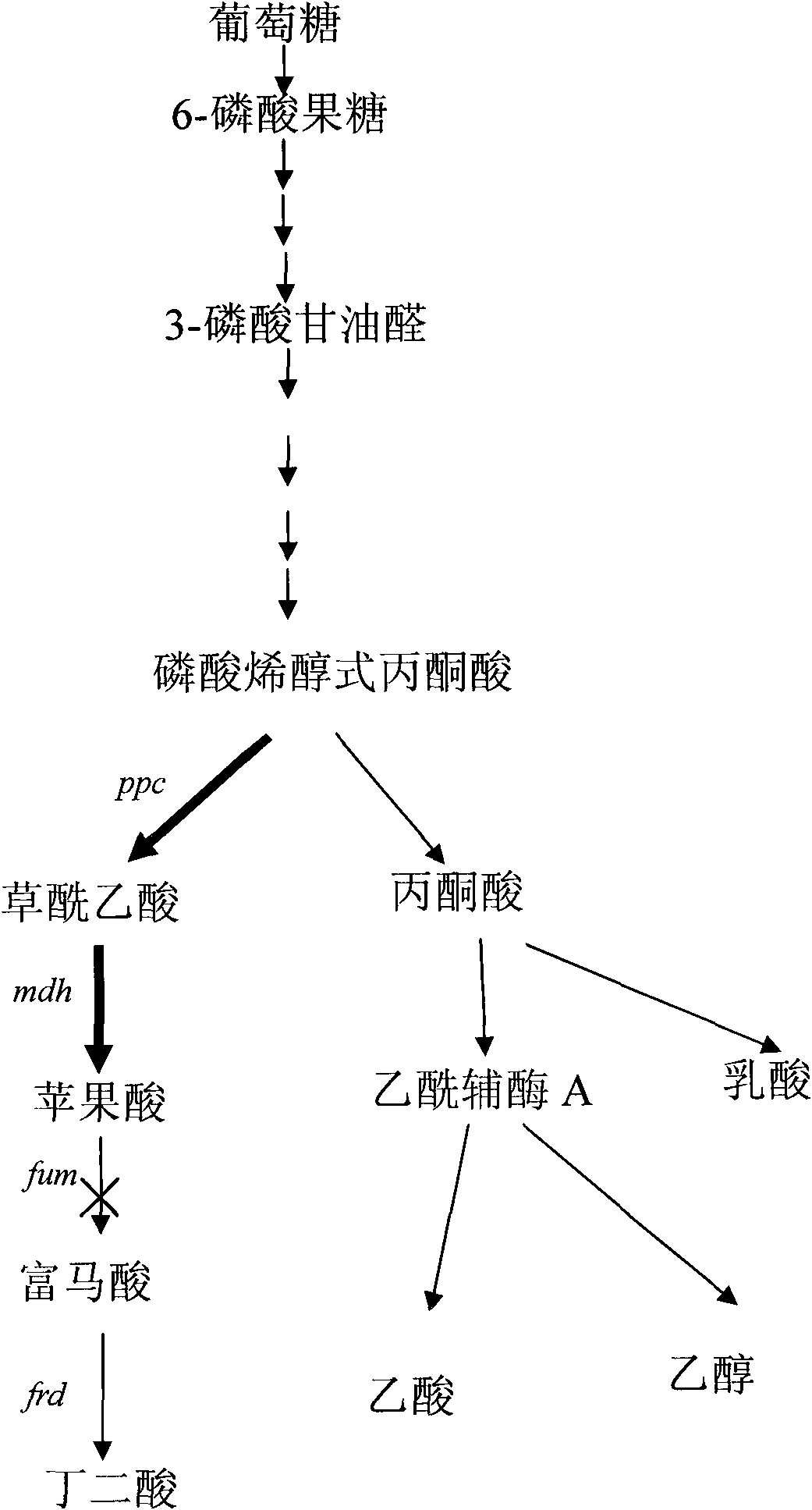
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and malic acid, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of narrow sources of raw materials, high extraction costs, and expensive equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
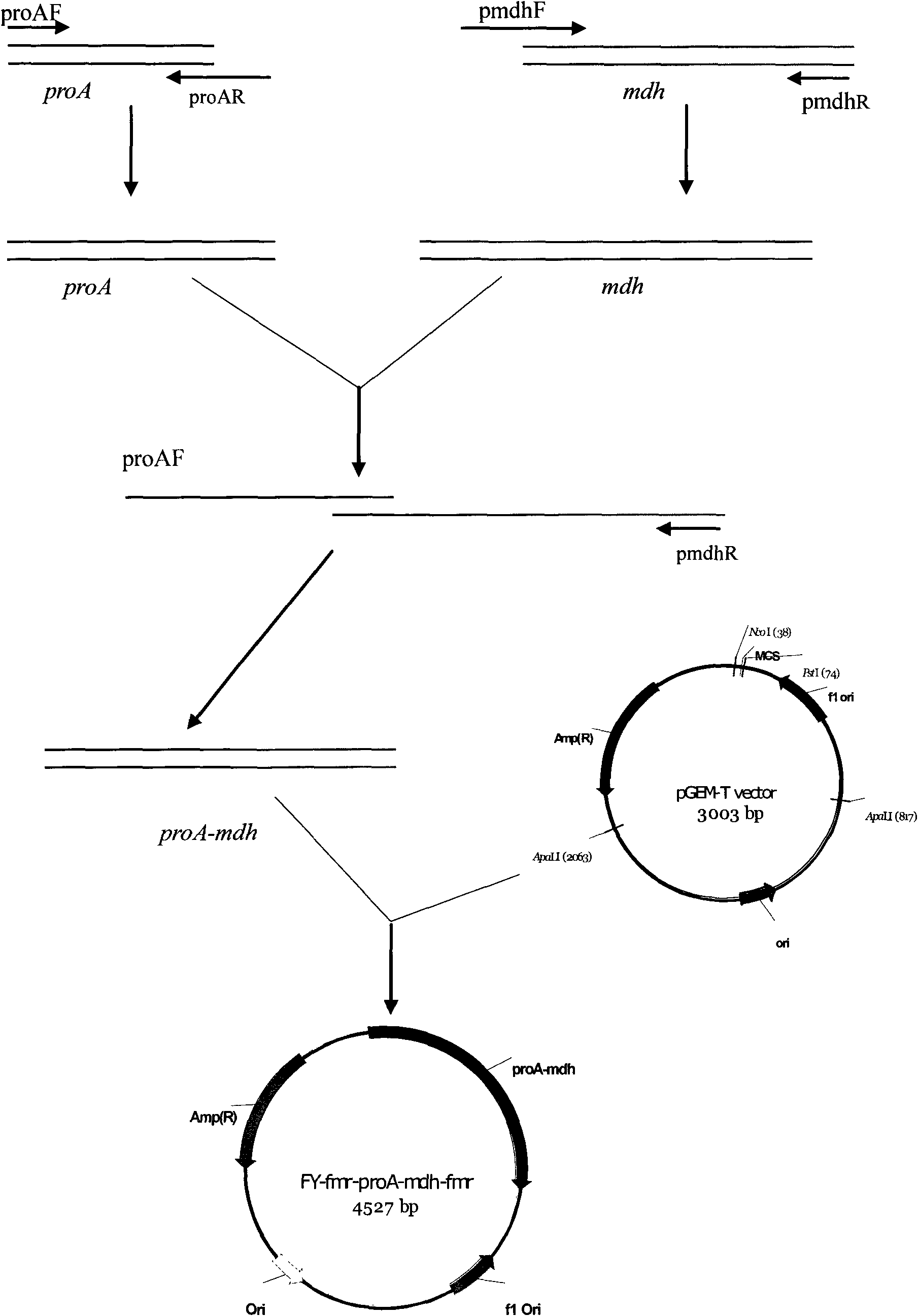
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The screening of embodiment 1SMF resistant bacterial strain
[0040] The rumen of freshly slaughtered cattle was taken, and microorganisms were enriched by anaerobic culture method, and a succinic acid-producing bacterium was obtained through primary screening on a flat plate and secondary screening in a shaker flask. After the identification of morphology, physiology and biochemistry, and 16S rRNA, it was determined that the screened strain belonged to Actinobacillus succinogenes, and the actinomycete was named AS-FY10.
[0041] Pick a single colony of AS-FY10 from the plate, activate and enrich it for 1-2 times, and culture it in a specific liquid medium (MA) at 37°C in a CO 2Under the conditions, culture in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask (with rubber stopper) with slight shaking for 1-4 days to