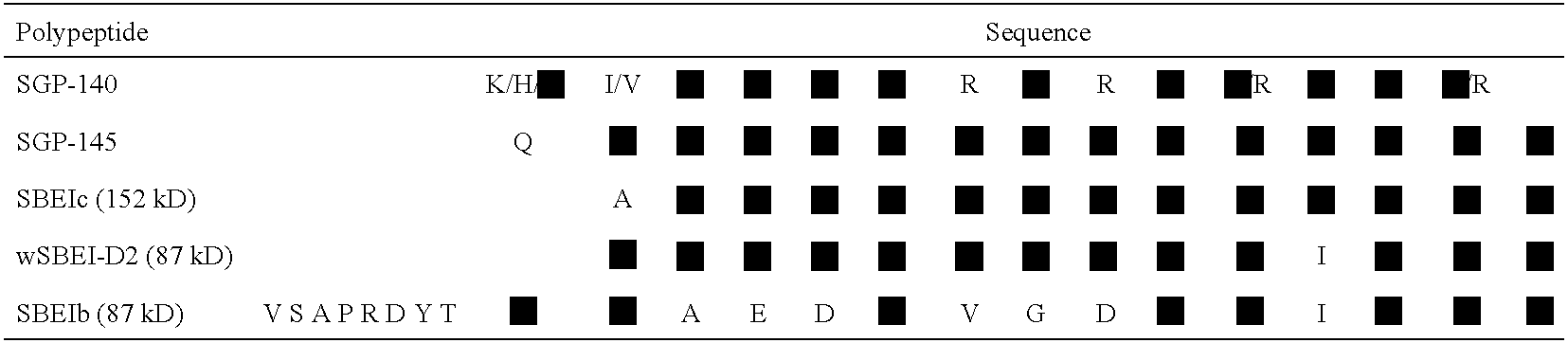
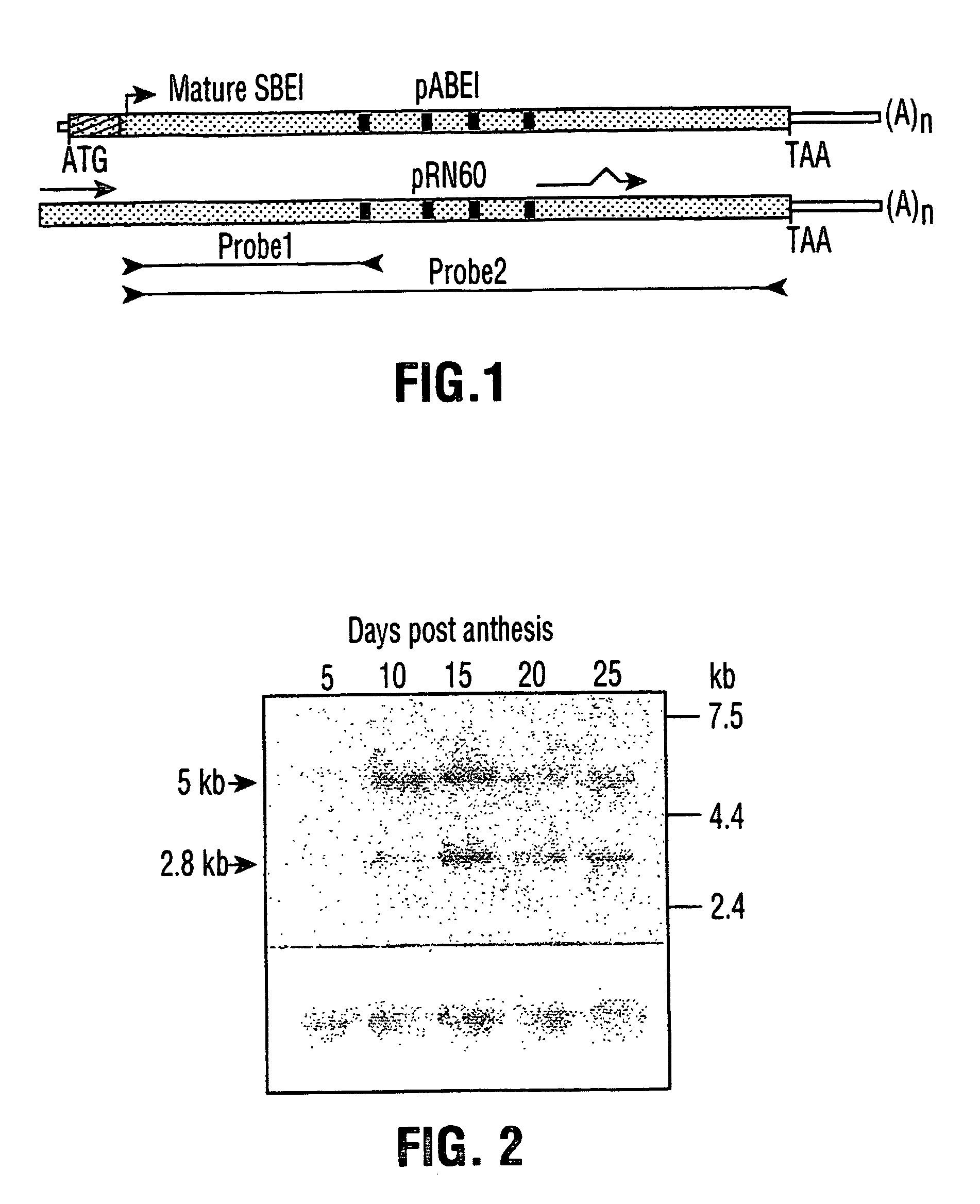
