Patents
Literature
6542results about "Glycosylases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
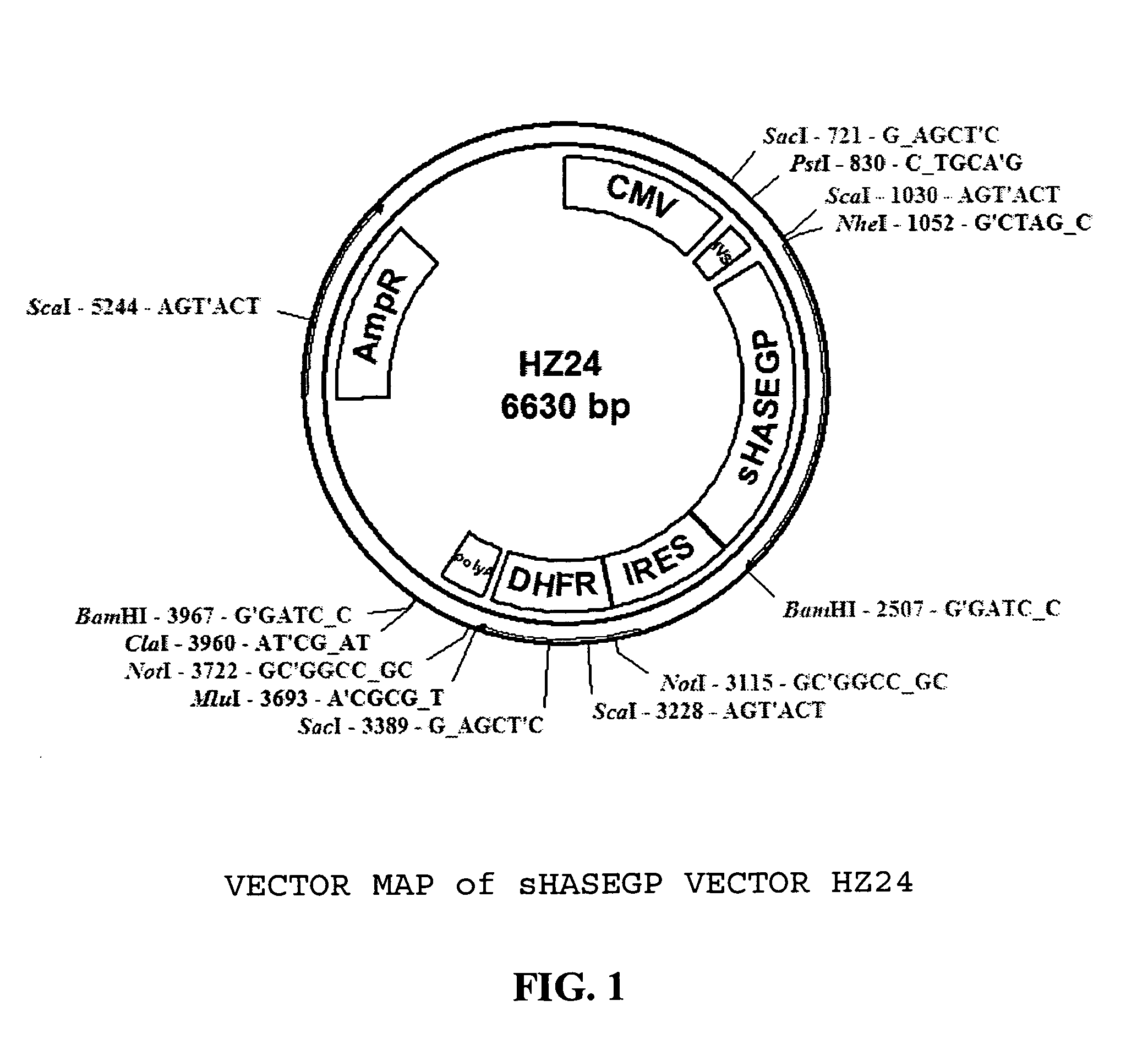
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
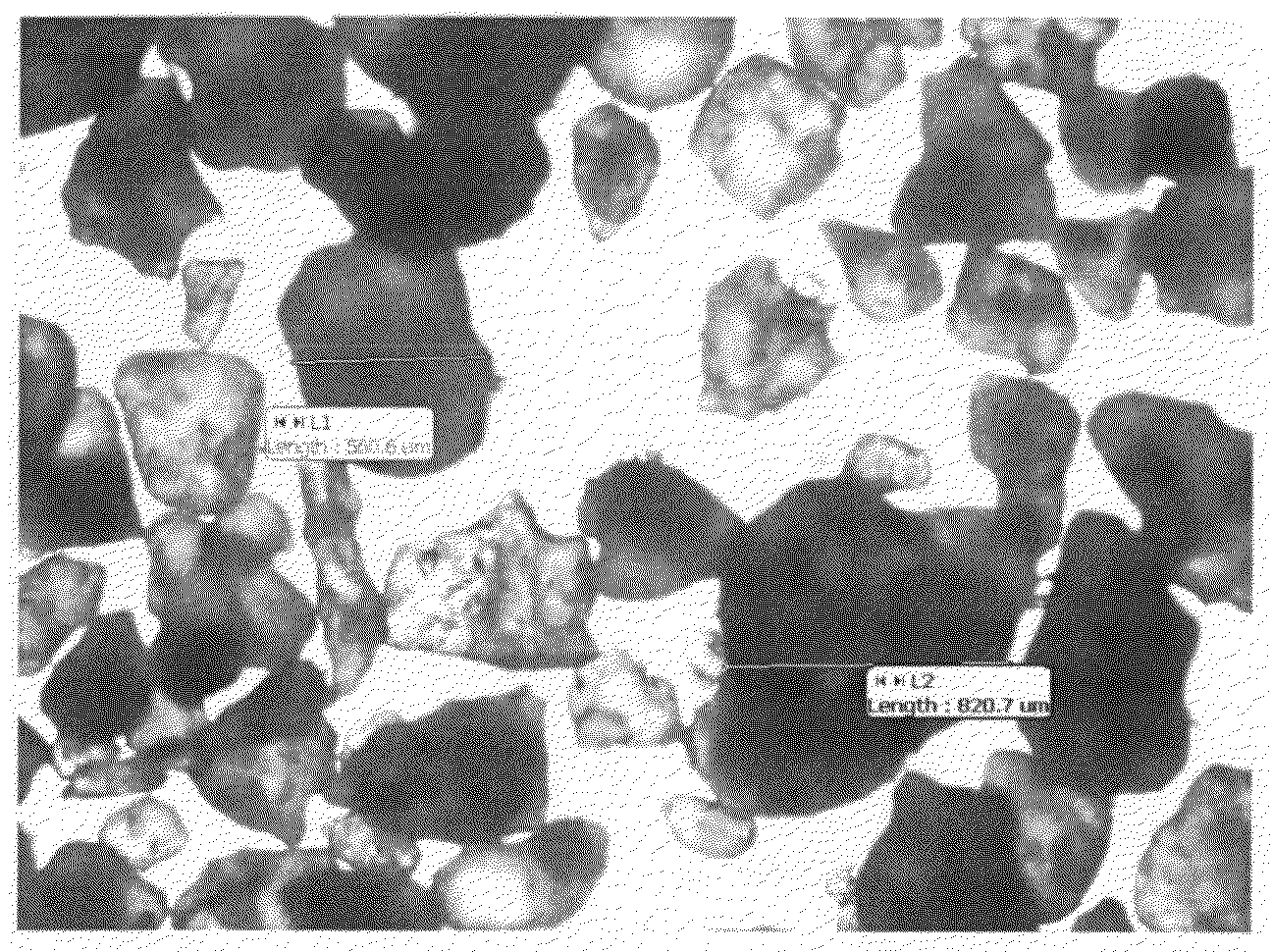
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
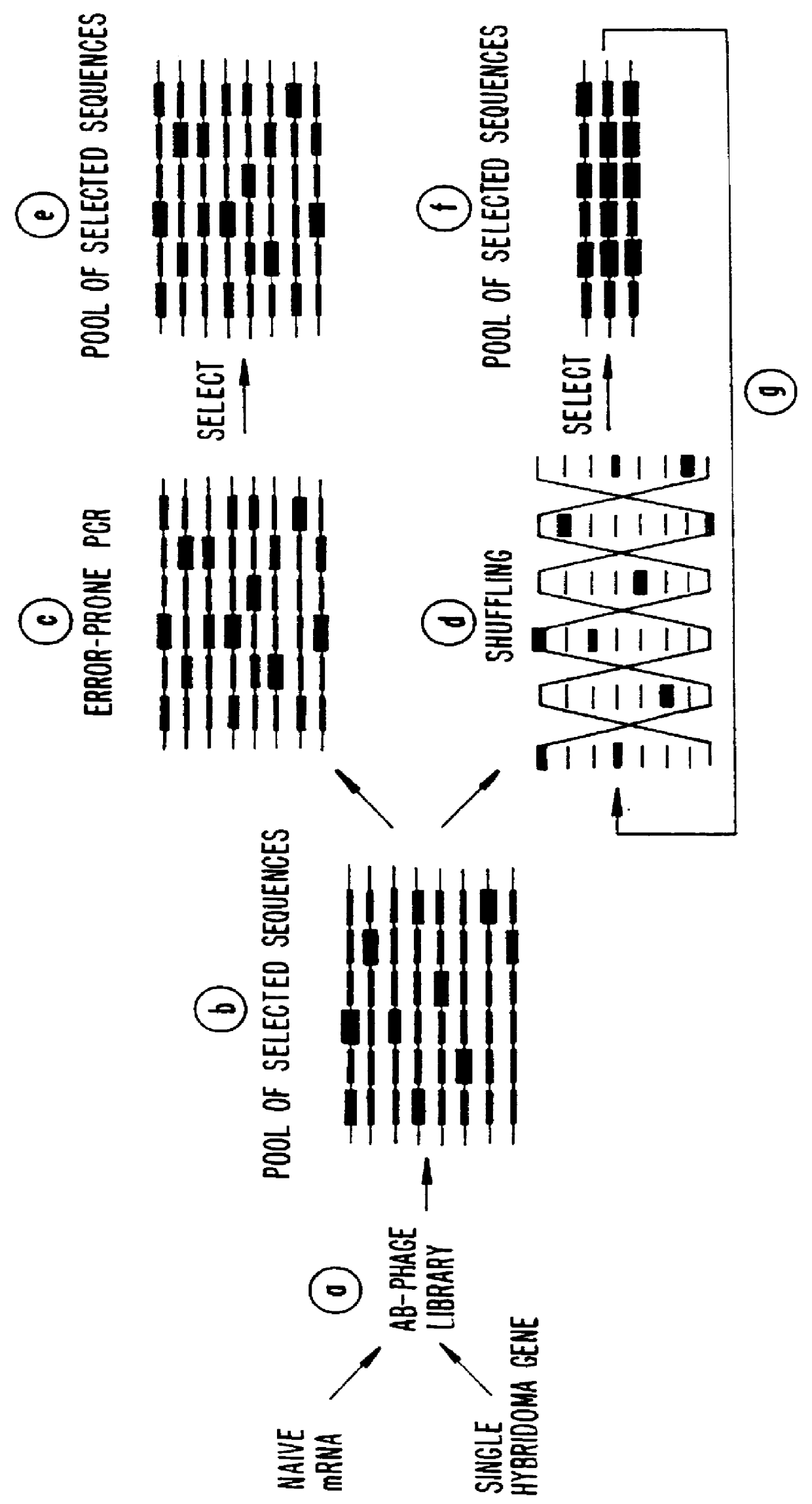
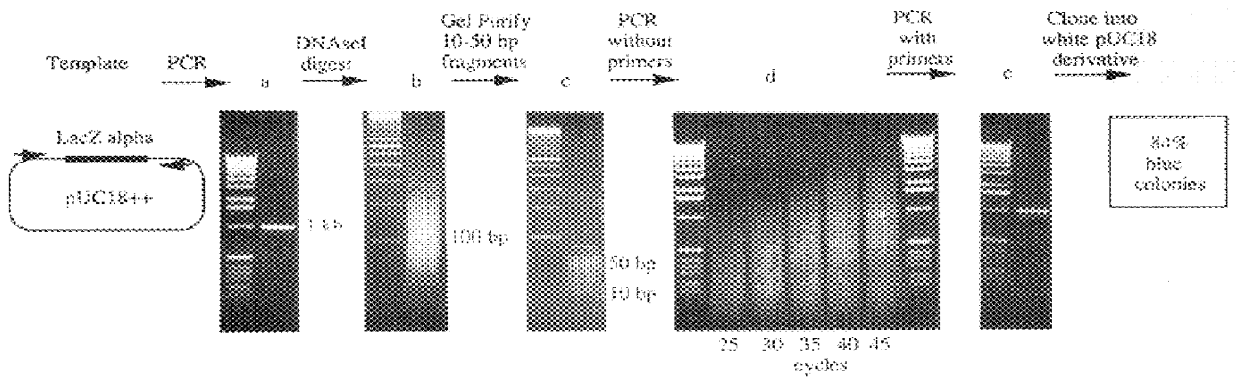
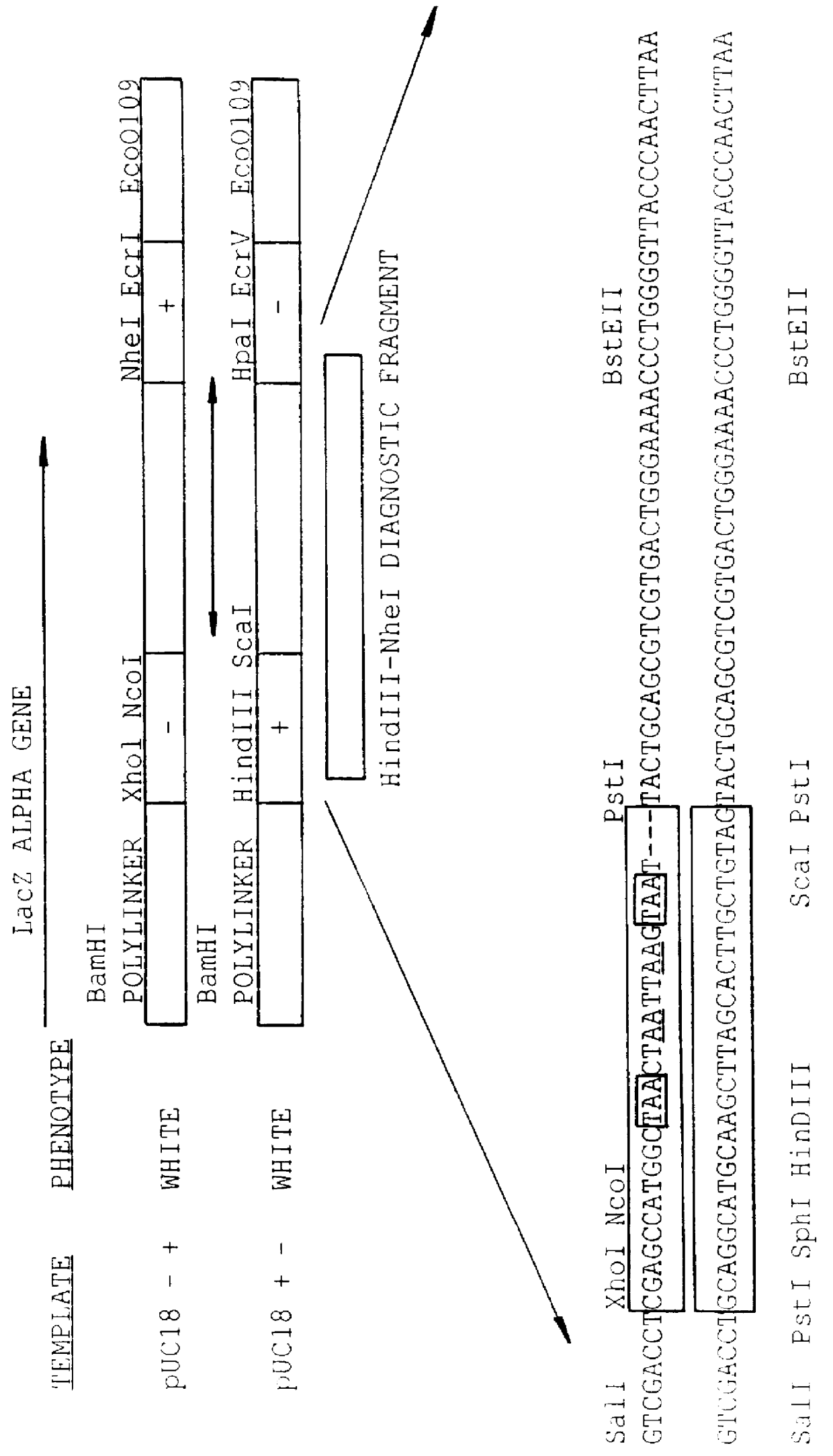
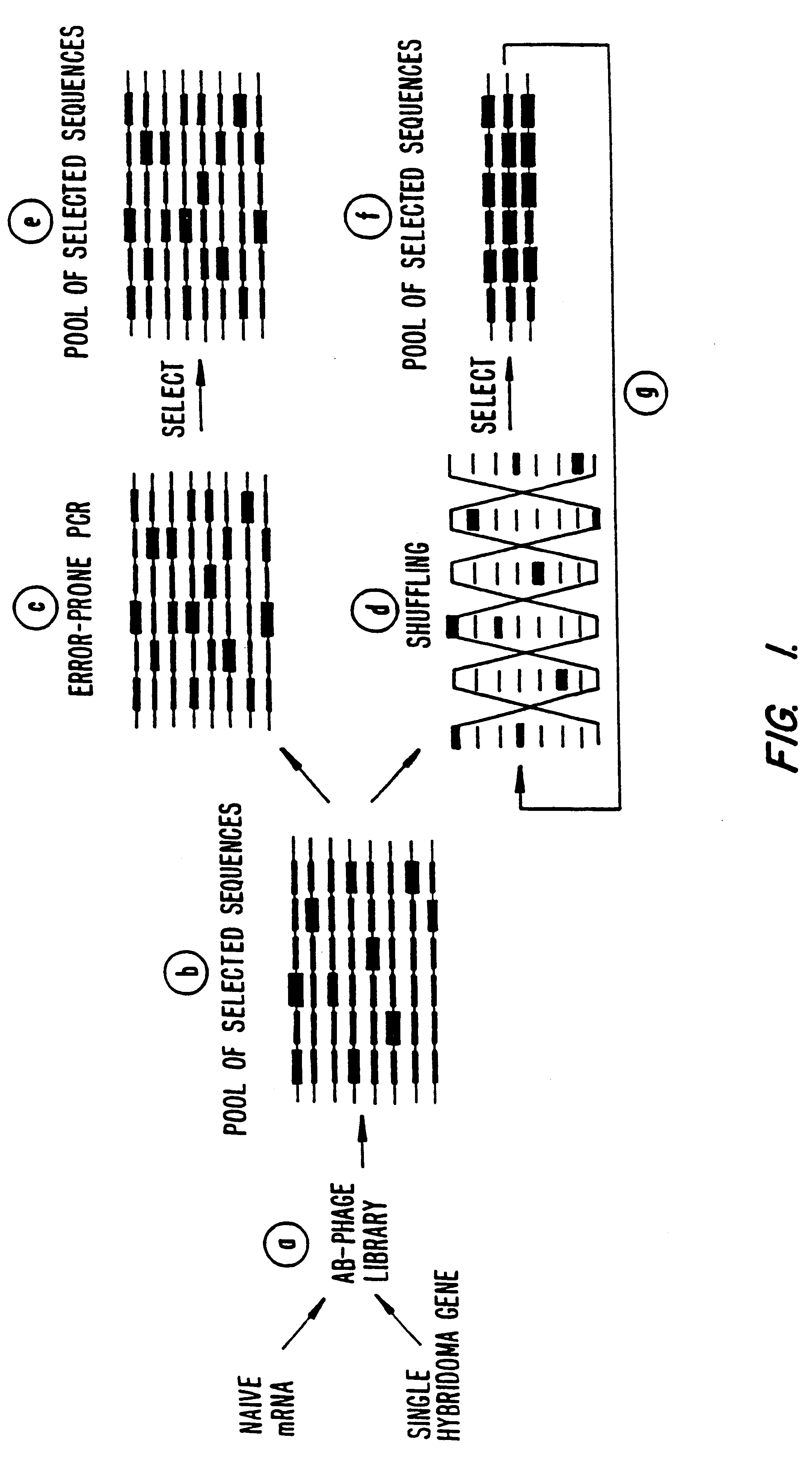
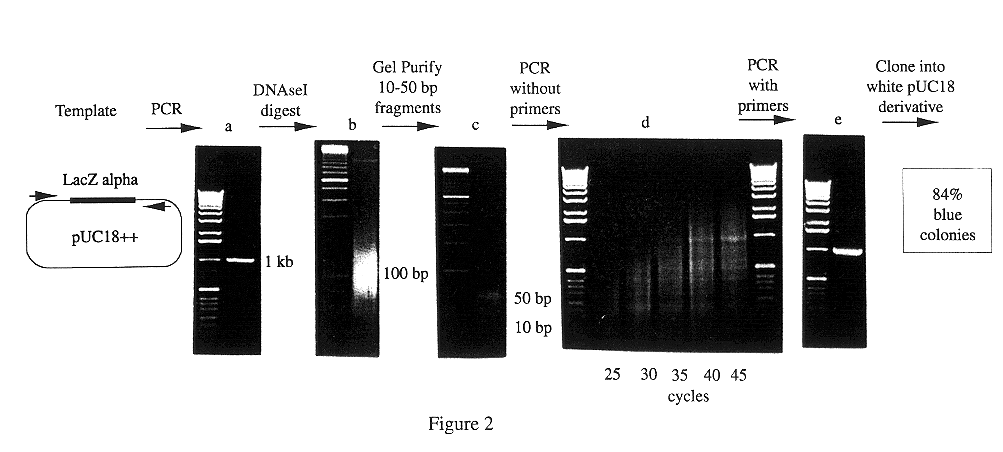
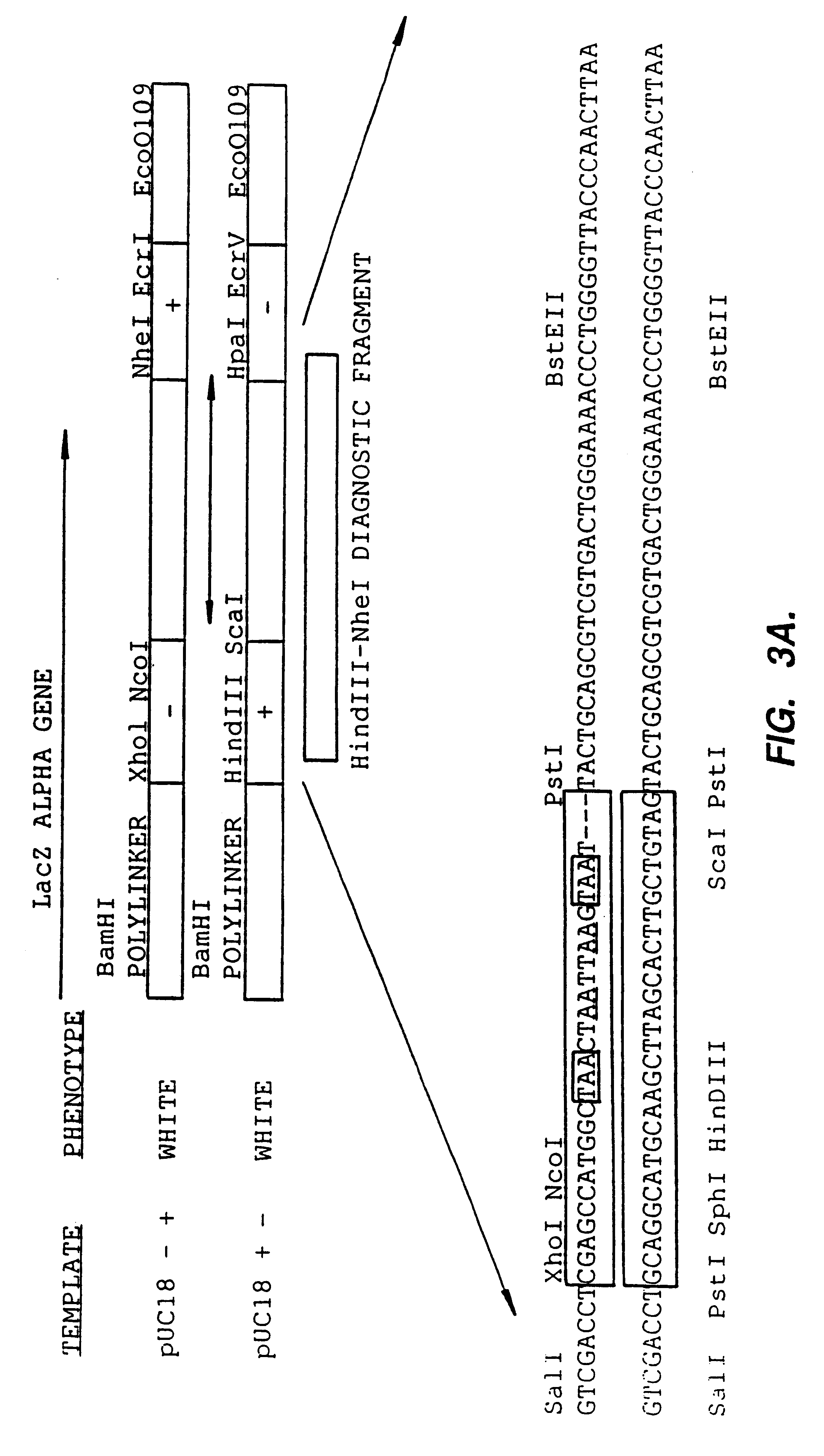
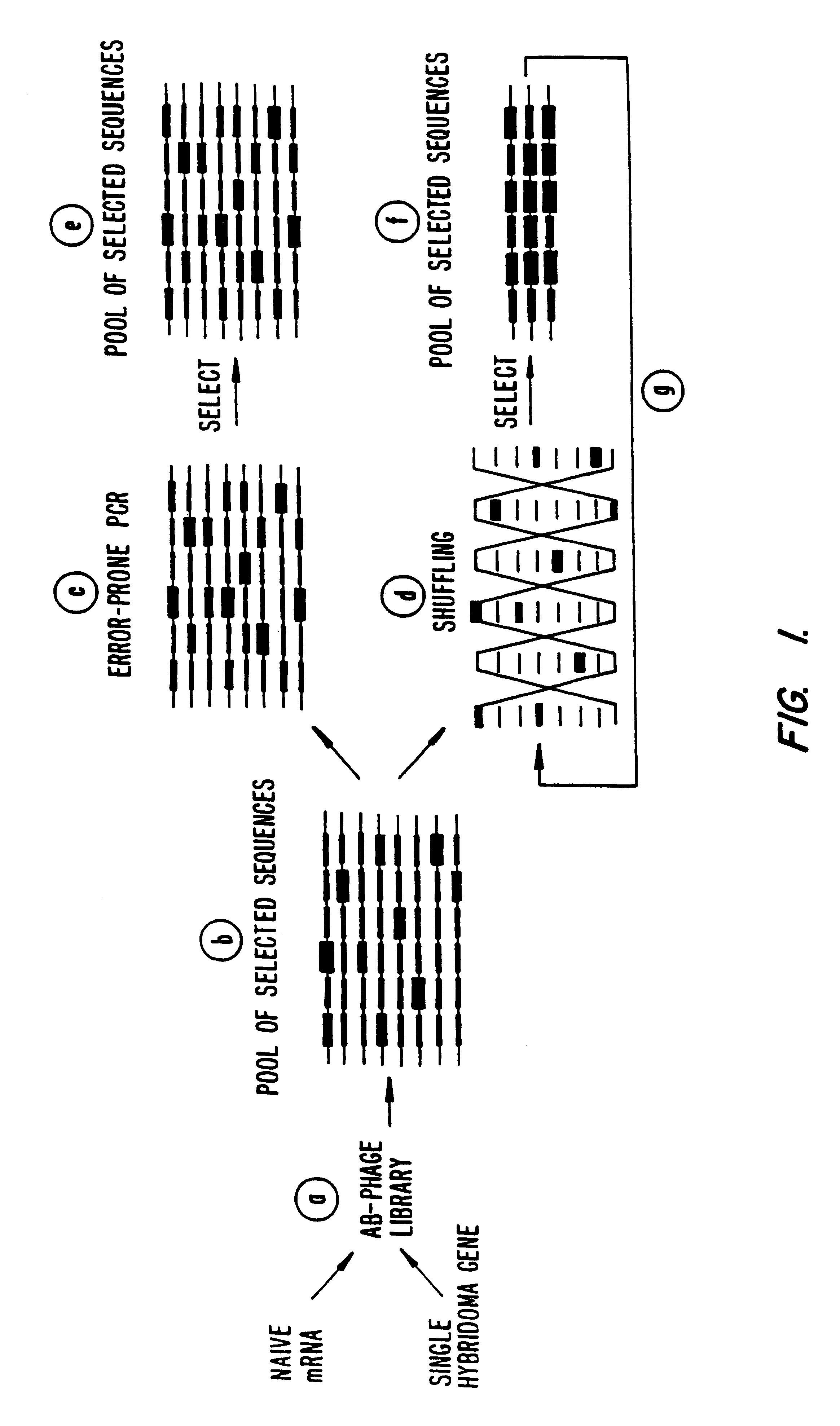
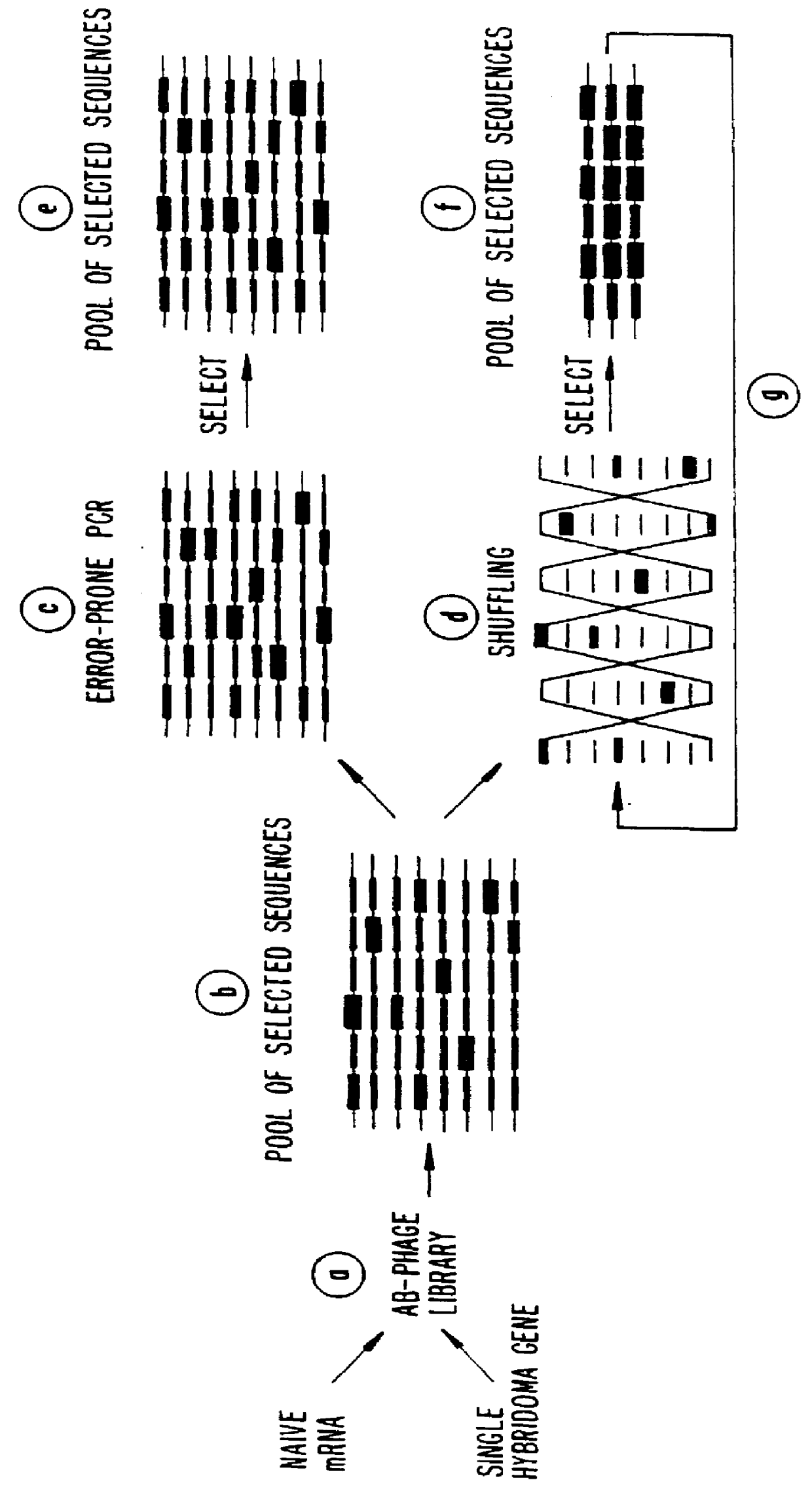
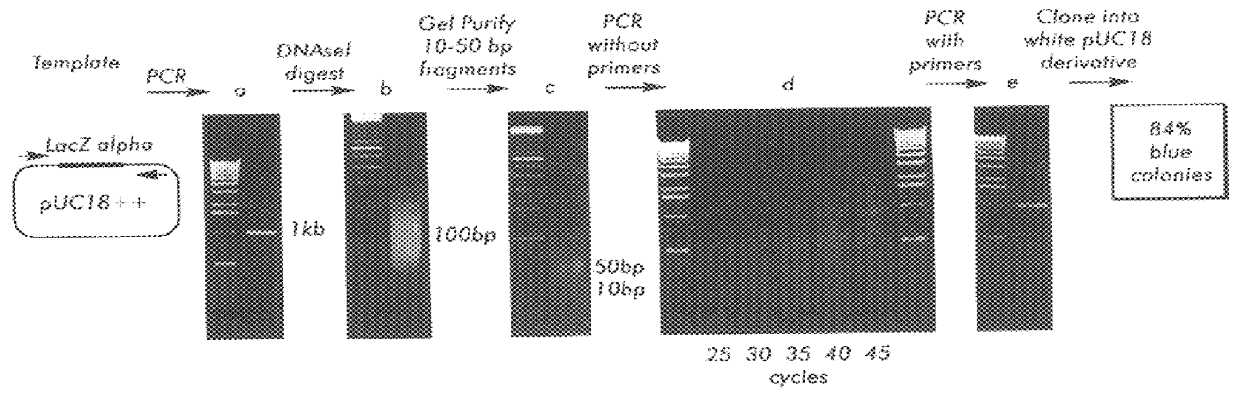
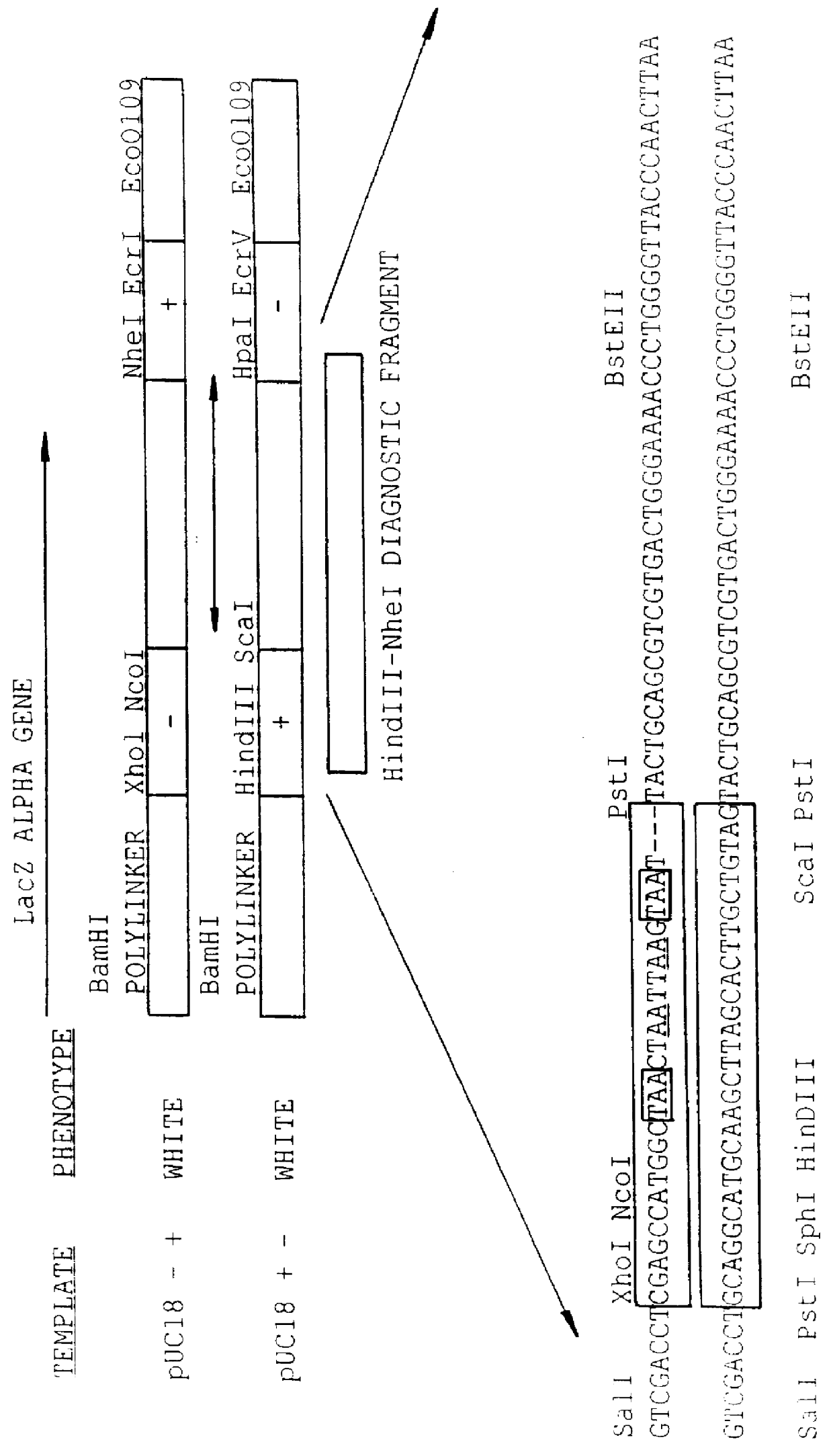
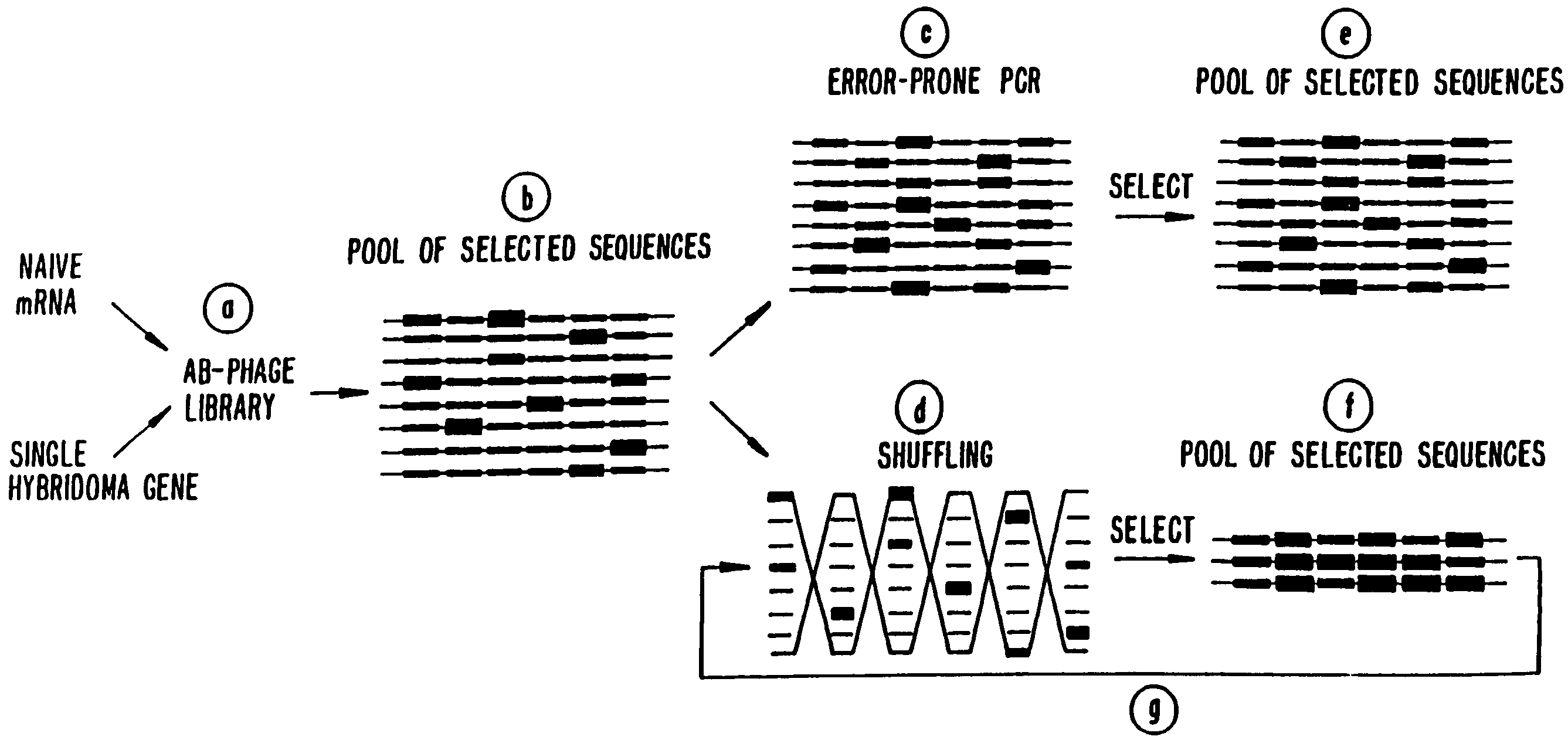
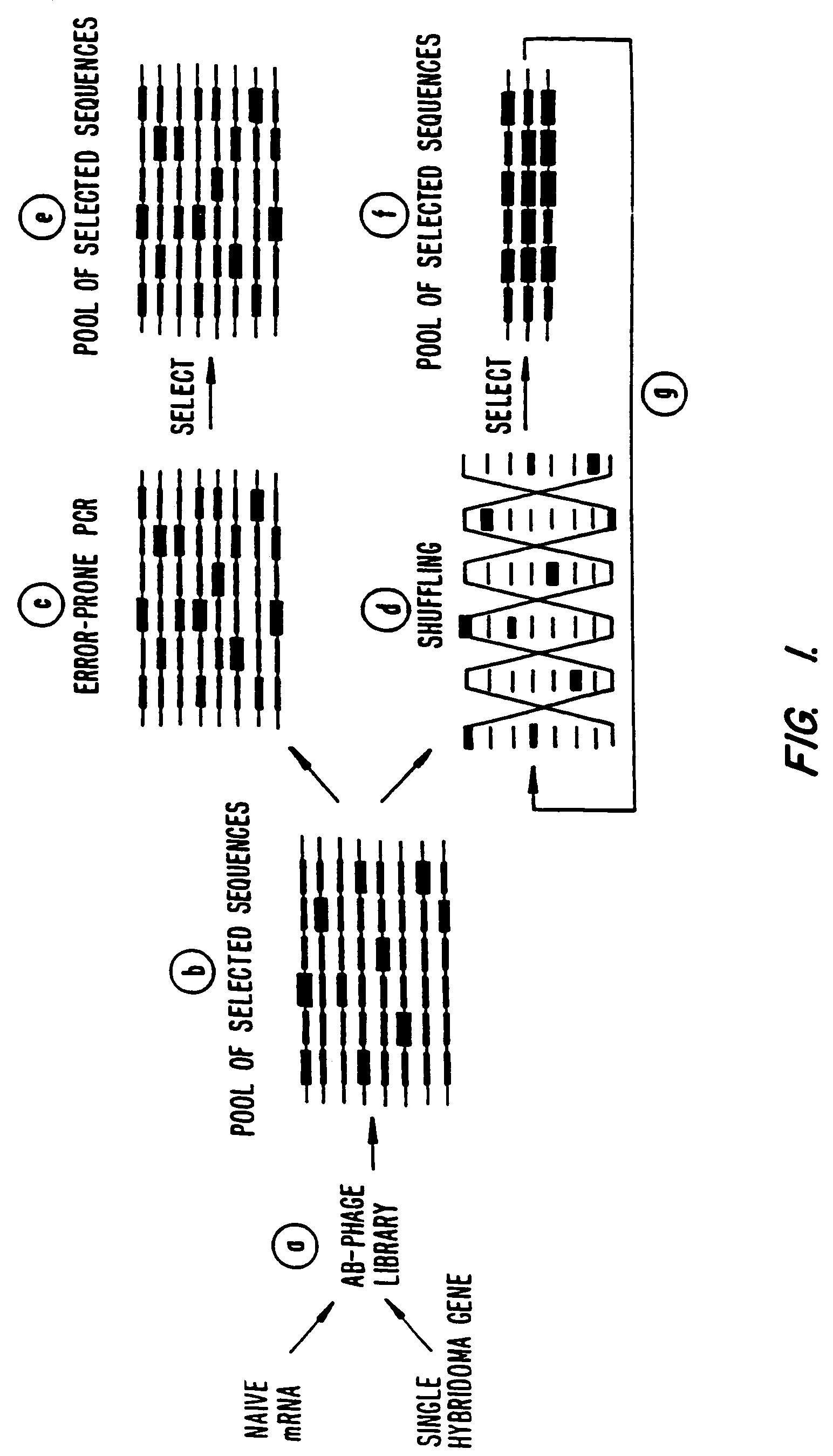
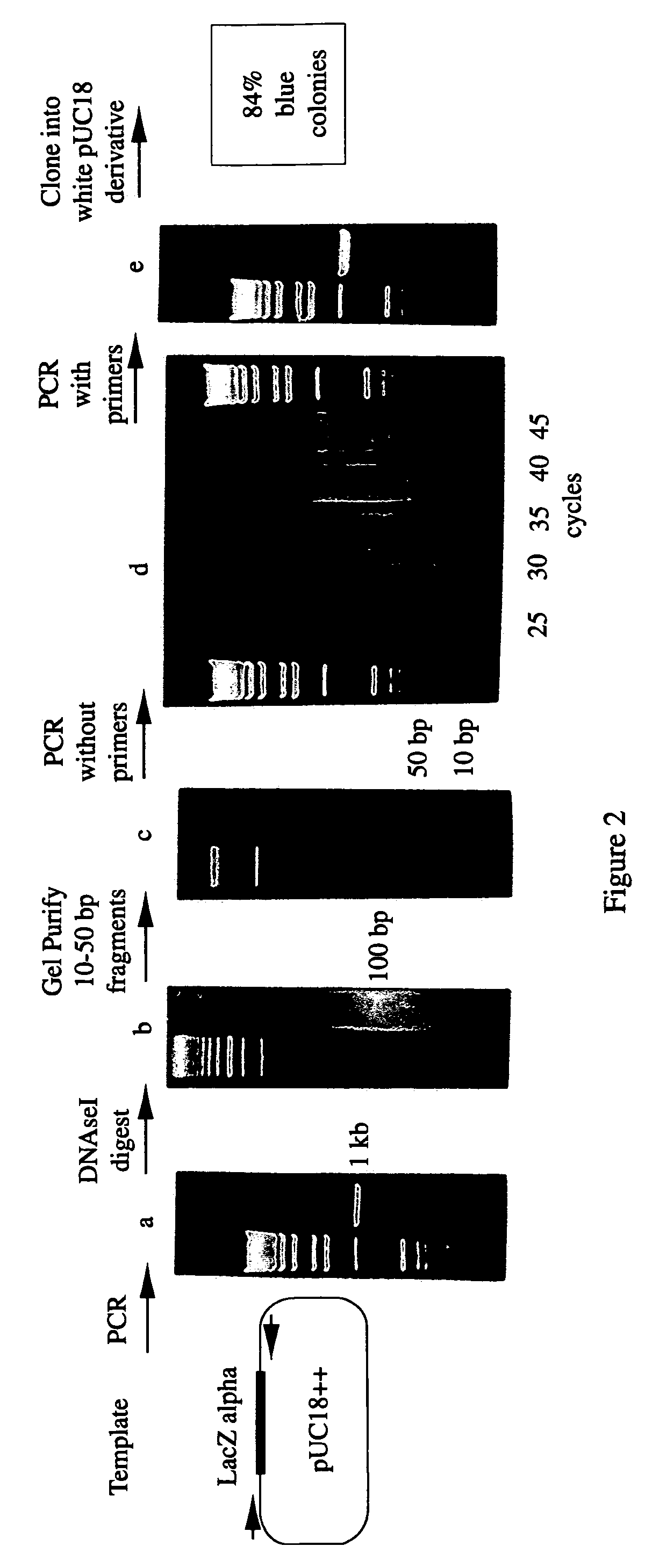
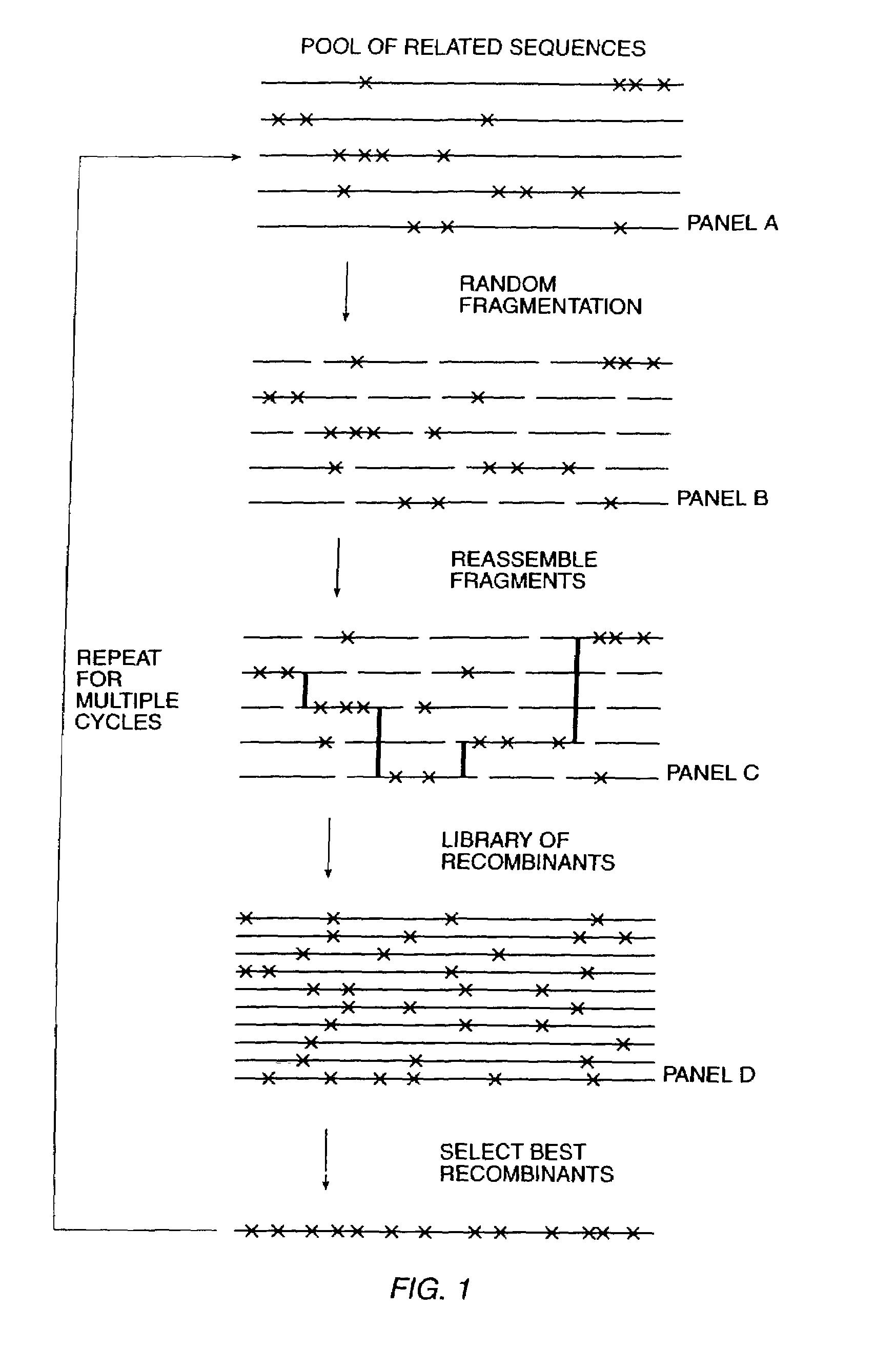
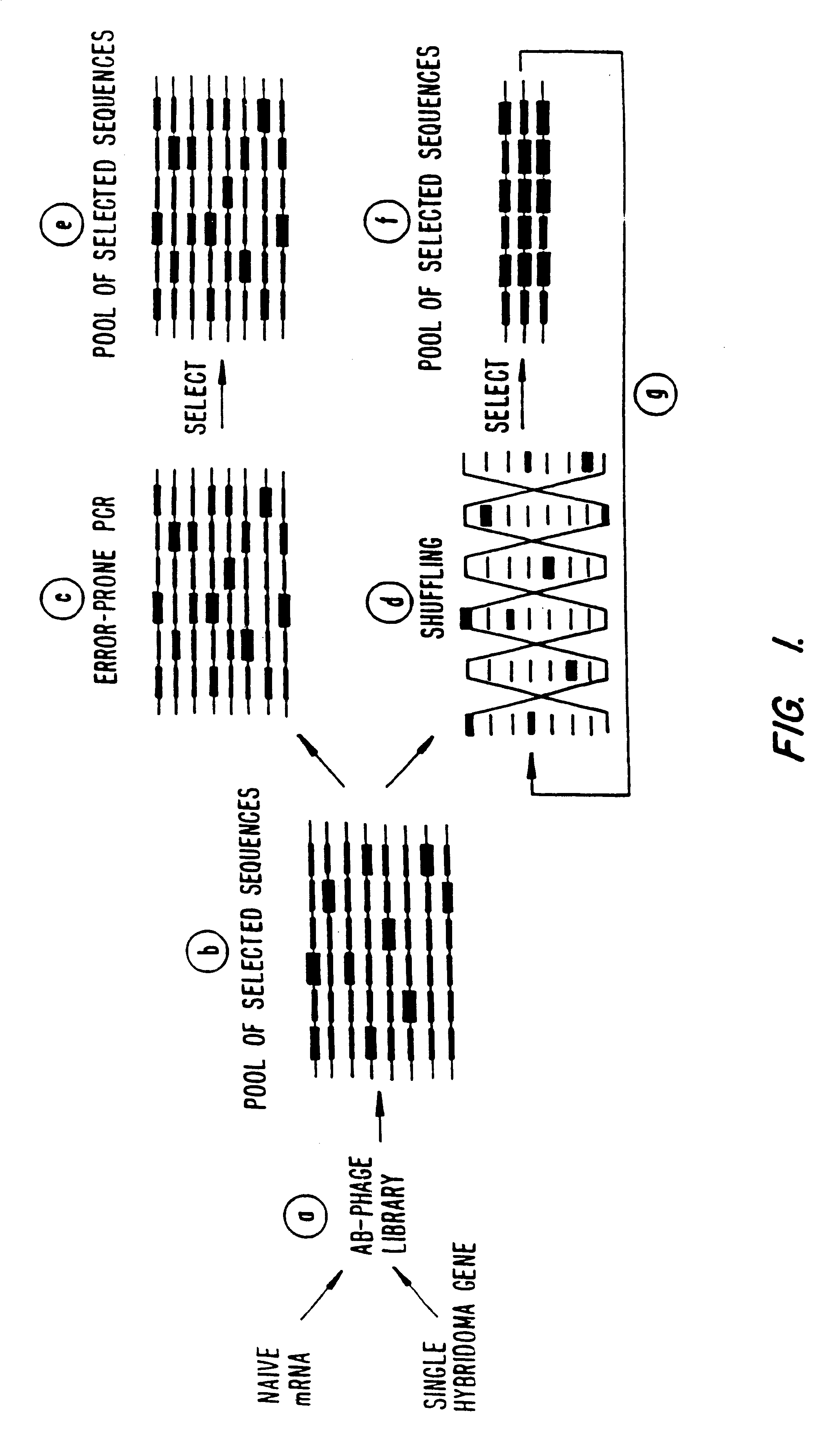
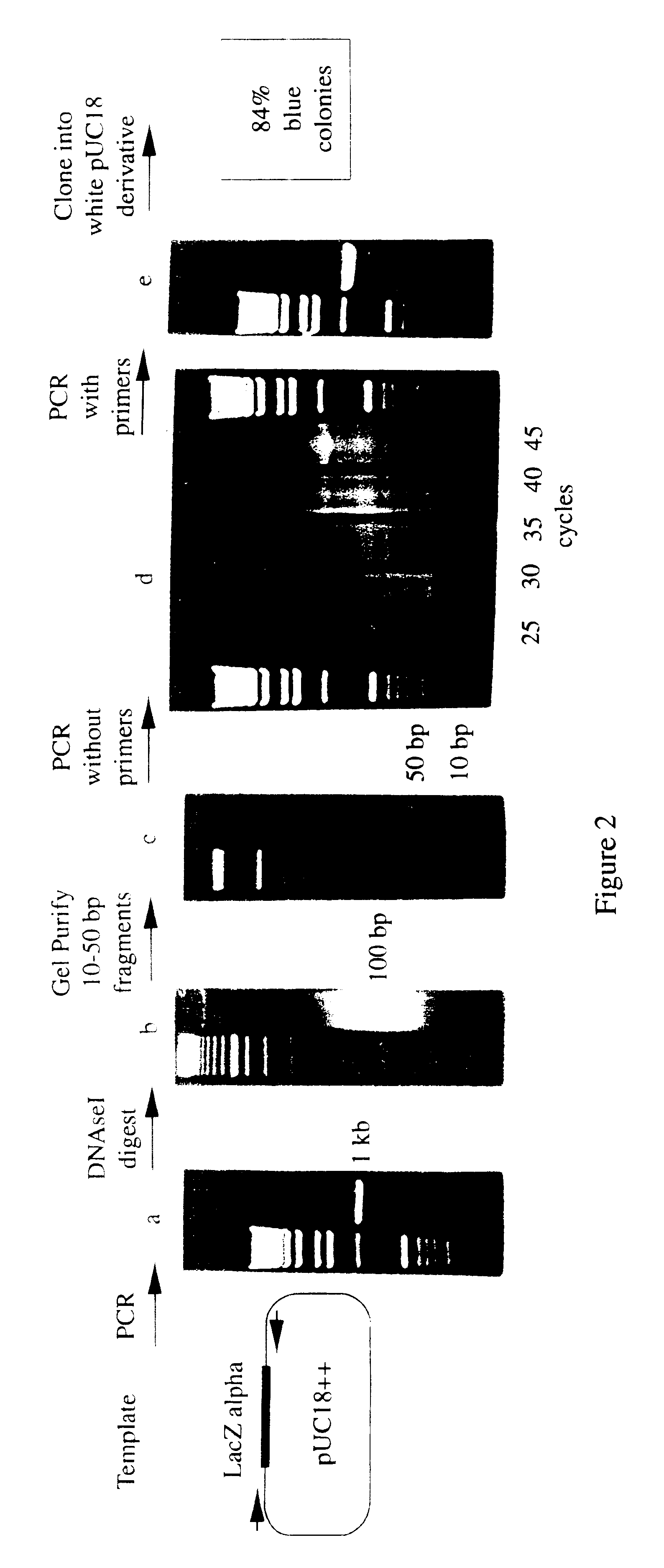
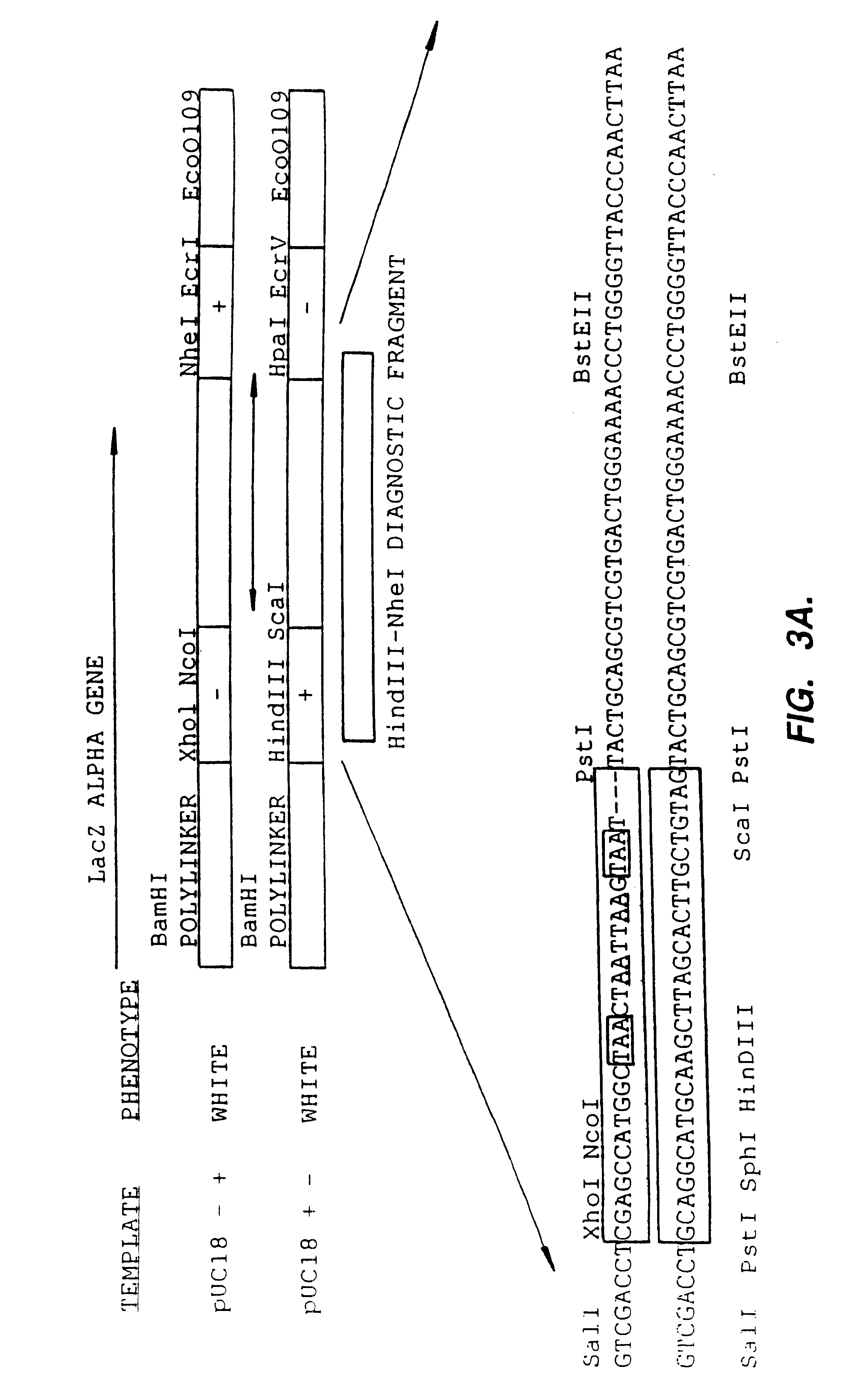
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
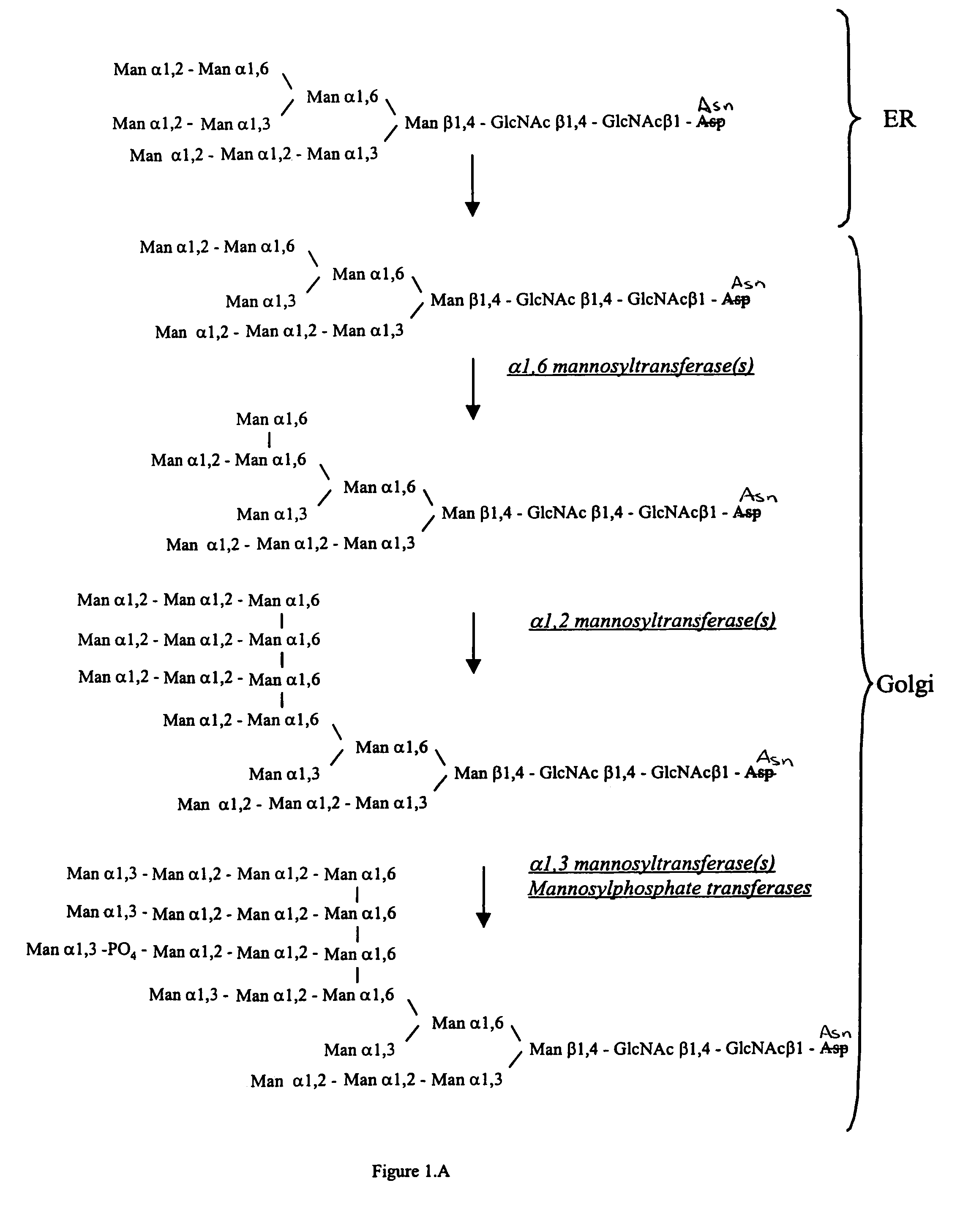
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
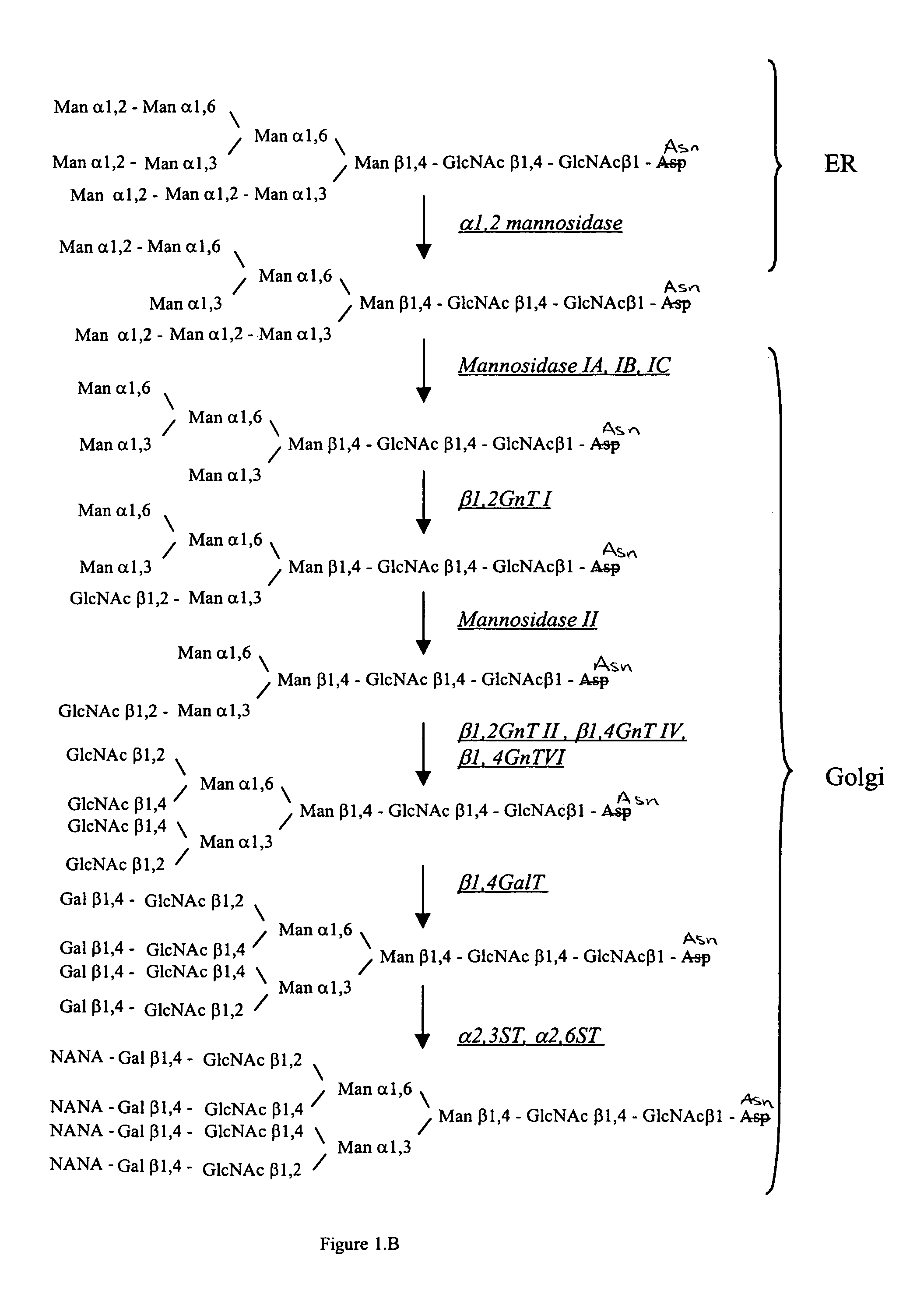
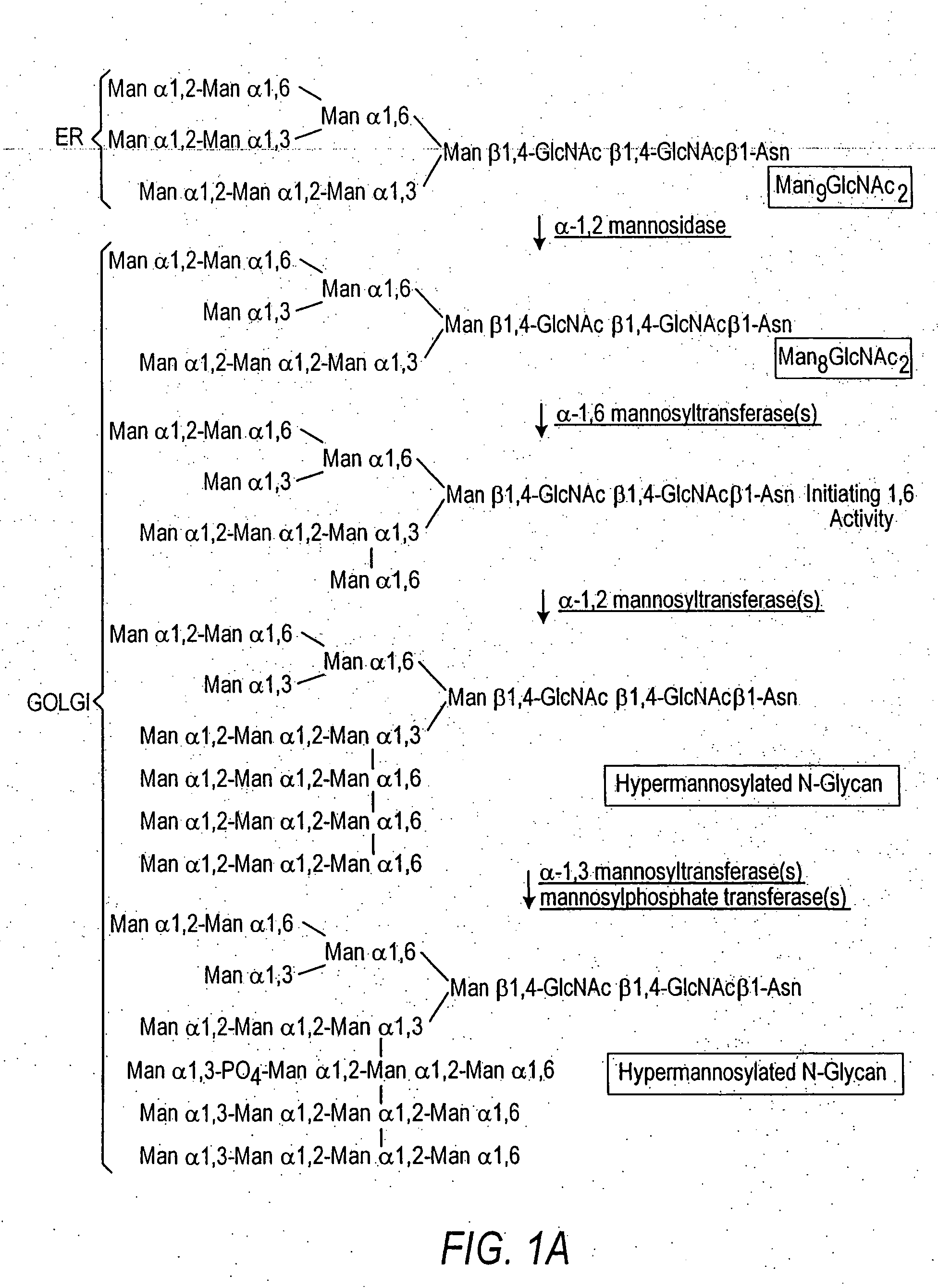
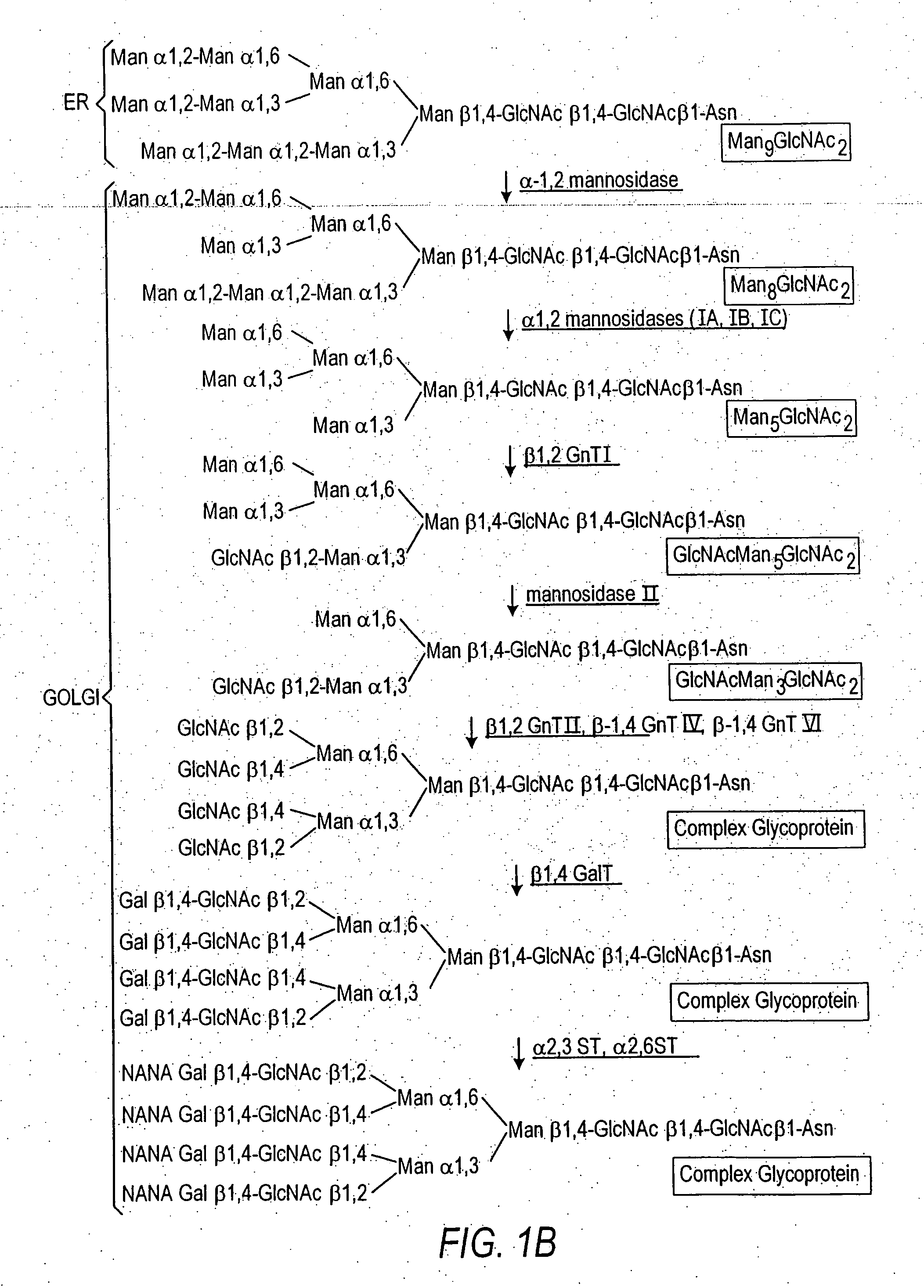
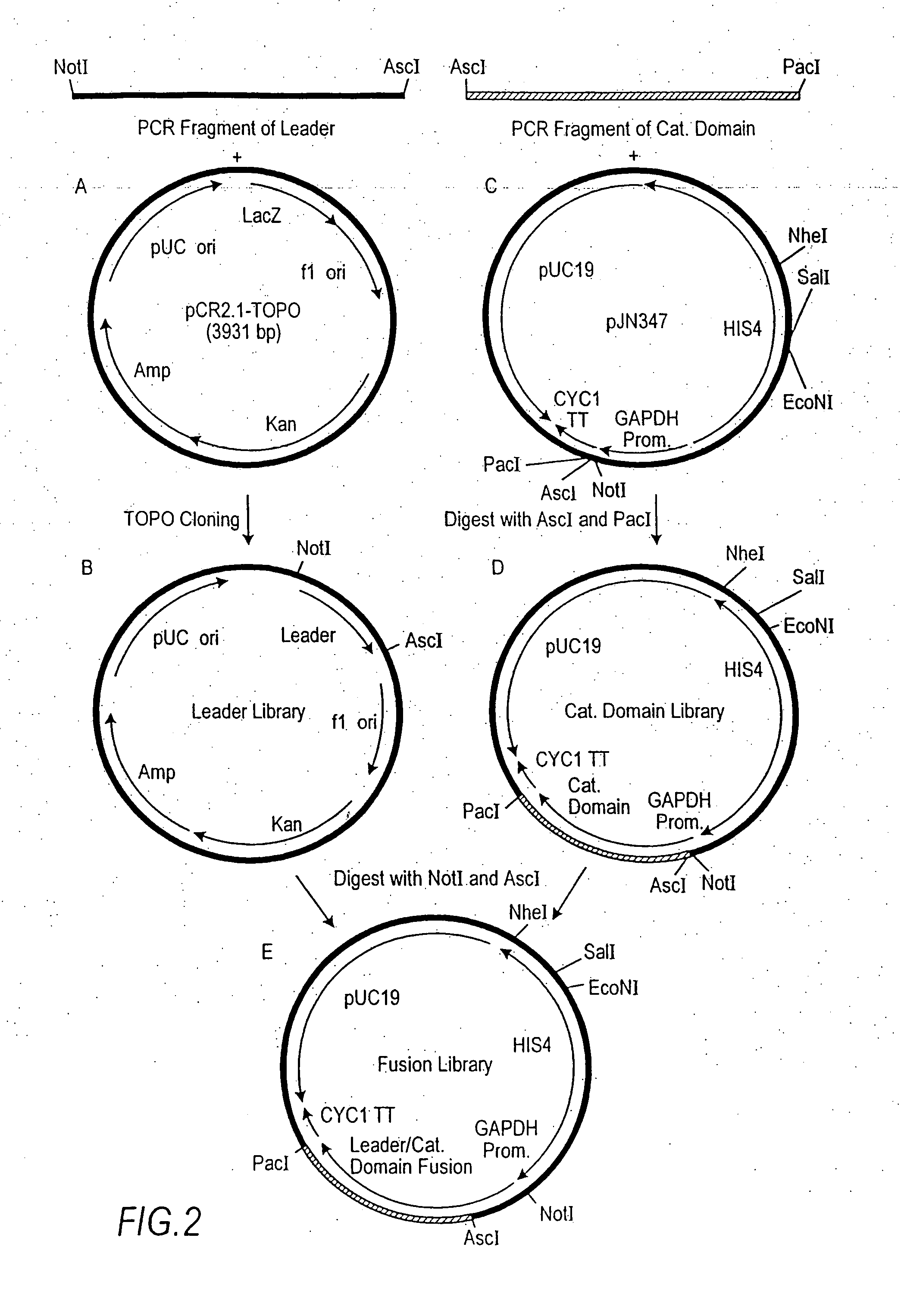
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Production of sialylated N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20060286637A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHeterologousSialic acid aldolase
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
