Patents
Literature
34 results about "Hydrophobic residue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Modified cytokine
InactiveUS7112660B1Increase intrinsic stabilityIncrease of to proteolytic degradationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsProtein secondary structureSolvent
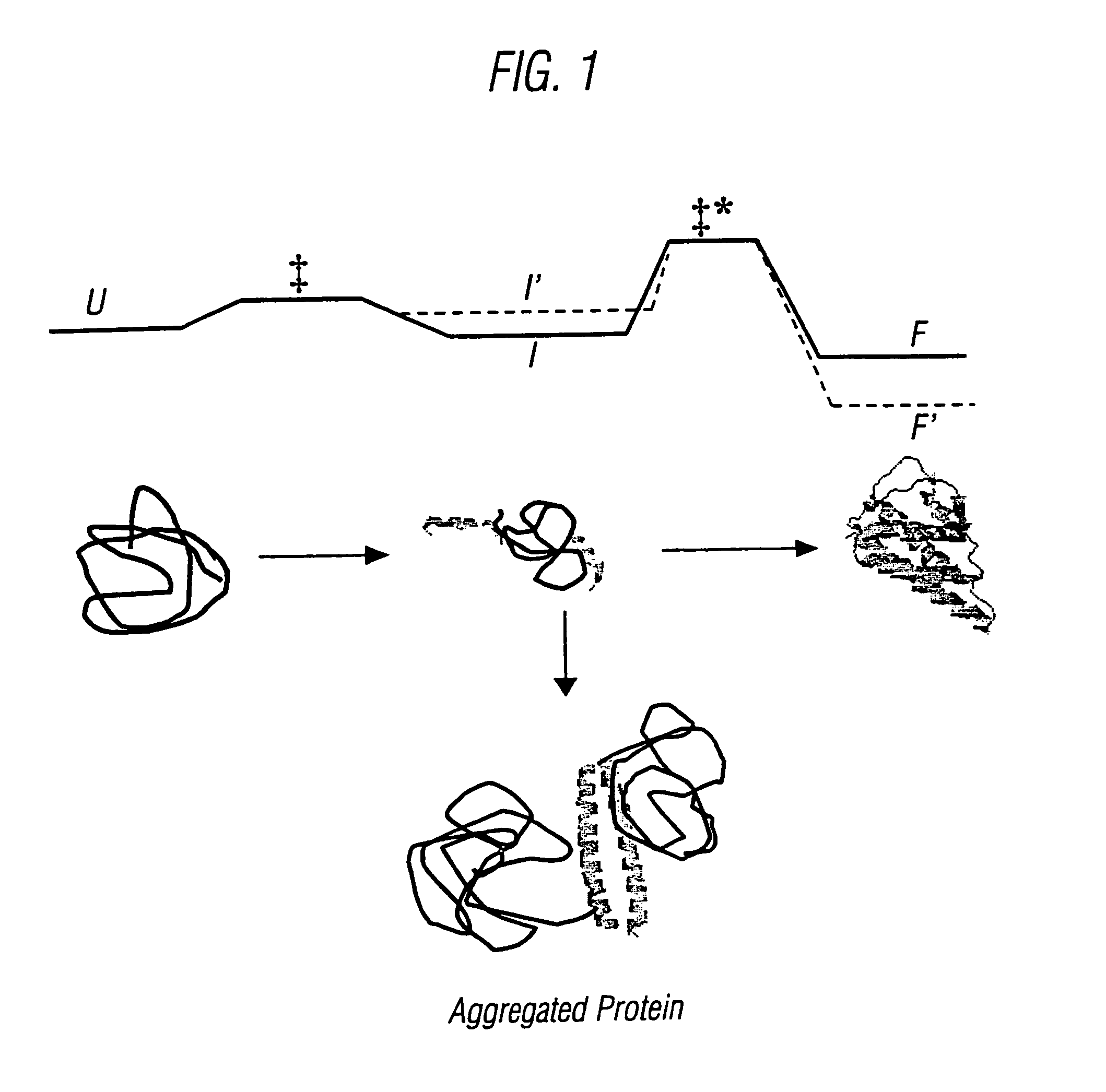
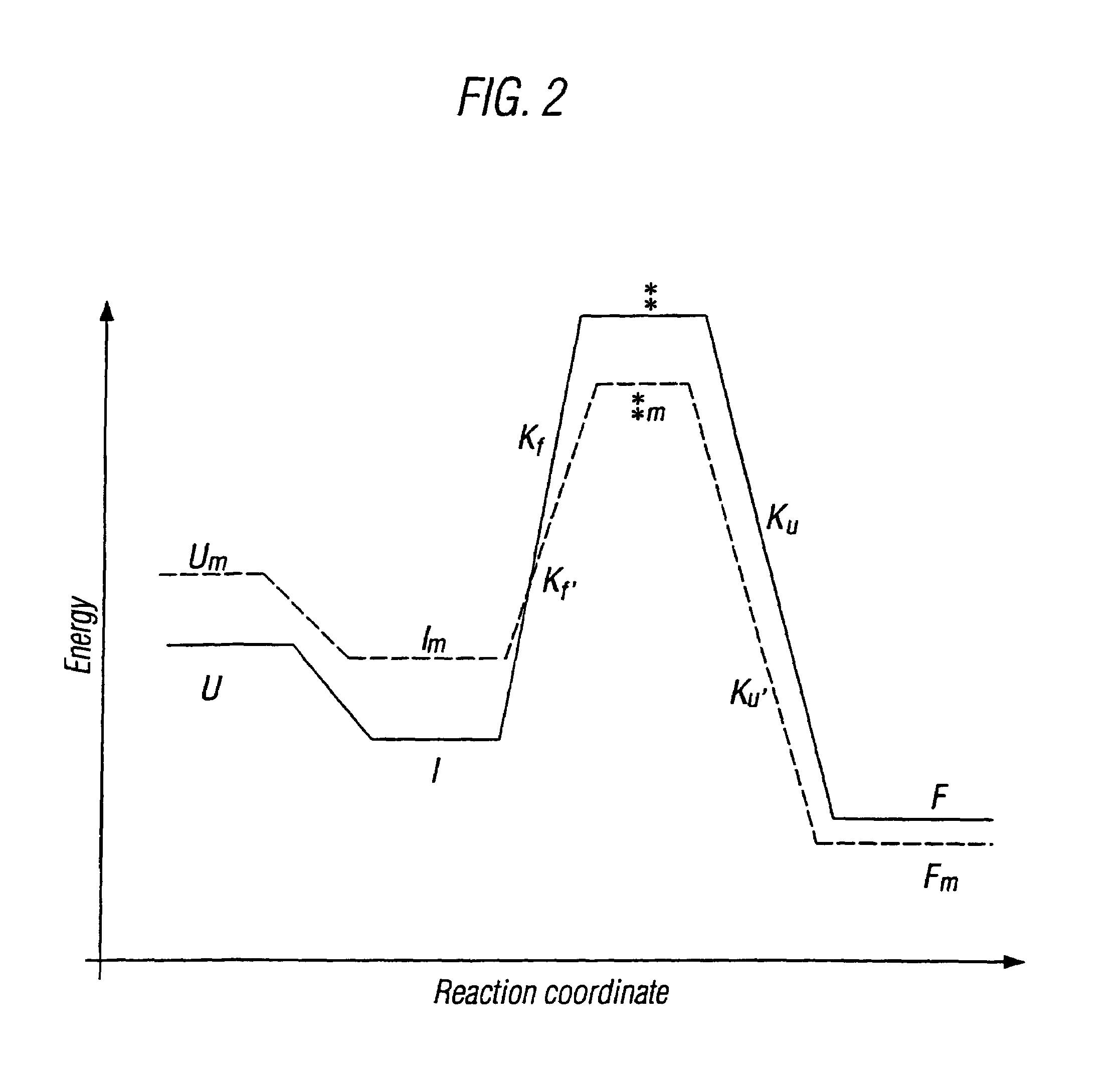
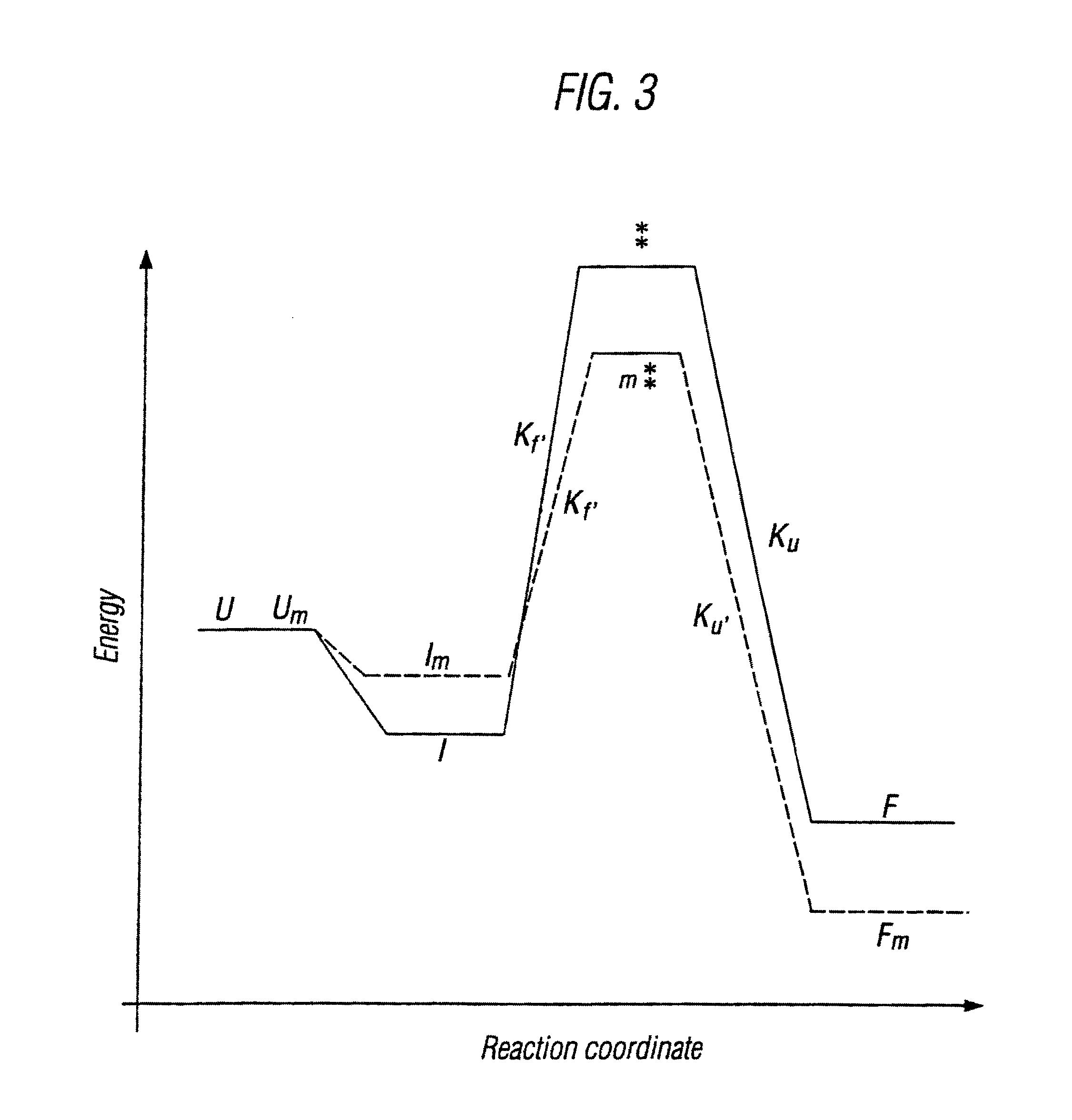
The invention relates to methods for the stabilisation of cytokines and to cytokines generated by such methods. The methods of the invention involve mutating the amino acid sequence of a cytokine so as to remove solvent-exposed hydrophobic residues, and / or mutating the amino acid sequence of the cytokine so as to stabilise one or more secondary structure elements in the molecule. These steps have the effect of destabilsing intermediates that are formed during the folding process, relative to the stability of the cytokine in its naturally folded state, so increasing the yield of the cytokine as produced in vitro.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA AG +1
Treatment of leaky or damaged tight junctions and enhancing extracellular matrix
ActiveUS20080274979A1Promote growthPromote repairAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseDiabetic retinopathy
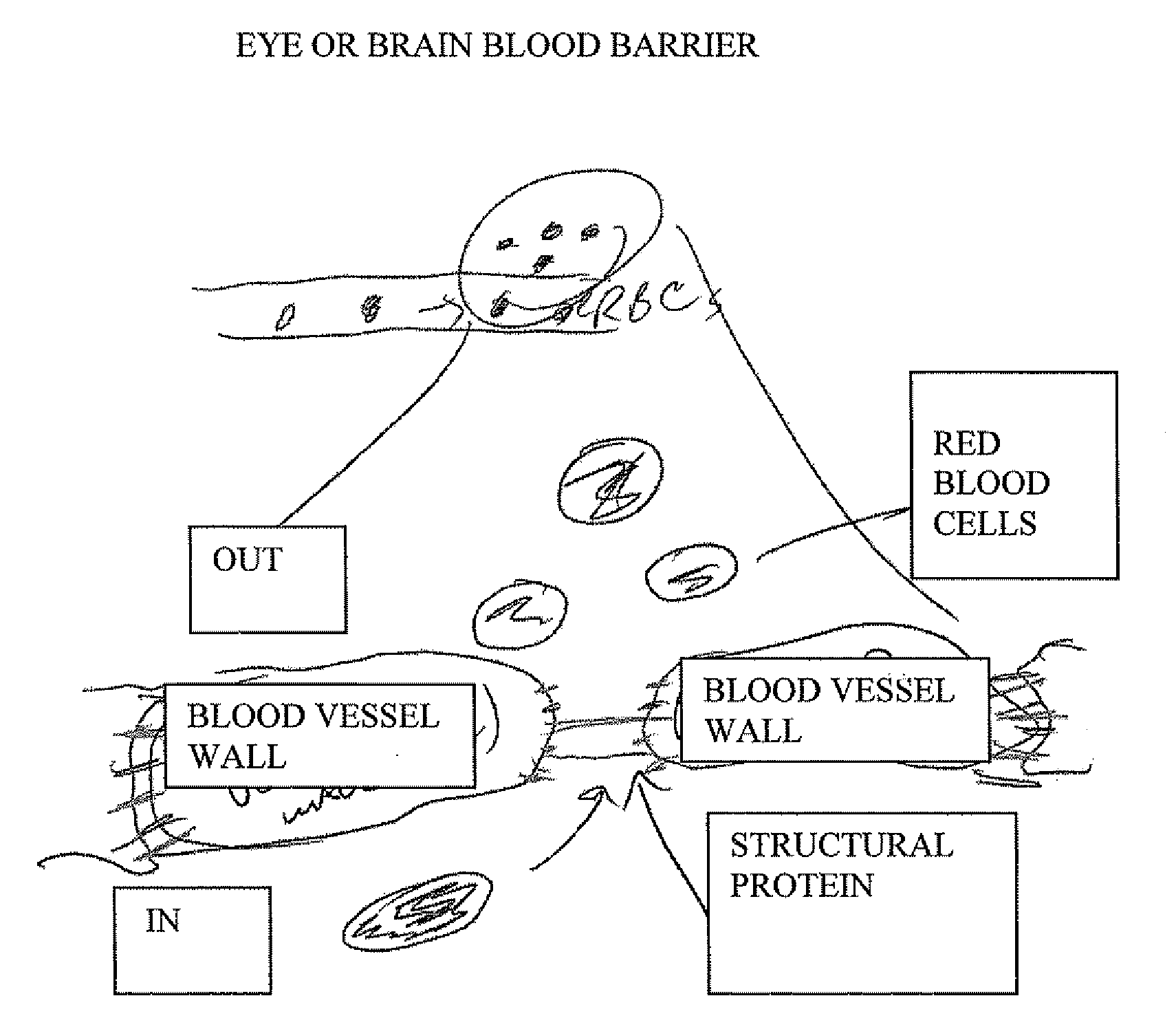
Self assembling peptides and peptidomimetics can be utilized for the treatment and support of disorders associated with leaky or damaged tight junction and weak, diseased, or injured extracellular matrix. The self-assembling materials generally have alternating hydrophilic or hydrophobic residues or hydrophobic and / or hydrophilic sections which allow the material to react or interact with the glycoproteins found in the ECM. Diseases in which treatment with these materials applied to or near the site in need of treatment include diabetic retinopathy, sepsis, burns, and certain neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. The formulations can be administered by injection, spraying, topically or by catheter or via a wound dressing or other material to which it is applied and then applied to the site in need of treatment.
Owner:ARCH BIOSURGERY
Antimicrobial hexapeptides
ActiveUS20060229252A1Growth inhibitionPrevent microbial infectionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryAcid-fastMammal
The invention encompasses hexapeptides consisting of alternating hydrophobic residues (B) at positions 2, 4, and 6, hydrophilic, hydrophilic, charged residues (X) at positions 1 and 3, and a naphthylalanine (Nal), an aliphatic or aromatic residue (O) at position five, represented generally by the formula XBXBOB, which exhibit antimicrobial activity against infections caused by a variety of pathogens. These pathogens may include gram positive or negative bacteria, acid-fast bacteria such a mycobacteria, parasites, dermatophytes, or fungal pathogens. Typical fungal pathogens include Candida albicans and typical dermatophytes include Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The hexapeptides of the present invention exhibit antifungal activity, antibacterial activity, desirable stability, and lack toxicity to the mammal receiving treatment.
Owner:HELIX BIOMEDIX INC
Treatment of leaky or damaged tight junctions and enhancing extracellular matrix
ActiveUS9415084B2Enhance growth and repairAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiabetic retinopathyDisease
Self assembling peptides and peptidomimetics can be utilized for the treatment and support of disorders associated with leaky or damaged tight junction and weak, diseased, or injured extracellular matrix. The self-assembling materials generally have alternating hydrophilic or hydrophobic residues or hydrophobic and / or hydrophilic sections which allow the material to react or interact with the glycoproteins found in the ECM. Diseases in which treatment with these materials applied to or near the site in need of treatment include diabetic retinopathy, sepsis, burns, and certain neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. The formulations can be administered by injection, spraying, topically or by catheter or via a wound dressing or other material to which it is applied and then applied to the site in need of treatment.