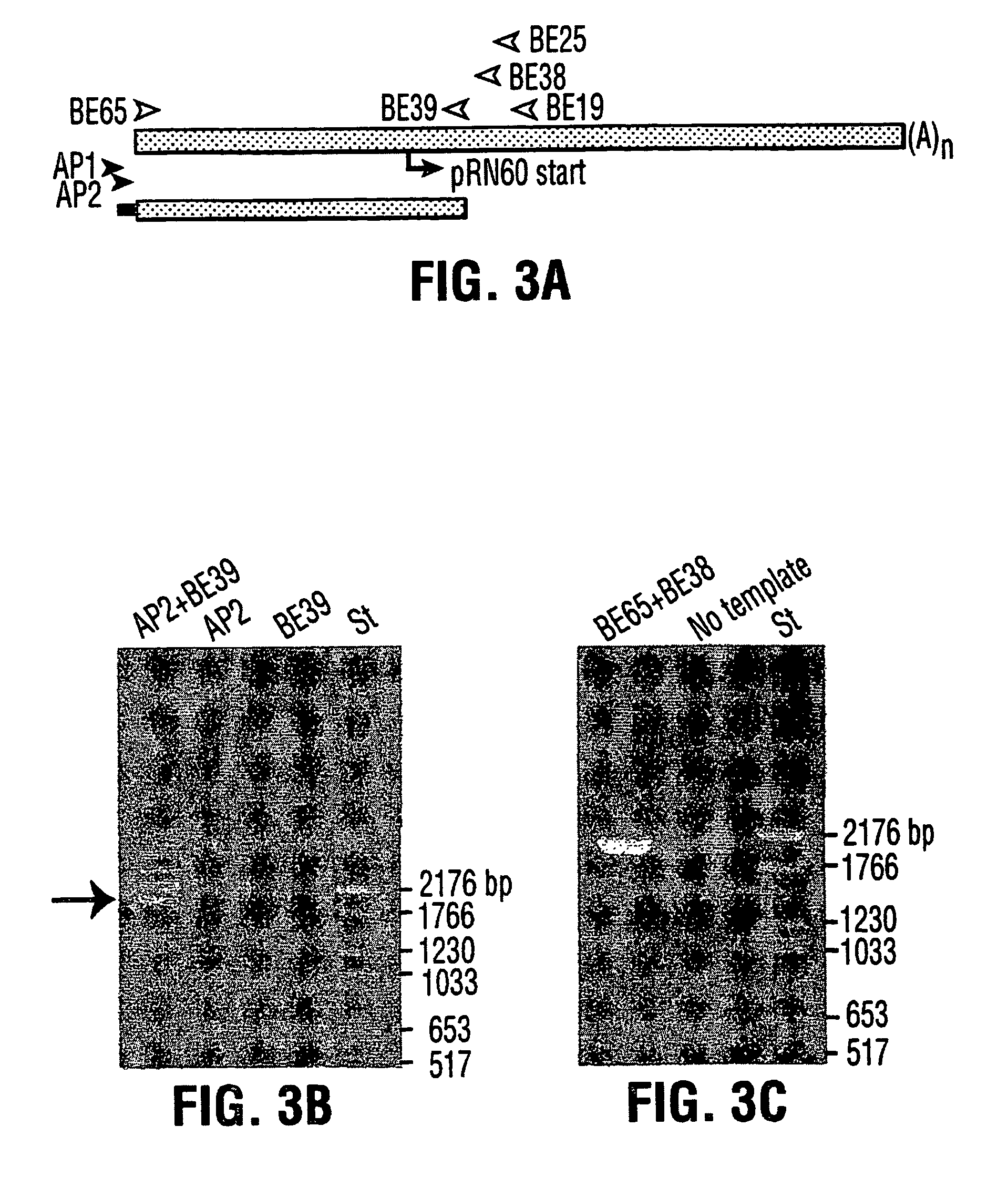
