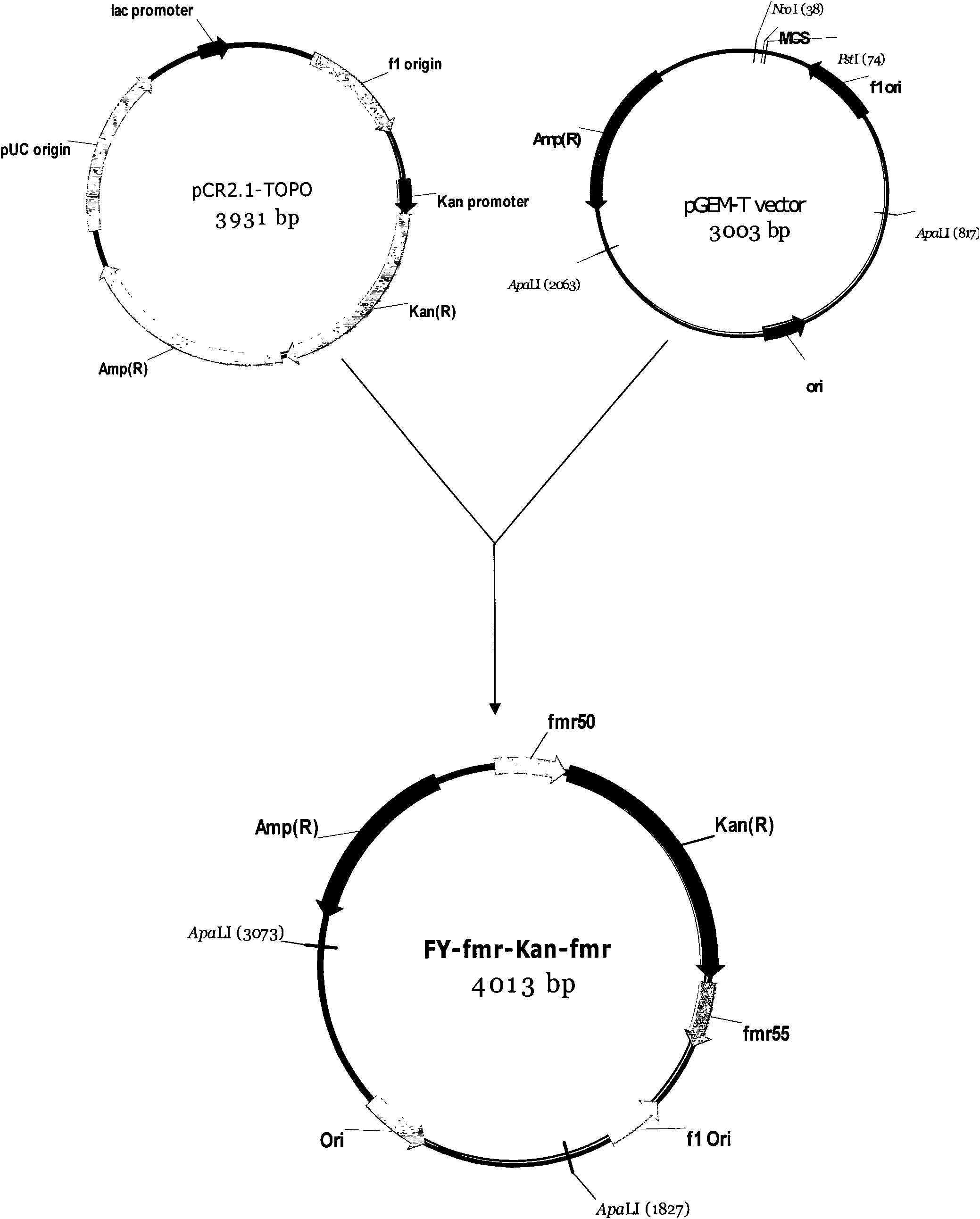
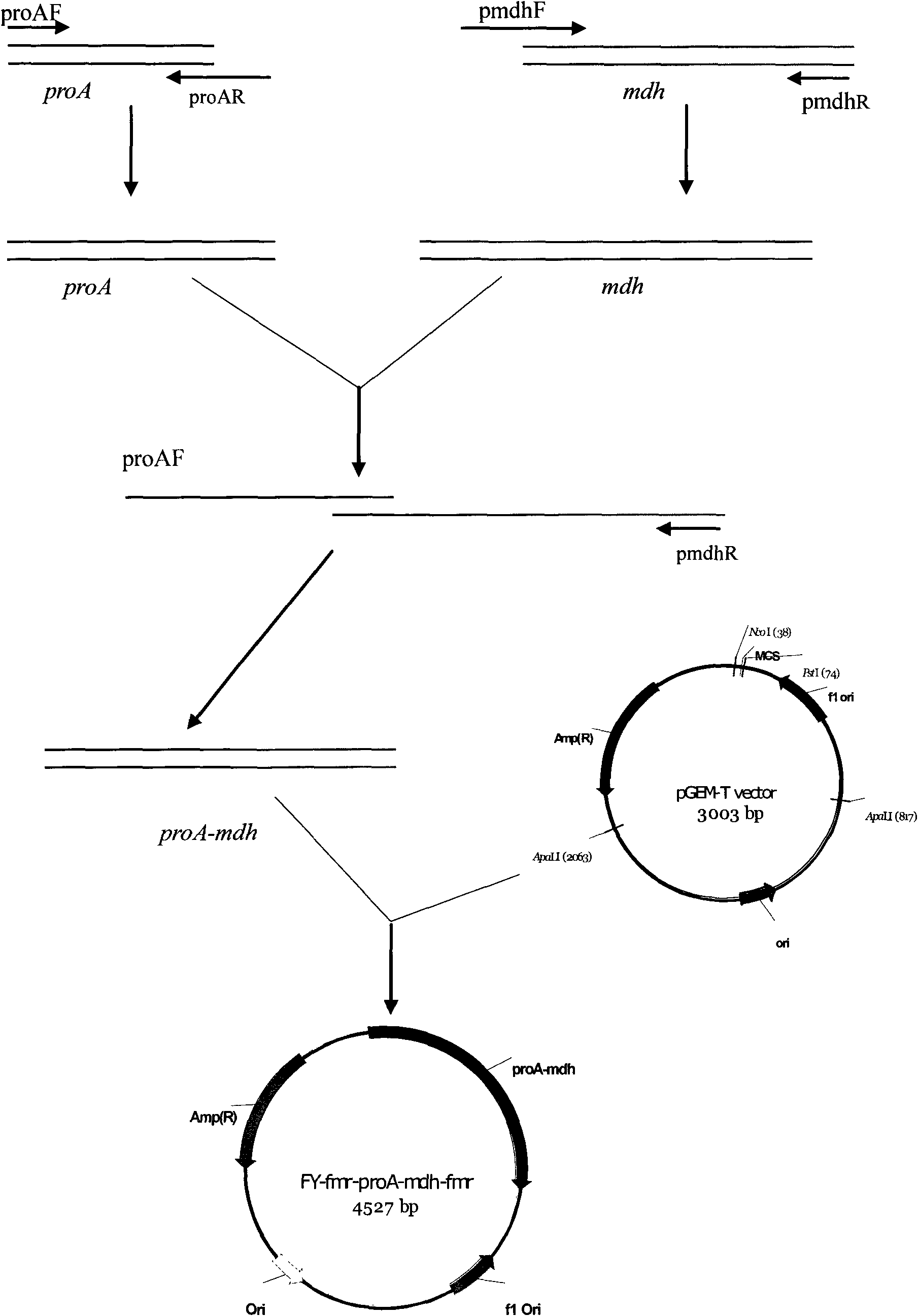
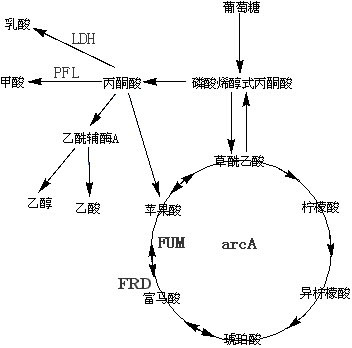
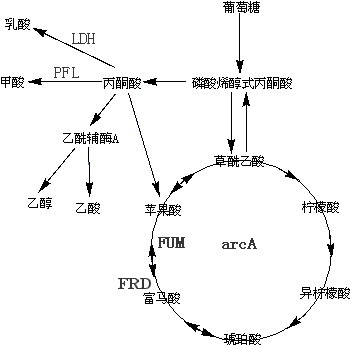
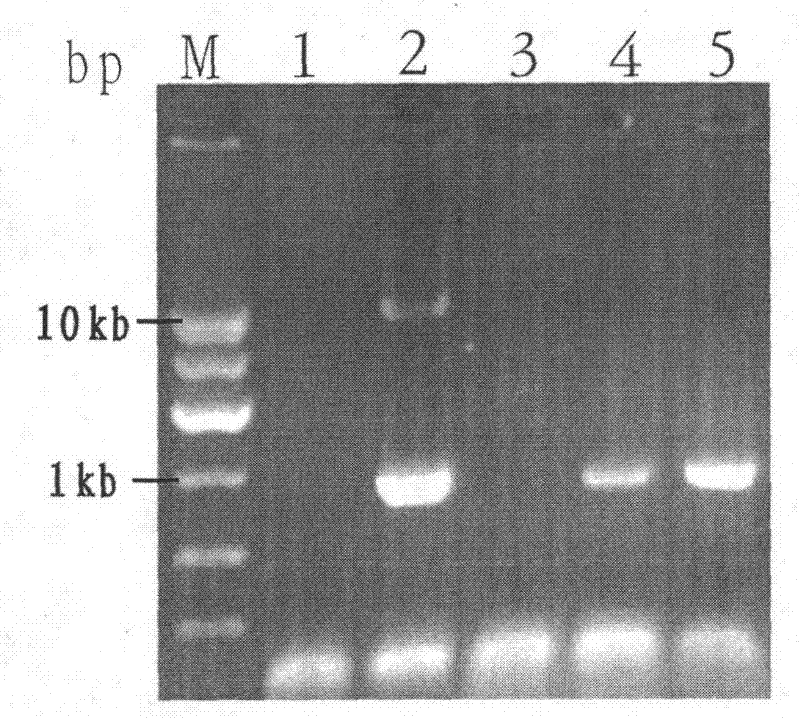
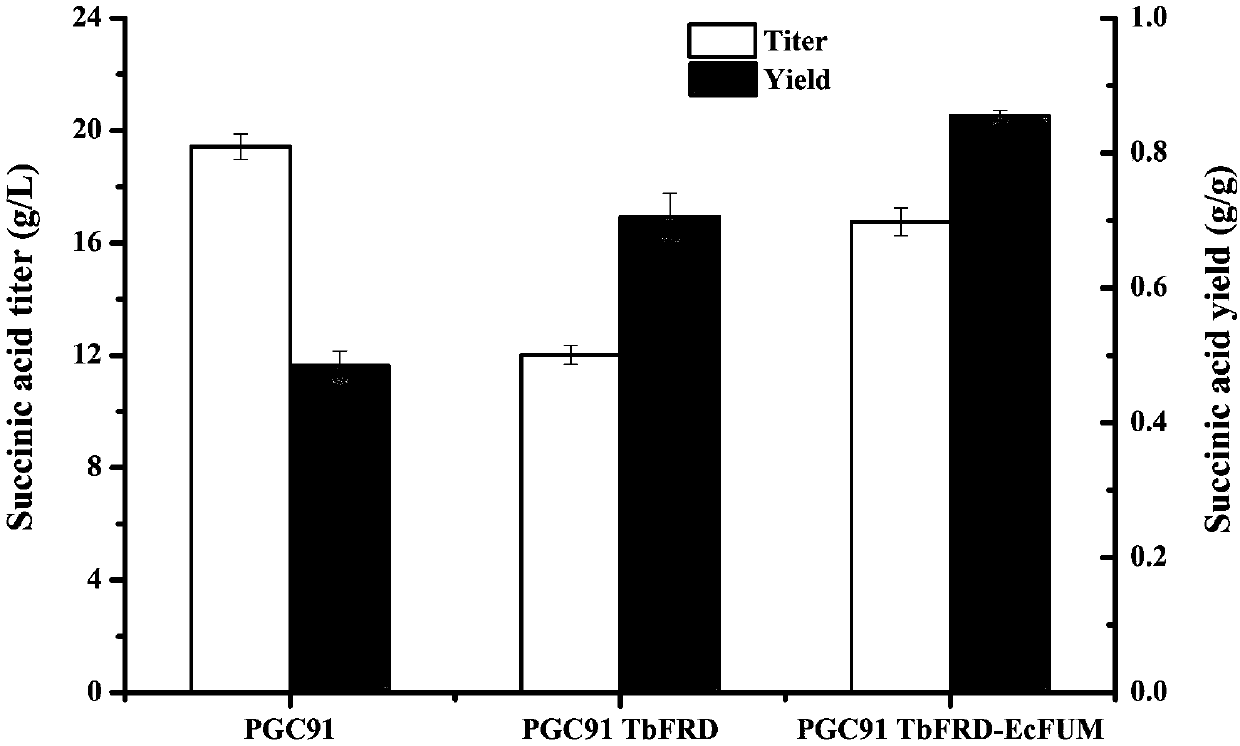
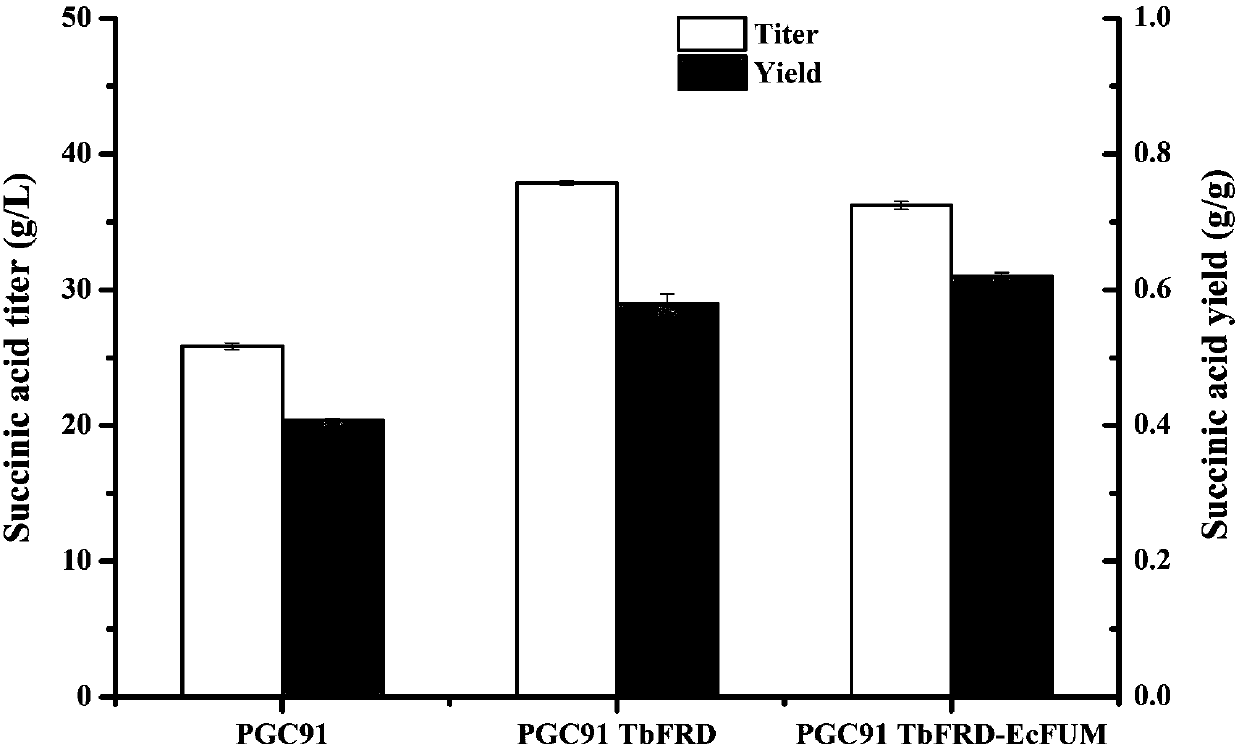
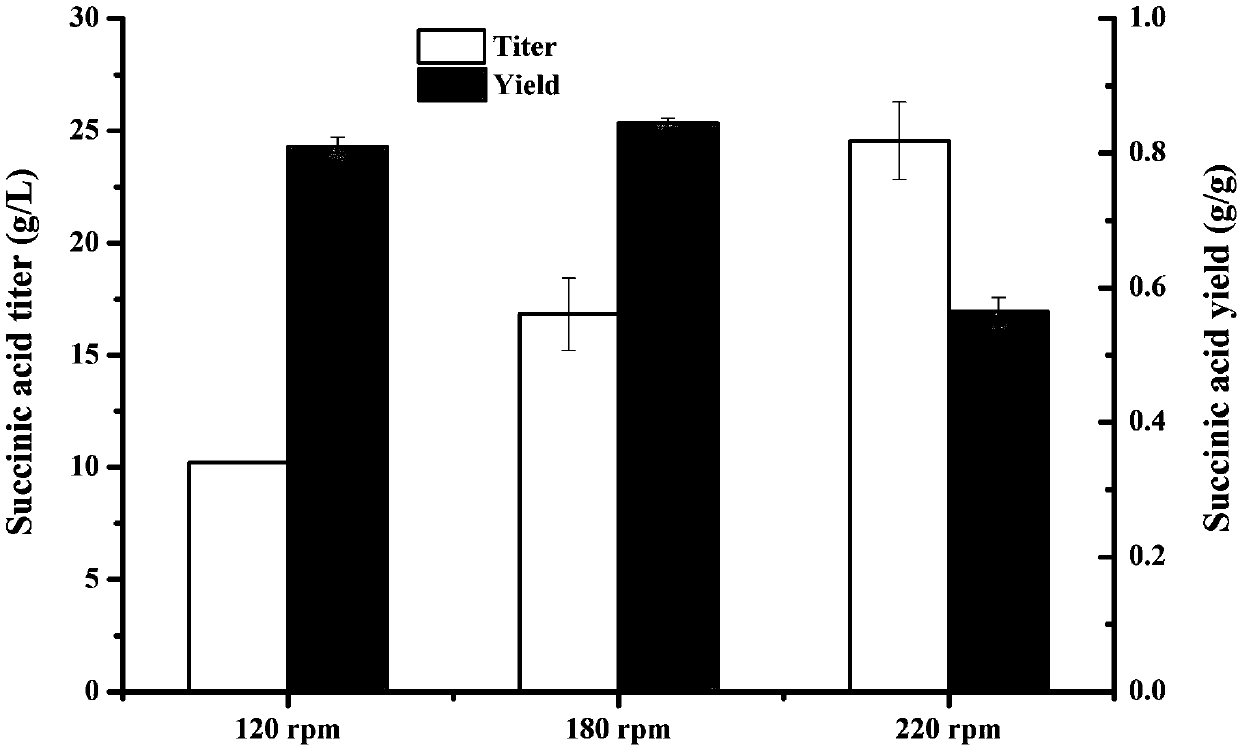
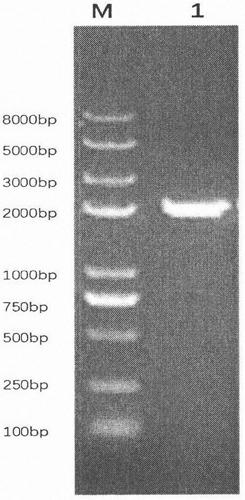
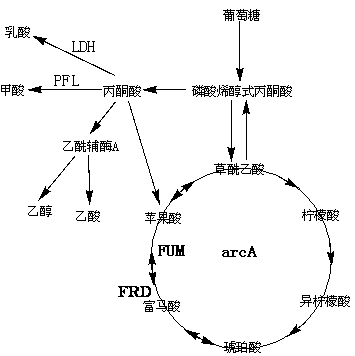
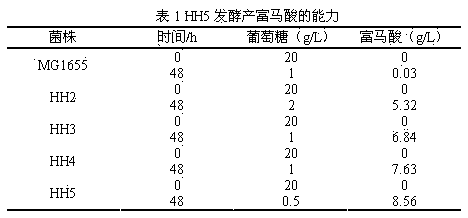
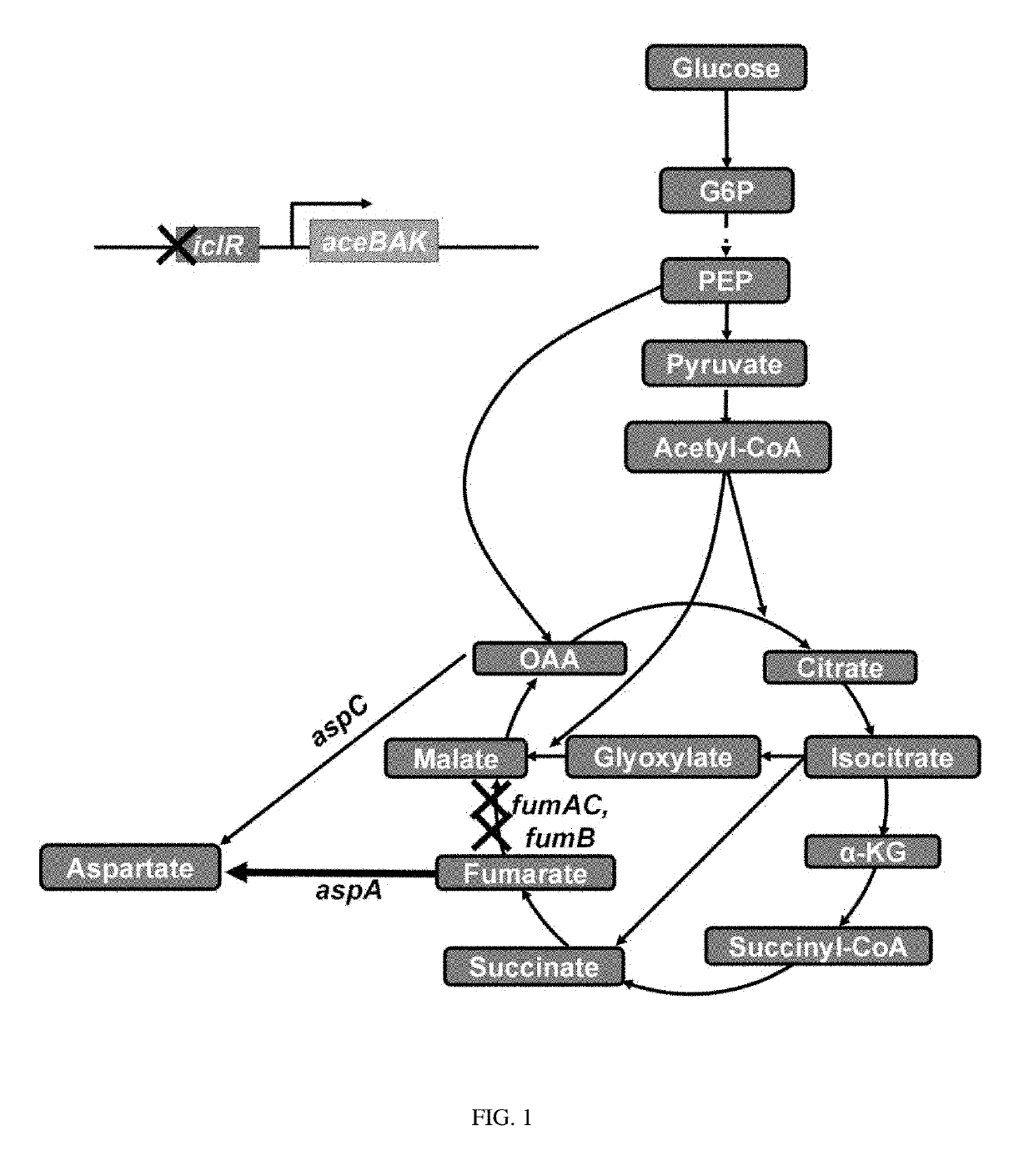
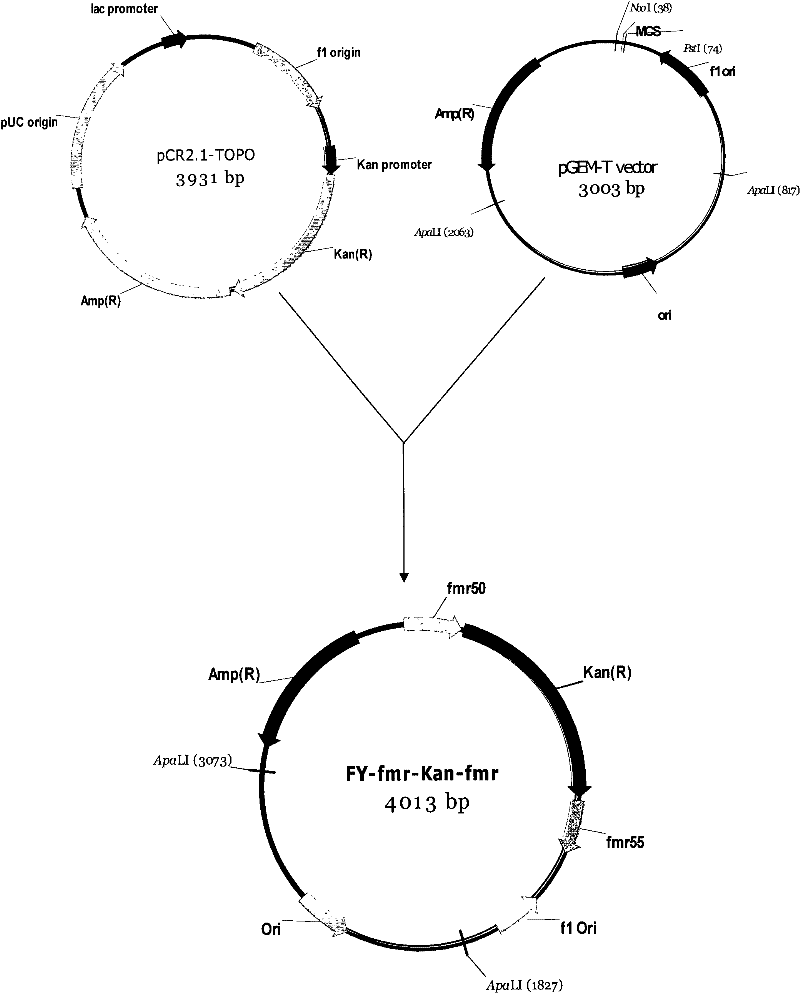
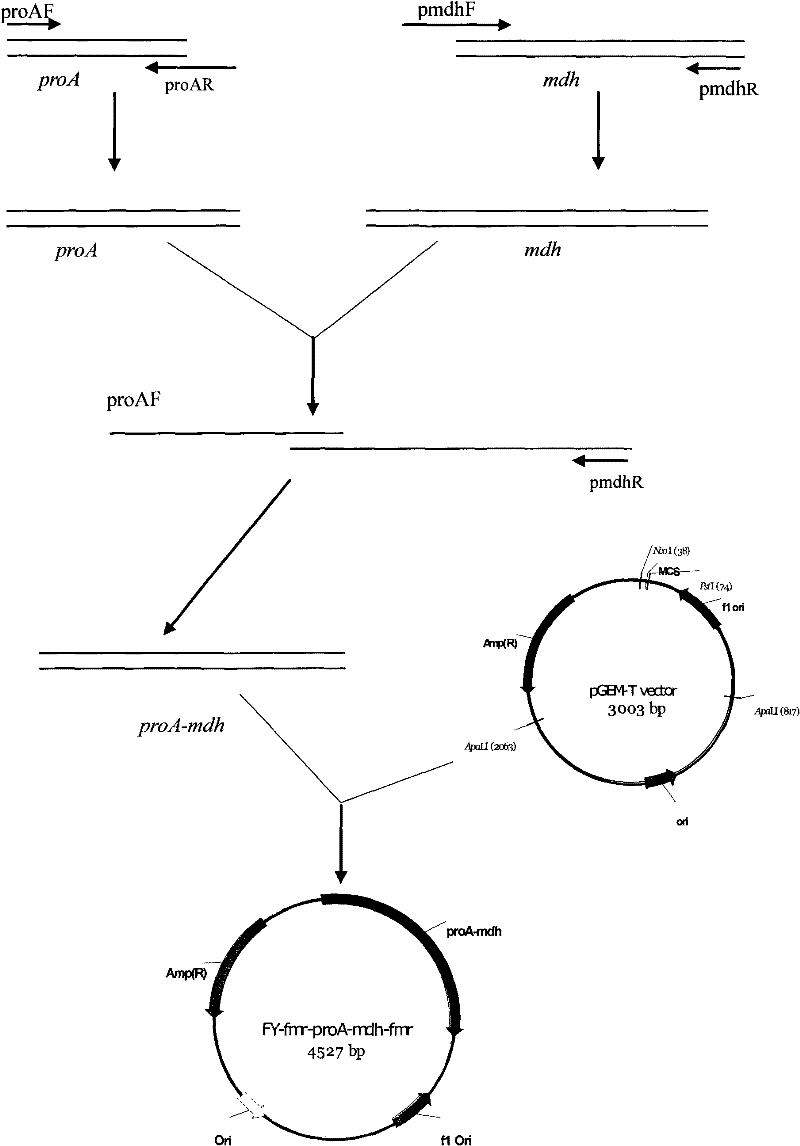
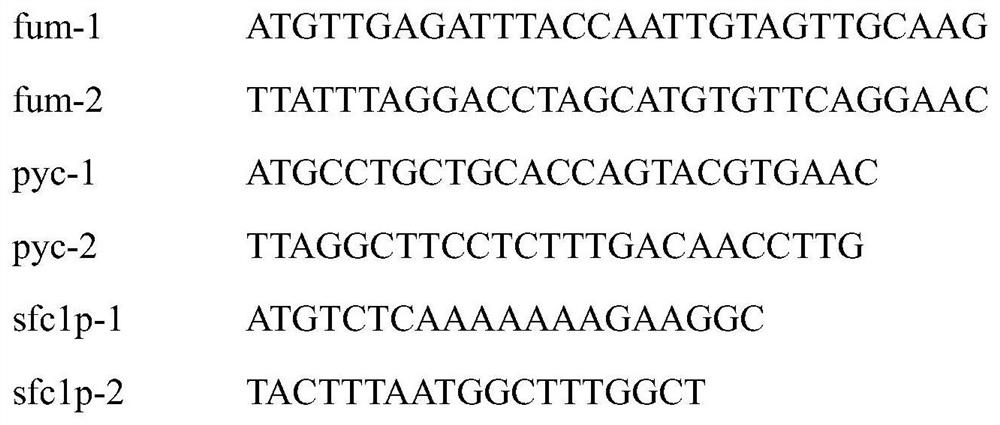Patents
Literature
30 results about "Fumarase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
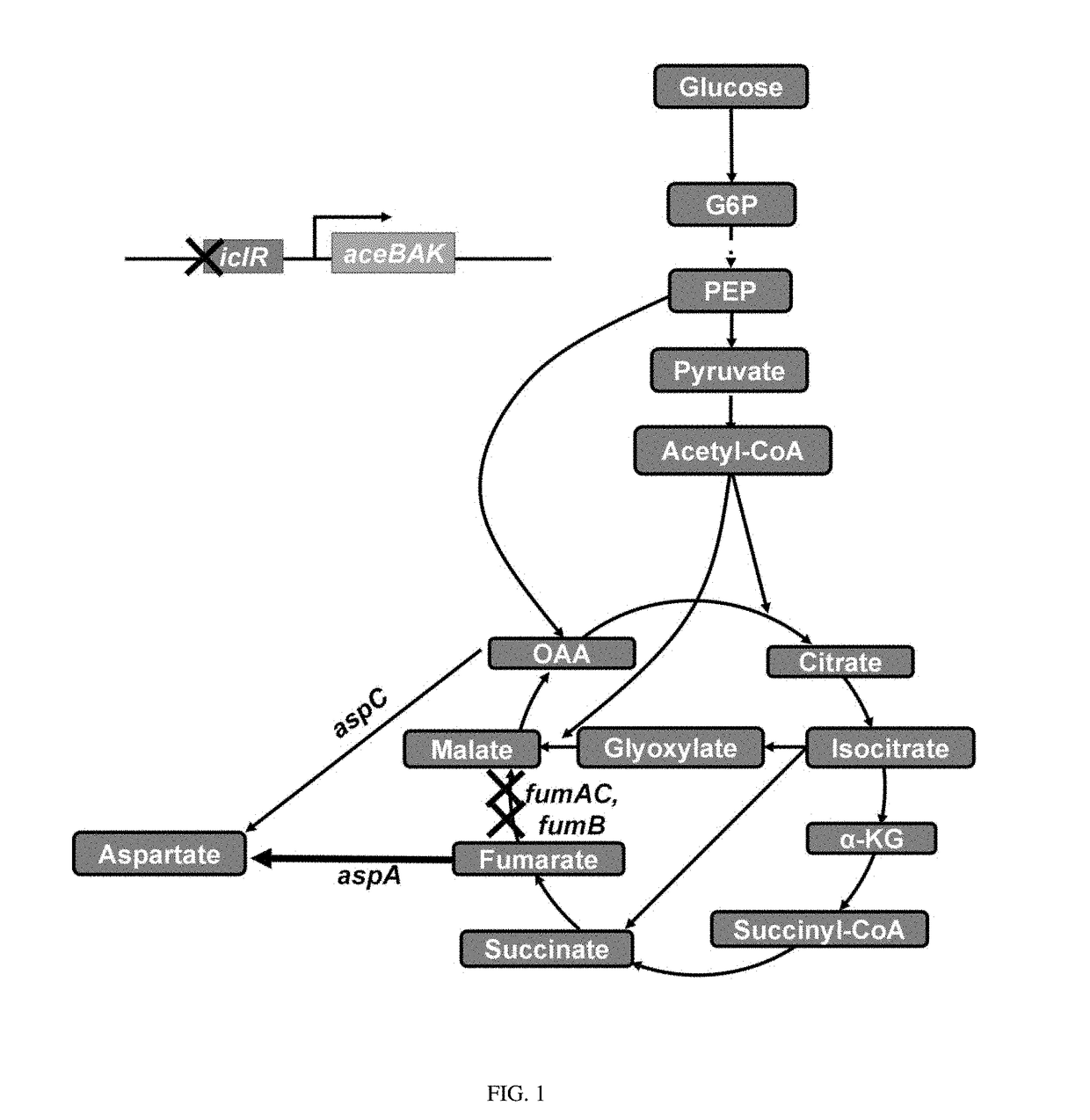
Fumarase (or fumarate hydratase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration/dehydration of fumarate to malate. Fumarase comes in two forms: mitochondrial and cytosolic. The mitochondrial isoenzyme is involved in the Krebs Cycle (also known as the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle [TCA] or the Citric Acid Cycle), and the cytosolic isoenzyme is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and fumarate. Subcellular localization is established by the presence of a signal sequence on the amino terminus in the mitochondrial form, while subcellular localization in the cytosolic form is established by the absence of the signal sequence found in the mitochondrial variety.
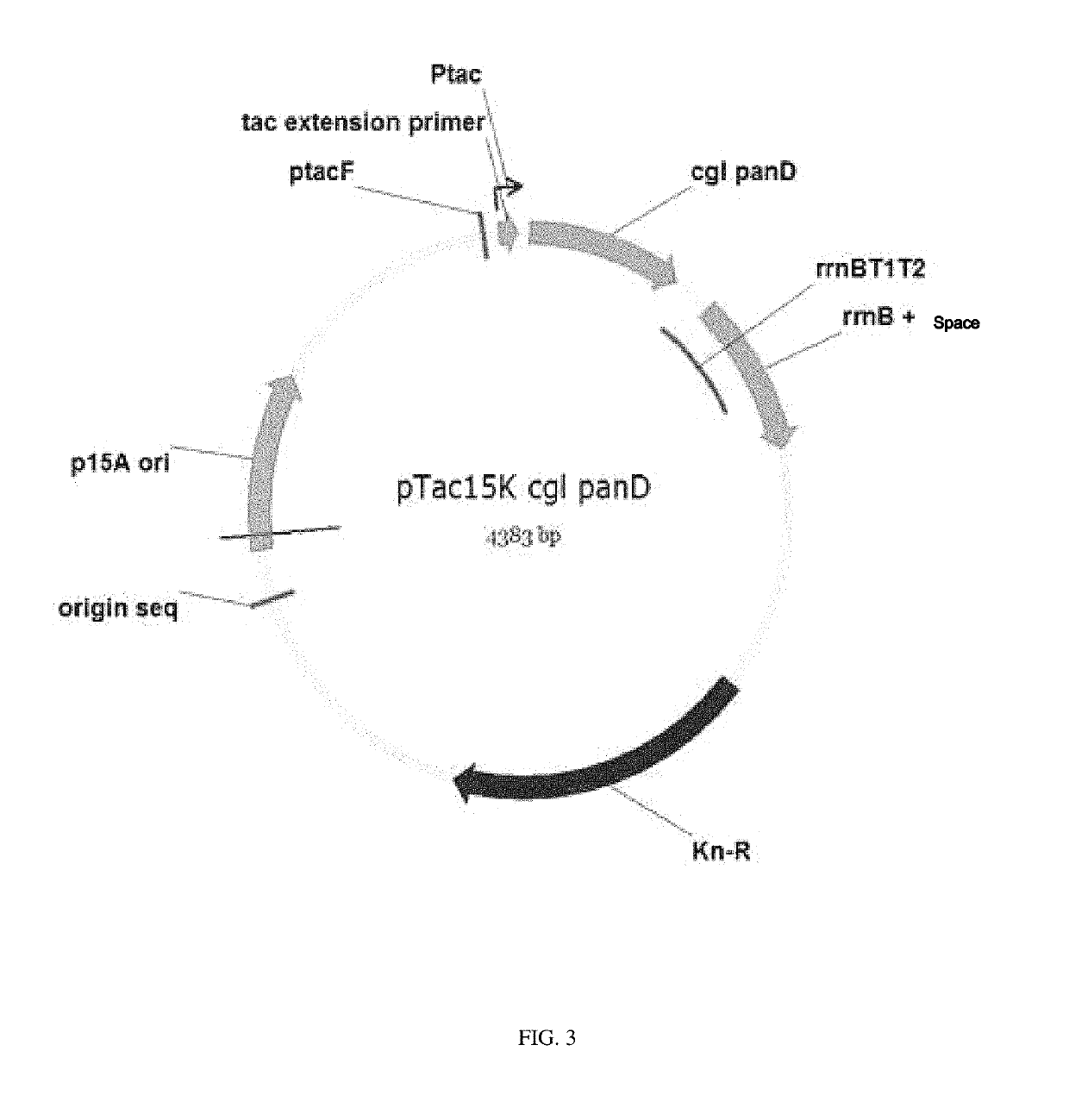
Malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and its construction and use
InactiveCN104046577AThe fermentation method is simpleGood effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFumaraseFermentation
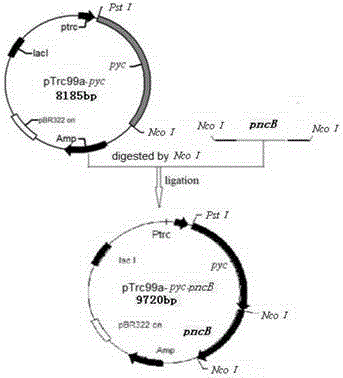
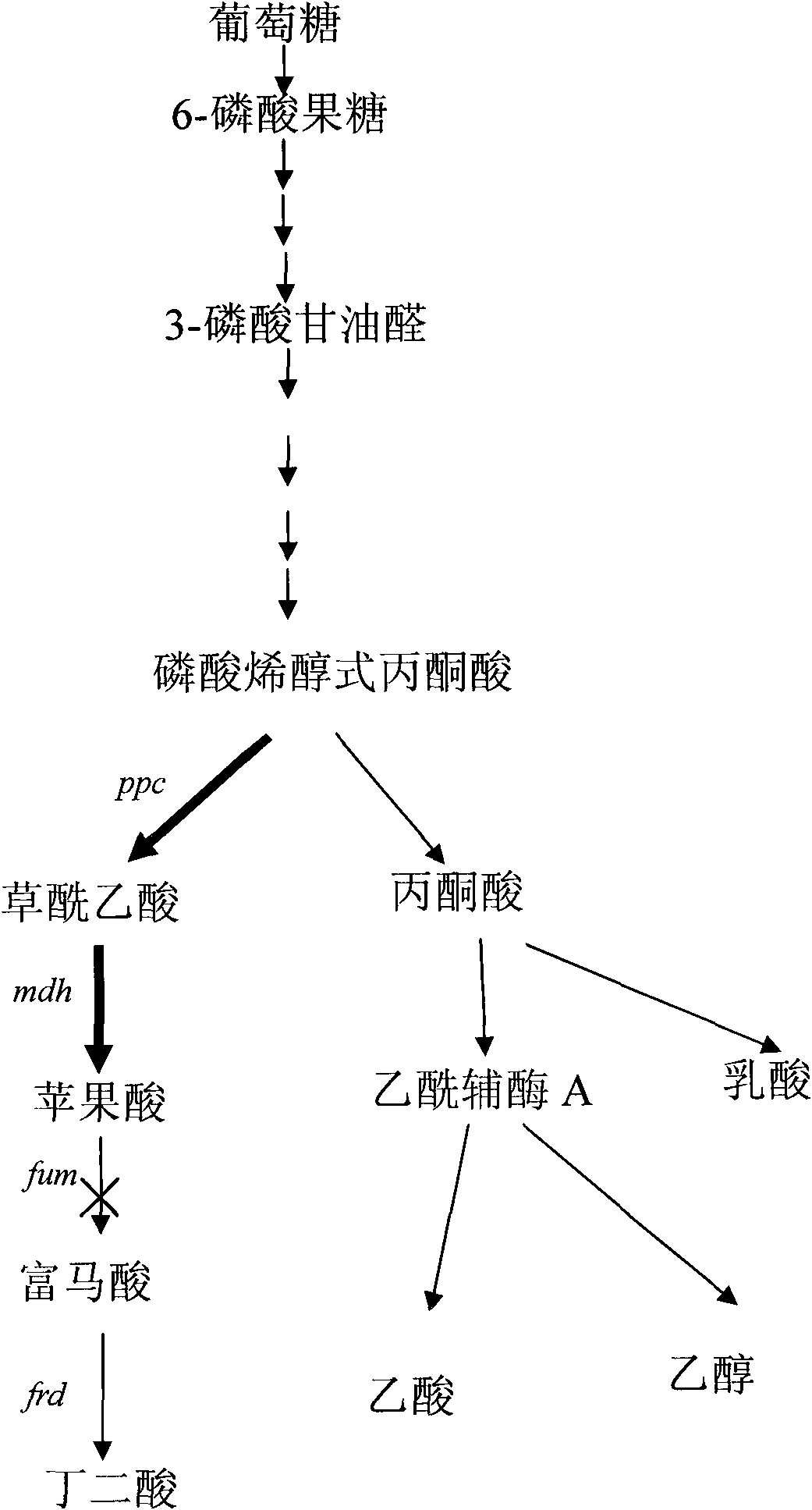
