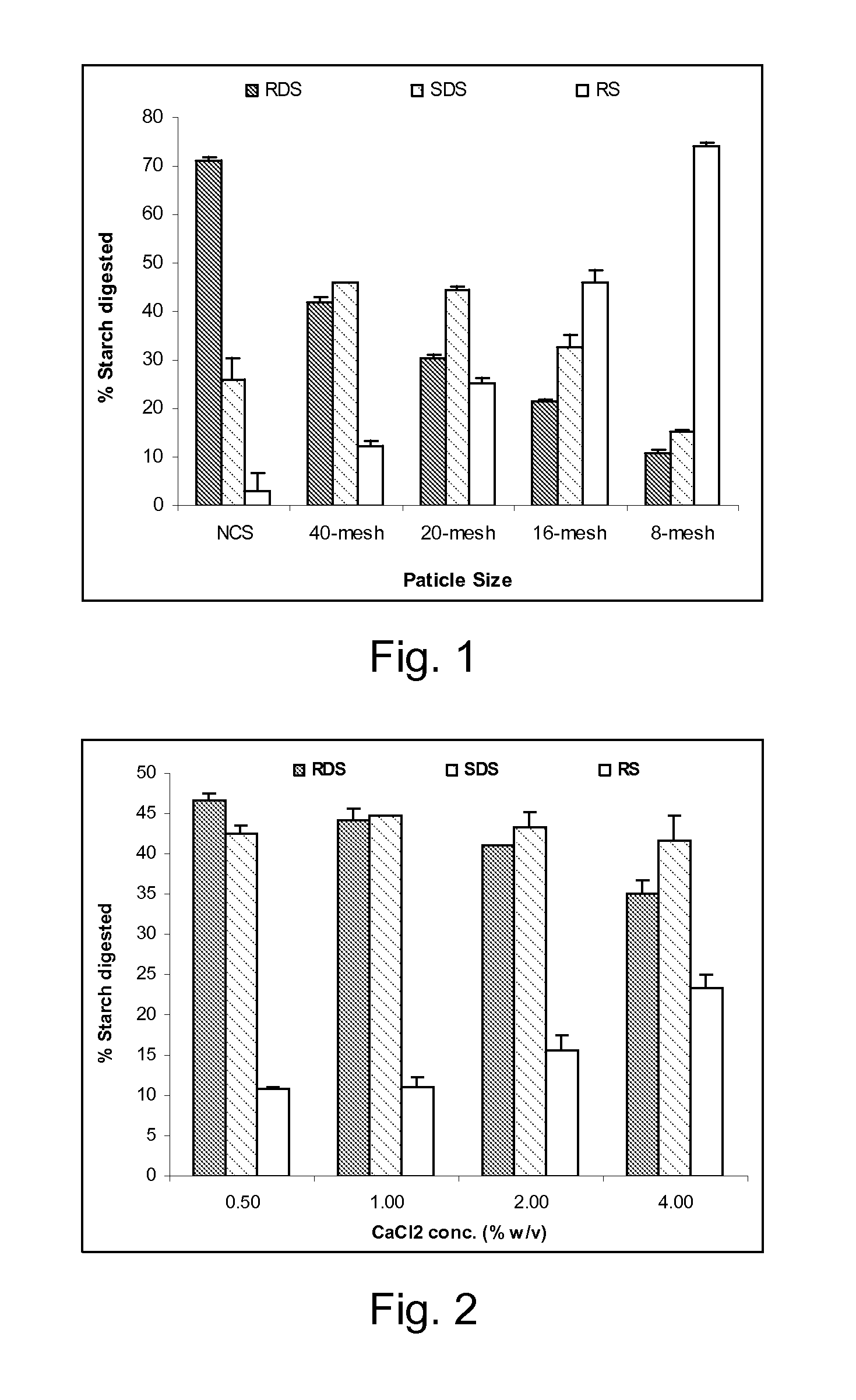
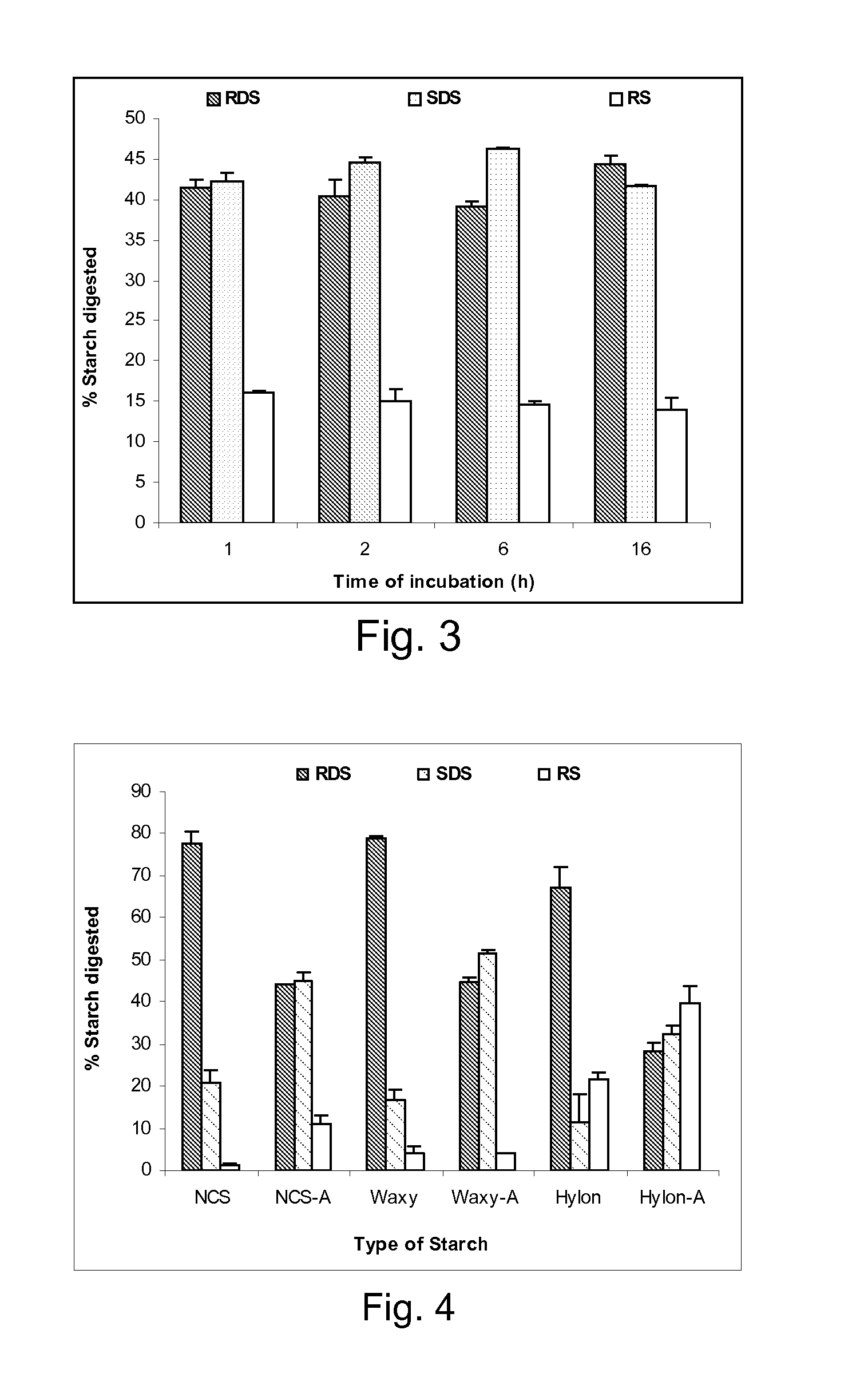
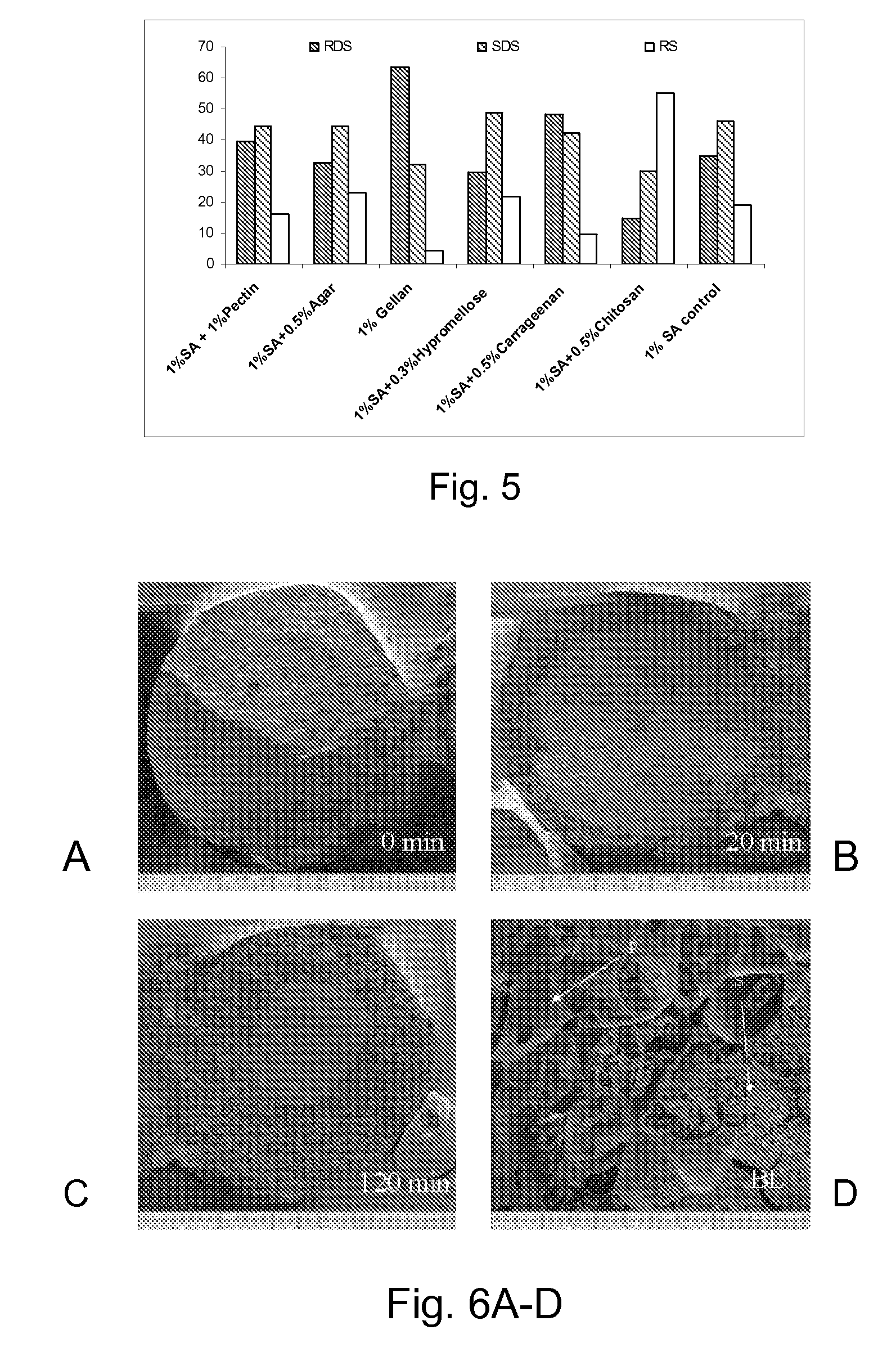
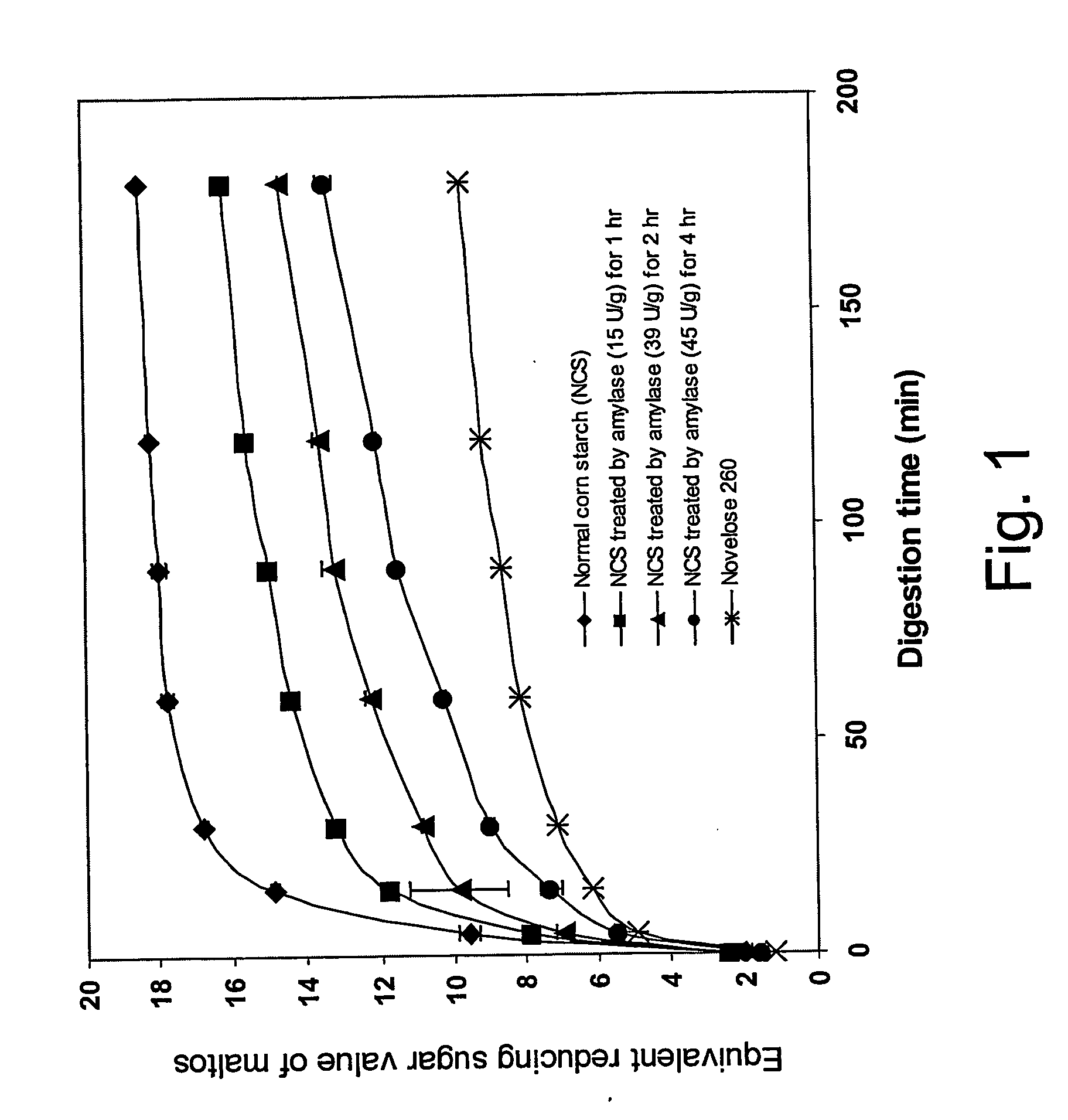
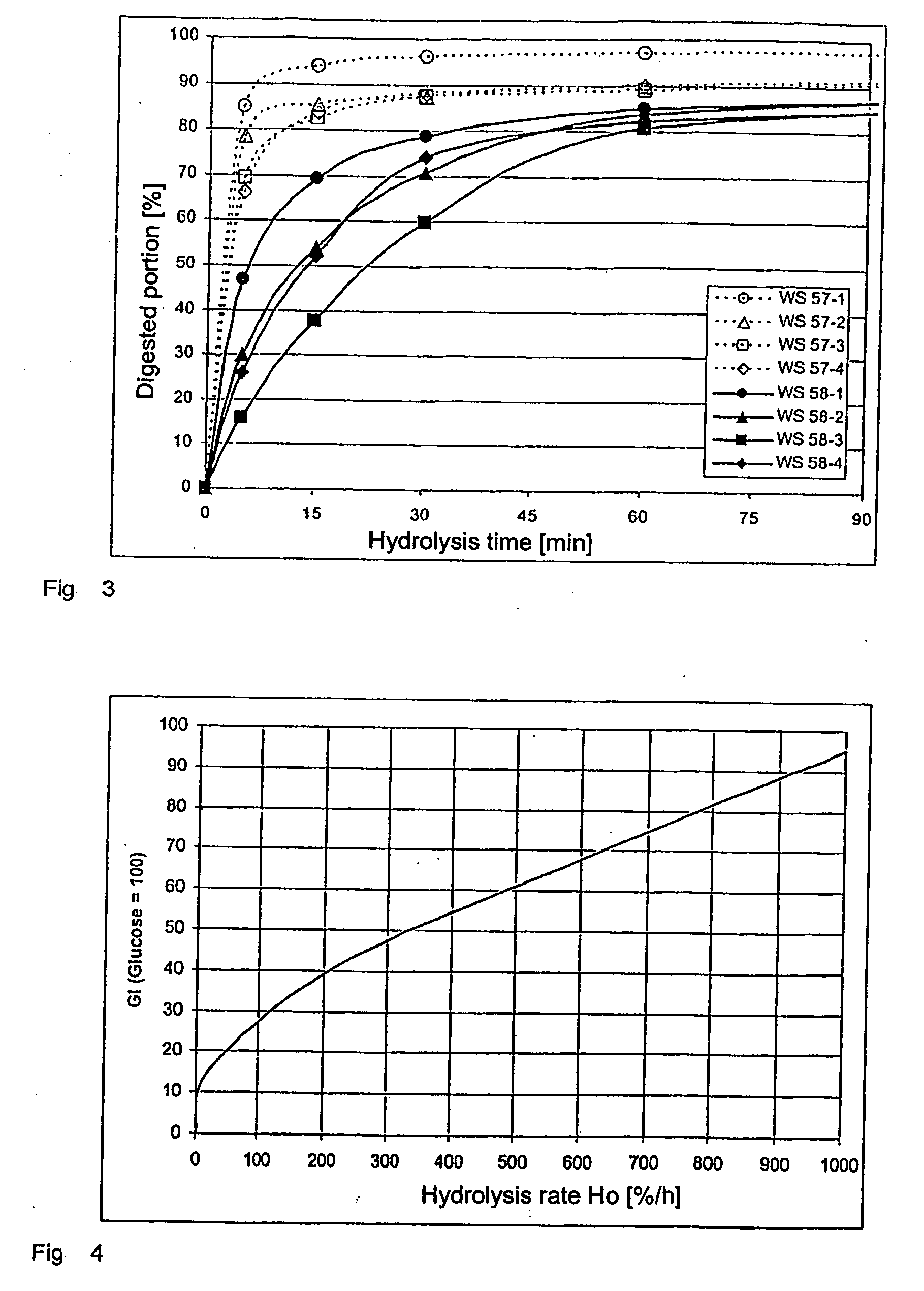
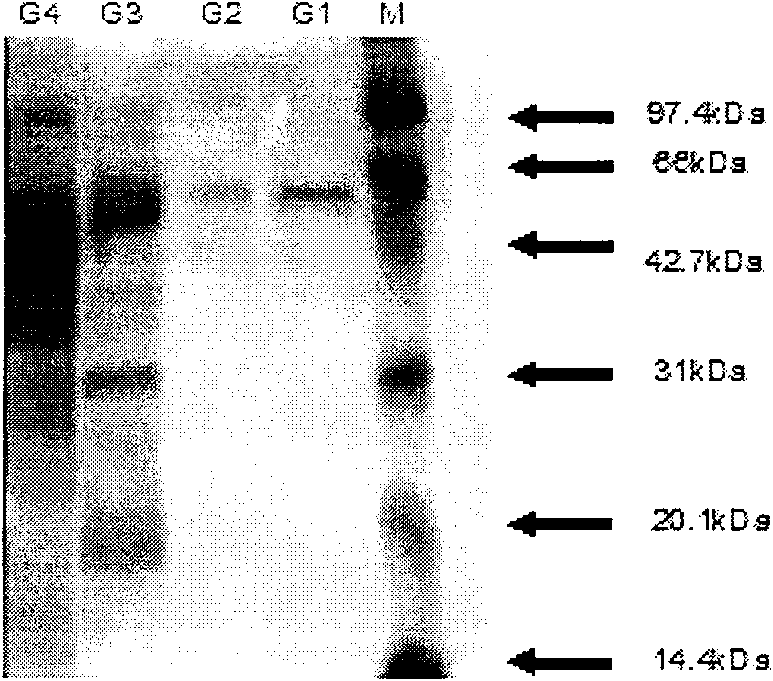
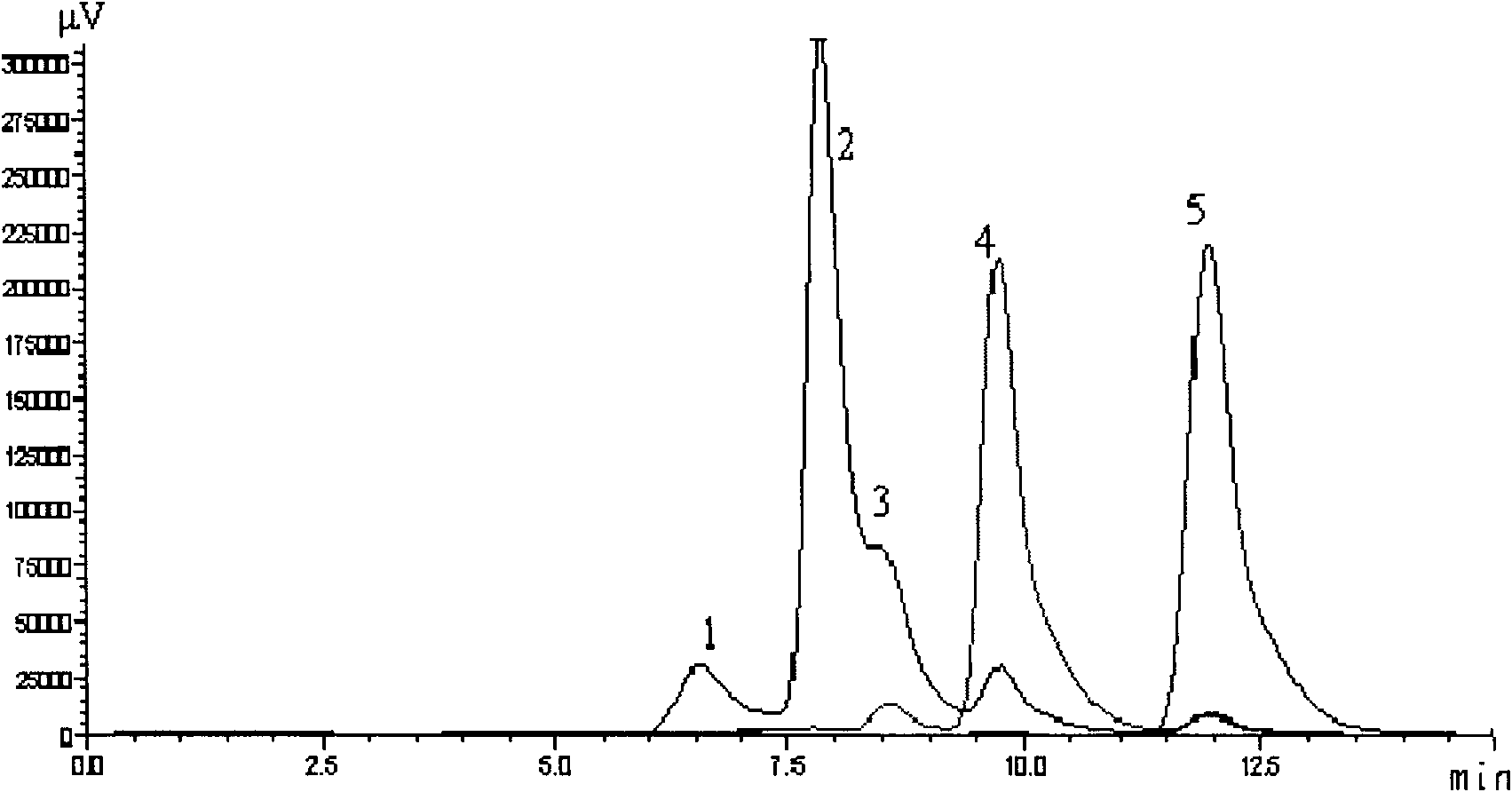
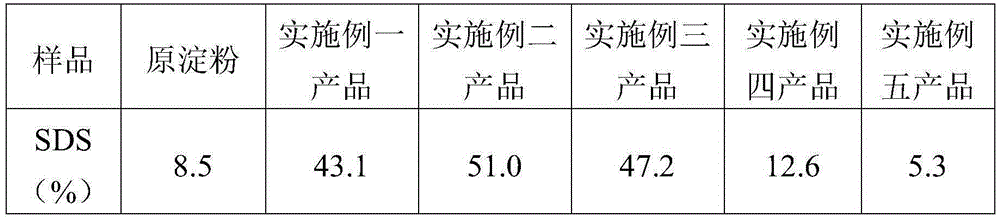
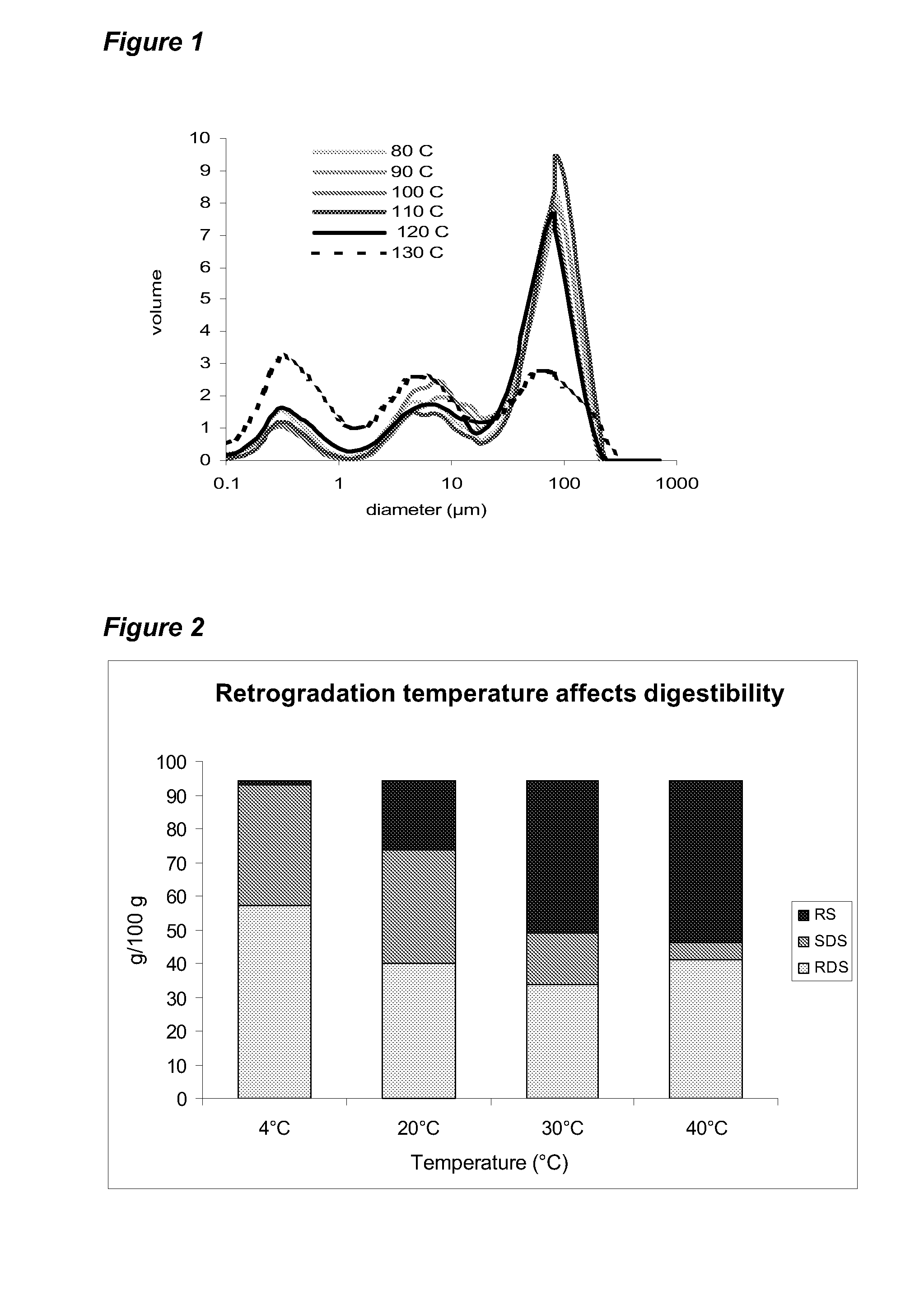
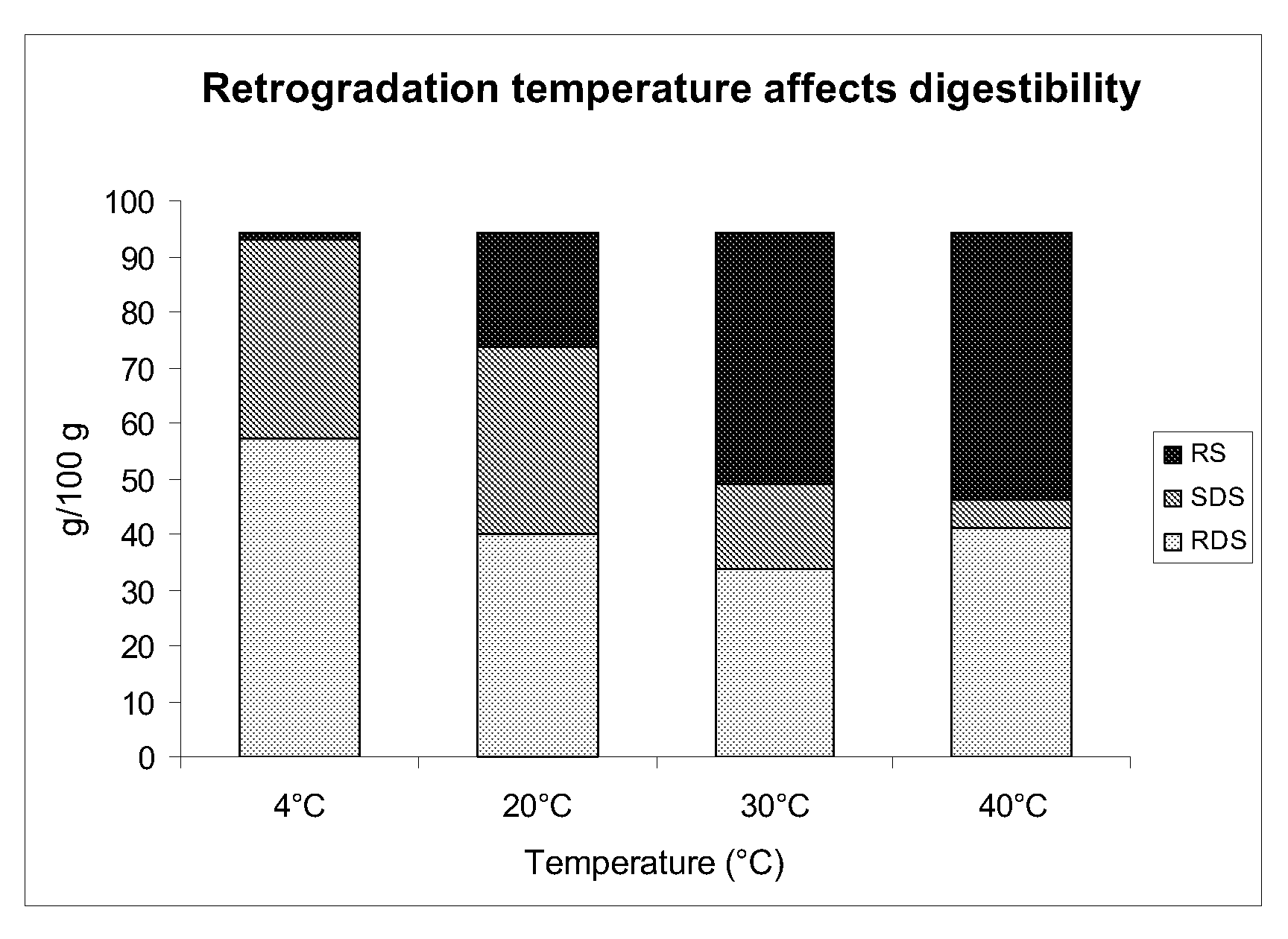
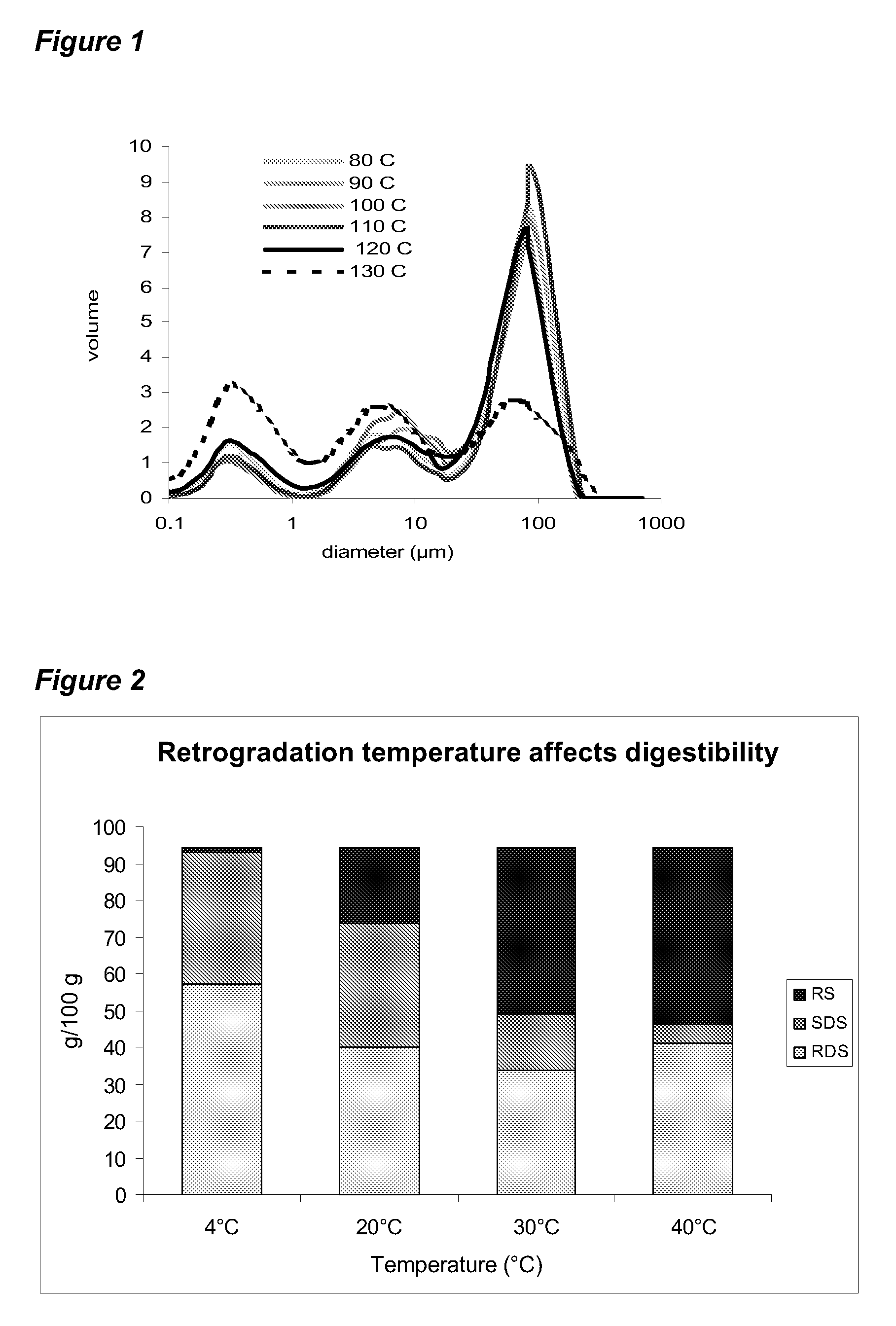
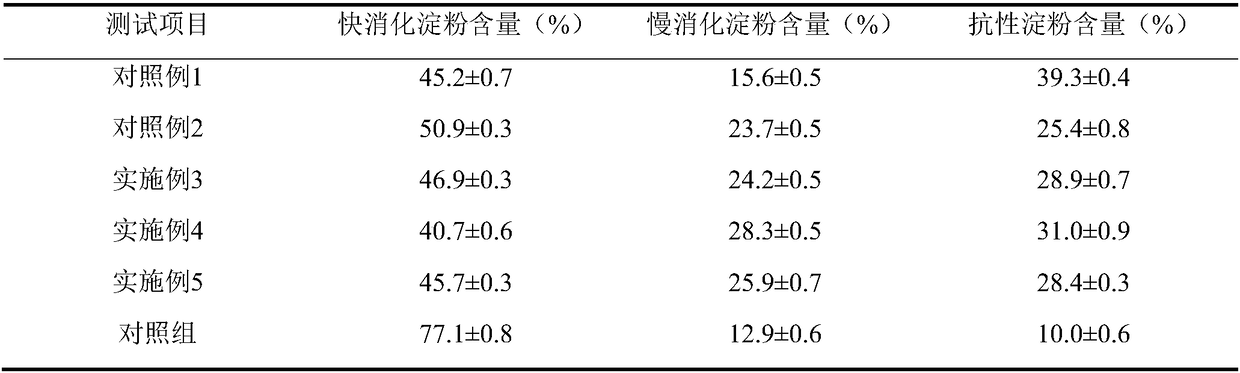
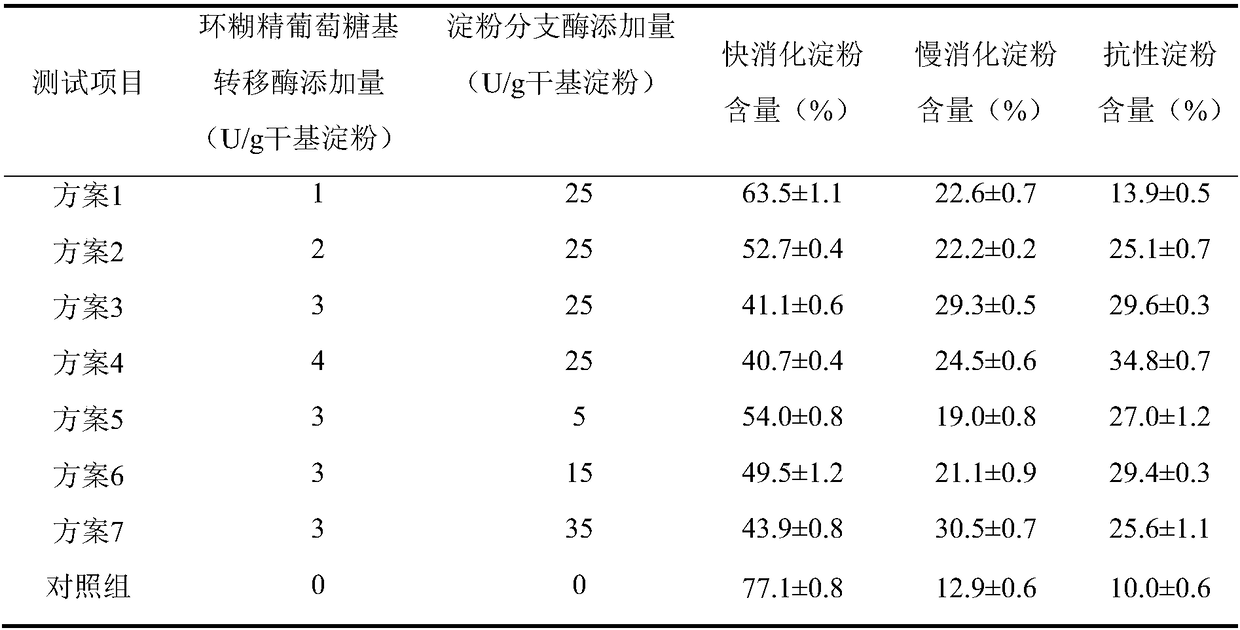
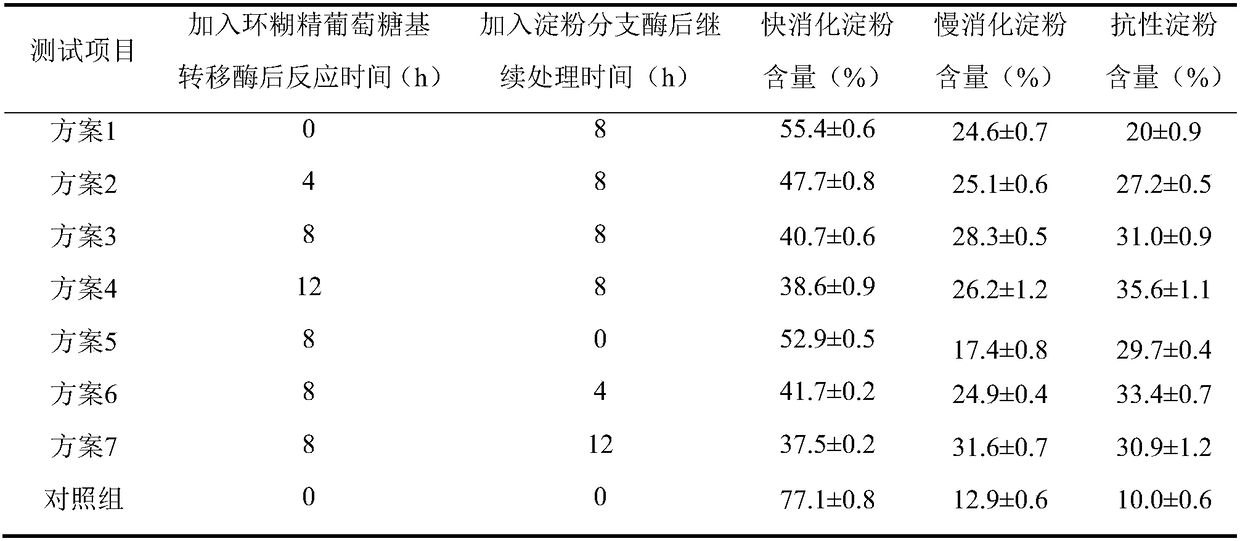
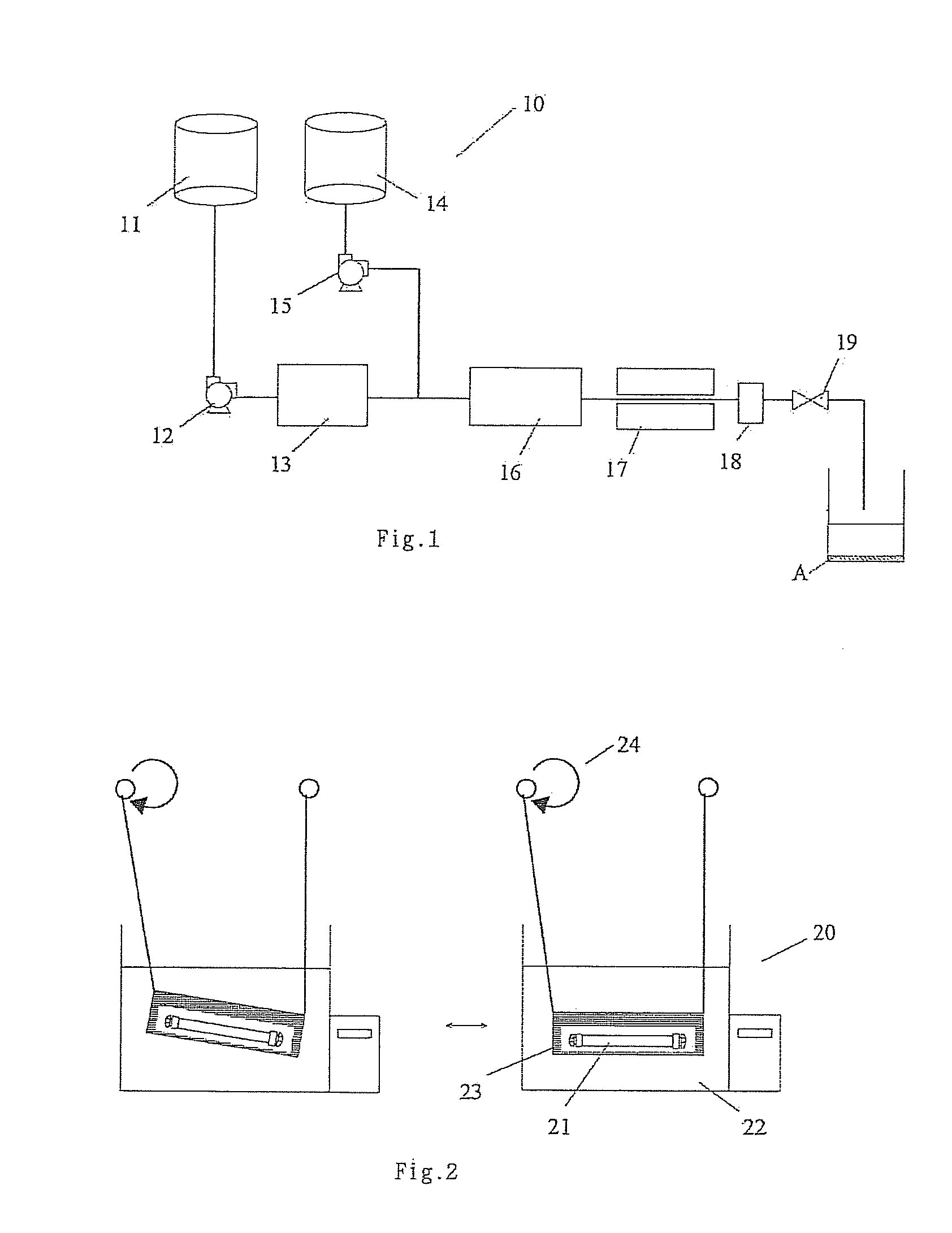
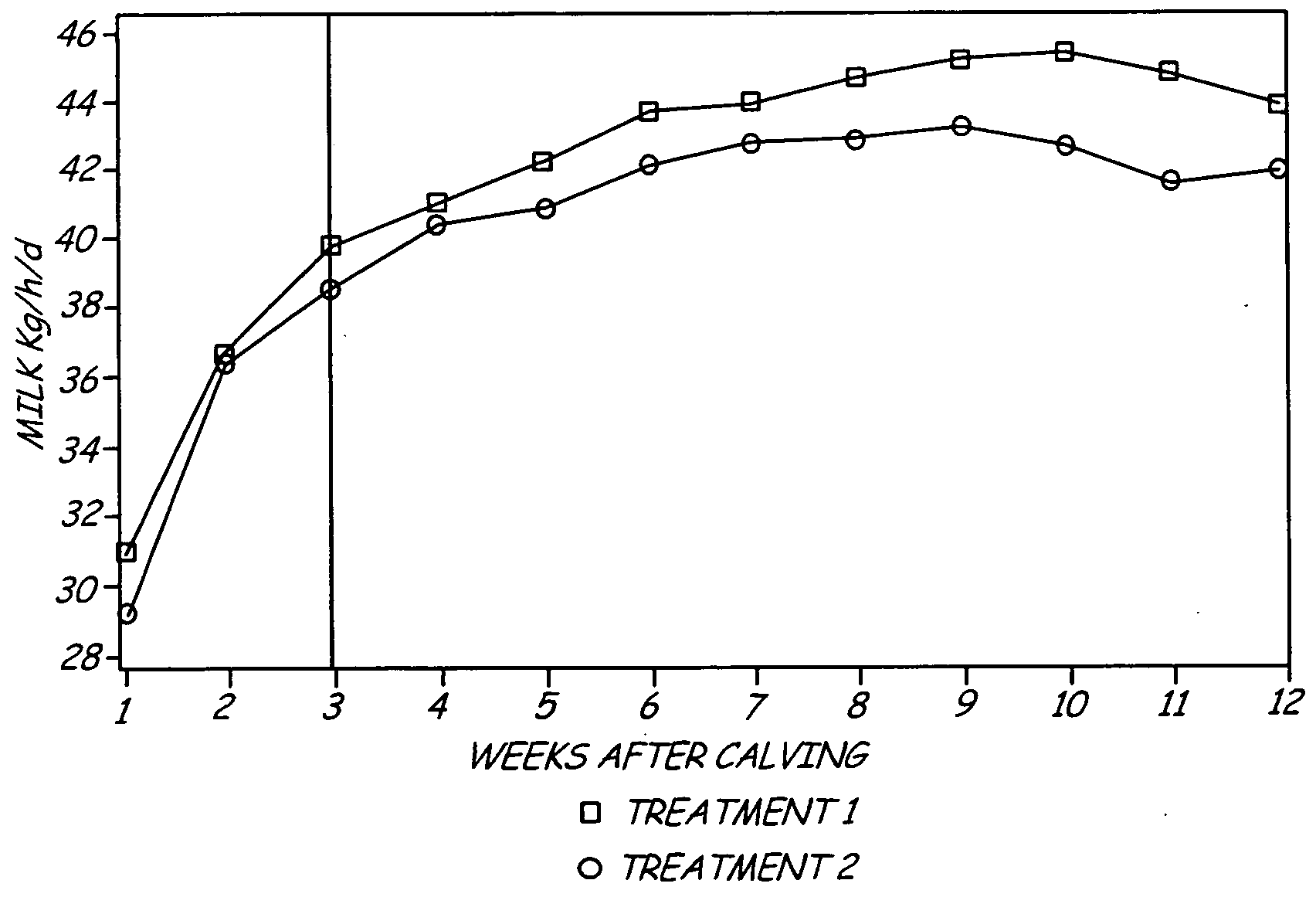
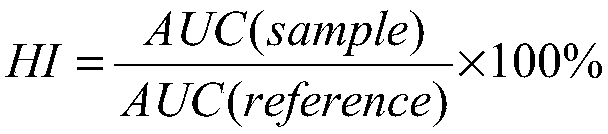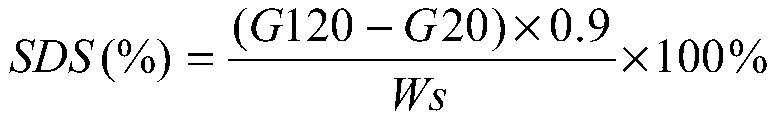Patents
Literature
133 results about "Digestible starch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
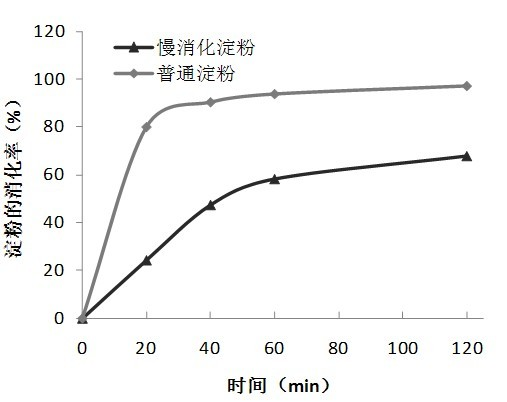
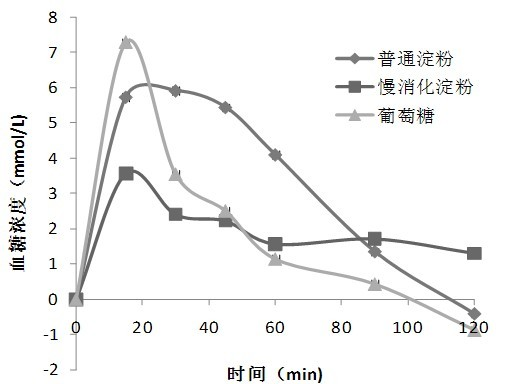
Slowly digestible starch is a slow-release carbohydrate that occurs naturally in starchy foods such as grains, legumes, roots and tubers. Its preservation is dependent on both the nature of the ingredients and food processing conditions, such as heat, pressure, and moisture. Slowly digestible starch takes longer to break down by...
Slowly digesting starch and fermentable fiber
ActiveUS20070196437A1Prevention and treatmentBenefit their healthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDigestible starchAdditive ingredient
Compositions which provide slowly digestible starch and a source of fermentable dietary fiber. Microparticles in which starch is entrapped in a crosslinked matrix to provide dietary benefit. Such microparticles are used to deliver glucose to targeted regions in the small intestine for beneficial physiological effects, and fermentable dietary fiber to the colon to improve colon health and to treat diseases of the colon. Microparticles can be employed to selectively deliver