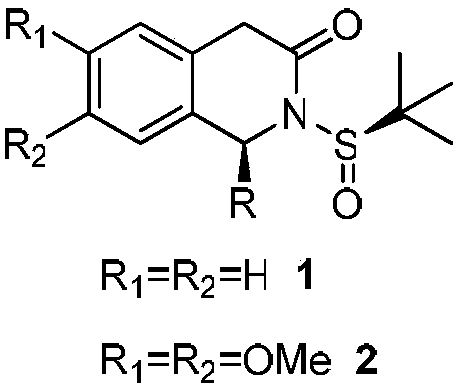
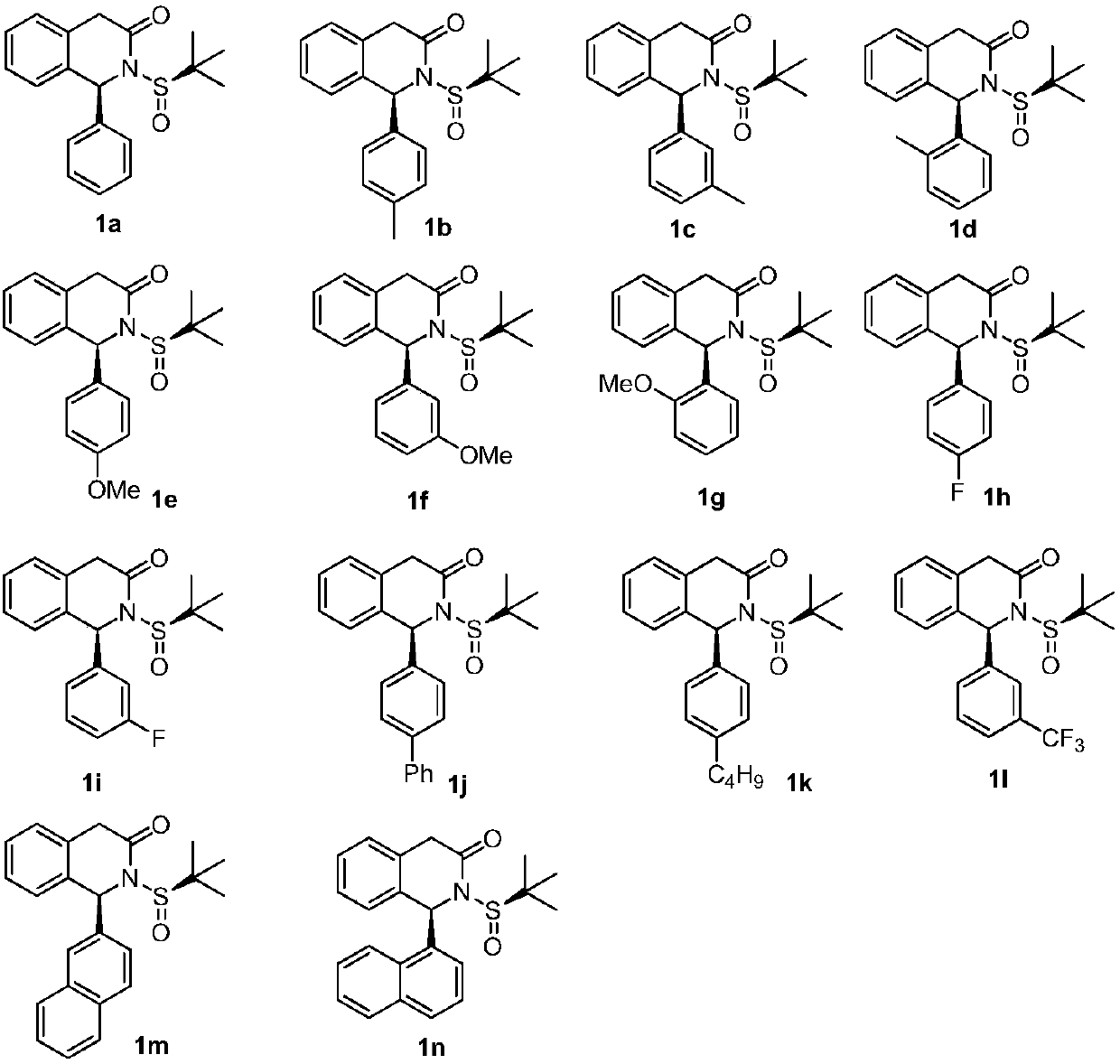
Patents
Literature
75 results about "Structure–activity relationship" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The structure–activity relationship (SAR) is the relationship between the chemical structure of a molecule and its biological activity. This idea was first presented by Crum-Brown and Fraser in 1865. The analysis of SAR enables the determination of the chemical group responsible for evoking a target biological effect in the organism. This allows modification of the effect or the potency of a bioactive compound (typically a drug) by changing its chemical structure. Medicinal chemists use the techniques of chemical synthesis to insert new chemical groups into the biomedical compound and test the modifications for their biological effects.
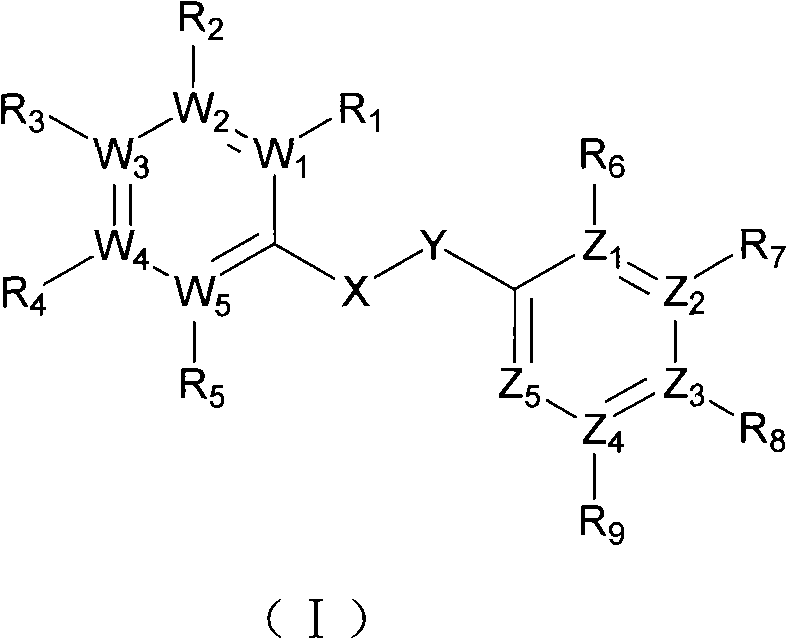
Substituted diaryl compound and preparation method and antiviral application thereof
ActiveCN102206172ALess likely to develop drug resistanceImprove securityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationSulfonic acid esters preparationMechanism of actionStructure–activity relationship
The invention provides substituted diaryl compounds as shown in general formula (I) or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, and also provides a preparation method; a class of novel broad-spectrum antiviral compounds and pharmaceutical salts targeting cytokines are screened and obtained through studies on structure-activity relationship and action mechanism of active compounds; the compounds not only have significant broad-spectrum antiviral activity, but also have the advantages of low toxicity and good pharmaceutical properties.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
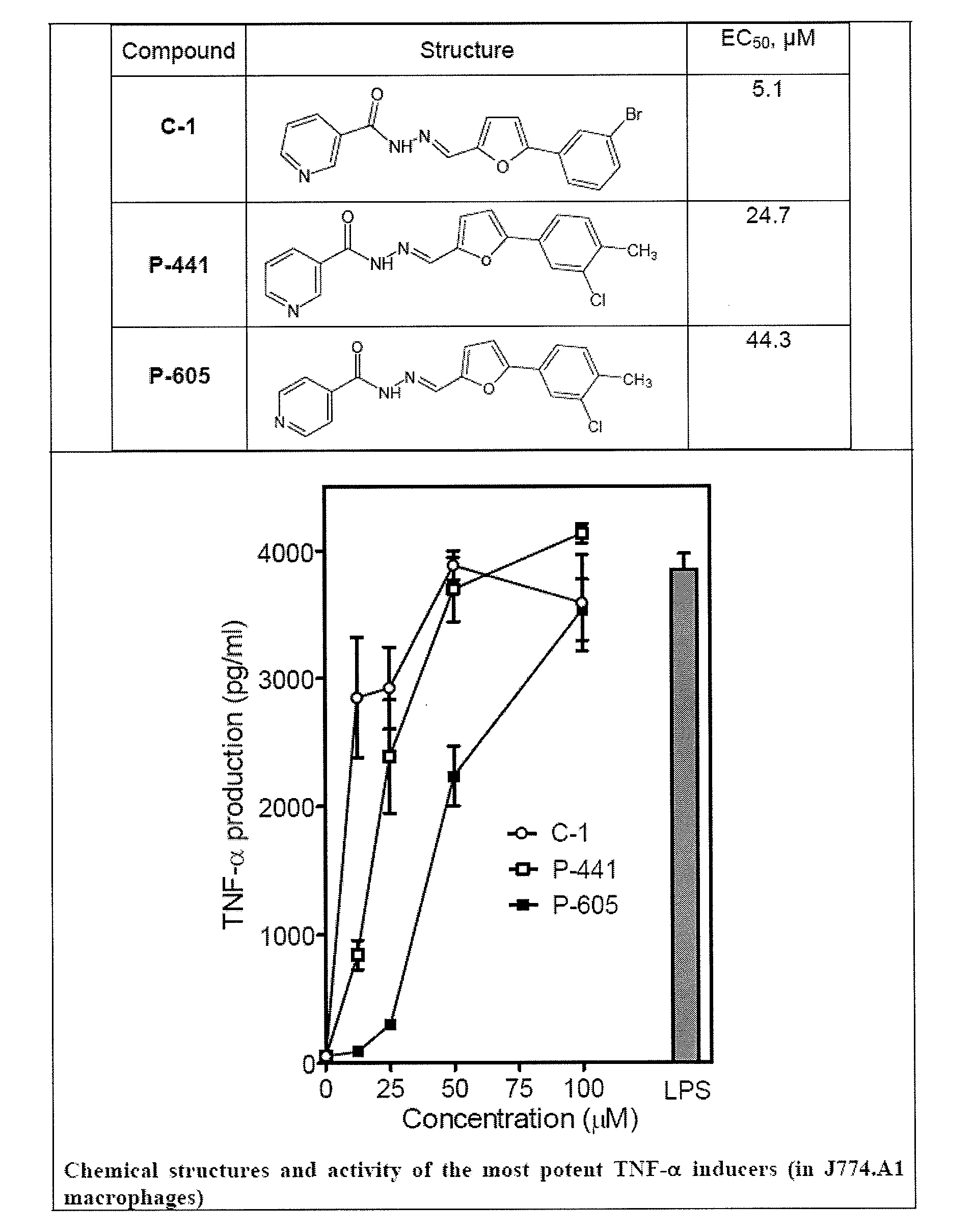
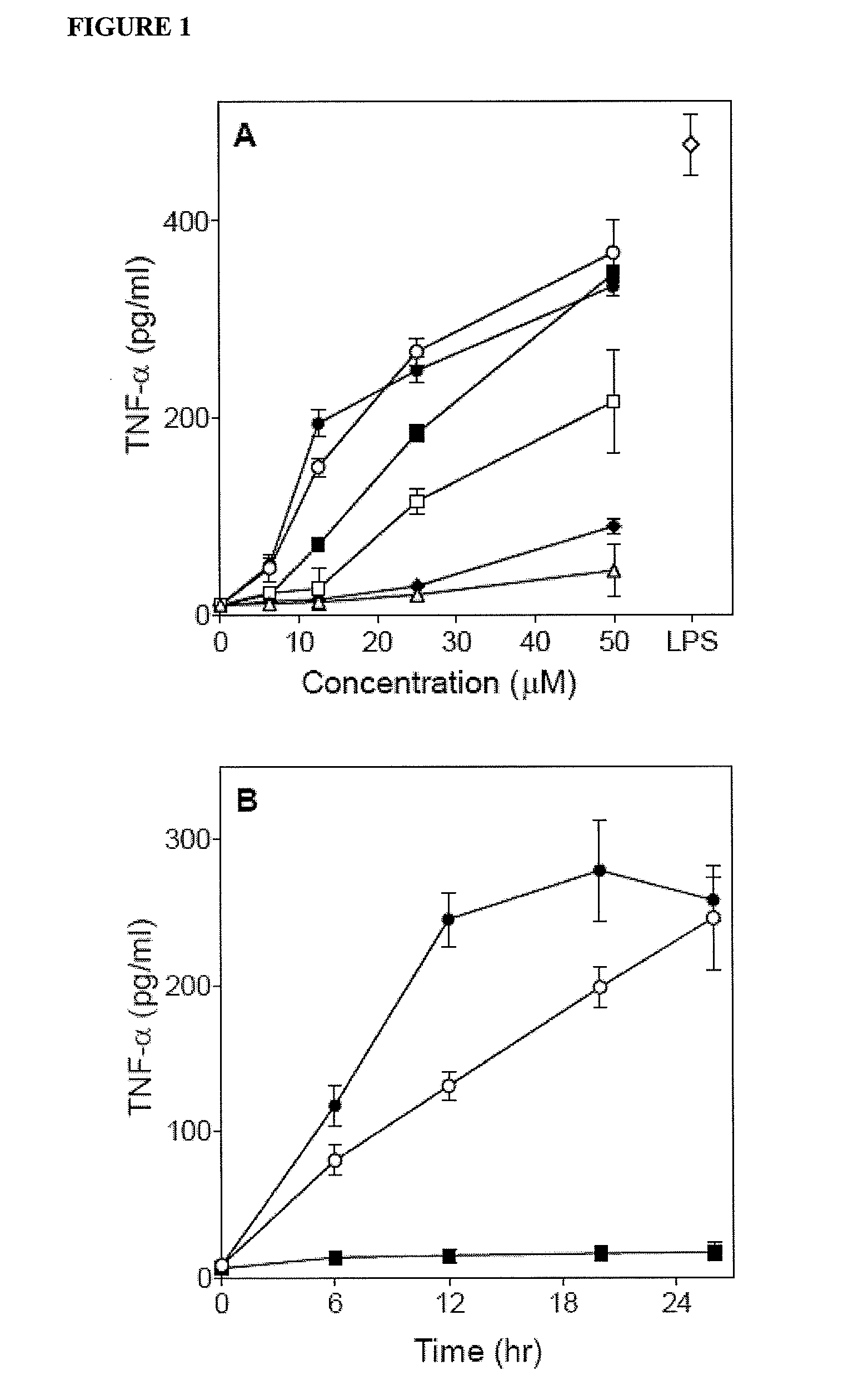
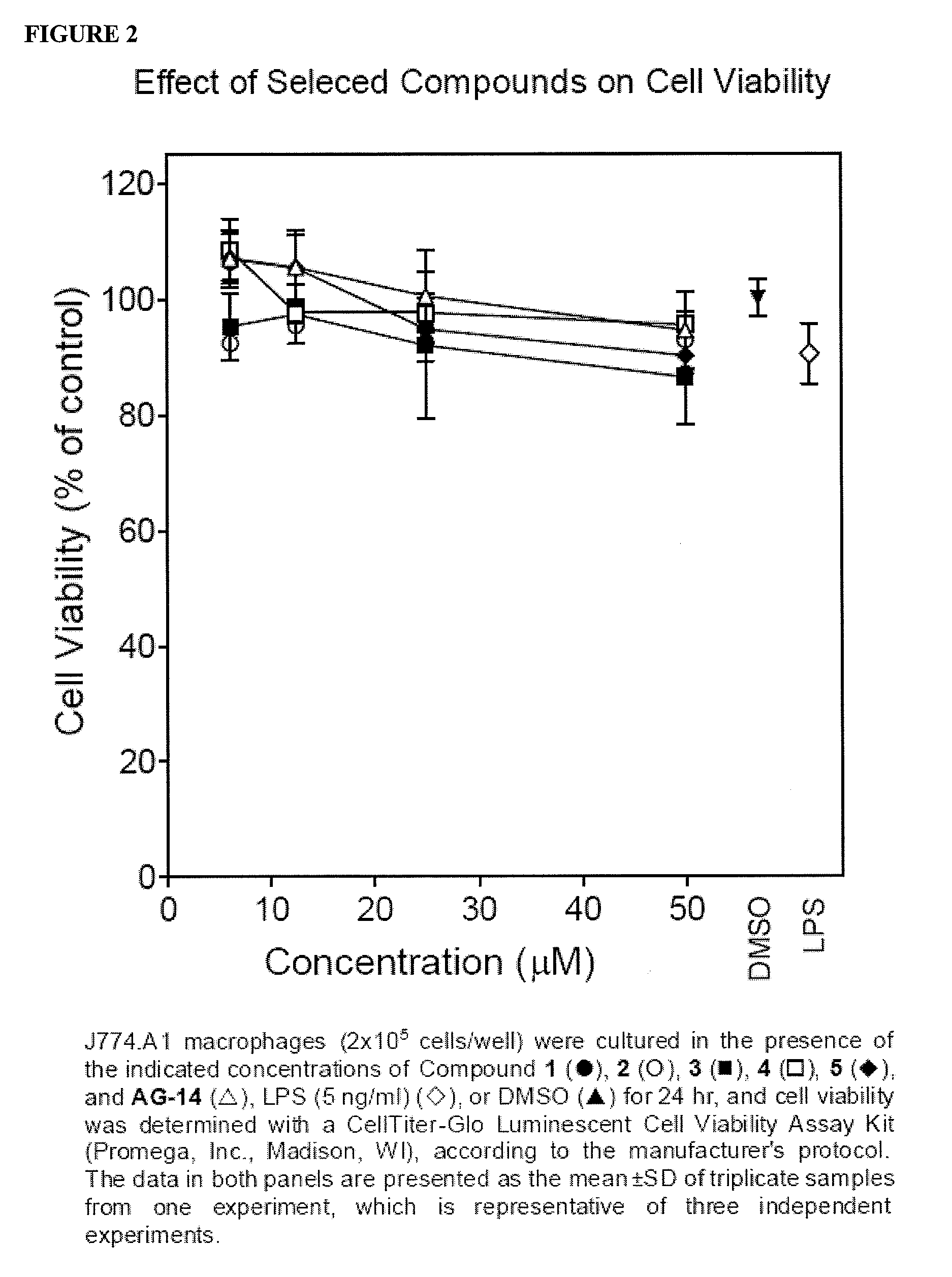
Novel formyl peptide receptor like 1 agonists that induce macrophage tumor necrosis factor alpha and computational structure-activity relationship analysis of thereof
The present invention provides compounds of structural formula (I), which are agonists of formyl peptide receptor (FPR), particularly formyl peptide receptor like 1 (FPRL1). The present invention also provides the therapeutic use of the compounds of formula (I).