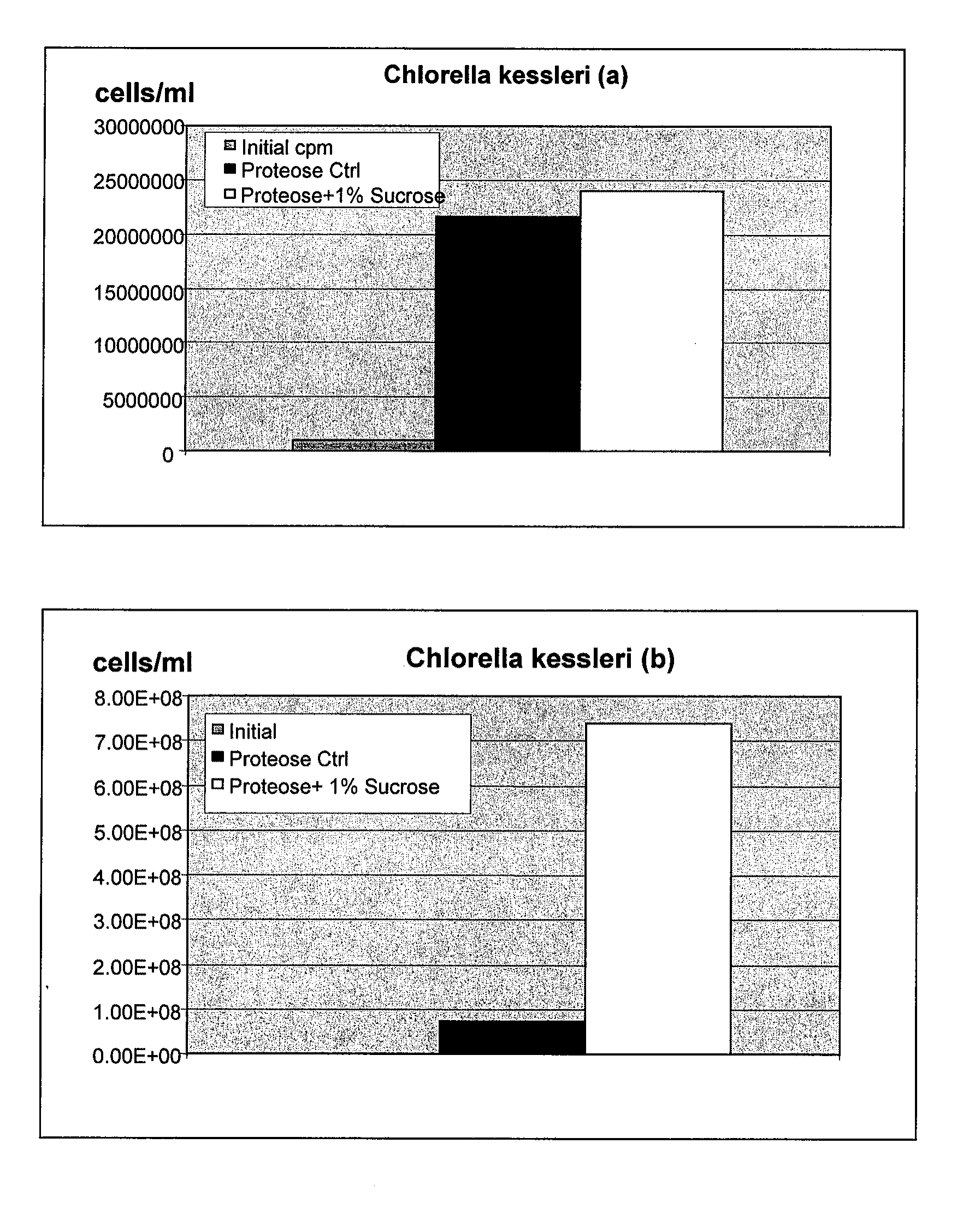
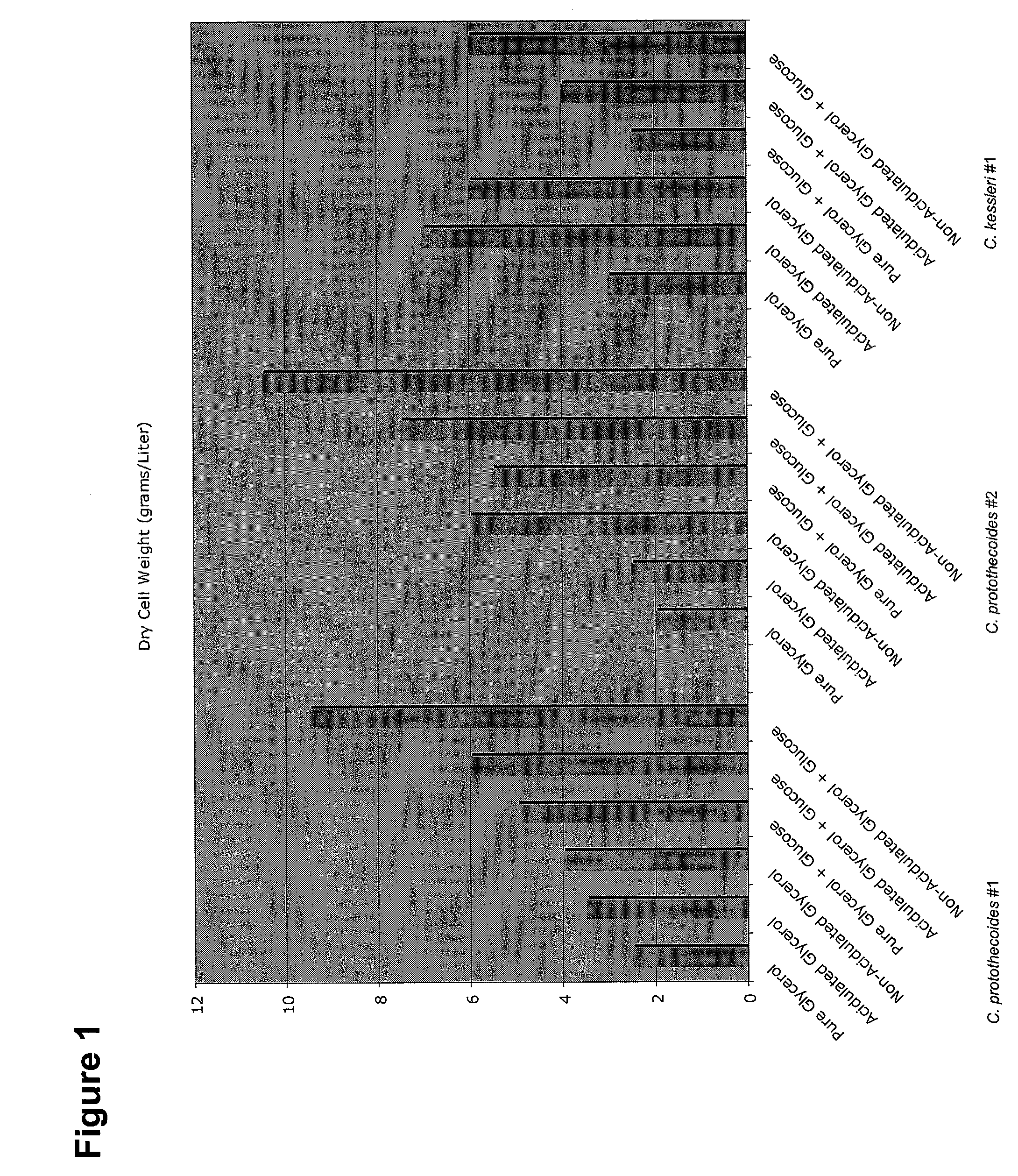
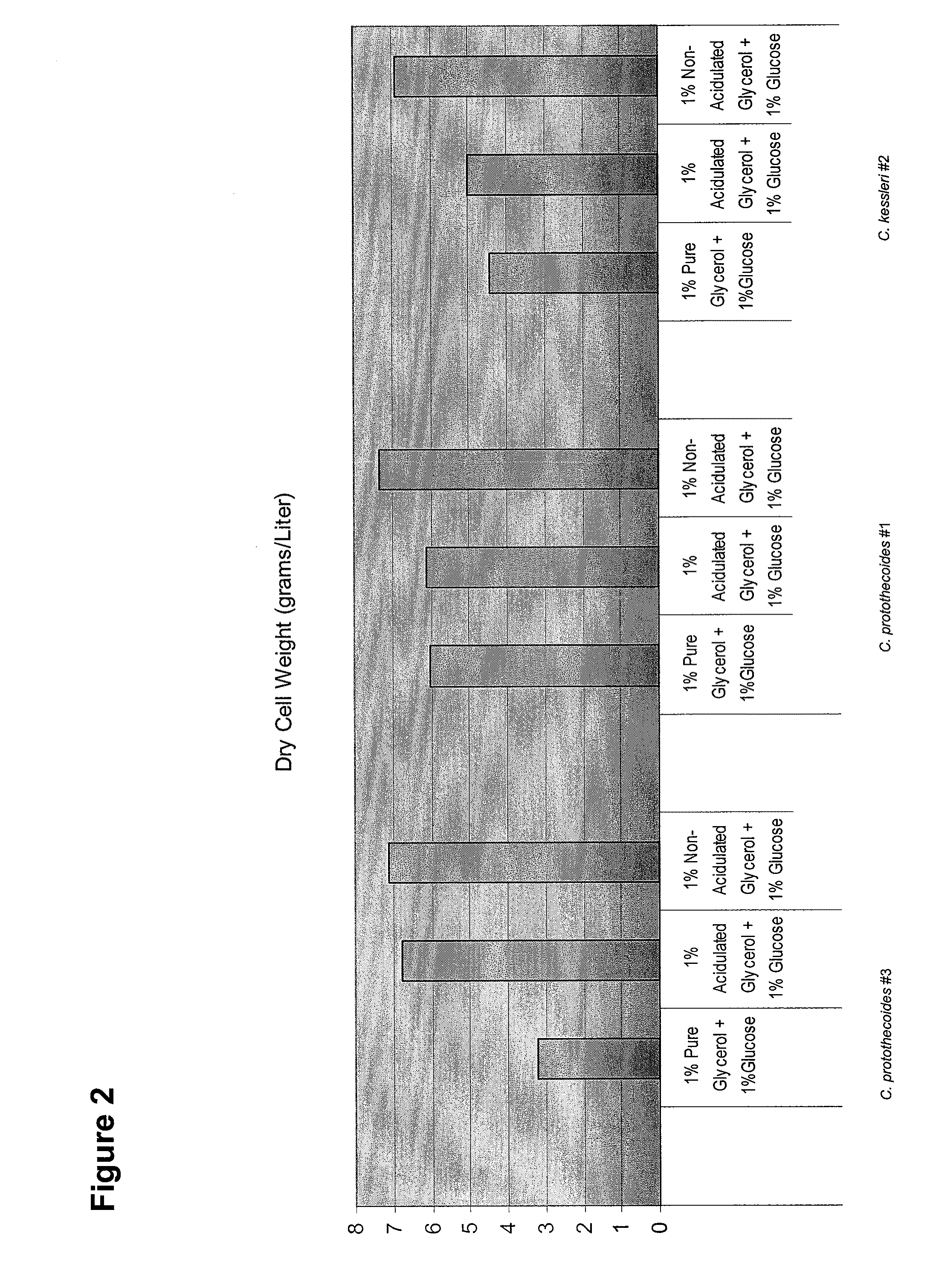
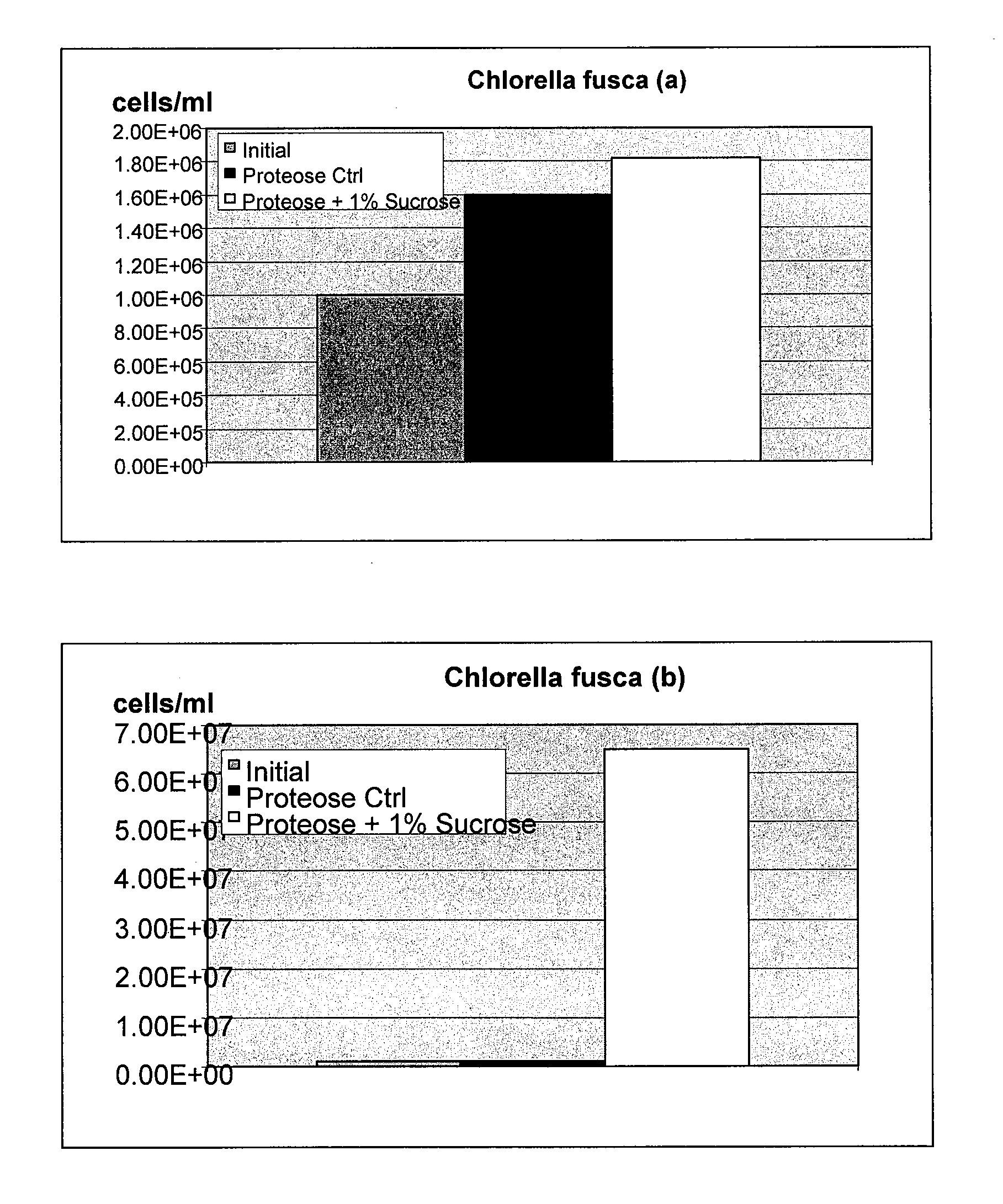
Use of Cellulosic Materials for Cultivation of Microorganisms
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
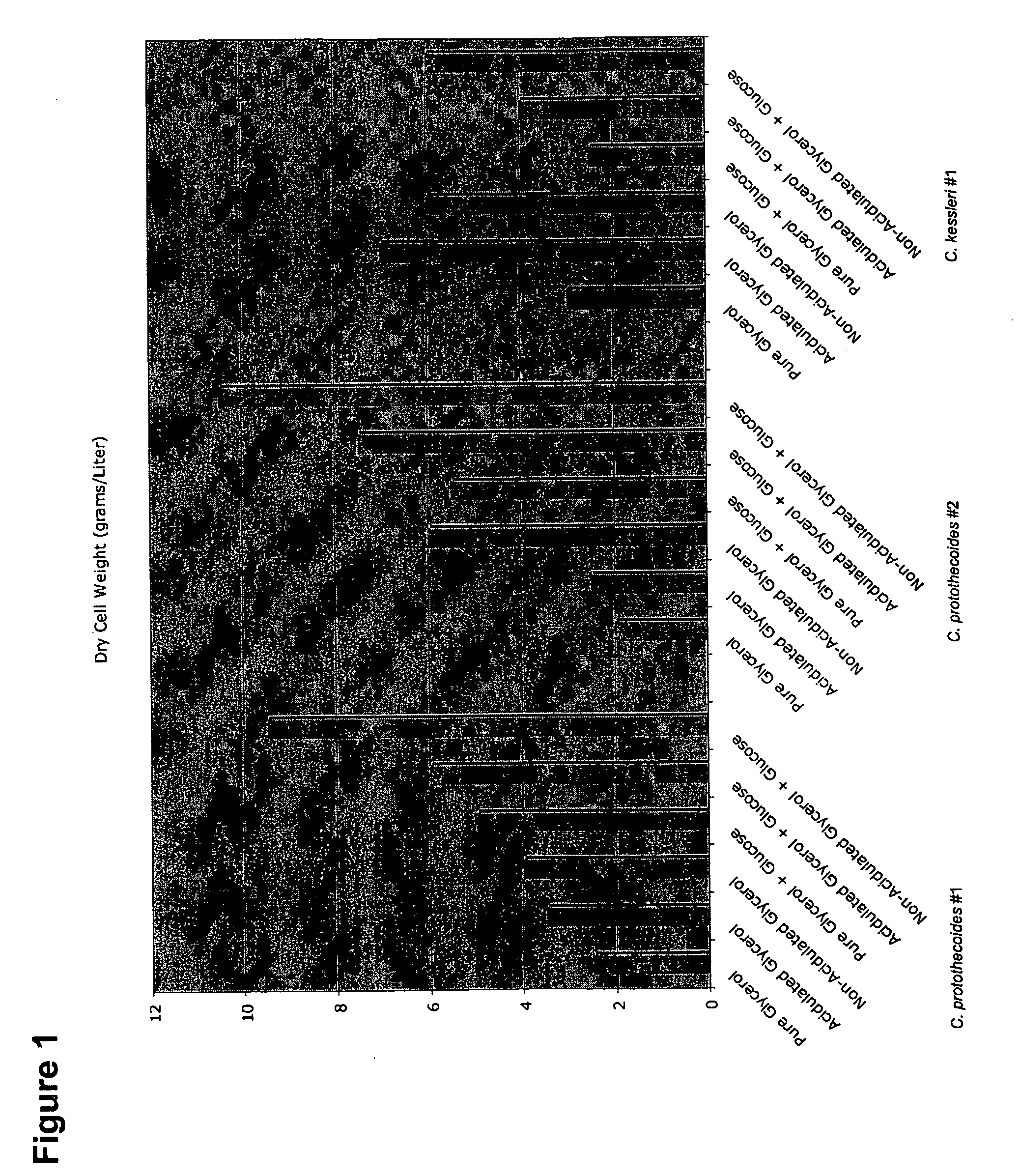
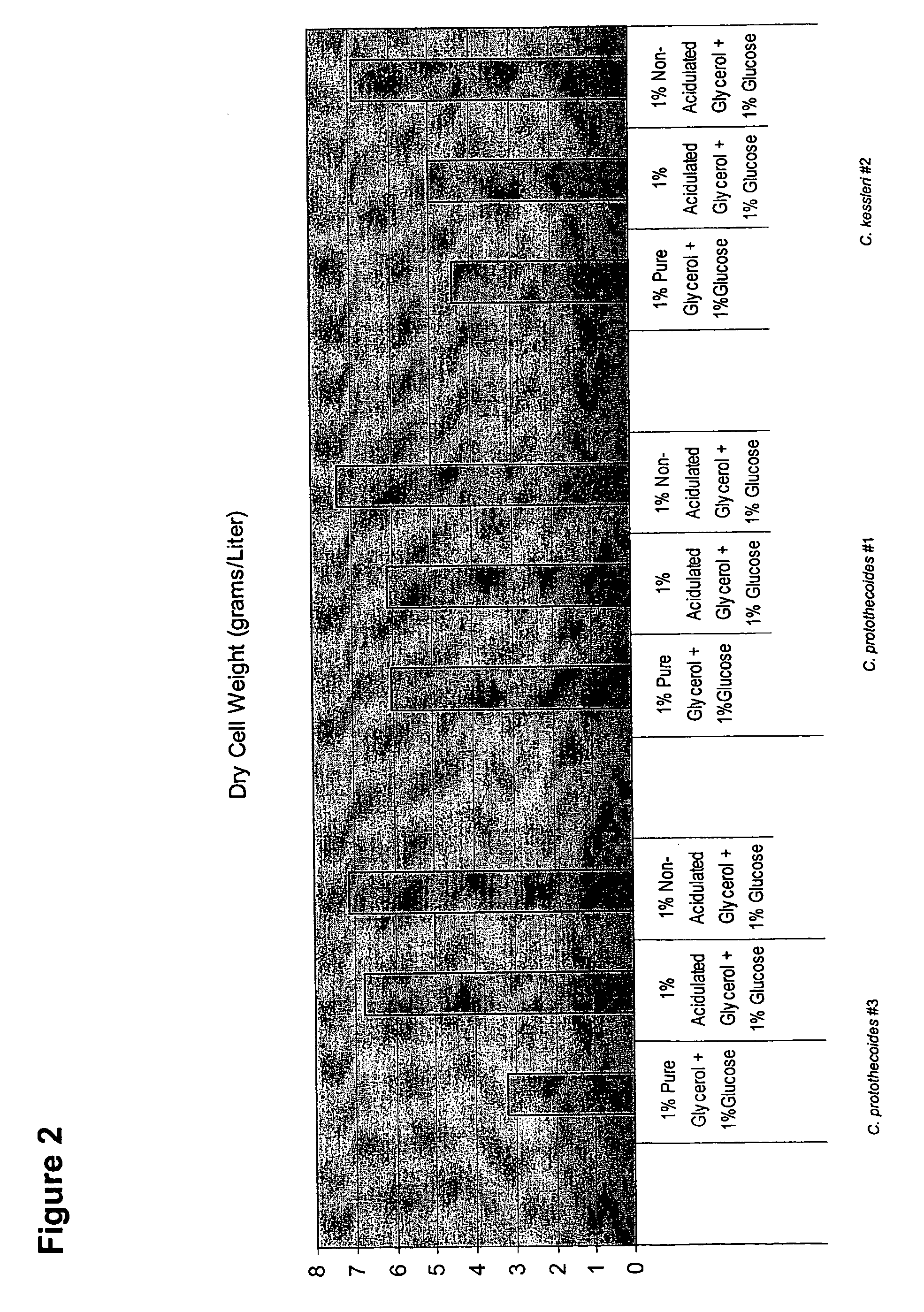
Glycerol Feedstock Utilization for Oil-Based Fuel Manufacturing
InactiveUS20090004715A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid chemical modificationMicroorganismTransesterification
The invention provides methods of manufacturing biodiesel and other oil-based compounds using glycerol and combinations of glycerol and other feedstocks as an energy source in fermentation of oil-bearing microorganisms. Methods disclosed herein include processes for manufacturing high nutrition edible oils from non-food feedstock materials such as waste products from industrial waste transesterification processes. Also included are methods of increasing oil yields by temporally separating glycerol and other feedstocks during cultivation processes. Also provided herein are oil-bearing microbes containing exogenous oil production genes and methods of cultivating such microbes on glycerol and other feedstocks.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS7288375B2Less immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods and compositions for cellular and metabolic engineering
InactiveUS7105297B2Improve abilitiesExcellent catalytic performanceImmunoglobulinsFermentationIndividual geneOrganism
