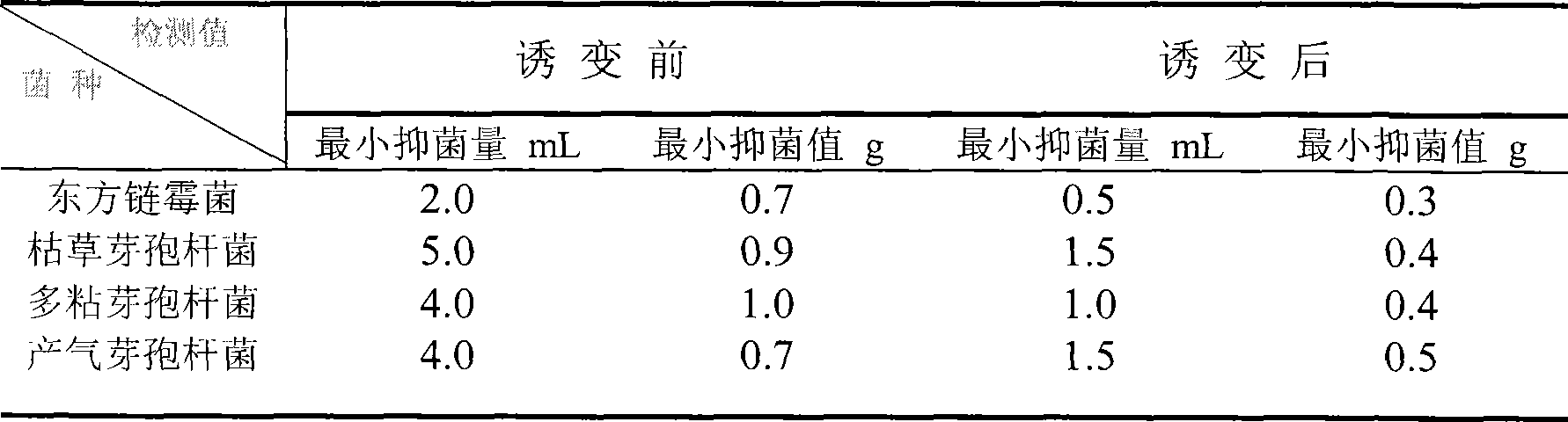
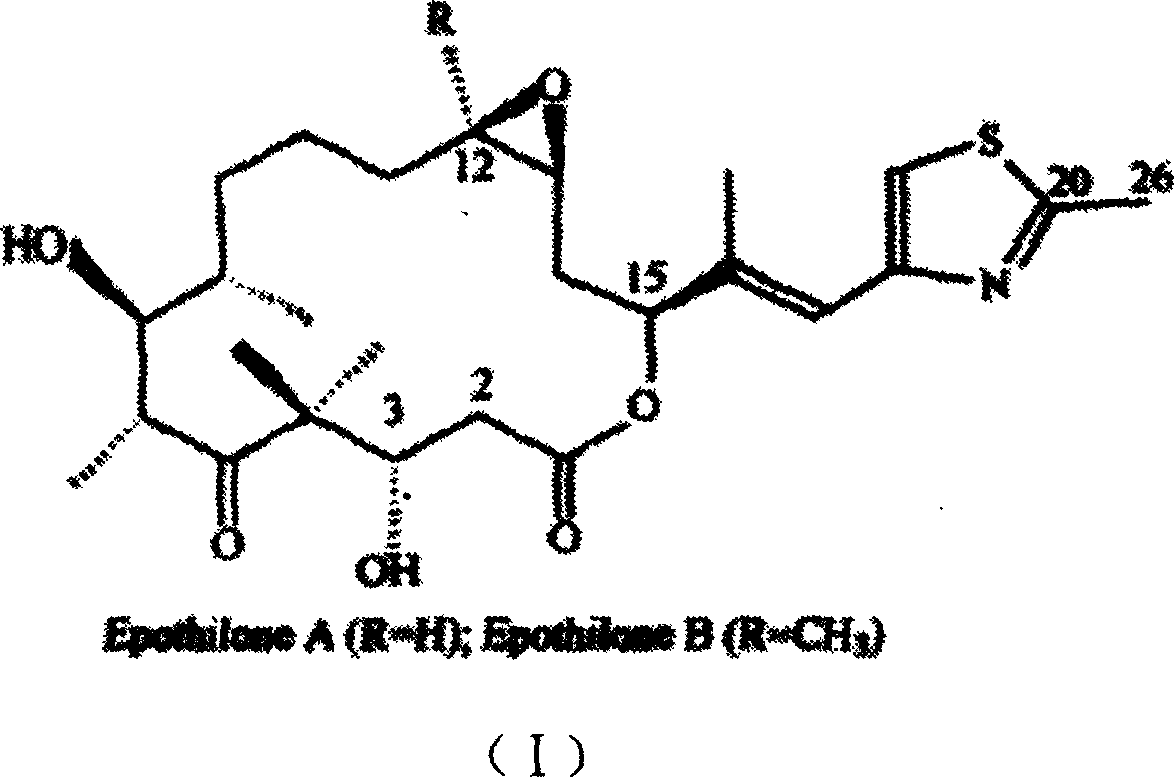
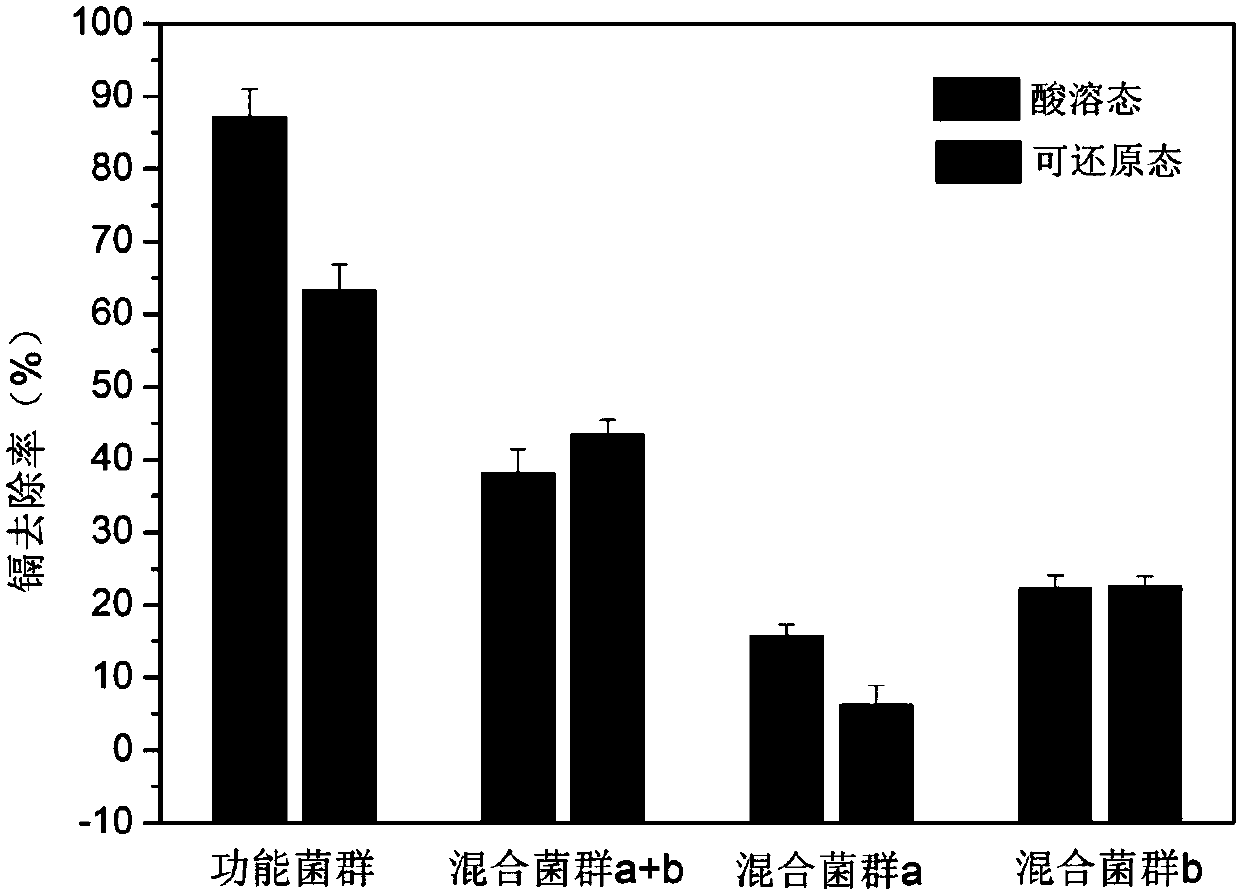
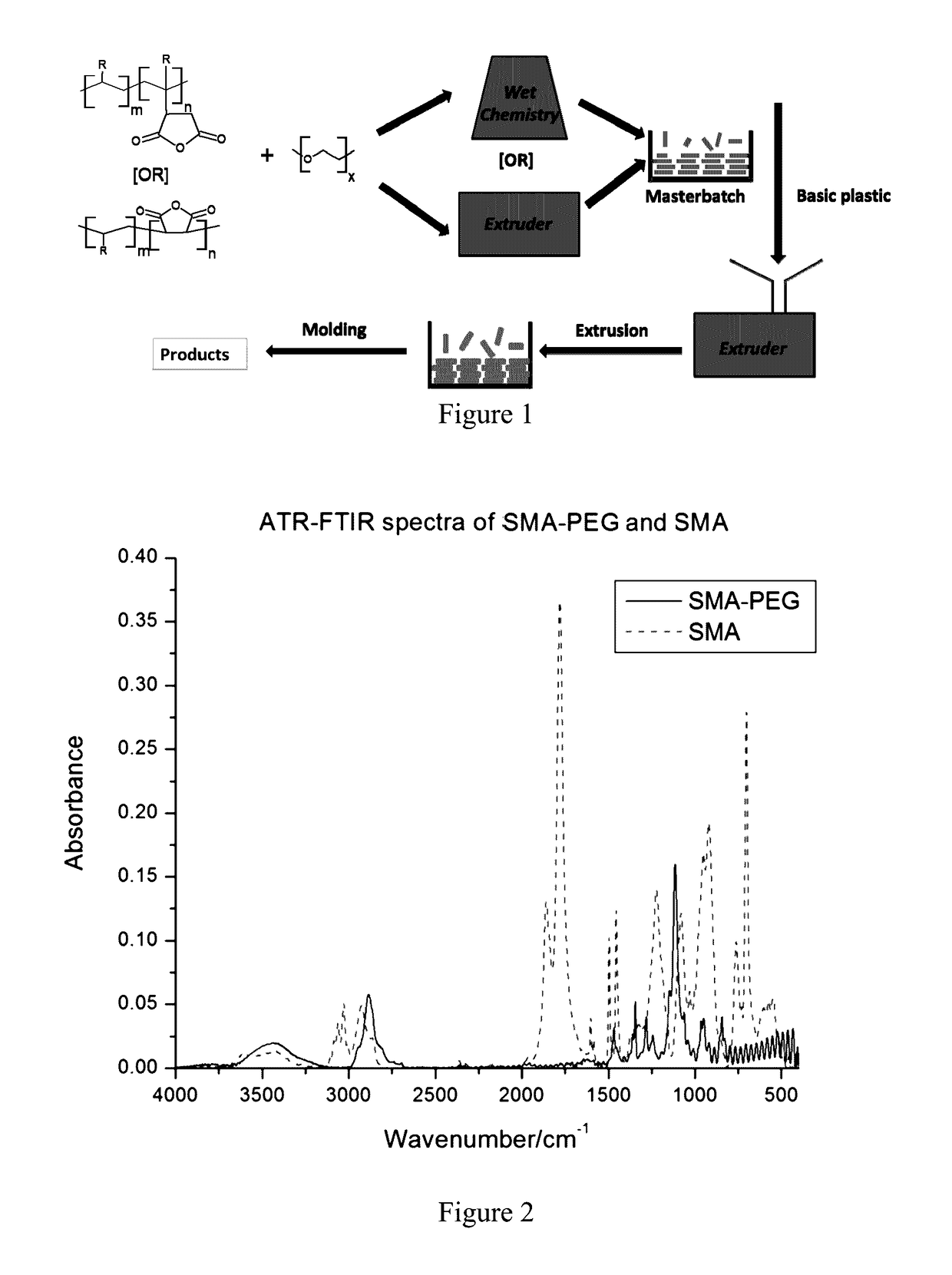
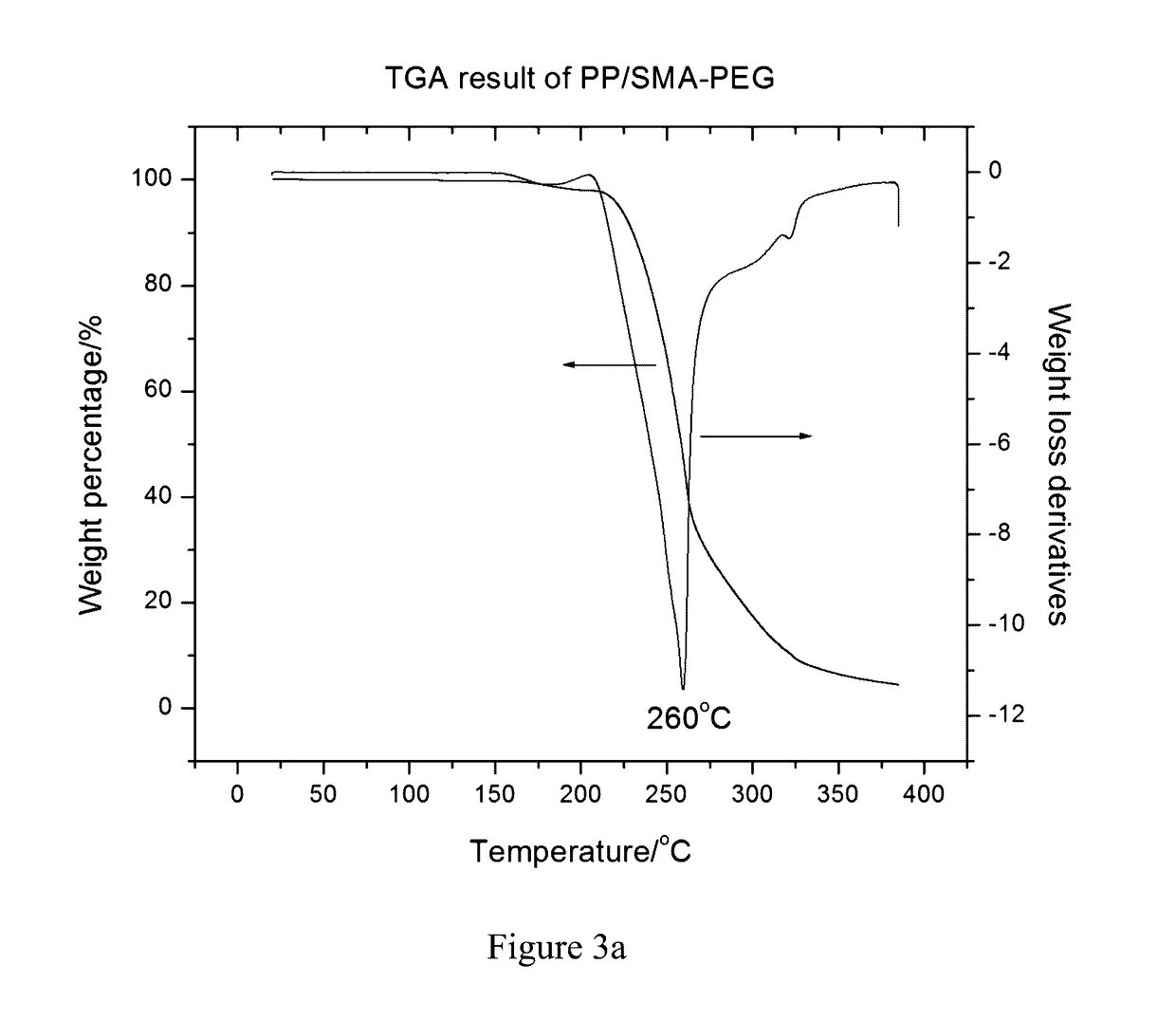
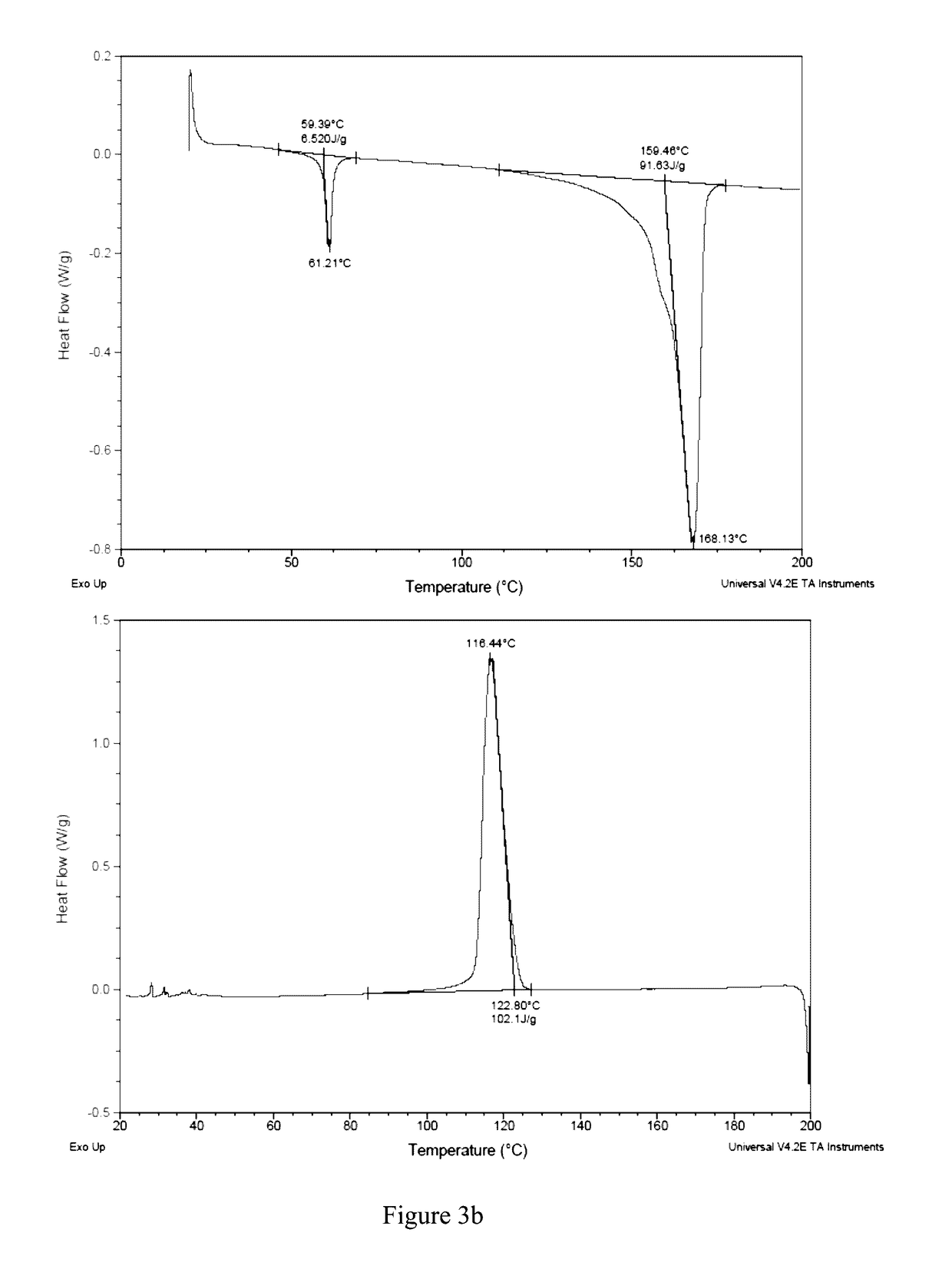
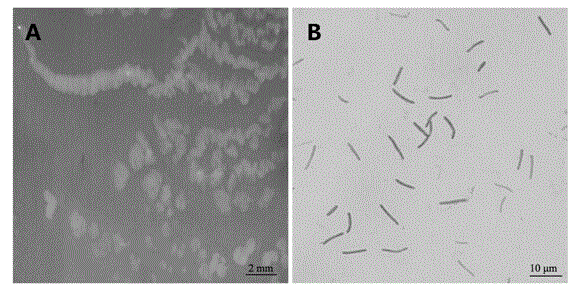
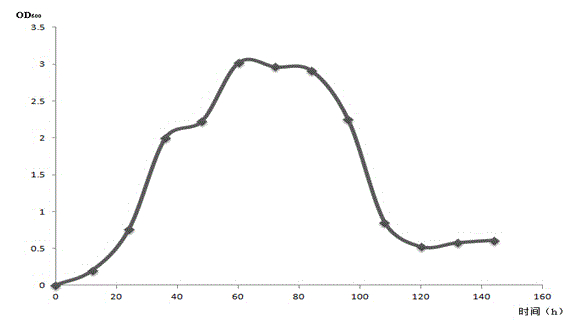
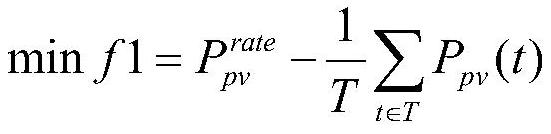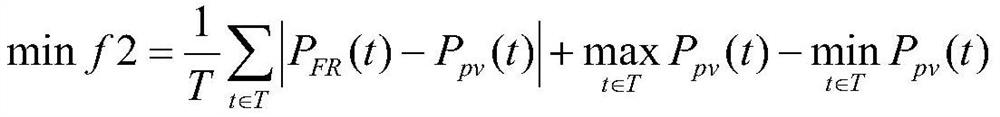Patents
Literature
59 results about "Myxobacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The myxobacteria ("slime bacteria") are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes, relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except for Anaeromyxobacter and Vulgatibacter. One of the myxobacteria, Minicystis rosea, has the largest bacterial genome with over 16 million nucleotides. The second largest is another myxobacteria Sorangium cellulosum. Myxobacteria are included among the delta group of proteobacteria, a large taxon of Gram-negative forms.
Sulfate reducing bacteria resisting microbial preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101235359AGrowth inhibitionReduce usageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMyxobacteriaLiquid product
The invention relates to a microbial agent of sulfate-reducing bacteria, which utilizes bacteria which can secrete antibiotic namely one or several of myxobacteria, streptomycete and bacillus to form single or mixed bacterial liquid product through culturing, or form single or mixed fermentation liquor after fermenting and extracting concentrated solution products. The process for preparing the microbial agent comprises the following steps: inoculating one or several of myxobacteria, streptomycete and bacillus whose bacterial strain is activated through a slant face on an optimum culture medium to culture, and then obtaining through project domestication and scale-up culture, or obtaining through fermenting the bacterial strain under pure culture condition and a mixed culture condition. The microbial agent can completely inhibit harmful bacterium from producing in membrane deposit, which can reduce the employment of chemical agent, and is beneficial for the protection of ecologic