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
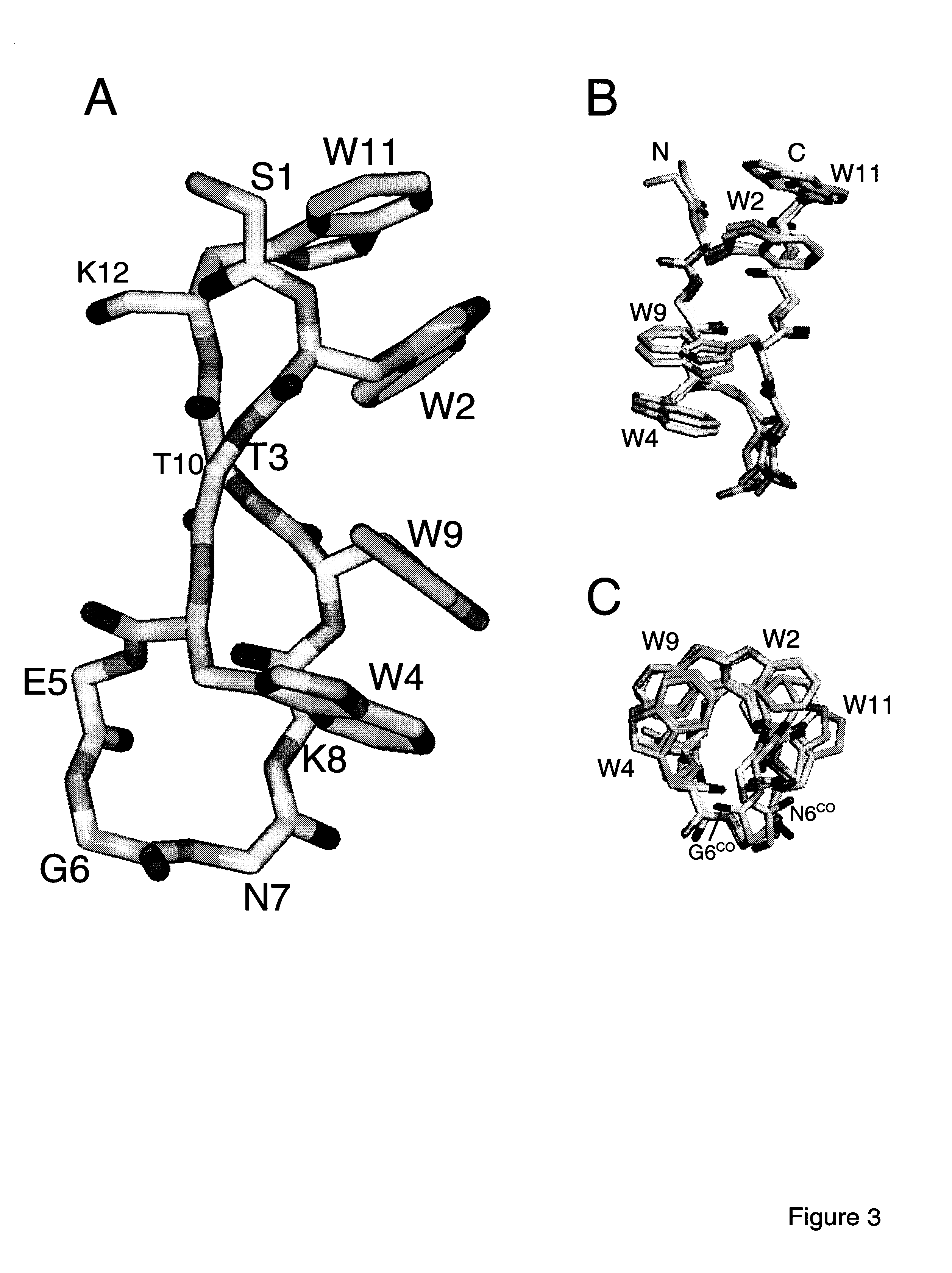
Hairpin peptides with a novel structural motif and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6914123B2Enable stabilizationImprove structural stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein moleculesModel system
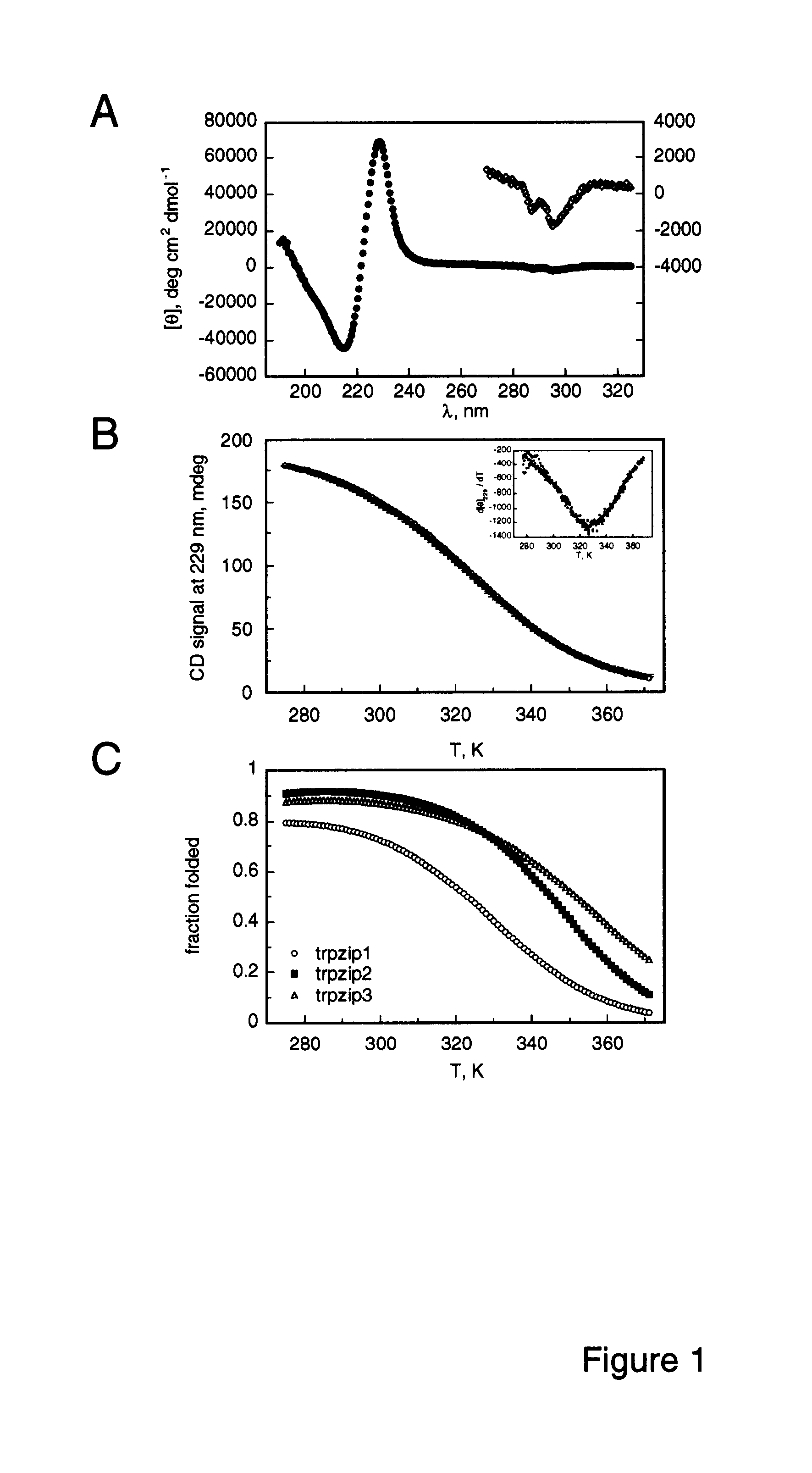
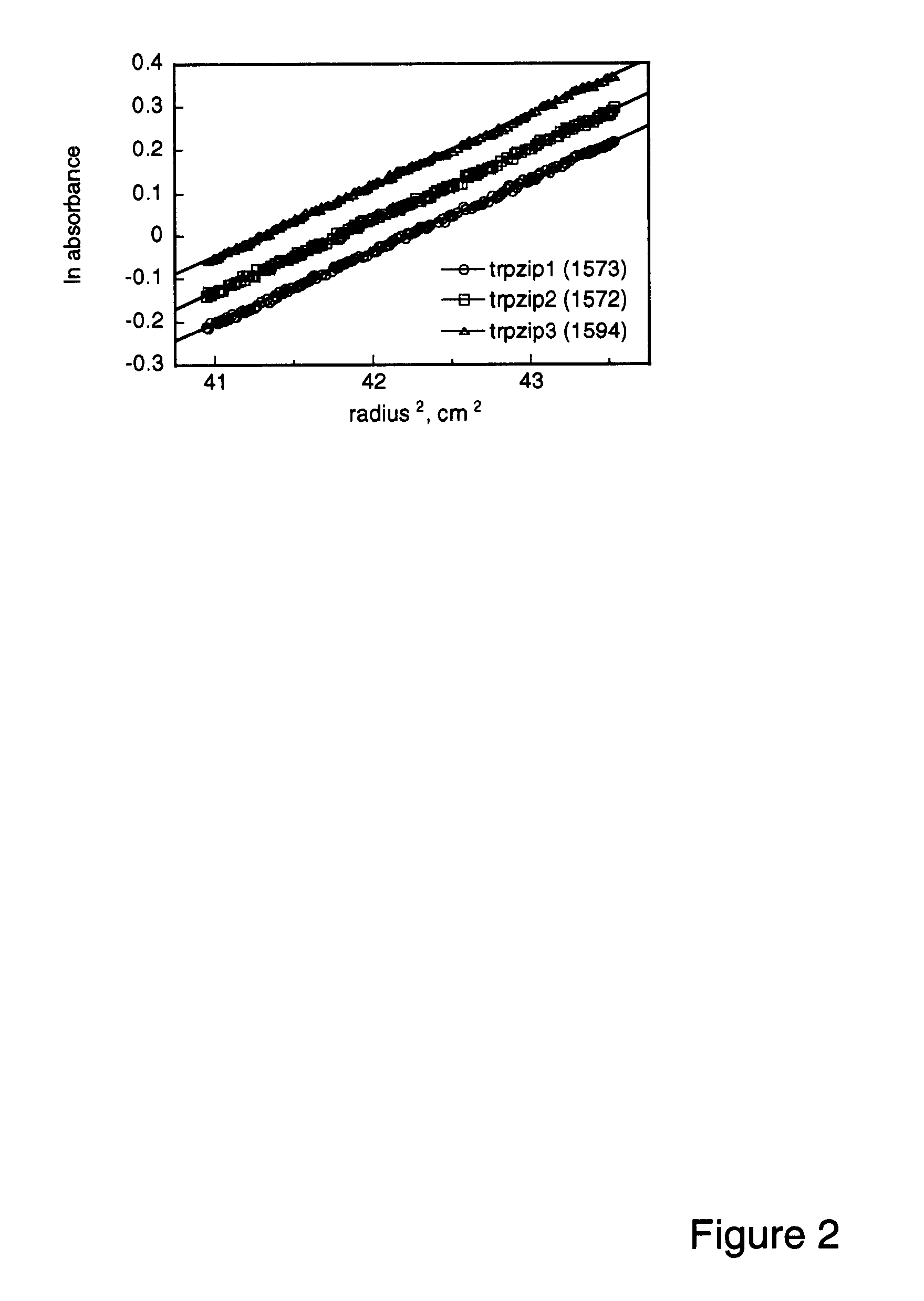
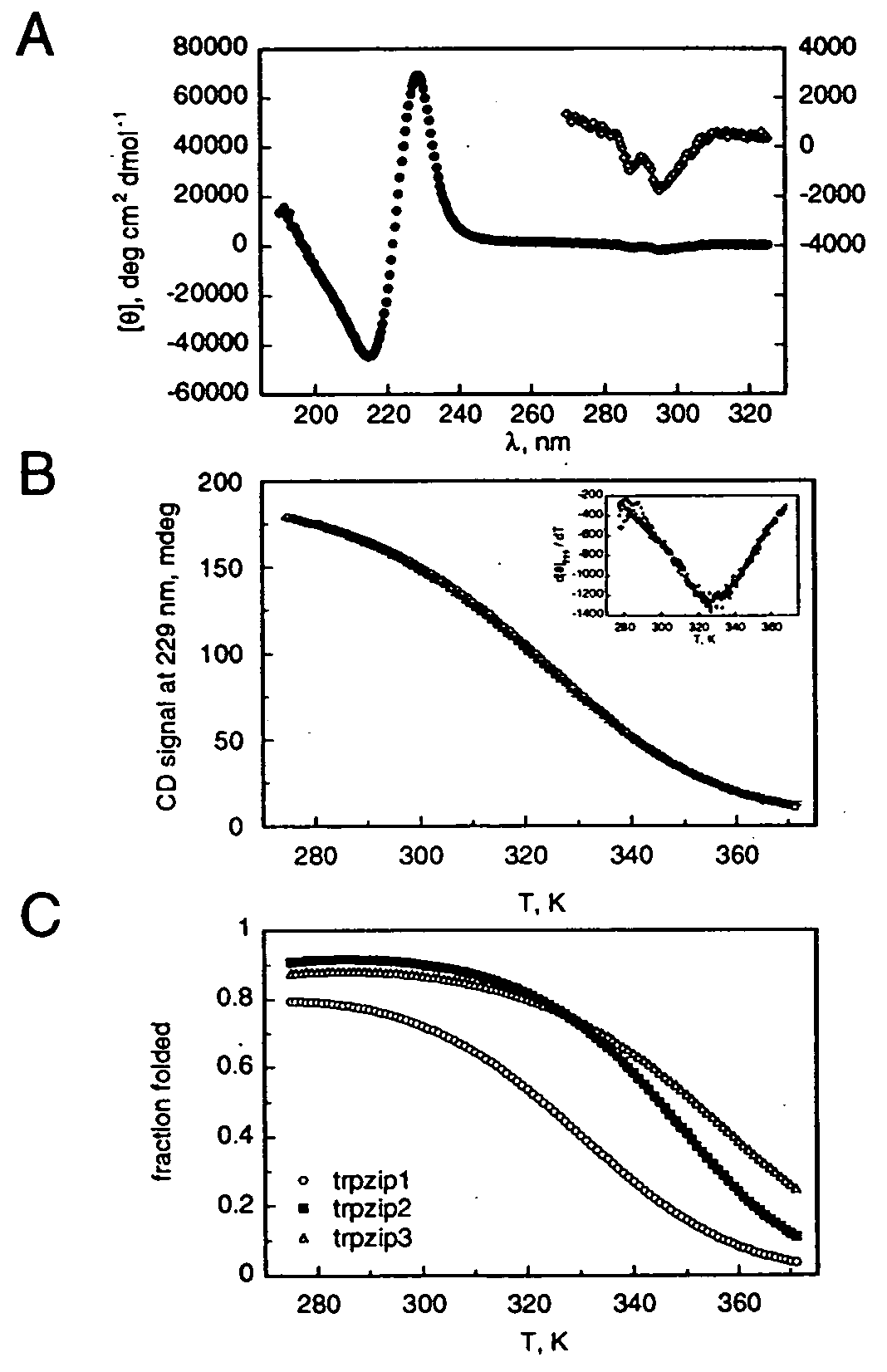
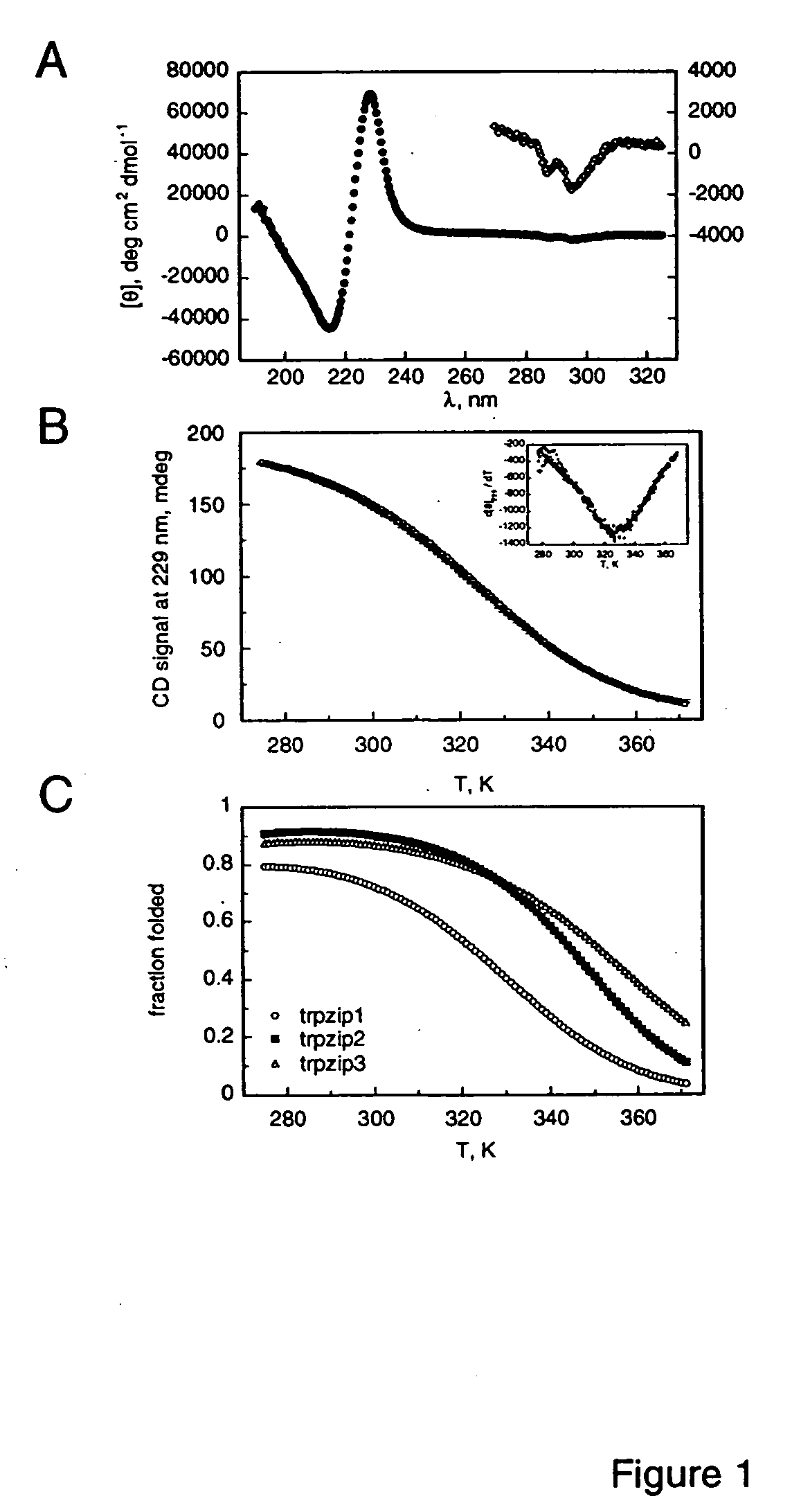
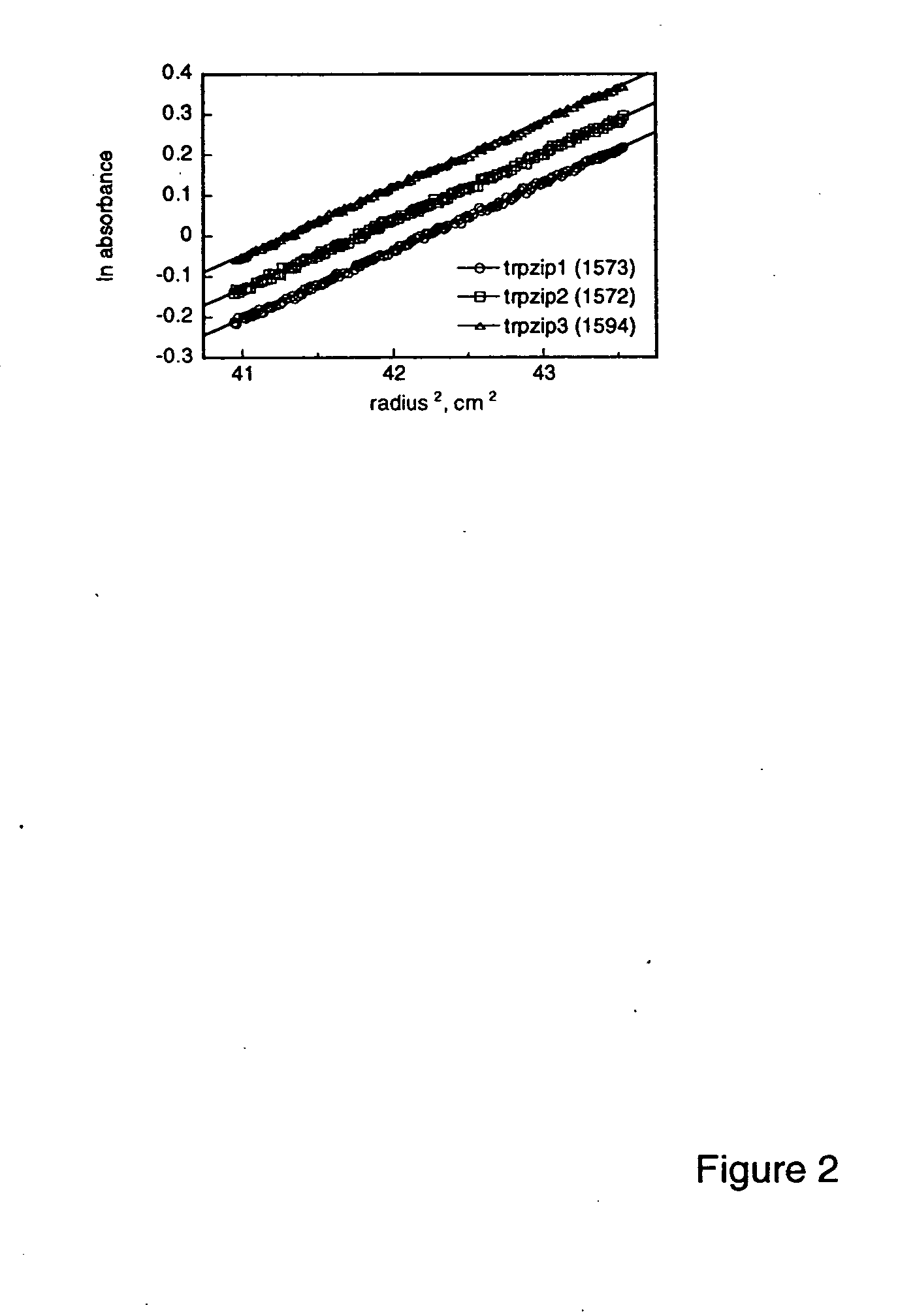
The invention is directed to a model system for structure-activity relationship analysis of peptide or protein molecules involved in important biological processes. Provided by the invention are combinatorial peptide libraries comprising peptides with a novel “tryptophan zipper” scaffold (trpzip) that forms stable β-hairpin structure in solution. Methods of selecting and using such scaffold are provided herein, which are useful for mimicking native protein structures and interactions and designing therapeutic agents. Thus, the invention has profound utility for biological studies and drug development.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Small molecule inhibitors of autotaxin and methods of use
InactiveUS20110110886A1Inhibit and reduce and growthInhibit and reduce likelihoodHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMetastatic melanoma
Autotaxin (ATX) is a prometastatic enzyme initially isolated from the conditioned media of human melanoma cells that stimulates a myriad of biological activities including angiogenesis and the promotion of cell growth, survival, and differentiation through the production of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). ATX increases the aggressiveness and invasiveness of transformed cells, and ATX levels directly correlate with tumor stage and grade in several human malignancies. To study the role of ATX in the pathogenesis of malignant melanoma, we developed antibodies and small molecule inhibitors against recombinant human protein. Immunohistochemistry of paraffin embedded human tissue demonstrates that ATX levels are markedly increased in human primary and metastatic melanoma relative to benign nevi. Chemical screens identified several small molecule inhibitors with binding constants ranging from nanomolar to low micromolar. Cell migration and invasion assays with melanoma cell lines demonstrate that ATX markedly stimulates melanoma cell migration and invasion, an effect suppressed by ATX inhibitors. The migratory phenotype can be rescued by the addition of ATX's enzymatic product, LPA, confirming that the observed inhibition is linked to suppression of LPA production by ATX. Chemical analogues of the inhibitors demonstrate structure activity relationships important for ATX inhibition and indicate pathways for their optimization. These studies suggest that ATX is an approachable molecular target for the rational design of chemotherapeutic agents directed against human malignancies driven by the ATX / LPA axis, especially including malignant melanoma, among numerous others including breast and ovarian cancers.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for synthesizing polycarboxylic acid series cement water reducer accelerated by microwave
The invention relates to a method for using microwave to accelerate the synthesis of polycarboxylic acid cement water reducerm belonging to organic synthesis technical field. The invention based n the property demand of cement water reducer and analysis on monomer molecule structure-activity relationship optimizes selection of monomer molecule structure and monomer proportioning. The invention uses methacrylic acid, methyl acrylate, carbowax methyl methyl methacrylate, and methacrylic mahogany as polymerization monomers, uses ammonium persulfate as initiator, uses microwave technique, uses microwave to rapidly synthesize polycarboxylic acid water reducer. The inventive method can significantly reduce reaction time, reduce energy consumption, reduce pollution, and improve product purified pulp flowing ability, as one safe, effective, energy-saving, environment-friend and simple method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Virtual screening method of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
ActiveCN108830041AReduce in quantityAvoid blindnessSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual screenIn vivo
The invention aims at disclosing a virtual screening method of an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, the virtual screening method and the application of screened compounds in pharmaceutical preparations forpreventing and / or treating 2-type diabetes. The method comprises the steps of 1, the obtaining, analyzing and treating of the three-dimensional structure of a large molecular protein; 2, the construction of a traditional Chinese medicine natural product library and the preparation of a small molecular compound; 3, the calibration of the prediction capability of a virtual screen model and the establishment of the screen model; 4, the virtual screening of the natural product library and the analyzing of a mutual impacting mechanism; 5, in vivo and in vitro biological activity verification of ascreening result. The method is used for screening and can be used for the discussing of a structure-activity relationship of compounds of the type, and the further modification of a structure based on a biological compound is guided.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Peptide library penetrating through blood brain barrier and screening method thereof
ActiveCN109666973AIncrease success rateReduce workloadPeptide librariesBacteriaMedicineScreening method