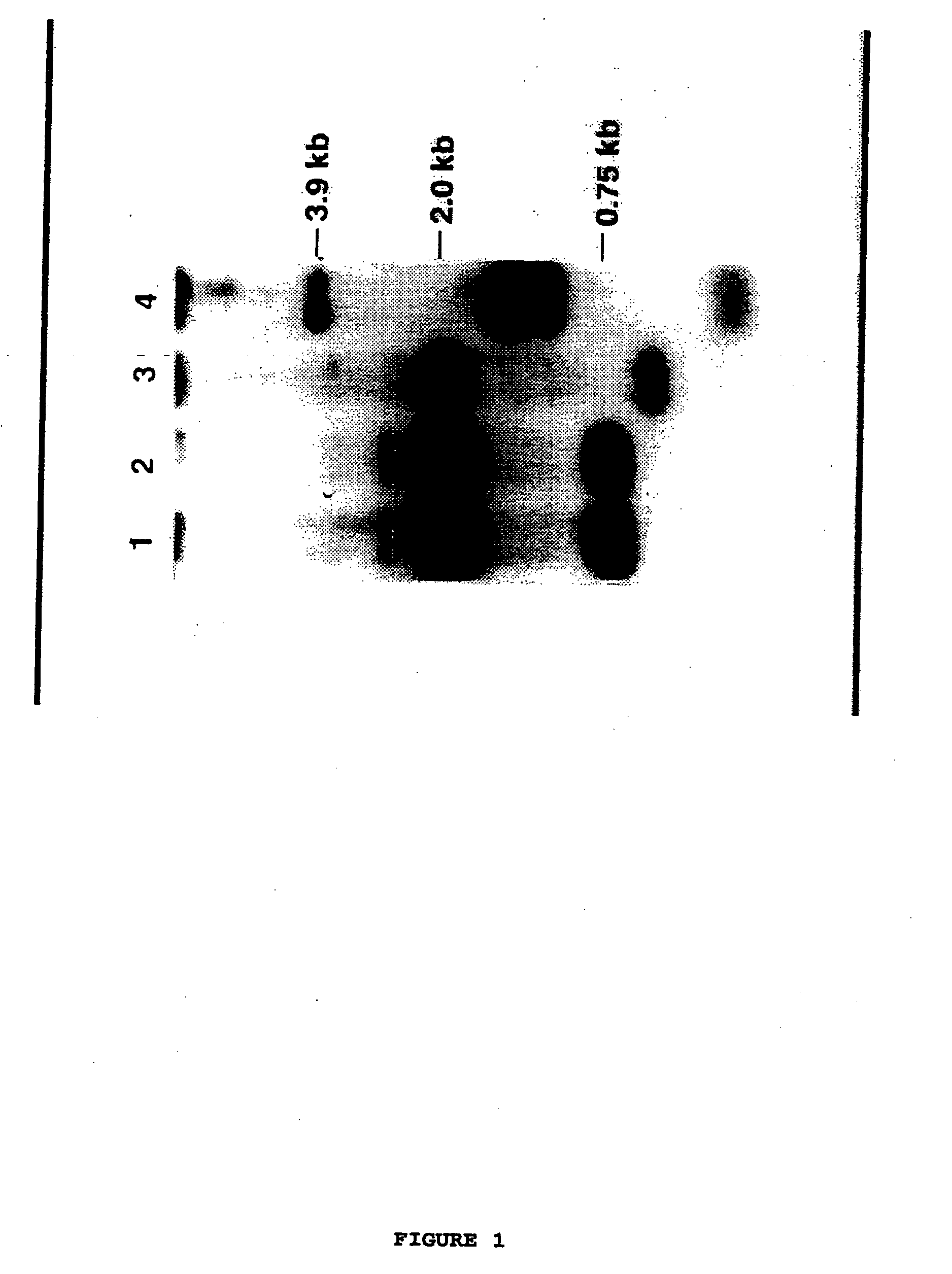
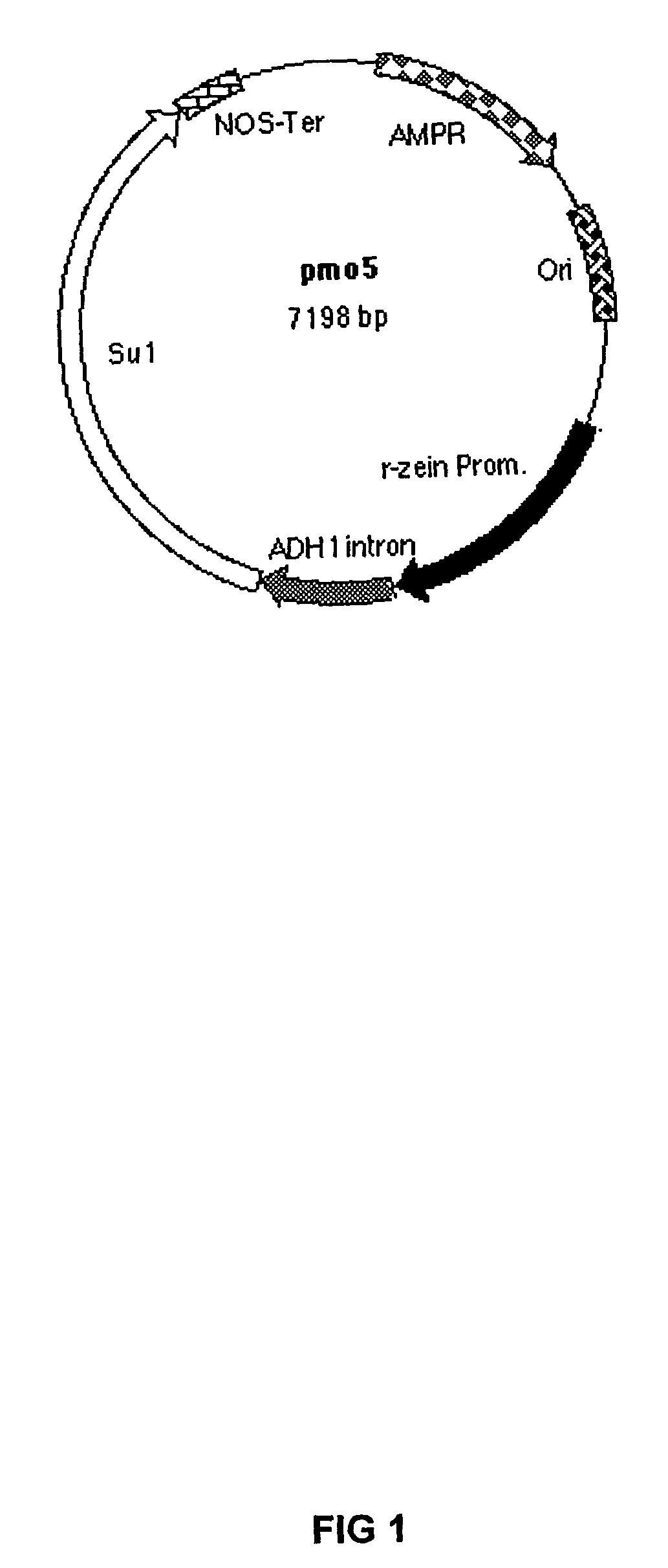