the logarithmic phase, centrifuge the AS-FY10 cells in the logarithmic growth phase (8000g, 20min), wash with 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer ( pH7.0) was washed twice, then the cells we...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Transformation of embodiment 2 recombinant plasmids, screening of recombinants
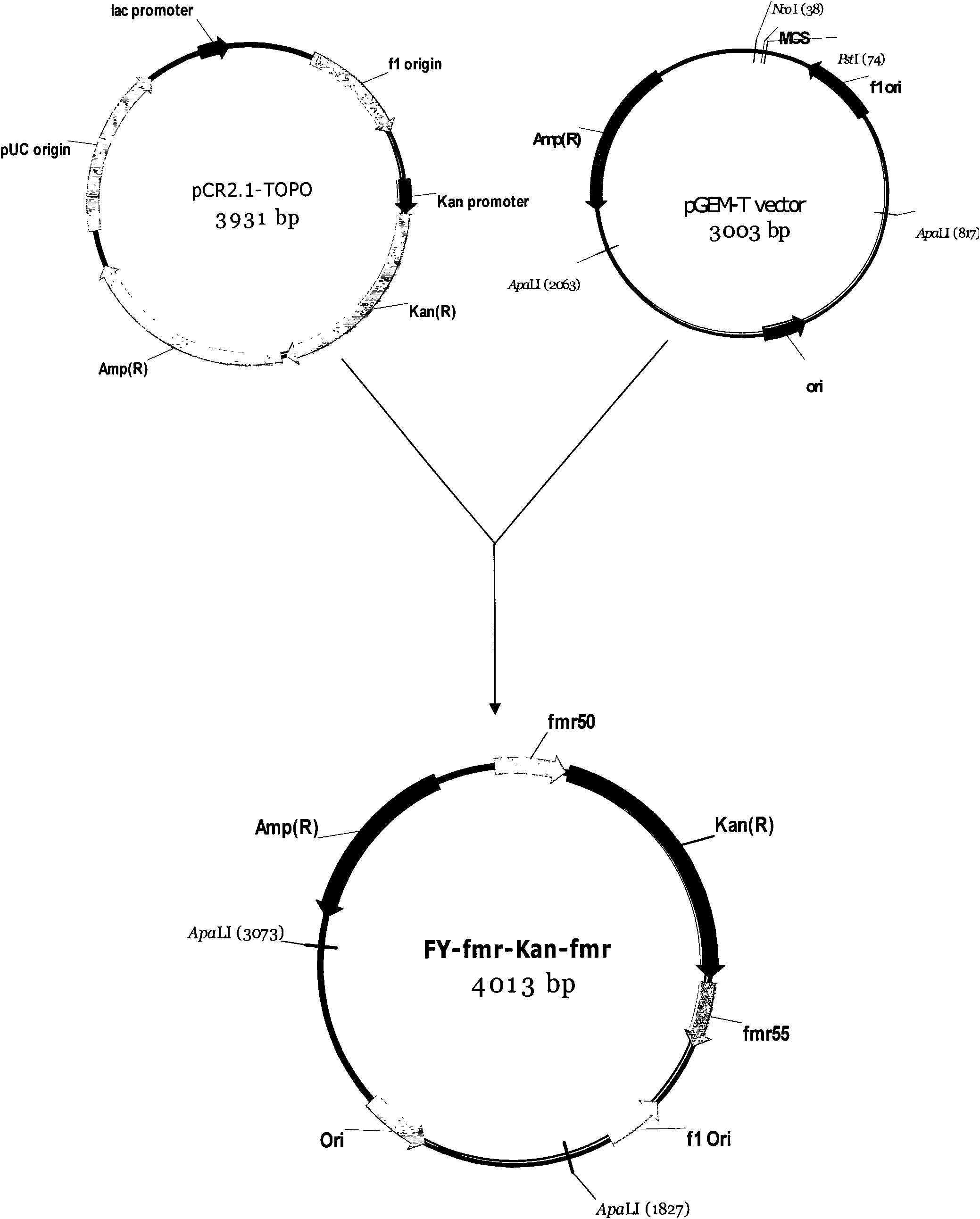
[0043] 1 Construction of recombinant plasmid FY-fmr-Kan-fmr
[0044] Use pCR2.1 (invitrogen) as a template, use primers Kan F and Kan R (see Table 1) to amplify the kanamycin resistance gene, pfu as a polymerase, and the total volume of PCR reaction is 50 μl Reaction conditions: 94 ° C pre-denaturation 5min, denaturation at 94°C for 1min, annealing at 55°C for 40sec, extension at 72°C for 2min, a total of 30 cycles, and finally extension at 72°C for 10min, adding ordinary Taq enzyme and continuing to incubate for 10min. The size of the electrophoresis analysis band was 1.0kb, which was consistent with the expected size ( Figure 4 ) Purify the PCR product with a kit from Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (see the instruction manual for specific methods), and ligate the product with pGEM-T vector (invitrogen) using T4 DNA ligase (product of Takara Company) overnight at 4°C. Transform Esche...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3PEPCE and MDH enzyme activity assay
[0050] 1 Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0051] At 37°C, AS-FY10 and AS-FY-Rec in CO 2 Cultivate under anaerobic conditions for 24 hours, take 1mL of bacterial suspension, centrifuge to obtain bacterial cells, dilute to 10mL with pH 7.5, 0.1mmol / L phosphate buffer, sonicate in an ice bath for 10min, and then freeze and centrifuge at 10000rpm for 15min. The obtained supernatant is the crude enzyme solution.
[0052] 2 PCEPCK enzyme activity assay
[0053] Take two cuvettes, add 2.3mL pH 7.5, 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer to one of them, and then add 50mmol / L MnCl in sequence 2 , 0.5mmol / L NaHCO 3 , 0.5mmol / L sodium phosphoenolpyruvate, 50mmol / L ADP, 0.1ml each of 5mmol / L NADH solution, add 3mL phosphate buffer saline to the control cuvette. Place the two cuvettes at 25°C for 2 minutes, and quickly add 0.1ml 500u / mL malate dehydrogenase pure enzyme solution and an appropriate amount of crude enzyme solution to star...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com