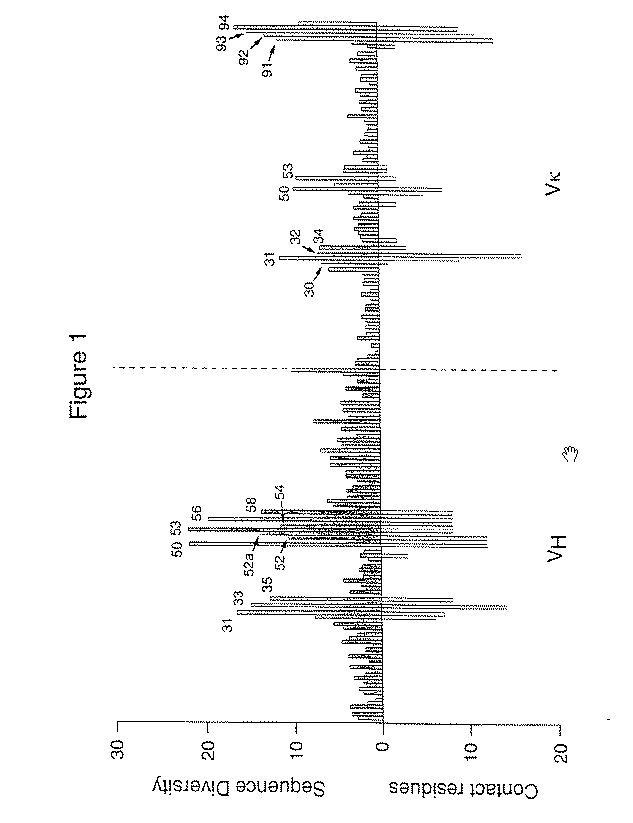
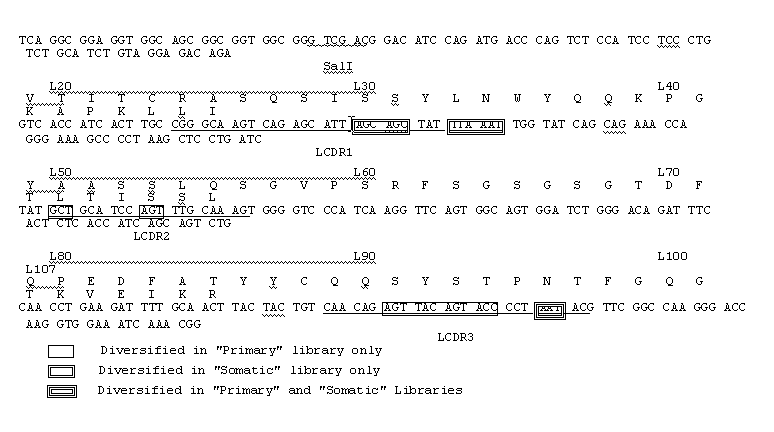
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
a technology of phages and libraries, applied in chemical libraries, animal/human proteins, combinational chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of antibody selection from these libraries may be poorly expressed, antibody folding cannot be correctly folded, and use consensus frameworks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0143] [0144]Example 2 Library construction and selection with the generic ligandsThe "primary" and "somatic" libraries were assembled by PCR using the oligonucleotides listed in Table 1 and the germline V gene segments DPK9 (Cox et al. (1994) Eur. J. Immunol., 24: 827) and DP-47 (Tomlinson et al. (1992) J. Mol. Biol., 227: 7768). Briefly, first round of amplification was performed using pairs of 5' (back) primers in conjunction with NNK or DVT 3' (forward) primers together with the corresponding germline V gene segment as template (see Table 1). This produces eight separate DNA fragments for each of the NNK and DVT libraries. A second round of amplification was then performed using the 5' (back) primers and the 3' (forward) primers shown in Table 1 together with two of the purified fragments from the first round of amplification. This produces four separate fragments for each of the NNK and DVT libraries (a "primary" VH fragment, 5A; a "primary" Vκ fragment, 6A; a "somatic" VH frag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conformation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com