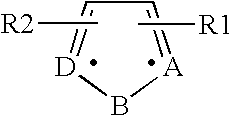Patents
Literature
55 results about "Structural motif" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a supersecondary structure, which also appears in a variety of other molecules. Motifs do not allow us to predict the biological functions: they are found in proteins and enzymes with dissimilar functions.
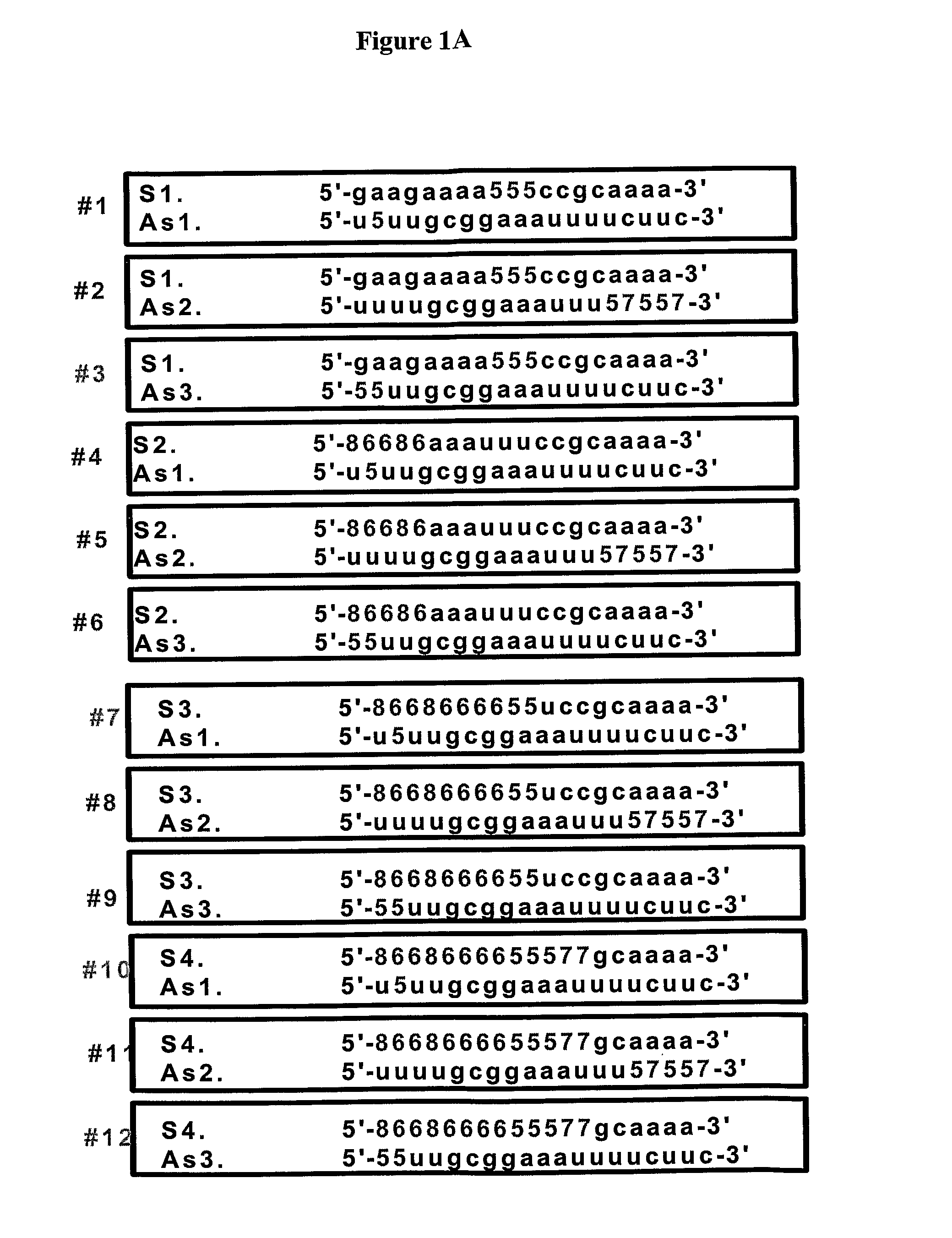
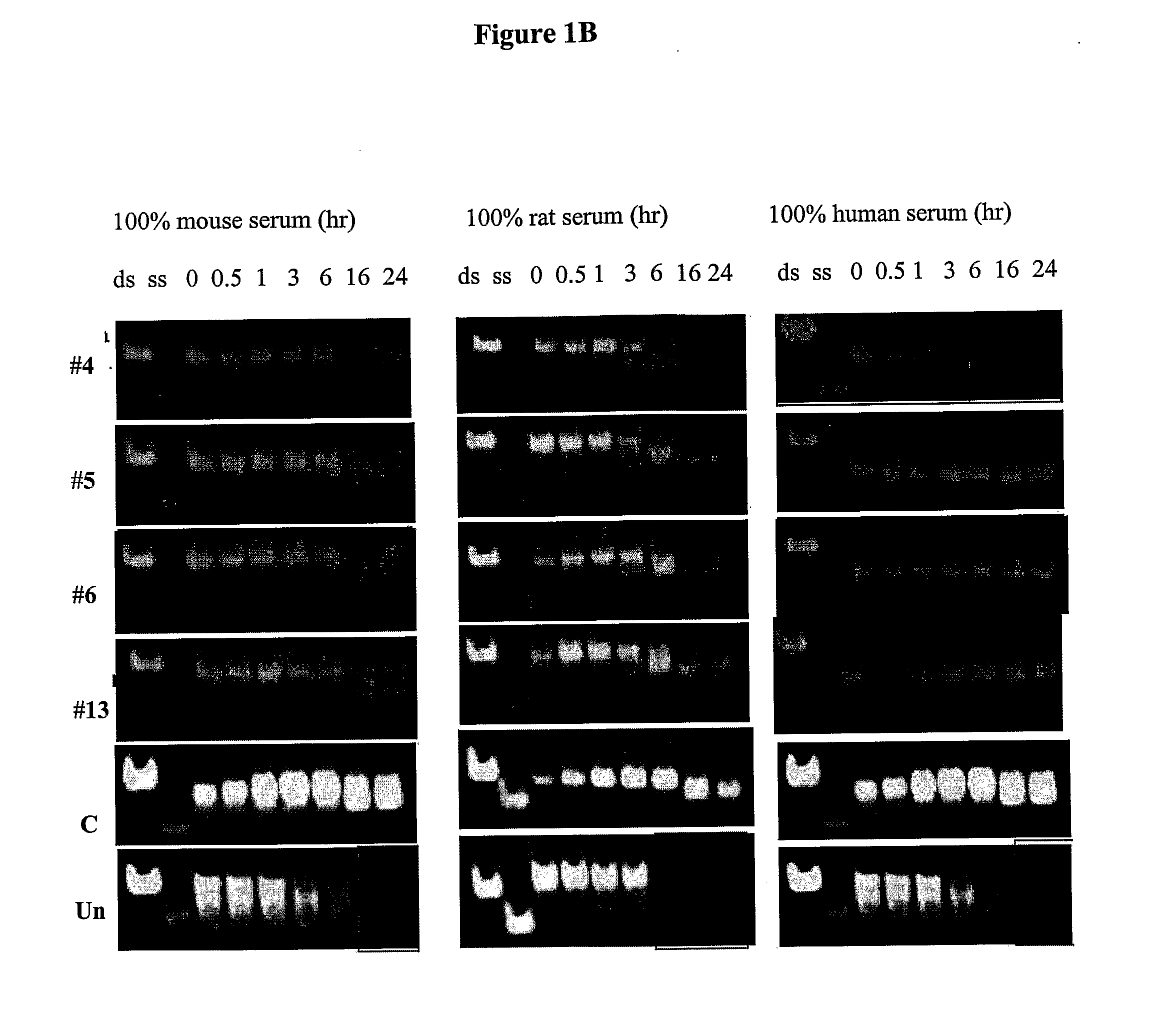
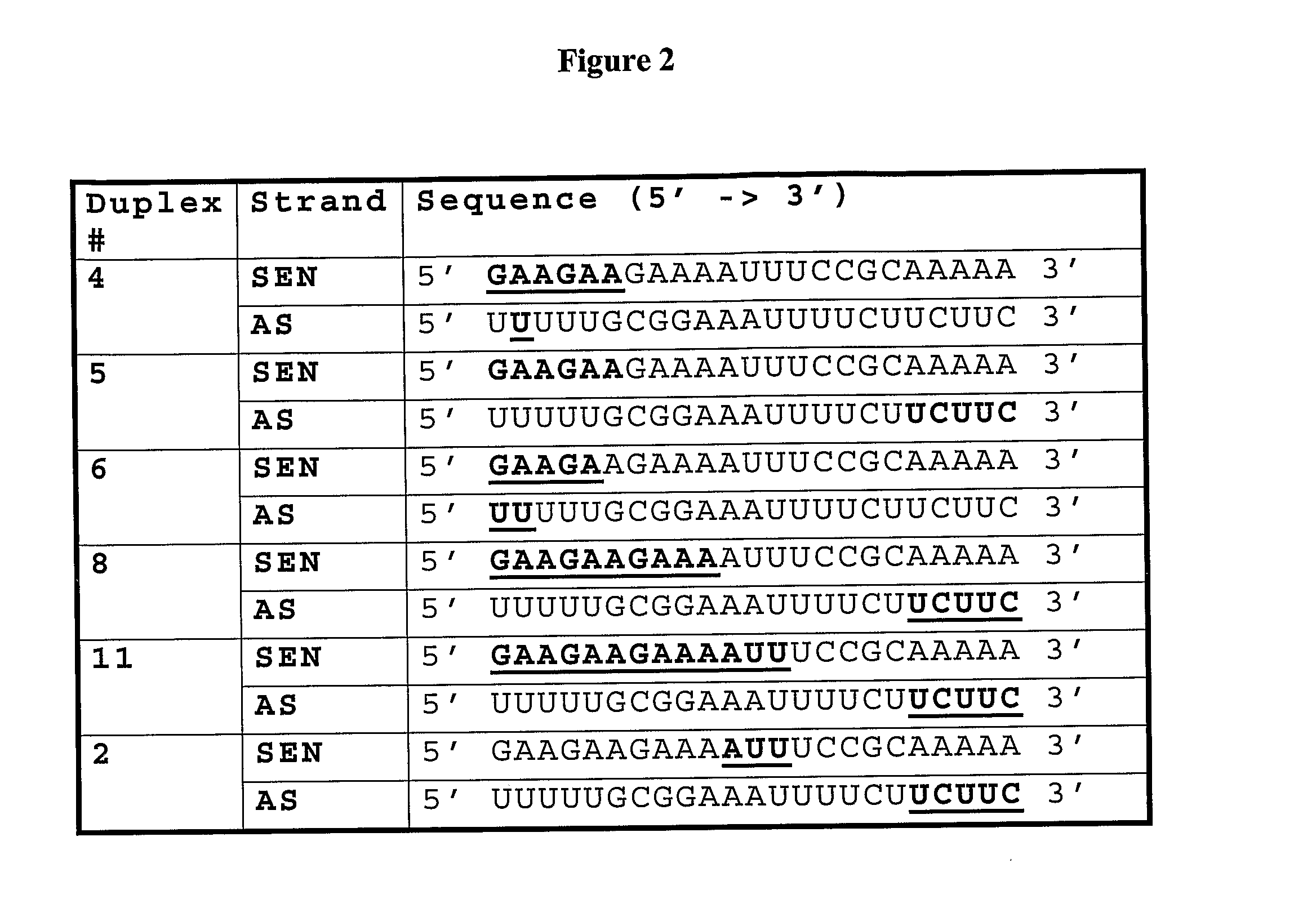
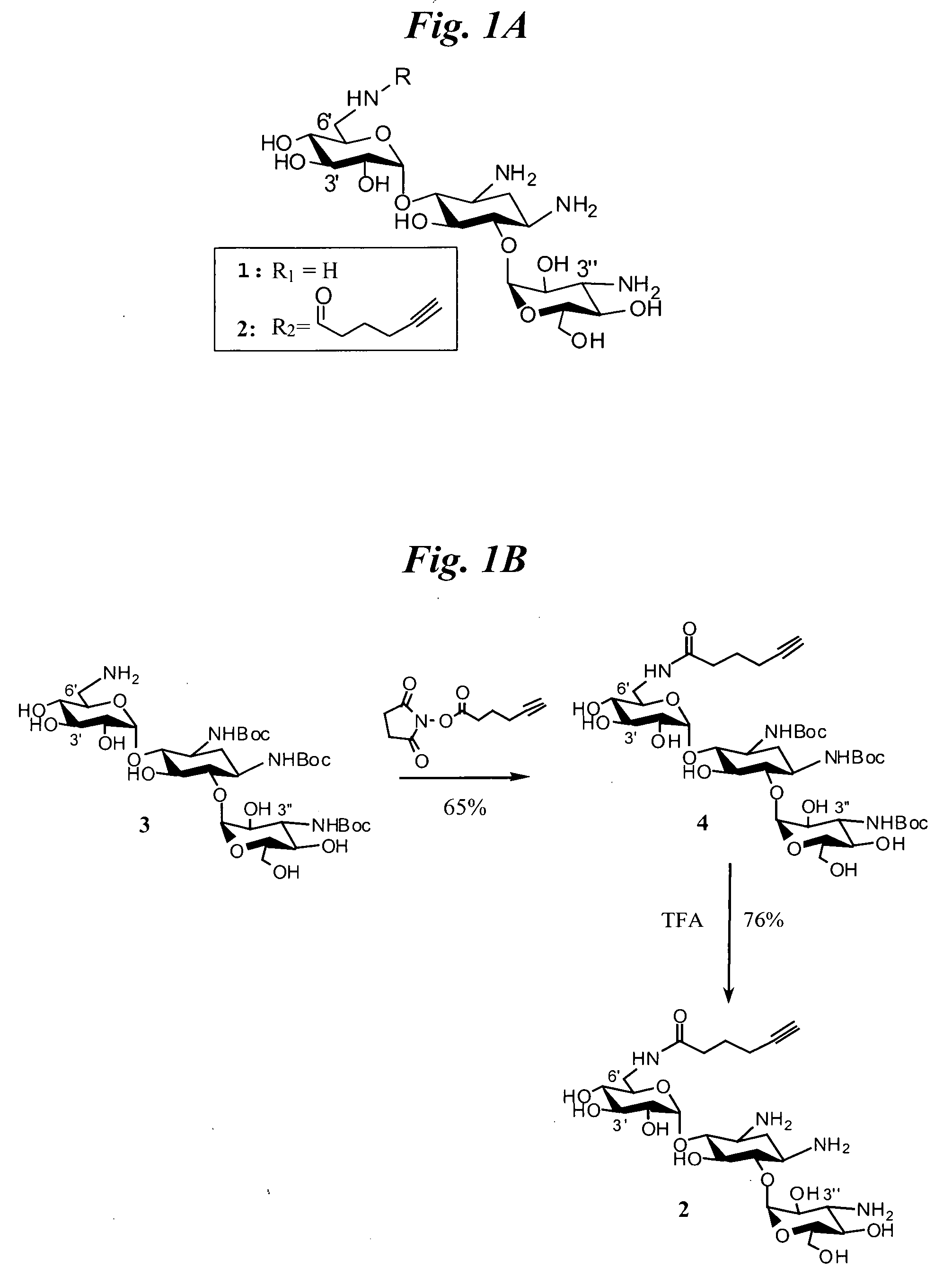
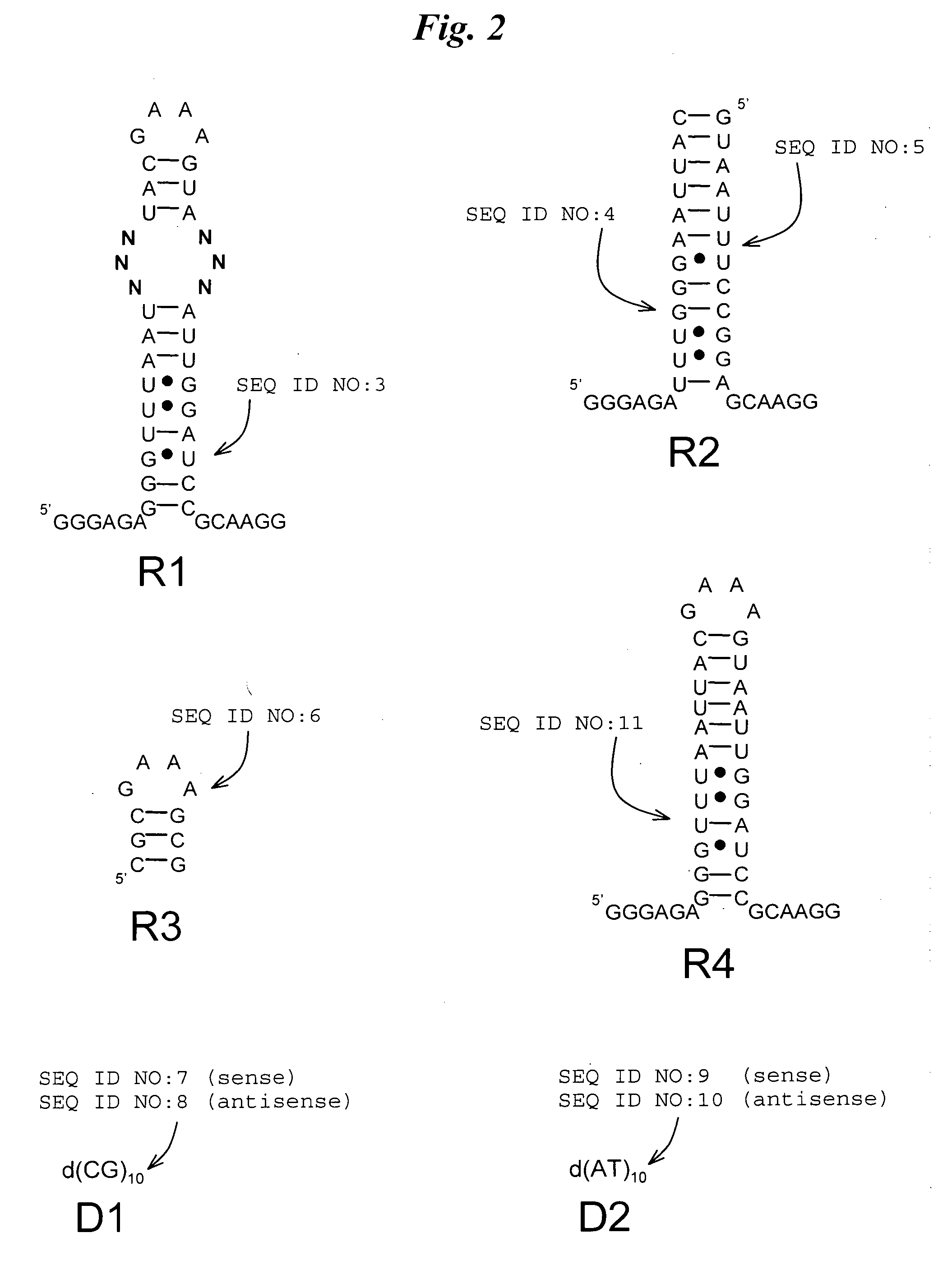
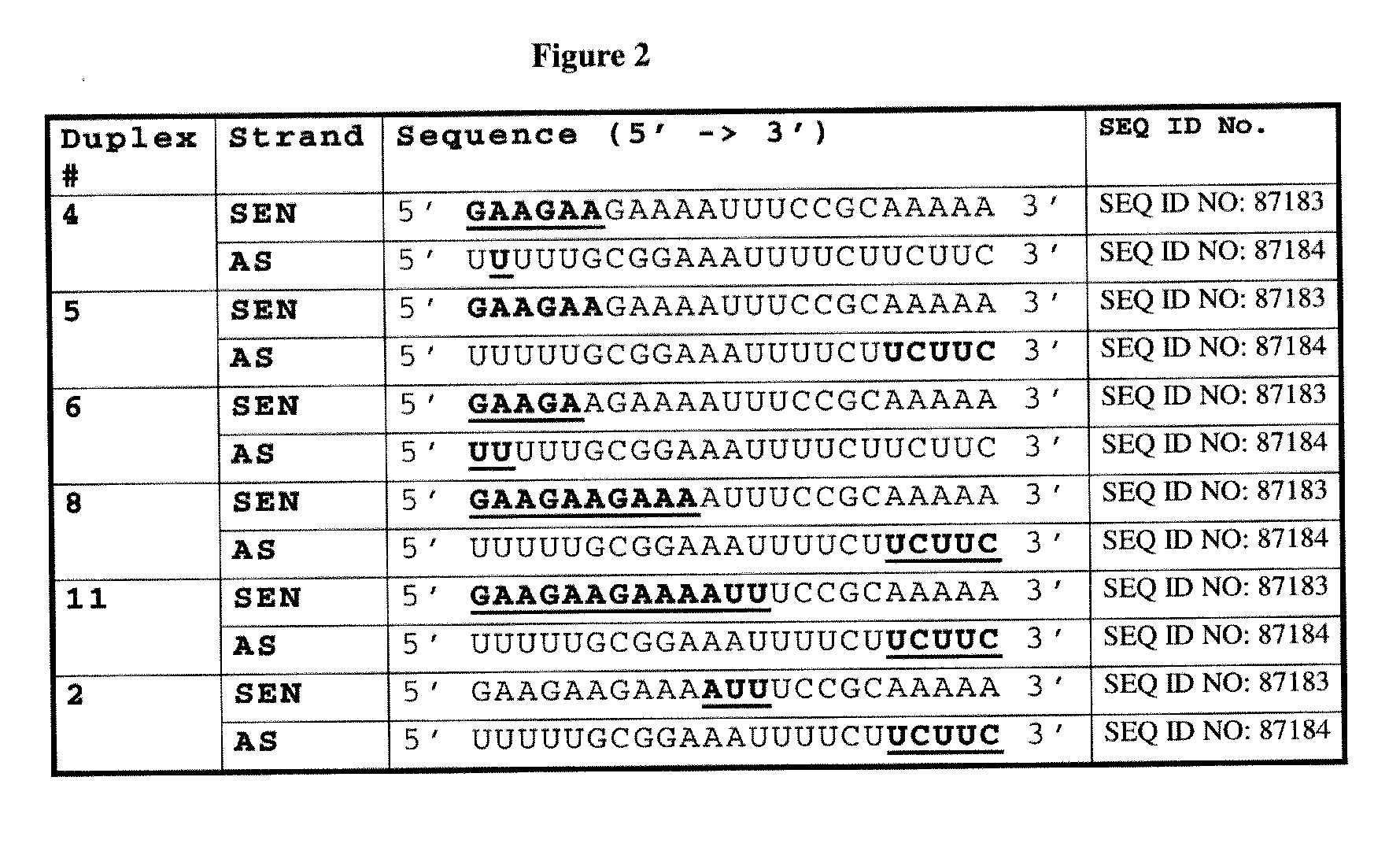
Novel sirna structures
The invention relates to siRNA compounds possessing novel sequences and structural motifs which down-regulate the expression of specific human genes. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides a method of treating and / or preventing the incidence or severity of various diseases or conditions associated with the genes and / or symptoms associated with such diseases or conditions comprising administering to a subject in need of treatment for such disease or condition and / or symptom the compound or the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the subject.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
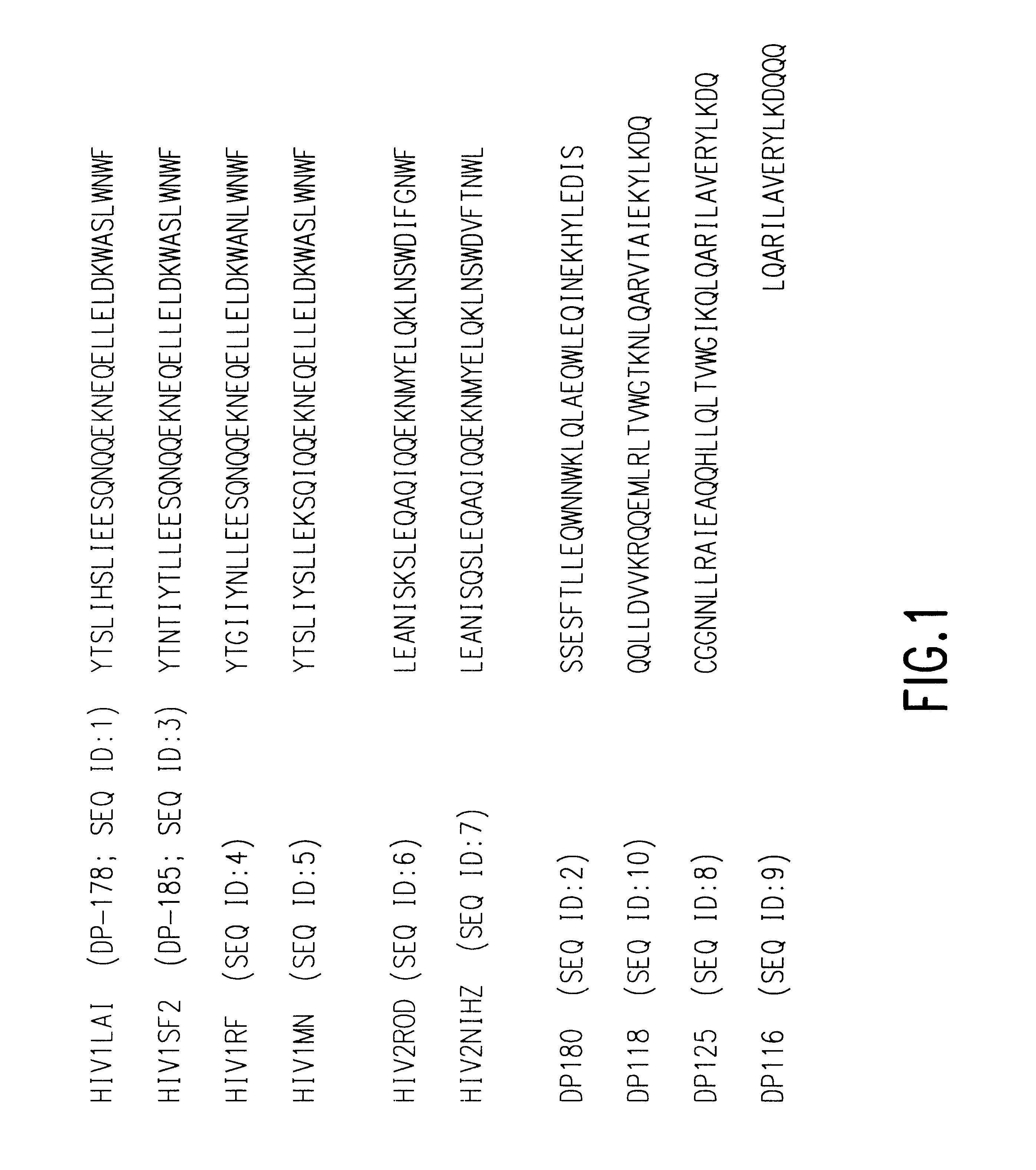
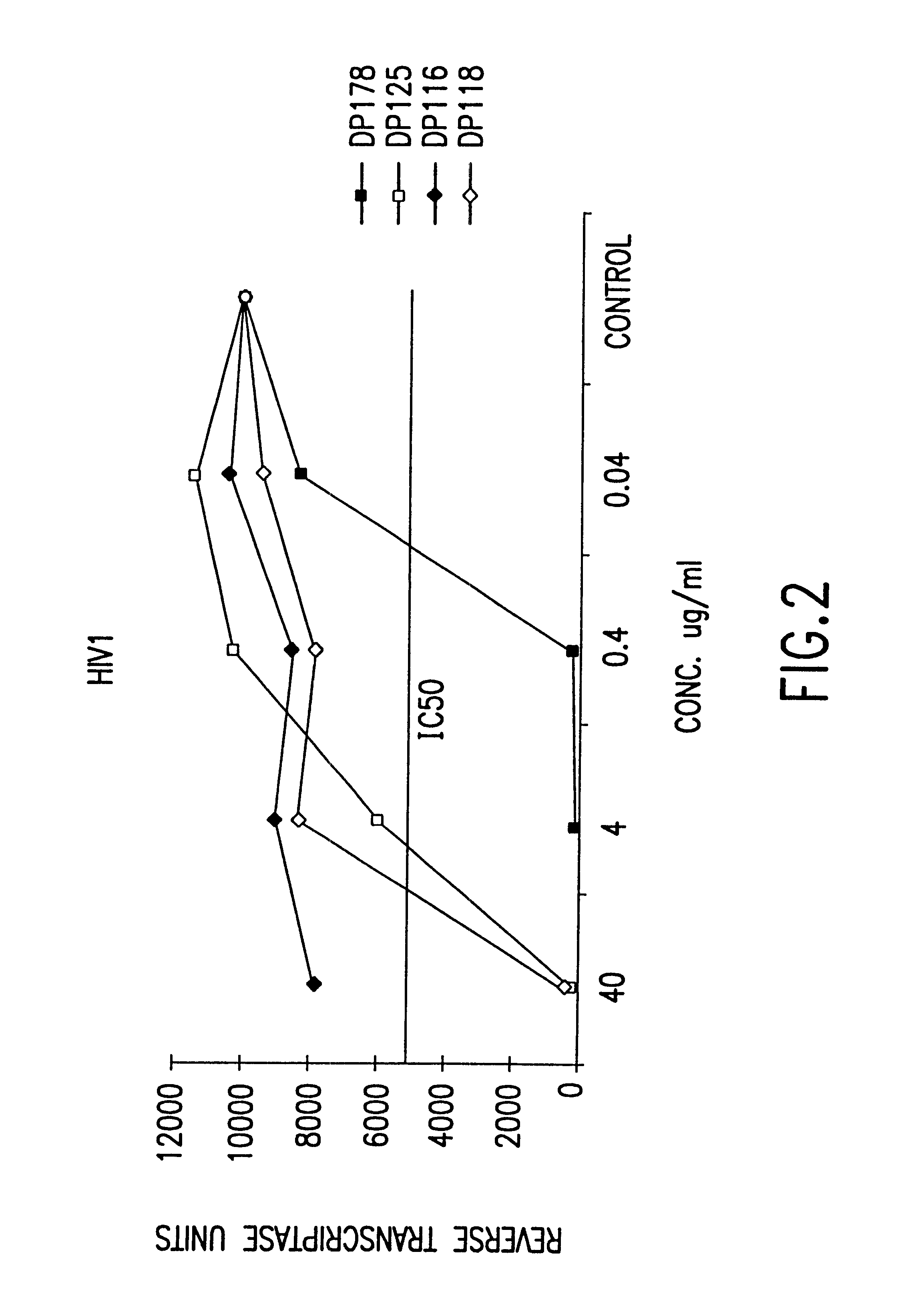
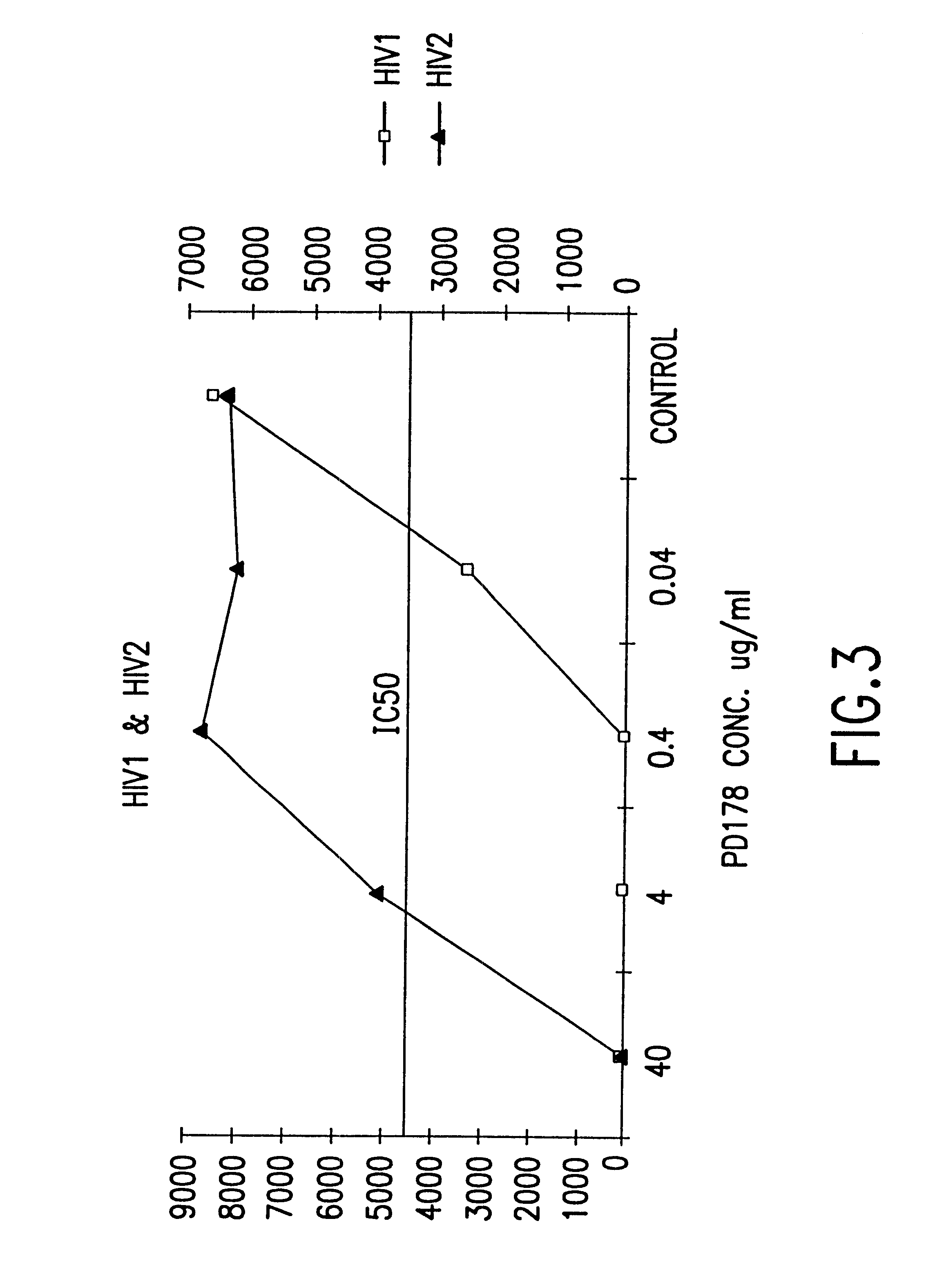
Methods for the inhibition of epstein-barr virus transmission employing anti-viral peptides capable of abrogating viral fusion and transmission
