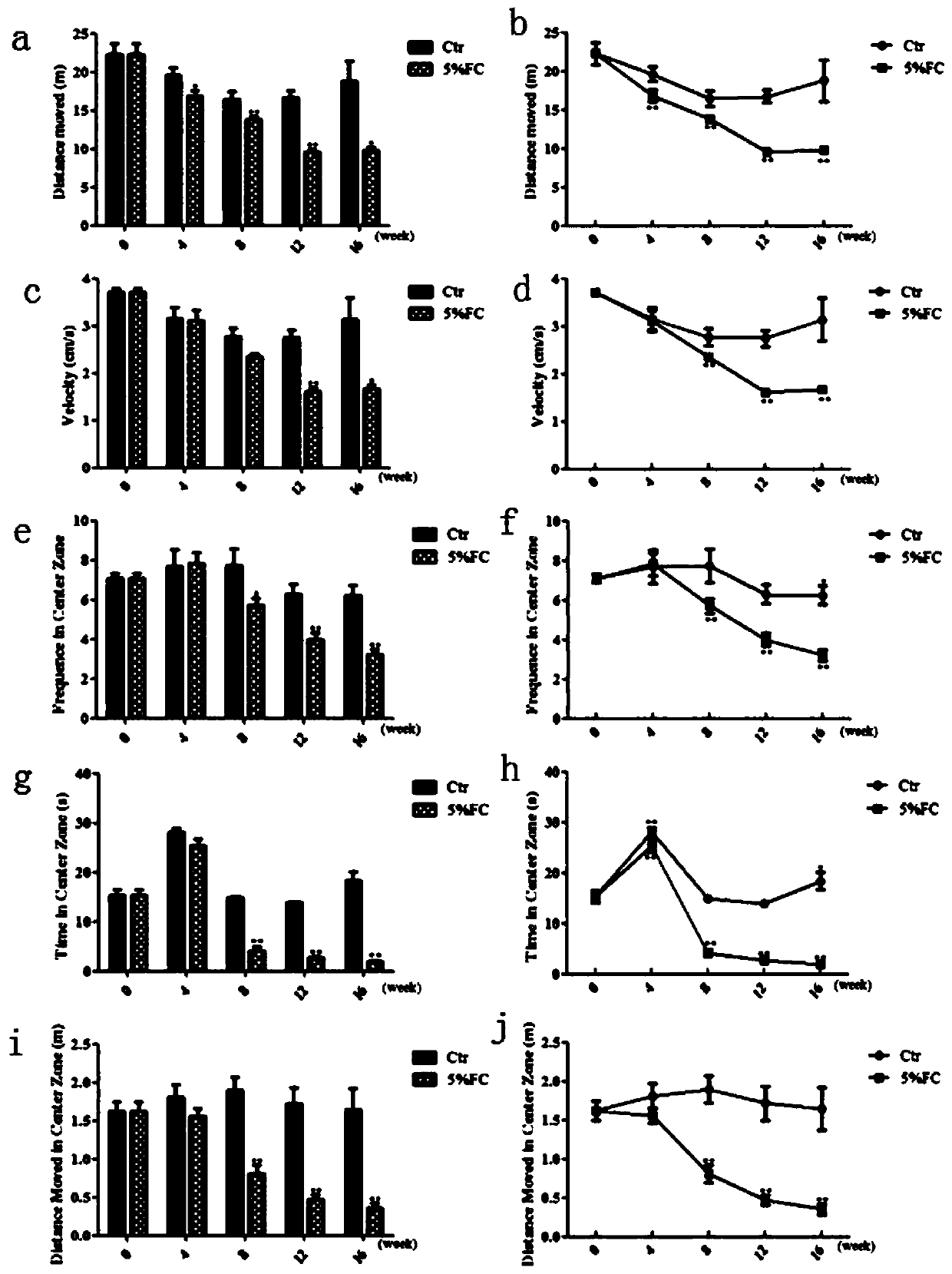
InactiveCN110663646AHigh incidenceScientific referenceHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsNeuronal degenerationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal model building and discloses a chronic food-borne Parkinson's disease mouse model and a building method and application thereof. The method includes: a 5% ferric citrate solution is used to continuous intervene a C57BL / 6 mouse for 16 weeks, behavioral evaluation is performed through open-field, speed-up rotation and pole climbing experiments every other 4 weeks, and the mouse of the 16th week is subjected to a suspension experiment and a food award type Y-maze experiment; the measured mouse total journey, average speed, center times, center journey, center time and on-rod time of the mouse are evidently reduced as compared with those of the control, turning time and pole climbing time of the mouse are evidently increased as compared with those of the control, the results are time-dependent, and mouse sports coordination, balance ability, muscular tension and activity are lowered evidently. The chronic food-borne Parkinson's diseasemouse model and the building method have the advantages that the occurrence conditions of Parkinson's disease are simulated, and the chronic model is suitable for monitoring early-stage change and screening the early-stage diagnosis indexes of the Parkinson's disease; behavioral disorder can be quantified, and the pathological characteristic of the Parkinson's disease is dopaminergic neuron degeneration and loss characteristic lesion.