Manufacturing method of soybean paste by protease and its processed products
A manufacturing method, soybean paste technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to produce enough protease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
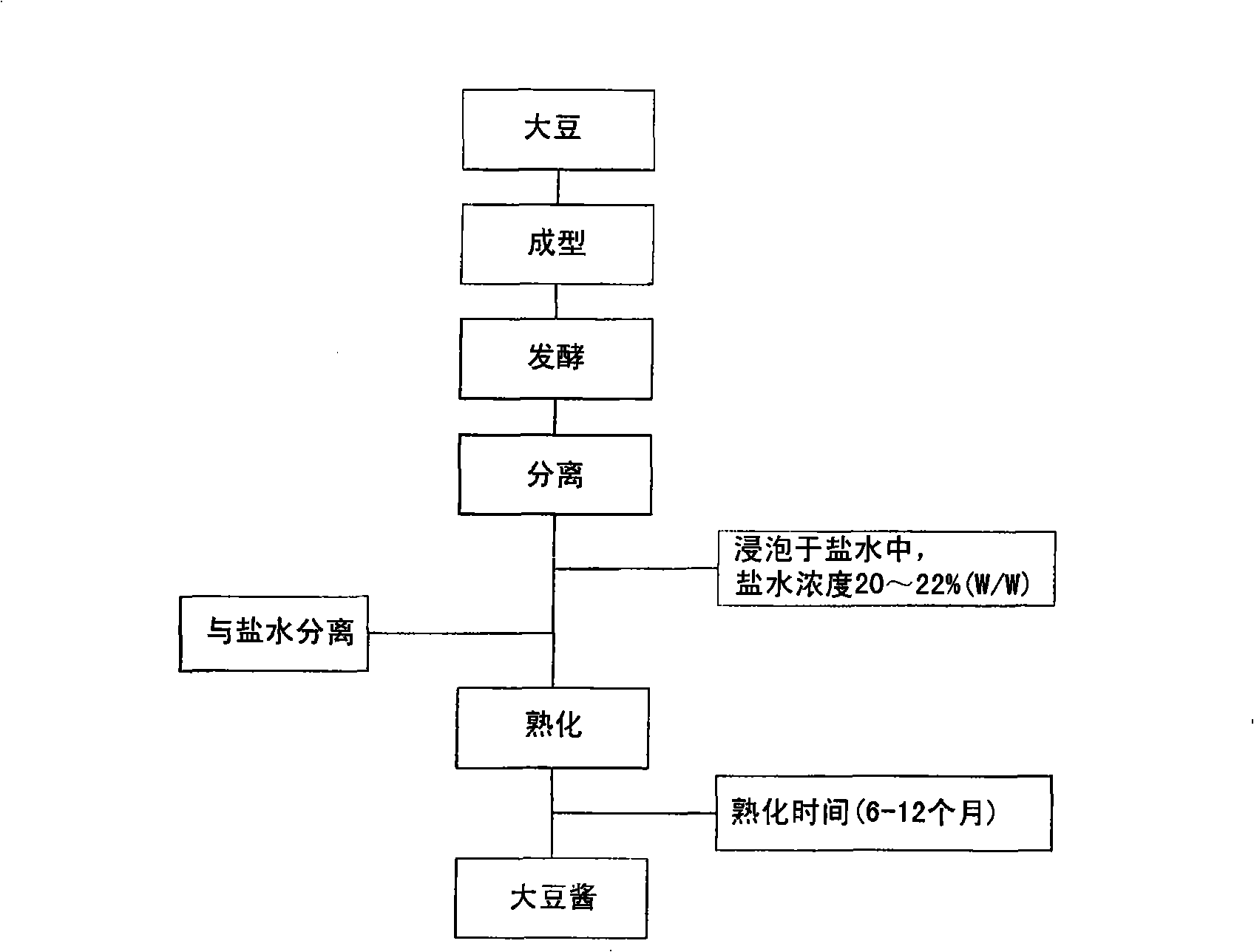
[0035] Embodiment 1 shortens the soybean paste preparation method of ripening period
[0036] Soybeans are shaped, dried and fermented according to traditional methods, then soaked in 20-25% brine for 90 days. Subsequently, the fermented soybeans are separated from the brine and ground. As shown in Table 1, 5% protease was added to fermented soybeans, and then aged for 40 days. The added enzymes were proteases of Aspergillus origin (Promod 279P; Biocatalysts, England), and proteases of Bacillus origin (Delvolase; DSM Food Specialties, Netherlands and Maxazyme NMP DS; DSM Food Specialties, Netherlands). As a result, compared with the control, the ripening degree of the soybean paste after adding the enzyme increased to 191-339mg% with the addition of the enzyme in the soybean paste.
[0037] Table 1 According to the ripening degree of Aspergillus-derived protease and Bacillus-derived protease added to soybean paste isolated from brine (unit: ripening degree mg%)
[0038] ...