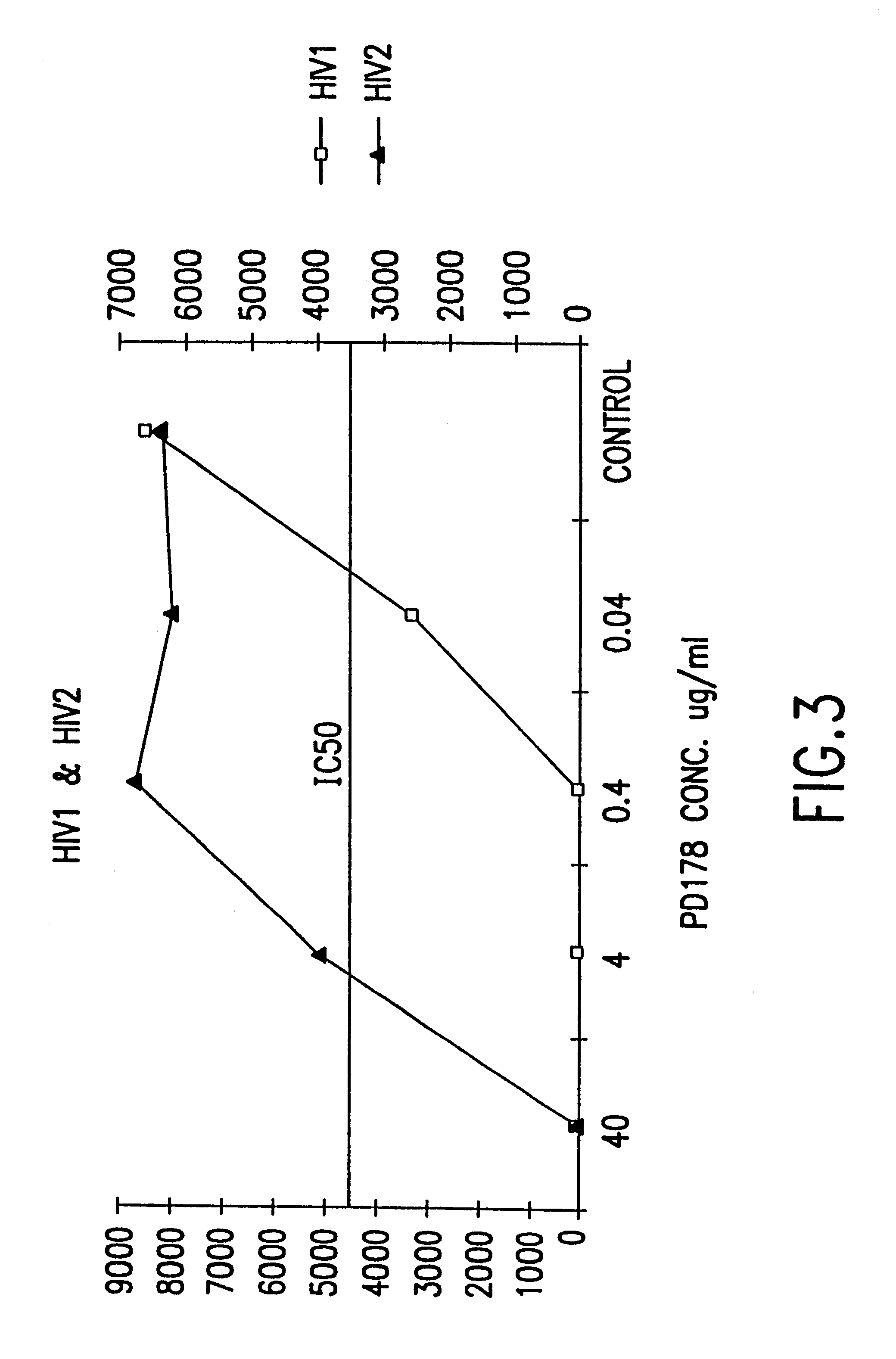
InactiveUS6518013B1SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCell membraneViral life cycle
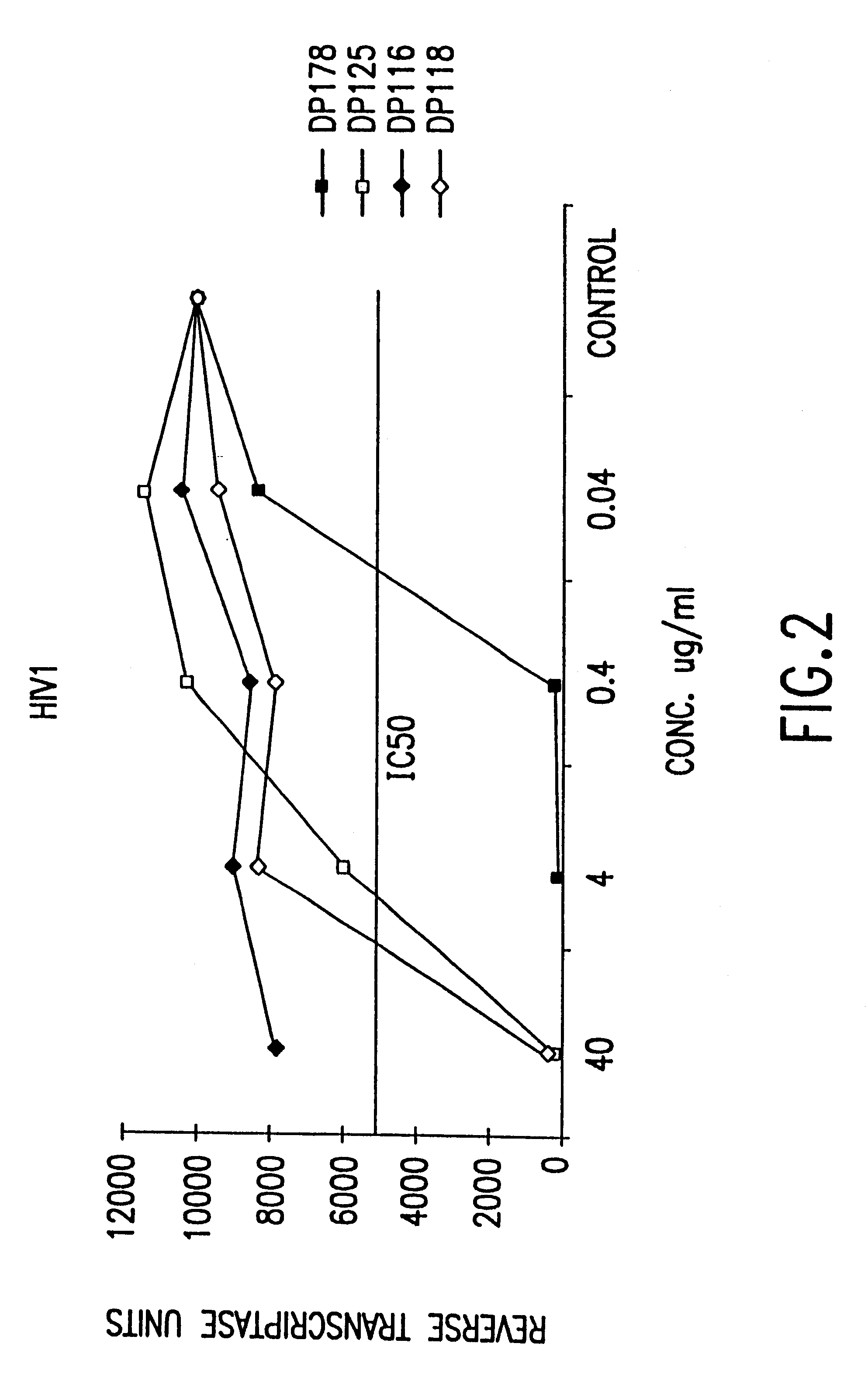
Fusion of the viral envelope, or infected cell membranes with uninfected cell membranes, is an essential step in the viral life cycle. Recent studies involving the human immunodeficiency virus type 1(HIV-1) demonstrated that synthetic peptides (designated DP-107 and DP-178) derived from potential helical regions of the transmembrane (TM) protein, gp41, were potent inhibitors of viral fusion and infection. A computerized antiviral searching technology (C.A.S.T.) that detects related structural motifs (e.g., ALLMOTI 5, 107x178x4, and PLZIP) in other viral proteins was employed to identify similar regions in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Several conserved heptad repeat domains that are predicted to form coiled-coil structures with antiviral activity were identified in the EBV genome. Synthetic peptides of 16 to 39 amino acids derived from these regions were prepared and their antiviral activities assessed in a suitable in vitro screening assay. These peptides proved to be potent inhibitors of EBV fusion. Based upon their structural and functional equivalence to the known HIV-1 inhibitors DP-107 and DP-178, these peptides should provide a novel approach to the development of targeted therapies for the treatment of EBV infections.