fermentable dietary fiber to targeted portions of the colon. A method for making the microparticles is provided as well as methods for using the microparticles for controlled digestion of starch on ingestion in the small intestine and methods for using the microparticles to deliver dietary fiber. The microparticles with entrapped starch provide a low glycemic index and extended glucose release in food products and food ingredients. The microparticles with entrapped starch can, in particular, be used as an ingredient in foods that are to be cooked.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Slowly digestible starch
InactiveUS20060257977A1Slowly digestibleSlow digestibilityOrganic active ingredientsFermentationDigestible starchAlpha-amylase
The invention provides processes to make slowly digestible starches from native and commercial starches. Slowly digestible starches are prepared by controlled hydrolysis of gelatinized starch by alpha amylase. The slowly digestible starches have a range of starch digestion rates and fall between normal, untreated commercial and native starch, and commercial resistant starches. The slowly digestible starches provide a range of starch functionalities. These slow digesting starches retain their digestion characteristic after cooling, and can used in a range of processed food products to modulate the rapid glucose release typical of many processed starchy foods. Edible products incorporating slowly digestible starch will exhibit lower glycemic index and increase satiety. The invention provides solid and liquid food, nutritional, and drug preparations containing the slowly digestible starch. The invention further provided edible products for extended energy release for example, for use in sports drinks and snack bars. The slowly digestible starches can also be employed as functional food grade additives to provided beneficial rheological or other properties to edible compositions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for producing high temperature stable slow-slaking amidon and uses thereof
