Processing method of lotus seed starch-lipid compound nanoparticles
A technology of lipid complex and lotus seed starch, which is applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of many by-products, low yield, and inability to adapt to industrial continuous production. , to achieve the effect of increasing the yield, increasing the degree of compounding, and shortening the preparation cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
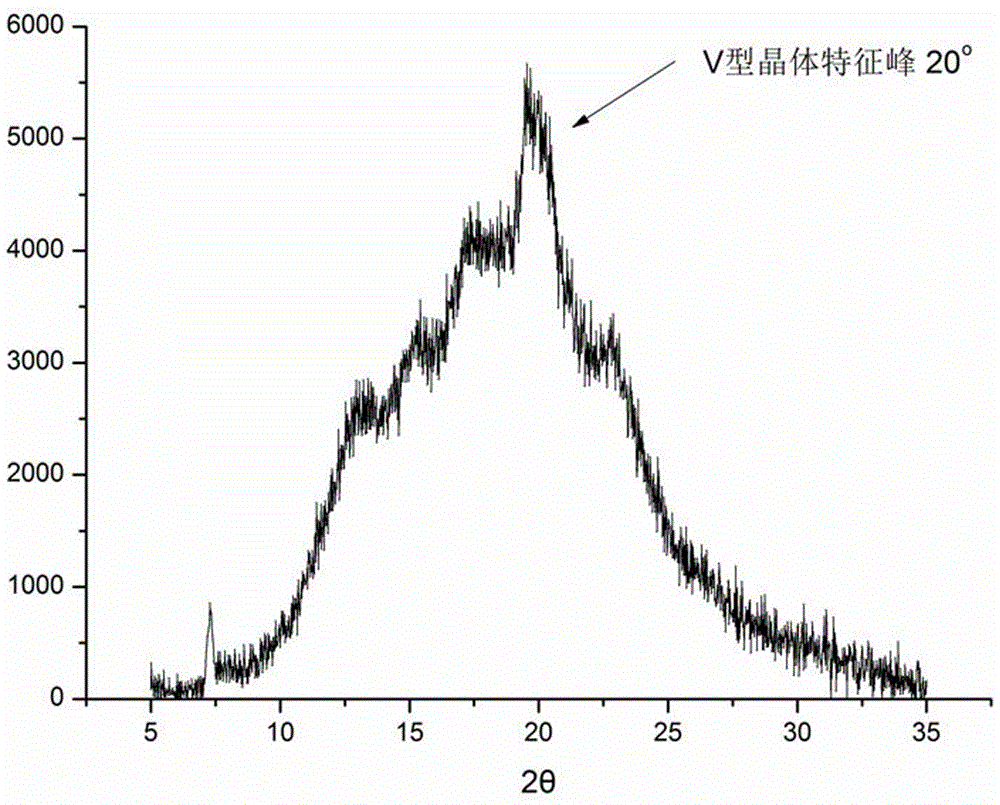
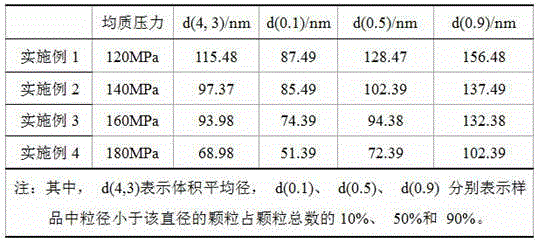
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for processing lotus seed starch-lipid complex nanoparticles, the specific steps are:
[0029] (1) Hydrolysis with α-amylase and isoamylase: add deionized water to 50.0g lotus seed starch to prepare a 10 wt% starch emulsion; after heating and gelatinizing in a water bath at 90°C for 15 minutes, add 500U / g based on the quality of starch High-temperature-resistant α-amylase was used for enzymatic hydrolysis for 3 h; after that, when the sample solution was cooled to 25 °C, 80 U / g of starch-based isoamylase was added for enzymatic hydrolysis for 10 h. After the enzymatic hydrolysis is completed, high-temperature enzymatic treatment is carried out, and the airtight container is ready for use;
[0030] (2) High-pressure micro-jet homogeneous compounding: 0.50 g of glyceryl monostearate was dissolved in 25 g of ethanol solution with a volume concentration of 50%, and then transferred to the lotus seed starch emulsion that had been enzymatically hydrolyzed for use, an...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for processing lotus seed starch-lipid complex nanoparticles, the specific steps are:
[0037] (1) Hydrolysis with α-amylase and isoamylase: Add deionized water to 50.0g lotus seed starch to prepare a 10 wt% starch emulsion; after heating and gelatinizing in a water bath at 90°C for 15 minutes, add 400U / g based on the quality of starch High-temperature resistant α-amylase was used for enzymatic hydrolysis for 3 h; after that, when the sample solution was cooled to 25°C, 100 U / g of starch-based isoamylase was added for enzymatic hydrolysis for 12 h. After the enzymatic hydrolysis is completed, high-temperature enzymatic treatment is carried out, and the airtight container is ready for use;
[0038] (2) High-pressure micro-jet homogeneous compounding: 0.60 g of glycerol monostearate was dissolved in 30 g of ethanol solution with a volume concentration of 50%, and then transferred to the lotus seed starch emulsion that had been enzymatically hydrolyzed for use, an...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A method for processing lotus seed starch-lipid complex nanoparticles, the specific steps are:
[0045] (1) Hydrolysis with α-amylase and isoamylase: add deionized water to 50.0g lotus seed starch to prepare a 10 wt% starch emulsion; after heating and gelatinizing in a water bath at 90°C for 15 minutes, add 500U / g based on the quality of starch High-temperature-resistant α-amylase was used for enzymatic hydrolysis for 3 h; after that, when the sample liquid was cooled to 25 °C, 60 U / g of starch-based isoamylase was added for enzymatic hydrolysis for 10 h. After the enzymatic hydrolysis is completed, high-temperature enzymatic treatment is carried out, and the airtight container is ready for use;
[0046] (2) High-pressure micro-jet homogeneous compounding: 0.50 g of glycerol monostearate was dissolved in 25 g of ethanol solution with a volume concentration of 50%, and then transferred to the lotus seed starch emulsion that had been enzymatically hydrolyzed for use, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com