Owner:TRIMERIS
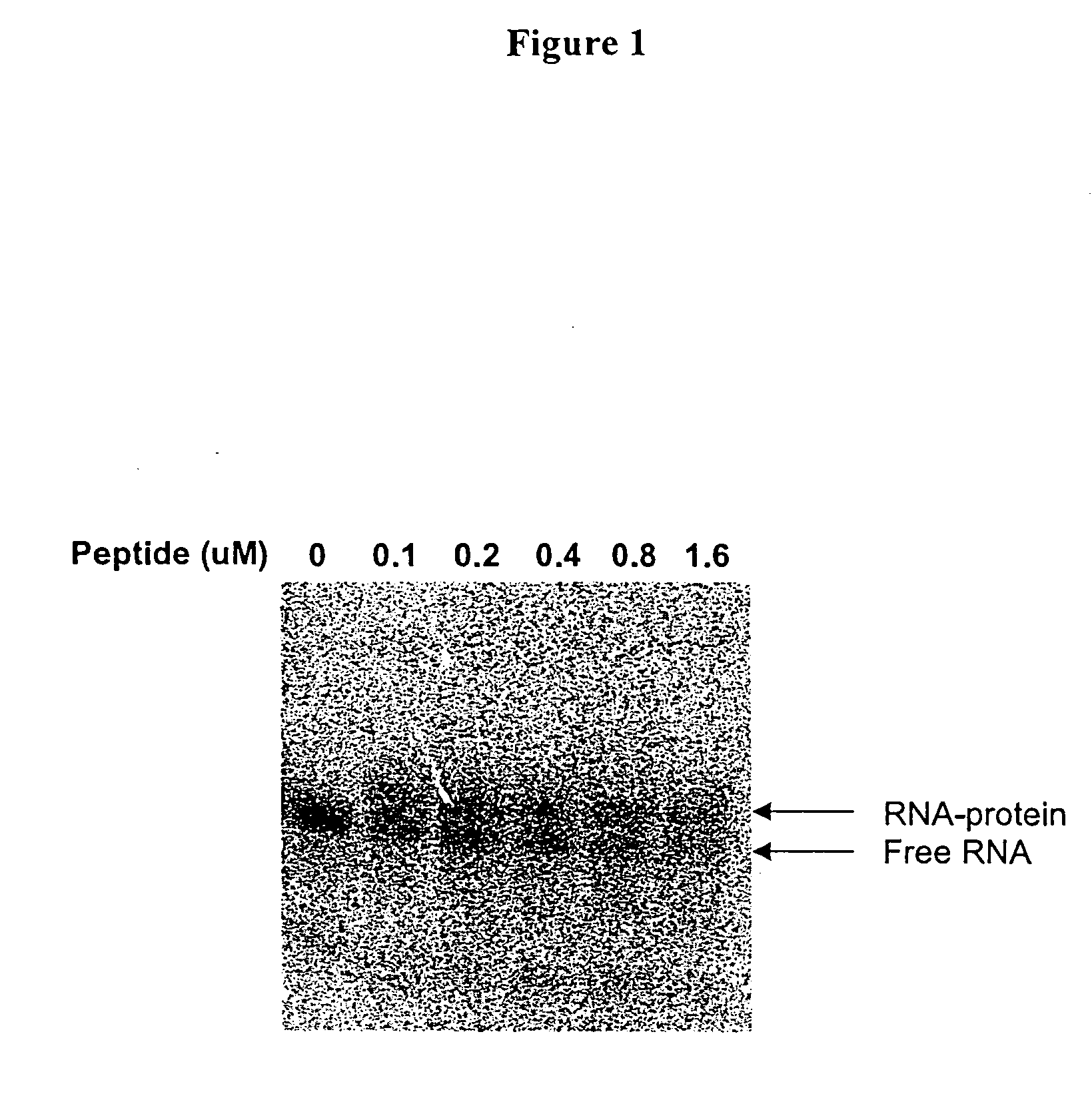
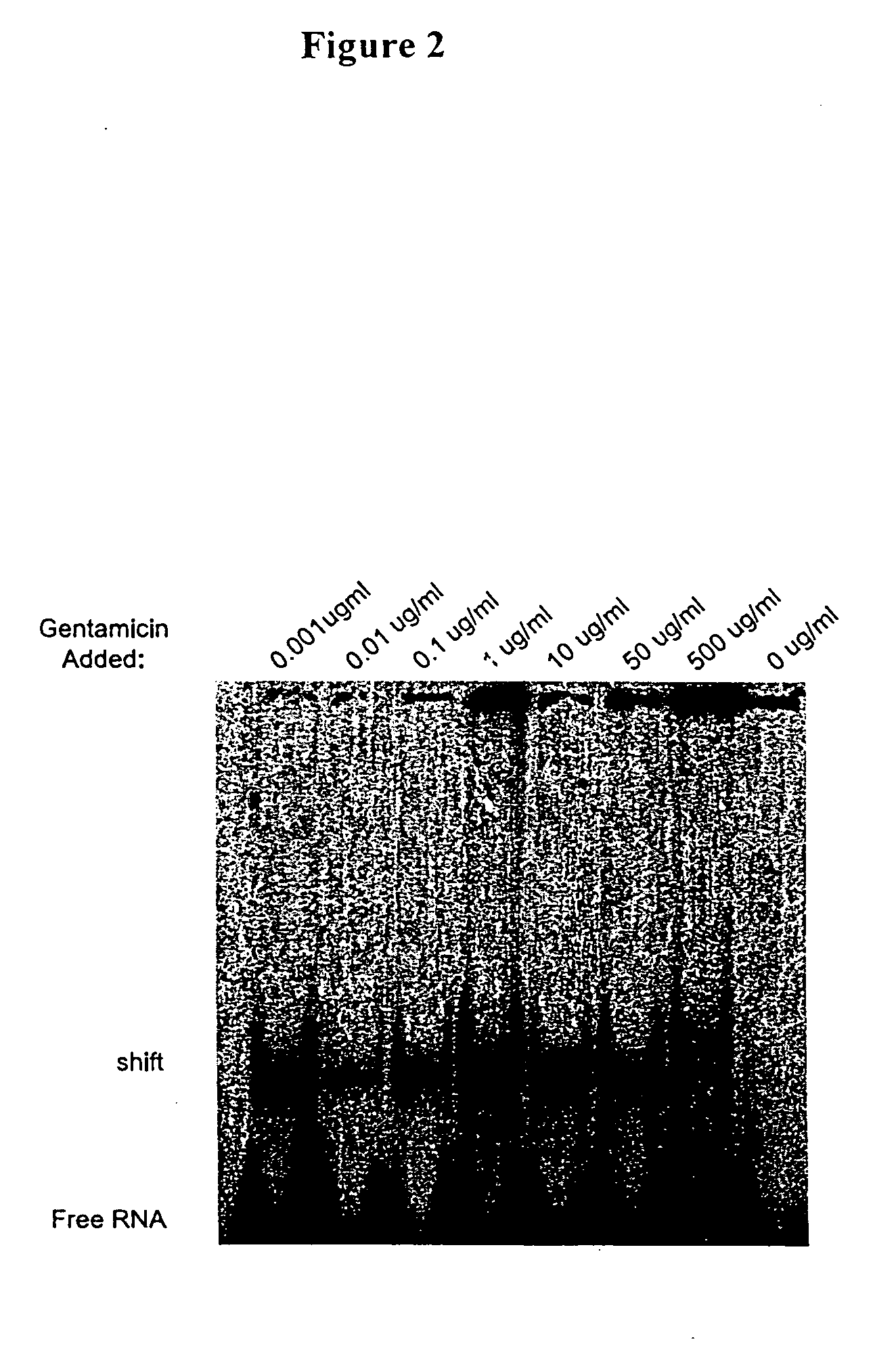
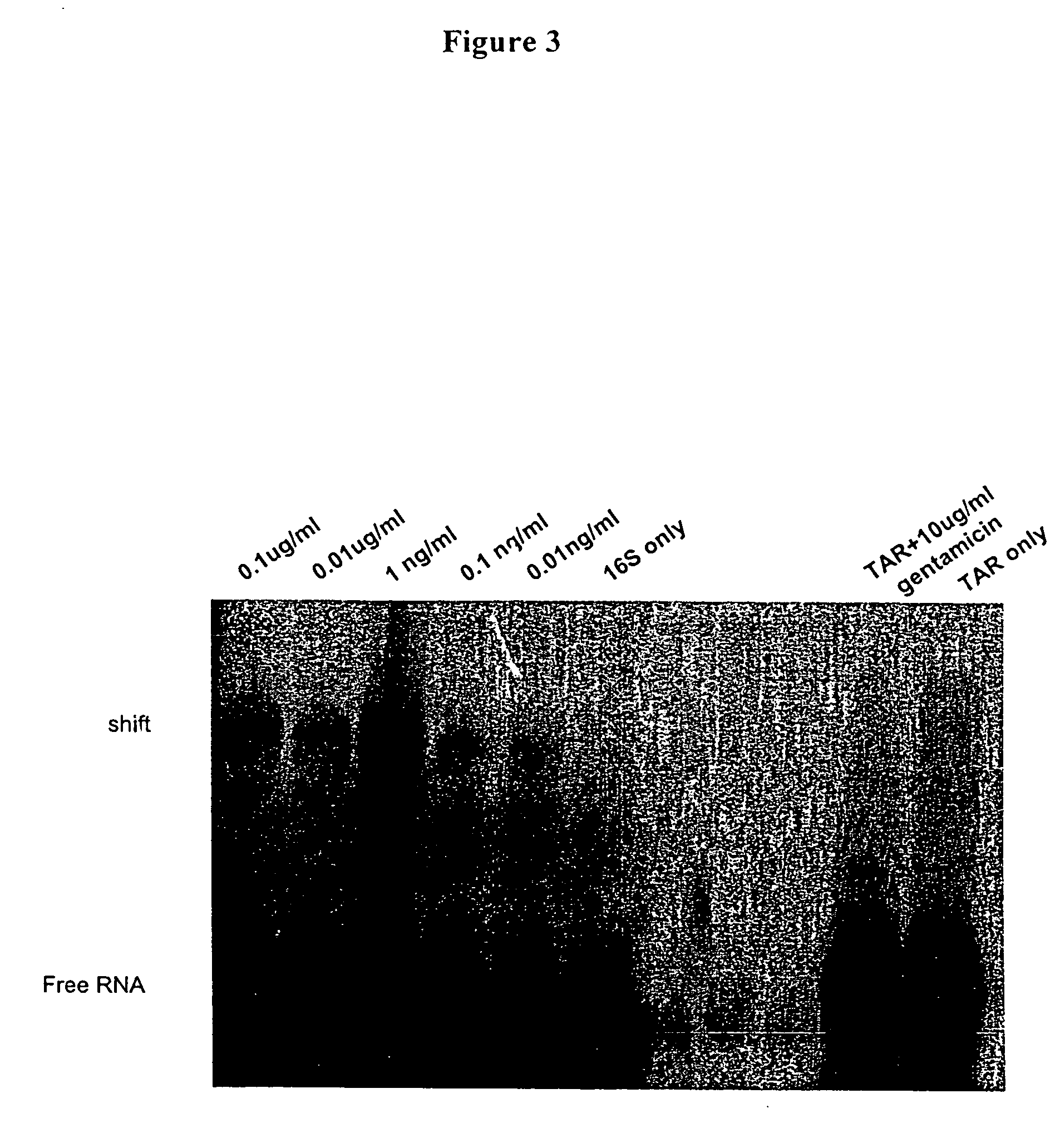
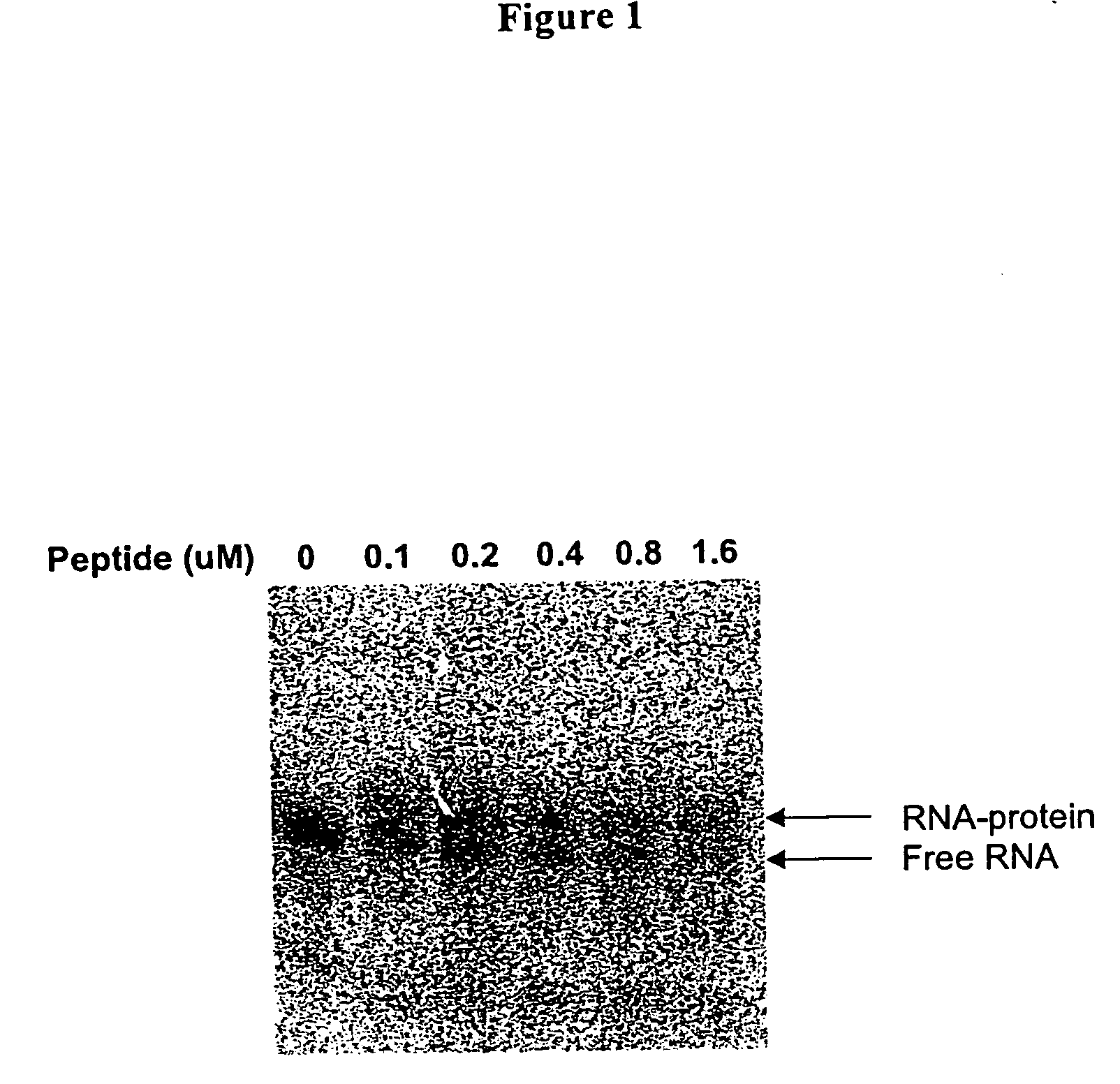
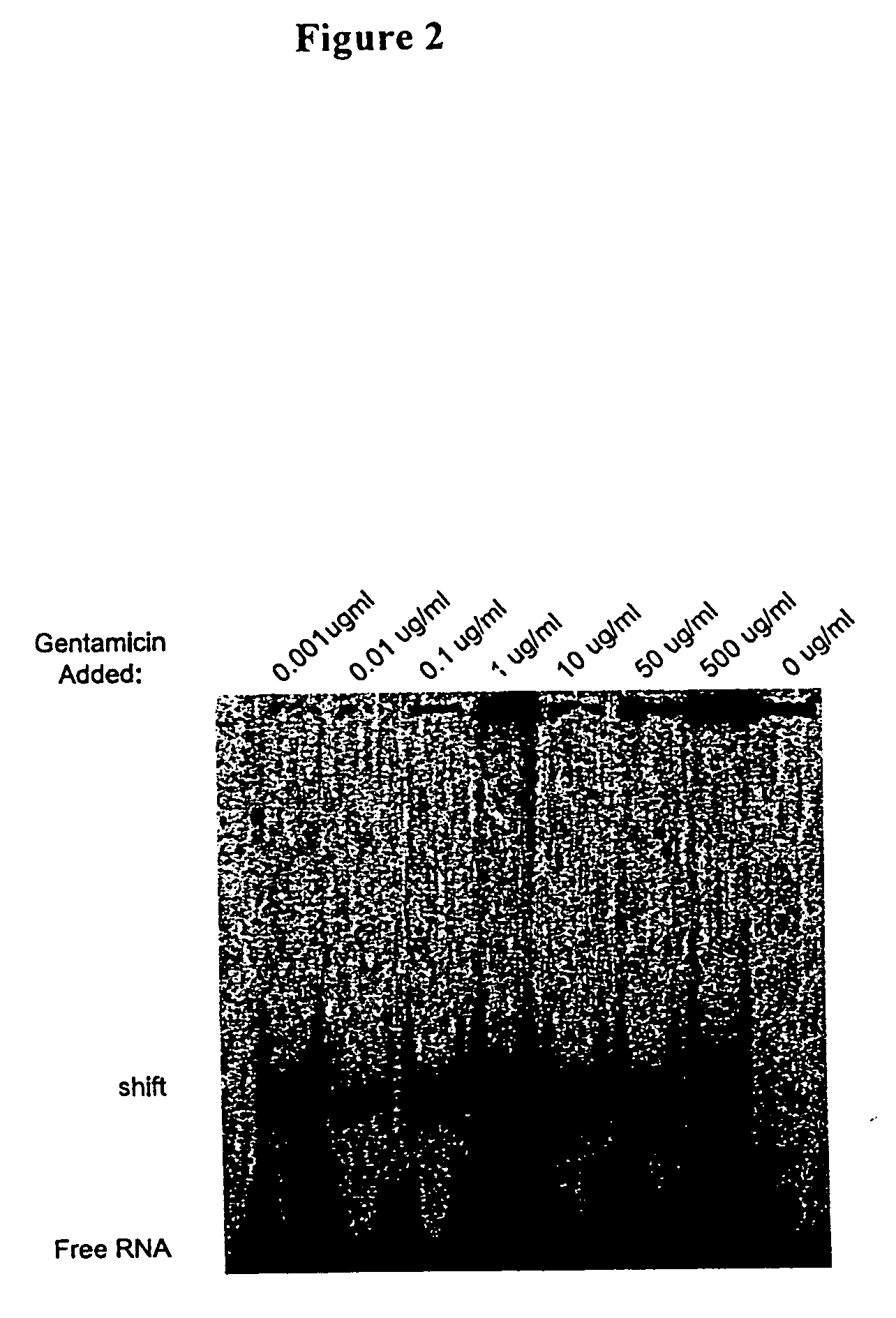
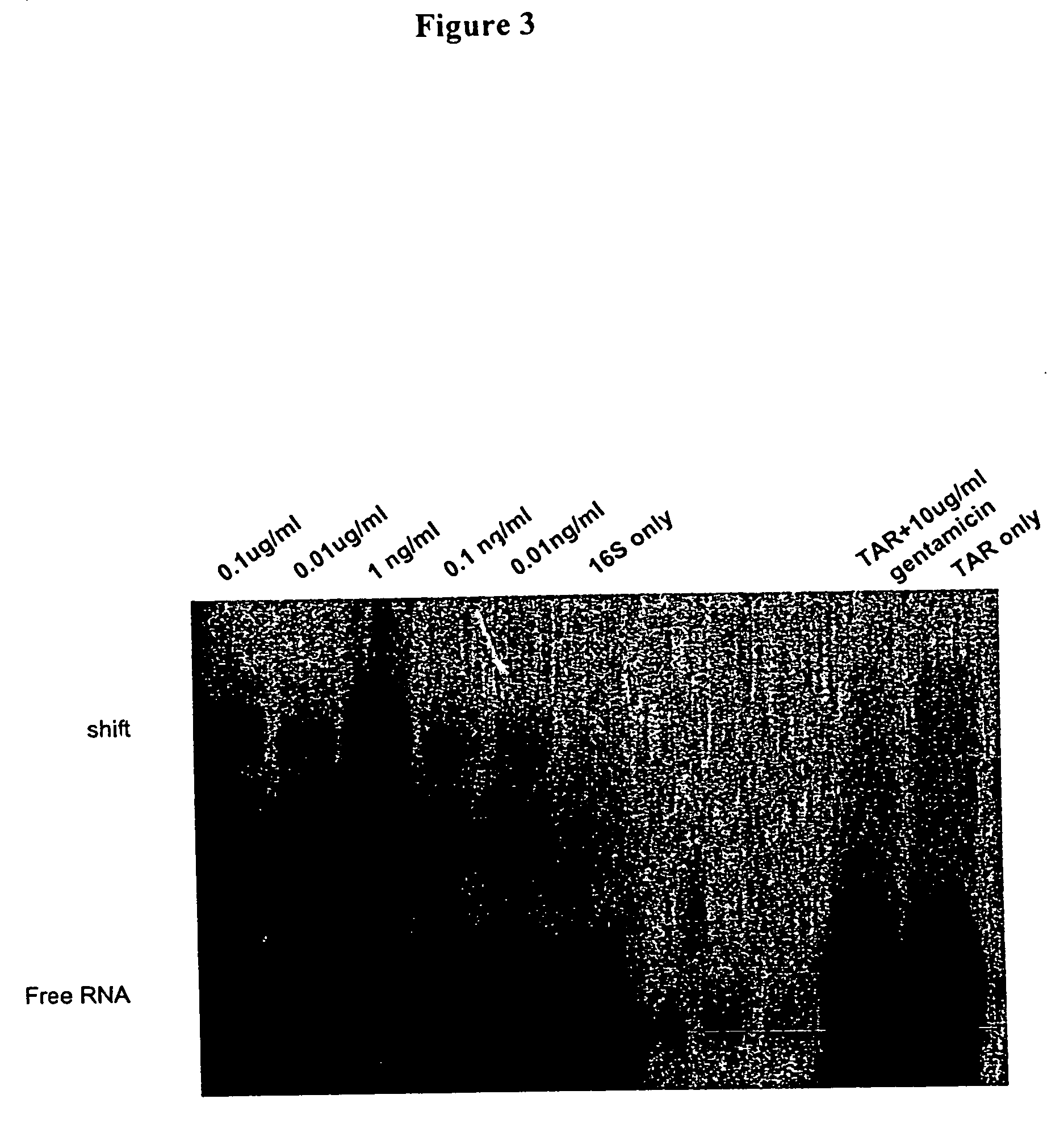
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific rna structural motifs
InactiveUS20040219545A1Easy to identifyEliminate biasMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsBiology
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid ("RNA"). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:RANDO ROBERT F +1
Methods for treating protein aggregation disorders
InactiveUS20050215562A1Easy clearanceIncreased toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsCell AggregationsChemical compound
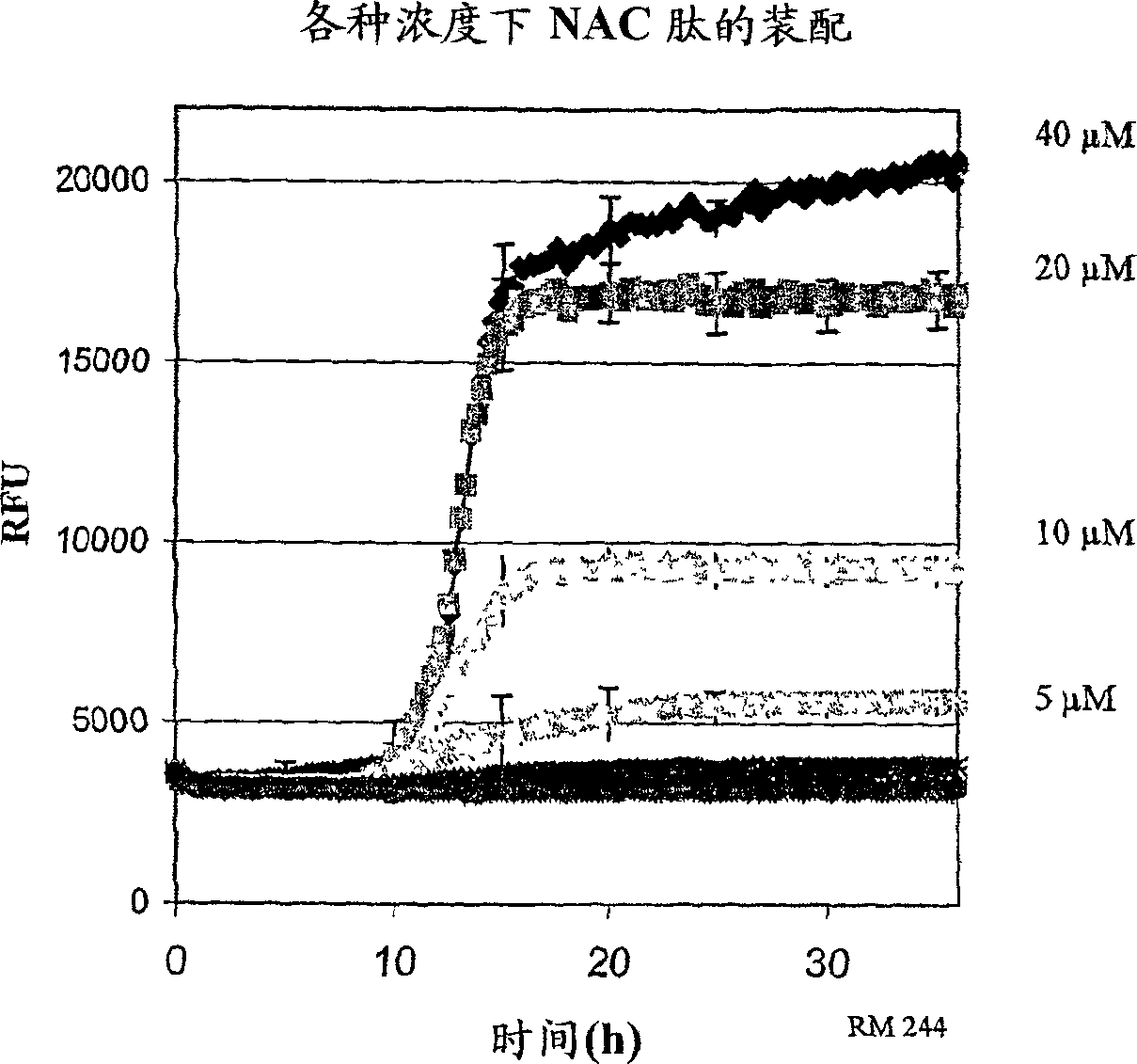
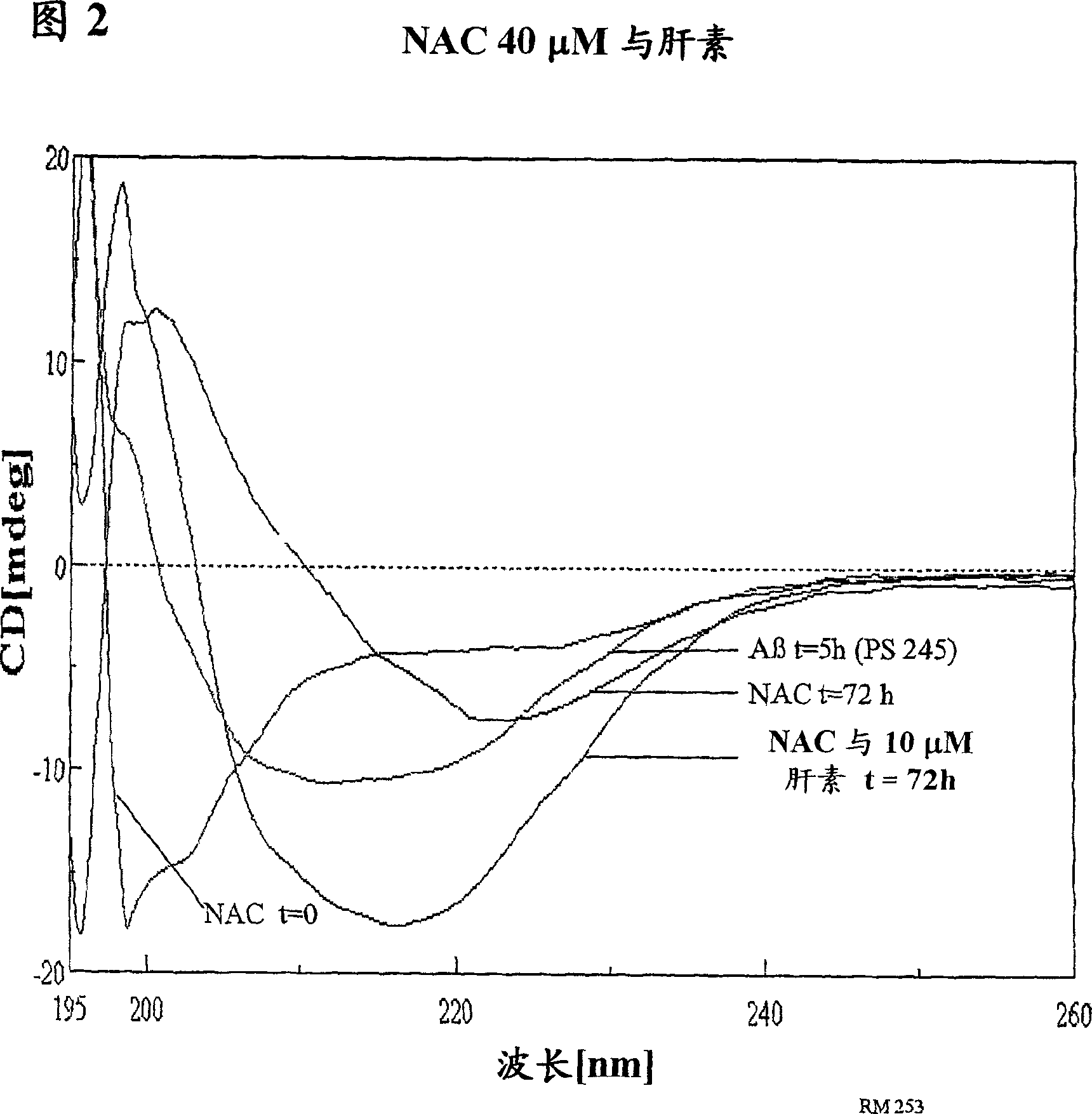
The present invention is based, at least in part on the discovery of therapeutic agents capable of preventing, inhibiting or modulating abnormal processing, misfolding or aggregation of protein. The therapeutic agents of the invention may prevent, inhibit or modulate the formation of inclusions. The therapeutic agents of the invention may also be capable of facilitating clearance and / or blocking the cellular toxicity of inclusions to treat or ameliorate disorders characterized by protein aggregation. Compounds which bind to structural motifs commonly found in protein aggregates, such as β-sheets, would represent strong candidates for such compounds and are therefore desirable.
