Patents
Literature
268 results about "Dihedral angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes. In chemistry it is the angle between planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry it is defined as the union of a line and two half-planes that have this line as a common edge. In higher dimension, a dihedral angle represents the angle between two hyperplanes.
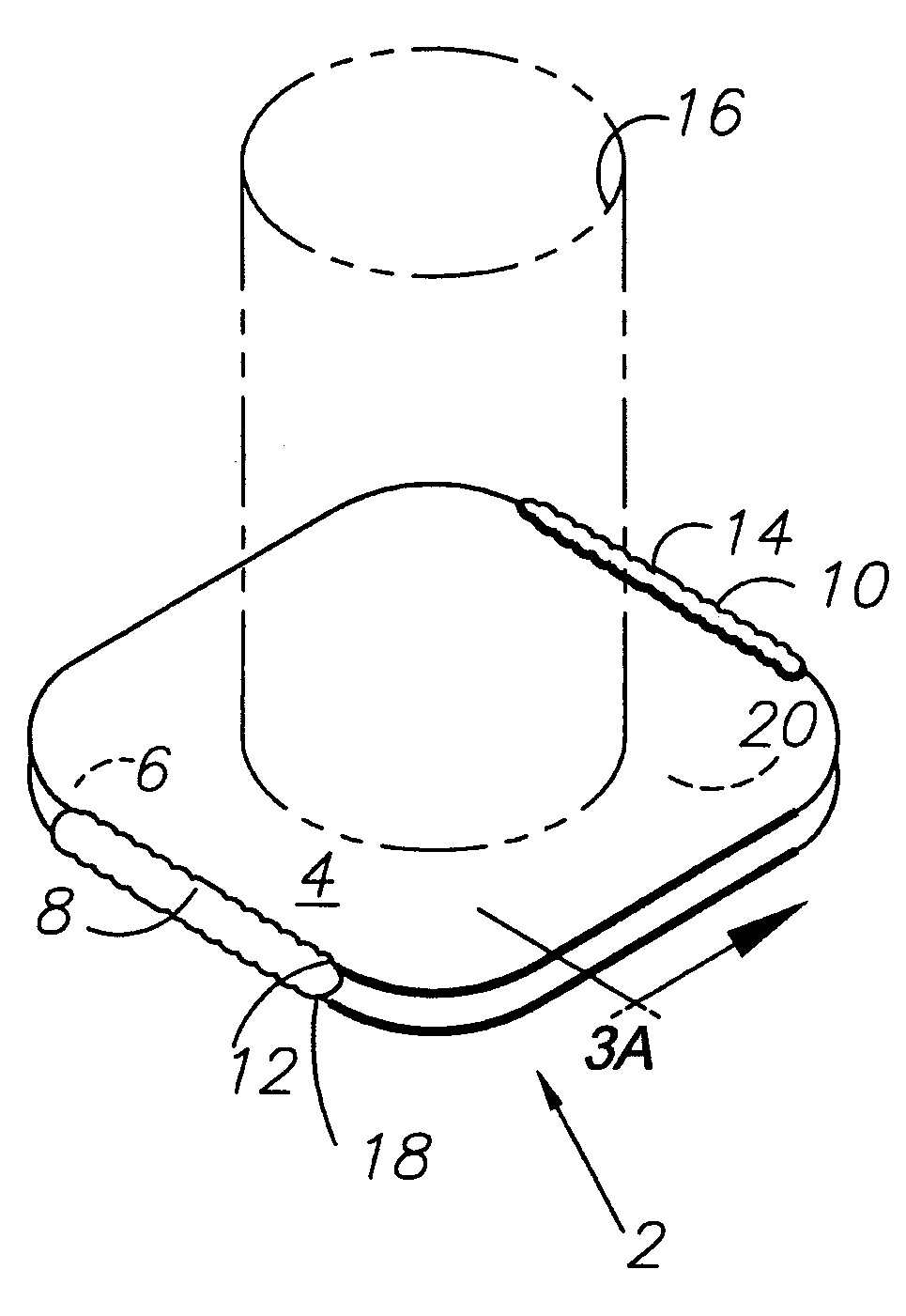
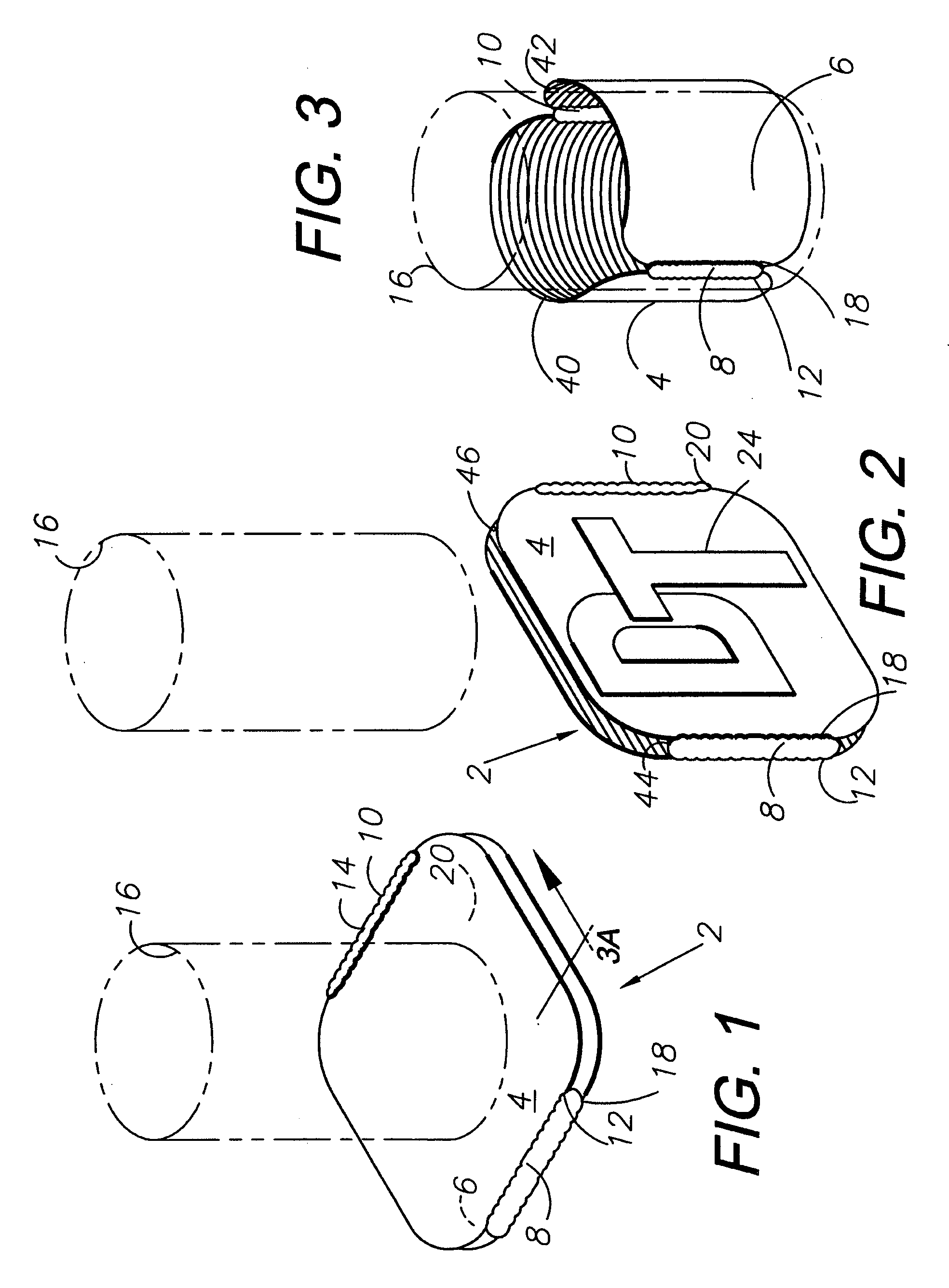
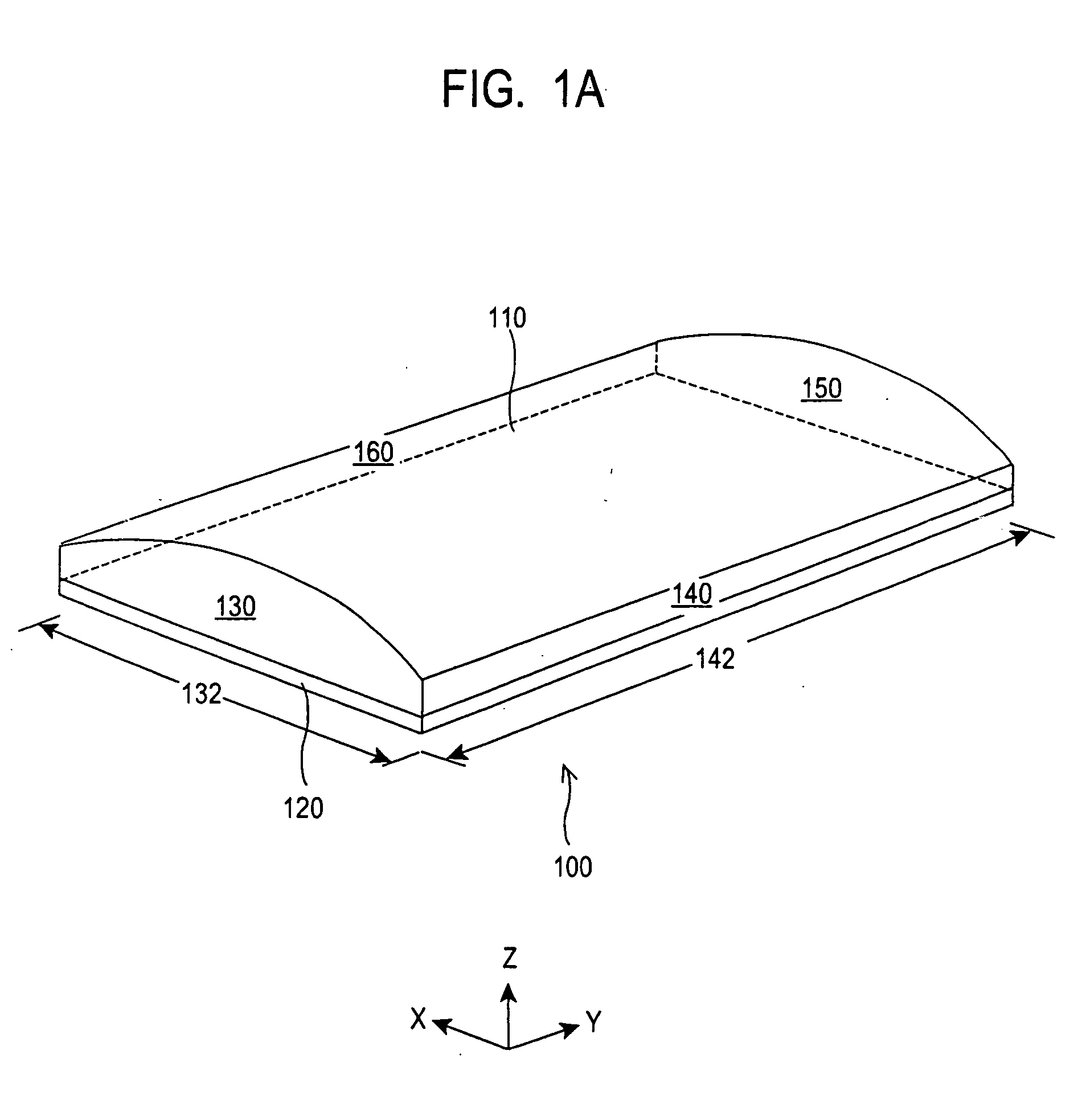
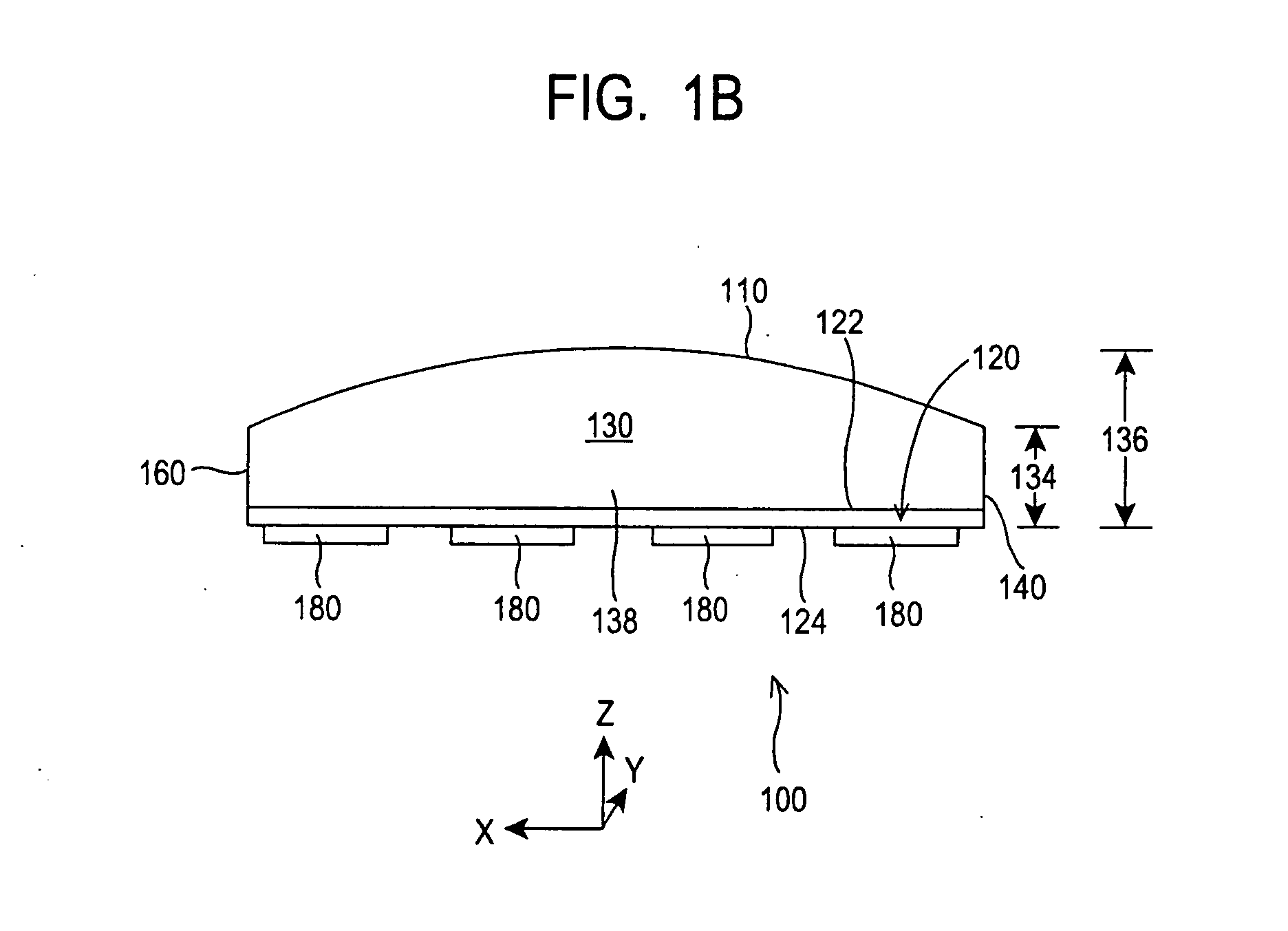
Combination coaster and sleeve apparatus
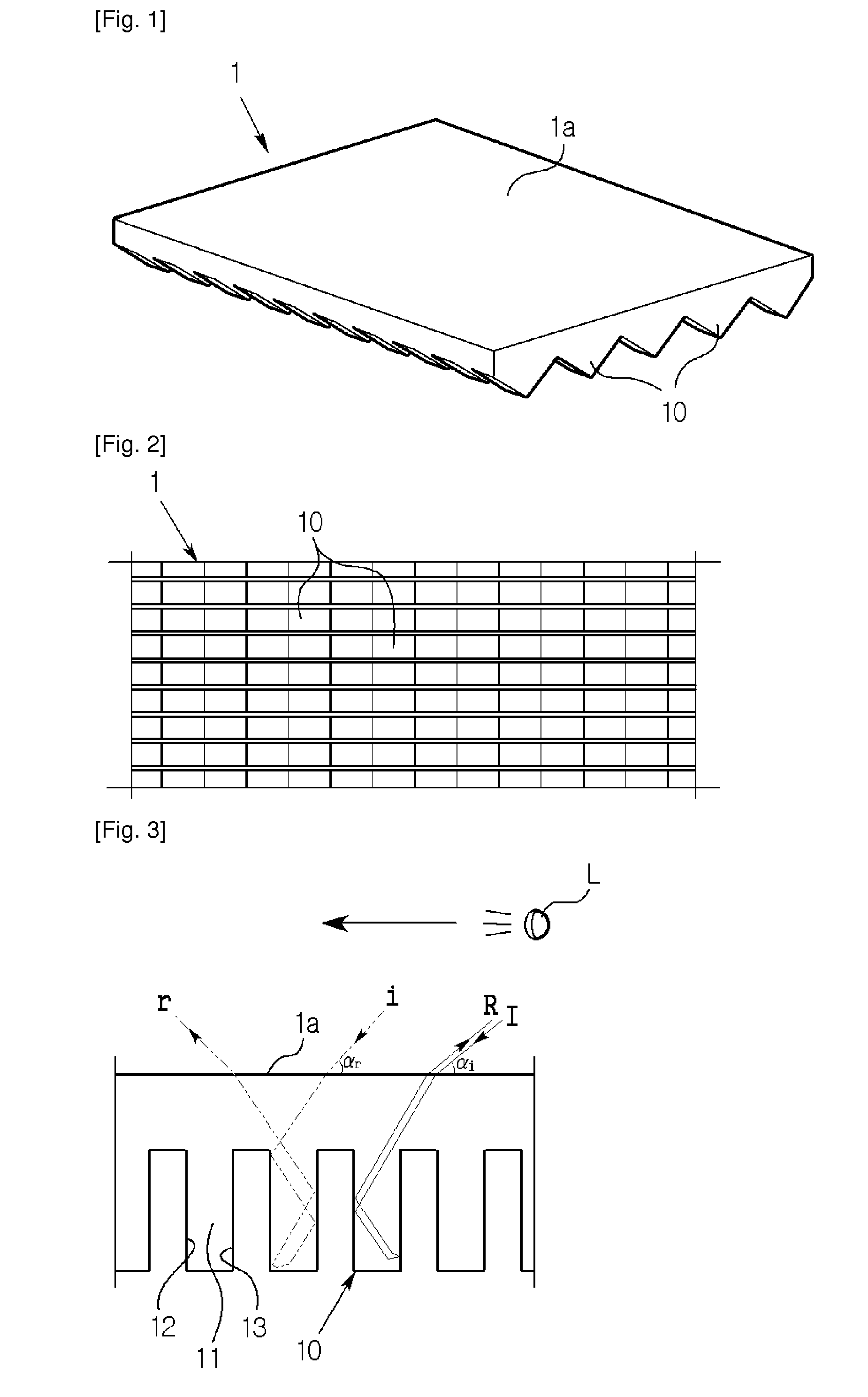
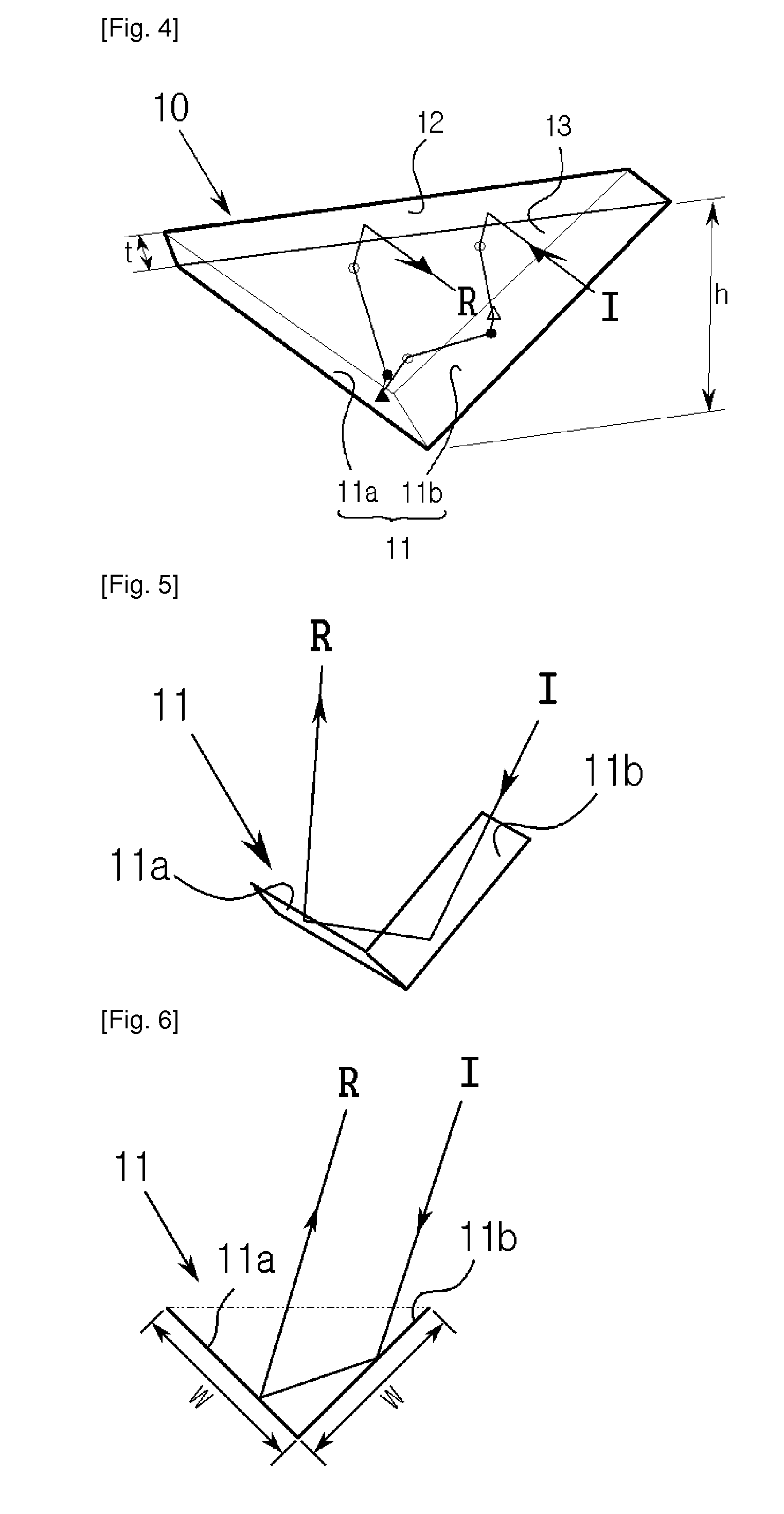
An improved combination holder and coaster apparatus for receiving a container or vessel which includes first and second thermally insulative, flexible panels joined together by a joint comprised of a stretchable, flexible, adhesive material adapted to return the device to a collapsed coaster configuration. While in receipt of the vessel or container, the device is adapted to an elliptical holder configuration in which the panels are separated by a projected dihedral angle generally between approximately 0 degrees through approximately 180 degrees allowing the elliptical holder to receive the vessel or container.