environment, and the microbial agent is particularly suitable for the prevention and cure of sulfate ash reducing bacteria corrosion in an oil field water re-injection system, various recycle water systems and a central air-conditioning cooling water system, preparation technology is simple, and the invention is easy to implement.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Special ferment bacterium biological water cleaning agent for fish ponds
InactiveCN101711512APromote circulationReduce oxygen consumptionPisciculture and aquariaBiological water/sewage treatmentDiseaseBacteroides
The invention relates to a special ferment bacterium biological water cleaning agent for fish ponds, which comprises a culture medium base material, a microbian compound preparation, a feather meal, multivitamins and a compound enzyme preparation. The invention has the advantages that the ferment bacteria can quickly decompose hydrogen sulfide, ammonia gas, methane and other harmful gases in the rearing pond; the favorable conditions of the water quality in the rearing pond is kept, the photosynthetic bacteria can accelerate the circulation of nutrient substances, improve the pH value, enhance the oxygen content and reduce the oxygen consumption of organic substances, and therefore, the water cleaning agent can effectively promote the circulation of phosphonium and nitrogen and reduce the accumulation of the bottom mud; and photosynthetic bacteria are beneficial, and have the functions of promoting the digestive absorption of animals, stimulating the growth and development, enhancing the immunologic function and inhibiting various pathogenic bacteria. The water cleaning agent is very effective for improving the water quality; and the water quality starts to become clear 3 hours generally after the water cleaning agent is used. The water cleaning agent has favorable actions on preventing and treating myxobacteria, gill rot, stigmatosis, desquamation, red fin disease, enteronitis and graze; and the water cleaning agent can enhance the yield per mu by 15-23%, reduce the feed coefficient by 18-23%, enhance the survival rate by 20-60% and increase the individual weight by 15%.
