Freeman decomposition and homo-polarization rate-based polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method
A classification method and co-polarized technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of arbitrary division of regions, deterioration of classifier performance, and high computational complexity, achieving clear edges and reducing Computational complexity, achieving simple and easy effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
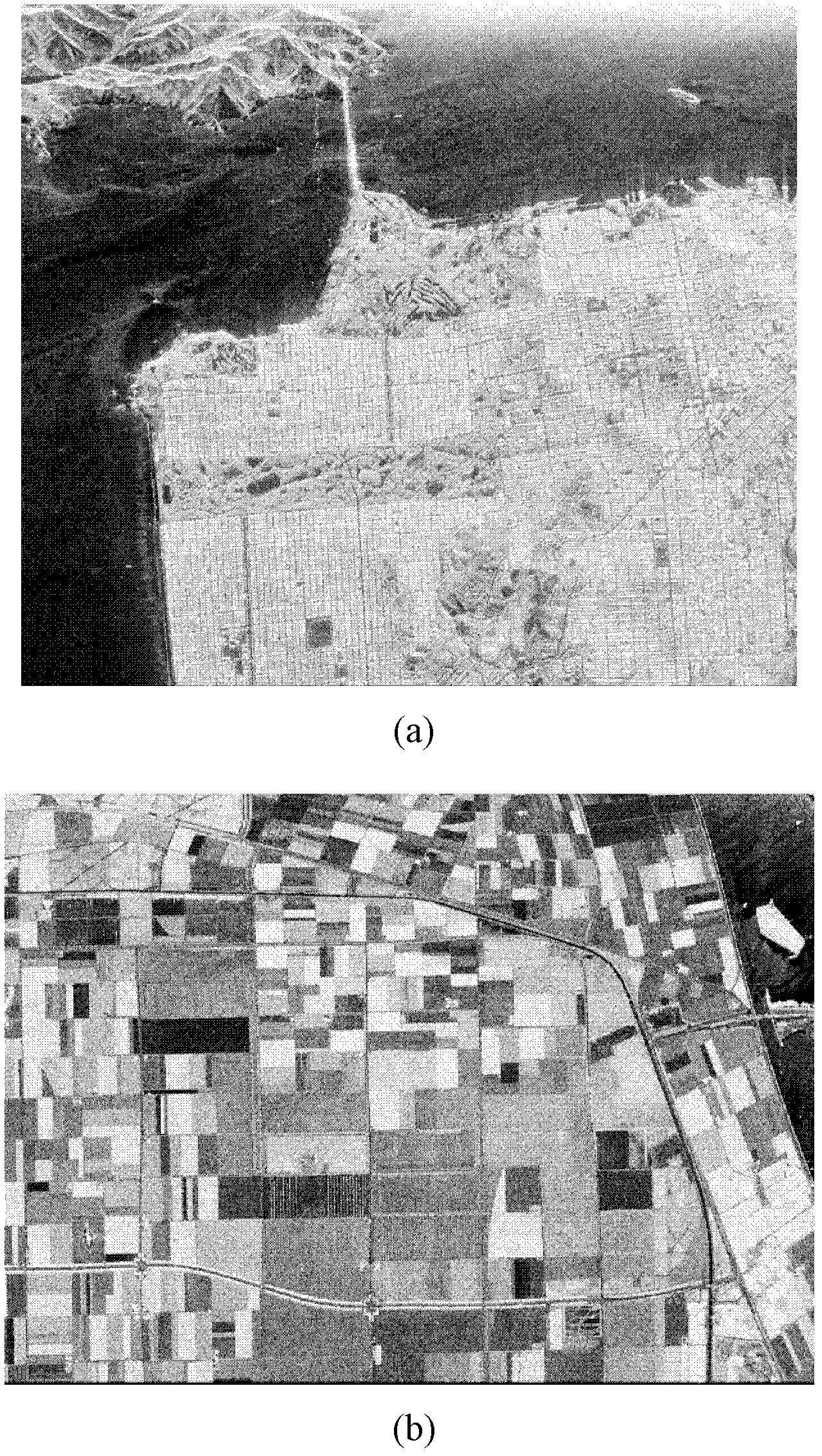
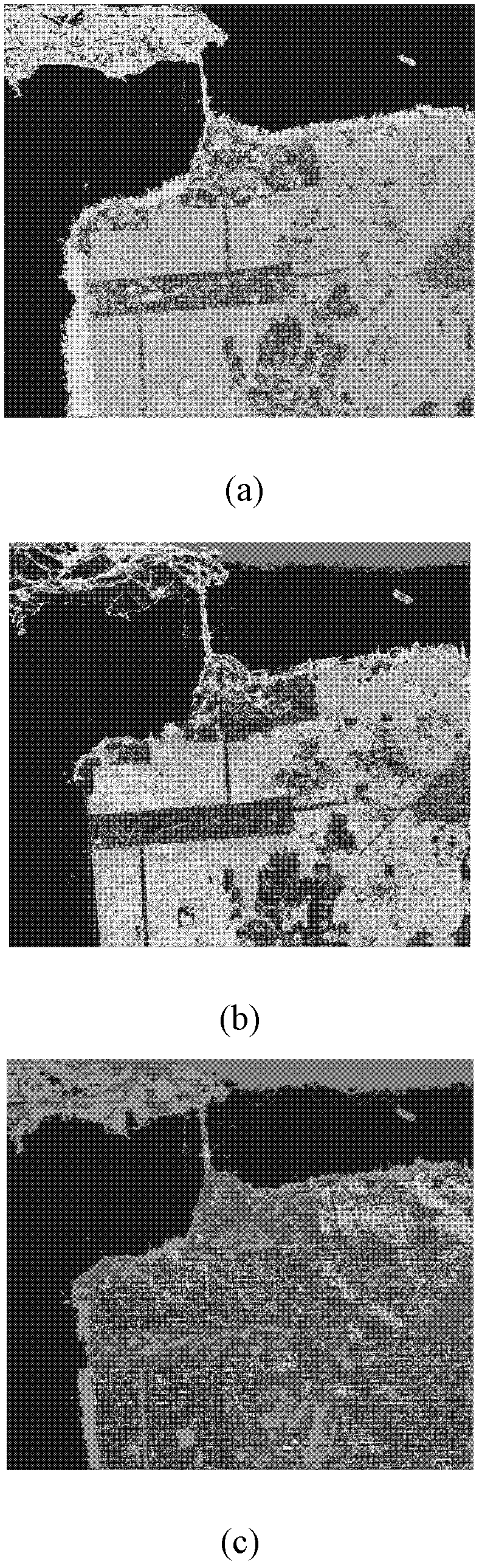
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
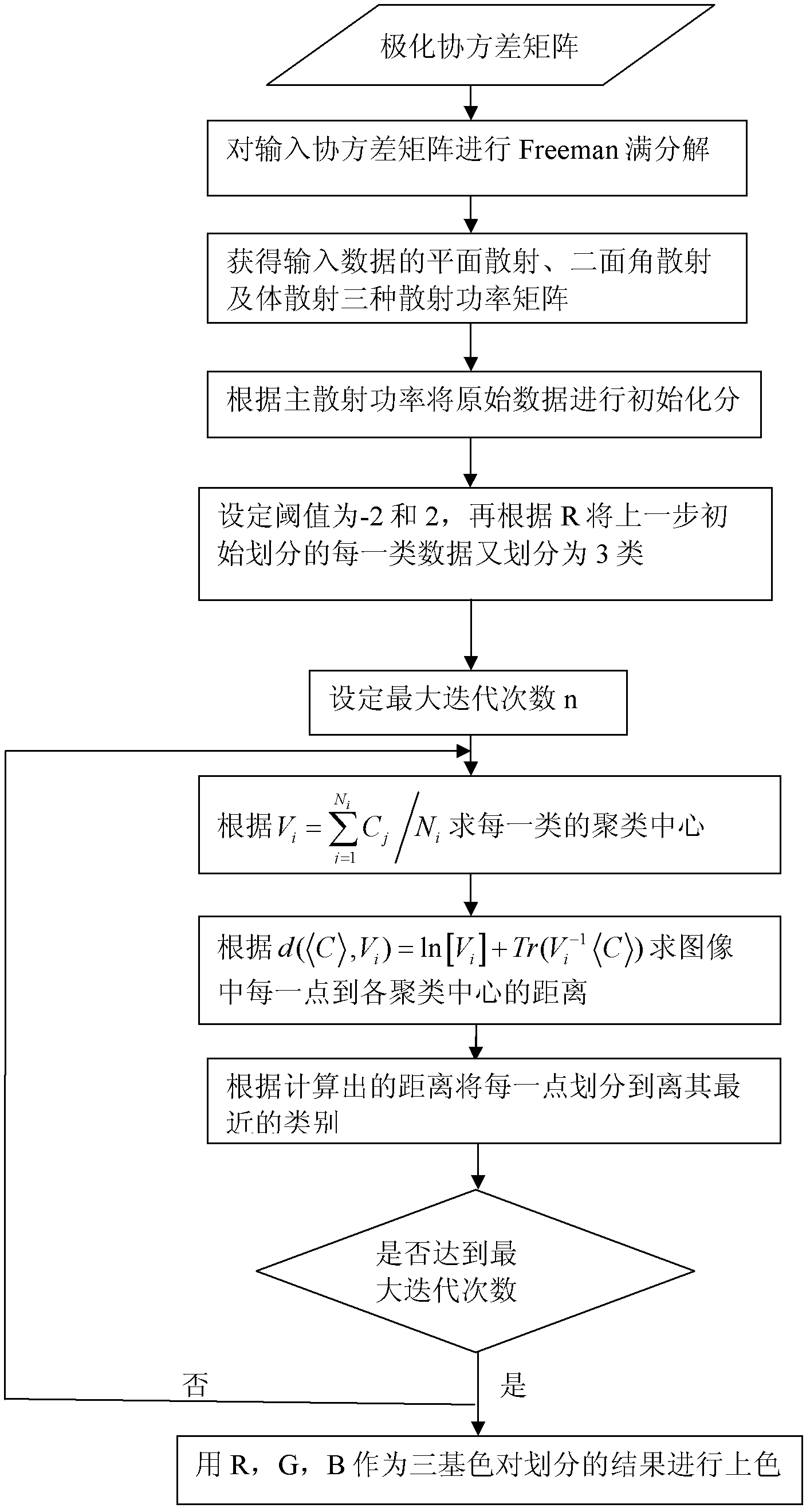
[0025] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0026] Step 1, perform Freeman decomposition on the input data to obtain the scattering power matrix P s , P d , P v , where P s represents the surface scattering power matrix, P d Denotes the dihedral scattered power matrix, P v represents the volume-scattered power matrix.
[0027] For Freeman’s decomposition, see Freeman A and Durden S.A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 1998, 36(3): 963-973. The specific steps are as follows:
[0028] 1a) Each pixel of the read-in data is a 3×3 polarization covariance matrix C containing 9 elements;
[0029] C = | S HH | 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com