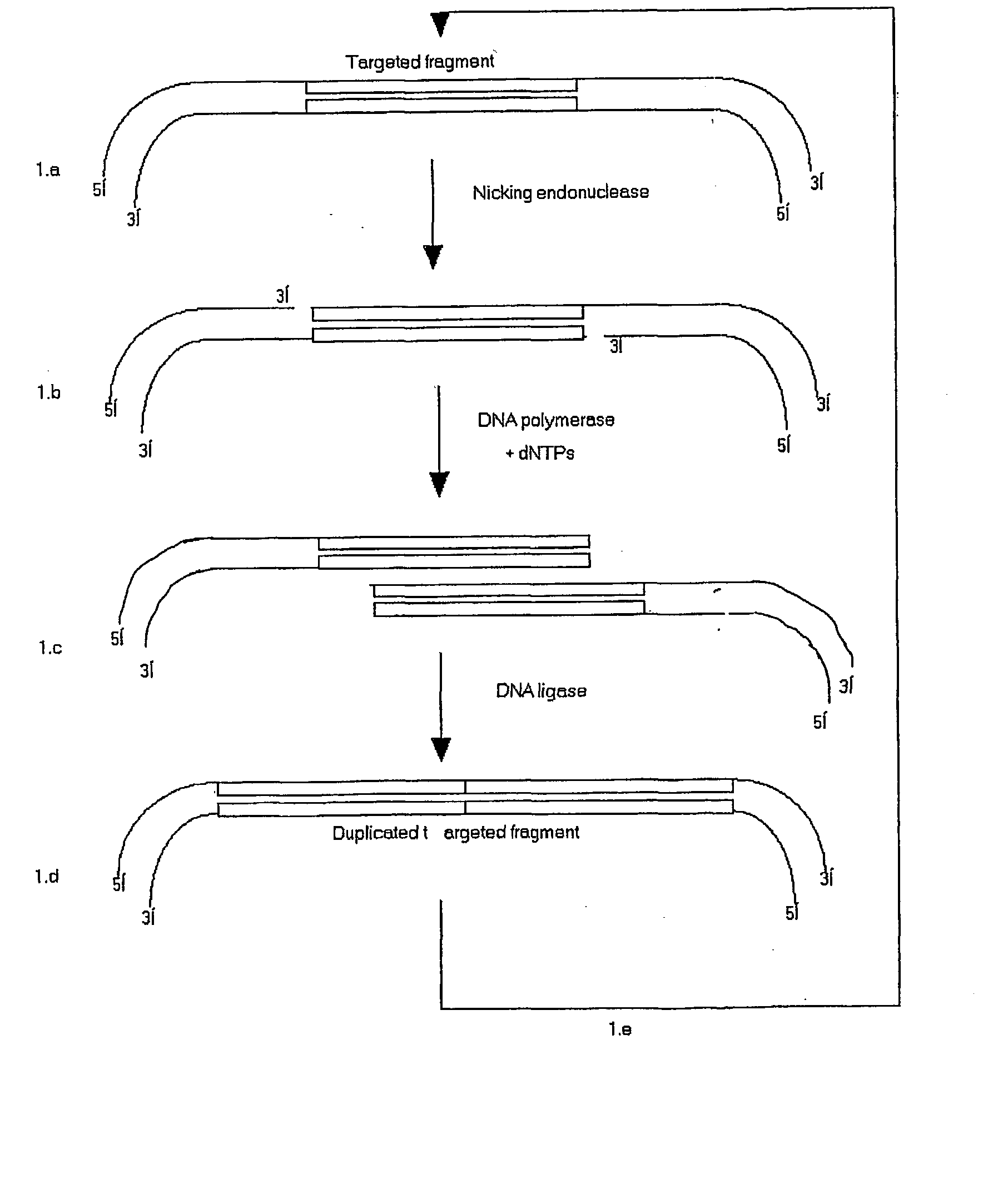
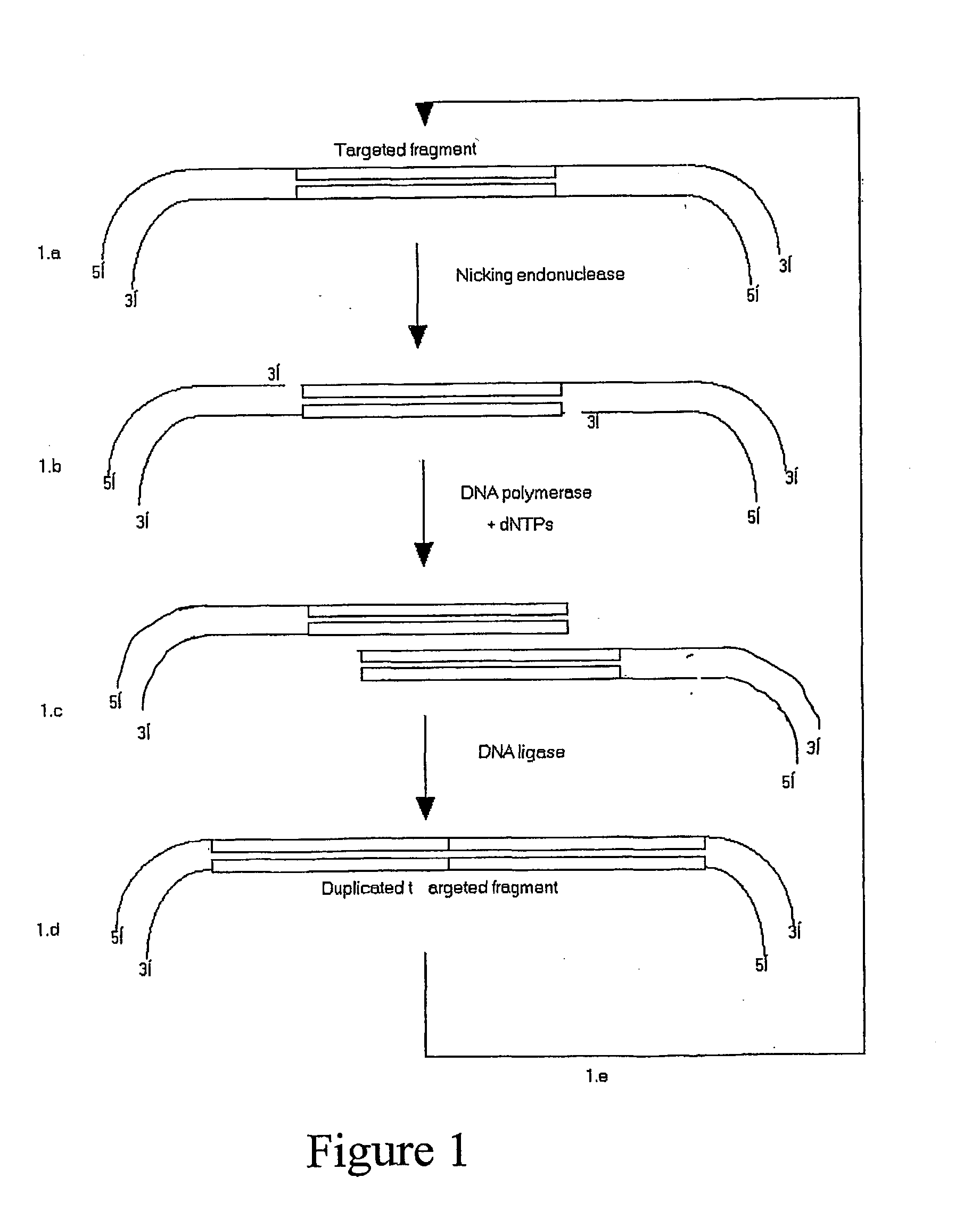
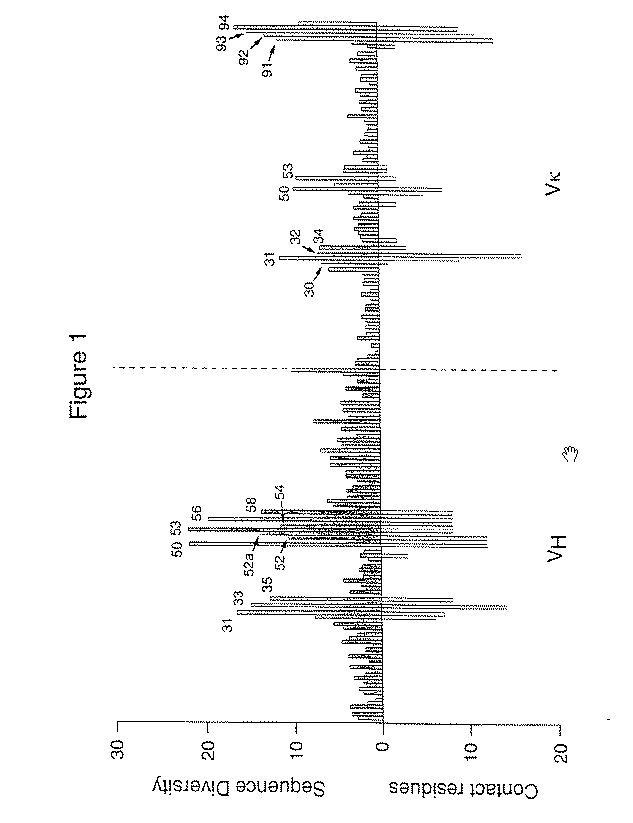
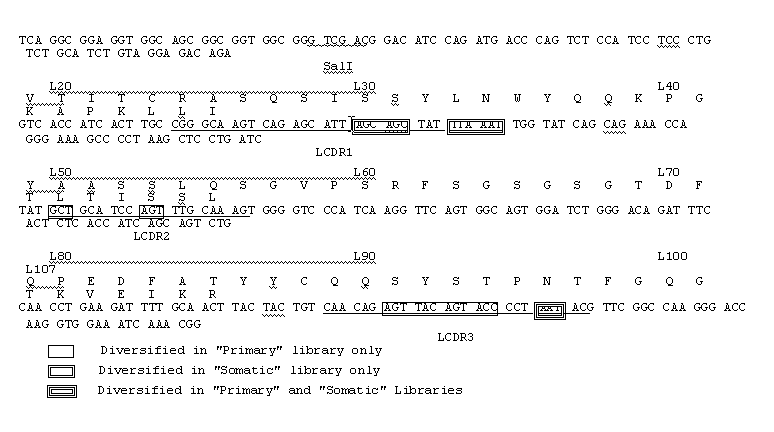
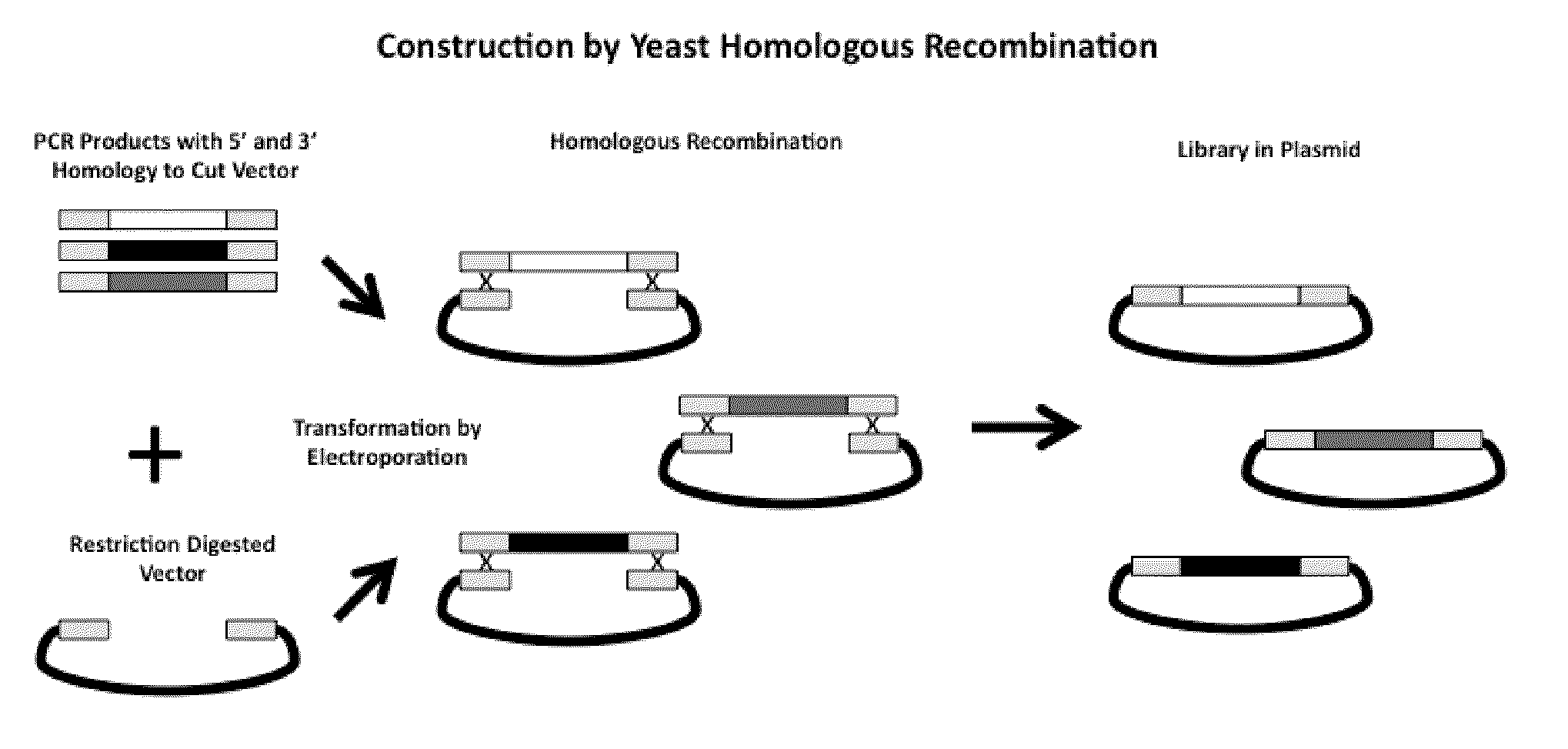
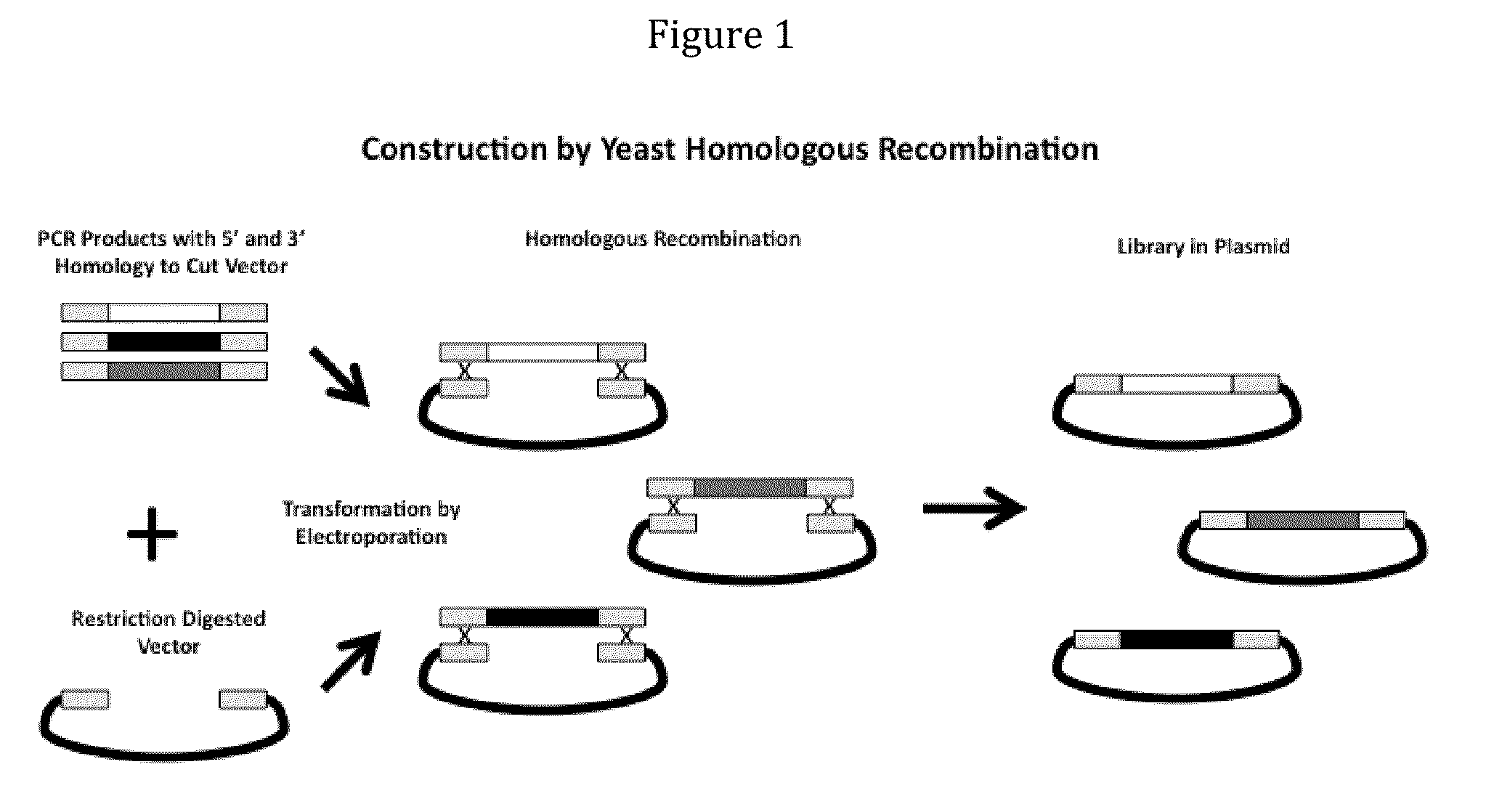
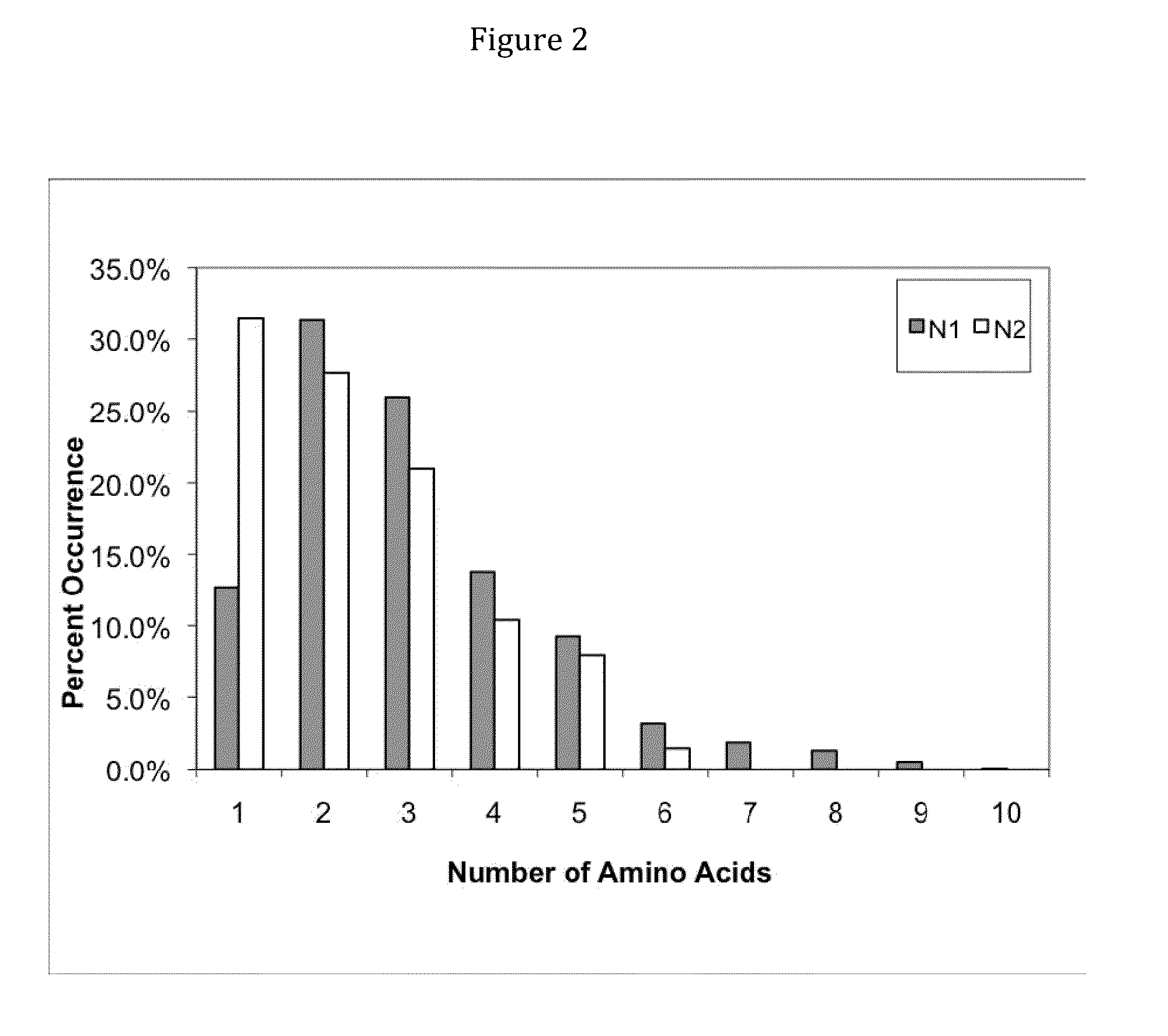
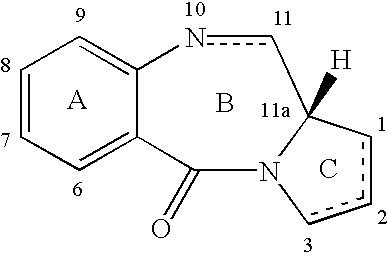
Patents
Literature
1104results about "Microorganism libraries" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
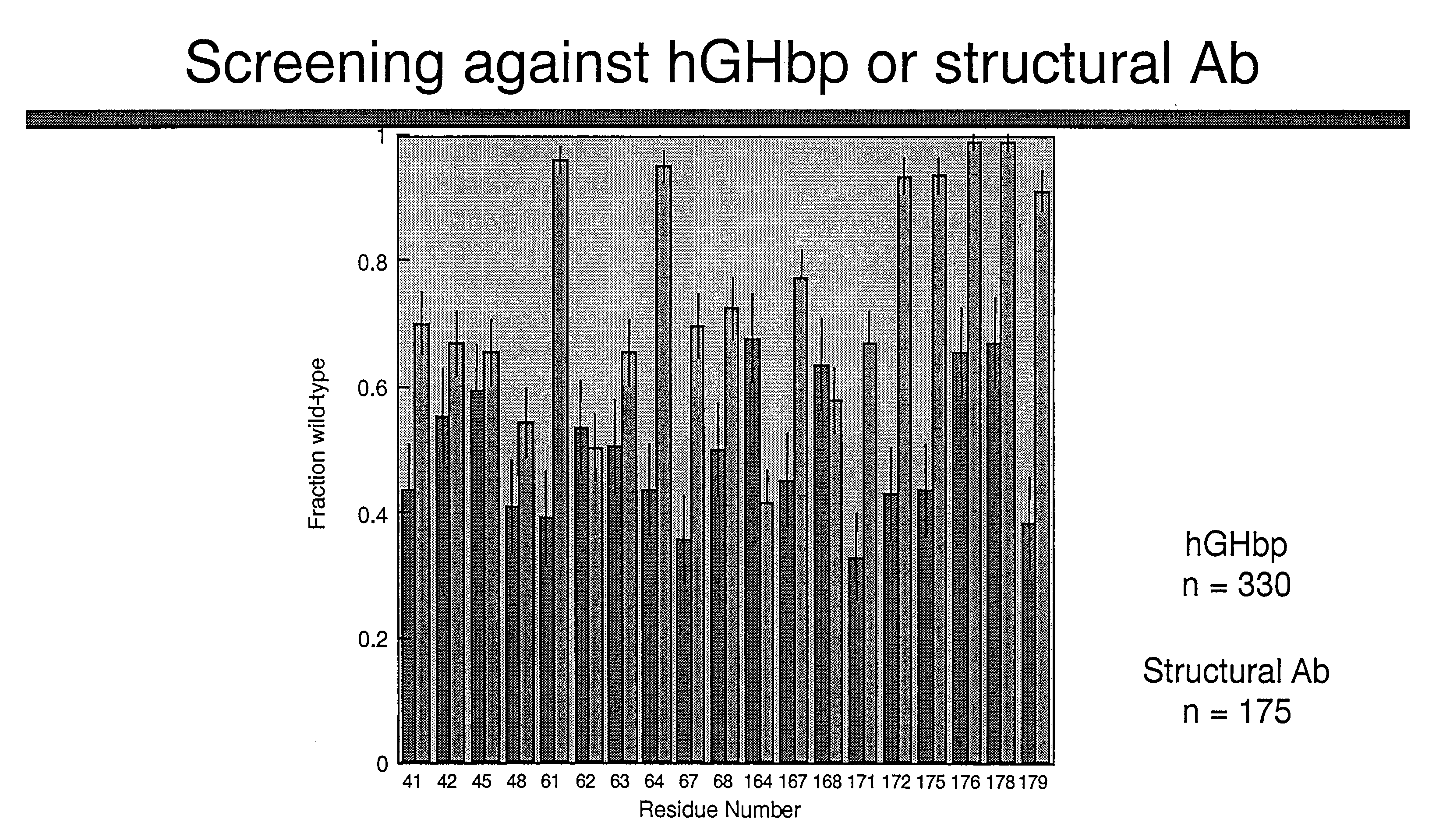
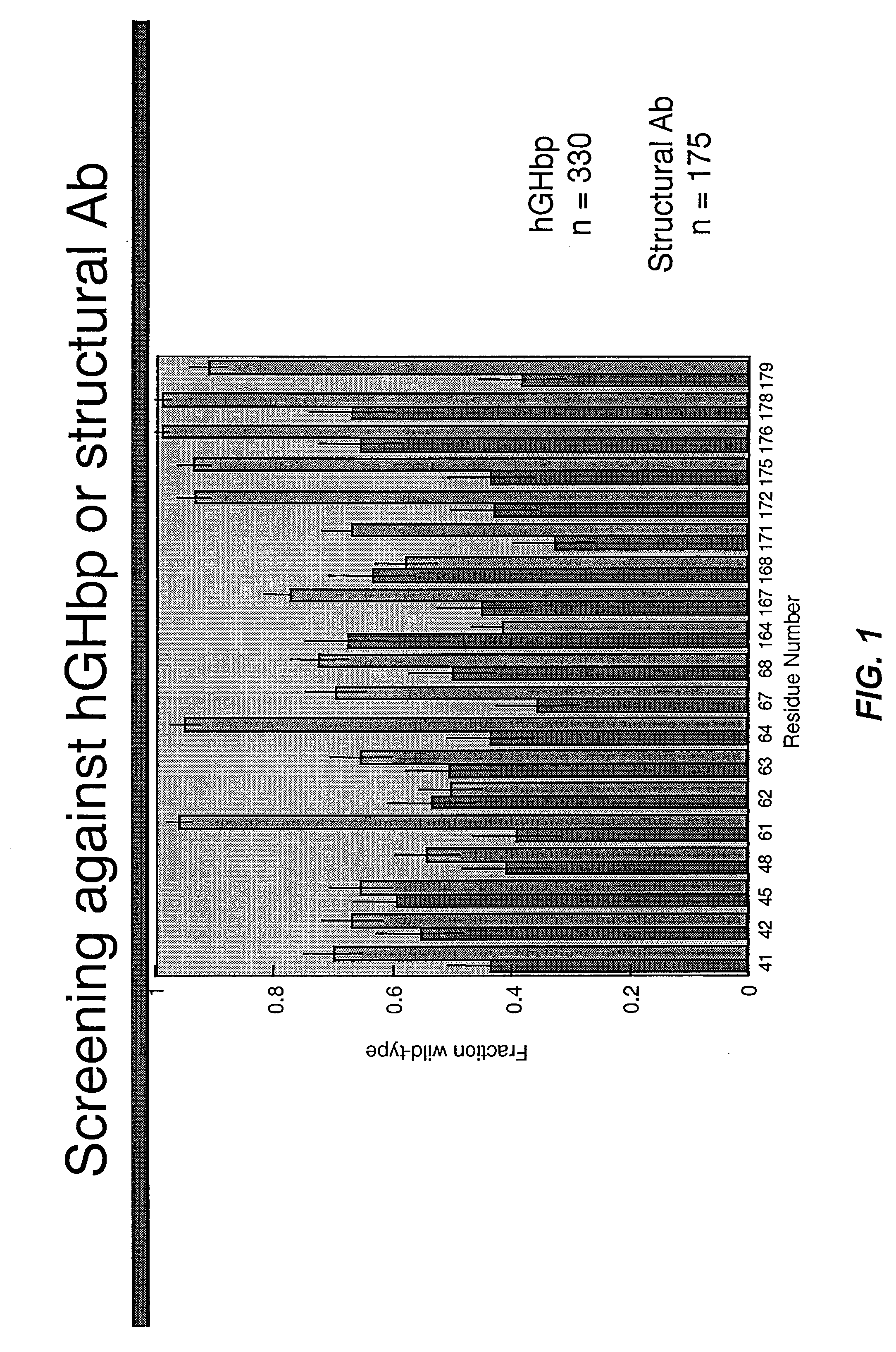
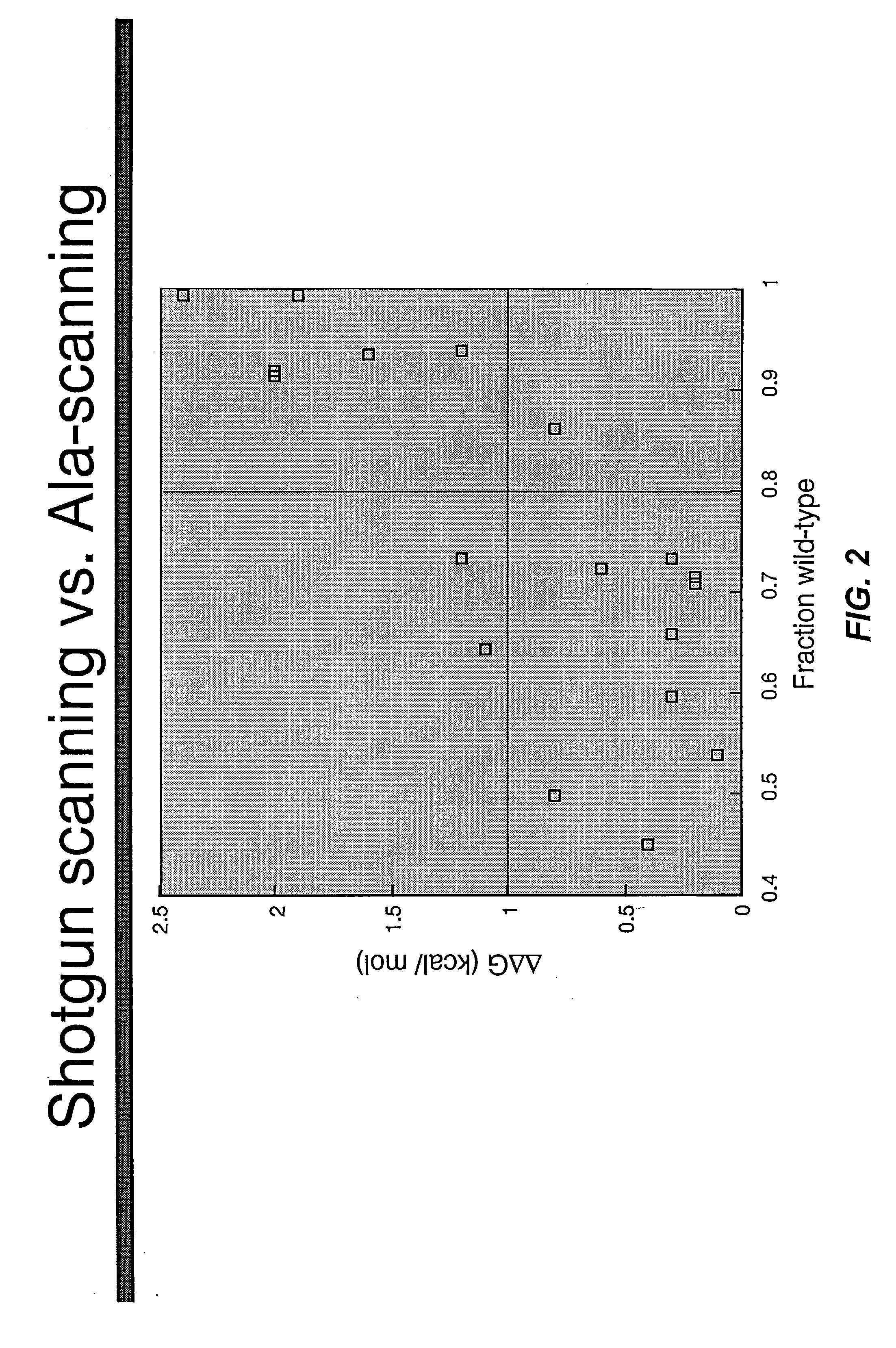
Shotgun scanning
A combinatorial method that uses statistics and DNA sequence analysis rapidly assesses the functional and structural importance of individual protein side chains to binding interactions. This general method, termed “shotgun scanning”, enables the rapid mapping of functional protein and peptide epitopes and is suitable for high throughput proteomics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
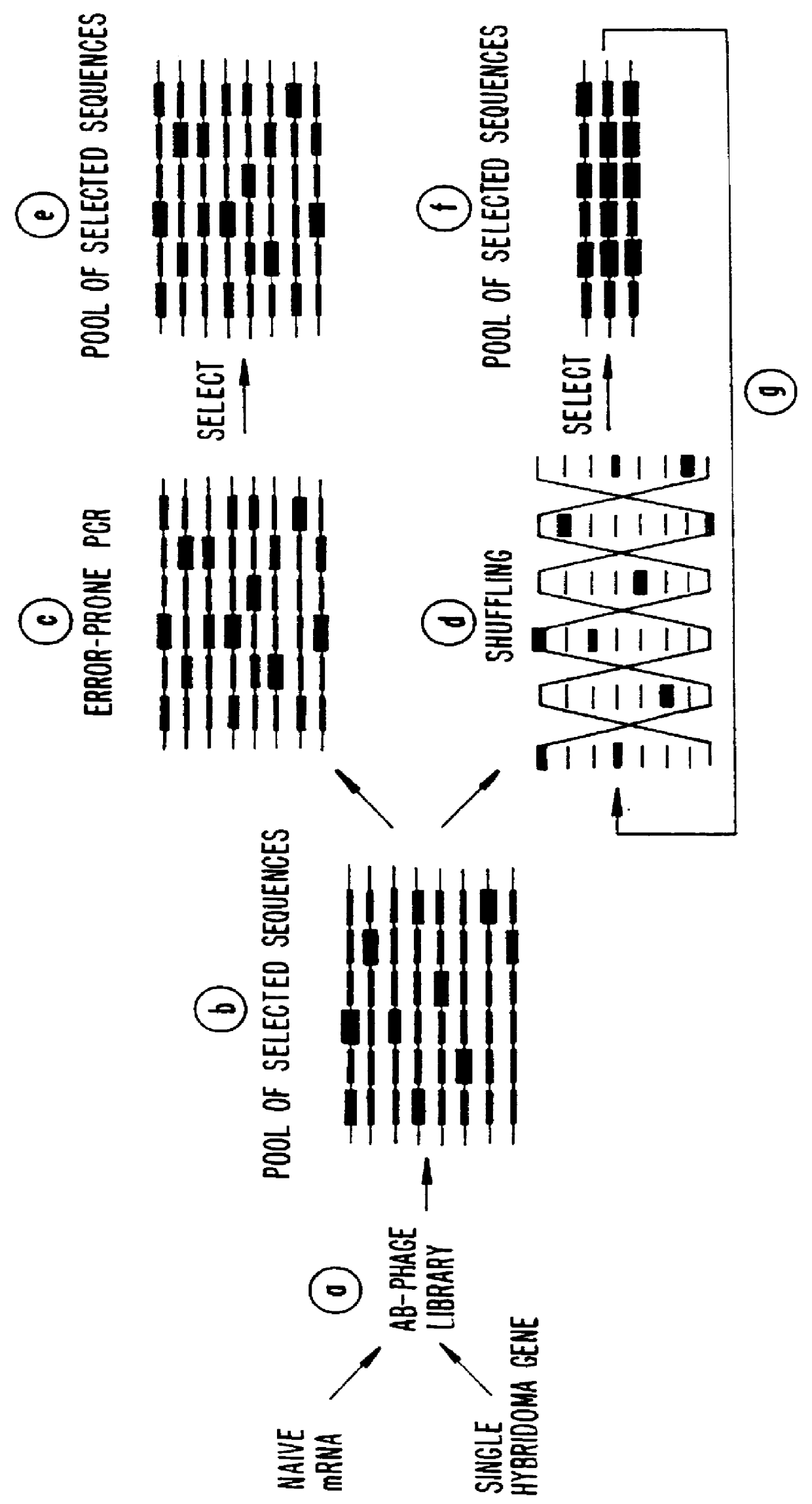
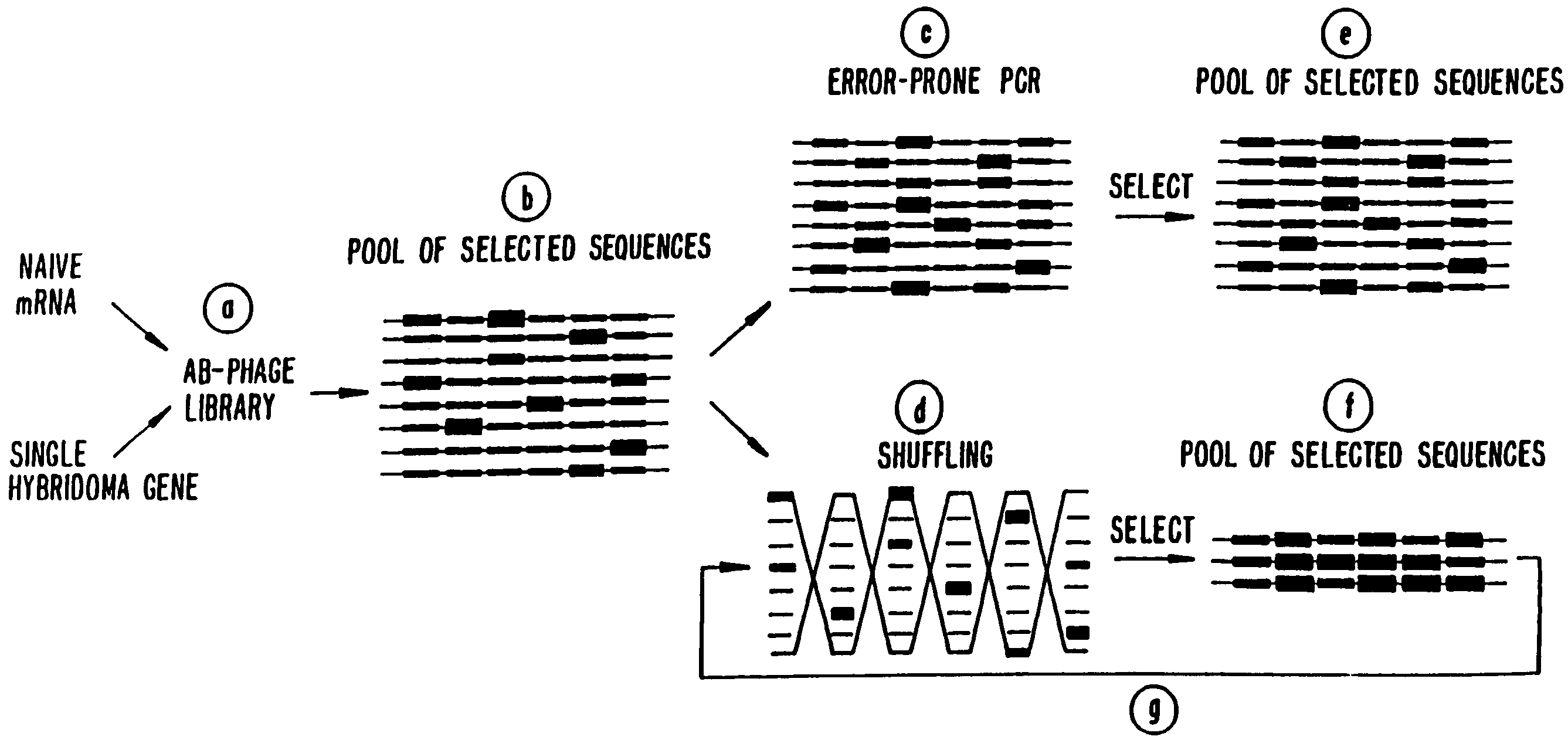
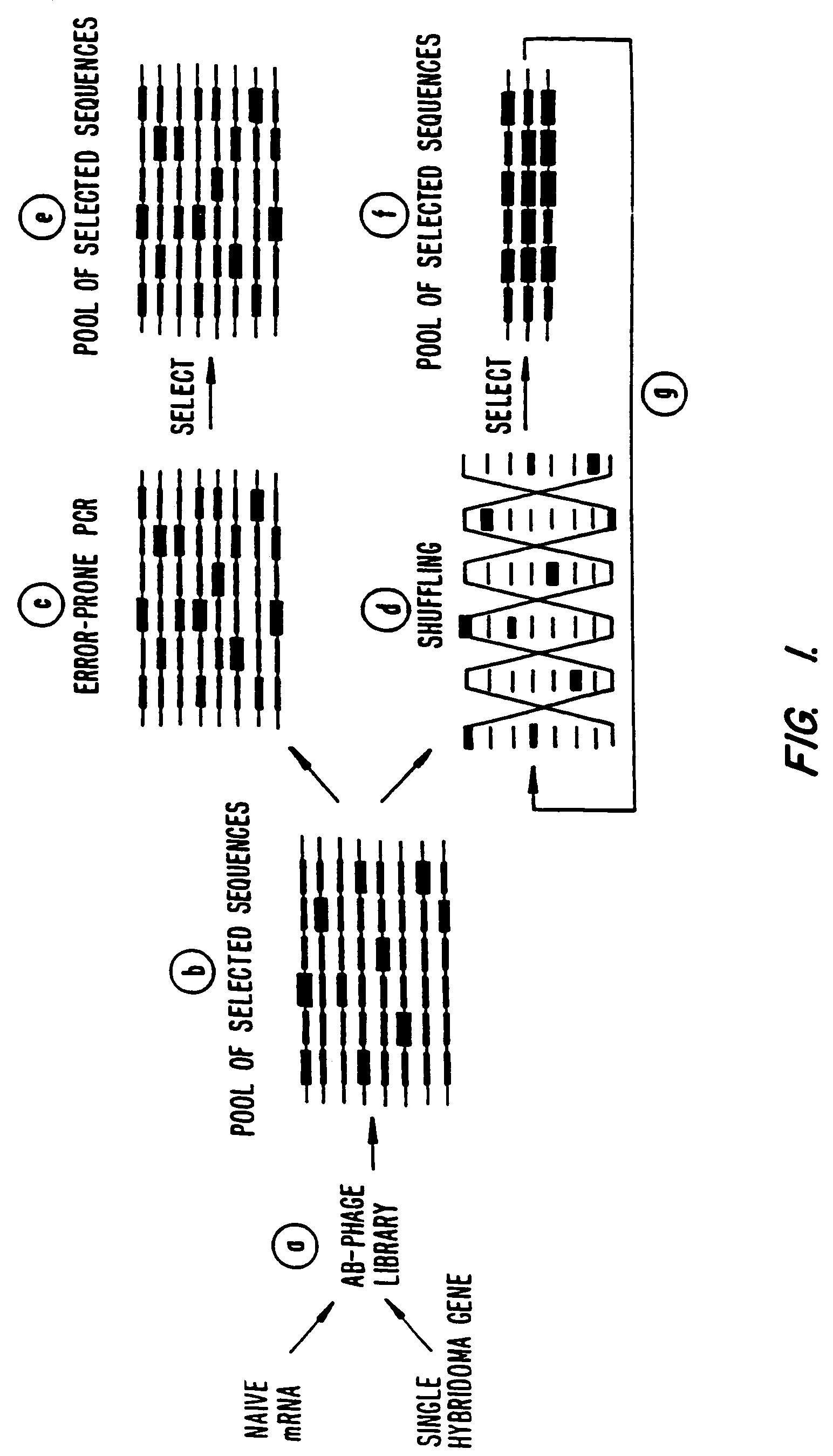
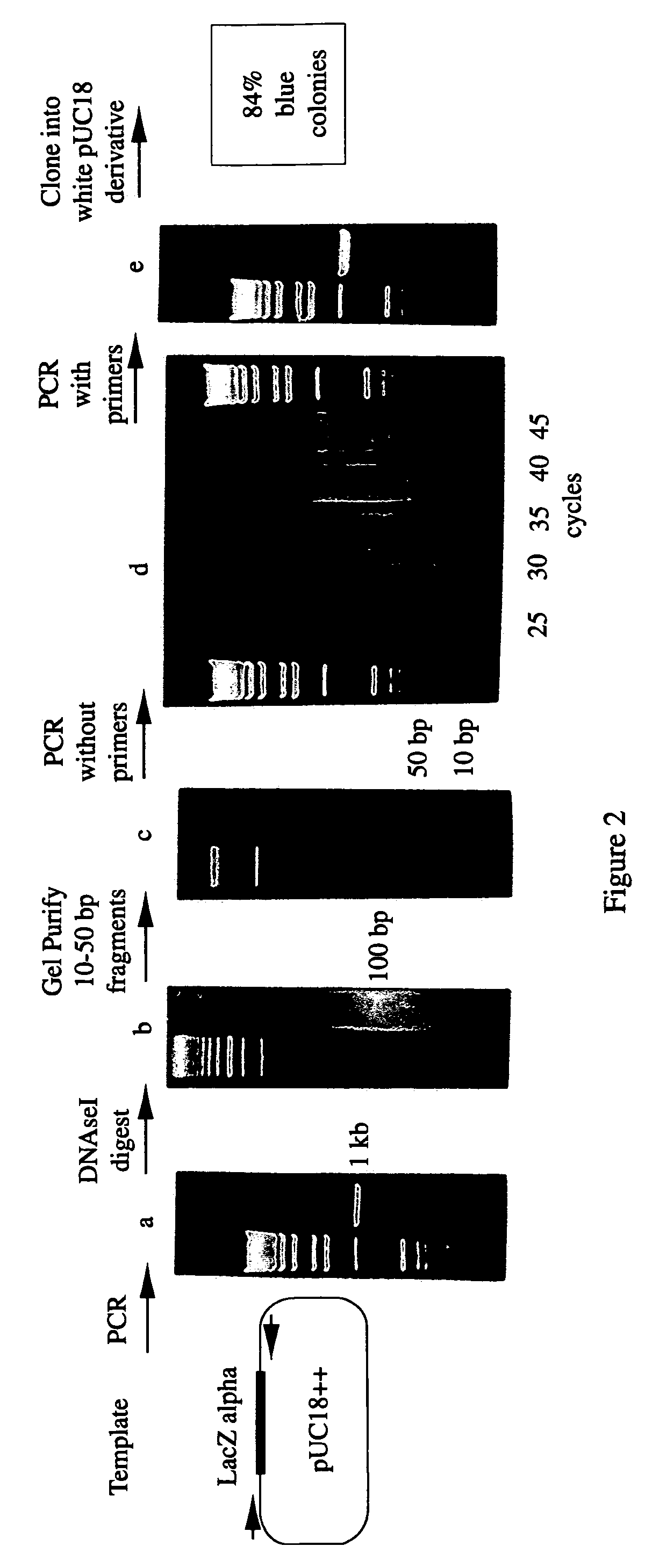
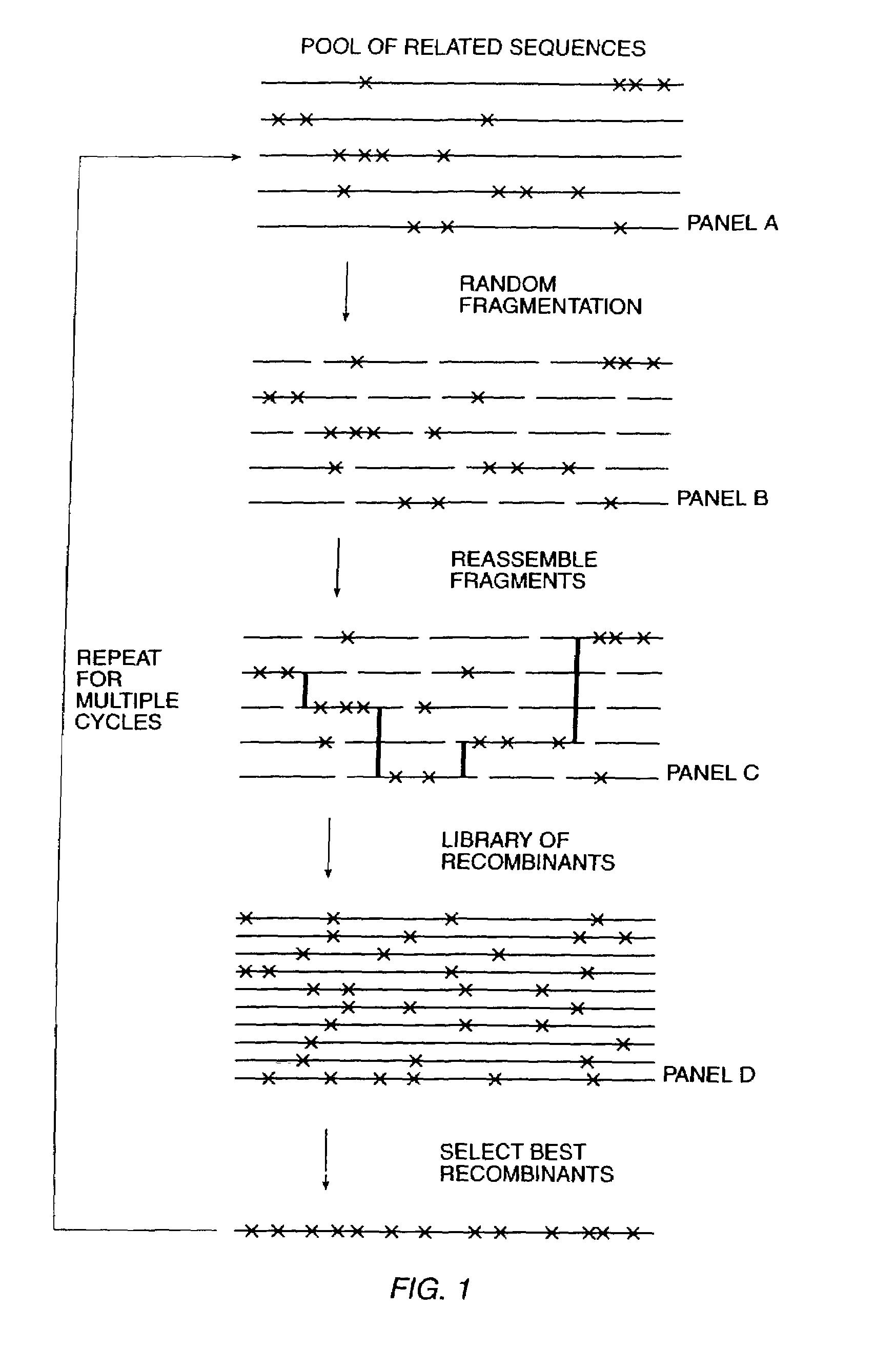
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
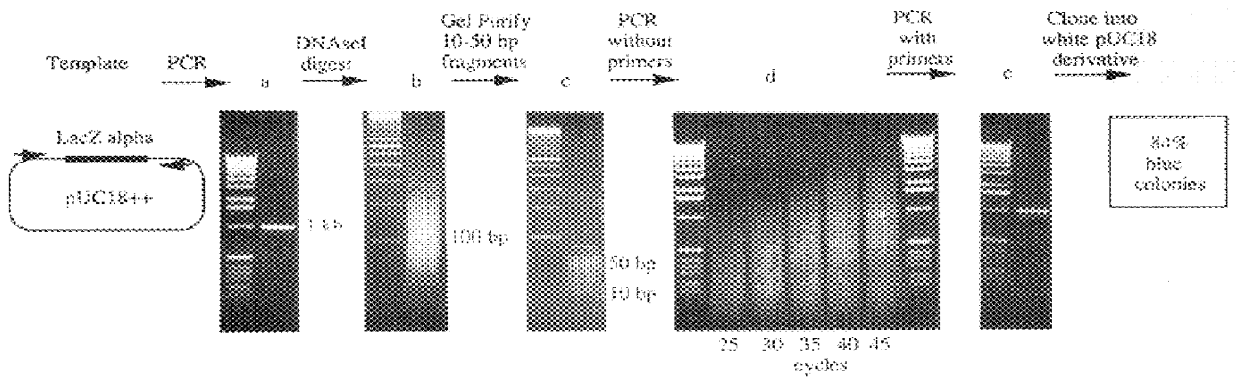
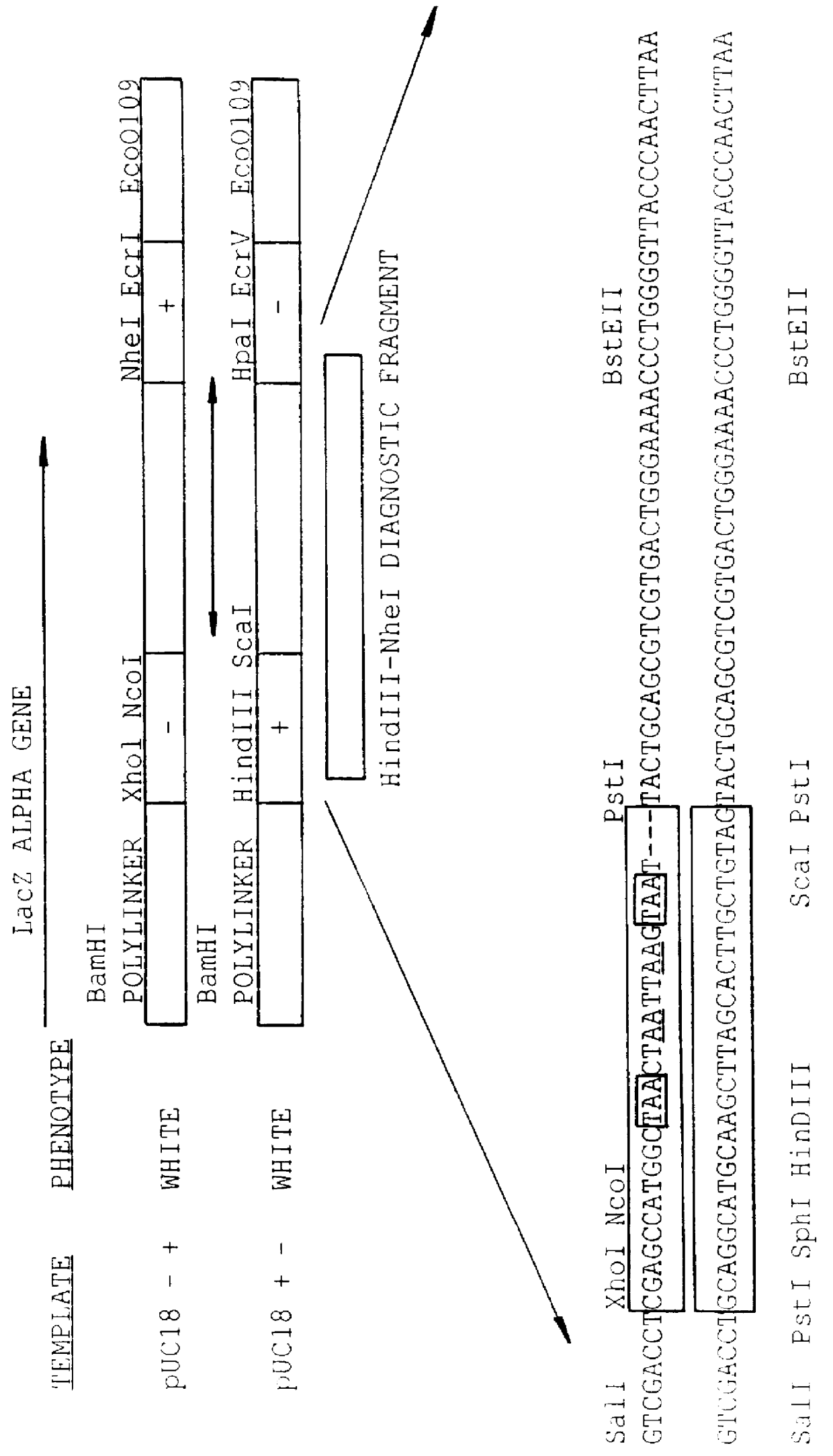
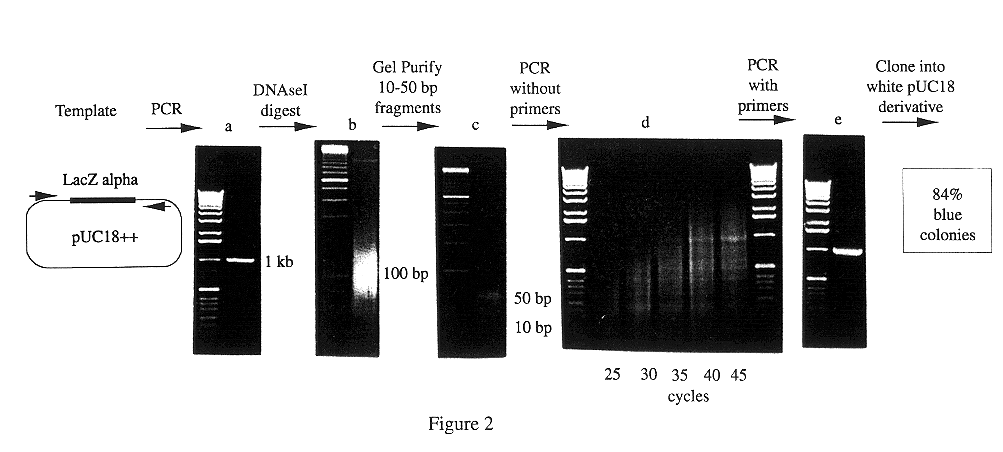
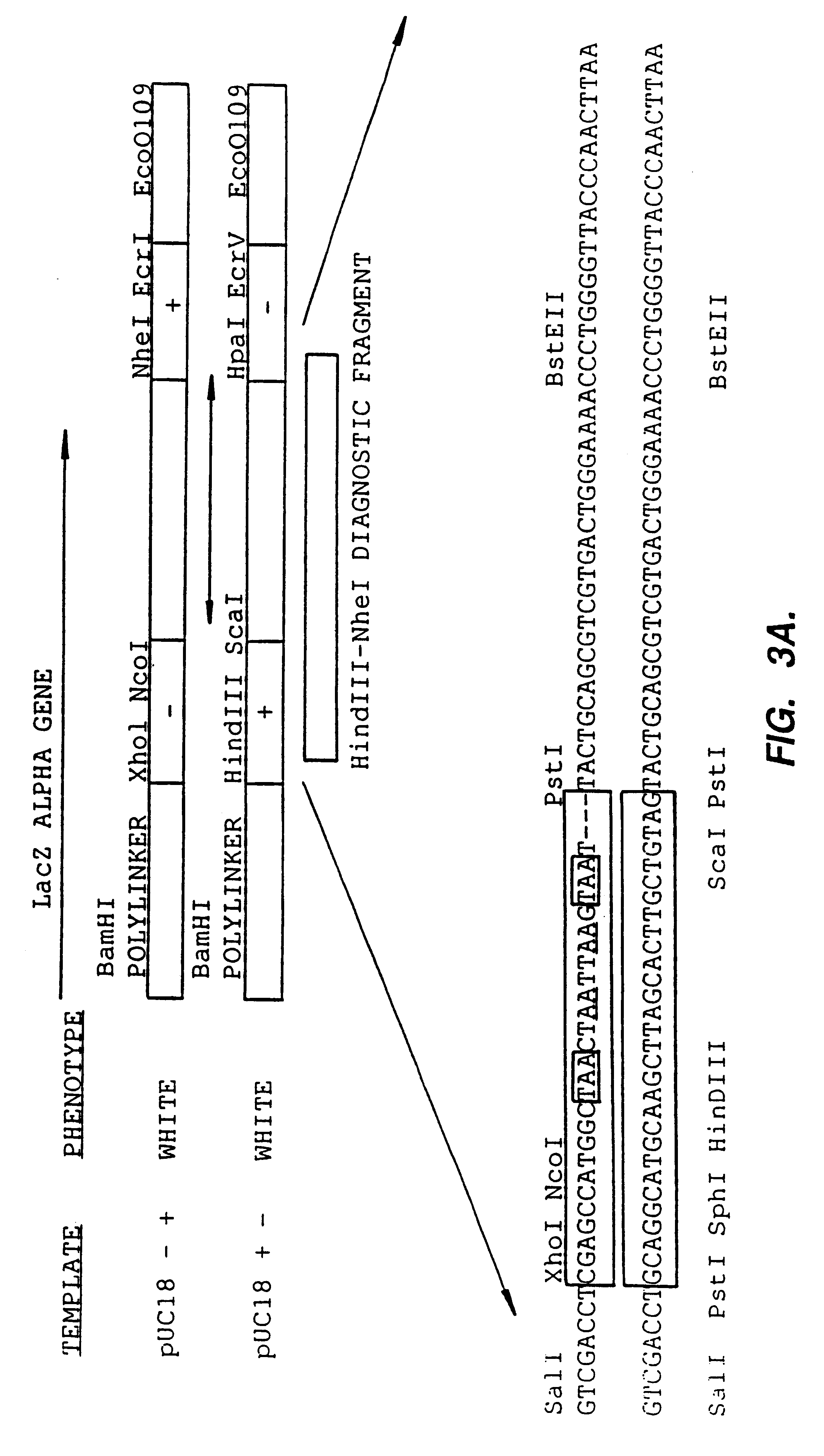
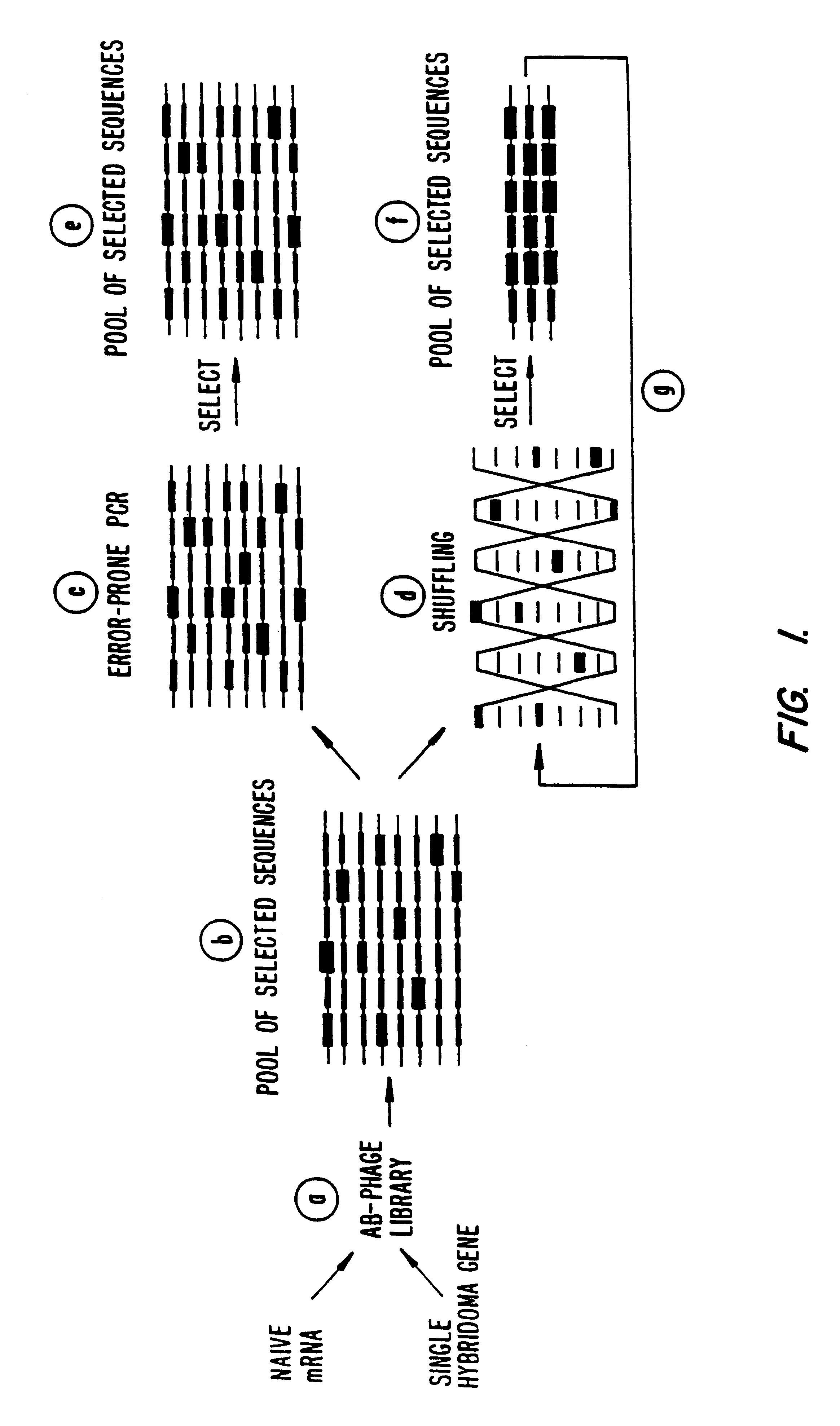
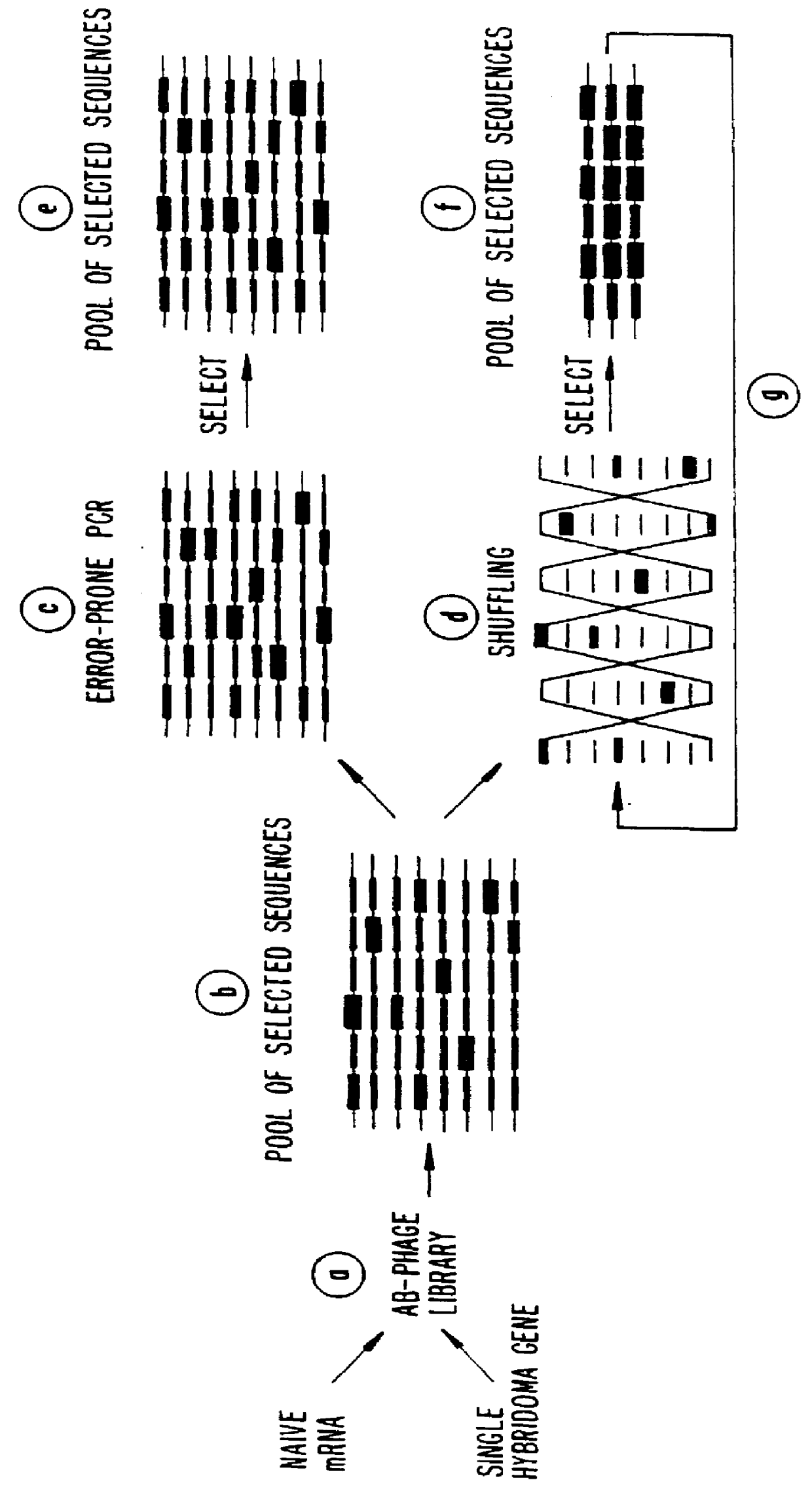
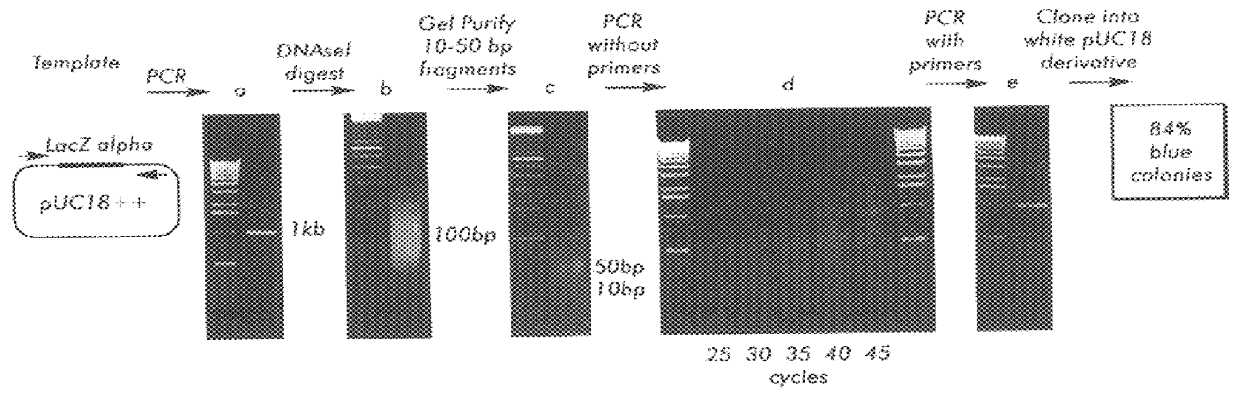
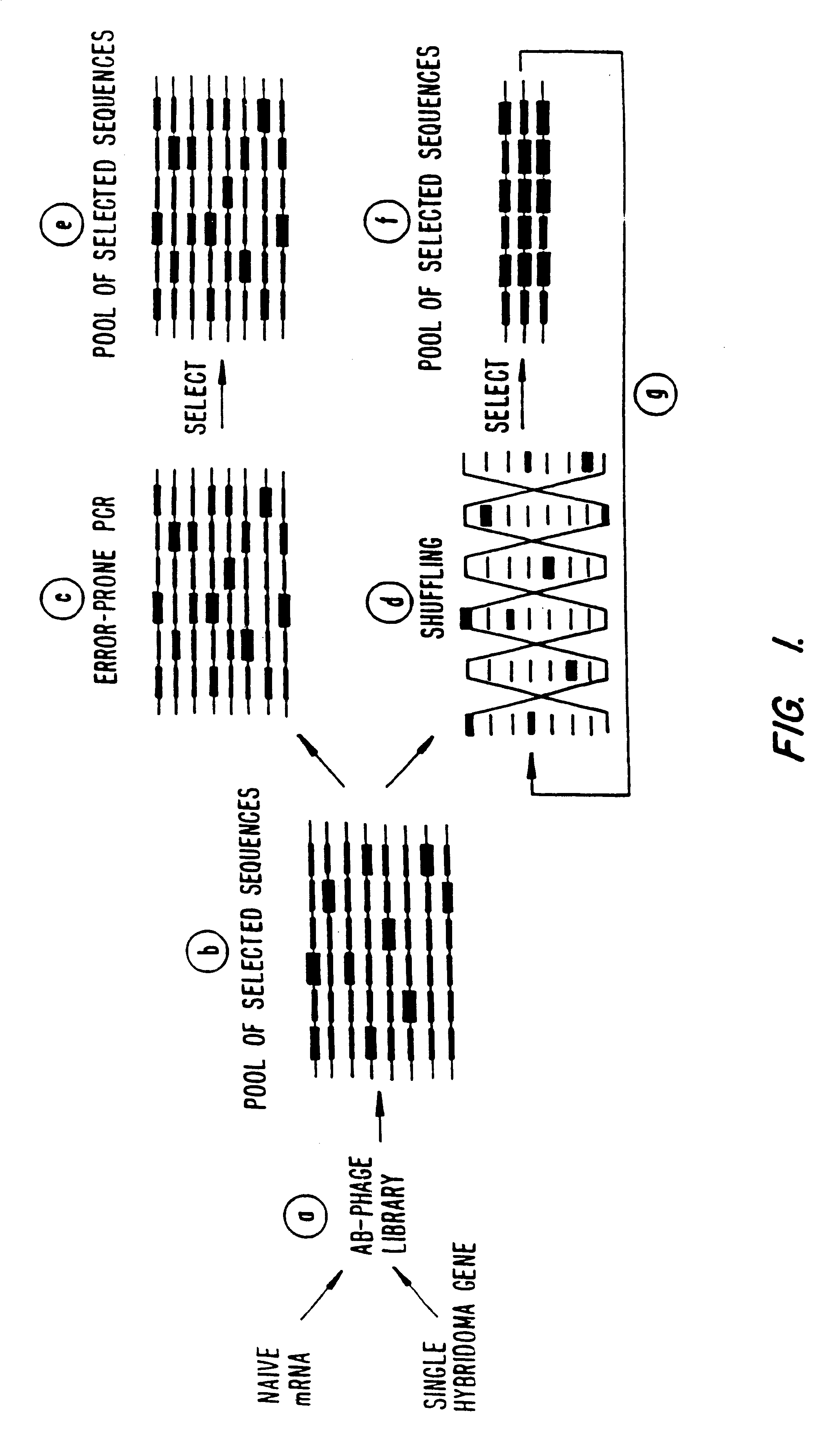
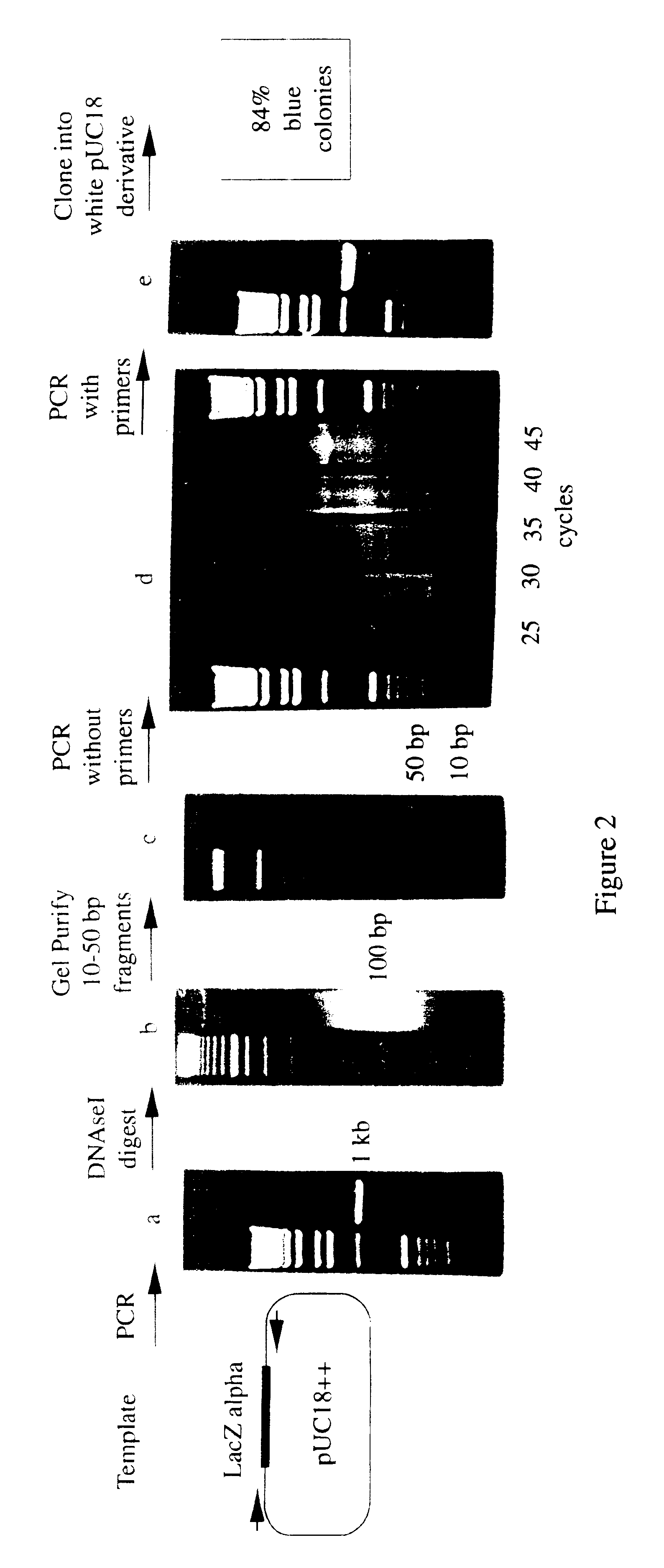
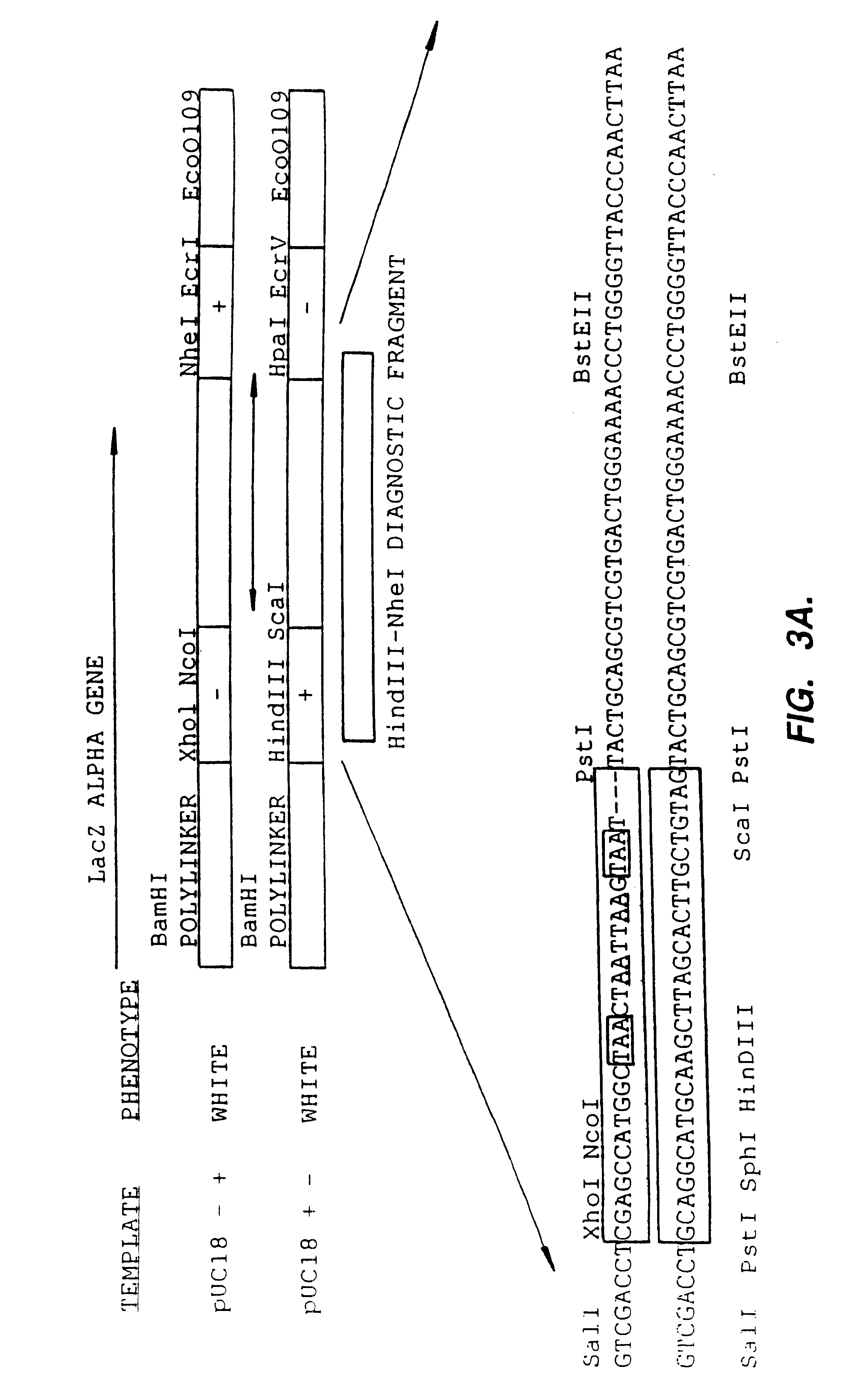
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Novel proteins with targeted binding
InactiveUS20050089932A1Stimulate and inhibit activityEasy screeningPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMonomerComputational biology
Methods for identifying discrete monomer domains and immuno-domains with a desired property are provided. Methods for generating multimers from two or more selected discrete monomer domains are also provided, along with methods for identifying multimers possessing a desired property. Presentation systems are also provided which present the discrete monomer and / or immuno-domains, selected monomer and / or immuno-domains, multimers and / or selected multimers to allow their selection. Compositions, libraries and cells that express one or more library member, along with kits and integrated systems, are also included in the present invention.