Owner:NEUROCHEM INT
Structural motifs and oligomeric compounds and their use in gene modulation
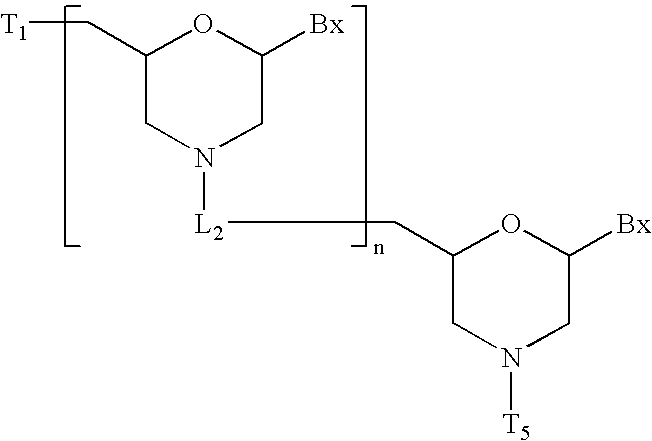
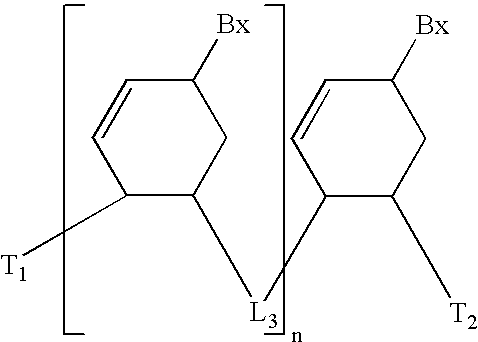
Oligomer compositions comprising first and second oligomers are provided wherein at least a portion of the first oligomer is capable of hybridizing with at least a portion of the second oligomer, at least a portion of the first oligomer is complementary to and capble of hybridizing to a selected target nucleic acid, and at least one of the first or second oligomers has a non-linear secondary structure or is part of a multiple oligomer assembly. Oligonucleotide / protein compositions are also provided comprising an oligomer complementary to and capable of hybridizing to a selected target nucleic acid and at least one protein comprising at least a portion of an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), wherein the oligomer has has a non-linear secondary structure or is part of a multiple oligomer assembly.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific rna structural motifs
InactiveUS20050142545A1Easy to implementHigh throughput screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAssay
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid (“RNA”). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen bead-based libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
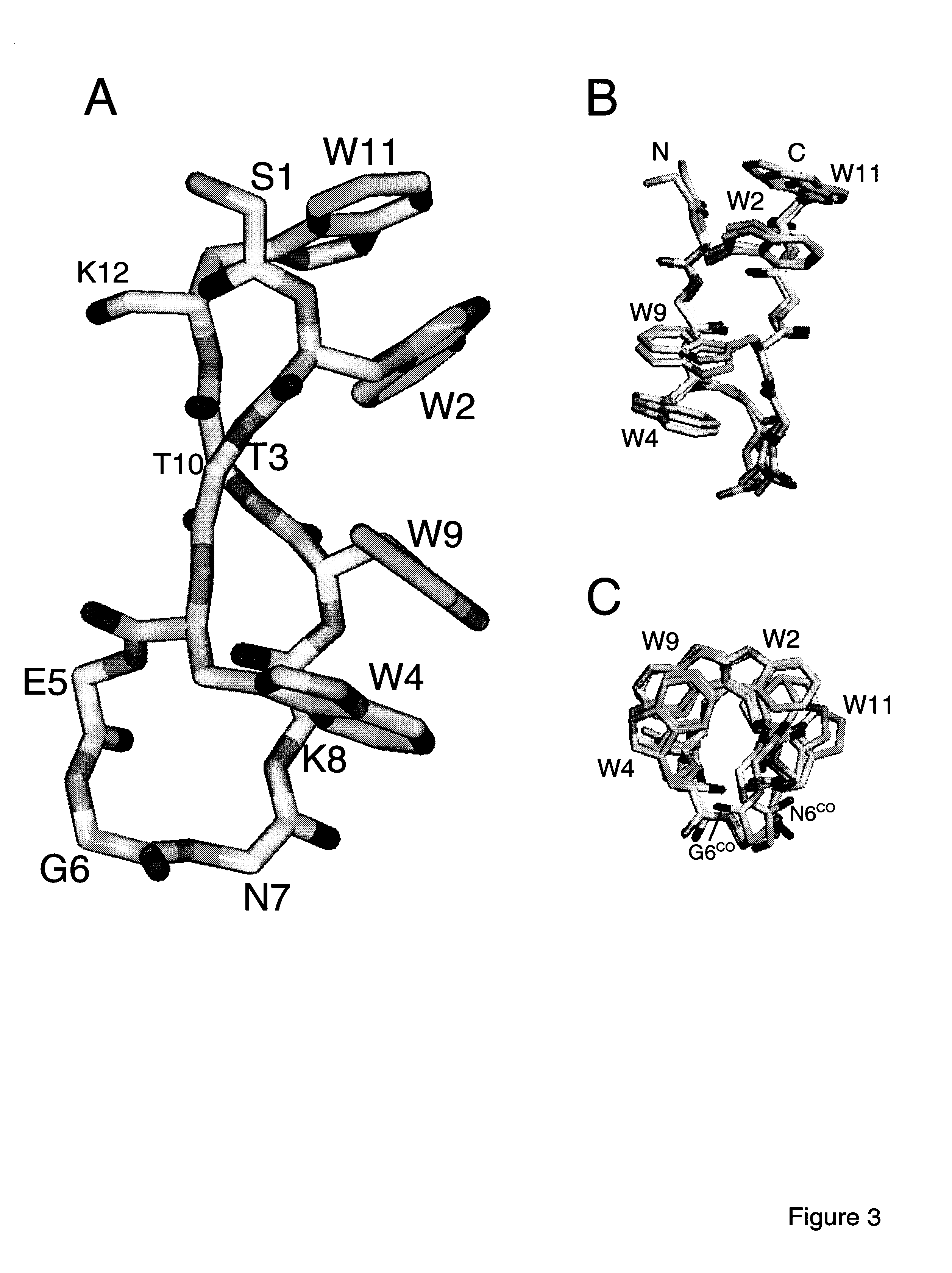
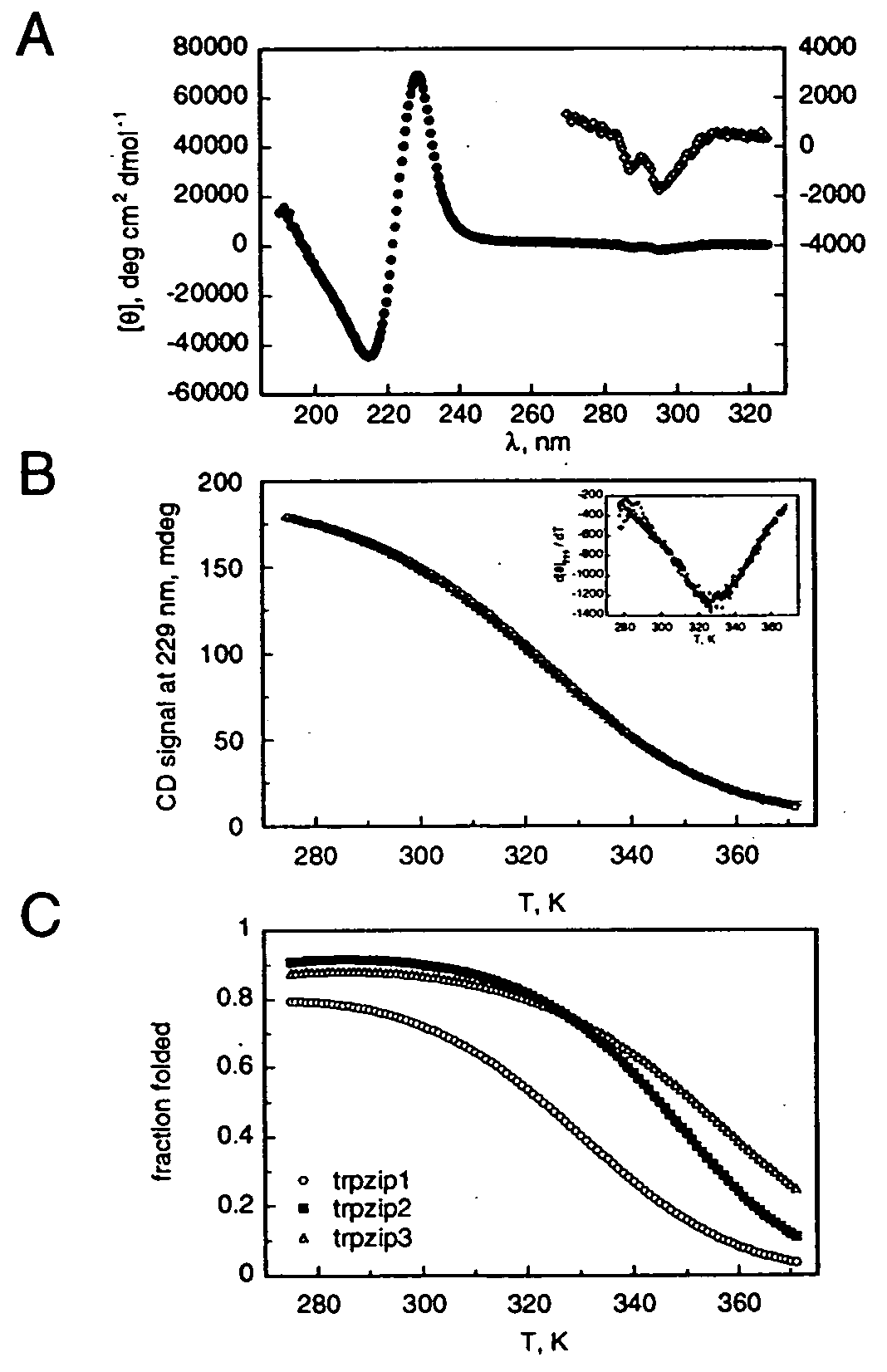
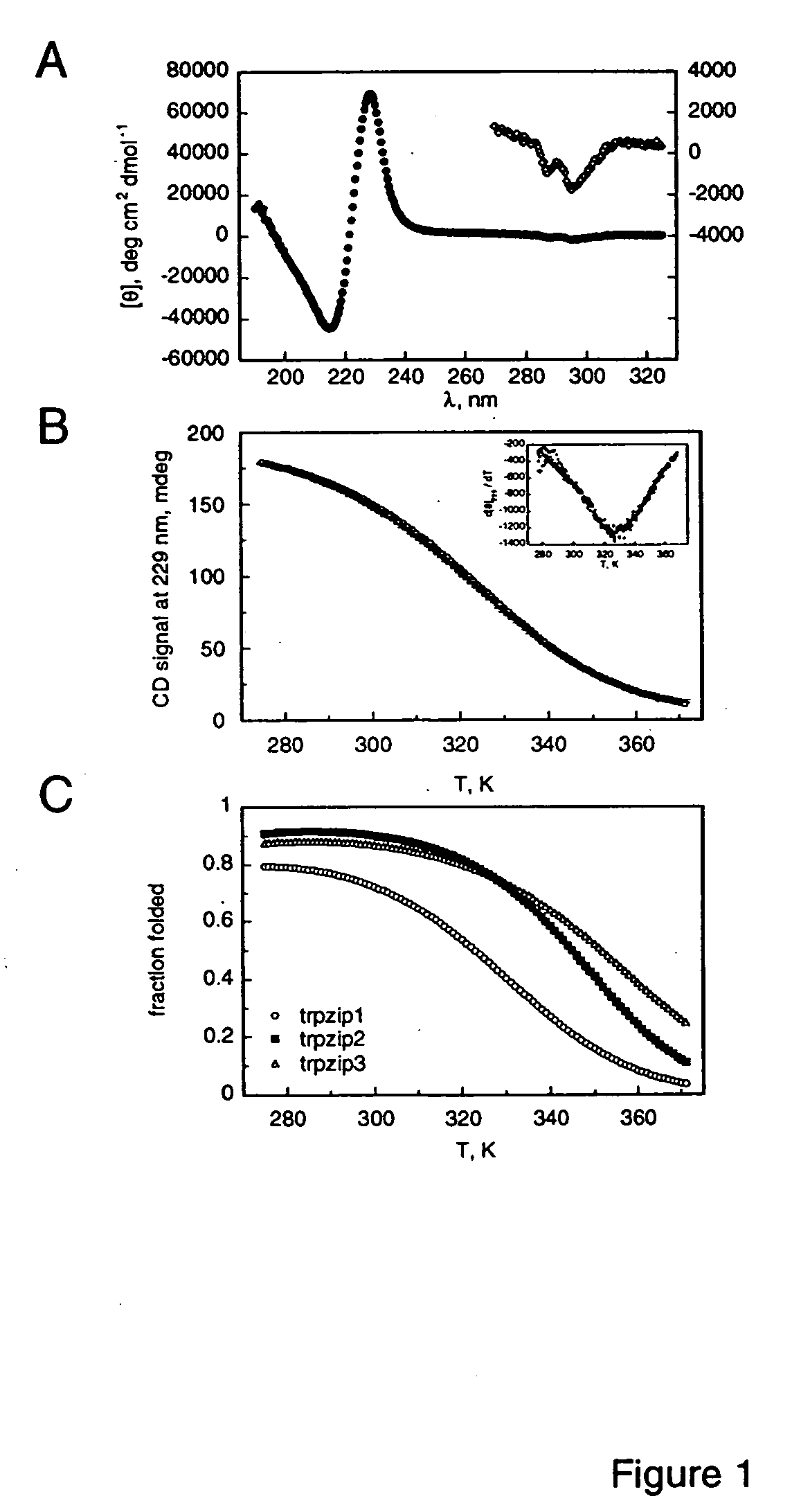
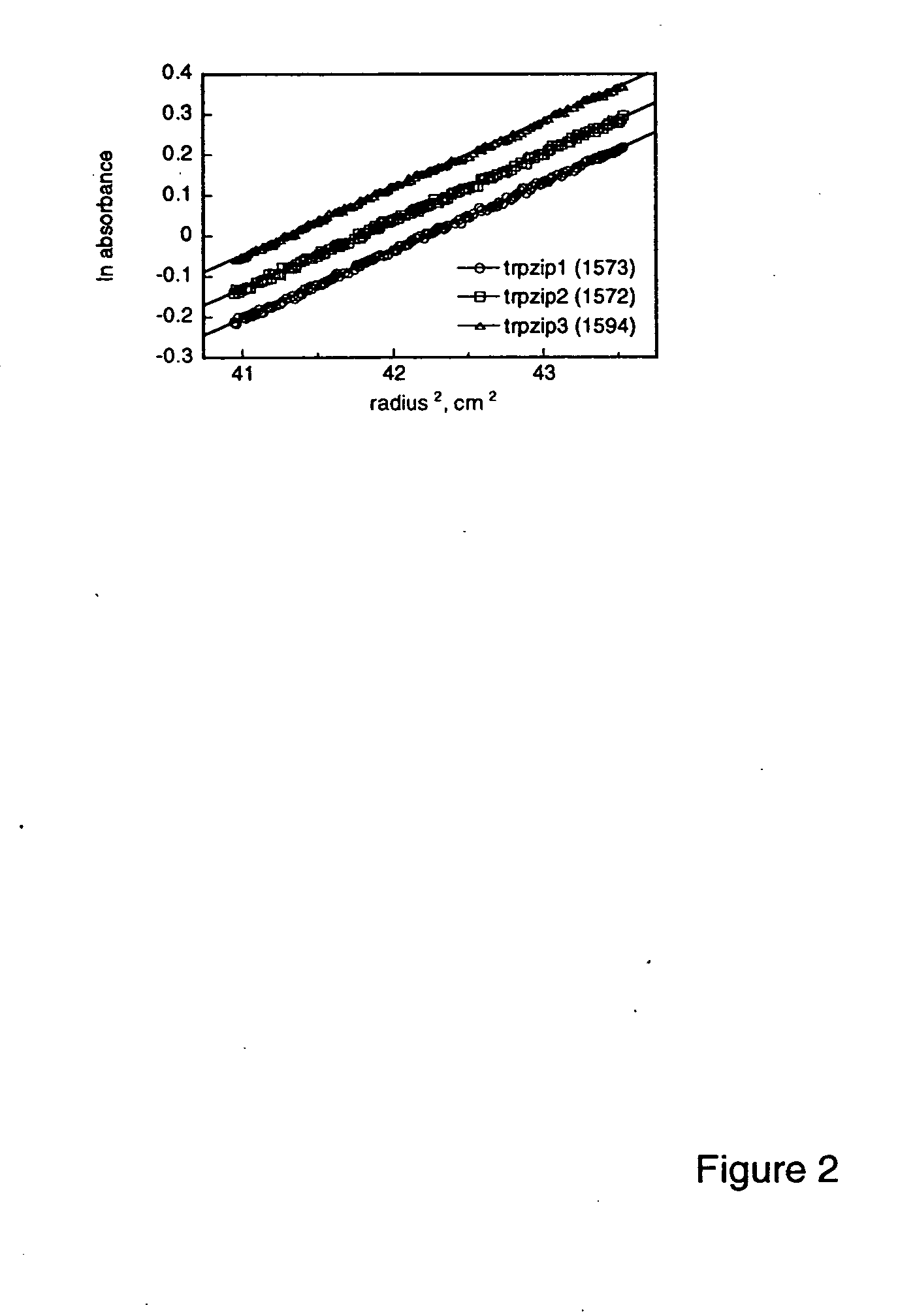
Hairpin peptides with a novel structural motif and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6914123B2Enable stabilizationImprove structural stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein moleculesModel system
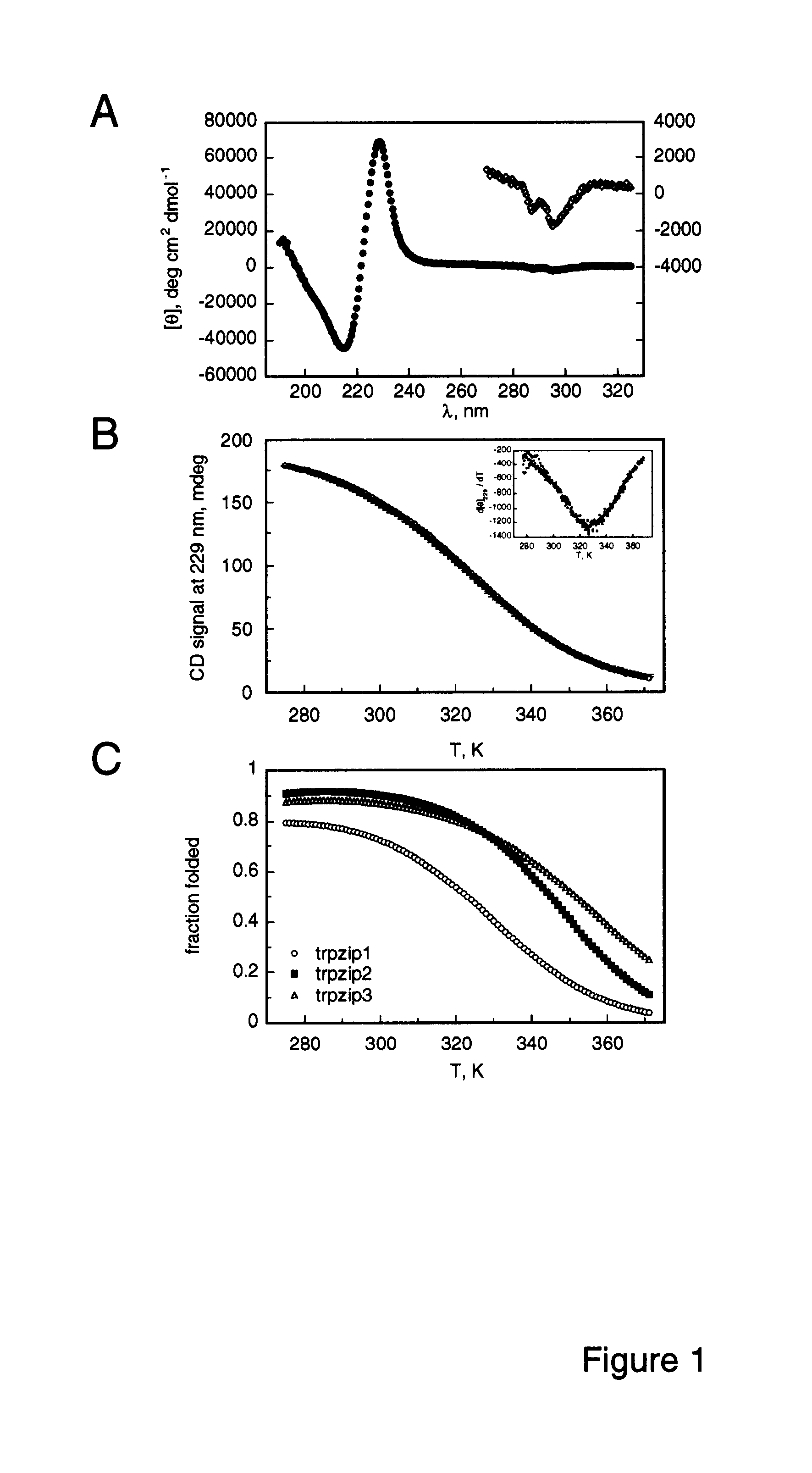
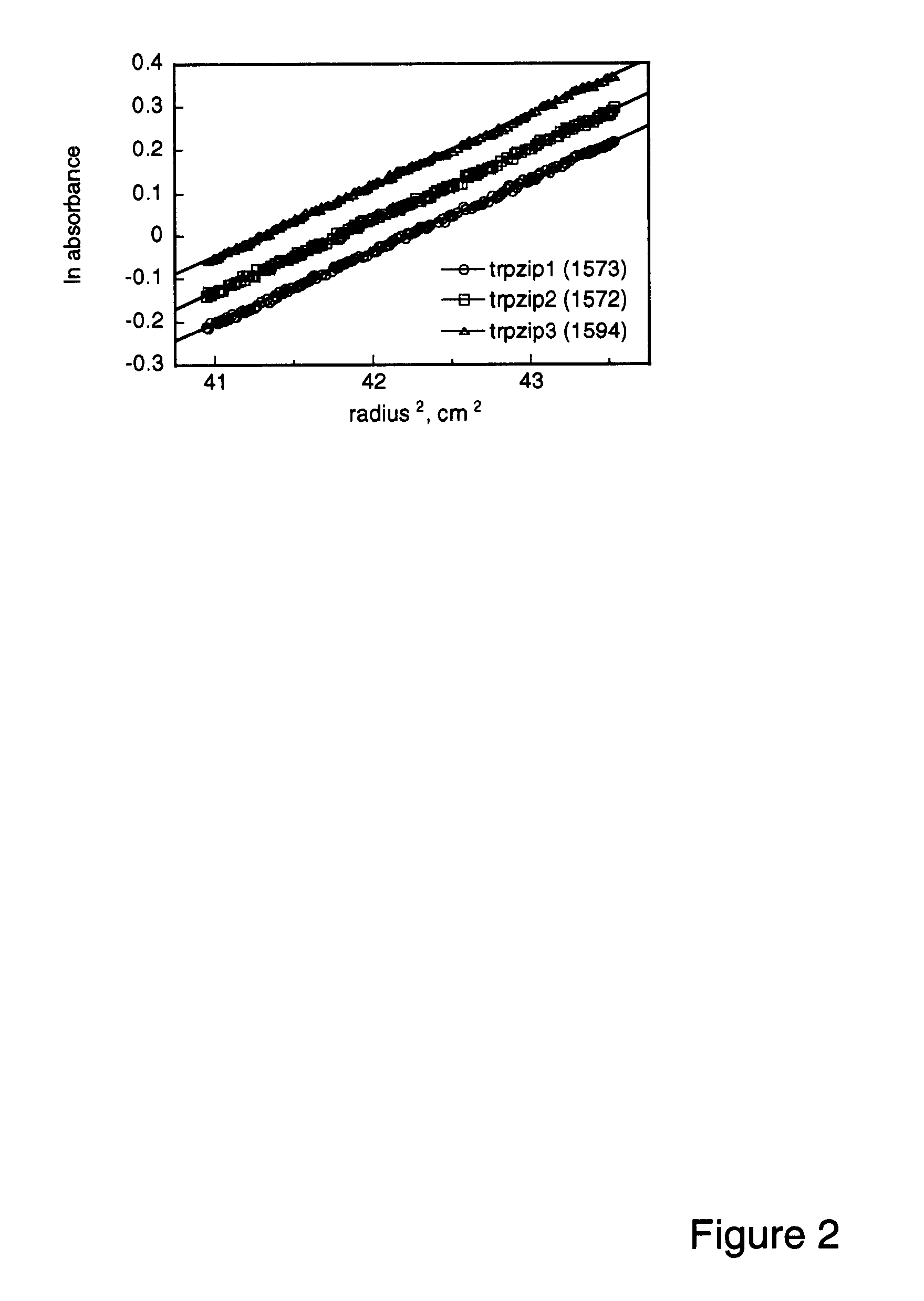
The invention is directed to a model system for structure-activity relationship analysis of peptide or protein molecules involved in important biological processes. Provided by the invention are combinatorial peptide libraries comprising peptides with a novel “tryptophan zipper” scaffold (trpzip) that forms stable β-hairpin structure in solution. Methods of selecting and using such scaffold are provided herein, which are useful for mimicking native protein structures and interactions and designing therapeutic agents. Thus, the invention has profound utility for biological studies and drug development.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methods for the inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus transmission
Fusion of the viral envelope, or infected cell membranes with uninfected cell membranes, is an essential step in the viral life cycle. Recent studies involving the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) demonstrated that synthetic peptides (designated DP-107 and DP-178) derived from potential helical regions of the transmembrane (TM) protein, gp41, were potent inhibitors of viral fusion and infection. A computerized antiviral searching technology (C.A.S.T.) that detects related structural motifs (e.g., ALLMOTI5, 107x178x4, and PLZIP) in other viral proteins was employed to identify similar regions in the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Several conserved heptad repeat domains that are predicted to form coiled-coil structures with antiviral activity were identified in the RSV genome. Synthetic peptides of 16 to 39 amino acids derived from these regions were prepared and their antiviral activities assessed in a suitable in vitro screening assay. These peptides proved to be potent inhibitors of RSV fusion. Based upon their structural and functional equivalence to the known HIV-1 inhibitors DP-107 and DP-178, these peptides should provide a novel approach to the development of targeted therapies for the treatment of RSV infections.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific RNA structural motifs
InactiveUS20060228730A1Easy to implementHigh throughput screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhysical approach
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid (“RNA”). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:RANDO ROBERT +1
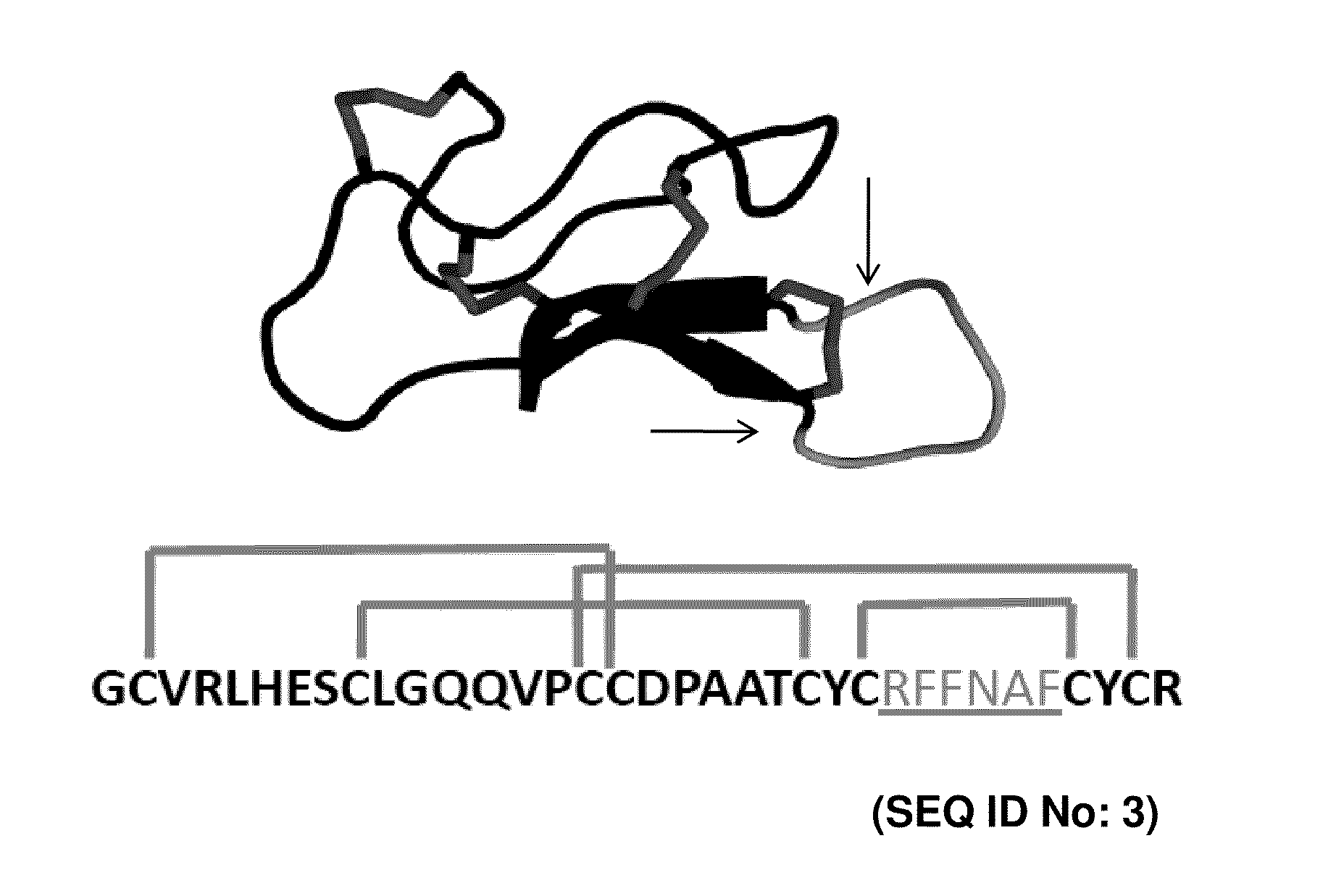
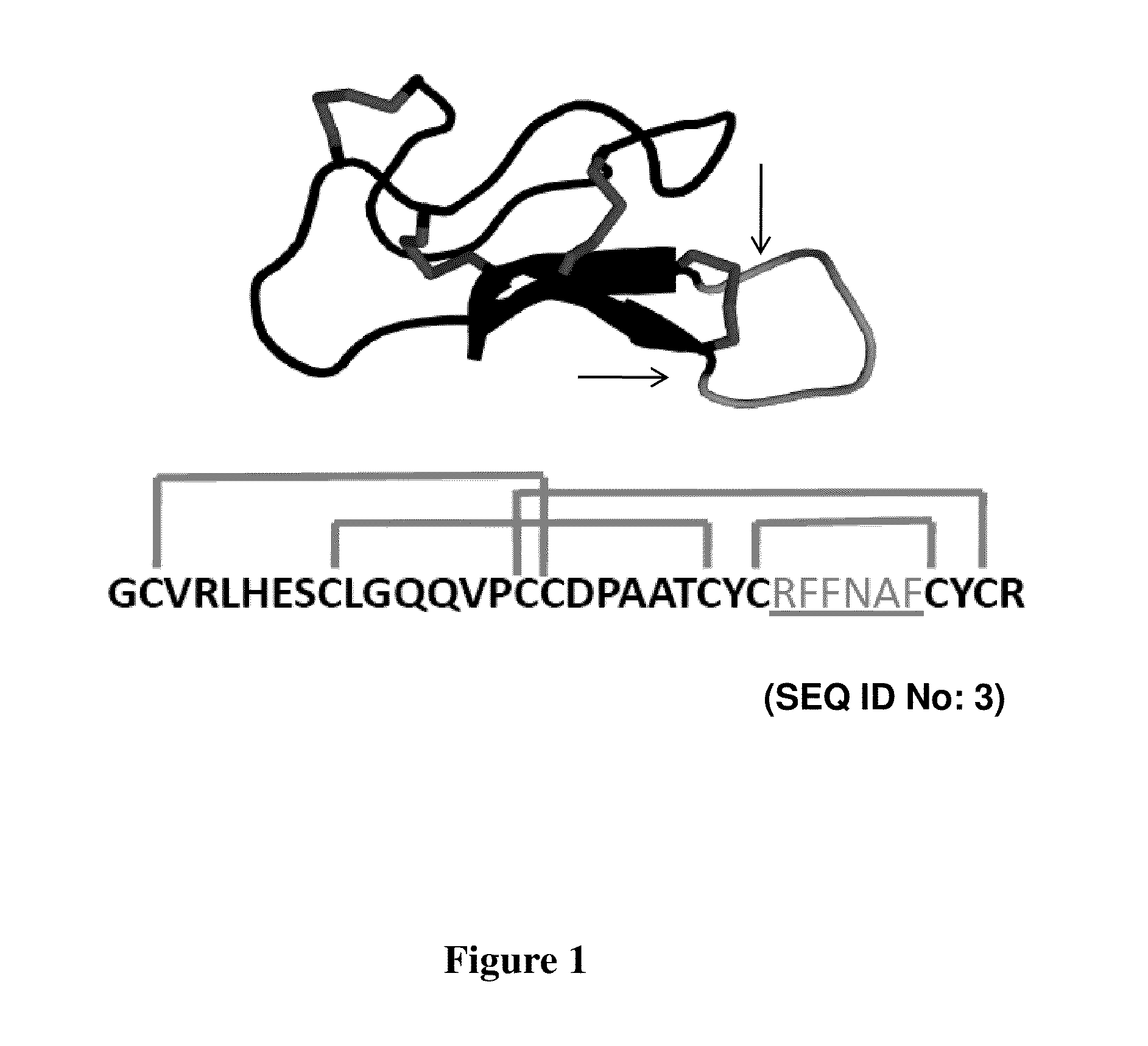
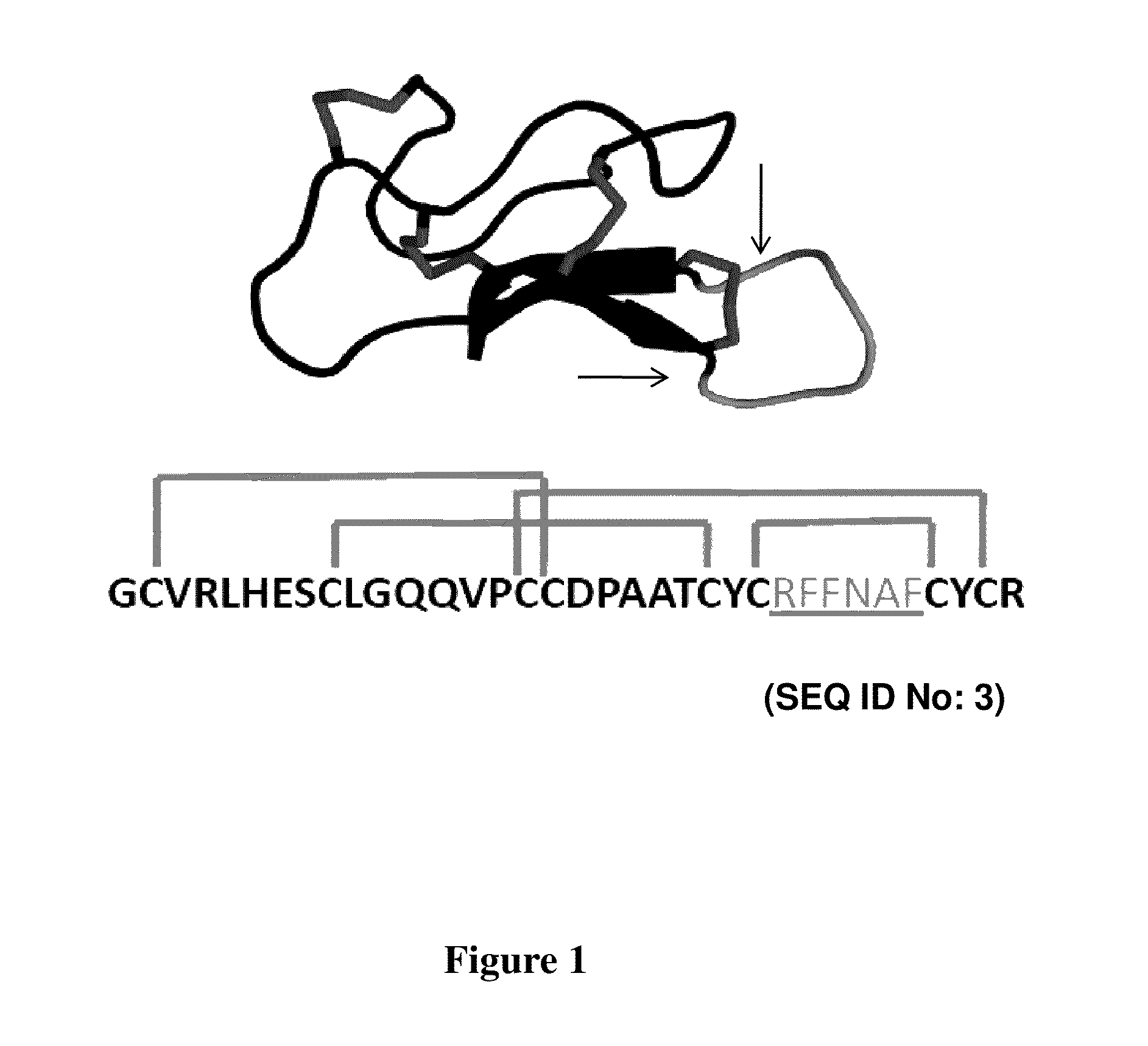
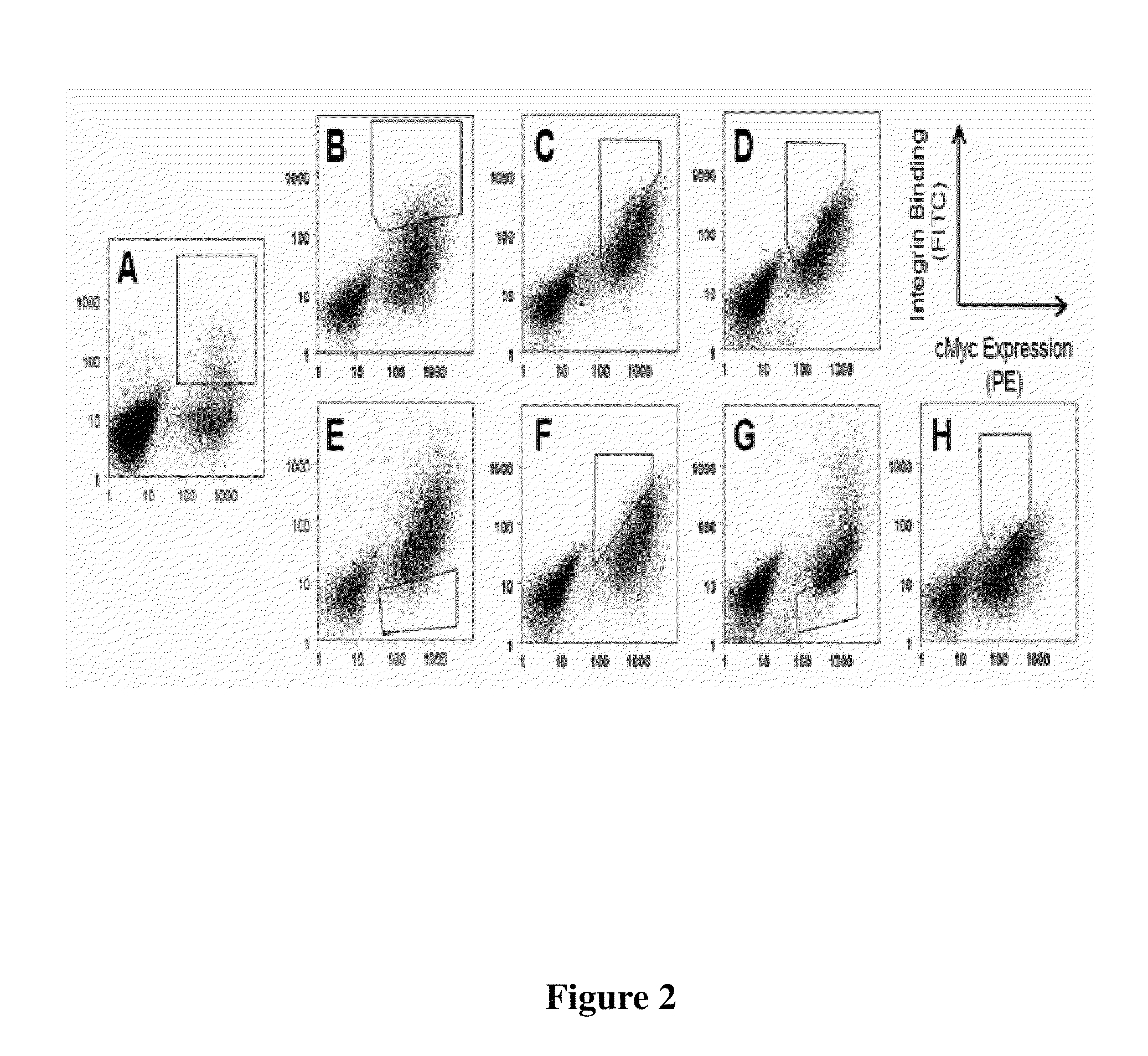
CYSTINE KNOT PEPTIDES BINDING TO ALPHA IIb BETA 3 INTEGRINS AND METHODS OF USE
InactiveUS20110136740A1Inhibits platelet aggregationImprove bindingDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCystine knotAlpha-IIb/Beta-3
