Starch branching enzyme derived from myxobacteria, gene of starch branching enzyme, engineering bacterium containing gene and application of starch branching enzyme
A starch branching enzyme and gene technology, applied in genetic engineering, application, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of low enzyme activity and catalytic efficiency, and low enzyme production of natural strains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
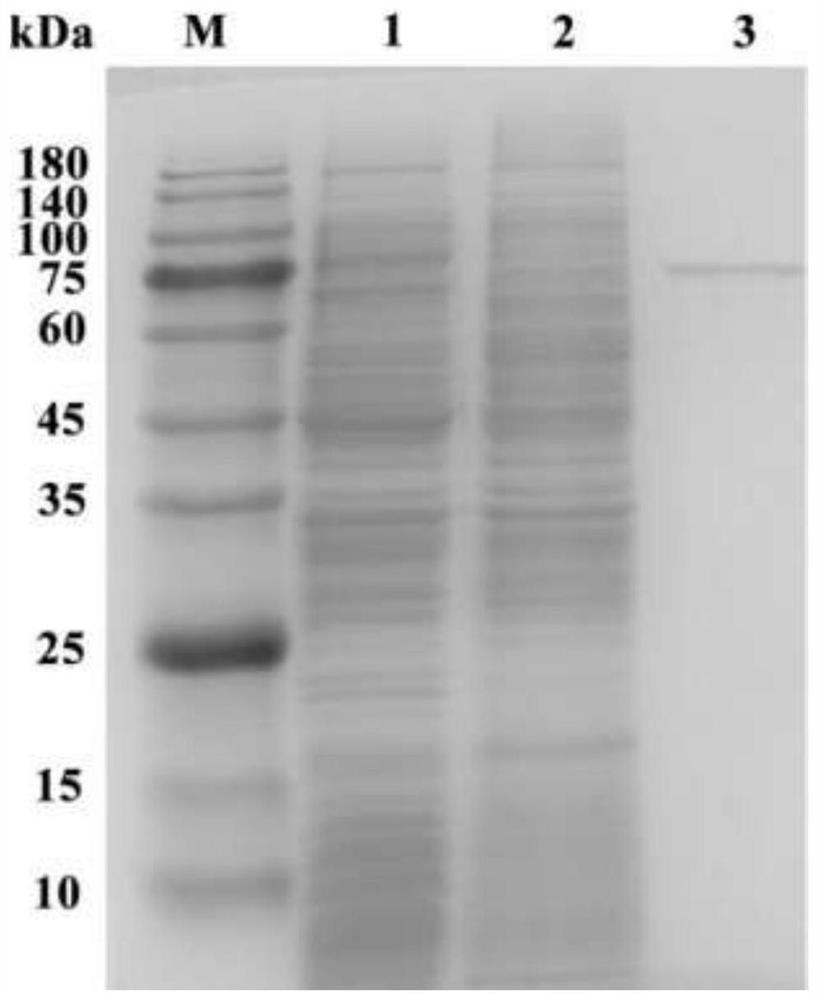
[0030] Expression purification and activity determination of embodiment 1 starch branching enzyme
[0031] 1.1 pCR amplification of starch branching enzyme gene
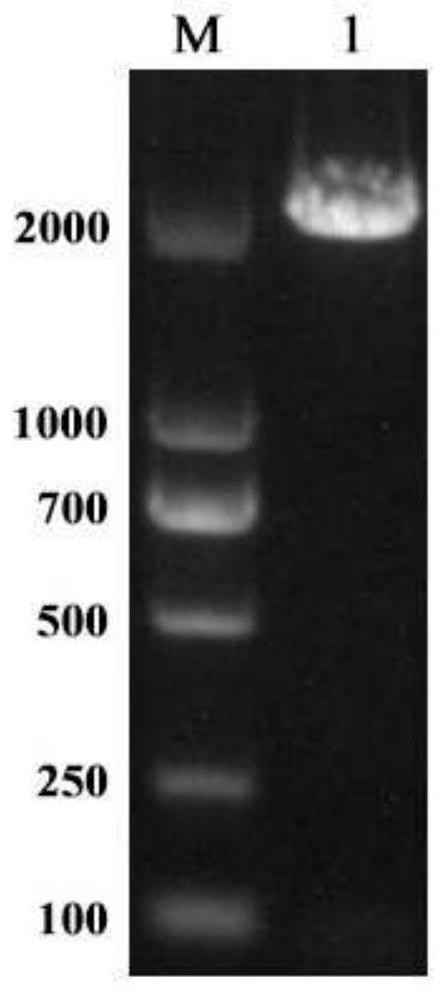
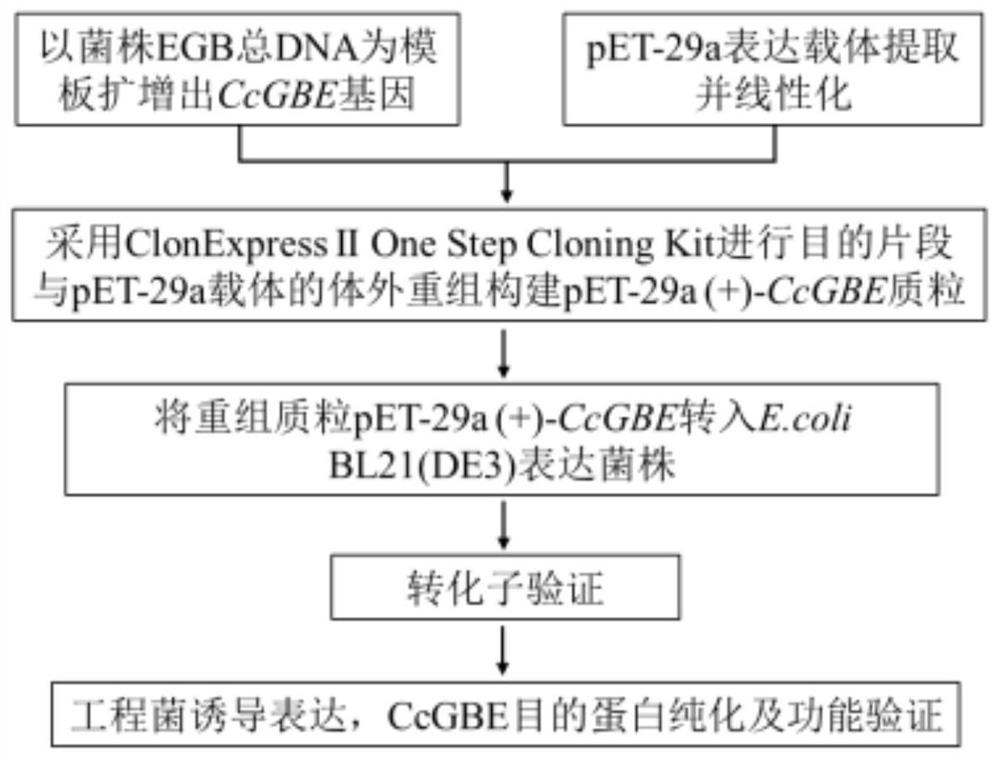
[0032] According to the completion map of the Corallococcus sp.strain EGB genome and combined with NCBI genome information for gene function prediction, starch branching enzyme primers were designed using the full length of the SEQ ID NO. Open) genome as a template, carry out the pCR amplification of the full-length starch branching enzyme gene, obtain the full-length sequence of the starch branching enzyme gene. The full length of the gene (from the start codon to the stop codon) is 2178bp, the GC content of the sequence is 69.65%, and it encodes 725 amino acids. The amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2 without signal peptide. The primers used for pCR amplification are F and R, and the amplification results are shown in electrophoresis figure 1 , the construction process of the expression plasmid refers to figure ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2. Study on Enzymatic Characteristics of Starch Branching Enzyme CcGBE
[0044] 3.1 Effect of temperature on enzyme activity
