Methods for increasing starch content in plant cobs
一种淀粉含量、穗轴的技术,应用在植物分子生物学领域,能够解决效率低等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0131] Generation of transgenic maize plants
[0132] Eight RNAi cassettes were constructed for plant expression. These cassettes are designed to downregulate the enzymes alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, dextran water dikinase (R1), phosphodextran water dikinase (PWD), and chloroplast alpha-amylase (AMY3) in maize cob tissue . The maize cDNA sequences for α-amylase (Genbank Accession No. L25805), β-amylase (Genbank Accession No. Z25871 ) and α-glucan water dikinase (R1 , Genbank Accession No. CD973834) were obtained from NCBI. The maize orthologue of Arabidopsis chloroplast phosphoglucan water dikinase (GenBank accession number AJ635427) was generated based on sequence homology to the maize genomic sequence. Likewise, a maize orthologue of Arabidopsis Amy3 (GenBank Accession No. NM105651 ) was generated based on sequence homology to the maize genomic sequence. RNAi fragment from the 3' end of the coding region of each gene (α-amylase of 495 bp, SEQ ID NO: 1; β-amylase of 500 b...
Embodiment 2
[0145] Sample collection and pre-screening of transgenic maize events.
[0146] 10 days after pollination from mature T 0 Cob samples were collected from corn plants. Then, fresh cobs were frozen at -80°C. Afterwards, the seeds were removed from the frozen cobs using a paint scraper. Freezing the cobs allows for better removal of corn seeds for cob analysis. After removing the cob seeds, each cob was then sliced into slices less than 1 / 4 inch thick. Two sections (one from the middle and one from the end) were used for Lugol's iodine staining. The method as described in Example 1 can be used by using T transformed with an empty binary vector without RNAi cassette 0 plants to generate control plants.