The invention relates to a peptide library penetrating through a blood brain barrier, a method for selecting blood brain barrier penetrating peptides by using the peptide library, and obtained blood brain barrier penetrating peptides. The invention also provides a coding nucleic acid, a nucleic acid construct, a host cell of the blood brain barrier penetrating peptides, and the application as a brain drug delivery carrier in preparing brain drugs. Based on the previously known structure-activity relationship and bioinformatics analysis of the blood brain barrier penetrating peptides, a methodfor efficiently screening and preparing the blood brain barrier penetrating peptides is provided by fully utilizing the blood brain barrier function of living animals and phage surface peptide librarydisplaying technology.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
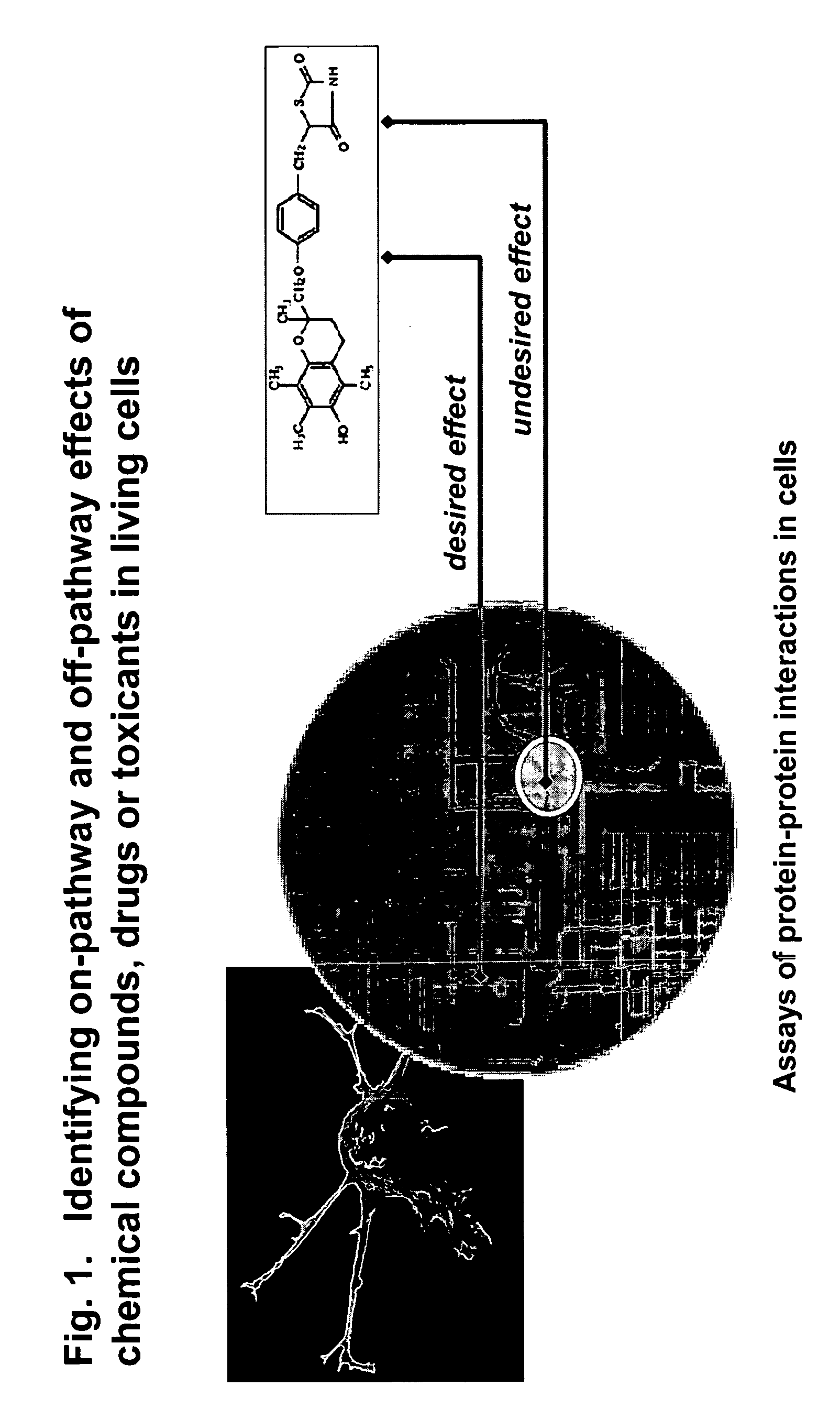
Protein-protein interactions for pharmacological profiling
InactiveUS20050221280A1Enable optimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningToxicantEfficacy
The present invention provides methods for performing pharmacological profiling of a chemical compound, in particular to improve drug safety and efficacy at an early stage in the drug development process. The chemical compound may be a test compound, drug lead, known drug or toxicant. The compound is profiled against a panel of assays. Preferred embodiments of the invention include high-content assays for protein-protein interactions. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to identify pathways underlying drug efficacy, safety, and toxicity; and to effect attrition of novel compounds with undesirable or toxic properties. The compositions and methods of the invention can also be used to identify new uses of therapeutic agents, to screen libraries of chemical compounds, to perform lead optimization, and to perform studies of structure-activity relationships in the context of intact cells. The compositions and methods of the invention can be applied to any test compound, drug, drug target, pathway, and therapeutic indication.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Resveratrol dimer derivative and preparation and application methods thereof
InactiveCN102180846AHas antioxidant activityHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer cellStructure–activity relationship
The invention discloses a resveratrol dimer derivative containing a Combretastin A-4 structure and preparation and application methods thereof, belonging to the technical field of medical engineering. By analyzing and researching reported anti-tumor activity and structure-activity relationship related to resveratrol and a derivative of the resveratrol, a series of derivatives with novel structures formed by polymerization of Combretastin A-4 and the resveratrol can be obtained through design and preparation. Through preliminary anti-tumor pharmacological tests, the prepared new compound is confirmed to have broad-spectrum tumor inhibitory activity to cancer cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for extracting salvia chinensis anthocyanin
InactiveCN102321061AIncrease the degree of liquefactionPromote leachingOrganic chemistryNatural dyesWater bathsAmyris
The invention provides a method for extracting salvia chinensis anthocyanin, belonging to the technical field of extraction of plant functional active ingredients. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pretreating raw materials; (2) hydrolyzing with alpha amylase; (3) extracting salvia chinensis anthocyanin in a water bath or in an intermittent way; (4) separating and concentrating theextracted mixture; and (5) eluting the concentrated solution with macroporous resin, purifying, drying and the like. In the invention, the raw material is hydrolyzed with alpha amylase, so that the extraction rate of anthocyanin is increased from about 80 percent conventionally to over 95 percent; and moreover, the preparation process has a mild condition and low energy consumption, the natural structure-activity relationship of anthocyanin is kept, the product is pure, and the color scale (defined in China) is over 40. The method can be popularized and applied in salvia chinensis culturing regions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUB TROPICS CROP INST
Dual inhibitors of farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I
ActiveUS9040563B2Easy to derivatizeExtensive structure-activity relationship (SAR) studyBiocideOrganic chemistryEthylenediamineAnticarcinogen
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
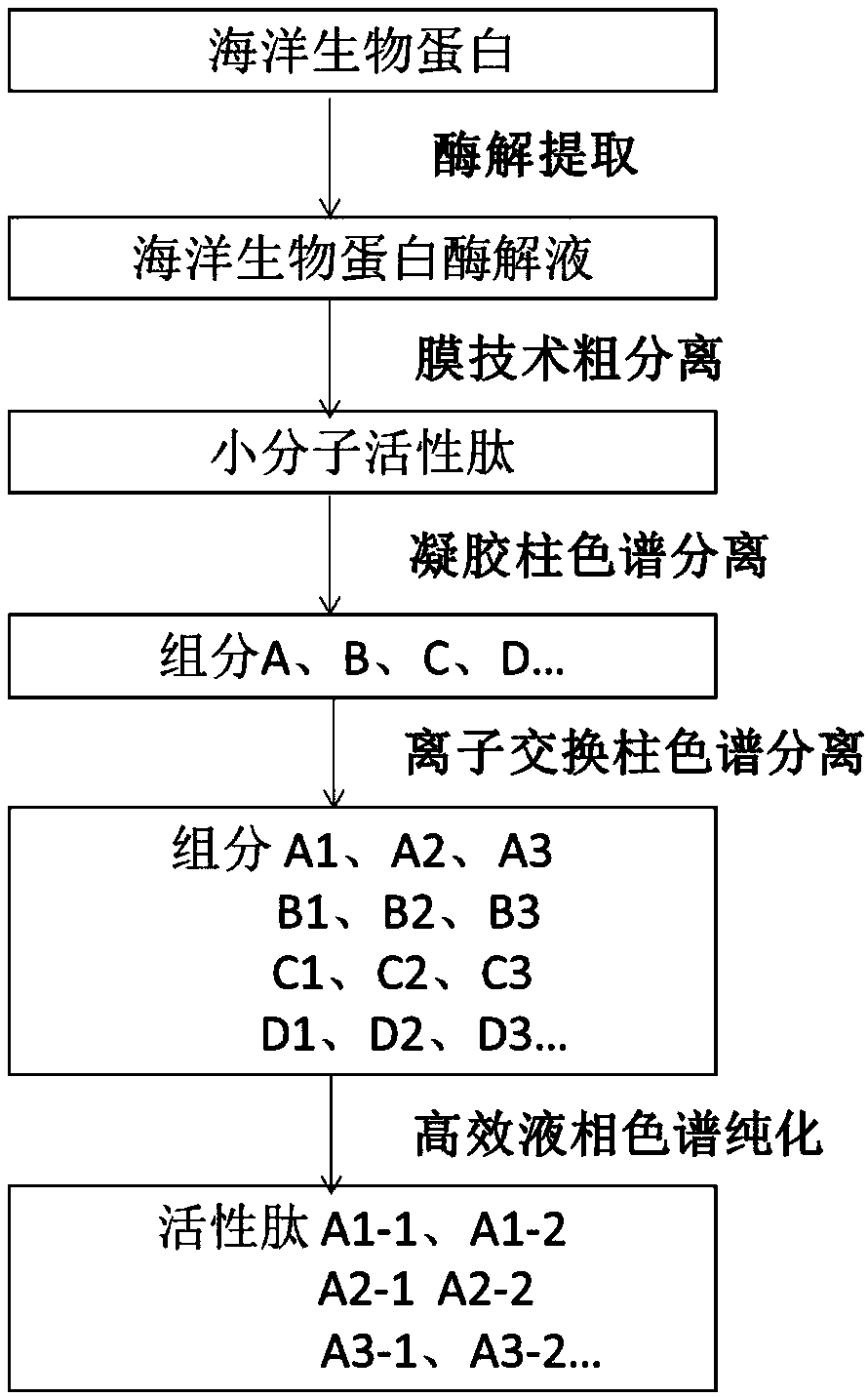
Combined technology for extracting and separating small-molecular active peptide from marine organism protein resources
PendingCN108103130ASimple technical routeEasy to implementPeptide preparation methodsFermentationChromatographic separationHydrolysate
The invention discloses a combined technology for extracting and separating small-molecular active peptides from marine organism protein resources. The combined technology comprises the steps as follows: (1) an enzymatic hydrolysate is prepared through enzymolysis of marine organism protein; (2) the marine organism protein enzymatic hydrolysate is subjected to crude separation with a membrane separation technology, and small-molecular active peptides are obtained; (3) all components are obtained through sephadex gel chromatographic separation of the small-molecular active peptides; (4) all thecomponents are further separated through ion exchange chromatography and separation products of different components are obtained; (5) the separation products are purified through reverse high performance liquid chromatography, and a series of small-molecular active polypeptide compounds are finally obtained. The technical route is simple, feasible and easy to implement, a series of small-molecular active polypeptide compounds can be directly obtained from multiple marine protein resources, and research work such as structure identification, pharmacological activity research, structure-activity relationship study of small-molecular active peptide compounds with different sources and types, screening of computer simulation drugs and the like can be carried out.