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Skin type lupus erythematosus mouse model and construction method and application thereof
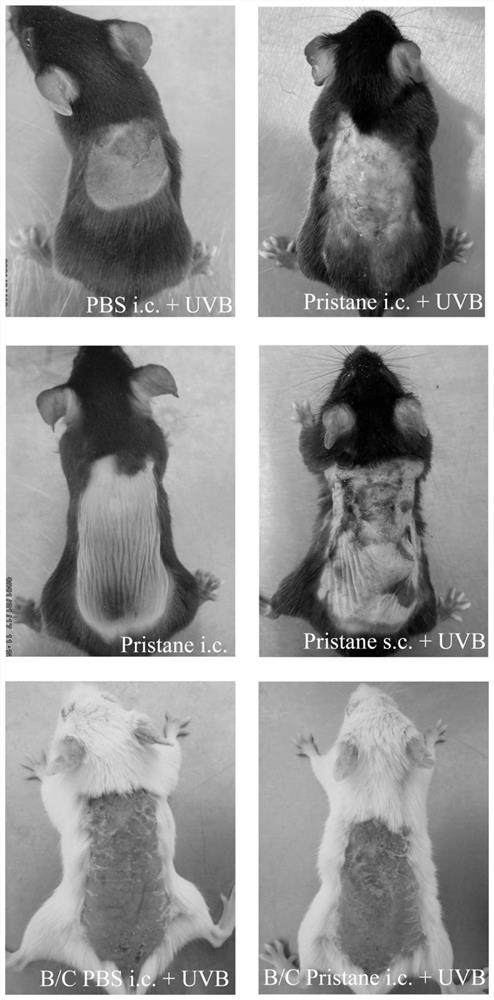
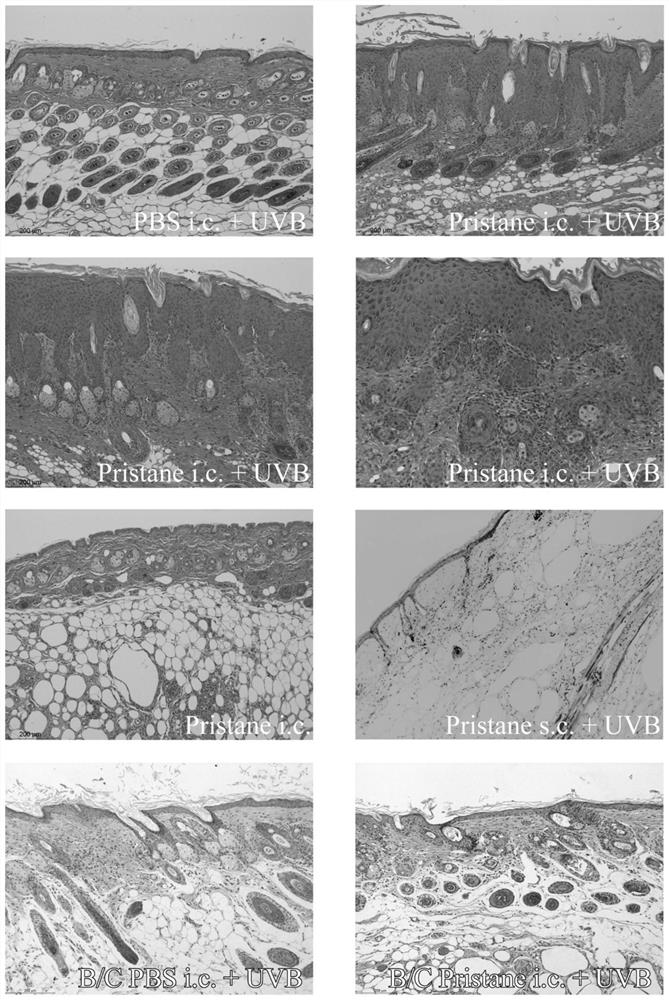
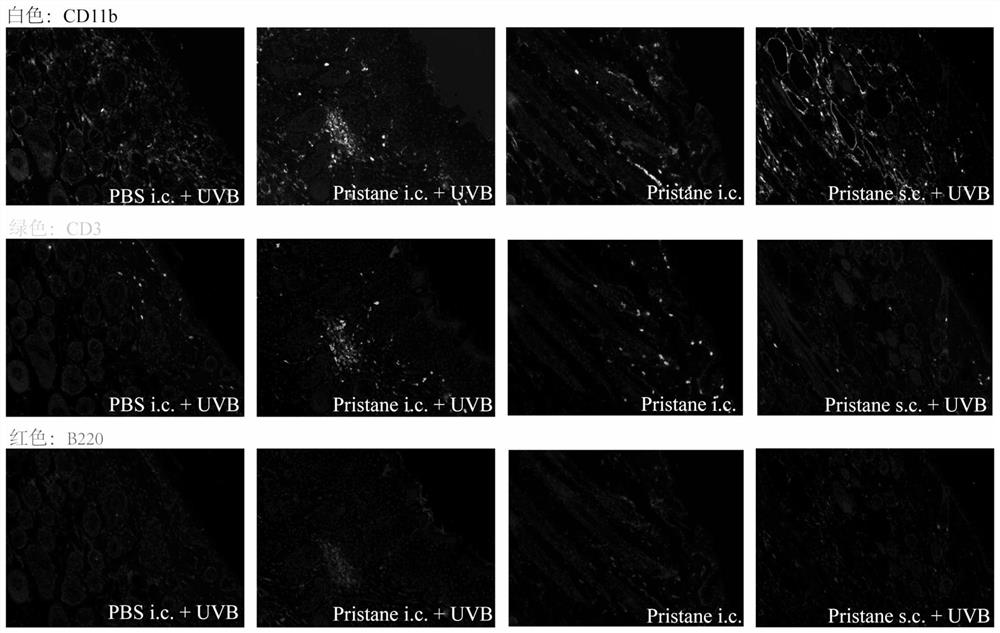
ActiveCN113412813AAccelerate the clinical transformation of scientific researchLight therapyVeterinary instrumentsDiseaseSystemic lupus erythematosus
The invention provides a skin type lupus erythematosus mouse model and a construction method and application thereof. According to the skin type lupus erythematosus mouse model constructed by the construction method, pristane is combined with ultraviolet (UVB) stimulation to construct the skin type lupus erythematosus mouse model. A C57BL / 6 mouse is continuously irradiated by a proper amount of UVB after being subjected to Pristane intradermal immune treatment. The skin type lupus erythematosus mouse model better simulates immune response generated by abnormal activation of mouse skin immune cells under UVB stimulation. The model can be used for discussing the occurrence mechanism of the disease progress of lupus erythematosus, researching and developing drugs for targeting lupus skin lesion and the like, and is of great significance in the aspect of accelerating and promoting scientific research and clinical transformation.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Construction method of type I diabetes animal model
InactiveCN109718240AGood modelingHigh molding rateOrganic active ingredientsIntraperitoneal routeDiabetes model
The invention provides a construction method of a type I diabetes animal model. The method comprises the following steps: selecting C57BL / 6 mice, performing first tail vein injection, continuously performing intraperitoneal injection of a streptozotocin reagent for 5 days, performing ambrosia for 12 hours before injection, and allowing the mice to freely drink water. Two days after the injection procedure is completed, the ambrosia is carried out for 4 hours, and a glucometer is used for measuring blood glucose until the blood glucose value is 10 mmol / L or above. The statistical analysis of the blood glucose measurement result of the type I diabetes animal model shows that the C57BL / 6 mouse type I diabetes model constructed by using the streptozotocin is feasible and can be used for researching the diabetes pathogenesis and the anti-hyperglycemia intervention of medicaments and health-care foods. Compared with the prior art, the C57BL / 6 mouse type I diabetes model constructed by the invention has the advantages of high film forming rate, simple operation, no death of animals and good reproducibility.