The present invention is generally directed to the evolution of new metabolic pathways and the enhancement of bioprocessing through a process herein termed recursive sequence recombination. Recursive sequence recombination entails performing iterative cycles of recombination and screening or selection to “evolve” individual genes, whole plasmids or viruses, multigene clusters, or even whole genomes. Such techniques do not require the extensive analysis and computation required by conventional methods for metabolic engineering.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
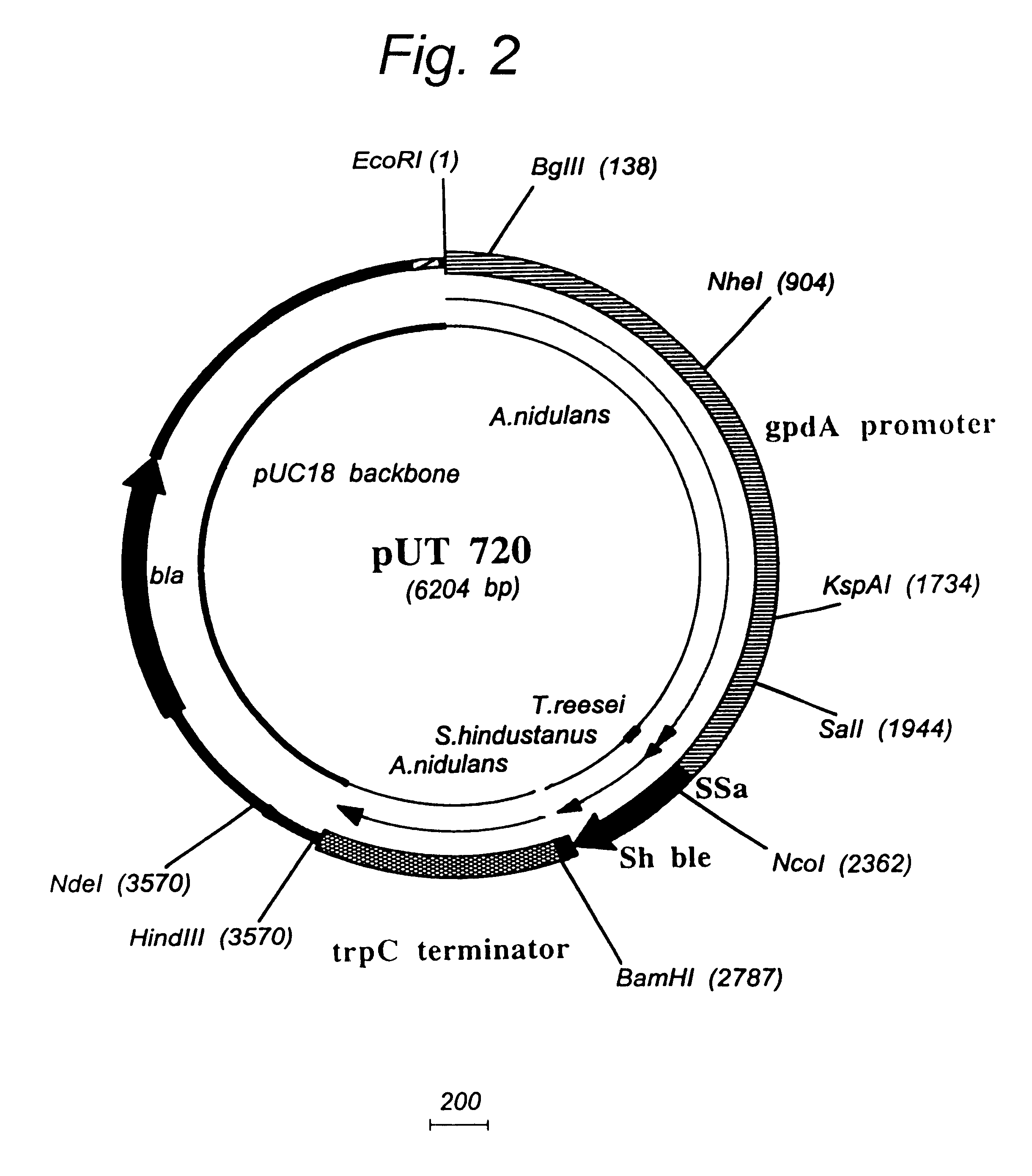
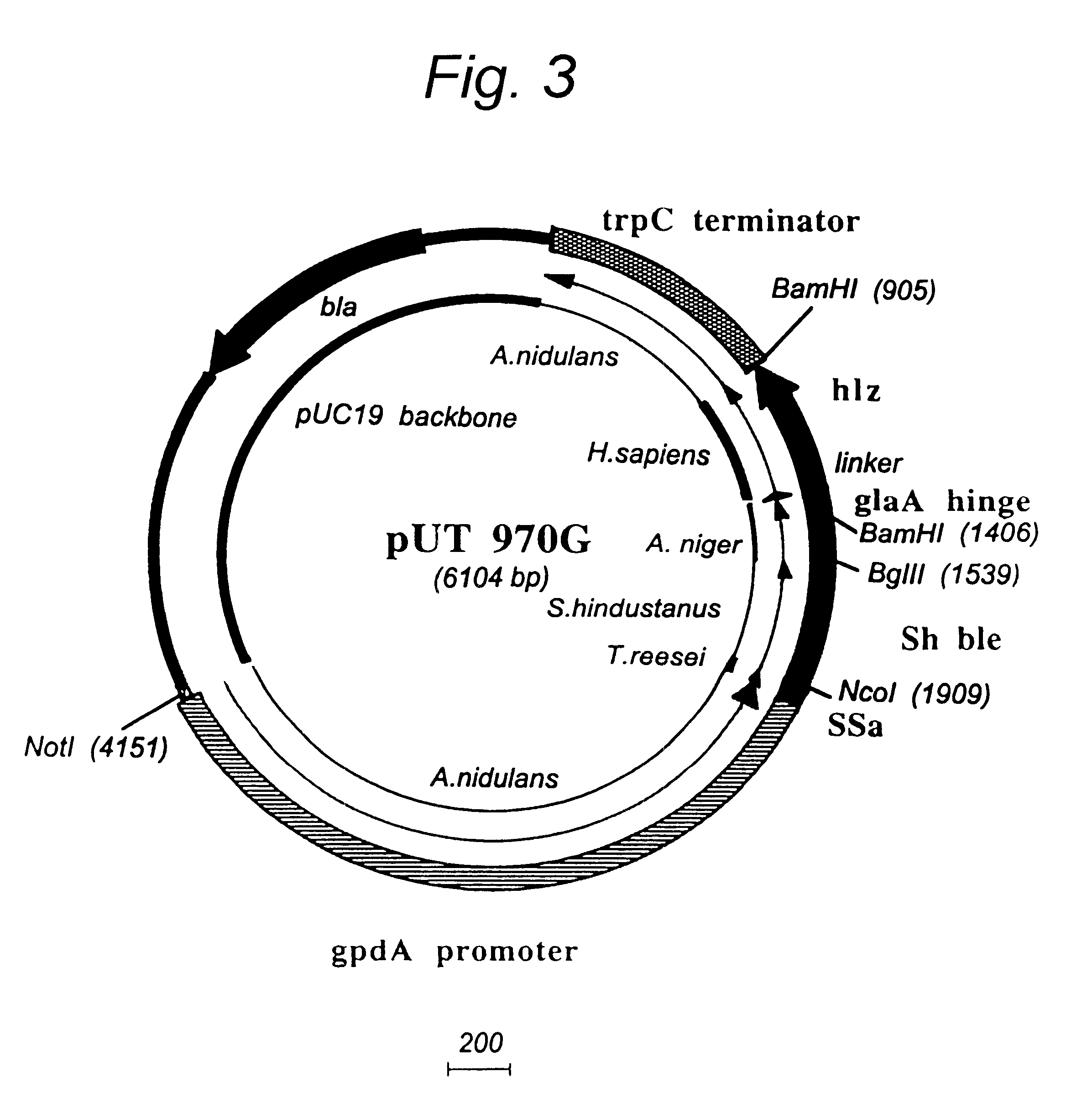
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
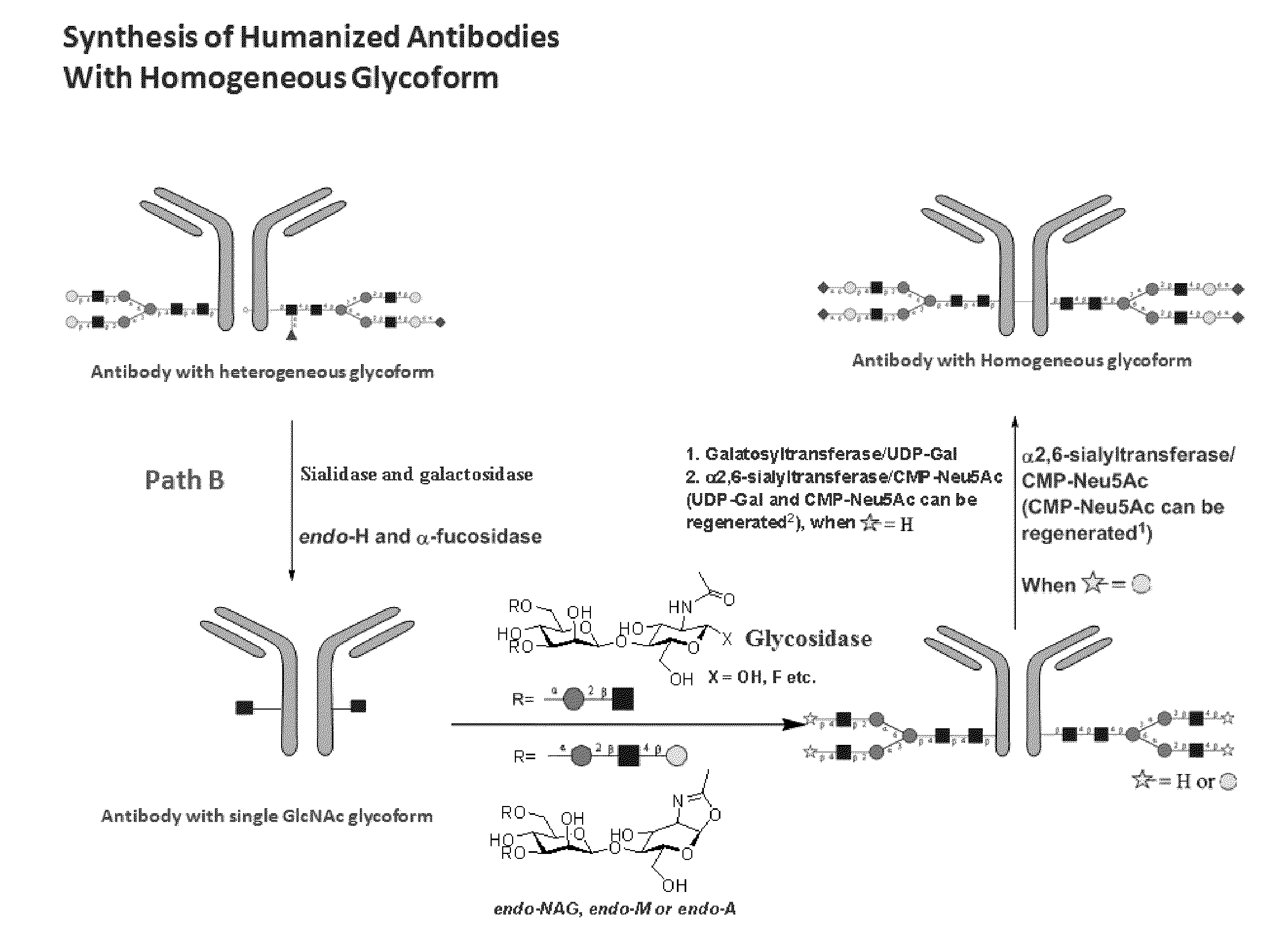
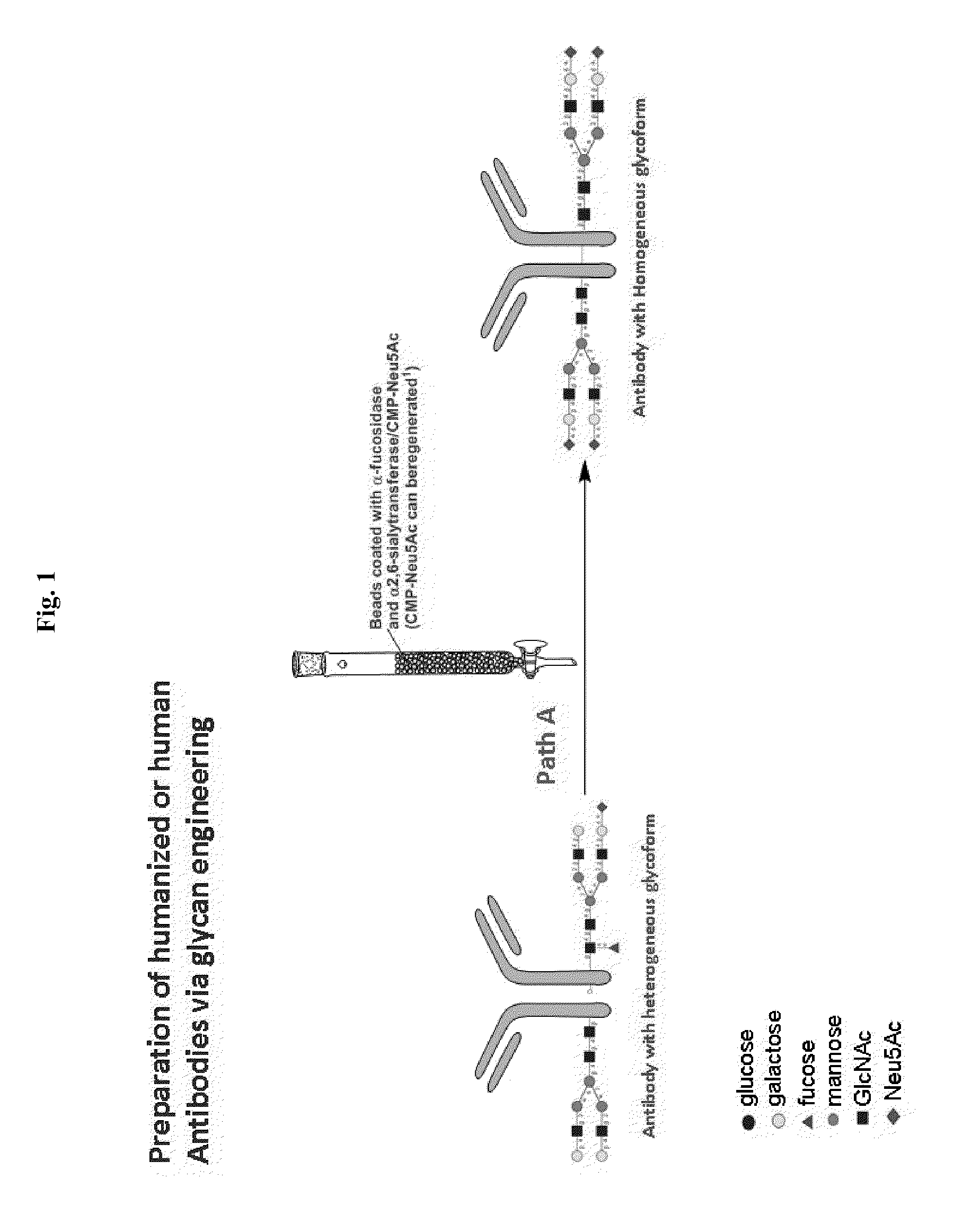
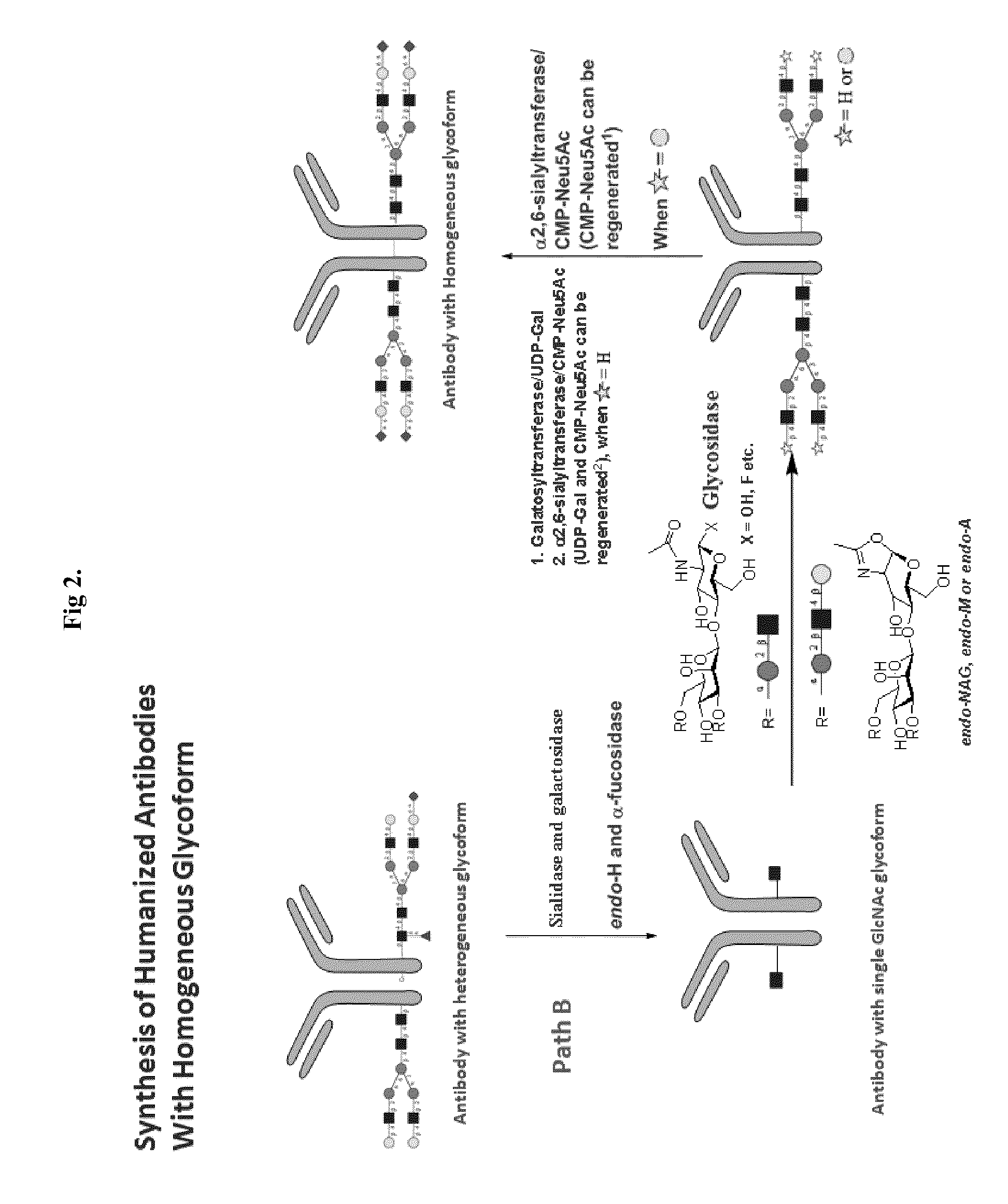
Methods for modifying human antibodies by glycan engineering
ActiveUS20110263828A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityImmunoglobulinsFermentationGlycanAntibody fragments
Modified Fc regions of antibodies and antibody fragments, both human and humanized, and having enhanced stability and efficacy, are provided. Fc regions with core fucose residues removed, and attached to oligosaccharides comprising terminal sialyl residues, are provided. Antibodies comprising homogeneous glycosylation of Fc regions with specific oligosaccharides are provided. Fc regions conjugated with homogeneous glycoforms of monosaccharides and trisaccharides, are provided. Methods of preparing human antibodies with modified Fc using glycan engineering, are provided.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6518065B1Less immunogenicImmunoglobulinsLibrary member identificationMutated proteinNucleotide