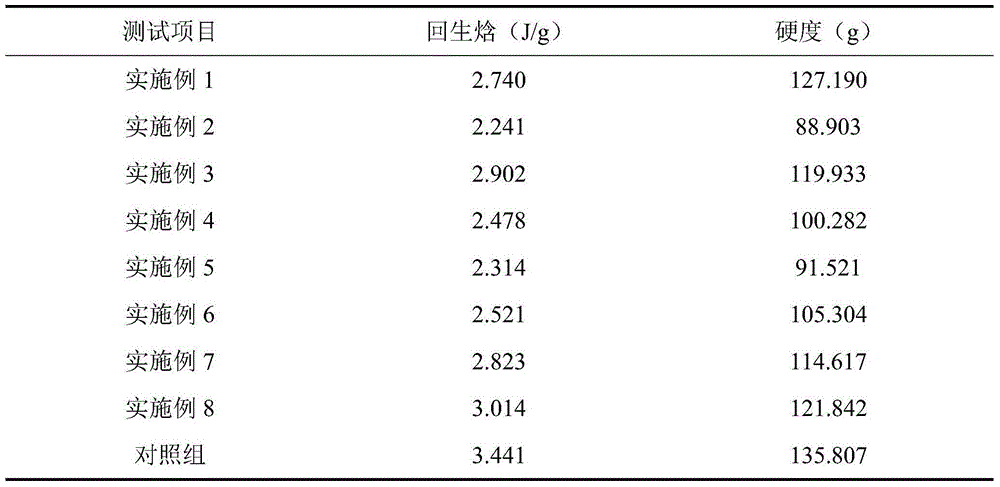