Owner:ARCH BIOSURGERY
Antimicrobial hexapeptides
The invention encompasses hexapeptides consisting of alternating hydrophobic residues (B) at positions 2, 4, and 6, hydrophilic, charged residues (X) at positions 1 and 3, and a naphthylalanine (Nal), an aliphatic or aromatic residue (O) at position five, represented generally by the formula XBXBOB, which exhibit antimicrobial activity against infections caused by a variety of pathogens. These pathogens may include gram positive or negative bacteria, acid-fast bacteria such as mycobacteria, parasites, dermatophytes, or fungal pathogens. Typical fungal pathogens include Candida albicans and typical dermatophytes include Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The hexapeptides of the present invention exhibit antifungal activity, antibacterial activity, desirable stability, and lack toxicity to the mammal receiving treatment.
Owner:HELIX BIOMEDIX INC
Nucleic acids encoding ara h 3 polypeptides
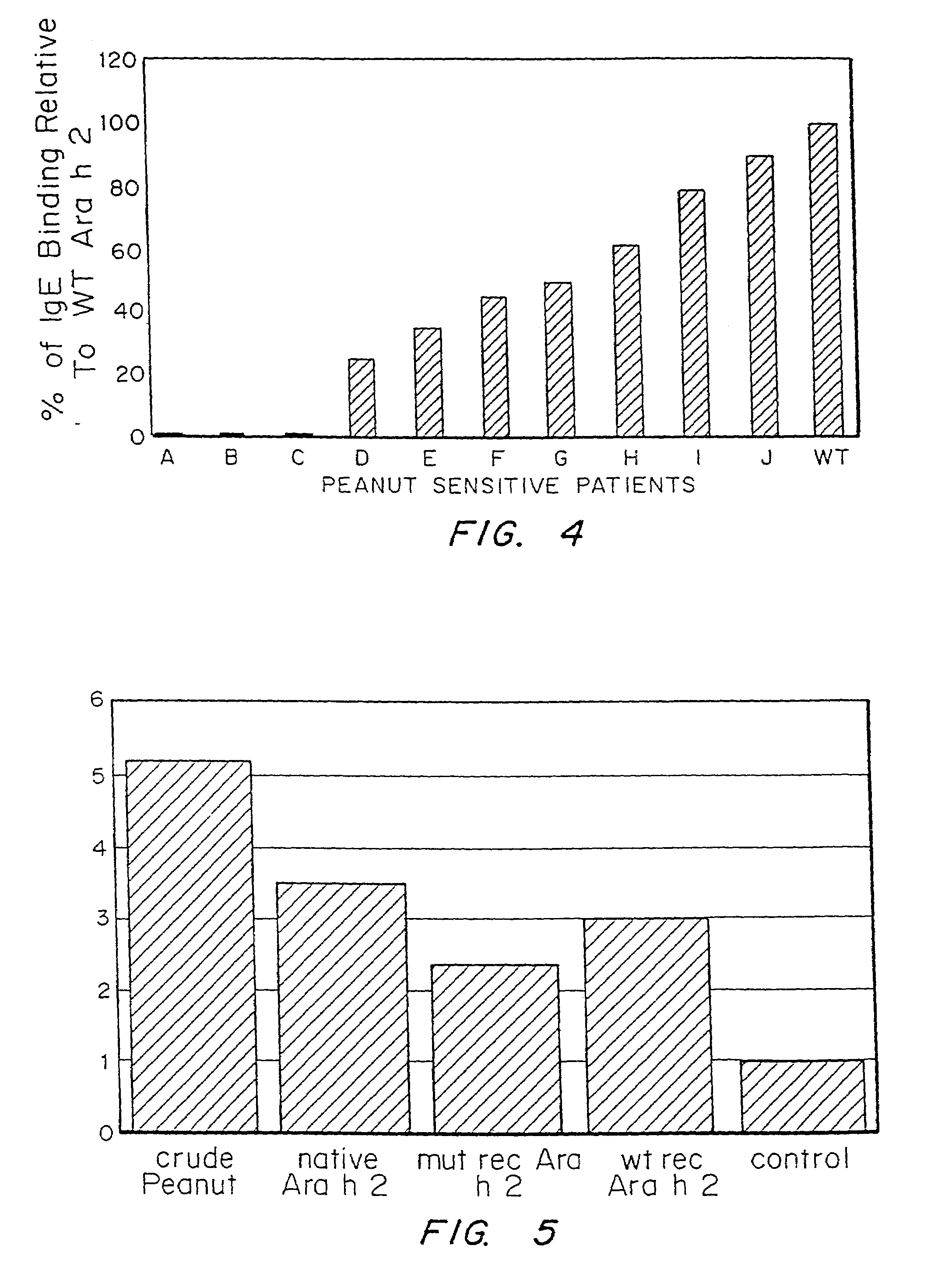
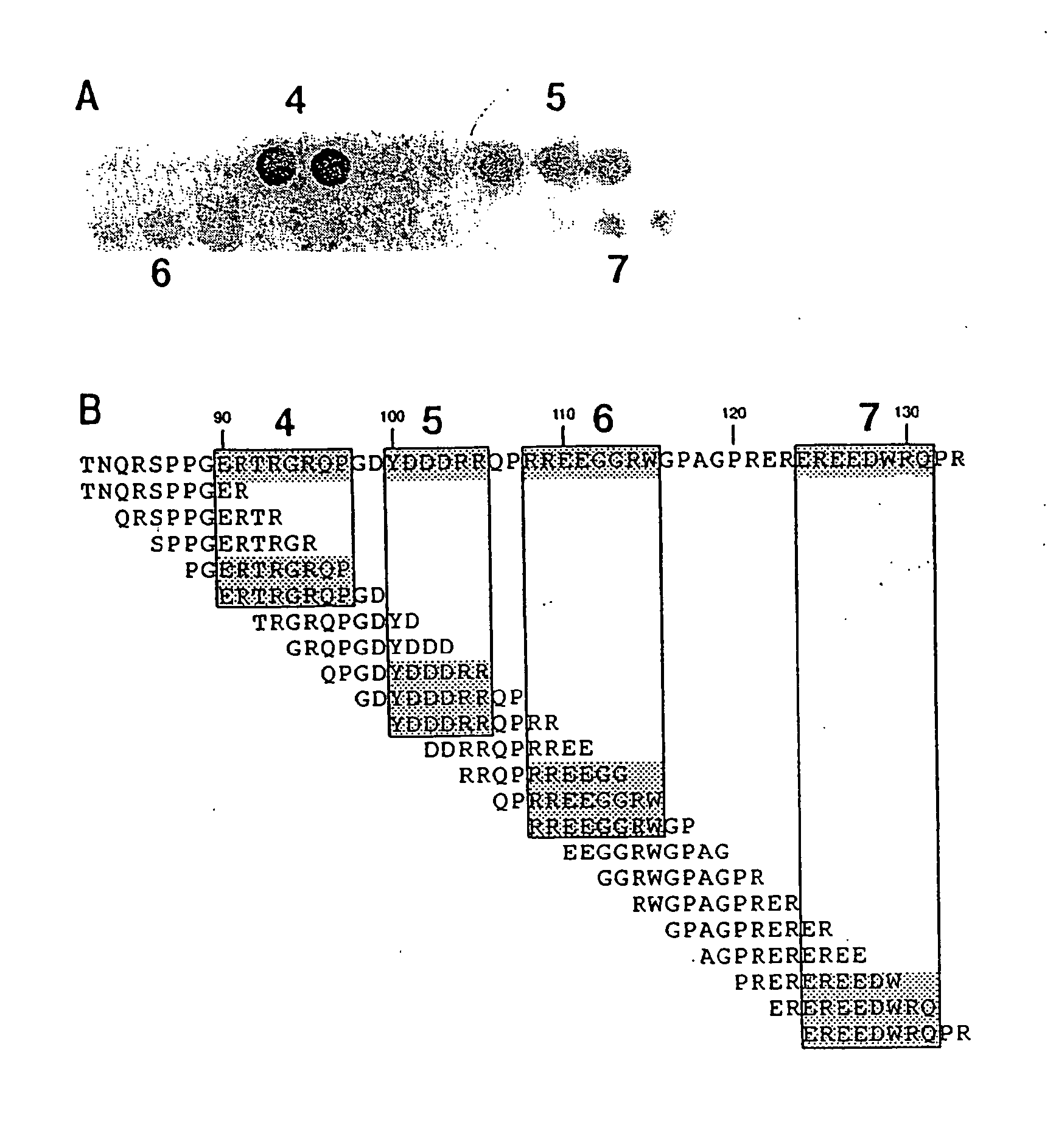
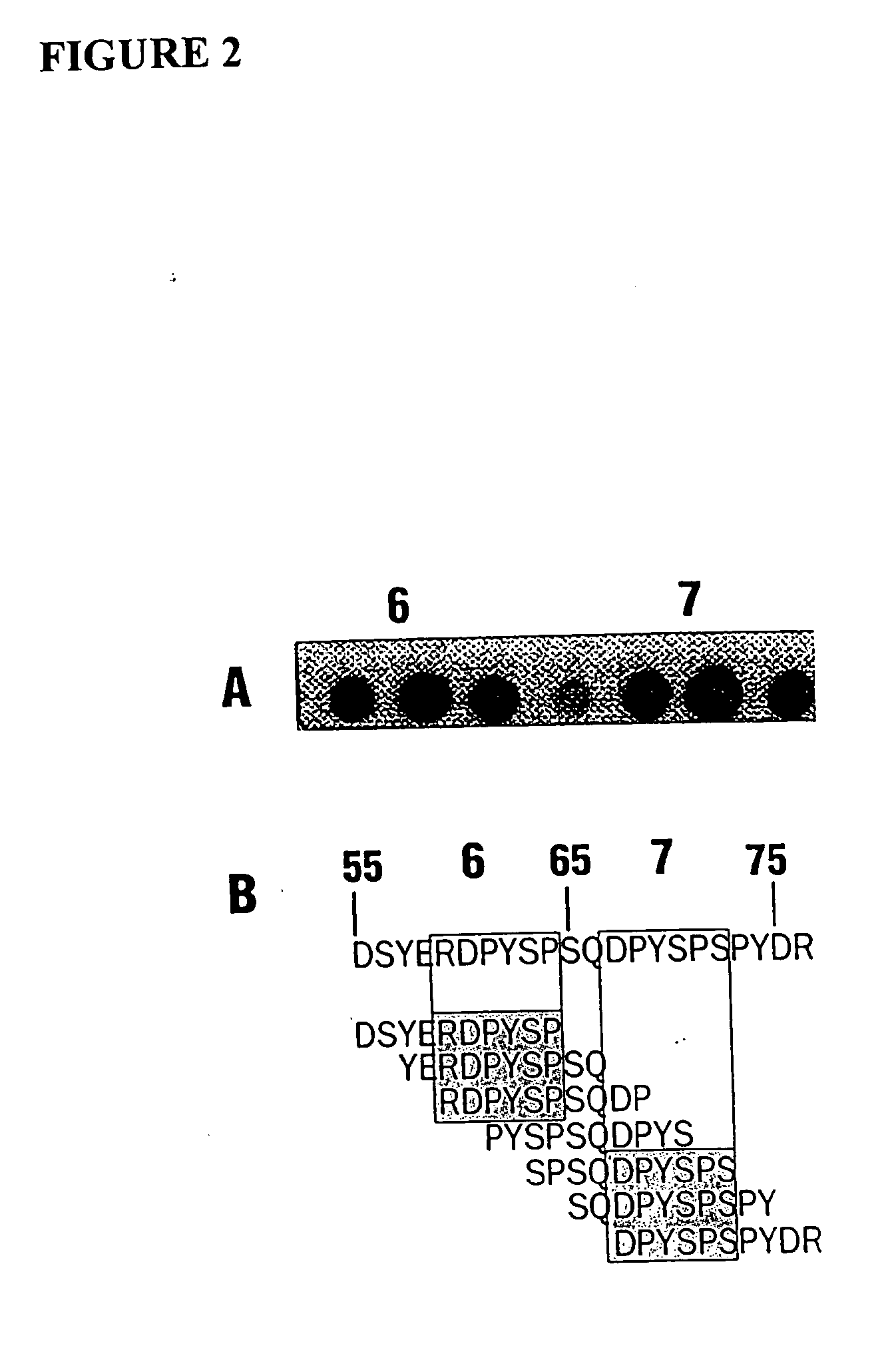
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity. The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS20070213507A1Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsFungi peptidesBinding siteT cell
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Antimicrobial agents
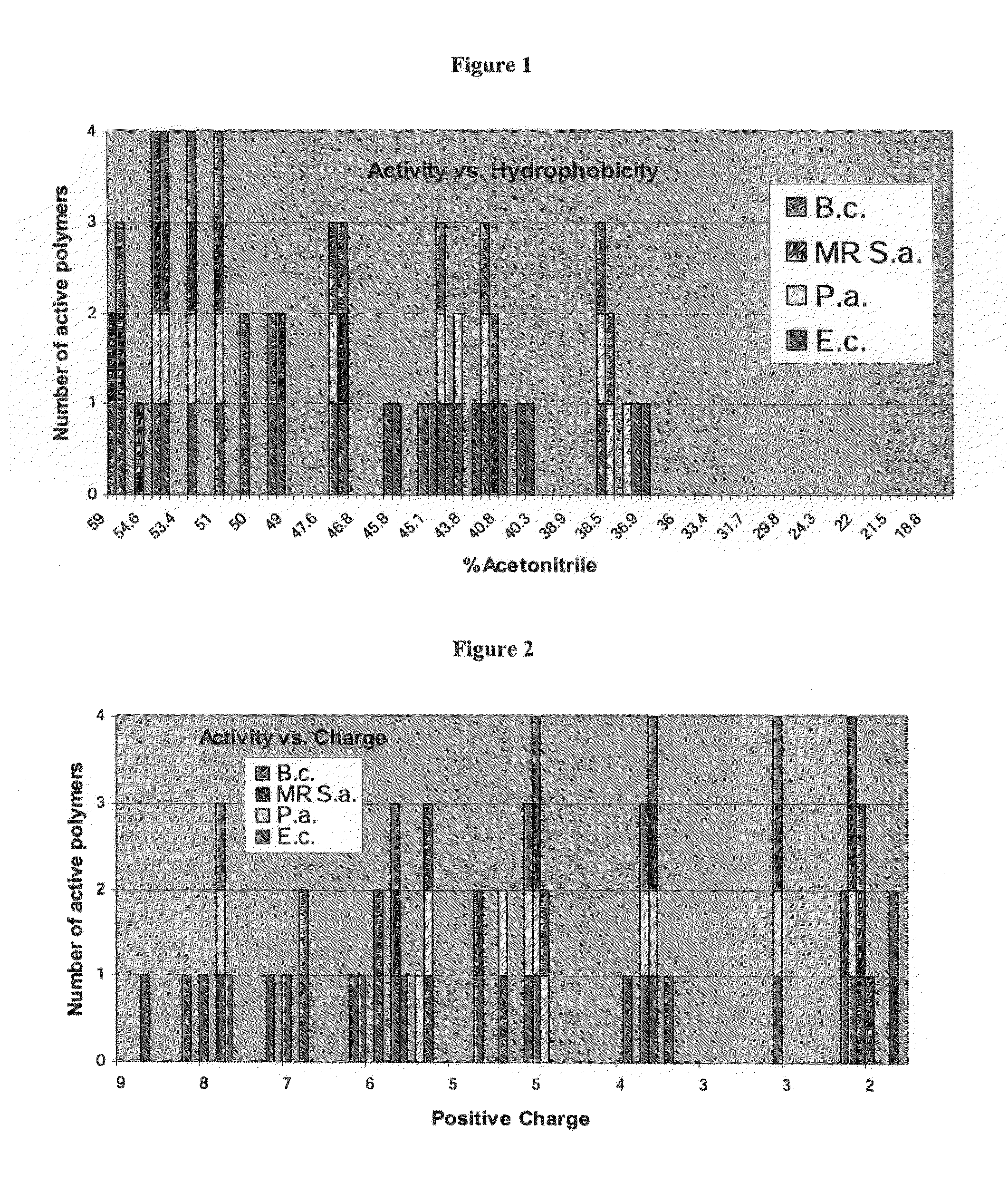
A novel class of antimicrobial polymeric agents, which include a plurality of amino acid residues, such as positively charged amino acid residues, and at least one hydrophobic residue linking there between. such as an omega-amino-fatty acid residue designed to exert antimicrobial activity while being stable, non-toxic and avoiding development of resistance thereto and a process of preparing same are disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions containing same and a method of treating medical conditions associated with pathological microorganisms, a medical device, an imaging probe and a food preservative utilizing same. Further disclosed are conjugates of an amino acid residue and a hydrophobic moiety residue and a process of preparing same.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Amphiphilic materials and liposome formulations thereof
InactiveUS7368129B1Suitable for useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideLiquid crystallineWhole blood product
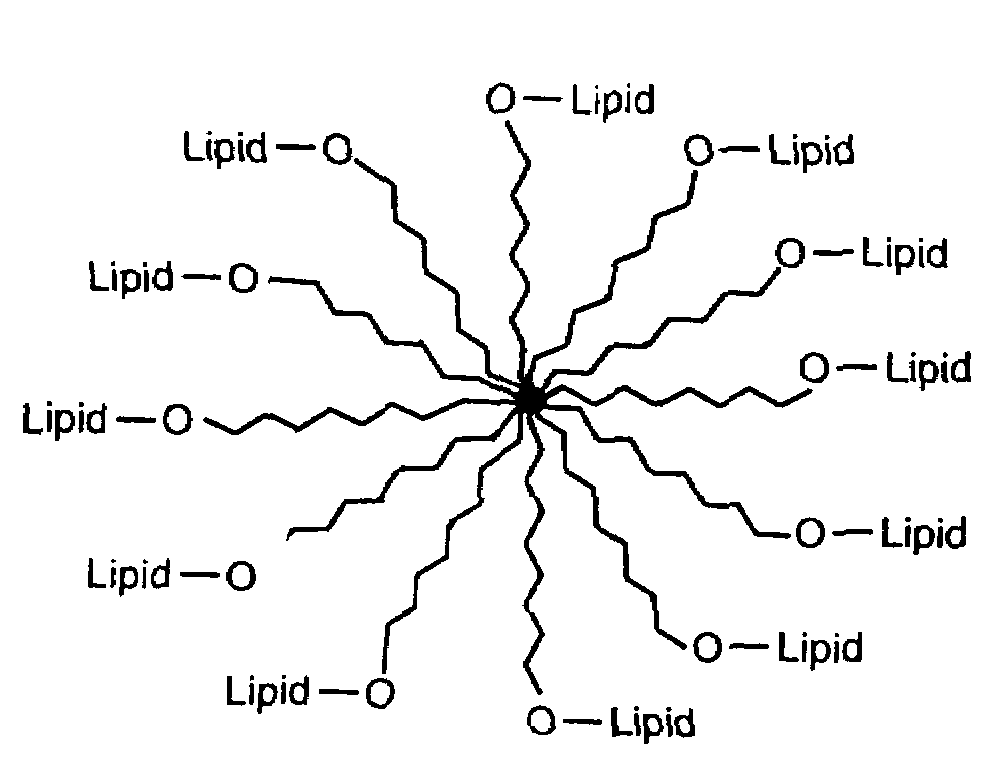
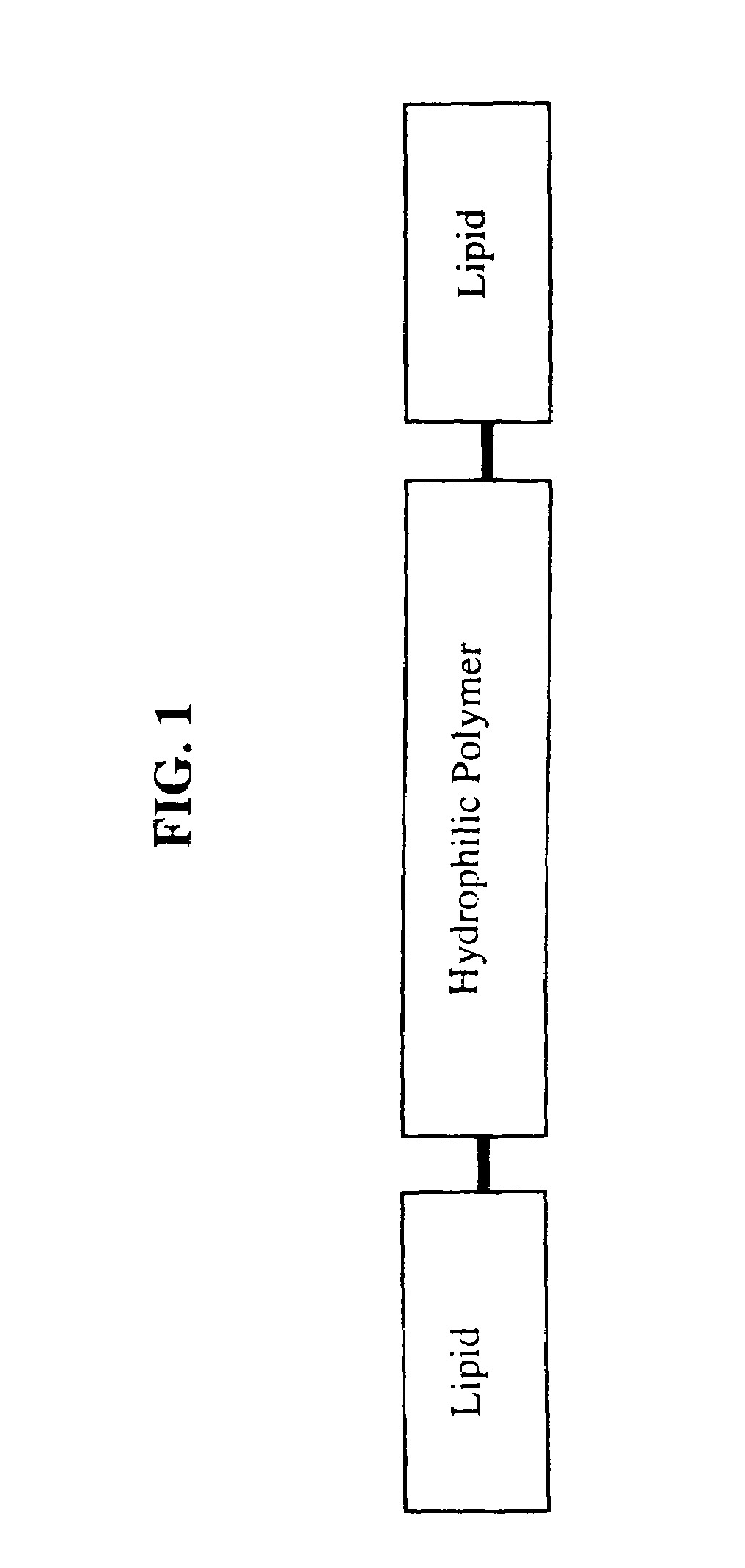
