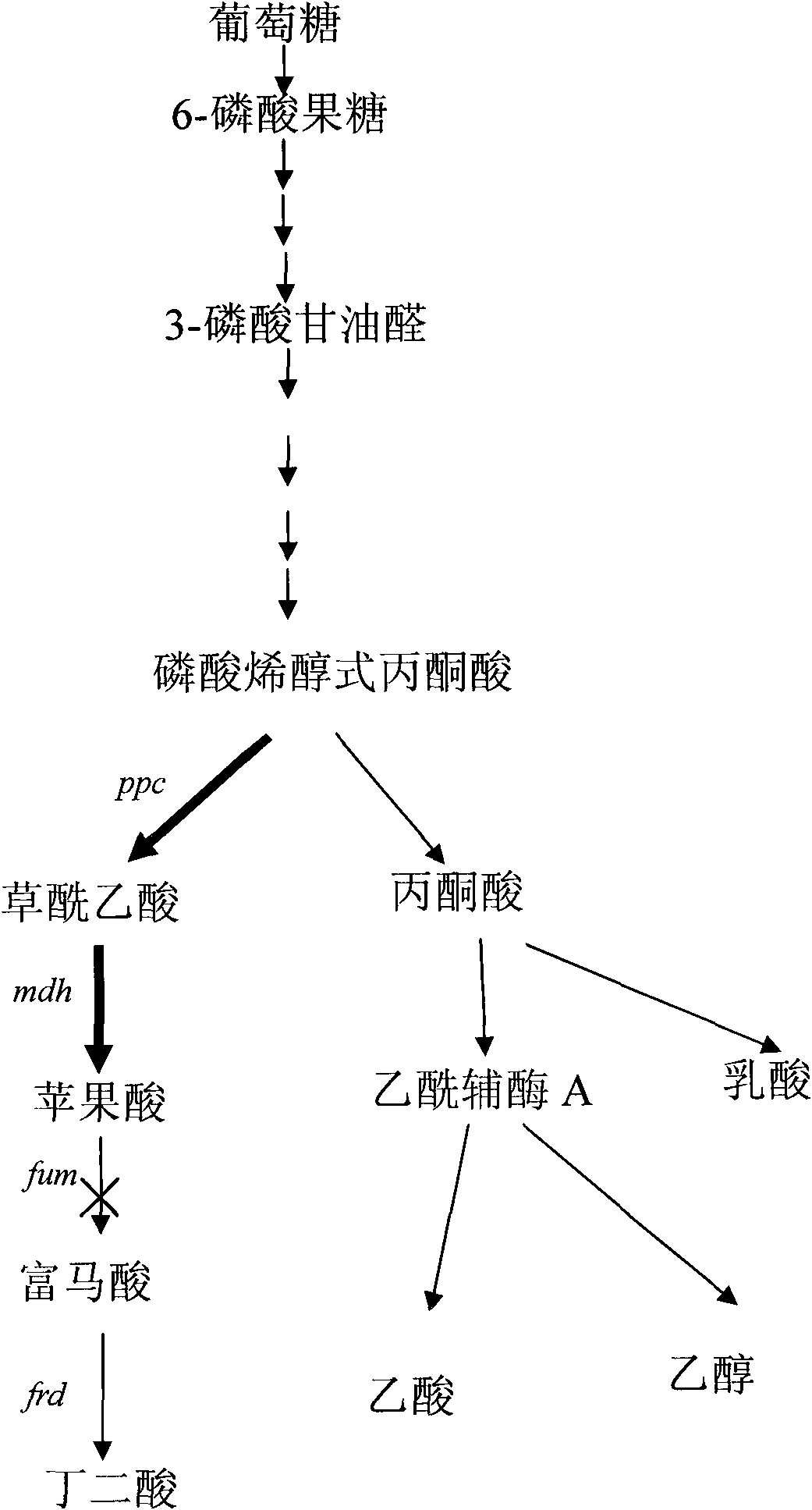
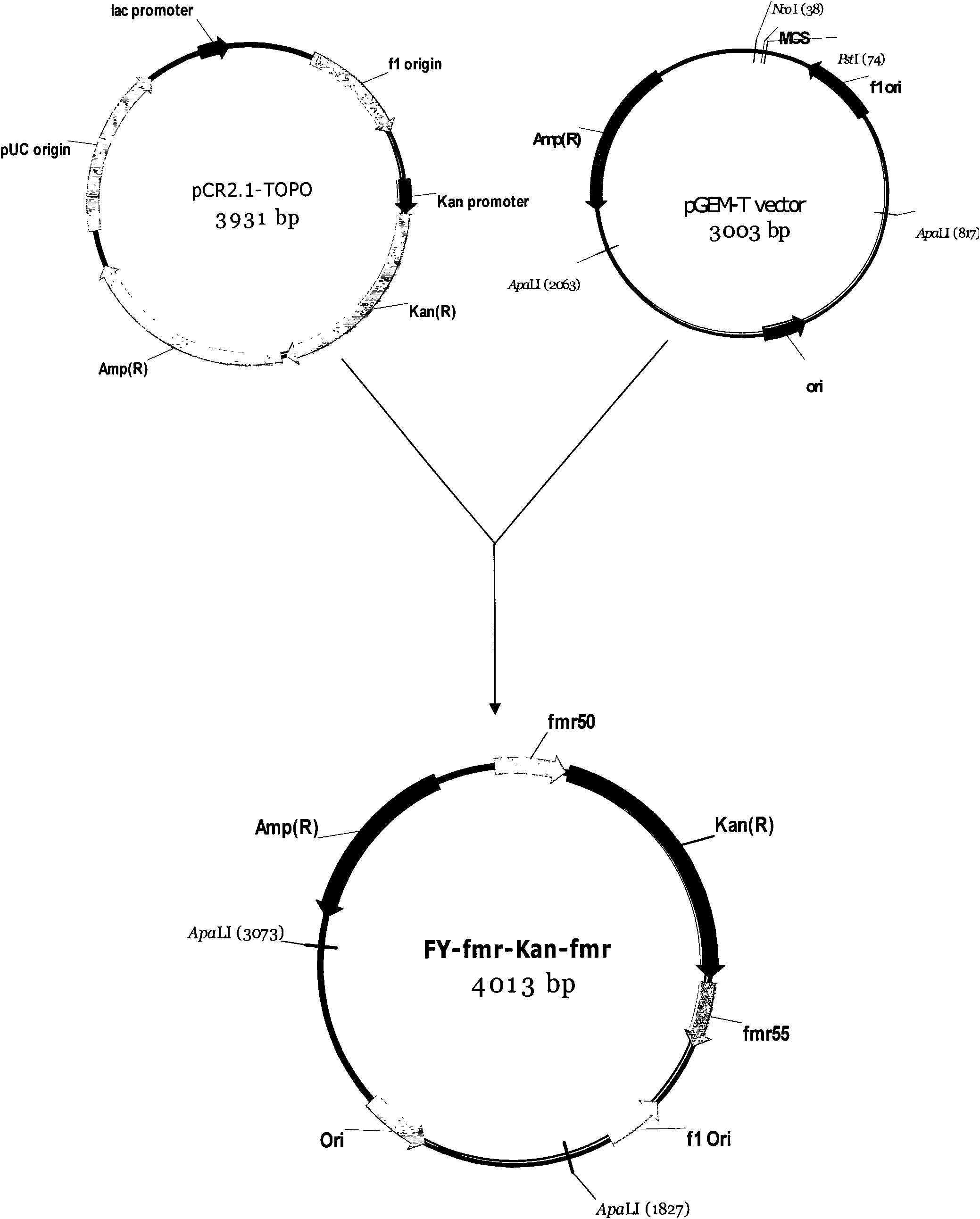
Patents
Literature
79results about How to "Reduce feedback inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
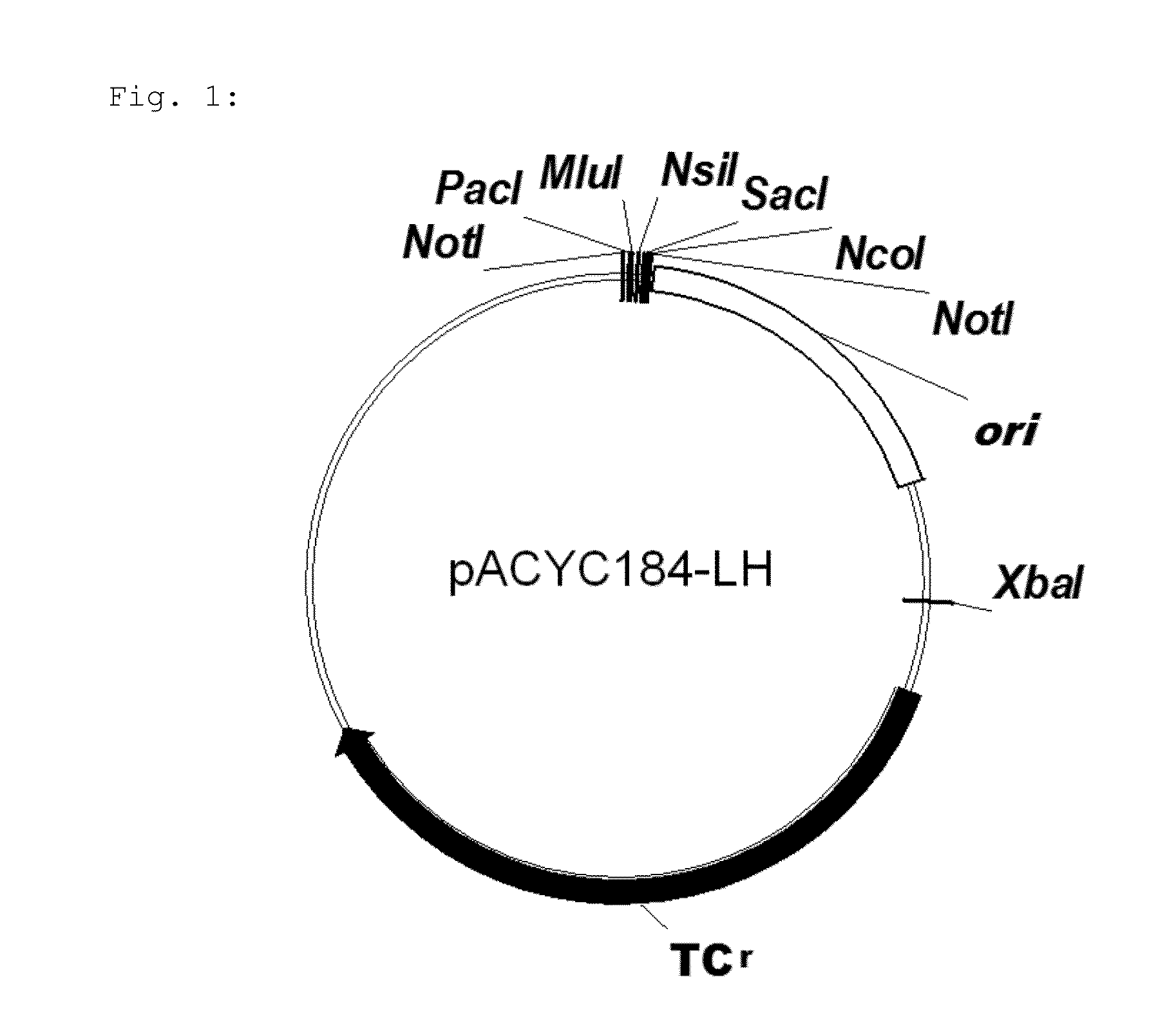
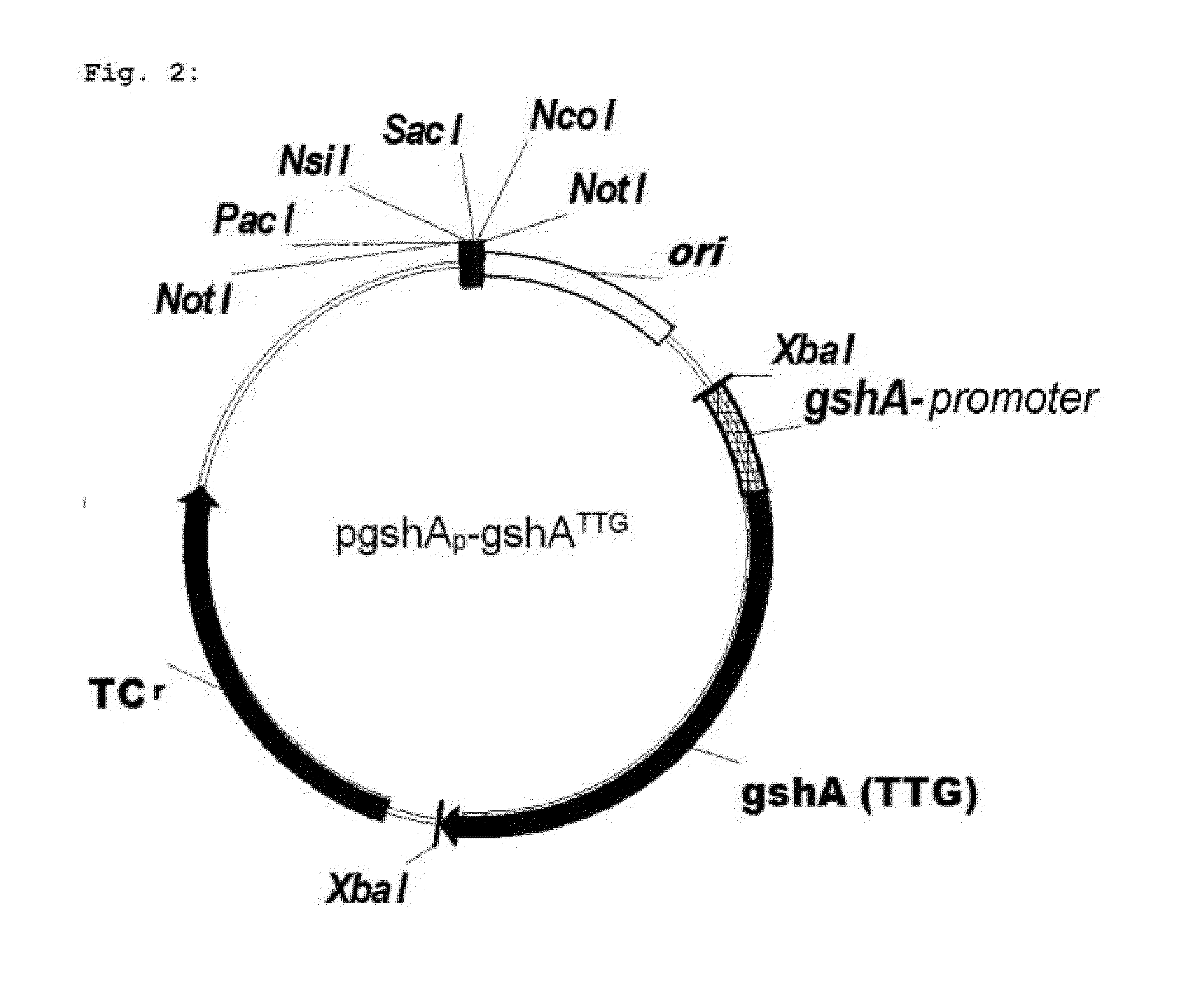
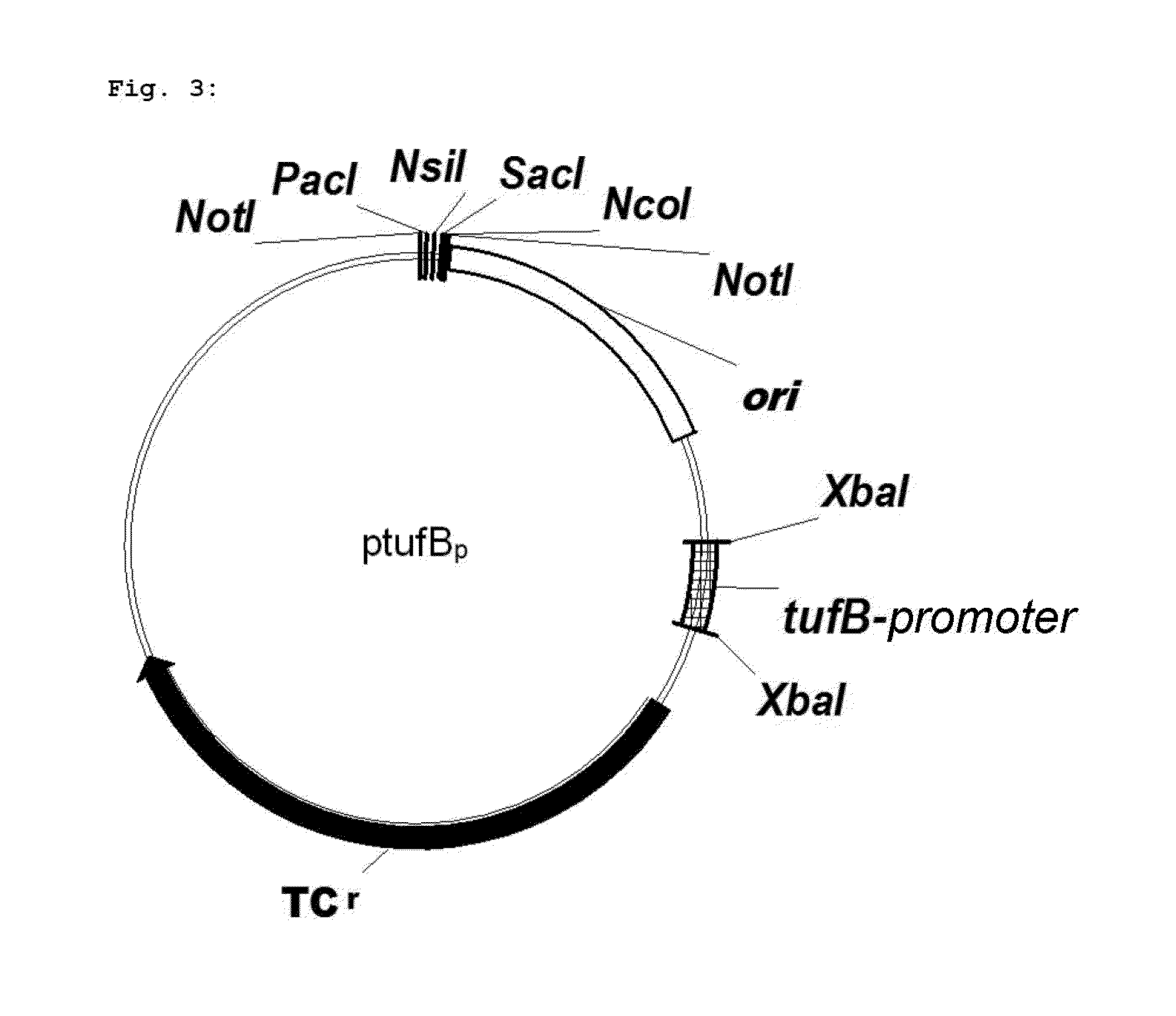
Method for fermentative production of L-methionine
A microorganism strain suitable for fermentative production of L-methionine and preparable from a starting strain, which comprises increased activity of a yjeH gene product or of a gene product of a yjeH homolog, compared to the starting strain.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Gas-phase double-dynamic solid fermentation technology and fermentation apparatus
InactiveCN1434113ASimple structureImprove sealingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGas phaseEngineering
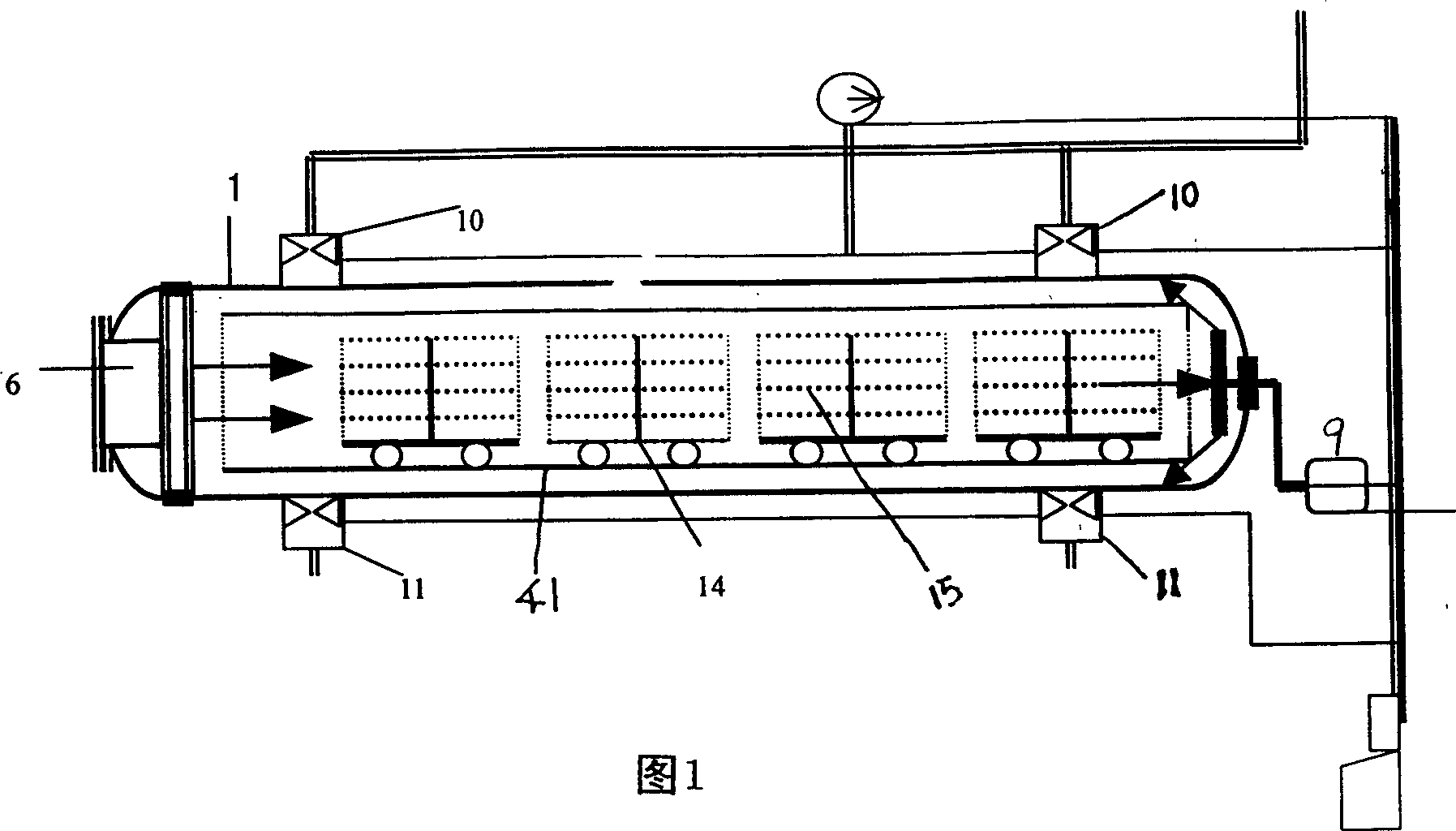
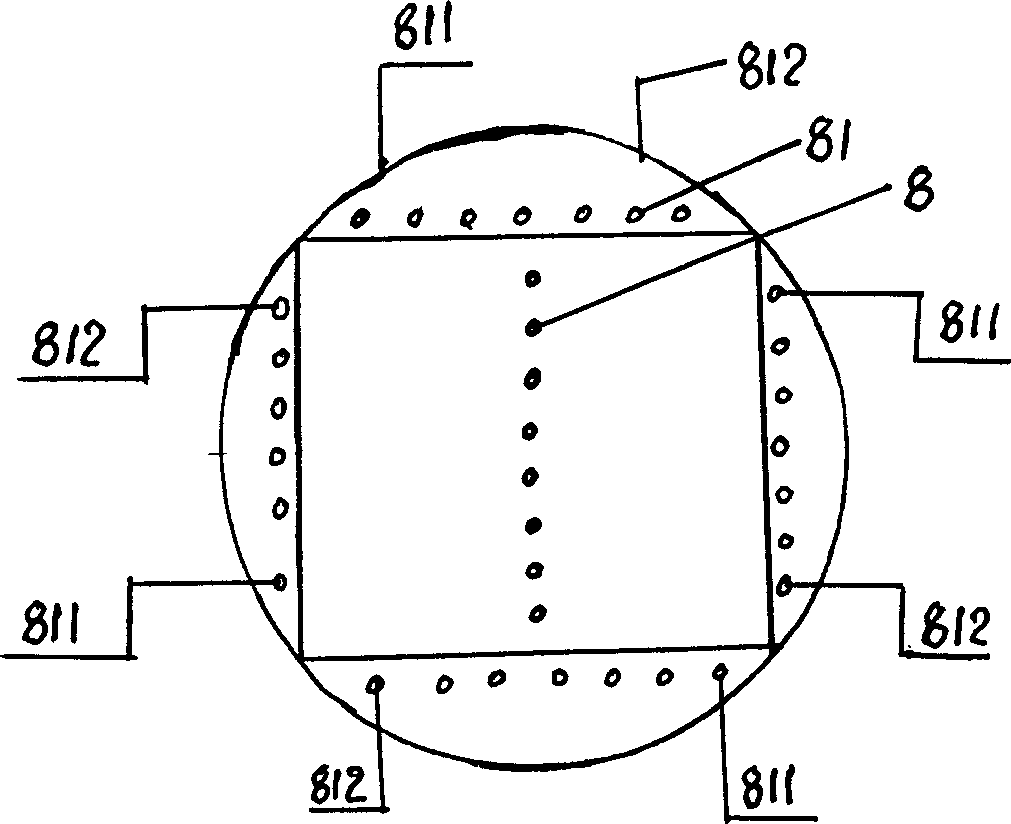
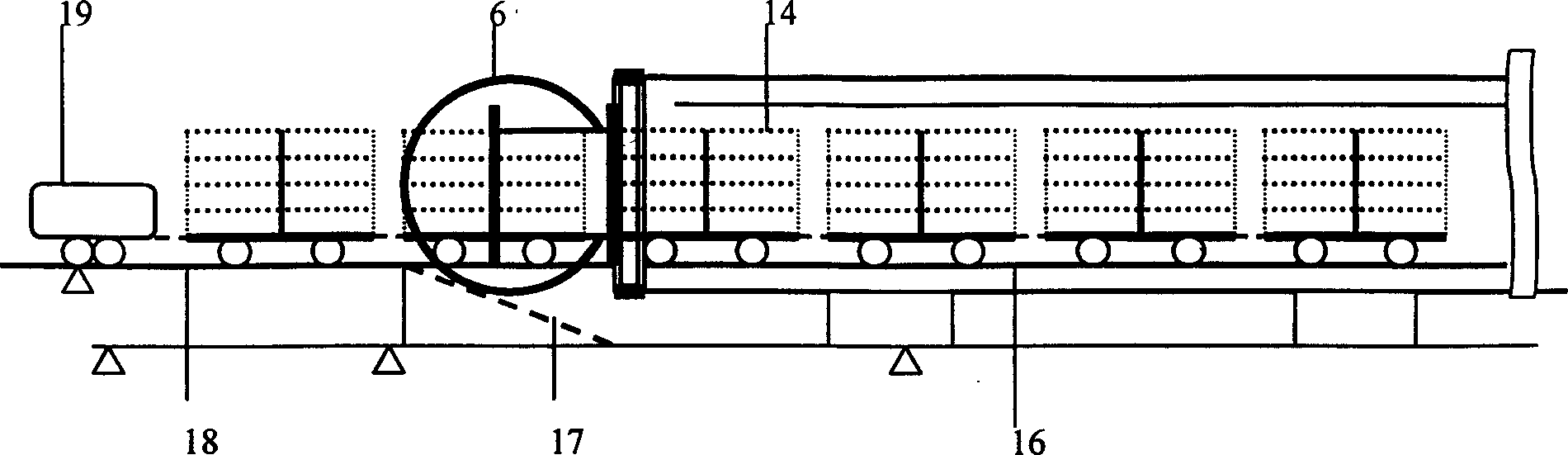
The present invention relates to a gas-phase double-dynamic solid fermentation techinque, and is characterized by that the solid material to be fermented is placed into a double-dynamic environment with pressure pulsatino and circular flowing air to make solid fermentation. Its fermentation equipment includes a horizontal cylindrical tank with a quickly-opening door, in the interior of the tank arectangular spacing cylinder which is formed from four partition boards and whose section is quadratic is axially placed, and in the space of partition board and tank wall a cooling calandria parallel to the partition board is arranged, and the vertical centre of the spacing cylinder is equipped with horizontally-arranged several groups of cooling calandria.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for realizing high-efficiency and low-consumption nitrogen and phosphorous removal of municipal sewage
ActiveCN108675450AEasy loadingLow mud productionWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesOxygenNitrogen gas
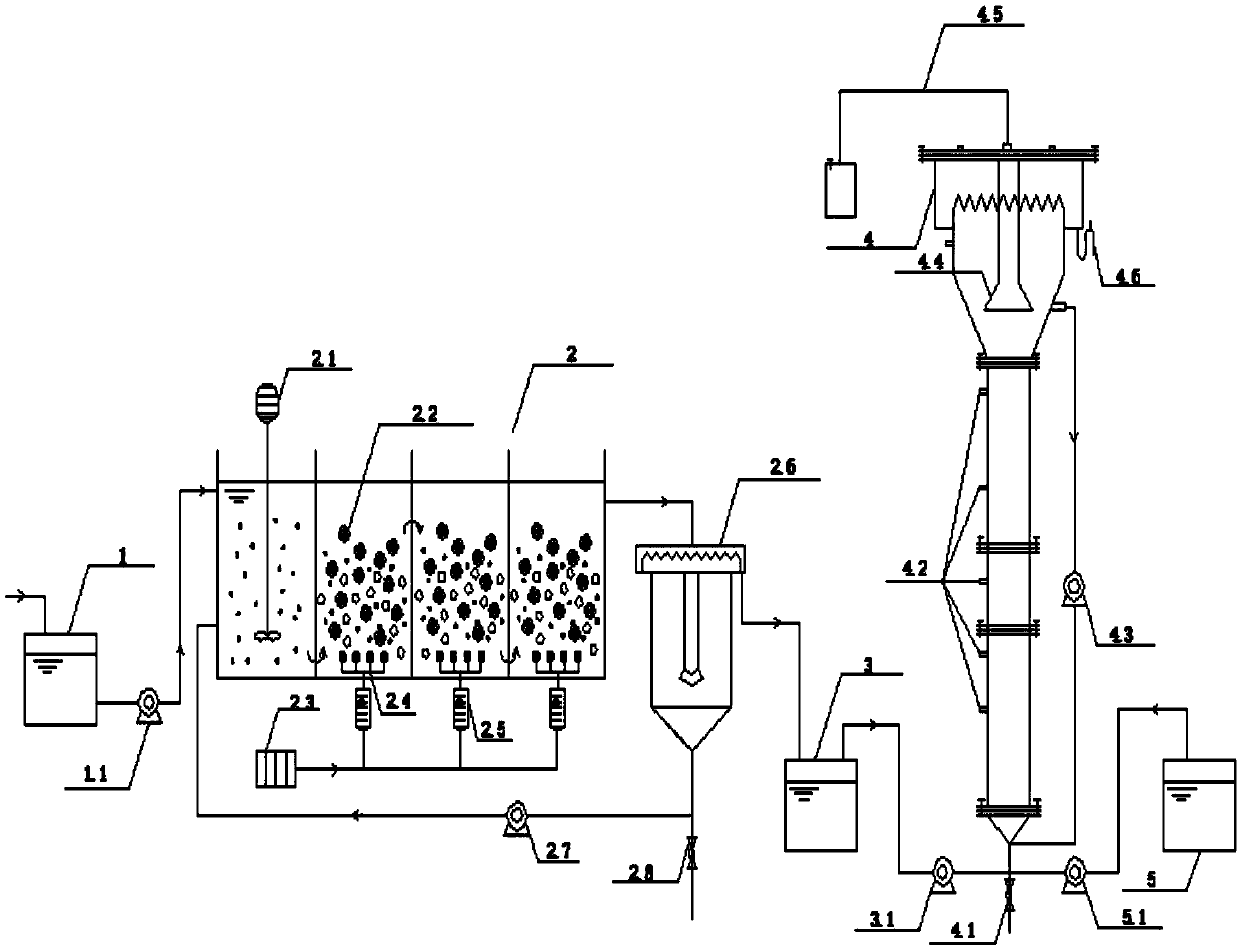