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Enzymes for starch processing
InactiveUS20060148054A1Good curative effectActivity be alteredFungiSugar derivativesCarbohydrate-binding proteinAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to polypeptides comprising a carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and,an alpha-amylase amino acid sequence as well as to the application of such polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
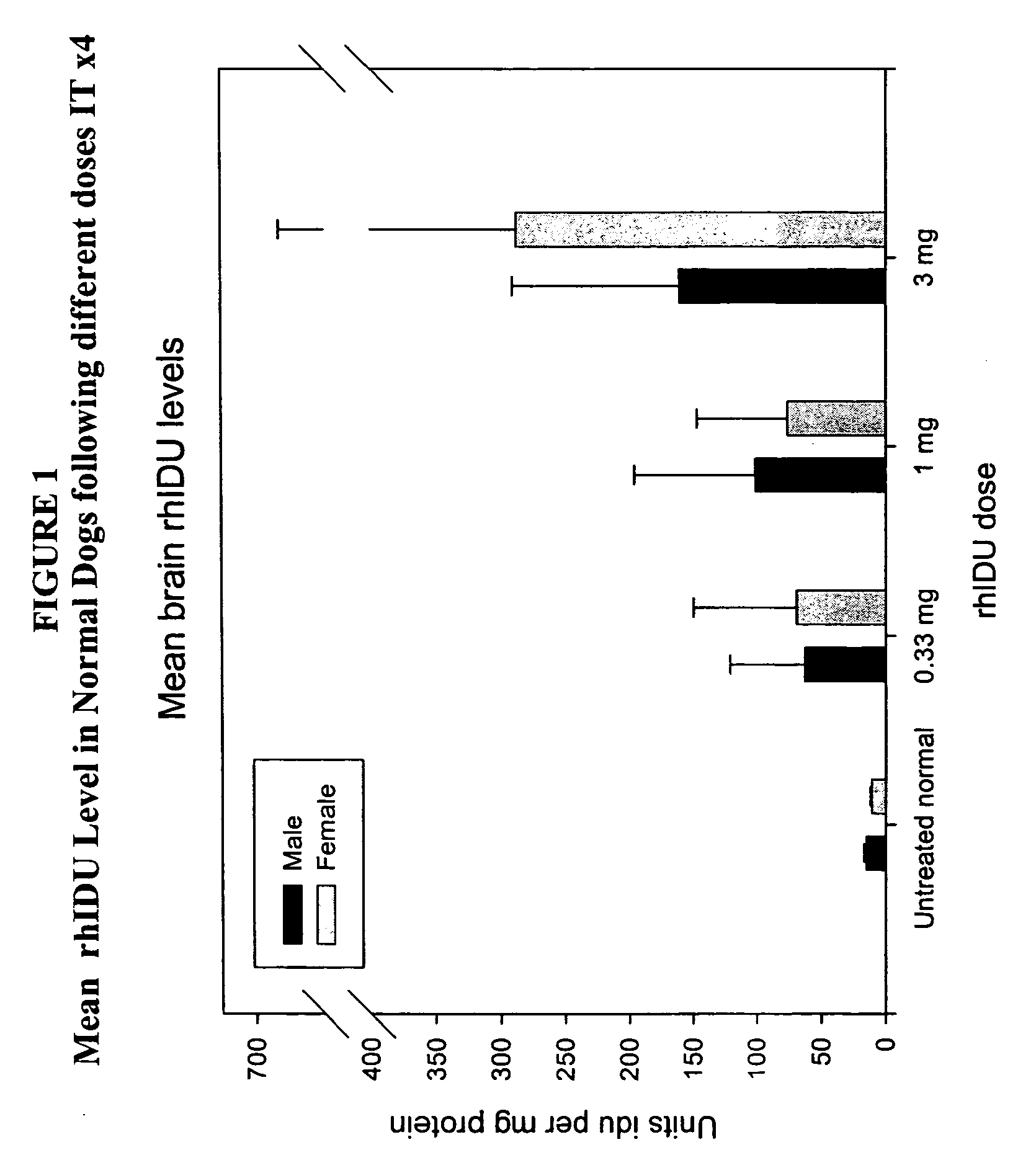
Delivery of therapeutic compounds to the brain and other tissues
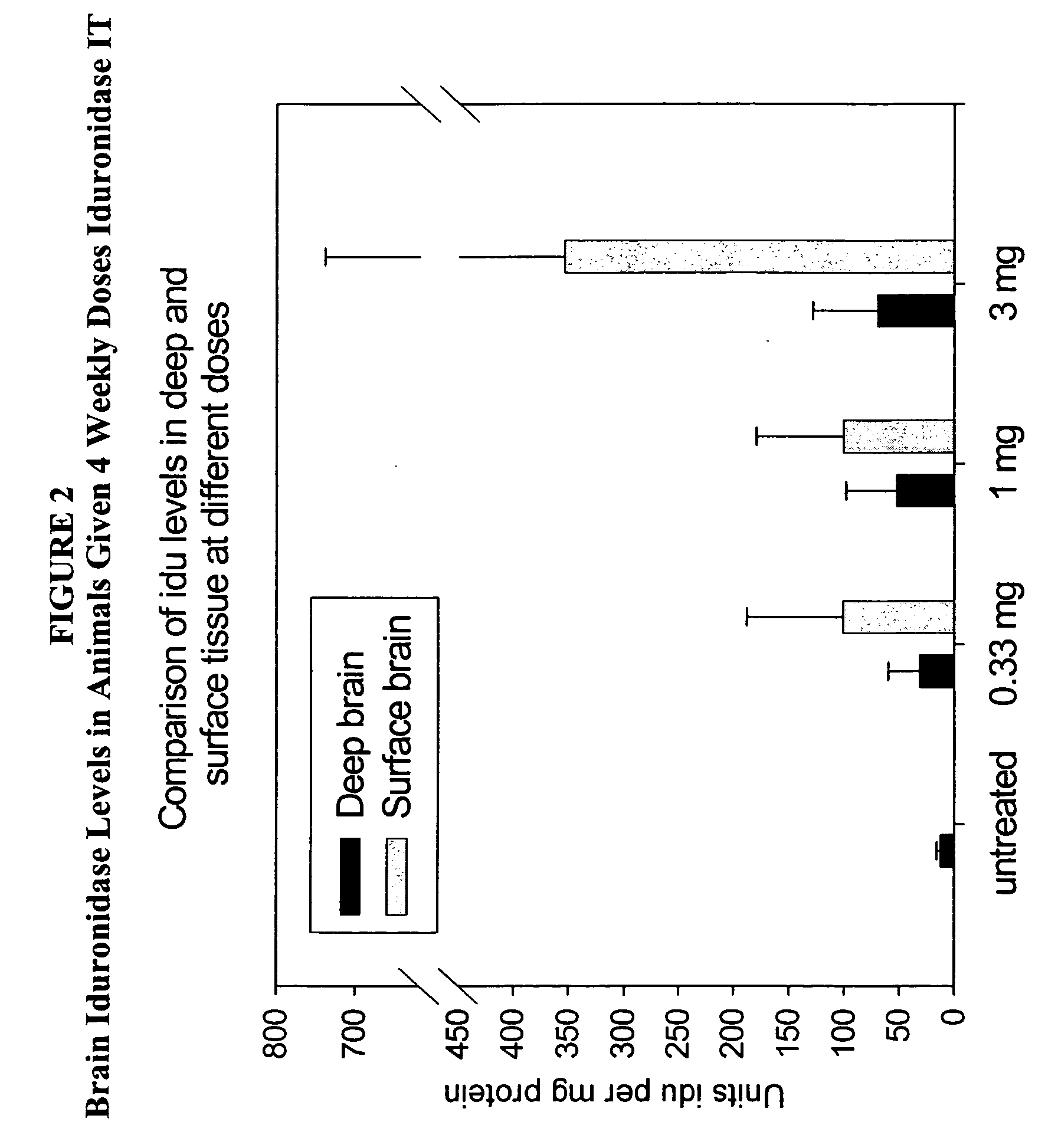
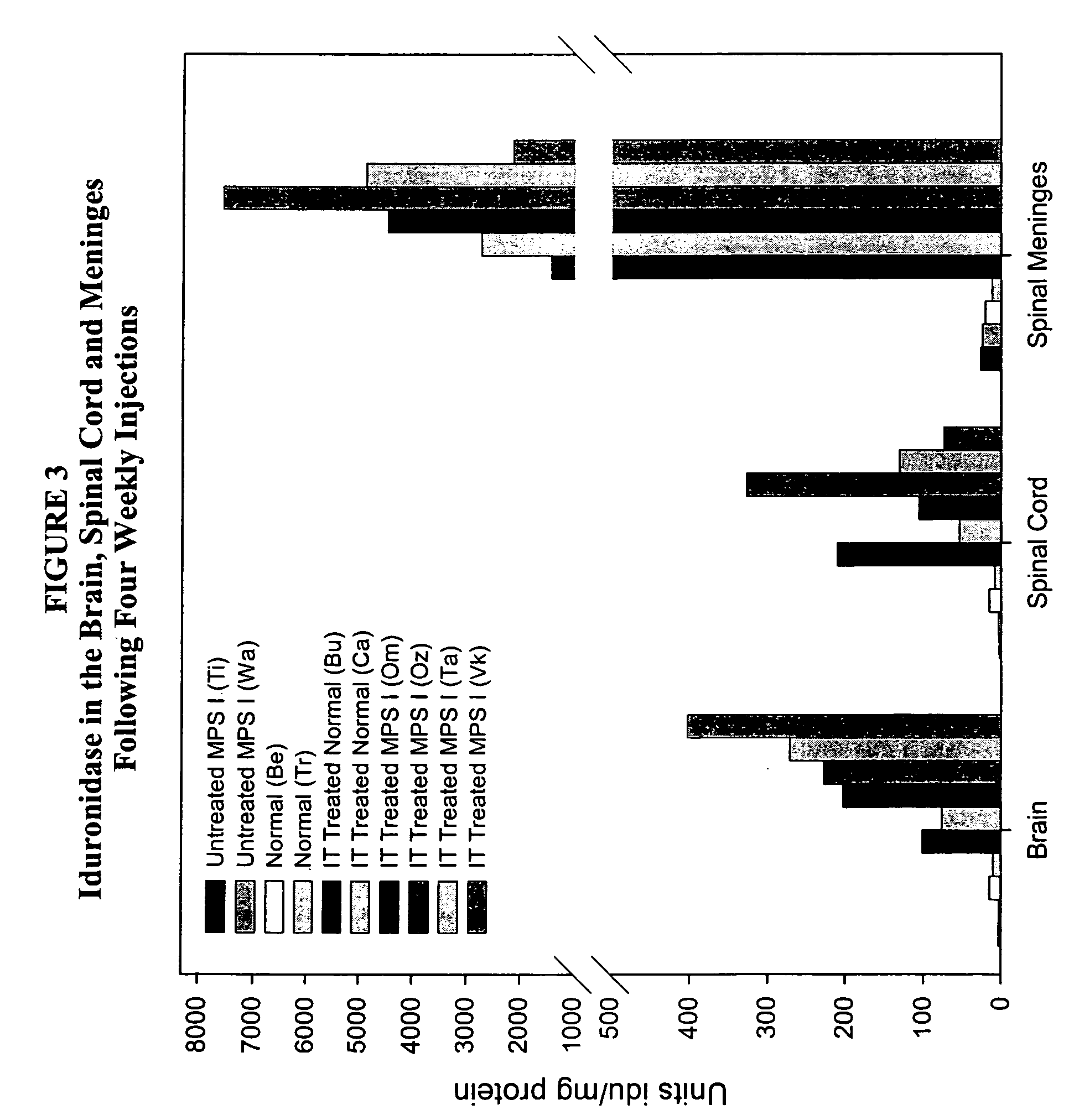
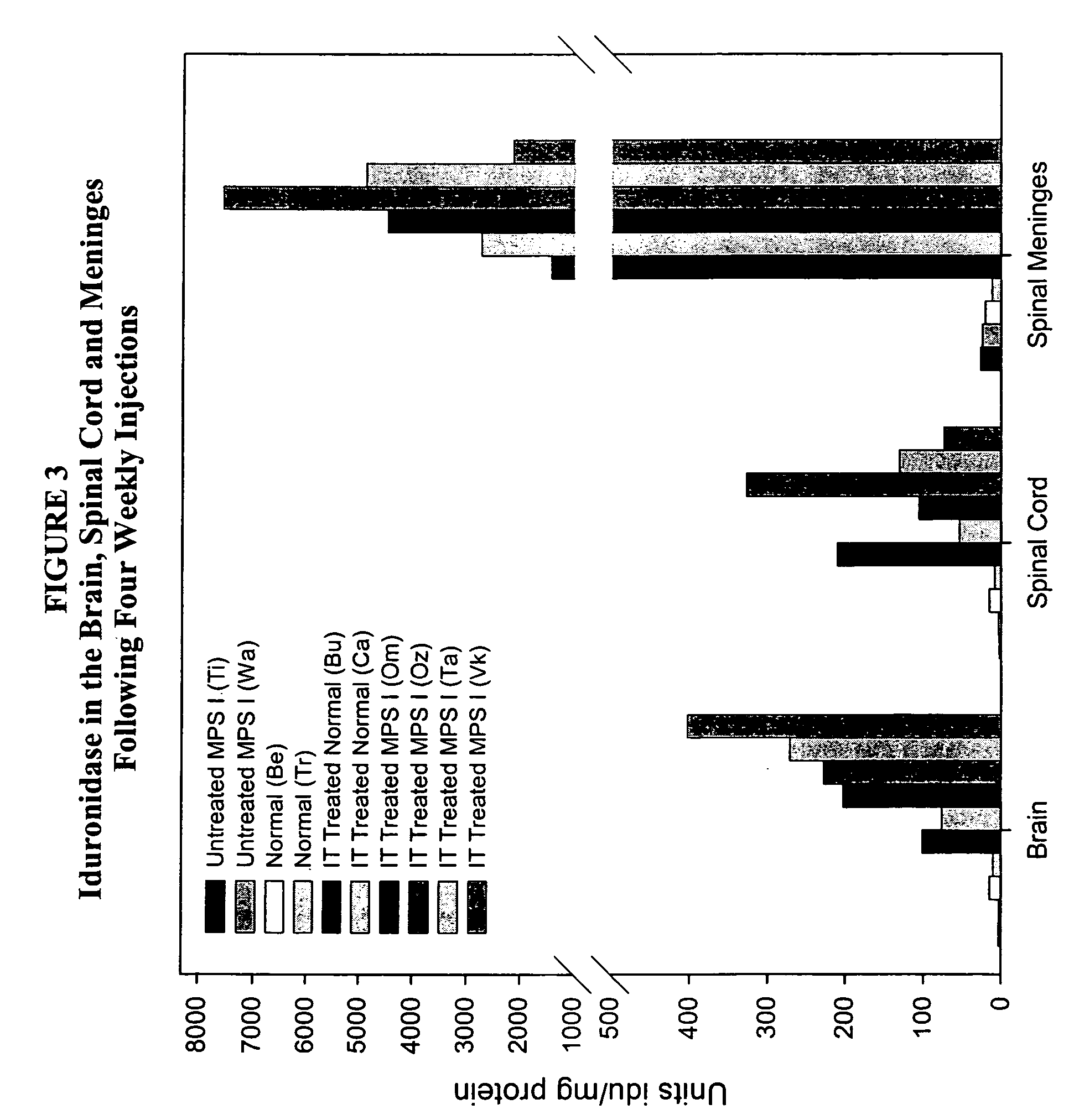
ActiveUS20050048047A1Reduces and eliminates glycogen storage granuleReduce eliminateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMeningesIntrathecal use
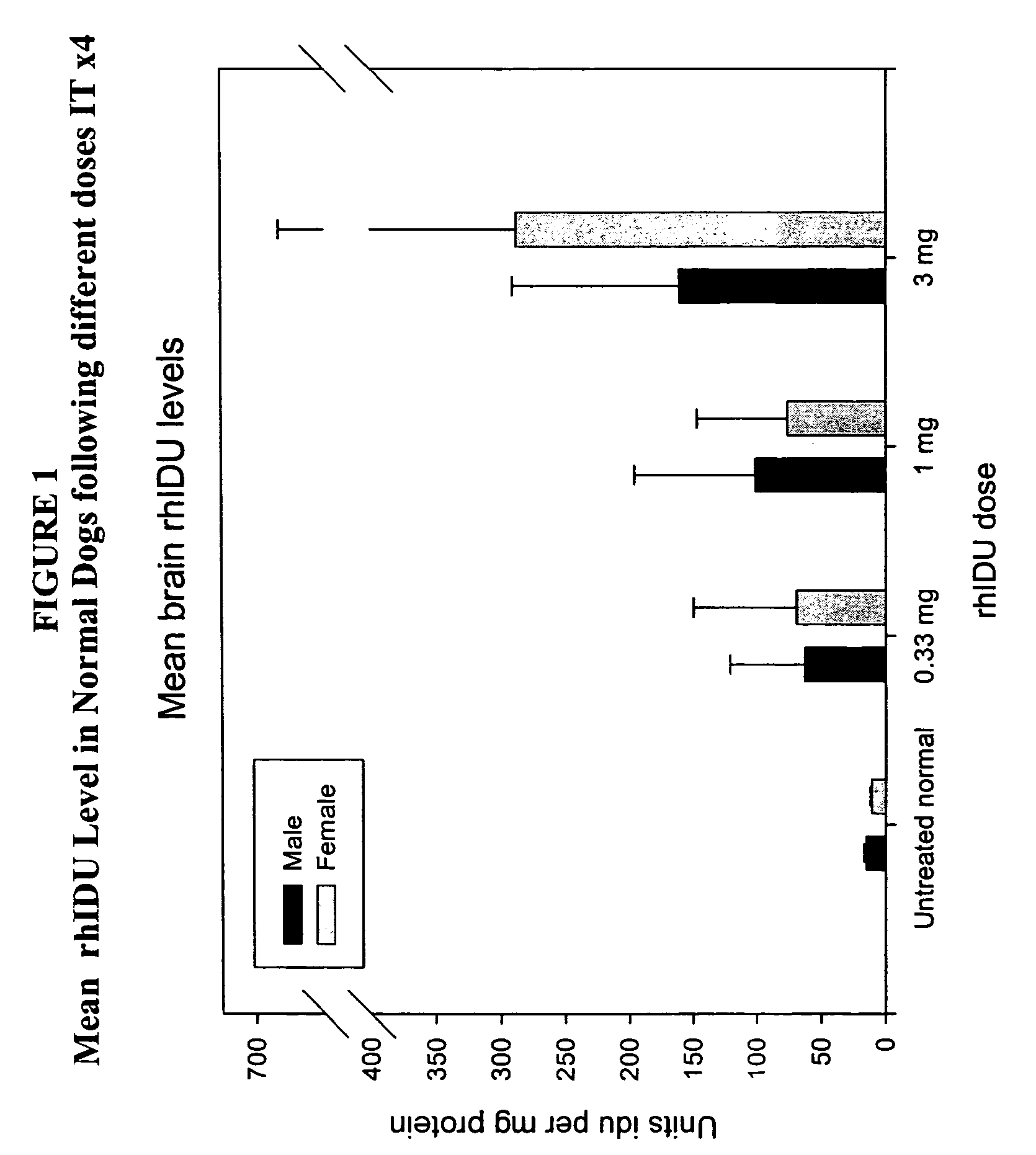
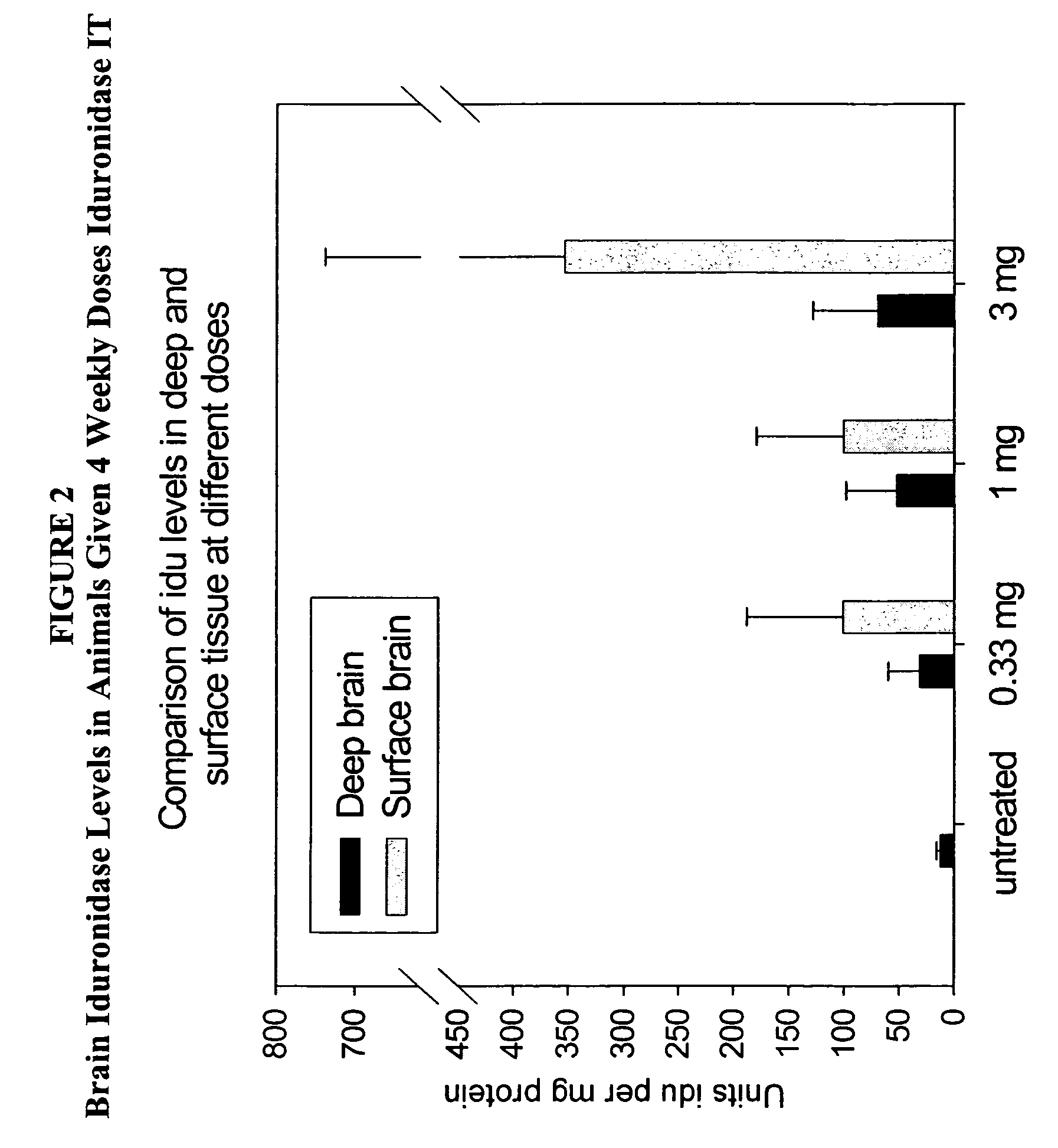
The present invention relates to the intrathecal (IT) administration of recombinant enzyme to treat lysosomal storage disorders. In an exemplary embodiment, intrathecal administration of human α-L-iduronidase (rhIDU) injections in MPS I affected animals resulted in significant enzyme uptake, significant rh-iduronidase activity in brain and meninges and a decrease of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) storage