Owner:贵州健安德科技有限公司 +1
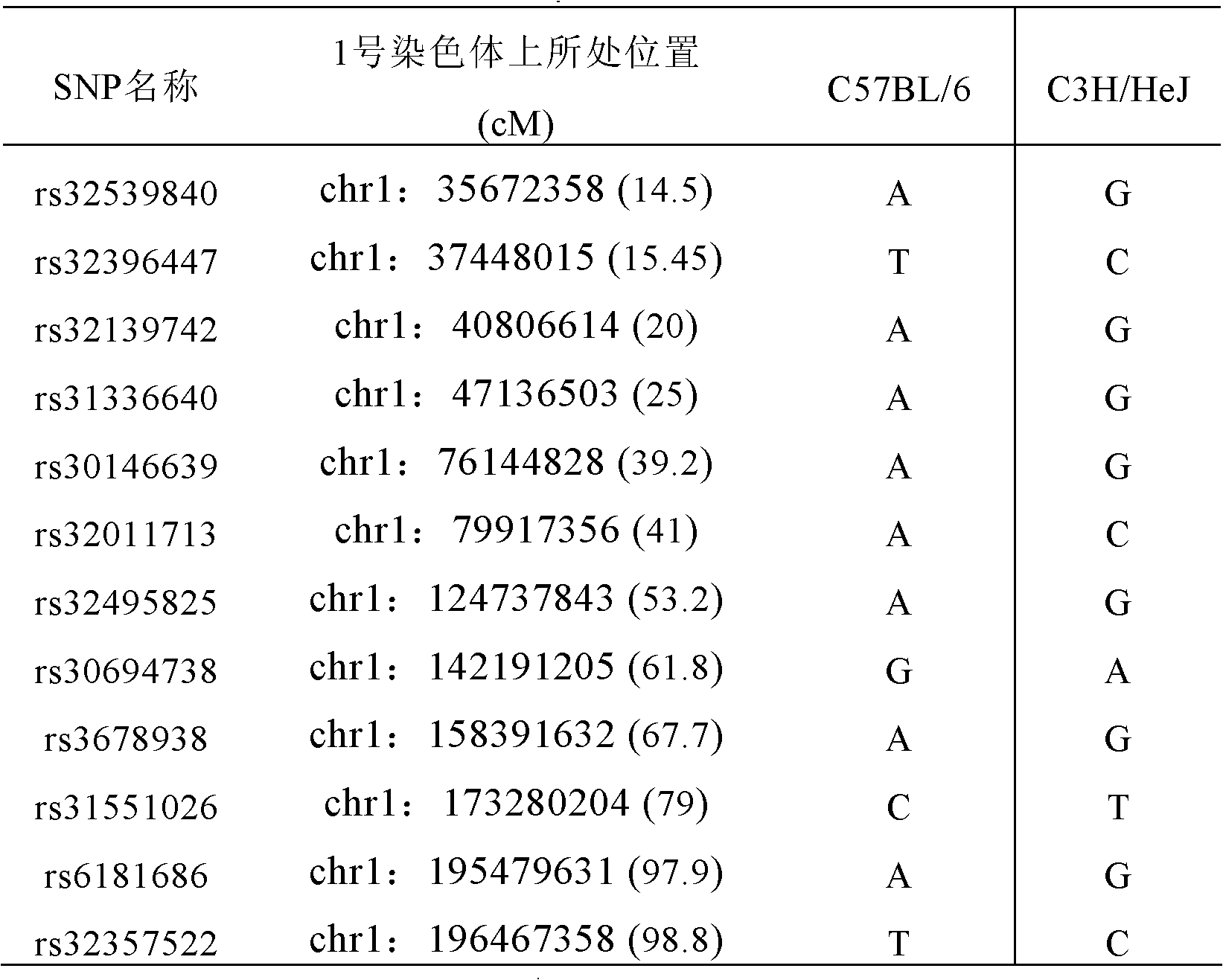
Construction for number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL/6-Chr1C3H/HeJ
The invention relates to construction for a number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1C3H / HeJ. According to the construction for the number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1C3H / HeJ, a new chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain is constructed. A genetic background of the chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain is based on a C57BL / 6 mouse, while wherein a number 1 chromosome is from a C3H / HeJ mouse. According to the construction for the number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1C3H / HeJ, the chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain can be used for research of character differences brought by different number 1 chromosome genomes under the same genome background, and can be a useful tool for research of the chromosome genome functions by adoption of a genetic method.
Owner:上海西普尔-必凯实验动物有限公司 +1
Sugar-reducing application of citrus changshanensis extract
InactiveCN104547176AImprove enduranceReduce resistanceMetabolism disorderFood preparationBiotechnologyDisease
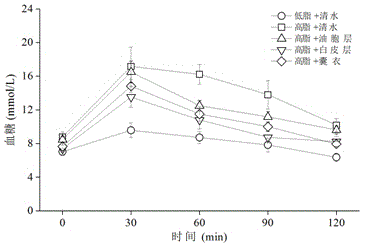
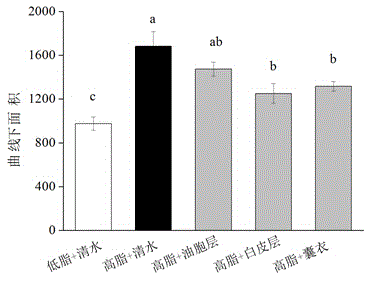
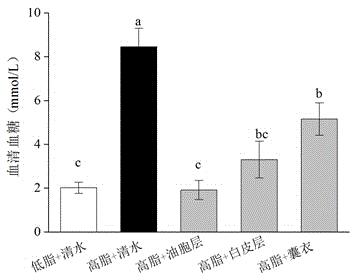
The invention provides an application of citrus changshanensis extract in preparing sugar-reducing functional foods, health-care products or sugar-reducing medicines. The citrus changshanensis extract comprises an oil-cell layer, a white-skin layer and a bag-coating extract, so that the fasting blood glucose and the serum glucose of a C57BL / 6 mouse with diabetes can be obviously reduced in vivo, the glucose tolerance can be increased and the insulin resistance can be reduced. The citrus changshanensis extract can be used for preventing and treating diseases related to abnormal glucose metabolism as a functional food, a health-care product or a preventing and treating medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of substance for improving activity and/or expression quantity of liver SIRT5 protein in treatment of acute myocardial infarction
ActiveCN112972685AReduce myocardial infarct sizeReduced area of myocardial fibrosisMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical active ingredientsMyofibrosisCardiac functioning
The invention discloses application of a substance for improving activity and / or expression quantity of liver SIRT5 protein in treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Experiments prove that compared with a C57BL / 6 mouse, the myocardial infarction area and the myocardial fibrosis area of the C57BL / 6 mouse of which a liver specifically overexpresses the SIRT5 protein are remarkably reduced, and the cardiac function is improved to a certain extent. Therefore, the substance for improving the activity and / or expression quantity of the liver SIRT5 protein can reduce the myocardial infarction area, reduce the myocardial fibrosis area and improve the cardiac function, and acute myocardial infarction is further prevented and / or treated. The application of the substance for improving the activity and / or expression quantity of the liver SIRT5 protein in treatment of acute myocardial infarction has an important application value.