Owner:DALIAN SHENLAN PEPTIDE TECH R & D CO LTD
Preparation of aconite primary diterpene alkaloid component and use in disinsection
The invention relates to a method for preparing main diterpenoid alkaloids of radix aconiti carmichaeli by means of extraction and separation from crude radix aconiti carmichaeli of the traditional Chinese medicine and a desinsection application thereof, pertaining to the technical field of the preparation of a natural active ingredient and the application thereof. The preparation method for the main diterpenoid alkaloids of the crude radix aconiti carmichaeli comprises the steps that the Mianyang radix aconiti carmichaeli is taken as a raw material which is extracted by ethanol after being dried and ground, then subjected to acid and alkali treatment and is leached by an organic solvent (such as chloroform, acetic ether, and the like) to obtain the general diterpenoid alkaloids; and the general diterpenoid alkaloid obtained is subjected to silica gel column chromatography and separation and then the main diterpenoid alkaloids are obtained through recrystallization. The main diterpenoid alkaloids in radix aconiti carmichaeli are proven to have relatively good desinsection activity by activity tests and can be used for developing pesticides with novel plant sources and also serving as a lead compound and a synthesized material of pesticides to study and create novel pesticides through the structure-activity relationship.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
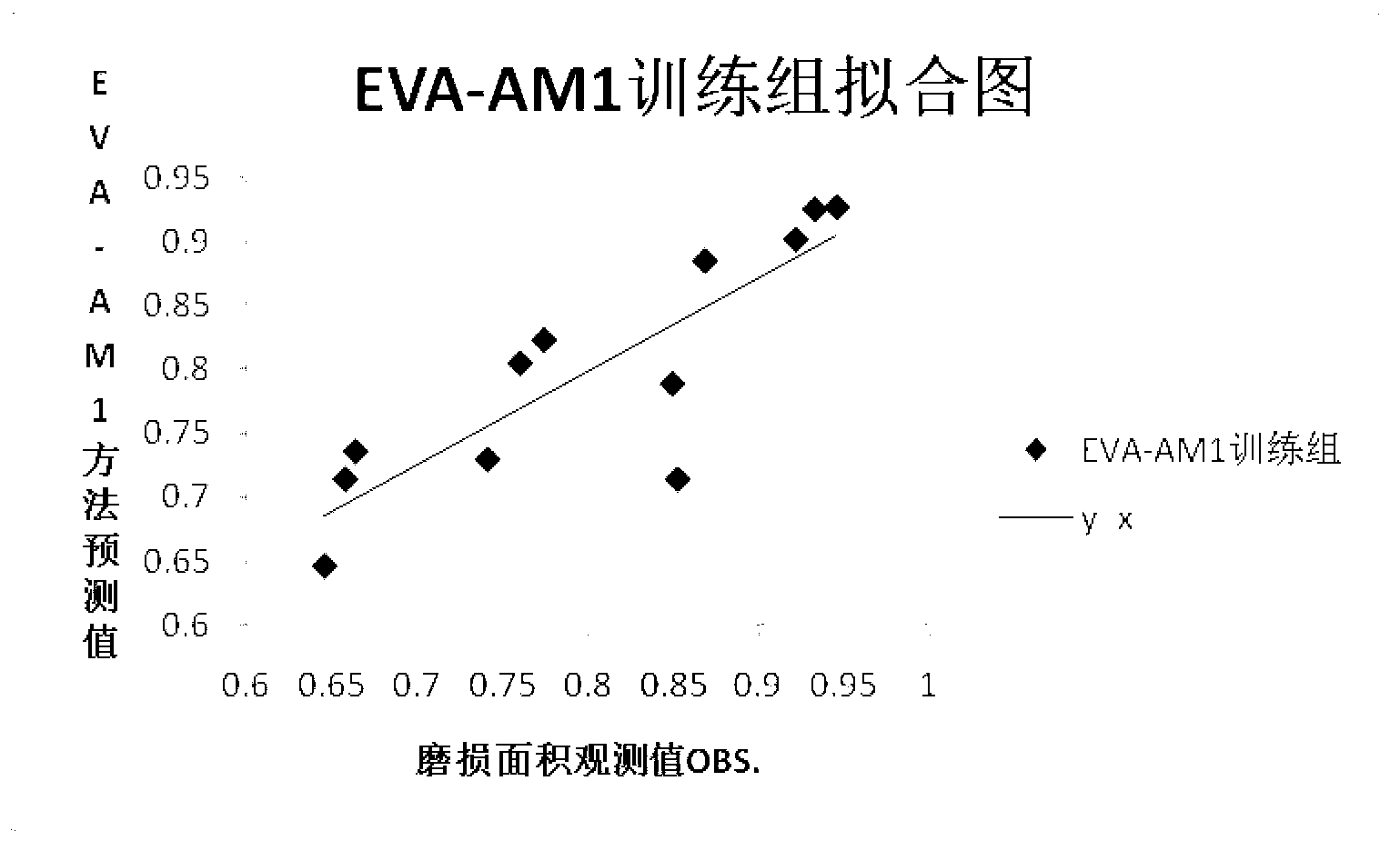
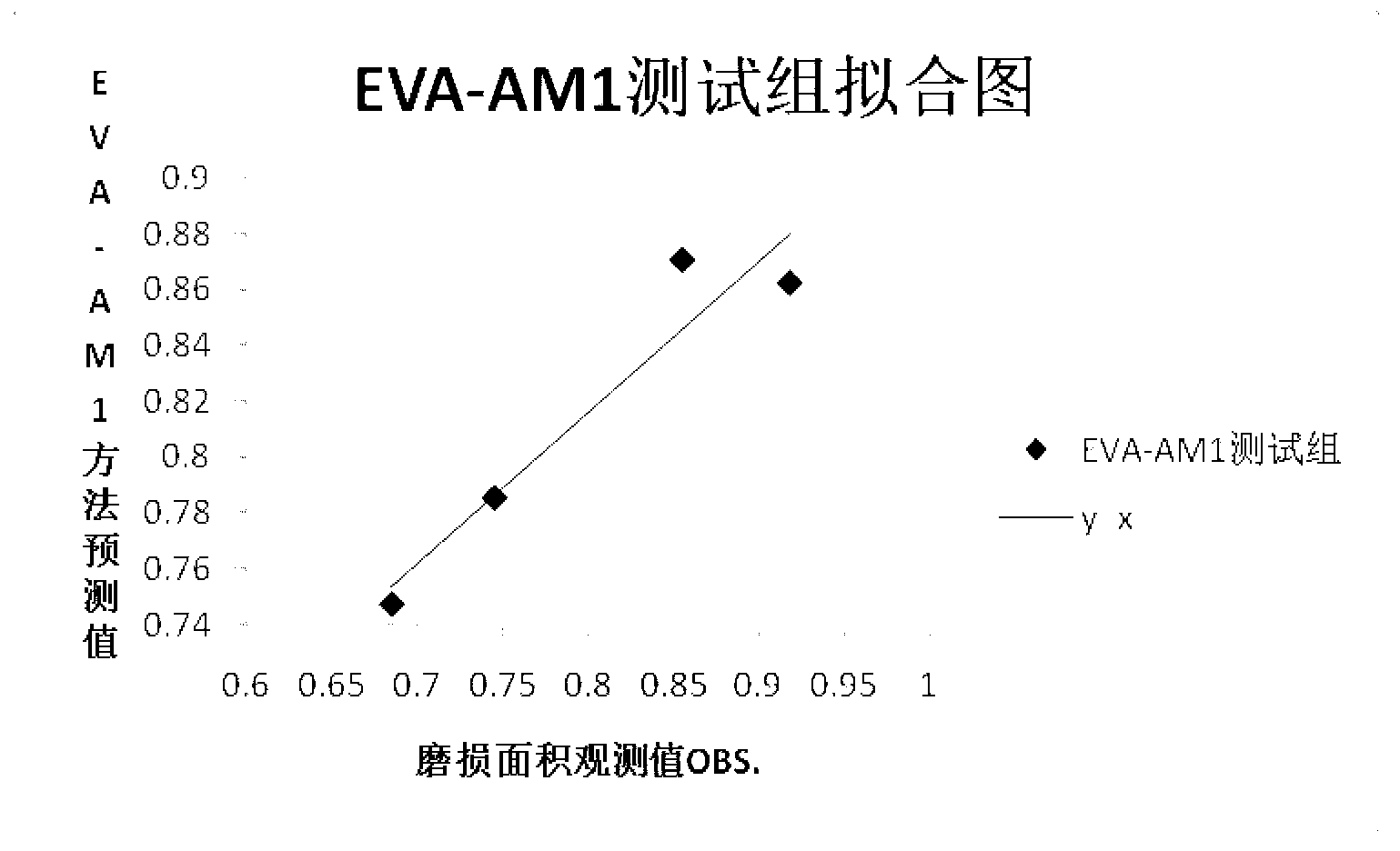
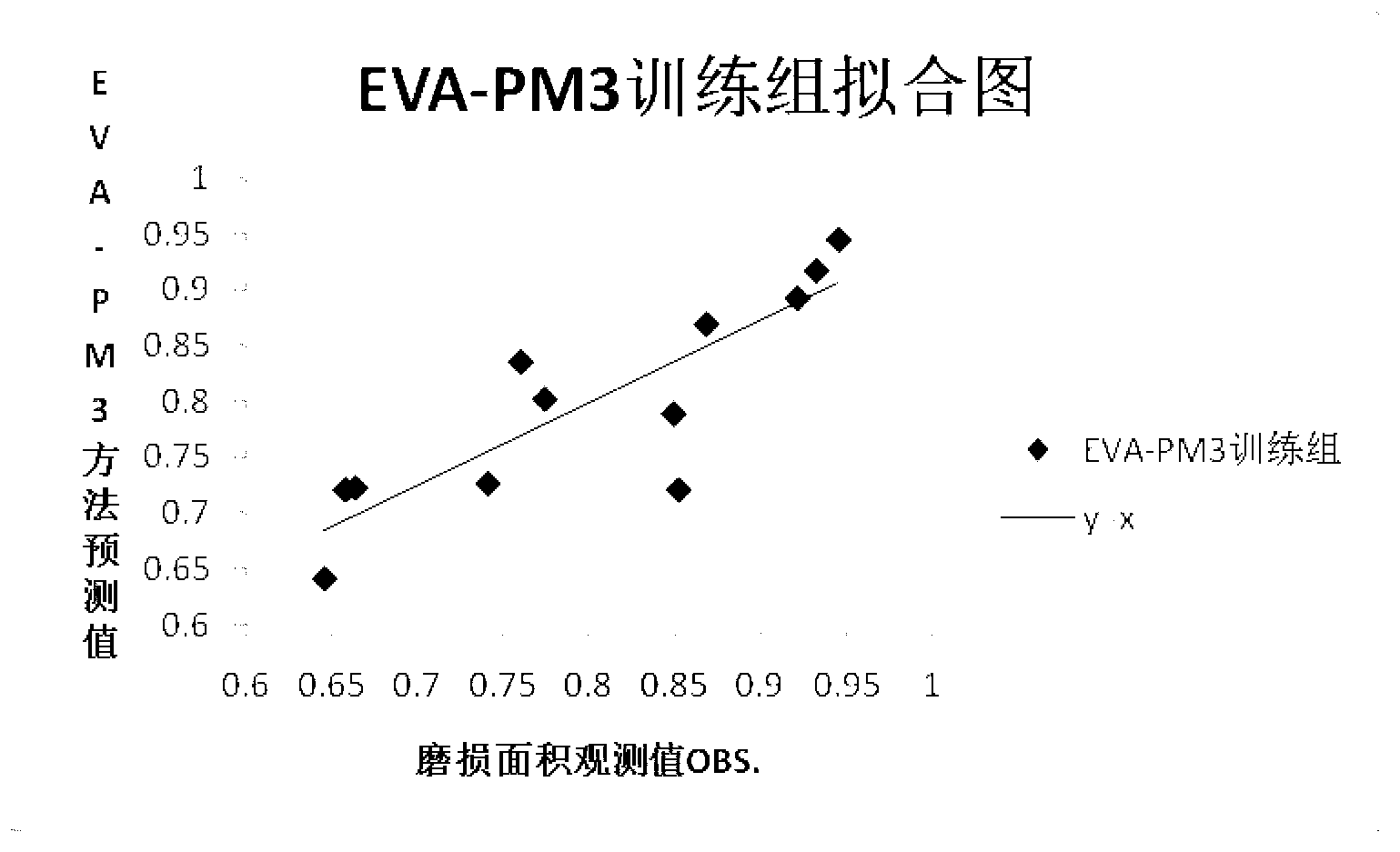
Method for predicting wear resistance of lubricating base oil according to chemical structures
ActiveCN103294863AReduce experimental workloadReduce riskSpecial data processing applicationsChemical structureMaterials science
The invention provides a method for predicting the wear resistance of lubricating base oil according to chemical structures. The method includes steps of 1), generating three-dimensional chemical structures of molecules of the lubricating base oil; 2), minimizing energy of the three-dimensional chemical structures; 3), computing an EVA (evaluation of an infrared vibration-based descriptor) parameter of each three-dimensional chemical structure; 4), preprocessing wear surface data of a friction pair sample after the lubricating base oil is applied to the friction pair sample; 5), performing regression on the EVA parameters and the wear surface data by means of partial least squares, and establishing a relationship between the preprocessed wear surface data and the EVA parameters so as to create a quantitative prediction model; 6), performing cross validation on the prediction model; 7), predicting the wear area of the friction pair sample according to the created prediction model when the lubricating base oil is applied to the friction pair sample in an experimental state. The method has the advantages that a computer-aided design process is introduced into the field of lubricating oil design for the first time on the basis of the quantitative structure-tribo-ability relationship, the method is beneficial to reducing lubricating oil design risks and research cost, and the lubricating oil development efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
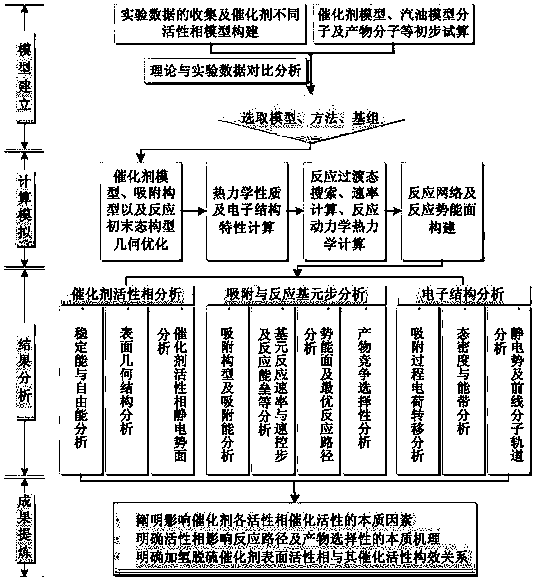
Analytical method for structure-activity relationship between surface active phase and catalytic activity of hydrodesulfurization catalysts
InactiveCN108636421AQuick Introduction to Computational MethodsThe result is accurateChemical processes analysis/designMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectronic structureHydrogenation reaction