in cells of MPS I subjects to that of normal subjects. Intrathecal administration proved more effective than intravenous treatment at alleviating MPS I symptoms, indicating it is a useful method of treating lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
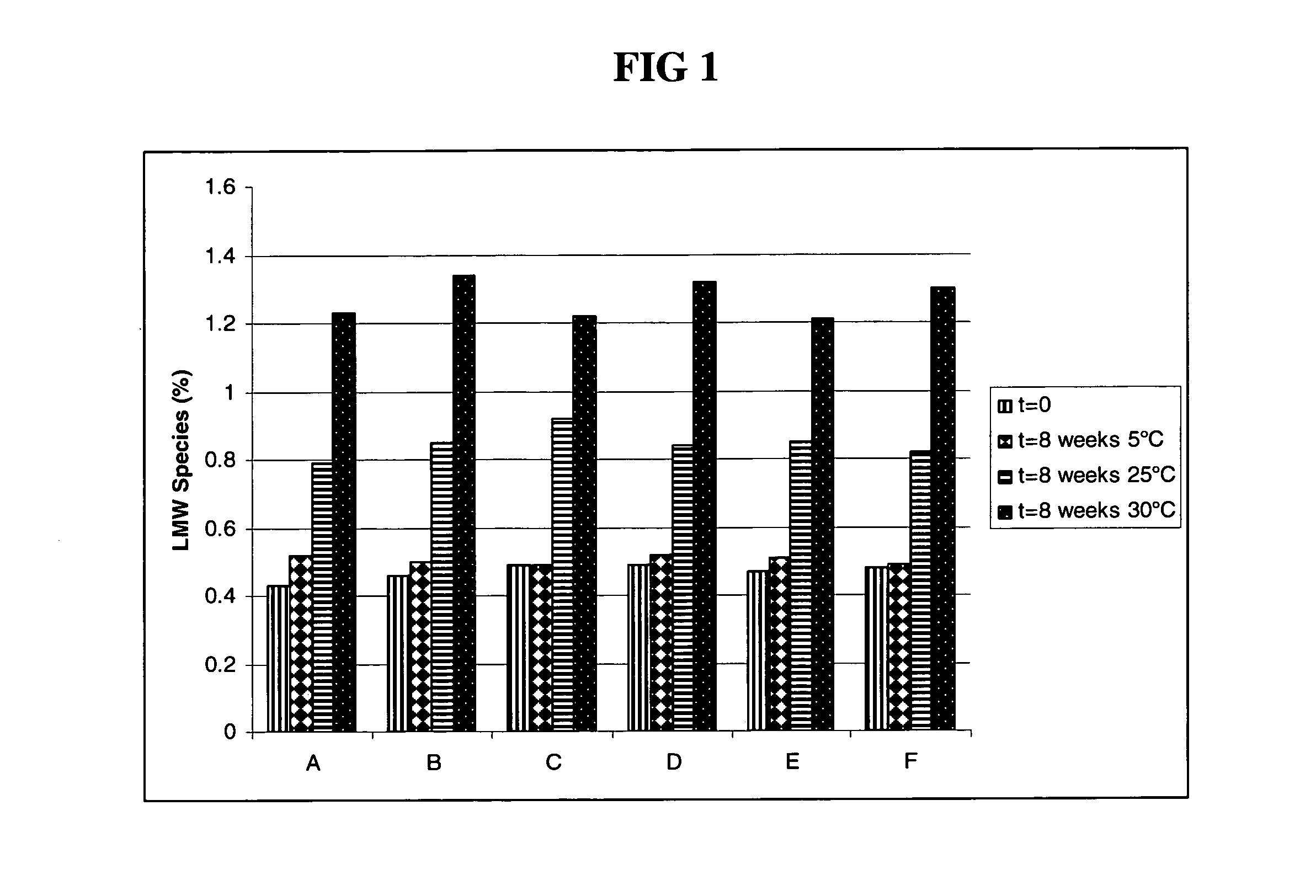
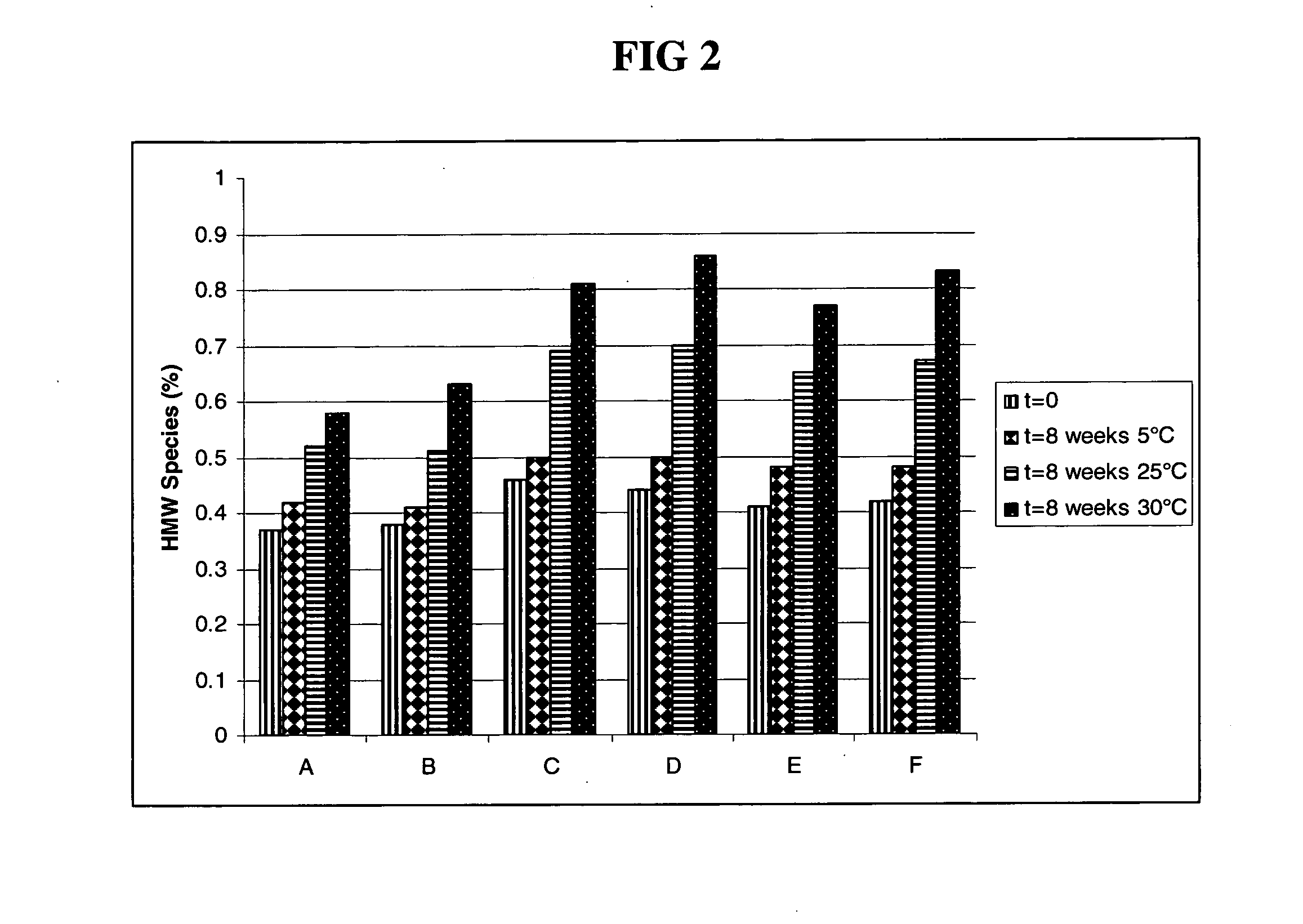
Subcutaneous anti-HER2 antibody formulations and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a highly concentrated, stable pharmaceutical formulation of a pharmaceutically active anti-HER2 antibody, such as e.g. Trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN™), Pertuzumab or T-DM1, or a mixture of such antibody molecules for subcutaneous injection. In particular, the present invention relates to formulations comprising, in addition to a suitable amount of the anti-HER2 antibody, an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme as a combined formulation or for use in form of a co-formulation. The formulations comprise additionally at least one buffering agent, such as e.g. a histidine buffer, a stabilizer or a mixture of two or more stabilizers (e.g. a saccharide, such as e.g. α,α-trehalose dihydrate or sucrose, and optionally methionine as a second stabilizer), a nonionic surfactant and an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme. Methods for preparing such formulations and their uses thereof are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
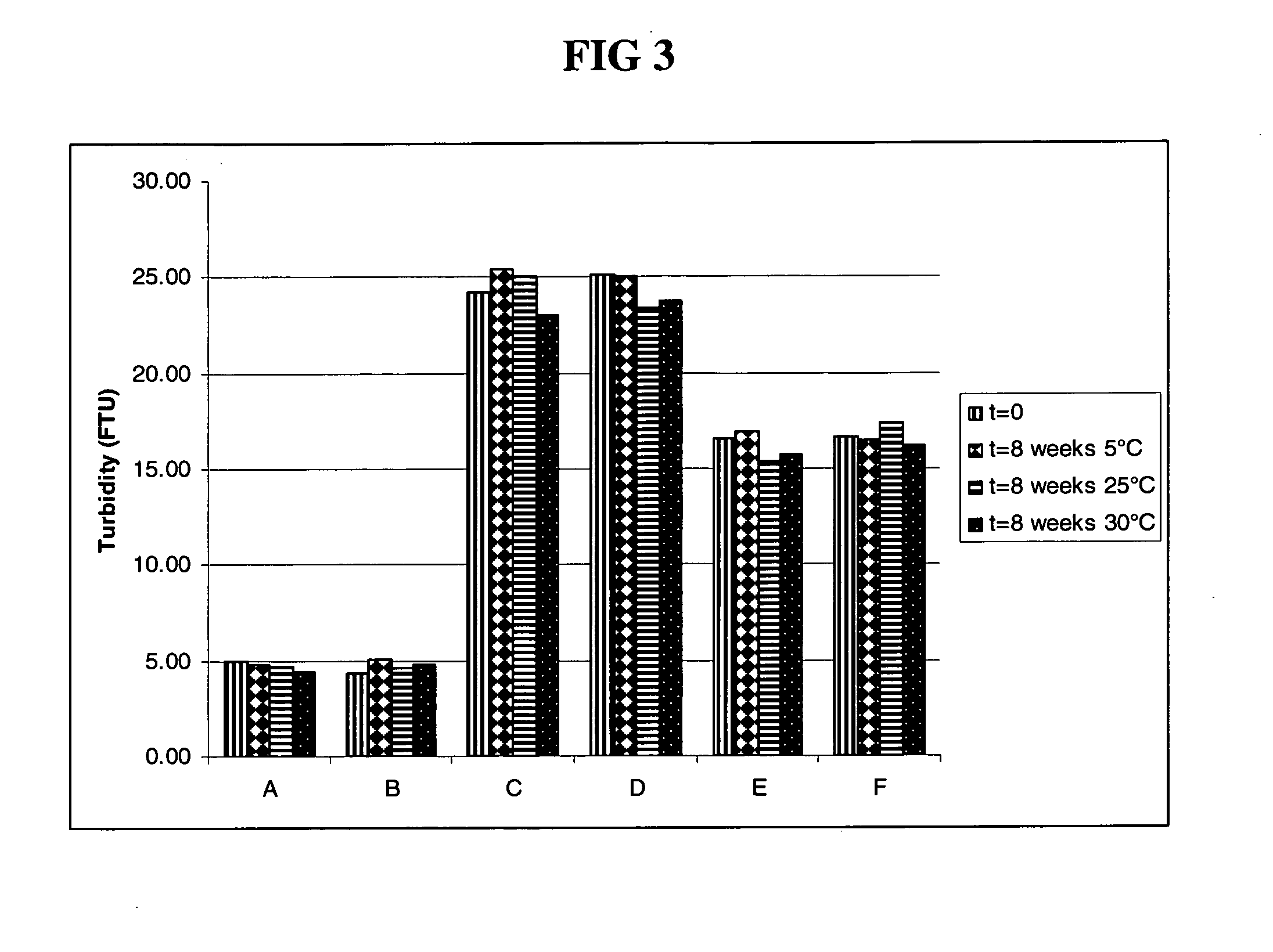
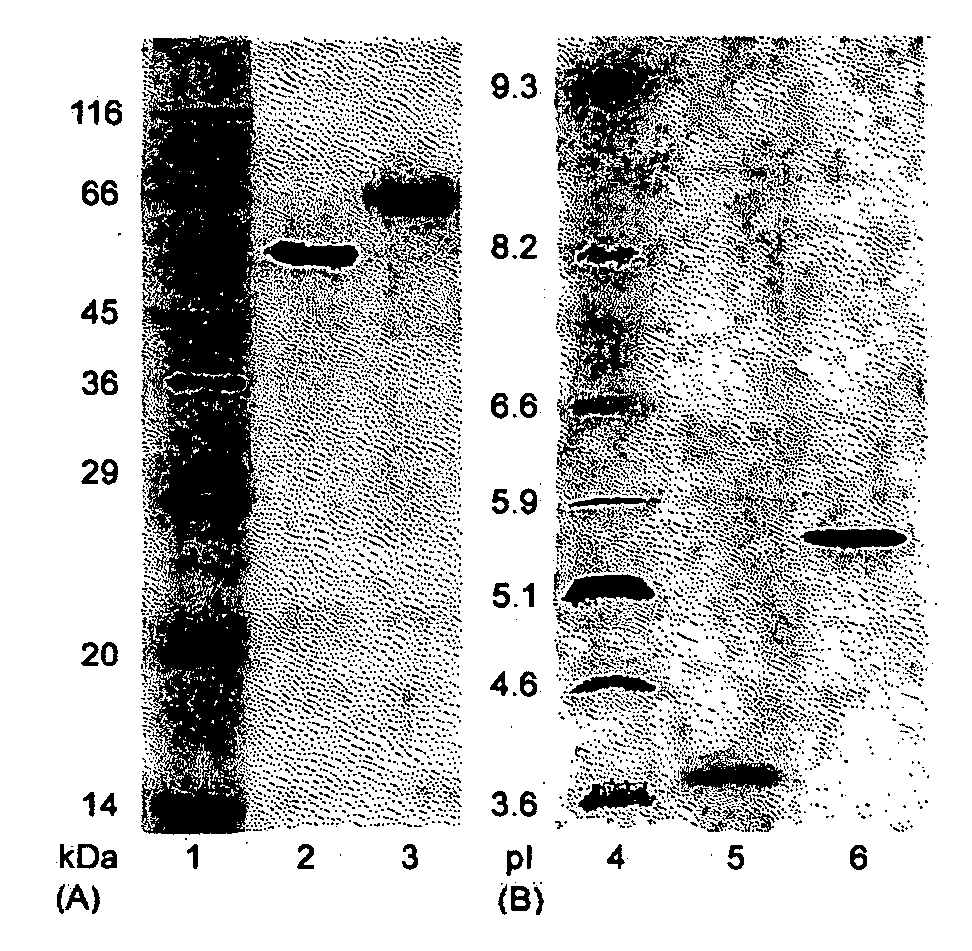
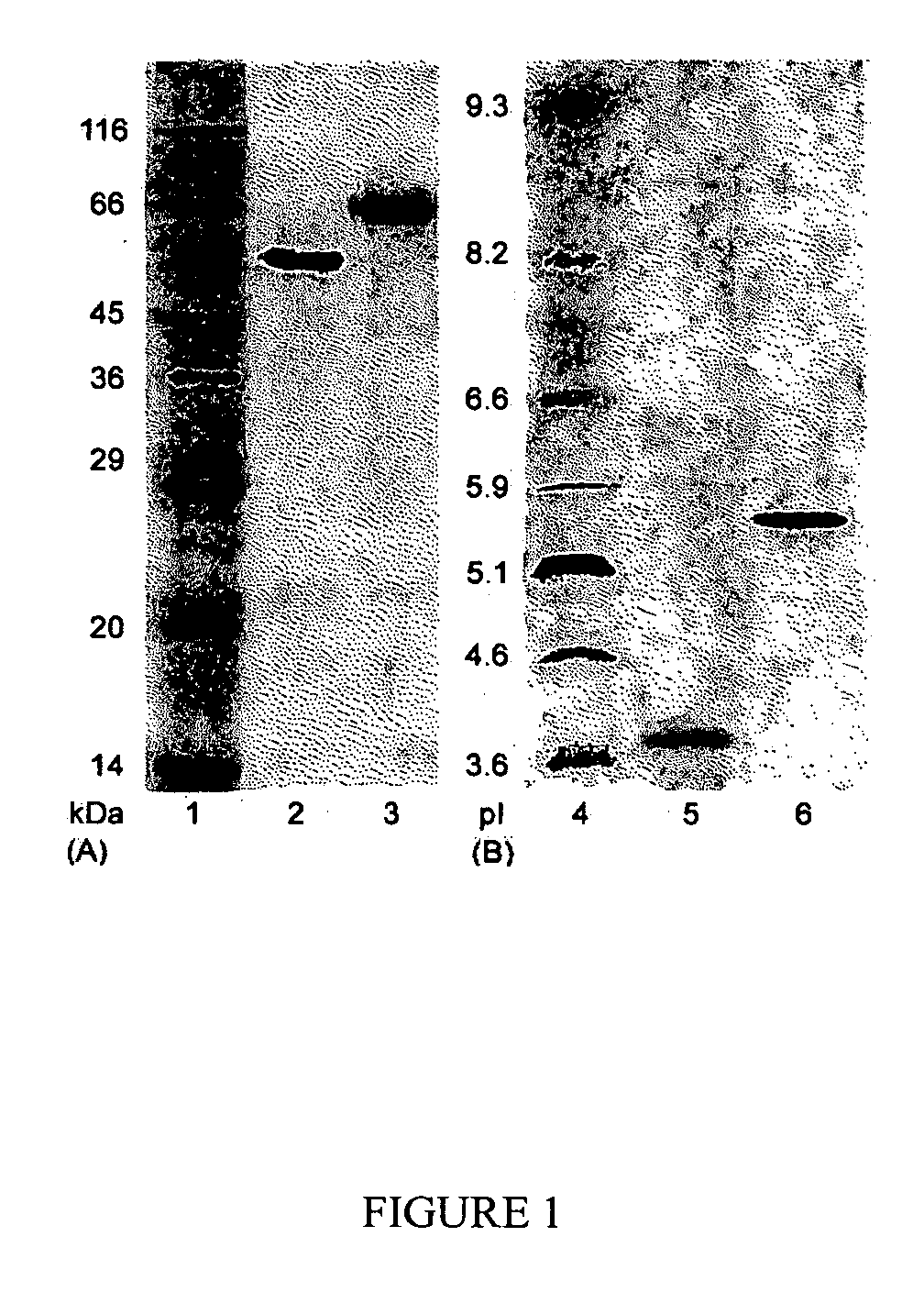
