Malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and its construction and use
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and malic acid, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as growth inhibition, inability to utilize glucose, etc., and achieve good effects and simple and feasible fermentation methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] This example illustrates the process of knocking out the fumarase gene fumB in the parental Escherichia coli NZN111 using homologous recombination technology to obtain a strain that eliminates apramycin resistance.
[0050] Using homologous recombination technology to knock out the fumarase (FUM) gene:
[0051] 1. Using LB medium, cultivate Escherichia coli NZN111 to OD at 37°C under aerobic conditions 600 =0.4~0.6, prepared to be electrotransfer competent.
[0052] 2. The plasmid pKD46 was electrotransformed into competent Escherichia coli NZN111, the electric shock conditions were: 200Ω, 25μF, electric shock voltage 2.3kV, electric shock time 4-5ms. Immediately after electric shock, the cells were added to pre-cooled 1mL SOC medium, cultured at 150r / min, 30°C for 1h, and then spread on LB medium plate with ampicillin (Amp) to screen out the positive transformant NZN111 (pKD46).
[0053] 3. Add 10 mM L-arabinose to LB medium, induce plasmid pKD46 to express λ recombi...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This example illustrates the process of eliminating the apramycin-resistant strain by further knocking out the fumarate reductase gene frdABCD by using homologous recombination technology on the basis of knocking out the fumarase gene fumB in the parental Escherichia coli NZN111.
[0066] Knockout of the fumarate reductase (FRD) gene by homologous recombination:
[0067] 1. Using LB medium, cultivate E. coli lacking ldhA, pflB and fumB at 37°C under aerobic conditions to OD 600 =0.4~0.6, prepared to be electrotransfer competent.
[0068] 2. The plasmid pKD46 was electrotransformed into the competent strain in the above step 1. The electric shock conditions were: 200Ω, 25μF, electric shock voltage 2.3kV, electric shock time 4-5ms. Immediately after electric shock, the cells were added to pre-cooled 1mL SOC medium, cultured at 150r / min, 30°C for 1h, and then spread on LB medium plate with ampicillin (Amp) to screen out positive transformants.
[0069] 3. Add 10 mM L-ara...
Embodiment 3
[0080] This example illustrates the construction process of the expression plasmid pTrc99a-pyc of exogenous pyruvate carboxylase.
[0081] 1. Synthesize primers with NcoI and PstI restriction sites:
[0082] Upstream primer: 5'-CATGCCATGGTCAGCTGATGAGAAACGTCGAGAAG-3'
[0083] Downstream primer: 5'-AAAACTGCAGGGTCATTCTCTTCAAAGCCAAAACGA-3'
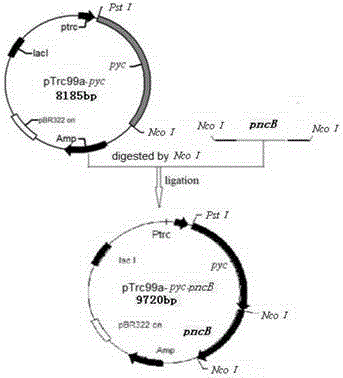
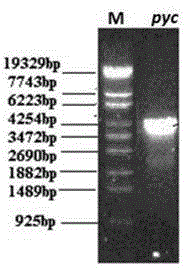
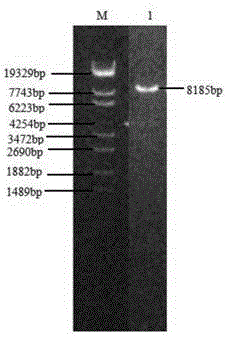
[0084] 2. Using Lactococcus lactis cremoris NZ9000 genomic DNA as a template, PCR amplifies the target gene fragment. The reaction conditions are: 94°C, 5min; (94°C for 45s, 53°C for 45s, 72°C for 300s, 35 cycles); 72°C, 10min , the agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR product pyc is as follows Figure 7 shown. After purifying the amplified pyc gene, it was cut with NcoI and PstI at the same time as the expression plasmid pTrc99a, and then ligated to obtain the recombinant plasmid pTrc99a-pyc. The construction map of the recombinant plasmid is as follows: Figure 8 shown. Figure 9 The result of single enzyme digestion identification of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com