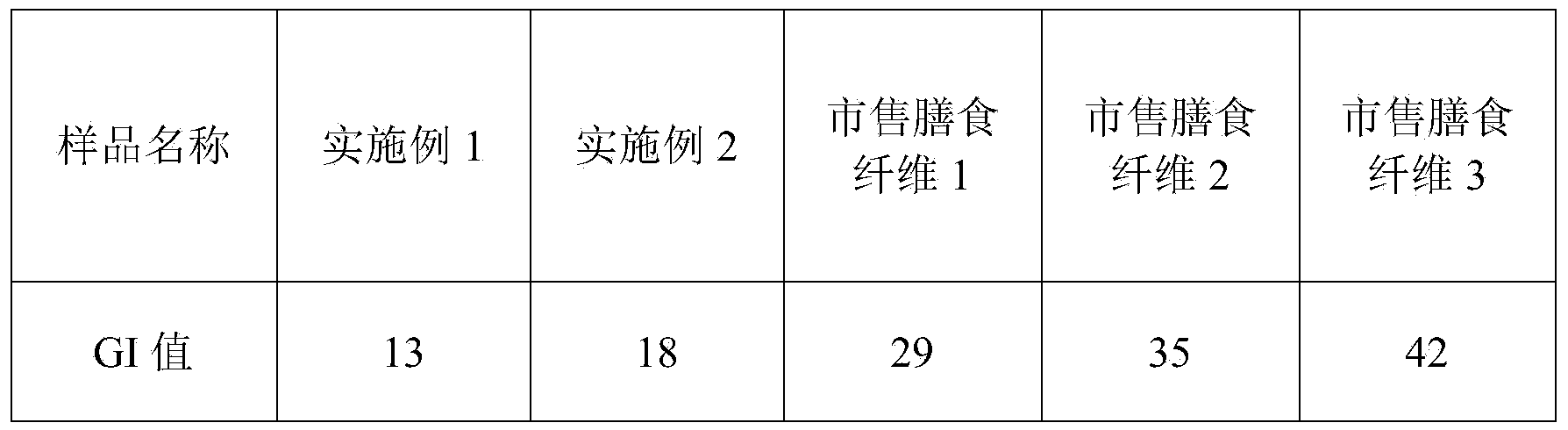
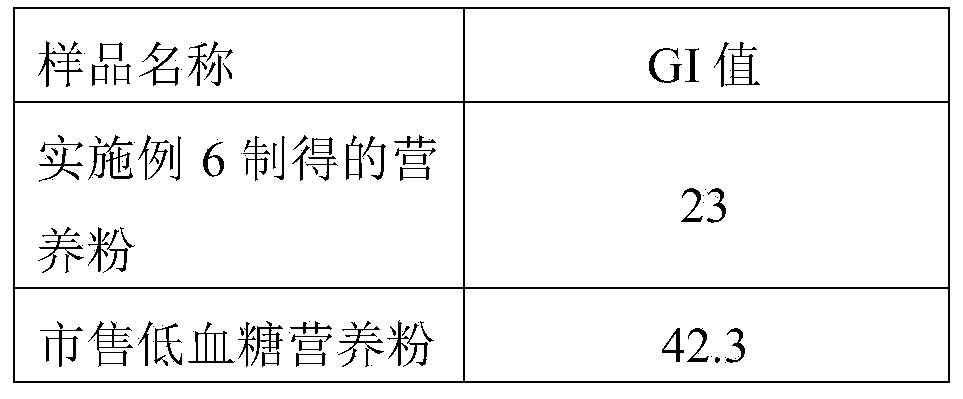