Owner:AMGEN MOUNTAIN VIEW
Protein scaffolds for antibody mimics and other binding proteins
InactiveUS7115396B2Easy to foldImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWAS PROTEINAntibody
Disclosed herein are proteins that include an immunoglobulin fold and that can be used as scaffolds. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
c-Met kinase binding proteins
InactiveUS20060008844A1Stimulate and inhibit activityCompound screeningPeptide librariesKinase bindingC-Met
Owner:AMGEN MOUNTAIN VIEW
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS6846634B1Overcome inherent biasGuaranteed effective sizePeptide librariesLibrary screeningBinding siteBacteriophage
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
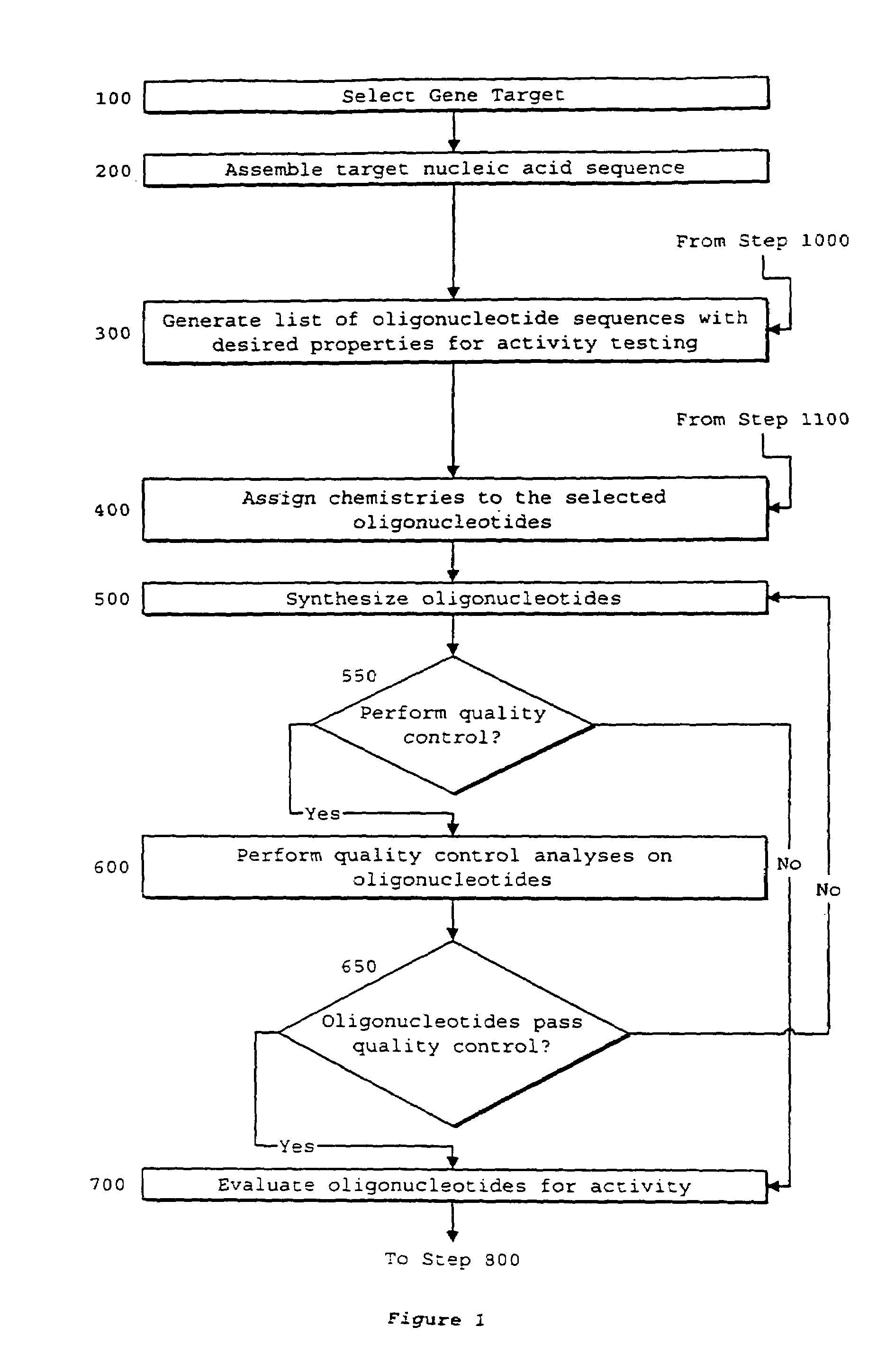
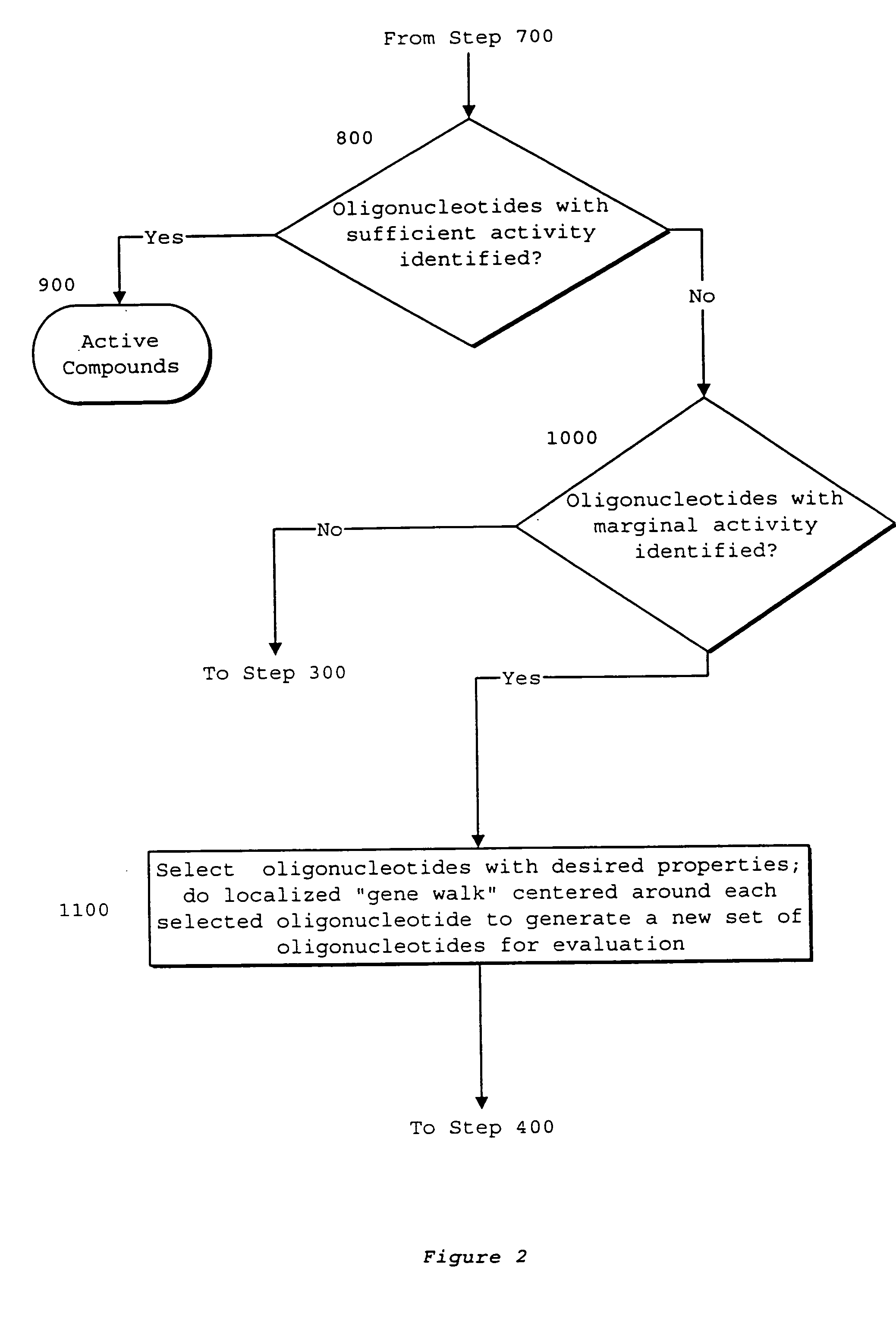
System of components for preparing oligonucleotides
Interative, preferably computer based iterative processes for generating synthetic compounds with desired physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties, i.e., active compounds, are provided. During iterations of the processes, a target nucleic acid sequence is provided or selected, and a library of candidate nucleobase sequences is generated in silico according to defined criteria. A “virtual” oligonucleotide chemistry is chosen and a library of virtual oligonucleotide compounds having the selected nucleobase sequences is generated. These virtual compounds are reviewed and compounds predicted to have particular properties are selected. The selected compounds are robotically synthesized and are preferably robotically assayed for a desired physical, chemical or biological activity. Active compounds are thus generated and, at the same time, preferred sequences and regions of the target nucleic acid that are amenable to oligonucleotide or sequence-based modulation are identified.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Recombinant binding proteins and peptides
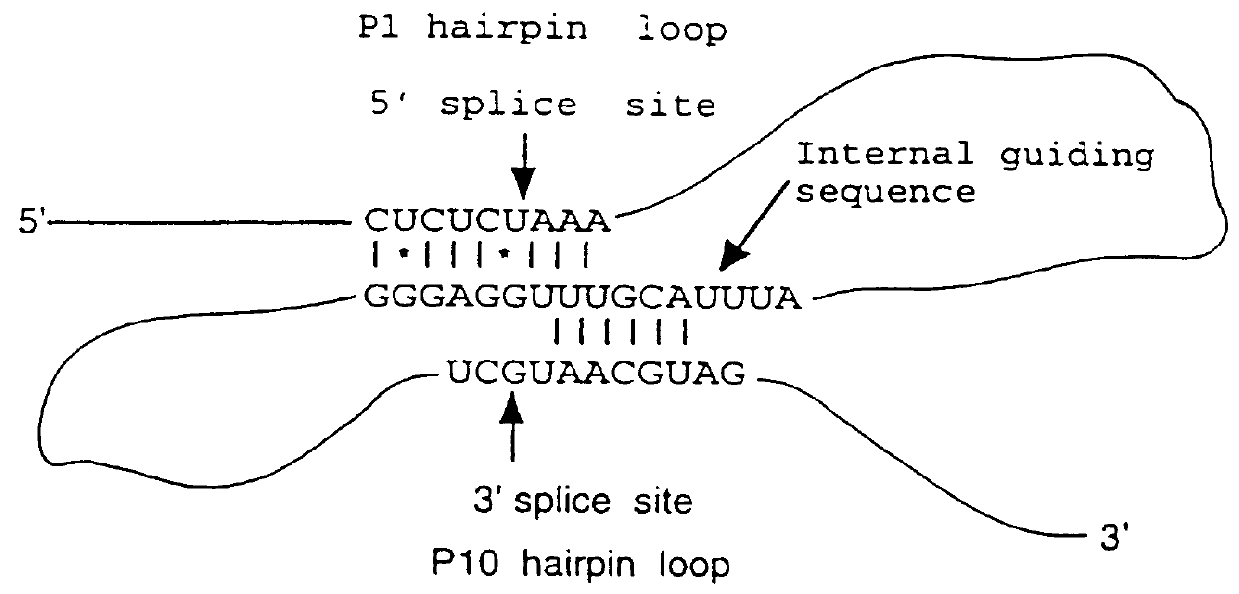
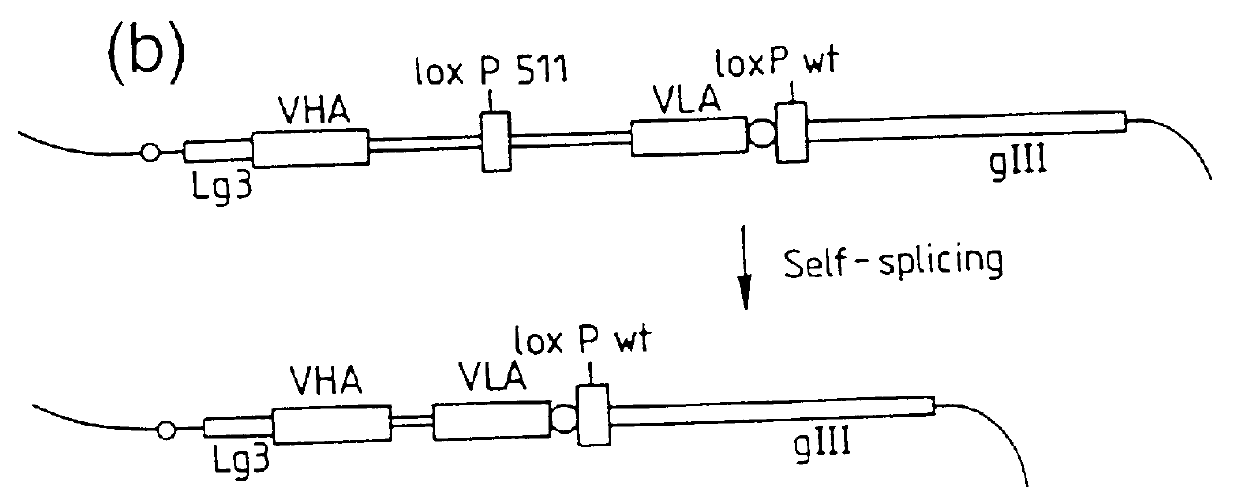