Disclosed is a new structural class of amphiphilic molecules which incorporate a hydrophilic material or polymer attached, at spatially distinct sites, to at least two hydrophobic residues. Certain of the amphiphilic molecules comprise a plurality of hydrophobic moieties. All such amphiphilic molecules have a common structural motif and, in contact with water, display surface activity and self-assemble into multimolecular aggregates and liquid crystalline phases. Also disclosed are enhanced stability liposomes that incorporate such amphiphilic molecules via unique interactions, and methods of using such formulations in a variety of applications including drug delivery, nutrition, bio-diagnostics, cosmetics, blood products and related applications.
Owner:NUTRIMED BIOTECH
Antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS7915223B2High efficacyStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsBiocideFatty acidMedicinal chemistry
A novel class of antimicrobial polymeric agents, which include a plurality of amino acid residues, such as positively charged amino acid residues, and at least one hydrophobic residue linking therebetween, such as an omega-amino-fatty acid residue, designed to exert antimicrobial activity while being stable, non-toxic and avoiding development of resistance thereto, and a process of preparing same, are disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions containing same and a method of treating medical conditions associated with pathological microorganisms, a medical device, an imaging probe and a food preservative utilizing same. Further disclosed are conjugates of an amino acid residue and a hydrophobic moiety residue and a process of preparing same.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
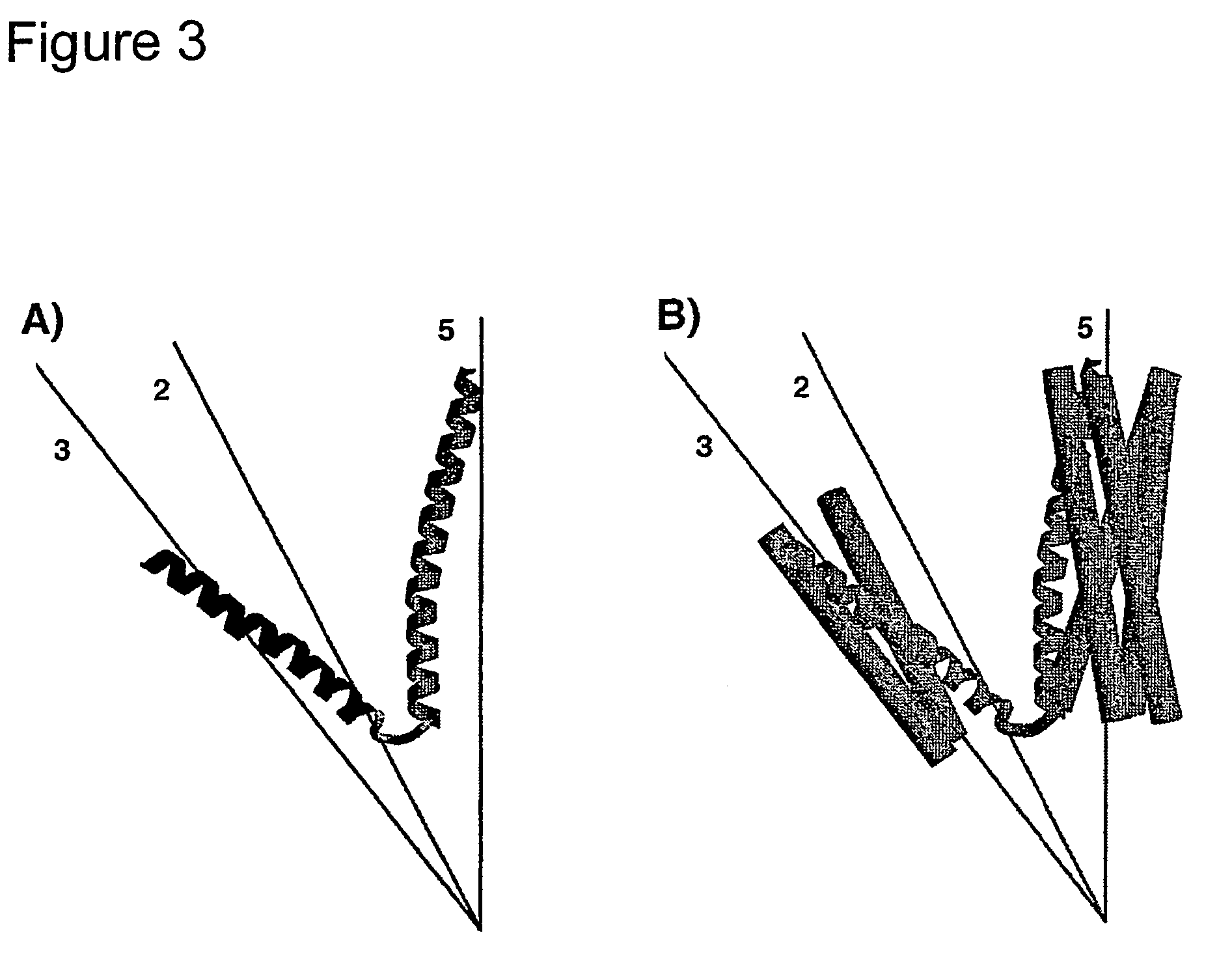
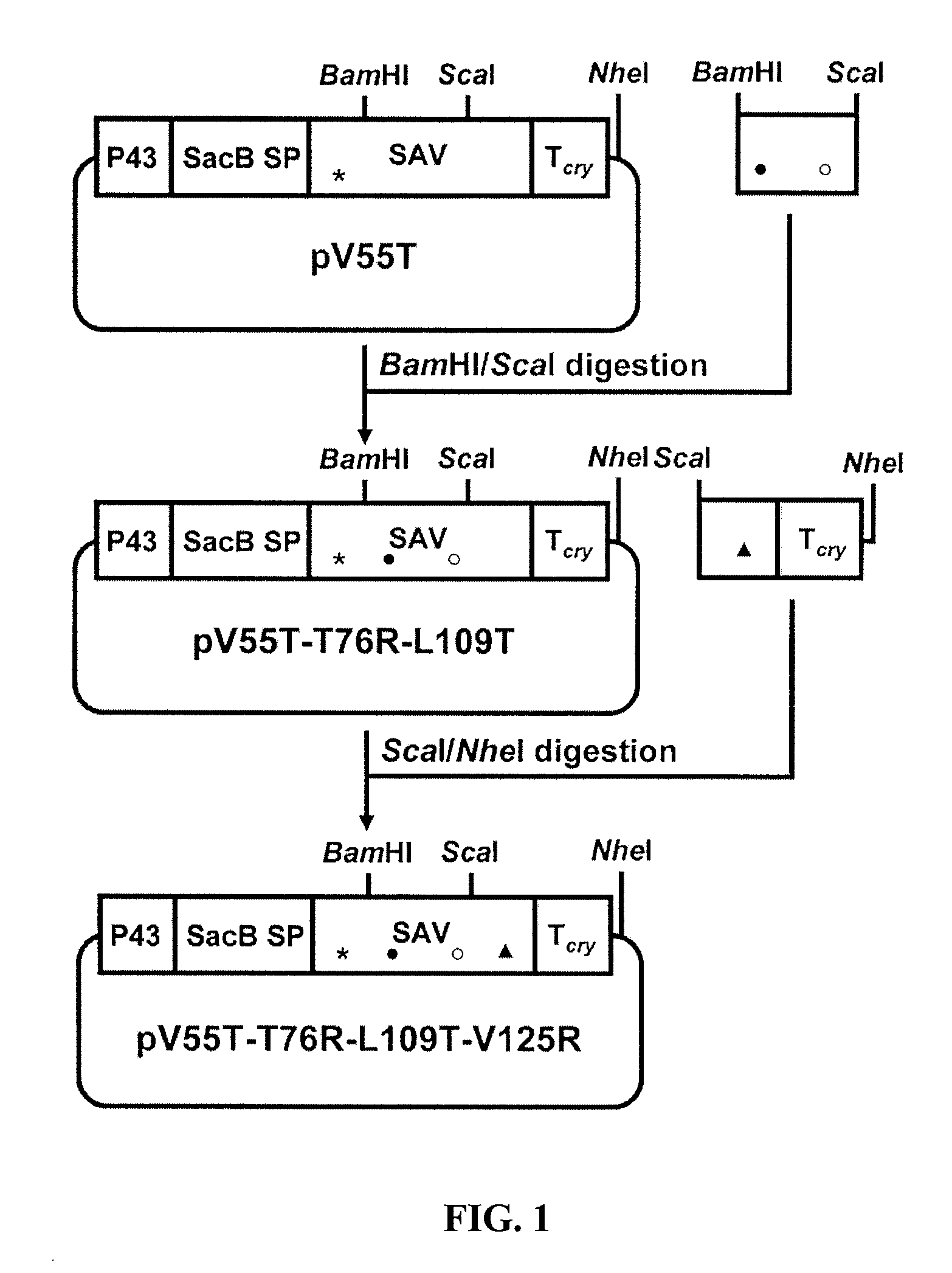
Monomeric streptavidin muteins
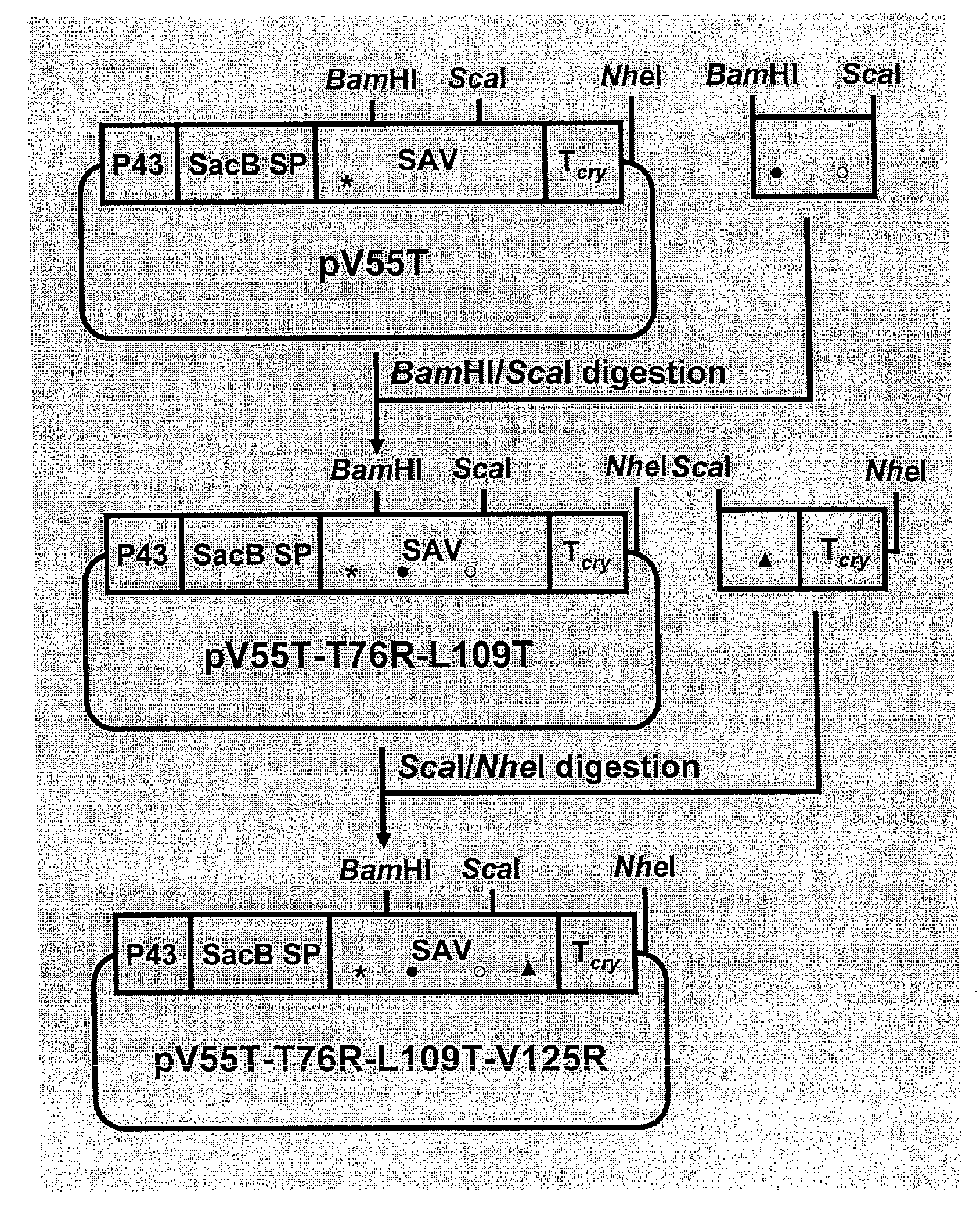
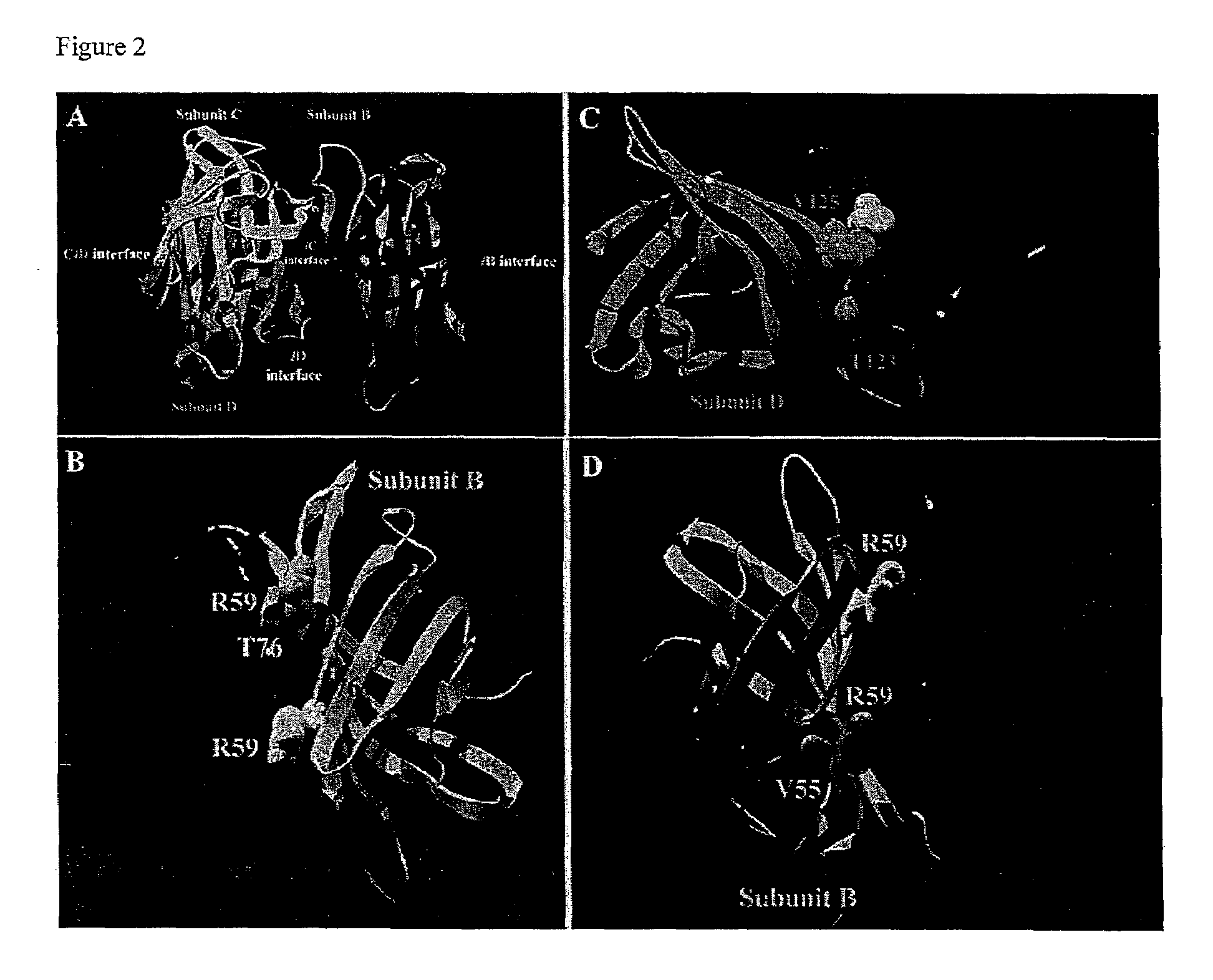
The invention includes a streptavidin mutein having at least one mutation chosen to cause one or more of steric hindrance, charge repulsion, or improvement of solubility by changing interfacial hydrophobic residues to less hydrophobic or hydrophilic residues. The mutein may exist in monomeric form even in the presence of biotin, and reversibly binds to biotin. The invention also includes polynucleotides encoding such muteins, expression systems and host cells for producing such muteins. The invention also includes a method of capturing biotinylated molecules using the muteins of the invention.