InactiveCN101117352AWide range of raw materialsNo pollution in the processDigestible starchPotato starch
A production method and the application of a high temperature stable slowly digestible starch belong to the non-chemical modified starch field. The material starch of the present invention, such as cornstarch, wheat starch, rice starch, potato starch, tapioca starch, sweet potato starch, mung bean starch, chick pea starch, sorghum starch, sago starch, and canna starch, is gelatinized, and the complex debranching treatment is conducted after adding the commodity diastases, pullulanase and alpha amylase, and finally, the slowly digestible starch is gained after preservation, recrystallization, and hydrothermal treatment. The content of the slowly available glucose is greater than or equal to fifty percent, and the residue of the slowly digestible starch is greater than or equal to 80 percent after high temperature processing treatment. The present invention relates to a plurality of fields, such as baking food, short order, candy, flavoring, dairy products, athlete special food, food for diabetes, slimming foods, oral intestinal target controlled release film coating, and animal feed.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Slowly digestible starch product
InactiveUS20070134392A1Slowly digestibleReduce hydrolysis rateDough treatmentBaking mixturesDigestible starchAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a starch product in the form of a foodstuff ingredient and to a foodstuff per se whose hydrolysis speed during digestion can be set to low and especially almost constant in that the starch is obtained as a partially crystalline network with a low degree of swelling by means of targeted conditioning, starting from an at least partly amorphous state.