The invention provides malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria Escherichiacoli BA043. The malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria is named as BA043 (Escherichiacoli BA043) and has a preservation registration number CCTCC NO: M2014034. The invention also provides a construction method of the malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and a method for fermentation production of malic acid. Through knockout or inactivation of fumarase and fumarate reductase and through over coexpression of exogenous pyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase, recombinant escherichia coli can reduce by-product pyruvic acid generation by glucose metabolism growth so that a malic acid yield and production intensity are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. In the invention, key phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase(PEPCK) related to the L-malic acid, malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and fumarase (FumC) are transformed to obtain the gene engineering bacterial strain; a deactivation mutation is carried out on the fumCto cause the interruption of a metabolic flux at the converting position from the malic acid to the fumaric acid so as to accumulate the target product L-malic acid; before the mdh, the promoter of aninner source pepck gene is added to generate the metabolic flux biased towards the malic acid; in addition, through the inducement of monofluorine sodium acetate, the activity of the PEPCK is improved, and the product feedback inhibition is greatly reduced. The bacterial strain applied to the fermentative production of the L-malic acid so as to obviously improve the yield of L-malic acid. The invention has advantages of simple technology, obvious effect and low cost and can satisfy the demand of markets.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Method for constructing escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria for producing fumaric acid
InactiveCN102618570ARealize accumulationCumulative acid production effect is idealBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFumarase
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for constructing escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria for producing fumaric acid. The method for constructing the escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria mainly comprises the following steps of: inactivating or knocking fumarase serving as key enzyme for converting fumaric acid into malic acid in a tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle out, and knocking a key gene arcA for inhibiting the TCA cycle out. Further, key enzyme genes in paths of succinic acid, lactic acid and formic acid can also be knocked out, so the fumaric acid can be accumulated under the anaerobic condition.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Engineered Escherichia coli and method of synthesis of catalyzing fumaric acid from maleic acid in presence of Engineered Escherichia coli
InactiveCN106222122AImprove expression efficiencyHigh densityBacteriaCis-trans-isomerasesFumaraseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to engineered Escherichia coli capable of high-yield production of fumaric acid; specifically, fumarase coded genes fumA and fumC of Escherichia coli are knocked off, and maleic cis-trans isomerase gene from Serratia marcescens is converted to obtain the engineered Escherichia coli. The invention also discloses a method of synthesis of catalyzing fumaric acid from maleic acid by using the engineered Escherichia coli. The method includes culturing the engineered Escherichia coli by fermenting, subjecting the engineered Escherichia coli to high-density inductive expression when OD600 reaches 40-80, and applying the obtained fermentation broth to biochemical catalysis of maleic acid in presence of Engineered Escherichia coli to obtain fumaric acid. The genes fumA and fumC in the Escherichia coli are knocked off by using Red homologous recombination, a metabolic pathway of its fumaric acid to L-malic acid is cut off, the maleic cis-trans isomerase from Serratia marcescens is then expressed, and the obtained genetically-engineered Escherichia coli can efficiently convert maleic matrix to synthesize high-purity fumaric acid, there is nearly no L-malic acid byproduct synthesized, and basis is provided for the industrialized production of fumaric acid by whole-cell process catalysis of maleic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Construction method and use of fumaric acid producing candida glabrata engineering strain