Owner:UTI LLP
Peptidic nanoparticles as drug delivery and antigen display systems
Described is a new type of nanoparticle using the concept of self-organization of a single continuous chain to form peptidic nanoparticles. In particular, nanoparticles of the invention consist of aggregates of a continuous chain comprising two peptidic oligomerization domains connected by a linker segment. Preferred are coiled-coil oligomerization domains with a contiguous pattern of hydrophobic residues spaced 3 and 4 residues apart. The invention provides a drug targeting and delivery system comprising a functionalized peptidic nanoparticle comprising ligands capable of binding a receptor and drugs, and a method of treating or diagnosing humans using such functionalized peptidic nanoparticles. The invention further provides an antigen display system to be used as efficient vaccines comprising a functionalized peptidic nanoparticle comprising an antigen, and a method of vaccinating humans or non-human animals using such functionalized peptidic nanoparticles. The invention also provides processes for making peptidic nanoparticles and functionalized peptidic nanoparticles, and monomeric building blocks suitable for forming such nanoparticles.
Owner:ALPHA O PEPTIDES
Monomeric streptavidin muteins
Owner:UTI LLP
Monomeric streptavidin muteins
ActiveUS20060246519A1Improve efficiencyEfficient developmentBacteriaSugar derivativesSolubilityPolynucleotide
The invention includes a streptavidin mutein having at least one mutation chosen to cause one or more of steric hindrance, charge repulsion, or improvement of solubility by changing interfacial hydrophobic residues to less hydrophobic or hydrophilic residues. The mutein may exist in monomeric form even in the presence of biotin, and reversibly binds to biotin. The invention also includes polynucleotides encoding such muteins, expression systems and host cells for producing such muteins. The invention also includes a method of capturing biotinylated molecules using the muteins of the invention.
Owner:UTI LLP
Dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide, dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113004432AClear structureStrong anti-aging effectOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsGlycosideSugar derivatives
The invention relates to dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide, a dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide derivative and a preparation method and application of the dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide and the dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide derivative, and the main technology is that the dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide contains 3-9 glycoside residues and has glucose residues at a non-reducing end; the derivative is obtained through substitution at the non-reducing end with hydrophobic residues . The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the two compounds. The invention has the beneficial effects that the dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide with the purity of more than or equal to 99% is prepared from the dendrobium officinale for the first time, the structure, the anti-aging activity effect and the immune regulation effect of the dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide are defined, and the dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide is found to be capable of well inhibiting collagenase and also has certain activity on TNF-alpha and IL-6; the method can be applied to the fields of medicine, food and daily necessity development.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS7879977B2Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from yeastsBinding siteADAMTS Proteins
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Monomeric streptavidin muteins
InactiveUS20080213801A1Improve efficiencyEfficient developmentDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsSolubilityBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention includes a streptavidin mutein having at least one mutation chosen to cause one or more of steric hindrance, charge repulsion, or improvement of solubility by changing interfacial hydrophobic residues to less hydrophobic or hydrophilic residues. The mutein may exist in monomeric form even in the presence of biotin, and reversibly binds to biotin. The invention also includes polynucleotides encoding such muteins, expression systems and host cells for producing such muteins. The invention also includes a method of capturing biotinylated molecules using the muteins of the invention.
Owner:UTI LLP
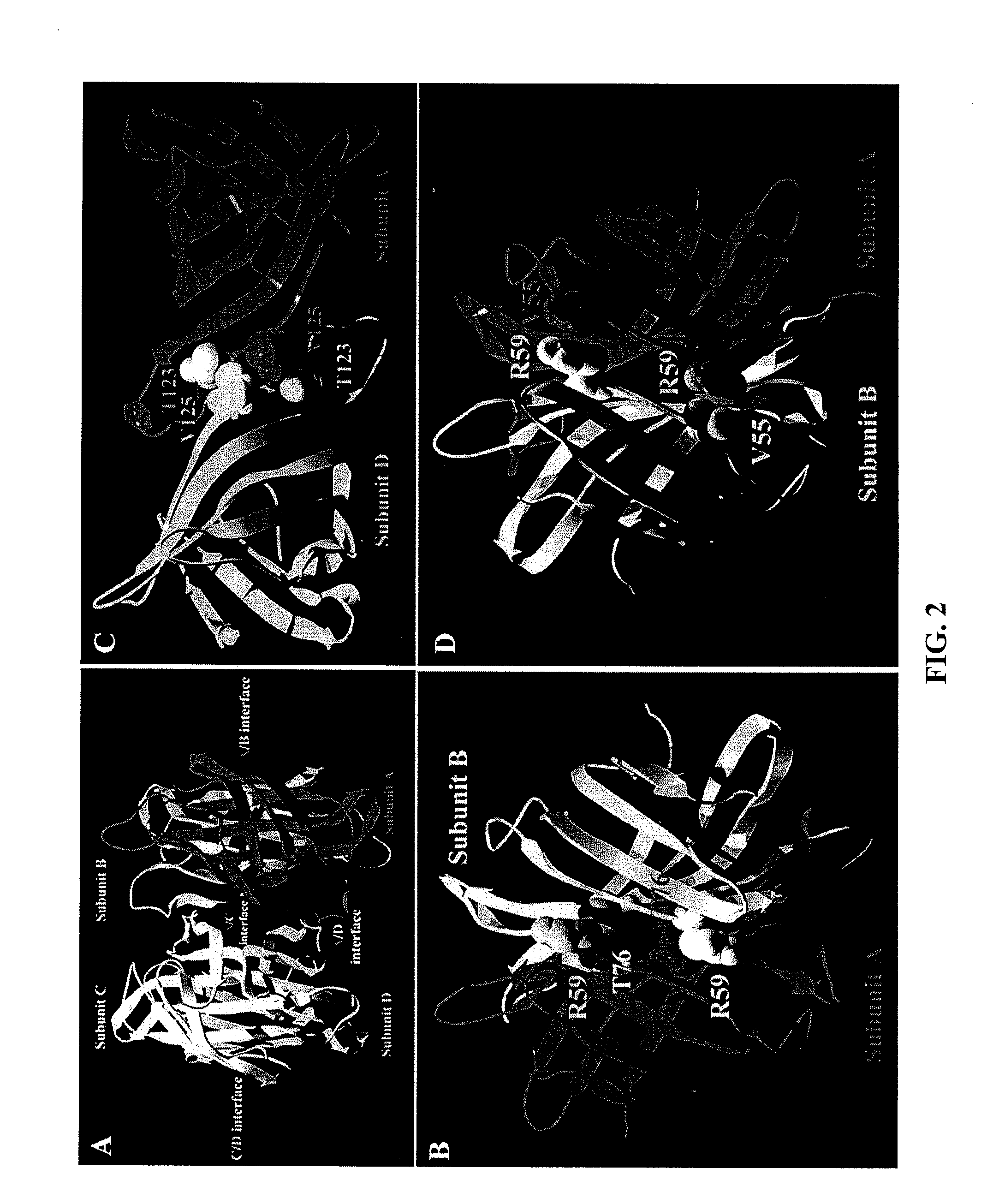
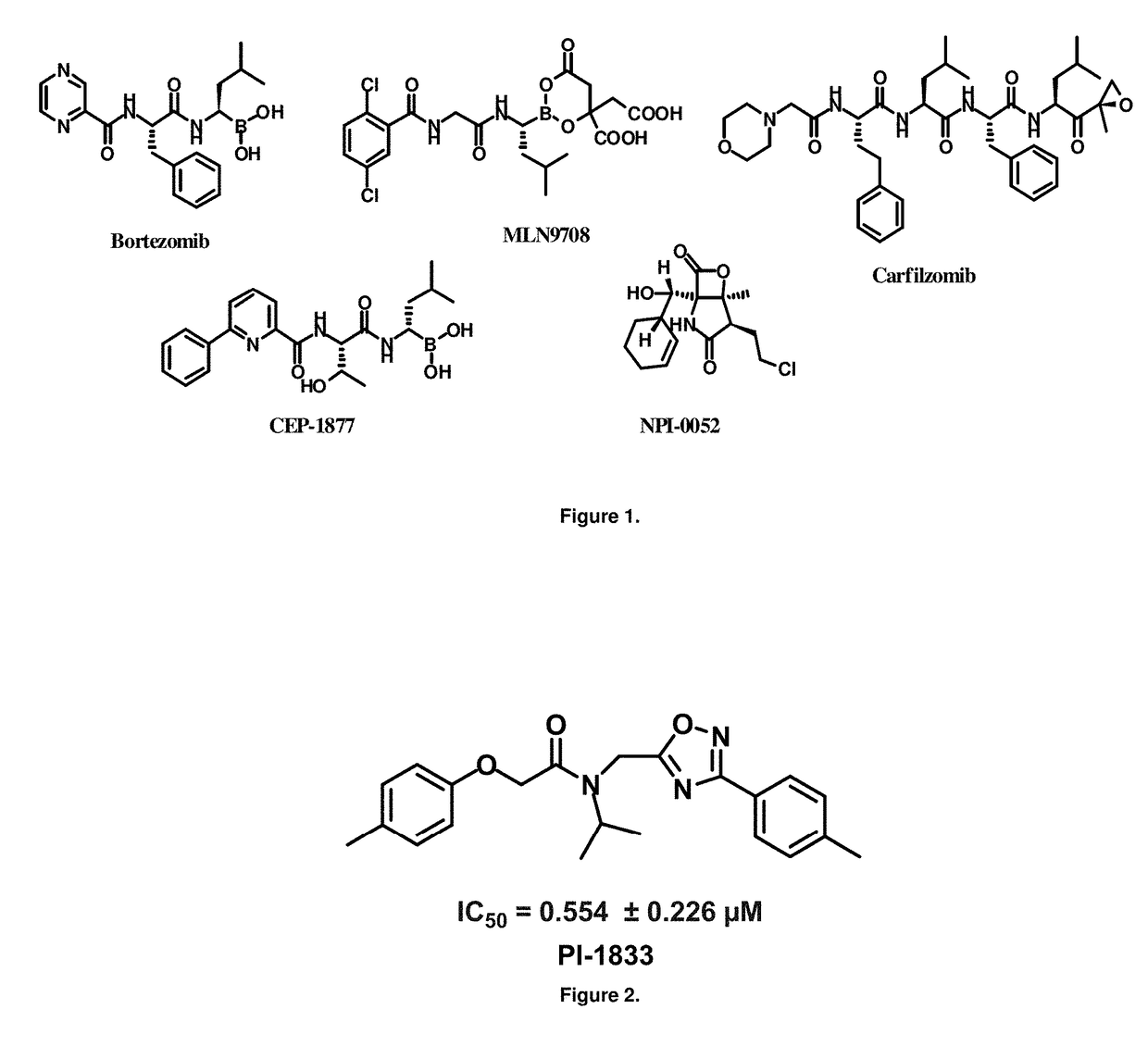
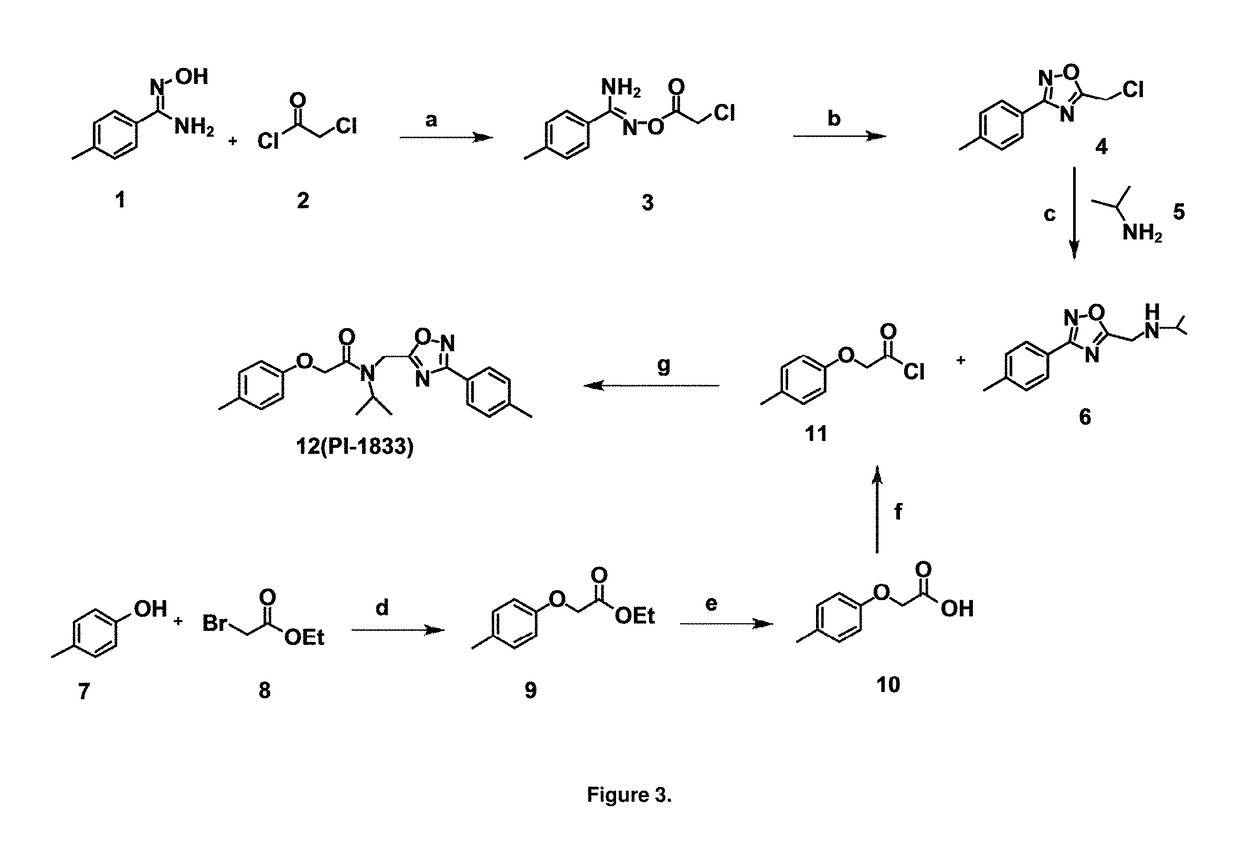
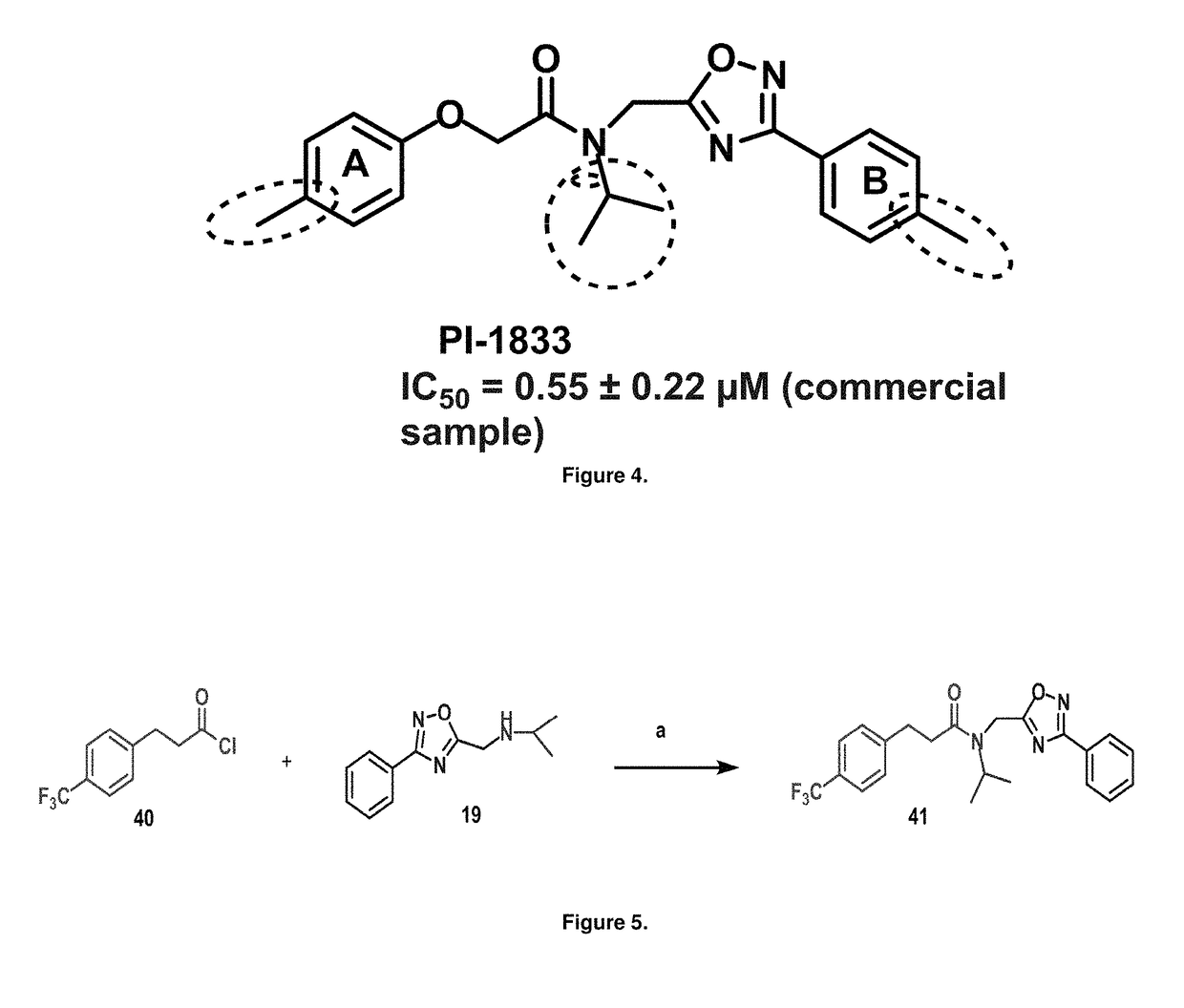
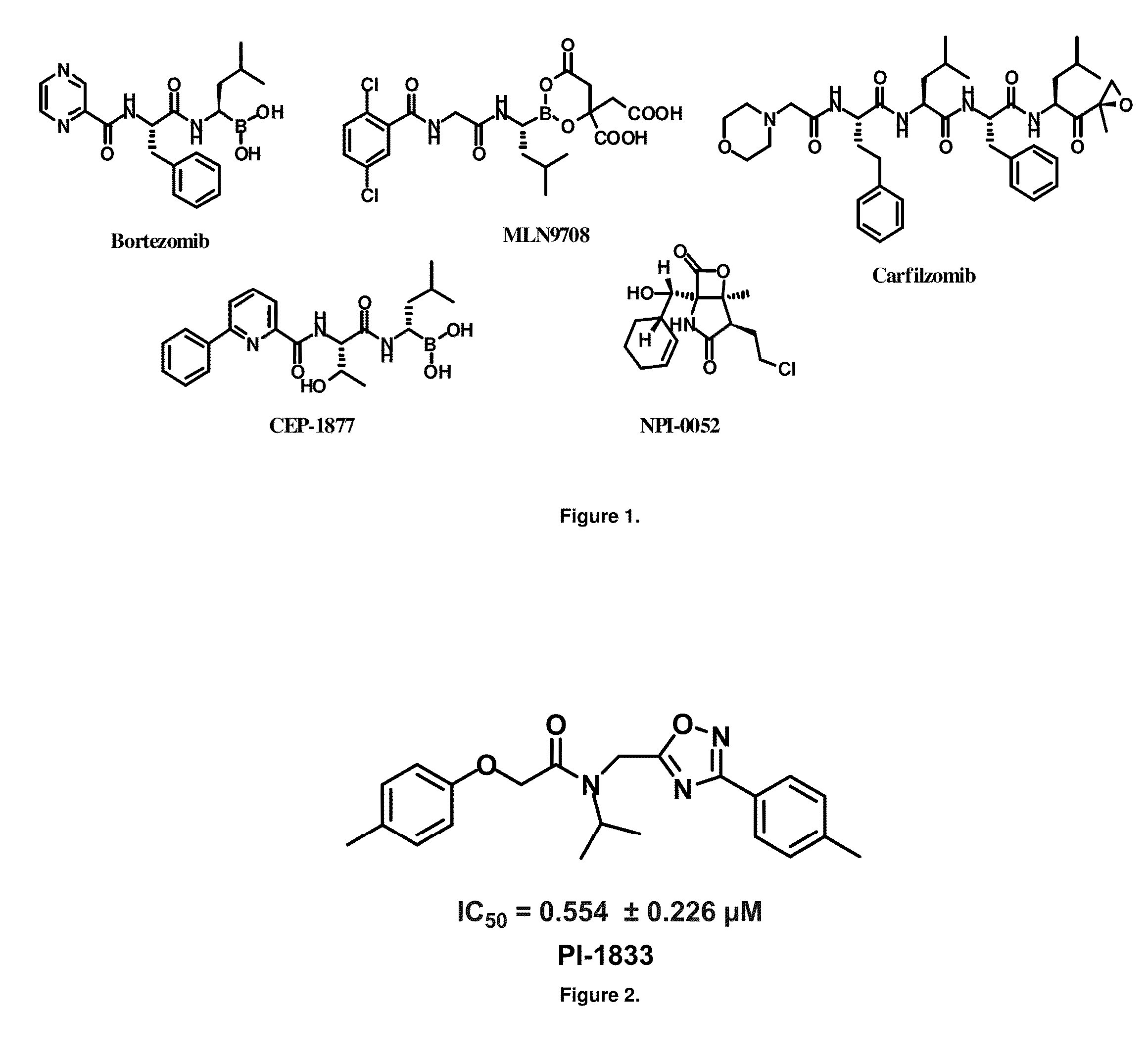
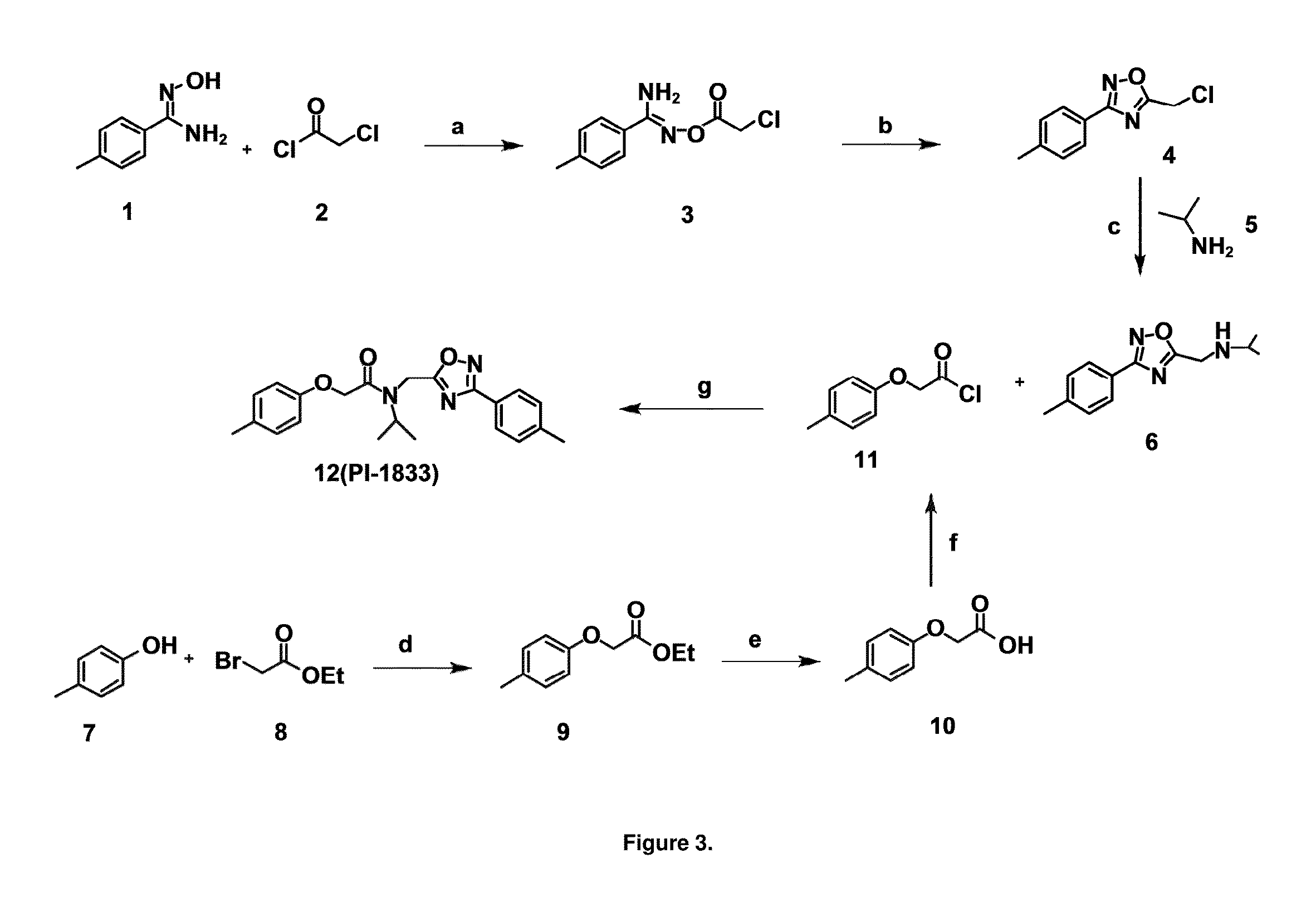
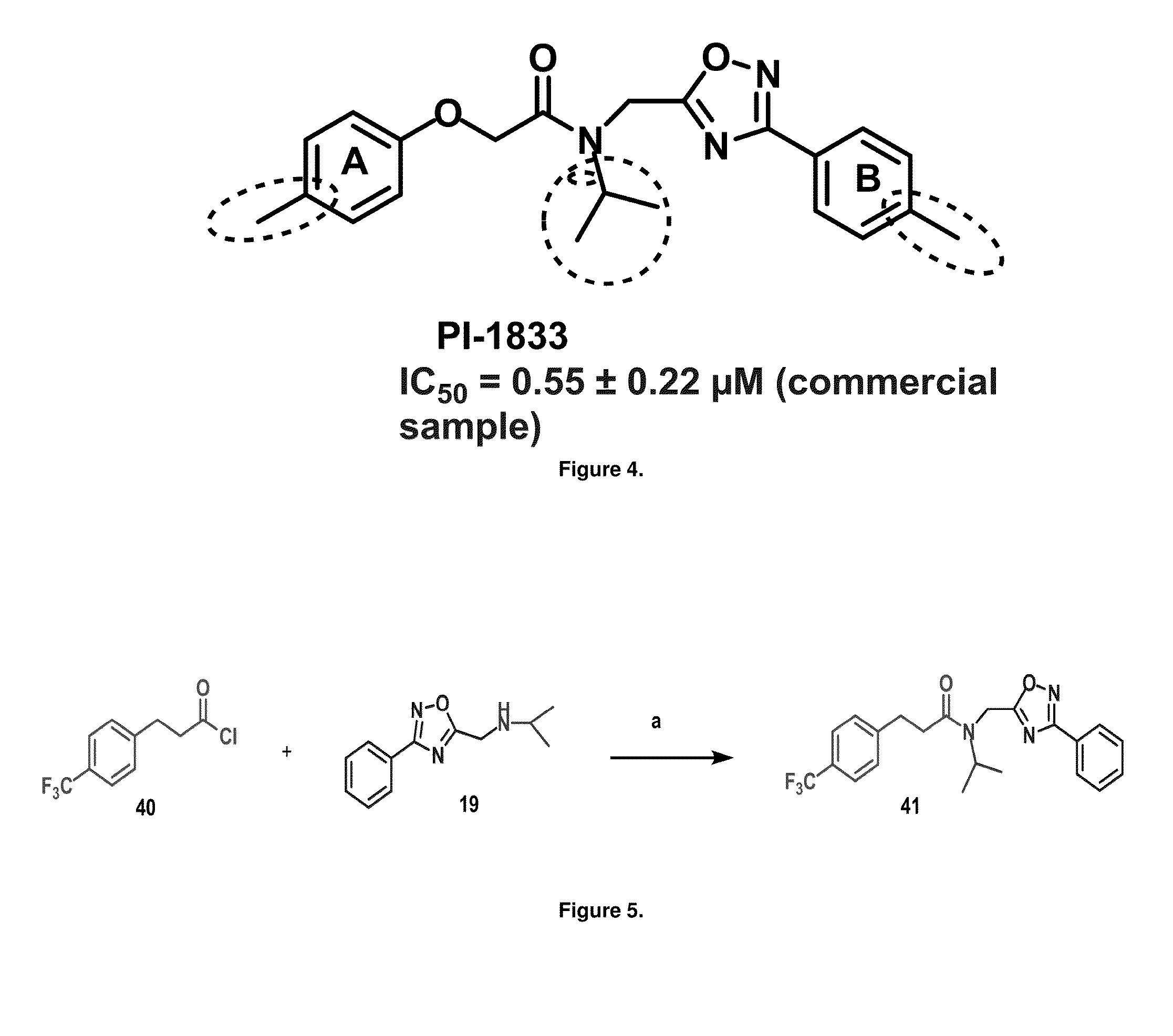
Proteasome chymotrypsin-like inhibition using PI-1833 analogs
Focused library synthesis and medicinal chemistry on an oxadiazole-isopropylamide core proteasome inhibitor provided the lead compound that strongly inhibits CT-L activity. Structure activity relationship studies indicate the amide moiety and two phenyl rings are sensitive toward synthetic modifications. Only para-substitution in the A-ring was important to maintain potent CT-L inhibitory activity. Hydrophobic residues in the A-ring's para-position and meta-pyridyl group at the B-ring significantly improved inhibition. The meta-pyridyl moiety improved cell permeability. The length of the aliphatic chain at the para position of the A-ring is critical with propyl yielding the most potent inhibitor, whereas shorter (i.e. ethyl, methyl or hydrogen) or longer (i.e. butyl, propyl and hexyl) chains demonstrating progressively less potency. Introduction of a stereogenic center next to the ether moiety (i.e. substitution of one of the hydrogens by methyl) demonstrated chiral discrimination in proteasome CT-L activity inhibition (the S-enantiomer was 35-40 fold more potent than the R-enantiomer).