Embodiment 2
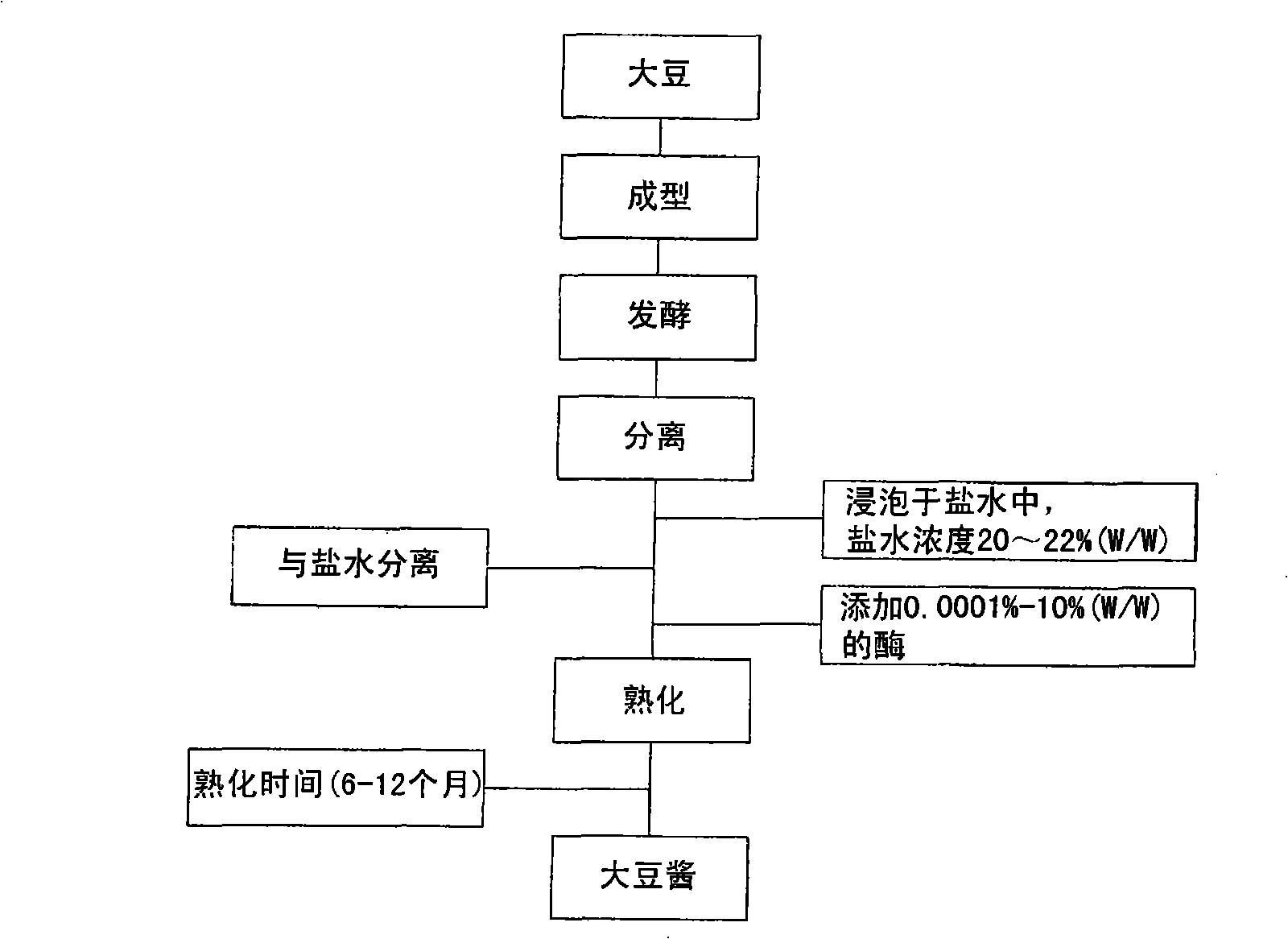
[0039] Embodiment 2 shortens the soybean paste preparation method of ripening period
[0040] Soybeans are shaped, dried and fermented according to traditional methods, then soaked in 20-25% brine for 90 days. Subsequently, the fermented soybeans are separated from the brine and ground. As shown in Table 2, 3% protease was added to the fermented soybeans, followed by aging for 50 days. The added enzymes were papaya-derived protease (Collupulin MG); pineapple-derived protease (Bromelain 1200GDU; Great Food, Thailand) and Aspergillus-derived protease (Promod 279P; Biocatalysts, England). As a result, compared with the control, the ripening degree of soybean paste after adding the enzyme increased to 230-268mg% with the enzyme added to the soybean paste. Compared with the control, the protease activity of the enzyme in soybean paste increased by 52-87%.
[0041] Table 2 Results after adding plant protease and protease complex to soybean paste isolated from brine
[0042] ...