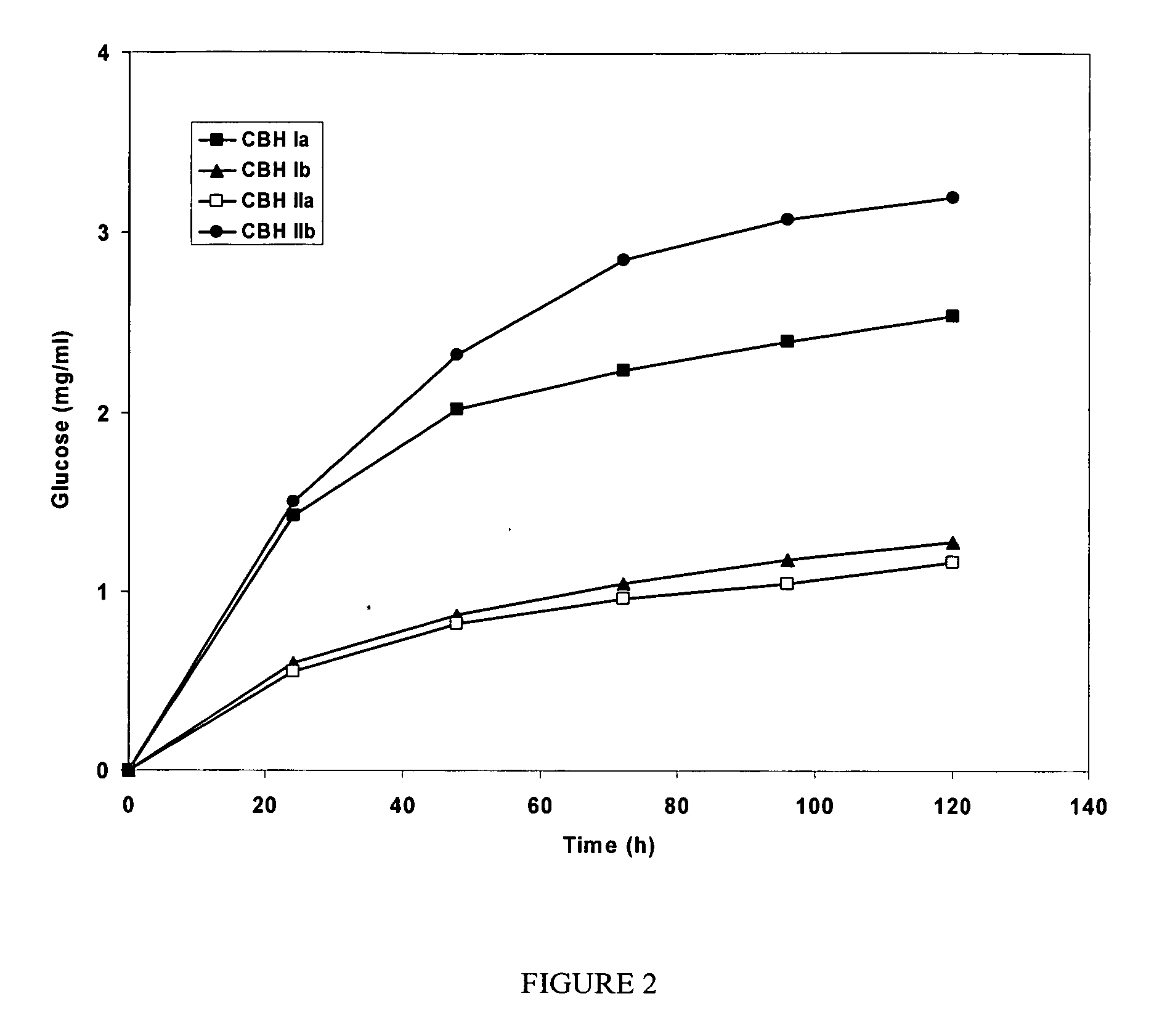
Construction of highly efficient cellulase compositions for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose
This invention provides novel enzyme compositions using newly identified and isolated C. lucknowense enzymes, including CBH Ib CBH IIb, EG II, EG VI, β-glucosidase, and xylanase II in conjunction with previously identified enzymes CBH Ia, CBH IIa (previously described as Endo 43), and EG V. These enzyme compositions demonstrate an extremely high ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass (e.g., Avicel, cotton, Douglas fir wood pretreated by organosolv) to glucose. CBH Ia and IIb, which both have a cellulose-binding module (CBM) displayed a pronounced synergism with three major endoglucanases (EG II, EG V, EG VI) from the same fungus in hydrolysis of cotton as well as a strong synergy with each other. The enzyme compositions are effective in hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Enzyme delivery systems and methods of preparation and use
ActiveUS20100260857A1Improve stabilityEnhanced administration propertyPowder deliveryNervous disorderDiseaseCystic fibrosis lungs
This invention relates to coated digestive enzyme preparations and enzyme delivery systems and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the preparations. This invention further relates to methods of preparation and use of the systems, pharmaceutical compositions and preparations to treat persons having ADD, ADHD, autism, cystic fibrosis and other behavioral and neurological disorders.