Disclosed are peptides having a cystine knot structural motif and comprising a sequence engineered for specificity against αIIbβ3 integrin, found on platelets, and a method of using the same in anti-thrombotic therapies. The present peptides utilize a cystine knot scaffold derived from modified agouti-related protein or agatoxin, An alternate library screening strategy was used to isolate variants of peptides that selectively bound to αIIbβ3 integrin or to both αIIbβ3 and αVβ3 integrins. Unique consensus sequences were identified within the identified peptides suggesting alternative molecular recognition events that dictate different integrin binding specificities. In addition, the engineered peptides prevented human platelet aggregation in a plasma-based assay and showed high binding affinity for αIIbβ3 integrin.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Pharmacological agents and methods of treatment that inactivate pathogenic prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and viruses by attacking highly conserved domains in structural metalloprotein and metalloenzyme targets
The invention relates to the treatment of viral, bacterial, parasitic, proliferative diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, immunological diseases, transplanted organ rejection, and diseases produced by intoxication with heavy metals. The invention relates to the use of specific metal chelating agents including, furoic acid, 2-thiophenecarboxylic acid and their derivatives, analogs and structurally related chemicals as pharmacological agents that can be used effectively to disrupt and inactivate specific transition metal ion containing zinc finger structural motifs in metalloproteins and specific transition metal ion containing catalytic sites in metalloproteinases, which in turn, inactivate the pathogenic virus, pathogenic prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells which produces disease conditions. The preparations can be administered topically or for systemic use. The preparations are novel wide-spectrum antibiotics which have antiviral, antiproliferative, antineoplastic, antiangiogenic, antibacterial, antiparasitic, antiinfective, and anti-inflammatory effects and can be used in the treatment and prevention of diseases such as AIDS, cancers, untoward angiogenesis, pulmonary anthrax, malaria, inflammatory responses, Alzheimer's disease and other diseases.
Owner:POLS LAB BIOTECH
Stromal collagen in the diagnosis and characterization of breast cancer
ActiveUS7805183B2Test accurateGood informationImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryAbnormal tissue growthPresent method
The present invention provides methods and systems for evaluating biological materials for the diagnosis of disease, such as gland abnormalities, and the cancerous and precancerous conditions. Nonlinear optical microscopy techniques, such as MP microscopy and harmonic generation microscopy, are used to generate high resolution, three dimensional images of a test tissue, such as a biopsy tissue sample and tissue in whole organisms, that are analyzed, optionally in combination, to detect, identify and characterize tumor-associated collagen signatures. The presence, abundance and extent of histological features and structural motifs comprising tumor-associated collagen signatures may be directly and accurately correlated with the onset and progression of cancer, such as breast cancer. The present methods are capable of providing an accurate and selective diagnosis of cancer, and provide diagnostic information complementary to conventional diagnostic methods.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific RNA structural motifs
InactiveUS20060194234A1Eliminate biasDirect methodMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsBiology
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for treating protein aggregation disorders
The present invention is based, at least in part on the discovery of therapeutic agents capable of preventing, inhibiting or modulating abnormal processing, misfolding or aggregation of protein. The therapeutic agents of the invention may prevent, inhibit or modulate the formation of inclusions. The therapeutic agents of the invention may also be capable of facilitating clearance and / or blocking the cellular toxicity of inclusions to treat or ameliorate disorders characterized by protein aggregation. Compounds which bind to structural motifs commonly found in protein aggregates, such as ss-sheets, would represent strong candidates for such compounds and are therefore desirable.