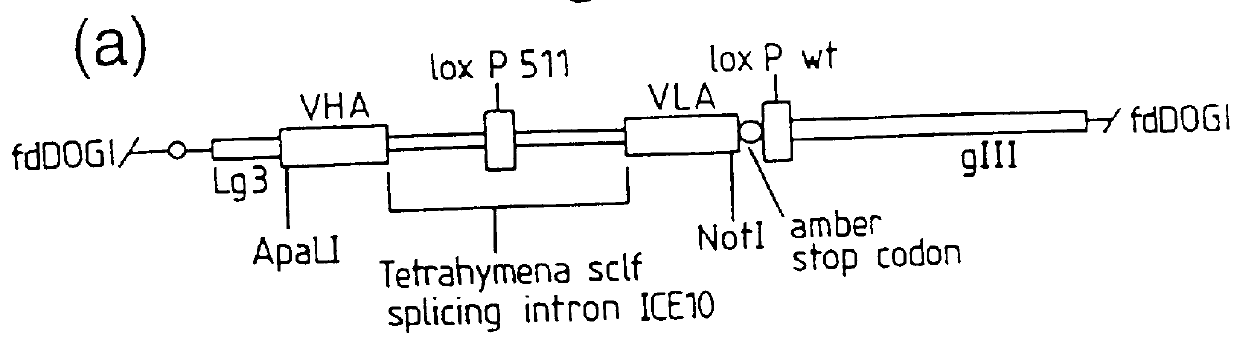
DNA constructs comprise a first exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a first peptide or polypeptide, a second exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a second peptide or polypeptide and a third sequence of nucleotides between the first and second sequences encoding a heterologous intron, for example that of Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear pre-rRNA, between RNA splice sites and a site-specific recombination sequence, such as loxP, within the intron, the exons together encoding a product peptide or polypeptide. Such constructs are of use in methods of production of peptides or polypeptides, transcription leading to splicing out of the intron enabling translation of a single chain product peptide or polypeptide. Isolated nucleic acid constructs consisting essentially of a sequence of nucleotides encoding a self-splicing intron with a site-specific recombination sequence within the intron, for use in creation of constructs for expression of peptides or polypeptides, are also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
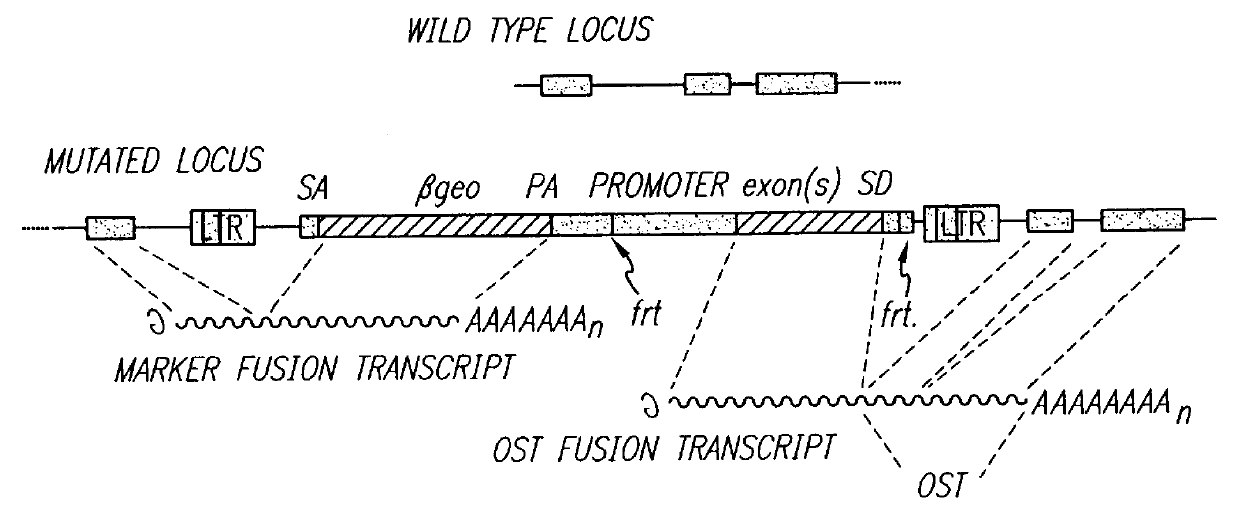
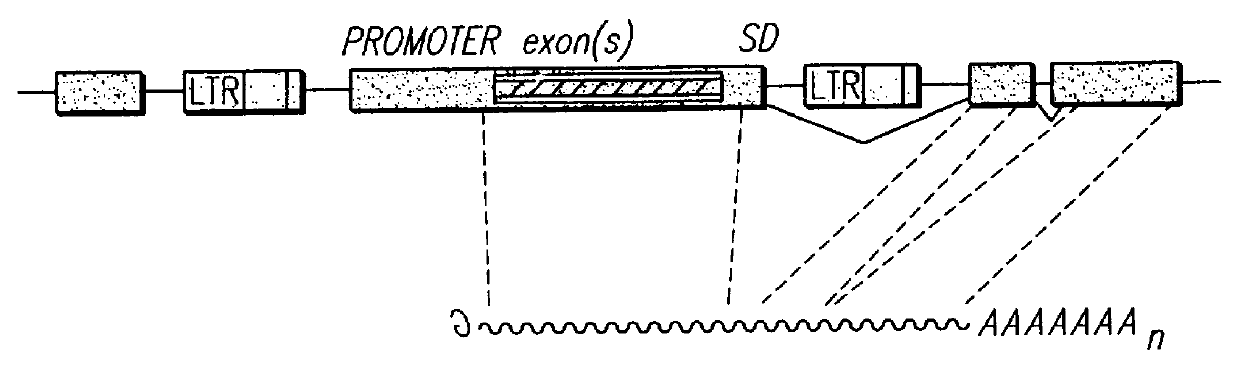
Vectors for gene trapping and gene activation
InactiveUS6080576AImprove efficiencySufficient efficiencyNucleic acid vectorMicroorganism librariesAntibiotic resistanceBiological activation
A novel 3' gene trap cassette is described that does not encode a marker conferring antibiotic resistance and can be used to efficiently trap and identify cellular genes. Vectors incorporating the presently 3' gene trap cassette find particular application in gene discovery, the production of transgenic cells and animals, and gene activation.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
Identication of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and virues
InactiveUS6881825B1Reduce deliveryFacilitating uptakeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionIn vivoCell type
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of the peptides, and methods of use for the peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Protein scaffolds for antibody mimics and other binding proteins