Owner:CUREMARK
Isolated nucleic acids encoding proteins with chitinase activity and uses thereof
InactiveUS7087810B2Increase resistanceMammal material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulinsBiotechnologyNematode infection
Owner:VERDIA +1
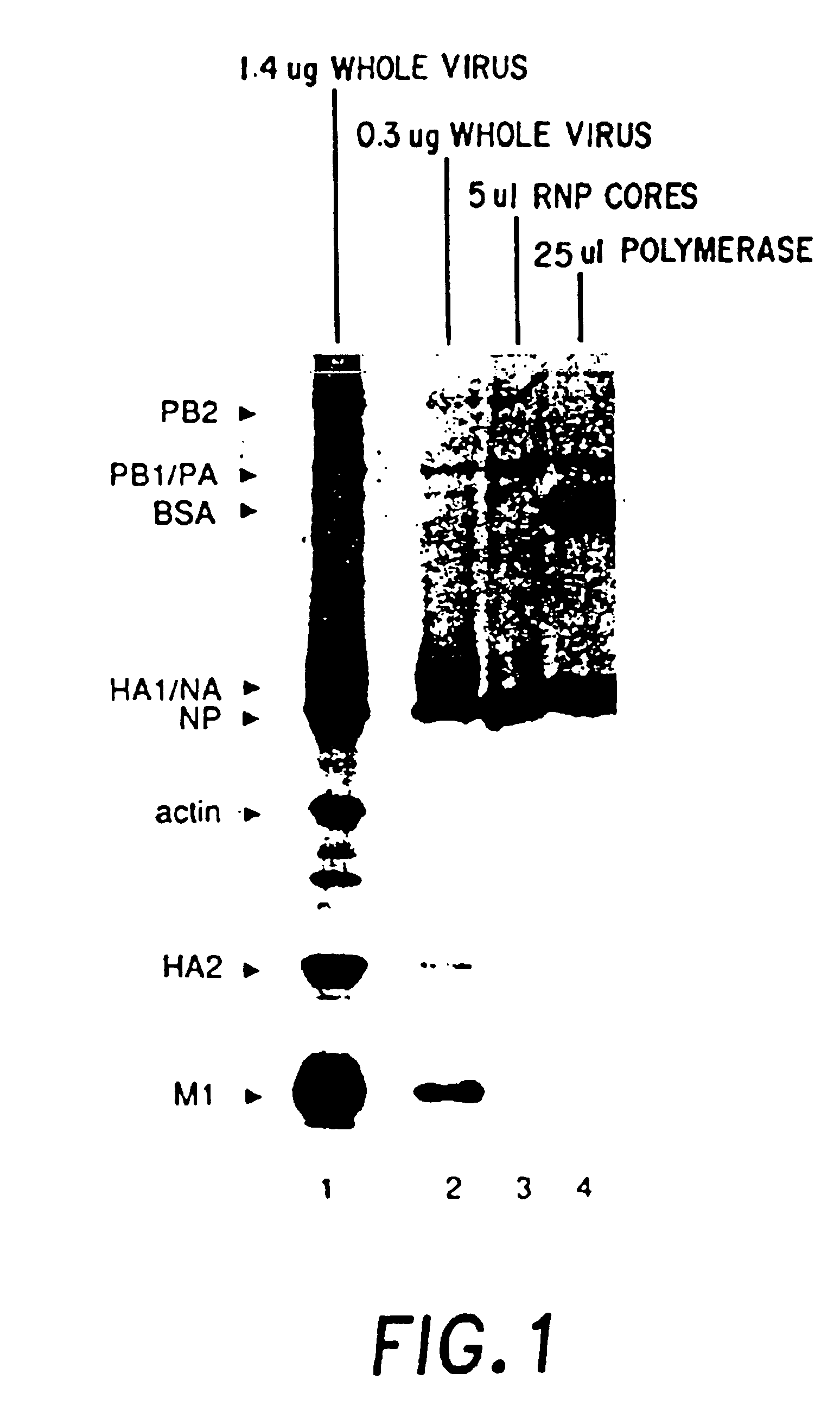
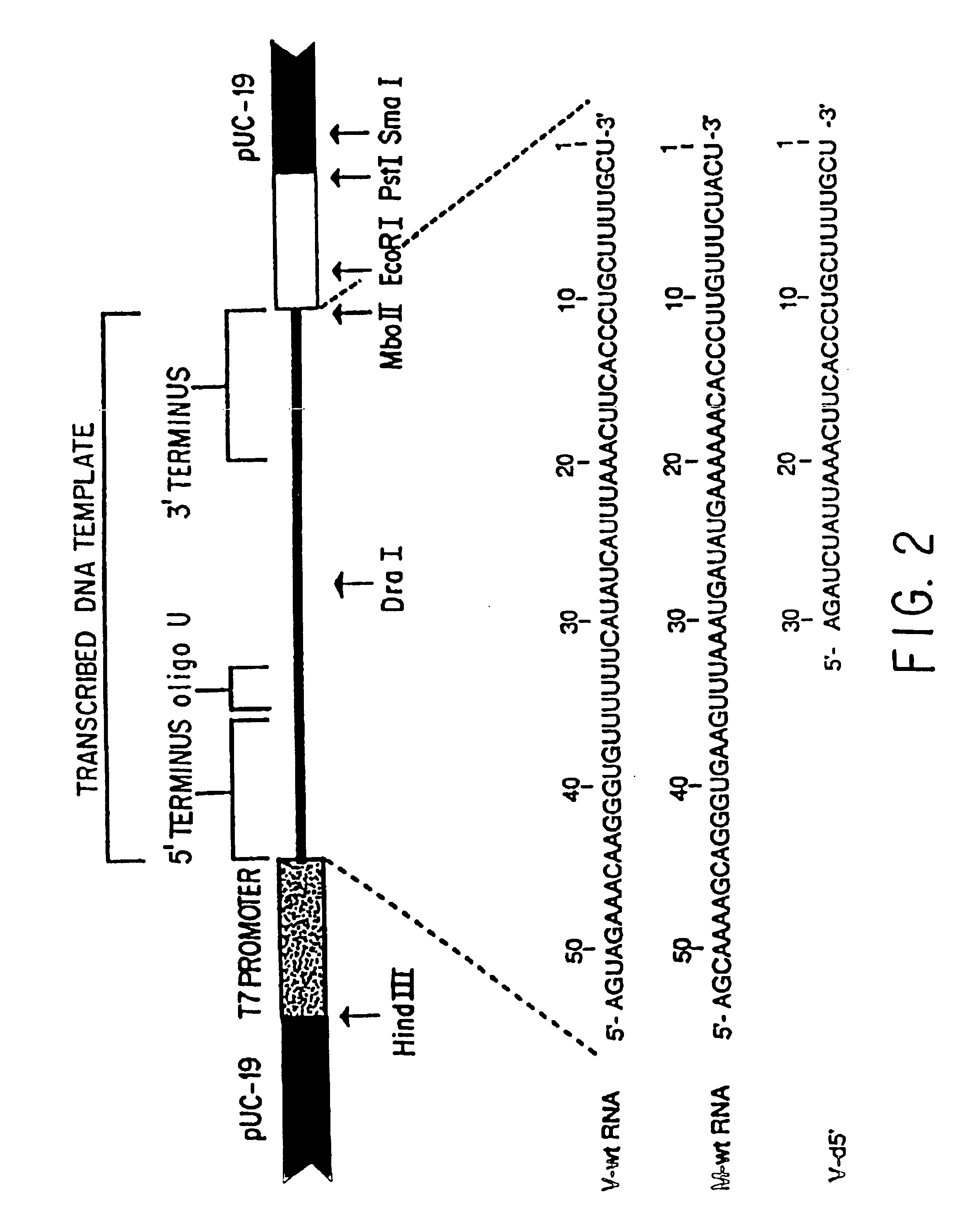
Recombinant negative strand RNA virus expression systems and vaccines
Owner:MEDIMMUNE VACCINES
Nucleic acid encoding a chitinase and methods of using it to make fungal resistant plants
InactiveUS7145060B2Increase temperatureSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyChitinase
The present invention provides a nucleic acid encoding a chitinase and methods for it to enhance resistance of plants to fungal infections.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Delivery of therapeutic compounds to the brain and other tissues
ActiveUS7442372B2Reduces and eliminates glycogen storage granuleReduce eliminateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMeningesIntrathecal use
The present invention relates to the intrathecal (IT) administration of recombinant enzyme to treat lysosomal storage disorders. In an exemplary embodiment, intrathecal administration of human α-L-iduronidase (rhIDU) injections in MPS I affected animals resulted in significant enzyme uptake, significant rh-iduronidase activity in brain and meninges and a decrease of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) storage in cells of MPS I subjects to that of normal subjects. Intrathecal administration proved more effective than intravenous treatment at alleviating MPS I symptoms, indicating it is a useful method of treating lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
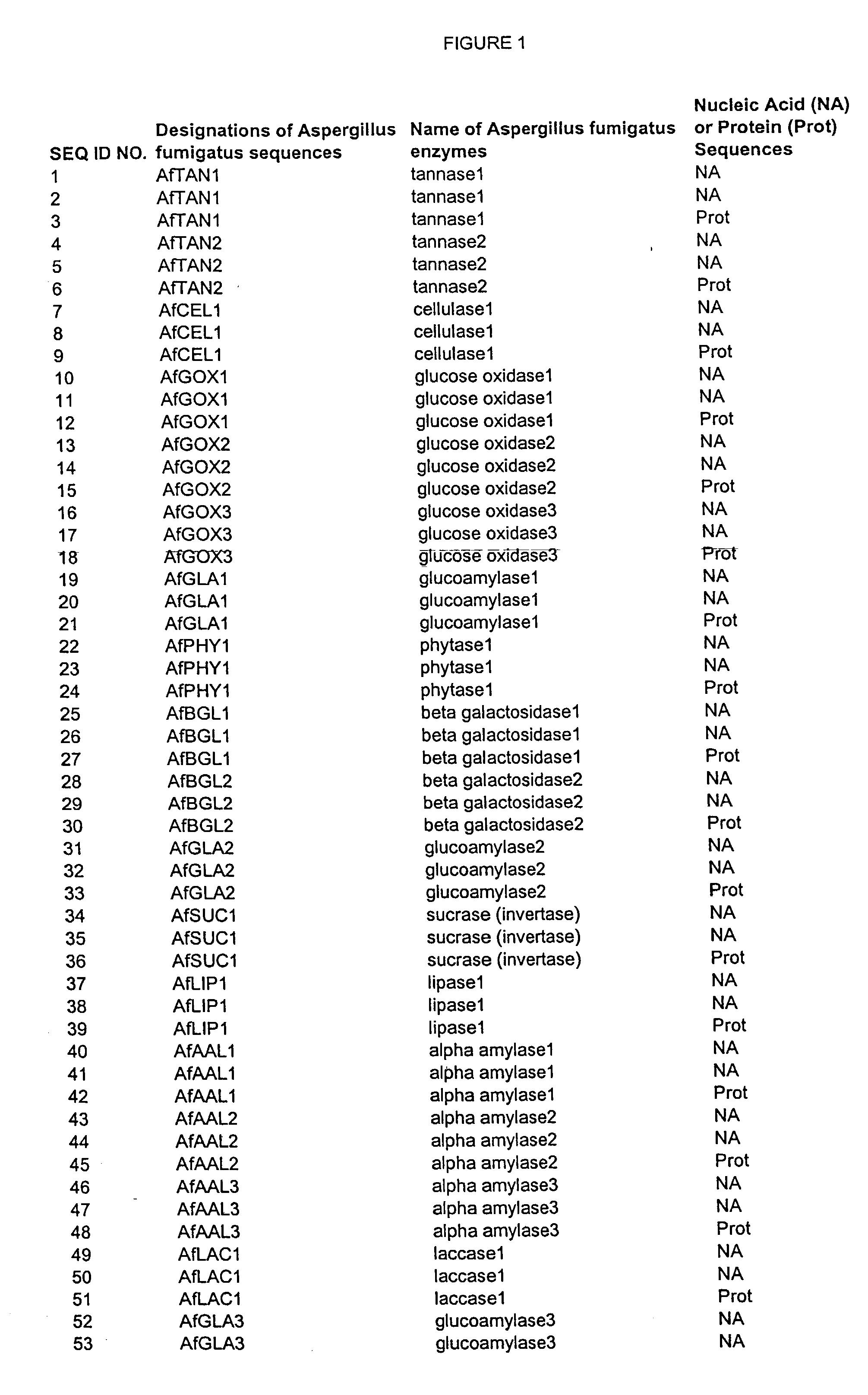
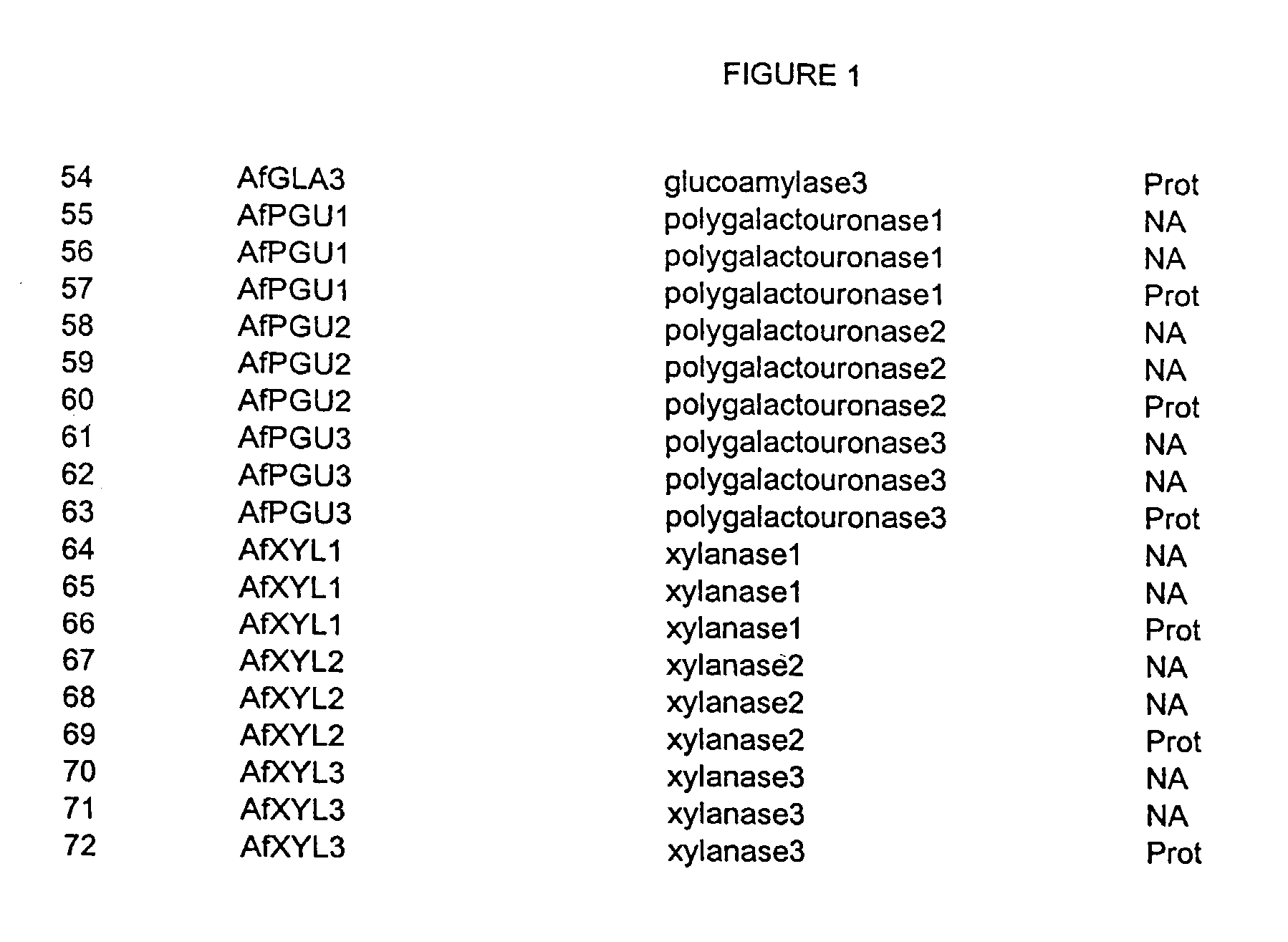
Nucleic acids of aspergillus fumigatus encoding industrial enzymes and methods of use
The present invention provides nucleotide sequences of Aspegillus fumigatus that encode proteins which exhibit enzyme activities. Vectors, expression constructs, and host cells comprising the nucleotide sequences of the enzyme genes are also provided. The invention further provides methods for producing the enzymes, and methods for modifying the enzymes in order to improve their desirable characteristics. The activities displayed by the enzymes of the invention include those of a tannase, cellulase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, phytase, beta-galactosidases, invertase, lipase, alpha-amylase, laccase, polygalacturonase or xylanase. The enzymes of the invention can be used in a variety of industrial processes. Enzymatically active compositions in various forms as well as antibodies to the enzymes and fragments thereof, are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
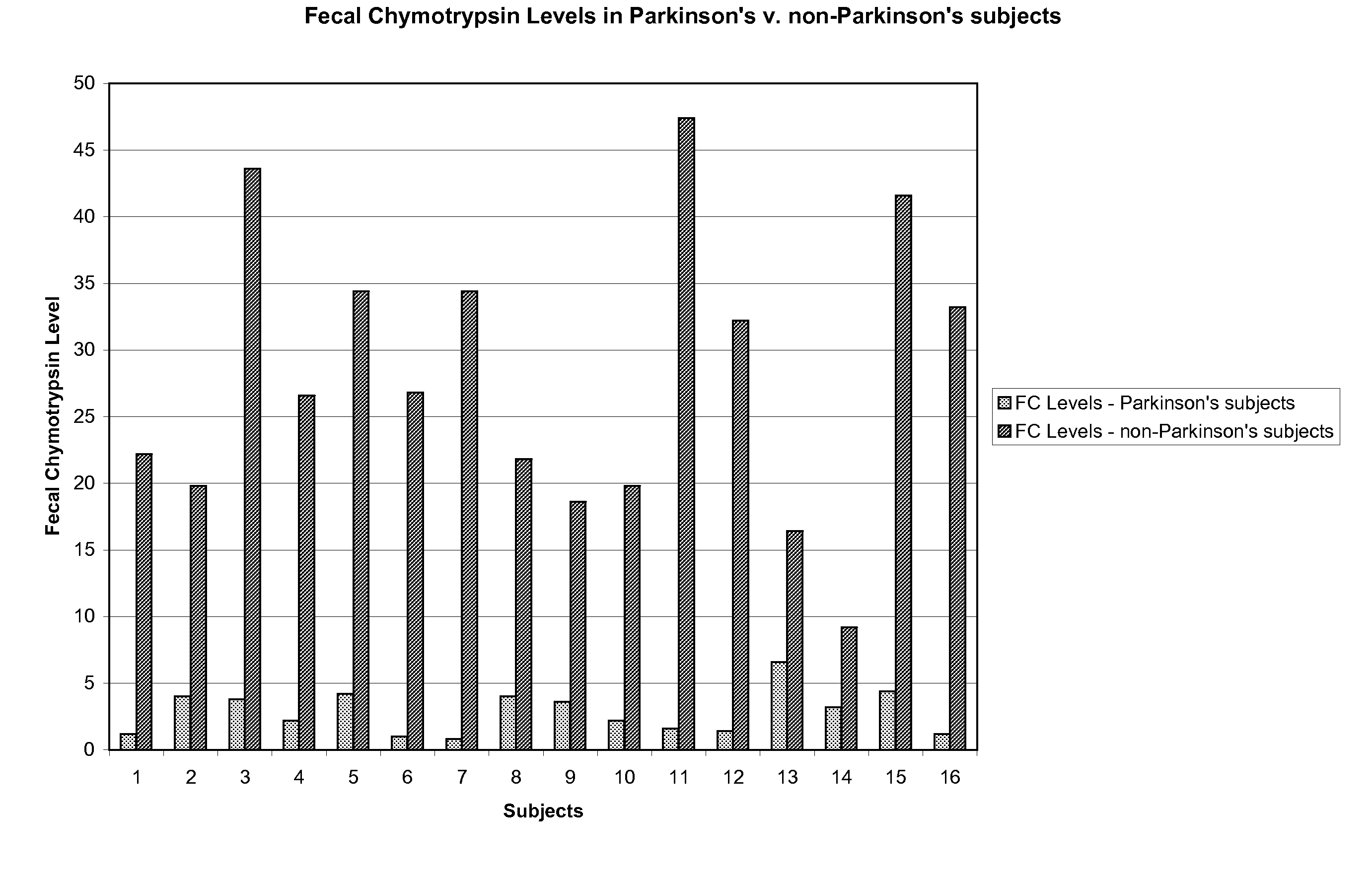
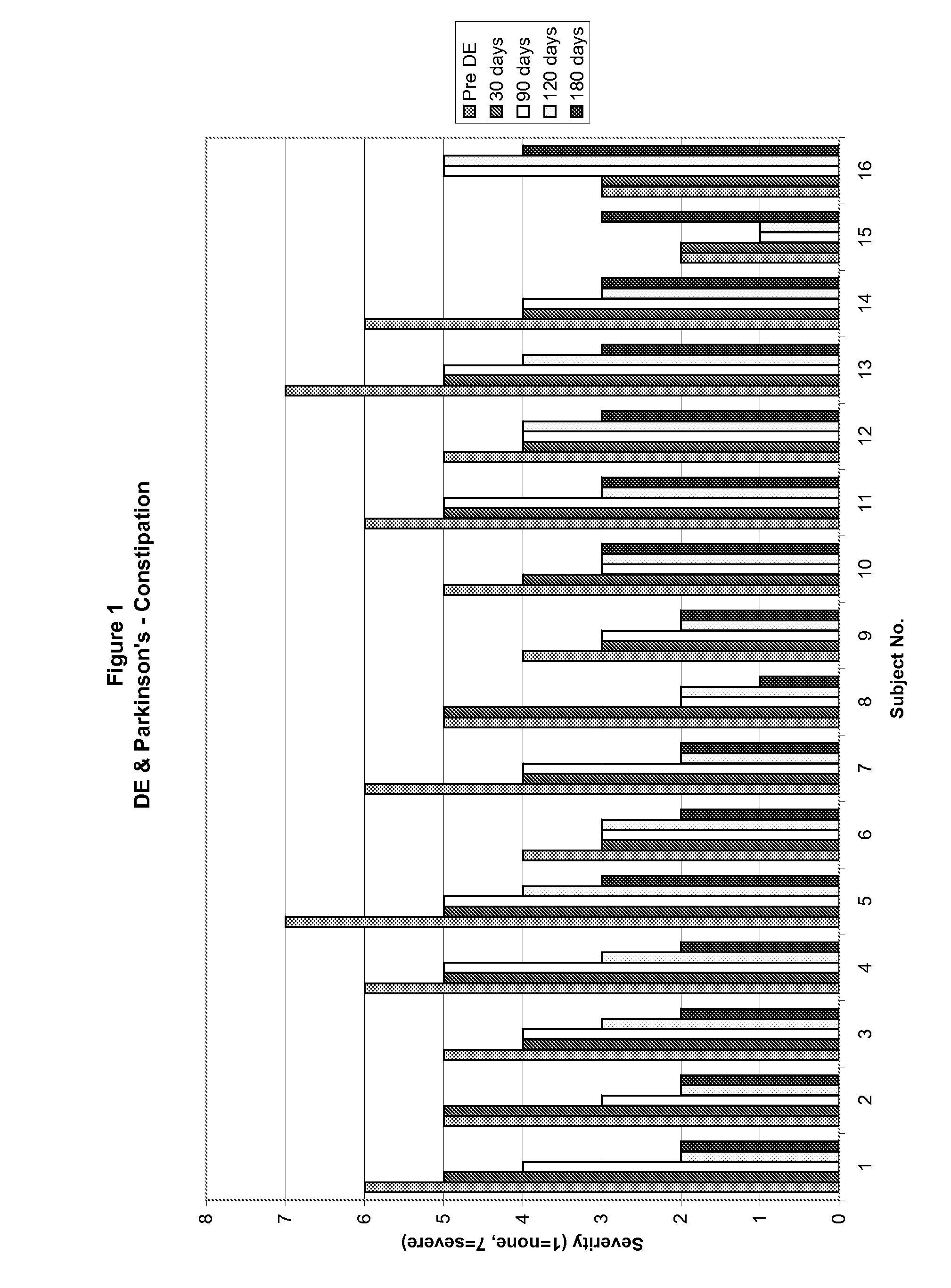
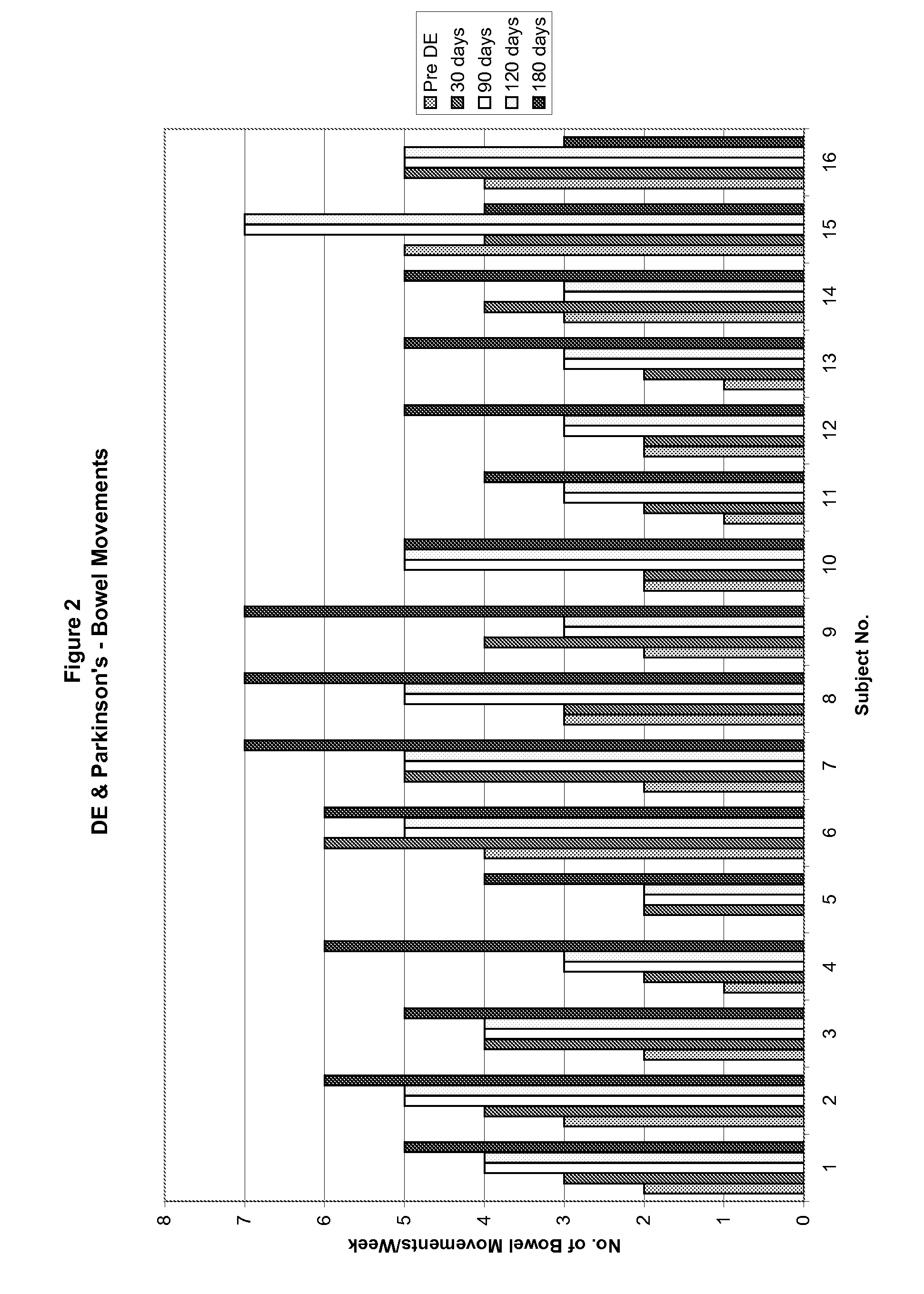
Method of treating and diagnosing parkinsons disease and related dysautonomic disorders
InactiveUS20070053895A1Symptoms improvedNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAutonomic bladder dysfunctionPsychiatry
A method for treating a Parkinson's patient with digestive / pancreatic enzymes involves administering an effective amount of digestive / pancreatic enzymes to an individual having the disorder in order to improve a symptom of the disorder. In addition, a method is provided for determining whether an individual has, or may develop, Parkinson's disease or related dysautonomic disorders and for determining whether an individual will benefit from the administration of pancreatic / digestive enzymes to treat the dysautonomic disorder.
Owner:CUREMARK
Targeting of glycoprotein therapeutics
Methods of making ligand-decorated polymer conjugates of therapeutic glycoproteins are described. Improved targeting of glycoproteins to specific tissues is achieved by masking the natural carbohydrate and other surface determinants with high molecular weight polymers, such as, e.g., PEG, polysialic acid, etc., which in turn are decorated with target-specific ligands. In some embodiments, acid-labile linkages in such conjugates or rapidly degradable masking groups allow for the intracellular release of the polymer from the glycoprotein, for example, under conditions found in lysosomes.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Novel pharmaceutical preparation for preeclampsia, eclampsia, and toxemia, and their related symptoms and related disorders of pregnancy
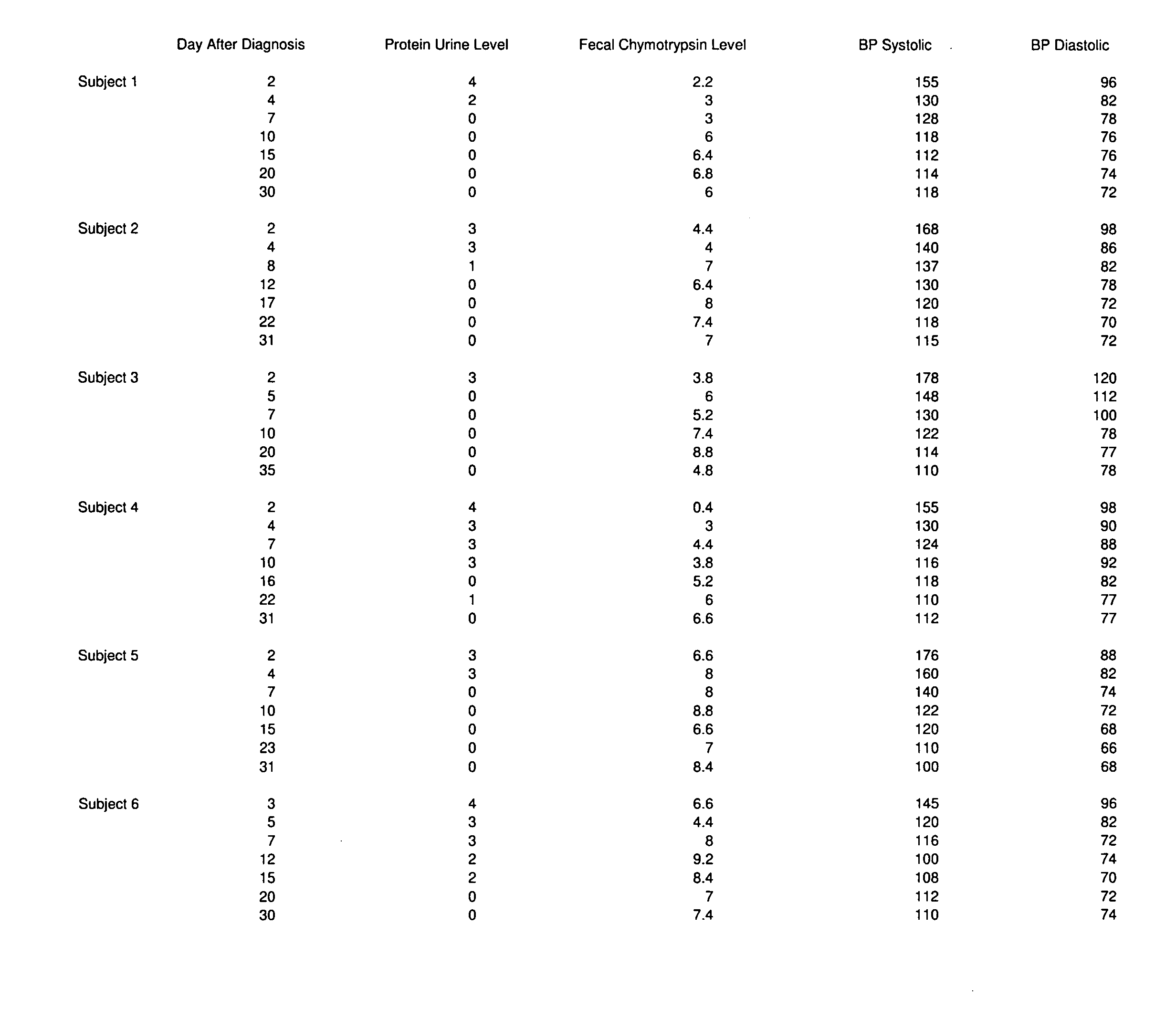
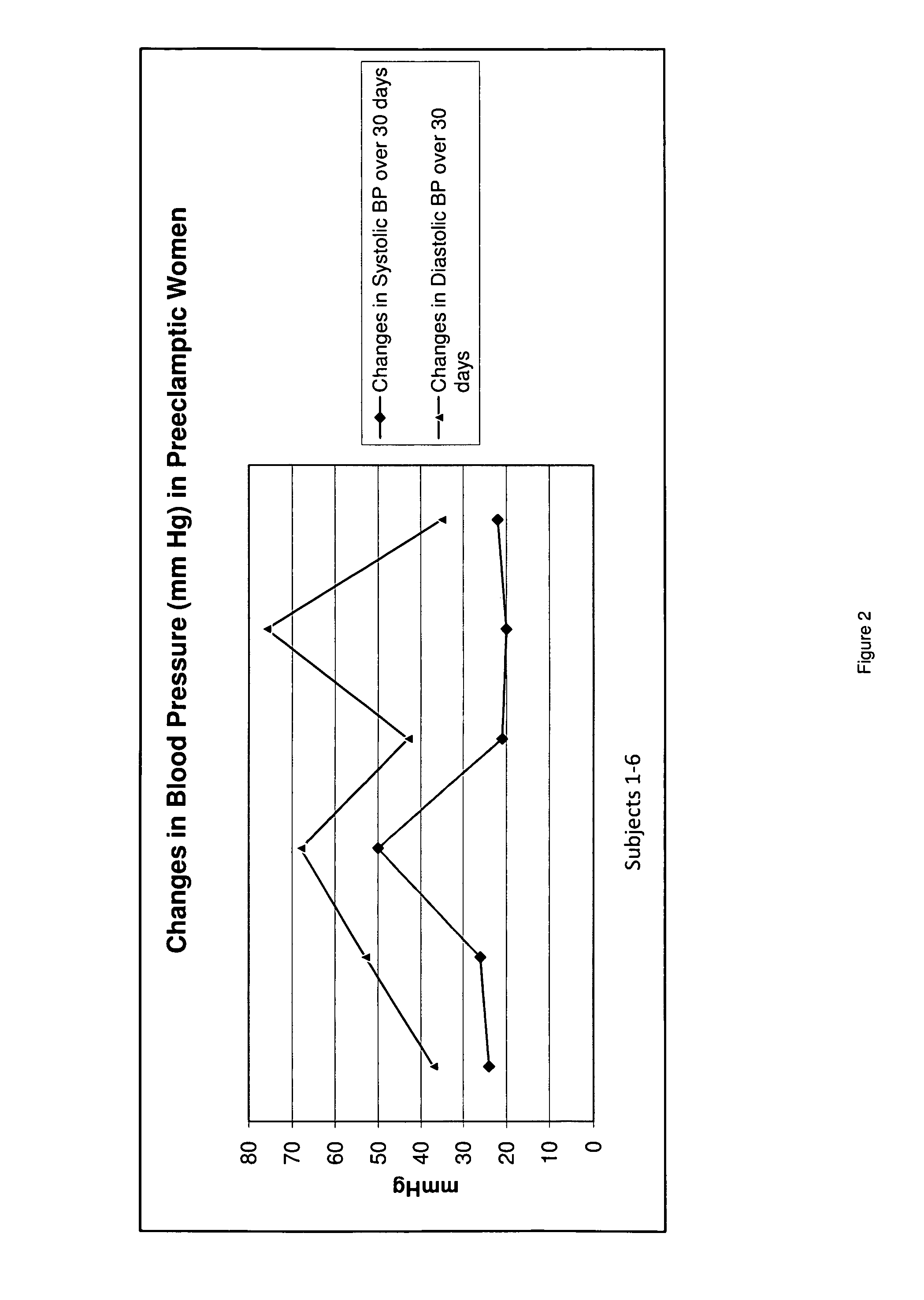
A therapeutic agent for the treatment of toxemia, preeclampsia and eclampsia and the method for preparing the therapeutic agents is disclosed. The therapeutic agent is a stable pharmaceutical preparation containing, but not limited to, digestive / pancreatic enzymes. The therapeutic agent may be manufactured by a variety of encapsulation technologies. Delivery of the therapeutic agent may be made orally, through injection, by adherence of a medicated patch or other method. Further, a method of using of a biomarker, the presence of chymotrypsin in the maternal GI tract to determine the likelihood of developing preeclampsia, pregnancy induced hypertension, and eclampsia / toxemia is disclosed.