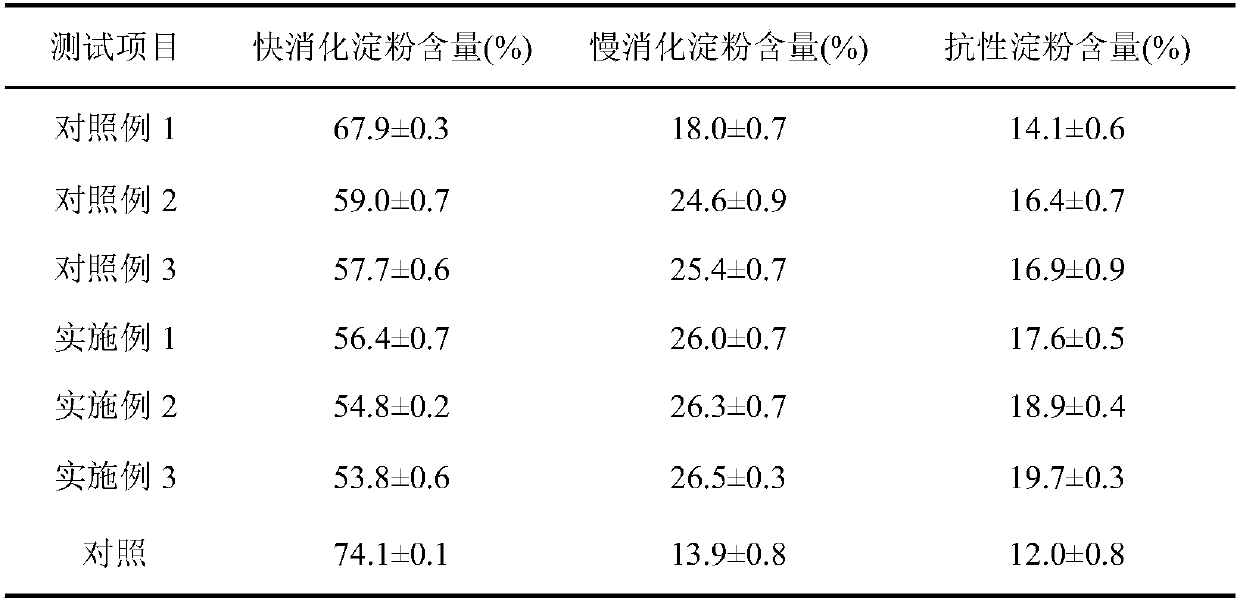