Owner:INNOGEL AG
Method for producing controlled/slow release starch derivative with hypoglycemia response characteristics
ActiveCN101731510AWide range of raw materialsIncrease contentFood preparationDigestible starchLow glucose
The invention discloses a method for producing a controlled / slow release starch derivative with hypoglycemia response characteristics, and belongs to the technical field of the production of functional food additives. The method utilizes a conventional industrial natural polymer to obtain the controlled / slow release starch derivative with the hypoglycemia response characteristics through micro-encapsulation embedding technology. The method adopts emulsification / internal gelatination technology, takes commercialized starch with different sources as a core material, and takes a compound of canageenen or sodium alginate and chitosan as a wall material to obtain a starch derivative with a particle size of between 10 and 150mu m through micro-encapsulation embedding treatment. The content of temperature-resistant slowly digestible starch (SDS) is remarkably improved (more than or equal to 15 percent) relative to native starch in the starch derivative, and the change range of the content thereof does not exceed 3 percent after high-pressure cooking treatment. A glycemic index (GI) is lower than 55 percent. The starch derivative not only can be taken as a functional ingredient to be added to develop novel slowly digestible hypoglycemia food, but also can be taken as a carrier material of stabilization and targeted controlled / slow release of functional factors such as probiotics, active polypeptide, protein, grease, vitamin and the like.
Owner:武汉森澜生物科技有限公司
Multifunctional slowly digestible starch and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106616914AWide variety of sourcesEasy to processClimate change adaptationFood preservationDigestible starchRoom temperature
The present invention belongs to the field of non-chemical modification and deep processing of starch, and specifically discloses multi-functional slowly digestible starch and a preparation method and an application thereof. The specific steps of the preparation method are as follows: the starch is prepared into starch milk at a starch content of 10-40% and the starch milk is heated at 70-95 DEG C for 30-60 min; fatty acids are added at a mass percentage of 5-25% of starch dry bases, the temperature is kept at 50-60 DEG C, and a stirring is conducted for 20-60 min; and then fat-soluble phenols at a mass percentage of 5-20% of the starch dry bases is added, the materials are stirred continuously for 10-40 minutes, after the stirring, the mixture is slowly cooled to a room temperature, the cooled mixture is washed with ethanol, the washed mixture is dried, the dried mixture is pulverized, and the pulverized mixture is sieved to obtain the multifunctional slowly digestible starch. The multifunctional slowly digestive starch has the slow digestion function, can effectively remove free radicals in body, and synergistically treats or prevents incidences of diabetes, obesity and other chronic diseases.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAIBAO MEDICAL SCI TECH
Method for producing slow digestion starch by hot-press acid-hydrolysis of cornstarch using organic acid
The invention relates to a method for adopting organic acid to treat common corn starch through autoclaving and acid hydrolysis so as to prepare the slow digestible starch. The method includes the following steps: the common corn starch is prepared with the organic acid of 0.1 to 10 percent (w / v) concentration into a corn starch cream of 2 to 30 percent (w / v) concentration; the obtained corn starch cream is stirred for 20 to 60 minutes and then is treated through acid hydrolysis and autoclaving for 5 to 90 minutes under the temperature of 100 to 150 DEG C; then the corn starch cream is centrifuged at a speed of 2000 to 10000rpm for 2 to 10 minutes; the sediment of centrifugation is frozen for retrogradation under the temperature of minus 10 to 10 DEG C for 12 to 240 hours and then the sediment is dried with blast under the temperature of 50 to 80 DEG C for 10 to 20 hours; and then after the mechanical smashing, the sediment is sifted with a mesh sieve of 80 to 150 meshes so as to obtain the product containing more than 20 percent of slow digestible starch. The slow digestible starch prepared by the invention can be applied to the food manufacturing industry.
Owner:胡耀辉
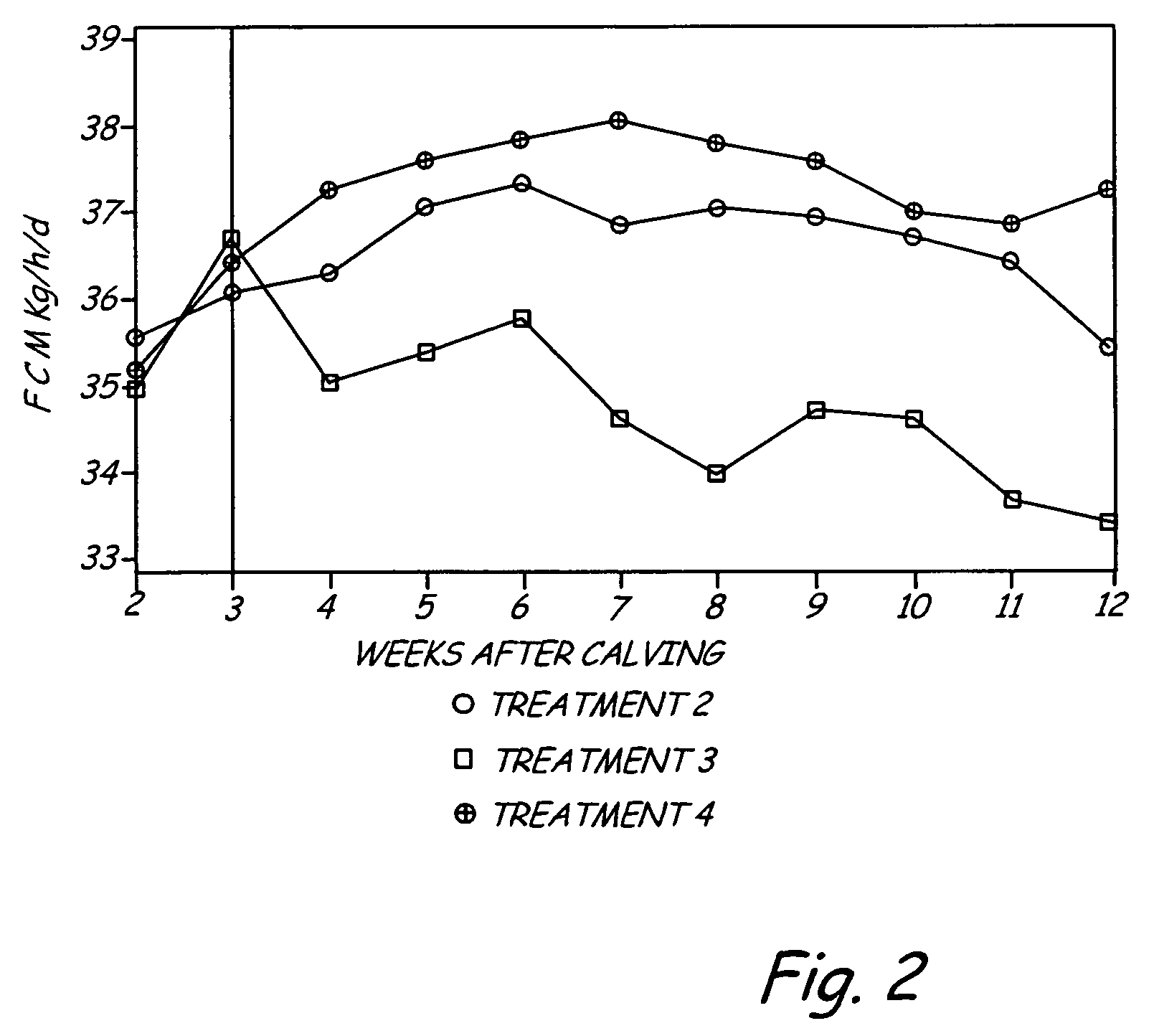
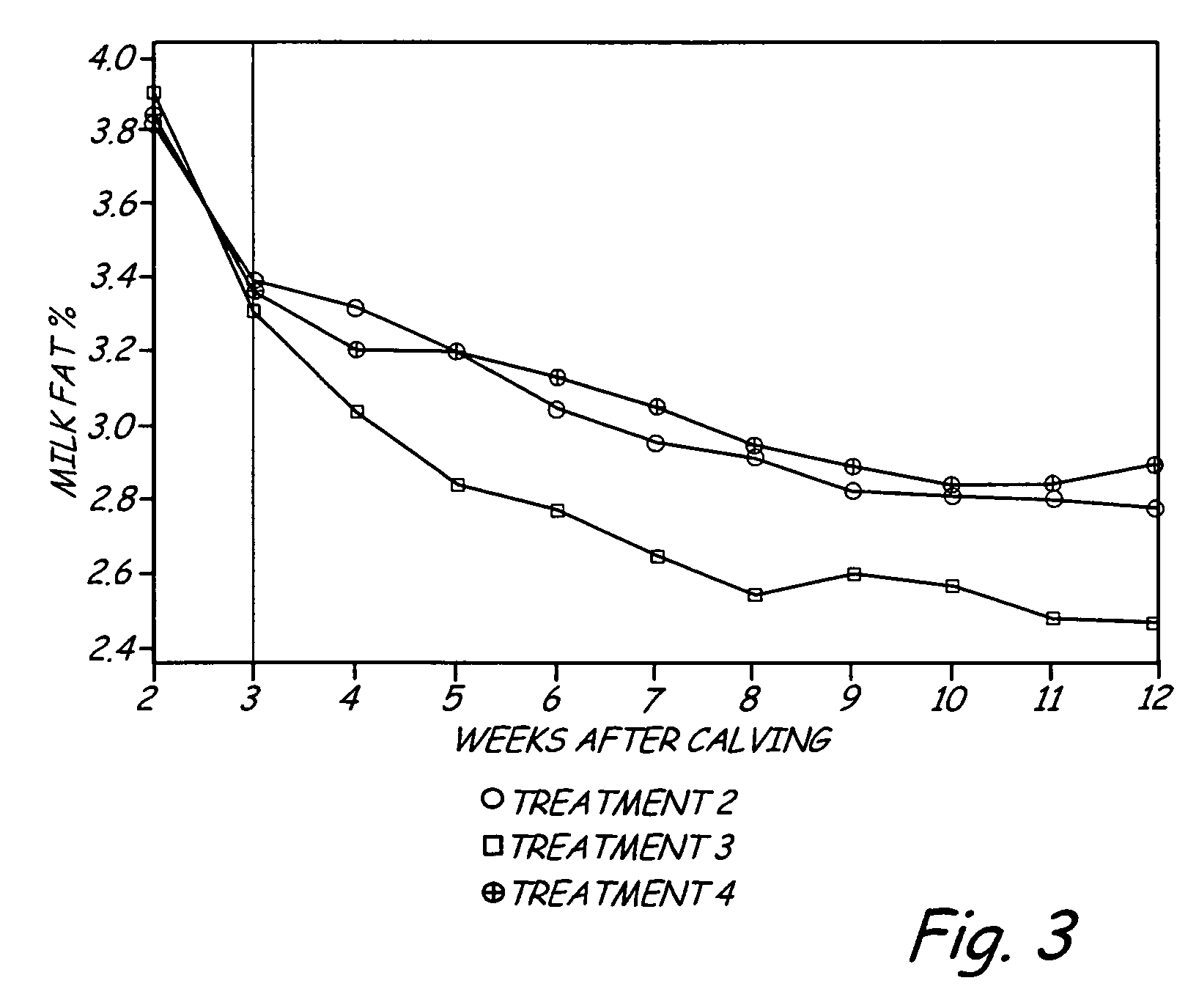
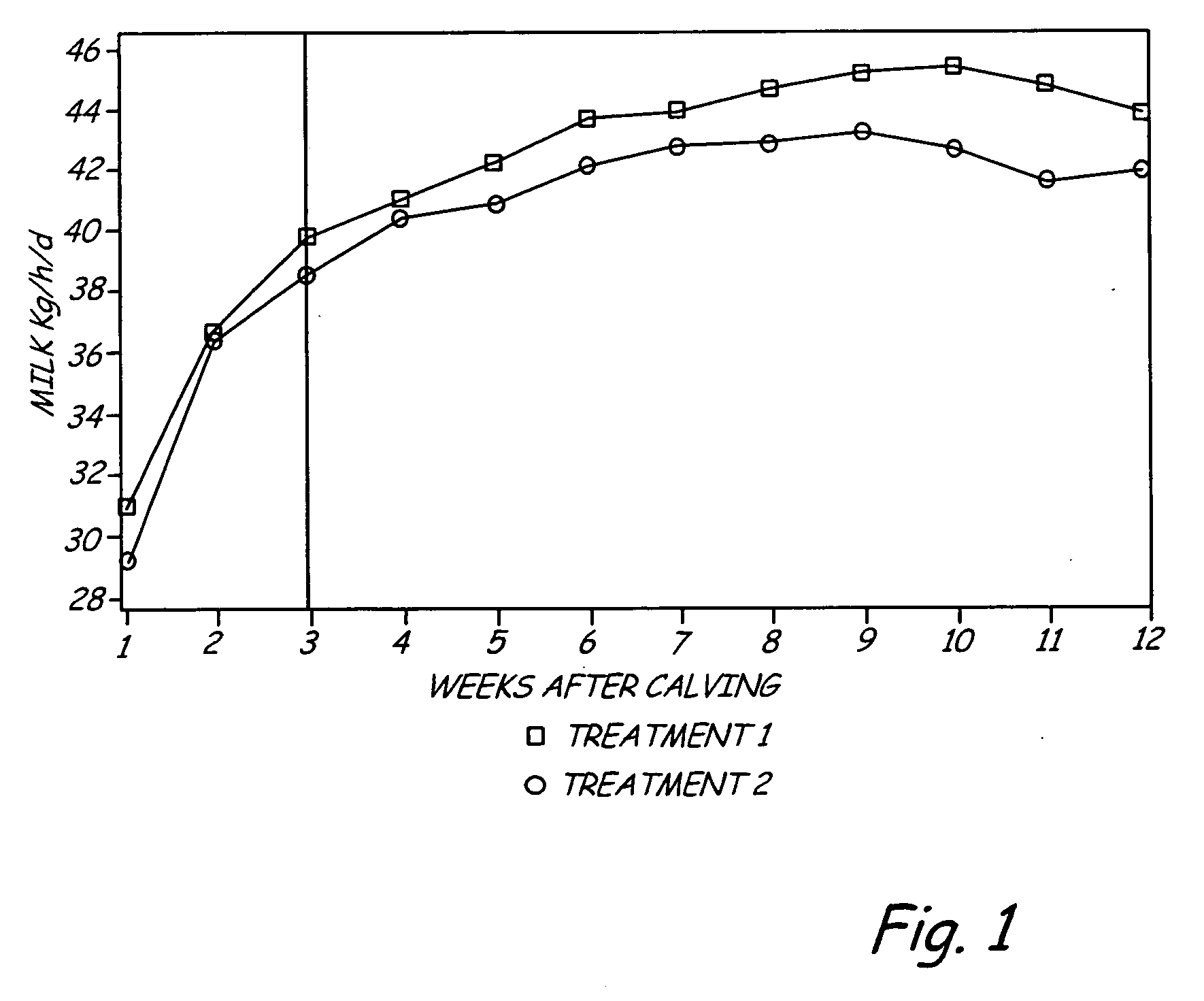
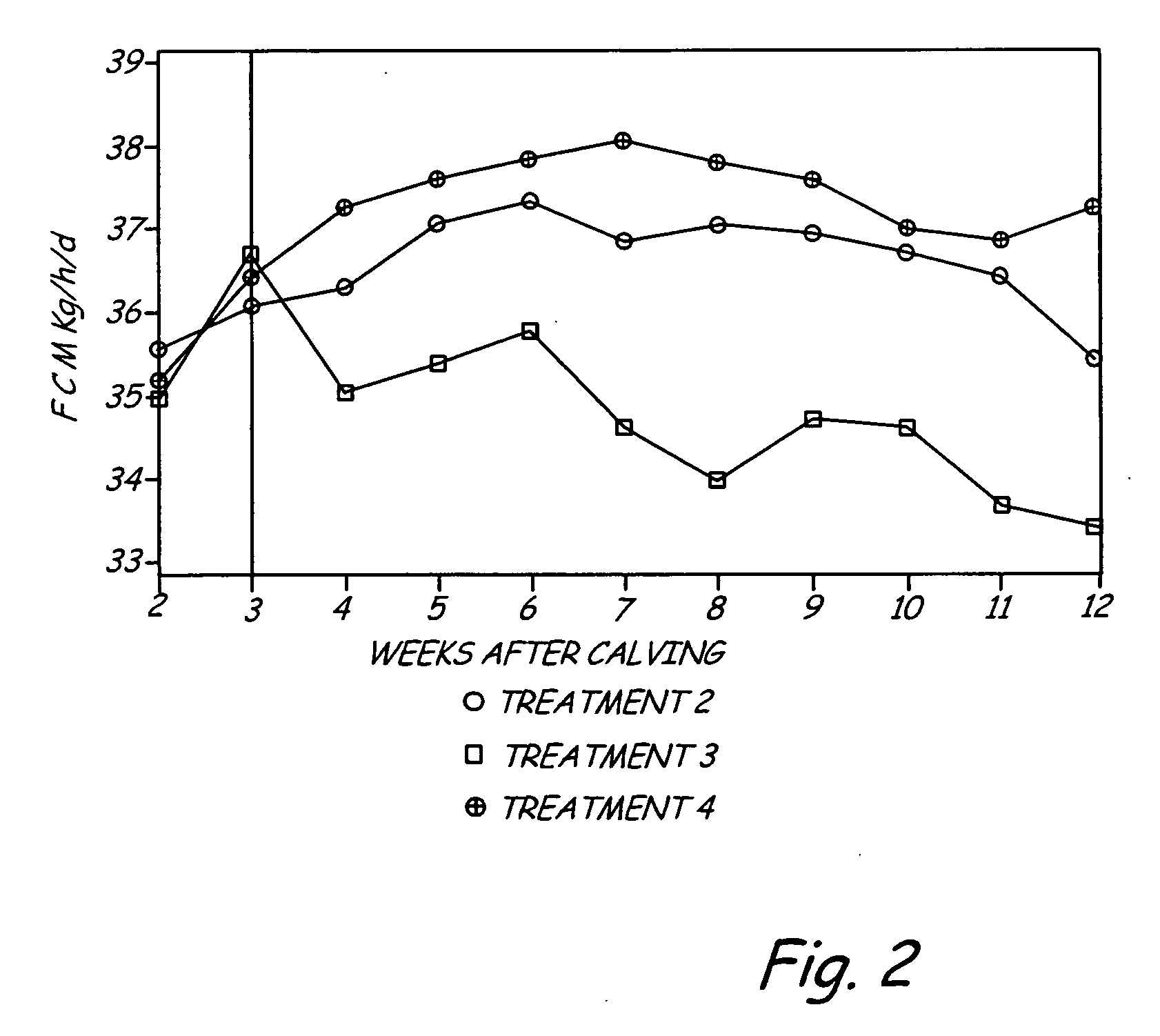
Selective feeding of starch to increase milk production in ruminants
ActiveUS7550172B2Improving milk production and dry matter intakeSugar food ingredientsMetabolism disorderDigestible starchRumen
The present invention includes a method for improving milk production in a ruminant. An amount of ruminally digestible starch in relation to the dry matter of a feed is manipulated to include a first selected ratio of ruminally digestible starch in relation to the dry matter of the feed which is fed to the ruminant during a first time interval after parturition. After the first time interval, the amount of ruminally digestible starch component in the dry matter of the feed is adjusted to a second ratio, lower than the first ratio, and fed to the ruminant.