InactiveUS20050255548A1Easy to foldImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsWAS PROTEINAntibody
Disclosed herein are proteins that include a fibronectin type III domain having at least one randomized loop. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Selection by compartmentalised screening
ActiveUS20060153924A1Rapid and high-throughput screeningLow costMicroorganism librariesGranular deliveryDrug developmentBiochemistry
The invention describes a method for the identification of compounds which bind to a target component of a biochemical system or modulate the activity of the target, by compartmentalizing the compounds into microcapsules together with the target, such that only a subset of the repertoire is represented in multiple copies in any one microcapsules; and identifying the compound which binds to or modulates the activity of the target. The invention enables the screening of large repertoires of molecules which can serve as leads for drug development.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
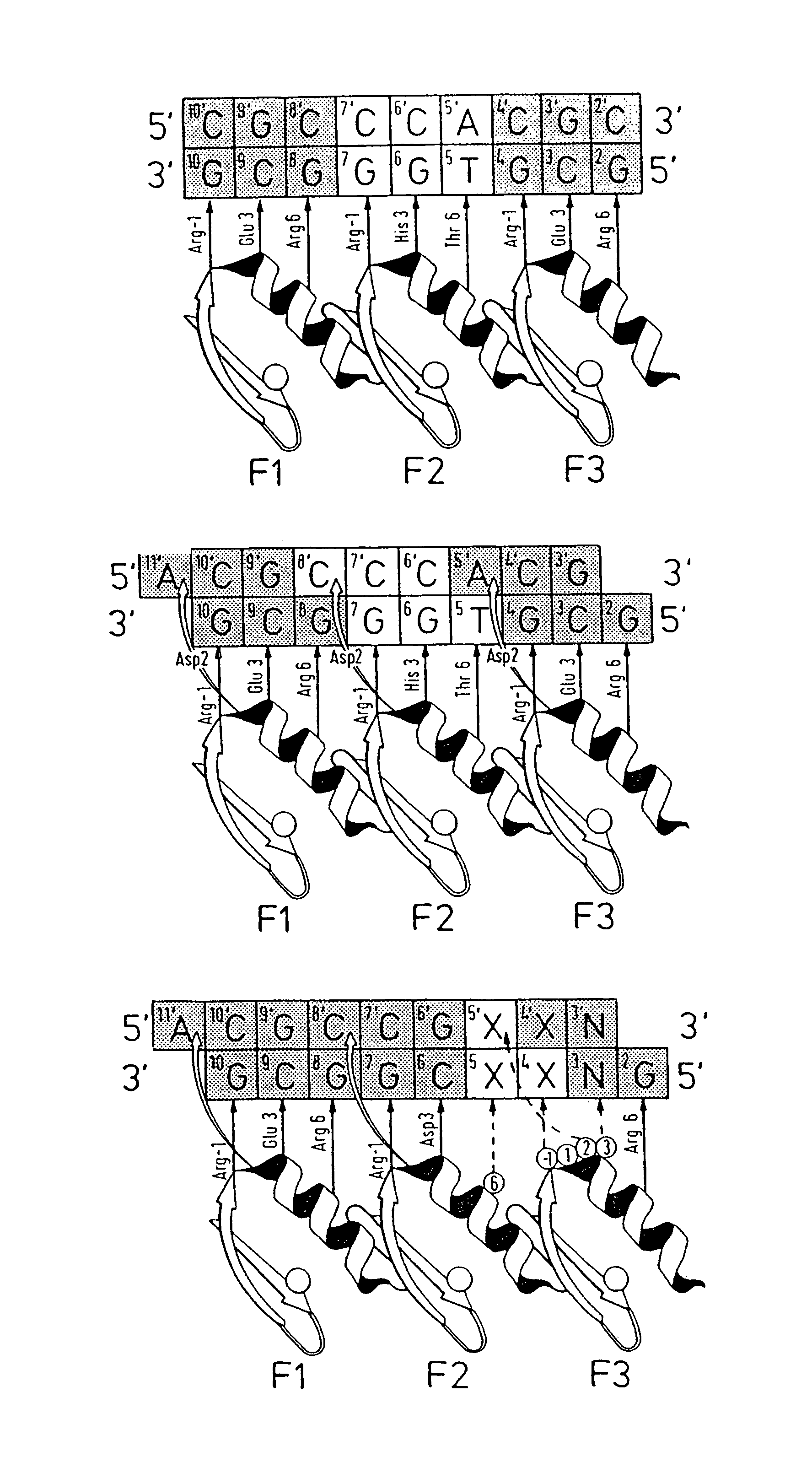
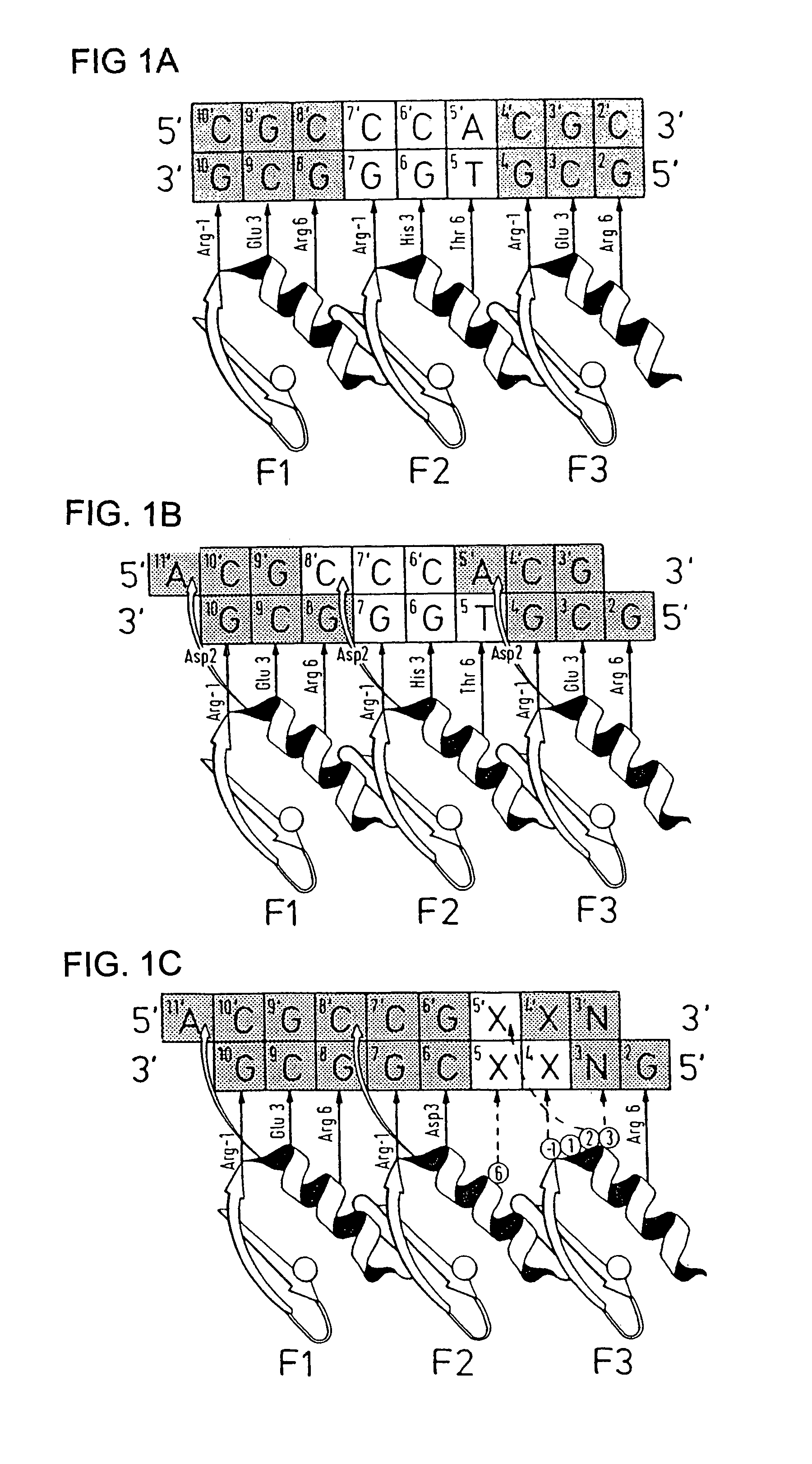
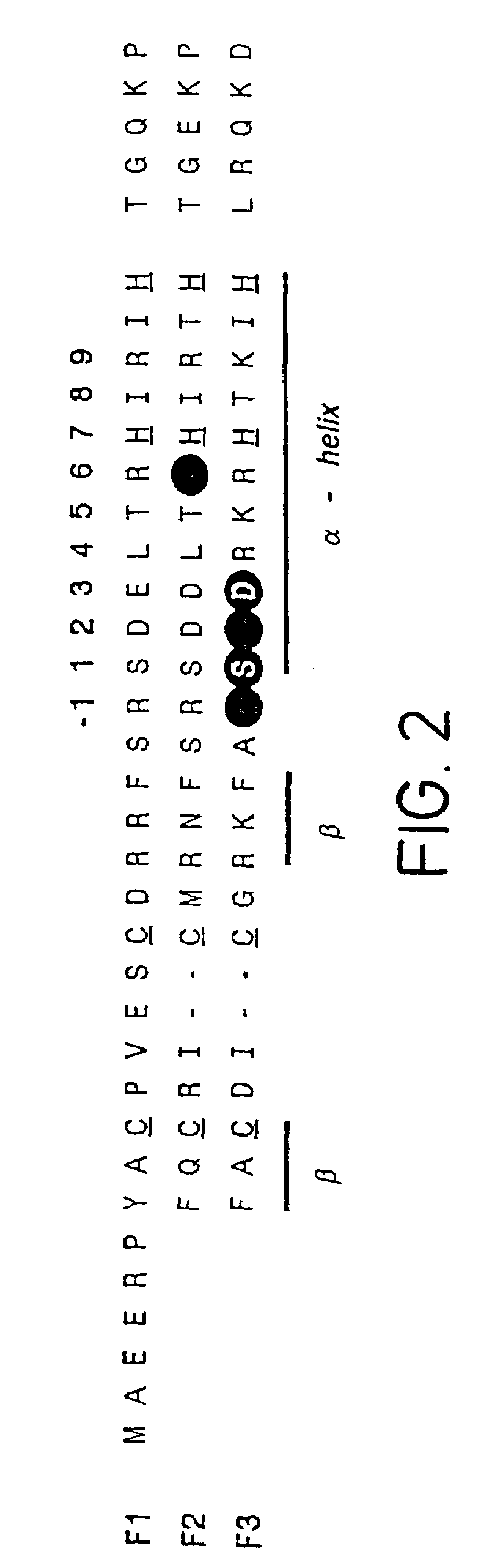
Nucleic acid binding proteins
Disclosed herein are methods for designing DNA binding proteins comprising a plurality of zinc fingers and methods for binding the proteins to target nucleotide sequences in cells.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Concatenated nucleic acid sequence
InactiveUS20040009507A1High frequencyDesigning can be facilitatedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingDNA
An in vitro method for constructing a concatenated head-to-tail repertoire of target nucleic acid sequences is revealed. In particular, the method relates to cycles of concatenation whereby after a single cycle of concatenation, not more than two identical copies of each target nucleic acid sequence are linked together head-to-tail on the same molecule of DNA. The present method ensures that each molecule of a concatenated repertoire is derived from a single template target sequence of the starting repertoire.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS20040038291A2Immunoglobulin superfamilyLibrary screeningPolyphageImmunoglobulin superfamily