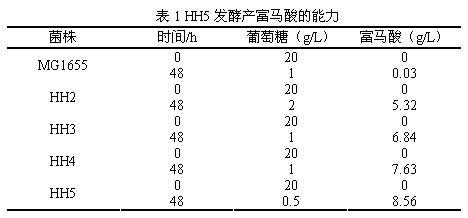
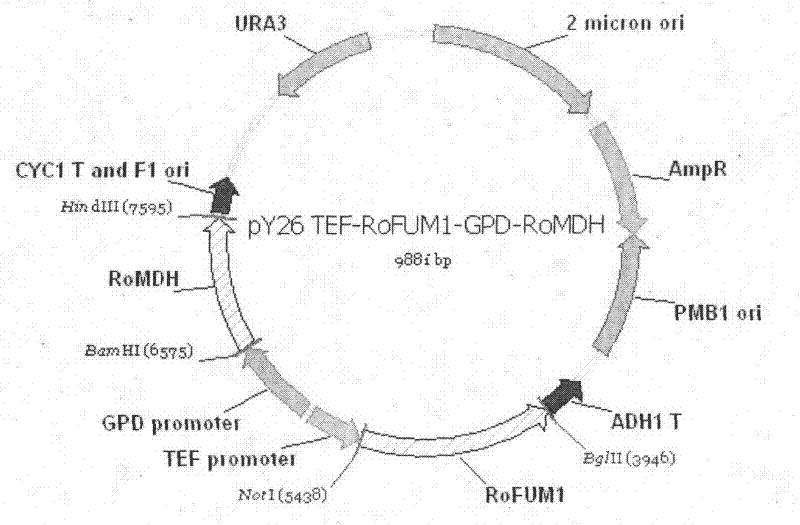
The invention discloses a construction method and use of a fumaric acid producing T.glabrata candida glabrata engineering strain and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. In the invention, a recombinant T.glabrata FMME045 strain is obtained by overexpression of a malic dehydrogenase (RoMDH) gene and a fumarase (RoFUM1) gene from rhizopus oryzae in a uracil deficient (Ura) T.glabratadeltaura3 strain of a pyruvic acid producing strain T.glabrata in a free expression mode. When the strain is used for fermentation production of fumaric acid, the fumaric acid yield after the fermentation is performed for 60 hours is increased by 6 times to 35mg / L compared with that of a starting strain. Thus, a new approach is provided for producing fumaric acid by a microbial fermentation process. The method has a bright application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of utilizing yarrowia lipolytica strain having reductive TCA path to aerobically synthesize succinic acid
ActiveCN107916275AHigh yieldGood resistance to acidic conditionsMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesFumaraseUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method of utilizing a yarrowia lipolytica strain having a reductive TCA path to aerobically synthesize succinic acid. The yarrowia lipolytica engineering strain heterogeneously expresses key enzymes: fumaric reductase (FRD) and fumarase (FUM) in the reductive TCA path, and theoretical yield is substantially increased when compared with that of conventional oxidative TCA paths. The process of electrodialysis or acidizing ultrafiltration is omitted in a step of separating and purifying succinic acid, and no ammonium sulfate which is a byproduct is generated, so that themethod has considerable application value and prospect.