Owner:BEIJING TSINGHUA CHANGGUNG HOSPITAL
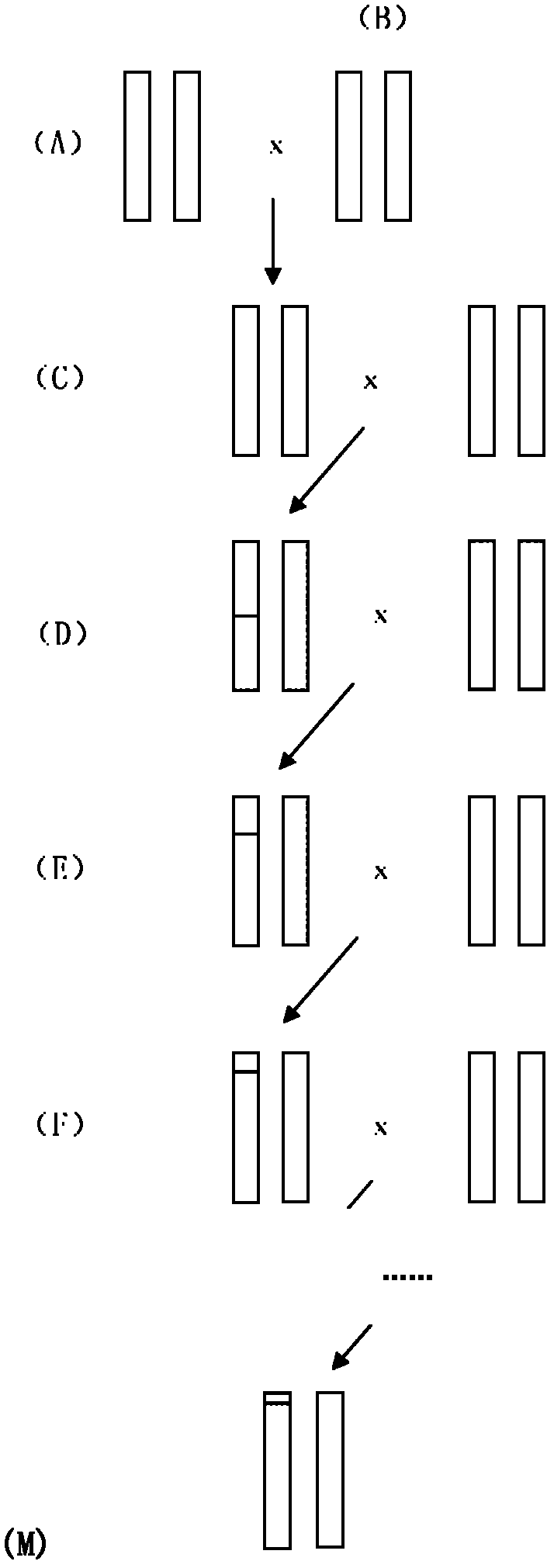
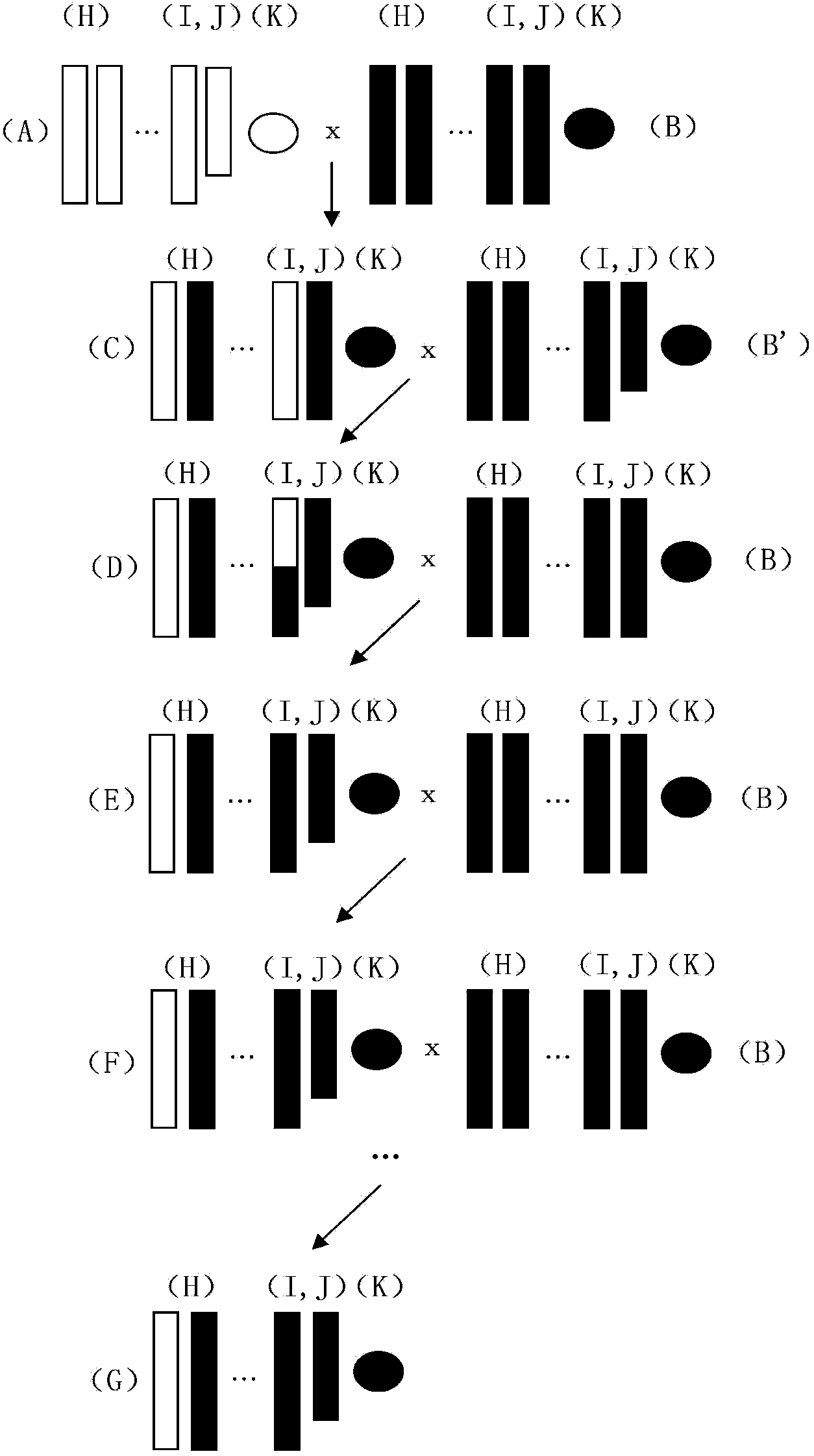
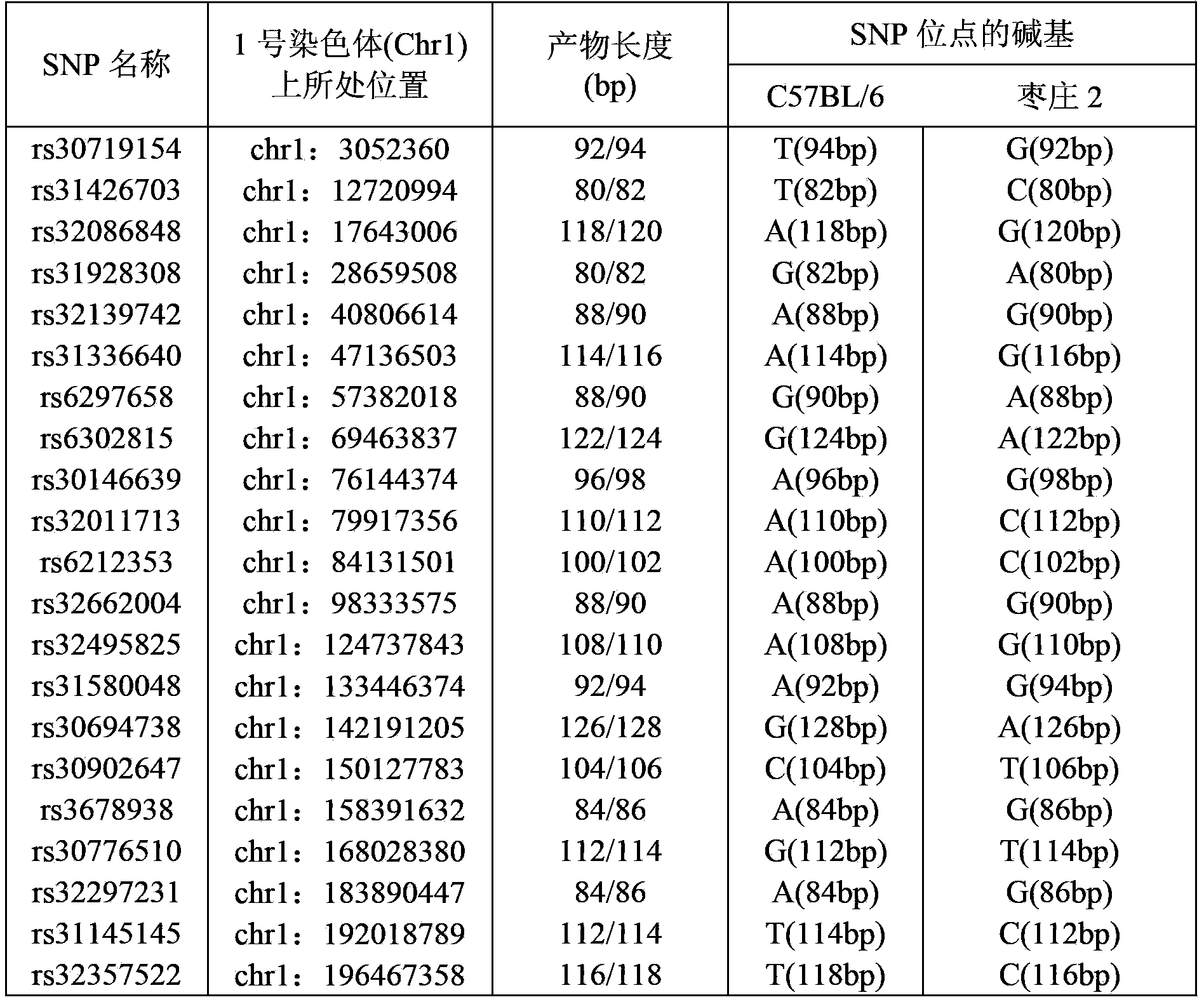
Construction for Chromosome 1 to replace wild mus musculus strain C57BL/6. Zaozhuang 2-Chr1
The invention relates to construction for Chromosome 1 to replace wild mus musculus strain C57BL / 6. Zaozhuang 2-Chr1. A novel Chromosome C57BL / 6 replacing experiment musculus strain is constructed, a C57BL / 6 musculus is mainly used as the genetic background of the musculus strain, and a Zaozhuang 2 musculus is mainly used in the Chromosome 1. The Chromosome replacing strain can be used for studying character difference brought by different Chromosome 1 genomes under the background of the same genome, and a useful tool for studying the functions of the genomes by using a genetics method is achieved.
Owner:上海西普尔-必凯实验动物有限公司 +1
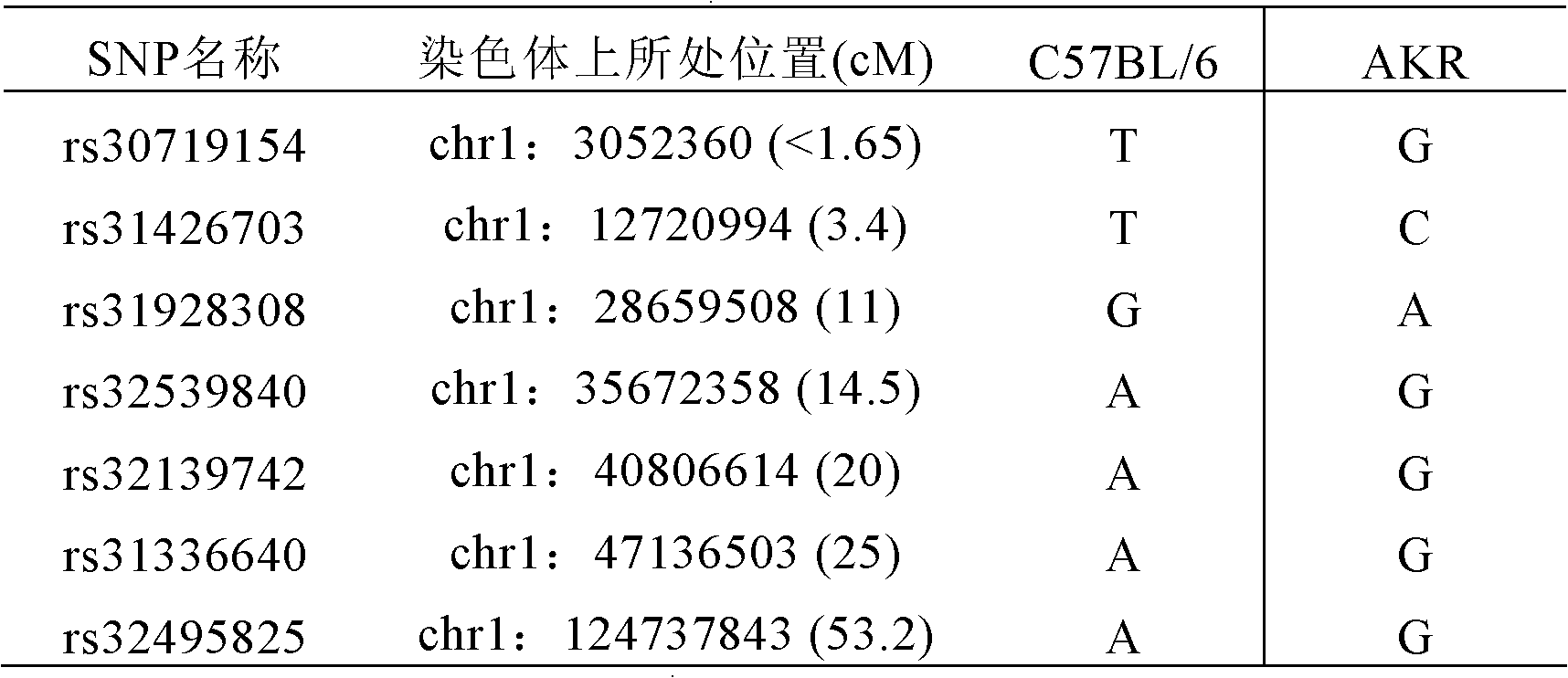
Construction for number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL/6-Chr1AKR