Abstract of the Disclosure The present invention relates to methods for selecting repertoires of polypeptides using generic and target ligands. In particular, the invention relates to a library comprising a repertoire of polypeptides of the immunoglobulin superfamily, wherein the members of the repertoire have a known main chain conformation.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS7288375B2Less immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods and compositions for cellular and metabolic engineering
InactiveUS7105297B2Improve abilitiesExcellent catalytic performanceImmunoglobulinsFermentationIndividual geneOrganism
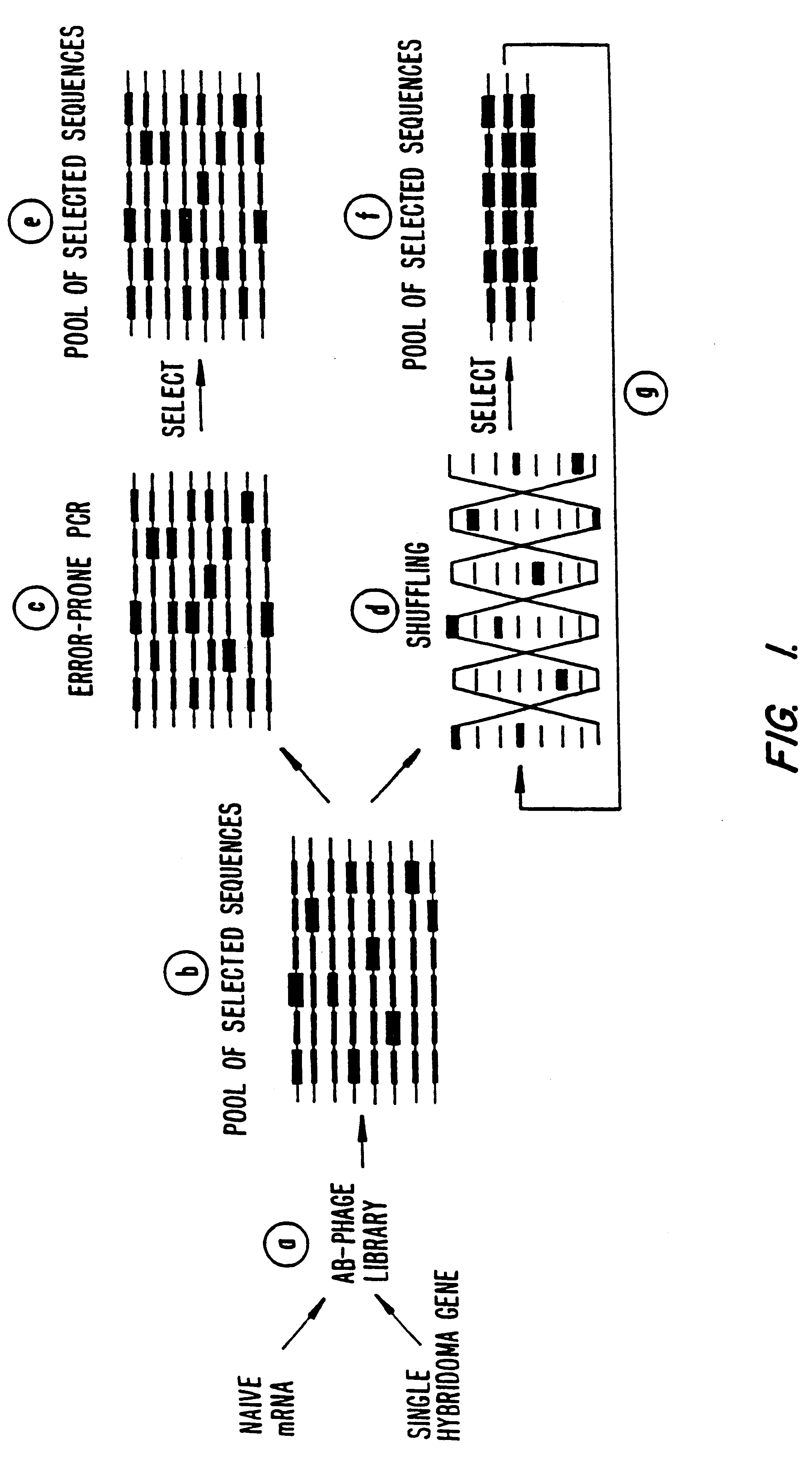
The present invention is generally directed to the evolution of new metabolic pathways and the enhancement of bioprocessing through a process herein termed recursive sequence recombination. Recursive sequence recombination entails performing iterative cycles of recombination and screening or selection to “evolve” individual genes, whole plasmids or viruses, multigene clusters, or even whole genomes. Such techniques do not require the extensive analysis and computation required by conventional methods for metabolic engineering.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods of generating novel peptides
The present invention describes peptides capable of specifically binding to preselected micromolecules or to their natural receptor. The preselected molecules include but are not limited to drugs, vitamins, neuromediators and steroid hormones. Methods of using the phage display libraries to identify peptide compositions in preselected binding interactions are also disclosed. The retrieved peptides mimicking a natural receptor binding site to preselected molecules are used as is or as ligands to re-screen the same or different libraries to find and / or derive new receptor ligands, or are used to elicit the production of antibodies capable of binding to the natural receptor. The two categories of effector molecules (peptides or antibodies) may find diagnostic, therapeutic or prophylactic uses. The peptides directly derived from the phage display libraries may be used as drug detectors or antidotes. The others may be used to identify, target, activate or neutralize the receptor for the preselected micromolecules, the receptor being known or unknown.