Owner:NEUROCHEM INT
Polypeptide structural motifs associated with cell signaling activity
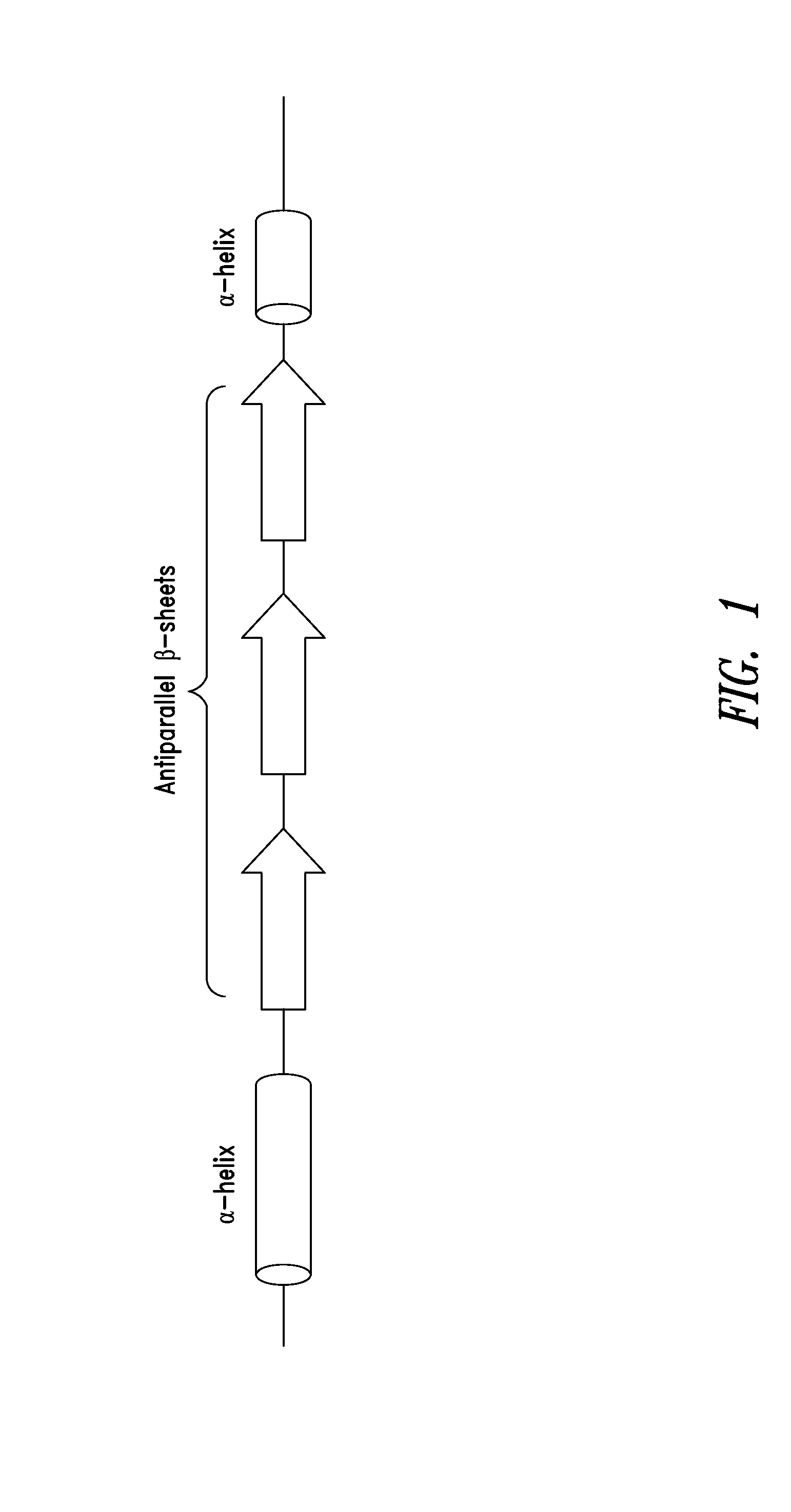
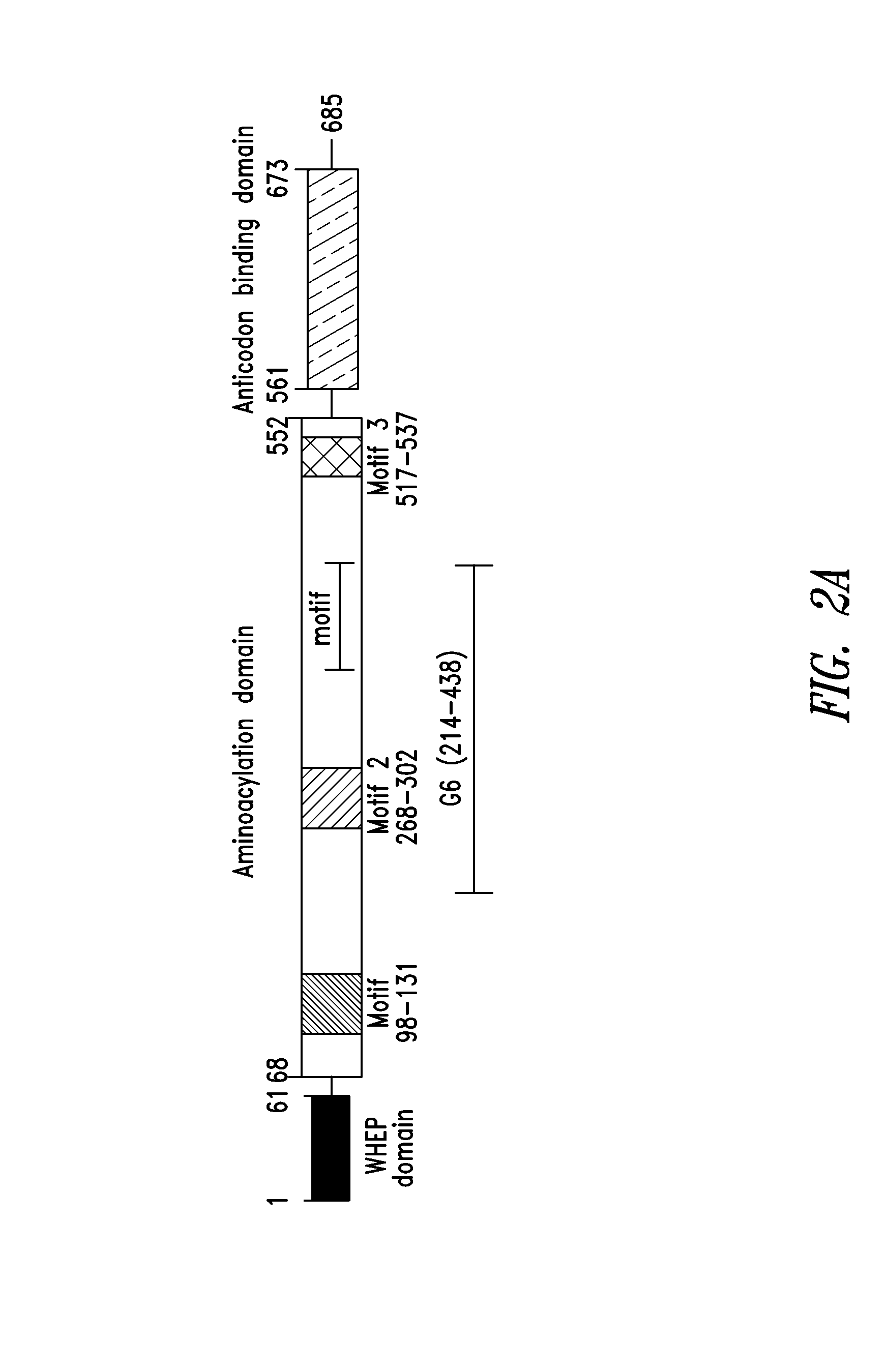
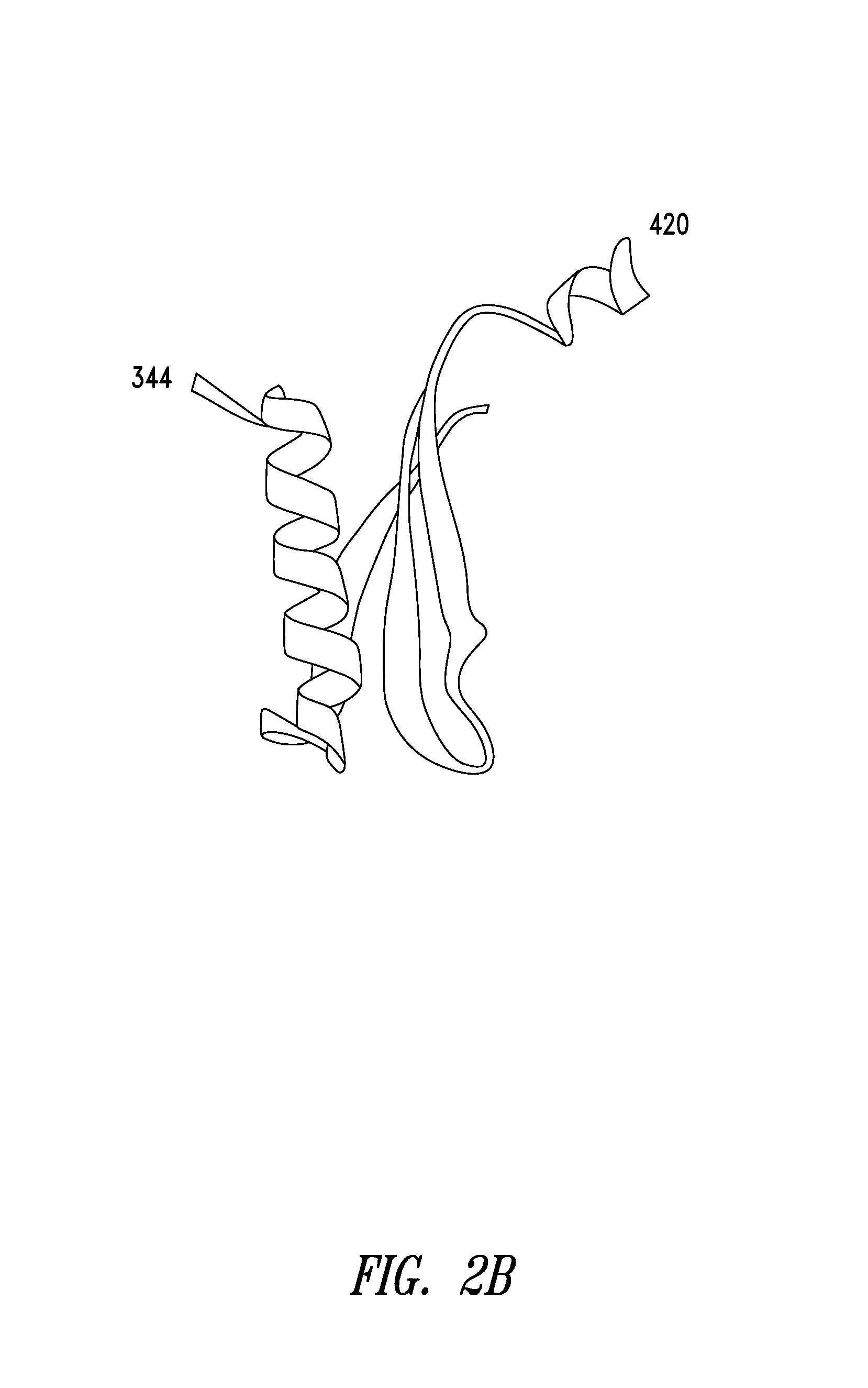
Isolated polypeptides comprising or consisting essentially of specific structural motifs (e.g., three β-sheets and two α-helices) are provided, wherein the polypeptides exhibit at least one cell signaling and / or other non-canonical activity of biological relevance. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding such polypeptides, binding agents that bind such polypeptides, analogs, variants and fragments of such polypeptides, etc., as well as compositions and methods of identifying and using any of the foregoing.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC
Preparation method of polymer-coated binary bifunctional nanocluster core-shell microspheres
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional nanoparticle assembly, and specifically relates to a method of preparing binary nanoclusters with nanoparticle as a structural unit and microemulsion droplets as a template, and preparing a polymer with binary nanoclusters as a core through surface-initiated polymerization. A new method for shell-composite nanoclusters. It includes three steps: synthesis of nanoparticles, preparation of nanoclusters, and surface-initiated polymerization. Oil-soluble nanoparticles can be synthesized by two-phase method, phase transfer method, and high-temperature pyrolysis method, and the size of nanoclusters can be regulated by changing the amount of surfactant and the concentration of nanoparticles. The invention is a new method for preparing bifunctional nano-clusters and compounding them with polymers, which realizes the integration and optimization of various nano-particle functions. After compounding with polymers, it can not only improve the stability of nano-clusters, but also introduce polymerization The special properties of materials can be obtained to obtain nano-micro-scale multifunctional composite materials, which have broad application prospects in the research fields of biology, catalysis, sensing, and optoelectronics.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
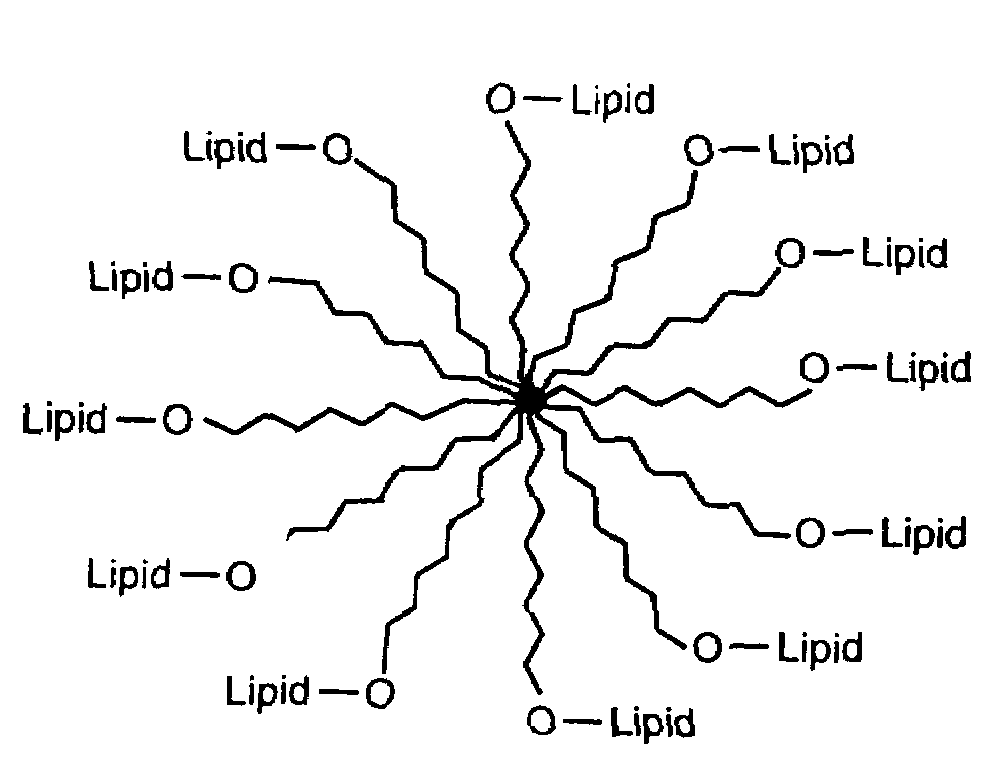
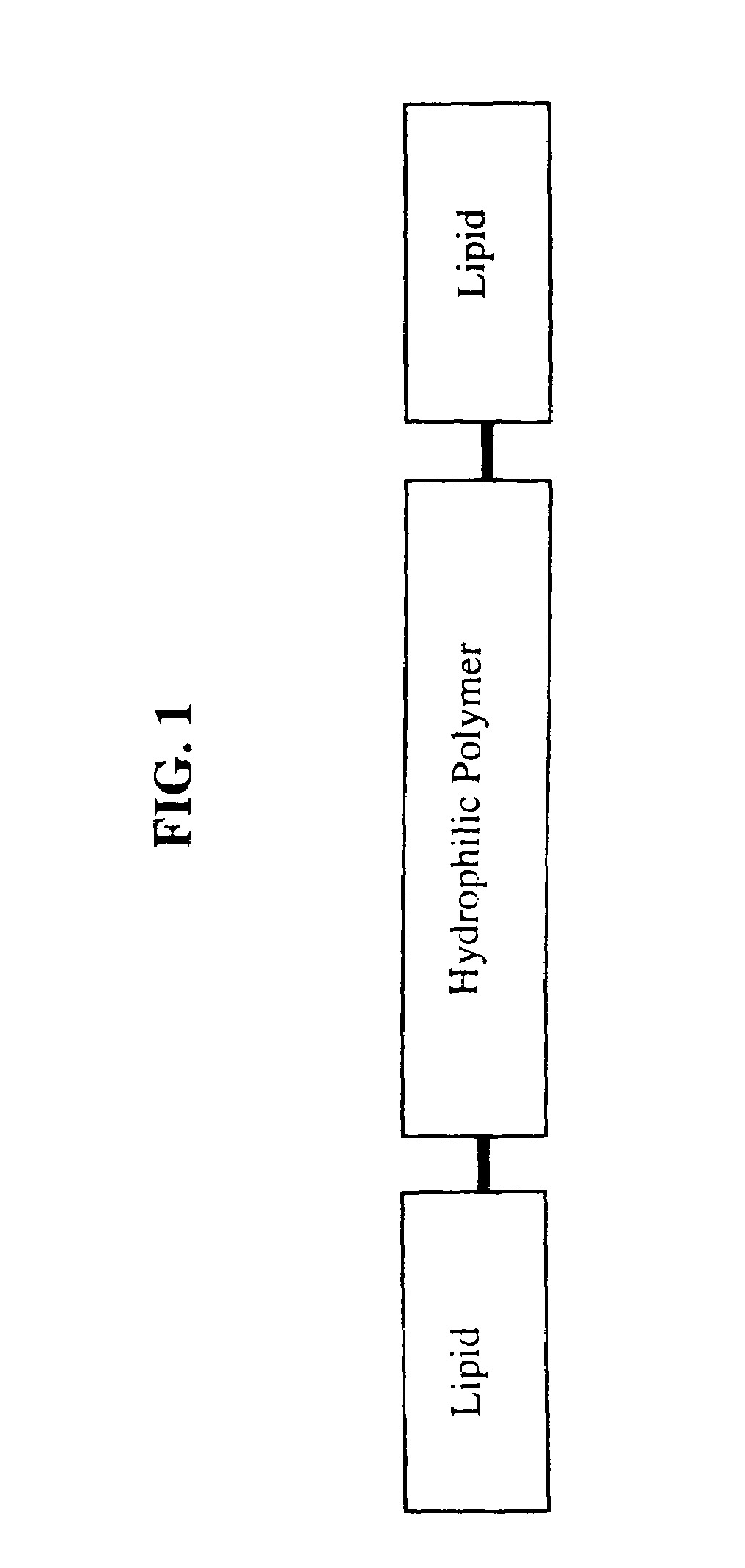
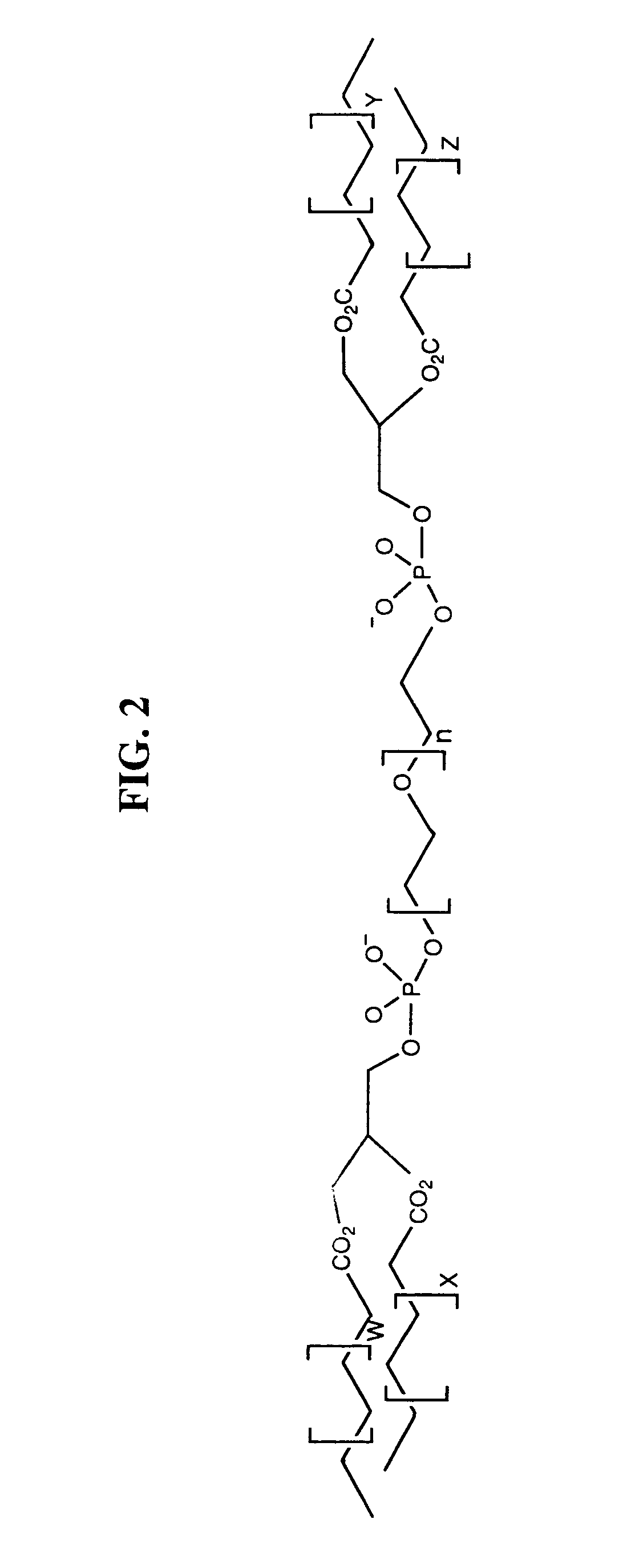
Amphiphilic materials and liposome formulations thereof
InactiveUS7368129B1Suitable for useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideLiquid crystallineWhole blood product
Disclosed is a new structural class of amphiphilic molecules which incorporate a hydrophilic material or polymer attached, at spatially distinct sites, to at least two hydrophobic residues. Certain of the amphiphilic molecules comprise a plurality of hydrophobic moieties. All such amphiphilic molecules have a common structural motif and, in contact with water, display surface activity and self-assemble into multimolecular aggregates and liquid crystalline phases. Also disclosed are enhanced stability liposomes that incorporate such amphiphilic molecules via unique interactions, and methods of using such formulations in a variety of applications including drug delivery, nutrition, bio-diagnostics, cosmetics, blood products and related applications.
Owner:NUTRIMED BIOTECH
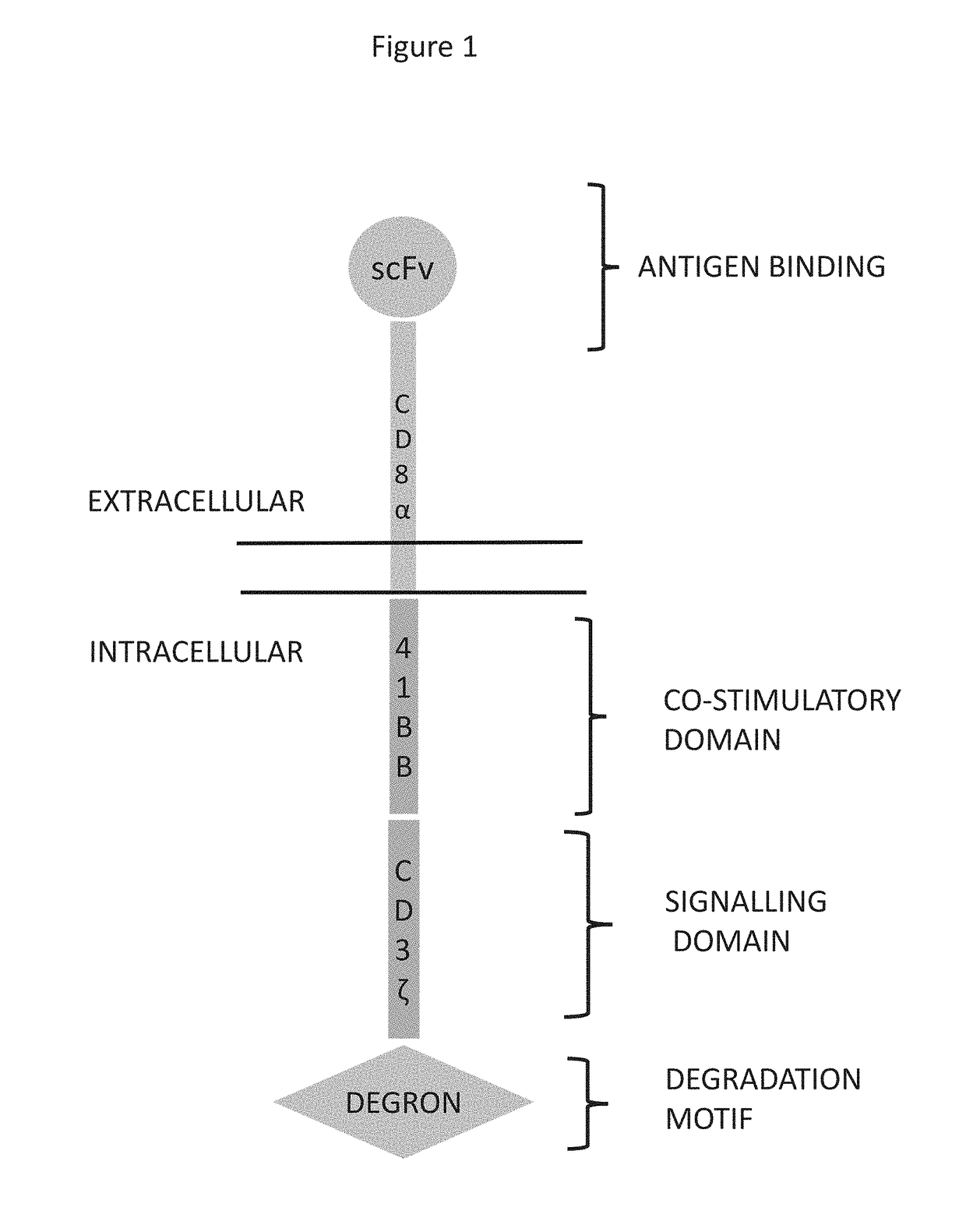
Targeted Protein Degradation
ActiveUS20190002578A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyProtein targetChimeric antigen receptor
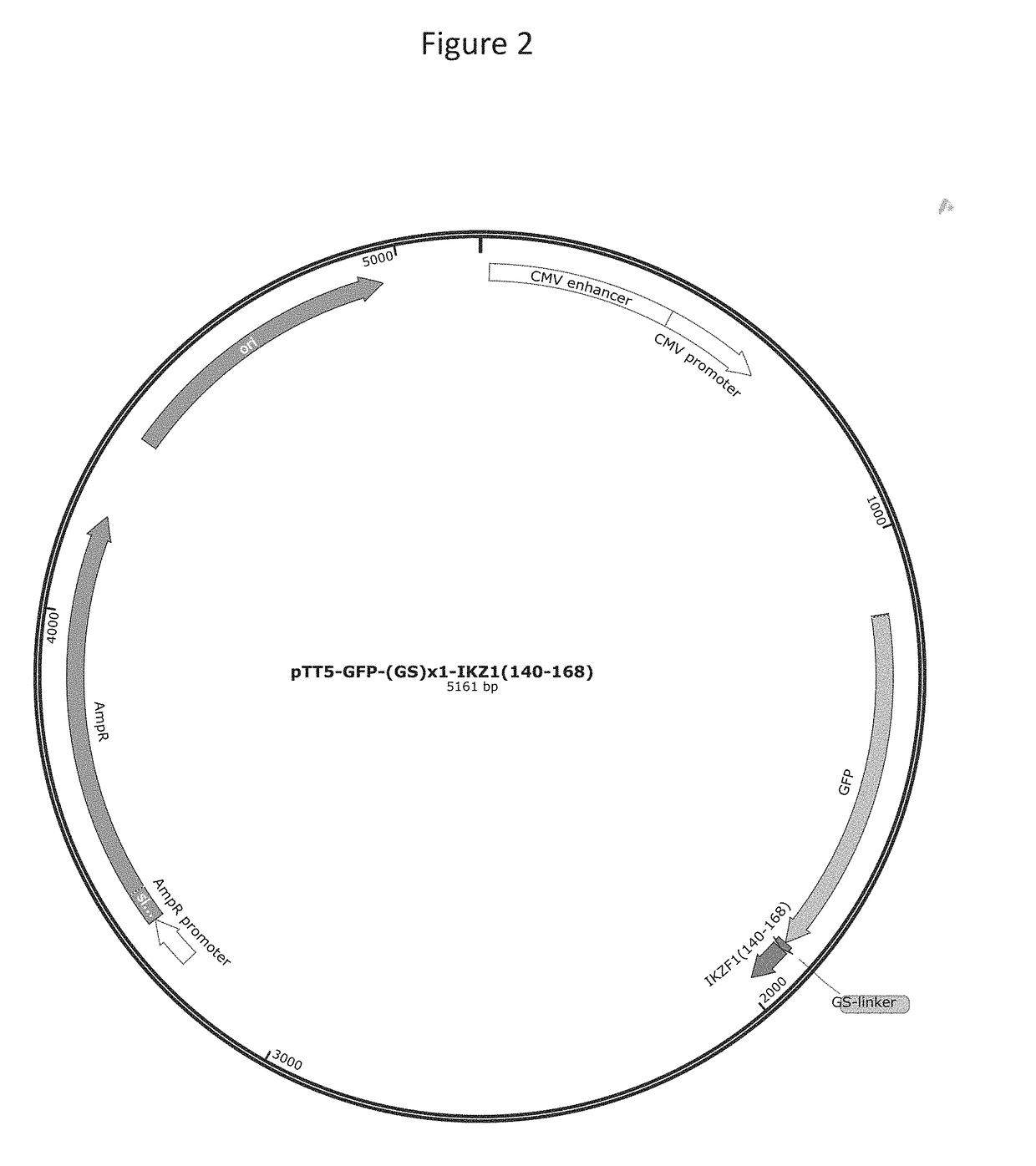
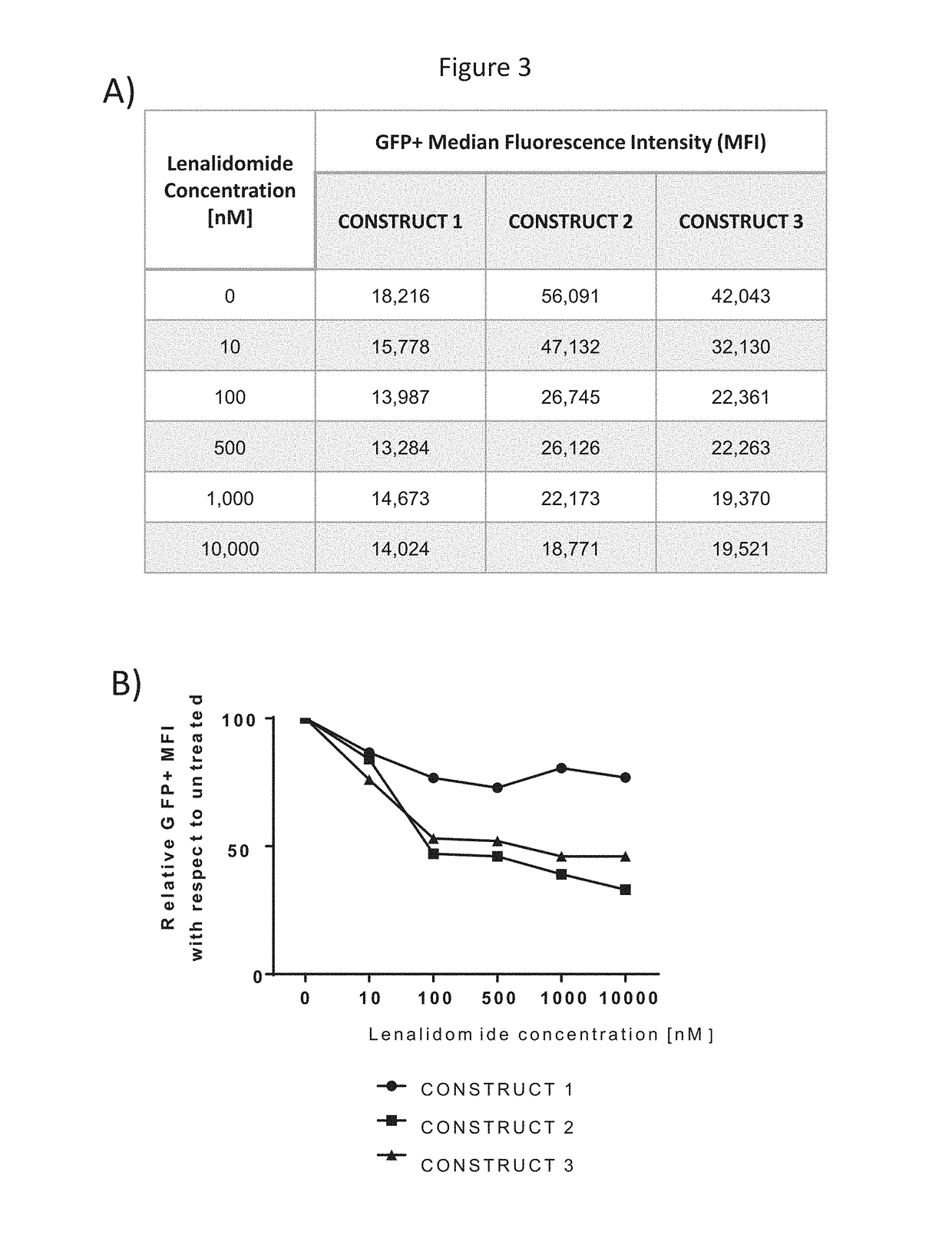
The invention relates to a method of controlling the level of a polypeptide sequence comprising administering a polypeptide sequence fused to a ubiquitin targeting protein which comprises a minimal degron structural motif. In particular, the polypeptide sequence comprises a chimeric antigen receptor therefore the present invention is useful in methods of cell and gene therapy where the activity of the chimeric antigen receptor needs to be controlled.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Prodrugs of cytotoxic active agents having enzymatically cleavable groups
PendingUS20190351066A1Improve tumour selectivityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsDiseaseTumor-Related Protein
The invention relates to novel prodrugs or conjugates of the general formula (Ia)in which La, n, R and D have the definitions given in the description and which have a structural motif reduced to an asparagine derivative as cleavage site for tumour-associated proteases such as legumain, in which cytotoxic drugs, for example kinesin spindle protein inhibitors, are released by legumain cleavage, and to the use of these prodrugs or conjugates for treatment and / or prevention of diseases, and to the use of these prodrugs or conjugates for production of medicaments for treatment and / or prevention of diseases, especially of hyperproliferative and / or angiogenic disorders, for example cancers. Reduction of the legumain-cleavable substrate peptide sequence to an asparagine derivative as structural motif, as a result of slowed legumain cleavage, achieves an increase in stability in the lysosomes of healthy organs while simultaneously maintaining the high anti-tumour effect.