[0147] Use Lugol's staining solution to perform T 0 Prescreening for starch accumulation in maize events. Lugol's solution selectively stains starch from dark blue to black and can be visualized under a microscope. The degree of staining relative to the null control a...
Embodiment 3
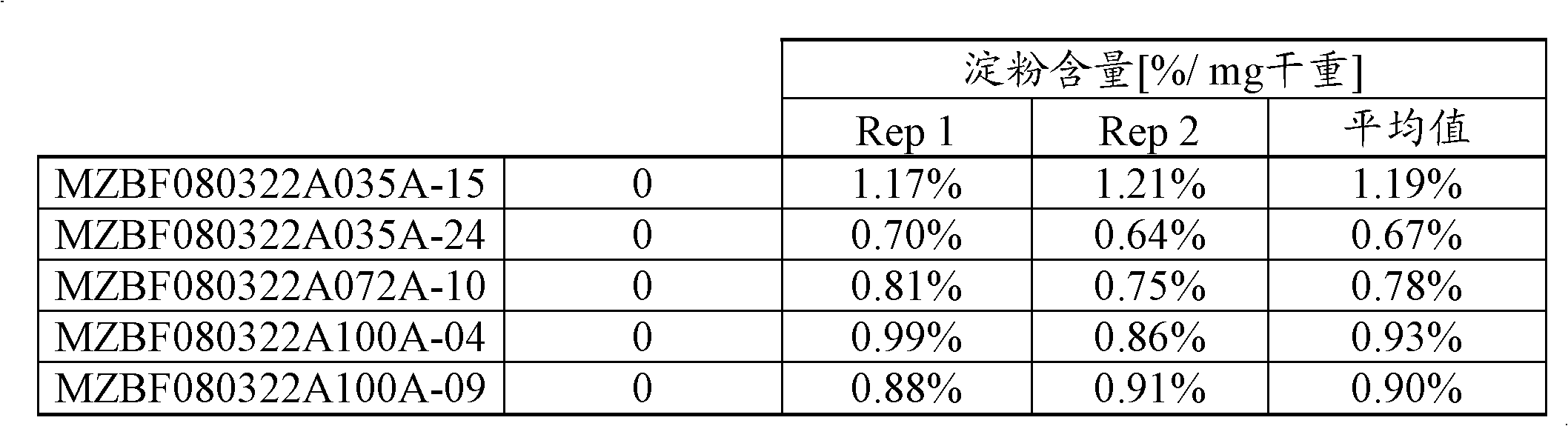
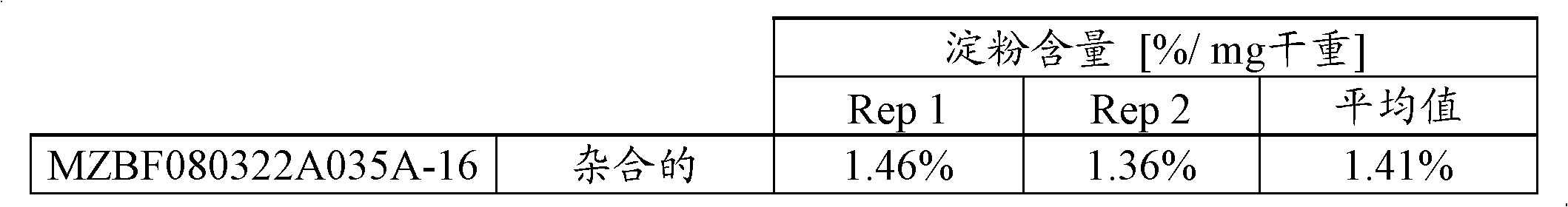
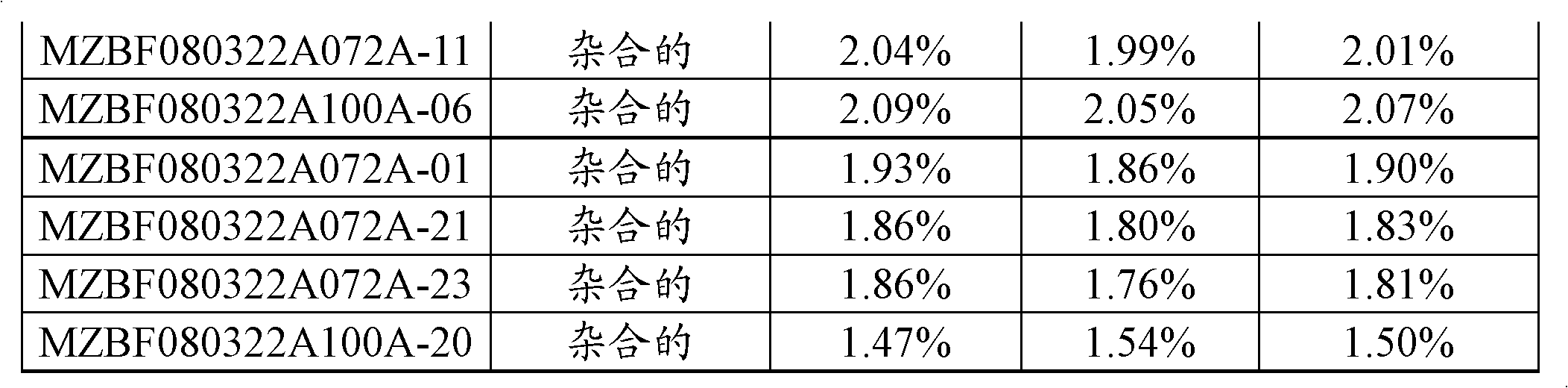
[0164] Starch and Sugar Evaluation in Corn Cob Tissue Samples
[0165] The following assay protocol was used to assess the amount of sugar and total starch by dry weight in cob samples. This method employs the Megazyme Total Starch Assay (MEGAZYME, Wicklow, Ireland) (AOAC Method 996.11 and AACC Method 76.13), which involves complete digestion of sample starch into free D-glucose by alpha-amylase and amyloglucosidase hydrolysis , followed by a glucose oxidase-peroxidase reaction and a colorimetric measurement of free D-glucose released from the sample. The amount of starch in the sample can be calculated via a simple conversion of the measured amount of D-glucose released. The sugars were extracted with water and the amount analyzed by HPAEC (High Performance Anion Exchange Chromatography).
[0166] Cob sample preparation
[0167]Fresh cobs were frozen at -80°C, photographs were taken, and a paint scraper was used to remove the seeds. Then, slice each cob into slices le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com