The invention discloses a device and method for realizing high-efficiency and low-consumption nitrogen and phosphorous removal of municipal sewage and belongs to the field of biological treatment of sewage and sludge. Sewage in a raw water tank sequentially enters an anaerobic zone and an aerobic zone of a reactor for enhanced biological phosphorus removal and whole-process nitrification through awater feeding pump; anaerobic phosphorus release is performed in the anaerobic zone; whole-process nitrification and aerobic phosphorus absorption effects are carried out in the aerobic zone; subsequently, the sewage is drained into a settling pond, supernate enters a reactor for fermentation coupling, short-cut denitrification and synchronous anaerobic ammonium oxidation of excess sludge. The excess sludge is quantitatively fed into the reactor for fermentation coupling, short-cut denitrification and synchronous anaerobic ammonium oxidation of the excess sludge each day; short-cut denitrifying bacteria transform nitric nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen by using organic matters produced by hydrolysis and fermentation of the sludge; anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria transform excess ammonia nitrogen and nitric nitrogen into nitrogen. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal of the municipal sewage is realized by using an enhanced biological phosphorus removal process, a short-cut denitrification process and an anaerobic ammonium oxidation process; moreover, sludge reduction is realized by the hydrolysis and fermentation effects of the sludge, so that energy conservation and consumption reduction are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Combined pretreatment method for efficiently separating bagasse biomass components
InactiveCN102180994ANo pollution in the processReduce energy consumptionBiofuelsFermentationAlkaline waterPretreatment method
The invention discloses a combined pretreatment method for efficiently separating bagasse biomass components, which mainly comprises the following steps: preimpregnating in dilute sulfuric acid; carrying out steam explosion treatment; washing with hot water; extracting; and carrying out enzymolysis. In the combined pretreatment method disclosed by the invention, on the basis of different physicochemical properties and structural features of the three components (hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin) in the