Owner:BAYER AG +1
Methods for identifying ligands that target nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid structural motifs
ActiveUS20080188377A1Microbiological testing/measurementSaccharide librariesNucleic acid structureDNA
Disclosed are methods for identifying a nucleic acid (e.g., RNA, DNA, etc.) motif which interacts with a ligand. The method includes providing a plurality of ligands immobilized on a support, wherein each particular ligand is immobilized at a discrete location on the support; contacting the plurality of immobilized ligands with a nucleic acid motif library under conditions effective for one or more members of the nucleic acid motif library to bind with the immobilized ligands; and identifying members of the nucleic acid motif library that are bound to a particular immobilized ligand. Also disclosed are methods for selecting, from a plurality of candidate ligands, one or more ligands that have increased likelihood of binding to a nucleic acid molecule comprising a particular nucleic acid motif, as well as methods for identifying a nucleic acid which interacts with a ligand.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Novel sirna structures
The invention relates to siRNA compounds possessing novel sequences and structural motifs which down-regulate the expression of specific human genes. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides a method of treating and / or preventing the incidence or severity of various diseases or conditions associated with the genes and / or symptoms associated with such diseases or conditions comprising administering to a subject in need of treatment for such disease or condition and / or symptom the compound or the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the subject.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
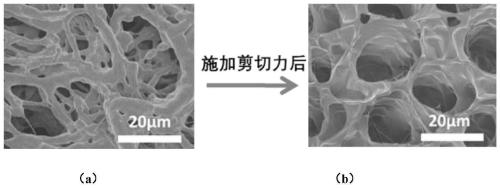
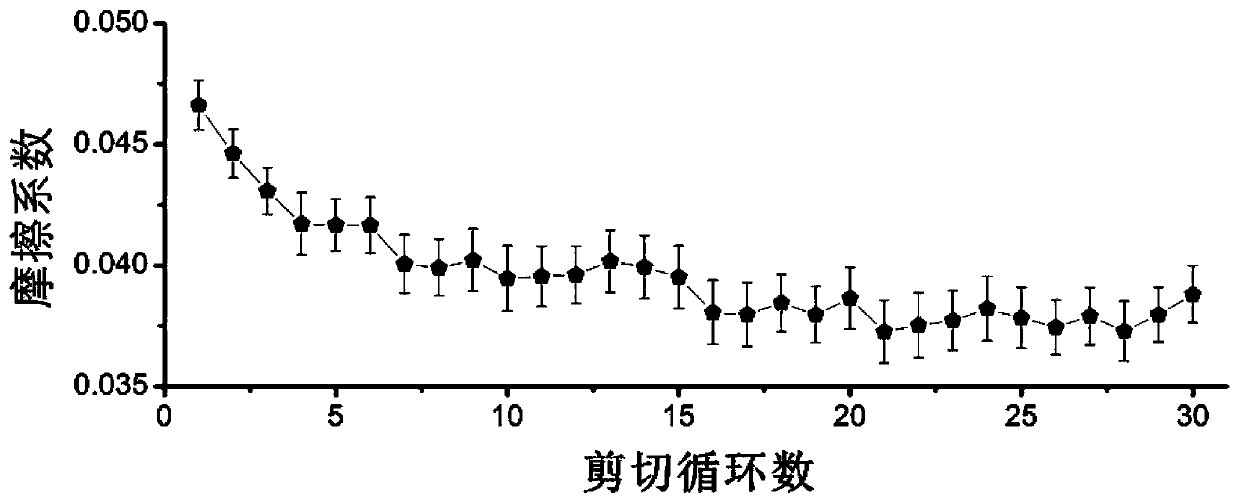
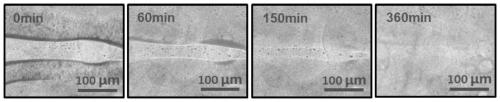
Shear force-responsive supramolecular bionic articular cartilage material with dynamic lubrication and self-repairing ability and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110180022AGood self-lubricating functionGood mechanical supportPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationArtificial jointsHigh intensity
The invention relates to a shear force-responsive supramolecular bionic articular cartilage material with dynamic lubrication and self-repairing ability and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of bionic self-repairing and lubricating articular cartilage materials and preparation thereof. Inspired by articular cartilage, a covalently crosslinked high-strength hydrogelnetwork, a shear force-responsive supramolecular network and an intrinsic self-repairing structural motif are organically combined to provide an intelligent hydrogel material having a function of bionic articular cartilage activity. The intelligent hydrogel material has good mechanical properties and a shear self-lubricating function; more importantly, through the interaction between a shear force-responsive exudation lubricating layer and a self-repairing motif, the dynamic exudation lubrication mechanism is simulated while realizing the double repair of a three-dimensional network structureand the shear force-responsive self-lubricating function after the material is worn. The design concept can be applied to the preparation of new artificial articular cartilage or self-repairing lubrication devices, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Hairpin peptides with a novel structural motif and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS20050196810A1Enable stabilizationImprove structural stabilityPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein moleculesModel system
The invention is directed to a model system for structure-activity relationship analysis of peptide or protein molecules involved in important biological processes. Provided by the invention are combinatorial peptide libraries comprising peptides with a novel “tryptophan zipper” scaffold (trpzip) that forms stable β-hairpin structure in solution. Methods of selecting and using such scaffold are provided herein, which are useful for mimicking native protein structures and interactions and designing therapeutic agents. Thus, the invention has profound utility for biological studies and drug development.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
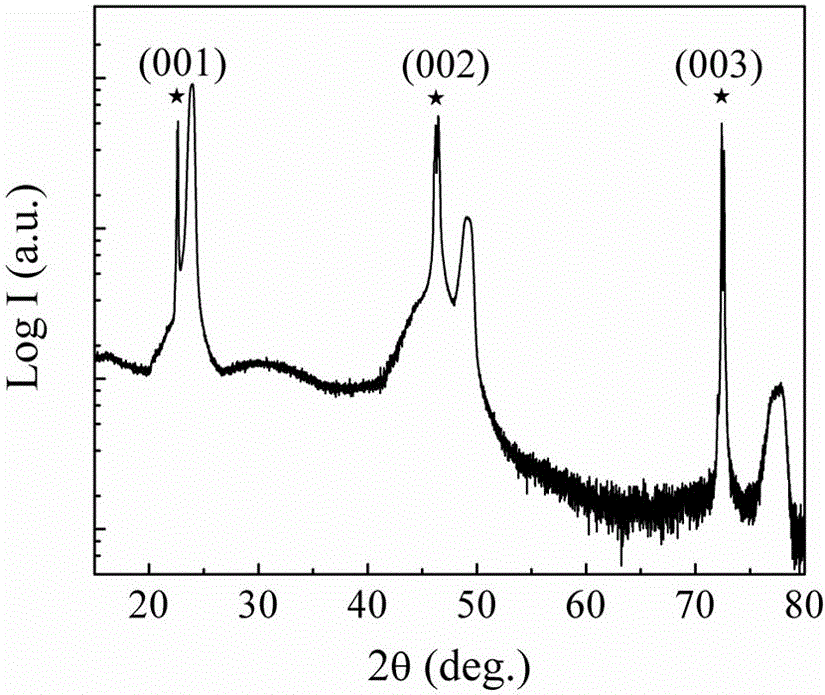
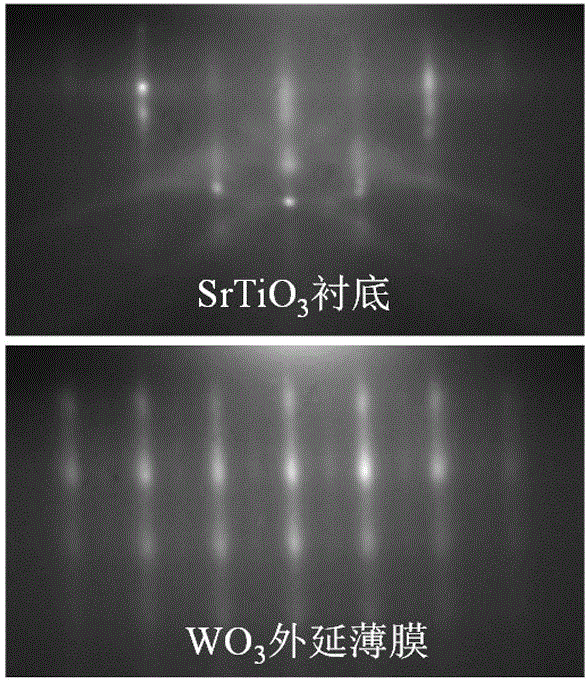
NO2 sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106124575AImprove detection abilityImprove stabilityMaterial resistanceOctahedronHigh surface
The invention discloses an NO2 sensor and a preparation method thereof. The sensor comprises an oxide single crystal substrate, a WO3 epitaxial thin film, test electrodes and noble metal catalysts. The concentration of the NO2 gas in the environment is calibrated by measuring change of the resistance value of the WO3 epitaxial thin film between the test electrodes. Distortion and tilting of a structural motif WO6 octahedron of the WO3 epitaxial thin film are achieved by regulating the stress on the interface of the oxide single crystal substrate and the WO3 epitaxial thin film to obtain the WO3 epitaxial thin film with specific crystalline phase and exposed crystal plane, higher surface activity and reaction site concentrations and stable properties, thereby improving the detectivity and stability of the NO2 sensor. The sensor provided by the invention can be used for detecting NO2 with concentration of 40mu g / m<3>-20mg / m<3>, has short response time and stable properties, can be used for monitoring the concentration of NO2 in the atmospheric environment in real time and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cystine knot peptides binding to alpha IIb beta 3 integrins and methods of use
Disclosed are peptides having a cystine knot structural motif and comprising a sequence engineered for specificity against αIIbβ3 integrin, found on platelets, and a method of using the same in anti-thrombotic therapies. The present peptides utilize a cystine knot scaffold derived from modified agouti-related protein or agatoxin, An alternate library screening strategy was used to isolate variants of peptides that selectively bound to αIIbβ3 integrin or to both αIIbβ3 and αVβ3 integrins. Unique consensus sequences were identified within the identified peptides suggesting alternative molecular recognition events that dictate different integrin binding specificities. In addition, the engineered peptides prevented human platelet aggregation in a plasma-based assay and showed high binding affinity for αIIbβ3 integrin.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Modeling system and extracting method for primal sketch of color image
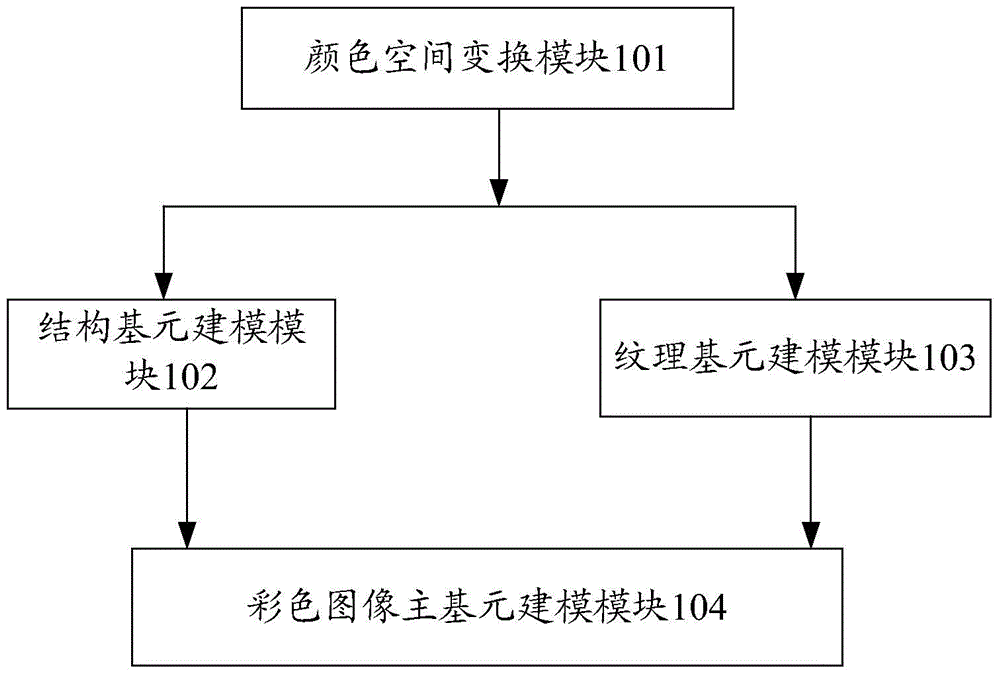
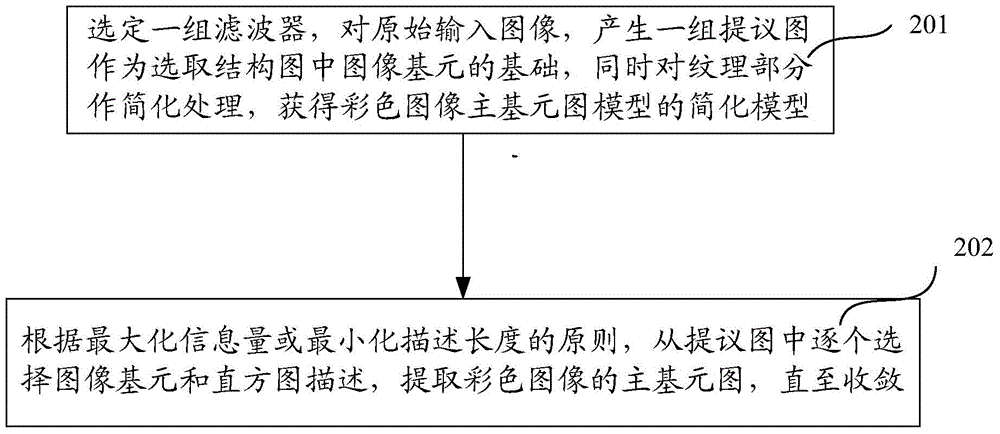
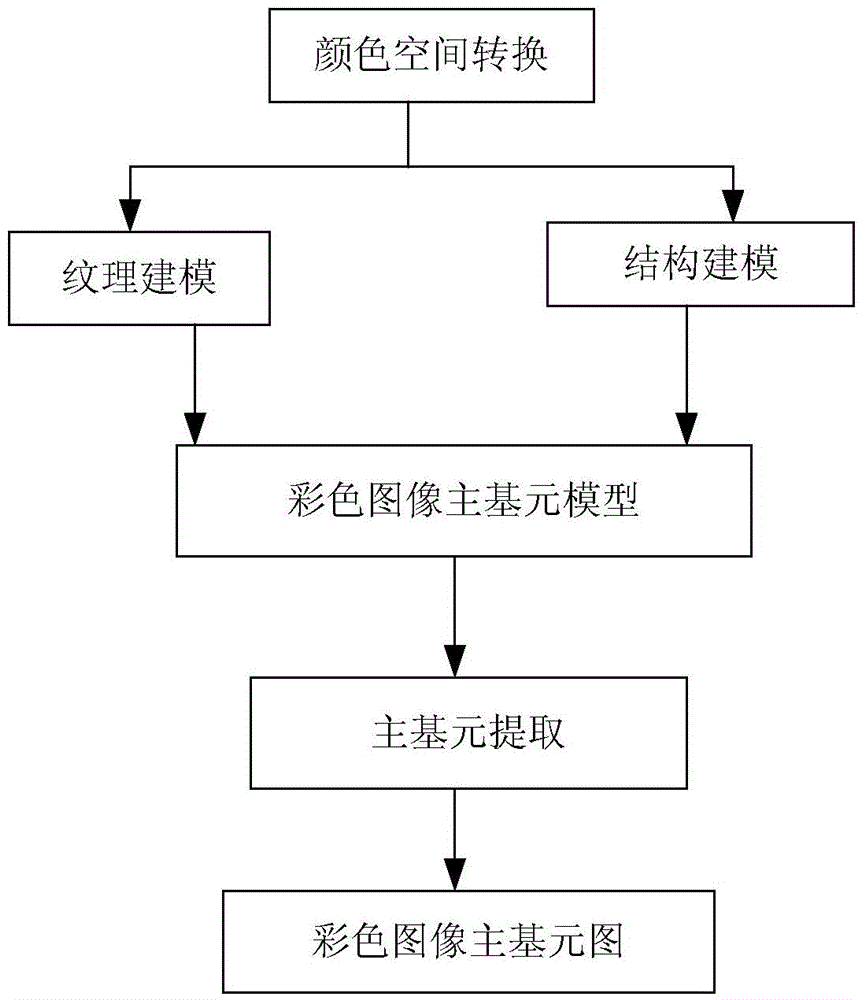
InactiveCN104537658AImplement extractionConform to perceptionImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageLab color space
The invention discloses a modeling system and extracting method for a primal sketch of a color image. The modeling system comprises a color space alternation module, a structural motif modeling module, a texture primitive modeling module and a color image primal sketch modeling module, wherein the color space alternation module transforms an original RGB image into a Lab color space through a color space, the structural motif modeling module divides a structure part in the image into a set of K disjointed image blocks, each set of image blocks are represented by an image primitive, and the structure part of the image is represented by a structure chart through a set of image primitives; the texture primitive modeling module clusters a texture part in the color image trough response of a set of selected filters and divides the texture part into a set of disjointed homogeneous texture areas, each homogeneous texture area is represented by a set of histograms in an implicit expression mode, and finally the texture areas in the image are marked; the color image primal sketch modeling module obtains a probability mathematic model represented by a primal sketch of a gray level image, and constructs a model for the primal sketch of the color image. Through the modeling system and extracting method for the primal sketch of the color image, the primal sketch neglected by the gray level primal sketch image can be extracted.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
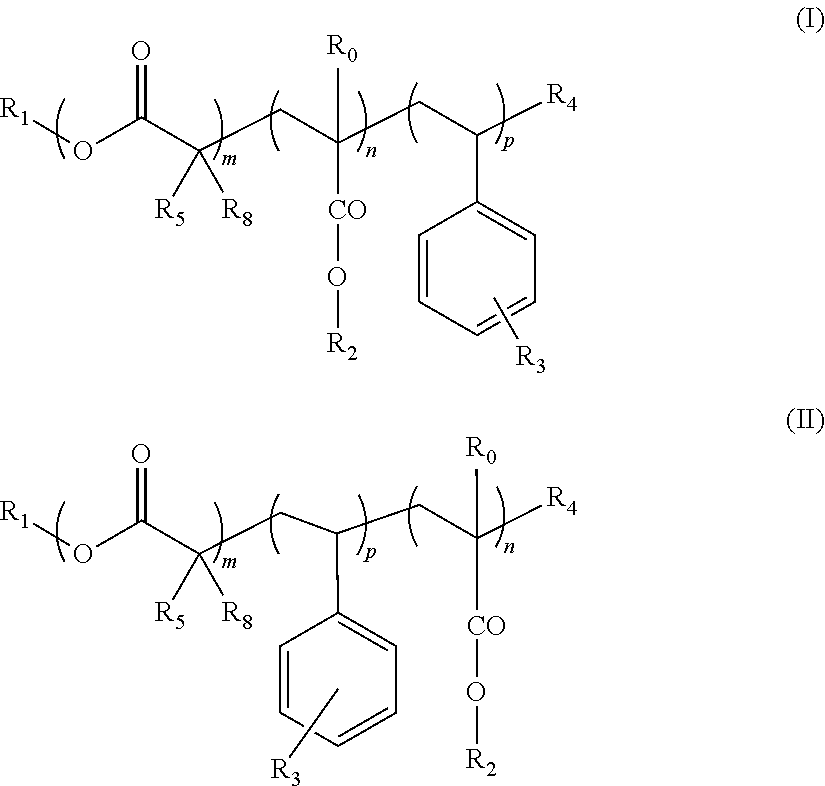
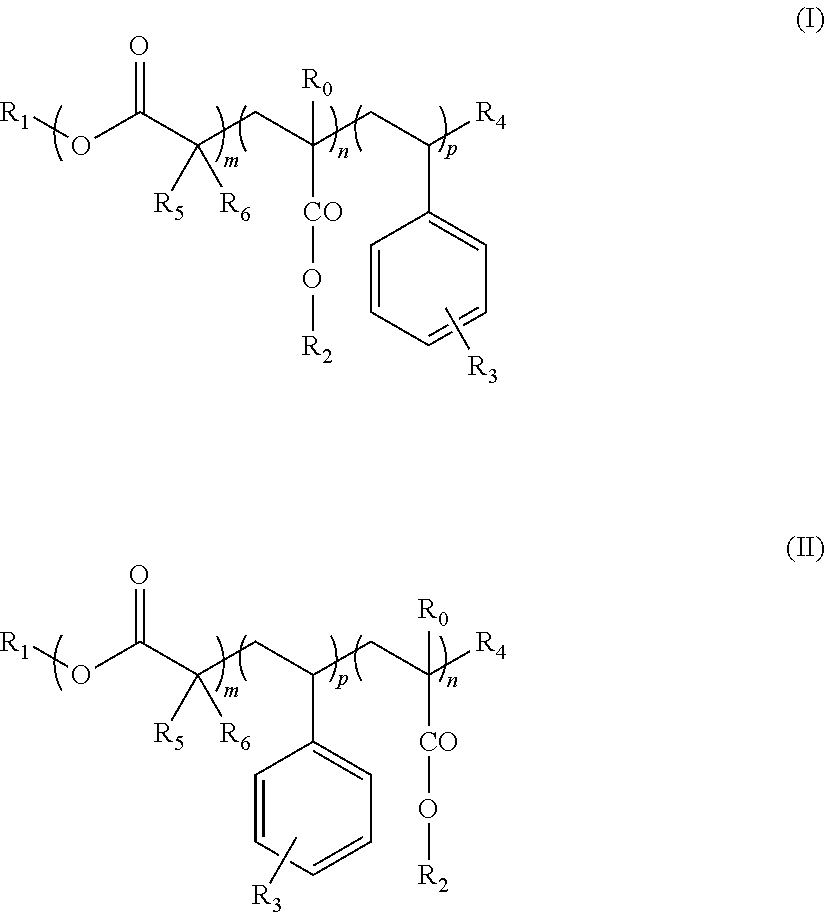
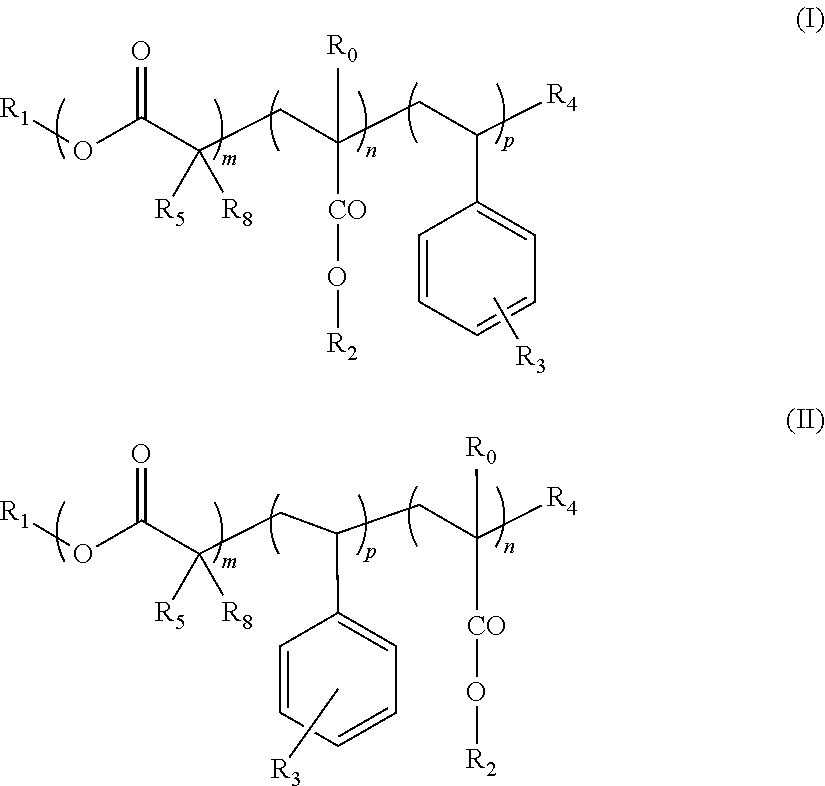
Block copolymers and the use thereof for improving the cold properties of fuels or combustibles
The invention relates to a block copolymer and the use thereof as a cold resistance additive of a fuel or combustible. The block copolymer comprises: (i) a block A consisting of a chain of structural motifs derived from at least one α,β-unsaturated alkyl methacrylate or acrylate monomer; and (ii) a block B consisting of a chain of structural motifs derived from at least one α,β-unsaturated monomer selected from styrene derivatives, the aromatic ring of which is substituted by at least one group R selected from the groups: C1 to C24 alkyl esters, and preferably acyclic linear or branched C1 to C12 hydrocarbonated chains, said chain being substituted by at least one group containing a quaternary ammonium salt. The invention also relates to an additive concentrate containing such a copolymer and to the use thereof as an anti-sedimentation additive, and advantageously, as a TLF booster additive.