Owner:FORAGE GENETICS INT
Method for preparing thermally stable slowly digestible starch
InactiveCN102030921AIncrease contentIncrease vitalityFermentationFood preparationDigestible starchPullulanase
The invention relates to a technology for preparing thermally stable slowly digestible starch, belonging to the technical field of preparation of slowly digestible starch in food processing. Ordinary starch is quickly digestible starch, and a thermally stable slowly digestible starch product can be obtained through the following processes (enzymolysis, tea polyphenol adding and spray drying): adding 20-50g of water to 1kg of starch raw material to blend into a 2-5 percent starch suspension, adding pullulanase (the addition is 1-5U / g) at 50 DEG C with a pH value of 5.0, and carrying out enzymolysis for 4-10h; adding 20-80g of tea polyphenol, mixing, heating to 100 DEG C for enzyme inactivating for 125n and cooling to room temperature; homogenizing by a high-voltage homogenizer under 20MPa, and drying into powder by using a spray dryer (the air inlet temperature is 160-200 DEG C, and the air outlet temperature is 80-100 DEG C); and packaging to obtain the slowly digestible starch product.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Slowly digestible starch and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106473100AAvoid contactReduce digestionFood ingredient as emulsifierDigestible starchGellan gum
The present invention discloses slowly digestible starch and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The slowly digestible starch is prepared by using a physical embedding method, "cores" are starch granules, and "shells" are prepared by compounding sodium alginate, gellan gum and chitosan. In the low temperature, a water-in-oil aqueous emulsion is prepared, the prepared aqueous emulsion is subjected to an electrostatic spraying, the sprayed aqueous emulsion is solidified, and the solidified material is subjected to a suction filtration to obtain solid microspheres of the slowly digestible starch. The structures are monodispersed core-shell capsules. In the preparation process, the starch is always in the low temperature, the starch granules are not gelatinized, and the original SDS content is not affected. The sodium alginate / gellan gum / chitosan has good film-forming ability and flexibility, and can always cover the outer layer of the starch granules, so that the slowly digestible starch is not affected by the processing environment and the effect of the processing process in the SDS content is minimized.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Method for preparing slowly digestible wheat starch through coordination of biological enzyme and low-temperature freeze-thawing
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly digestible wheat starch through the coordination of a biological enzyme and low-temperature freeze-thawing, which comprises the following steps: performing debranching treatment on starch through a biological enzyme method; forming a structure the most of which is in the form of a compact perfect crystal under retrogradation action; and performing low-temperature repeated freeze-thawing treatment to destroy the perfect crystal of the starch so as to form a structure the most of which is in the form of an imperfect crystal, thus increasing content of the slowly digestible starch. The slowly digestible starch content in the slowly digestible wheat starch is no less than 30%; and after high-temperature cooking (at 100 DEG C), the residual content of the slowly digestible starch is up to 95% or above. Thus, the slowly digestible wheat starch is especially suitable for being developed into a food for diabetics, has the characteristics of stable property, high safety, low blood sugar generation index, high glucose utilization rate and the like, and is easy to realize industrial production.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of slowly-digestible starch-based recombinant rice with low glycemic index
ActiveCN109393333AIncrease added valueIncrease the added value of technologyFood thermal treatmentFood shapingDigestible starchEnzymatic hydrolysis
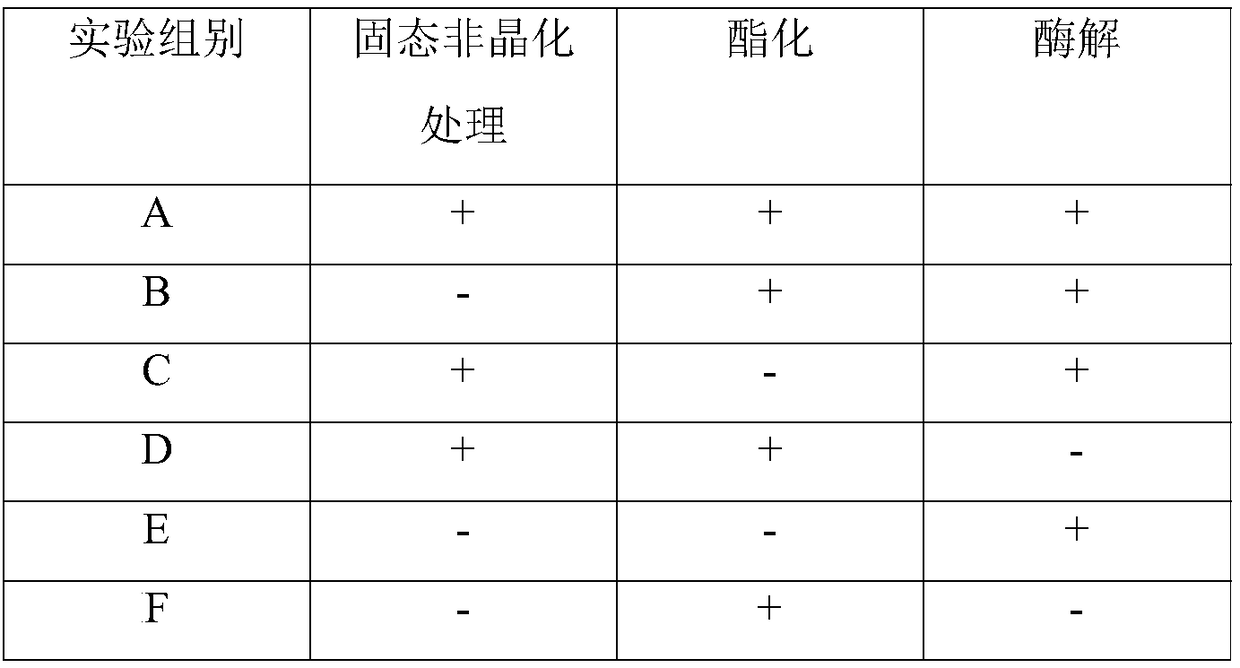