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
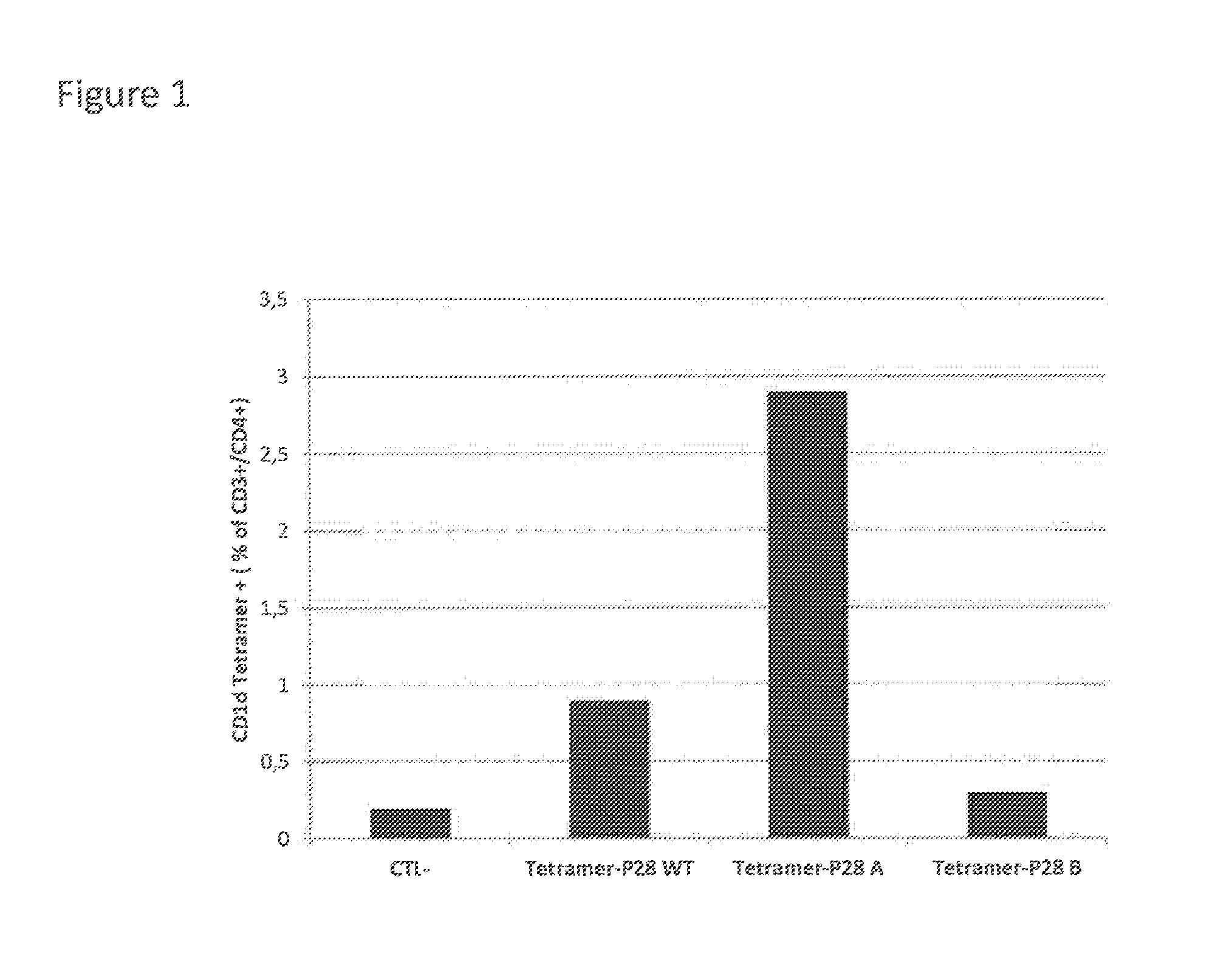
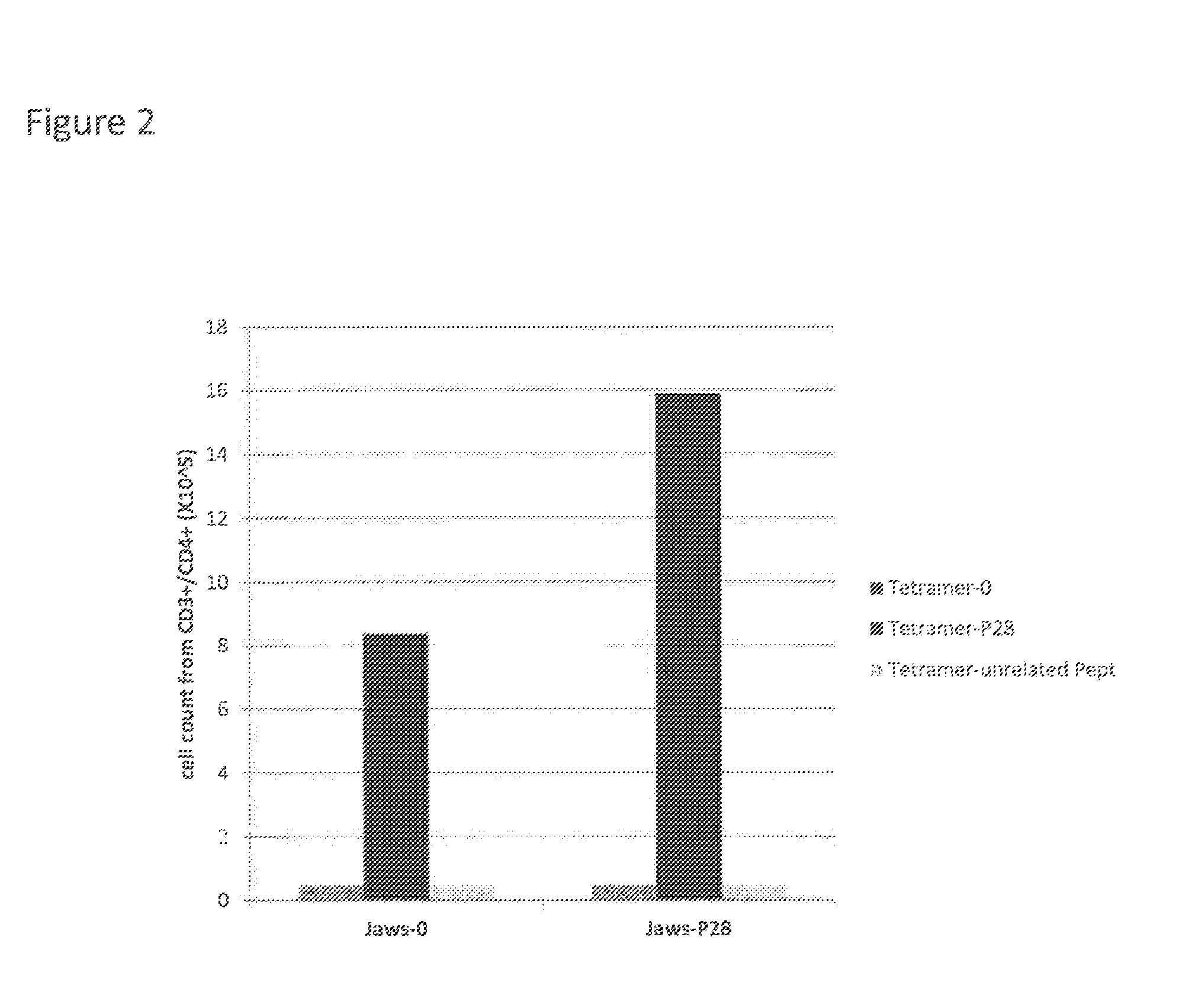
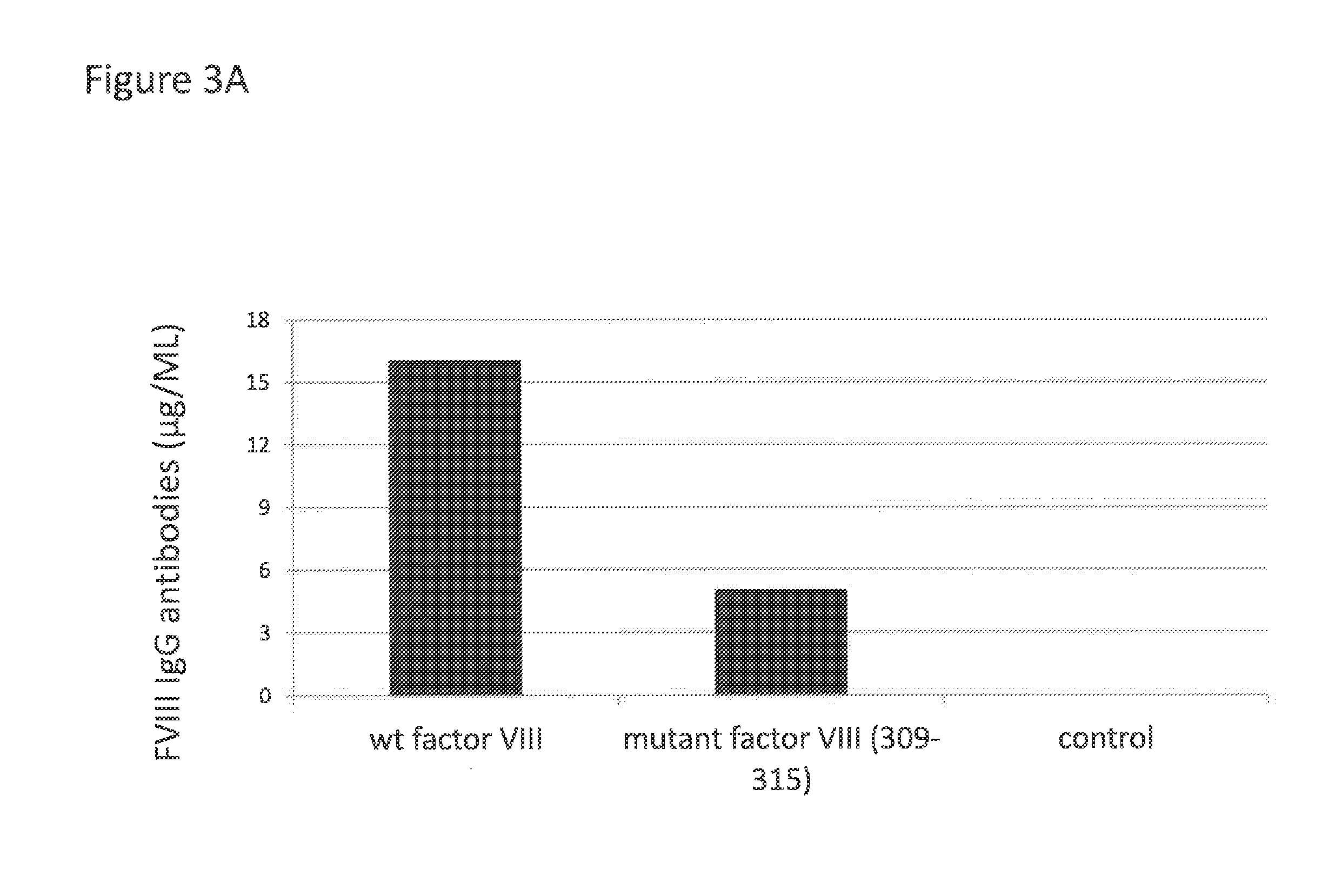
Coagulation factor viii with reduced immunogenicity
ActiveUS20150087593A1Limited degreeMinimal constraintFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeFactor ii
The invention describes factor VIII molecules with reduced capacity to elicit activation of NKT cells for use in the treatment of congenital and / or acquired haemophilia A and in bleeding disorders. Said factor VIII molecule is obtainable by:a. identification of at least one NKT cell epitope wherein said epitope comprises hydrophobic aminoacid residues in position P1 and / or P7b. modification of said epitope(s) by eliminating at least one hydrophobic aminoacid residues in position P1 and / or P7, substituting at least one hydrophobic aminoacid residue in position P1 and / or P7 with a non-hydrophobic residue, or adding a non-hydrophobic residue in position P1 and / or P7.
Owner:IMNATE SARL
Proteasome chymotrypsin-like inhibition using pi-1833 analogs
Focused library synthesis and medicinal chemistry on an oxadiazole-isopropylamide core proteasome inhibitor provided the lead compound that strongly inhibits CT-L activity. Structure activity relationship studies indicate the amide moiety and two phenyl rings are sensitive toward synthetic modifications. Only para-substitution in the A-ring was important to maintain potent CT-L inhibitory activity. Hydrophobic residues in the A-ring's para-position and meta-pyridyl group at the B-ring significantly improved inhibition. The meta-pyridyl moiety improved cell permeability. The length of the aliphatic chain at the para position of the A-ring is critical with propyl yielding the most potent inhibitor, whereas shorter (i.e. ethyl, methyl or hydrogen) or longer (i.e. butyl, propyl and hexyl) chains demonstrating progressively less potency. Introduction of a stereogenic center next to the ether moiety (i.e. substitution of one of the hydrogens by methyl) demonstrated chiral discrimination in proteasome CT-L activity inhibition (the S-enantiomer was 35-40 fold more potent than the R-enantiomer).
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Maltose functionalized nanometer composite material based on ion complementation type peptide self-assembly and preparation method and application of composite material
The invention discloses a maltose functionalized nanometer composite material based on ion complementation type peptide self-assembly and a preparation method and application of the composite material. By modifying self-assembly, on the surfaces of SiO2@Fe3O4, C@Fe3O4 and other nanometer materials, of the ion complementation type peptide with alternating hydrophilic and hydrophobic residues on maltose, the stable maltose functionalized nanometer composite material is obtained. The composite material can selectively enrich glycopeptides in standard glycoprotein and biological sample enzymolysisliquid, the enrichment efficiency is high, the selectivity is high, the detection limit is low, the performance is stable, and the composite material can be reused. The composite material is simple in preparation method, mild in condition, green, free of toxin and capable of being used for one-step surface functionalization of various nanometer enrichment materials.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Bidentate motif and methods of use
InactiveUS20070219117A1Inhibit bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementThreonineTyrosine
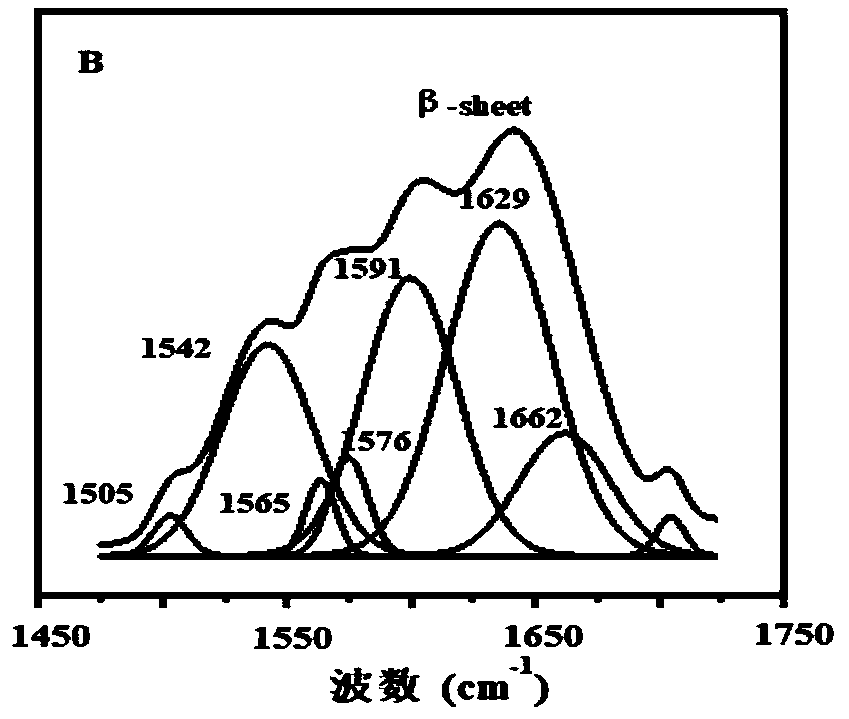
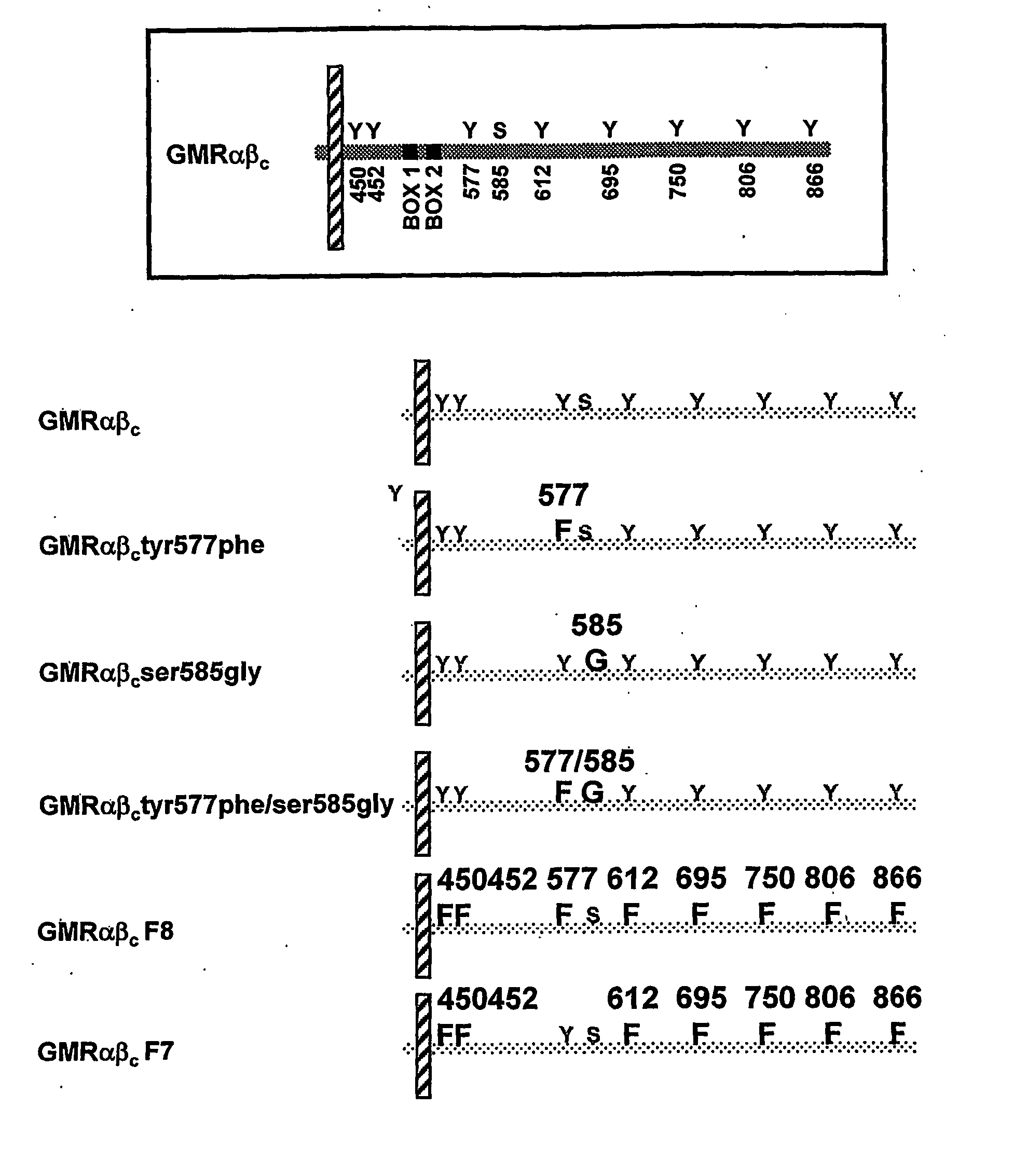
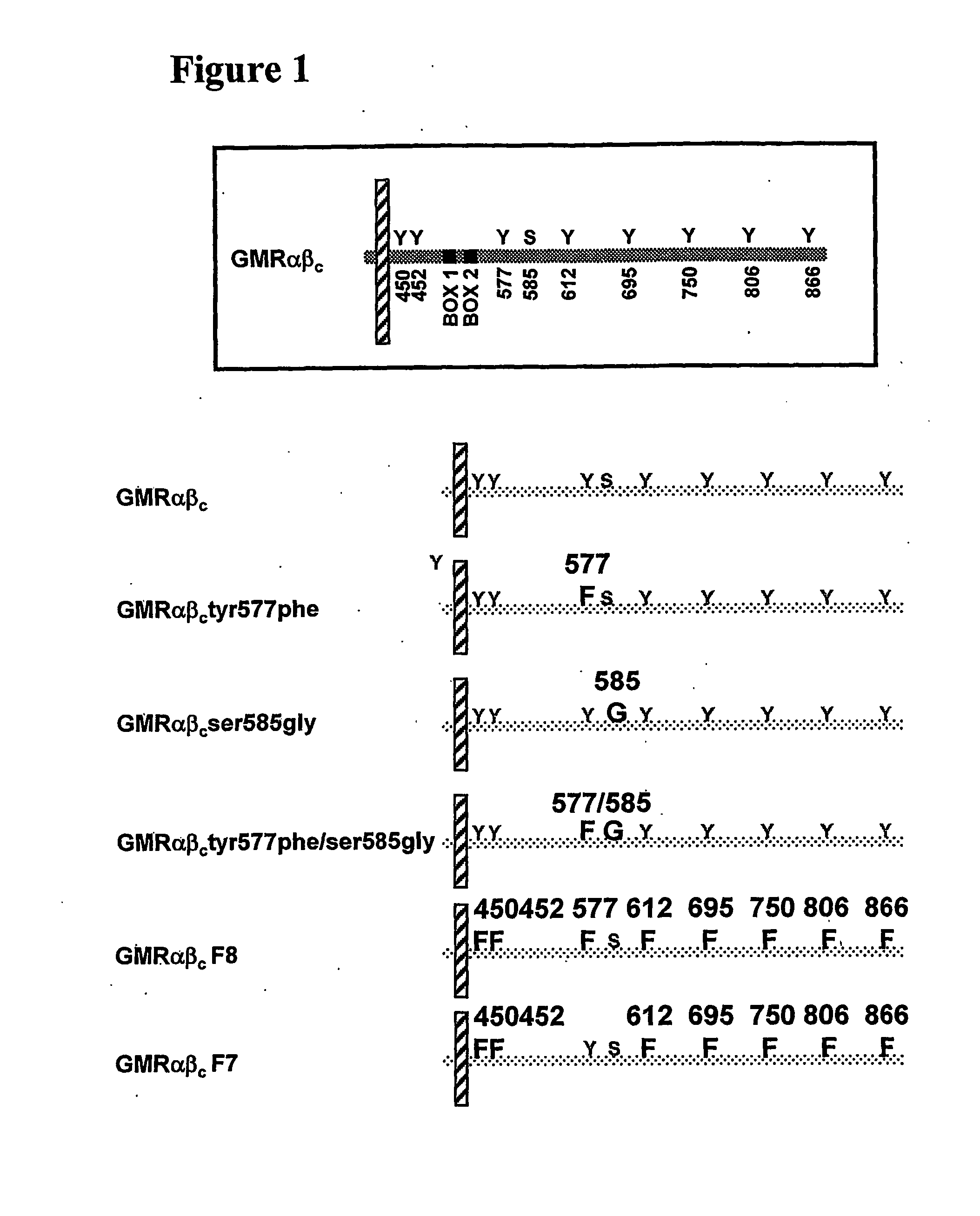
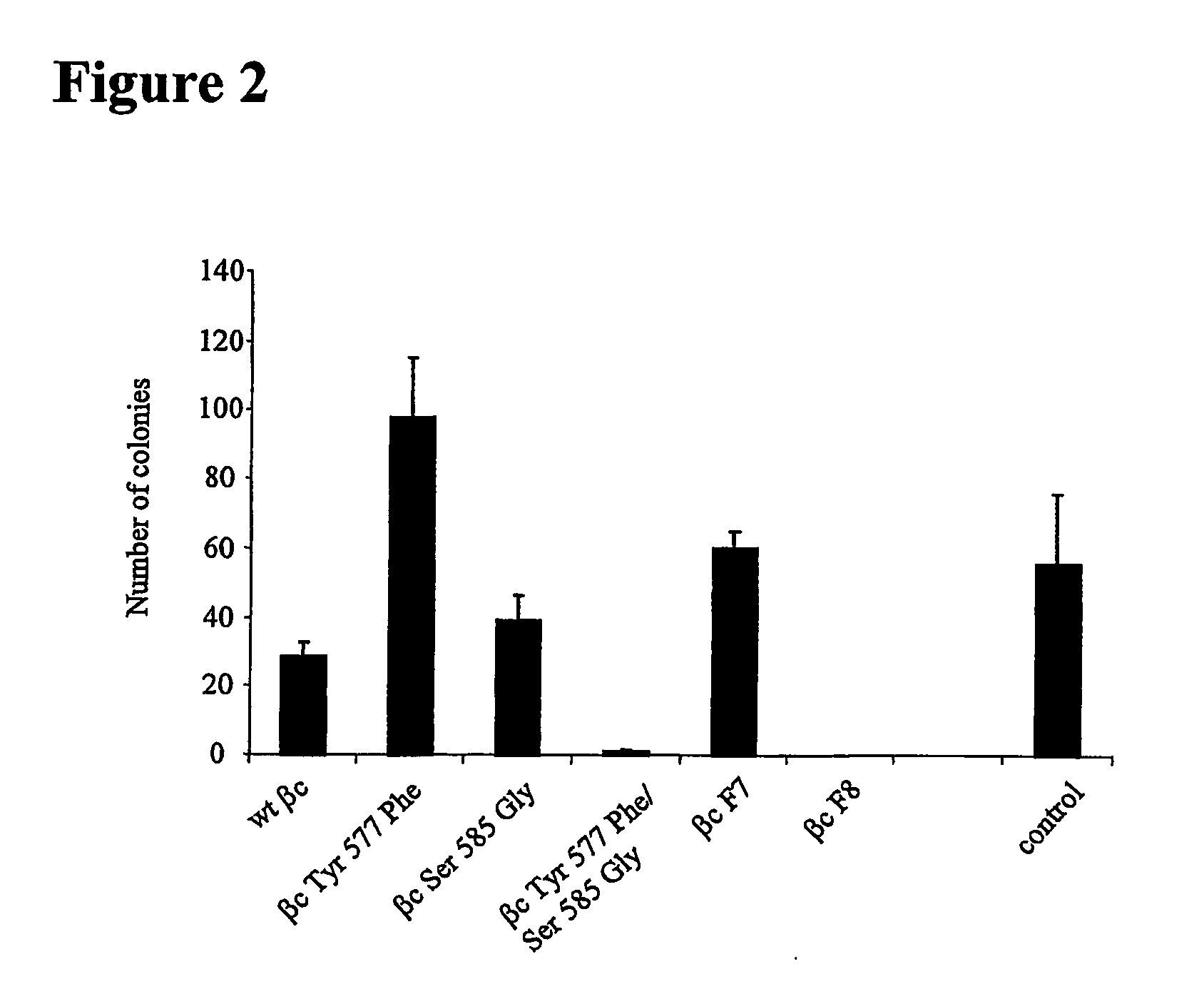
The present invention relates to a novel bidentate motif that is composed of two adjacent residues of tyrosine and serine which have been found to be involved in the binding of crucial cytoplasmic proteins which are involved in cell signalling pathways. In some cases, the cytoplasmic proteins are ubiquitous proteins involved in cell signalling pathways that may include mitogenesis, transformation and survival. The bidentate motif may have a sequence alignment (SEQ ID NO: 71)N-X-X-Y- (X) 1-13-[R / K / H / Q]-[X / Ψ] 2-3-S / T-X-P;(SEQ ID NO: 72)Y- (X) 1-16-[R / K / H / Q]-[X / Ψ] 2-3-S / T-X-P;or(SEQ ID NO: 73)N-X-X-Y-[X]1-30-[R / K / Q / H]-[X]1-4-[S / T]-X-pwherein X is any residue, Y is tyrosine, S / T is serine or threonine and Ψ is a hydrophobic residue or an equivalent thereof. Preferably the residues are Tyr577 and Ser585 of the common βc of the GM-CSF / IL-5 / IL-3 receptor.
Owner:MEDVET SCI
A modification method of natural anticancer peptide
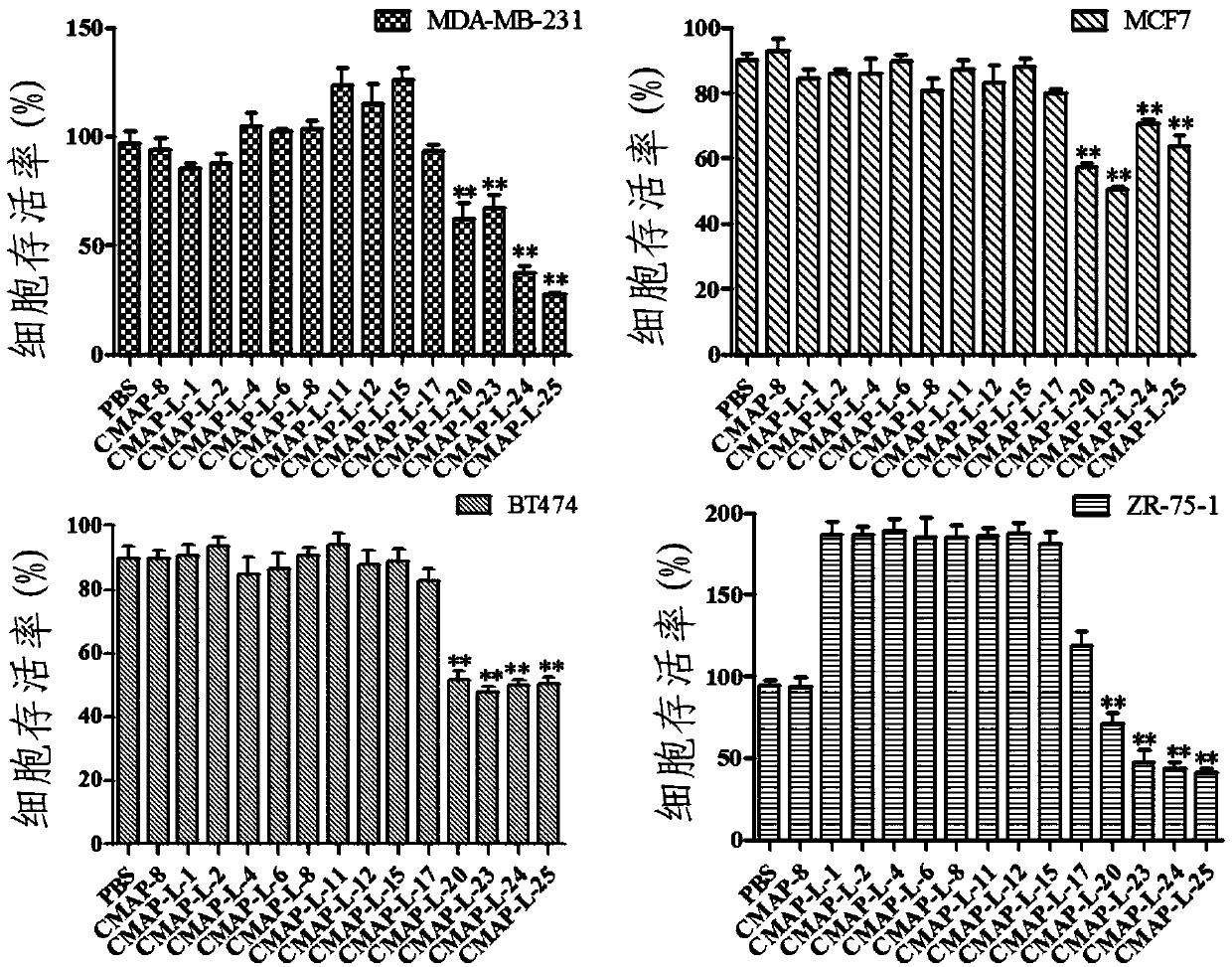
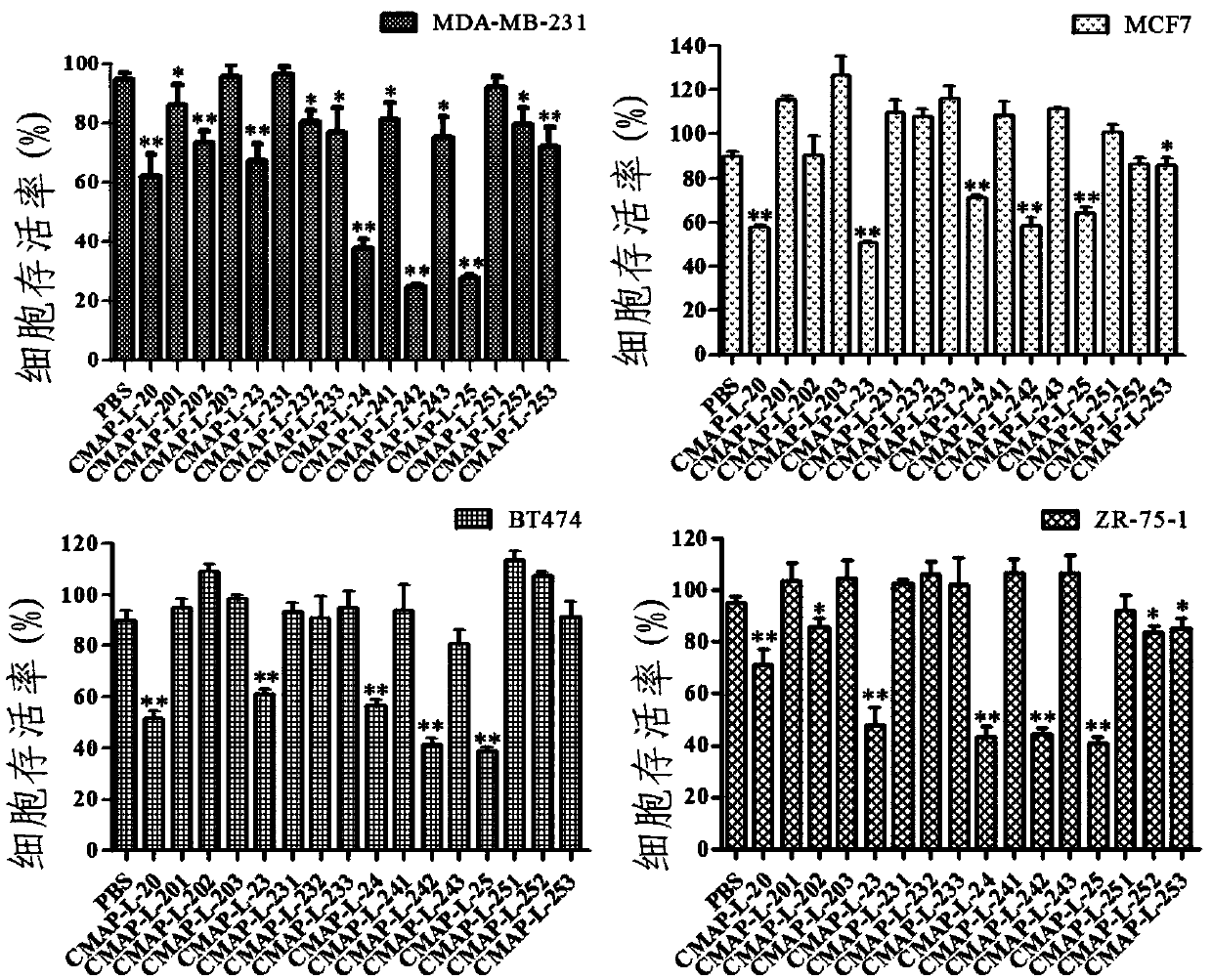
The invention relates to the biotechnology field, specifically relates to an improvement method of natural anticancer peptide. The method comprises the design improvements at two stages by use of natural polypeptide as a template; in the design improvement at the first stage, a series of polypeptide derivatives are obtained by changing the percentage of polypeptide net charge and the hydrophobic residue in the polypeptide; in the design improvement at the second stage, the variety and the number of the screened polypeptide amino acid residue are unchanged, only the primary amino acid sequence is changed, so that the alpha-helix in the high-level structure is located at different positions or disappeared to obtain the series of polypeptide again. The anticancer peptide prepared by use of the method disclosed by the invention is not only high in anticancer property, but also small in toxicity and safer to the human body.
Owner:贵州源熙生物研发有限公司
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor
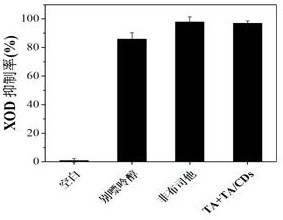
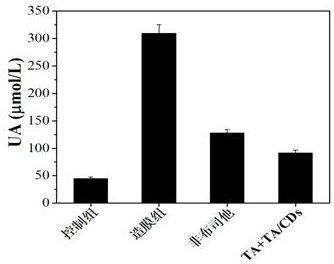
PendingCN114869910AEnhanced inhibitory effectLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic active ingredientsXanthineOxidative enzyme
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, in particular to a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. A tannic acid carbon dot and tannic acid mixture which has good water solubility, low toxicity and biocompatibility and has a xanthine oxidase inhibition effect is used as a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, and the tannic acid carbon dot and the tannic acid are combined with hydrophobic residues of xanthine oxidase to form hydrogen bonds or generate a hydrophobic effect; and when being inserted into hydrophobic gaps of the xanthine oxidase, the xanthine oxidase occupies a catalytic activity center, and competes with a substrate xanthine to be combined with an active site of the xanthine oxidase, so that the substrate is prevented from entering, and the activity of the xanthine oxidase is reduced. In-vitro and in-vivo animal experiment results show that the xanthine oxidase inhibitor disclosed by the invention can be equivalent to hyperuricemia drugs in the prior art, is low in toxicity, and can be applied to health-care foods or drugs for preventing and treating hyperuricemia.