Owner:TULP DAVID W
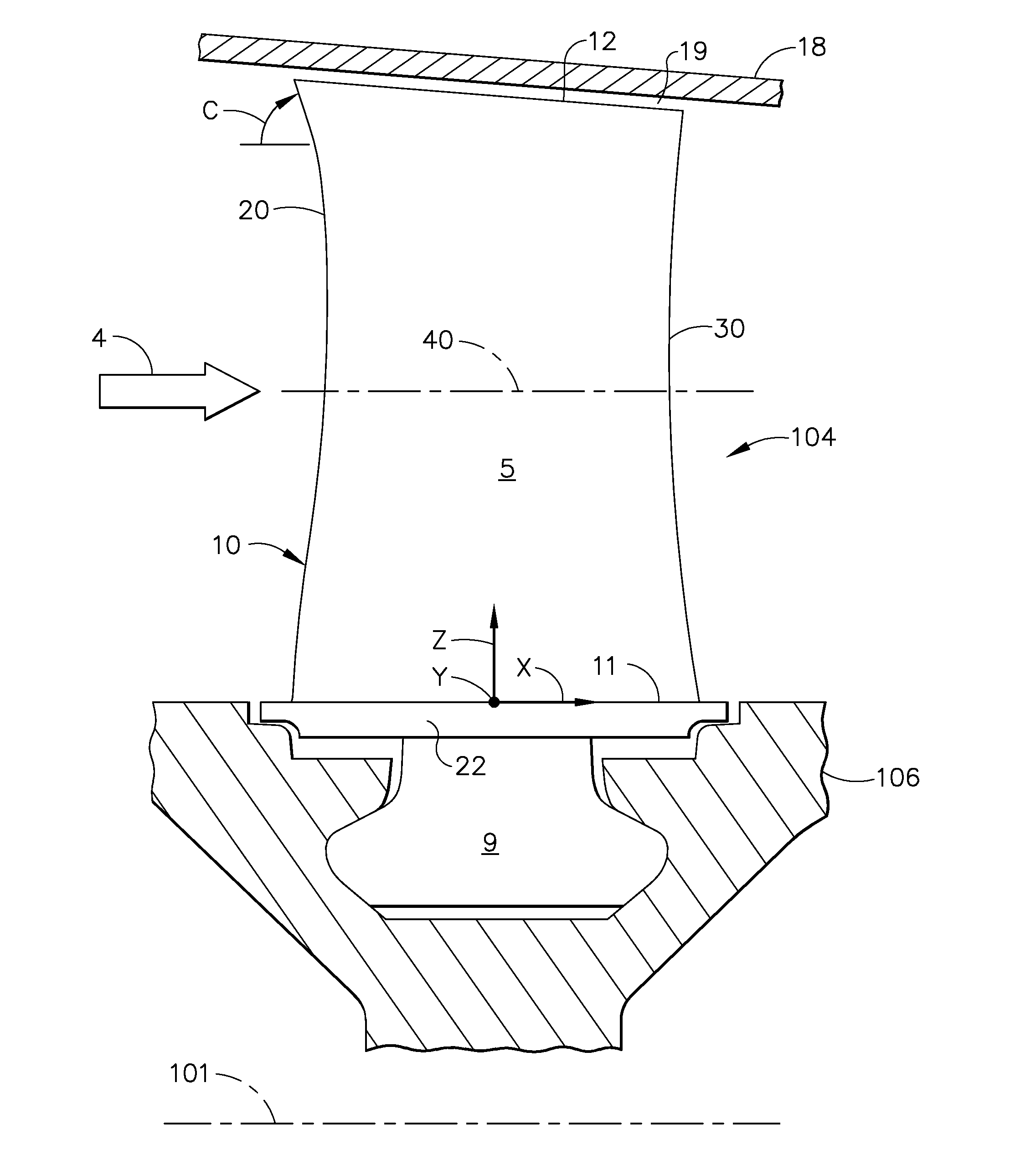
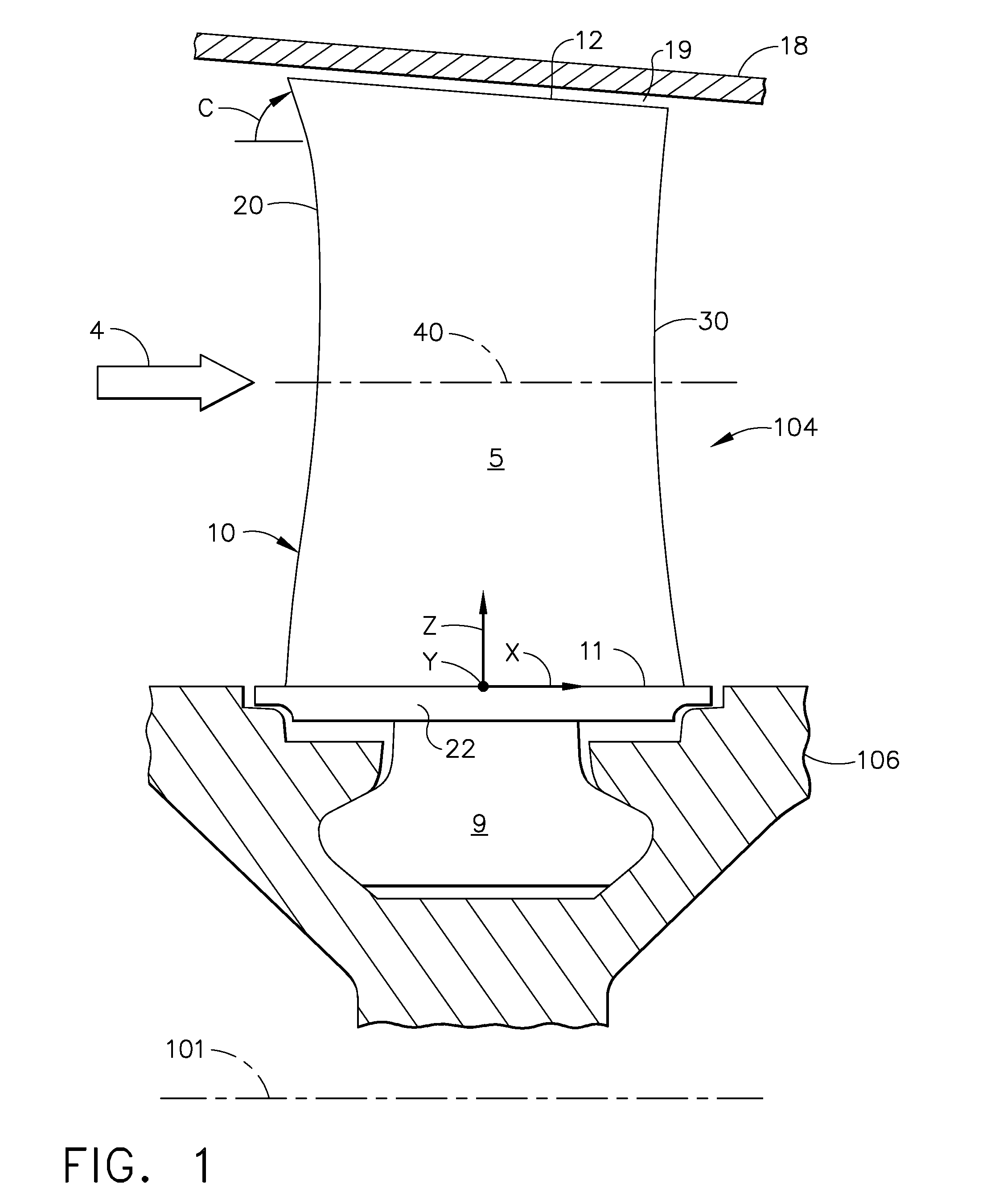
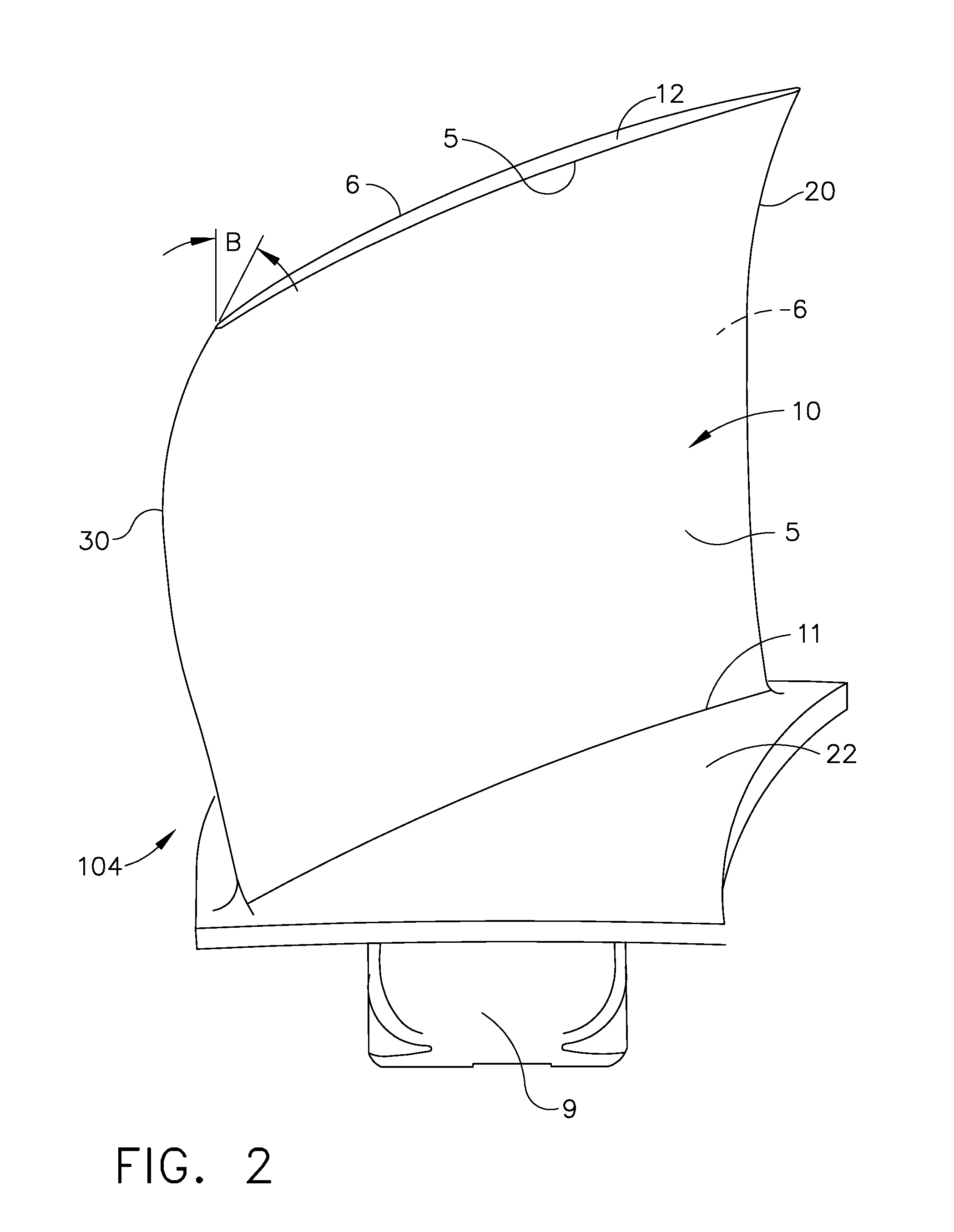
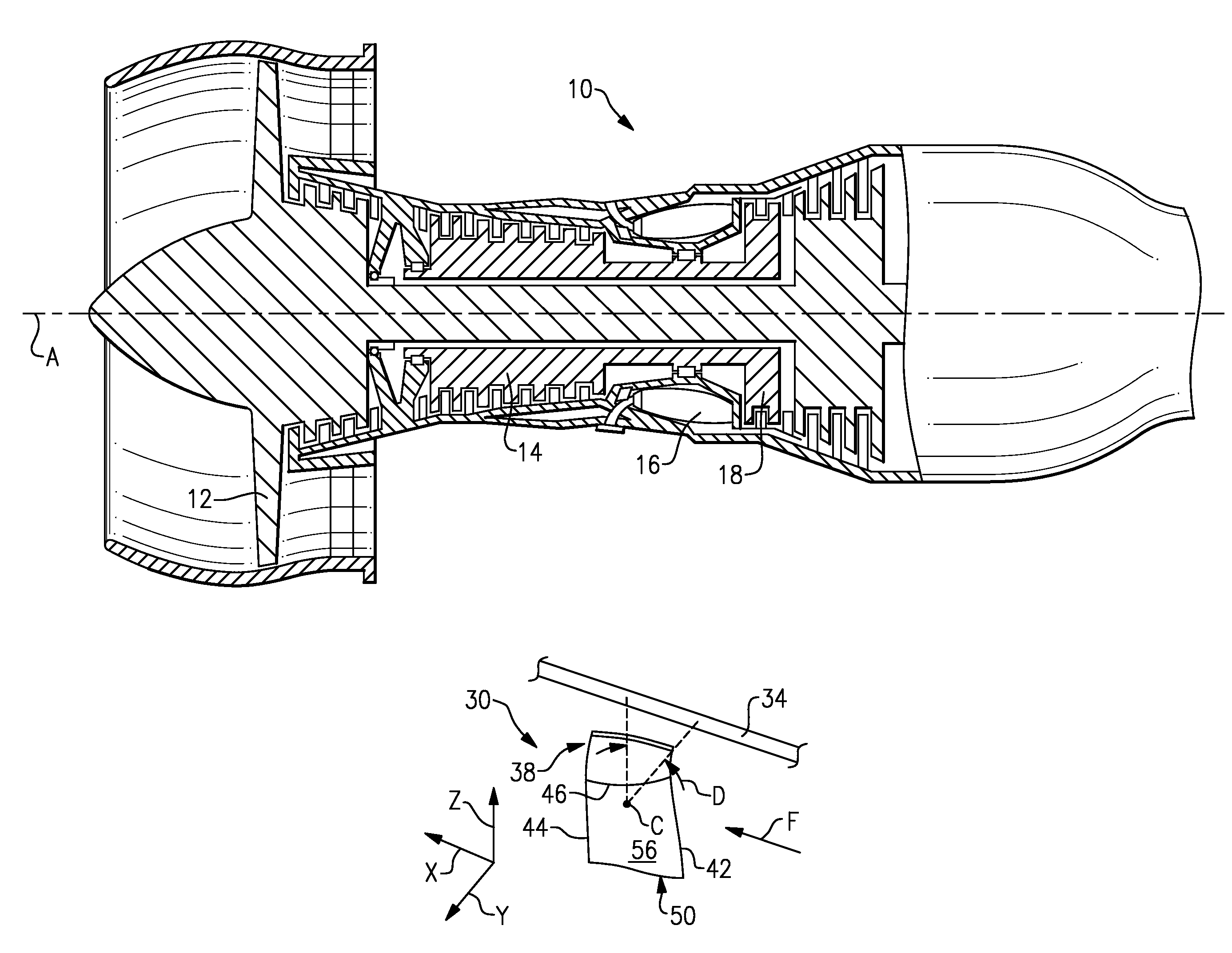
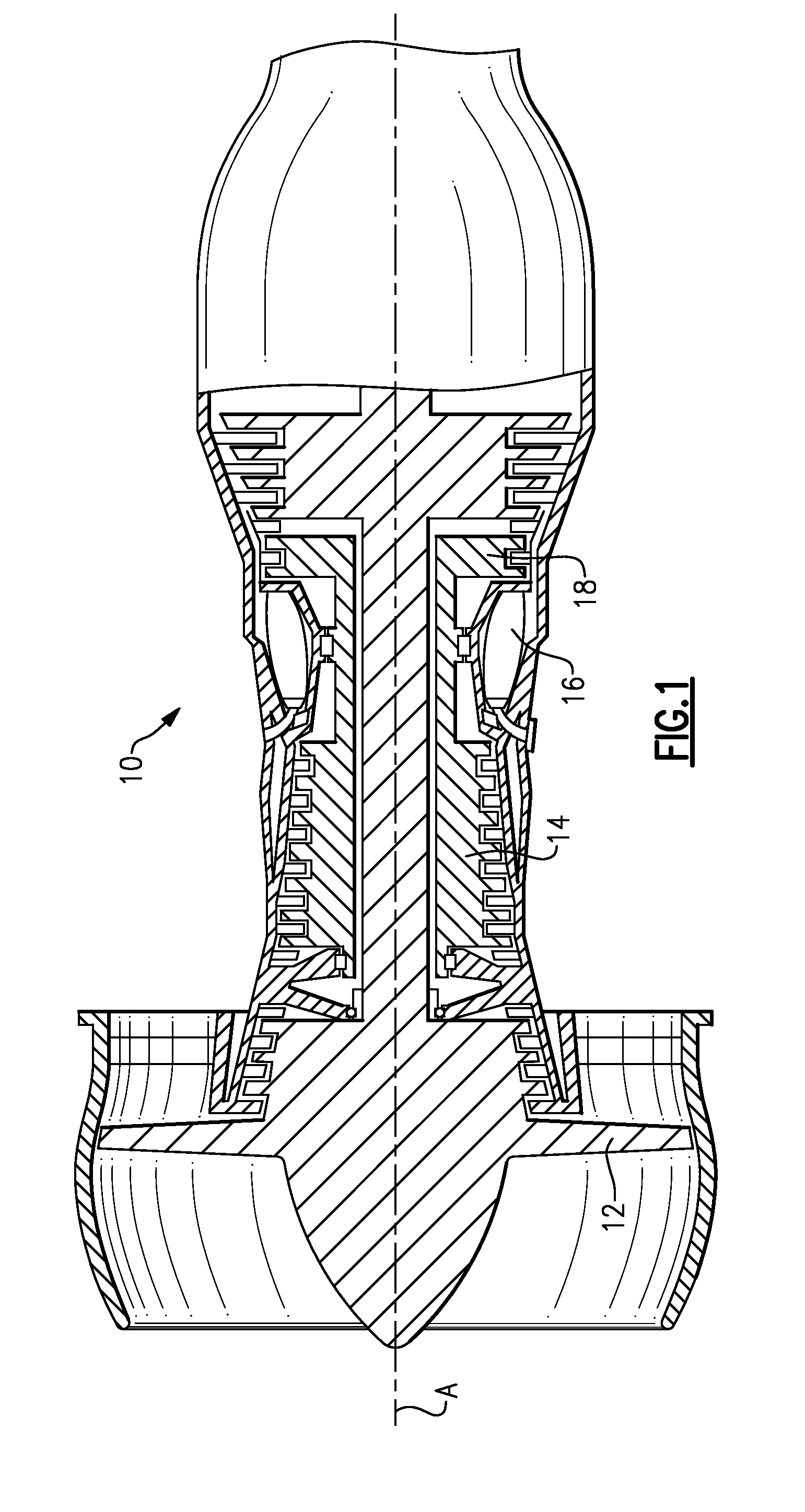
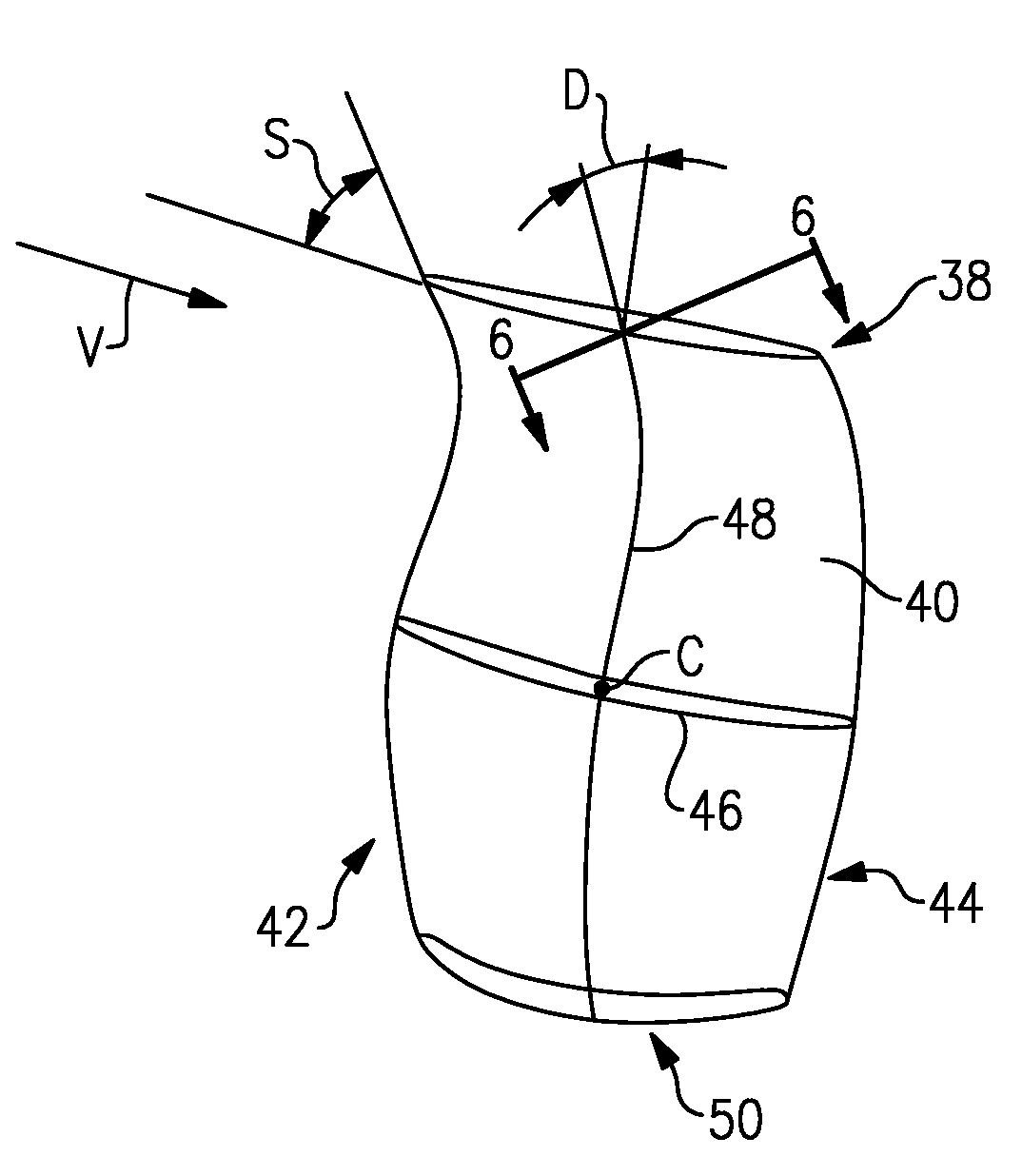
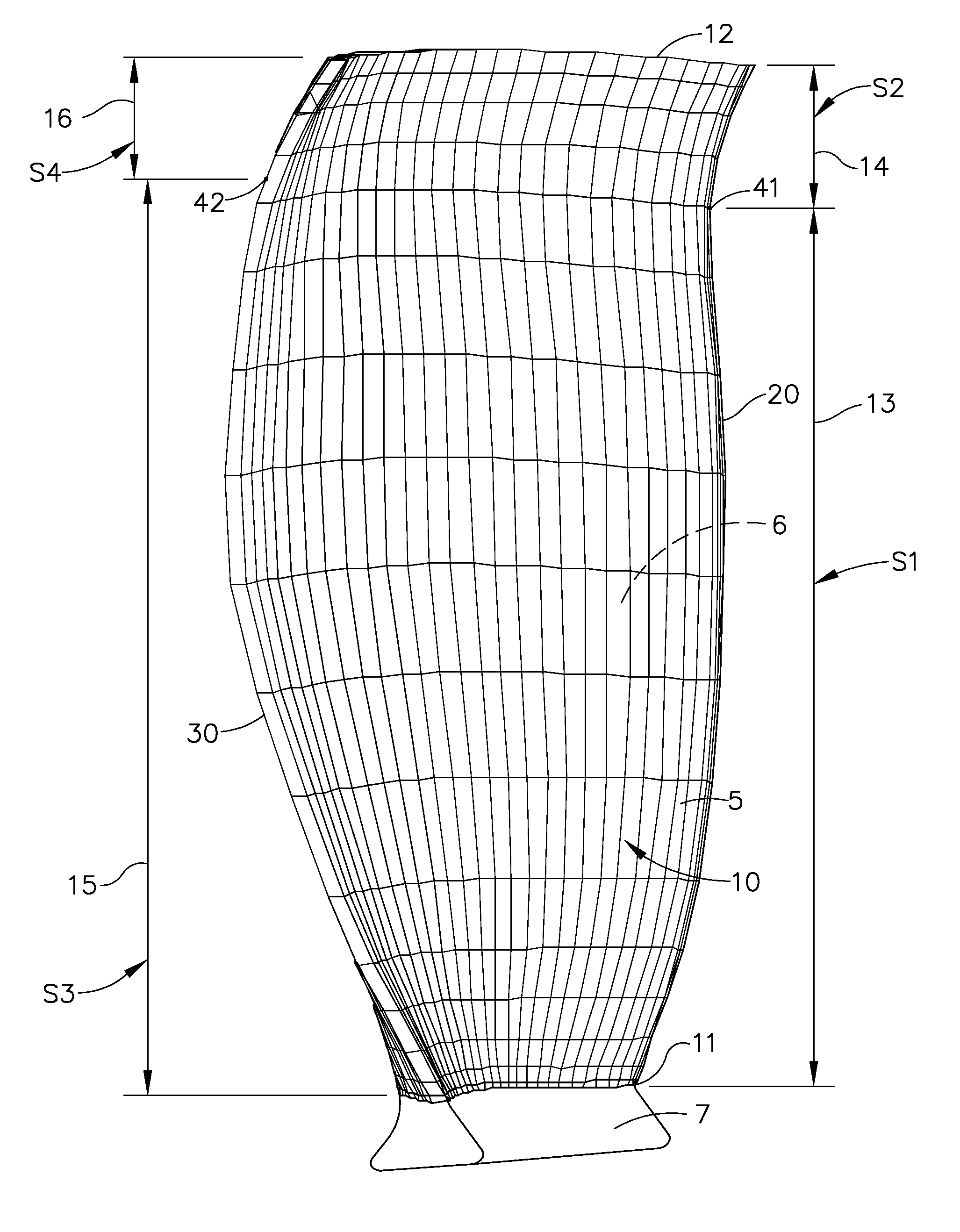
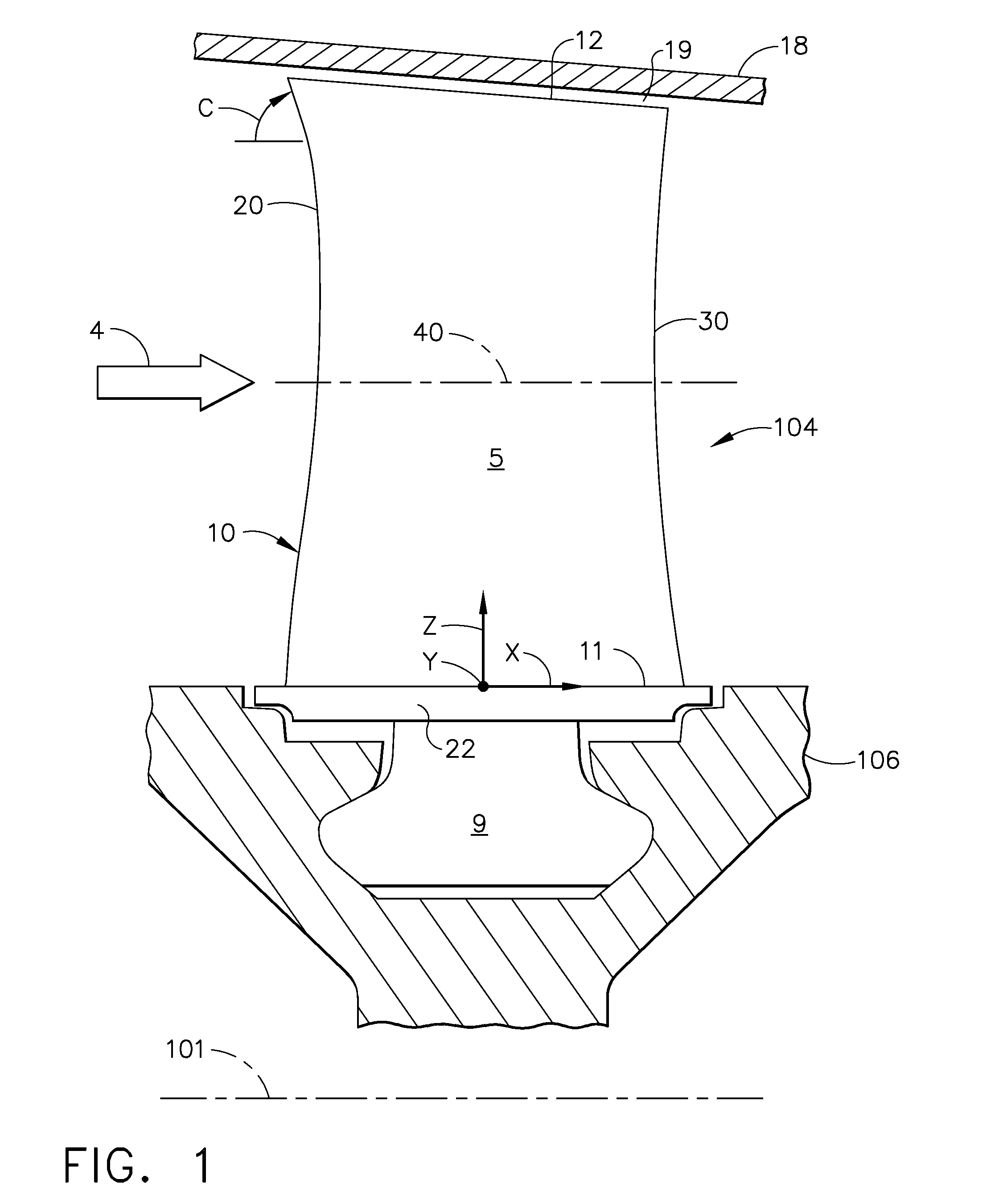
Compressor airfoil with tip dihedral
An airfoil for a compressor is described. The airfoil has a root, an airfoil tip, a leading edge, a trailing edge, airfoil pressure and suction sides extending between the leading edge and the trailing edge. The airfoil has an inner span region and an outer span region and the trailing edge has a dihedral profile such that the trailing edge dihedral angle decreases in at least a portion of the inner span region and the outer span region.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
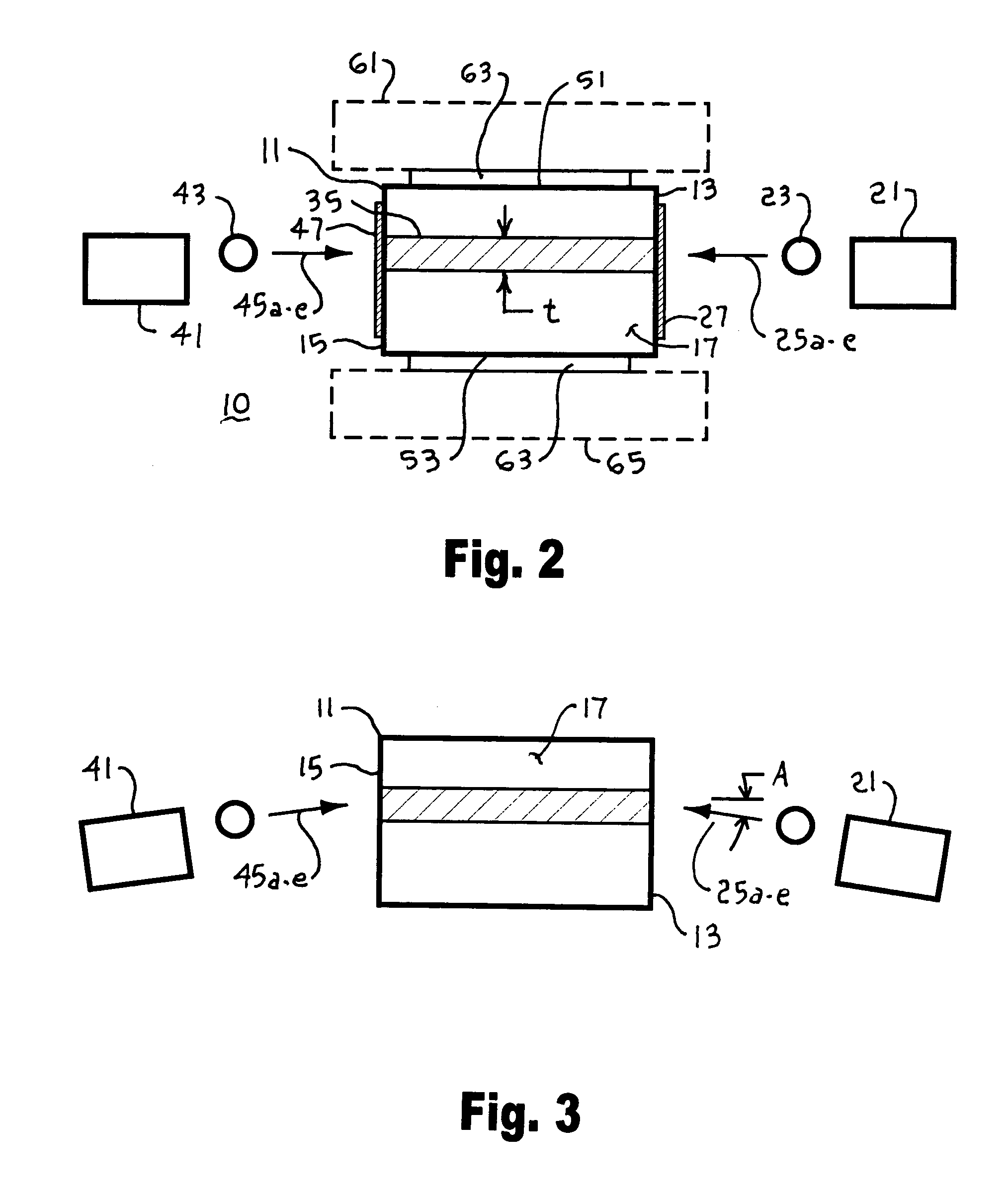
High-gain diode-pumped laser amplifier
InactiveUS20060114961A1Minimize parasitic amplified spontaneous emissionActive medium shape and constructionOptical devices for laserAudio power amplifierOptical coating
A laser amplifier includes a laser active slab with a source of pump power to amplify an input laser beam, the laser active slab including a block of laser active material having opposed lateral faces defining a wedge lateral dihedral angle, opposed longitudinal faces, and opposed parallel transverse faces, the wedge lateral dihedral angle specified to minimize parasitic amplified spontaneous emission. The source of pump power may be one or more laser diode bars and microlenses producing a gain sheet in the laser active slab. The lateral faces may include optical coatings highly transmitting at a wavelength of the pump power and highly reflecting at a lasing wavelength to provide a folded path for the input laser beam though the gain sheet. The laser amplifier may optionally include one or more external mirrors highly reflecting at the lasing wavelength positioned and oriented to provide one or more additional zig-zag passes through the gain sheet for the input laser beam and to provide a multi-pass-amplified laser beam.