The present invention discloses a preparation method of slowly-digestible starch-based recombinant rice with a low glycemic index, and belongs to the technical field of food processing. After a high-temperature fluidization technology is used to conduct a non-crystallizing treatment of a solid-phase broken rice raw material in a short time, materials are subjected to a one-step reactive extrusiontechnology, enzyme-adding enzymatic hydrolysis and an esterification treatment are combined, and the recombinant rice with high slowly-digestible starch content and low glycemic index is obtained. Therecombinant rice prepared by the one-step shaping extrusion technology is suitable for consumption of patients with type II diabetes. At the same time, the preparation method increases added value ofagricultural and sideline products, reduces production cost, and improves production efficiency.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Slowly digestible starch-containing foodstuffs
InactiveUS20070082109A1High reduction in GISlowly digestibleDough treatmentPreservation by heat treatmentDiseaseDigestible starch
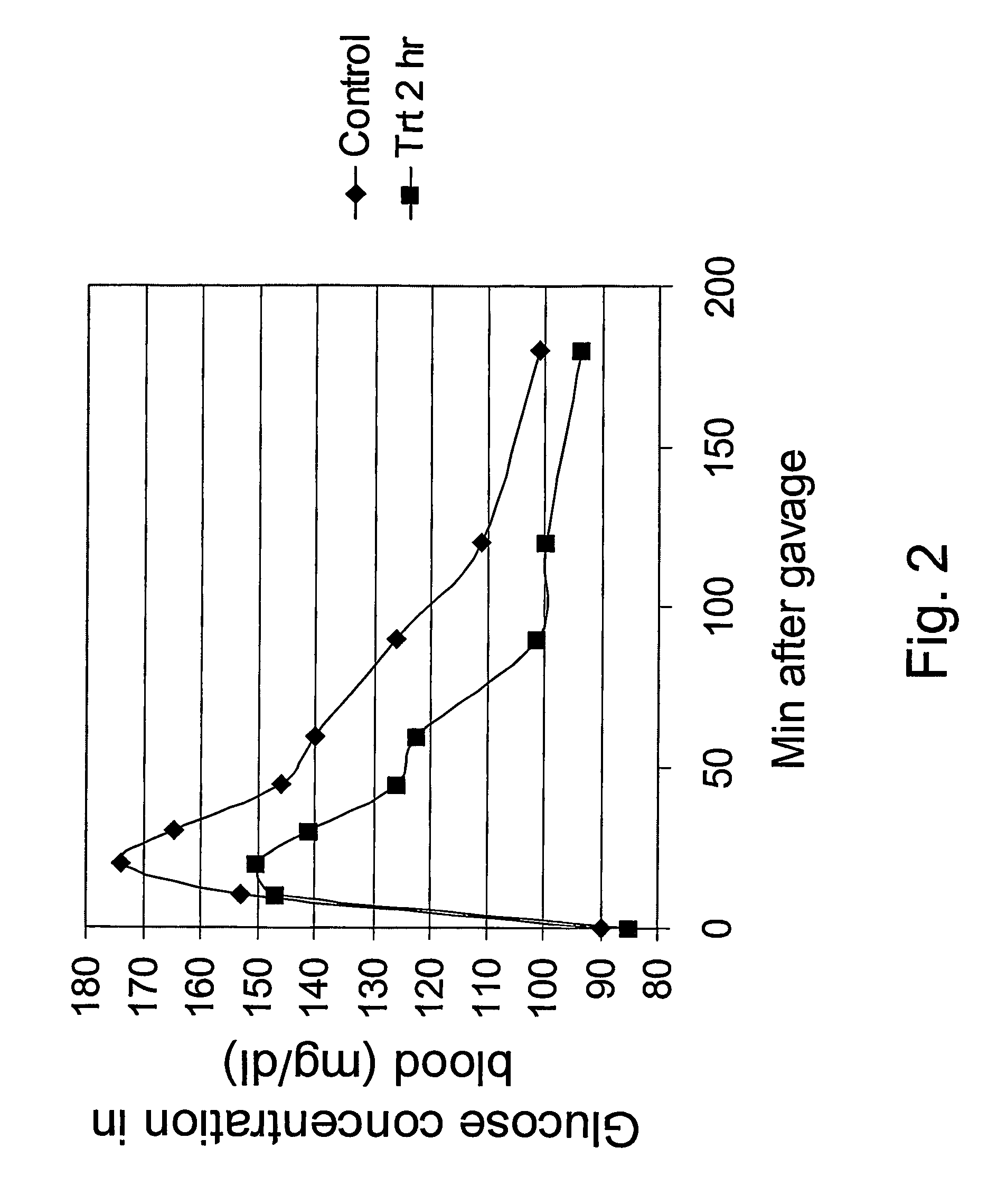
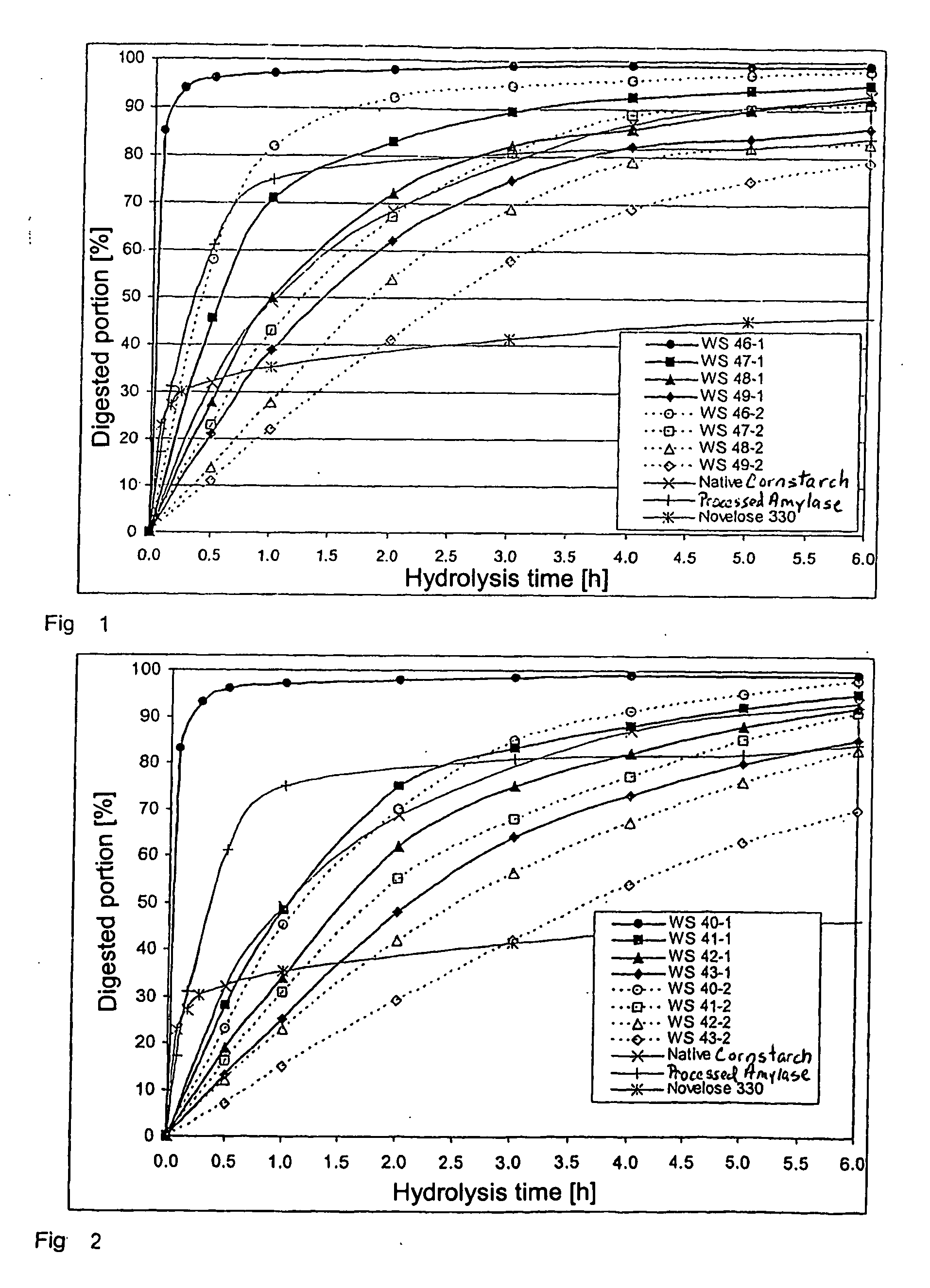
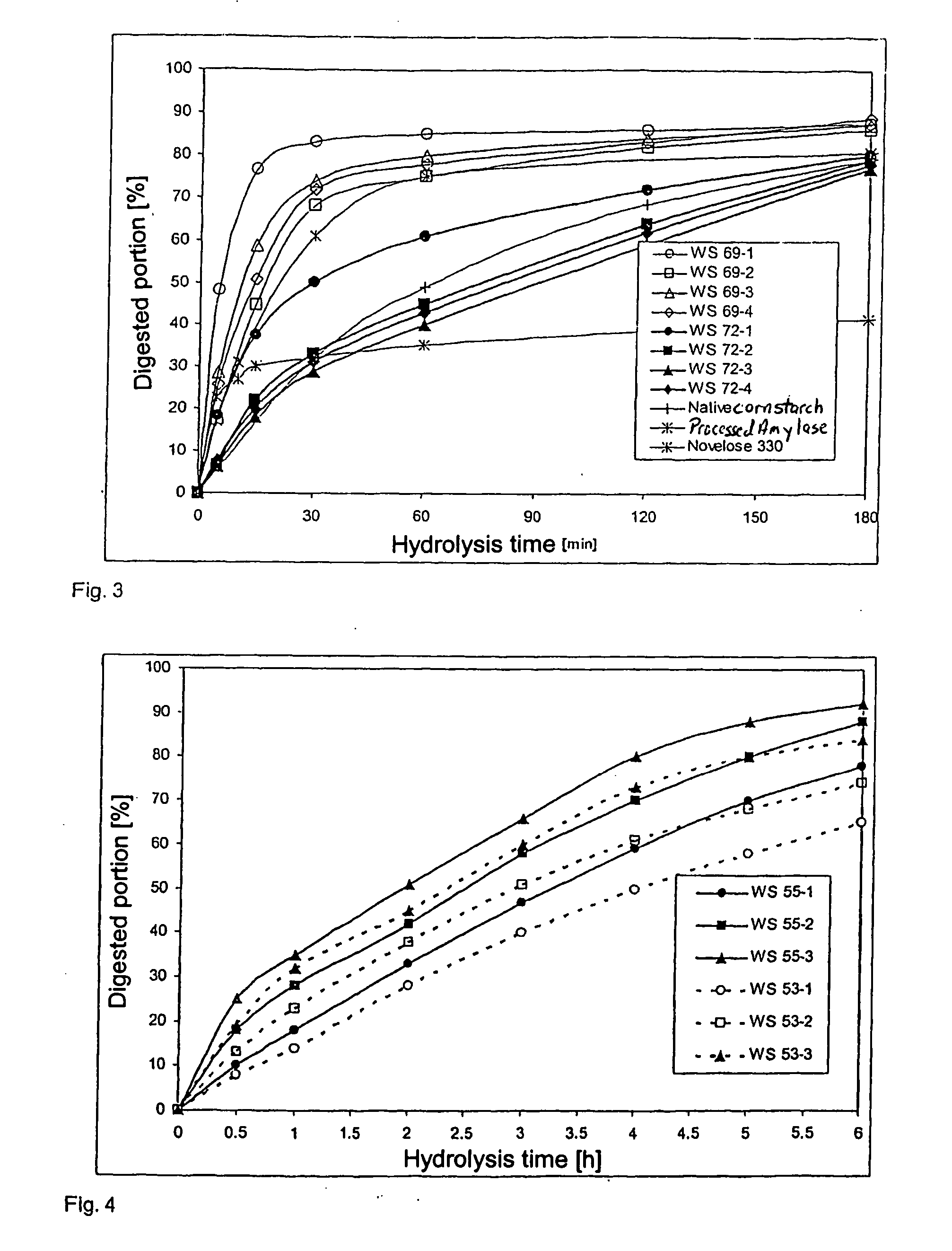
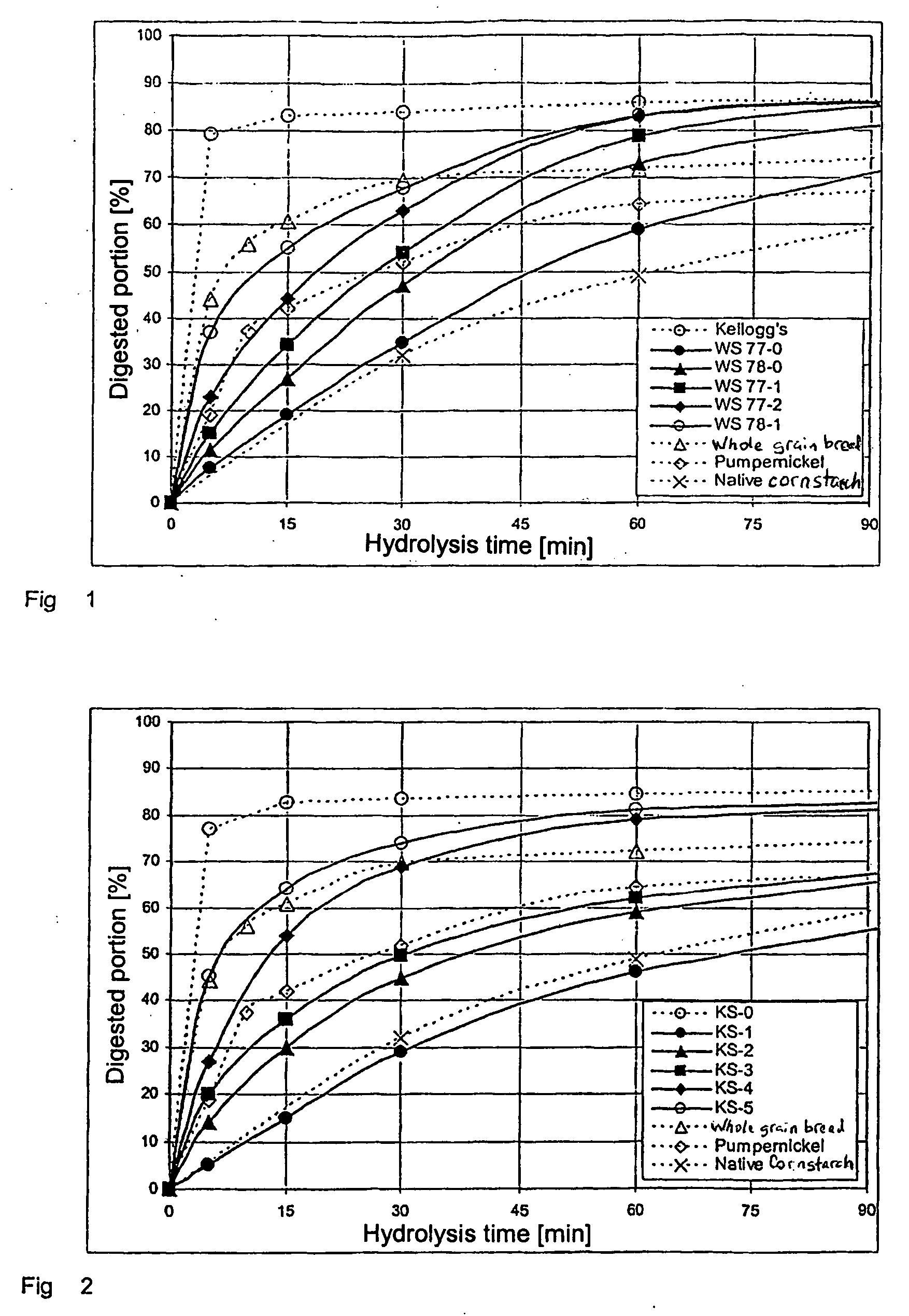
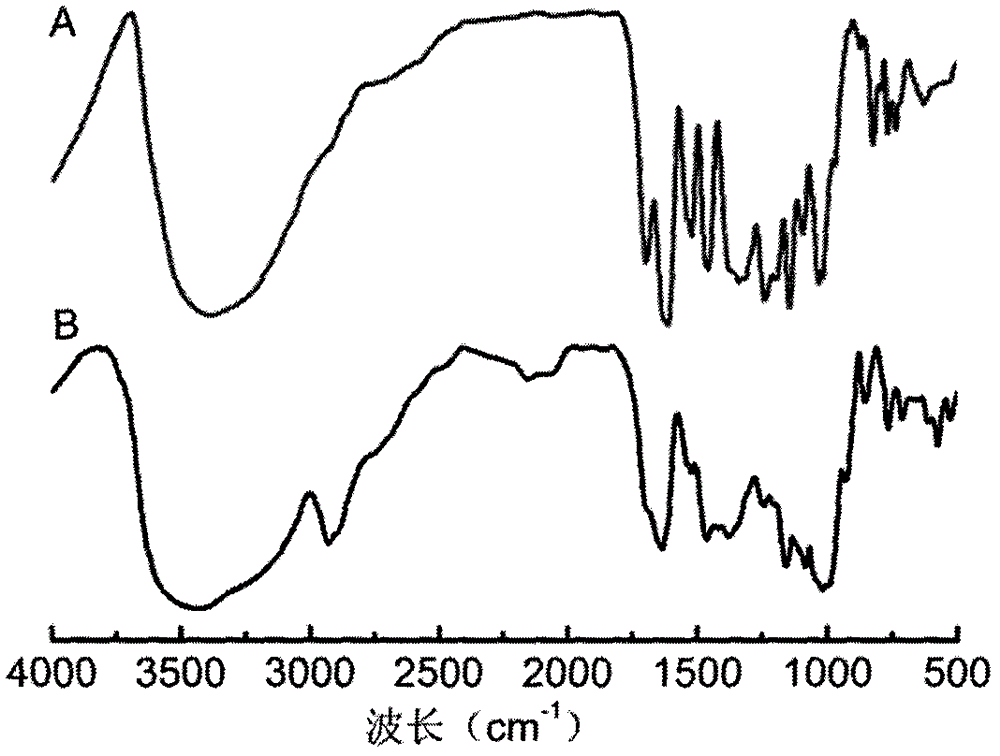
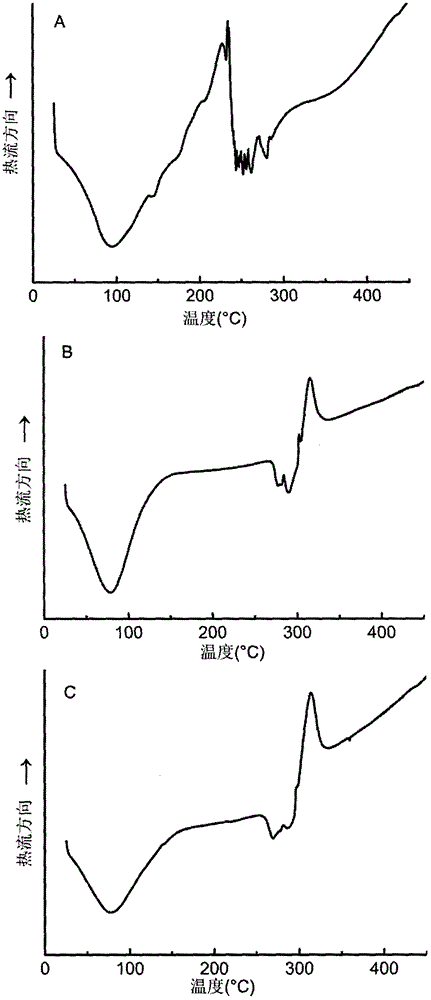
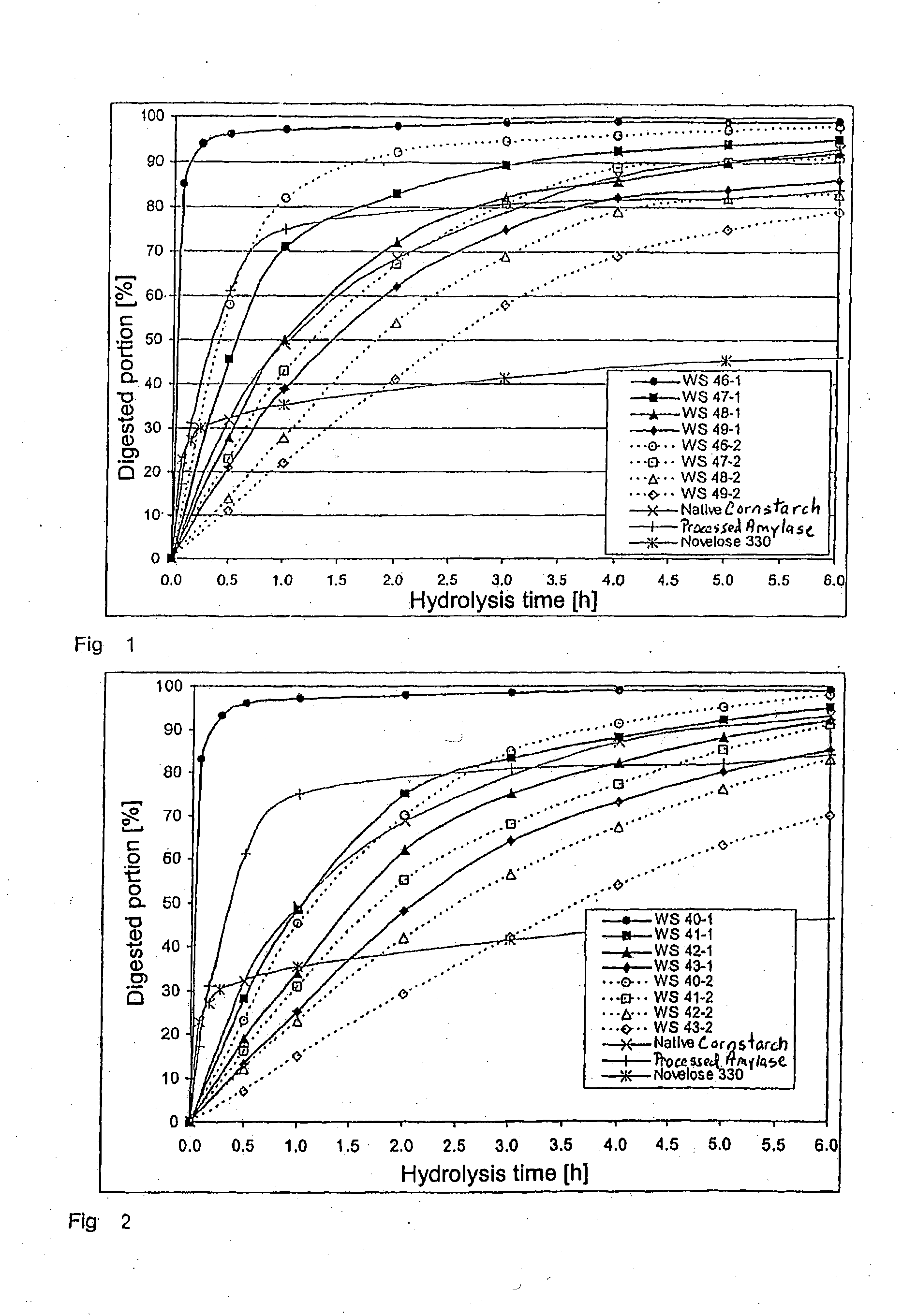
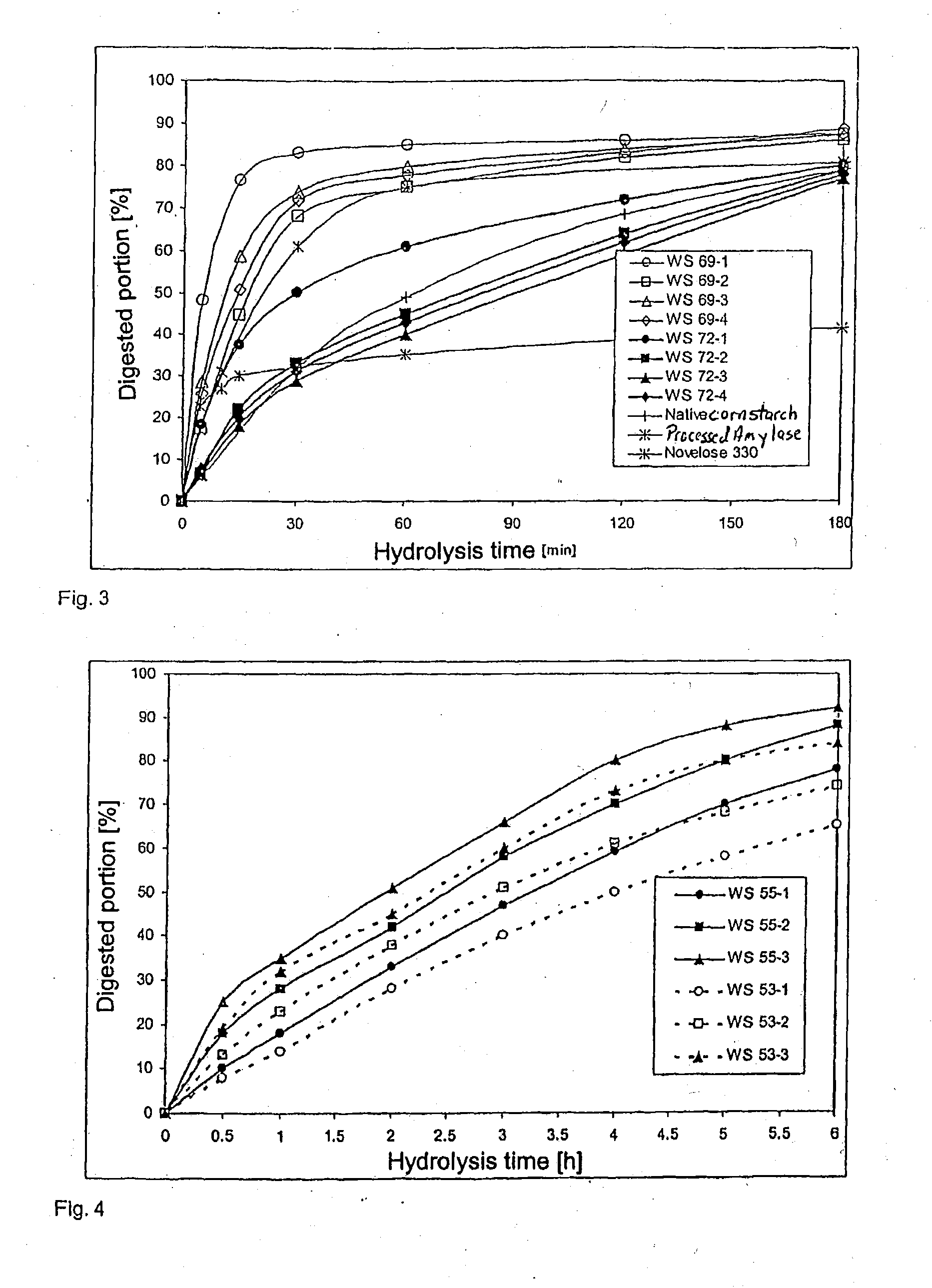
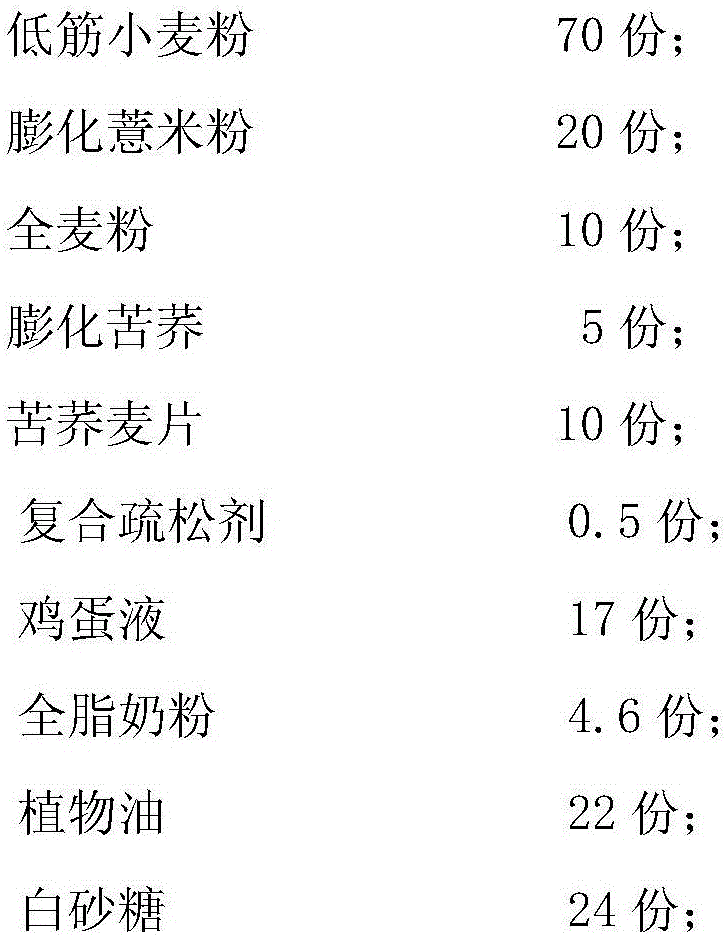
The invention relates to slowly digestible starch-containing foodstuffs, such as cereals and snacks, while a substantial percentage of the starch phase of starch-containing foodstuffs is transformed into a slowly digestible form in situ during foodstuff manufacture by modifying the method typical for the respective foodstuff, and if necessary, the recipe. During the manufacture of starch-containing foodstuffs, the starch is most often prepared to the extent where it digested exceedingly quickly, and converted into glucose in the process. This leads to a rapid rise in the blood sugar level (high sugar), followed by a speedy to severe drop in the blood sugar level (low sugar). These foodstuffs have a high glycemic index (GI). A high number of more recent studies suggest that foodstuffs with a high GI are a significant cause of diabetes, obesity and cardiopulmonary diseases. The WHO believes that indicating GI values on foodstuff packaging would effectively help in preventing the mentioned diseases. Therefore, there is a need for starch-containing foodstuffs that have a reduced GI, i.e., are slowly digested. Within this context, the ideal scenario involves a foodstuff with a constant hydrolysis over time, wherein precisely the amount of glucose consumed for metabolism is released per unit of time. Such a foodstuff would be exceedingly desirable in particular for diabetics. The best currently existing solution for diabetics in this regard is uncooked, i.e., native corn starch (WO 95 / 24906), which is digested relatively slowly. However, the consumption of native cornstarch in the form of an aqueous slurry is unattractive on the one hand, and only a limited time-constant release of glucose can here be achieved on the other. In addition, the temperature stability of native cornstarch is limited, so that only very limited incorporation in processable foodstuff preparations is possible. Other forms of slowly digestible starches include resistant starches (e.g., high corn, Novelose, ActiStar, CrystaLean). These starches exhibit a high crystalline percentage, and about 50% can be digested in the small intestine. The remainder is fermented in the large intestine. The percentage that can be digested in the small intestine is predominantly digested very quickly, so that it makes sense to use only a limited amount of resistant starches as food additives for reducing the GI. Other slowly digestible starches are described in WO 2004 / 066955 A2. These starches are obtained by gelatinizing a suspension of about 5% starch in water,
Owner:MULLER ROLF +1
Method for preparing slowly-digestible starch through malic acid modification
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly-digestible starch through malic acid modification. The method comprises the following steps of: blending the starch by use of a malic acid solution with mass concentration of 15-35% to obtain starch milk in which the mass ratio of malic acid to starch is (1:5)-(4:5), and uniformly mixing; adjusting the pH to 2.5-4.5 by use of a NaOH solution, uniformly mixing, and standing for 8-16 hours at room temperature; putting the product into an air-blowing drying oven at 45-55 DEG C, grinding and sieving with a 100-mesh standard sieve; putting the product in a high-temperature reaction kettle and keeping for 4-8 hours at 120-150 DEG C; taking out the product and cooling; washing the product with distilled water to remove residual malic acid and keep the pH value of the starch at 6-7; and drying in the air-blowing drying oven for 12-36 hours, grinding and sieving with the 100-mesh standard sieve to obtain the product. The malic acid is a harmless additive and can be used as a nutrient supplement. The method disclosed by the invention greatly increases the content of the product slowly-digestible starch, and simplifies the technology for preparing slowly-digestible starch.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing cycloamylose 4-alpha-glycosyl transferase production