Owner:盛虹控股集团有限公司
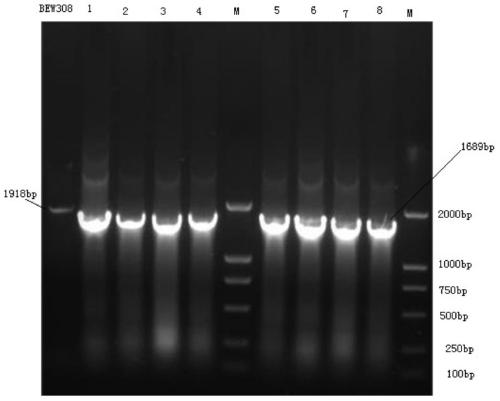
Recombinant escherichia coli efficiently transforming fumaric acid into L-asparagine as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105925520ALow fumarase activityImprove conversion yieldCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliFumarase
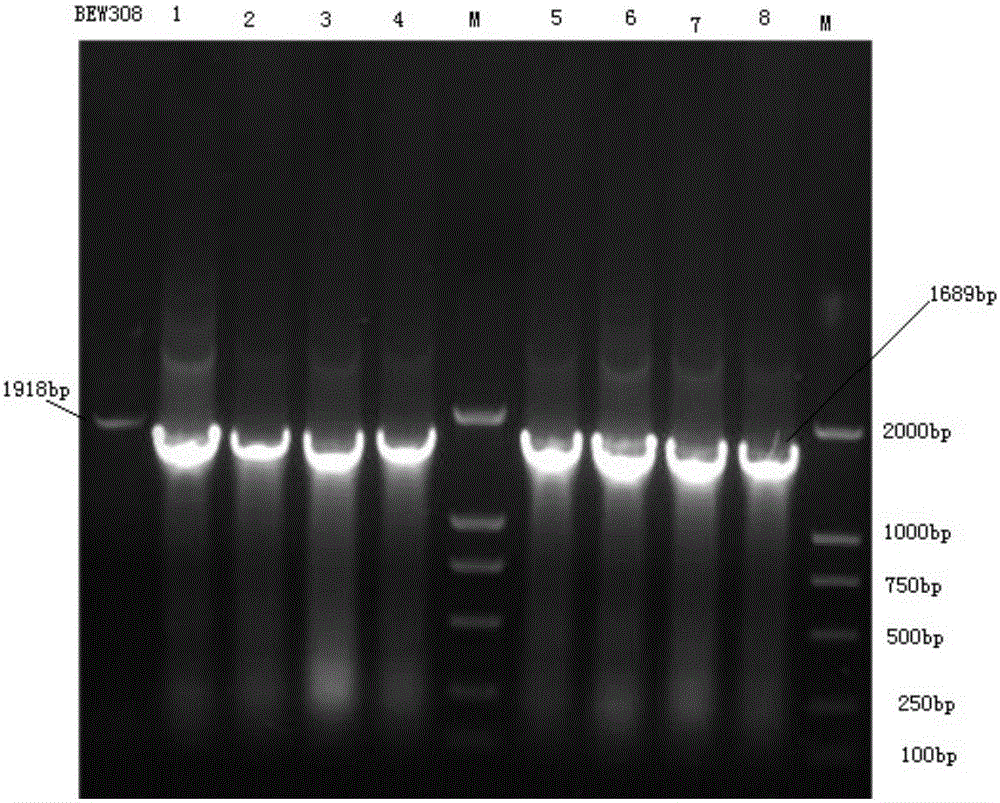
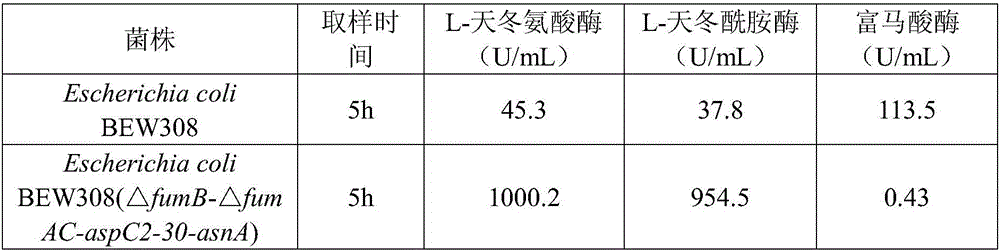
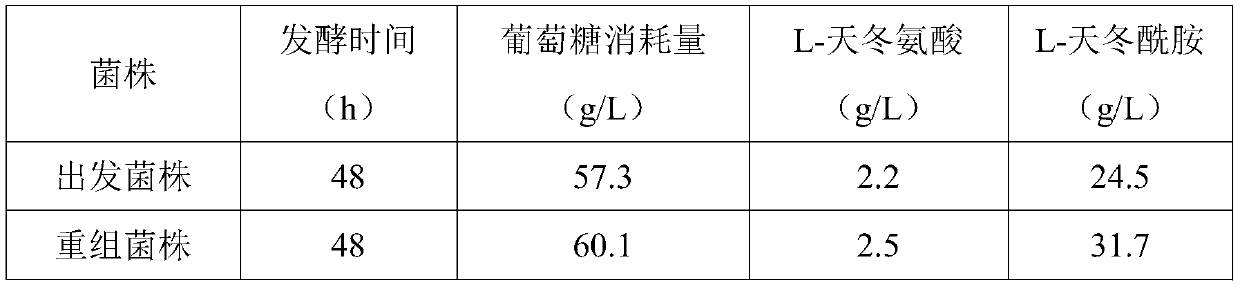
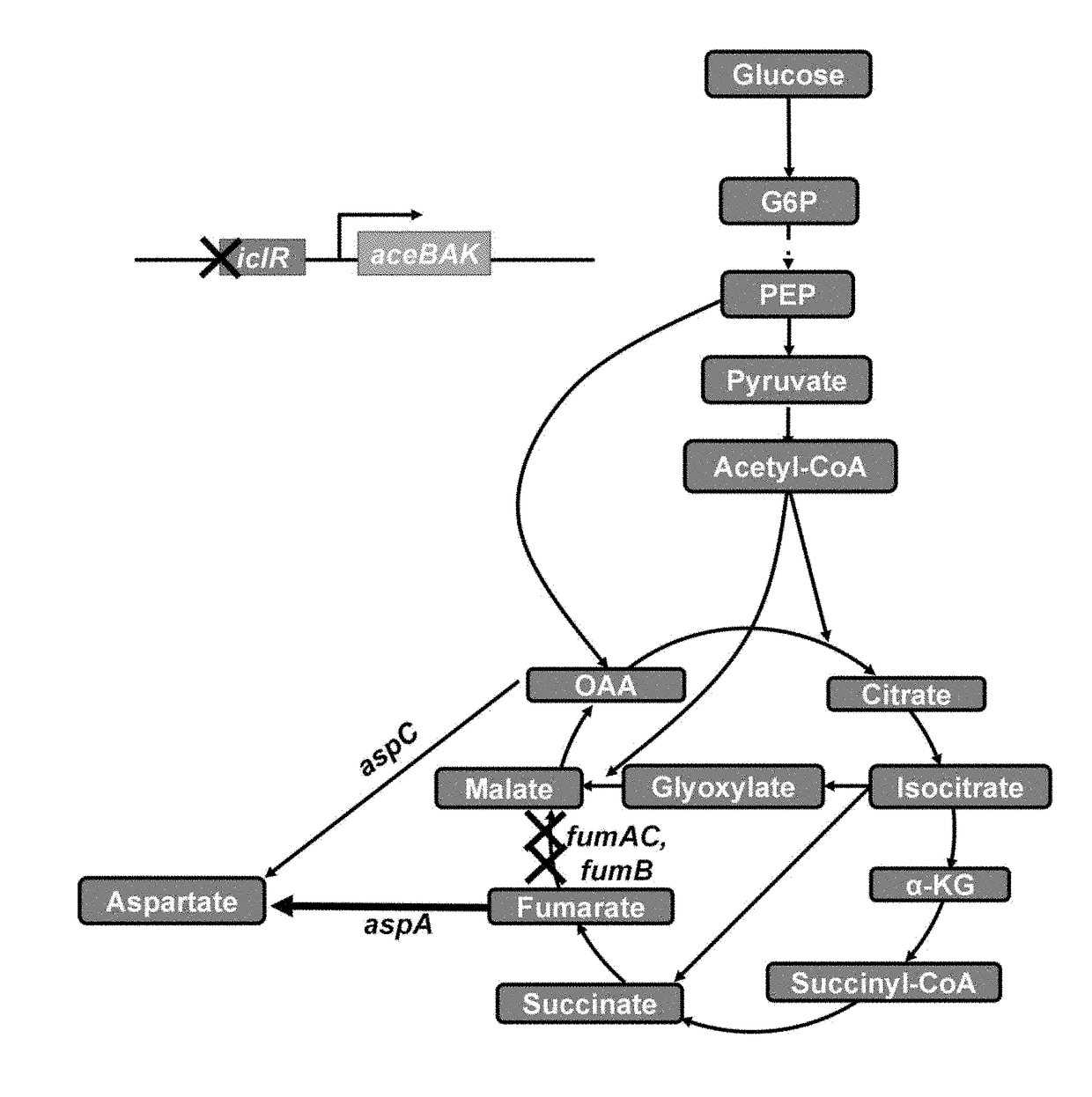
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli efficiently transforming fumaric acid into L-asparagine as well as a construction method and an application thereof. Fumarase encoding genes fumA, fumB, fumC in an ammonium-tolerant escherichia coli BEW308 are inactivated, and then L-aspartase encoding and L-asparaginase encoding genes are inserted into the positions of the fumarase encoding fumAC genes, thereby obtaining the recombinant escherichia coli having no malic acid by product, less L-aspartic acid accumulated, and a major product L-asparagine. The invention also discloses a construction method and an application of the bacterial strain. The recombinant escherichia coli can realize constitutive high-activity expression of L-aspartase and L-asparaginase, and ultimately achieve transformation of fumaric acid into L-asparagine.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
One-step enzyme transformation method for producing L-malic acid
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of L-malic acid in the enzyme engineering domain, which comprises the following steps: loading fumarase liquid in the biological reacting crystallizer according to weight; adding calcium fumarate and enzyme activity adjuster in the crystallizer with fumarase liquid under normal pressure at 30-45 deg. c; setting the weight rate of fumarase liquid, fumarate and enzyme activity adjuster at 1 25-50 0.0001-0.0005; separating; selecting the enzyme activity adjuster from one or composition of magnesium sulfate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and zinc sulfate; coupling; reacting for 18-26h; obtaining the crystal of L-malic acid; separating; purifying; obtaining the product.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium synthesizing L-asparaginate and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN110218691AReduce consumptionPromote accumulationCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium synthesizing L-asparaginate. The genetically engineered bacterium is classified and named Escherichia coliDeltafumABCDeltaarcADeltaptsGDeltagltADeltaargG / pAA, and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC NO:M2019170. The construction process of the genetically engineered bacterium comprises the steps that aspawn running strain fumarase encoding gene, a DNA transcription binding regulatory factor encoding gene, a glucose transport related gene, a citrate synthase encoding gene and an argininosuccinate synthase encoding gene are knocked out; an aspartase encoding gene and an asparagine synthetase A encoding gene are cloned to an expression plasmid, the recombinant plasmid is transformed into recombinant escherichia coli after gene knockout, and a target strain is obtained. The genetically engineered bacterium is synthesized into the L-asparaginate through fermentation, achieves a route for biosynthesizing and preparing the L-asparaginate by completely using glucose as a raw material, is efficient, green and environmentally friendly, and has economy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for fermenting and producing L-malic acid with raw material of citric acid broth
ActiveCN102242160AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesFumaraseSodium fumarate
The invention discloses a method for fermenting and producing L-malic acid with a raw material of citric acid broth. According to the method, citric acid broth is carbon source, through fermentation fumarase is generated, and by utilizing broth of fumarase and an enzyme conversion method, sodium fumarate generates the L-malic acid. After conversion of 20 to 26 hours, malic acid content reaches 78-85g / L, and conversion rate reaches 81.2%-85.5%. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple technology, low energy consumption, cheap raw material and substantial saving of production cost.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Mutant microorganism producing l-aspartic acid derivatives, and method for producing l-aspartic acid derivatives using same
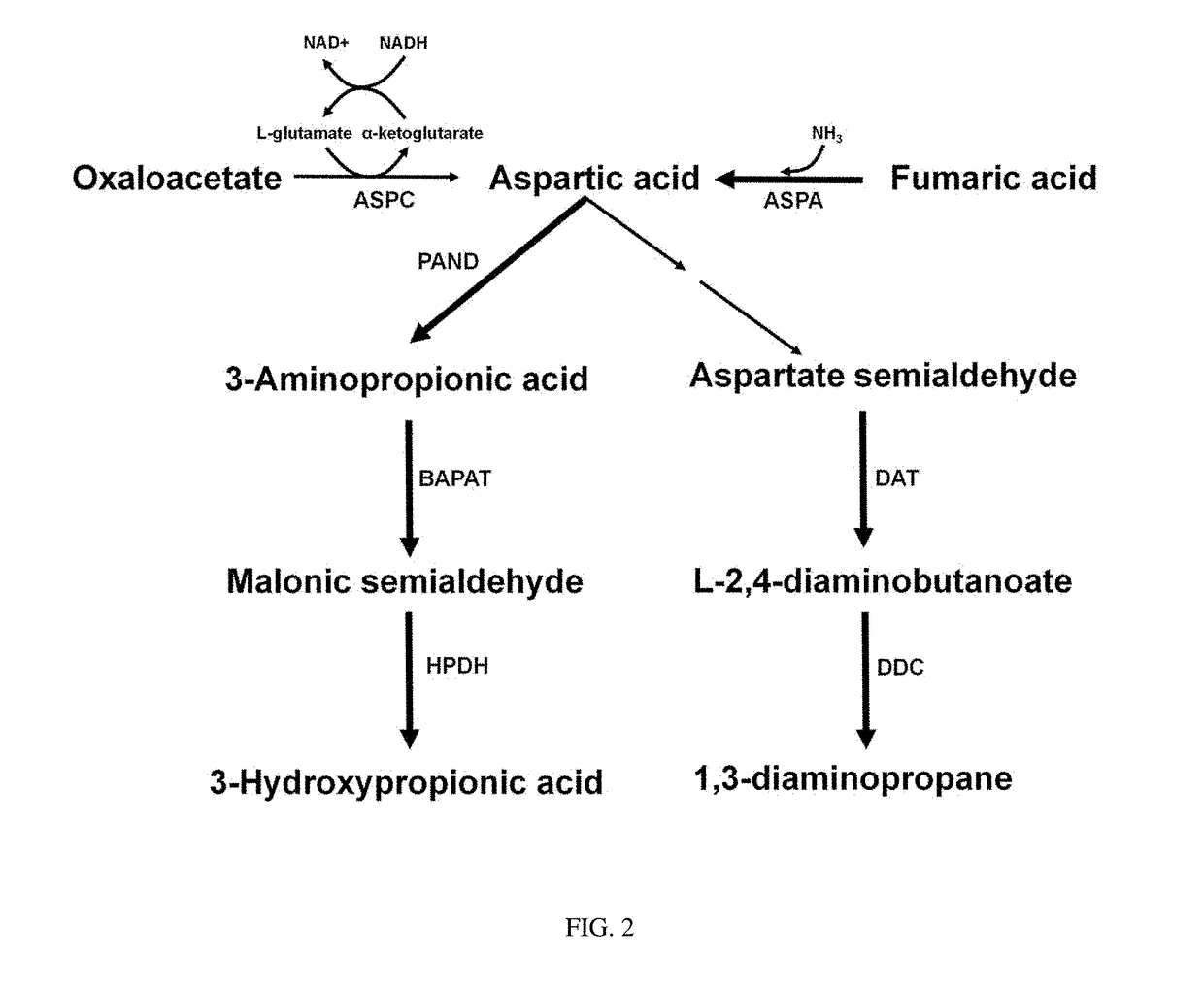
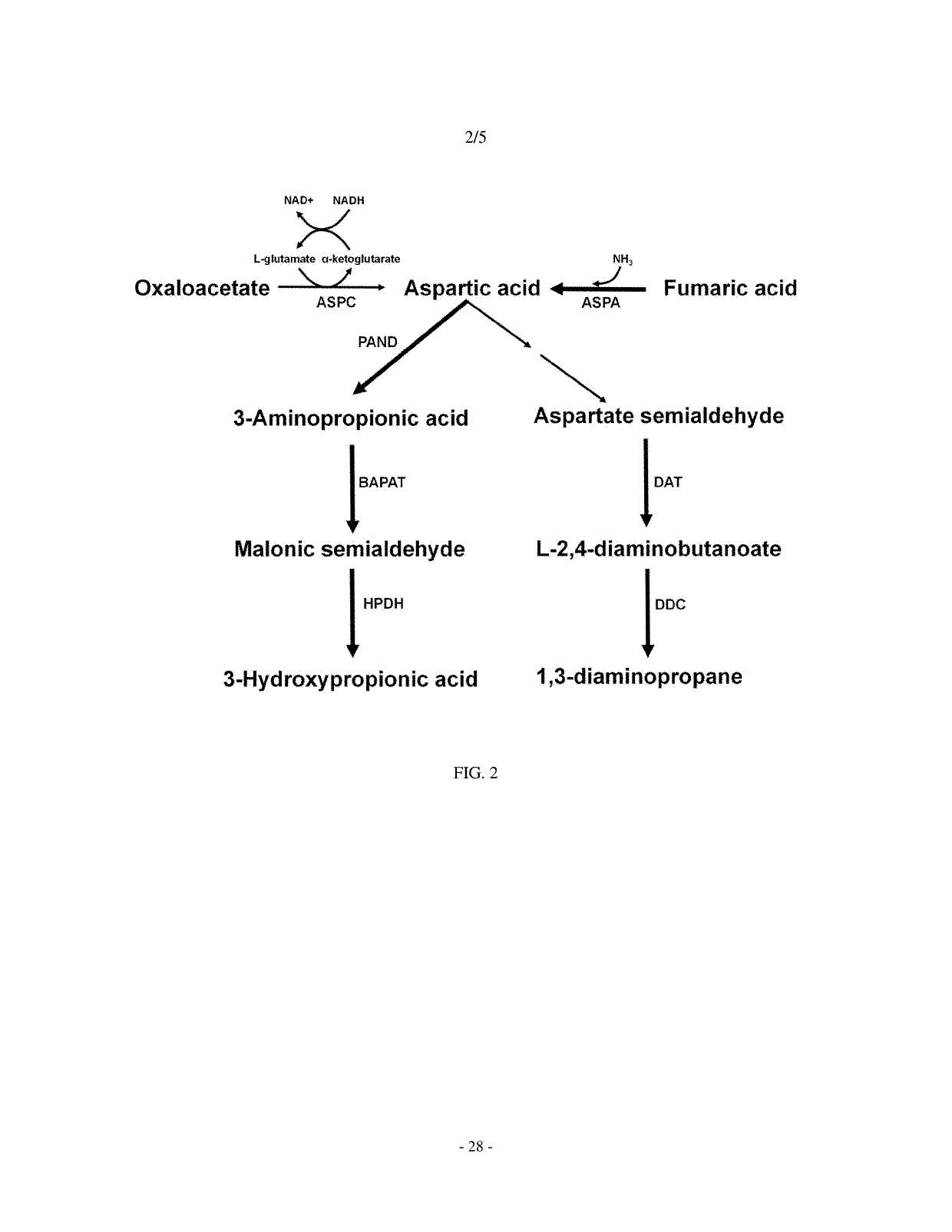
The present invention relates to a mutant organism having the ability to produce aspartic acid derivatives, wherein a gene encoding the glyoxylate shunt regulator and a gene encoding fumarase are deleted and a gene encoding aspartase is overexpressed compared to that in a wild-type strain, and to a method for producing L-aspartic acid derivatives using the same. According to the present invention, various aspartic acid derivatives, including L-alanine, 3-aminopropionic acid, threonine, 1,3-diaminopropane, lysine, methionine, 3-hydroxypropionic acid, cadaverine, 5-aminovaleric acid, etc., can be produced by biological methods.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Brevibacterium and method for separating and purifying fumarase from Brevibacterium fermentation broth
InactiveCN105647834ASimple processHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFumaraseInorganic salts
The invention relates to Brevibacterium and a method for separating and purifying fumarase from Brevibacterium fermentation broth. Latin name of this bacterium is Brevibacterium sp., reference is made to a microorganism: NJWGY2133, and Brevibacterium sp. is collected on 26th May, 2008 under CGMCC No. 2520. The method for separating and purifying fumarase comprises the specific steps: preparing crude enzyme liquid through Brevibacterium sp. fermentation broth culturing and ultrasonic crushing, and preparing a polyethylene glycol-inorganic salt two aqueous phase extraction system; carrying out two aqueous phase extraction; preparing fumarase through dialytic desalting and freeze drying. The process of the invention is simple, production cycle is short, operation conditions are mild, cost is low, high-purity enzymes may be acquired from microorganisms, and enzyme activity yield is higher than 90%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of EDDS lyase immobilized enzymes