The invention relates to construction for a number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1AKR. According to the construction for the number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1AKR, a new chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain is constructed. A genetic background of the chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain is based on a C57BL / 6 mouse, while wherein a number 1 chromosome is from an AKR mouse. According to the construction for the number 1 chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain C57BL / 6-Chr1AKR, the chromosome substitution laboratory mouse strain can be used for research of character differences brought by different number 1 chromosome genomes under the same genome background, and can be a useful tool for research of the chromosome genome functions by adoption of a genetic method.
Owner:上海西普尔-必凯实验动物有限公司 +1
Building method of mouse stomach cancer model
InactiveCN103750916APromote gastric cancerSignificant chronic stress responseAmide active ingredientsAnimal fetteringNitro compoundMouse Stomach
The invention discloses a building method of a mouse stomach cancer model. A four-week-old C57BL / 6 mouse is taken and placed in a tubular device, wherein movement of the mouse is restrained but the mouse can breathe freely in the tubular device; every stress period lasts for 25-30 days, and six to eight hours are needed every day; the interval between every two stress periods is 5-7 days, and two to three stress periods are needed; when stress is carried out, the mouse drinks water containing N-nitro compounds is provided for the mouse, medicine is fed for a week and is fed again after a week, normal drinking water is provided for the mouse at the medicine feeding intervals, and the mouse needs to be fed with medicine for five weeks; the mouse is bred for 35 weeks conventionally after the medicine feeding, and the mouse suffering the stomach cancer is obtained. According to prior literatures and reports, the stomach cancer formation rate obtained after MNU treatment is carried out on a C57BL / 6 mouse purely is about 30%; after the MNU treatment and the stress treatment are combined, the stomach cancer formation rate of the C57BL / 6 mouse increases to be 60%.
Owner:徐泽宽
Preparation method of enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model and model application
InactiveCN107361012AHigh xenotransplantation efficiencyGood effectAnimal husbandryFluorescenceT lymphocyte
The invention discloses a preparation method of an enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model. The method comprises the following steps: adopting the mode of crossing and backcrossing among multiple generations of C57BL / 6-Tg (CAG-EGFP) mice and NOD / SCID mice and screening the multiple generations to establish steadily hereditary NOD / SCID / EGFP mice systemically expressing green fluorescence, namely, an enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model sheet. The preparation method employs the breeding method featuring crossing and backcrossing among multiple generations to raise NOD / SCID mice expressing enhanced green-florescent protein genes. Compared with nude mice, the SCID mice have more severe immune deficiency including combined T and B cell deficiencies. The invention further discloses an application of the enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model. In terms of xenotransplantation study, the SCID mice are more efficient in xenotransplantation than the nude mice with deficient t lymphocytes. The method of the model is an excellent model for fluorescent animals with immune deficiencies.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com