InactiveCN101633900AImprove heat resistanceChange propertiesBacteriaTransferasesDigestible starchEscherichia coli
The invention provides a method for preparing cycloamylose 4-alpha-glycosyl transferase production, belonging to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The method uses Escherichia coli CGMCC No. 3093 as a parent strain to prepare pure enzyme 4-alpha-transferase through preparing a seed culture medium by jar fermentation, fermenting and culturing the culture medium in a fermentation cylinder, collecting strains, extracting crude enzyme by ultrasonication and purifying. The transferase prefers a temperature at 75 DEG C and pH of 7.5, and has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, high enzyme activity and the like, wherein, vitality of the 4-alpha-transferase which is primarily purified, frozen and dried can reach 7,000-10,000U / g. The 4-alpha-transferase can act on amylase to generate cycloamylose, and can modify amylopectin to generate slowly digestible starch. Therefore, the transferase can be widely applied in foods, pharmacy and other industries, and has enormous potential commercial value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Food helpful to controlling blood sugar production
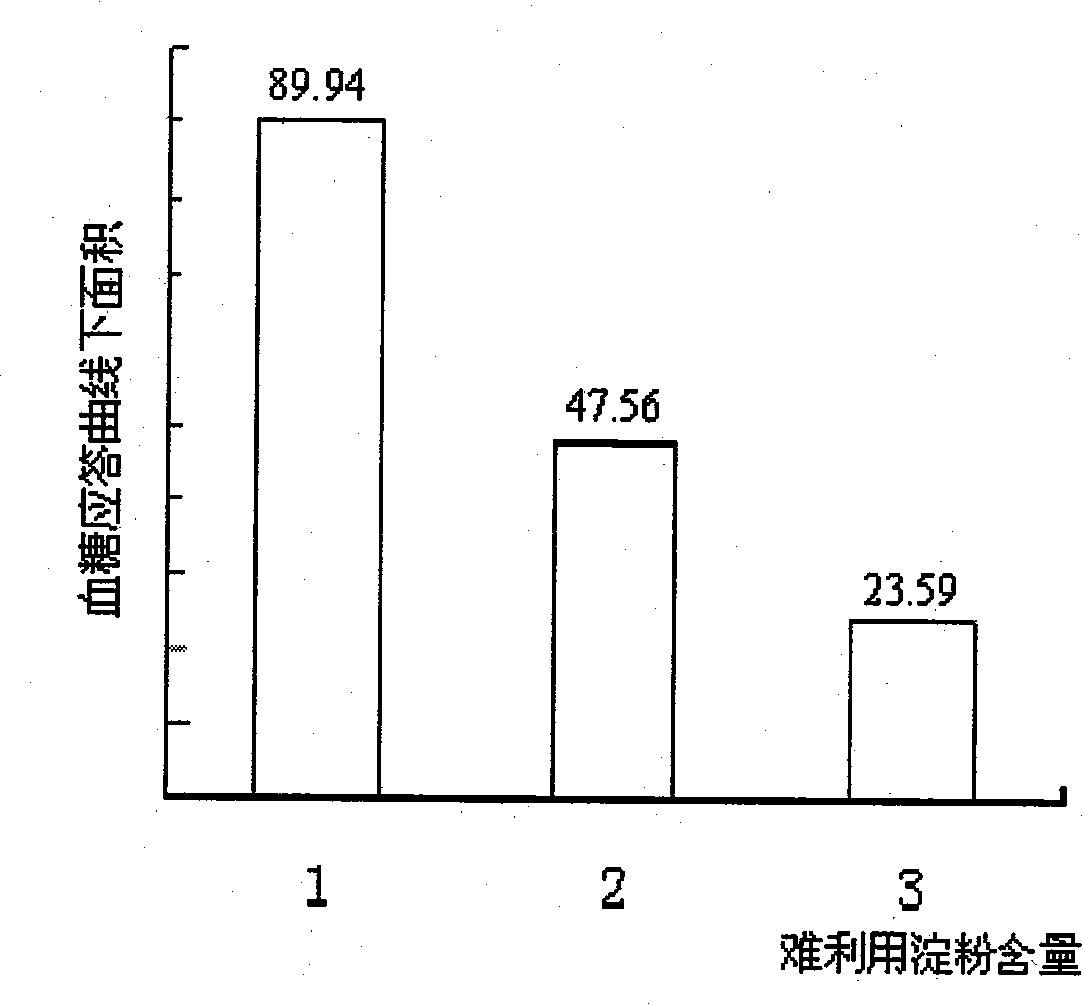
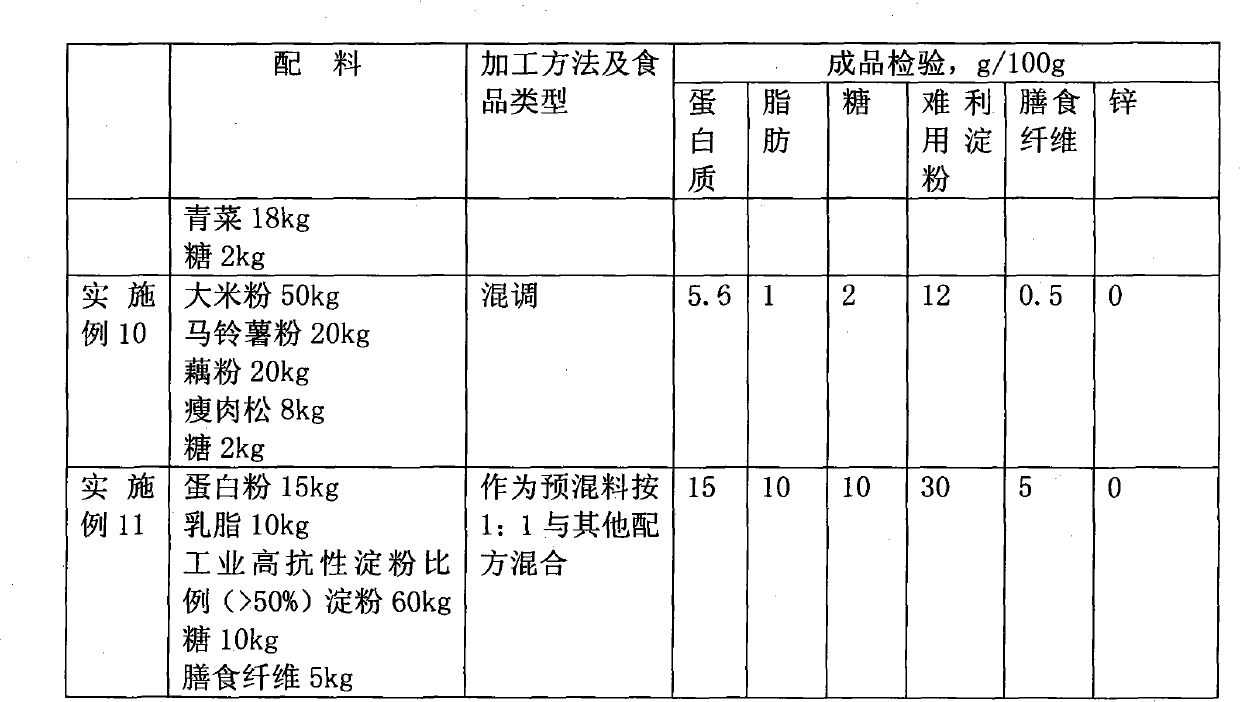
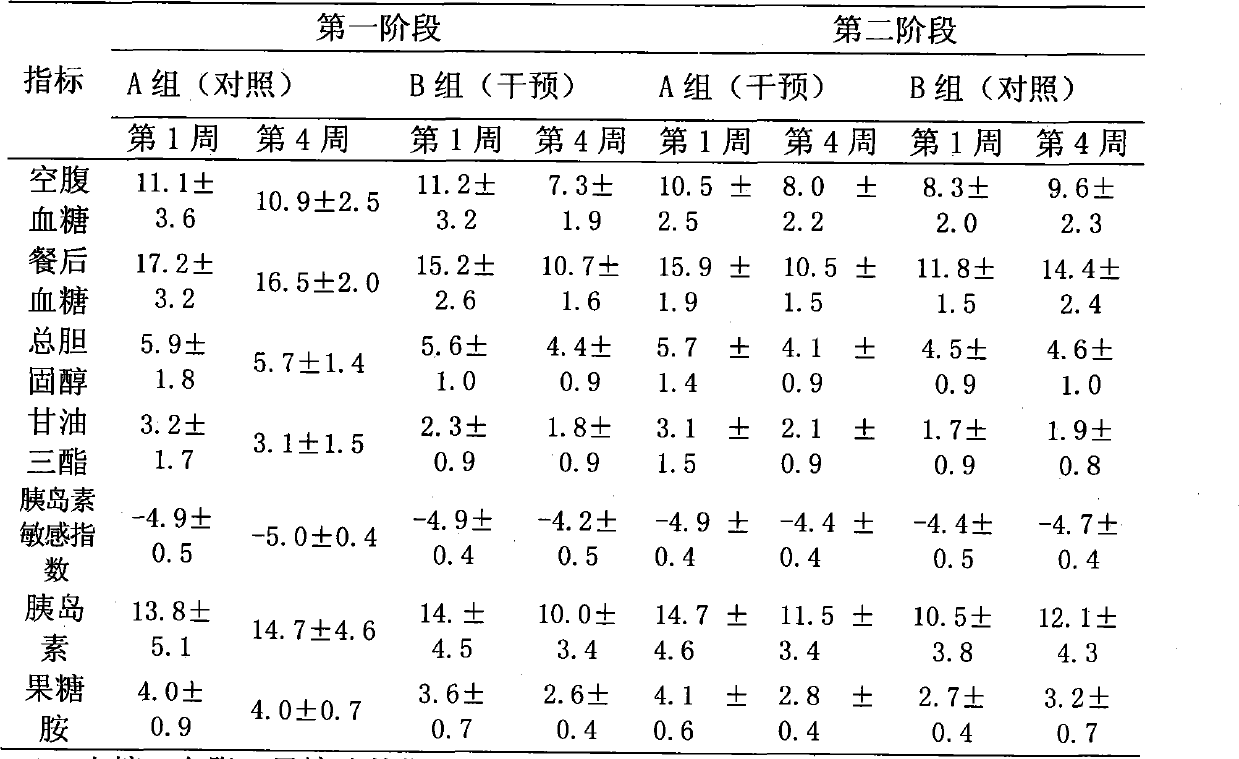
The invention relates to a food helpful to controlling blood sugar production for diabetic patients. The food is characterized in that nutrient in dry substance of every 100g of the food comprises 5 to 20g of protein, 0.5 to 12g of fat, 0 to 10g of sugar, 5 to 30g of difficulty utilizable starch and 0.5 to 6g of dietary fiber, wherein the difficulty utilizable starch is combination of slowly digestible starch and resistant starch according to any proportion. In the formula of the food, the proportion of three major nutritive materials is adjusted so as to obtain the food with high proportion of slowly digestible carbohydrate by means of the digestion characteristic of natural starch, so that good mouthfeel is kept and the requirement of the diabetic patients on control over the blood sugar can also be met.
Owner:王竹 +1
Method for efficiently preparing thermal-stability-type slowly digestible starch by combining chemical method and enzymic method
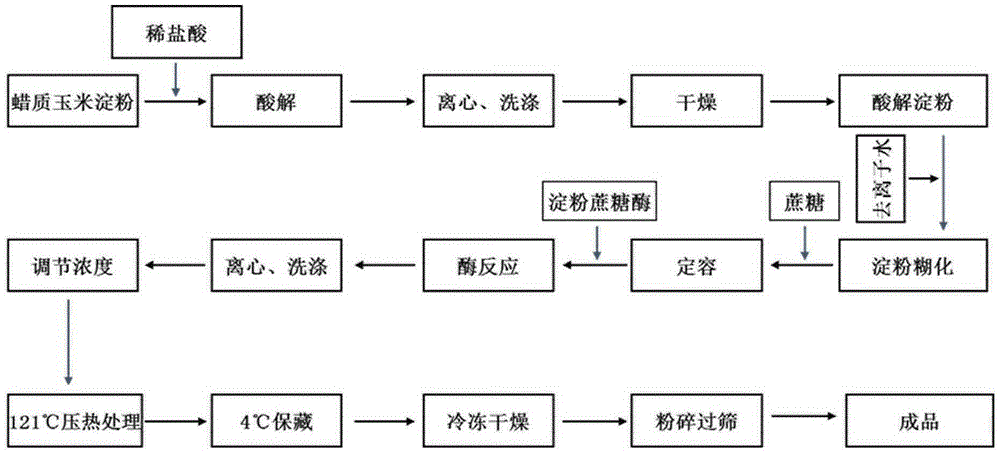
The invention relates to a method for efficiently preparing thermal-stability-type slowly digestible starch by combining a chemical method and an enzymic method. Waxy corn is taken as a raw material, and a preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) acid decomposition treatment; (2) washing and drying; (3) heating and pre-gelatinization treatment; (4) amylosucrase treatment; (5) washing, autoclaving treatment and preserving at 4 DEG C; (6) freezing and drying. According to the method provided by the invention, the defects that the waxy corn is high in viscosity and low in enzyme reaction efficiency under the condition of high concentration, the prepared slowly digestible starch is good in stability, and can be used as an original auxiliary material of food processing for being subjected to hot-working treatment, so the slowly digestible starch has wide market prospect and the method is a novel, simple, efficient and safe thermal-stability-type slowly digestible starch preparation method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cooking appliance and method for starch-based foodstuffs
ActiveUS20200260907A1Reduce decreaseReduction in rapidly digestible starch,Time-controlled ignitorsBiotechnologyDigestible starch
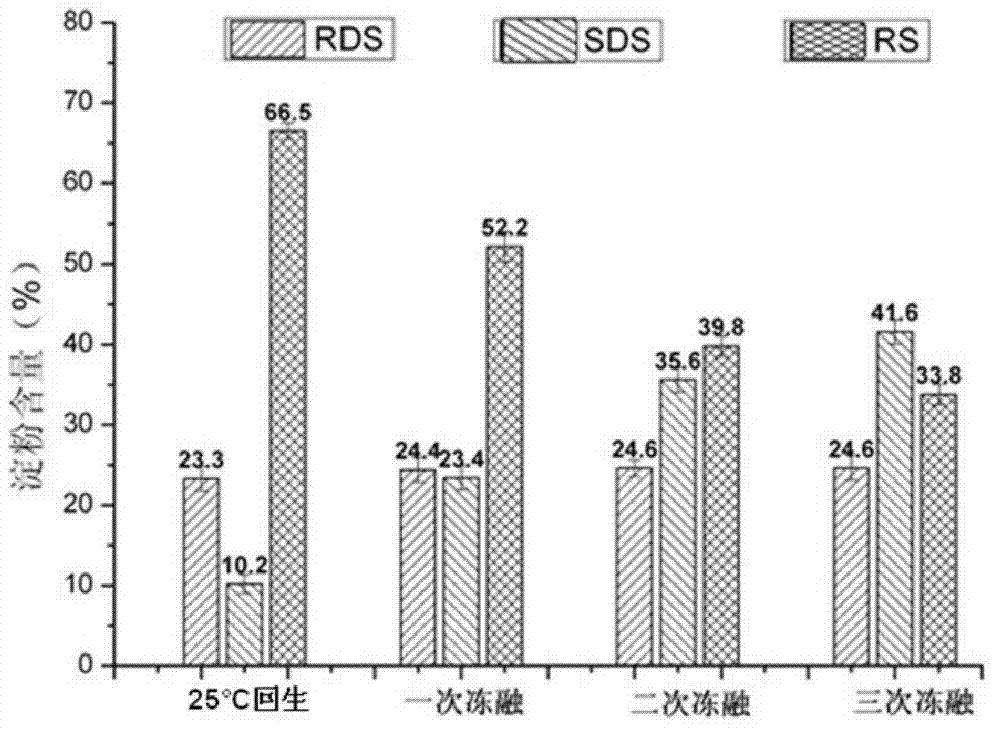
A device for cooking a starch-based food item is provided in which there is a drying cycle at a temperature below the gelatinization temperature and a cooking cycle at a temperature above the gelatinization temperature. The drying provides a relative weight drop by a first amount and the cooking provides a further relative weight drop. The weight is monitored during drying and cooking to provide feedback control of the duration of the drying and cooking times. The device and method make healthy food with reduced rapid digestible starch (RDS) and increased resistant starch (RS) content. In this way the glycemic index (GI) of a food item is reduced and the resistant starch is increased, which is beneficial to health especially for diabetes and obese groups.