Owner:TOTAL MARKETING SERVICES SA
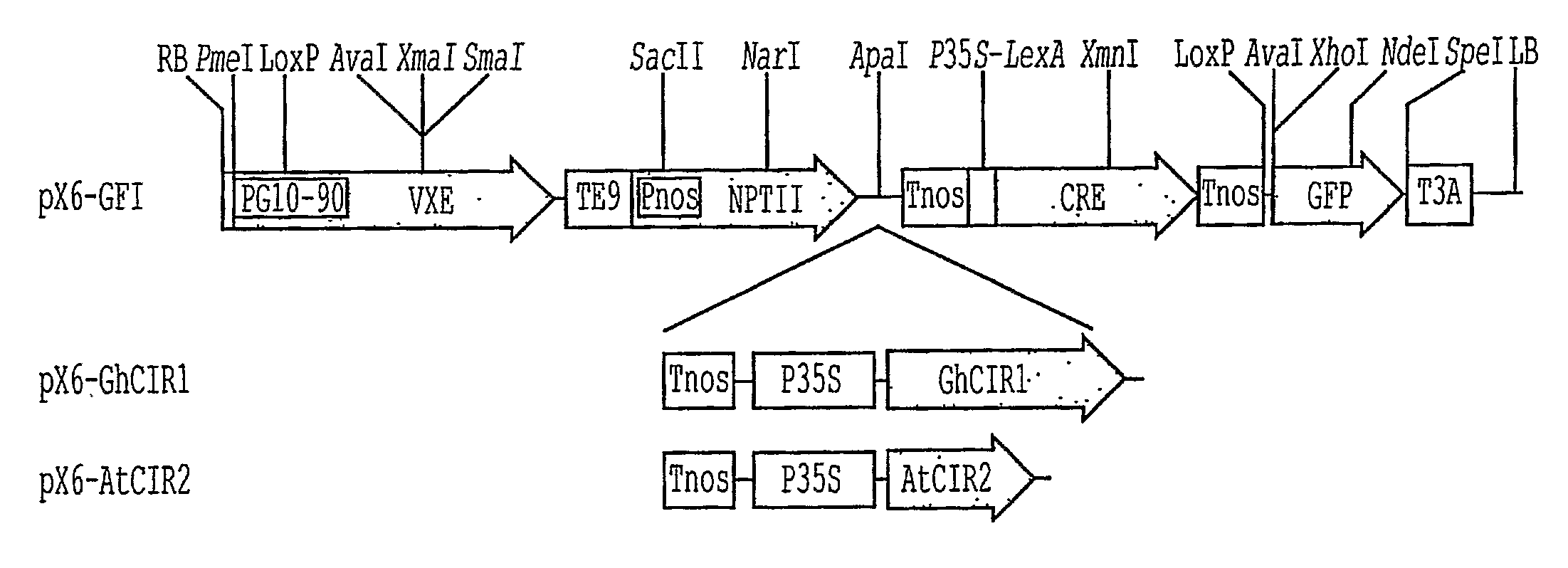
Novel plant homeodomain protein-encoding genes and their uses
InactiveUS20100293662A1Improve efficiencyPromote regenerationBacteriaImmunoglobulinsBiotechnologyTransformation efficiency
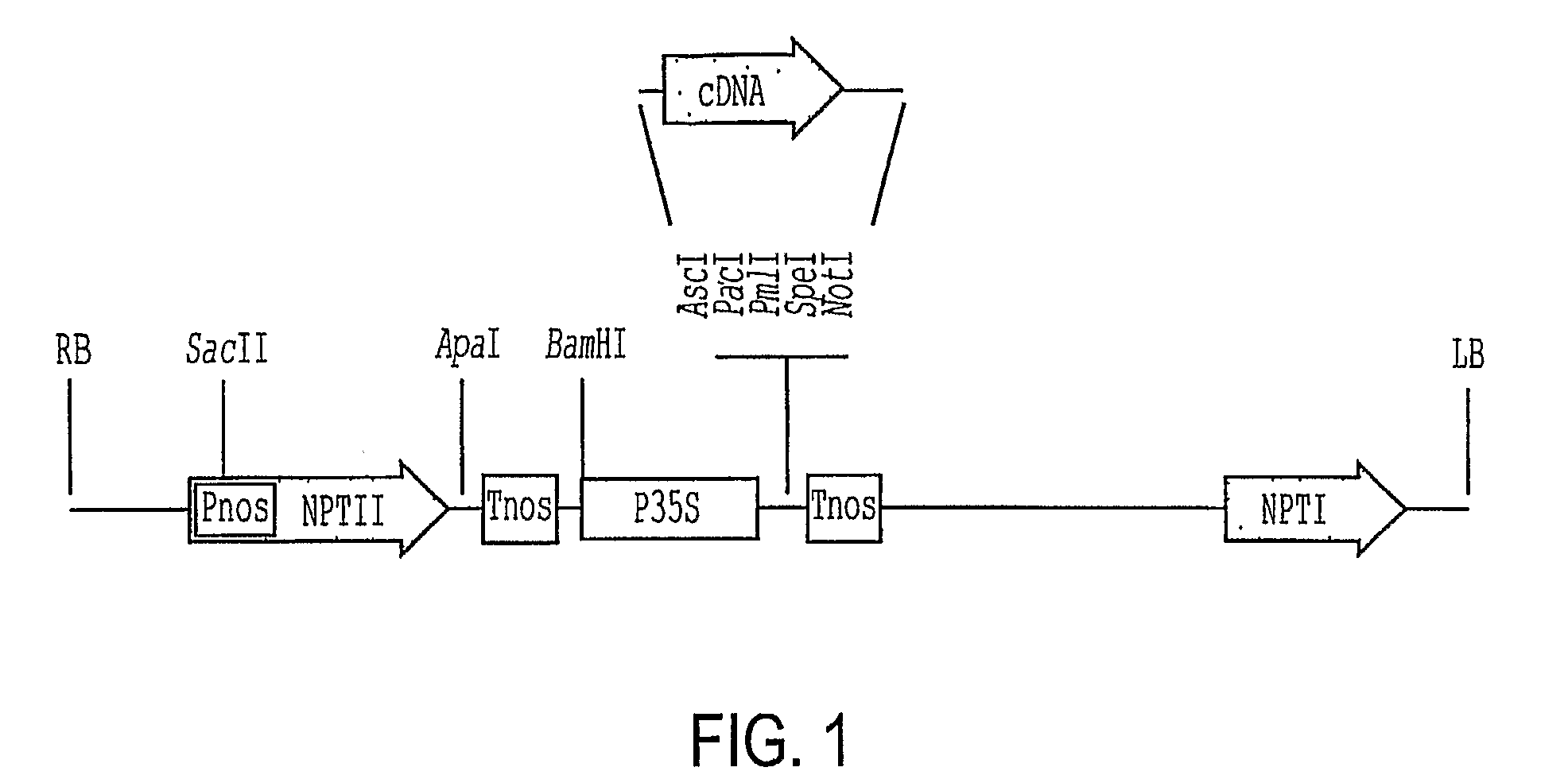
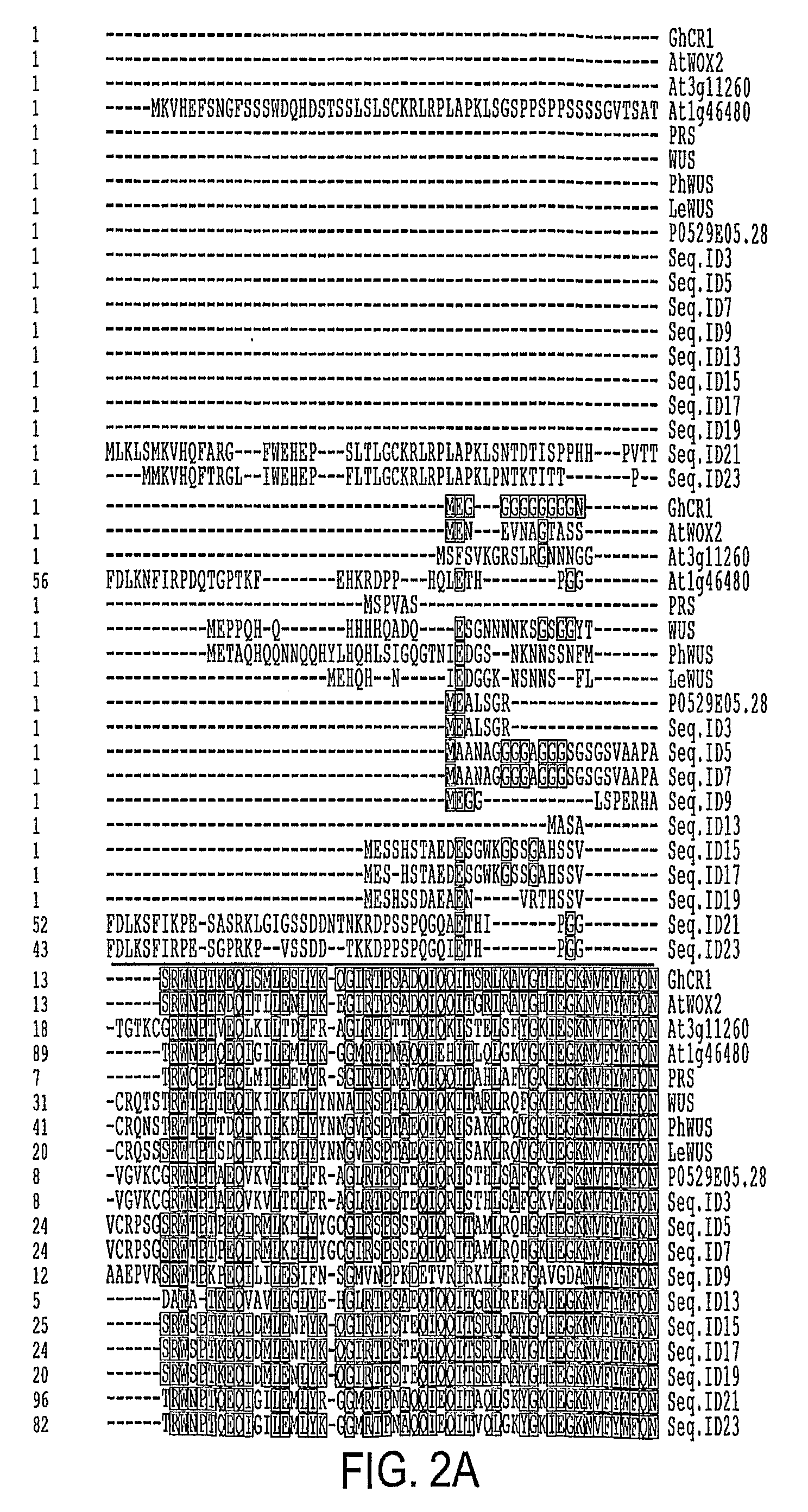
A group of genes including GhCIR1 from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum), and AtCIR1 and AtCIR2 from Arabidopsis thaliana promote shoot regeneration in plants even in the absence of cytokinin. In the presence of cytokinin, the genes significantly improve transformation efficiency. The genes can be used as an enhancer as well as a selectable marker of transformation in plants. The proteins encoded by the novel genes have a homeodomain (HD) at the N-terminus and a highly divergent domain at the C-terminus. The proteins share a common structural motif.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
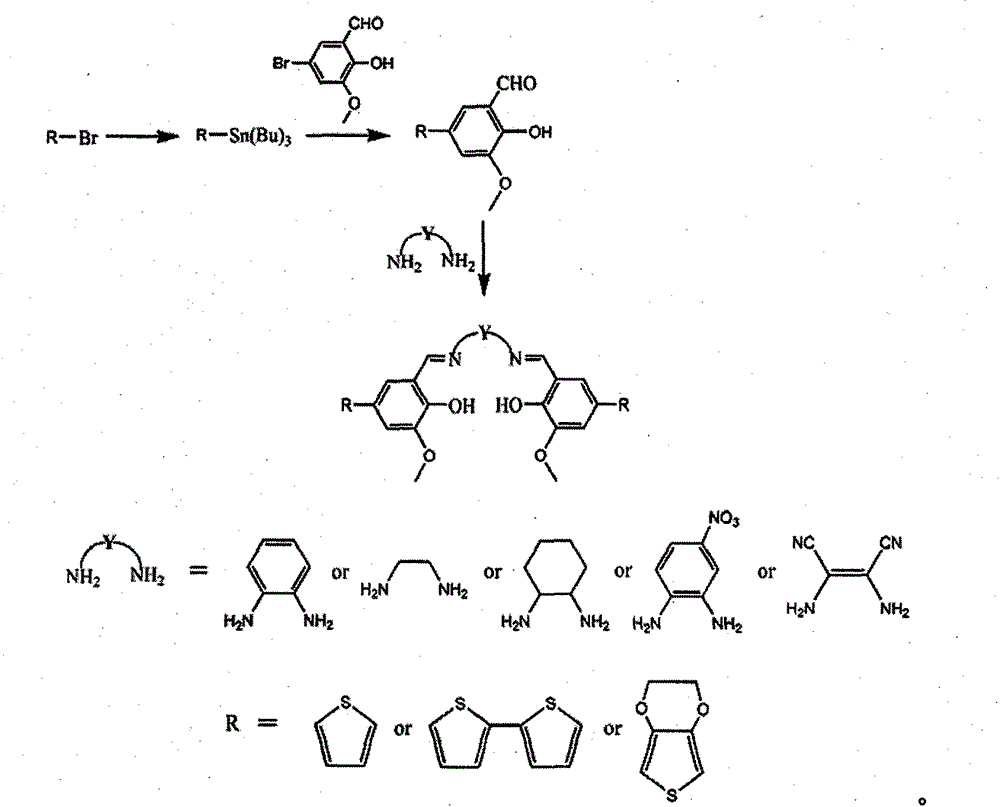
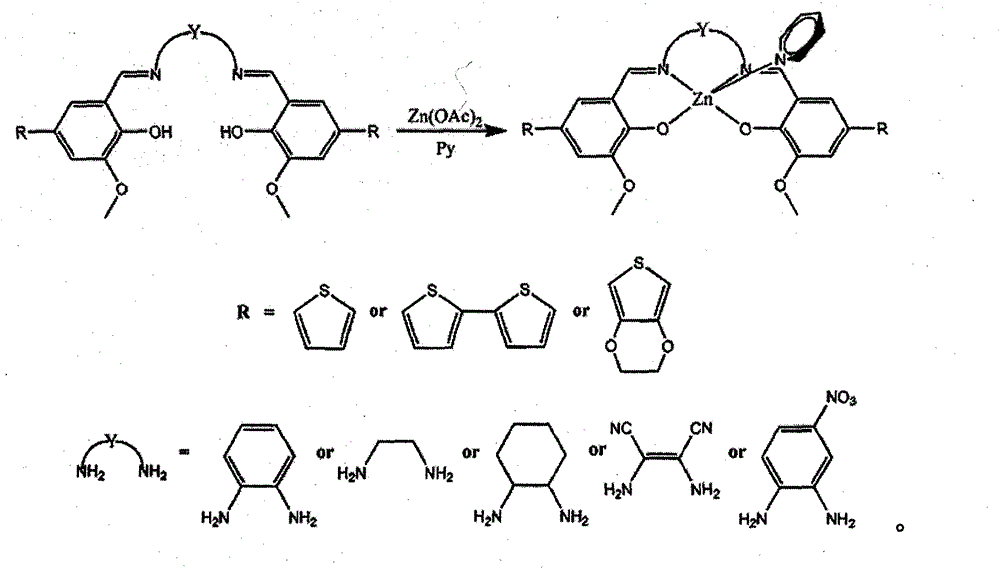
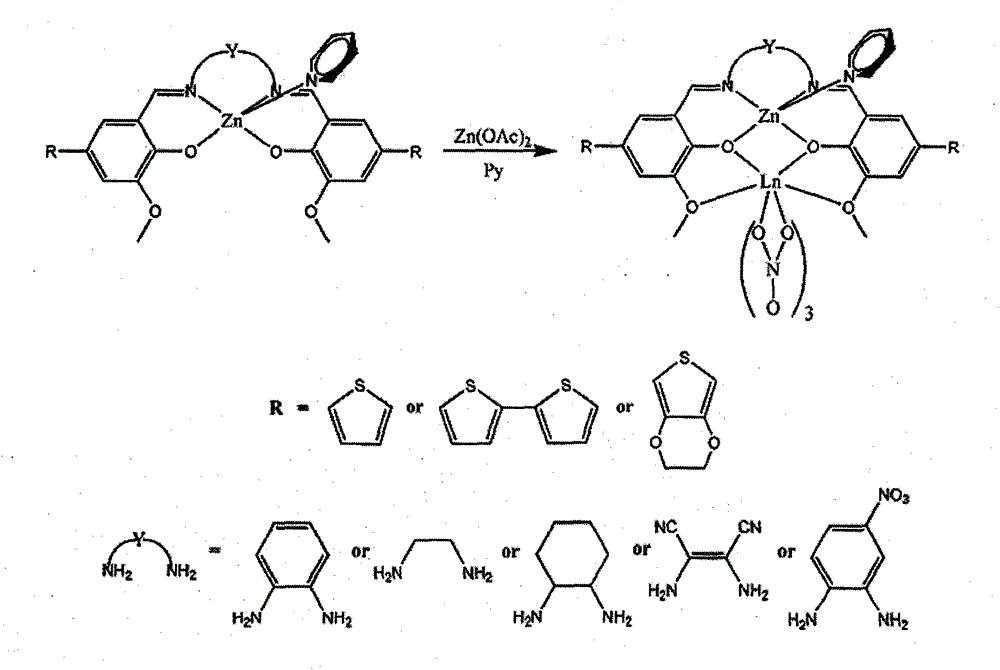
Preparation method of conductive mixed metal polymer film material
InactiveCN104004508ALong fluorescence lifetimeHigh fluorescence intensityElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionQuantum yieldNear infrared luminescence
The present invention discloses a preparation method of conductive mixed metal polymer film material, belonging to the field of metal polymer. The method comprises: obtaining aldehyde compound through synthesis reactions, then obtaining Salen series Schiff base ligand L which contains functional group substituents through aldehyde-amine condensation reaction with diamine compounds; and assembling the Salen series Schiff base ligand L with Zn2+ and Ln3+ (Ln equals to Nd, Yb, Er, Gd, Eu or Tb) according to the properties of the molecular system of a structural motif of a Zn-Ln heteronuclear bimetallic complex. Through revealing the energy transfer mechanism of the molecular system of conductive mixed metal polymer which contains Zn and Ln, the invention discloses the breakthrough solution and method of acquiring luminescent devices with a long fluorescence lifetime, strong fluorescence intensity and high quantum yields when the material is used in visible and near-infrared light-emitting materials.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Oligonucleotide mediated specific cytokine induction and prophylaxis and treatment of viral infection in a mammal
InactiveUS7700570B2Easy to produceWithout causing unwanted toxic side effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMammalIn vivo
The invention provides new methods for modulating specific CMI-inducing cytokines in vivo. Such new methods result in stimulation of the cytokines IL-6, IL-12 MIP-1β and MCP without substantially inducing undesired cytokines. The methods according to the invention are based upon administration of oligonucleotides containing particular structural motifs which lead to specific cytokine induction.
Owner:IDERA PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com