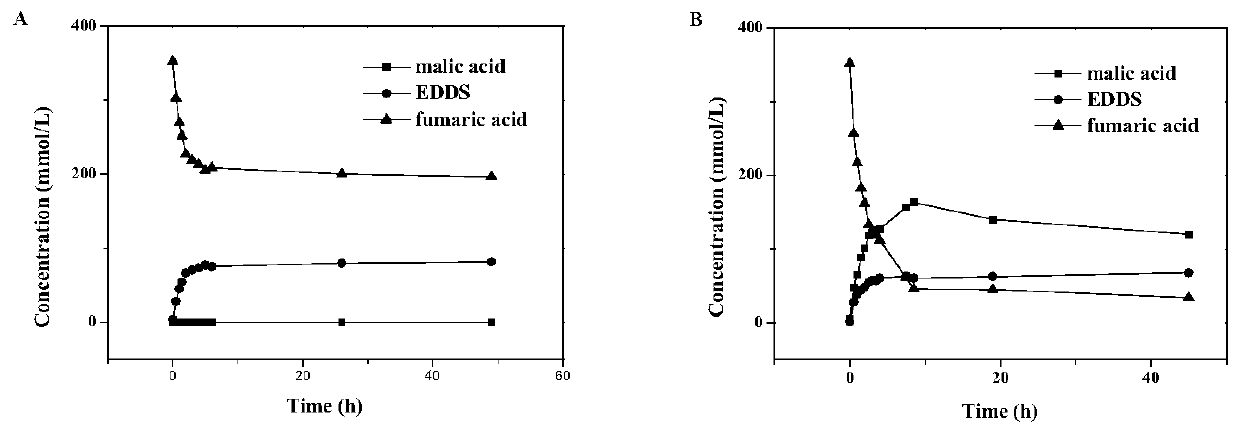
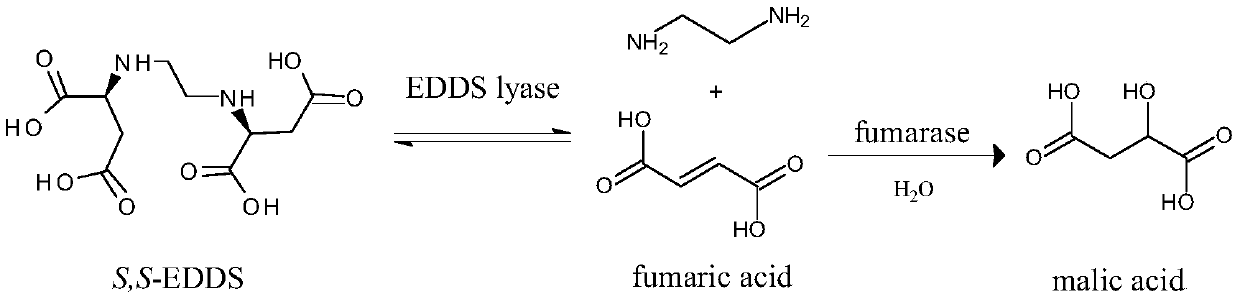
ActiveCN111454934AEfficient removalAchieve high enzyme activityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesOn/in organic carrierFumaraseLyase
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of EDDS lyase immobilized enzymes, and belongs to the technical field of biology. In order to solve existing problems of being poor in purity and low in conversion rate, the invention provides a preparation method of the EDDS lyase immobilized enzymes. The method comprises the steps of performing fermentation and coarse extraction on EDDS lyase genetic engineering bacteria having His-tag to obtain EDDS lyase coarse enzyme liquid; enabling the coarse enzyme liquid to be in contact with a metal compatible carrier, enabling EDDS lyaseto be adsorbed onto the metal compatible carrier, and performing purification; eluting the EDDS lyase on the metal compatible carrier to obtain purified enzyme liquid; and immobilizing the enzyme liquid and the immobilized carrier to obtain EDDS lyase immobilized enzymes having His-tag for synthetizing (S,S)-EDDS by using fumaric acid and ethylenediamine as substrates. According to the preparationmethod disclosed by the invention, fumarase in the enzyme liquid can be effectively removed, the efficient purification effect can be achieved, and the preparation method has efficient enzyme activity capacity and high reutilization rate.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV +1
Construction method for producing fumaric acid based on pichia stipitis synthetic strain fermented xylose
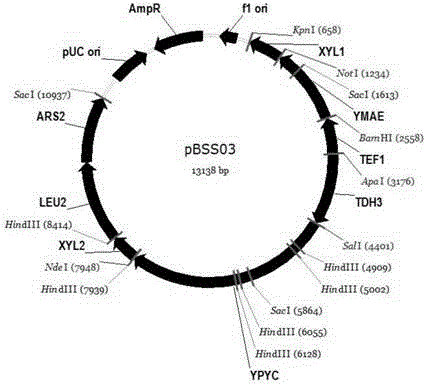
The invention provides a construction method for producing fumaric acid based on pichia stipitis synthetic strain fermented xylose. The method comprises the following steps: using pichia stipitis having a natural xylose metabolic capability as a host; deleting genes PSfum1 and PSfum2 that encode fumarase in tricarboxylic acid cycle of pichia stipitis, to acquire fumarase deficient mutants; heterologously expressing a modified fumaric reduction synthesis module on the basis of the acquired mutants, using xylose to ferment yeast synthesis strains of fumaric acid; on the basis of the yeast synthesis strains, expressing translocator YMAE that is modified with codons and originated from Chestnut wine fission yeasts, to acquire pichia stipitis synthesis strains for producing fumaric acid by fermented xylose; efficiently fermenting the acquired strains in a fully synthesized fermentation culture medium to produce fumaric acid by fermentation of xylose; cultivating by fermentation for 3-4 days at a temperature of 30 degrees centigrade with a stirring speed of 150-200rpm. The content of fumaric acid is greater than 4g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
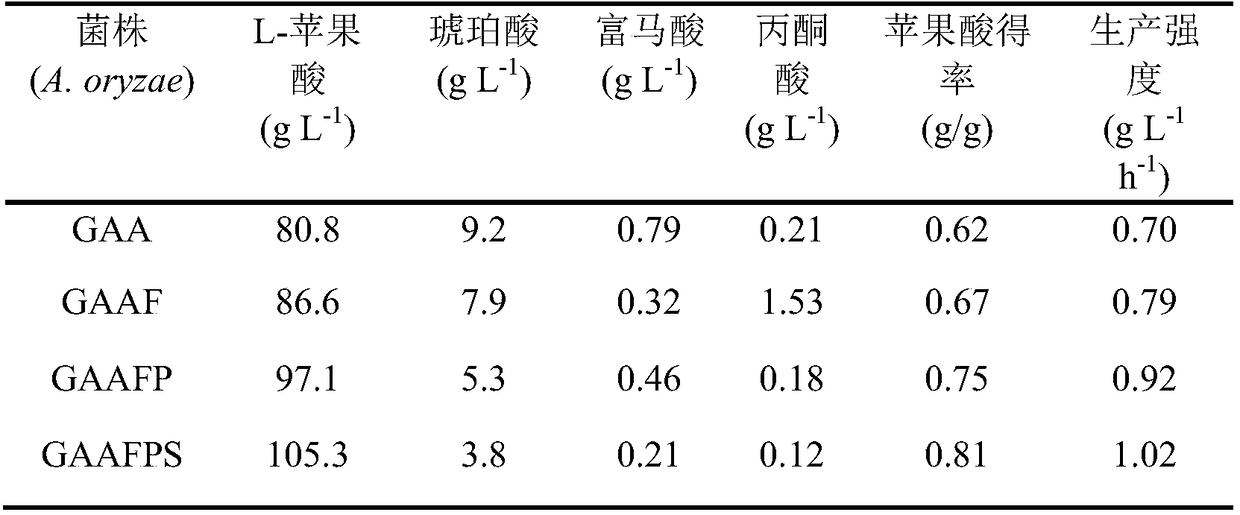
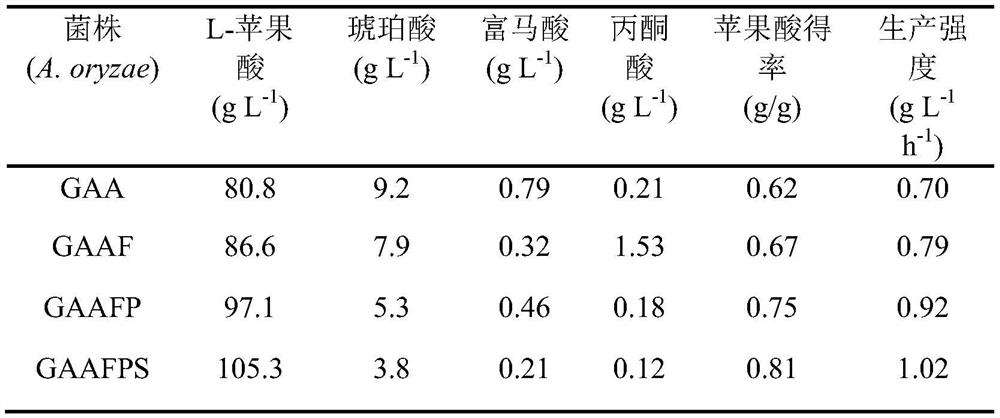
Aspergillus oryzae capable of reducing accumulation of by-product in synthesis process of malic acid and application of aspergillus oryzae
ActiveCN108641970AThe method is simple and efficientSimple and efficient strategyFungiMicroorganism based processesFumaraseRhizopus oryzae
The invention discloses aspergillus oryzae capable of reducing accumulation of a by-product in a synthesis process of aspergillus oryzae and an application of the aspergillus oryzae, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, on the basis of A.oryzae GAA, over-expression of a fumarase coding gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae, a pyruvate carboxylase codinggene derived from rhizopus oryzae, a succinic acid-fumaric acid mitochondria transport protein coding gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae is implemented, so that conversion of fumaric acid andpyruvic acid in cytoplasm and mitochondria towards the malic acid and material exchange of cytoplasm and mitochondria are further enhanced. As for the finally obtained recombinant bacterium A.oryzaeCMPFS, a yield of L-malic acid undergoing shake-flask fermentation for 102h reaches 105.3g / L, concentration of succinic acid is 3.8g / L and concentration of fumaric acid is 0.21g / L; therefore, the concentration of the by-product is obviously reduced and product yield is improved; and a foundation is laid for production of the L-malic acid which is higher in purity through further metabolic transformation.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
A Recombinant Escherichia coli Efficiently Transforming Fumaric Acid into L-Asparagine and Its Construction Method and Application
ActiveCN105925520BLow fumarase activityImprove conversion yieldCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliFumarase
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli efficiently transforming fumaric acid into L-asparagine as well as a construction method and an application thereof. Fumarase encoding genes fumA, fumB, fumC in an ammonium-tolerant escherichia coli BEW308 are inactivated, and then L-aspartase encoding and L-asparaginase encoding genes are inserted into the positions of the fumarase encoding fumAC genes, thereby obtaining the recombinant escherichia coli having no malic acid by product, less L-aspartic acid accumulated, and a major product L-asparagine. The invention also discloses a construction method and an application of the bacterial strain. The recombinant escherichia coli can realize constitutive high-activity expression of L-aspartase and L-asparaginase, and ultimately achieve transformation of fumaric acid into L-asparagine.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Strain for maleic acid whole-cell catalysis synthesis of L-aspartic acid and method
InactiveCN110004102AGet rid of the problem of dependence on petroleum-based fumaric acid as a raw materialChoose cheapCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliFumarase
The invention discloses a strain for maleic acid whole-cell catalysis synthesis of L-aspartic acid and a method. The strain is named as Escherichia coli delta fumABC delta gltA delta argG / pMA, the preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M 2019171, and the method comprises the construction processes that knocking out fumarase encoding gene, a citrate synthase encoding gene and an argininosuccinate synthase encoding gene in an original strain, meanwhile, aspartase encoding gene mutation N217K-T233R-V367G and maleic cis-trans isomerase encoding gene mutation G8A-G179A are cloned to expression plasmids to form recombinant plasmids, the recombinant plasmids are converted into the strain with knockout genes, and the target strain is obtained. According to the method for genetically engineered bacterium whole-cell catalysis synthesis of L-aspartic acid, the path for catalysis synthesis of L-aspartic acid by adopting maleic acid as raw materials is achieved, the production cost is lowered, efficient catalysis is achieved, and economy is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A construction method based on the production of fumaric acid by fermenting xylose with a synthetic strain of Pichia stipitis
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for producing malic acid by fermentation of citric acid mother liquor
ActiveCN102191282ASimple processReduce energy consumptionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFumaraseSodium fumarate
The invention relates to a method for producing malic acid by fermentation of citric acid mother liquor. In the method, with the citric acid mother liquor as a carbon source, a strain capable of producing fumarase by fermentation produces fumarase, and fermentation liquor is used as a raw material to convert sodium fumarate. After 20 to 25 hours of conversion, the content of L-malic acid reaches about 1.1 mol / L, and the conversion rate is about 94 percent. In the invention, performed separately, the fumarase production and conversion both can be performed under more proper conditions; the process is simple; energy consumption is small; the raw material is cheap; and the substrate conversion rate is high.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
A kind of Aspergillus oryzae that reduces the accumulation of by-products in the process of malic acid synthesis and its application
ActiveCN108641970BThe method is simple and efficientFungiMicroorganism based processesFumaraseSuccinic acid
The invention discloses aspergillus oryzae capable of reducing accumulation of a by-product in a synthesis process of aspergillus oryzae and an application of the aspergillus oryzae, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, on the basis of A.oryzae GAA, over-expression of a fumarase coding gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae, a pyruvate carboxylase codinggene derived from rhizopus oryzae, a succinic acid-fumaric acid mitochondria transport protein coding gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae is implemented, so that conversion of fumaric acid andpyruvic acid in cytoplasm and mitochondria towards the malic acid and material exchange of cytoplasm and mitochondria are further enhanced. As for the finally obtained recombinant bacterium A.oryzaeCMPFS, a yield of L-malic acid undergoing shake-flask fermentation for 102h reaches 105.3g / L, concentration of succinic acid is 3.8g / L and concentration of fumaric acid is 0.21g / L; therefore, the concentration of the by-product is obviously reduced and product yield is improved; and a foundation is laid for production of the L-malic acid which is higher in purity through further metabolic transformation.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
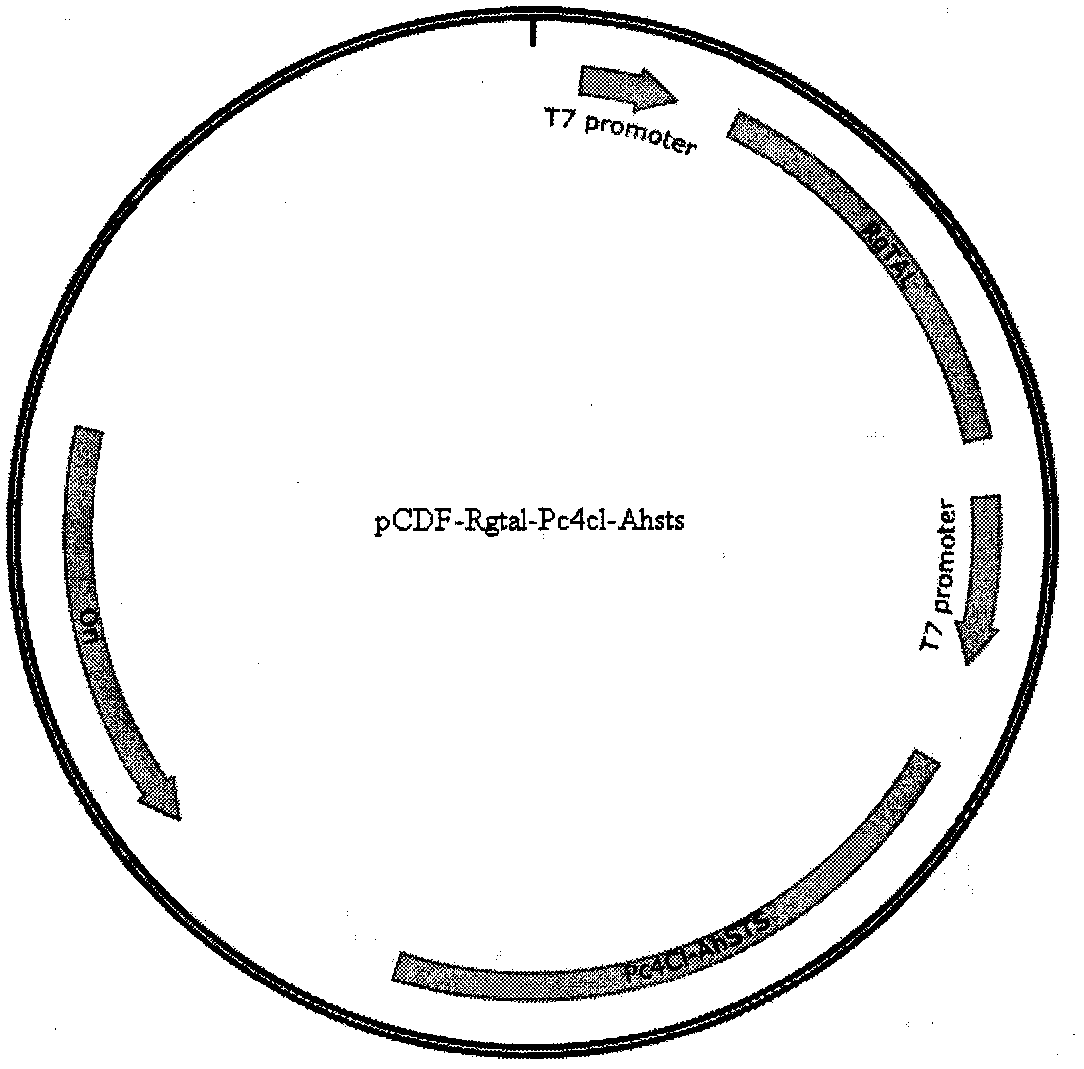
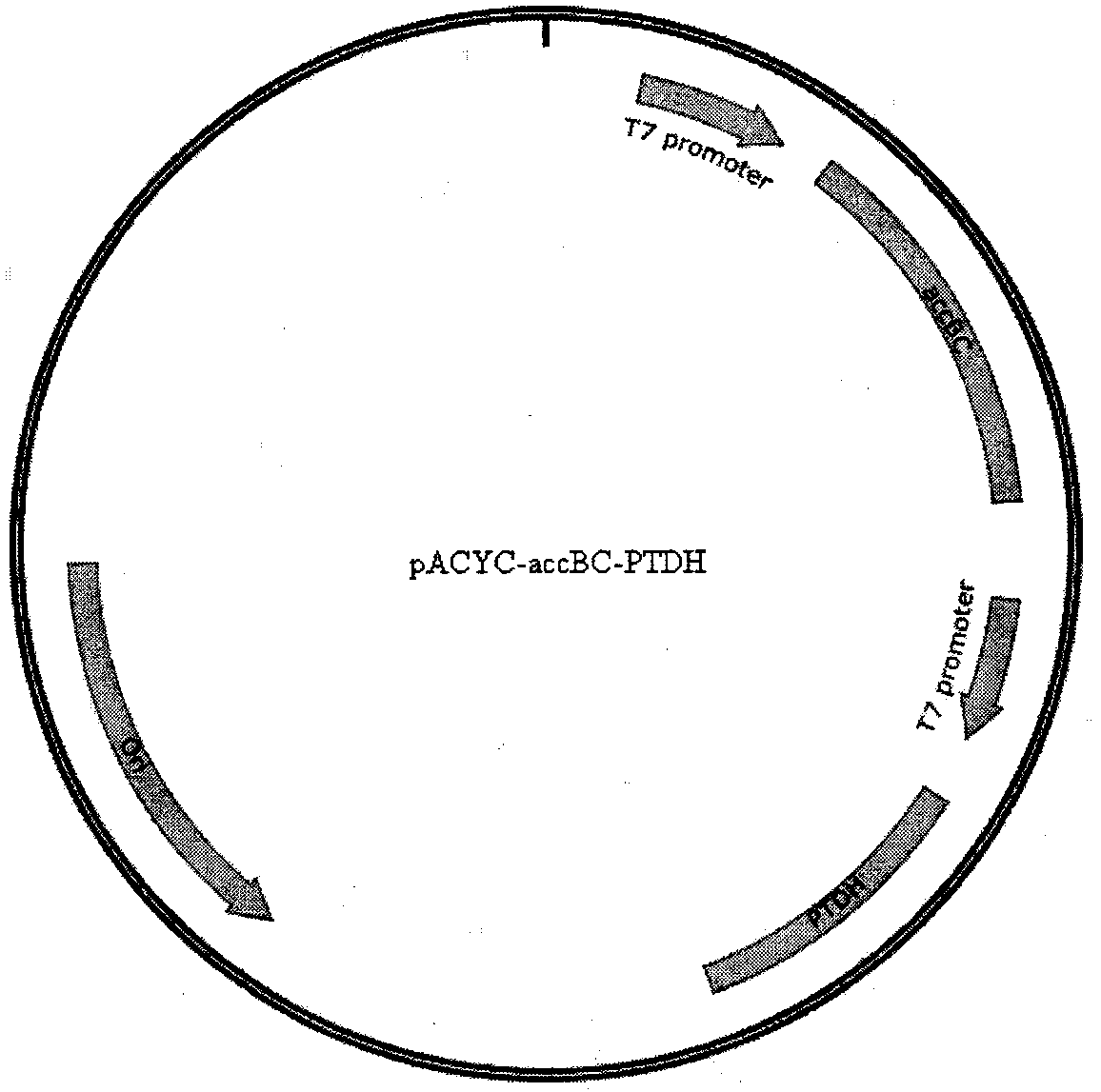
Biological method capable of increasing resveratrol accumulation amount
InactiveCN109609421AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMalonyl-coenzyme A synthetase
The invention discloses a gene-defective-type Escherichia coli strain containing a resveratrol synthase system and a malonyl coenzyme-A synthase system and a construction method thereof, as well as amethod for increasing resveratrol accumulation amount. A recombinant plasmid composed of the resveratrol synthase system and the malonyl coenzyme-A synthase system provided by the invention includes Rgtal, Pc4cl, Ahsts, accBC and PTDH sequences as well as two suitable vector fragments. The biological method capable of increasing resveratrol accumulation amount provided by the invention comprises the following steps: transforming the recombinant plasmids composed of the resveratrol synthase system and the malonyl coenzyme-A synthase system, namely pCDF-Rgtal-Pc4cl-Ahsts and pACYC-accBC-PTDH, into Escherichia coli strains with fumarinase gene deficiency (delta-fumB) so as to obtain engineering strains; and then, carrying out culturing with an optimized medium. Thus, yield of resveratrol withthe optimized medium can be up 22.62 mg / L, which is increased by 5.73 times compared with yield of original strains.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for constructing escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria for producing fumaric acid
InactiveCN102618570BRealize accumulationCumulative acid production effect is idealBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFumarase
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for constructing escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria for producing fumaric acid. The method for constructing the escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria mainly comprises the following steps of: inactivating or knocking fumarase serving as key enzyme for converting fumaric acid into malic acid in a tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle out, and knocking a key gene arcA for inhibiting the TCA cycle out. Further, key enzyme genes in paths of succinic acid, lactic acid and formic acid can also be knocked out, so the fumaric acid can be accumulated under the anaerobic condition.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Mutant microorganism producing L-aspartic acid derivatives, and method for producing L-aspartic acid derivatives using same