Owner:荆门市农润生物科技有限公司
Method for highly-effective producing epothilone using myxobacteria sorangium cellulosum
InactiveCN1769468ASuitable for growthGrowth does not affectMicroorganism based processesFermentationMyxobacteriaEpothilone
The invention provides a process for producing Epothilones by utilizing Sorangium cellulosum, which comprises improving fermentation culture medium of Sorangium cellulosum, and charging cyclodextrins or cyclodextrin derivatives into the fermentation culture medium. The process can realize higher output of Epothilones production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Mixotroph-type functional microbial flora capable of removing acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium in cadmium-polluted soil, and preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN108102970AReduced effectivenessHigh removal rateFungiBacteriaAcidithiobacillus thiooxidansTrichoderma
The invention discloses a mixotroph-type functional microbial flora capable of removing acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium in cadmium-polluted soil, and a preparation method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial treatment of heavy metal polluted soil. In the invention, the mixotroph-type functional microbial flora, which can high-effectively remove the acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium soil, is prepared by compounding autotrophic and heterotrophic microorganisms, i.e., the flora not only includes heterotrophic microorganisms, such as Geobacter metallireducens, Alicyclo bacillus, Acetobacter diazotrophicus, Anaeromyxobacter and trichoderma, but also includes autotrophic microorganisms, such as Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Thiobacillus caldus and bacillusacidoohilus. The invention solves the problems that compound functional microbial flora is poor in adaptability and is difficult to colonize when being appliedto polluted soil. The functional microbial flora guarantees high removal rate of the acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium in the polluted soil, significantly reduces bioavailability of cadmium and plant availability, and lays a certain fundament for promotion and application of microbial treatment of the cadmium-polluted soil.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +2
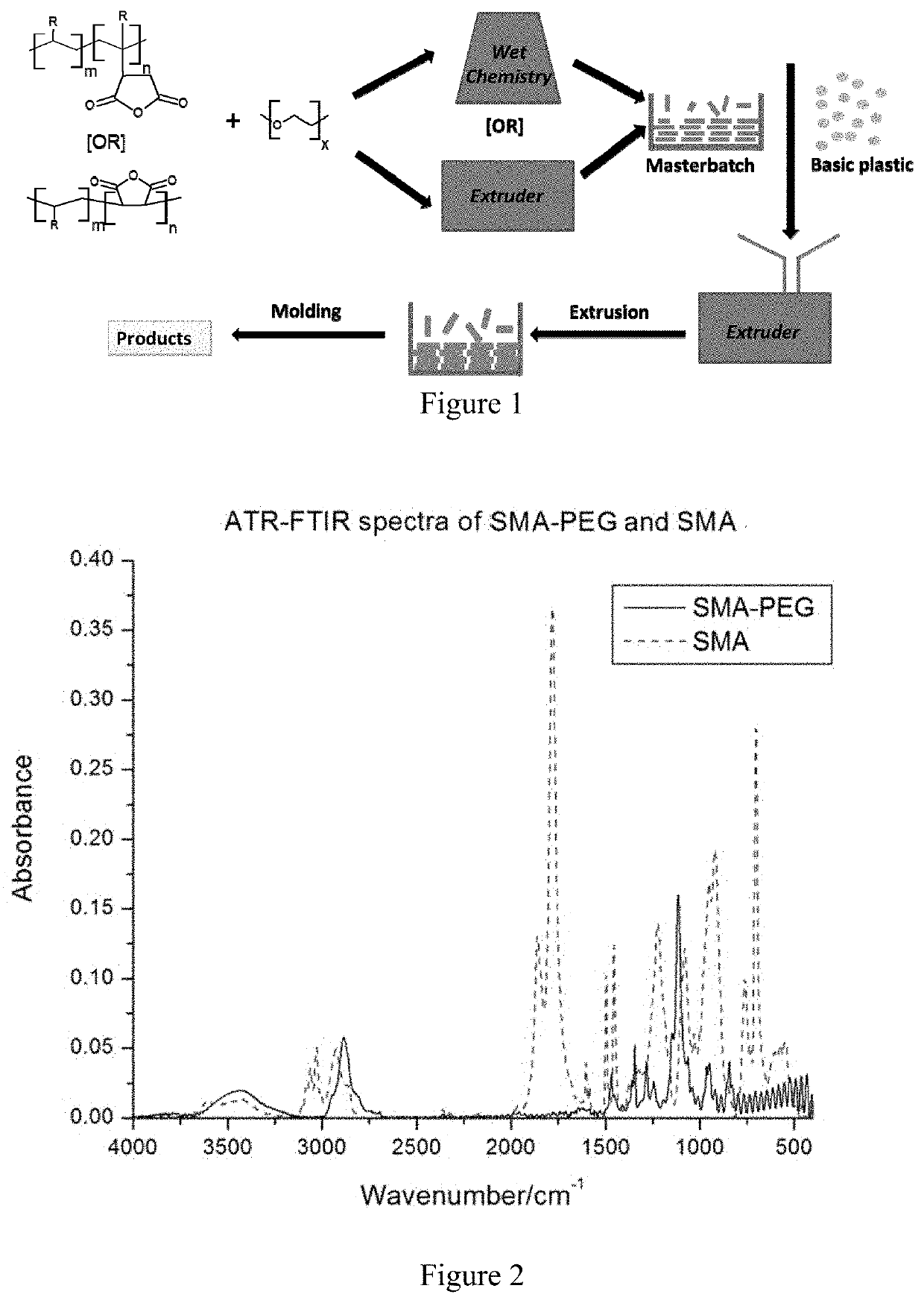
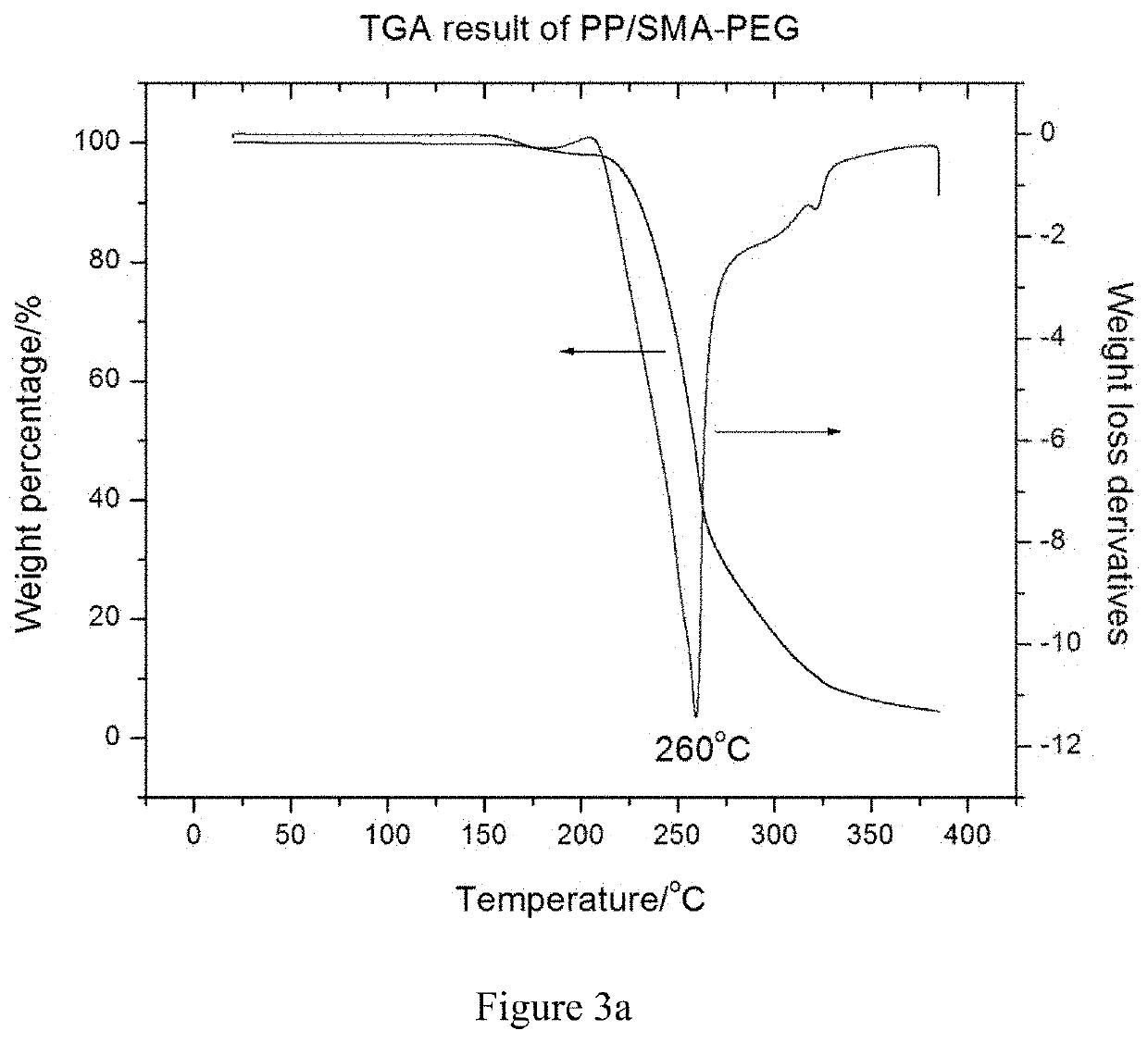
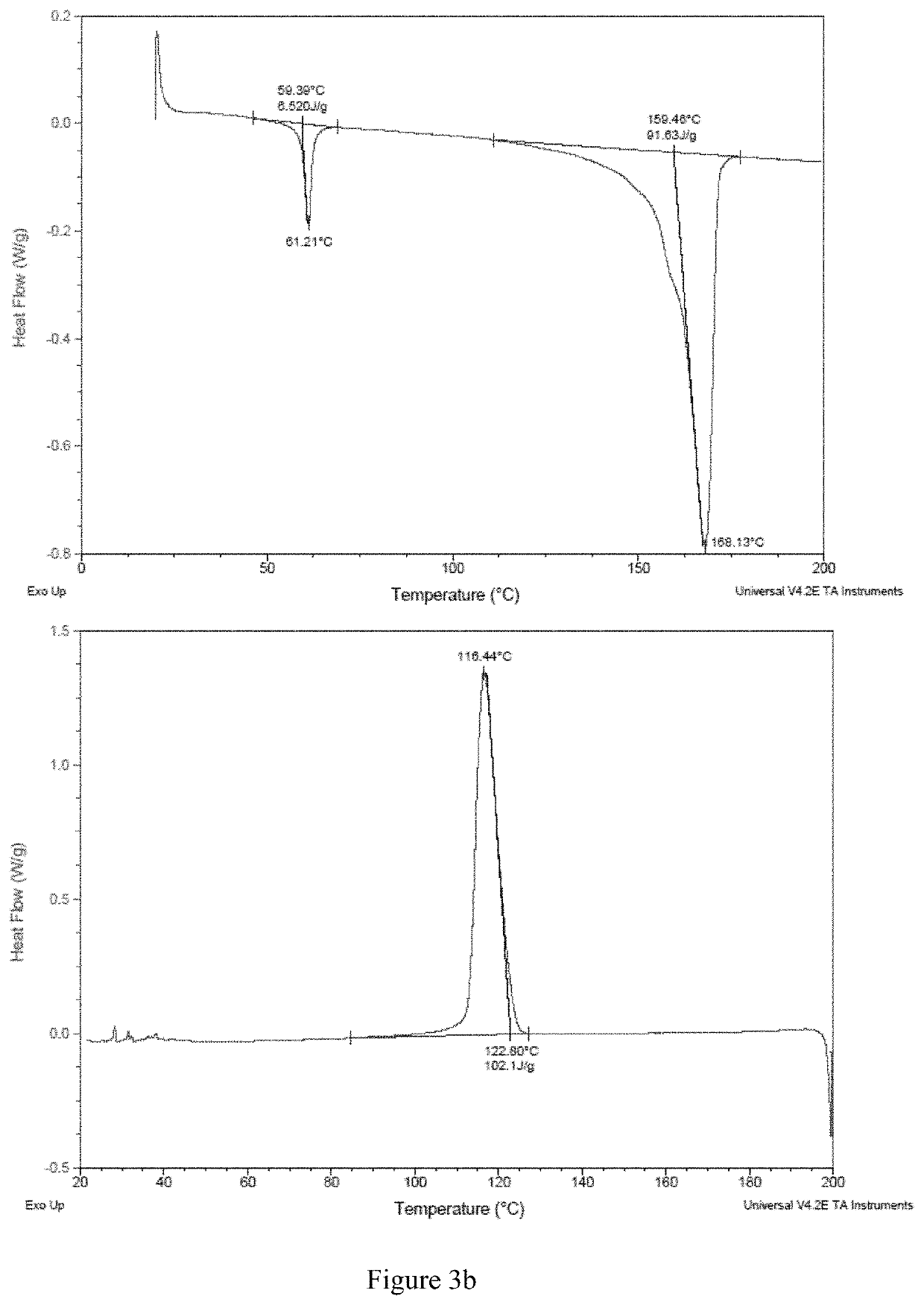
Built-in antimicrobial plastic resins and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20170129139A1Good chemical stabilityEliminate chanceBiocideAnimal repellantsFiberThermoplastic
A built-in and process-adaptive formulation of antimicrobial commodity thermoplastic resins with mixed compositions comprising of a polymer, a backbone linker, and a non-labile antifouling and biocompatible coupling agent which is melt-processable and enabled to be manufactured into finished products in the form of solid, monolith, tube, composite, fiber, film, sheet and varnish without the prerequisite of biocides or antimicrobial additives is disclosed. The said formulation is adapted to thermoforming and thermal curing processes including but not limited to melt compounding, spinning, extrusion, molding, compression foaming and drawing. The antimicrobial property is attributed to the persistent formation of a non-stick bacteria-repellent tethered layer in which the antifouling component of the said formulation is heterogeneously phase separated and / or surface migrated to the surface after product forming in order to minimize adsorption and / or colonization of bacteria.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Myxobacteria strain and antitumor activity metabolite thereof
The invention relates to a myxobacteria strain and an antitumor activity metabolite thereof. The myxobacteria strain is the myxococcus STXZ72, Myxococcus sp.STXZ72, and the preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M2015353. The invention further comprises a separation and purification method of the antitumor activity metabolite of myxobacteria. The metabolite of Myxococcus sp.STXZ72 is prepared by utilizing the separation and purification method. Antitumor activity determination proves that the myxobacteria strain is capable of effectively inhibiting the activity of a variety of tumor cells and also has very low toxicity to normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Owner:湖南晴天生物科技有限公司
Myxobacteria and applications thereof
ActiveCN111621435AHas a broad-spectrum inhibitory effectVarious suppression strategiesBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMyxobacteria
The invention discloses myxobacteria and applications thereof. The myxobacteria M34 is assigned the accession number GDMCC No: 61026. The myxobacteria M34 can obviously inhibit the growth of plant pathogenic fungi and includes Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn causing rice sheath blight and Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense race 4 and Colletotrchum musarum Cooke et Mass causing banana vasicular wilt, and canprey on Pseudomonas syringae GIM 1.330, Ralstonia solanacearum GIM 1.70, Xanthomonas campestris JCM 20466 and Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens GIM 1.343. The strain has broad-spectrum inhibition effectson plant pathogens, is various in inhibition strategy including the direct inhibition of fungal growth and the predation of bacteria and has good application values on preparing Microbial fertilizer additives and biocontrol bacterial agents.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
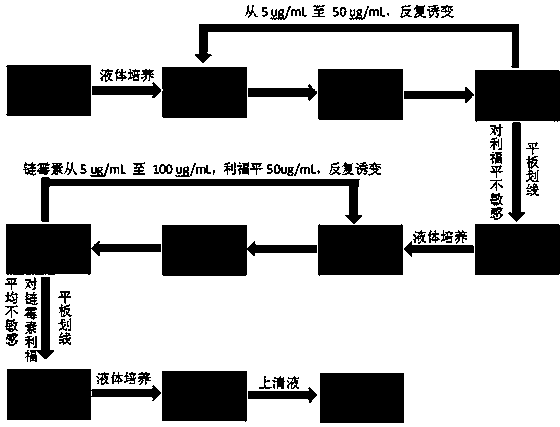
Mutation screening method and application of streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1
The invention discloses a mutation screening method of a streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1. The mutation screening method comprises the steps of inducing mutation of streptomyces coelicolor and streptomyces Lzsg6 through nitrosoguanidine to obtain a streptomyces mutant library, and screening the mutant library through rifampicin and streptomycin to obtain a strain with a transcription system and a translation system in mutation. The invention also discloses a streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1 and application thereof. The streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1 disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the strain contains substances having bacteriostatic activities, and the method of nitrosoguanidine (NTG) inducing as well as rifampicin and streptomycin screening can activate silent genes of the streptomyces to obtain a new metabolite, thus obtaining a new antibiotic; meanwhile, the mutation screening method has the advantages of simple operation, short cycle and high efficiency, and is not only applicable to streptomyces but also suitable for such microorganisms as myxobacteria rich in secondary metabolites; the mutation screening method has good popularization and application values.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
Three-strain balloon slime bacteria and sifting motion purification process
The invention relates to three bacteria Angiococcus and a method for screening and purifying Angiococcus. Rabbit excrement is used as raw material for screening, and an antifungal is used to inhibit the growth of fungi such as mold and so on. Flat screening, streaking, dilution and purification, low-temperature freezing and thawing, heat treatment and so on are adopted in turn for screening and purification. A calcium chloride water culture medium which is crossways streaked by microzyme and colibacillus (living or dead fungi) is further screened to get three bacteria through separation. The three bacteria belong to Angiococcus according to the characteristics of mycology. According to Bergey Manual of Determinative Bacteriology (the ninth edition), the three bacteria belong to three new bacterial strains.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Microecological preparation for green aquaculture
InactiveCN107523520AMaintain ecological balancePromote healthy and stable developmentFungiBacteriaMyxobacteriaAquaculture industry
The invention discloses a microecological preparation for green aquaculture. The microecological preparation comprises the following components in parts by weight: 25-35 parts of bacilli, 5-8 parts of myxobacteria, 3-5 parts of lactic acid bacteria, 20-30 parts of saccharomycetes, 10-15 parts of nitrobacteria, 2-5 parts of photosynthetic bacteria, and 1 part of a culture medium. According to the microecological preparation for green aquaculture, the prepared strain is outstanding and high in viable organism content through the scientific strain selection and the culture medium design, and can be stored for more than 24 months. The microecological preparation is capable of effectively removing inorganic nitrogen and organic nitrogen in culture wastewater, and the nitrogen removing effect is outstanding; the ecological balance at the bottom part of water is maintained; in addition, the microecological preparation is stable in quality, safe, reliable, green, environmentally friendly, free from pollution, and obvious in effect of promoting the healthy and stable development of the aquaculture industry.