bagasse, the component hemicellulose is sufficiently degraded and separated by dilute acid preimpregnation-steam explosion pretreatment, thereby reserving most of the cellulose and lignin; and the lignin is extracted by using a lower alcohol-alkaline water system, leaving high-cellulose-content residues. On the premise of low concentration of the added enzyme, the invention obviously increases the enzymolysis rate, and raises the conversion rate and comprehensive utilization rate of the bagasse biomass resource.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YOURUI BIOSCI
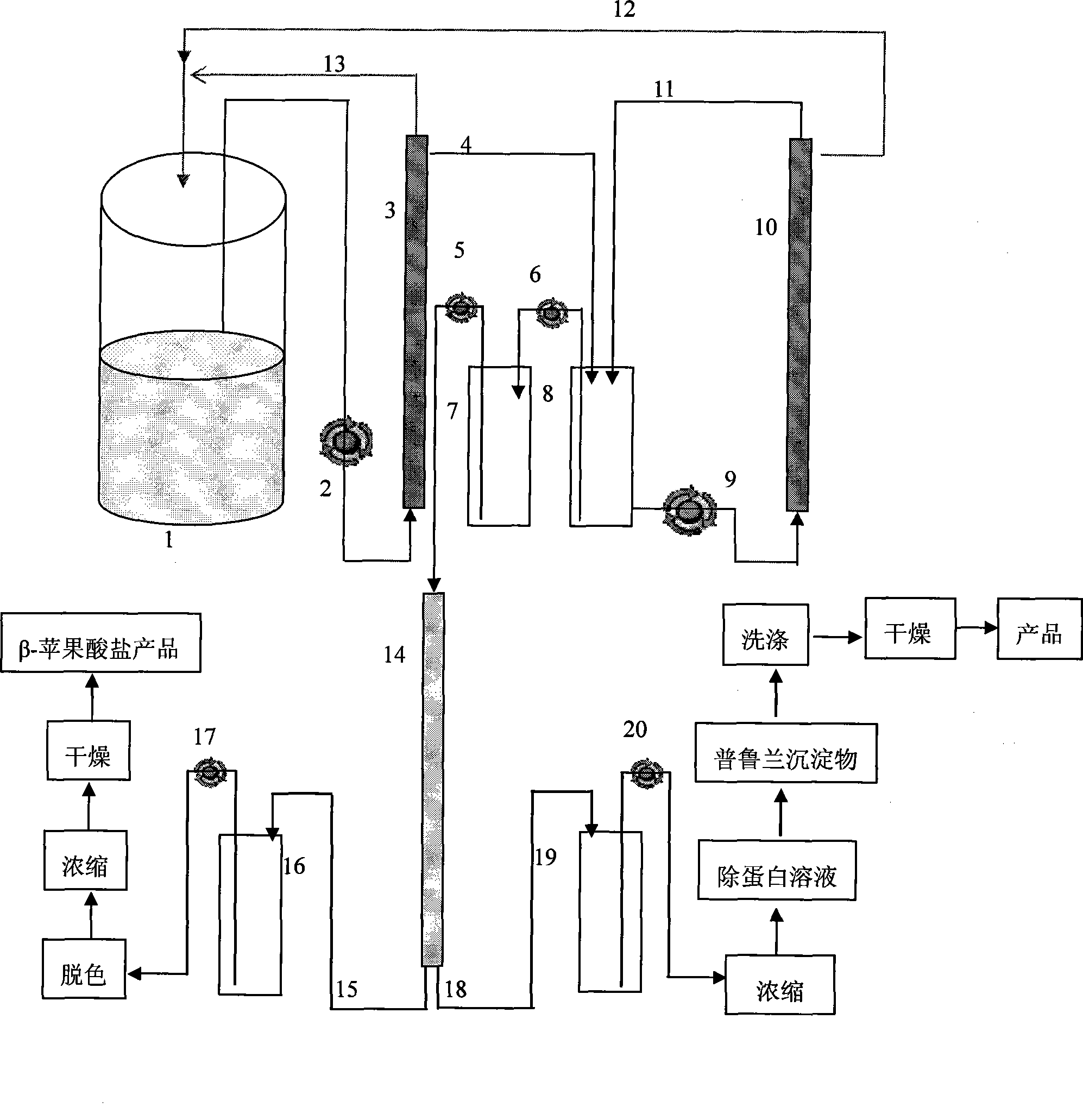
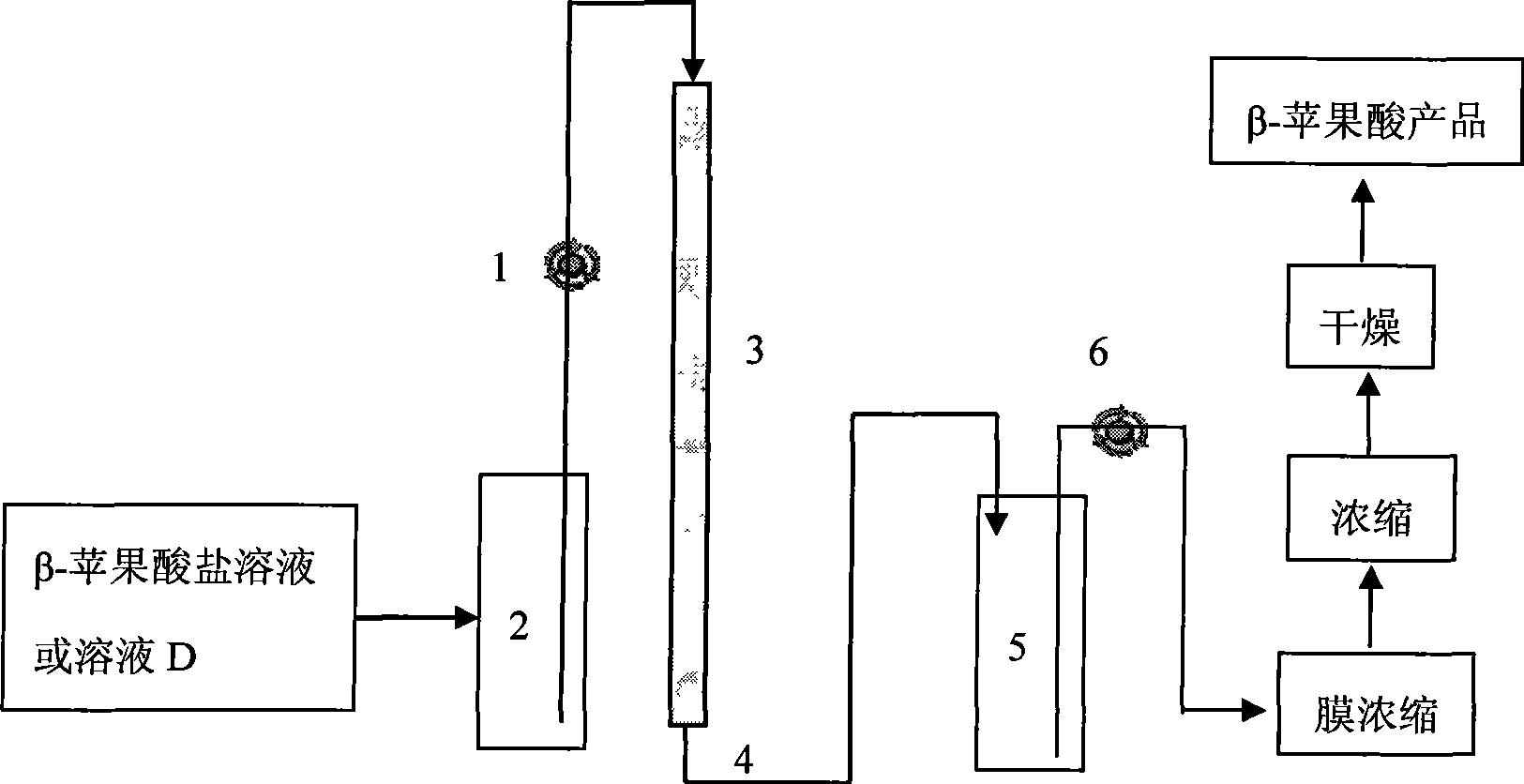
Preparation f beta-poly malic acid and salt thereof
ActiveCN101487034AHigh yieldReduce feedback inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPullulanStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for preparing Beta-poly malic acid and a salt thereof and simultaneously obtaining a byproduct pullulan. The method is realized by adopting the following technical proposal: return thalli and interception are implemented by a membrane technique in a fermentation process, high molecular weight Beta-poly malic acid is concentrated, and low molecular weight Beta-polymalic acid, pullulan and other components are recycled in a fermentation system; a weakly basic anion exchange resin is adopted to absorb the Beta-poly malic acid and lead pullulan solution to penetrate, alkaline solution is adopted to elute the Beta-poly malic acid that is adsorbed on the resin, and eluting solution is purified and dried, thus obtaining the salt product of the Beta-poly malic acid; a penetrating fluid is concentrated, chloroform and butanone mixture solution is adopted to remove protein, and the pullulan is precipitated by ethanol alcohol precipitation, orderly washed by acetone and ethyl ether, and dried by P2O5, thus obtaining a powder pullulan product; a strong acid cation exchange resin is adopted to absorb salt ions in salt solution of the Beta-poly malic acid, a membrane is used for removing extra acid in the desalted solution, and the obtained solution is concentrated and dried, thus obtaining the Beta-poly malic acid product.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