The present invention relates to a mutant organism having the ability to produce aspartic acid derivatives, wherein a gene encoding the glyoxylate shunt regulator and a gene encoding fumarase are deleted and a gene encoding aspartase is overexpressed compared to that in a wild-type strain, and to a method for producing L-aspartic acid derivatives using the same. According to the present invention, various aspartic acid derivatives, including L-alanine, 3-aminopropionic acid, threonine, 1,3-diaminopropane, lysine, methionine, 3-hydroxypropionic acid, cadaverine, 5-aminovaleric acid, etc., can be produced by biological methods.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
A kind of fumarase mutant and its application
ActiveCN109609486BImprove responseIncrease useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydroxybutyric acid
The present invention discloses a fumarase mutant and application thereof. The fumarase mutant of SEQ ID NO: 4 derived from Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 is obtained by a directed evolution method, the mutant or expression microorganisms thereof is capable of catalyzing a hydration reaction of crotonic acid to prepare (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid, the product ee value exceeds 95%, and the fumarase mutant has industrial development and application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for producing malic acid by fermentation of citric acid mother liquor
ActiveCN102191282BSimple processReduce energy consumptionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFumaraseSodium fumarate
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
A method for improving the efficiency of Escherichia coli to synthesize fumaric acid
ActiveCN106520812BHigh synthesis efficiencyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliFumarase
The invention provides a method for improving efficiency of escherichia coli on synthesizing fumaric acid. Specificity labels are added on two ends of three key enzymes (pyruvate dehydrogenase, malic dehydrogenase and fumarase) synthesized by the fumaric acid, so that covalent binding of the three enzymes is realized, a substrate channel is shortened, and the synthetic efficiency of the fumaric acid in the escherichia coli is promoted.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. In the invention, key phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) related to the L-malic acid, malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and fumarase (FumC) are transformed to obtain the gene engineering bacterial strain; a deactivation mutation is carried out on the fumCto cause the interruption of a metabolic flux at the converting position from the malic acid to the fumaric acid so as to accumulate the target product L-malic acid; before the mdh, the promoter of an inner source pepck gene is added to generate the metabolic flux biased towards the malic acid; in addition, through the inducement of monofluorine sodium acetate, the activity of the PEPCK is improved, and the product feedback inhibition is greatly reduced. The bacterial strain applied to the fermentative production of the L-malic acid so as to obviously improve the yield of L-malic acid. The invention has advantages of simple technology, obvious effect and low cost and can satisfy the demand of markets.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
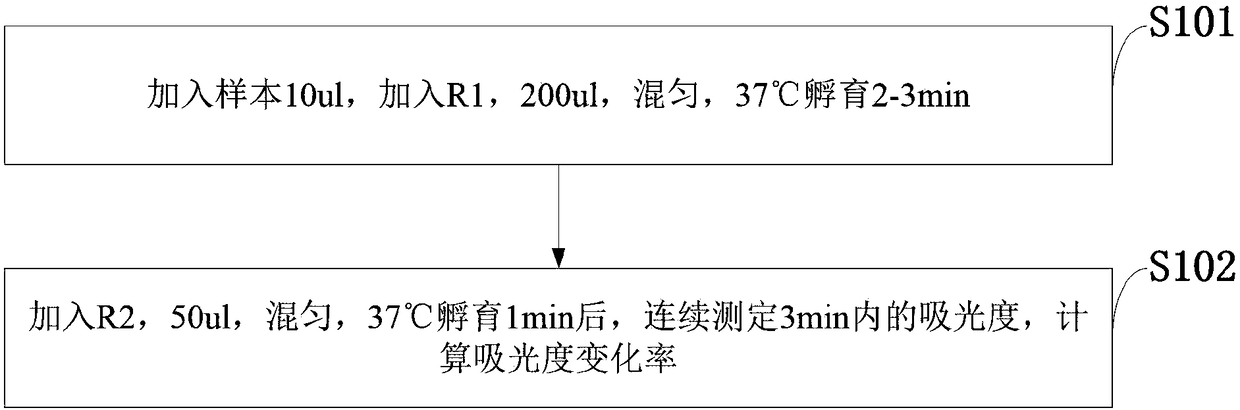
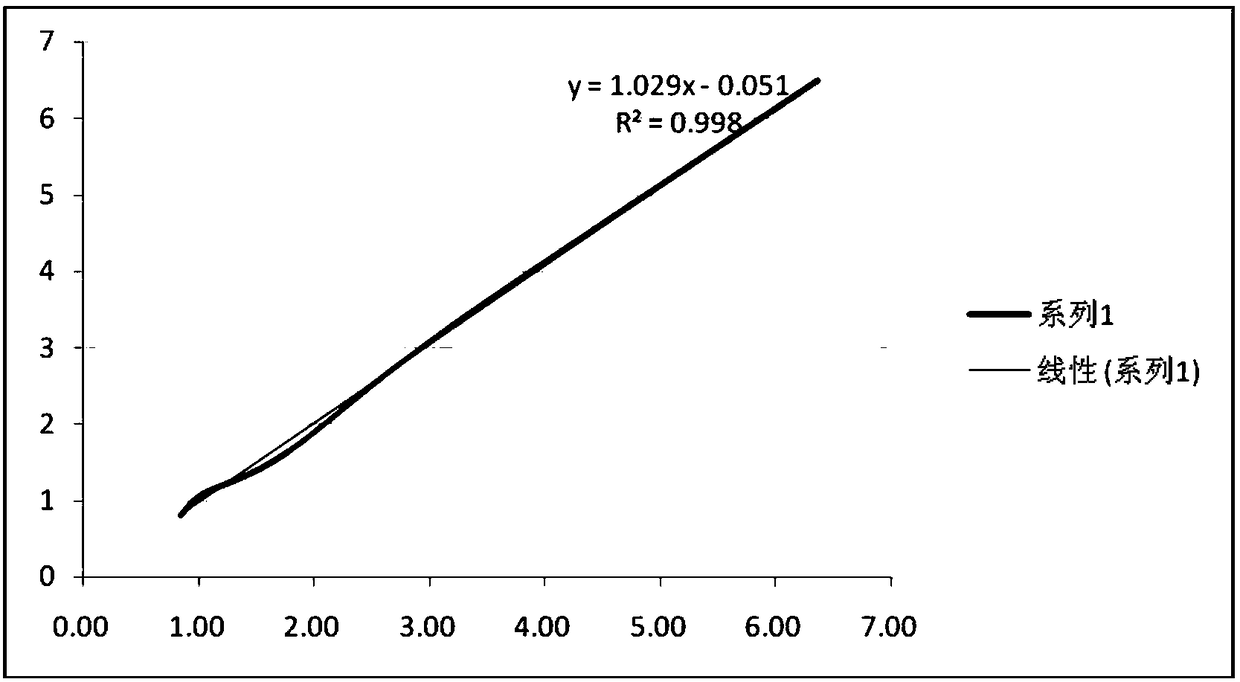
Reagent for detecting argininosuccinic acid lyase in serum and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of argininosuccinic acid lyase, and discloses a reagent for detecting argininosuccinic acid lyase in serum and a preparation method thereof. The reagent consists of R1 and R2, wherein R1 consists of a buffer solution, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, fumarase, malic dehydrogenase, an enzyme protective agent, a preservative, a surfactant and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and R2 consists of a buffer solution, disodium arginine succinate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and hydrazine sulfate. The method comprises: adding 10ul of a sample, adding 200ul of R1, mixing the sample and R1 uniformly, and carrying out incubation at 37 DEG C for 2-3min; and adding 50ul of R2, mixing the components uniformly, carrying out incubation at 37 DEG C for 1 min, then continuously measuring the absorbance in 3min, and calculating an absorbance change rate. According to the invention, fumarase, another product generated by catalyzing argininosuccinic acid by ASAL, is detected, and the amount of ASAL is detected by a full-automatic biochemical instrument by utilizing the characteristic that NAD+ has an absorption peak at a 340nm position.
Owner:湖北海卓生物科技有限公司
A kind of preparation method of L-malic acid
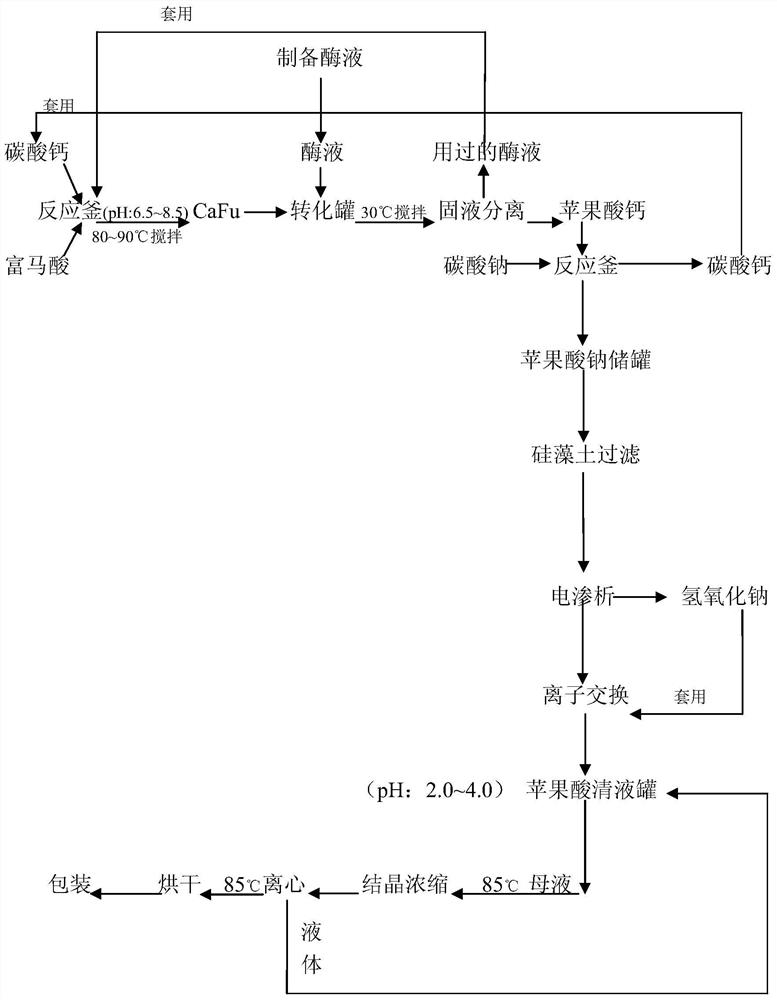
The invention provides a preparation method of L-malic acid. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: firstly, fumaric acid and calcium carbonate react to generate calcium fumarate, and generated calcium fumarate is converted into calcium malate under the action of fumarase; secondly, calcium malate and carbonate react in an aqueous solution, and a malate solution is generated; finally, the generated malate solution is converted into a malic acid solution with an electrodialysis method, and L-malic acid is obtained. According to the method, sulfuric acid is not utilized, no byproducts are produced, the method is environment-friendly, an extraction process is simple, intermediate products can be recycled, the cost is saved, and the enzymatic conversion rate is higher than 99.9%.
Owner:ANHUI XUELANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for fermenting and producing L-malic acid with raw material of citric acid broth
ActiveCN102242160BIncrease productionImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesFumaraseSodium fumarate
The invention discloses a method for fermenting and producing L-malic acid with a raw material of citric acid broth. According to the method, citric acid broth is carbon source, through fermentation fumarase is generated, and by utilizing broth of fumarase and an enzyme conversion method, sodium fumarate generates the L-malic acid. After conversion of 20 to 26 hours, malic acid content reaches 78-85g / L, and conversion rate reaches 81.2%-85.5%. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple technology, low energy consumption, cheap raw material and substantial saving of production cost.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com