Owner:苏州苏湘特种水产养殖场
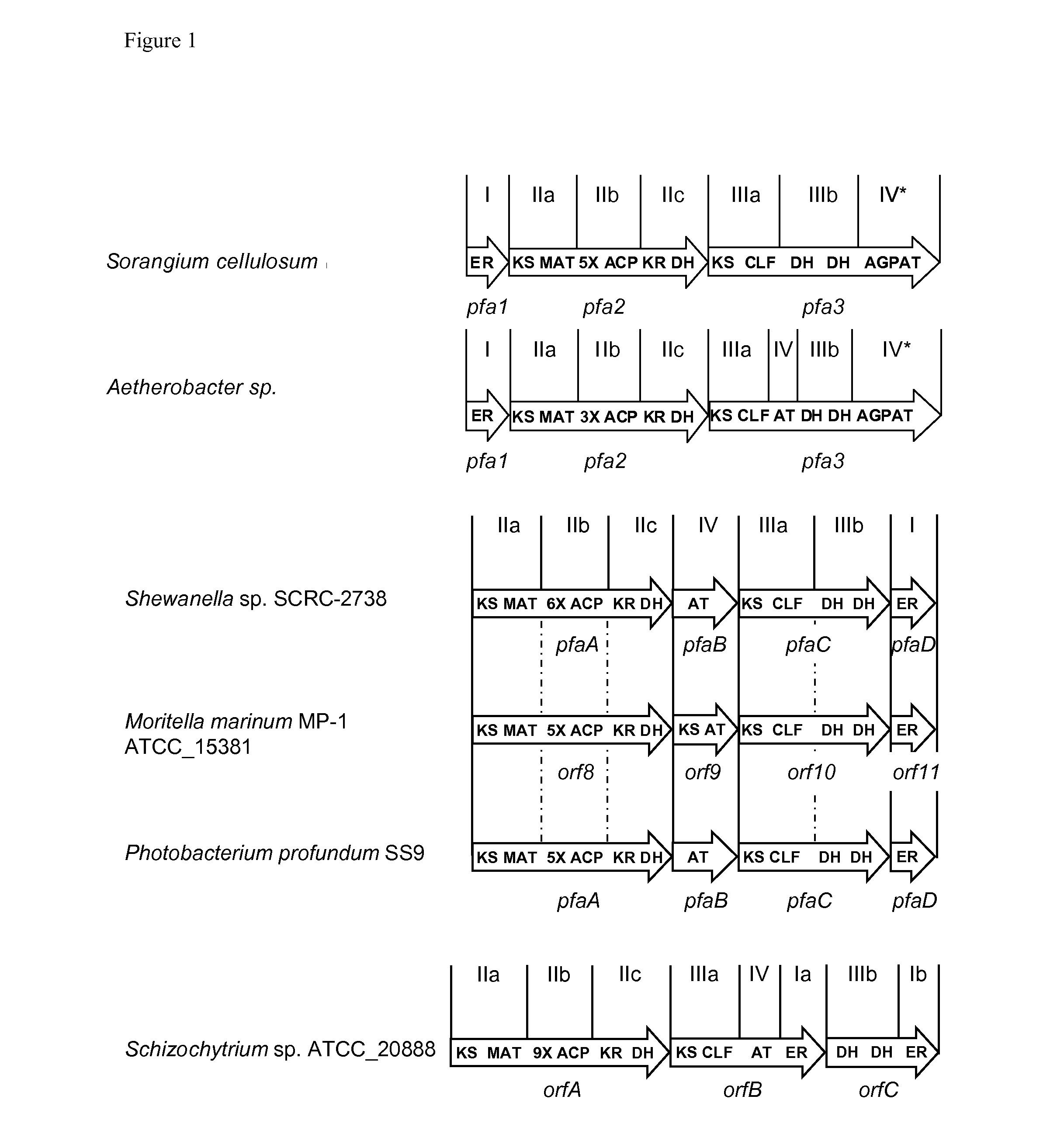
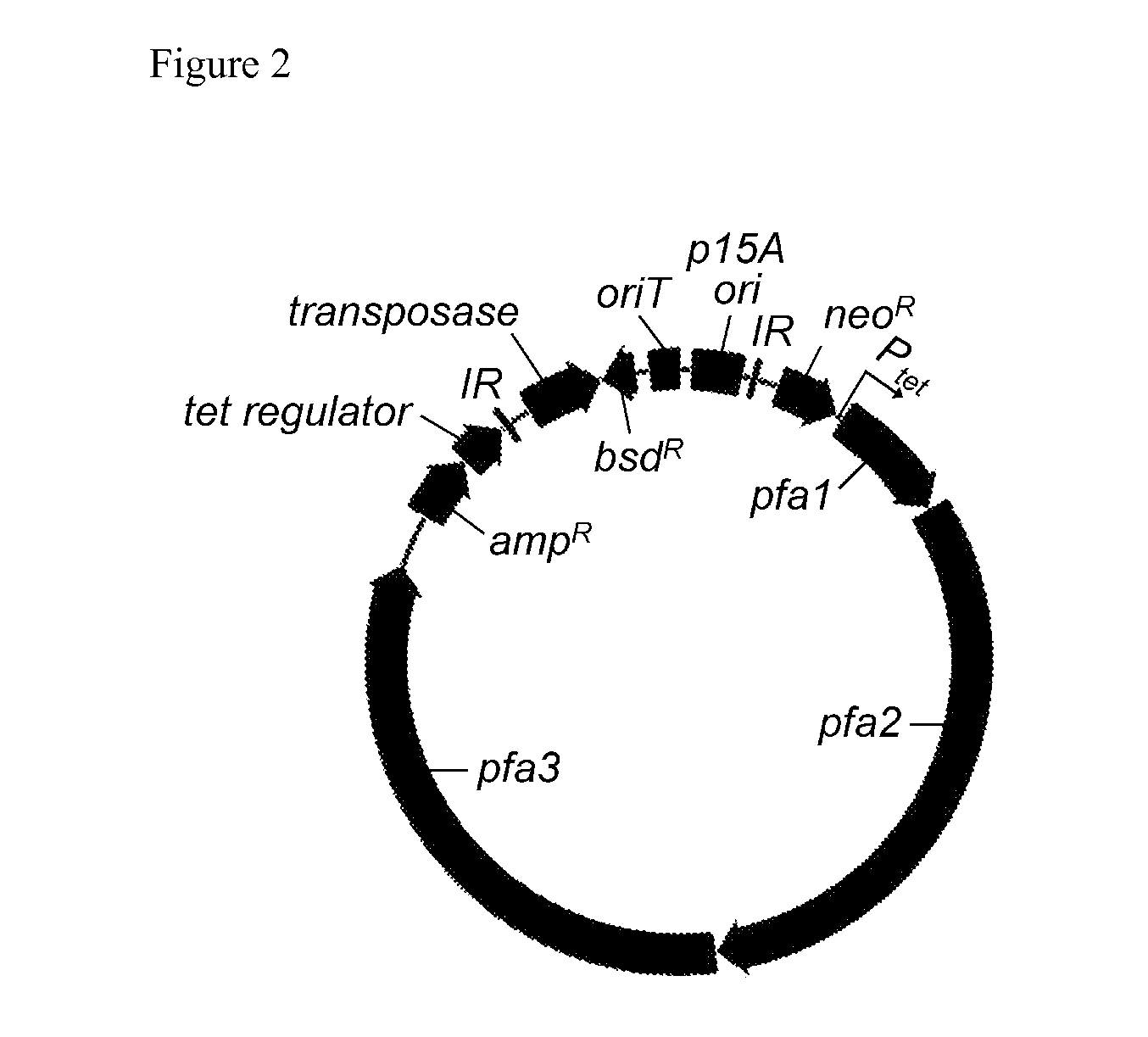
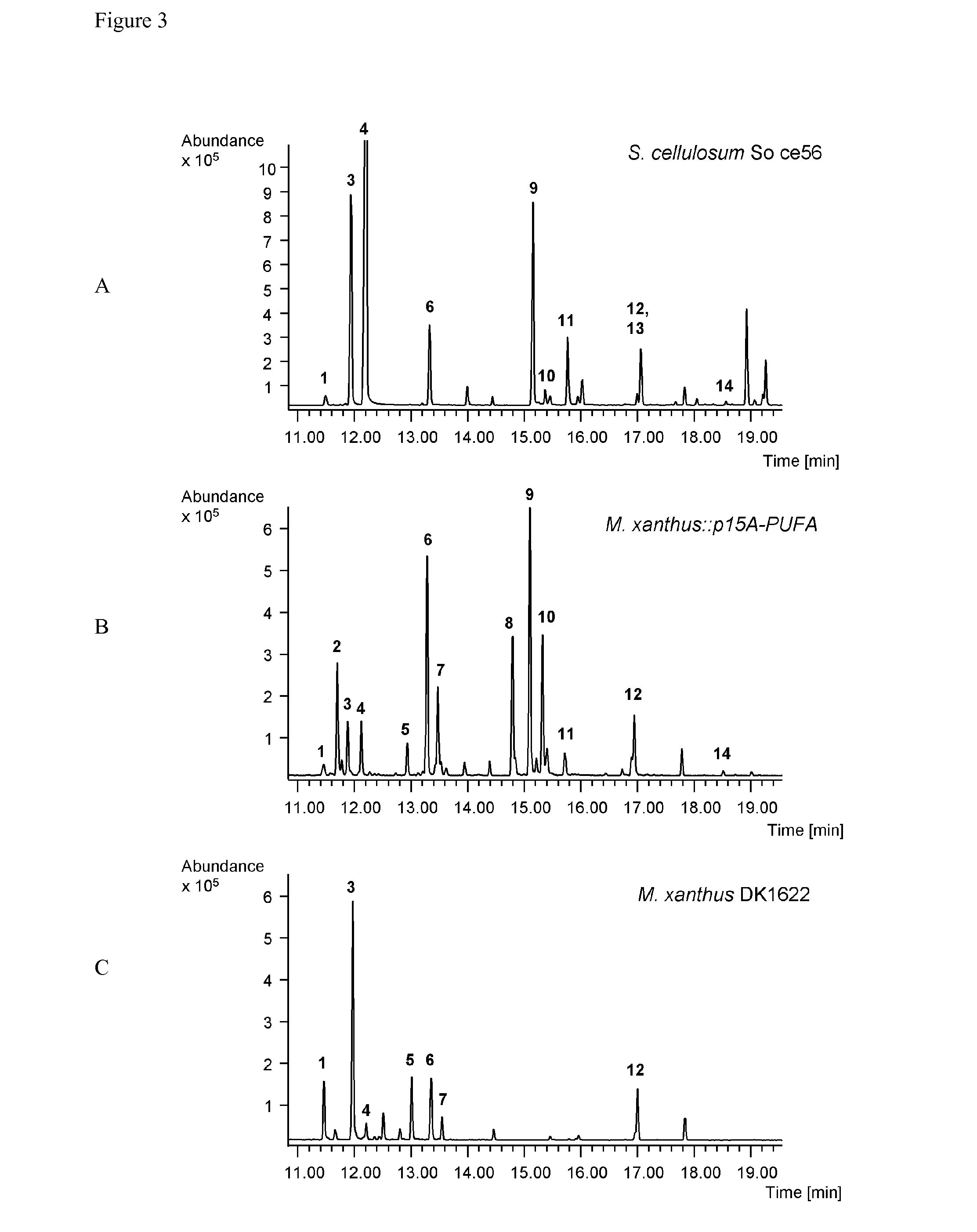
Production of fatty acids by heterologous expression of gene clusters from myxobacteria
The invention relates to a process for producing one or more polyunsaturated fatty acids by means of heterologous gene expression comprising the steps of providing a production organism which comprises a heterologous gene cluster encoding a polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic pathway encompassing a subsequence ER encoding an enoylreductase and a subsequence AT encoding an acyltransferase, growing the production organism in the presence of a fermentable carbon source whereby one or more polyunsaturated fatty acids are produced, and optionally recovering the one or more polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:UNIV DES SAARLANDES
Microbial flocculating agent for phosphorus removal, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108060179AIncrease profitImprove production efficiencyMicroorganismsWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMyxobacteria
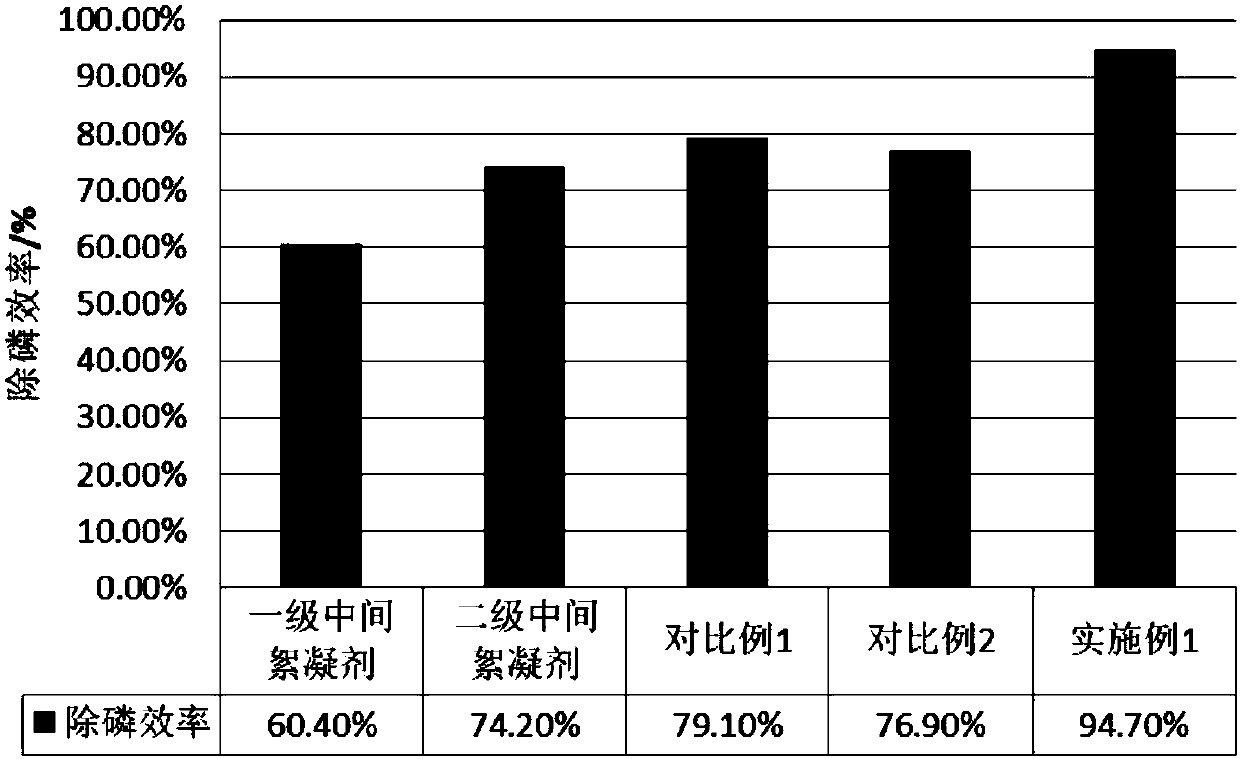
The invention discloses a microbial flocculating agent for phosphorus removal, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: inoculating acrude fiber raw material with flocculant-producing bacteria, and carrying out aerobic fermentation to obtain a primary fermentation material; inoculating the primary fermentation material with Clostridium cellulolyticum, and carrying out anaerobic fermentation to obtain a secondary fermentation material; inoculating the secondary fermentation material with myxobacteria, and carrying out aerobic fermentation to obtain a tertiary fermentation material; and extracting the tertiary fermentation material with ethyl acetate to obtain the microbial flocculating agent. The the crude fiber raw materialis inoculated with the flocculant-producing bacteria, the flocculant-producing bacteria are used to perform primary biological conversion on the crude fiber raw material, the primary fermentation material is continuously inoculated with the Clostridium cellulolyticum, the secondary fermentation material is continuously inoculated with the myxobacteria, and the myxobacteria can use dead or low-activity flocculant-producing bacteria in the secondary fermentation material as a nutrient source and further generate metabolites capable of precipitating phosphates in sewage, so the raw material utilization rate and the production efficiency are greatly improved.