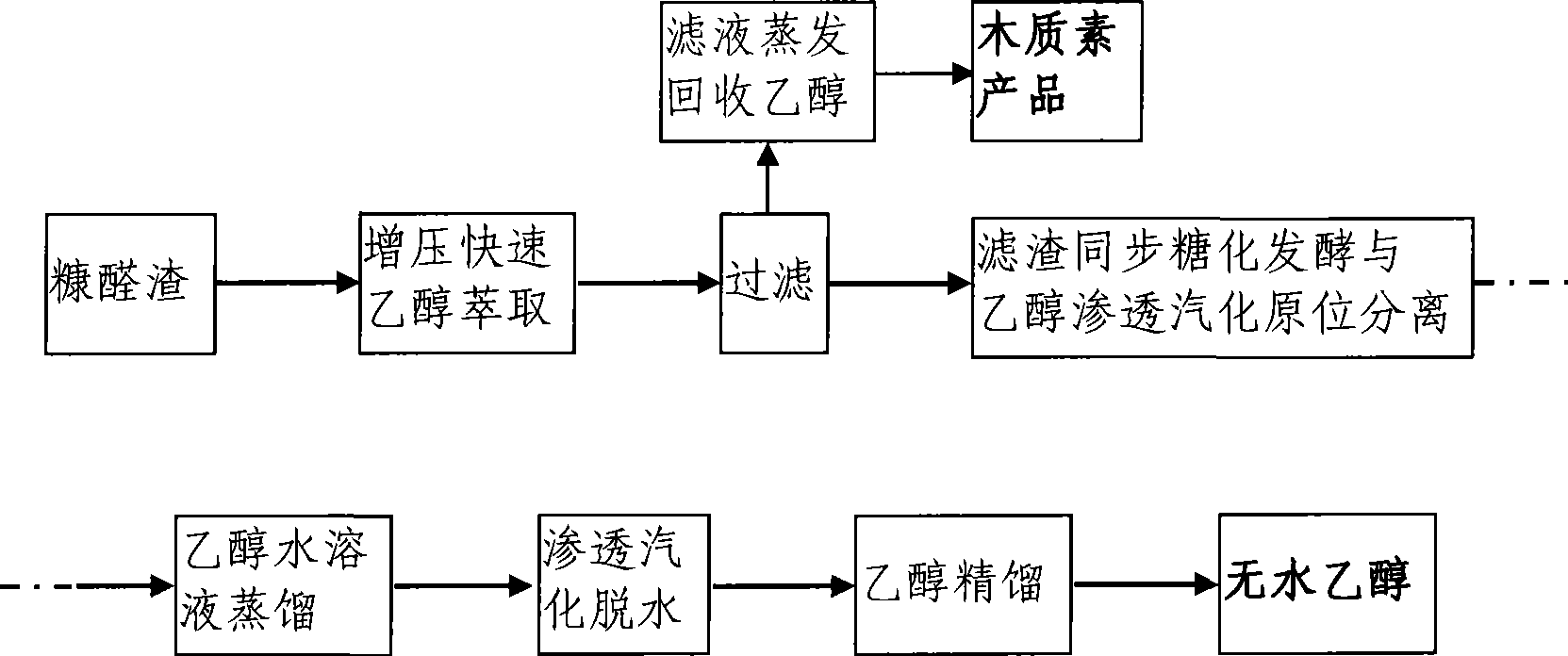
Method for preparing absolute ethyl alcohol from furfural residue
InactiveCN101413017ALarge amount of resourcesLow priceMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberAlcohol
The invention provides a method for preparing absolute ethyl alcohol by furfural residues. A furfural residue cellulose raw material is adopted, lignin is separated, and then the absolute ethyl alcohol is obtained through synchronous diastatic fermentation and pervaporation coupling separation of alcohol, then distillation, pervaporation dehydration and rectification. The method has the advantages that the method organically combines the prior mature rectification technology with a modern advanced separation technology to improve the production efficiency when high fiber raw materials are used to prepare the absolute ethyl alcohol.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Construction method of genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN102304539AReduce the content of intermediate productsIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme GeneTryptophan
The invention discloses a construction method of a genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing an escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out; 2, constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 containing key enzyme genes aroGFBR, aroE, aroB, aroD, tktA and ppsA in the metabolic pathway of the shikimic acid, so that the genes are subjected to transcriptional control of a tryptophan promoter Ptrp; and 3, transferring the recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 into the escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out to obtain a production strain for expressing the shikimic acid. In the method, the aim of interrupting the metabolism of the shikimic acid is fulfilled by the knock-out of the single gene aroA, a small number of genes are knocked out, the operating difficulty is low, and the expression of the genes is in the state of starting and stopping automatically and is started automatically in the middle and late period without the induction of inducers, so the possibility of adding toxic substances into a culture medium is reduced, and the shikimic acid has high yield.