Owner:VERSUNI HLDG BV
Method for preparing slowly digestible starch by pressure and heat collaborative double-enzyme treatment
InactiveCN103194508AReduce digestionIncrease nutritionFermentationDigestible starchGlycoside formation
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly digestible starch by pressure and heat collaborative double-enzyme treatment. The method comprises the steps of putting 5-45% of starch milk into a high-pressure sterilization pan to carry out pressure heat reaction, adjusting pH to 4.0-7.5, adding beta-amylase of which the dosage is 50-450U / g of starch at 45-75 DEG C to keep for 1-8hrs; carrying out high-temperature enzyme deactivation; adjusting pH to 4.0-7.5, adding glucose glycosides enzyme at 40-75 DEG C, wherein the dosage is 100-500U / g of starch; keeping for 6-48hrs; carrying out high-temperature enzyme deactivation; naturally cooling, drying by an air dry oven, crushing and screening to obtain the product. By adopting the method, the starch is taken as the material; the content of the slowly digestible starch is greatly improved by a biotechnology in cooperation with a physical treatment method; the technology of preparing the slowly digestible starch is simplified; the yield is effectively improved; and the energy consumption is reduced. The slowly digestible starch produced by the method has the characteristics of retarding digestion, strengthening nutrition and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing digestible starch with resistance improved
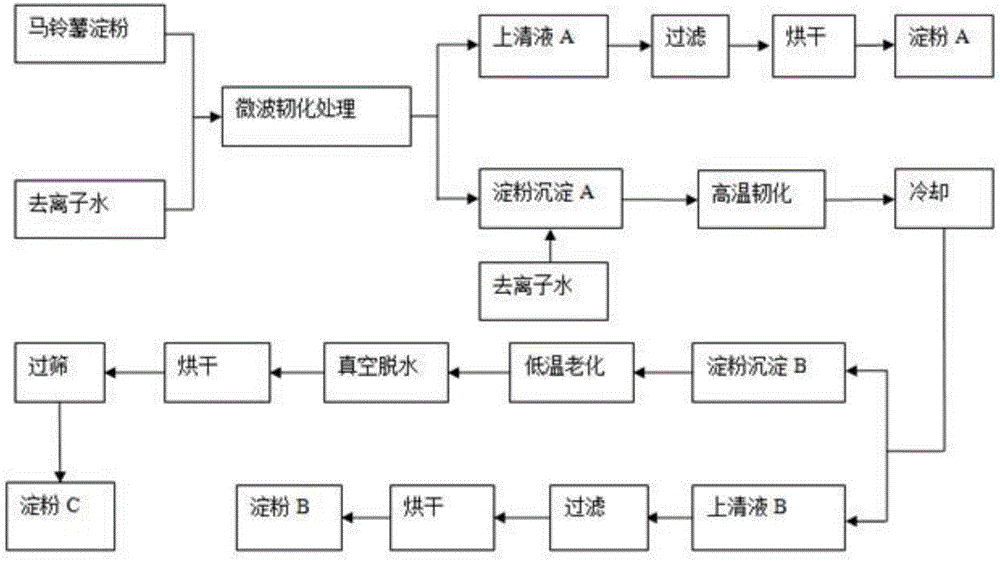
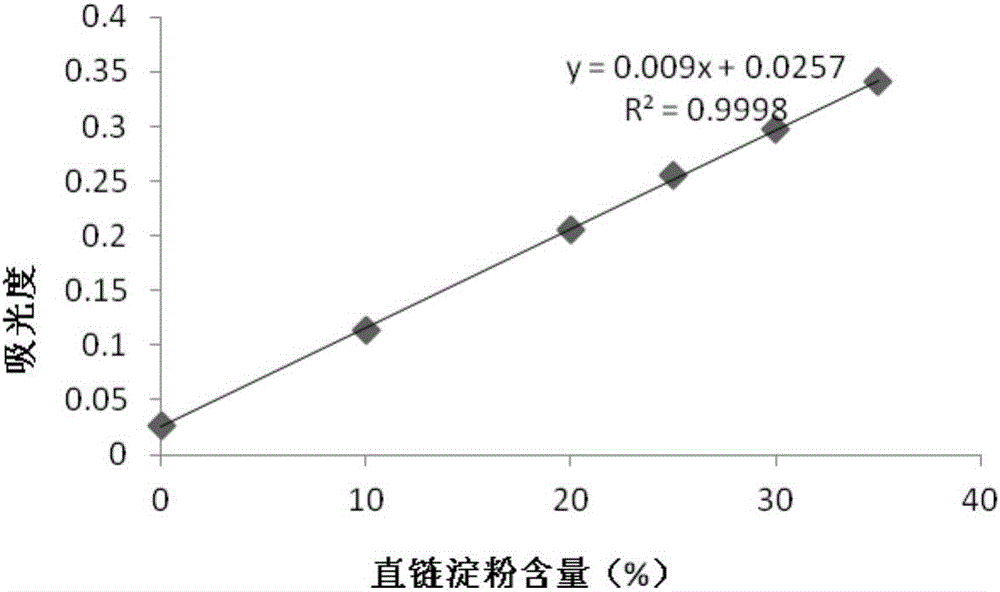
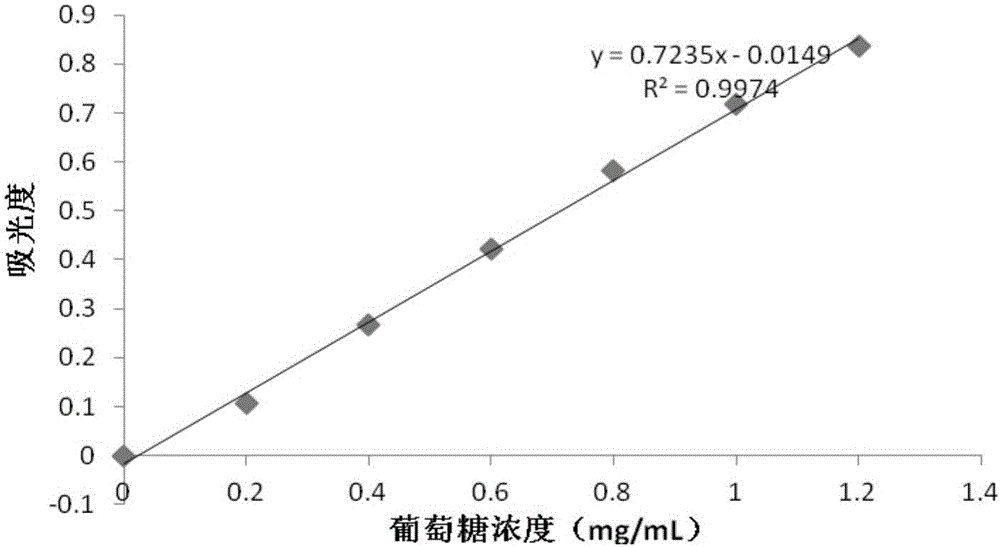
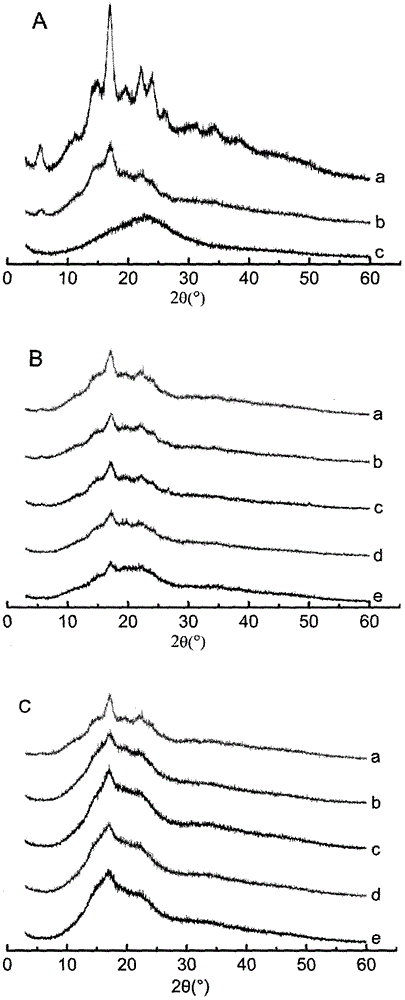
The invention belongs to the field of starch processing and in particular relates to a method for improving resistance of potatoes and enabling the potatoes to be digested more easily. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) adding deionized water into potato starch, and preparing into potato starch emulsion; (2) uniformly stirring the potato starch emulsion obtained in the step (1), toughening with microwave, then taking out and standing, and separating to obtain supernate A and starch sediment A; (3) adding deionized water into the starch sediment A, carrying out high temperature toughening treatment, cooling to room temperature, collecting supernate B, cleaning starch sediment B, then carrying out low temperature ageing, dehydrating, drying, smashing, sieving, and collecting the obtained starch C; and (4) respectively filtering the supernate A and the supernate B, drying the obtained sediment, then smashing and sieving, so that respective corresponding starch A and starch B are obtained respectively. Branch of the potato starch can be removed through the microwave and high temperature toughening treatment, and content of amylose of the potato starch is improved, so that the digestible starch with the resistance improved is obtained.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing starch-tea polyphenol compound by grinding technology
InactiveCN107434829ABelongs to green manufacturing processSimple preparation processDigestible starchX-ray
The invention belongs to the technical field of clathrates, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a starch-tea polyphenol compound by grinding technology. Mainly use starch as the main body, use grinding method, grind tea polyphenols and starch in a certain proportion at room temperature until the required time, use the ability of starch hydrophobic helical cavity to form complexes, embed tea polyphenols, The compound is formed, the method overcomes the shortcomings of the prior art, and the preparation process is simple and convenient, with low energy consumption and low cost. The starch-tea polyphenol complex was prepared by grinding method, the yield was 90.27%, the highest content of slow digestible starch was 80.17%, and the highest content of resistant starch was 36.48%. The formation of starch-tea polyphenol complex was proved by X-ray diffraction, infrared scanning and differential scanning calorimetry. The product prepared by the invention can not only improve the bioavailability of tea polyphenols, change the digestibility of starch, but also prolong the shelf life of the product, and provide a new method for preparing starch-tea polyphenol compound.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Slowly digestible starch product
InactiveUS20110117265A1Slowly digestibleReduce hydrolysis rateDough treatmentPreservation by heat treatmentDigestible starchAdditive ingredient
Owner:INNOGEL AG
Crispy cereal biscuits and making method thereof
InactiveCN105660796AImprove sensory qualityLow sensory qualityDough treatmentBakery productsDigestible starchPolygonum fagopyrum
The invention provides crispy cereal biscuits.The crispy cereal biscuits are prepared from, by weight of dry powder, 70-80 parts of low-gluten wheat flour, 15-20 parts of puffed coix seed flour, 5-10 parts of whole wheat flour, 5-10 parts of puffed tartary buckwheat, 5-10 parts of bitter tartary buckwheat pieces, 0.5-2 parts of a composite bulking agent, 17 parts of egg liquid, 0.3 part of salt, 4.6 parts of whole milk powder, 22-26 parts of vegetable oil, 24-26 parts of white granulated sugar, 2-4 parts of high fructose syrup, 0.5-1 part of phospholipid and 3-4 parts of water.The invention further provides a making method of the crispy cereal biscuits.According to the prepared crispy cereal biscuits, the content of flavonoid compounds like rutin, the content of 18 kinds of amino acid needed by the human body and the content of mineral are higher than those of common crispy biscuits sold in the market, the content of slow digestible starch is no smaller than 35 g / 100 g, and when being eaten frequently, the prepared crispy cereal biscuits have a nutrition function of balancing food and have nutrition effects of softening blood vessels and resisting oxidation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Preparation method of slowly digestible starch
ActiveCN111264840AInhibit enzyme activityIncrease contentPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFood ingredient as flavour affecting agentBiotechnologyDigestible starch
The invention discloses a preparation method of slowly digestible starch, and belongs to the technical field of starch modification. According to the invention, common rice starch and corn starch areused as raw materials; starch is fully declustered through dry heat non-crystallization treatment, traditional hydrothermal gelatinization is replaced, amino acid and starch milk are induced to be complexed through ultrasonic waves to form VI-type crystals, finally, the VI-type crystals are converted into VII-type crystals through an extrusion technology, and the content of slowly digestible starch is remarkably increased to 55%-60%. The preparation method is efficient, simple, convenient and environment-friendly, and the prepared product can be used as a drug sustained-release carrier or a low-glycemic-index food ingredient and has important practical value for regulation and control of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for producing slowly digestible starch
InactiveUS20100086668A1Provide quicklyVast supplyFood ingredient functionsFood preparationDigestible starchGlucose polymers
A sterilised food product containing starch, the starch having: (a) an amylose content of at least 60 wt. %; (b) a median particle size of between 1 and 15 &mgr;m, at least 90 wt. % of the starch particles having a particle diameter of less than 50 &mgr;m; and (c) a non-digestible starch content of less than 50 wt. %; and (d) a slowly digestible starch content of 15-75 wt. %. The product is obtained by heating and rapidly cooling the starch product and has a high slowly digestible starch content. It is suitable for use in the treatment of diabetes, obesitas, insulin resistance, or for postprandial glucose response.
Owner:NUTRICIA
Process for producing slowly digestible starch
InactiveUS8642110B2Provide quicklyVast supplyFood ingredient functionsFood preparationDigestible starchGlucose polymers
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes
ActiveCN108251475ADelayed digestionTightly branched structureOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDigestible starchCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes and belongs to the field of biologically modified starch. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the starch is cooperatively treated by utilizing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a starch branching enzyme; the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase is catalyzed to generate cyclodextrin and a lot of short-chain segments are generated; a fine and long type starch molecule is converted into a short and fat structure which is a tighter branch structure under the action of the starch branching enzyme, so that the slow digestion of the starch is more remarkable. By changing an adding manner of the two enzymes, an enzyme adding amount and reaction time, a cooperative effect between the two enzymes is promoted, the content of the cyclodextrin and the branching degree of amylopectin are improved; the content of the slowly digestible starch and resisting starch is further increased andthe digestion speed of the starch is reduced; a novel concept is provided for preparing the slowly digestible starch through biological modification.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of producing starch having high-less digestible starch content
InactiveUS20100183797A1High production costIncrease contentFood preparationDigestible starchThermal water
It is intended to provide a method of easily and economically producing starch which has an increased content of less digestible starch. The method of producing starch having a high content of less digestible starch is characterized by comprising contacting starch with hot water at a temperature of 160 to 260° C. which has a pressure corresponding to the saturated vapor pressure at that temperature or more.
Owner:J OIL MILLS INC +1
Selective feeding of starch to increase milk production in ruminants
ActiveUS20080152754A1Increase milk productionImproving milk production and dry matter intakeSugar food ingredientsMetabolism disorderDigestible starchRumen
The present invention includes a method for improving milk production in a ruminant. An amount of ruminally digestible starch in relation to the dry matter of a feed is manipulated to include a first selected ratio of ruminally digestible starch in relation to the dry matter of the feed which is fed to the ruminant during a first time interval after parturition. After the first time interval, the amount of ruminally digestible starch component in the dry matter of the feed is adjusted to a second ratio, lower than the first ratio, and fed to the ruminant.
Owner:FORAGE GENETICS INT
Okra seed dietary fiber gluten-free biscuits high in slowly-digestible starch content and high in resistant starch content and making method of okra seed dietary fiber gluten-free biscuits
ActiveCN109463417AMature manufacturing technologyHas an anti-digestive effectDough treatmentModified nutritive productsDigestible starchBlood sugar
The invention relates to okra seed dietary fiber gluten-free biscuits high in slowly-digestible starch content and high in resistant starch content. The okra seed dietary fiber gluten-free biscuits consist of the raw materials in parts by weight of based on 100 parts of rice flour and okra seed powder by total weight, 94-98 parts of the rice flour, 2-6 parts of the okra seed powder, 20-30 parts ofbutter, 30-80 parts of eggs, 0.5-2 parts of baked powder, 0.5-1 part of salt and 6-20 parts of water. The rice flour and the okra seed powder are used, so that the okra seed dietary fiber gluten-freebiscuits high in slowly-digestible starch content and high in resistant starch content are made. The preparation technology of products is mature, and the okra seed dietary fiber gluten-free biscuitscan maintain blood sugar stable and satiety, reduce the hungry feeling, and besides, have positive role on the effect of regulating intestinal flora. According to the okra seed dietary fiber gluten-free biscuits, in the range of the required additive amount of the okra seed powder, the products are uniform in appearance color, light golden, and crisp, fragrant and sweet in mouth feel.
Owner:河北玉桥食品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com