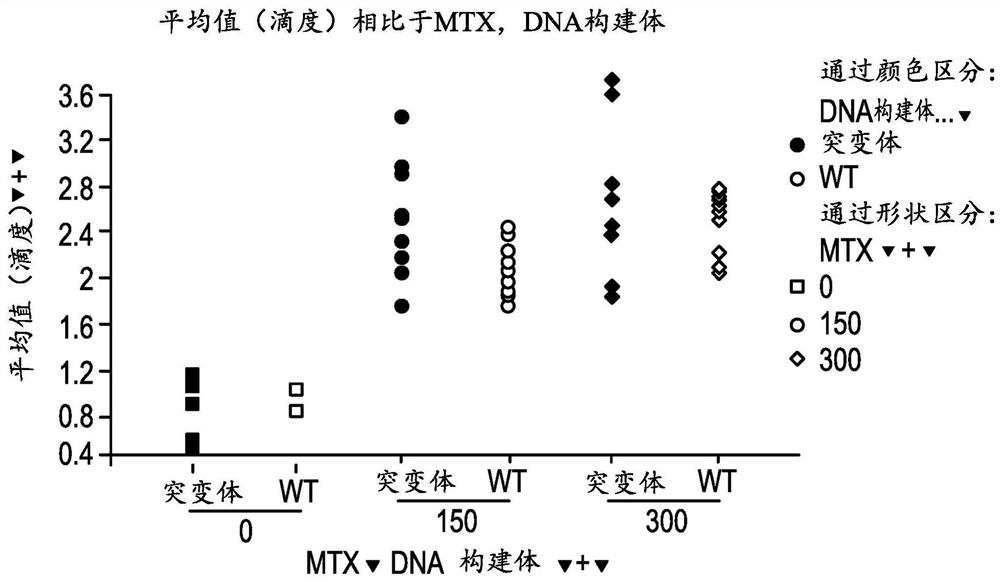
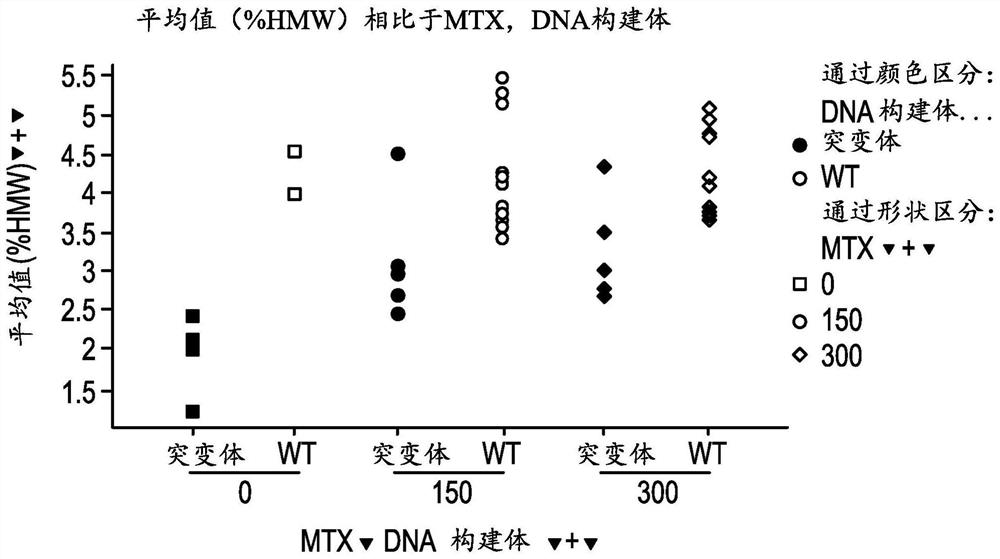
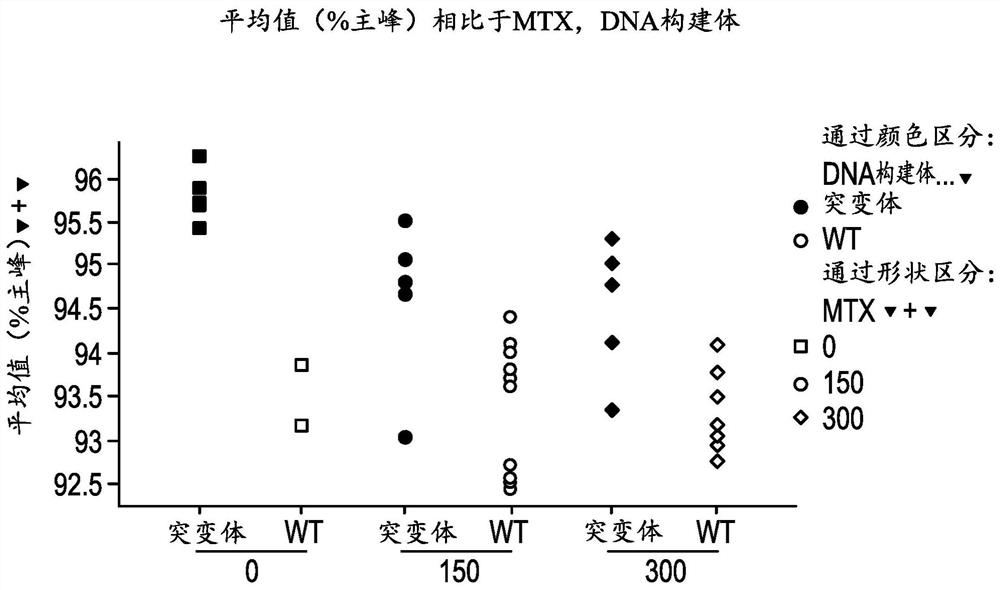
Engineering monoclonal antibodies to improve stability and production titer
A stability and antibody technology, applied in the field of protein engineering, can solve problems such as lack of stability, affecting the shelf life of mAb, and increasing production costs due to production levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] Example 1. A method of increasing the stability of a primary antibody comprising substituting glycine, alanine, or serine at position 56 (AHo numbering) of the heavy chain to generate a secondary antibody, wherein the secondary antibody is more stable than the unidentified antibody Substituted primary antibodies are more stable. For example, at position 56 of the heavy chain, a glycine can be substituted. For example, at position 56 of the heavy chain, glycine or alanine may be substituted. For example, at position 56, glycine or serine may be substituted.
Embodiment 2
[0112] Embodiment 2. The method of embodiment 1, wherein at position 56 of the heavy chain, the glycine is substituted.
Embodiment 3
[0113] Embodiment 3. The method of any one of embodiments 1-2, wherein the second antibody is further substituted with a hydrophobic amino acid residue at position 80 (AHo numbering) of the heavy chain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com