Owner:卢梅雅
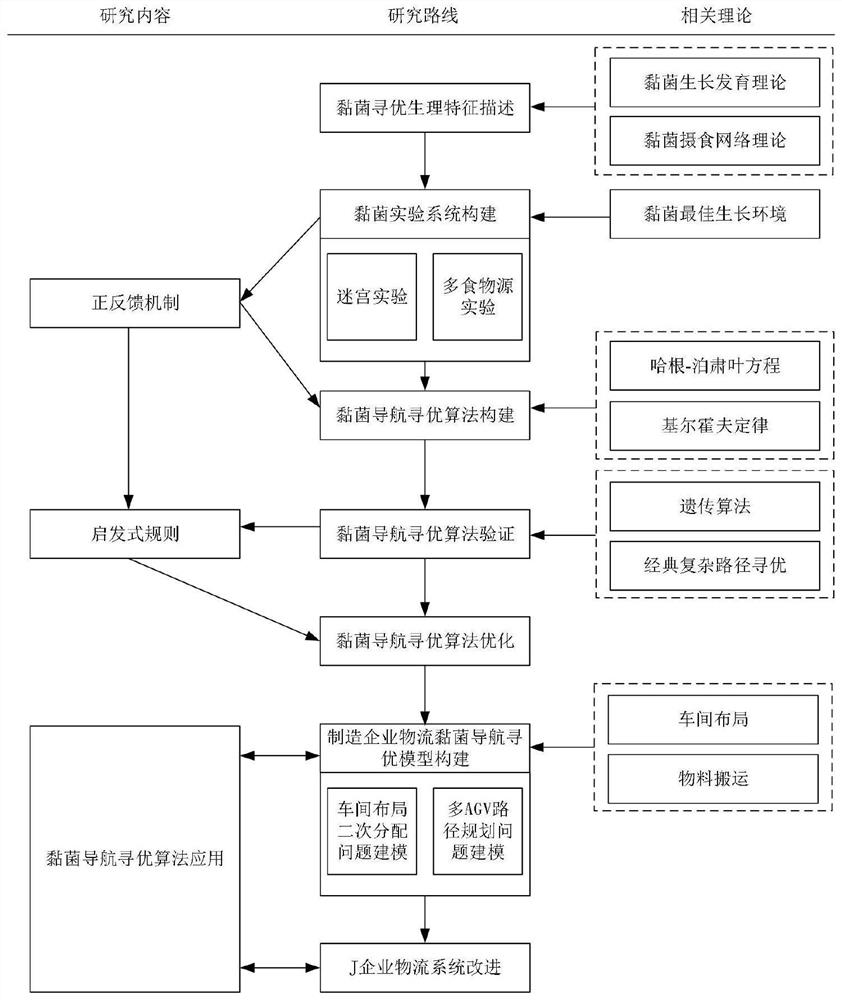
Optimization algorithm for manufacturing enterprise logistics based on myxobacteria navigation
PendingCN113589811ASolve the logistics problems of manufacturing enterprisesSolve logistics problemsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesMyxobacteriaLogistics management
The invention discloses an optimization algorithm for manufacturing enterprise logistics based on colistia navigation. The optimization algorithm comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a colistia culture environment, giving a positive feedback mechanism for colistia navigation optimization, constructing a colistia navigation optimization algorithm, proposing a heuristic rule, and designing a non-shortest path elimination model; and constructing a workshop secondary distribution problem model based on a myxus navigation optimization algorithm, designing a multi-objective function covering the minimum logistics quantity, the maximum area utilization rate and network cross congestion correction parameters, setting constraint conditions including boundary constraints and spacing constraints, and performing optimization processing for the material handling problem in a manufacturing enterprise logistics system. According to the method, a new intelligent bionic algorithm is provided based on the intelligent behavior of the myxobacteria, the method can effectively solve the problem of path optimization of the logistics system of the manufacturing enterprise, and the future logistics scheme of the enterprise can be predicted more accurately.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating white head-mouth disease of fishes
InactiveCN103933184AEasy to solveGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsAnthropod material medical ingredientsDiseaseMyxobacteria
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating white head-mouth disease of fishes and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines. The composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 4-15 parts of gallnuts, 6-18 parts of cyrtomium fortunei, 1-8 parts of pomegranate barks, 4-15 parts of radix sophorae flavescentis, 6-18 parts of golden cypress, 2-10 parts of encalyptus robusta, 2-10 parts of hairyvein agrimony, 1-8 parts of quispualis indica and 1-8 parts of cortex acanthopanacis. The traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating white head-mouth disease of fishes provided by the invention is reasonable in compatibility and can inhibit and eliminate myxobacteria in fishes by the effect of traditional Chinese medicines which supplement each other so as to better prevent and treat the white head-mouth disease. The effective rate for treatment reaches up to over 99%. The traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention is green and pollution-free, free from any toxic effect and suitable for being popularized and used on a large scale.
Owner:湖州天健兽药有限公司
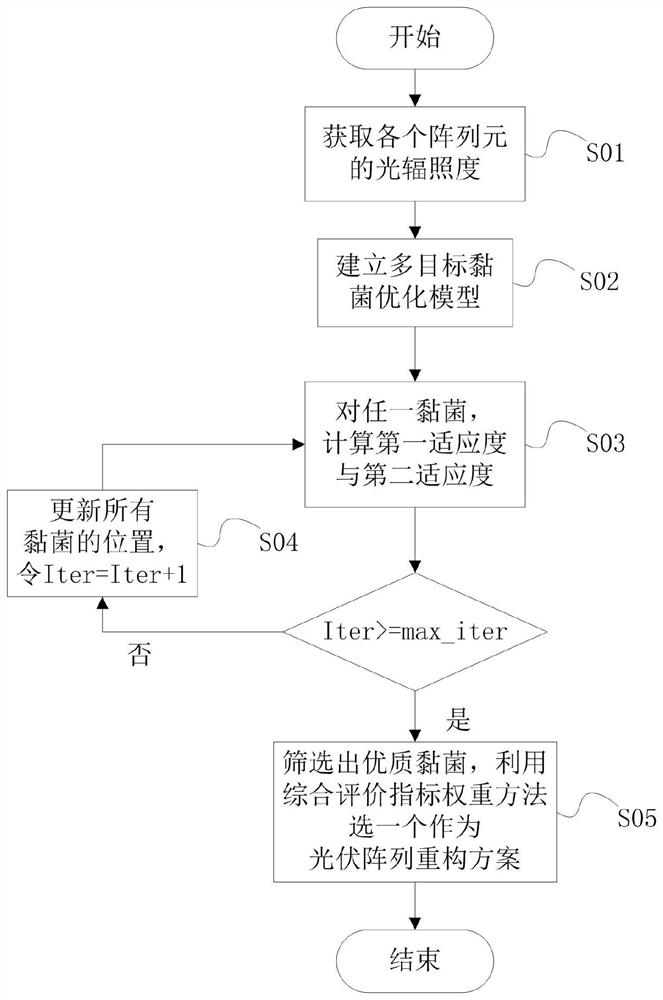
Method and system for reconstructing photovoltaic array based on multi-target myxobacteria optimization algorithm
ActiveCN113268931AIncrease output powerAcquisition speed is fastArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationMyxobacteriaAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of power system control, and provides a method and a system for reconstructing a photovoltaic array based on a multi-target myxobacteria optimization algorithm. The method for reconstructing the photovoltaic array based on the multi-target myxobacteria optimization algorithm comprises the steps of acquiring light irradiance of each array unit of the photovoltaic array under local shadow, establishing a photovoltaic array model, utilizing the multi-target myxobacteria optimization algorithm to carry out multiple iterations on all myxobacteria positions, and in each iteration, according to the current position, obtaining the output power of the photovoltaic array by each myxobacteria, updating the two fitness degrees, obtaining all the colistis of the last iteration, screening all the high-quality colistis from the colistis, selecting one colistis from the high-quality colistis by using a comprehensive evaluation index weight method, and restoring the position of the colistis into a reconstruction scheme of the photovoltaic array. According to the method for reconstructing the photovoltaic array based on the multi-target myxobacteria optimization algorithm, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the photovoltaic array is improved, and the method can better participate in secondary frequency modulation of a power grid.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Cultivation method of ganoderma lucidum
ActiveCN112970509AAwaken Growth PropertiesFavorable for large-scale production applicationsBacteriaCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologyMyxobacteria
A cultivation method of ganoderma lucidum comprises the following steps of 1, putting female parent ganoderma lucidum into an aqueous solution, controlling the water temperature to be 13 DEG C-15 DEG C, standing for 7-10 days, and then performing coarse filtration to obtain a myxobacteria fission cell solution for later use; 2, replacing the female parent ganoderma lucidum with a new aqueous solution, and controlling the temperature at 18 DEG C-26 DEG C to obtain a fungal spore and bacterial propagule solution; and 3, mixing the myxomycete fission cell solution with the fungal spore and bacterial propagule solution, and adding food-grade condensate gel into the mixed solution, so that myxomycete and fungal bacteria in artificially synthesized jelly ganoderma lucidum continue to generate the ganoderma lucidum which gradually becomes a natural state. By means of the cultivation method, artificial domestication of wild ganoderma lucidum is achieved, and the growth characteristics of the wild ganoderma lucidum are aroused; therefore, a foundation is laid for quick conversion into normal production, and large-scale production and application of the ganoderma lucidum are facilitated; the formed ganoderma lucidum are bright in color, good in shape, rich in nutrition and excellent in quality.