Owner:MANNI JEFFREY G
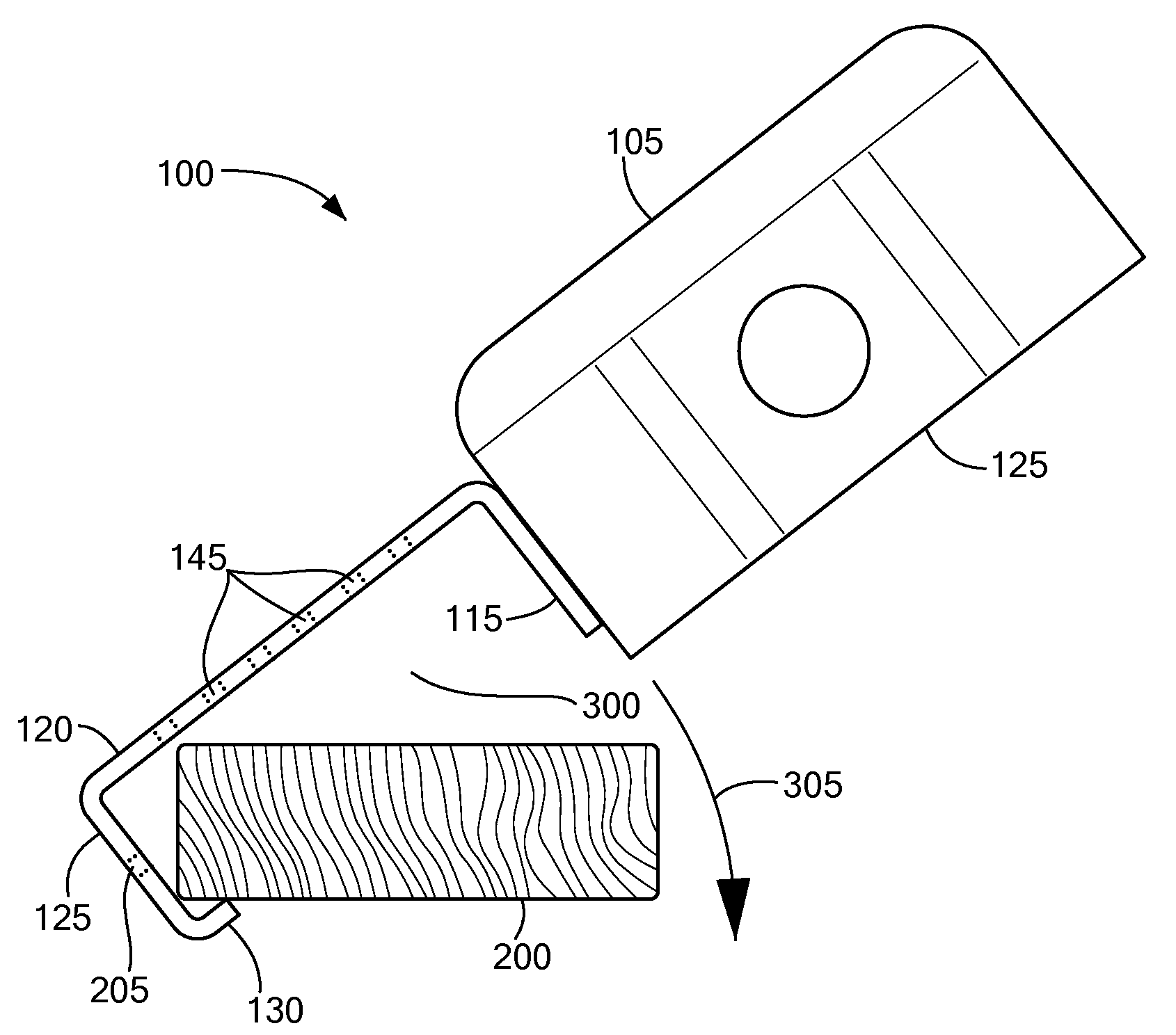
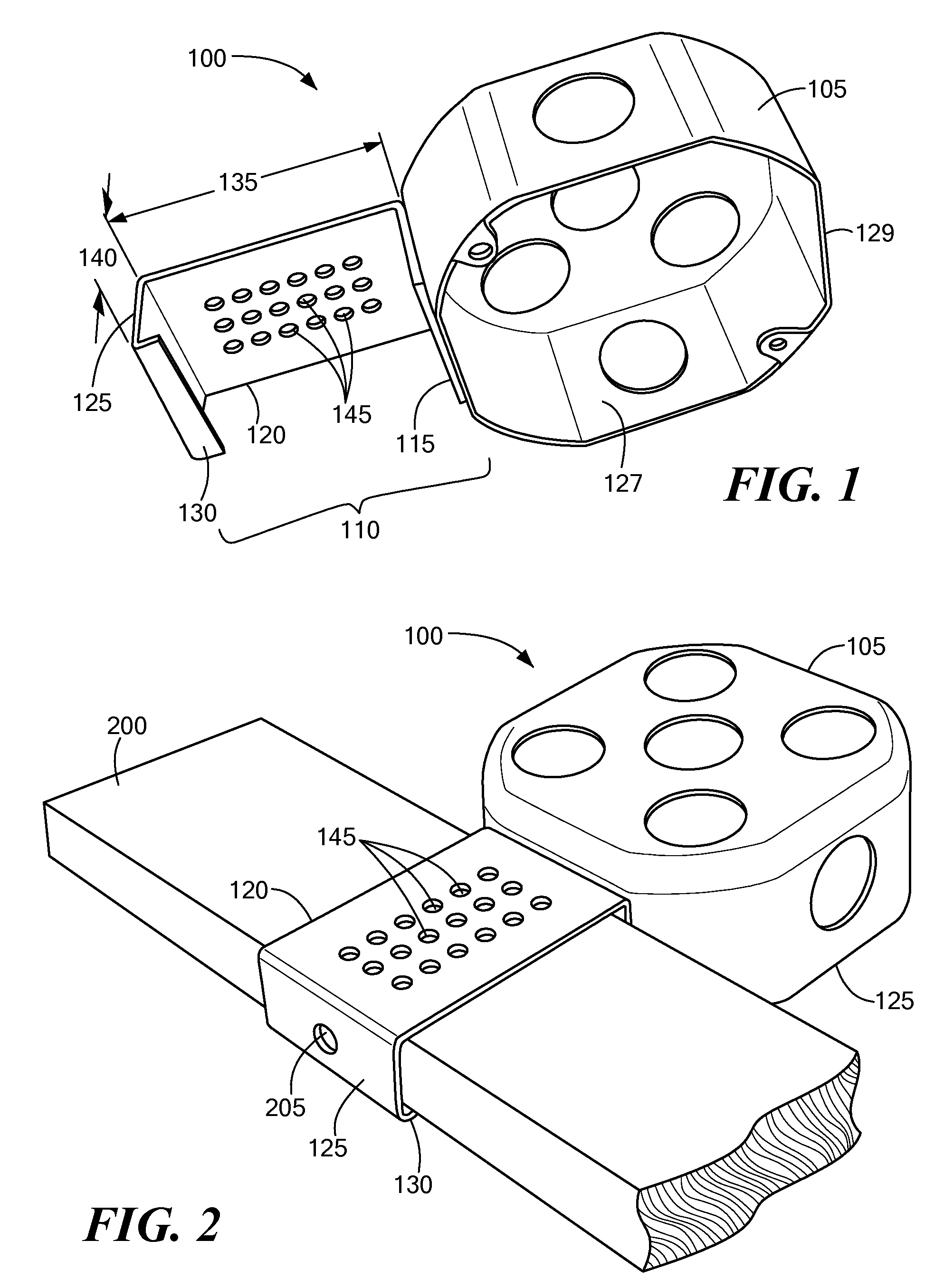
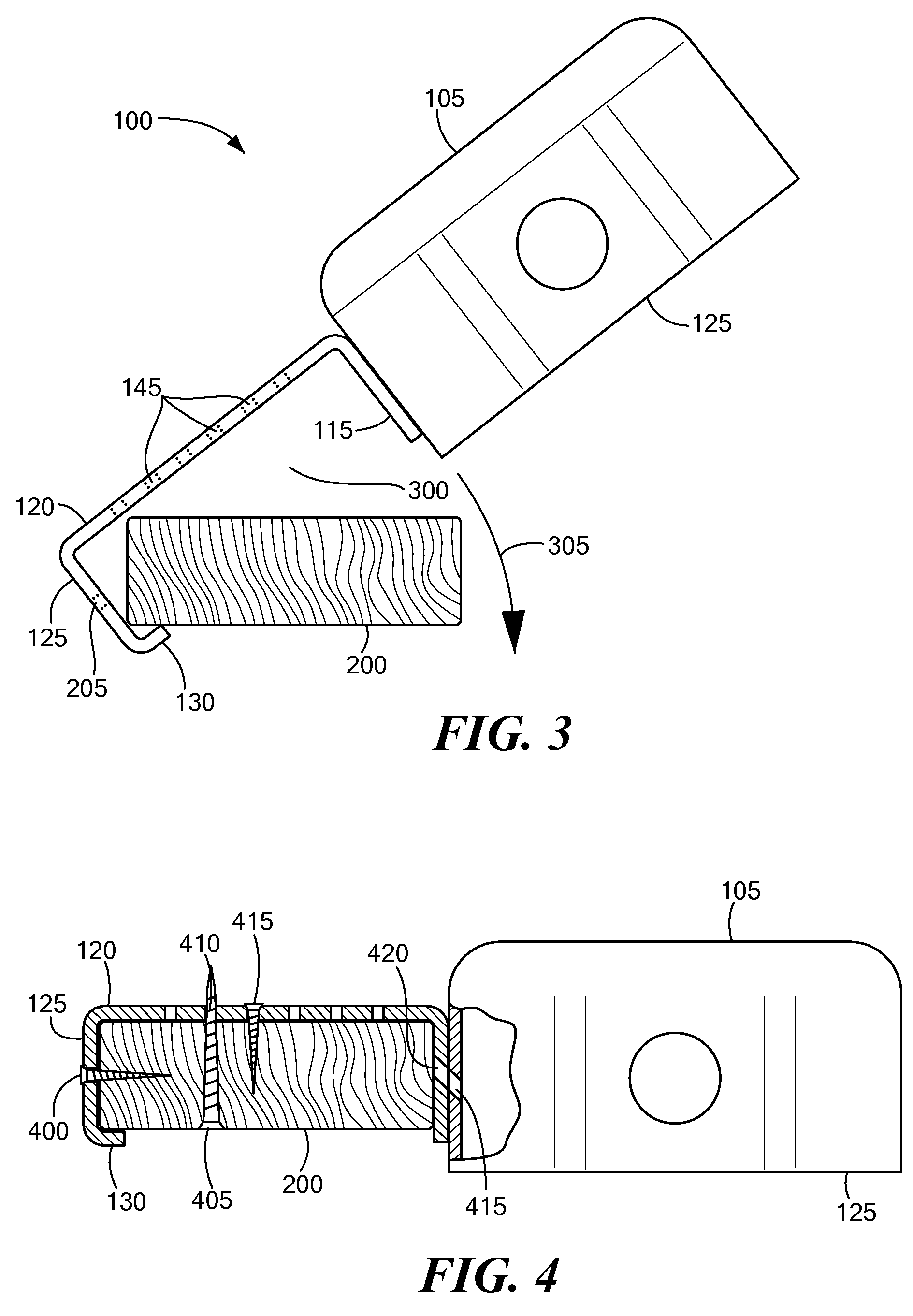
Mounting bracket for electrical junction box, luminaire or the like
Electrical fixtures, such as junction boxes or recessed luminaires, include mounting brackets that support the fixtures from structural members while fasteners, such as screws or nails, are driven through the mounting brackets, thereby facilitating mounting the fixtures. Each of the mounting brackets has a general U-shape that includes at least three generally planar sides. The top side is generally perpendicular to the other two sides, and the top side connects the other two sides and together. The three sides define (in cross-section) a structural member receiver opening. An inside dimension of the structural member receiver opening is such that bracket fits snugly around at least a portion of a commonly sized wood or metal structural member, such as a furring strip or joist, used in ceiling construction. In one embodiment, two of the sides of the structural member receiver opening define an acute dihedral angle to hood around the edge of a metal furring strip.
Owner:GOODE JOHN A
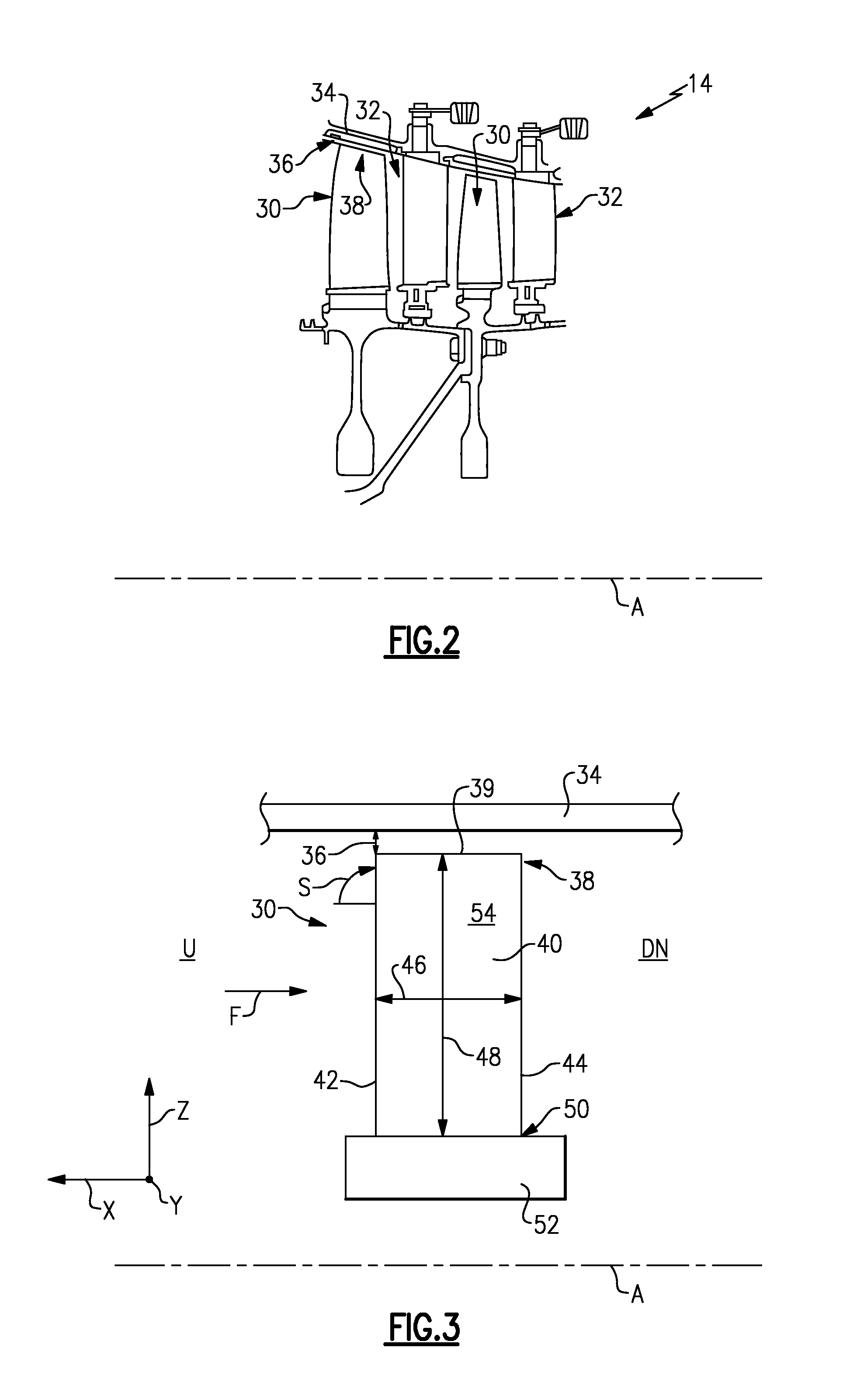
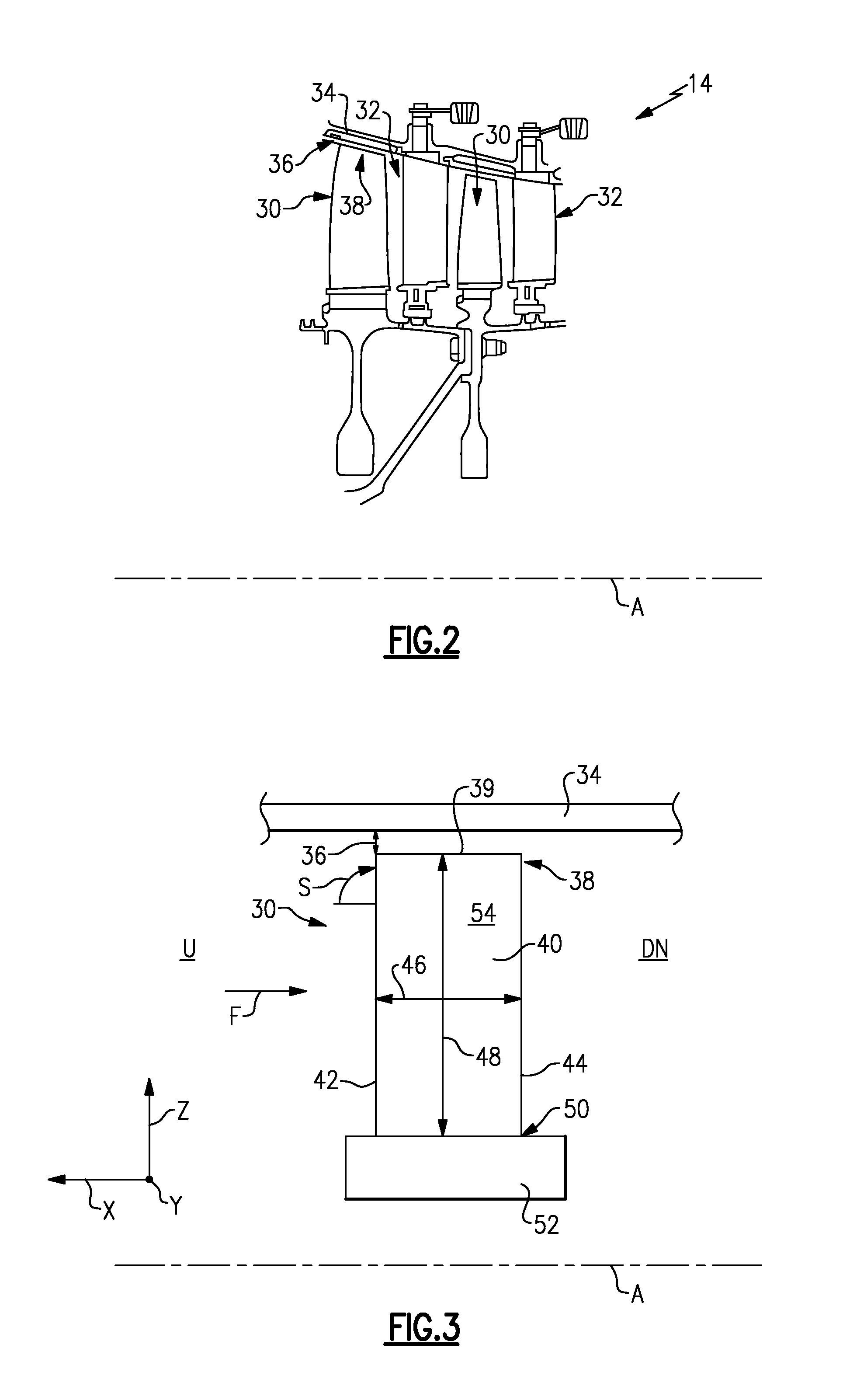
Gas turbine engine airfoil
A rotor blade for a gas turbine engine includes an airfoil that extends in span between a root and a tip region. A leading edge and a trailing edge of the airfoil section extend between a chord line of the airfoil. A sweep angle is defined at the leading edge of the airfoil section, and a dihedral angle is defined relative to the chord line of the airfoil section. The sweep angle and the dihedral angle are localized at the tip region of the airfoil section.
Owner:RTX CORP
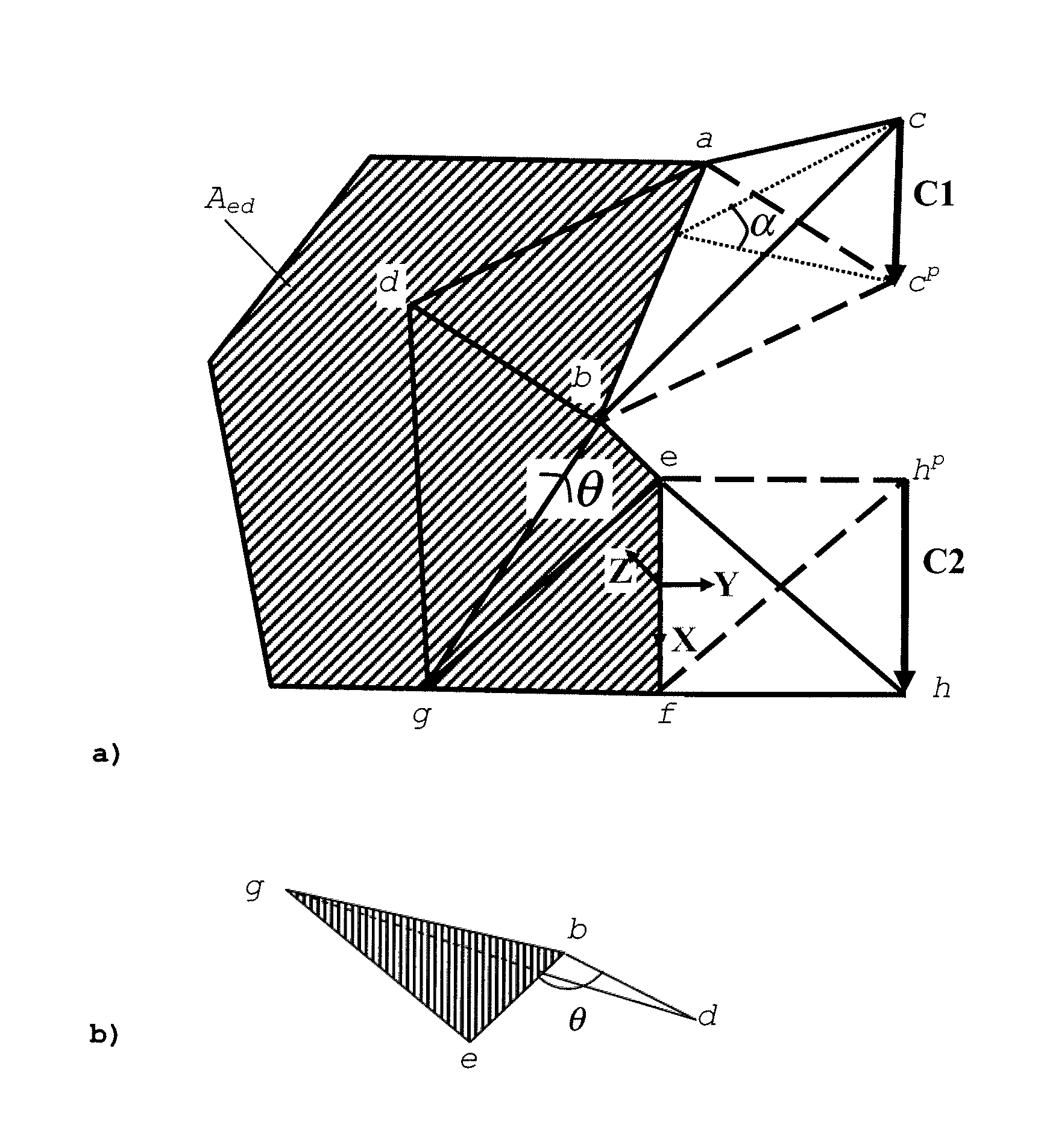
Method and apparatus for encoding 3D mesh models, and method and apparatus for decoding encoded 3D mesh models
ActiveUS8884953B2Reduce redundancyImprove coding efficiencyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmColatitude
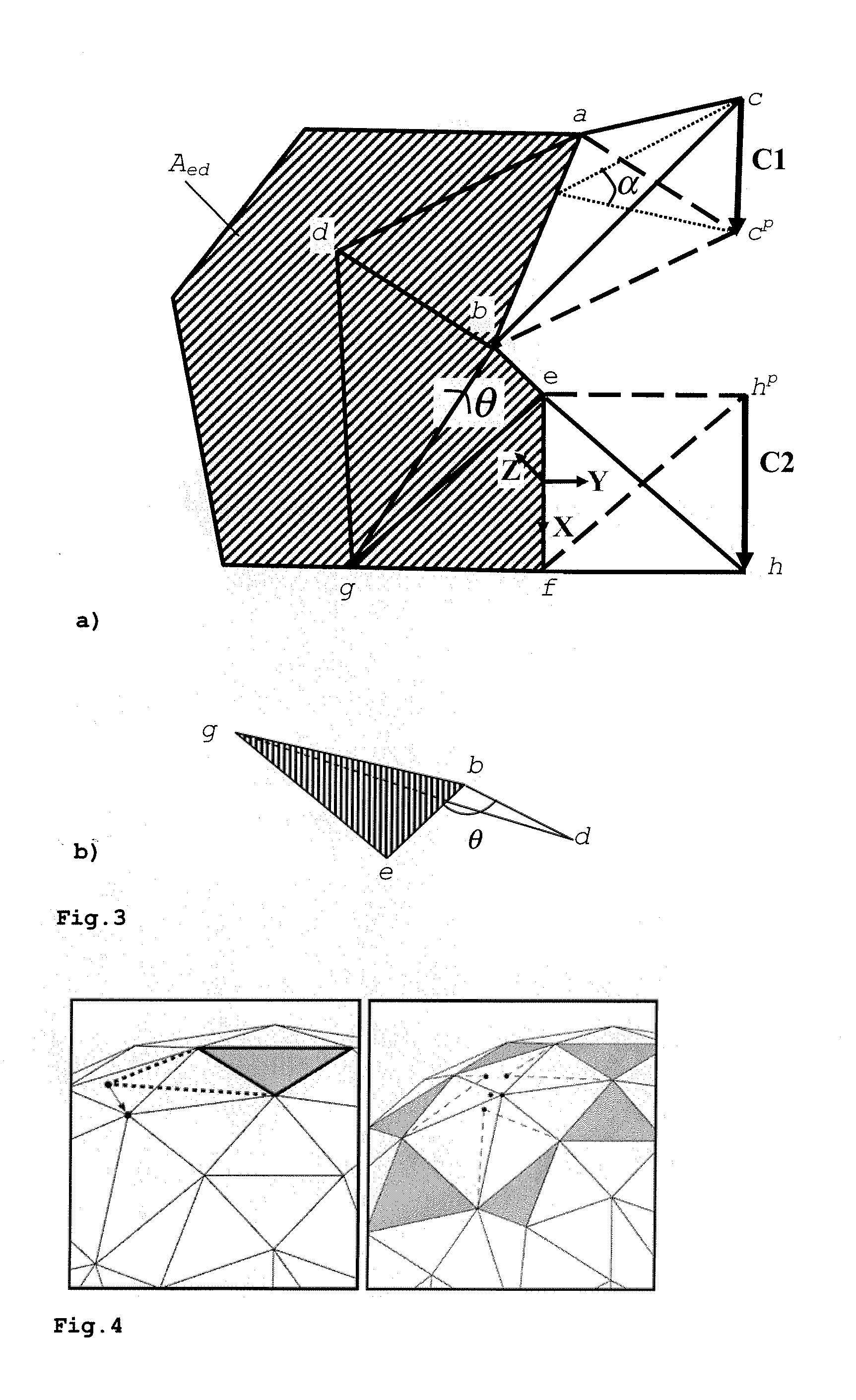
3D mesh models are widely used in various applications for representing 3D objects. These models are made of vertices and corresponding triangles, which can be compressed based on prediction and residuals. The present invention improves the accuracy of parallelogram prediction, particularly near sharp features. The proposed 3D mesh model encoding comprises analyzing the spatial or dihedral angles between triangles, clustering triangles with similar or equal dihedral angles, and defining a representative dihedral angle for each cluster. Triangles of each cluster are then encoded relative to individual prediction triangles having the representative dihedral angle according to the cluster. Additionally, the prediction triangle may be mirrored. An indication of the encoding mode is inserted into each vertex of the encoded bitstream. A decoder extracts the encoding mode indication, reconstructs the individual prediction triangles based on the respective representative dihedral angles and performs triangle prediction and reconstruction.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
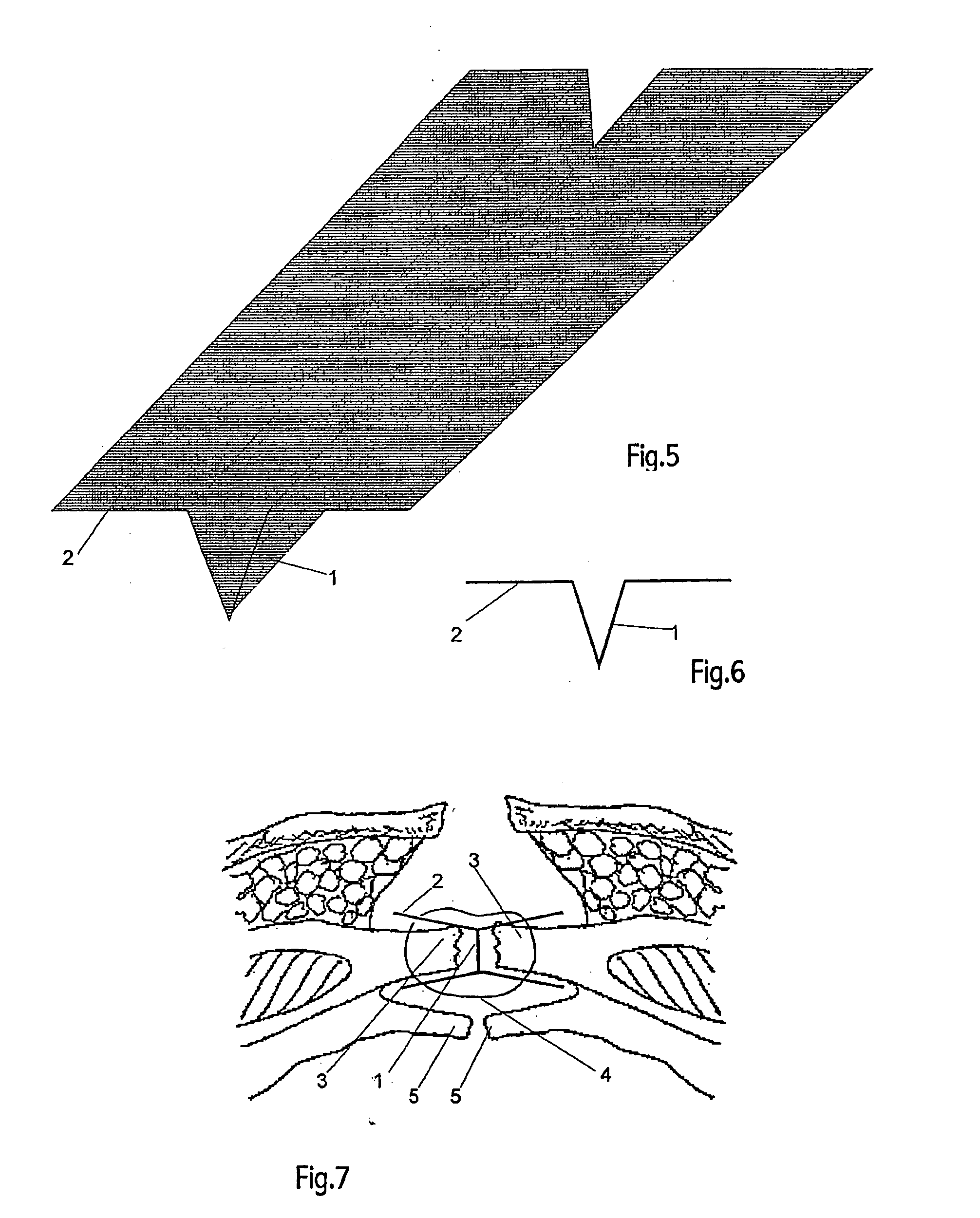
Wall prosthesis that can be implanted in the center of a wound to reinforce abdominal wall closure
ActiveUS20050043818A1Improve the immunityReduce the possibilityProsthesisWound clampsAbdominal wall closureAponeurosis
The invention relates to a prosthesis that can be implanted in the centre of wall wound scarring. The inventive prosthesis, which is intended for use in abdominal surgery, is provided with a geometric shape in the form of sheets that converge in dihedral angles. The sheets or planes are made from a synthetic biotolerated material in porous form with large pores. One of said planes is inserted into the centre of the scarring between the two aponeurotic surfaces to be joined. The other plane(s) of the prosthesis, which is perpendicular to the aforementioned plane, is arranged so as to overlap the aponeurotic edges of the edge of the section. The proliferation obtained around the prosthesis, in the scarring centre and close thereto, provides stress resistance greater than that obtained in standard closures, thereby greatly reducing the risk of hernias caused by a badly healed wound.