Owner:CUREMARK
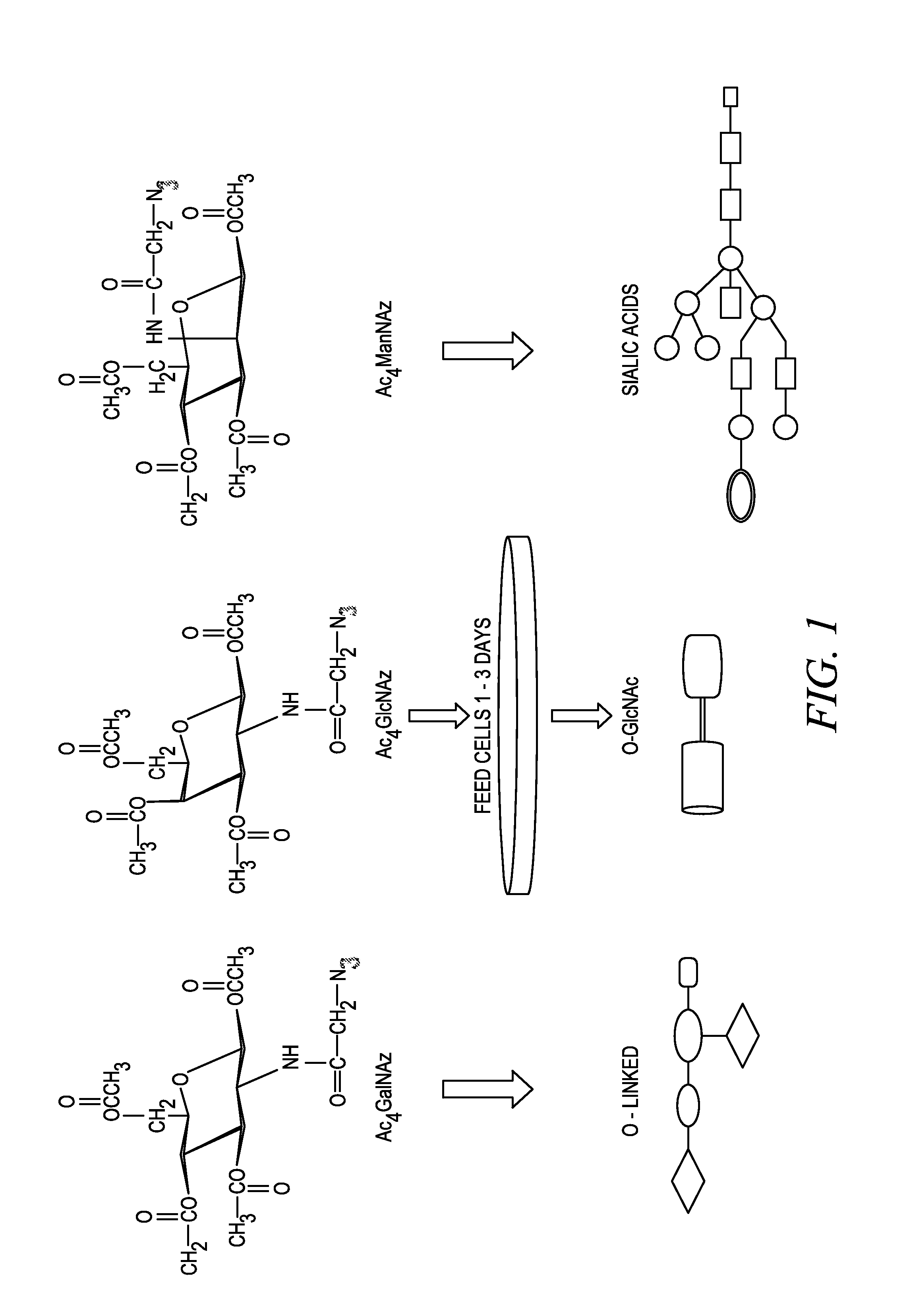
Labeling and detection of post translationally modified proteins
Provided in certain embodiments are new methods for forming azido modified biomolecule conjugates of reporter molecules, carrier molecules or solid support. In other embodiments are provided methods for enzymatically labeling a biomolecules with an azide group.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
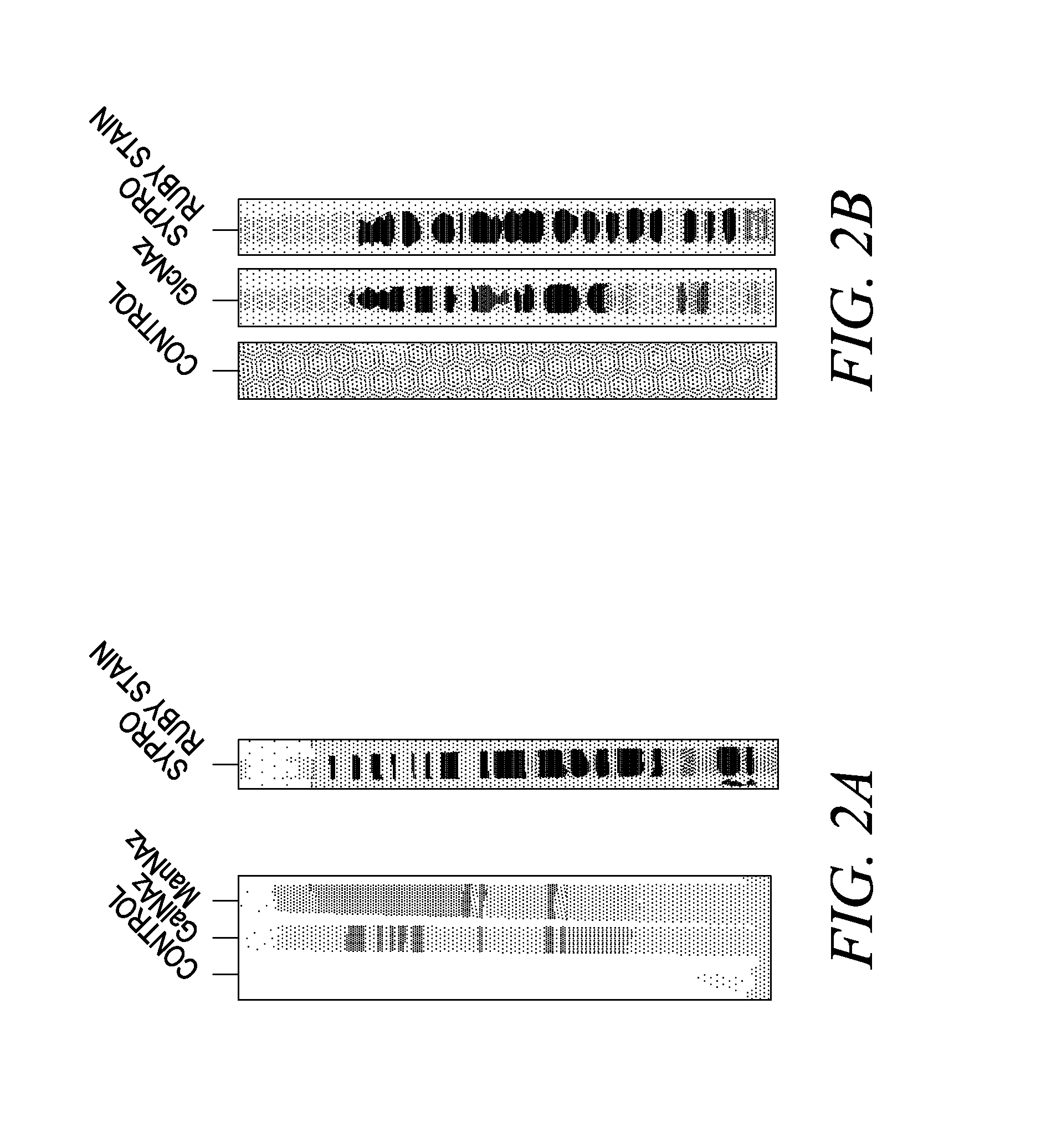
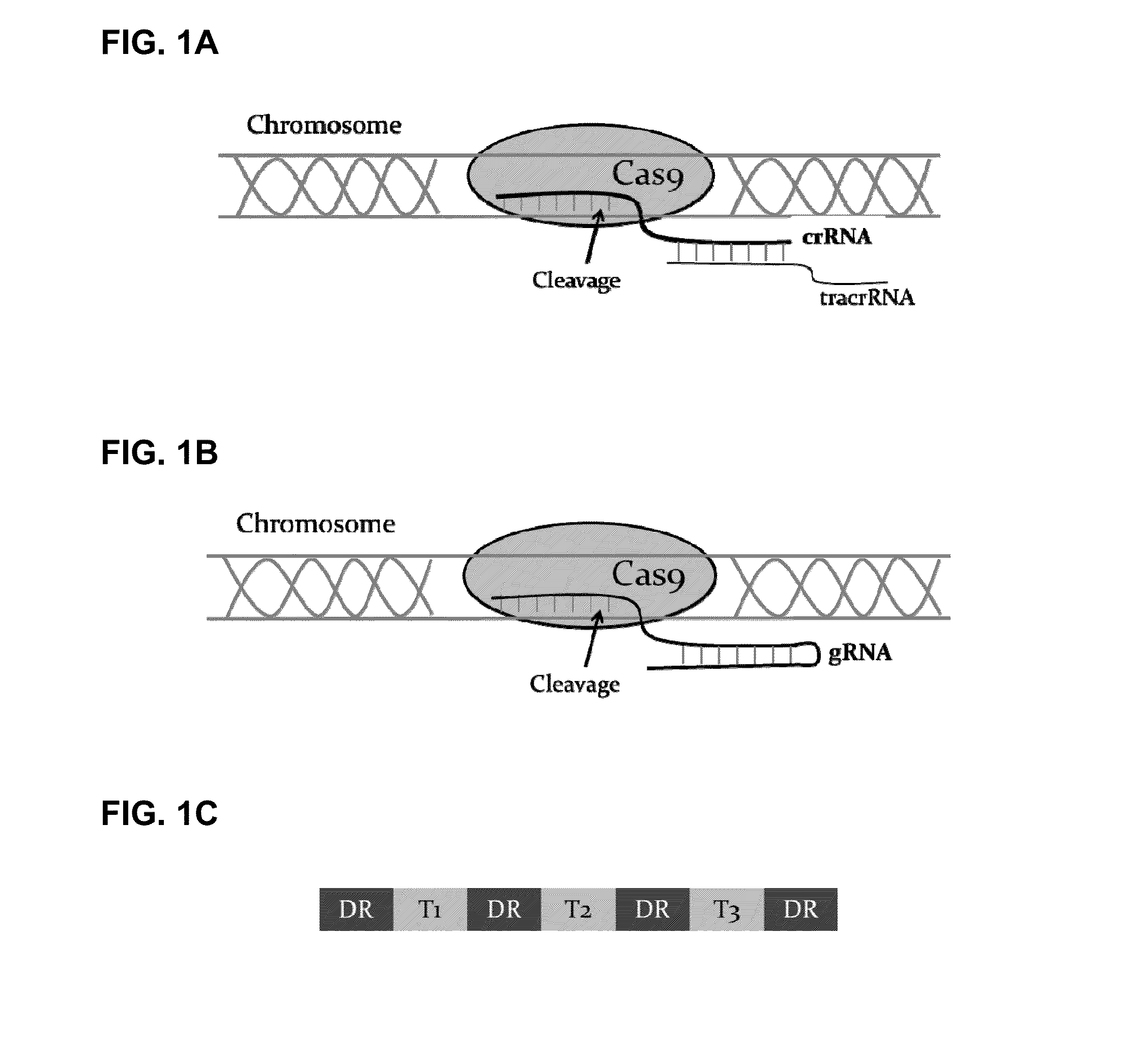
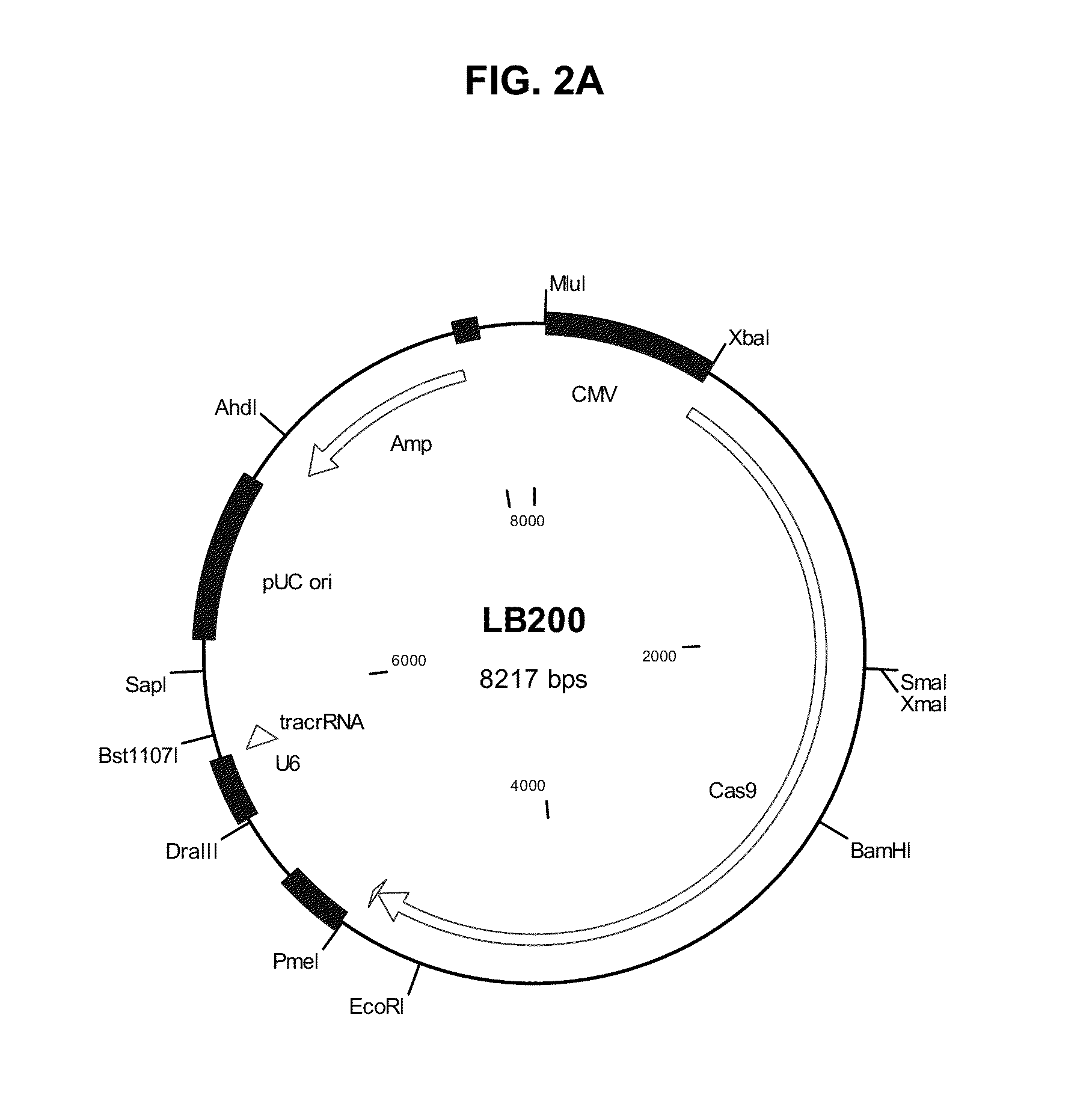
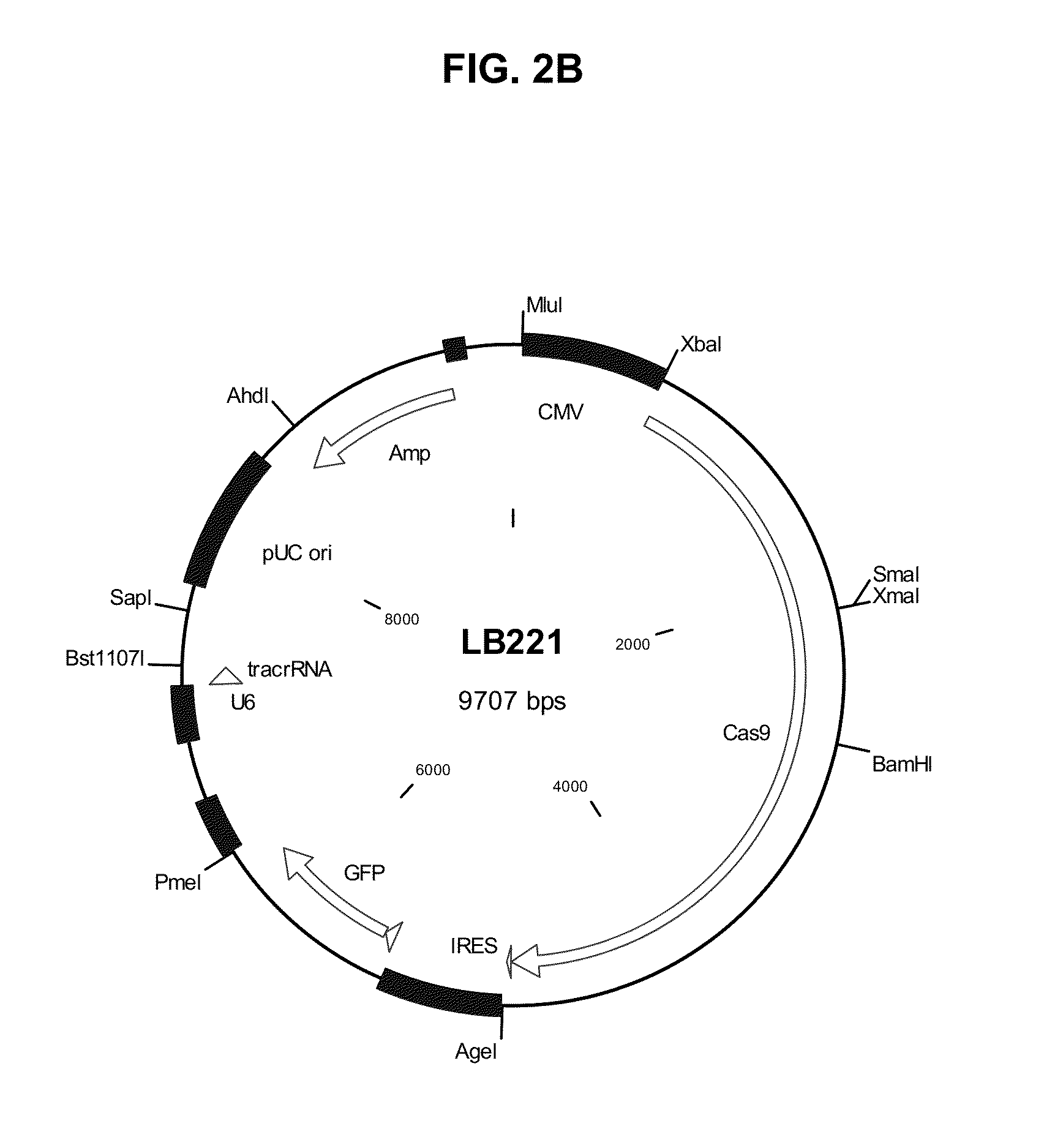
Methods and compositions for producing double allele knock outs
The present invention provides a method and compositions utilizing the CRISPR system to disrupt a target gene in eukaryotic cells to produce double allele knock outs. The method finds use in producing afucosylated antibodies with enhanced ADCC activity.
Owner:LARIX BIOSCI
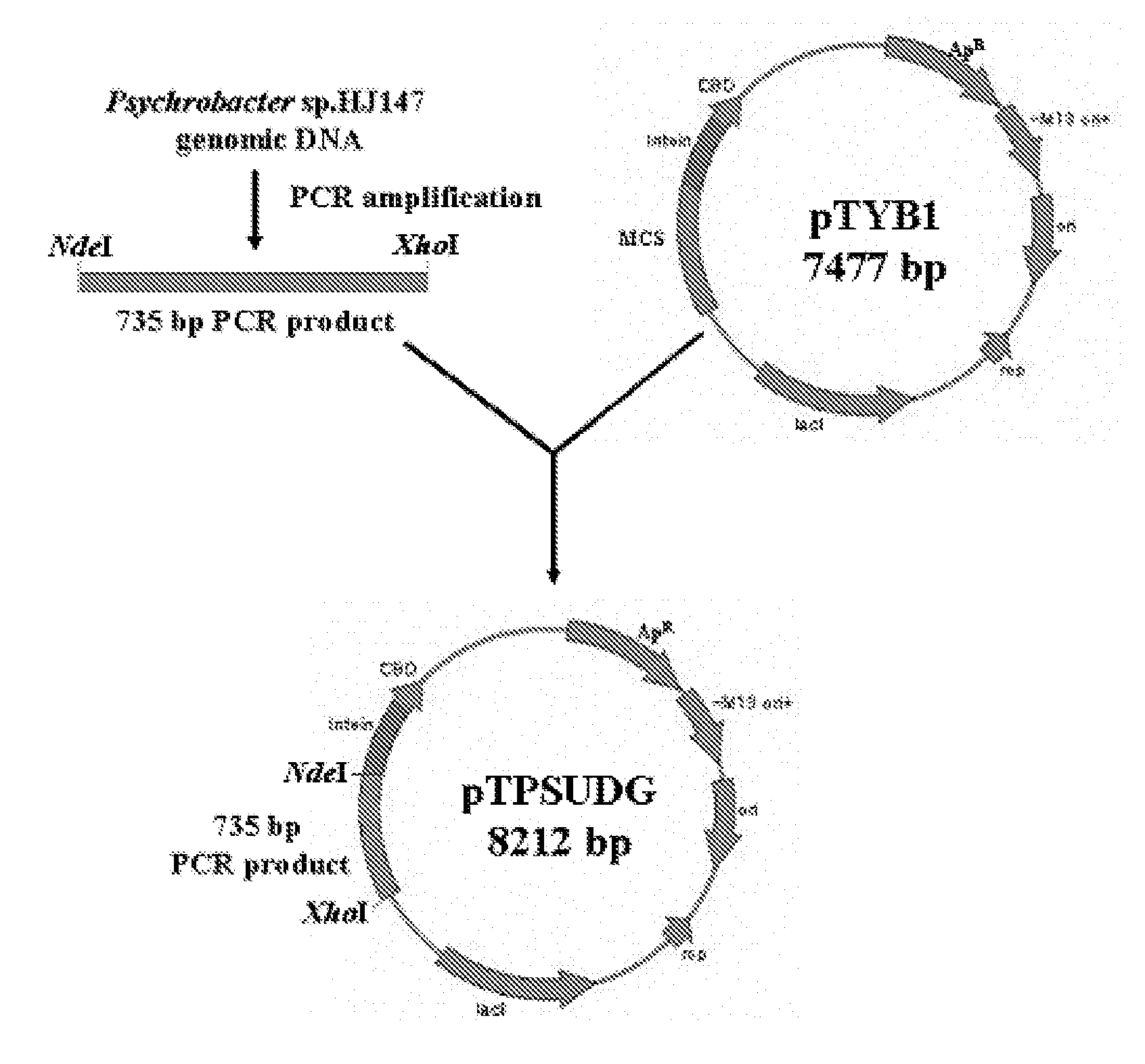
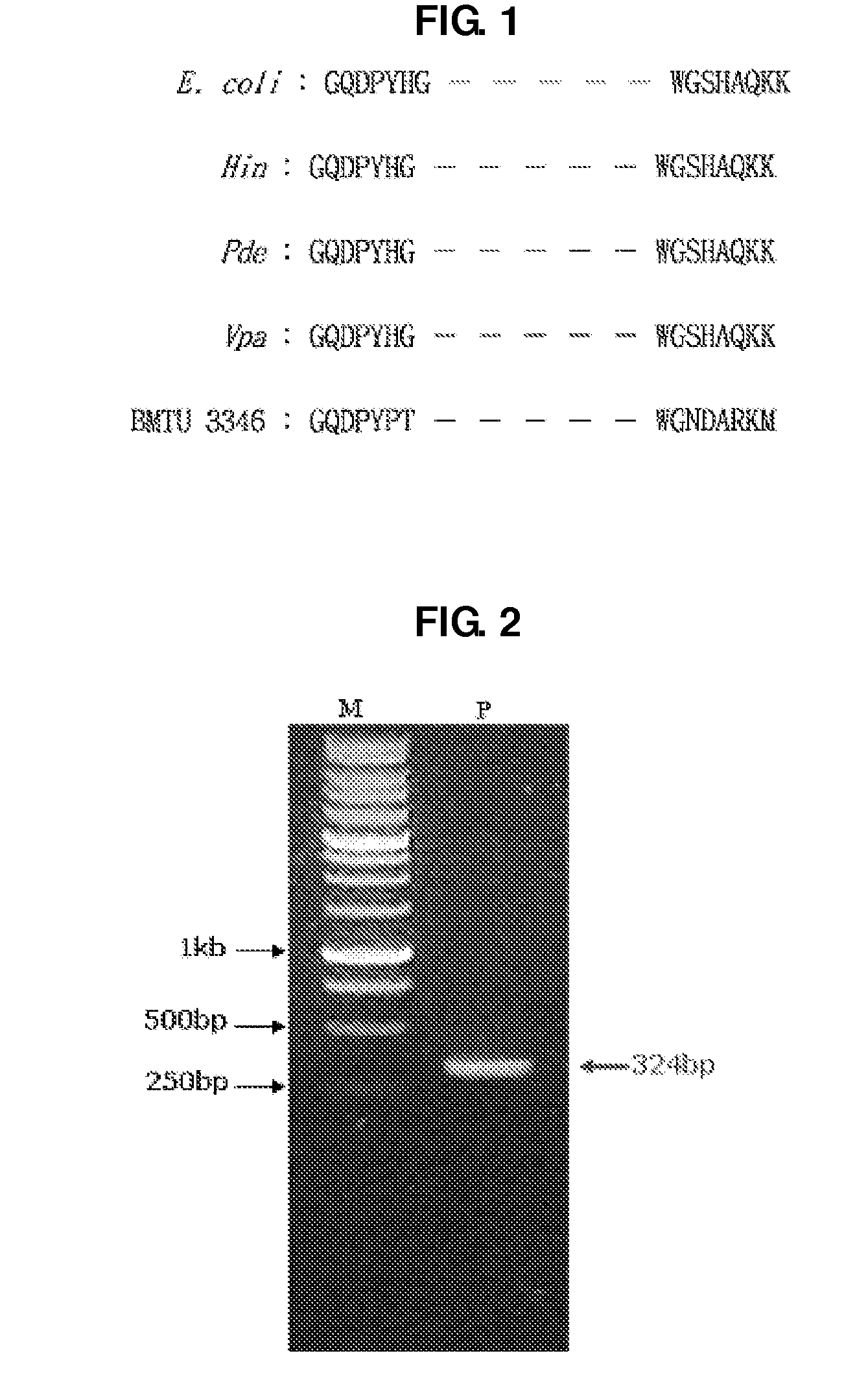
Uracil-DNA glycosylase of psychrobacter sp. HJ147 and use thereof
ActiveUS20080299609A1Eliminating contamination carry-overEliminating cross contaminationBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliPsychrobacter sp.
The present invention provides uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) gene originating from Psychrobacter sp. HJ147, and amino acid sequences deduced from the gene; expression and purification of Psp HJ147 UDG gene in Escherichia coli; and characterization of UDG obtained therefrom, and the use thereof in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The UDG according to the present invention has a specific activity of excising uracil bases in a uracil-containing DNA substrates at a low temperature, and is easily heat-inactivated. It thus can effectively eliminate cross contamination and carry-over contamination of PCR templates often occurring after a PCR process using dUTP. Therefore, it is useful for increasing preciseness (elimination of false positives), purity and amplification efficiency of PCR.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com