Owner:河南孟成生物药业股份有限公司
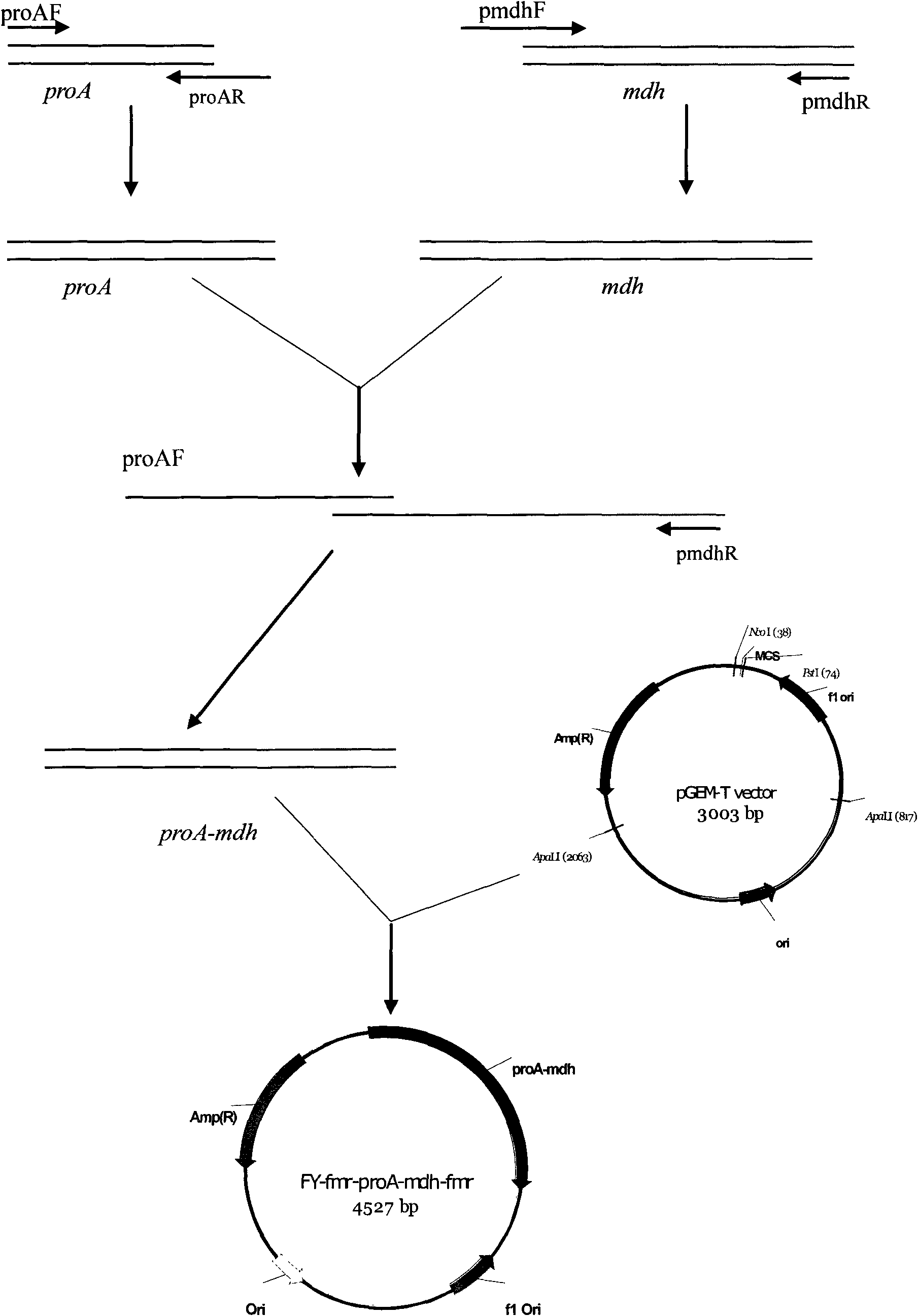
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. In the invention, key phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase(PEPCK) related to the L-malic acid, malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and fumarase (FumC) are transformed to obtain the gene engineering bacterial strain; a deactivation mutation is carried out on the fumCto cause the interruption of a metabolic flux at the converting position from the malic acid to the fumaric acid so as to accumulate the target product L-malic acid; before the mdh, the promoter of aninner source pepck gene is added to generate the metabolic flux biased towards the malic acid; in addition, through the inducement of monofluorine sodium acetate, the activity of the PEPCK is improved, and the product feedback inhibition is greatly reduced. The bacterial strain applied to the fermentative production of the L-malic acid so as to obviously improve the yield of L-malic acid. The invention has advantages of simple technology, obvious effect and low cost and can satisfy the demand of markets.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Yeast engineering bacterium for producing d-limonene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102071153AReduce feedback inhibitionGood application prospectFungiFermentationMevalonate pathwayMevalonic acid
The invention discloses a yeast engineering bacterium for producing d-limonene and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of gene engineering. In the invention, limonene synthetase from Citrusunshiu is heterologously expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C by metabolic engineering modification to increase ways (mevalonic acid (MVA) carbon metabolic flux) for synthesizing terpenoids, thereby obtaining a yeast engineering bacterium strain CEN.PK2 limonene for producing d-limonene at high yield. Compared with the original strain CEN.PK2-1C, the modified yeast engineering bacterium can produce d-limonene by metabolism, the feedback inhibition on d-limonene is obviously lowered, and the yield of d-limonene can reach 13 mg / L, thus the invention has wide application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain and building method thereof
InactiveCN102071155AReduce feedback inhibitionEasy to buildFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousLinalool
The invention discloses a high-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain and a building method, which belong to the field of genetic engineering. Through the metabolic engineering reformation, linalool synthetase from actinidiaarguta is expressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1 in a heterologous way, the terpene synthesis path-mevalonic acid (MVA) path carbon metabolizing flow is increased, and the high-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain CEN. PK2 linalool is obtained. Compared with an initial strain CEN. PK2-1C, the modified genetic engineering strain CEN. PK2 linalool can metabolize and produce s-linalool, in addition, the feedback inhibition of the s-linalool is obviously reduced, the yield of the s-linalool can reach 12 mg / L, and the genetic engineering strain has good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fermentation process for raising ebomycin A yield
The present invention discloses a method for raising secondary metallic product output of myxobacteria, i,e, a method for raising output of metabolic product epothilone A of sorangium cellulosum of ephothilone in myxobacteria, and the said method incldues: 1). naturalization method of lump-grown myxobacterial liquid uniform growth; (2). selecting potato starch and hydrolyzed lactoprotein, etc. suitable for production of epothilone A; and 3). addition method of mixed resin for integrally-eliminating product metabolic accumulation so as to make the output of ephothiloue A product be up to 62.7 mg / L level.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Construction and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for extracellular transport of vitamin D3 precursor squalene
PendingCN113684141AReduced intracellular storage burdenImprove the effectFungiTransferasesVitamin PrecursorsMolecular biology
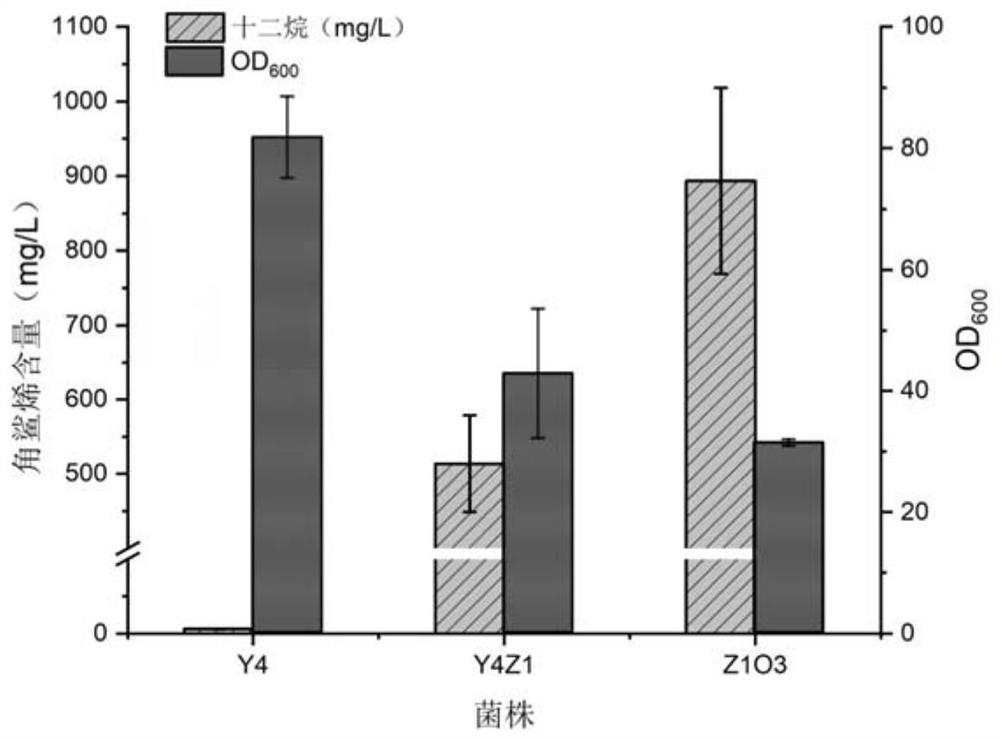
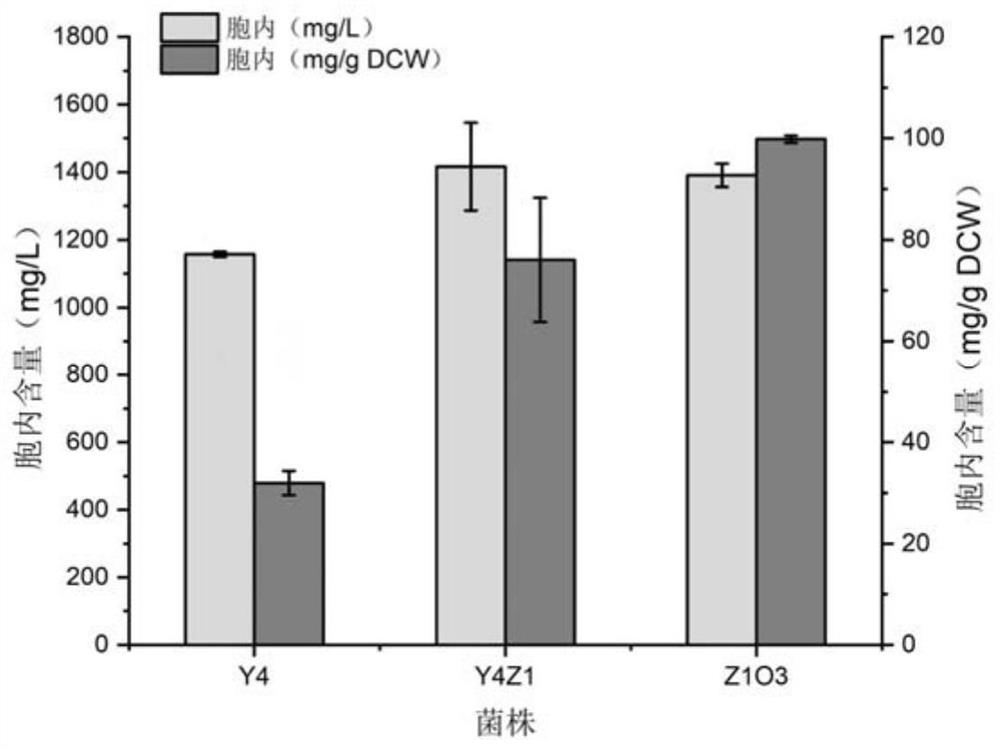
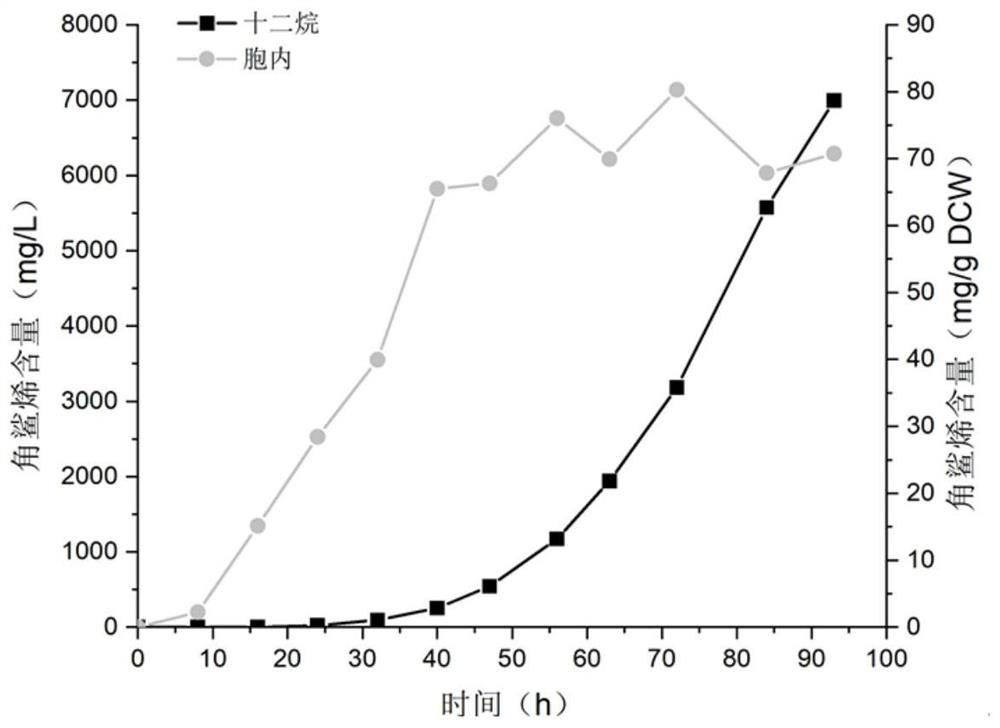
The invention discloses construction and application of a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for extracellular transport of vitamin D3 precursor squalene, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. The construction comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain Z1O3 for high yield of squalene, wherein the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae intensively expresses 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase, farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, and related genes INO2, Pdr5 protein and Osh3 protein of endoplasmic reticulum size regulating factors; knocking out ROX1 gene; when the strain is subjected to shake flask fermentation, the content of squalene in extracellular dodecane of the strain reaches 893.58mg / L; and when the strain is cultured in a fermentation tank, the content of squalene in extracellular dodecane of the strain can reach 6995.81mg / L. The recombinant strain constructed by the invention not only has the ability of extracellular transport of squalene, but also has stronger squalene production performance, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for fermenting lactic acid bacteria
ActiveCN102134581AShorten the enzymatic digestion timeDisinhibition effectFermentationHigh concentrationRaw material