Owner:BUJAN VARELA JULIA +2
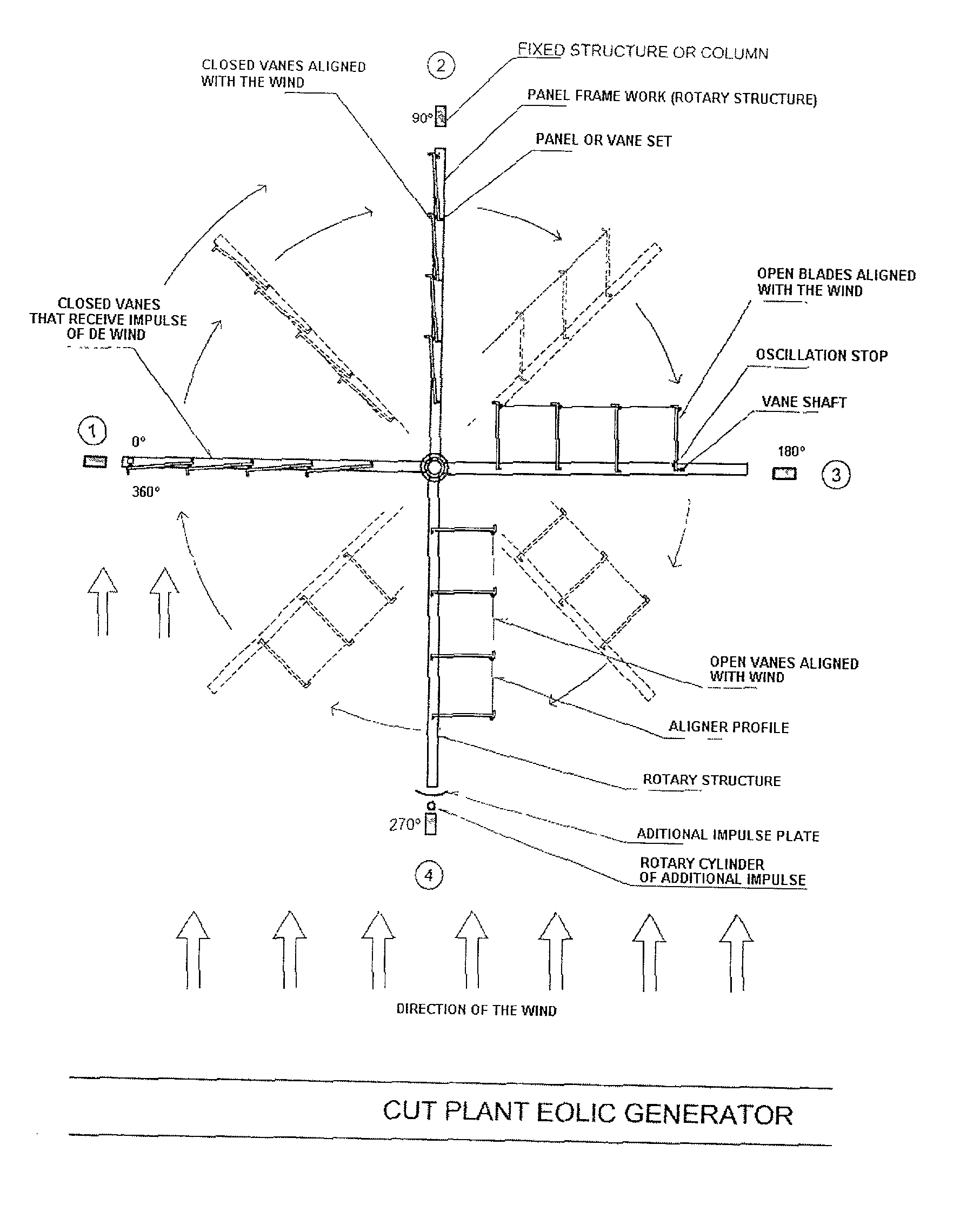
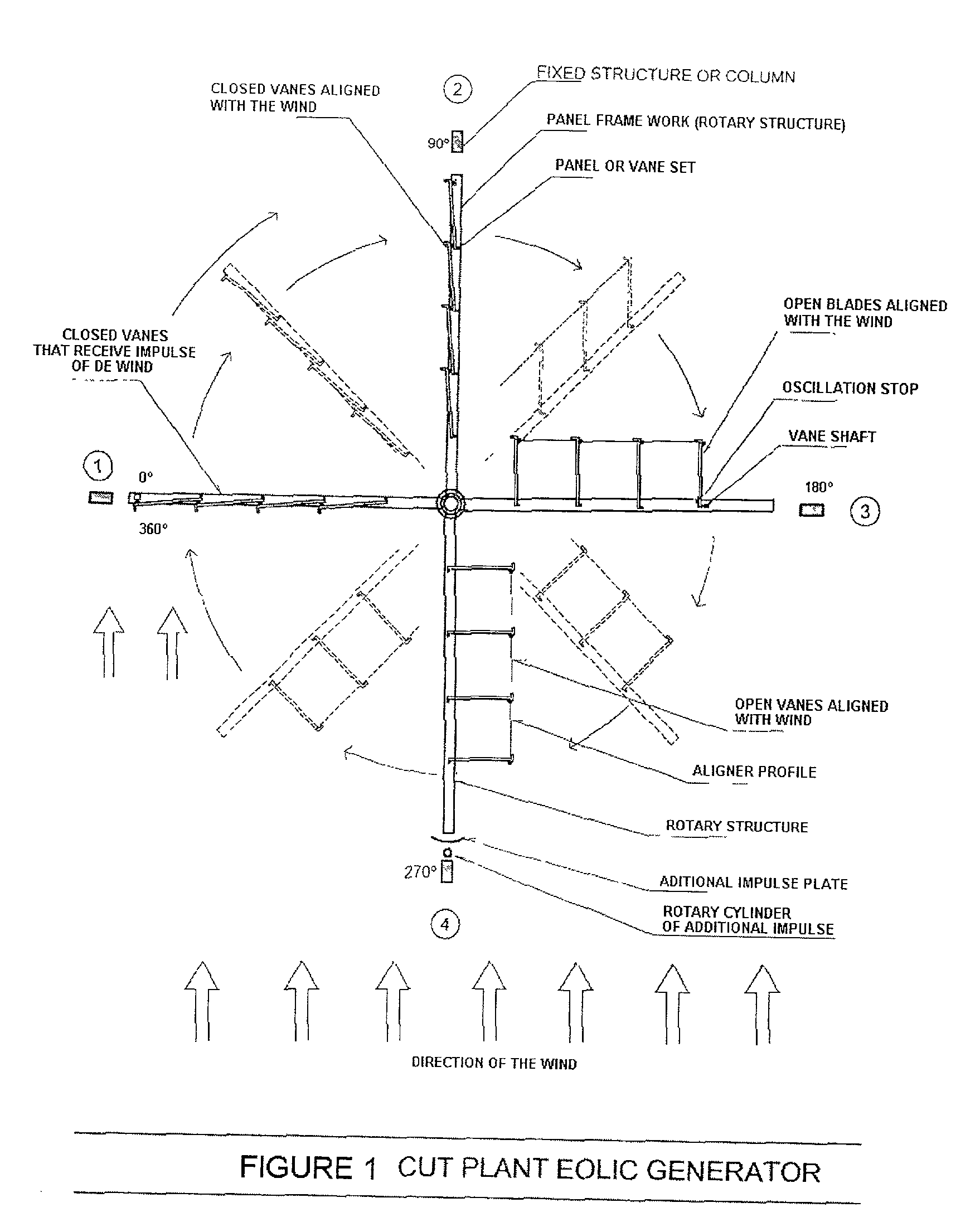
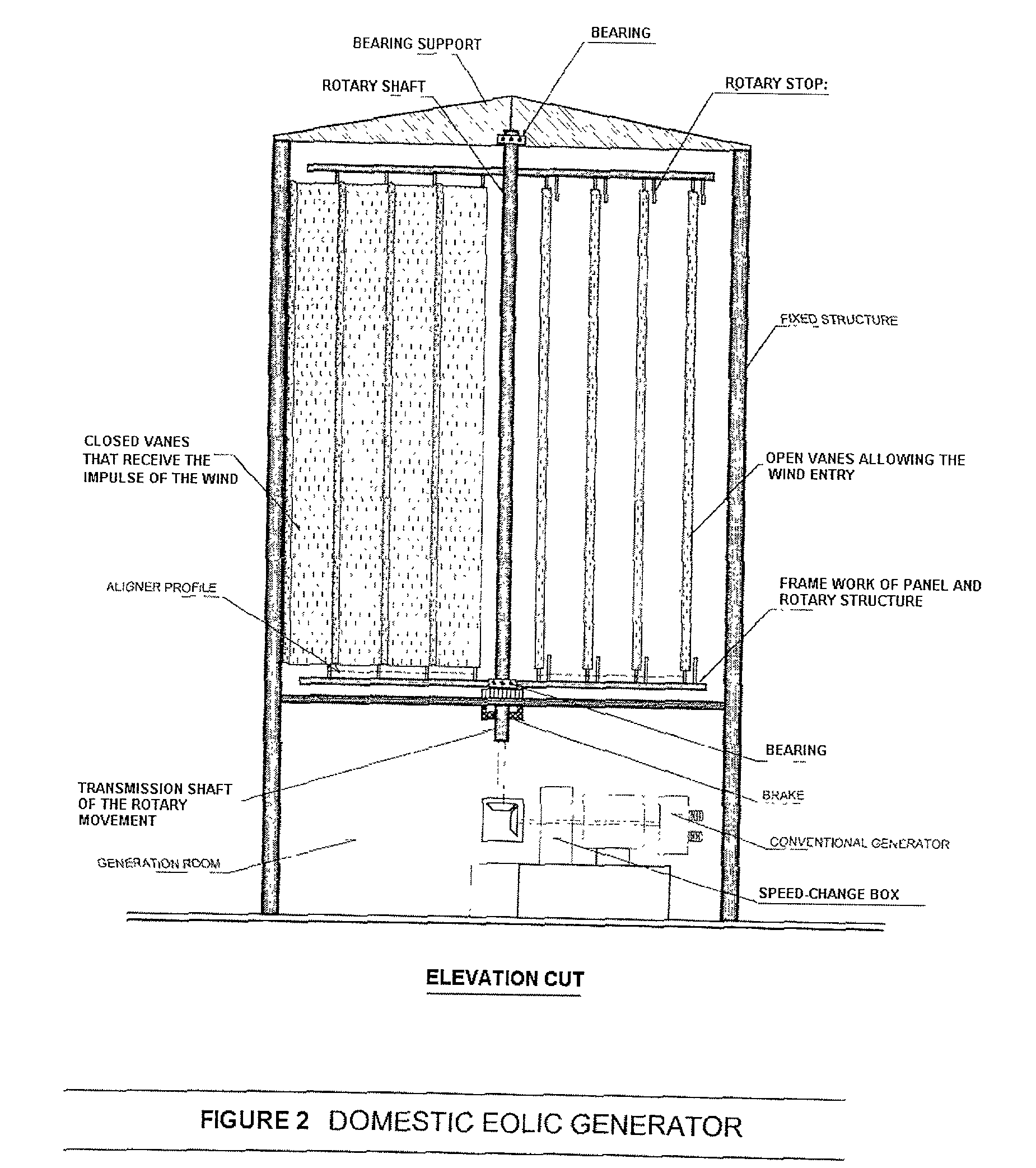
Eolic marine electrical generator geem
InactiveUS20030201645A1Improve system efficiencyImprove efficiencyEngine fuctionsRailway vehiclesMechanical energyInternal combustion engine
In short, the Eolic Marine Electrical Generator "GEEM" is an extraordinary invention used for capturing the huge impulse force of water or wind, to generate mechanical energy and to transform the mechanical energy into electrical energy, clean and ecological, without consuming vital oxygen thanks to the invention of immense split, self-regulating panels, radially fixed in dihedral angle to a rotary central shaft, panels which capture by shock the inexhaustible energy of the wind, the waves or the ocean currents; or fixed on rotary or flying machines of high speed, with panels formed at the same time by oscillating vanes that at a certain time of a turn of 360° will face the natural energy as a single group or panel, capturing therefrom the impulse force and converting it into rotary movement through the central rotary shaft. Said vanes in other rotation, by oscillation, will divide the panel and will align themselves with the natural vector, permitting its free passage, eliminating the turning resistance of the panel against water or wind and generating a constant rotation movement, independent of the direction of water or wind, and then transforming said mechanical energy into electrical energy by existing conventional means. The invention will allow men to renew their resources and to obtain electrical energy from anywhere in the planet such as cities, countryside, deserts, forests, mountains, seas, floating cities or spaces such as the Arctic and the Antarctic, neither polluting the environment, nor depending on costly networks or non-renewable inputs. The invention will also generate electrical energy on fleets, land vehicles or airship without consuming non-renewable fuel or destroying oxygen. Moreover, this invention replaces the internal combustion engines by eolic electrical motors, changing the scenery of the modern world and recovering the ozone lost in the Antarctic. And this invention will also be used when men in future colonize planets, without rivers or seas but with plenty of wind, to generate electrical energy without polluting this new vital space of the human race.
Owner:PACHECO PEDRO SAAVEDRA
Gas turbine engine airfoil
A rotor blade for a gas turbine engine includes an airfoil that extends in span between a root and a tip region. A leading edge and a trailing edge of the airfoil section extend between a chord line of the airfoil. A sweep angle is defined at the leading edge of the airfoil section, and a dihedral angle is defined relative to the chord line of the airfoil section. The sweep angle and the dihedral angle are localized at the tip region of the airfoil section.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
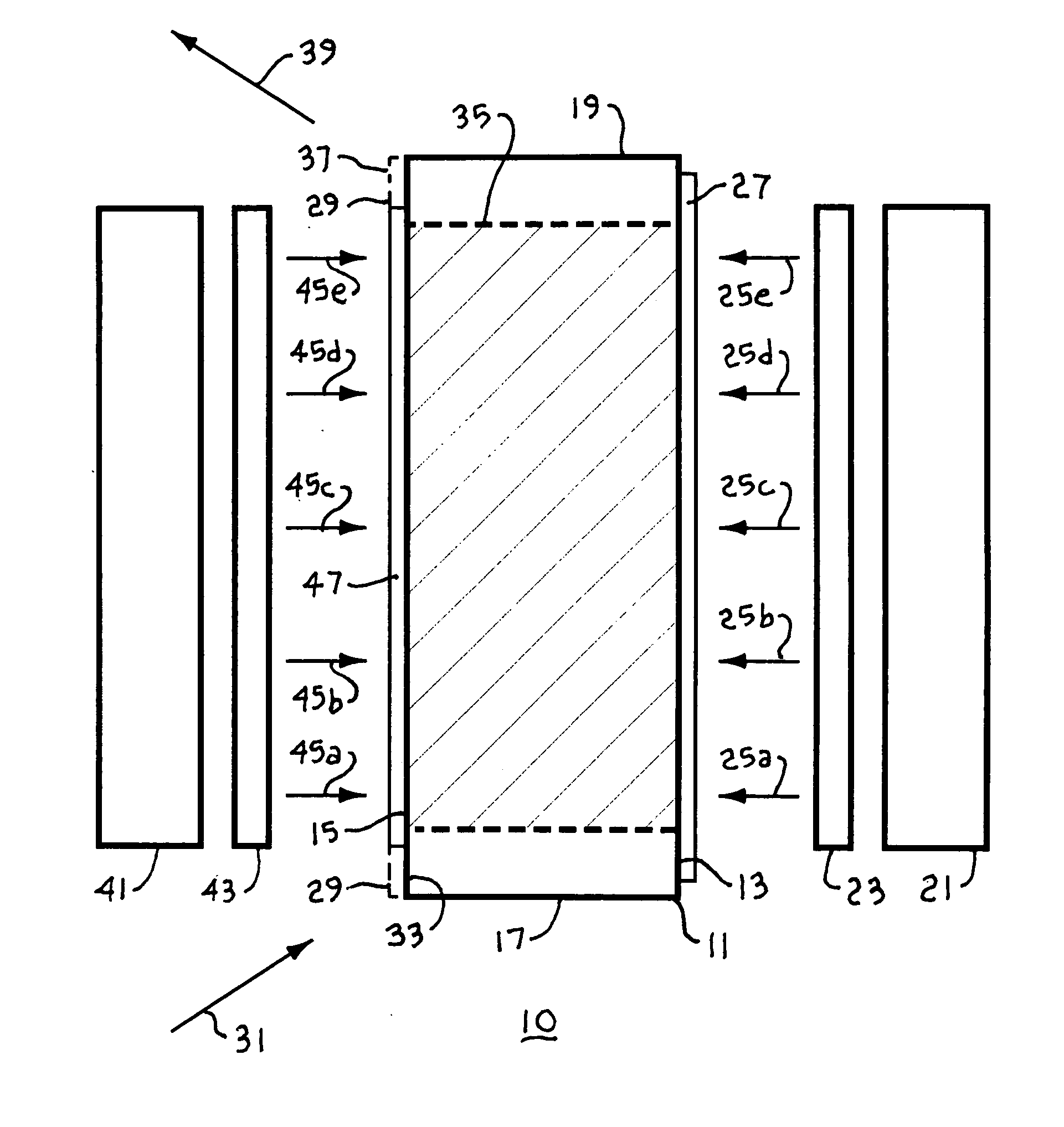
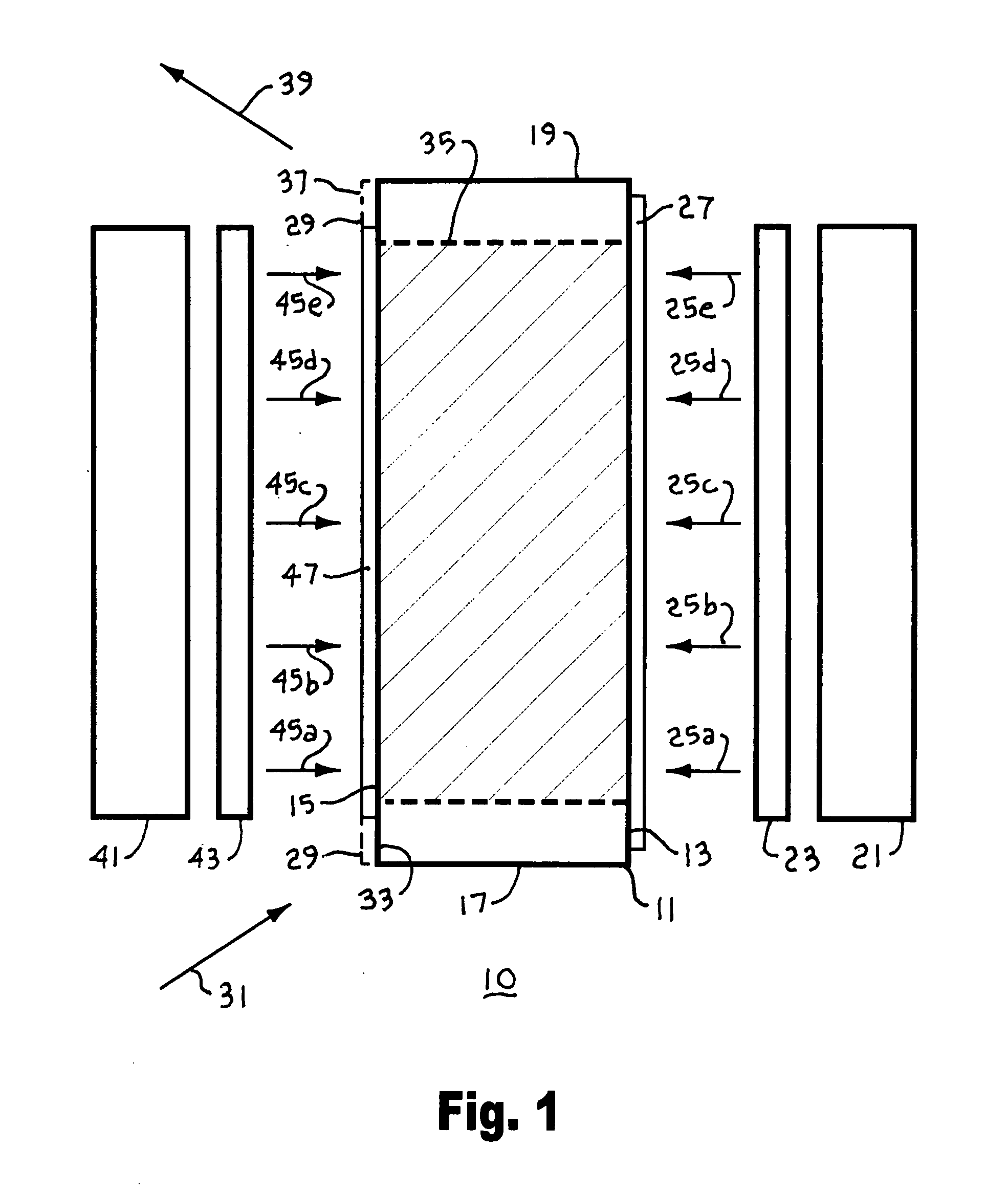
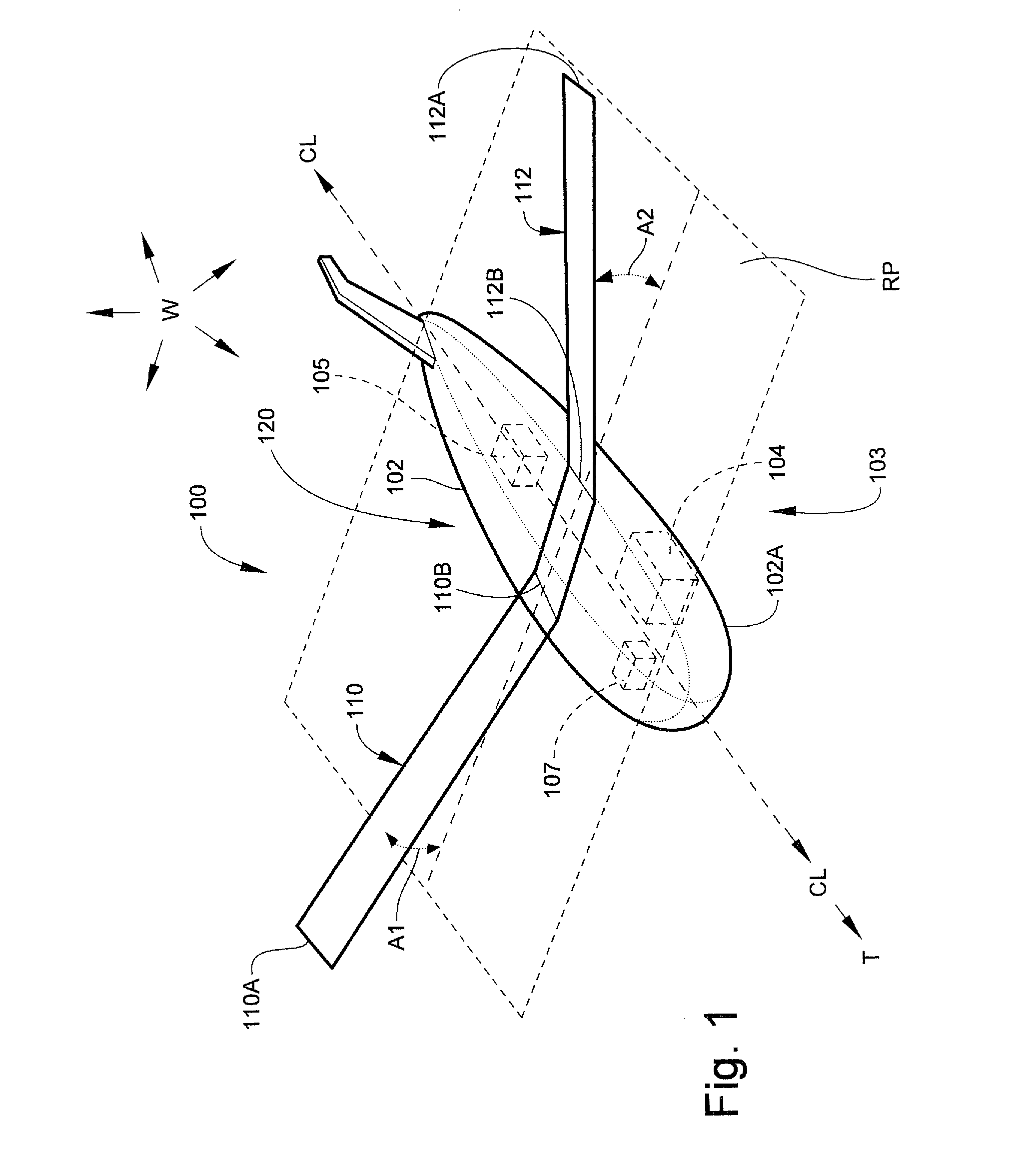
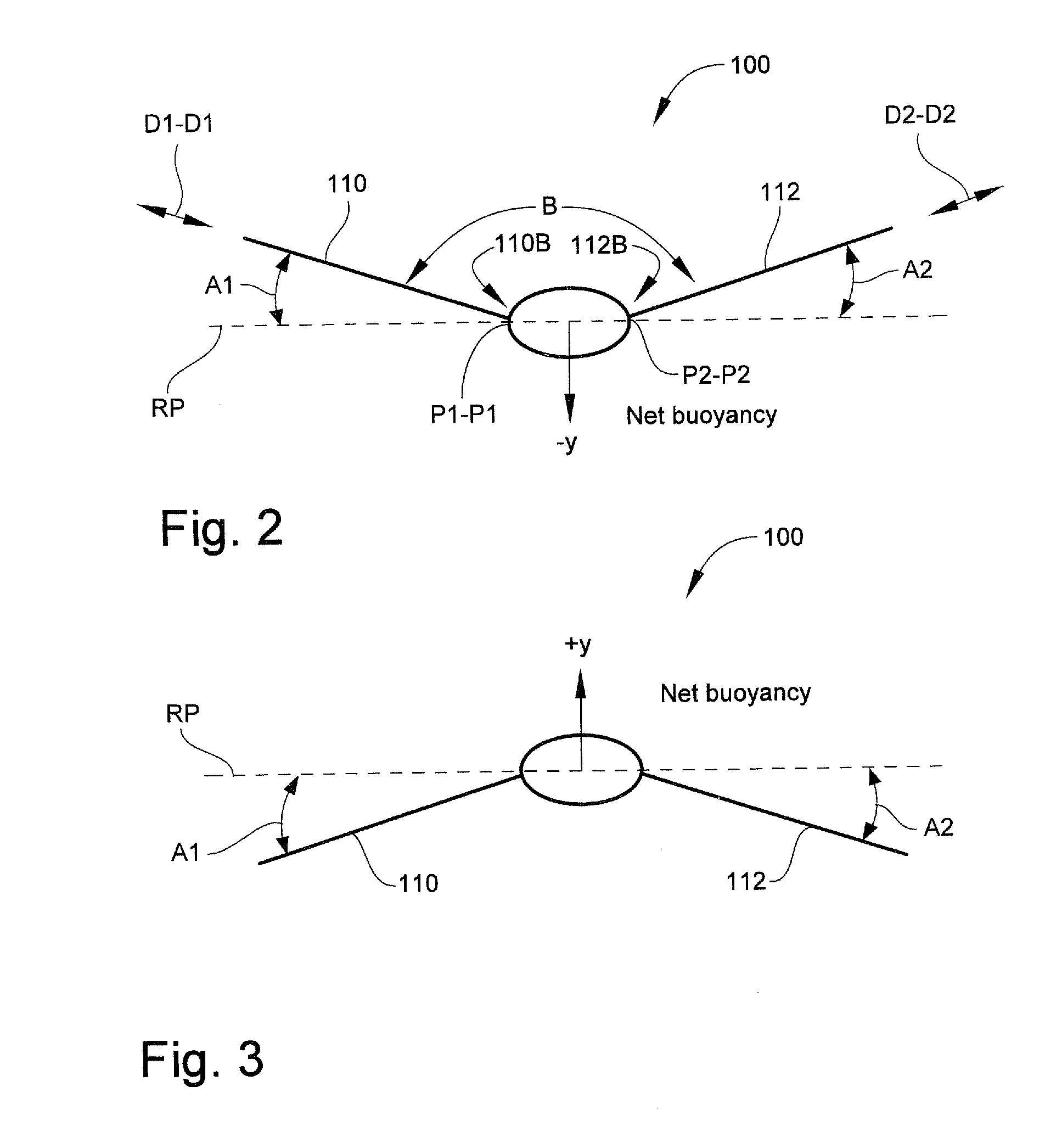
Submersible vehicles and methods for transiting the same in a body of liquid
A submersible vehicle for use in a body of liquid includes a vehicle body, a pair of fins coupled to the vehicle body on opposed sides thereof, and a dihedral angle control system. The dihedral angle control is system operative to vary a fin dihedral angle of each of the fins.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Method and apparatus for encoding 3D mesh models, and method and apparatus for decoding encoded 3D mesh models
ActiveUS20110285708A1Reduce redundancyImprove coding efficiencyCode conversionImage codingDihedral angleAlgorithm