The invention discloses an analytical method for the structure-activity relationship between the surface active phase and the catalytic activity of hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Based on DFT calculation, the characteristics of different active phases of catalysts and the reaction networks of catalytic desulfurization of model molecules on the surface of the catalysts are studied by DFT. The structure-activity relationship between the active phase and the desulfurization activity of catalysts is recognized by studying the surface characteristics of the catalysts with different active phases and the adsorption and the desulfurization reaction networks of the model molecules on the surface of the catalysts and combining the analysis of surface electronic structure characteristics, reactionbarriers and reaction rates and thermodynamic and kinetic analysis. Finally, the desulfurization-hydrogenation reaction mechanism is concluded, and the structure-activity relationship between the surface active phase and the desulfurization catalytic activity of the hydrodesulfurization catalysts is clarified by combining the analysis of a geometrical structure and an electronic structure of the catalysts. The calculation method is simple and fast and accurate in results, and provides theoretical guidance for the design of industrial desulfurization catalysts, showing important practical significance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Hairpin peptides with a novel structural motif and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS20050196810A1Enable stabilizationImprove structural stabilityPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein moleculesModel system
The invention is directed to a model system for structure-activity relationship analysis of peptide or protein molecules involved in important biological processes. Provided by the invention are combinatorial peptide libraries comprising peptides with a novel “tryptophan zipper” scaffold (trpzip) that forms stable β-hairpin structure in solution. Methods of selecting and using such scaffold are provided herein, which are useful for mimicking native protein structures and interactions and designing therapeutic agents. Thus, the invention has profound utility for biological studies and drug development.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Preparation method of single component of extracellular polysaccharide of lachnum hyalopus
InactiveCN101649338AAchieve fractional separationMicroorganism based processesFermentationStructure analysisFractionation
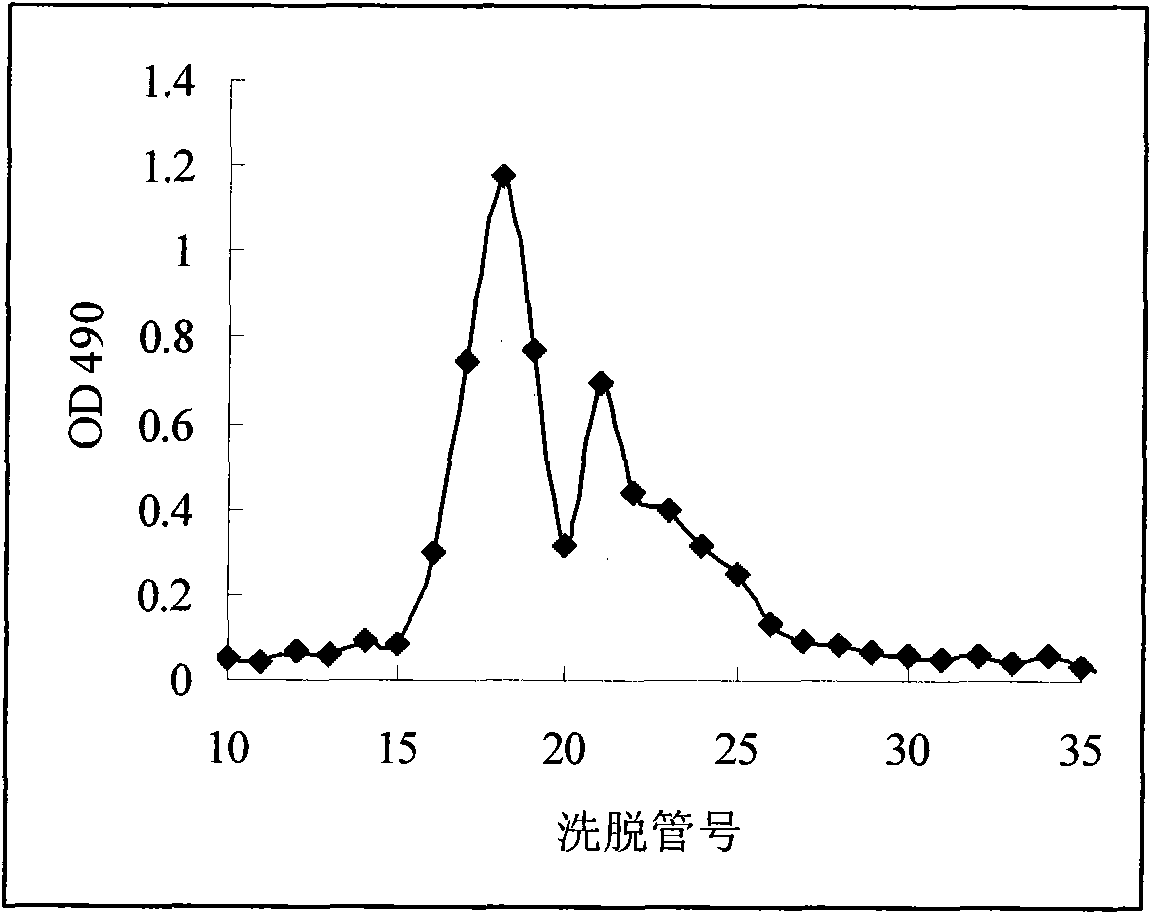
The invention relates to a preparation method of a single component of polysaccharide of lachnum, which comprises the steps of lachnum culture, extraction and purification of extracellular polysaccharide and fractionation. The invention is characterized by comprising the following steps: fractionating the extracted and purified extracellular polysaccharide by a sephadex chromatographic column; using double distilled water as an eluant, and collecting the eluate in order in different tubes; determining the absorbance at the place of 490nm; numbering the tubes according to the absorbance to obtain an elution curve by a graph; merging the single peak parts in the curve according to the elution curve; and obtaining the single component of extracellular polysaccharide of lachnum hyalopus by vacuum drying. The single component of polysaccharide can be used for the research of structure analysis and structure-activity relationship of polysaccharide of lachnum hyalopus.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
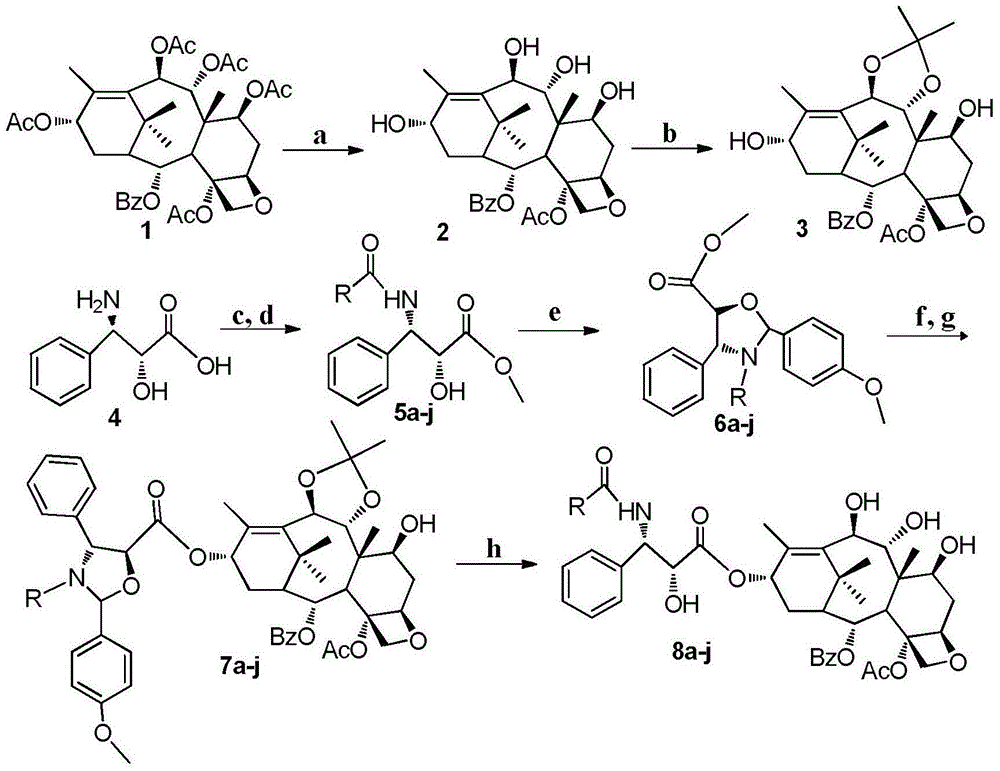
9,10-dihydroxy-1-deoxy-taxol analogue and preparation method thereof
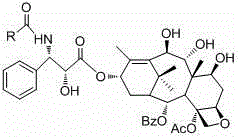
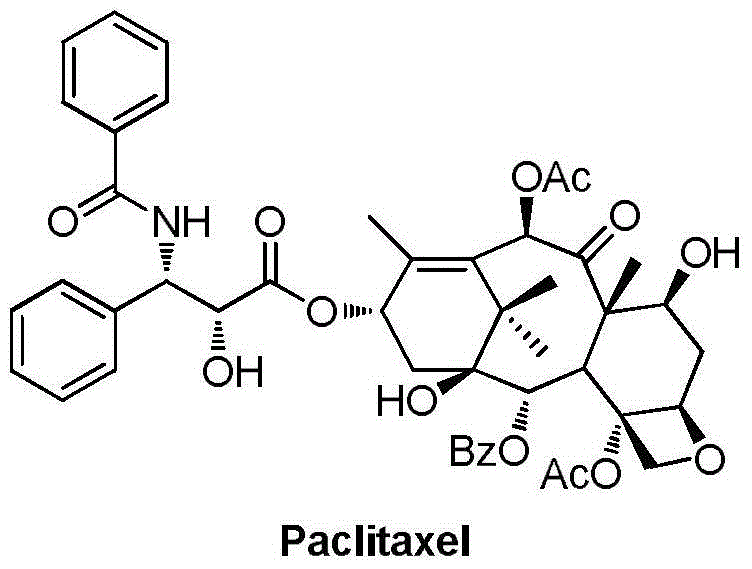
The invention relates to a 9,10-dihydroxy-1-deoxy-taxol analogue and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula of the analogue is shown in the specification, wherein R is methylphenyl, methoxyphenyl, propylphenyl, ethylphenyl, fluorophenyl, methyl chlorophenyl, bromophenyl, furyl, thienyl or benzofuranyl. The 9,10-dihydroxy-1-deoxy-taxol analogue has exposed hydroxyls on sites 7, 9 and 10, so that the water solubility of compounds can be greatly improved; various substituents are located on a side chain on a site 13, so that the compounds are enriched, and a very important foundation is laid for the authentication of structure-activity relationship of the compounds.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
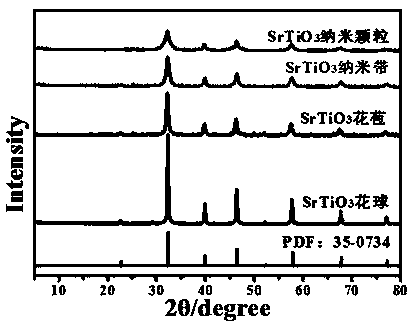
Shape-controllable SrTiO3 flowerlike series nanomaterial preparation and application