Owner:河北兴华圣缘生物科技有限公司
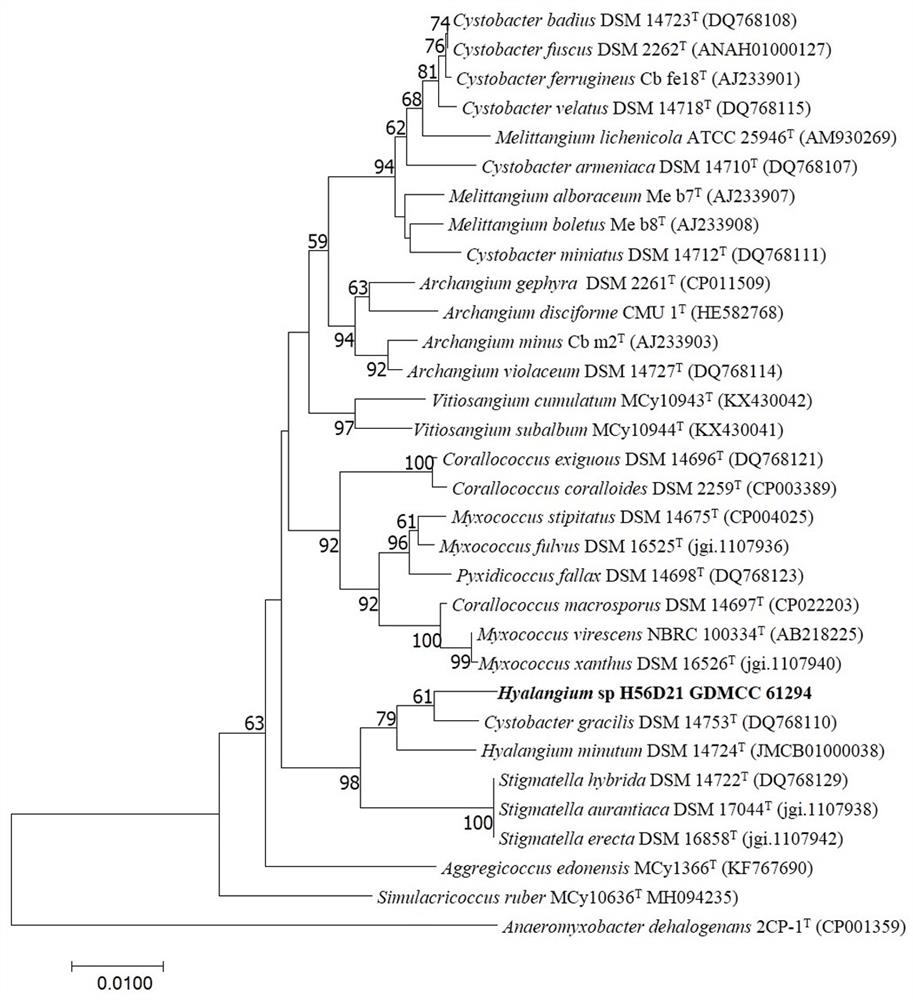
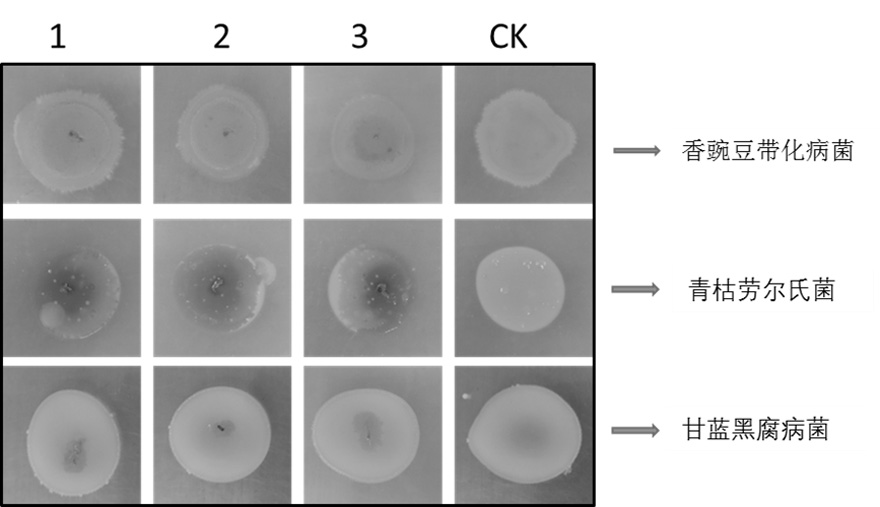
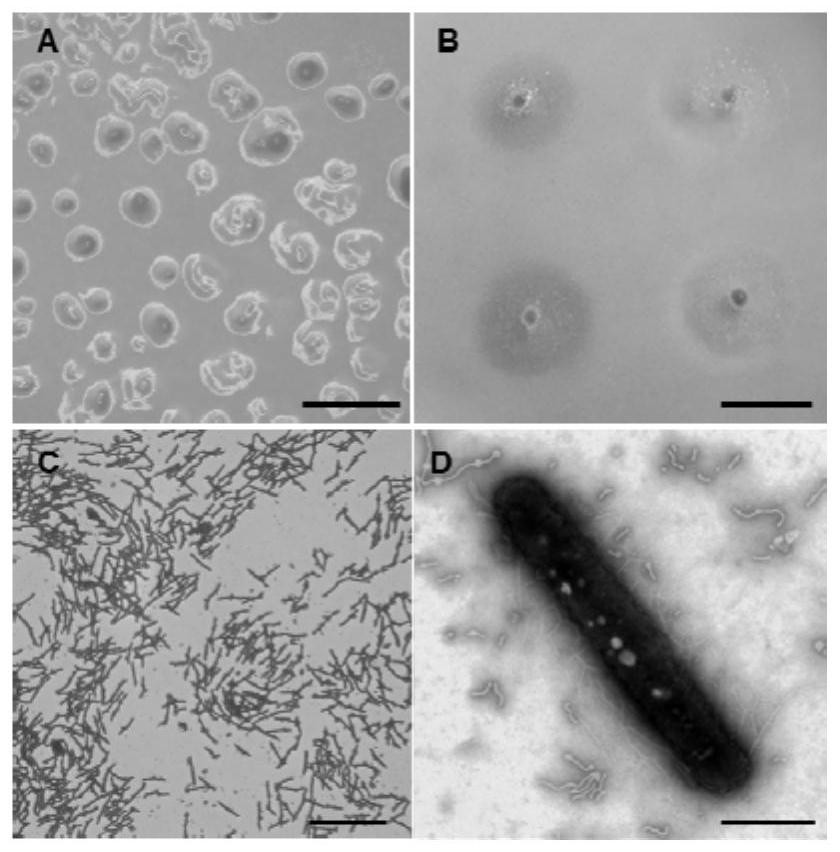
Myxobacteria H56D21 preying on phytopathogen and application of myxobacteria H56D21
The invention discloses myxobacteria H56D21 preying on phytopathogen and application of the myxobacteria H56D21, and belongs to the field of microbial technology and biological control. The ANI value and the dDDH value of the strain H56D21 and the similar model strain are analyzed, and the result shows that the strain H56D21 is a new species of Hyalangium. The Hylalangium sp.H56D21 is preserved in the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on November 17, 2020, the address is the 5th floor of the building 59, No.100 courtyard, Xianlie Middle Road, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, the postcode is 510070, the preservation number is GDMCC No: 61294, and the Hylalangium sp.H56D21 can prey plant pathogenic bacteria, has broad-spectrum predation characteristics and can be used for biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Myxococcus xanthus preying on ralstonia solanacearum and application of myxococcus xanthus in biological prevention and control of tomato bacterial wilt
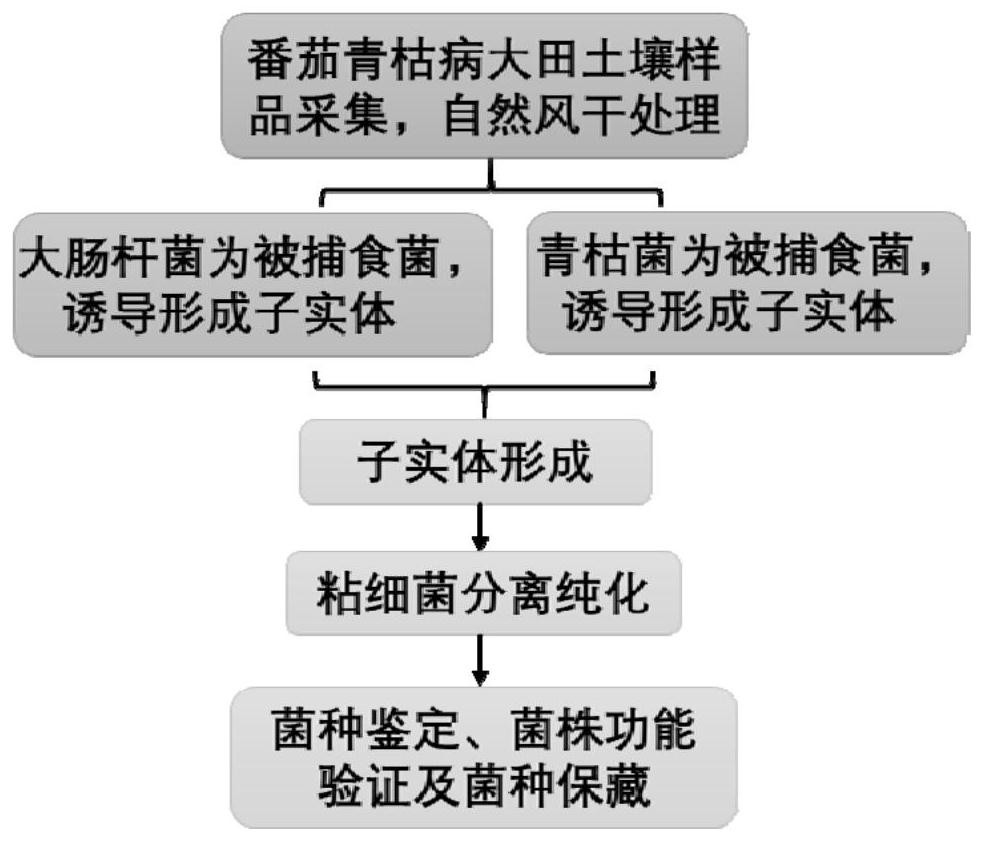
The invention discloses myxococcus xanthus preying on ralstonia solanacearum and application of the myxococcus xanthus in biological prevention and control of tomato bacterial wilt. The invention discloses Myxococcus xanthus R31, and the preservation number of the Myxococcus xanthus R31 is GDMCC No: 61842. According to the invention, plant pathogen ralstonia solanacearum is innovatively adopted as a predatory bacterium, a myxobacteria strain R31 is successfully separated and screened from a collected soil sample by using a predatory bacterium induction method, the myxobacteria strain R31 is identified as myxobacteria xanthus, the strain can prey on multiple strains of ralstonia solanacearum with different pathogenicity in the growth process and pathogenic bacteria are split to provide nutrients for self growth. The myxobacteria preys on ralstonia solanacearum, and physiological and biochemical characteristics and physiological differentiation of strains are not distinguished, so that broad-spectrum resistance of the myxobacteria to ralstonia solanacearum is shown. On the basis of predation experiments and potting experiments of Zhongshu No.4 tomatoes, experiments show that the myxobacteria Myxococcusx anthus R31 has huge application potential in the aspect of biological prevention and control of tomato bacterial wilt.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
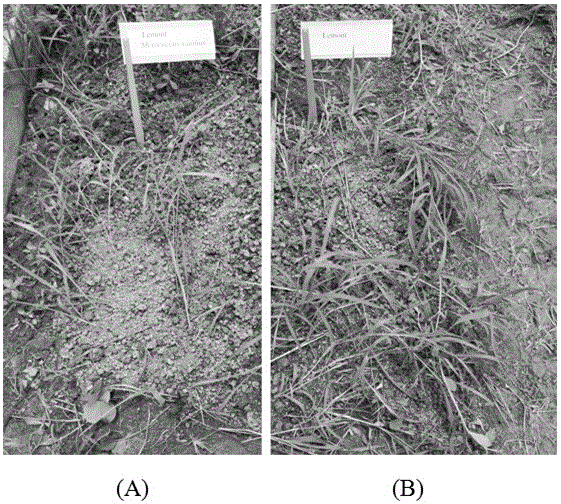
Method for suppressing growth of paddy field weeds by virtue of rice straw powder and myxobacteria
InactiveCN104663328ARich sourcesEasy to prepareBacteriaPlant protectionMyxobacteriaEcological safety
The invention provides a method for suppressing the growth of paddy field weeds by virtue of rice straw powder and myxobacteria. The method comprises the following steps: crushing dry rice straws, and sieving and applying rice straw powder into field blocks; inductively separating myxobacteria from soil in a paddy field by adopting a rabbit manure induction method, purifying the myxobacteria, performing enlarging cultivation, mixing the myxobacteria and sterilized crushed rabbit manure, and applying the mixture into the field blocks applied with the rice straw powder to suppress the growth of the paddy field weeds by virtue of interaction of the rice straw powder and the myxobacteria. According to the method, a novel paddy field weeding method which is easy to operate, low in cost and high in ecological safety is established by the technologies, and a reference for the utilization and the development of green and safe weeding of the paddy field can be provided.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Anti-inflammatory compounds
InactiveUS20120190651A1Useful in treatmentOrganic active ingredientsMaterial nanotechnologyMyxobacteriaDisease
This invention relates to novel compounds obtained by fermentation of Myxobacteria strain (PM0670013 / MTCC 5570). The present invention further relates to the processes for the production of the novel anti-inflammatory compounds, to the culture no. PM0670013 (MTCC 5570), and to pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of the present invention as an active ingredient and its use in medicines for the treatment of inflammatory diseases or disorders mediated by proinflammatory cytokines such as Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) and / or interleukins such as IL-6, having anti-inflammatory activity The invention also includes all stereoisomeric forms of compounds of the present invention.