3D mesh models are widely used in various applications for representing 3D objects. These models are made of vertices and corresponding triangles, which can be compressed based on prediction and residuals. The present invention improves the accuracy of parallelogram prediction, particularly near sharp features. The proposed 3D mesh model encoding comprises analyzing the spatial or dihedral angles between triangles, clustering triangles with similar or equal dihedral angles, and defining a representative dihedral angle for each cluster. Triangles of each cluster are then encoded relative to individual prediction triangles having the representative dihedral angle according to the cluster. Additionally, the prediction triangle may be mirrored. An indication of the encoding mode is inserted into each vertex of the encoded bitstream. A decoder extracts the encoding mode indication, reconstructs the individual prediction triangles based on the respective representative dihedral angles and performs triangle prediction and reconstruction.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Freeman decomposition and homo-polarization rate-based polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method
ActiveCN102208031AEffective divisionAvoid divisionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexitySynthetic aperture radar
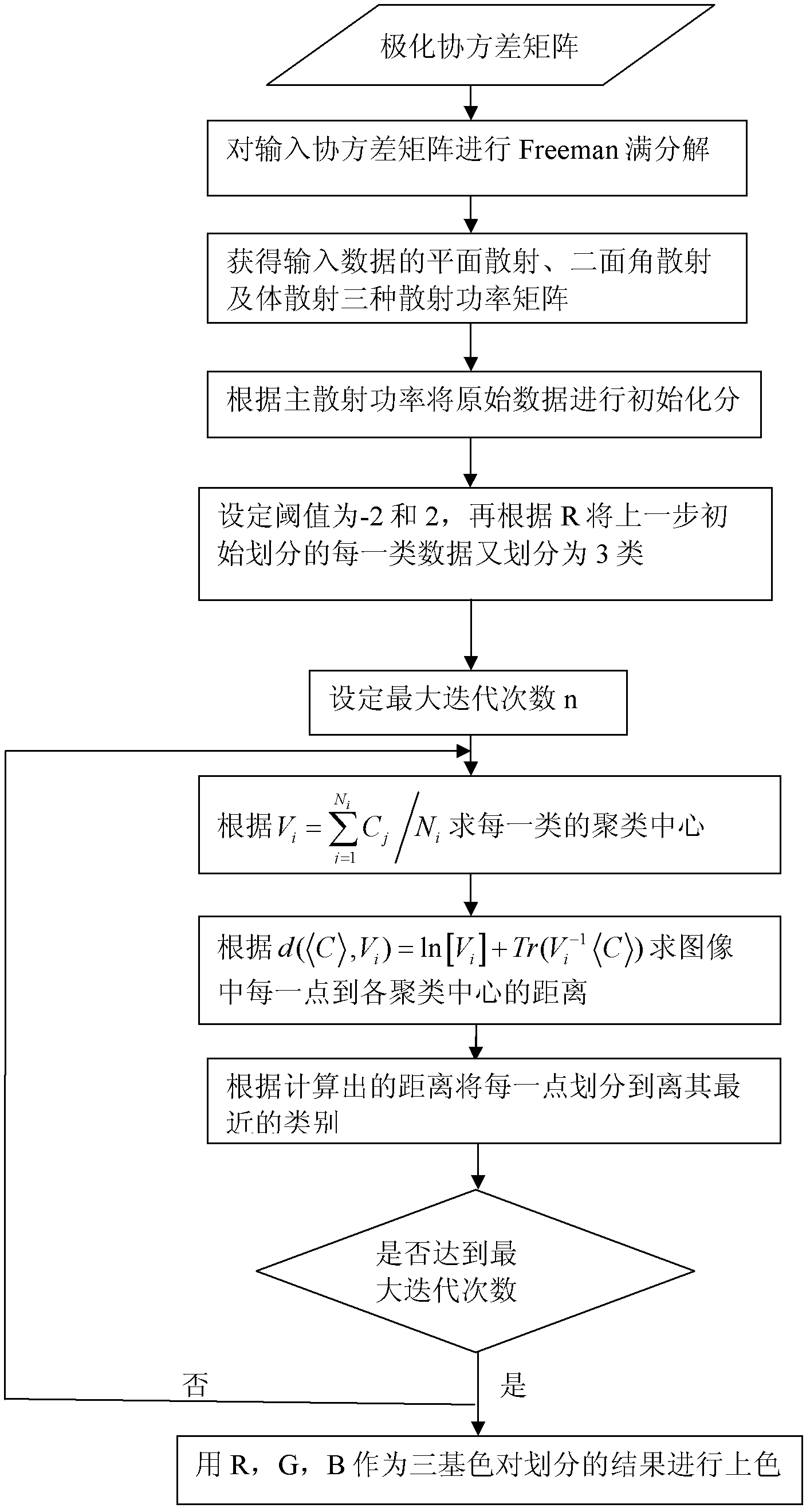
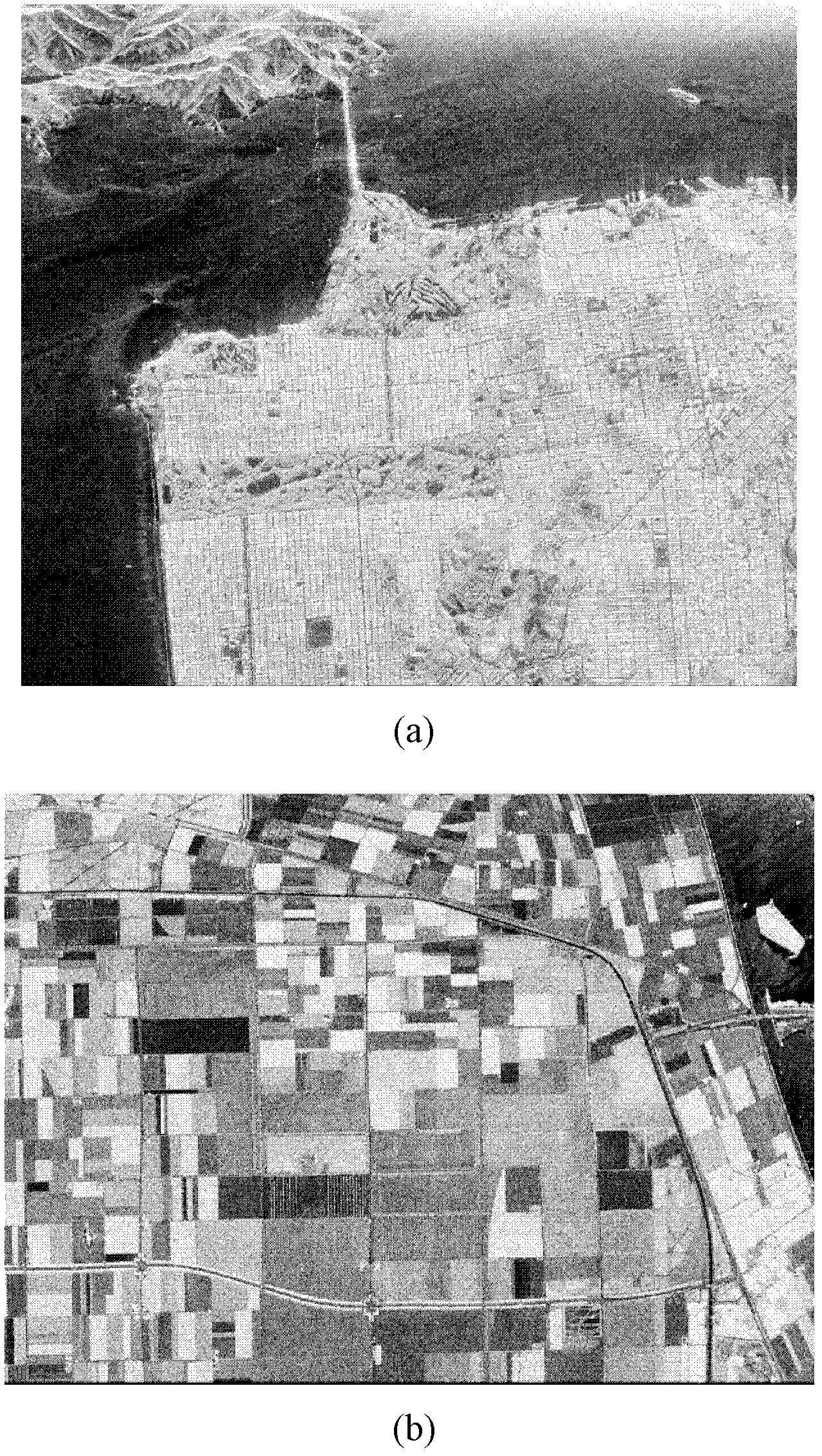
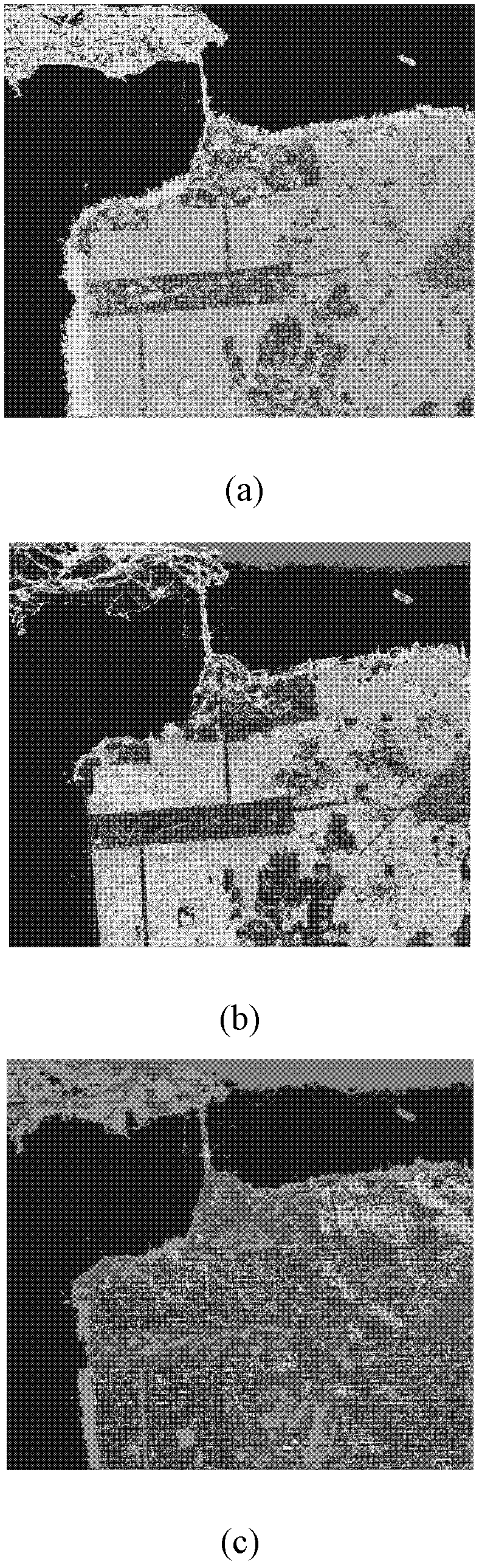
The invention discloses a Freeman decomposition and homo-polarization rate-based polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method for mainly solving the problems of higher calculation complexity and poor classification effect in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) inputting a covariance matrix of polarized SAR data; (2) performing Freeman decomposition on the input matrix to acquire three types of scattering power matrixes of plane scattering, dihedral angle scattering and volume scattering; (3) performing initial division on the polarized SAR data according to the three types of scattering power matrixes; (4) calculating the homo-polarization rate of all pixel points of the polarized SAR data of each class; (5) selecting a threshold value, and dividing the polarized SAR data of each class in the step (3) into 3 classes according to the homo-polarization rate, so that the whole polarized SAR data are divided into 9 classes; and (6) performing repeated Wishart iteration and coloring on the division result of the whole polarized SAR data to obtain a final color classification result graph. Compared with the classical classification method, the method has the advantages that the division of the polarized SAR data is stricter, the classification result is obvious and the calculation complexity is relatively low.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Submersible vehicles and methods for transiting the same in a body of liquid
A submersible vehicle for use in a body of liquid includes a vehicle body, a pair of fins coupled to the vehicle body on opposed sides thereof, and a dihedral angle control system. The dihedral angle control is system operative to vary a fin dihedral angle of each of the fins.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
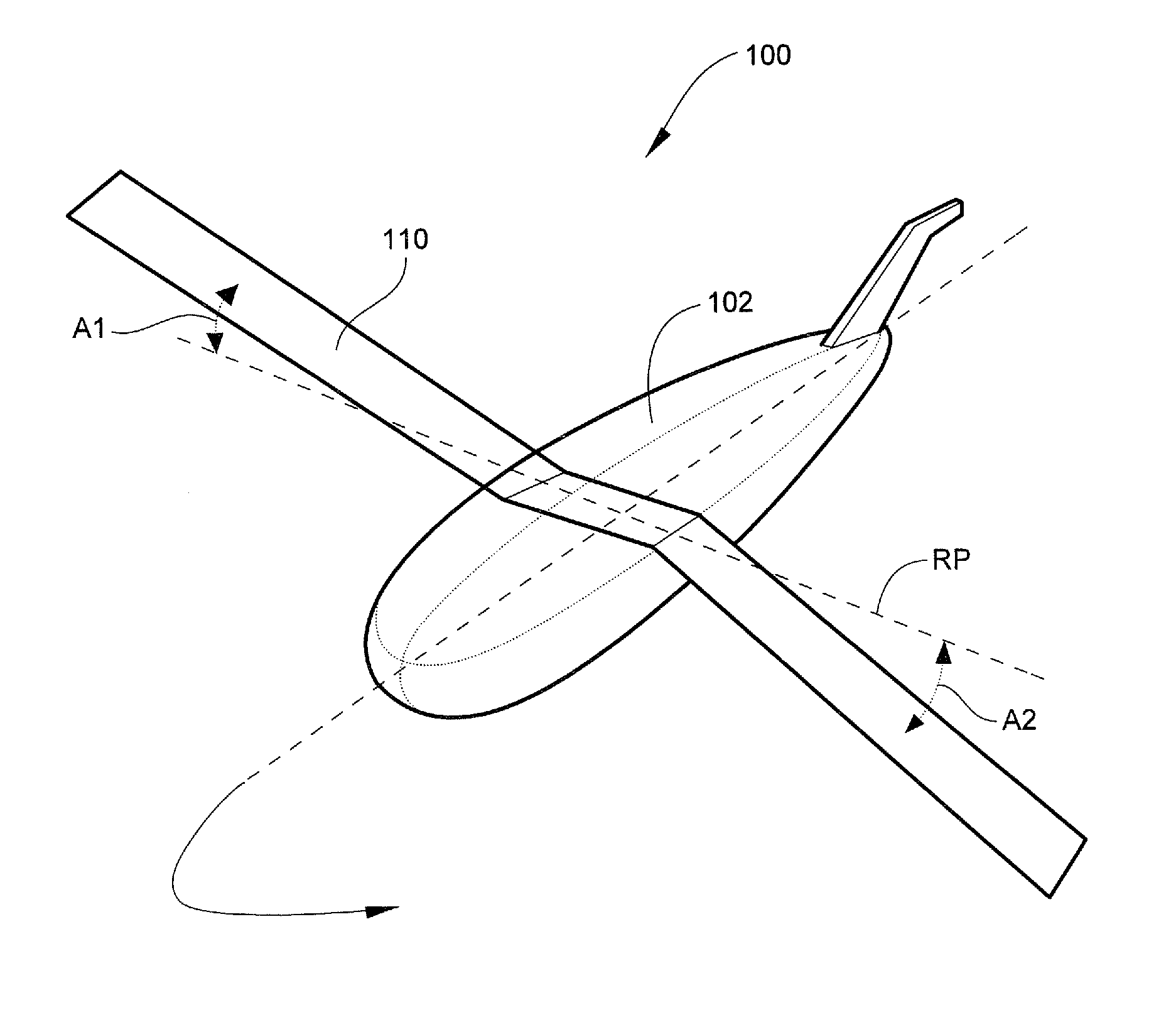
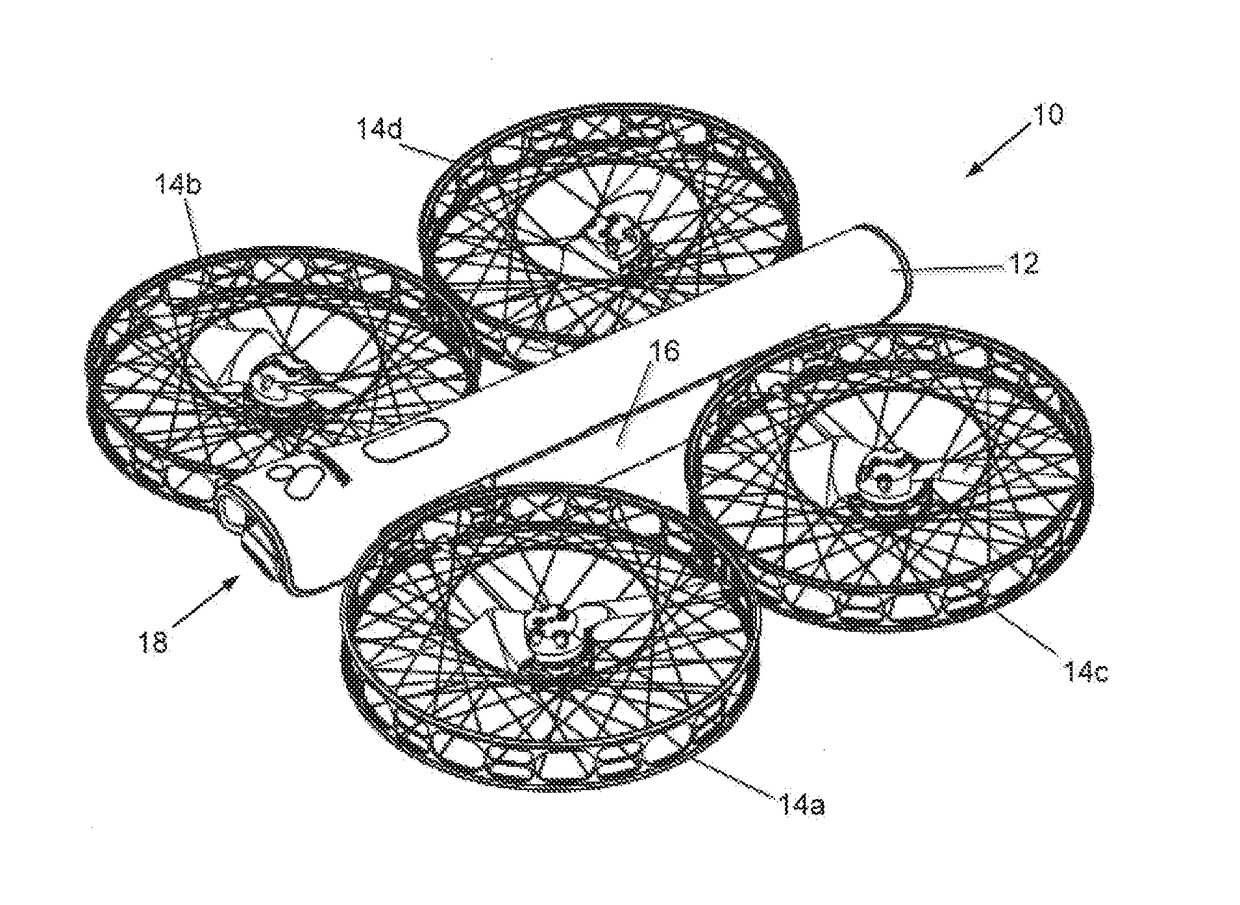
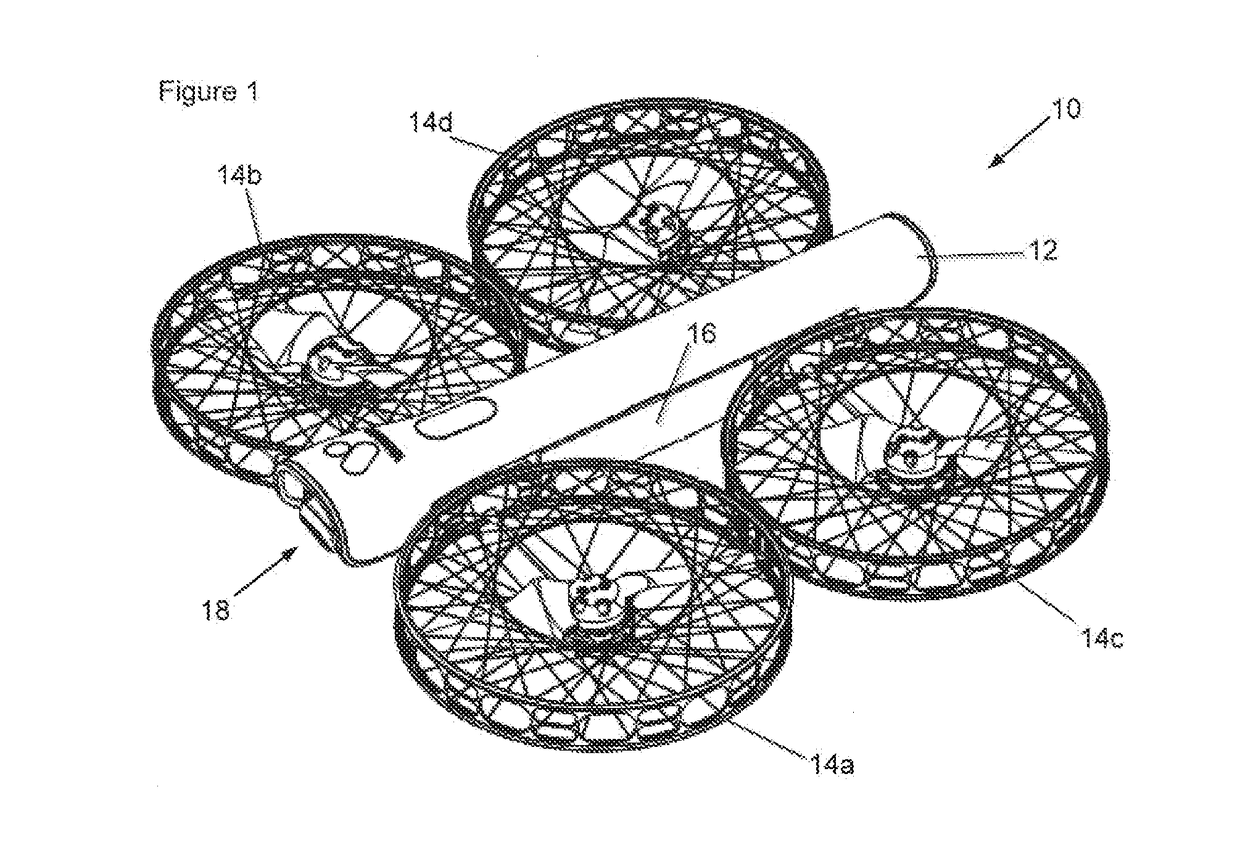
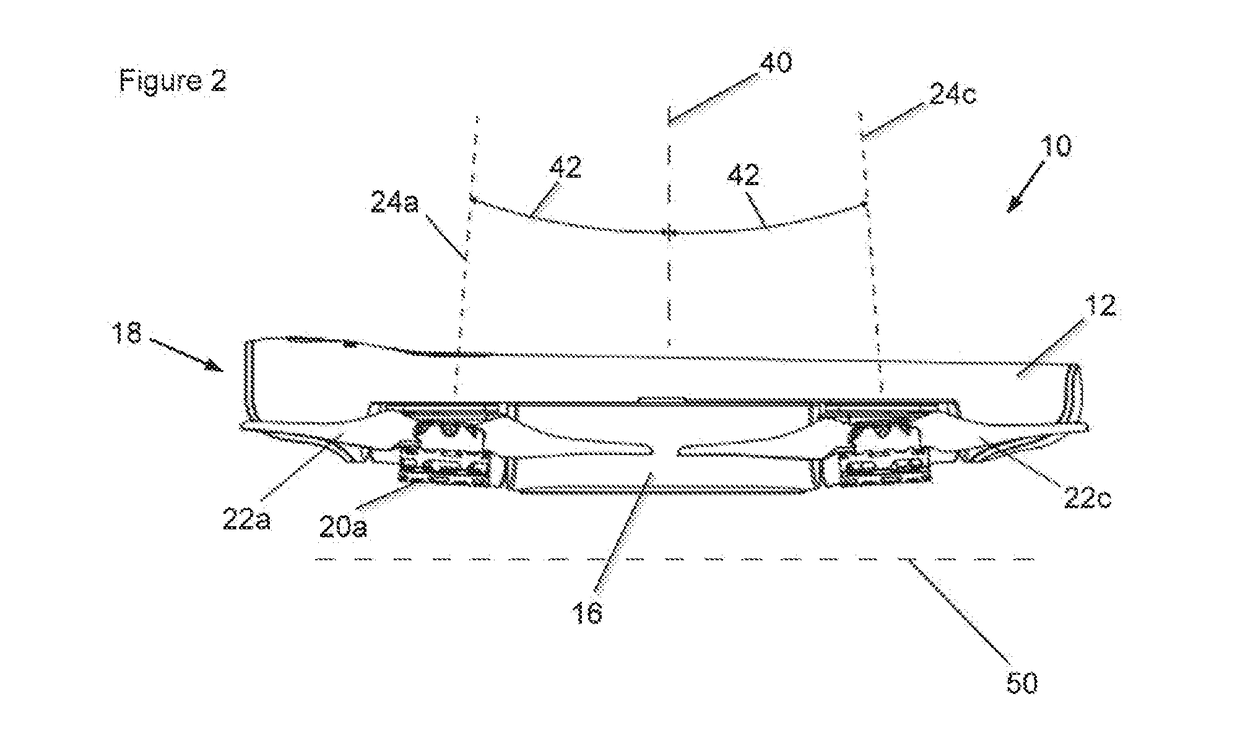
Quadcopter with pitched propeller configuration
ActiveUS20170121034A1Process stabilityProvide stabilityAircraft navigation controlTelevision system detailsPropellerDihedral angle
A quadcopter has a fuselage and four rotors, each defining a thrust vector. An onboard camera system includes a gimbal with a roll axis and a pitch axis. Right side motors are mounted with a dihedral angle so that their respective thrust vectors intersect at a common focal point located above the fuselage. Left side motors are mounted with a dihedral angle so that their respective thrust vectors intersect at a common focal point located above the fuselage. The tilted thrust vectors provide yaw stability which allows flight yaw control to be used as yaw control of the onboard camera.