Owner:云南伦扬科技有限公司
Identification of broadly reactive DR restricted epitopes
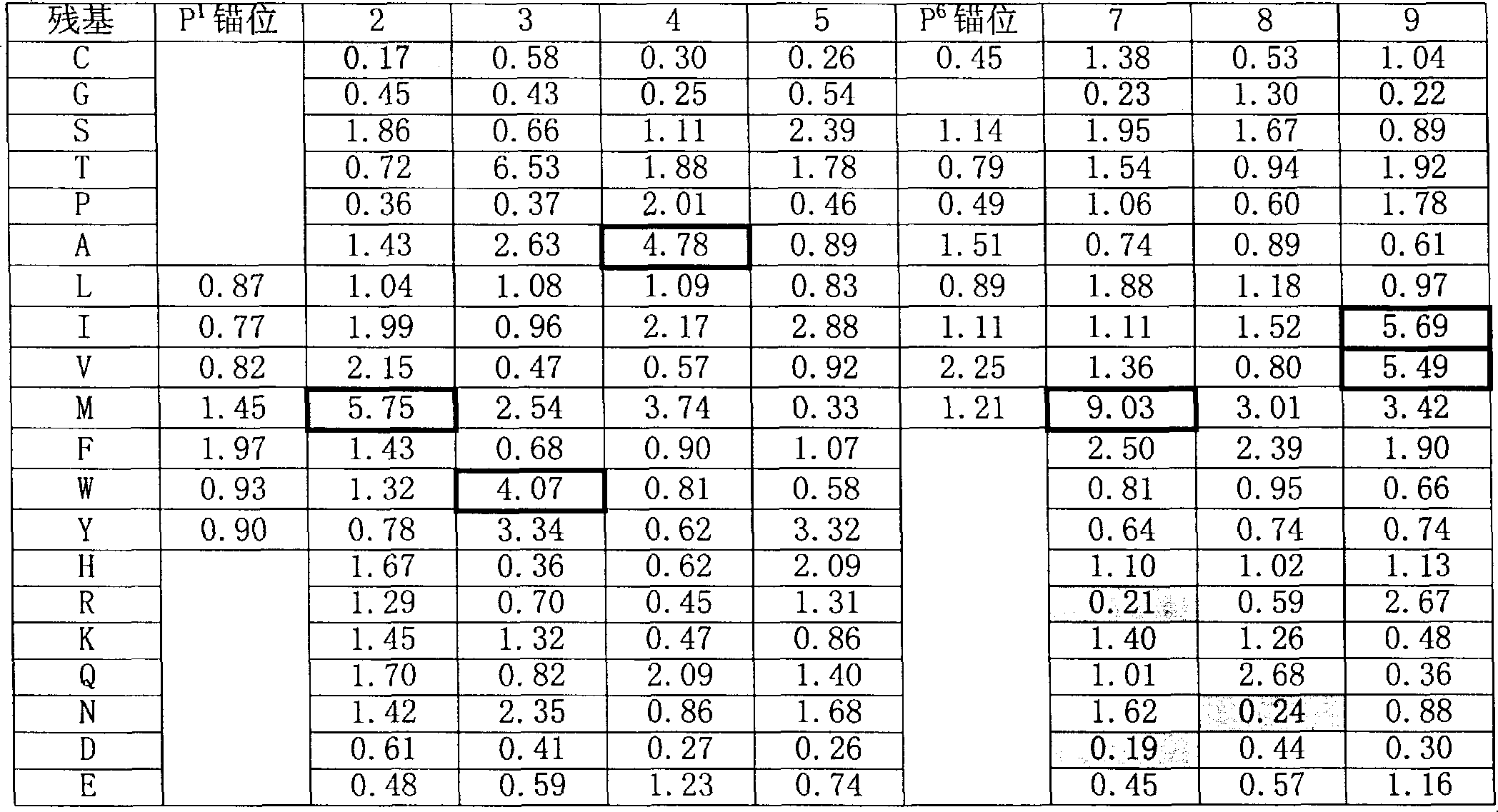
The present invention is based on peptide binding specificities of HLA DR4w4, DR1 and DR7. Peptides binding to these DR molecules have a motif characterized by a large aromatic or hydrophobic residue in position 1 (Y, F, W, L, I, V, M) and a small, non charged residue in position 6 (S, T, C, A, P, V, I, L, M). In addition, allele-specific secondary effects and secondary anchors are defined, and these results were utilized to derive allele specific algorithms. By the combined use of such algorithms peptides capable of degenerate DR1, 4, 7 binding were identified.
Owner:埃皮缪纳股份有限公司
Parathyroid hormone analogues for the treatment of osteoporosis
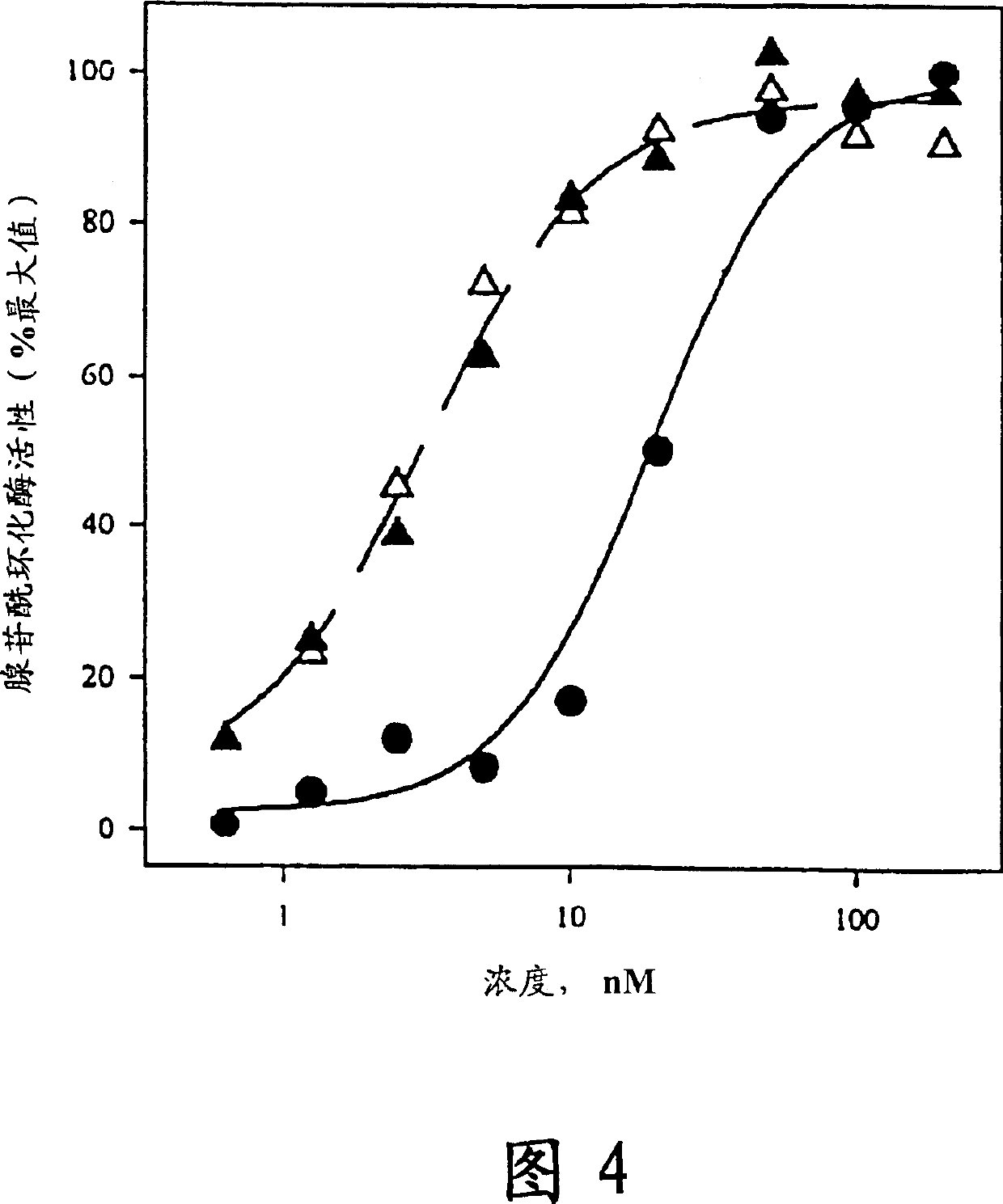
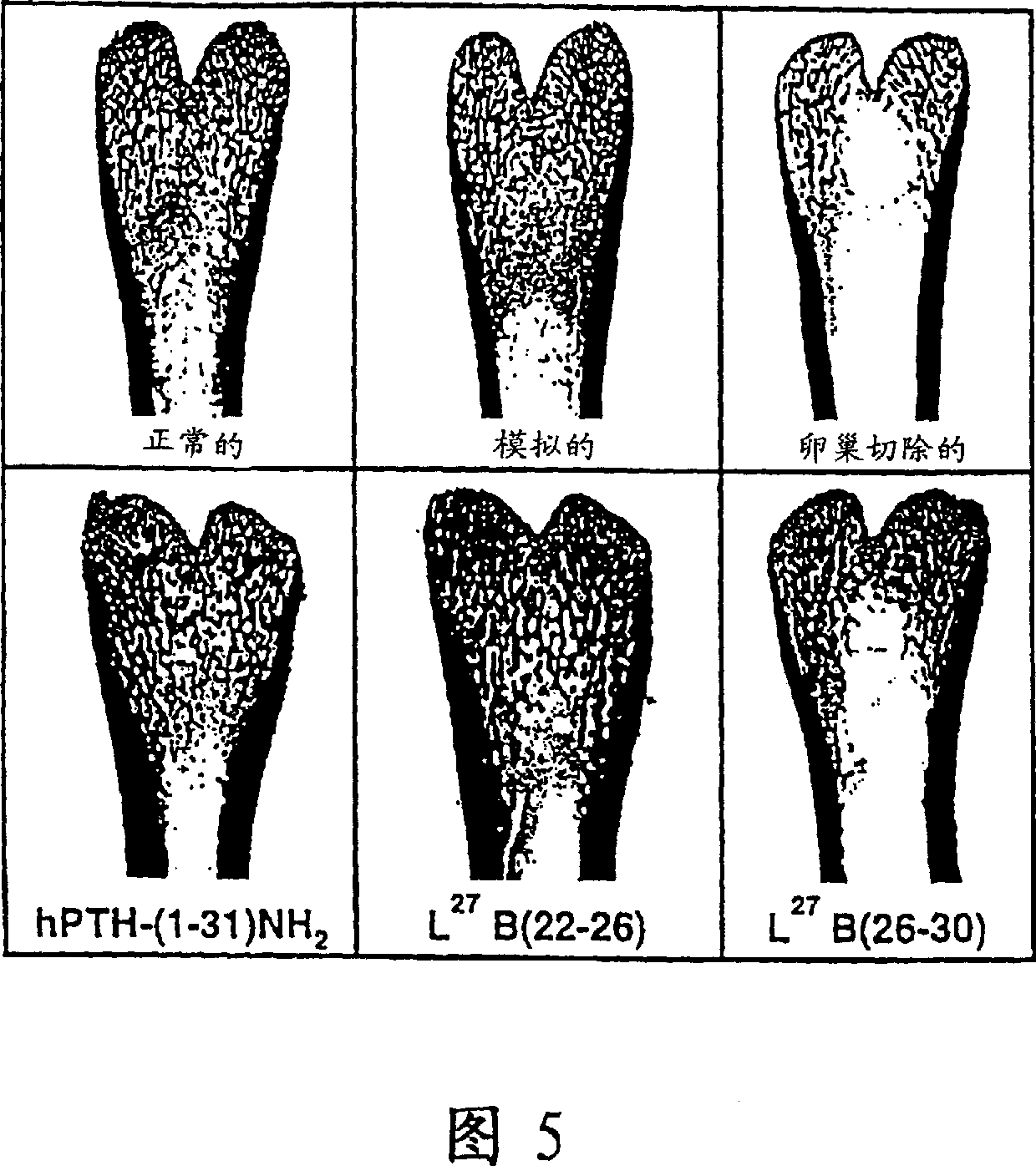
This invention describes analogues of human parathyroid hormone which have increased activities in bone restoration, and increased bioavailabilities. The peptides described are derivatives of hPTH-(1-31) which are cyclized for example, by formation of Lactams between either Glu<22> and Lys<26> or Lys<26> and Asp<30>. In addition, the natural Lys<27> may be substituted by either a Leu or other hydrophobic residues, such as Ile, norleucine, Met, Val, Ala, Trp, or Phe. Typically, these analogues have enhanced abilities to stimulate adenylyl cyclase in rat osteosarcoma cells, and show increased activities in bone restoration, using the ovariectomized rat model. The analogues also show enhanced activities and bioavailabilities, as demonstrated by their hypotensive effects in the rat. An assay which correlates hypotensive activity with osteogenic activity is also described.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Engineering monoclonal antibodies to improve stability and production titer
Provided herein are methods directed to engineering monoclonal antibodies and antibody variants to improve stability and their production in culture. Specifically, the monoclonal antibodies can be engineered at heavy chain residue 56 (AHo numbering) to a glycine, alanine, or serine, and / or engineered at position 80 (AHo) to be a hydrophobic residue such as alanine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, leucine, methionine, or valine.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Ultrafine iron oxide nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging T1 contrast agent
PendingCN113924129AGuaranteed uniformityDistribute quicklyMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismActive agentGadolinium-based Contrast Agent
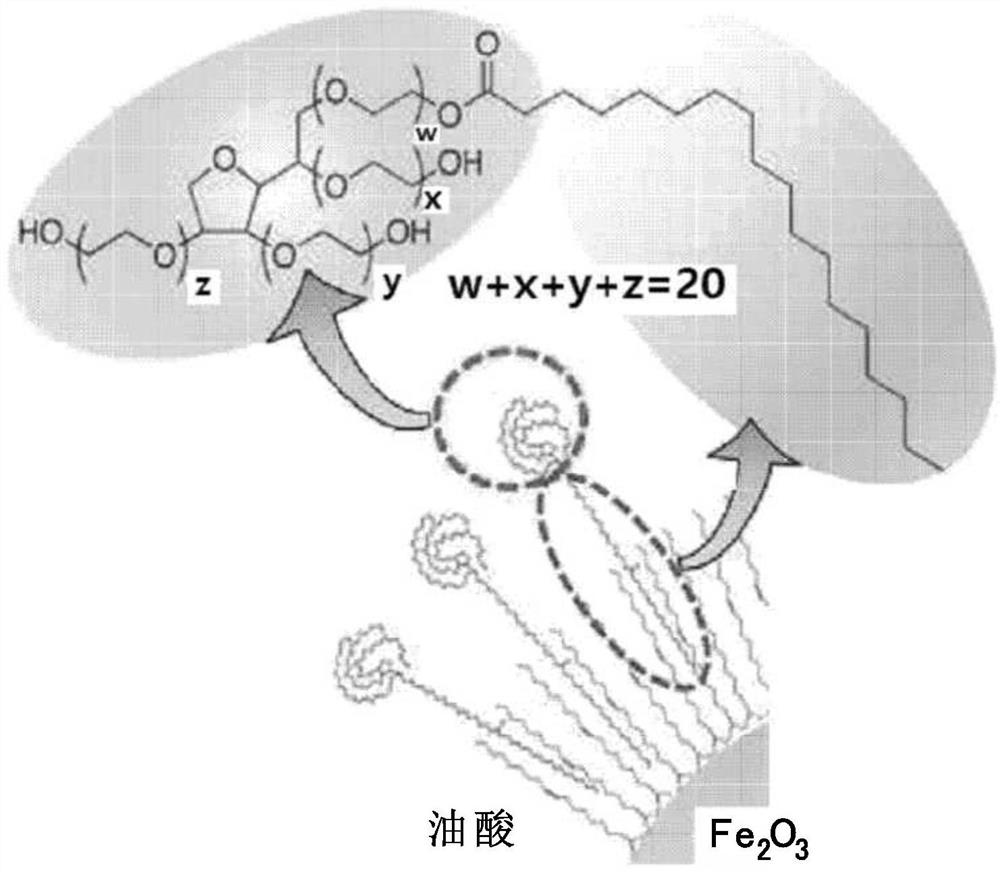
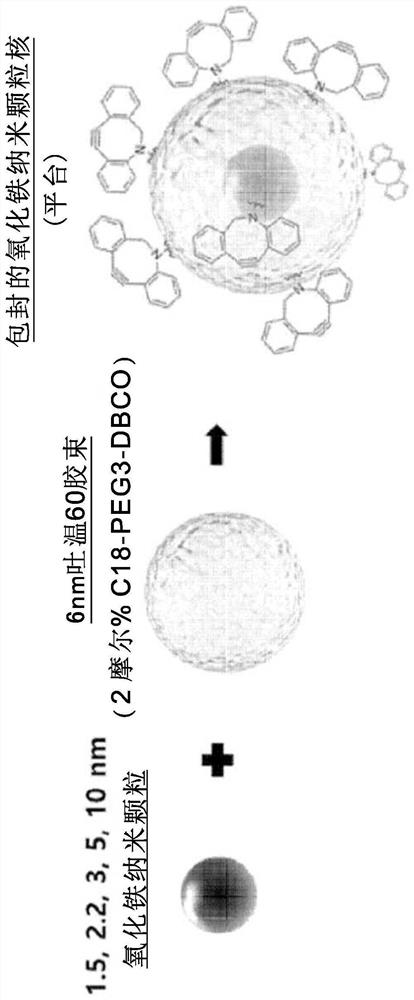
Provided is a magnetic resonance imaging T1 contrast agent comprising: a fine iron oxide nanoparticle core; and a micelle for encapsulating the core particles, wherein the micelle comprises a non-ionic surfactant containing: a hydrophilic residue containing at least two chains; and a hydrophobic residue consisting of at least one C10-C30 hydrocarbon chain. The T1 contrast agent of the present invention is a novel fine iron oxide nanoparticle-based T1 contrast agent that can replace conventional gadolinium-based T1 contrast agents, is not harmful to the human body, and exhibits a uniform contrast effect due to rapid distribution in blood and the uniform size. In addition, the T1 contrast agent enables image observation for at least 1 hour, or up to a maximum of 2 hours and is excreted through the kidneys and liver, and thus can address the problems of conventional gadolinium-based contrast agents.
Owner:セラベスト カンパニーリミテッド
A kind of dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide, dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide derivative and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN113004432BClear structureImprove anti-aging effectOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyGlycoside
The invention relates to a Dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide, a Dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The main technology is that the Dendrobium officinale oligosaccharide contains 3-9 glycoside residues and has glucose at the non-reducing end residue; its derivatives are obtained by substituting hydrophobic residues at the non-reducing end, and the preparation method and application of the two are also provided. The beneficial effects of the present invention are as follows: for the first time, Dendrobium candidum oligosaccharides with a purity ≥ 99% were prepared from Dendrobium candidum, and the structure, anti-aging activity and immune regulation of Dendrobium candidum oligosaccharides were clarified, and it was found that it can well inhibit Collagenase also has certain activity on TNF-α and IL-6; it can be used in medicine, food, daily necessities development and other fields.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com