PendingCN110054215AReduce usageUse hasAlkaline earth titanatesCatalyst carriersPhotocatalytic reactionActive agent
The invention relates to a flowerlike SrTiO3 photocatalyst preparation method. The method includes that shape-controllable flowerlike SrTiO3 photocatalytic materials are greenly and efficiently synthesized without use of organic templates. The method has advantages that under the condition that adding of any surfactants and template agents is avoided, a series of SrTiO3 photocatalytic materials indifferent surface appearances are obtained according to a simple hydrothermal method by reaction time modulation, and a structure-activity relationship is researched through photocatalytic reaction while self-assembly process control is realized.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
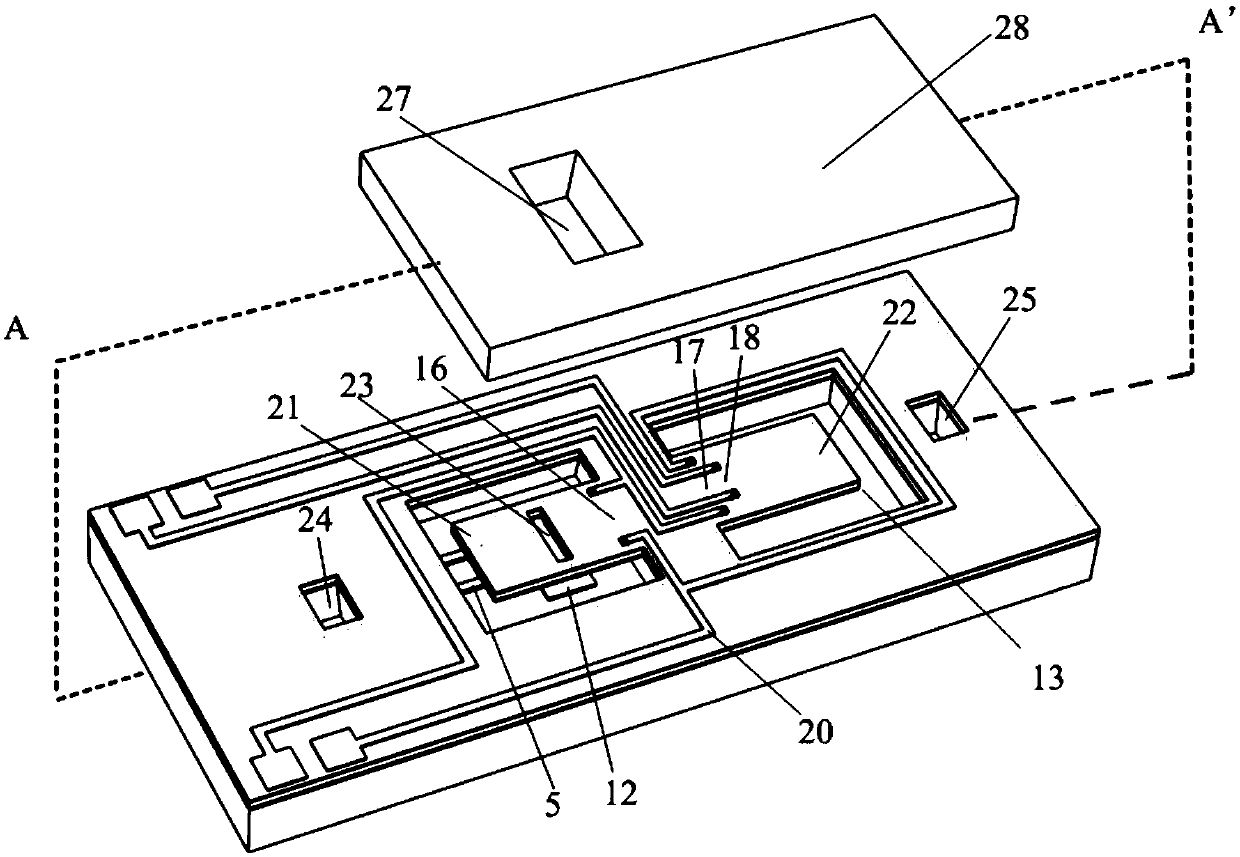
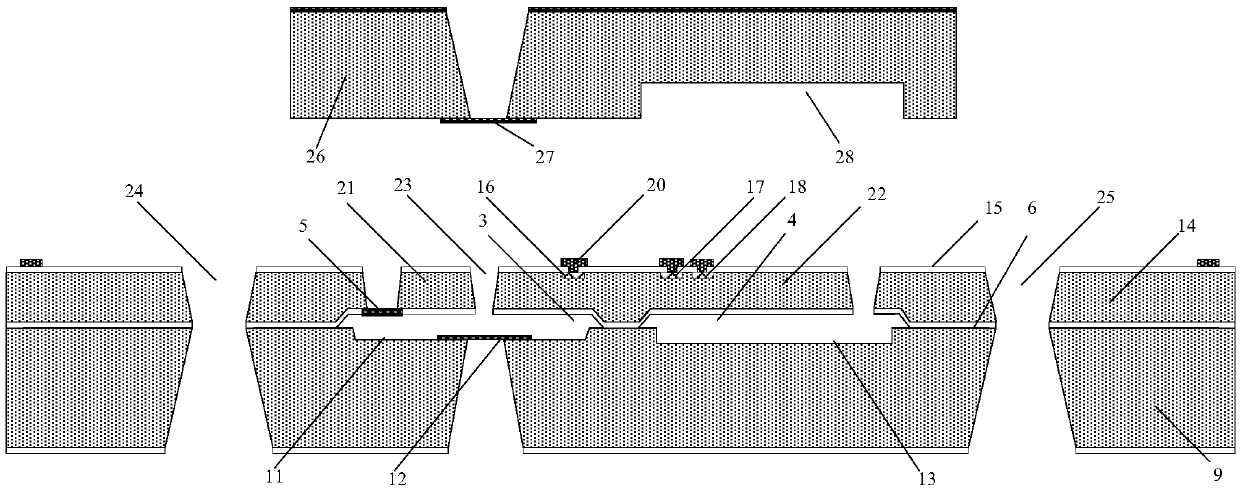
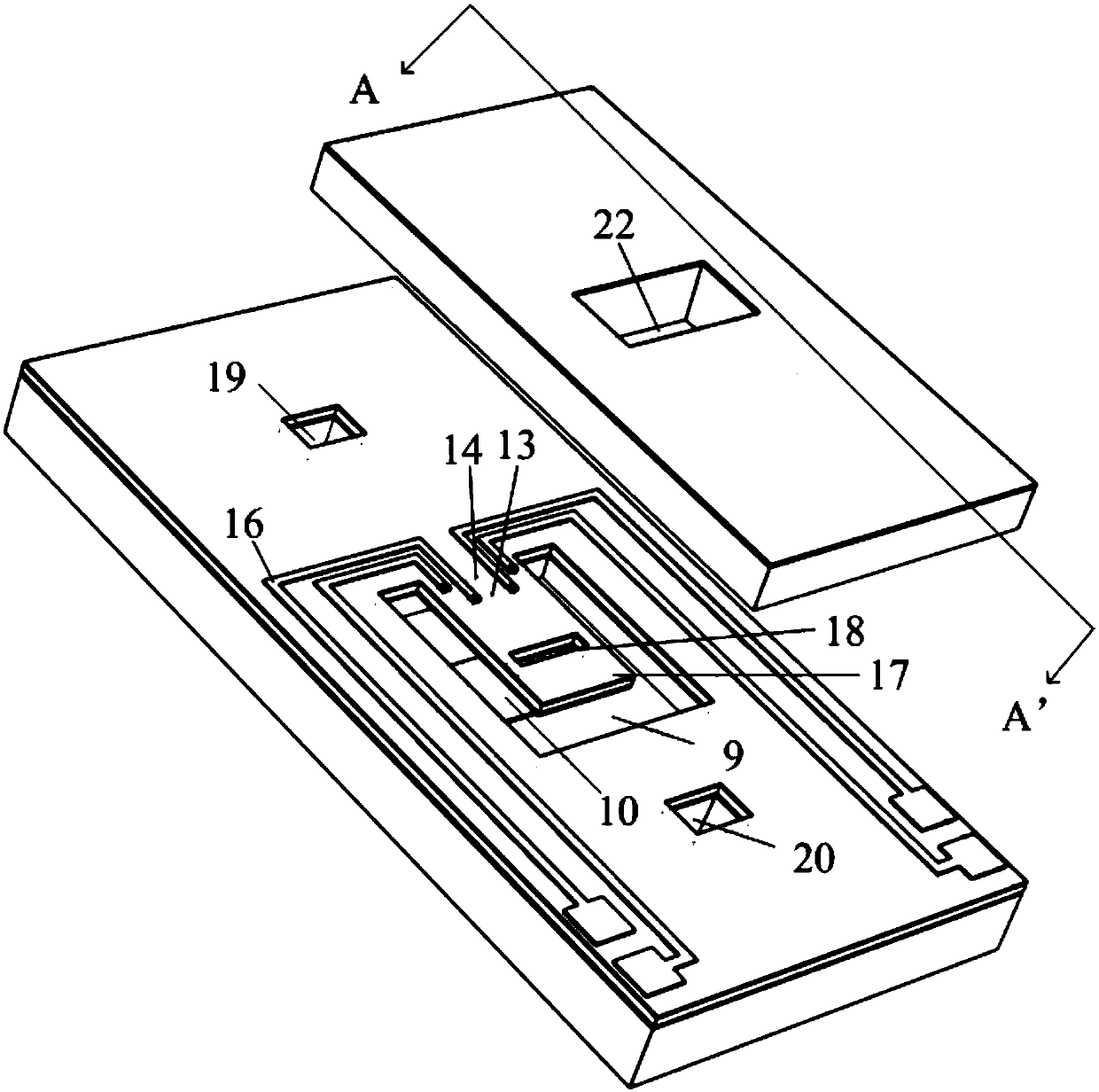
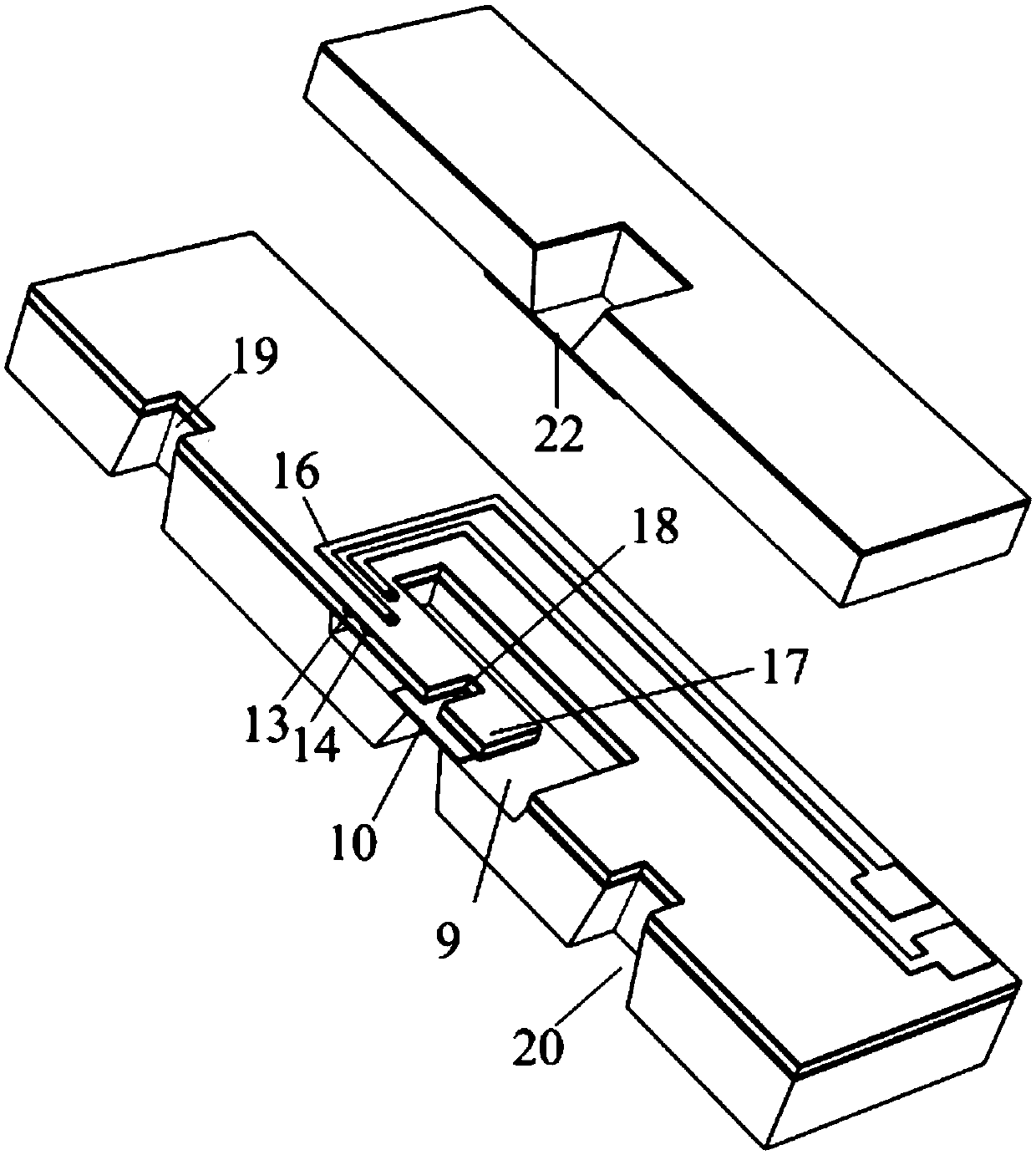
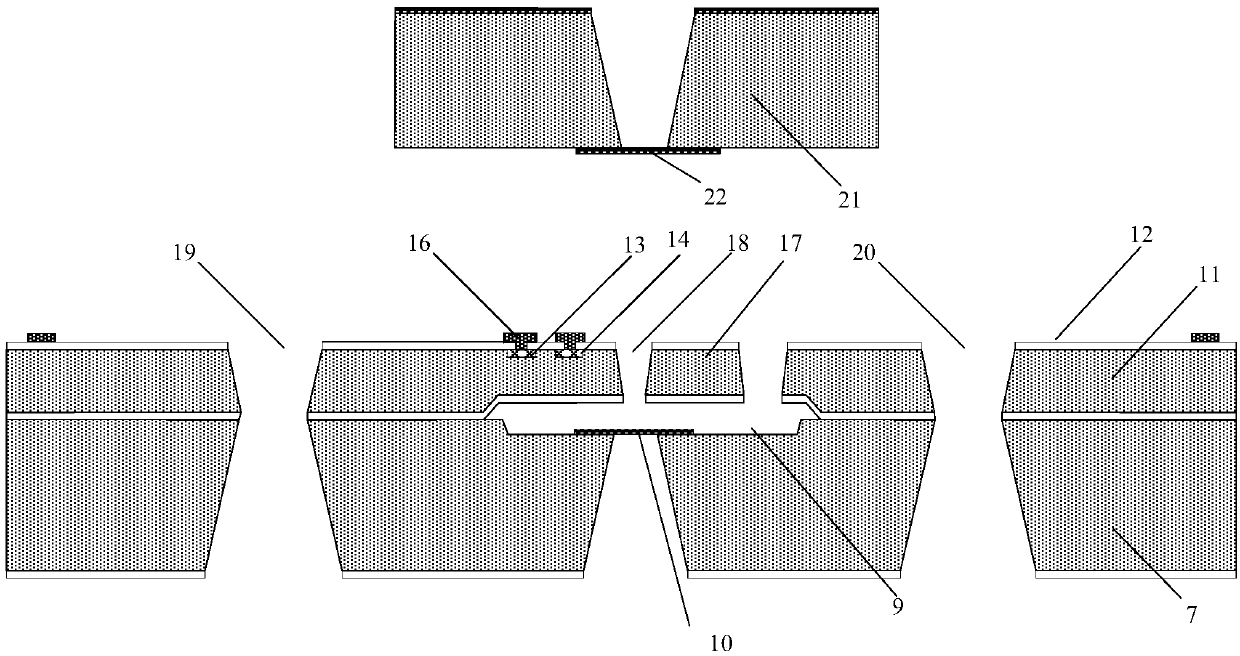
Chip used for realizing structure activity relationship indirect in-situ characterization with TEM and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109682710AAvoid destructionCapture quality changes in real timeElectric discharge tubesPreparing sample for investigationResonanceEngineering
The invention provides a chip used for realizing structure activity relationship indirect in-situ characterization with a TEM and a manufacturing method thereof. The chip comprises a main chip body and an auxiliary chip body, the main chip body comprises a detection cantilever beam, a main chip body groove, an observing cantilever beam with an observing hole, a main chip body window and an air hole; the auxiliary chip body comprises an auxiliary chip body window used for detecting the quality change of a to-be-detected sample located on the detection cantilever beam through the resonance of the cantilever beam; the main chip body and the auxiliary chip body are arranged oppositely and separately fixed to a TEM sample pole, and a closed space is formed by the main chip body, the auxiliary chip body and the TEM sample pole; the TEM observes the morphology change of the to-be-detected sample located on the observing cantilever beam through the auxiliary chip body window, the observing hole and the main chip body window. Through the chip, indirection in-situ real-time characterization of the morphology change and the quality change can be realized in the TEM, and the chip can be widelyapplied to TEM in-situ characterization of a nanometer material during a gas-solid reaction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
BCG-polysaccharide and preparation and analysis identification methods thereof
ActiveCN105367674AImprove the immunitySimple and fast operationComponent separationCelluloseFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a BCG-polysaccharide and a preparation method and an analysis identification method thereof. The preparation method includes using BCG-PSN as raw material, using DEAE-32 cellulose chromatographic column to perform elution by using deionized water as an eluant according to physical property and chemical property differences of polysaccharide and nucleic acid, collecting an eluate, performing dialysis and desalting, performing condensation, and performing freeze drying to obtain BCG-polysaccharide with molecular weight of 1.78*10<4>Da. The analysis identification method includes performing complete acid hydrolysis and methylation of the BCG-polysaccharide, identifying the BCG-polysaccharide by means of GC-MS, IR, and NMR. The BCG-polysaccharide is a glucan having a main chain of (1->4)-alpha-D-Glcp and containing a few branches of ->4,6)-alpha-D-Glap-(1->, the BCG-polysaccharide has one branch in average eight main chain residue, and the main chain has a deoxidized methyl doublet on the position C6. The preparation method is simple, high-efficient, and without damage, and the BCG-polysaccharide obtained by separating and purifying has high product purity. The structural characterization of the BCG-polysaccharide has important meaning on the researches of effective component and structure-activity relationship of BCG-polysaccharide.