Owner:VANTAGE ROBOTICS LLC
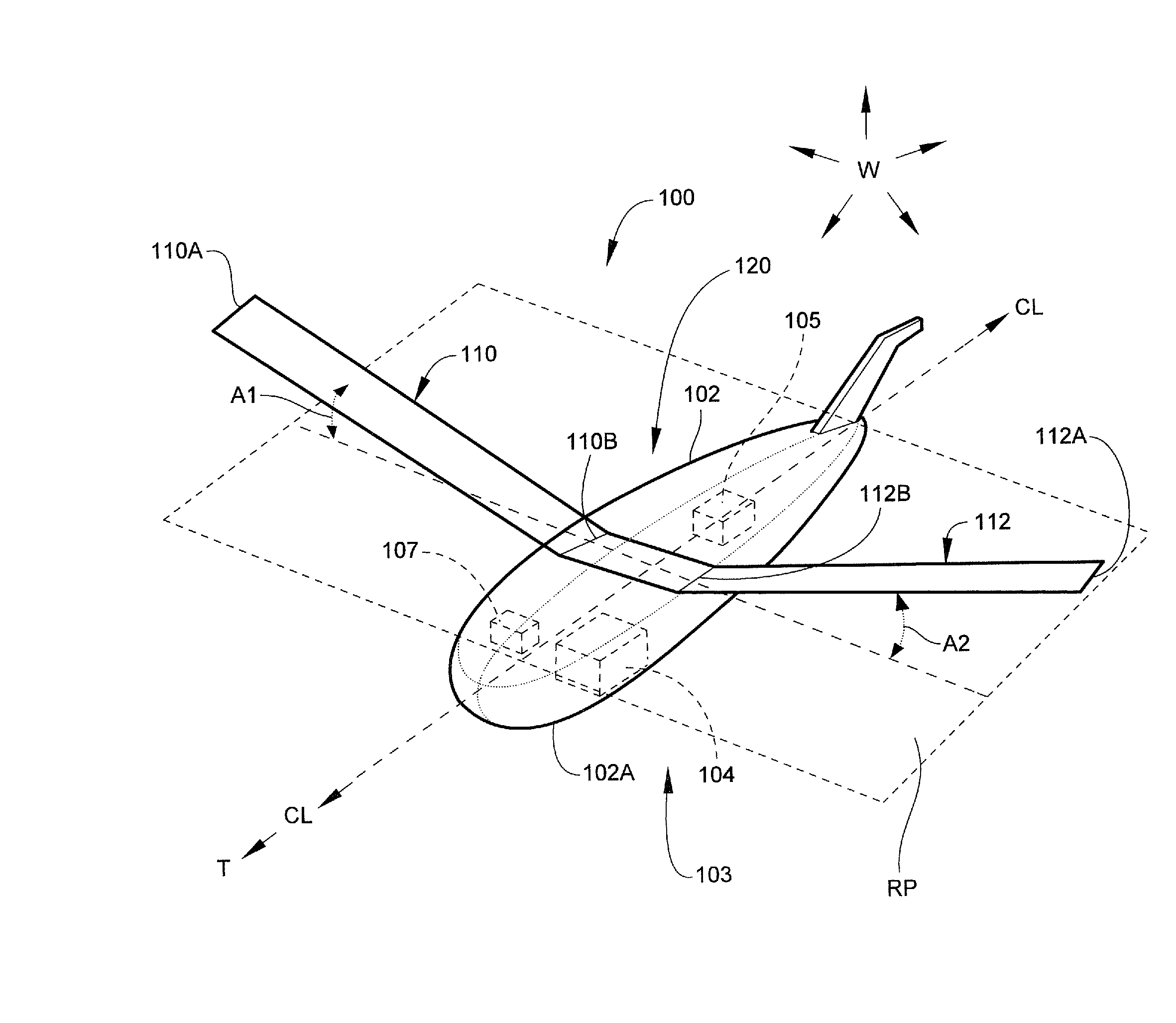
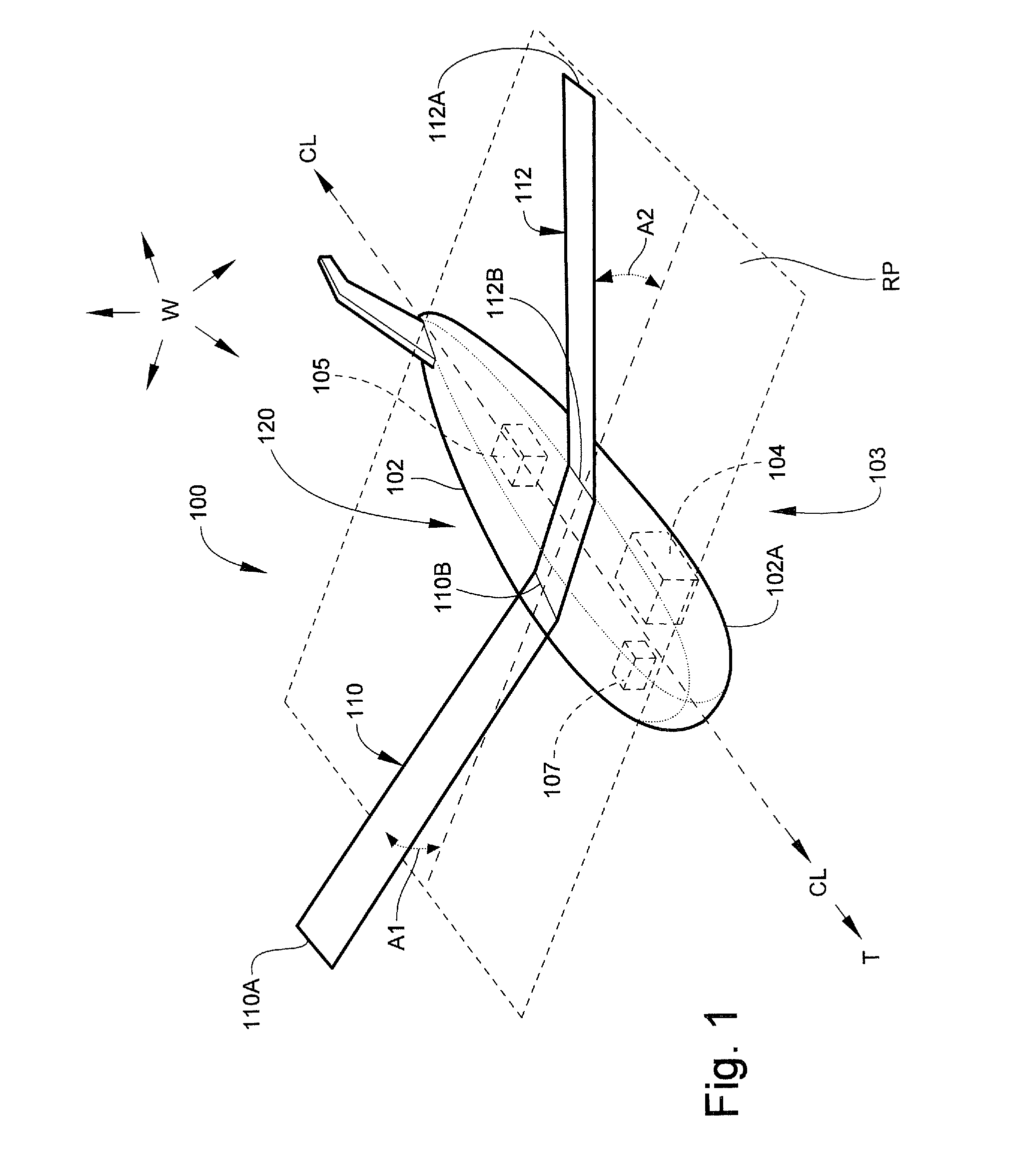
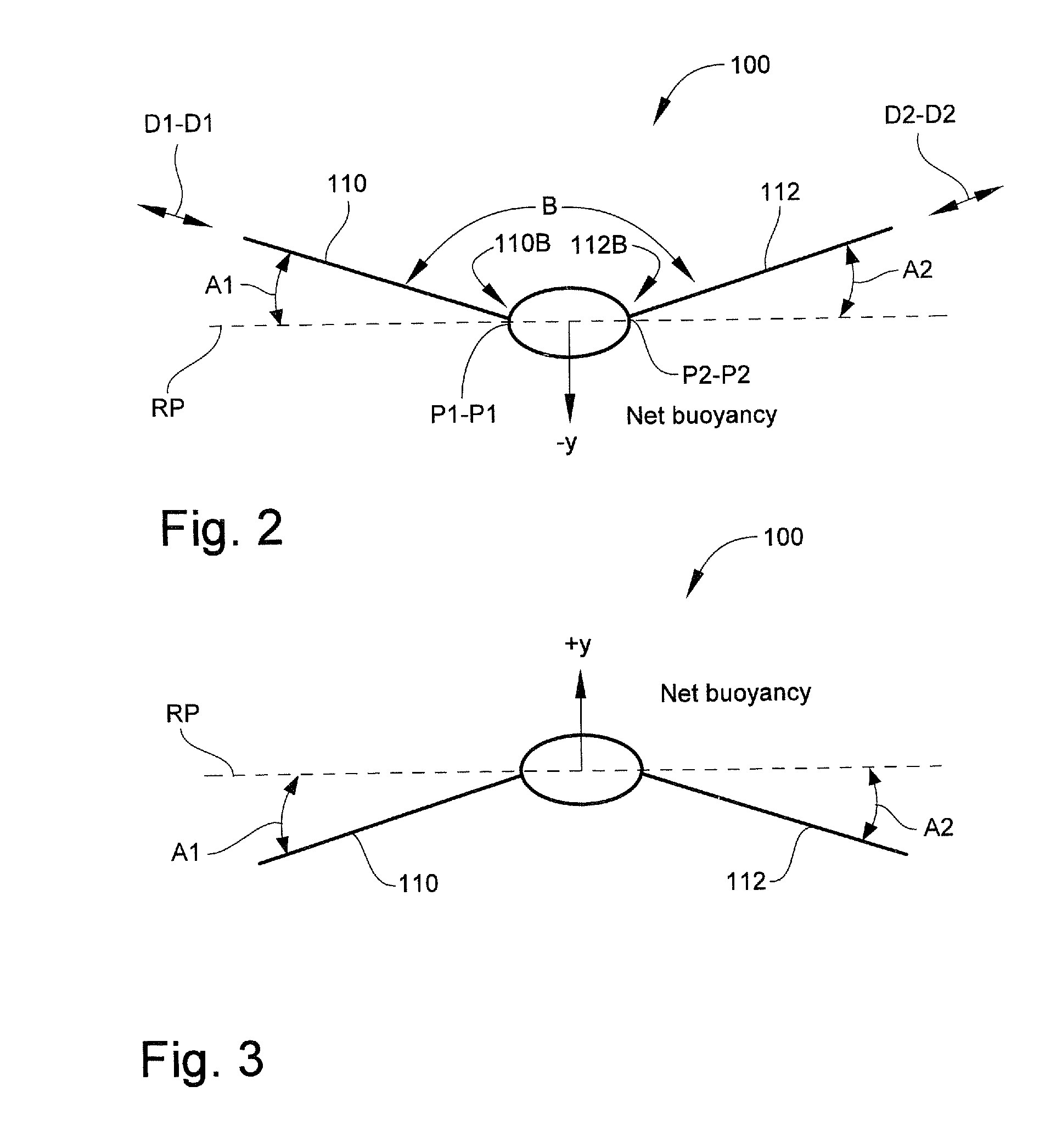
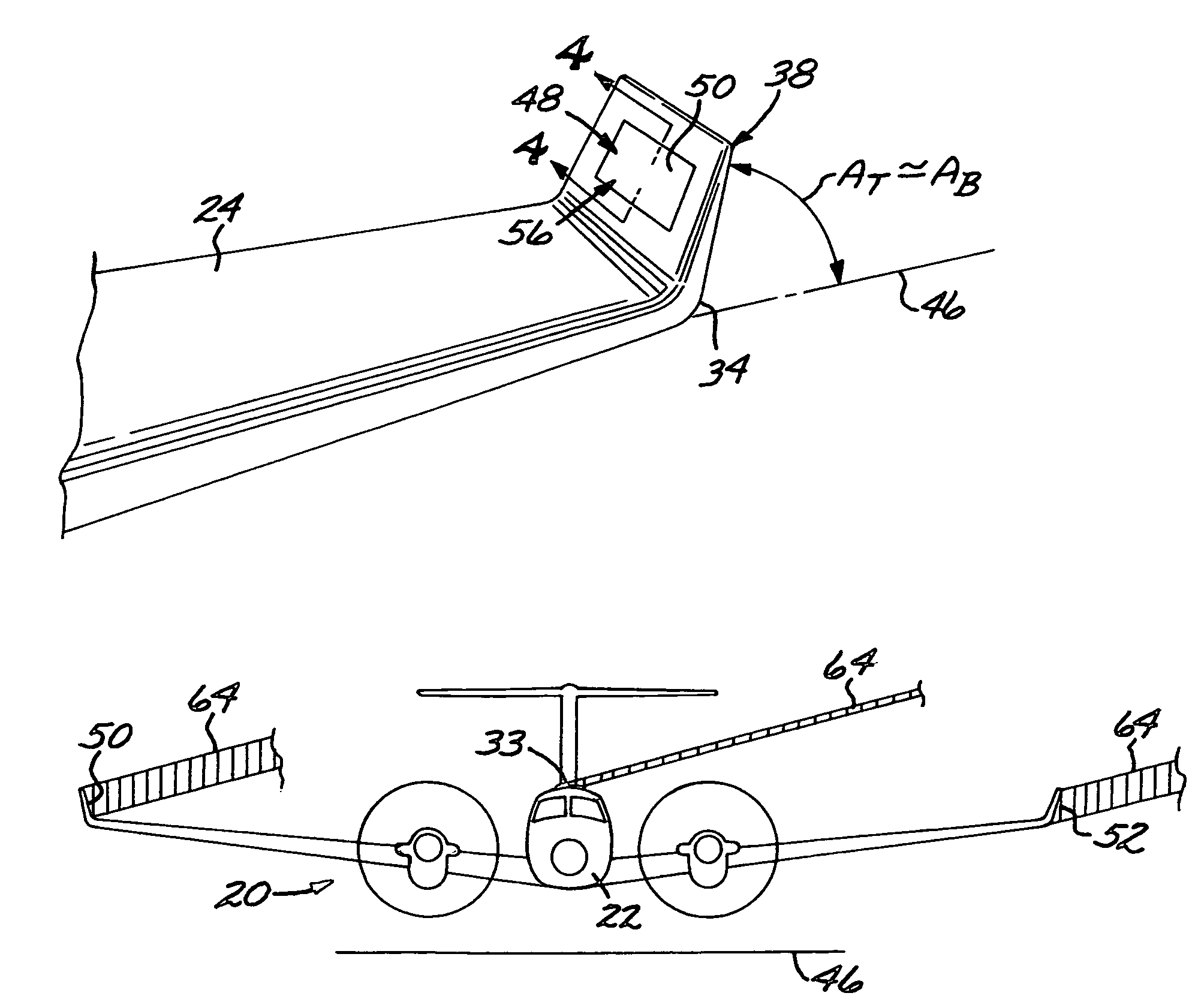
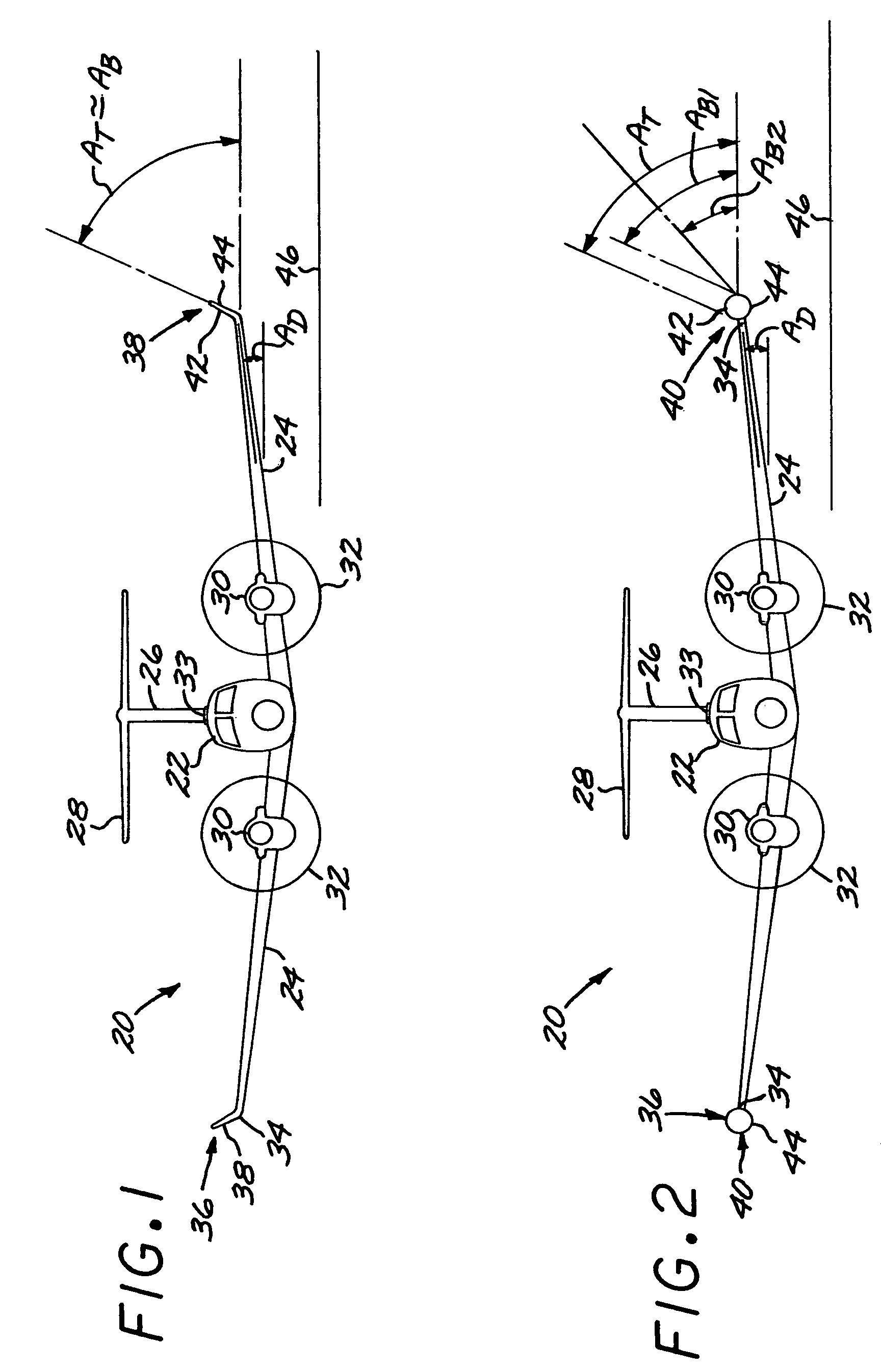
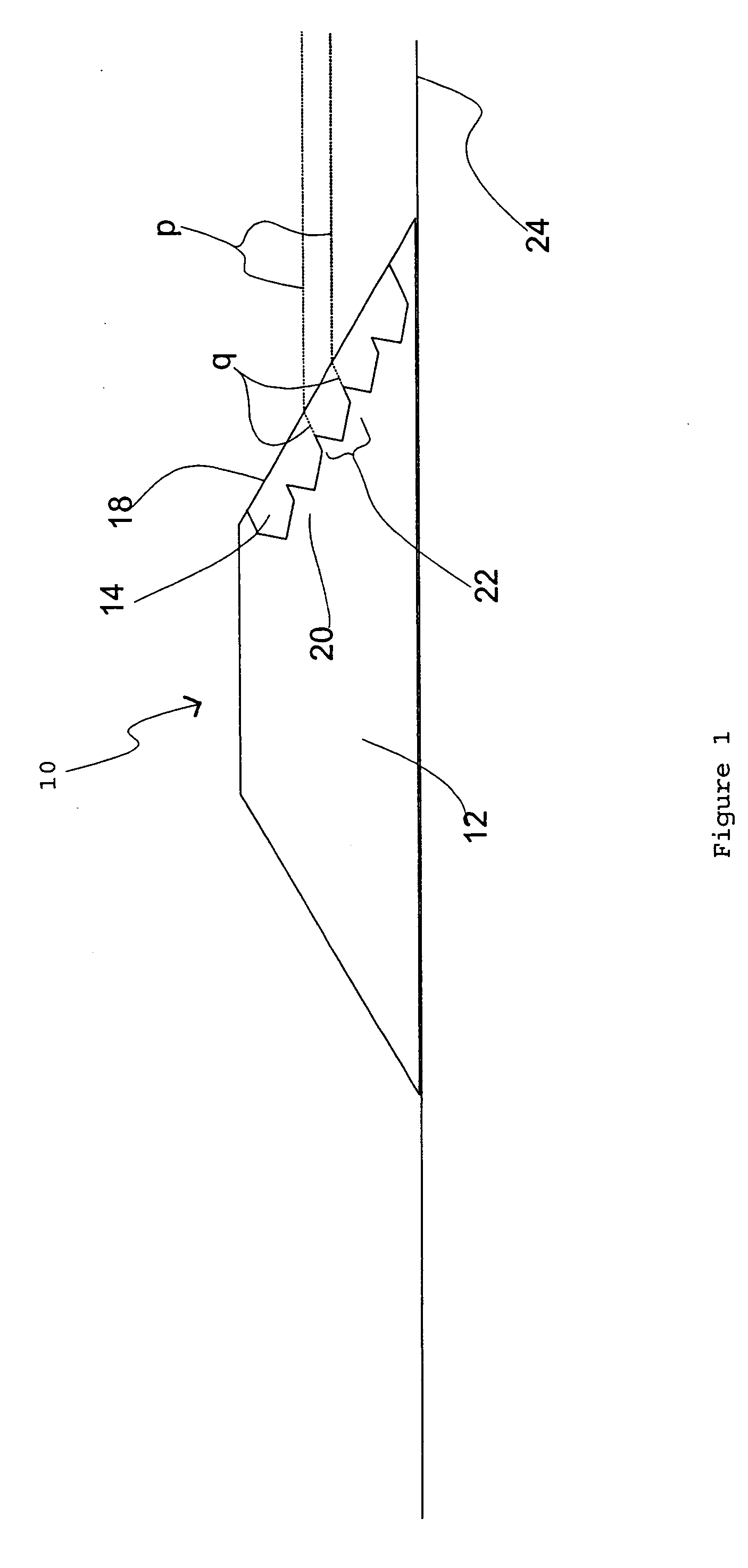
Aircraft with antennas mounted on the tops and bottoms of aerodynamic-surface extensions
InactiveUS7624951B1Effective electronic steeringReduce weightInfluencers by generating vorticesAntenna arraysDihedral angleFuselage
An aircraft has a fuselage and a pair of wings joined to the fuselage at a dihedral angle. A wing extension, such as an angled winglet or a wing-tip pod, is joined to a distal end of each of the wings. A top-surface antenna lies in each of the top surfaces, and a bottom-surface antenna lies in each of the bottom surfaces. The antennas are preferably flat-panel antennas such as phased-array antennas.
Owner:BEECHCRAFT
Event driven ambulatory electrocardiograph
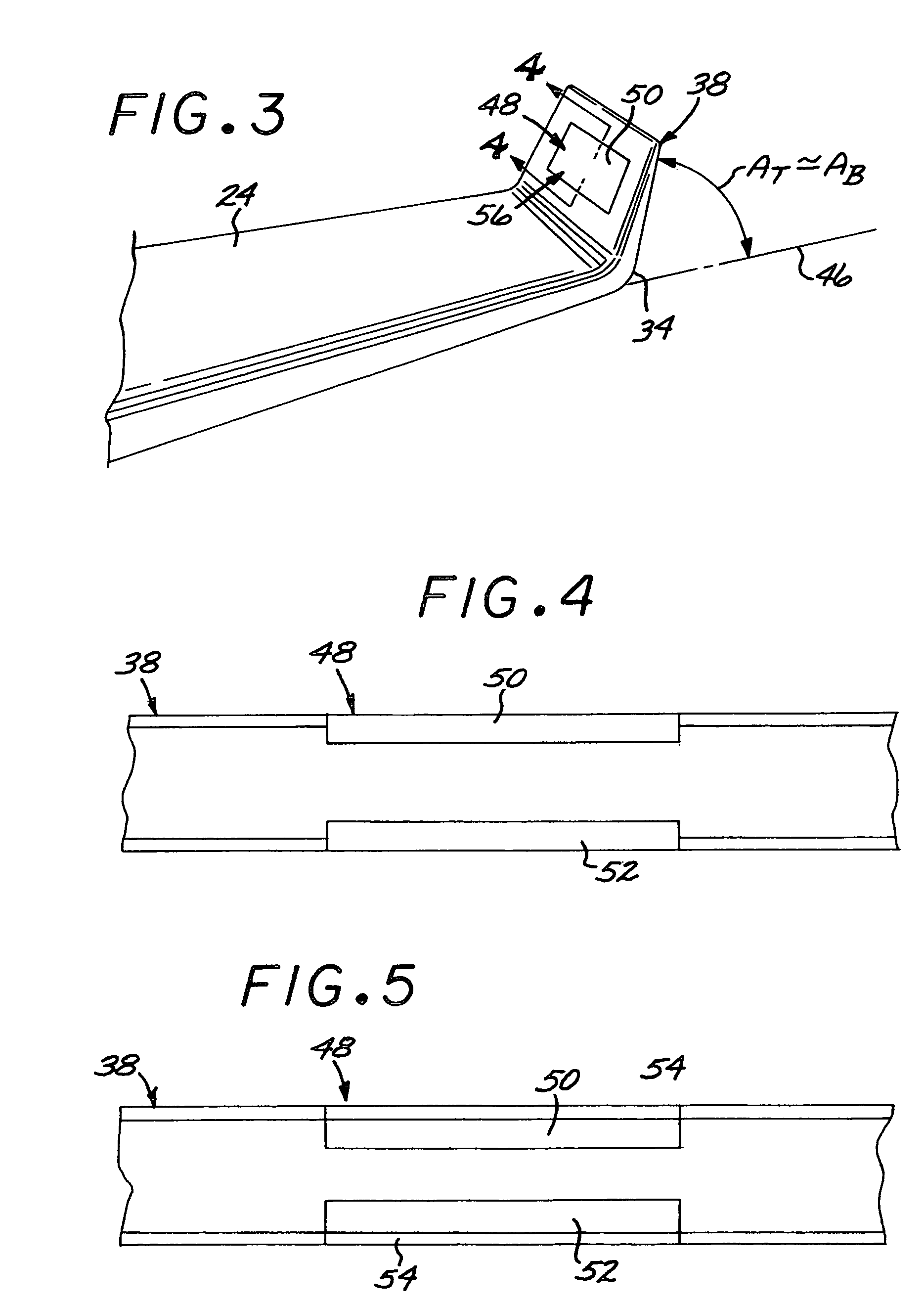
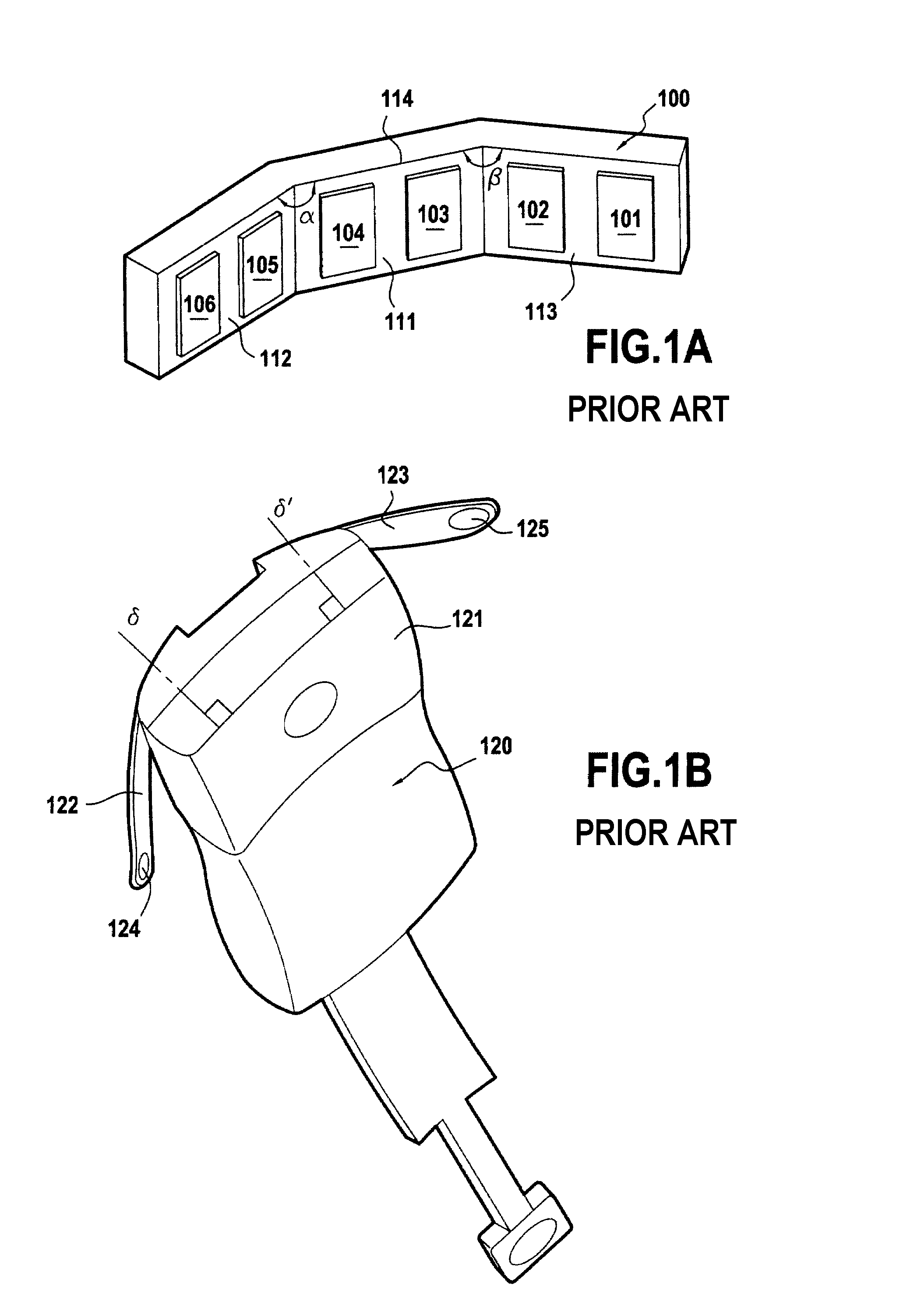
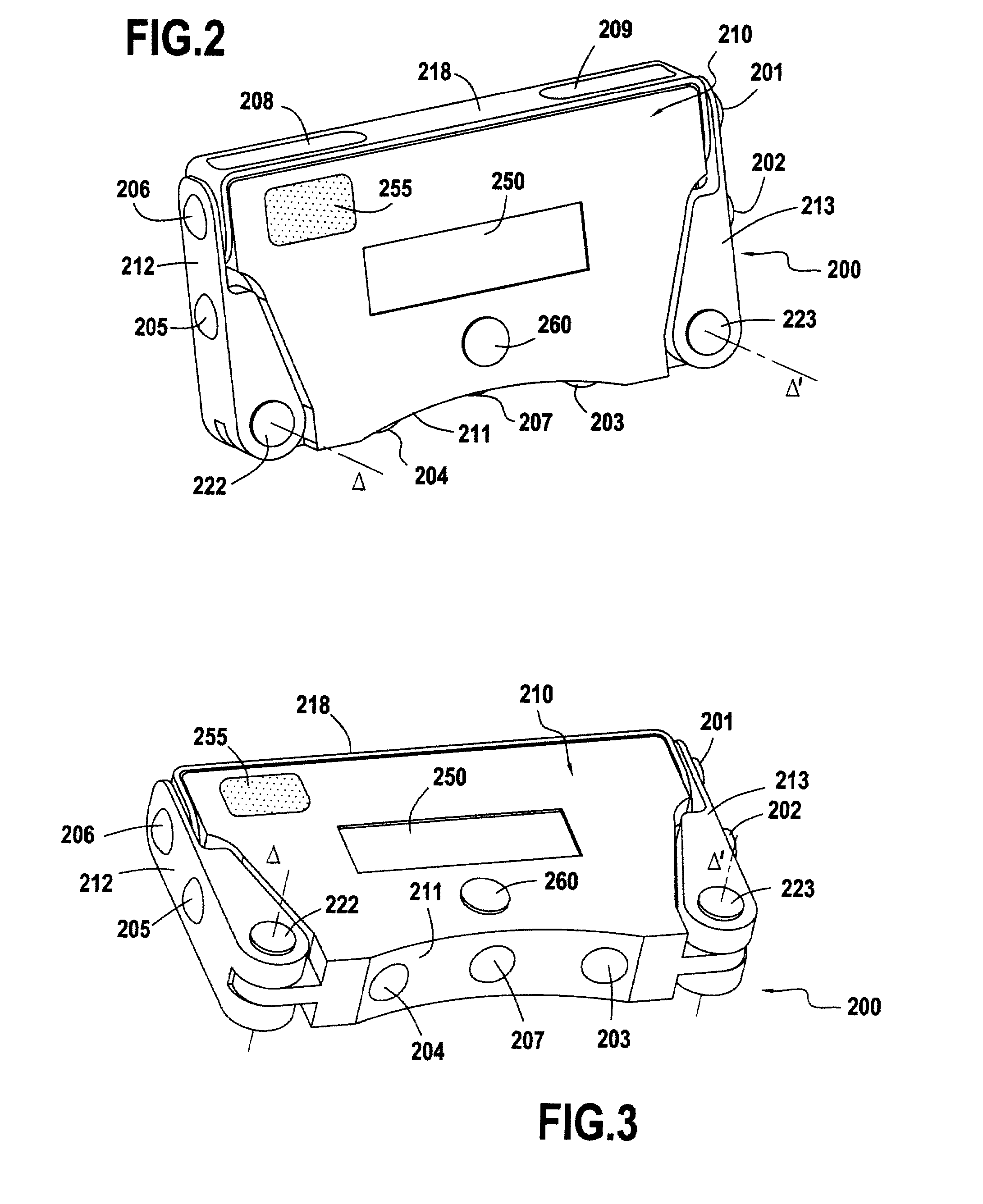
The electrocardiograph (200) of the invention is suitable for capturing a twelve-lead electrocardiogram from signals representative of the cardiac activity of a patient and acquired with the help of at least nine electrodes. The electrocardiograph comprises a body (210) having a front face (211) and at least one arm (212, 213) suitable for being folded beside the body and pivotable about an axis that is substantially parallel to the front face. Each arm is adapted to form a variable dihedral angle with the front face so that the substantially concave surface (214) formed by the front face and the or each arm and having six precordial electrodes (201-206) distributed thereon, is capable of adapting to the patient's morphology so as to enable the precordial electrodes to be properly positioned on the patient's chest. The electrocardiograph also includes means enabling said good positioning of the precordial electrodes on the patient's chest to be maintained.