Embodiment 3
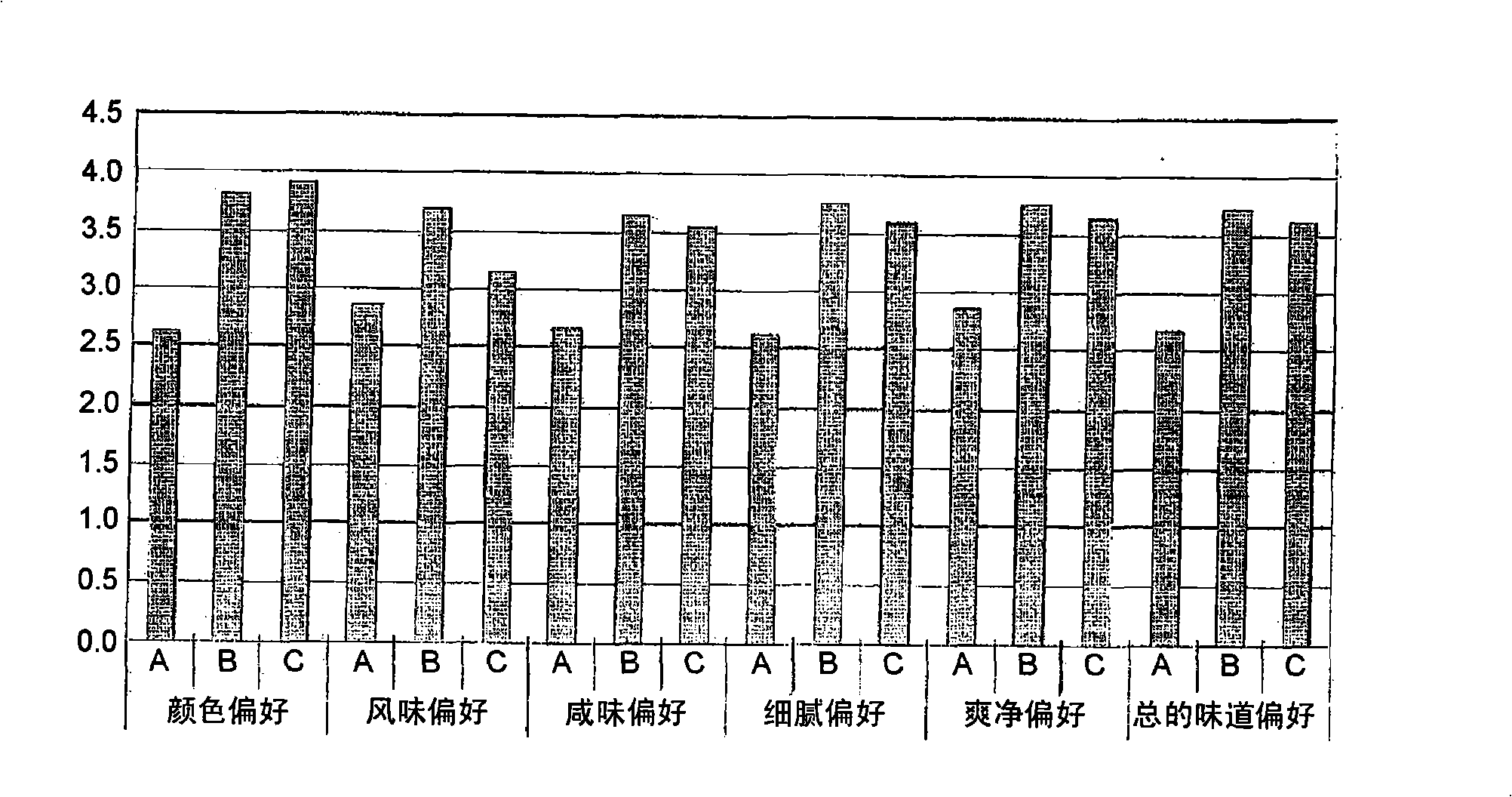
[0047] The sensory evaluation result of the prepared soybean paste of embodiment 3 with the shortened ripening period
[0048] Soybeans are shaped, dried and fermented according to traditional methods, and soaked in 20-25% brine for 80 days. Subsequently, the fermented soybeans are separated from the brine and ground. As shown in Table 2, 3% protease was added to fermented soybeans, and then aged for 60 days. Group A is the control group, group B is the enzyme derived from papaya (Collupulin MG), and group C is the protease derived from Bacillus subtilis (Maxazyme NMP DS). As soon as the aging was over, each soybean paste (control, papaya-derived enzyme-added group, and Bacillus protease-added group) was handed over to inspectors to investigate color preference, flavor preference, salty taste preference, delicate taste preference (delicate taste preference), refreshing Net preference (celanstate preference), and total taste preference, wherein the testers consisted of 5 male...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com