Owner:PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD
Hypoglycemic medicine contg. slime bacteria sporocarp and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN1435255AIncrease valueSimple production methodMetabolism disorderUnknown materialsBiotechnologyMyxobacteria
A hypoglycemic medicine is prepared from myxobacterial sporophore or its extract and conventional auxiliaries through proportional mixing. Its advantages are high effect on reducing blood sugar and treating diabetes, and no toxic by-effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
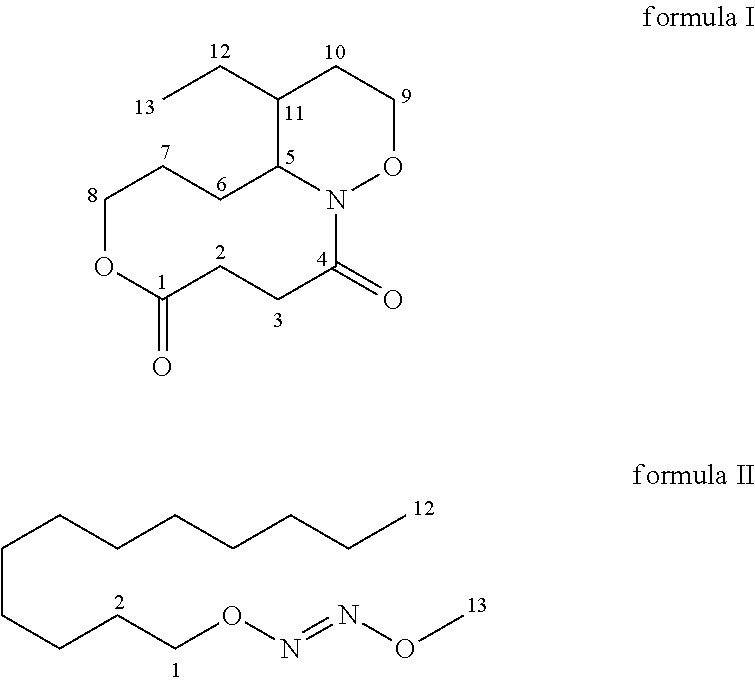
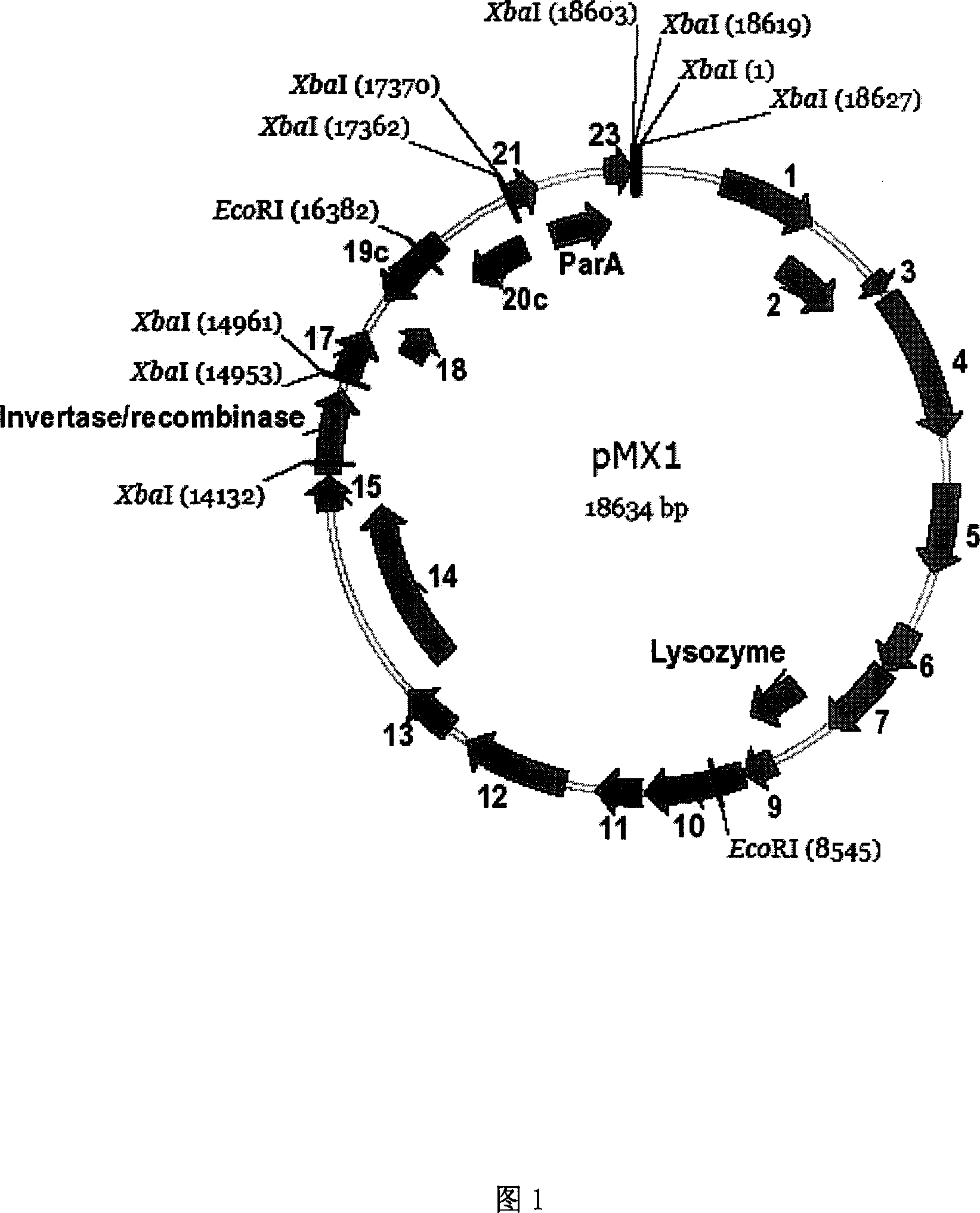
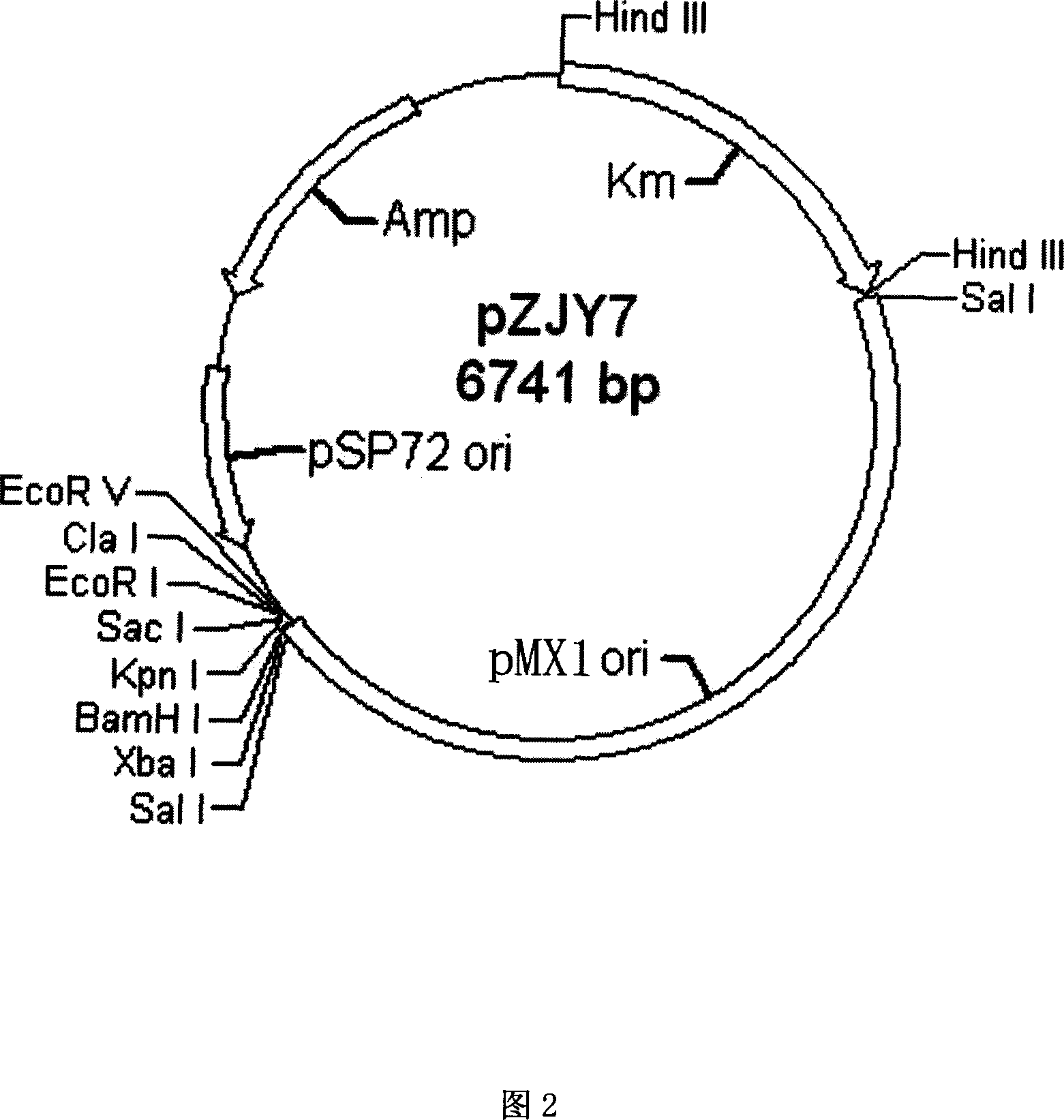
Myxobacteria specific plasmid and its use
The present invention discloses one Myxococcus fulvus 124B02 strain in the preservation number of CCTCC M 206081, and one plasmid, pMX1, originated from Myxococcus fulvus 124B02 and with the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The recombinant carrier or recombinant plasmid via reconstituting pMX1 plasmid may convert or conjugating myxobacteria, especially myxococcus, and is used in the genetic analysis and genetic engineering research of myxobacteria resource.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +3
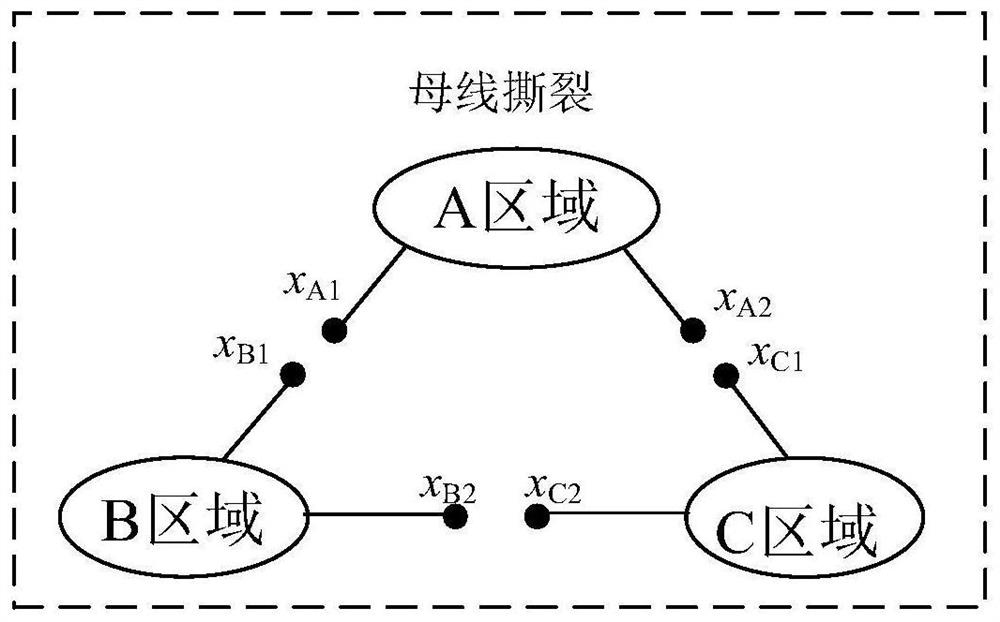
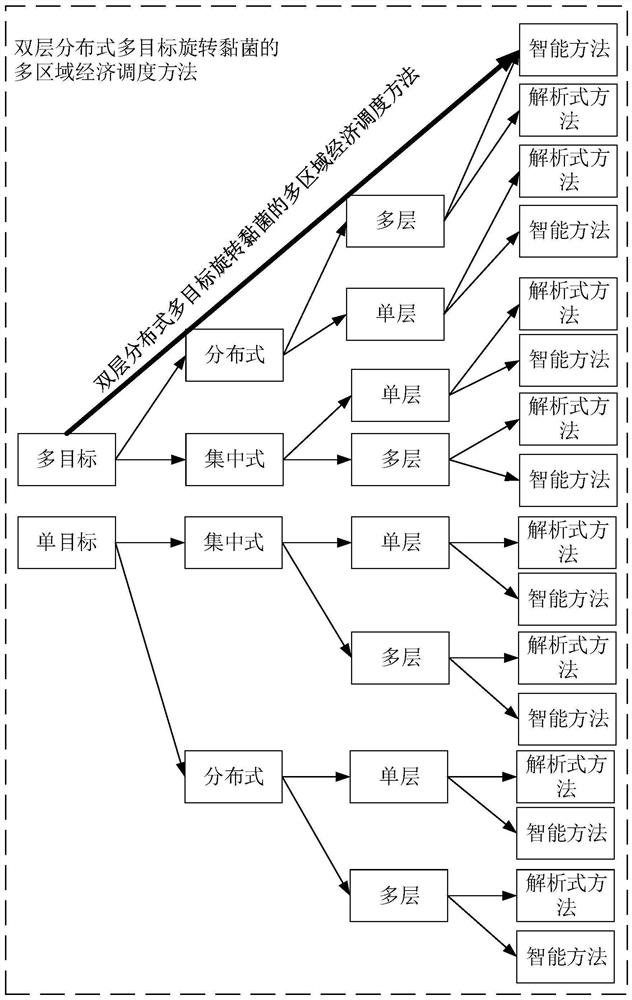
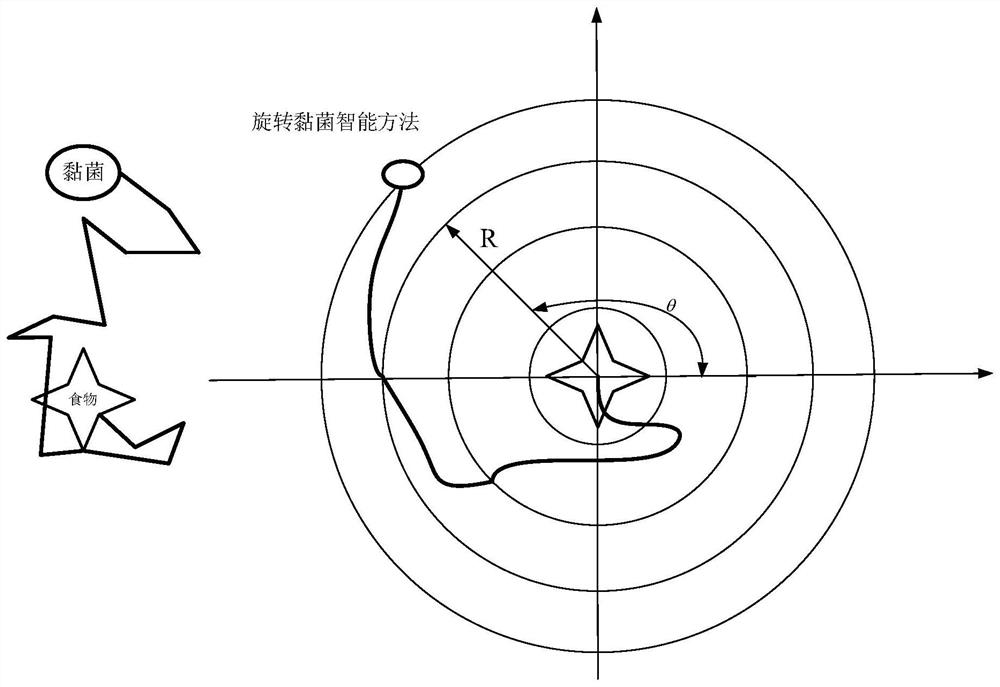
Double-layer distributed multi-target multi-region economic dispatching method for rotational myxobacteria
ActiveCN113285445ASingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationMyxobacteriaElectric power system
The invention provides a double-layer distributed multi-target multi-region economic dispatching method for rotational myxobacteria, which is a multi-target distributed double-layer intelligent optimization method and is used for solving the problem of multi-region economic dispatching. The method comprises the following steps of dividing a large-scale power system into a plurality of sub-region systems through a bus tearing method to form a first layer, continuously dividing the plurality of sub-region systems into a plurality of sub-sub-region systems to form a second layer, and then, sharing part of information of boundary virtual nodes, and safely, quickly and effectively solving the problem of multi-region economic dispatching by adopting a distributed consistency multi-target rotation myxus intelligent optimization method.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Genome extraction method for improving DNA quality of myxobacteria by virtue of pretreatment
InactiveCN104498478AEvenly dispersedSolve problems that cannot be fully decentralizedDNA preparationWater bathsMyxobacteria
The invention provides a genome extraction method for improving DNA quality of myxobacteria by virtue of pretreatment. The method comprises the following steps: in light of a phenomenon that in the culture process of myxobacteria, a lot of mucoid exopolysaccharides are generated to wrap the bacterium, so that cells in the liquid are hard to disperse, adding a nonionic surfactant into washed myxobacteria during pretreatment and oscillating by using an ultrasonic oscillator; and then, adding a SDS gene extraction buffer liquid and protease k for water bath so as to further uniformly mix the surfactant in the liquid, so that the cells are fully split. The method provided by the invention is integrally fast and simple to operate, and reagents and experimental instruments used are common instruments and reagents for a laboratory, so that the method is suitable for common and conventional experimental operations. The method is wide in application range, suitable for genome DNA extraction of all myxobacteria and strong in purifying capacity. The obtained DAN can be used for satisfying operations such as subsequent PCR amplification and DNA sequencing.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Microecological preparation for freshwater aquaculture
InactiveCN112624350AHigh content of live bacteriaEfficient removalWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryBiotechnologyMyxobacteria
The invention relates to a microecological preparation for freshwater aquaculture, which is characterized in that the microecological preparation is paste with the water content of 15-25% and comprises the following components in parts by weight: 23-32 parts of bacillus, 4-7 parts of myxobacteria, 4-6 parts of lactic acid bacteria, 23-32 parts of saccharomycetes, 12-18 parts of nitrifying bacteria, 1-5 parts of photosynthetic bacteria and 2-3 parts of culture medium. Bacillus, myxobacteria, lactic acid bacteria, saccharomycetes, nitrifying bacteria and photosynthetic bacteria are fermented in a culture medium with the pH value of 6.0-7.5 at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C under illumination, the content of viable bacteria is high, the shelf life is as long as 24 months or longer, the microecological preparation can effectively remove inorganic nitrogen and organic nitrogen in aquaculture wastewater, the denitrification effect is remarkable, and ecological balance of the bottom of water is kept. The microecological preparation is stable in quality, safe, reliable, green, environment-friendly and pollution-free, and has a remarkable effect of promoting healthy and stable development of the aquaculture industry.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Microbe flocculating agent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107937473AGood phosphorus removal effectLow costWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesMyxobacteriaFiber
The invention discloses a microbe flocculating agent and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) flocculant-producing bacteria can beinoculated in a crude fiber raw material, aerobic fermentation is carried out, and a primary fermentation object is obtained; 2) clostridium pasteurianum CGMCC1.208 is inoculated in the primary fermentation object, anaerobic fermentation is carried out, and a secondary fermentation object is obtained; 3) after the water content of the secondary fermentation object is reduced to 25-30%, myxobacteria is inoculated in the secondary fermentation object, and a third fermentation matrix with the water content being lower than 40% and a pH value being 6-8 is obtained; 4) aerobic fermentation is carried out, and a third fermentation object is obtained; and 5) the third fermentation object is extracted by using ethyl acetate, leaching liquor is taken, filtering is carried out to take clear liquid,and drying is carried out to obtain the microbe flocculating agent. The method employs the flocculant-producing bacteria-clostridium pasteurianum-myxobacteria for successively performing aerobic fermentation, anaerobic fermentation and aerobic fermentation on the crude fiber raw material, and the obtained flocculating agent has excellent phosphate removing effect on phosphor enriched sewage.