Owner:PARSYS LIMITED
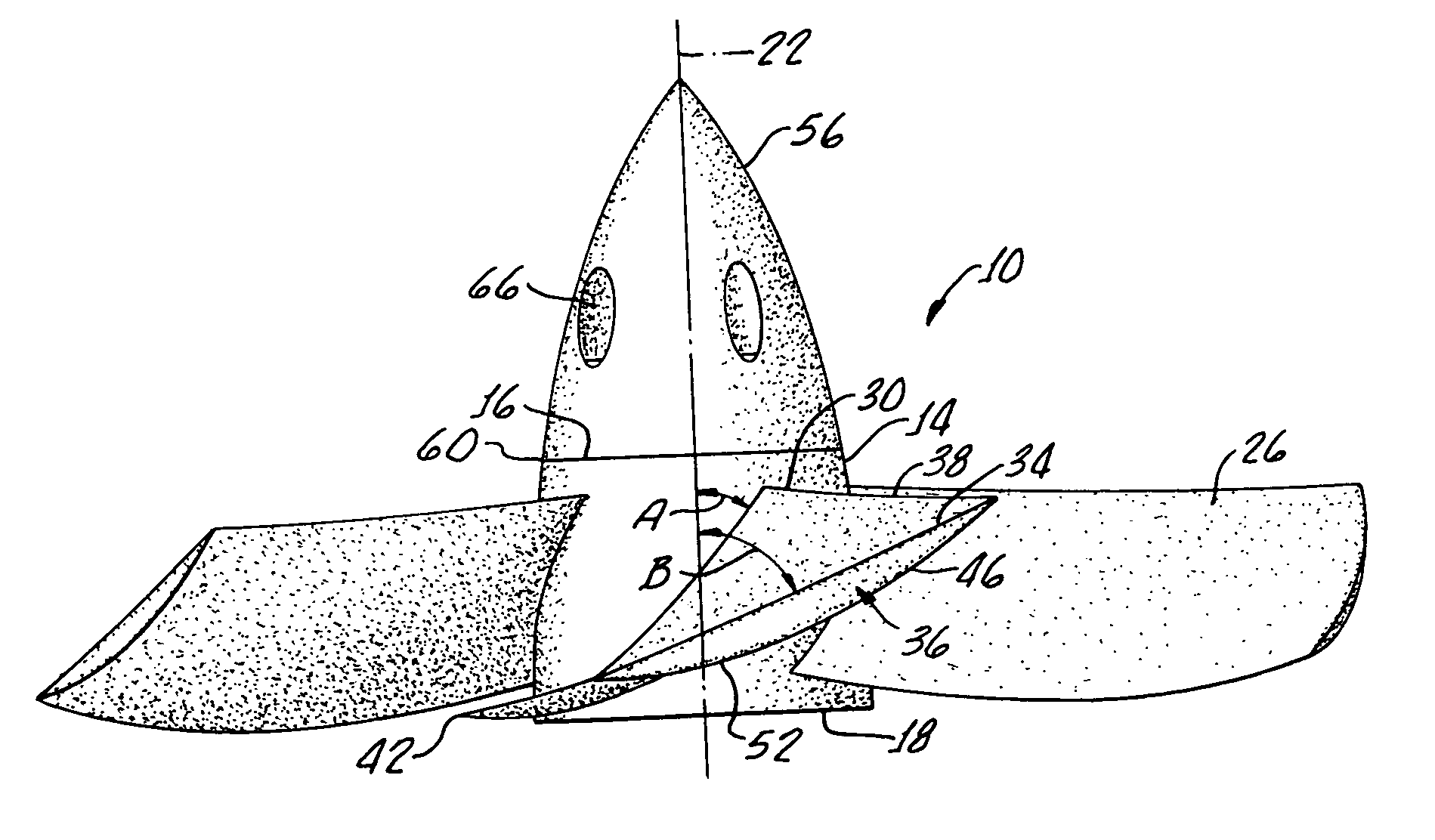
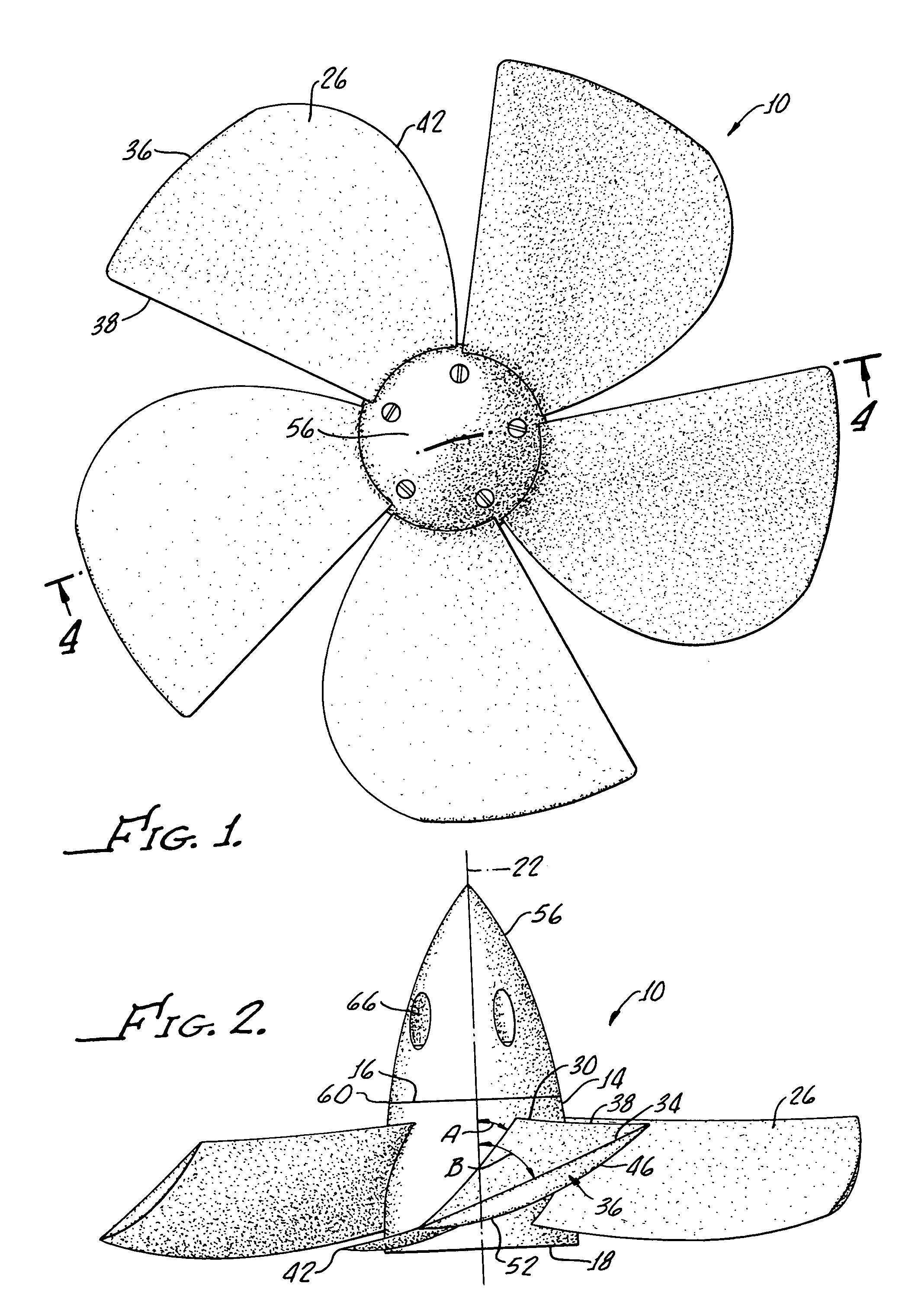
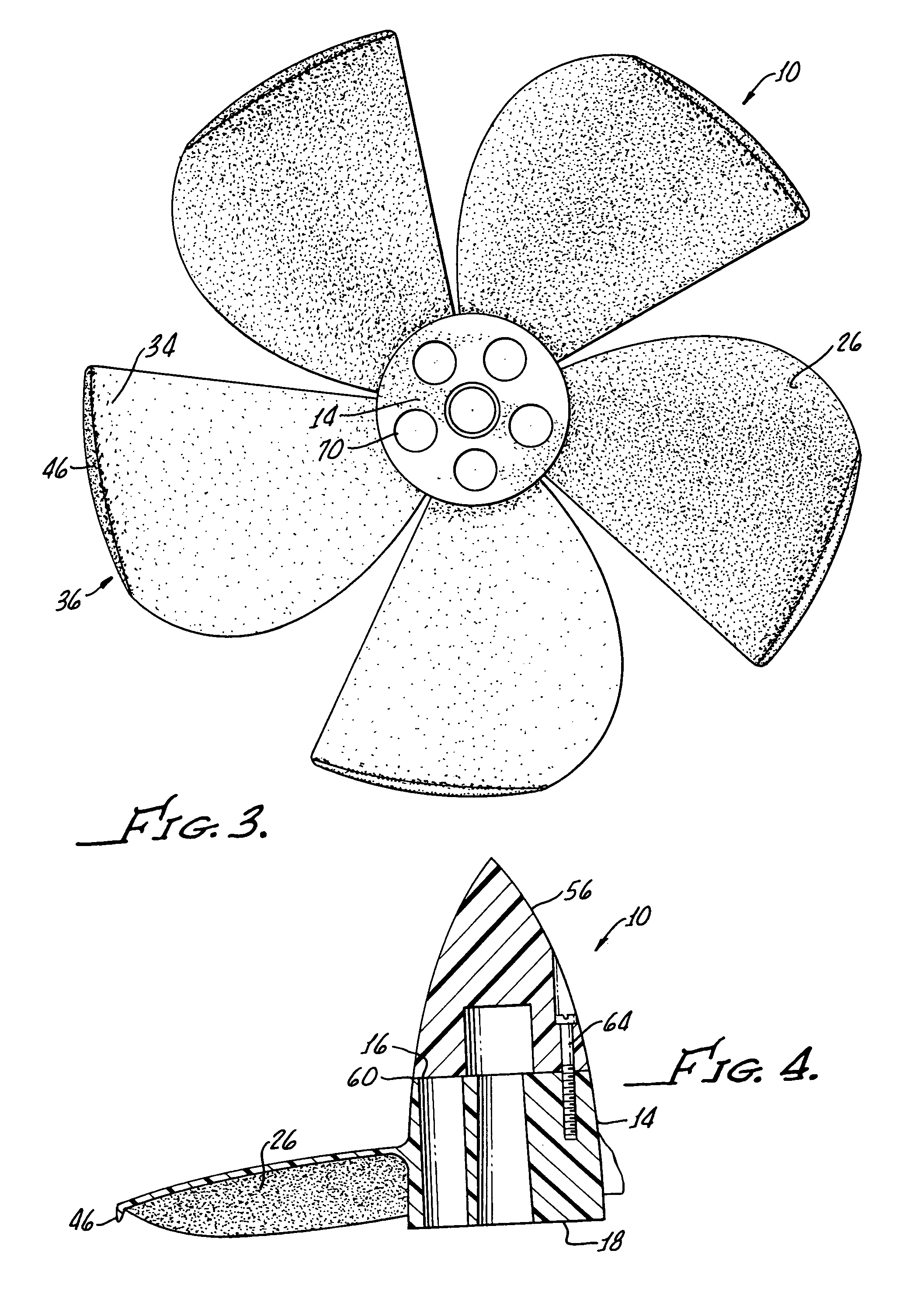
Boat propeller
InactiveUS7025642B1Streamline flow of waterPrevent shrinkagePropellersPump componentsLeading edgePropeller
A boat propeller includes a hub having a front, back, and an axis of revolution extending therebetween. A plurality of blades provide and extend from the hub between the front and back. Each blade includes a surface adjacent of the hub disposed at an oblique angle to the hub axis and a blade tip having an adjacent surface forming a dihedral angle with a surface adjacent to the hub extended on the forward camber only. The surface adjacent to the blade tip is inclined at a greater angle to the hub axis than the surface adjacent to the hub. Each blade includes a trailing edge extending radially from the hub with each trailing edge being substantially straight and a tip is provided joining the trailing edges at approximately a 90° angle. An arcuate leading edge is provided between each blade tip and a hub and a flange is disposed on each blade tip and extends parallel to the hub axis toward the hub back.
Owner:BAYLOR WESLEY TERRAN
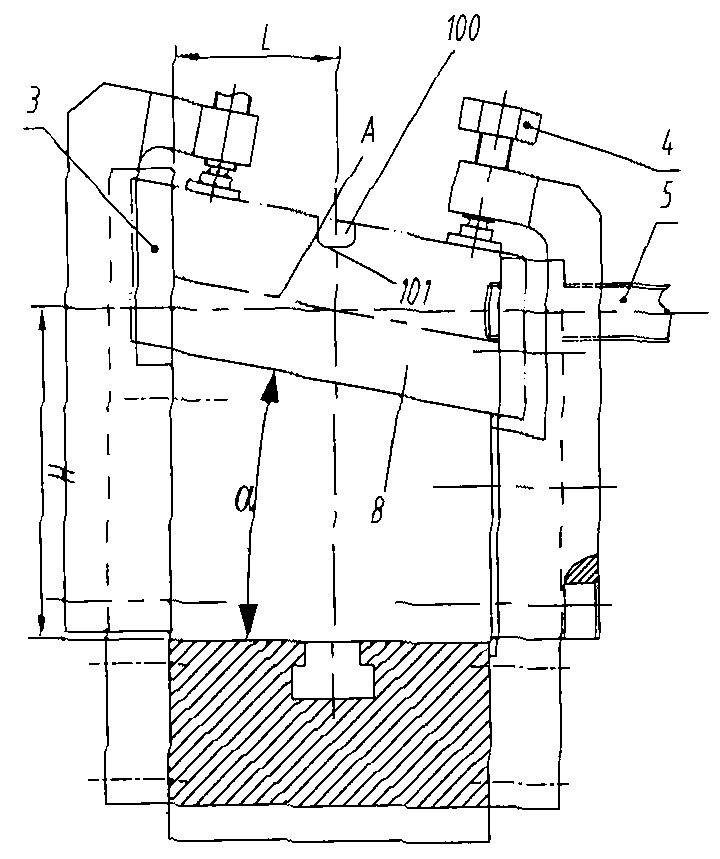
Special fixture used for processing open slot on spatial dihedral angle slope of turbine blade
ActiveCN102371491AExpand the scope of processingComply with positioning installation requirementsPositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSurface finishBaseboard
The invention provides a special fixture used for processing an open slot on a spatial dihedral angle slope of a turbine blade, and the special fixture is characterized by comprising a slope baseboard component capable of adjusting a radial gradient, wherein a tailstock tip component and an end face positioning component are oppositely arranged at two radial ends of the slope baseboard component; a slope cushion component which is capable of adjusting an axial gradient and a height is arranged on the slope baseboard component between the tailstock tip component and the end face positioning component; a side wall positioning component is also arranged on the slope baseboard component; the side wall positioning component can axially feed a side wall positioning element which is contained in the side wall positioning component; a clamping component is also arranged on the slope baseboard component; and a pressing head capable of feeding downward is arranged at the tail end of the clamping component. The fixture provided by the invention can firmly and accurately position a device, can quickly and efficiently process the open slot meeting a design demand on a size precision and a position precision, and has ultrahigh surface glossiness.
Owner:四川省自贡市海川实业有限公司
Compressor airfoil with tip dihedral
An airfoil for a compressor is described. The airfoil has a root, an airfoil tip, a leading edge, a trailing edge, airfoil pressure and suction sides extending between the leading edge and the trailing edge. The airfoil has an inner span region and an outer span region and the trailing edge has a dihedral profile such that the trailing edge dihedral angle decreases in at least a portion of the inner span region and the outer span region.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
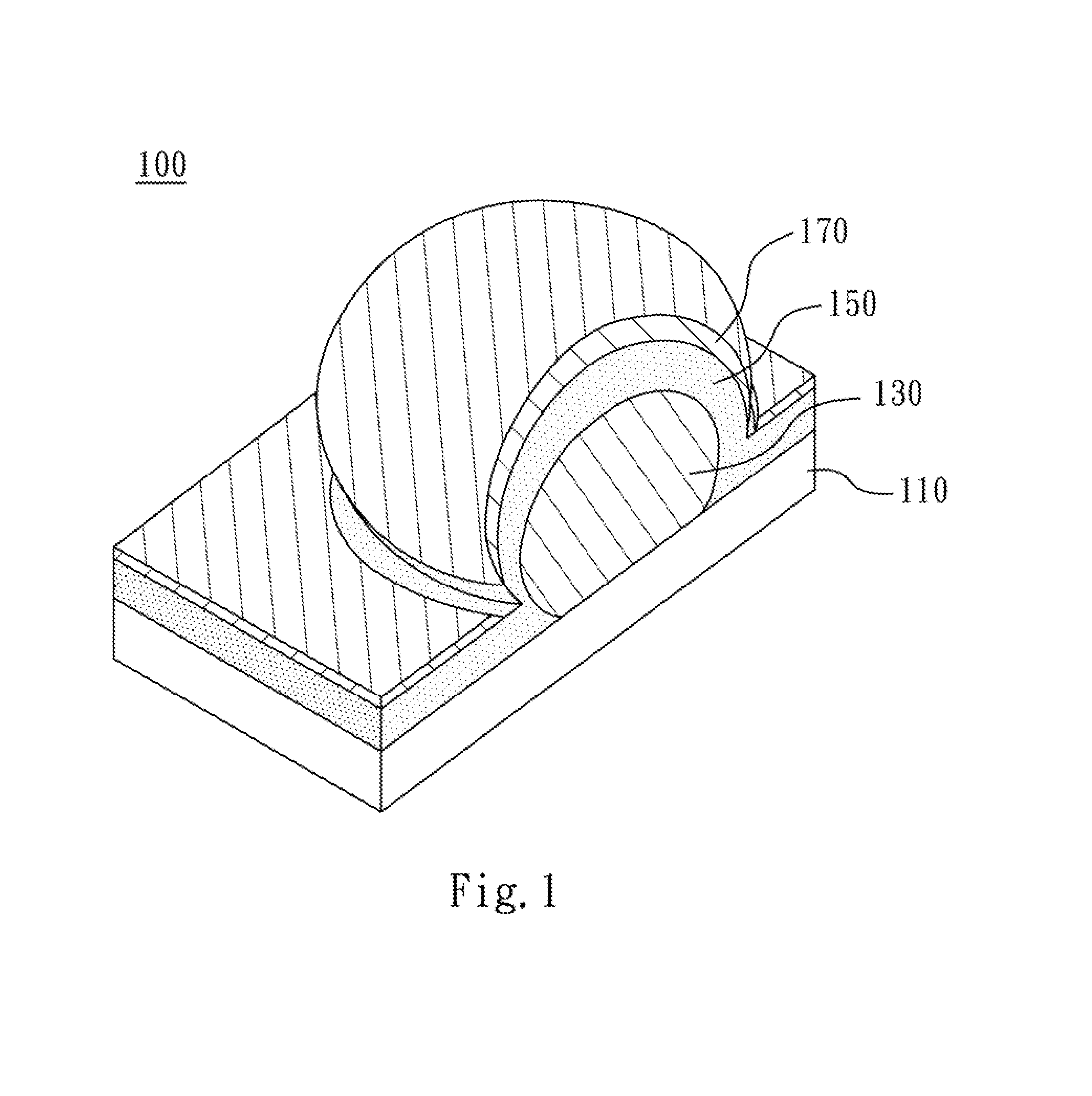
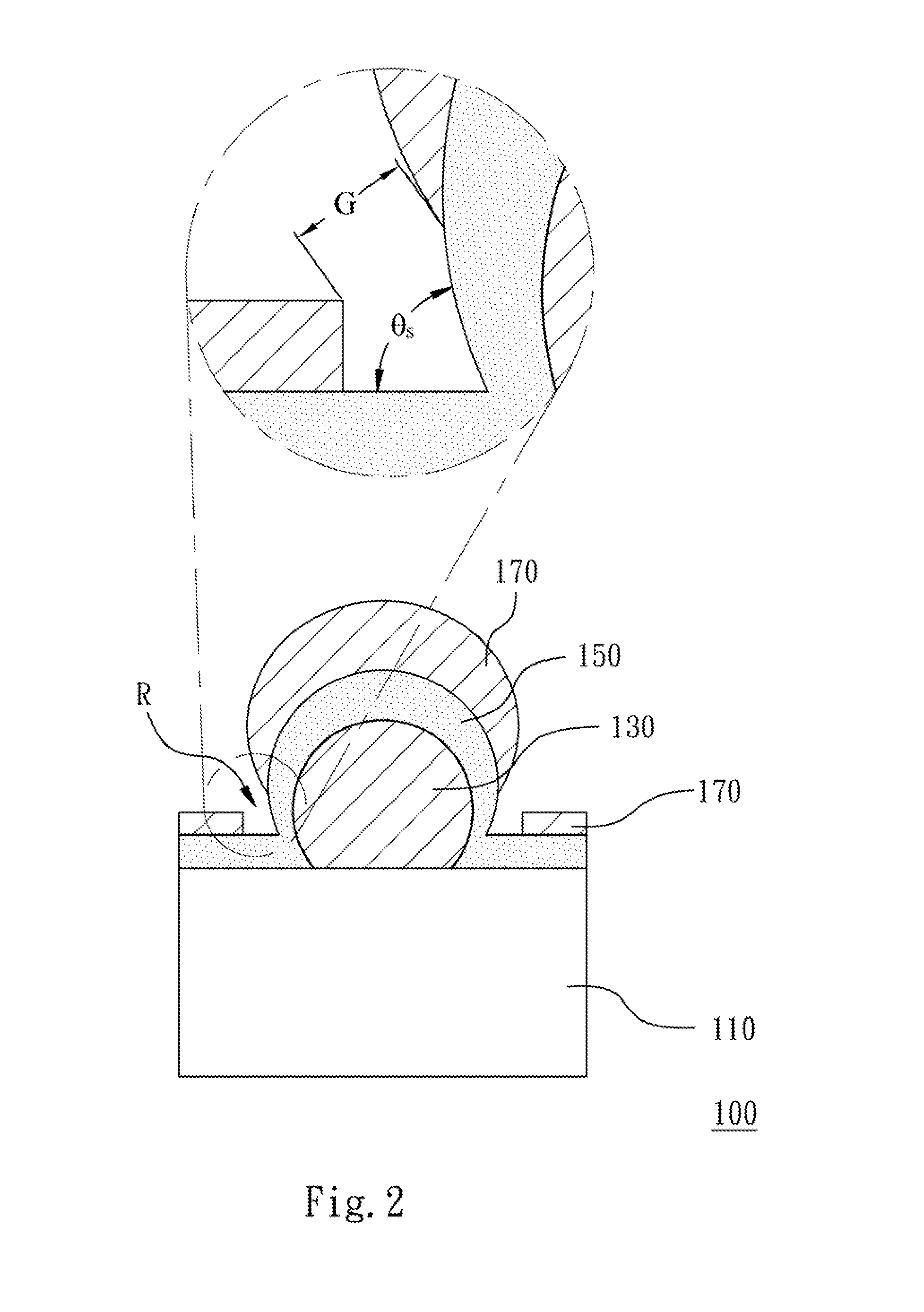
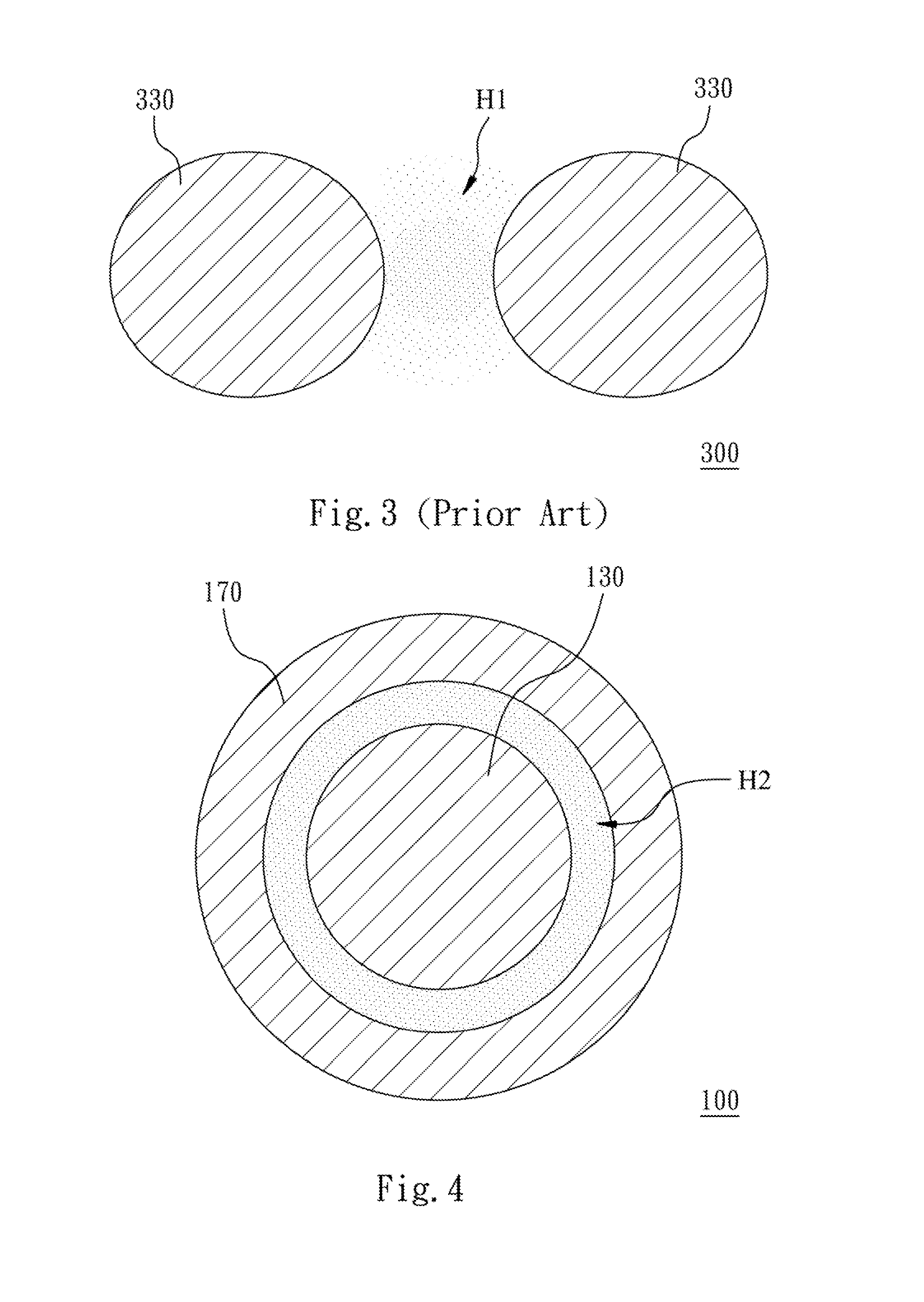
Sers-active structure, fabrication method thereof, and sers system comprising the same
ActiveUS20140043605A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansDihedral angleDielectric layer
A SERS-active structure includes a substrate, at least one metal nanoparticle, a dielectric layer and a metal nanolayer. The metal nanoparticles are disposed on the substrate. The substrate and the metal nanoparticles are covered by the dielectric layer, so that the dielectric layer forms a recessed portion with a dihedral angle formed by a surface of the dielectric layer at which the at least one metal nanoparticle contacts the substrate. The dielectric layer is covered by the metal nanolayer and the metal nanolayer has a gap located at and exposing the recessed portion.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Polarization four-component decomposition method for city area
InactiveCN103529447AAlleviate Negative Power IssuesResolve Surface ScatteringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionPolarimetric synthetic aperture radar
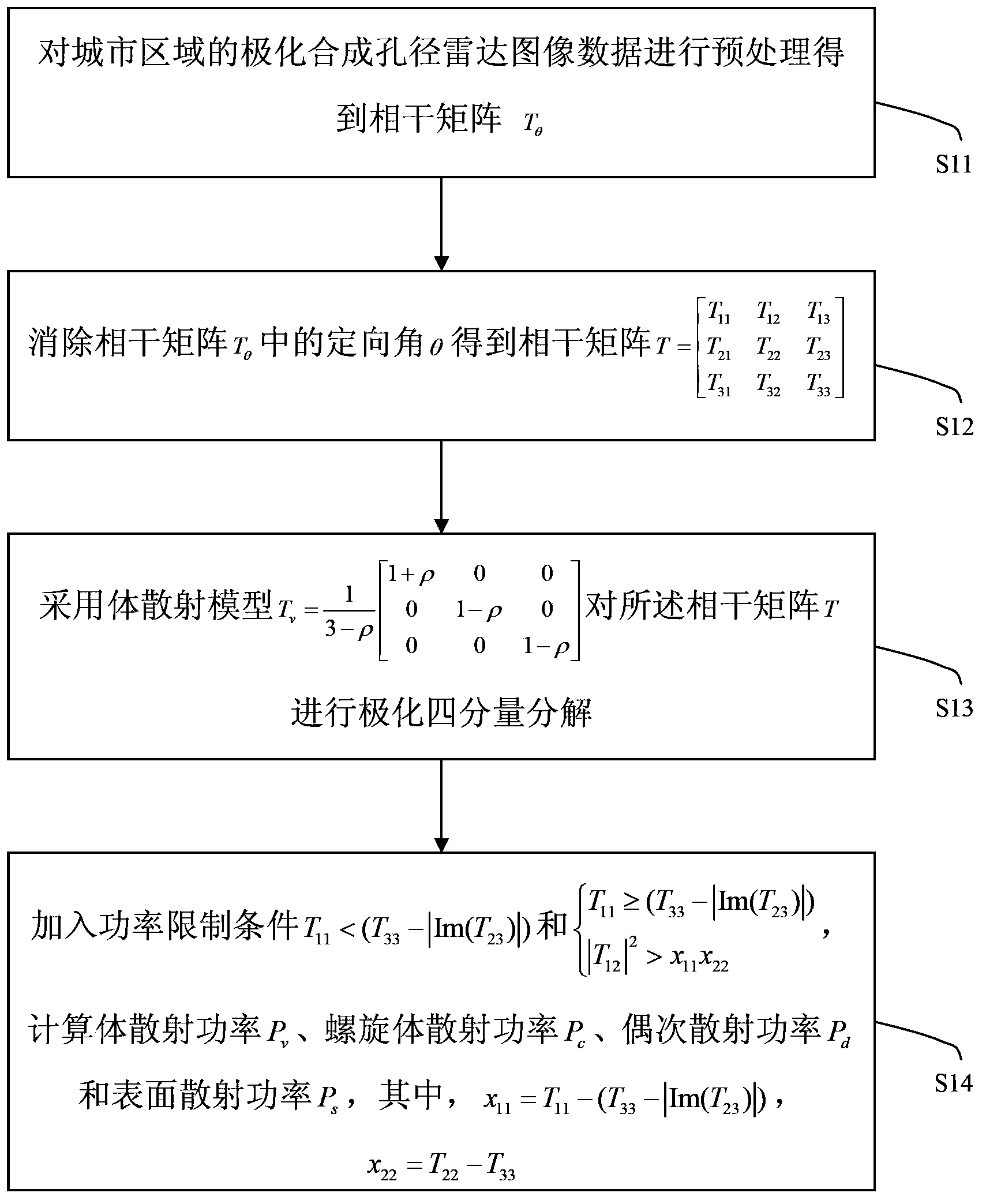
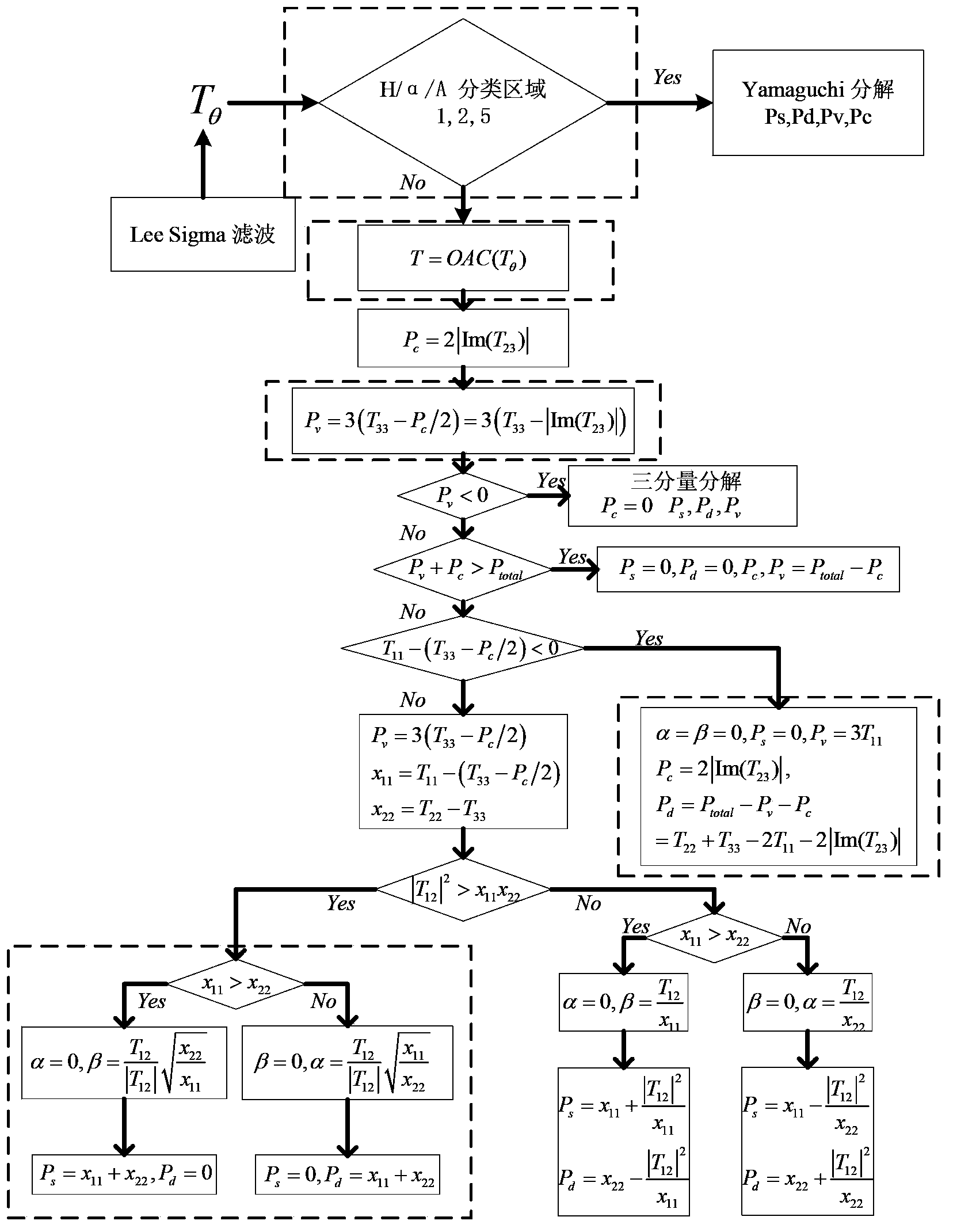
The invention discloses a polarization four-component decomposition method for a city area. The method comprises the following steps of: performing preprocessing on the polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image data of the city area so as to obtain a coherent matrix T theta; S12: eliminating the orientation angle theta in the coherent matrix T theta so as to obtain coherent matrix T; and S13: performing polarization four-component decomposition on the coherent matrix T by using a volume scattering model Tv. Through the orientation angle compensation performed on a coherent matrix and using a new volume scattering model to describe the volume scatting in polarization decomposition, the negative power problems of surface scattering and dihedral angle scattering, which are caused by overestimated volume scattering power, can be released to a certain extent.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Retro-reflector
InactiveUS20100265585A1Increase its retroreflective ratioWiden retroreflective rangePortable emergency signal deviceTraffic signalsDihedral angleReflectivity
The present invention relates to a retroreflective article enabling to retroreflect incident light in its incident direction, and the retroreflective article including at least one retroreflective element, the retroreflective element comprising at least one reflecting corner comprised of a pair of corner reflecting surfaces which meet at dihedral angle of about 90 degree; and a pair of vertical reflecting surfaces which are formed on both ends of the reflecting corner to be substantially perpendicular to a corner of the reflecting corner with a distance which is smaller than the highest vertical height and which meet at dihedral angle of about 90 degree for the pair of corner reflecting surfaces. This retroreflective article has higher retroreflective ratio and wider available retroreflective range, and it is designed to be freely changed its main reflecting direction having the highest retroreflective ratio.