[0045] The determination scheme of the optimum reaction temperature is as follows: at different temperatures (20°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 60°C), under the condition of 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH9.0) The activity of recombinase, set the highest enzyme activity as 100% ( Figure 4 A). Determination of thermal stability: Incubate the recombinant enzyme at 20°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C and 60°C, 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH9.0) for 1-9h, and place on ice Rapid cooling on the surface, the residual enzyme activity was determined respectively, and the enzyme activity without incubation was taken as 100% ( Figure 4 B). It has been determined that the optimum reaction temperature of the starch branching enzyme CcGBE is 40°C, and it remains relatively stable between 20°C and 45°C.
[0046] 3.2 Effect of pH on enzyme activity
[0047]...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3 Utilizes starch branching enzyme CcGBE to prepare highly branched modified starch
[0054] Prepare 0.5% cassava starch for 30 minutes in a boiling water bath to fully gelatinize. After cooling to room temperature, add starch branching enzyme CcGBE in an amount of 25000 U / kg starch, react at 40°C for different times, and terminate the reaction in a boiling water bath. Add isoamylase (100 U / g starch) to the prepared modified starch, react at 38° C. for 24 hours for debranching reaction, and terminate the reaction in a boiling water bath. Polymerization analysis of branched chains was performed using high performance anion exchange chromatography (Thermo ICS 5000+, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The results showed that the content of branched chains with a degree of polymerization DP>25 in the modified starch after CcGBE treatment for 15 minutes increased significantly, and the content of branched chains with a degree of polymerization DP<7 in the modified st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com