Owner:JIUZHITANG +1
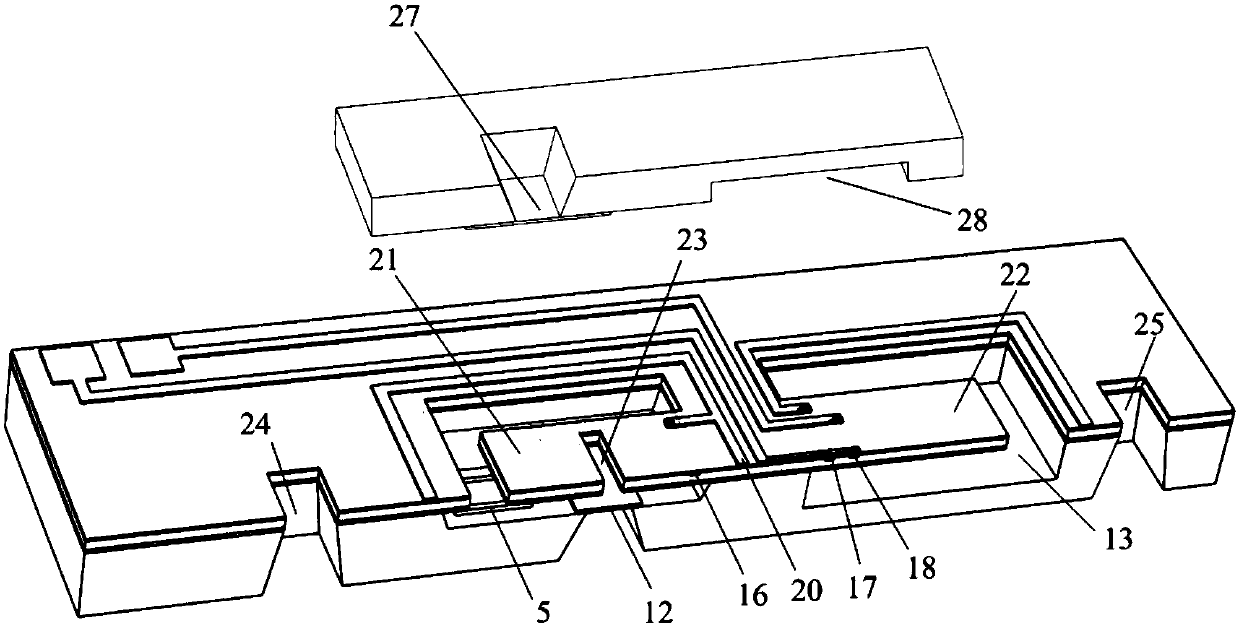
Chip for realizing structure activity relationship direct in-situ characterization through TEM and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109682711ACapture quality changes in real timeAvoid destructionElectric discharge tubesPreparing sample for investigationResonanceEngineering
The invention provides a chip used for realizing structure activity relationship direct in-situ characterization with a TEM and a manufacturing method thereof. The chip comprises a main chip body andan auxiliary chip body, the main chip body comprises a cantilever beam with an observing hole, a main chip body groove, a main chip body window and an air hole; the auxiliary chip body comprises an auxiliary chip body window used for detecting the quality change of a to-be-detected sample located on the cantilever beam through the resonance of the cantilever beam; the main chip body and the auxiliary chip body are arranged oppositely and separately fixed to a TEM sample pole, and therefore a closed space is formed by the main chip body, the auxiliary chip body and the TEM sample pole; the morphology change of the to-be-detected sample located on the cantilever beam is observed through the auxiliary chip body window, the observing hole and the main chip body window. Through the chip, observation of the morphology change and detection of the quality change can be realized for the same to-be-detected sample in the TEM so as to conduct direct in-situ real-time characterization, and the chip can be widely applied to TEM in-situ characterization of a nanometer material during a gas-solid reaction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
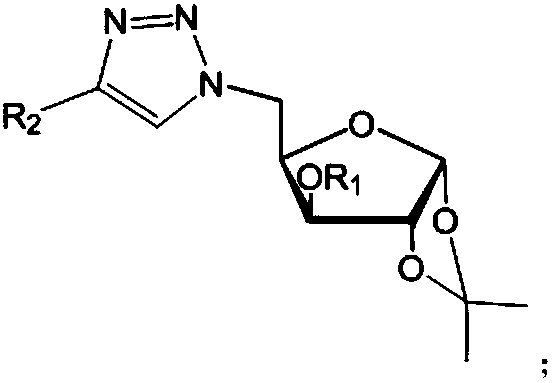
Furan glucosyl triazole type compound and preparation method and bactericide thereof
ActiveCN107857782AHigh antibacterial activityGood antibacterial effectBiocideSugar derivativesFuranPhenyl group
The invention relates to the field of bactericidal compounds, in particular to a furan glucosyl triazole type compound and a preparation and a bactericide thereof. The molecular formula of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound is shown in the following description, wherein R1 is methyl or benzyl, and R2 are phenyl and derivative of the phenyl or ethyl derivatives. Based on structural characteristics of the substrate fructose-6-phosphate and an ISOM catalytic hypothesis mechanism, the inventor adopts a five-membered furan glucose derivative with a similar structure as a basic skeleton, introduces an effective active group triazole structure of pesticides, designs a series of novel furan glucosyl triazole type compounds for the first time, studies the biological activities of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound, examines structure-activity relationships of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound, and lays the foundation for selecting better inhibitors.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
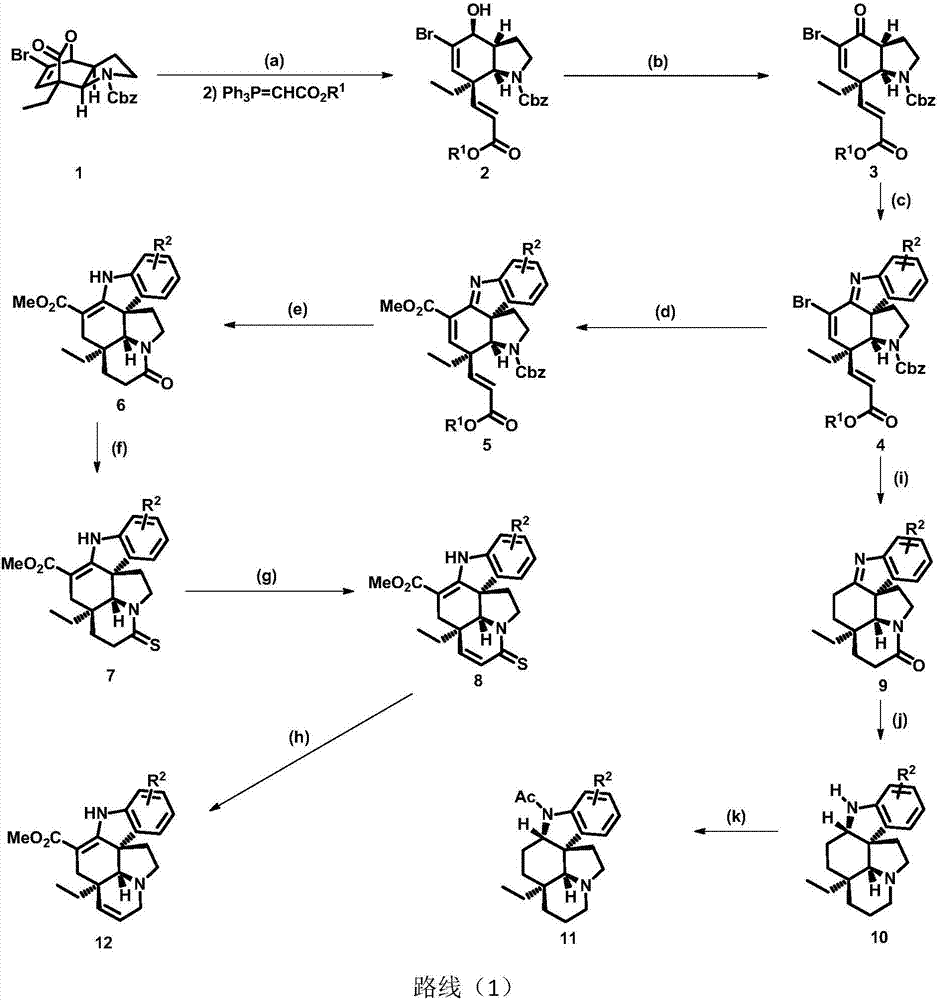
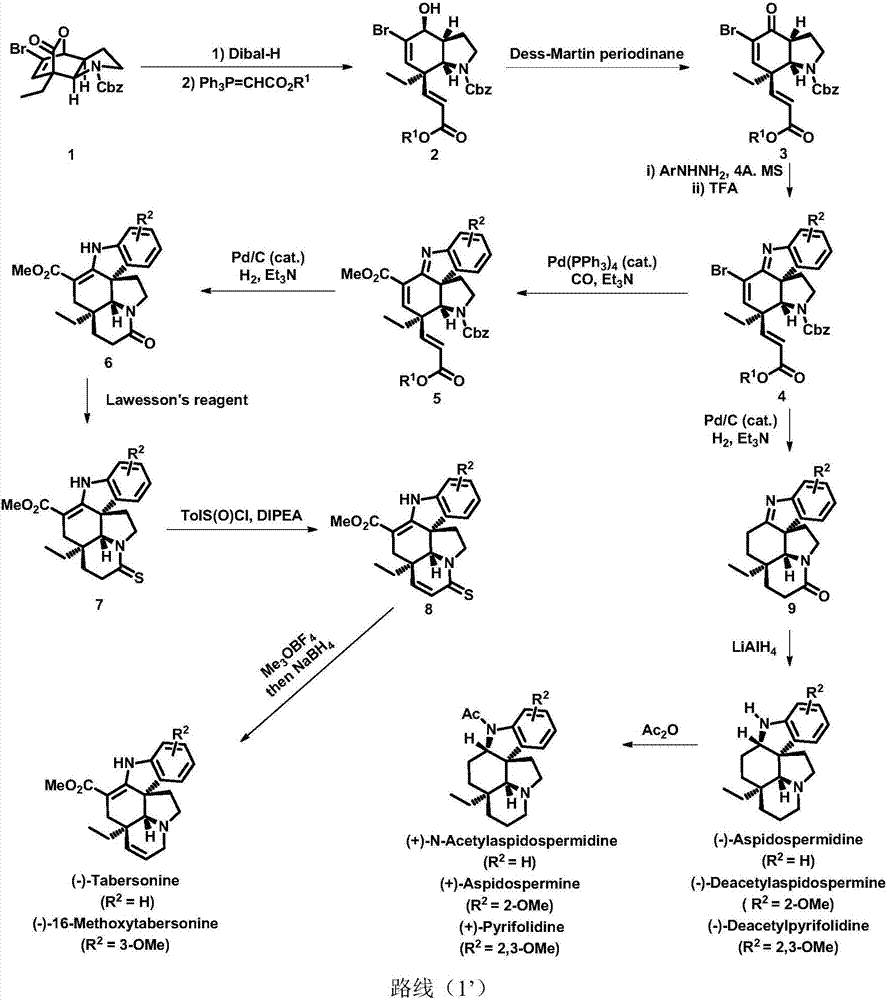
Method for asymmetric synthesis of Aspidosperma alkaloids
ActiveCN107312001AHigh yieldShort synthetic routeAsymmetric synthesesWittig reactionEnantioselective synthesis
The invention discloses a method for asymmetric synthesis of Aspidosperma alkaloids. According to the method, a bridged ring compound as shown in a formula (1) is subjected to reduction, the Wittig reaction, oxidation, Fischer indole rearrangement and the like so as to obtain a key intermediate, i.e., a compound as shown in a formula (4); the compound as shown in the formula (4) undergoes a variety of conversion so as to obtain a series of Aspidosperma alkaloids; and reaction routes are as shown in a route (1). The method provided by the invention starts with the compound as shown in the formula (1) and can provide good technical support for subsequent mass production of Aspidosperma alkaloids and research on structure-activity relationship.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
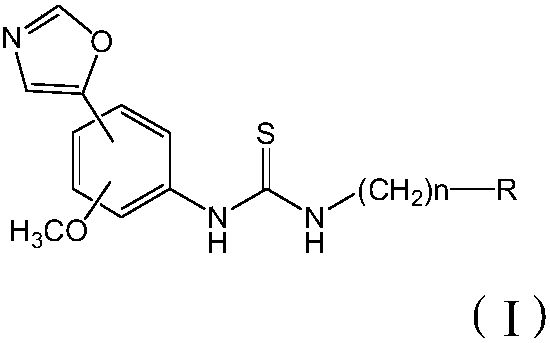
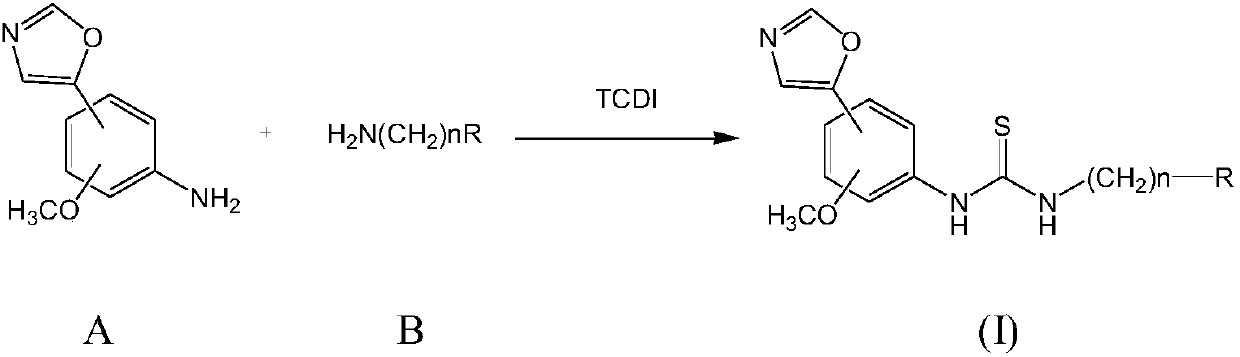
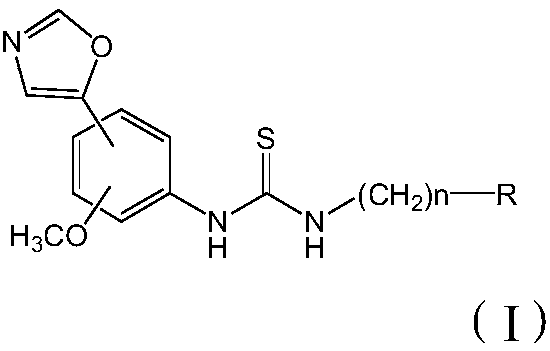
Thiourea compounds and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109970675ACtiveHas antiviral activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryThioureaMechanism of action
The invention discloses a group of thiourea compounds and a preparation method and application thereof. The oxazole phenylthiourea compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof has a structure represented by the general formula (I). According to the present inventors, a class of compounds having both IMPDH inhibitory activity and broad-spectrum antiviral activity and pharmaceutical saltsthereof are screened and obtained by studying the structure-activity relationship and the action mechanism of active compounds, wherein the virus comprises influenza virus, hepatitis B virus, coxsackie virus and herpes simplex virus. The invention lays a foundation for the development and application of the compounds as antiviral and other related drugs and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, andprovides a new technical means for antiviral treatment.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
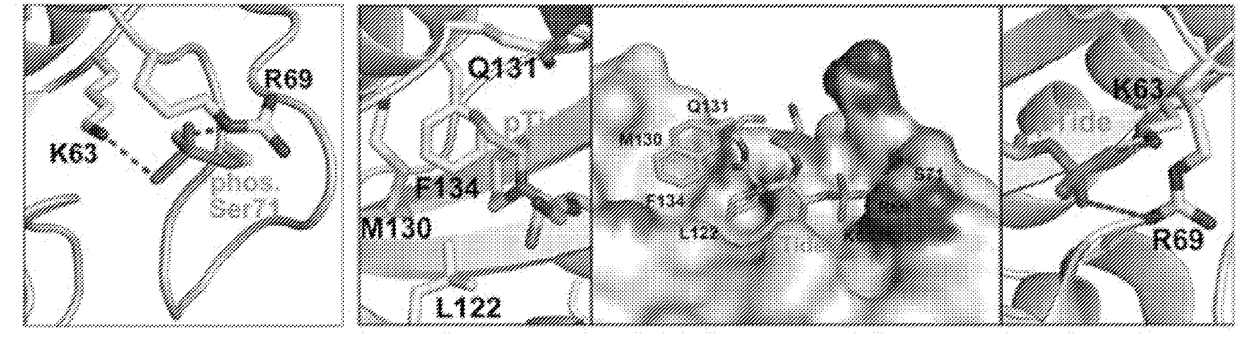
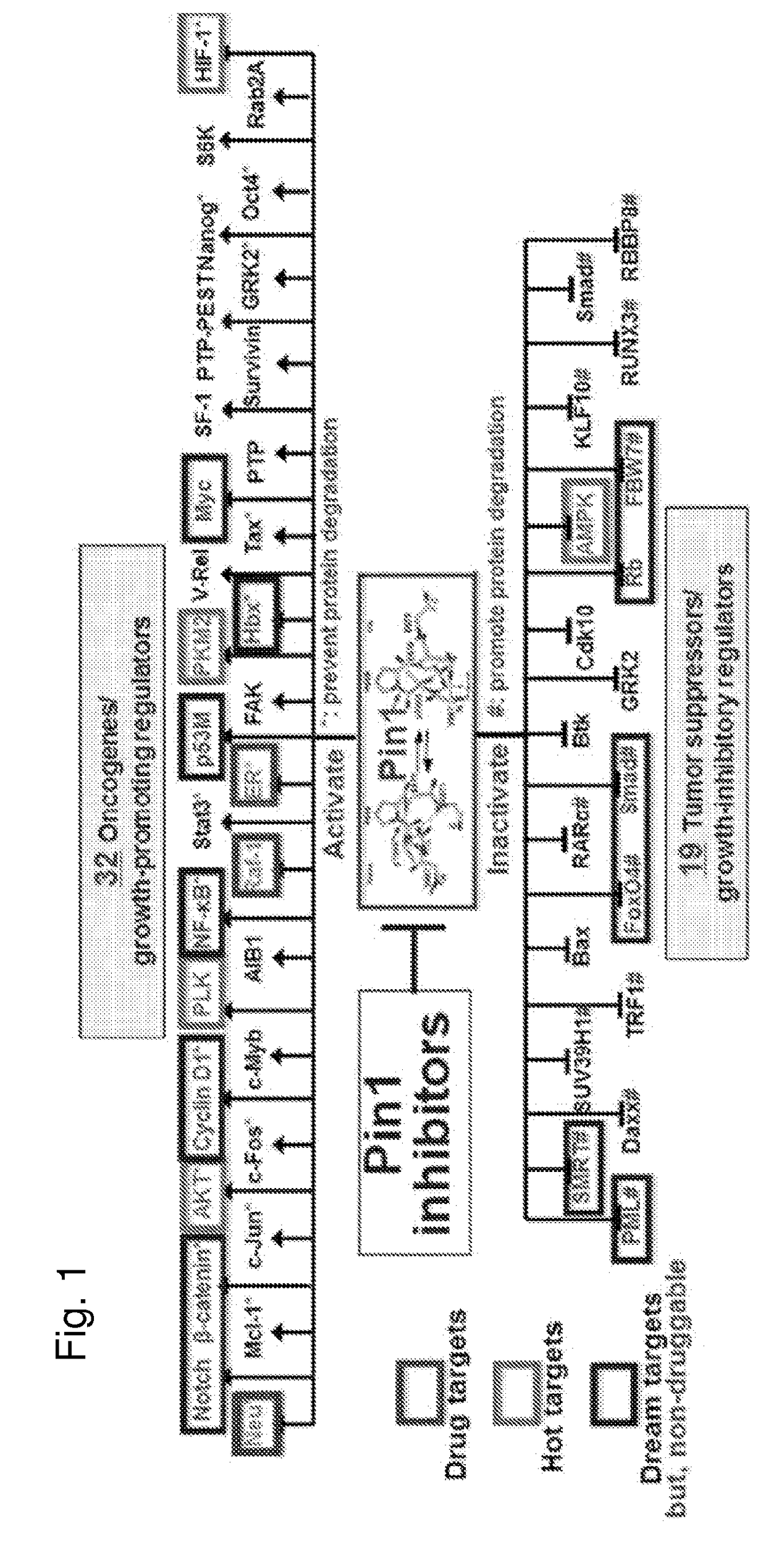
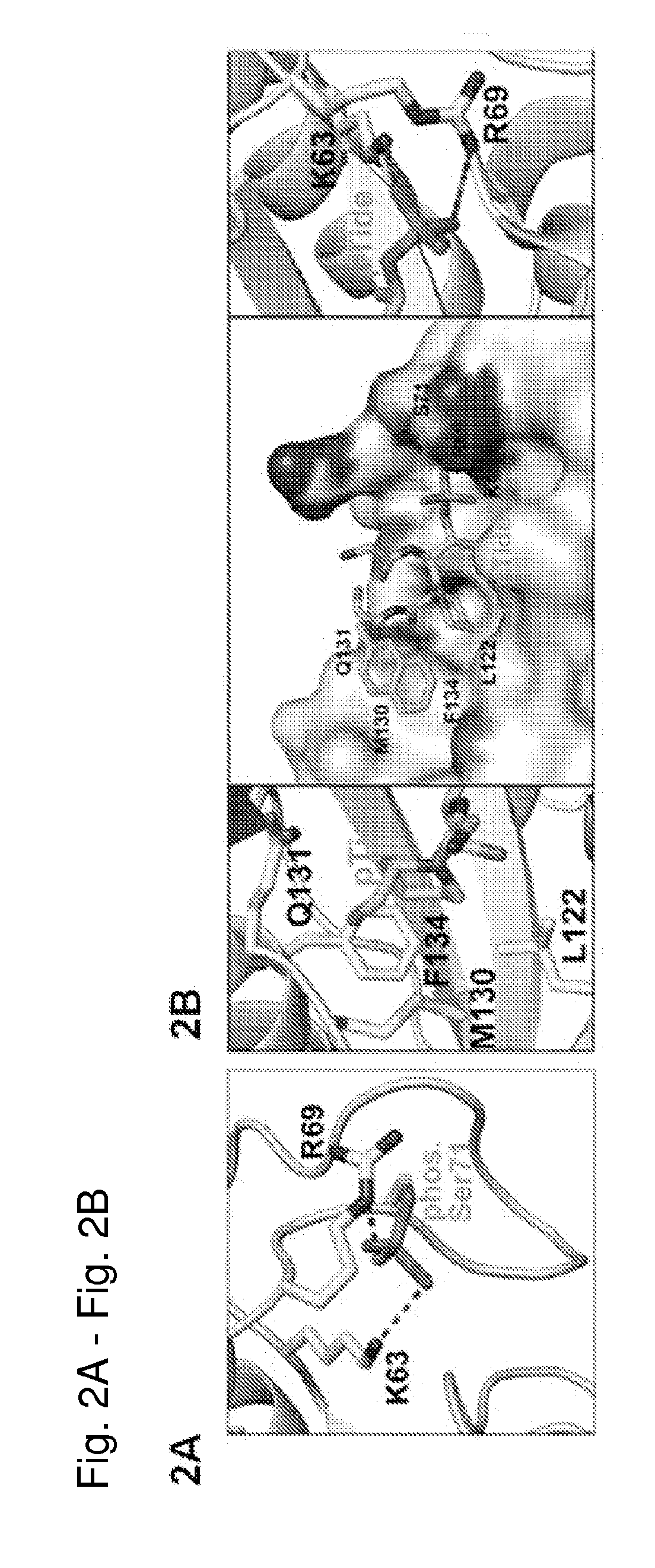
Enhanced atra-related compounds derived from structure-activity relationships and modeling for inhibiting pin1