Owner:KIM HYEONSIK +1
Background extraction and offset processing method for RCS (Radar Cross Section) measurement of low detectable target
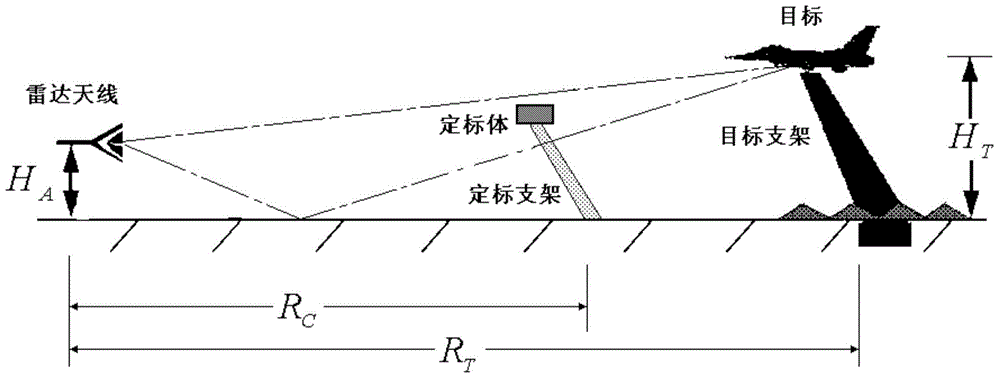
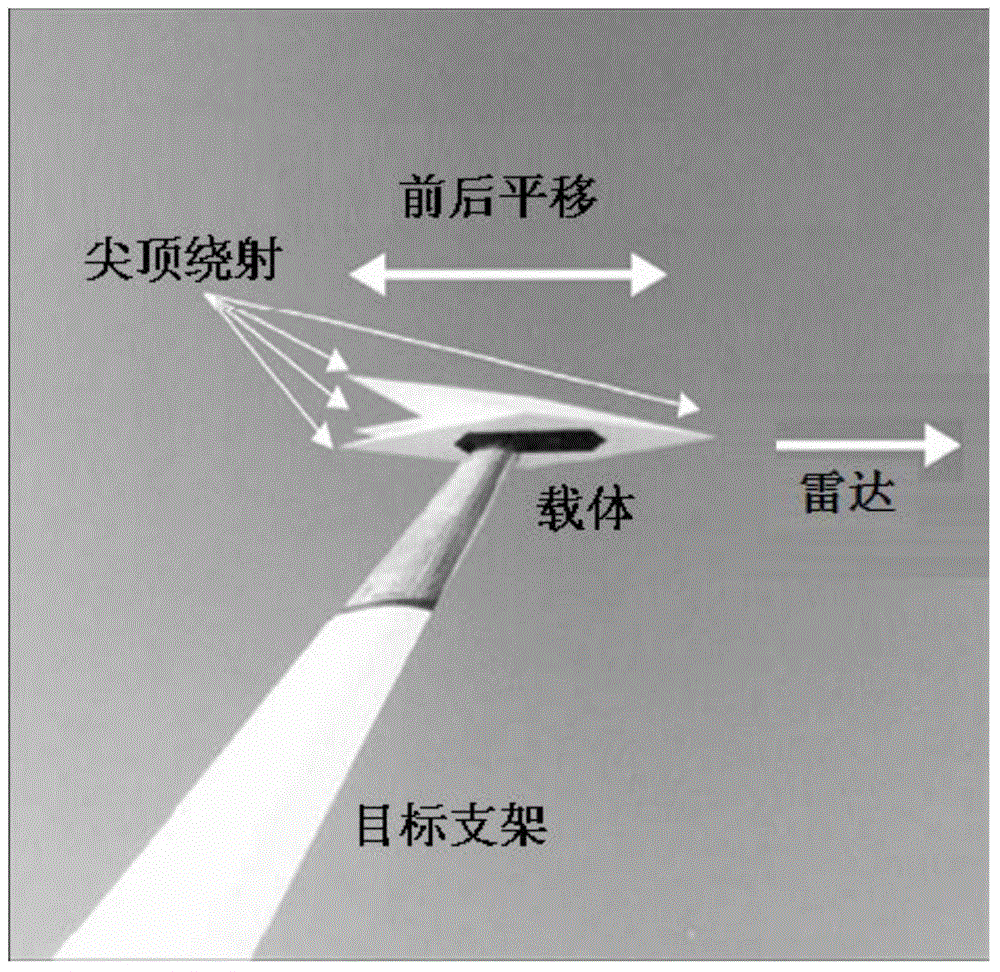
ActiveCN104635222AImproving Measurement Calibration AccuracyHigh measurement accuracyWave based measurement systemsWorkloadDihedral angle
The invention discloses a background extraction and offset processing method for RCS (Radar Cross Section) measurement of a low detectable target. The method can cover, but is not limited to, the existing operation including rectilinear translation of an auxiliary measurement carrier, azimuth rotation of an eccentric cylinder or rotation measurement of a dihedral angle reflector around a radar sight line. According to the method, a fixed background can be extracted by utilizing measurement data of various different auxiliary measurement bodies, thereby greatly expanding the application range of auxiliary background measurement, background extraction and offset technologies in the RCS measurement of the low detectable target. Particularly, when double-calibration bodies serve as the auxiliary measurement bodies, calibration measurement and auxiliary background extraction measurement can be simultaneously completed at a time; when targets self serve as the auxiliary measurement bodies, target measurement and auxiliary background extraction measurement are simultaneously completed at a time. According to the method, the measurement process and the workload are greatly simplified, and the problem of non-ideal background offset processing effect caused by the factors such as shifting of a measurement system is further solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Process for the carbonylation of a conuugated diene
InactiveUS20060235241A1Improve rigidityPromote resultsOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen atomDiphosphines
A process for the carbonylation of a conjugated diene, which involves reacting the conjugated diene with carbon monoxide and a co-reactant having a mobile hydrogen atom in the presence of a catalyst system including: (a) a source of palladium; and (b) a bidentate diphosphine ligand of formula II, R1R2>P1—R3m—R—R4n—P2<R5R6 (II) wherein P1 and P2 represent phosphorus atoms; R1, R2, R5 and R6 independently represent the same or different optionally substituted organic radical containing a tertiary carbon atom through which each radical is linked to the phosphorus atom; R3 and R4 independently represent the same or different optionally substituted methylene groups; R represents an organic group having the bivalent bridging group C1—C2 through which R is connected to R3 and R4; m and n independently represent a natural number in the range of from 0 to 4, wherein the rotation about the bond between the carbon atoms C1 and C2 of the bridging group is restricted a temperature in the range of from 0° C. to 250° C., and wherein the dihedral angle between the plane occupied by the three atom sequence composed of C1, C2 and the atom directly bonded to C1 in the direction of P1, and the plane occupied by the three atom sequence C1, C2 and the atom directly bonded to C2 in the direction of P2, is in the range of from 0 to 120°; and (c) a source of an anion.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Structured abrasive article and method of using the same
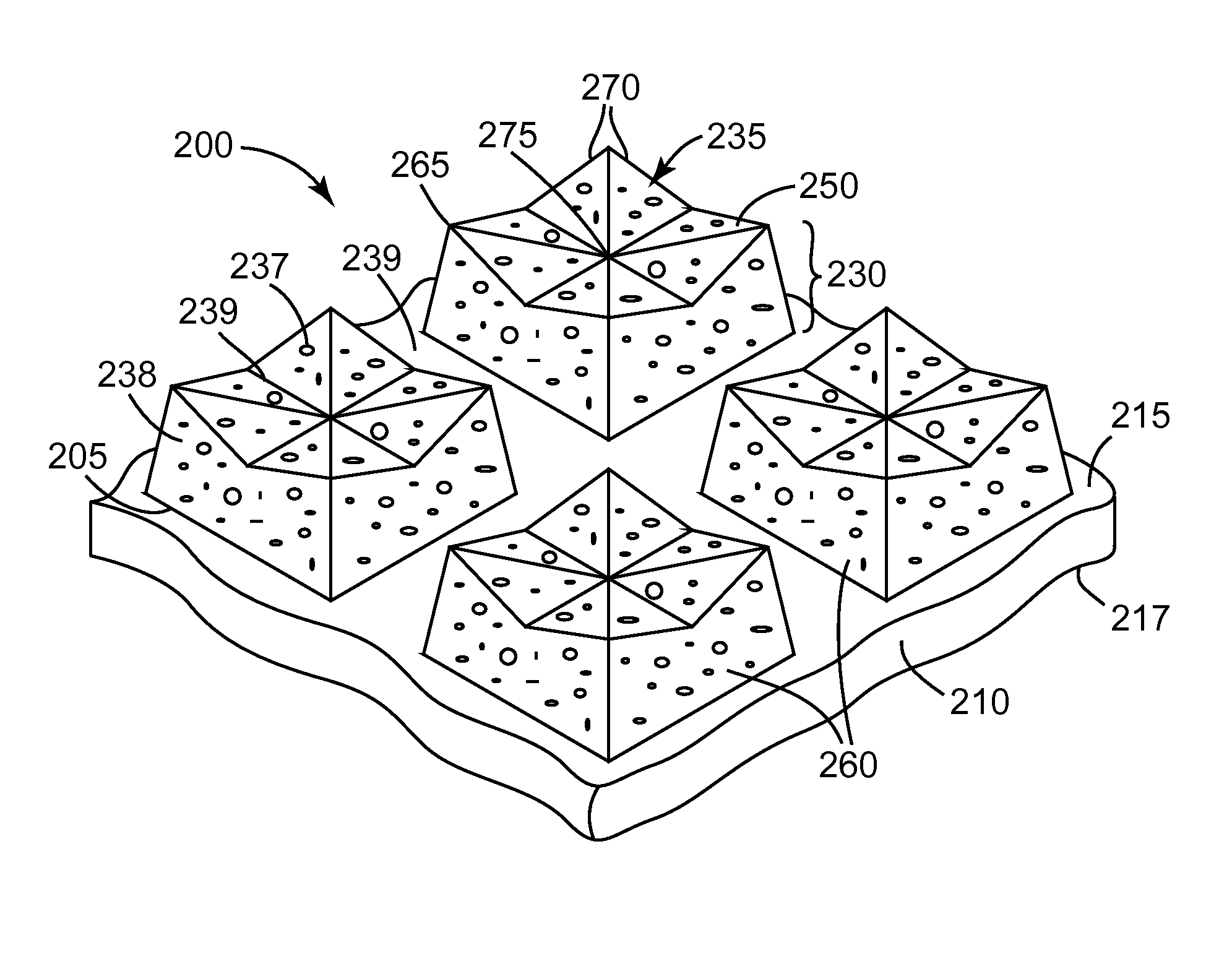
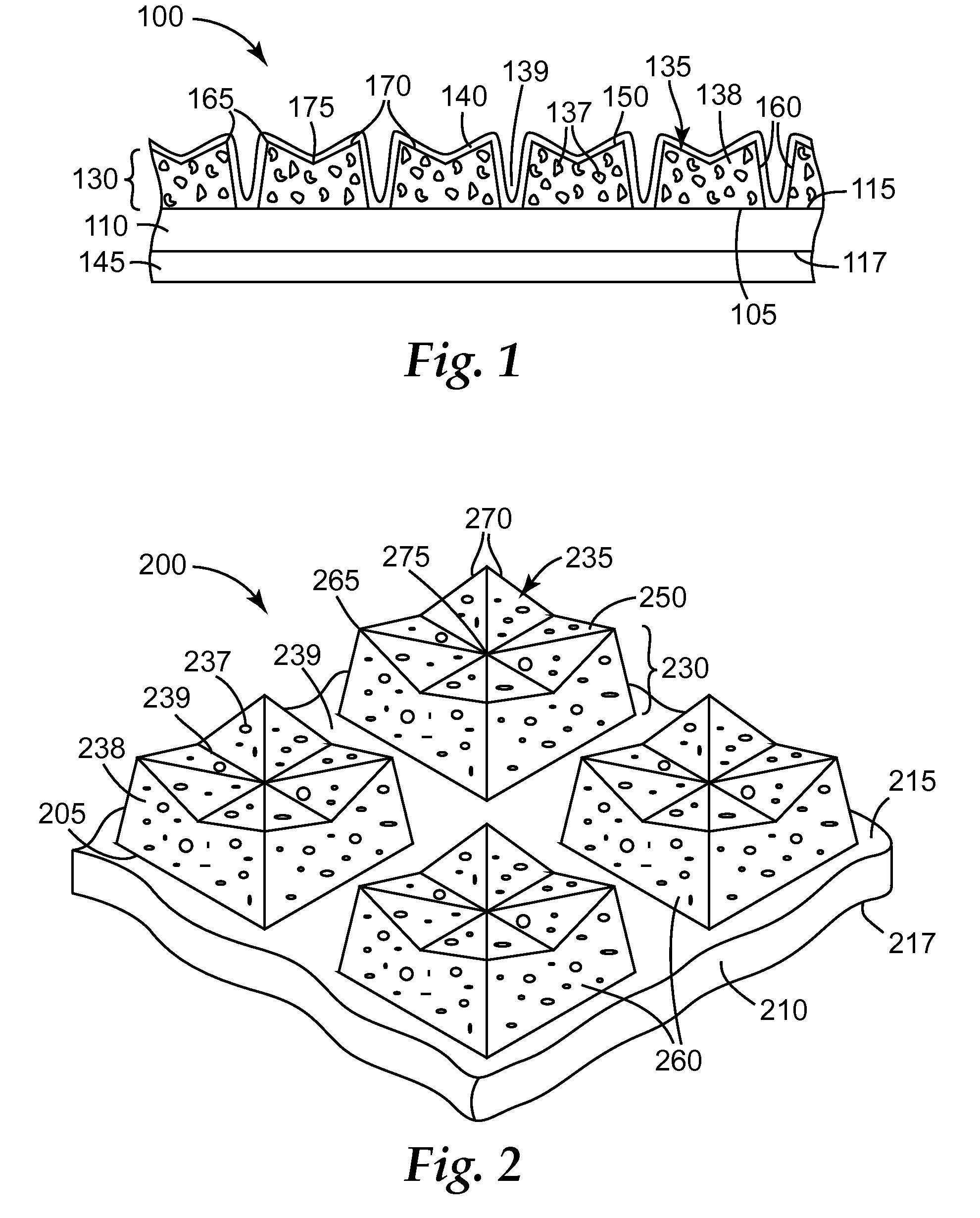
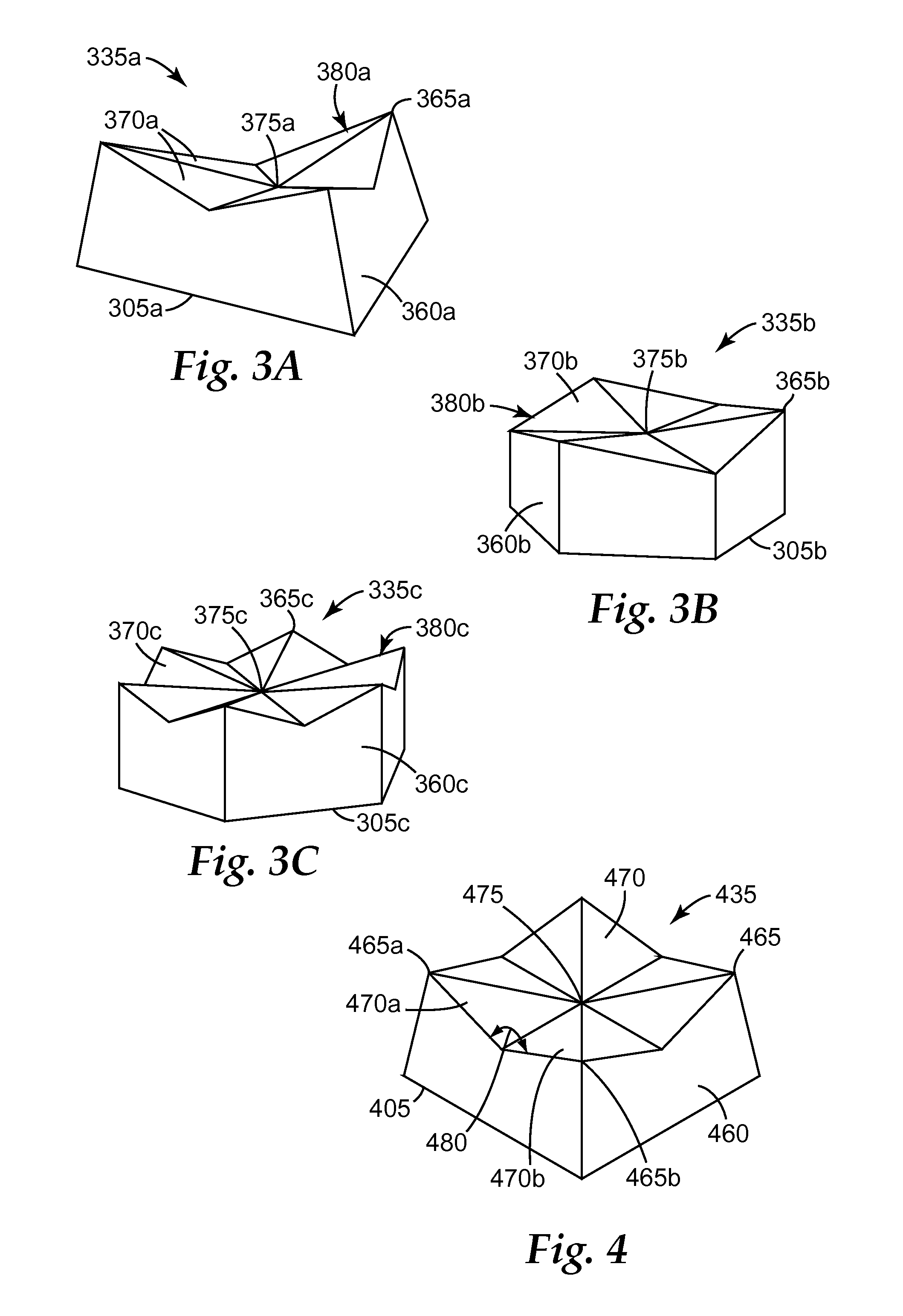
ActiveUS8425278B2Improve practicalityComparable initial cut rateLayered productsAbrasion apparatusDihedral anglePolymer chemistry
A structured abrasive article comprises a backing, and an abrasive layer disposed on and secured to the backing. The abrasive layer comprises shaped abrasive composites, each comprising abrasive particles dispersed in a binder. Each the shaped abrasive composites independently comprises: a base disposed on the backing; a plurality of walls extending away from the base, and a grinding surface not contacting the base. Adjacent walls share a common edge. Each wall independently forms a dihedral angle with the base of less than or equal to 90 degrees. The grinding surface has a plurality of: cusps, and facets that contact a recessed feature. At least a portion of the recessed feature is disposed closer to the base than each of the cusps. Each cusp is formed by an intersection of two of the walls and at least one of the facets. Use of the structured abrasive article to abrade a workpiece is also disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Multi-hedral rotary wing
InactiveUS20050281676A1Improve hover performanceAcceptable forward flight performanceRotary propellersReaction enginesEngineeringDihedral angle
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
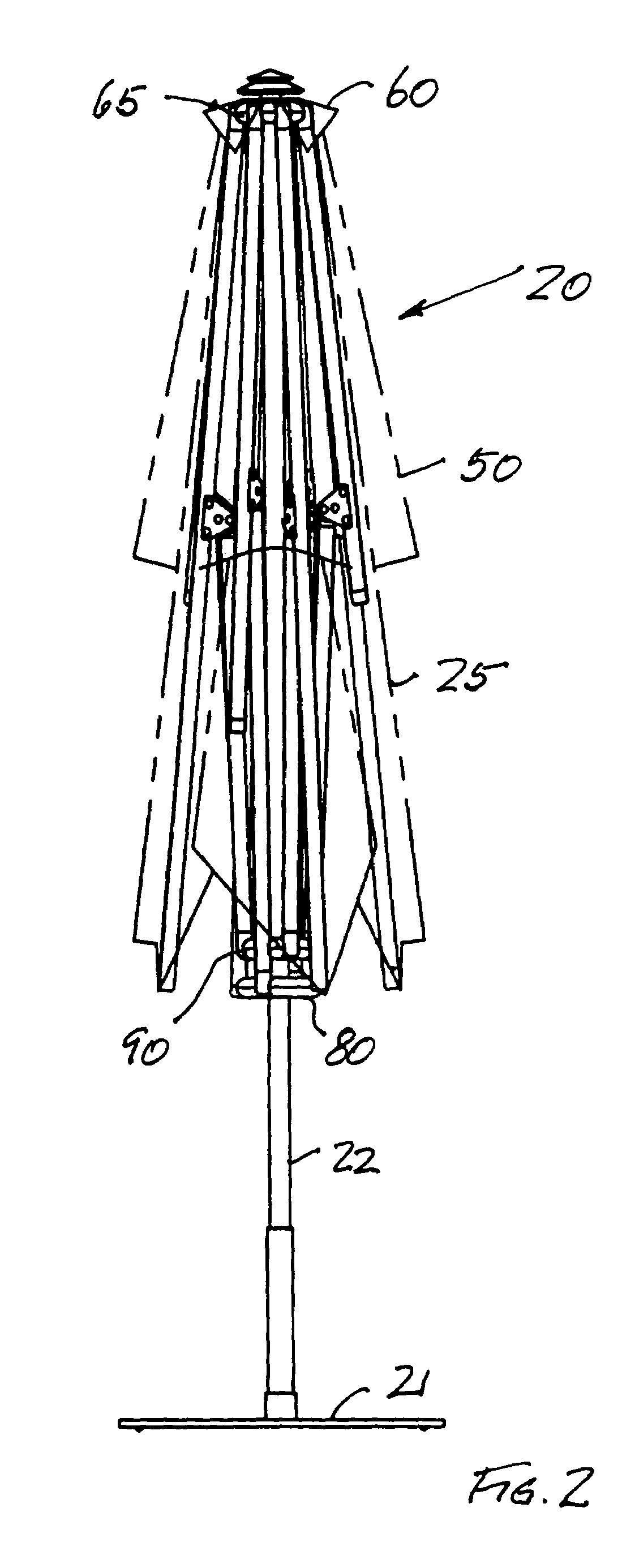
Umbrella with a vented canopy deployable and retractible to a dihedral shape with a positively moved canopy and vent cover
An umbrella assembly providing a dihedral shelter atop a pole which can be deployed to different dihedral angles and retracted to a compact configuration. It further includes a vent port in a cavity which is overhung by a positively positioned vent port cover.
Owner:CALDWELL JOHN W
Cube corner retroreflector with limited range
ActiveUS20050141092A1Avoid excessive road previewLimited rangeOptical articlesTraffic signalsVisibilityDihedral angle
Retroreflective articles having cube corner elements are disclosed, with the dihedral angle errors of the cube corner elements selected to limit the visibility range of the retroreflective article. Also disclosed are methods for making the cube corner elements and the retroreflective articles.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
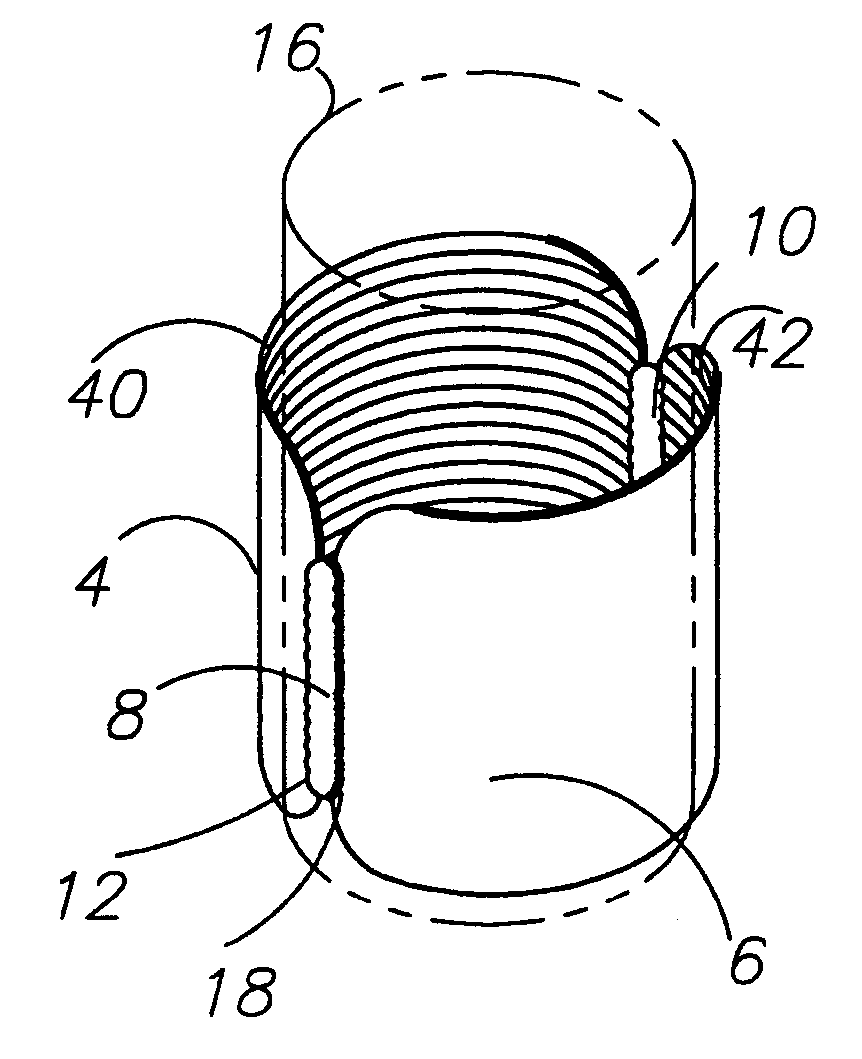
Combination coaster and sleeve apparatus
An improved combination holder and coaster apparatus for receiving a container or vessel which includes first and second thermally insulative, flexible panels joined together by a joint comprised of a stretchable, flexible, adhesive material adapted to return the device to a collapsed coaster configuration. While in receipt of the vessel or container, the device is adapted to an elliptical holder configuration in which the panels are separated by a projected dihedral angle generally between approximately 0 degrees through approximately 180 degrees allowing the elliptical holder to receive the vessel or container.
Owner:TULP DAVID W
Ultrasound emitting device comprising a head frame
InactiveUS20070167765A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An ultrasound emitting device is disclosed. The ultrasound emitting device includes a sound head matrix comprising a first planar member, and a second planar member, wherein the first planar member is attached to the second planar member to form a V-shaped assembly comprising a first interior dihedral angle, where that first interior dihedral angle is between about 155 degrees and about 175 degrees. The ultrasound emitting device further comprises a first plurality of ultrasound transducers disposed on the first planar member, and a second plurality of ultrasound transducers disposed on the second planar member.
Owner:CEREVAST THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com