Owner:BIOPHAGE
Protein/(poly)peptide libraries
InactiveUS6828422B1Reduce in quantityRemoving unwanted cleavages sitesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman DNA sequencingSynthetic DNA
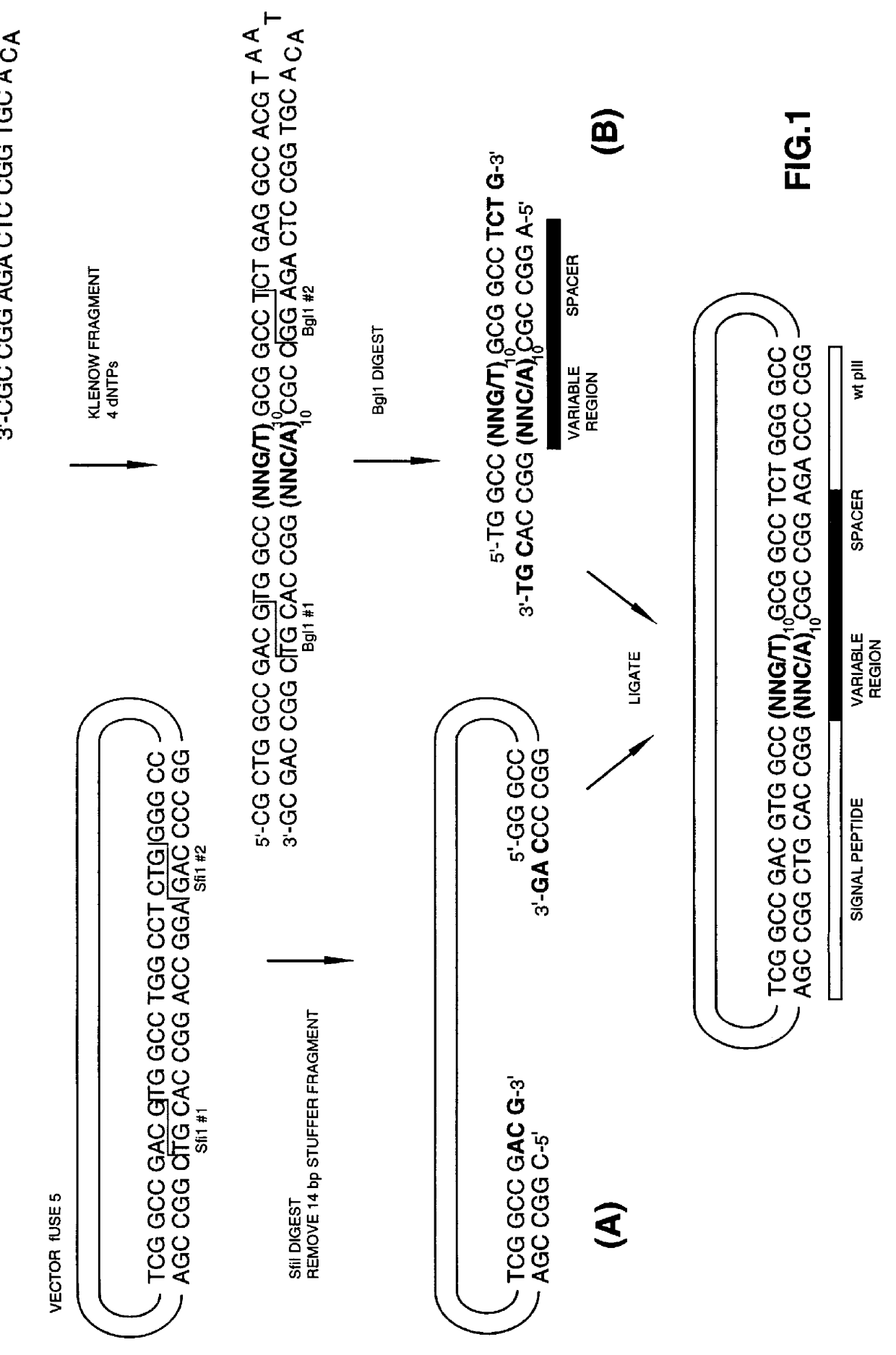
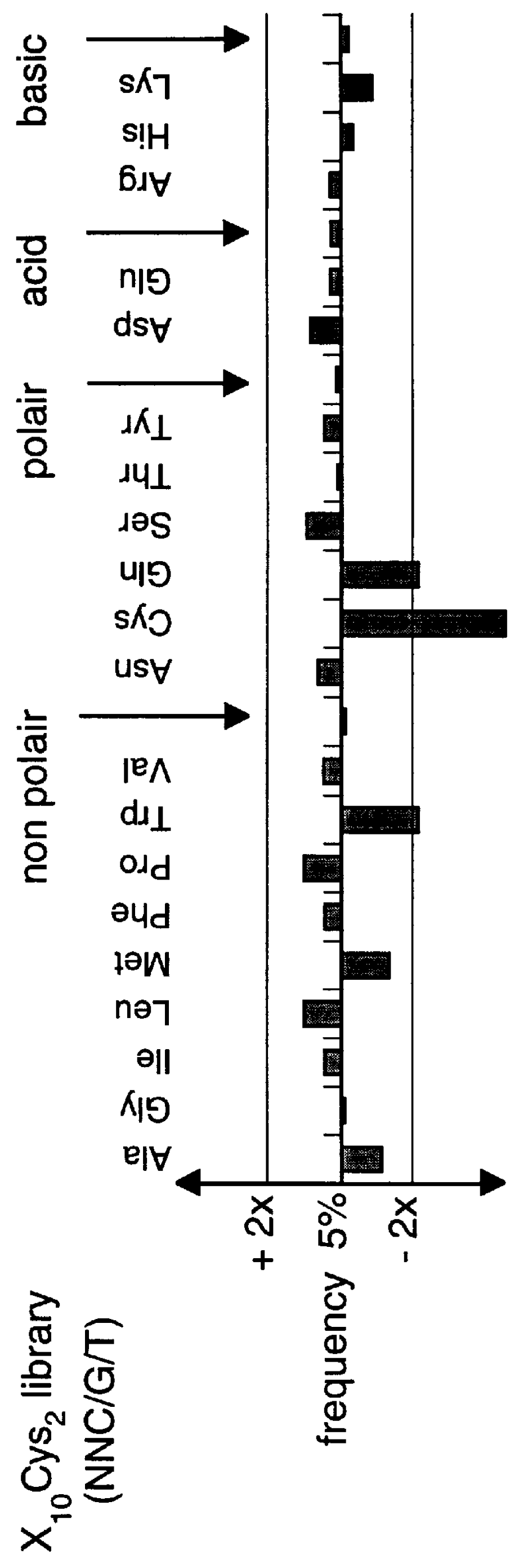
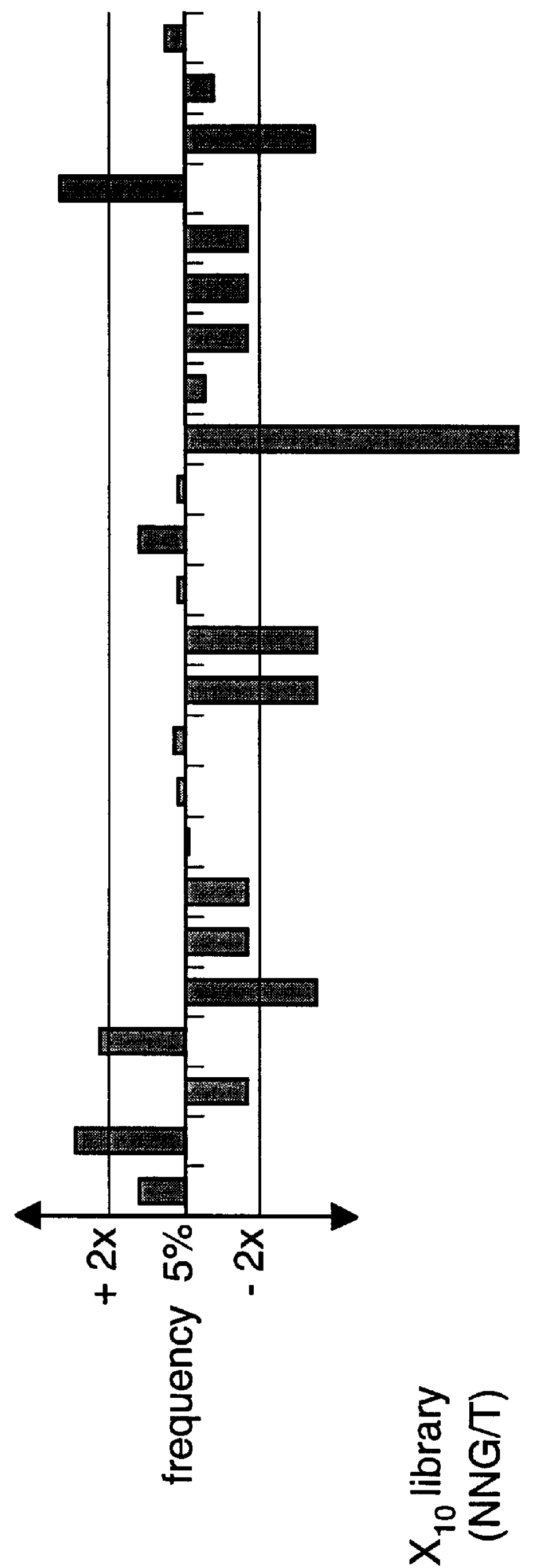
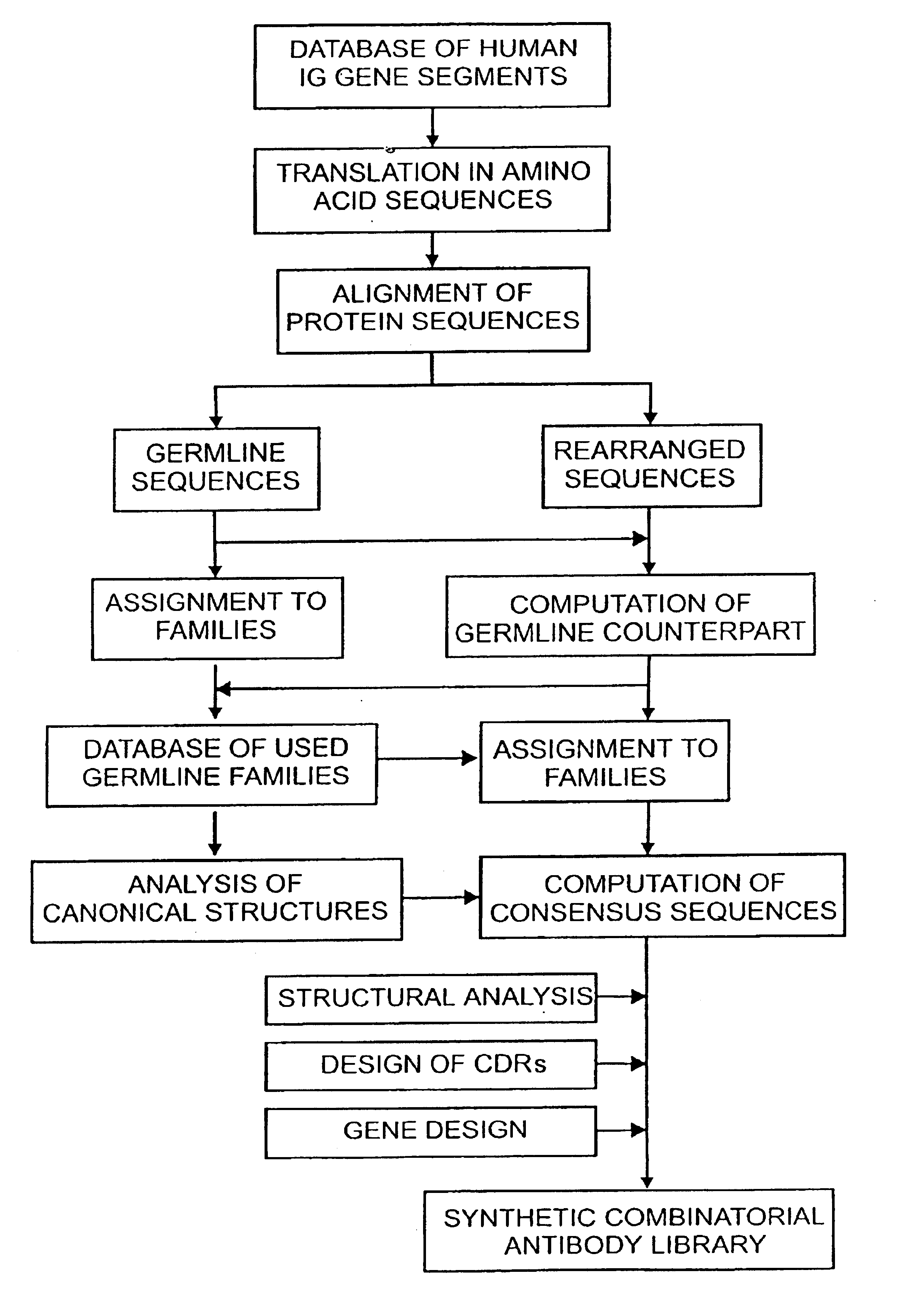
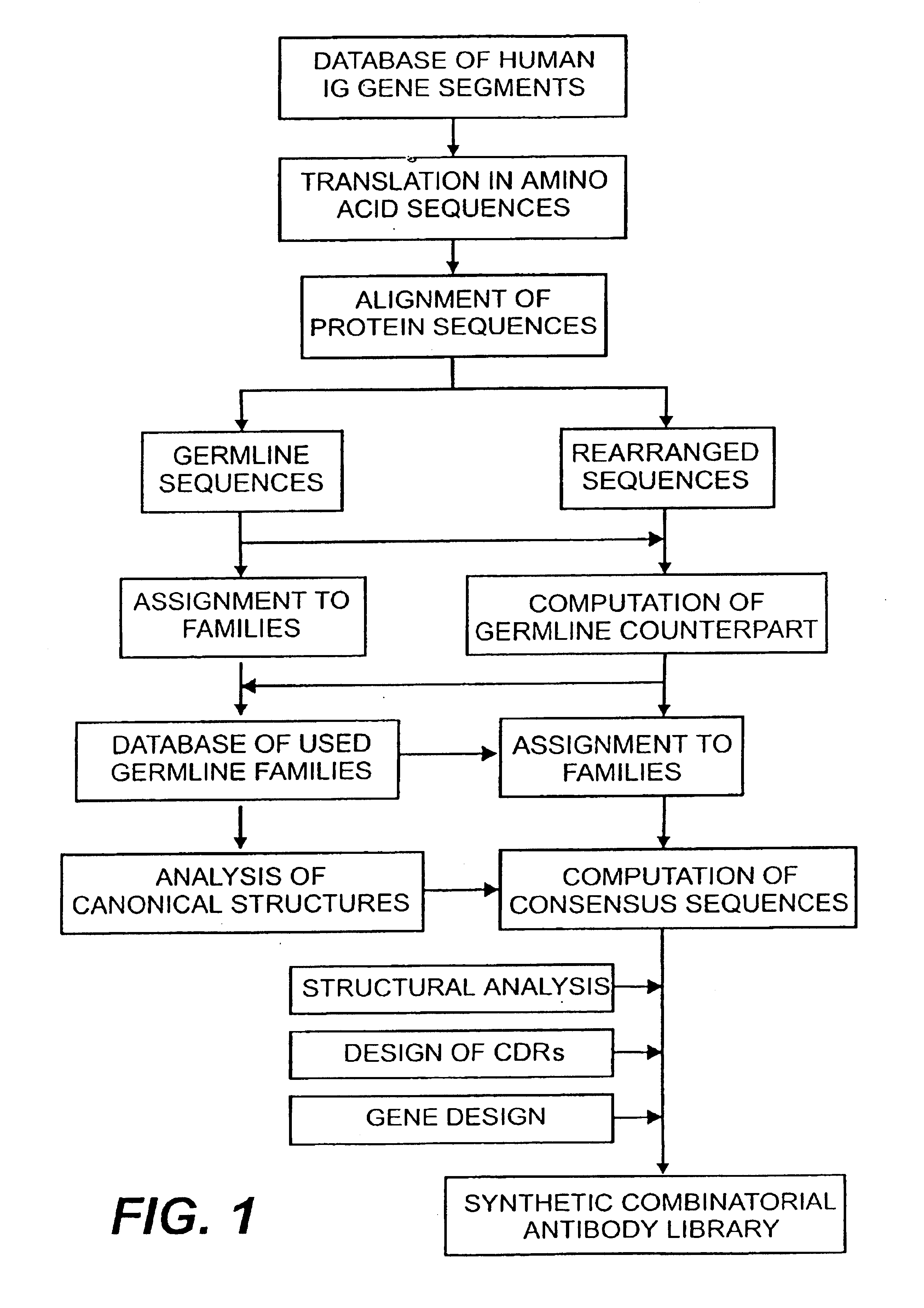
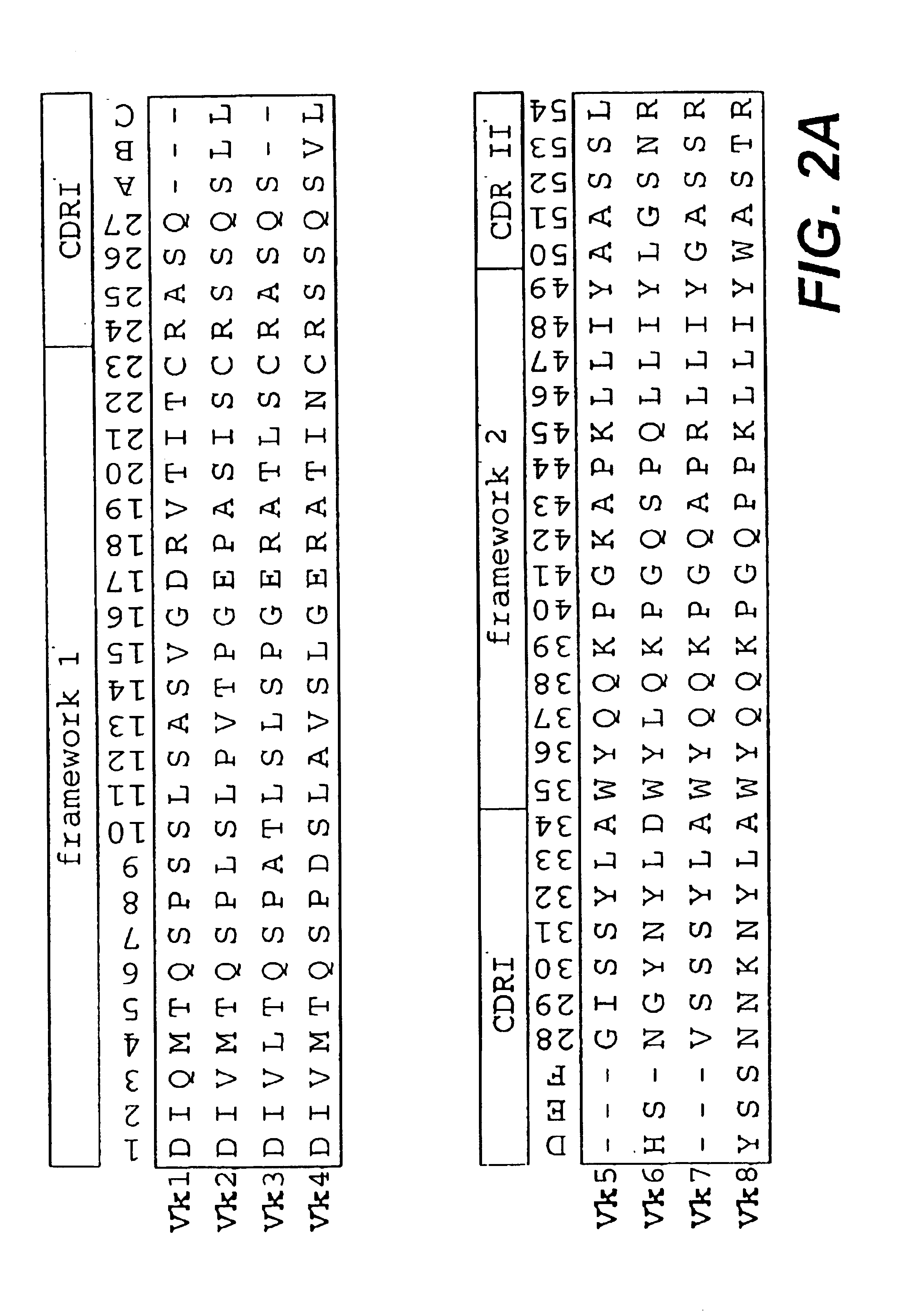
The present invention relates to synthetic DNA sequences which encode one or more collections of homologous proteins / (poly)peptides, and methods for generating and applying libraries of these DNA sequences. In particular, the invention relates to the preparation of a library of human-derived antibody genes by the use of synthetic consensus sequences which cover the structural repertoire of antibodies encoded in the human genome. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of a single consensus antibody gene as a universal framework for highly diverse antibody libraries.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
Mammalian viral vectors and their uses
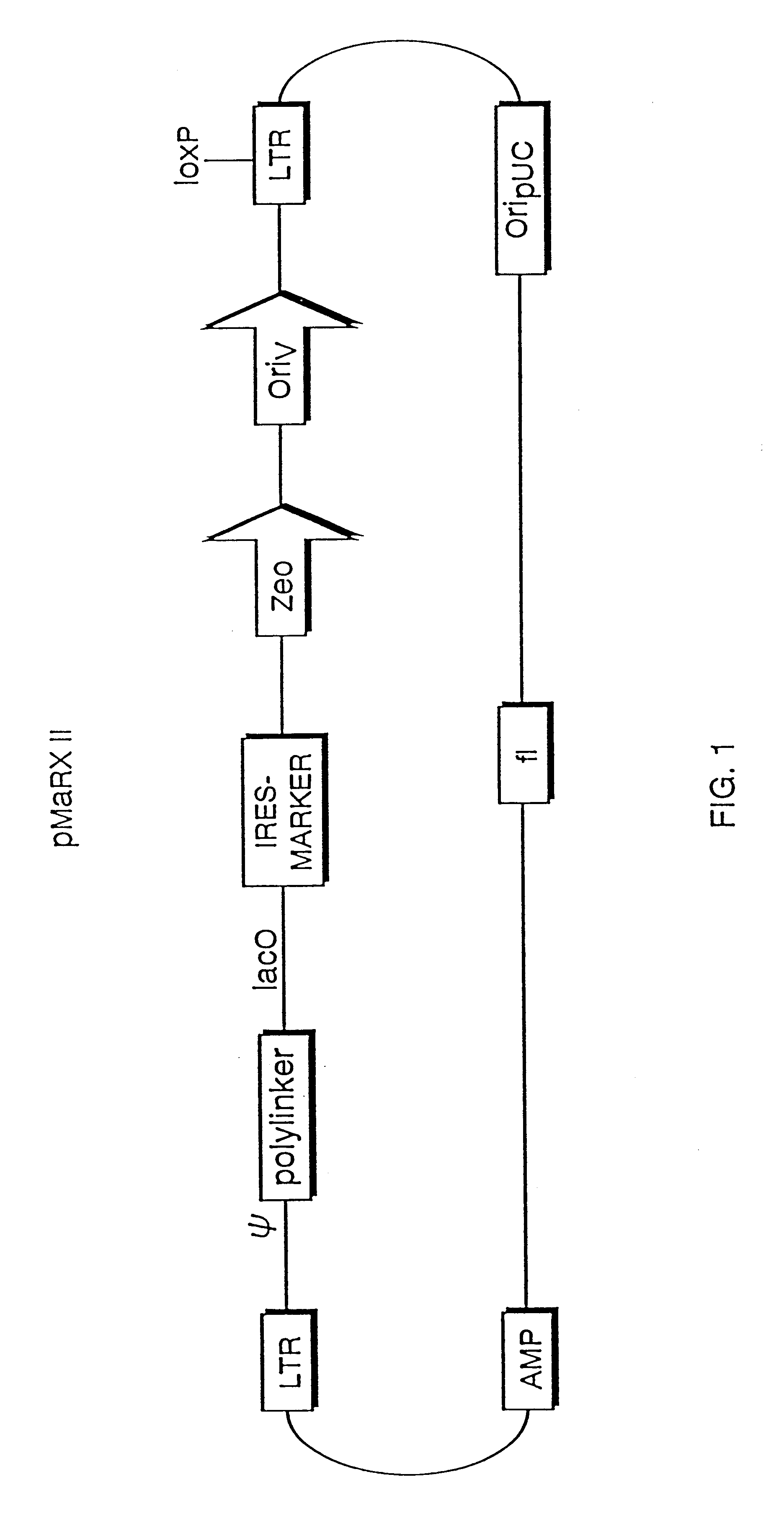
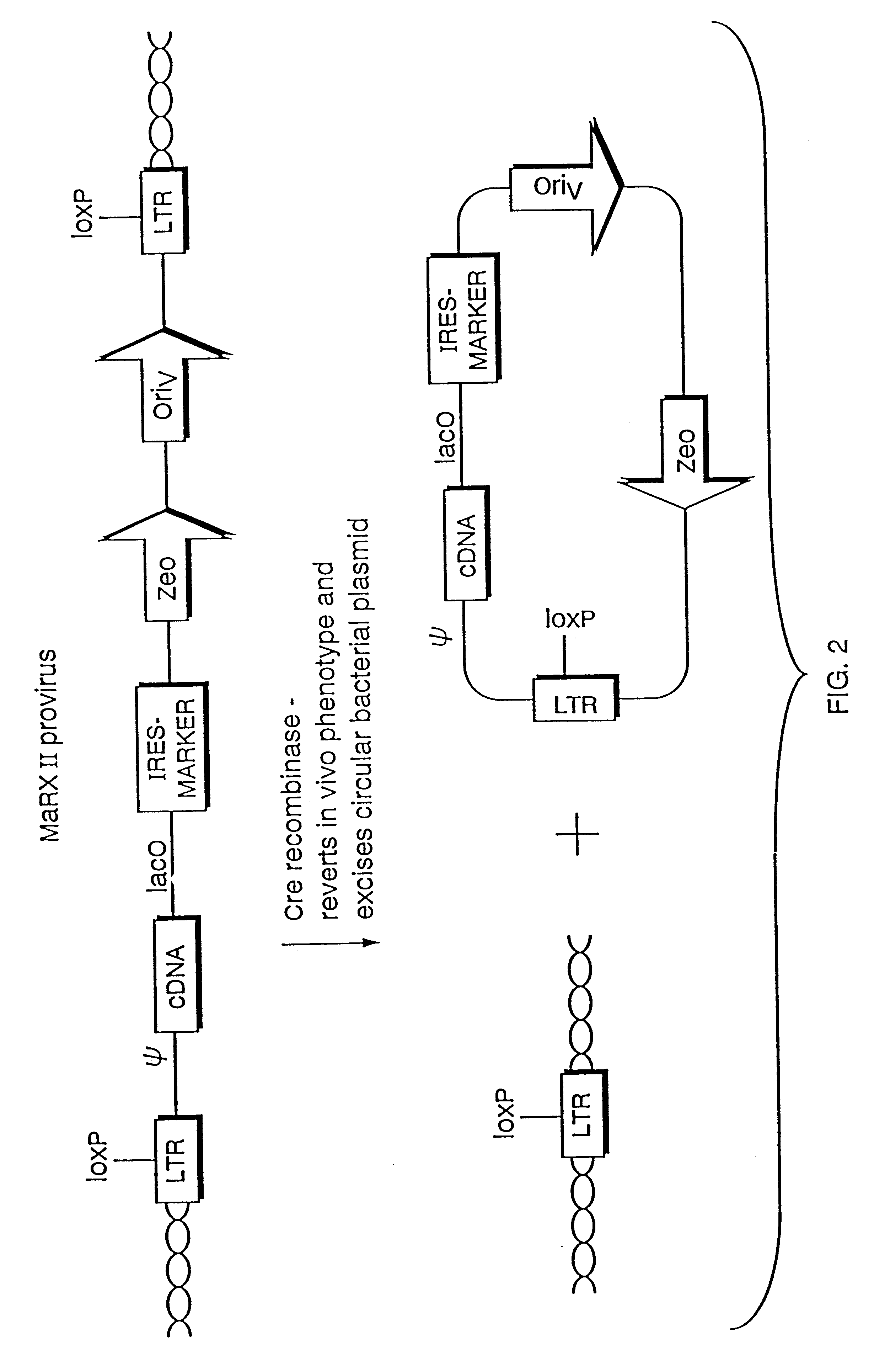
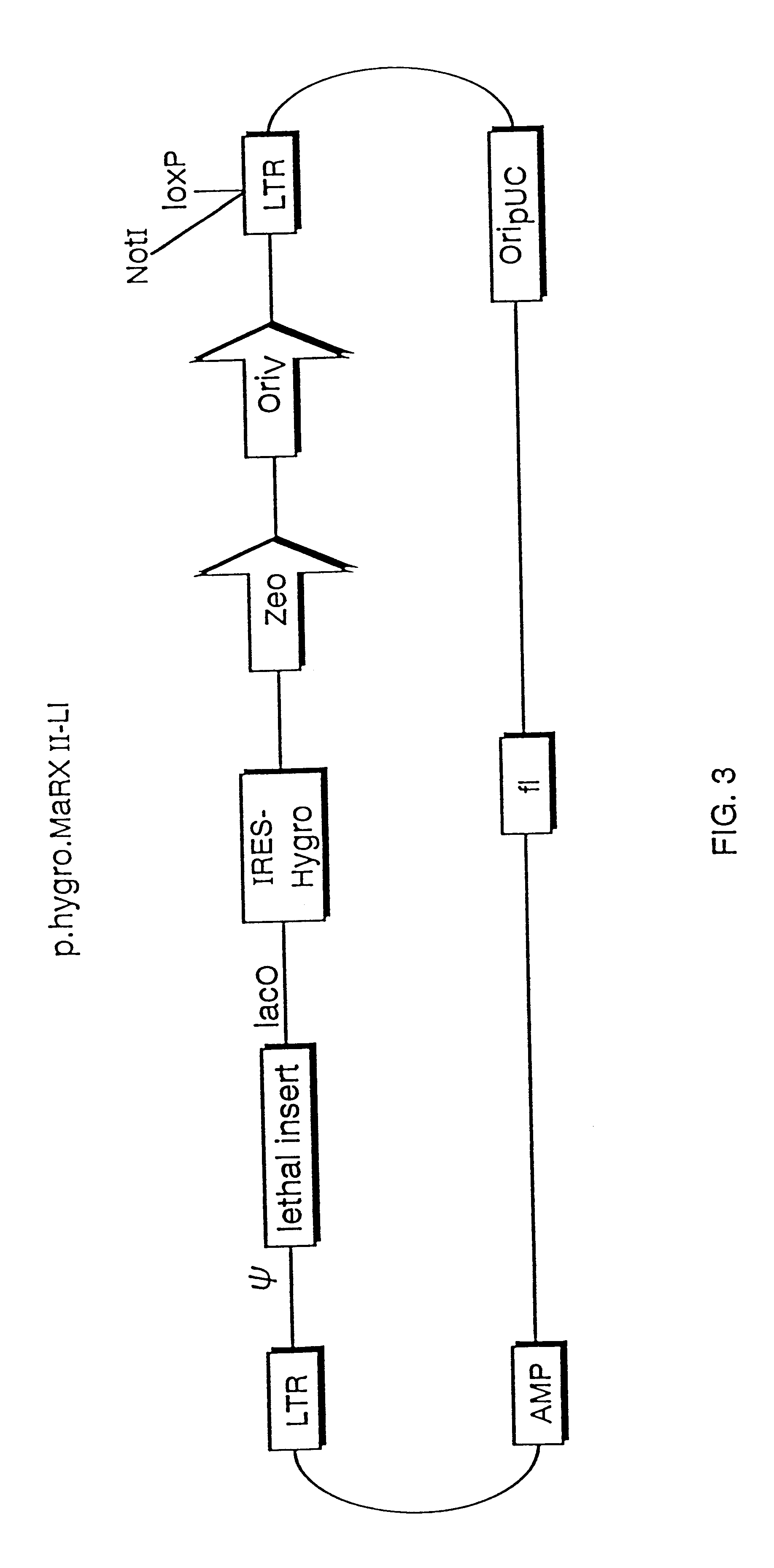
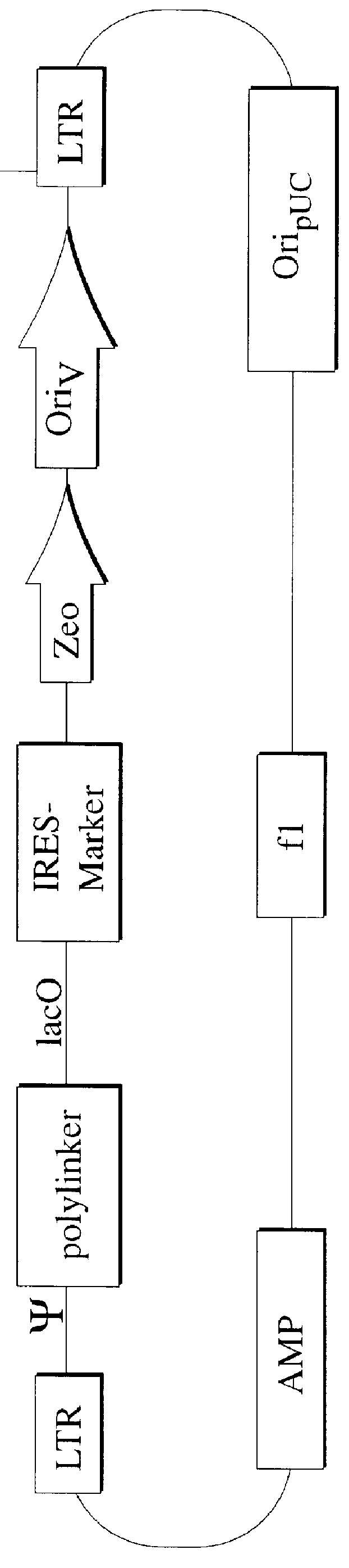
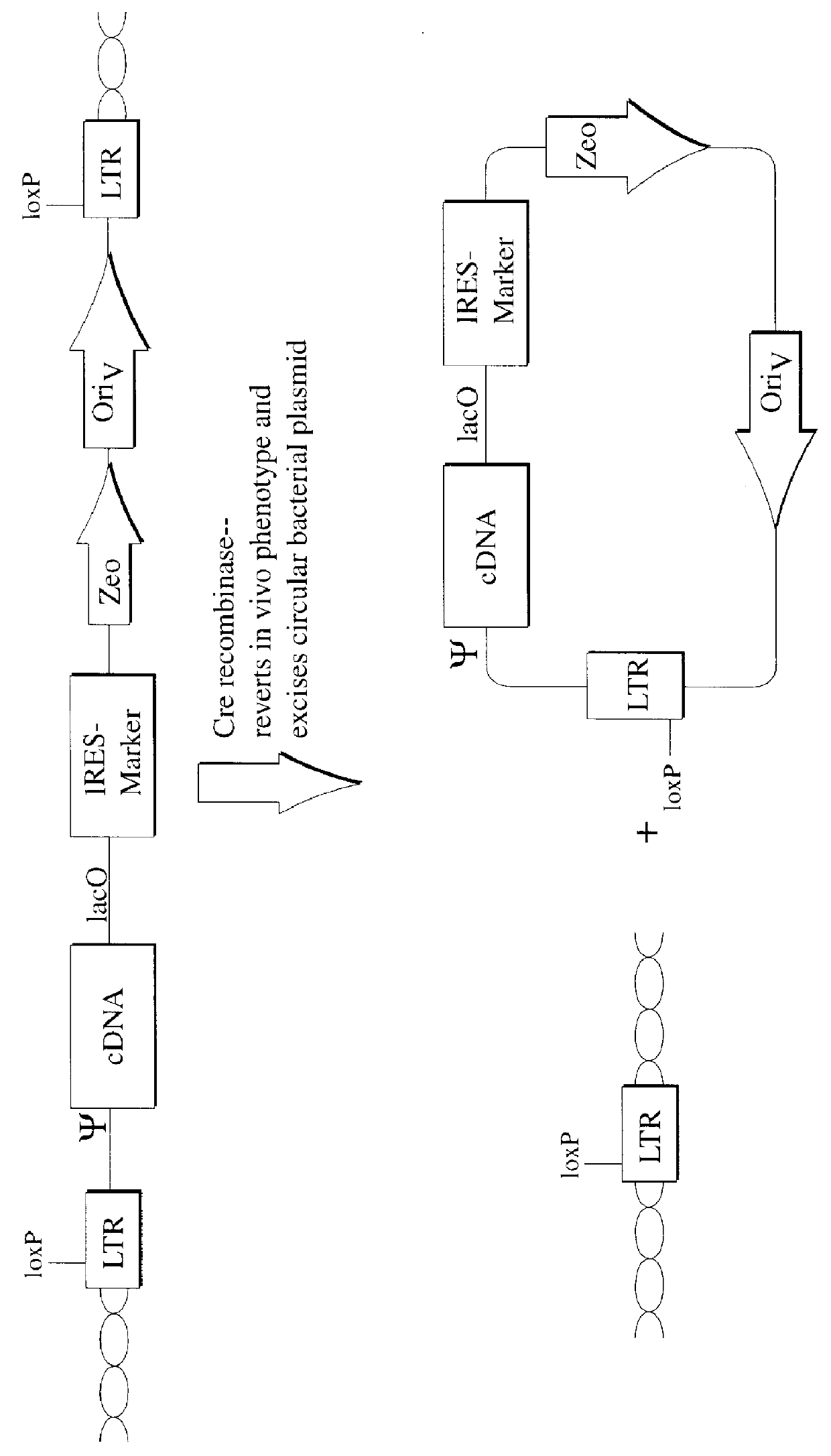
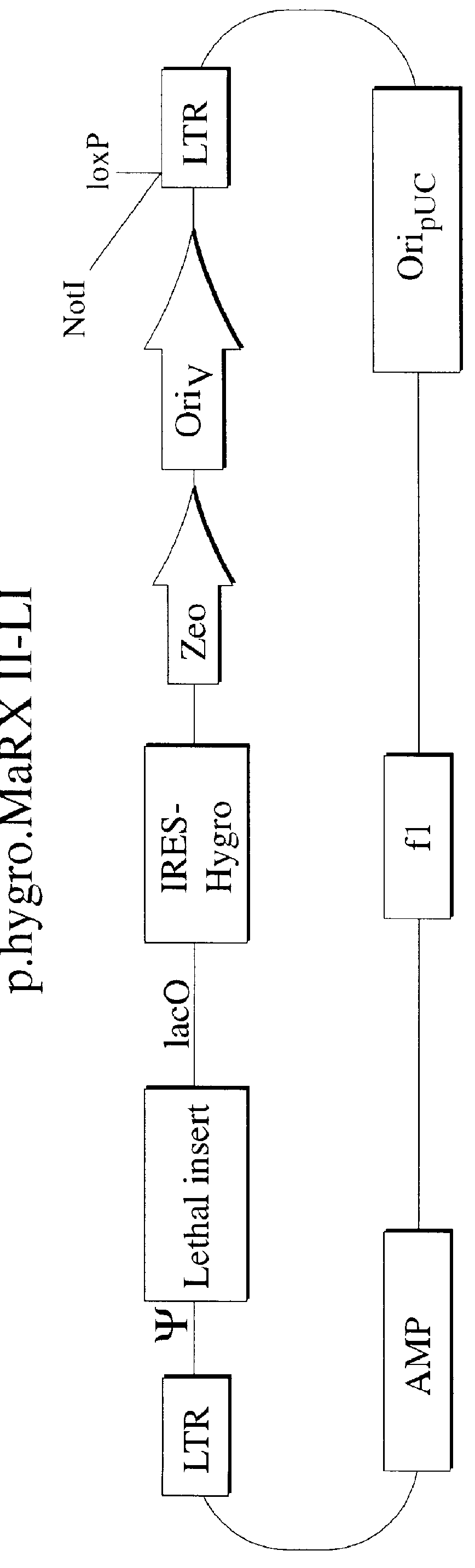
InactiveUS6255071B1Stable episomal maintenanceMaintain relatively stableSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRetroviral provirusMammal
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the elucidation of mammalian gene function. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved mammalian complementation screening, functional inactivation of specific essential or non-essential mammalian genes, and identification of mammalian genes which are modulated in response to specific stimuli.In particular, the compositions of the present invention include, but are not limited to, replication-deficient retroviral vectors, libraries comprising such vectors, retroviral particles