InactiveUS20170112792A1Increasing and decreasing sizeIncreasing and decreasing and lengthCompound screeningOrganic chemistryDiseasePhosphorylation
The invention features all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-related compounds capable of associating with Pin1 and methods of identifying the same. The invention also provides methods of treating a condition selected from the group consisting of a proliferative disorder, an autoimmune disease, and an addiction condition characterized by elevated Pin1 marker levels, Pin1 degradation, and / or reduced Pin1 Ser71 phosphorylation in a subject by administering a retinoic acid compound. Additionally, the invention features methods of treating proliferative disorders, autoimmune diseases, and addiction conditions (e.g., diseases, disorders, and conditions characterized by elevated Pin1 marker levels) by administering a retinoic acid compound in combination with another therapeutic compound. The invention also features a co-crystal including Pin1 and a retinoic acid compound. Finally, the invention also provides methods of developing and identifying enhanced Pin1-targeted ATRA-related compounds based on the newly defined unique binding pockets in the Pin1 active site revealed from the co-crystal structure, structure-activity relationship, and structural modeling.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
1-substituted isoquinoline ketone compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110317169AEasy to operateEasy to routeOrganic chemistry methodsChemical synthesisSide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis and relates to a 1-substituted isoquinoline ketone compound and a preparation method thereof. A benzoazacyclo 1-substituted isoquinoline skeleton serving as an important heterocyclic skeleton exists in many natural products or medicines, shows various types of biological activity and mainly has antibacterial, anti-inflammation, anti-depression, anti-oxidation, anti-pathogenic microorganism, blood pressure and blood glucose reducing, immune regulating, pain alleviating and anti-irrhythmia functions and the like. Therefore, developing a novel synthesis method for implementing mass synthesis of the 1-substituted isoquinoline ketone compound is remarkably beneficial to research of a structure-activity relationship, a clinical novel process and the like so as to discover a series of excellent lead compounds with high activity and less toxic and side effects.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Application of aromatic ester compounds in preparing anti-tumor drugs
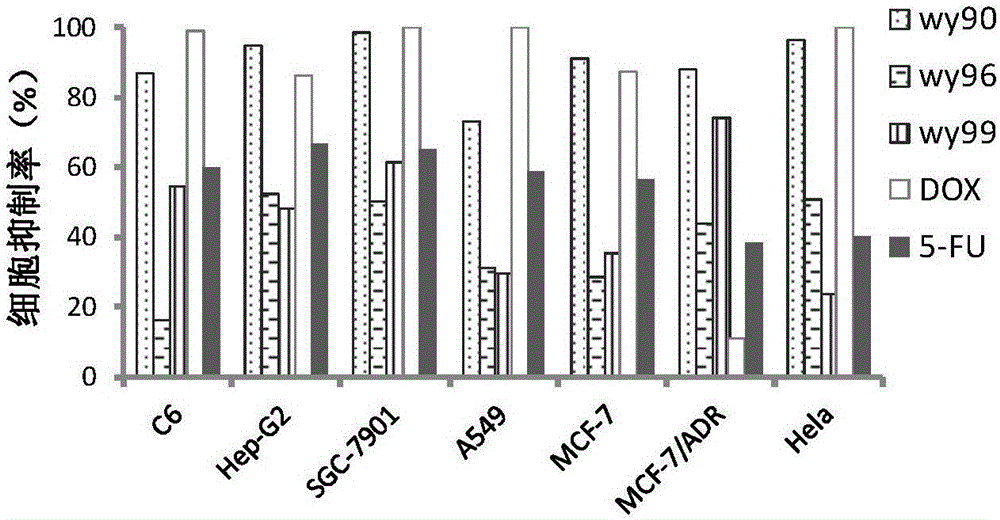
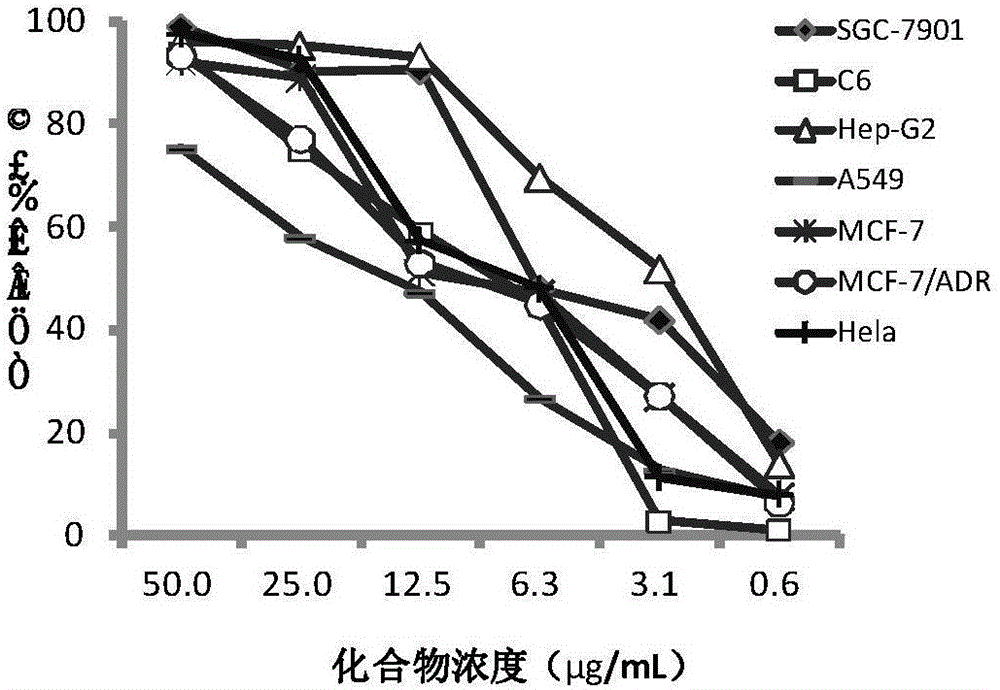
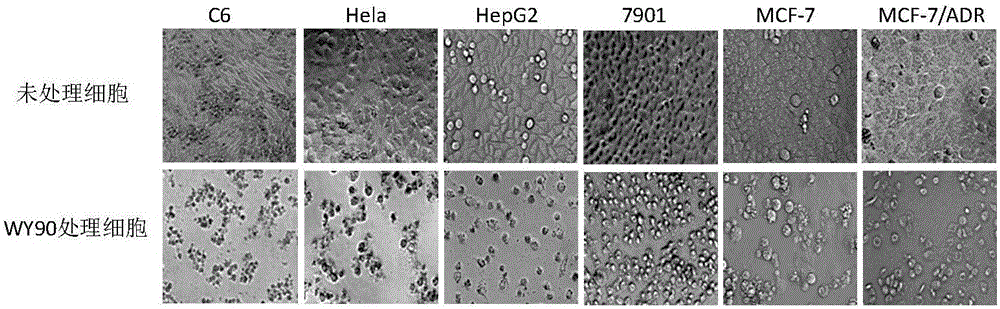
The invention relates to the field of anti-tumor drugs and provides an application of aromatic ester compounds in preparing anti-tumor drugs. The aromatic ester compounds are compounds shown by WY90, WY96 and MY99. According to anti-tumor activity study experiments, the compounds all show activity in resisting tumor cell proliferation in different degrees, wherein the WY90 shows the strongest inhibiting effect and can efficiently inhibit the tumor cell growth at low concentration to promote tumor cell apoptosis, and the inhibiting effect is stronger than that of a positive control compound. The preparation process of the compounds is simple and easy to implement, and the raw materials are cheap and easily available; and anti-tumor effect targets can be found through structure-activity relationship study, so that a valuable guide effect is provided for further drug development. The aromatic ester compounds provided by the invention provide a foundation for new drug screening.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN107226870AGood effectEasy to prepareComponent separationSkeletal disorderChemical structurePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and health care products and particularly relates to an Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer and its preparation method and application. The Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer comprises an Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer ABP3-2, an Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer ABW1-1, an Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer ABP1-2 and an Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer ABP4-3, and has molecular weight of 1000-100000Da. The preparation method has simple processes, mild reaction conditions and large-scale production feasibility. The high-purity Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer chemical structure is identified so that the structure is ensured and the structure basis is provided for study of a pharmacological activity mechanism. The pure Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer lays the foundation for Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer drugs and health products, quality control of the Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide polymer drug and health product and deep research of the structure-activity relationship and action mechanism.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
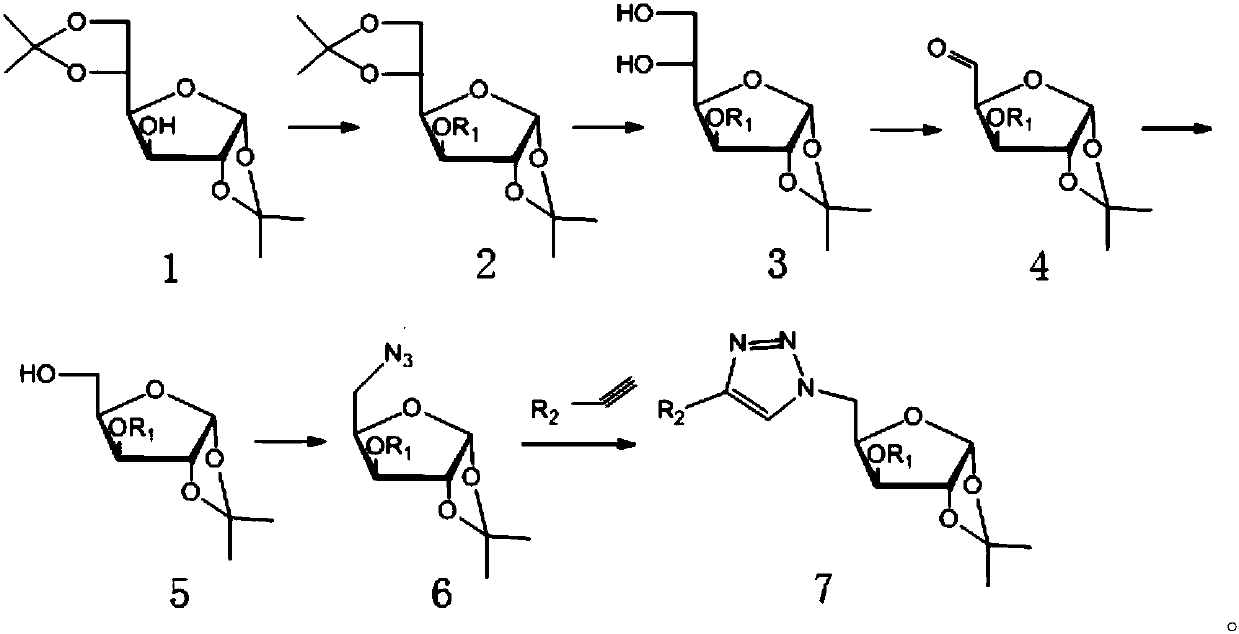
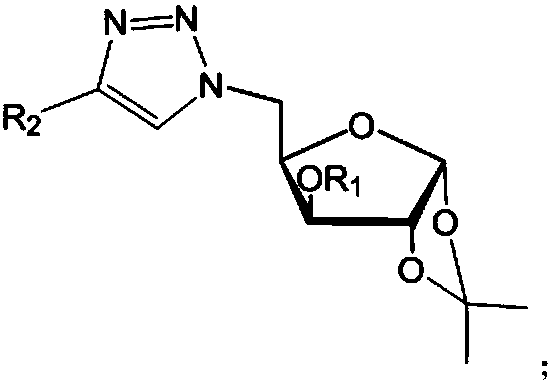
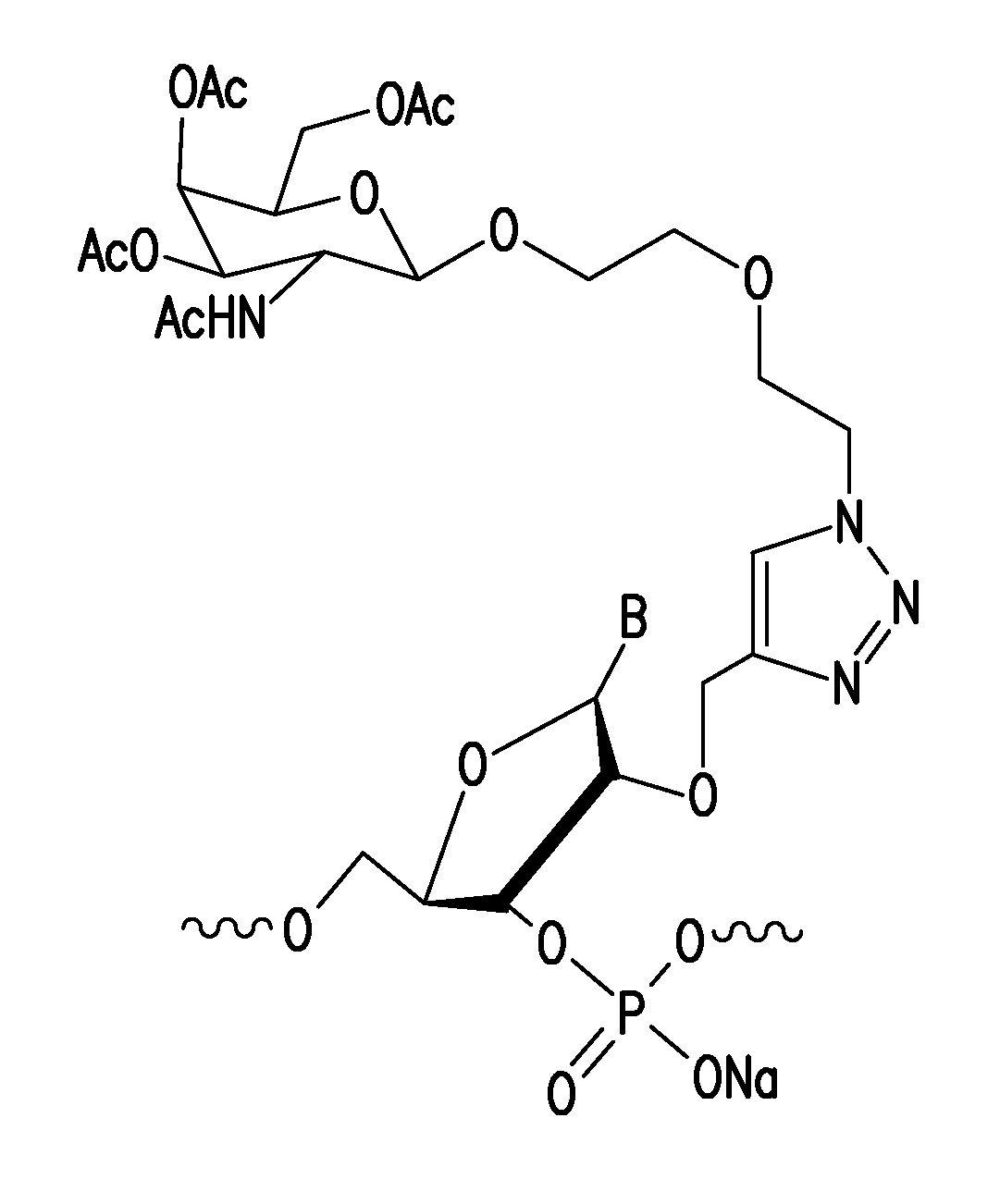
Post-synthetic chemical modification of RNA at the 2'-position of the ribose ring via "click" chemistry
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com