Combined technology for extracting and separating small-molecular active peptide from marine organism protein resources
A technology for small molecule active peptides and marine organisms, applied in the field of active peptides, can solve the problems of cumbersome extraction and separation process, low efficiency, and inability to effectively combine separation technologies, and achieve the effect of simple and feasible technical route, easy implementation, and promotion of development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
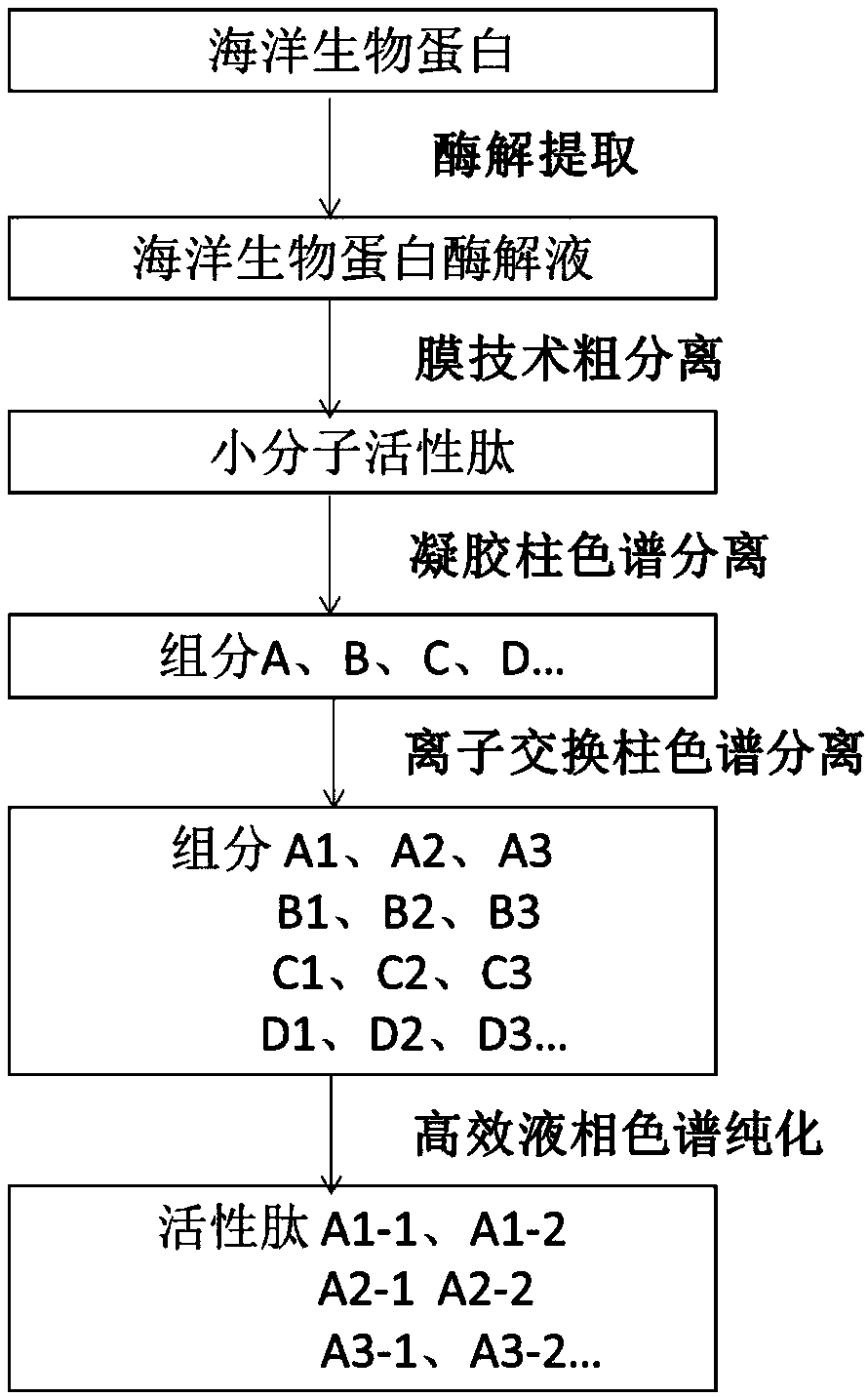
[0023] The combined process of separating and purifying active peptides from marine biological protein resources, the specific steps are as follows:
[0024] Step (1), preparation of blue mussel protein enzymatic hydrolyzate: add water and homogenate the blue mussel viscera, add 4 times the volume of water, and then add 0.2% of the total liquid volume of compound protease (mass ratio: neutral protease: alkali Protease: Flavor protease = 3:3:4), enzymatic hydrolysis at 50°C for 3 hours, the pH value of the enzyme reaction was controlled at 9, after the enzymolysis was completed, the temperature was raised to 80°C to inactivate the enzyme for 15 minutes, and the enzymatic hydrolyzate of blue mussel protein was obtained .
[0025] Step (2), rough separation of enzymatic hydrolyzate: centrifuge the proteolyzate obtained in step (1) to remove particulate matter and deformed macromolecular proteins, and then use an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 5000 Da ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The joint process of separating and purifying active peptides from marine biological protein resources, the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] Step (1), preparation of oyster shell protein enzymatic hydrolyzate: add 20 times the volume of water after the dried oyster is crushed, and then add 0.4% composite protease of the total liquid volume (mass ratio: neutral protease: alkaline protease: flavor protease=4 :3:3), enzymatic hydrolysis at 40°C for 6 hours, the pH value of the enzyme reaction was controlled at 8.5, and after the end of the enzymolysis, the temperature was raised to 90°C to inactivate the enzyme for 10 minutes to obtain oyster protein enzymatic hydrolyzate.
[0032] Step (2), rough separation of the enzymatic hydrolyzate: centrifuge the proteolyzate obtained in step (1) to remove particulate matter and deformed macromolecular proteins, and then use an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 5000 Da for rough separation to remove po...
Embodiment 3
[0037] The joint process of separating and purifying active peptides from marine biological protein resources, the specific steps are as follows:
[0038] Step (1), preparation of shrimp protein enzymatic hydrolyzate: add 20 times the volume of water after the dried shrimp is crushed, and then add 0.5% of the total liquid volume of compound protease (mass ratio: neutral protease: alkaline protease: flavor protease=4: 4:2), enzymolysis at 40°C for 5 hours, the pH value of the enzyme reaction was controlled at 8.8, after the end of the enzymolysis, the temperature was raised to 90°C to inactivate the enzyme for 10 minutes, and the shrimp protein enzymatic hydrolyzate was obtained.
[0039] Step (2), rough separation of the enzymatic hydrolyzate: centrifuge the proteolyzate obtained in step (1) to remove particulate matter and deformed macromolecular proteins, and then use an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 5000 Da for rough separation to remove polysac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com