produced by such vectors in conjunction with retroviral packaging cell lines, integrated provirus sequences derived from the retroviral particles of the invention and circularized provirus sequences which have been excised from the integrated provirus sequences of the invention. The compositions of the present invention further include novel retroviral packaging cell lines.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Modified retroviral vectors
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the elucidation of mammalian gene function. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved mammalian complementation screening, functional inactivation of specific essential or non-essential mammalian genes, and identification of mammalian genes which are modulated in response to specific stimuli. In particular, the compositions of the present invention include, but are not limited to, replication-deficient retroviral vectors, libraries comprising such vectors, retroviral particles produced by such vectors in conjunction with retroviral packaging cell lines, integrated provirus sequences derived from the retroviral particles of the invention and circularized provirus sequences which have been excised from the integrated provirus sequences of the invention. The compositions of the present invention further include novel retroviral packaging cell lines.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Rationally Designed, Synthetic Antibody Libraries and Uses Therefor
ActiveUS20090181855A1Peptide librariesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPolynucleotideSynthetic antibody
The present invention overcomes the inadequacies inherent in the known methods for generating libraries of antibody-encoding polynucleotides by specifically designing the libraries with directed sequence and length diversity. The libraries are designed to reflect the preimmune repertoire naturally created by the human immune system and are based on rational design informed by examination of publicly available databases of human antibody sequences.