The invention relates to a method for fermenting lactic acid bacteria. The method comprises the steps of: utilizing celluloses of plant straws, which are treated with partial enzymolysis, as a carbon source for the fermentation of lactic acid bacteria so as to produce lactic acid by fermentation, and causing the sugar content of celluloses of plant straws, which are treated with partial enzymolysis, to range from 1 to 10 in percentage by weight; and partial enzymolysis comprises the steps of: carrying out enzymolysis on the celluloses of plant straws for 12 to 72 hours through cellulose at the temperature from 45 to 55 DEG C so that sugar generated through enzymolysis and celluloses which are not treated with the enzymolysis can be contained in fermentation liquor and the lactic acid can be prepared through enzymolysis and fermentation simultaneously. Compared with the prior art, the production cycle is shortened to 64 hours from 136 hours, the inhibition of high-concentration glucose on lactic acid bacteria fermentation lactic acid is gotten rid off, and the fermentation level is increased to 6.8 from 3.6 in percentage by weight. The method utilizes the plant straws as raw materials for fermentation, makes waste profitable, reduces environmental pollution and has positive significance to guarantee food security.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Hydrogen manufacturing method for high-density culture and hydrogen production integration of platymanas subcordiformis
InactiveCN101748154AReduce hydrogen partial pressureRemove inhibitionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesShort termsHydrogen production
The invention utilizes a flat plate photobioreactor integrating a fuel battery to integrate microalgae high-density culture and irradiation hydrogen production so as to form an integrative hydrogen production system. Two sections of processes of microalgae culture and photosynthetic hydrogen production are generally divided in space time, and the cultured low-density frustule needs to be concentrated and then irradiated to produce hydrogen, so that the operations need to be respectively carried out in two photobioreactors. In the microalgae hydrogen production of the invention, the low-density microalgae is inoculated into a reactor, a culture mode of enriching carbon dioxide is utilized, the biomass required by the hydrogen production can be reached by short-term culture, then dark induction is carried out, and the operation can enter a continuous irradiation hydrogen production stage. The generated hydrogen gas can be integrated into a fuel battery on a reactor and is converted into electric energy, and the hydrogen production condition can be monitored at real time by the change of current. The invention combines the two sections of processes of the microalgae culture and the hydrogen production for the first time, utilizes the fuel battery to convert the hydrogen into the electric energy and provides reliable technical support for the large-scale microalgae hydrogen production.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production method for pullulan based on cell metabolism regulation strategies
ActiveCN103805651AImprove permeabilityReduce feedback inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPullulan
Owner:SHANDONG FREDA BIOTECH
Efficient hydrolytic acidification method suitable for treating agricultural wastes with high solid content and fermentation device
InactiveCN108165478AEasy to operateLow input costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWater circulationOxygen
The invention discloses an efficient hydrolytic acidification method suitable for treating agricultural wastes with a high solid content and a fermentation device. The fermentation device comprises ahydrolytic acidification reactor (1), a hot water circulation system (2), a leachate and biogas liquid spraying adjustment system (3) and an aeration system (4), wherein the hydrolytic acidification reactor (1) is suitable for treating the agricultural wastes with the high solid content; a forklift is adopted to directly feed and discharge materials; the hot water circulation system (2) continuously supplies a heat source to the reactor for fermentation at a medium temperature; through the leachate and biogas liquid spraying adjustment system (3), leachate (acidizing fluid) and biogas liquid are refluxed and sprayed to enhance continuous hydrolysis and acidification ability of the materials; the aeration system (4) provides a micro-aerobic hydrolytic acidification environment for a hydrolytic acidification reaction so as to enhance hydrolysis. The efficient hydrolytic acidification method suitable for treating the agricultural wastes with the high solid content and the fermentation device provided by the invention can effectively improve difficult feeding and discharging, hydrolysis easy to be inhibited by acid production feedback and other difficulties of a continuous operation reactor using the agricultural wastes as raw materials, and have management convenience, low operation energy consumption, and relatively good application prospect and promotion value.
Owner:ACADEMY OF PLANNING & DESIGNING OF THE MINIST OF AGRI
Method for fermentation production of bacitracin
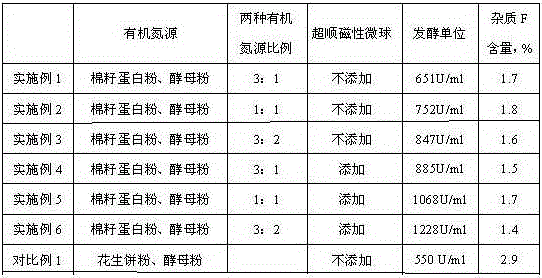
InactiveCN105483064AIncrease productionGuaranteed stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrosphere
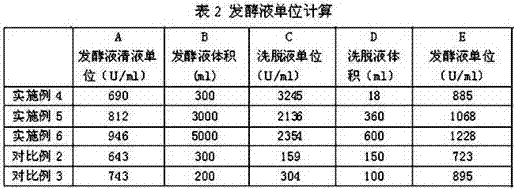
The invention belongs to the field of fermentation engineering, and particularly relates to a method for improving the yield of bacitracin produced through microbial fermentation. According to the method, by optimizing an organic composite nitrogen source and fermentation conditions, batch fermentation unit stability is ensured, and the content of impurities F is lowered; superparamagnetism microspheres are added in the bacitracin synthesis period to adsorb bacitracin in a fermentation solution, and therefore feedback restraint of a fermentation production for producing bacteria is lowered. After fermentation is finished, the fermentation unit of bacitracin can reach 1228 U / ml, the yield of bacitracin can be improved by 123% compared with the yield obtained before optimization, the yield is improved, energy consumption is lowered, and waste discharge is reduced.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
Method of preparing ethanol through cellulose solid phase enzymolysis and liquid fermentation coupling and its installation
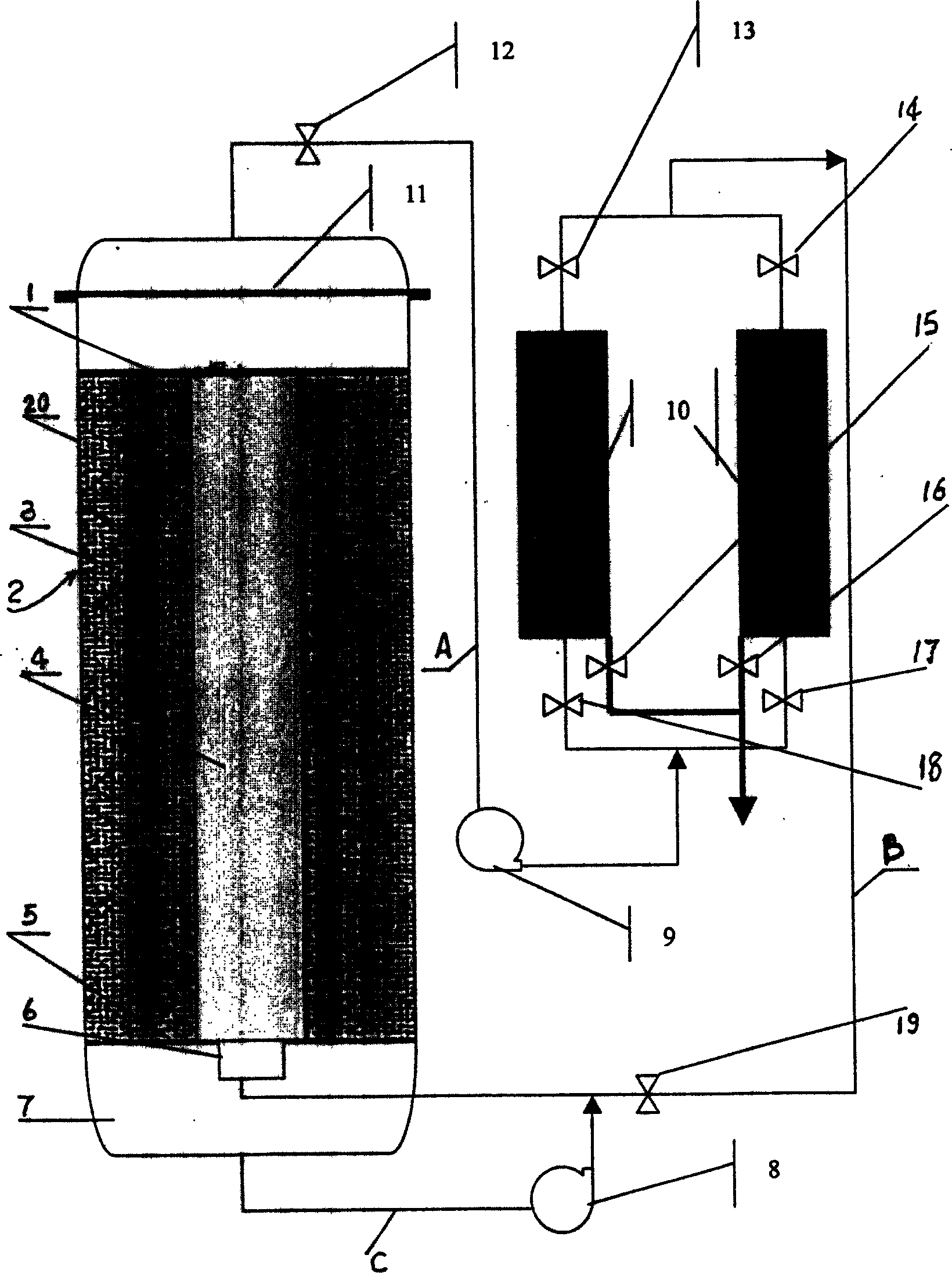
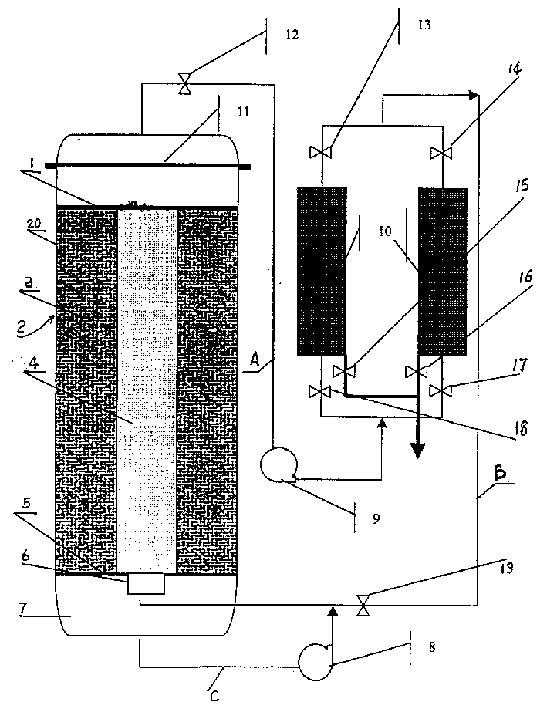
InactiveCN1493694AReduce feedback inhibitionAvoid inhibitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseAlcohol
A process and equipment for preparing alcohol by the coupled solid-phase cellulose enzymolysis and liquid fermentation are disclosed. Its equipment is composed of vertical reactor consisting of internal and external cylinder, upper and lower closure heads, upper and lower plate filters, air-floating valve connected to lower part of internal cylinder, CO2 gas circulating pump, and enzymolyzed liquid circulating pump. Said process includes adding cellulose and cellulose into the cavity between internal and external cylinders, leaching the enzymolyzed substance of cellulose, pumping the liquid into internal cylinder, adding yeast into internal cylinder, fermenting, and separating and recovering alcohol.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing L-lactic acid by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
ActiveCN112725386AIncrease concentrationHigh optical purityBacteriaBiofuelsBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method for producing L-lactic acid by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, which comprises the following steps: by using lignocellulose as a raw material, carrying out simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in the presence of an enterococcus faecalis DLY-FLYC seed solution and cellulase under enzymolysis conditions. The newly separated and screened enterococcus faecalis DLY-LFYC can be used for synchronous saccharification and fermentation at a high temperature, the concentration and optical purity of the L-lactic acid produced by fermentation are high, particularly, cellobiose can be used as a strain, the feedback inhibition effect is small, and the lactic acid fermentation effect is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
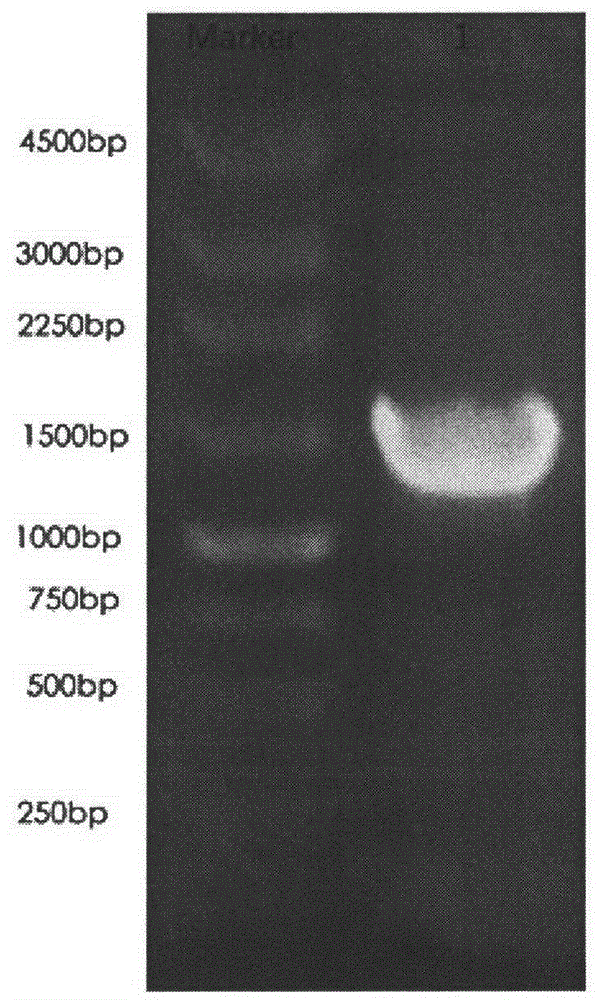
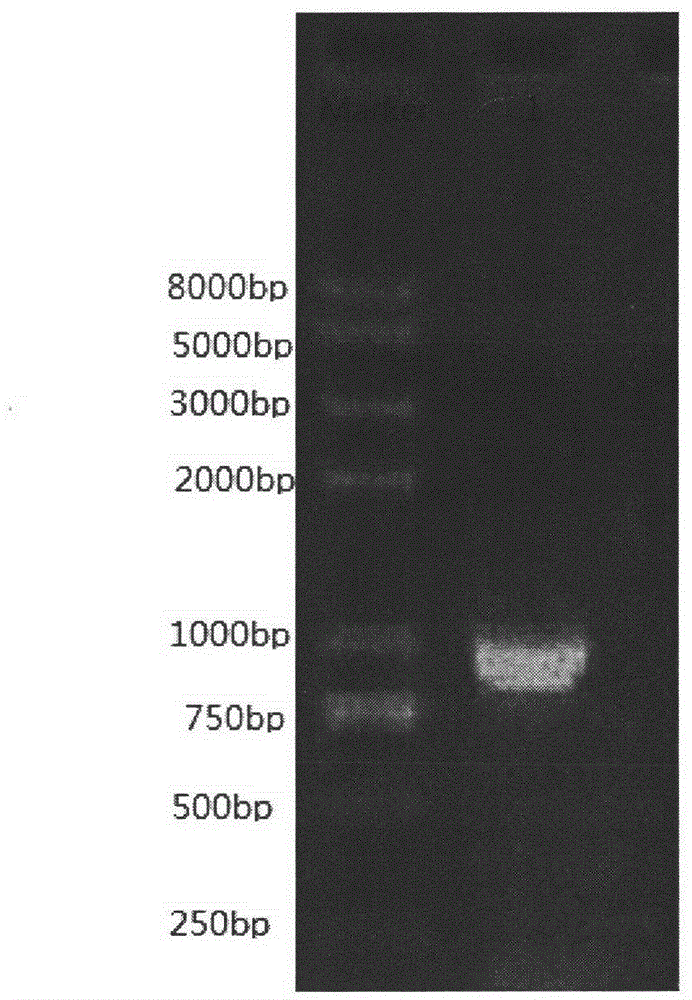
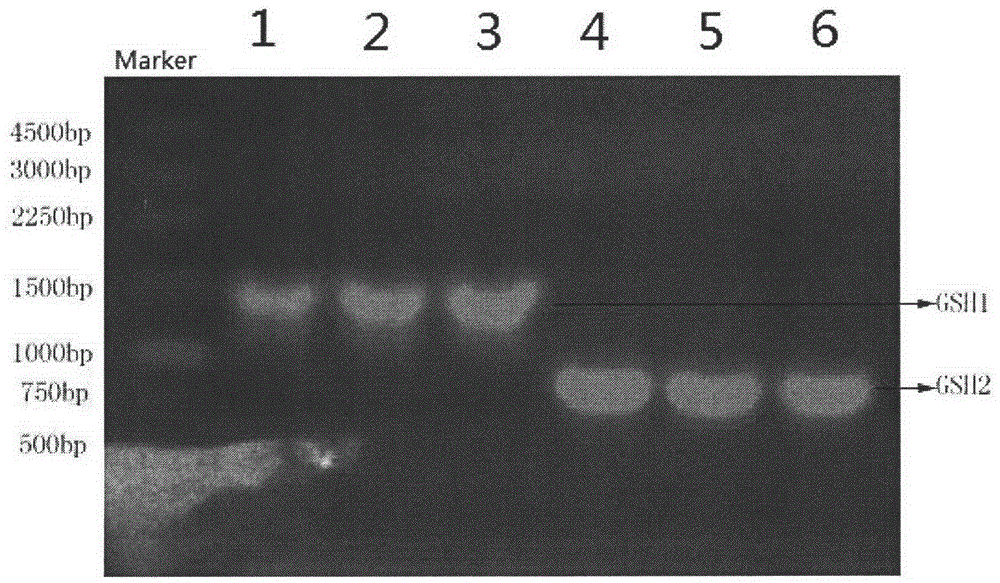
Feedback inhibition weakening method for producing glutathione by bacterial strains
InactiveCN102911960AReduce feedback inhibitionIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyFeedback inhibition
The invention provides a glutathione synthetase-based recombinant plasmid, a construction method and application thereof, and a method for accumulating glutathione. The glutathione synthetase-based recombinant plasmid provided by the invention includes sequences GSH1 and GSH2 as well as two appropriate vector segments; the principle of the method lies in that as GSH1 and GSH2 are connected onto vectors with different promoters, step-by-step expression of GSH1 and GSH2 can be realized through adding inducers at different time to reduce feedback inhibition; with the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the feedback inhibition can be weakened remarkably, the yield of glutathione is improved, the utilization ratio of raw materials is improved, and a base model is established for further studying synthesis of glutathione by a biological method. In addition, the method and the idea can be applied to target products of which the yield improvement is restricted due to the feedback inhibition, and provide a new idea for producing valuable products.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
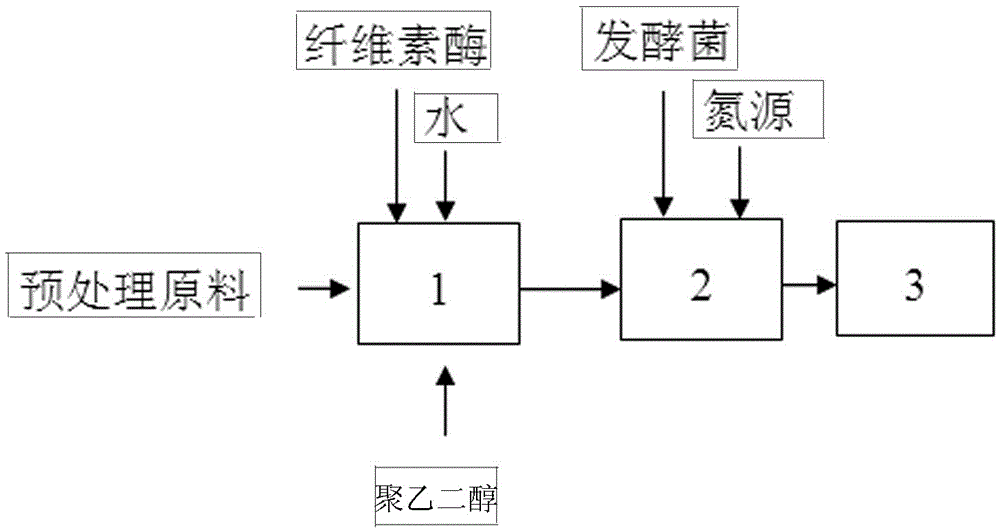
Method for producing ethanol by high-temperature enzymolysis and fermentation of lignocellulose
InactiveCN105624207AImprove high temperature performanceHigh activityBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for producing ethanol by high-temperature enzymolysis and fermentation of lignocellulose. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating a lignocellulose raw material to obtain a pretreated raw material; (2) adding the pretreated raw material, cellulase, water and polyethylene glycol into an enzymolysis tank to perform pre-enzymolysis, and controlling the dry matter concentration of an enzymolysis system to be 15-25wt%; (3) adding a feed liquor after enzymolysis into a fermentation tank and adding a butanol fermentation strain to perform synchronous saccharification and fermentation; and (4) adding a fermentation liquor into a rectification device to separate ethanol. According to the method, polyethylene glycol is added in the enzymolysis system, so that the high-temperature tolerance of the cellulase is improved, the activity of cellulase enzymolysis under the high-temperature condition is high, the cellulase consumption is reduced, the lignocellulose enzymolysis efficiency is raised, and the economy is improved.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Method for fermentation production of bacitracin
ActiveCN106893751AIncrease productionGuaranteed stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the field of fermentation engineering, and particularly relates to a method for improving yield of bacitracin by microbial fermentation. According to the method, by a step 1) of optimization of organic compounding of a nitrogen source and fermentation conditions, stability of fermentation units between batches is ensured, and the content of impurities F is reduced; and by a step 2) of adding superparamagnetic microspheres during the synthesis of bacitracin, feedback inhibition of produced bacteria by fermentation products is reduced. After fermentation, the fermentation unit of bacitracin can reach 1228U / ml, which can increase the yield of bacitracin by 123%, improve the productivity and reduce energy consumption and waste discharge.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
Construction method of genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN102304539BReduce the content of intermediate productsIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a construction method of a genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing an escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out; 2, constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 containing key enzyme genes aroGFBR, aroE, aroB, aroD, tktA and ppsA in the metabolic pathway of the shikimic acid, so that the genes are subjected to transcriptional control of a tryptophan promoter Ptrp; and 3, transferring the recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 into the escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out to obtain a production strain for expressing the shikimic acid. In the method, the aim of interrupting the metabolism of the shikimic acid is fulfilled by the knock-out of the single gene aroA, a small number of genes are knocked out, the operating difficulty is low, and the expression of the genes is in the state of starting and stopping automatically and is started automatically in the middle and late period without the induction of inducers, so the possibility of adding toxic substances into a culture medium is reduced, and the shikimic acid has high yield.