Owner:卢梅雅
Built-in antimicrobial plastic resins and methods for making the same
A built-in and process-adaptive formulation of antimicrobial commodity thermoplastic resins with mixed compositions comprising of a polymer, a backbone linker, and a non-labile antifouling and biocompatible coupling agent which is melt-processable and enabled to be manufactured into finished products in the form of solid, monolith, tube, composite, fiber, film, sheet and varnish without the prerequisite of biocides or antimicrobial additives is disclosed. The said formulation is adapted to thermoforming and thermal curing processes including but not limited to melt compounding, spinning, extrusion, molding, compression foaming and drawing. The antimicrobial property is attributed to the persistent formation of a non-stick bacteria-repellent tethered layer in which the antifouling component of the said formulation is heterogeneously phase separated and / or surface migrated to the surface after product forming in order to minimize adsorption and / or colonization of bacteria.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Feed for reducing shell rot disease of sea shrimps as well as preparation method and application of feed
PendingCN111296692ANot easy to moldNot perishableClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffMyxobacteriaHouttuynia
The invention discloses feed for reducing shell rot disease of sea shrimps as well as a preparation method and application of the feed. The feed consists of fish oil, purple potato powder, shrimp shell powder, phospholipid oil, superoxide dismutase SOD, a dandelion root extract, an antioxidant, a mildew inhibitor, a hylocereus undatus extract, an epimedium herb extract, neutral protease, carotenoid, polygonum multiflorum vine extract, choline chloride, a herba houttuyniae extract, betaine, a medicated leaven extract and a fructus lycii extract. The feed is difficult to get mildew and go bad, and caking and odor smells are avoided; and the feed is high in stability in water, cannot be scattered in 4 hours to 5 hours, and has no residues and side effects; pH of intestinal tracts of the sea shrimps can be kept at 5 to 7, vibrio cell outer membranes are damaged, vibrio parahaemolyticus, aeromonas, myxobacteria and flavobacterium can be killed, survival ratios of the sea shrimps are increased by 15 percent to 25 percent, the anti-stress capability of the sea shrimps is improved, the proliferation capability is improved, the palatability of feed is good, a digestion ratio is increased, the growth speed of the sea shrimps is high, the body length is increased by 20 percent to 50 percent, and the sea shrimps are 29cm to 36cm long.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
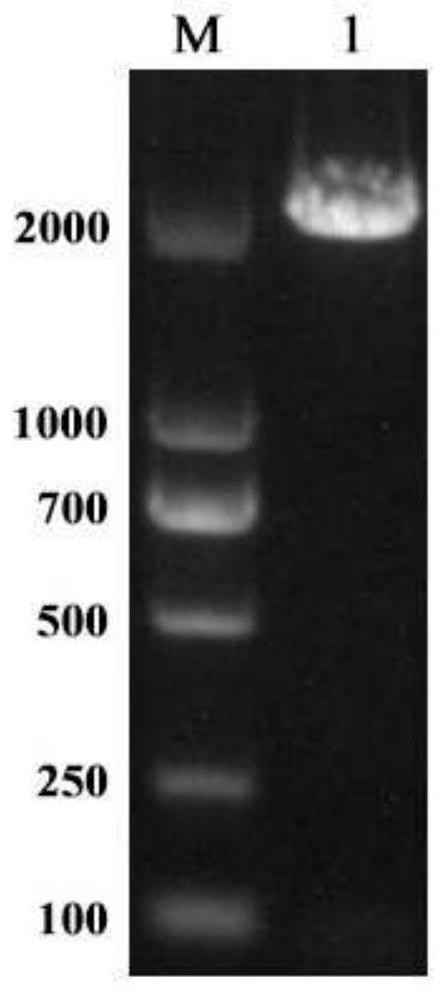
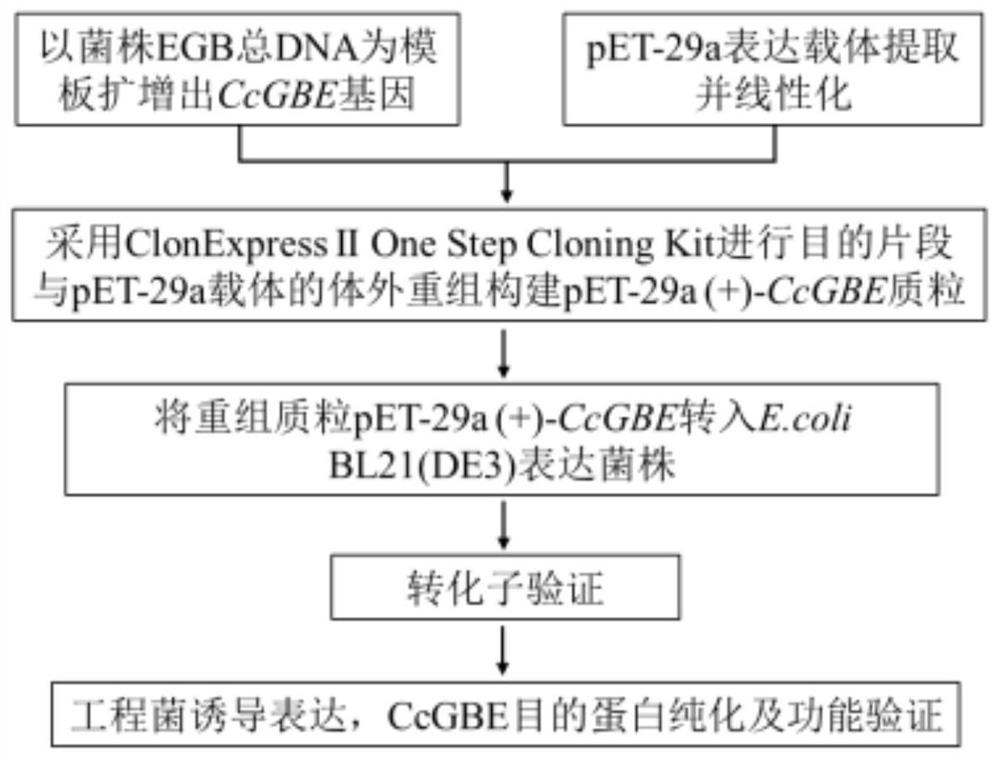
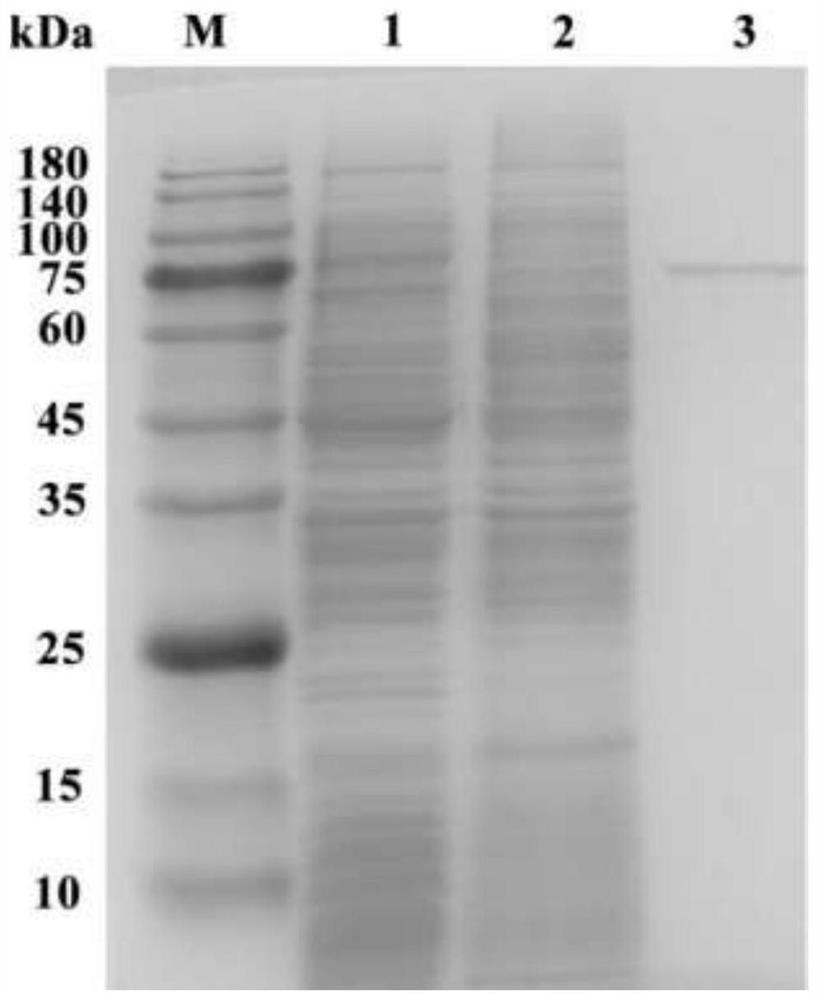
Starch branching enzyme derived from myxobacteria, gene of starch branching enzyme, engineering bacterium containing gene and application of starch branching enzyme
ActiveCN114317565AIncreased specific enzyme activityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaFood processingMyxobacteriaDigestible starch
The invention discloses a myxobacteria-derived starch branching enzyme and a gene thereof, an engineering bacterium containing the gene and application of the engineering bacterium. The nucleotide sequence of the starch branching enzyme gene provided by the invention is SEQ ID NO. 1, and the amino acid sequence of the coded protein is SEQ ID NO. 2. The recombinant starch branching enzyme obtained by using an engineering strain constructed by the gene takes cassava starch as an activity detection substrate, and the specific activity of the recombinant starch branching enzyme is 19439.9 + / -62.4 U / mg through iodine solution detection under the optimal reaction condition. The starch branching enzyme produced by using the gene can be used for starch modification, including preparation of slowly digestible starch or resistant starch, preparation of high-branching modified starch with anti-aging characteristic, preparation of cold water soluble starch and the like. The prepared modified starch can be widely applied to the industries of food, brewing, fermentation, textile industry, medicine and the like, and considerable economic benefits can be obtained while practical problems are solved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A method of inhibiting the growth of weeds in paddy fields by using rice straw powder and sticky bacteria
InactiveCN104663328BRich sourcesEasy to prepareBacteriaPlant protectionMyxobacteriaEcological safety
The invention provides a method for suppressing the growth of paddy field weeds by virtue of rice straw powder and myxobacteria. The method comprises the following steps: crushing dry rice straws, and sieving and applying rice straw powder into field blocks; inductively separating myxobacteria from soil in a paddy field by adopting a rabbit manure induction method, purifying the myxobacteria, performing enlarging cultivation, mixing the myxobacteria and sterilized crushed rabbit manure, and applying the mixture into the field blocks applied with the rice straw powder to suppress the growth of the paddy field weeds by virtue of interaction of the rice straw powder and the myxobacteria. According to the method, a novel paddy field weeding method which is easy to operate, low in cost and high in ecological safety is established by the technologies, and a reference for the utilization and the development of green and safe weeding of the paddy field can be provided.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com