Owner:ADIMAB LLC
Collections of compounds
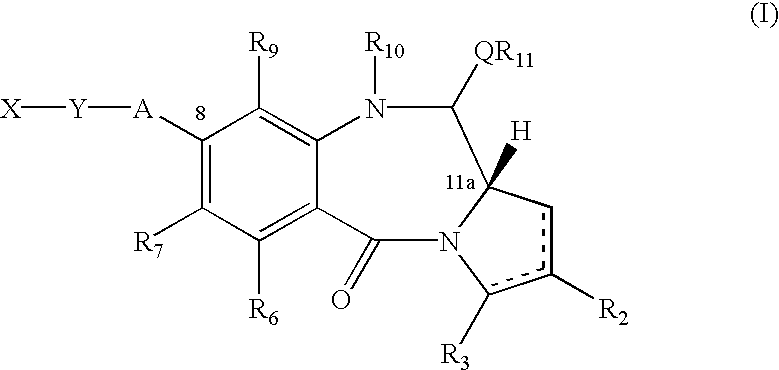
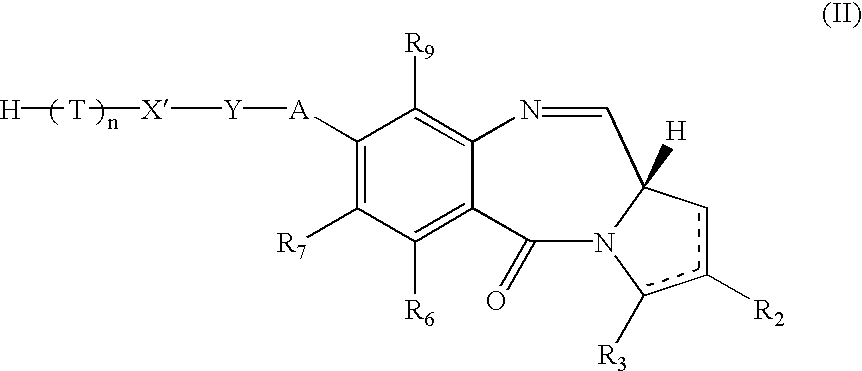
A compound of formula (IV): O is a solid support; L is a linking group or a single bond; X' is selected from CO, NH, S, or O; A is O, S, NH, or a single bond; R2 and R3 are independently selected from: H, R, OH, OR, =O, =CH-R, =CH2, CH2-CO2R', CH2-CO2H, CH2-SO2R, O-SO2R, CO2R, COR, CN and there is optionally a double bond between C1 and C2 or C2 and C3; R6, R7, and R9 are independently selected from H, R, OH, OR, halo, nitro, amino, Me3Sn; R11 is either H or R; Q is S, O or NH; R10 is a nitrogen protecting group; and Y is a divalent group such that HY=R, and other related compounds and collections of compounds.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
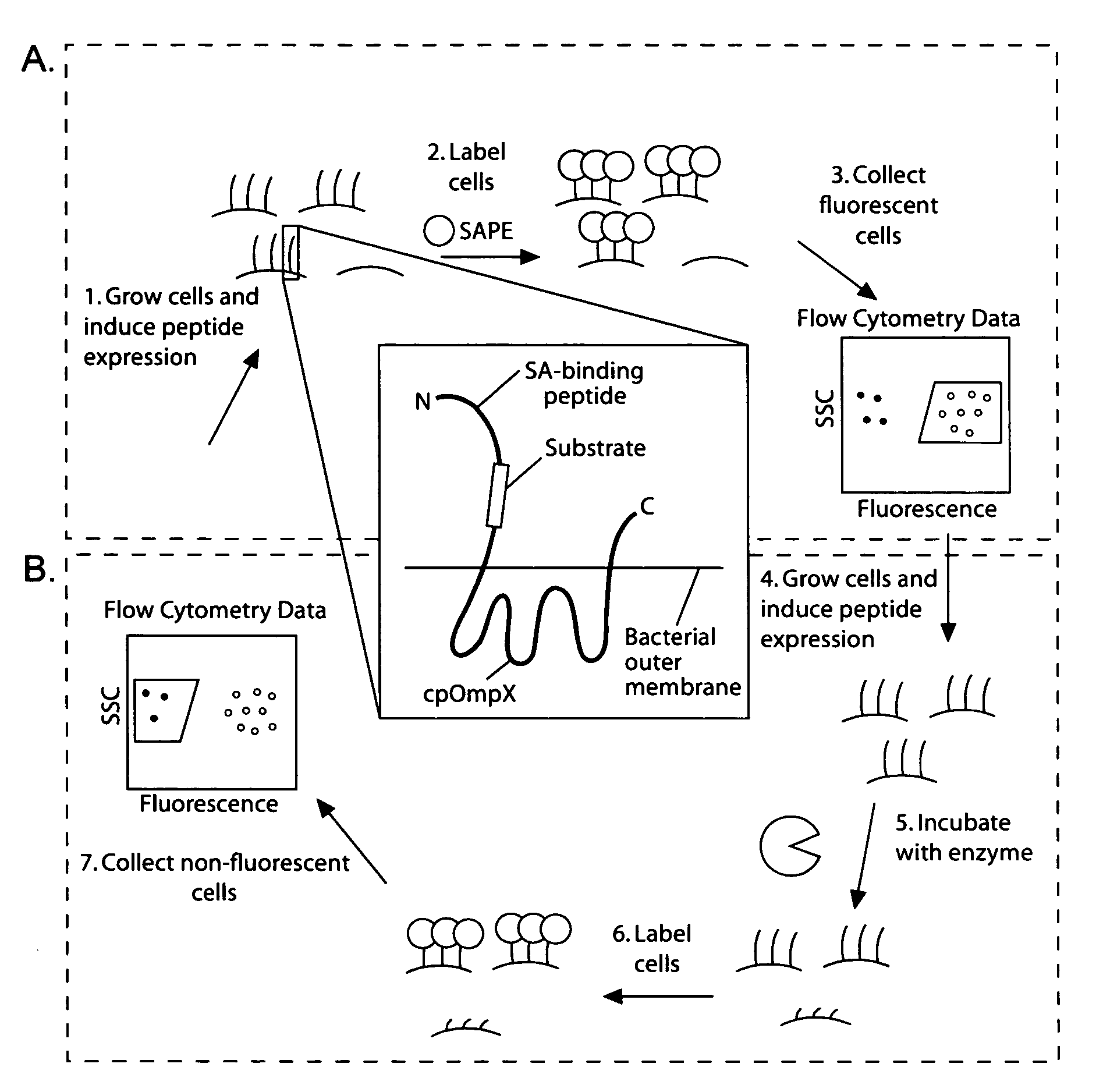
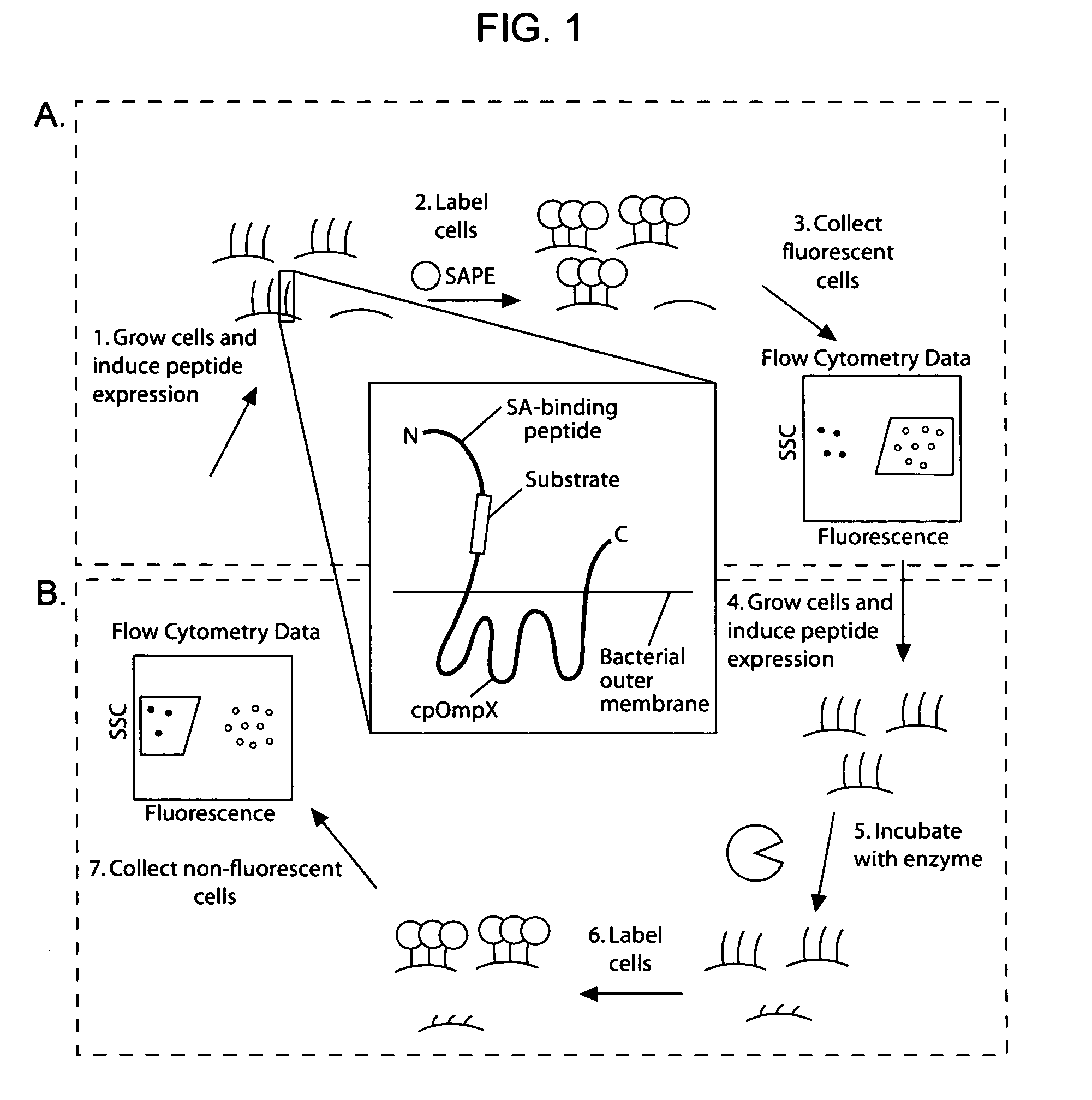
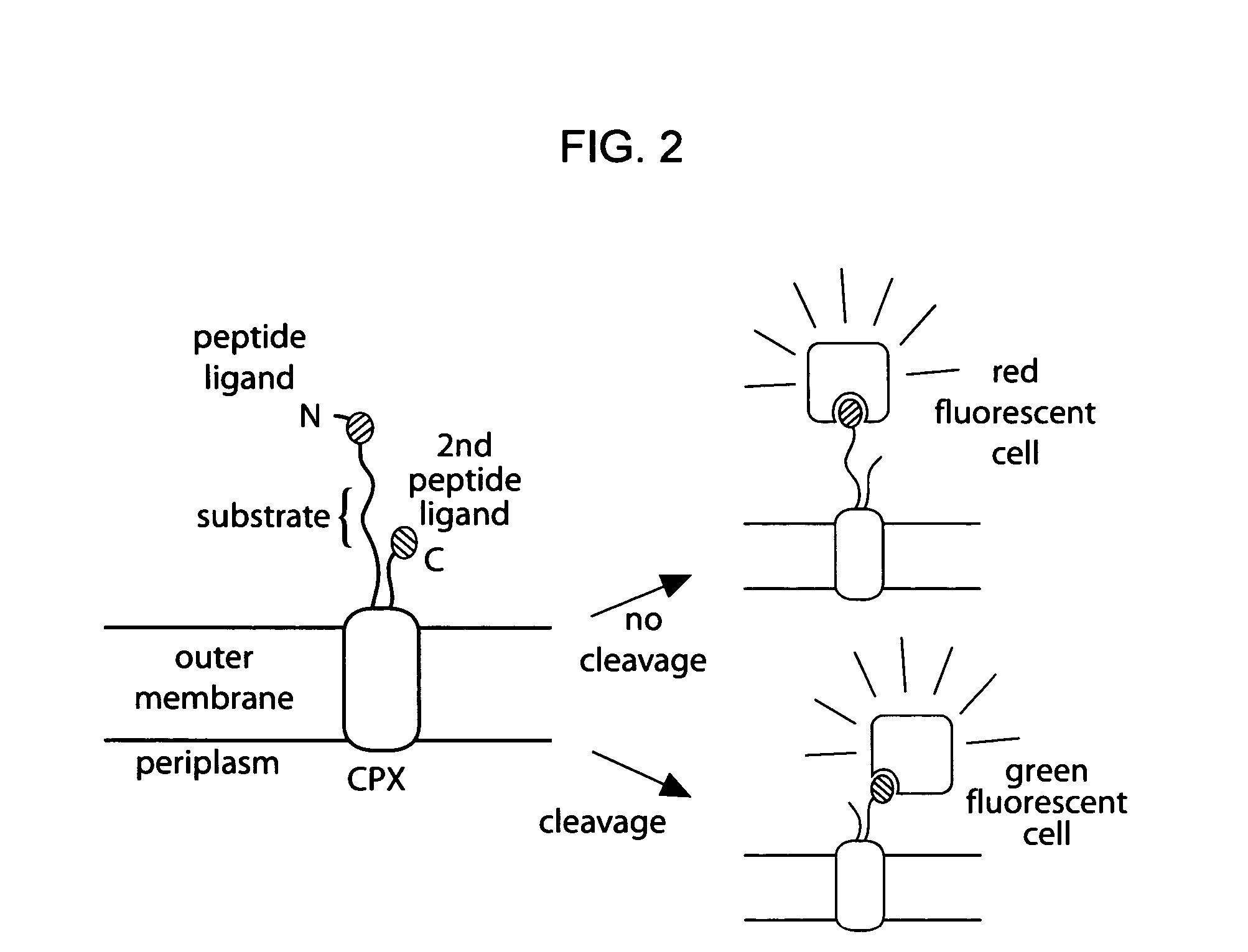
Cellular libraries of peptide sequences (CLiPS) and methods of using the same
The present invention provides compositions including peptide display scaffolds that present at least one candidate peptide and at least one detectable moiety in at least one of the N-terminal and C-terminal candidate peptide presenting domains that when expressed in a cell are accessible at a surface of the cell outermembrane. In addition, the present invention also provides kits and methods for screening a library of cells presenting the candidate peptides in peptide display scaffolds to identify a ligand for an enzyme.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
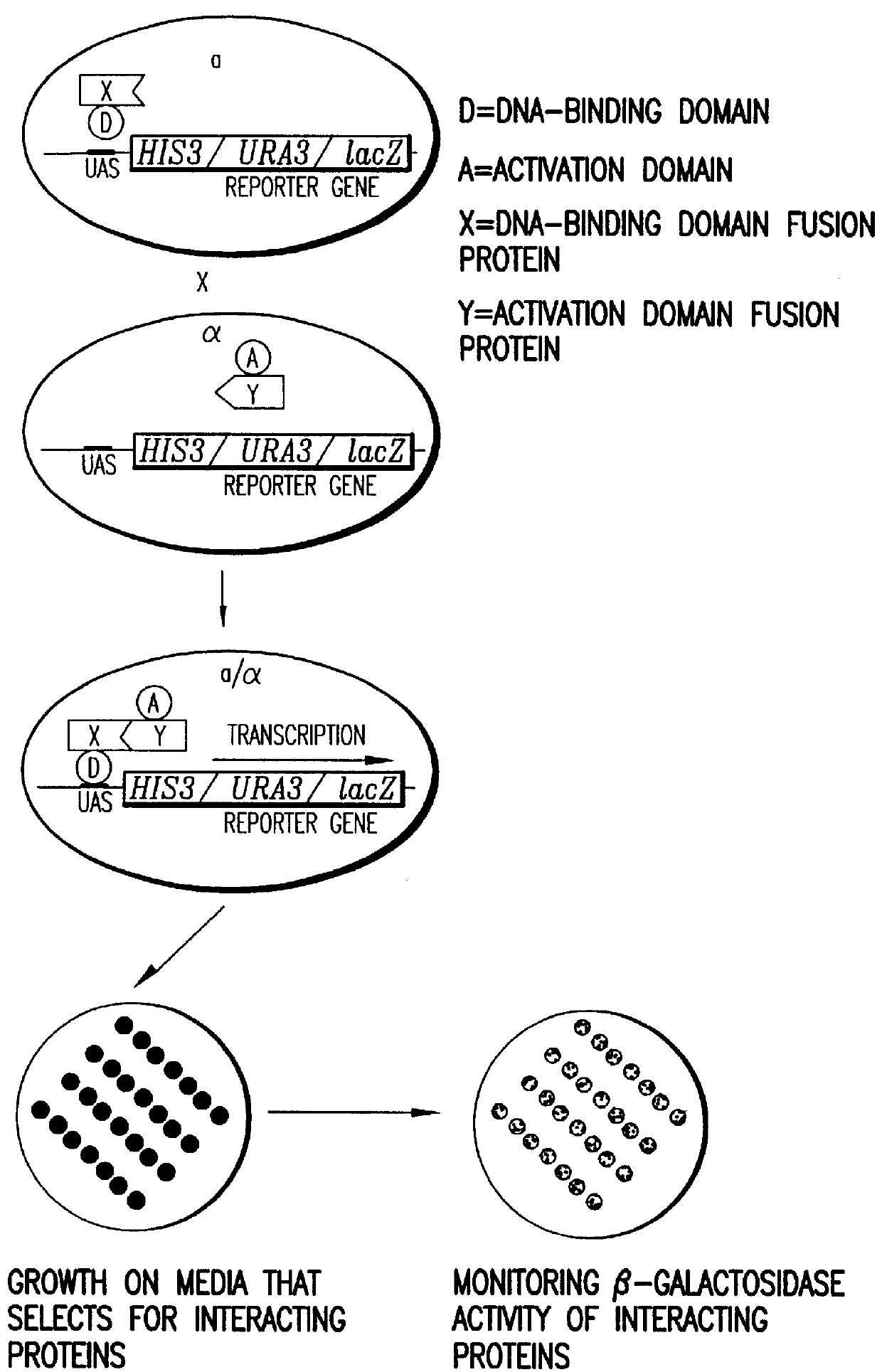
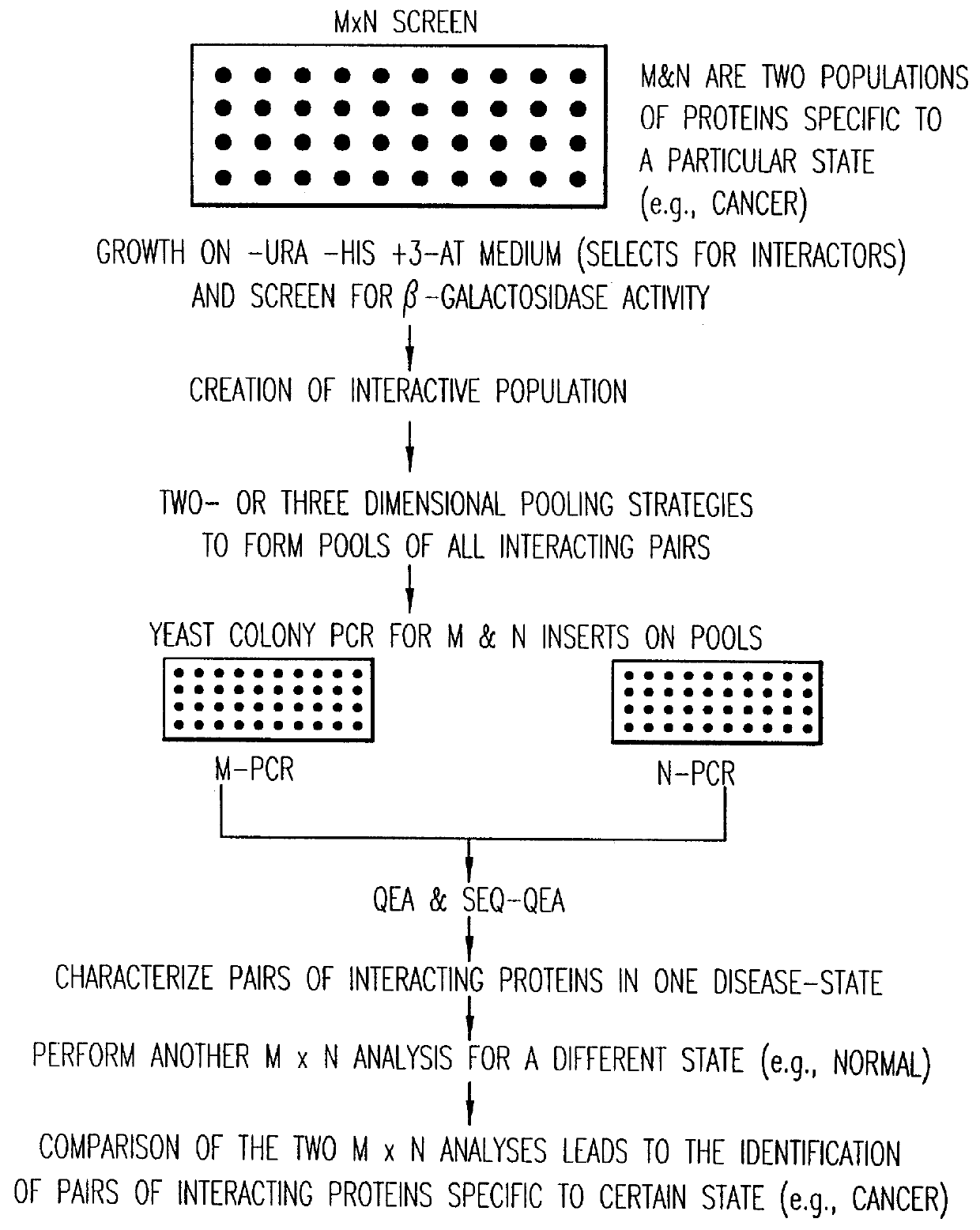
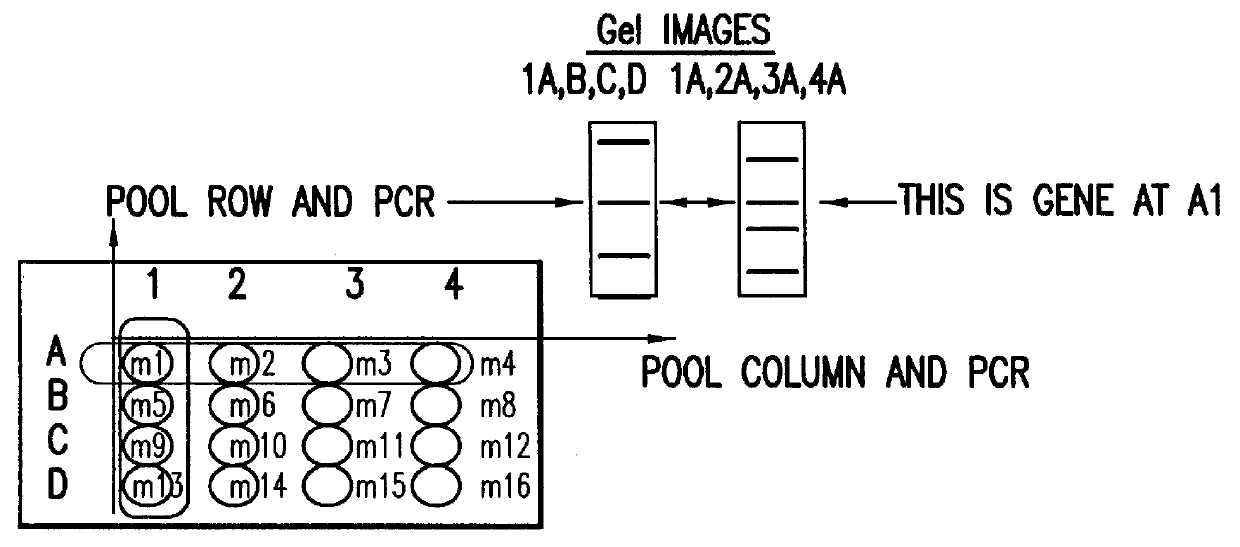
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6518065B1Less immunogenicImmunoglobulinsLibrary member identificationMutated proteinNucleotide
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
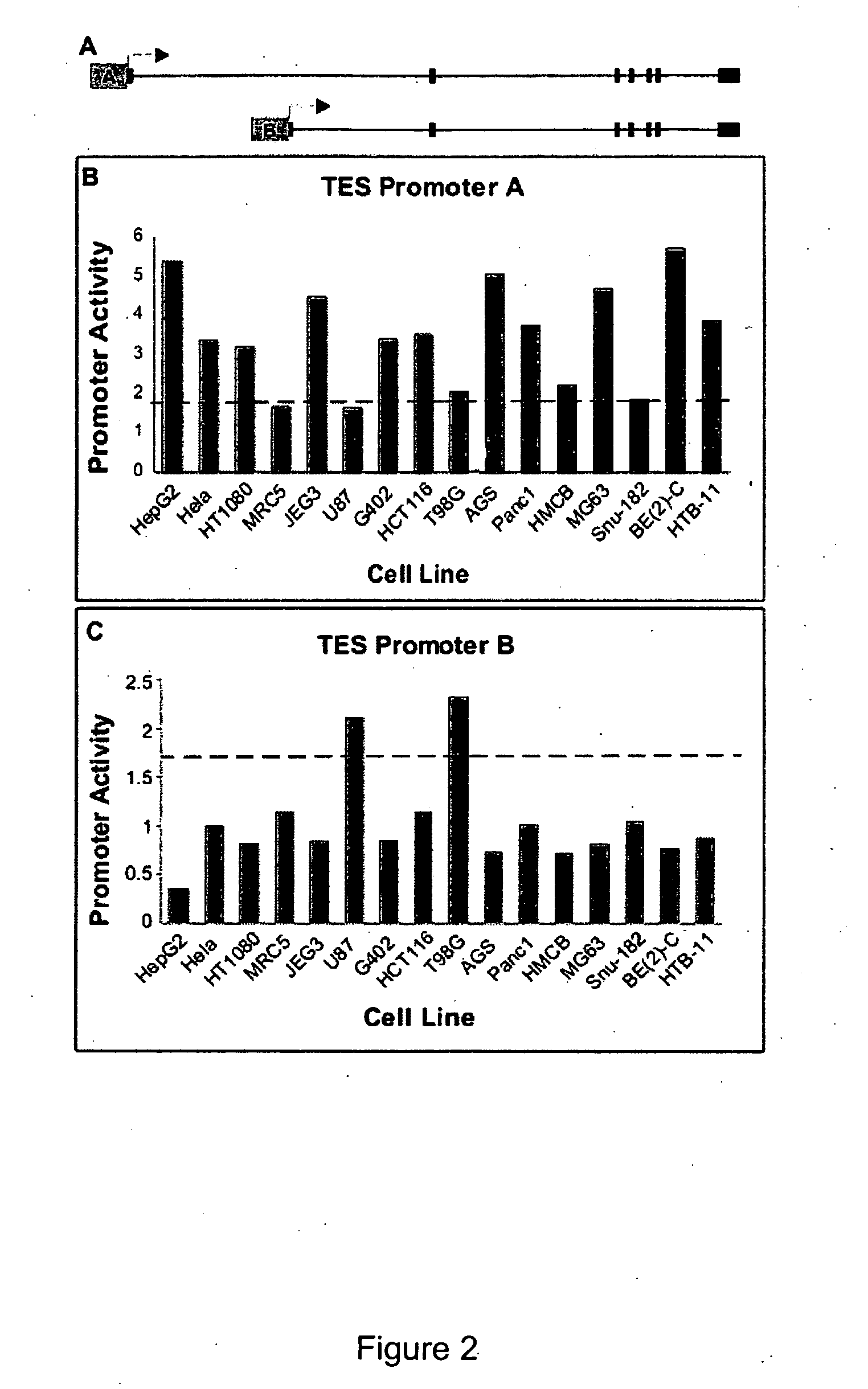
Functional arrays for high throughput characterization of gene expression regulatory elements
InactiveUS20070161031A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment, the nucleic acid segment varying in the library and having a diversity of at least 50. The nucleic acid segments can be a large library of gene expression regulatory elements such as transcriptional promoters. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com