Owner:河南孟成生物药业股份有限公司
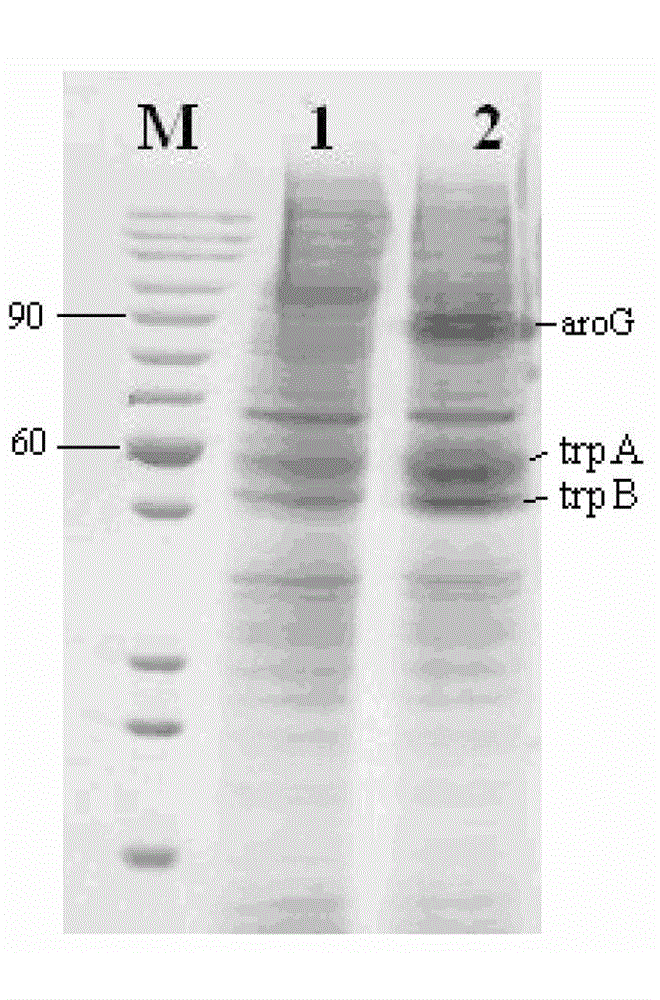
Method for building gene engineering strains of producing tryptophan
InactiveCN102719469AIncrease production capacityPromote productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for building engineering strains of producing tryptophan and relates to the method for building gene engineering strains of producing tryptophan. The problem to be solved is that the method for producing tryptophan at present is low in yield of tryptophan and high in cost. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) augmentation by taking escherichia coli JM109 genome DNA as a template to obtain target genes aroG and trpBA; building pMD18-T-aroG, connecting with a pET-32a vector after enzyme digestion to obtain a connection product X; building pMD18-T-trpBA, connecting with a pET-30a vector after enzyme digestion, thus obtaining a connection product Y; converting the connection product X into a competent cell, and converting the connection product Y into a positive recombinant strain namely an engineering strain of producing tryptophan. The engineering strain built by the method can excessively express DAHP (EC 2.5.1.54,3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase) synthetase and tryptophan synthetase, reduce feedback inhibition of a reaction product on the tryptophan synthetase, and increase the yield of the tryptophan. The method is used for producing the tryptophan.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing ethanol by carrying out high temperature enzymolysis and fermentation on lignocellulose
InactiveCN105671090AImprove high temperature performanceHigh activityBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAlcohol ethyl
The invention discloses a method for producing ethanol by carrying out high temperature enzymolysis and fermentation on lignocellulose. The method for producing the ethanol by carrying out the high temperature enzymolysis and fermentation on the lignocellulose comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating a lignocellulose raw material, so as to obtain a pretreated raw material; (2) adding the pretreated raw material, cellulase, water and xanthan gum into an enzymatic vessel for carrying out pre-enzymolysis, and controlling dry material concentration of an enzymolysis system to be 15-25wt%; (3) pumping an enzymolyzed feed liquid into a fermentation tank, adding temperature-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae, and carrying out simultaneous saccharification and fermentation; and (4) pumping fermentation liquor into a rectification device and separating ethanol. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the xanthan gum is added into the enzymolysis system, high temperature tolerance of cellulase is improved, activity of the cellulase under high temperature enzymolysis condition is high, usage amount of the cellulase is reduced, enzymolysis efficiency of the lignocellulose is improved, and economy is improved.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
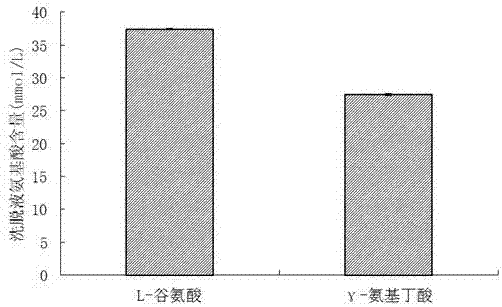
Double column production method of gamma-aminobutyric acid by immobilized cell and D101 resin
ActiveCN107287253AIncrease productionAchieve separationMicroorganism based processesFermentationManufacturing technologyGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention relates to a double column production method of gamma-aminobutyric acid by immobilized cell and D101 resin, which belongs to the technical field of green biological production; according to the double column production method, a D101 macroporous adsorption resin column is taken as an auxiliary reaction column and is coupled mutually with an immobilized enterococcus faecium cell reaction column, and the coupled macroporous adsorption resin column and the immobilized enterococcus faecium cell reaction column are connected with other auxiliary installation or equipment to form a cyclic reaction system, efficient conversion is realized as a reaction substrate is cycled between the D101 macroporous adsorption resin column and the immobilized enterococcus faecium cell reaction column, and productivity of the gamma-aminobutyric acid is improved; compared with a catalytic reaction method only using the immobilized enterococcus faecium cell reaction column, the output of the gamma-propalanine produced by the invention can be increased by 196.32%. Besides, purification of the gamma-aminobutyric acid also can be realized through the adsorption effect of the D101 resin column, a downstream process is simplified, the cost is reduced, and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Production method of tacrolimus
ActiveCN101280283AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismStreptomyces hygroscopicus
The invention discloses seed medium and fermentation medium for culturing streptomyces hygroscopicus (ACCC No.40417) and a new production method for tacrolimus, and belongs to the biomedical field. Through the microorganism fermentation and culturing, the amount of the dissolved oxygen and the flow acceleration of the substrate during the fermentation process are regulated and controlled, so as to improve the yield of the tacrolimus. The final yield of the tacrolimus can reach 380 mg / L finally, the operation in the overall fermentation process is simple, the concentration of the fermentation product (tacrolimus) in the fermentation liquid is high, the versatile is high, the popularization is easy, and industrialized production can be performed.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Microorganism and method for overproduction of gamma-glutamylcysteine and derivatives of this dipeptide by fermentation
InactiveUS20140342399A1Reduce cell viabilityReduce feedback inhibitionBacteriaPeptidesMicroorganismDipeptide
The invention relates to a prokaryotic microorganism strain capable of overproducing γ-glutamylcysteine and its derivatives bis-γ-glutamylcystine and γ-glutamylcystine, which can be prepared from a parent strain, wherein said strain has a reduced cellular glutathione synthetase activity compared to the parent strain, and has a cellular γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase activity which is more greatly increased than in a strain with similarly reduced cellular glutathione synthetase activity.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
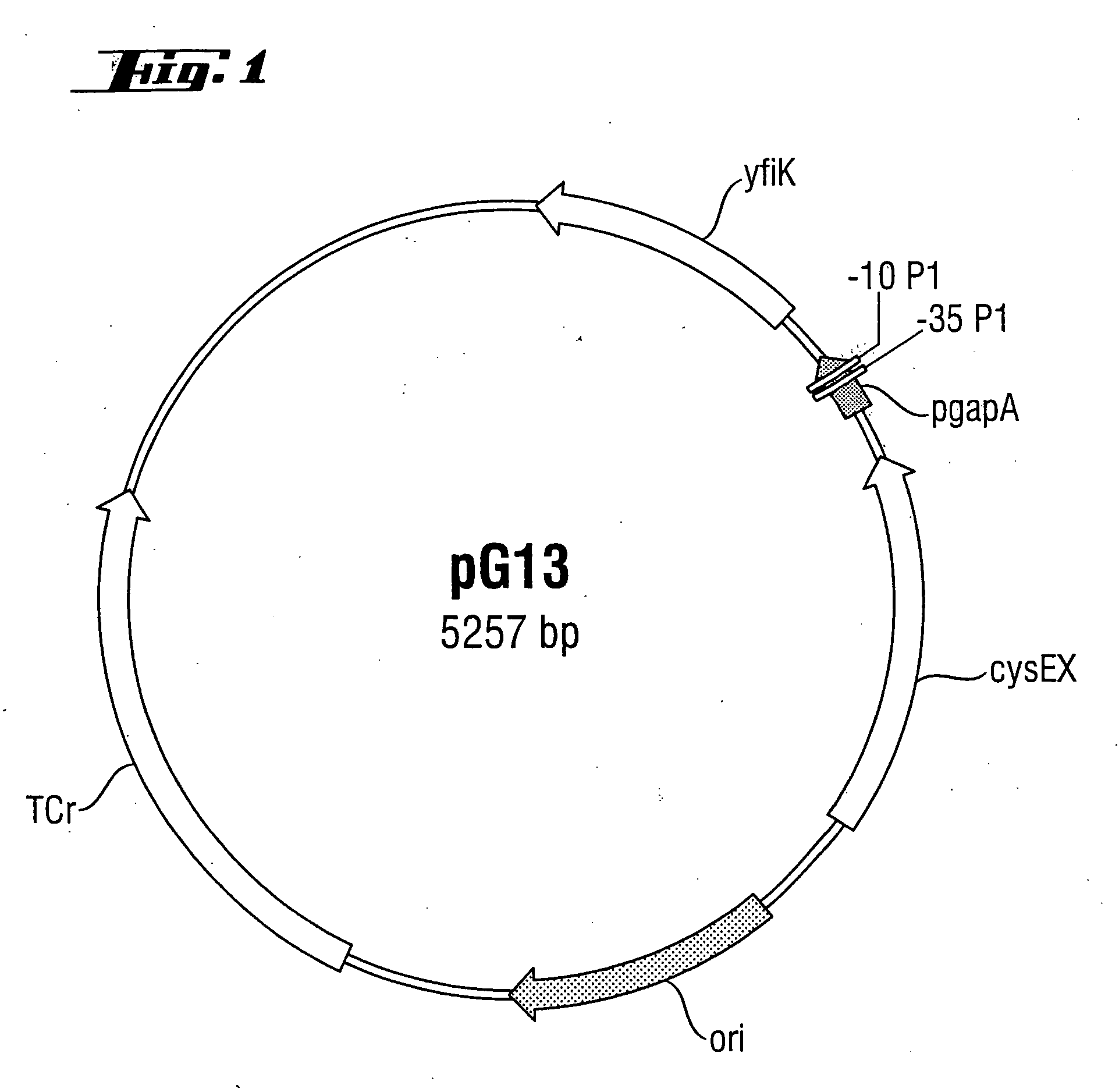
Method for fermentative production of amino acids and amino acid derivatives of the phosphoglycerate family
InactiveUS20060148041A1High activityHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCysteine thiolate
A microorganism strain suitable for fermentative production of amino acids of the phosphoglycerate family or derivatives thereof and producible from a starting strain, is based upon a starting strain having an increased activity of a yfiK-gene product or of a gene product of a yfiK homologue. The microorganism strain is a member of the family Enterobacteriaceae and is a member of the species E. coli. A plasmid has a Yfik-gene with a promoter and a genetic element for the deregulation of cysteine metabolism coding for a serine O-acetyl transferase and being subject tot a reduced feedback inhibition by L-cysteine.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
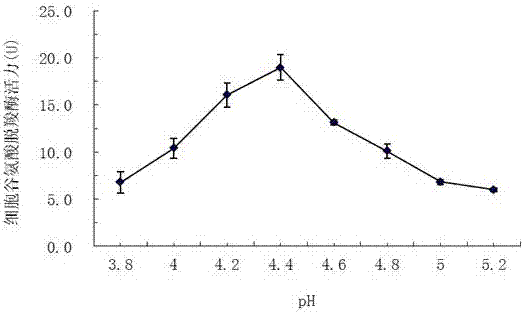
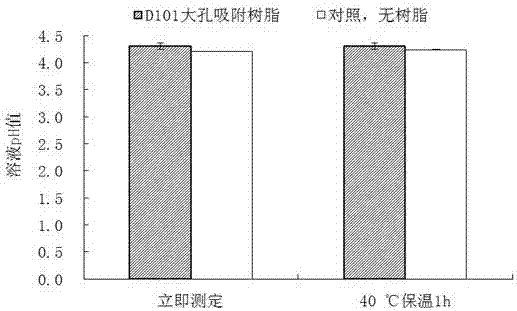
Method for increasing activity of GAD (Glutamate Decarboxylase) by using D101 macroporous adsorption resin
ActiveCN107326052AAvoid inactivationAccelerate the speed of leaving the active center of glutamic acid decarboxylaseMicroorganism based processesFermentationWater bathsGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a method for increasing the activity of enterococcus faecium Glutamate Decarboxylase by using D101 macroporous adsorption resin, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the D101 microporous adsorption resin is used as an enzyme activity accelerator of enterococcus faecium GAD, and a D101 microporous adsorption resin-GAD composite catalytic system is constructed according to a proportion that the mass of the D101 macroporous adsorption resin to the volume of a substrate solution to the volume of an enterococcus faecium bacterial suspension solution or a GAD free enzyme solution is 1 to 1 to 1; when the D101 microporous adsorption resin-GAD composite catalytic system is subjected to reaction in a water bath oscillator of which the temperature is 37 to 43 DEG C at 80r / min or stirring reaction in a stirring tank at a low speed for 24 to 36 hours, the yield of GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) can be increased by 18.54 to 149.11 percent; the D101 macroporous adsorption resin is capable of remarkably increasing the activity of the GAD, an exchange adsorption function of the D101 microporous adsorption resin on the GABA is also a purifying process of the GABA, a downstream extracting and purifying technology is simplified, and the production cost is reduced; the method is simple, green and environment-friendly.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com