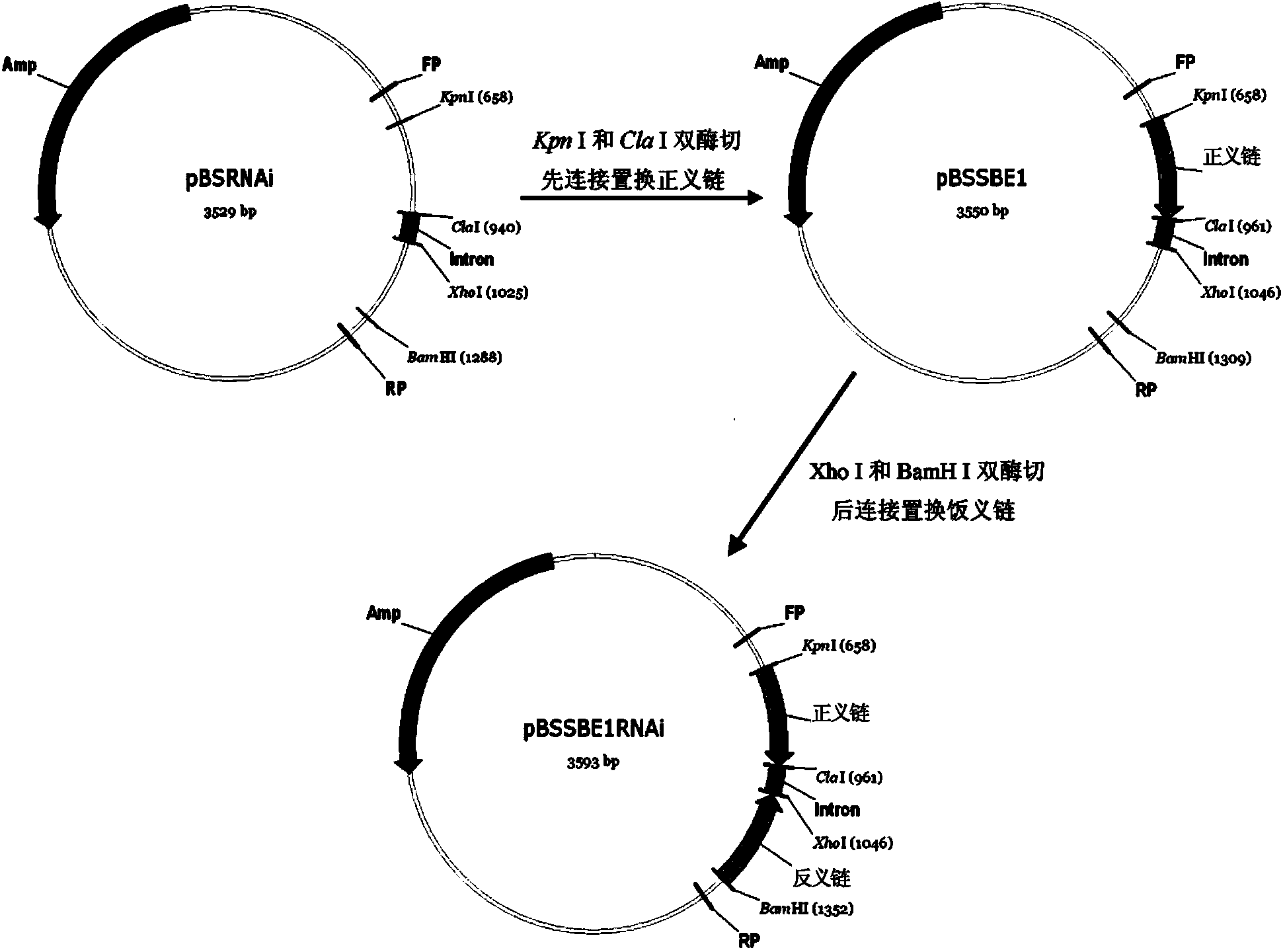
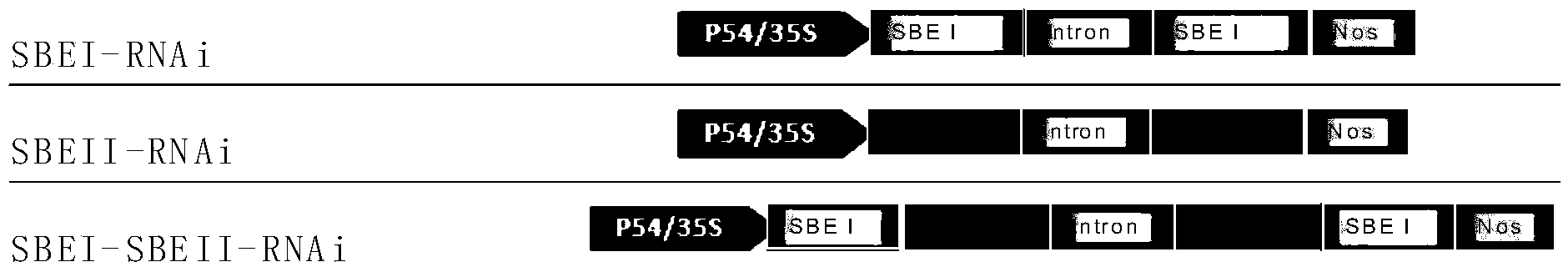
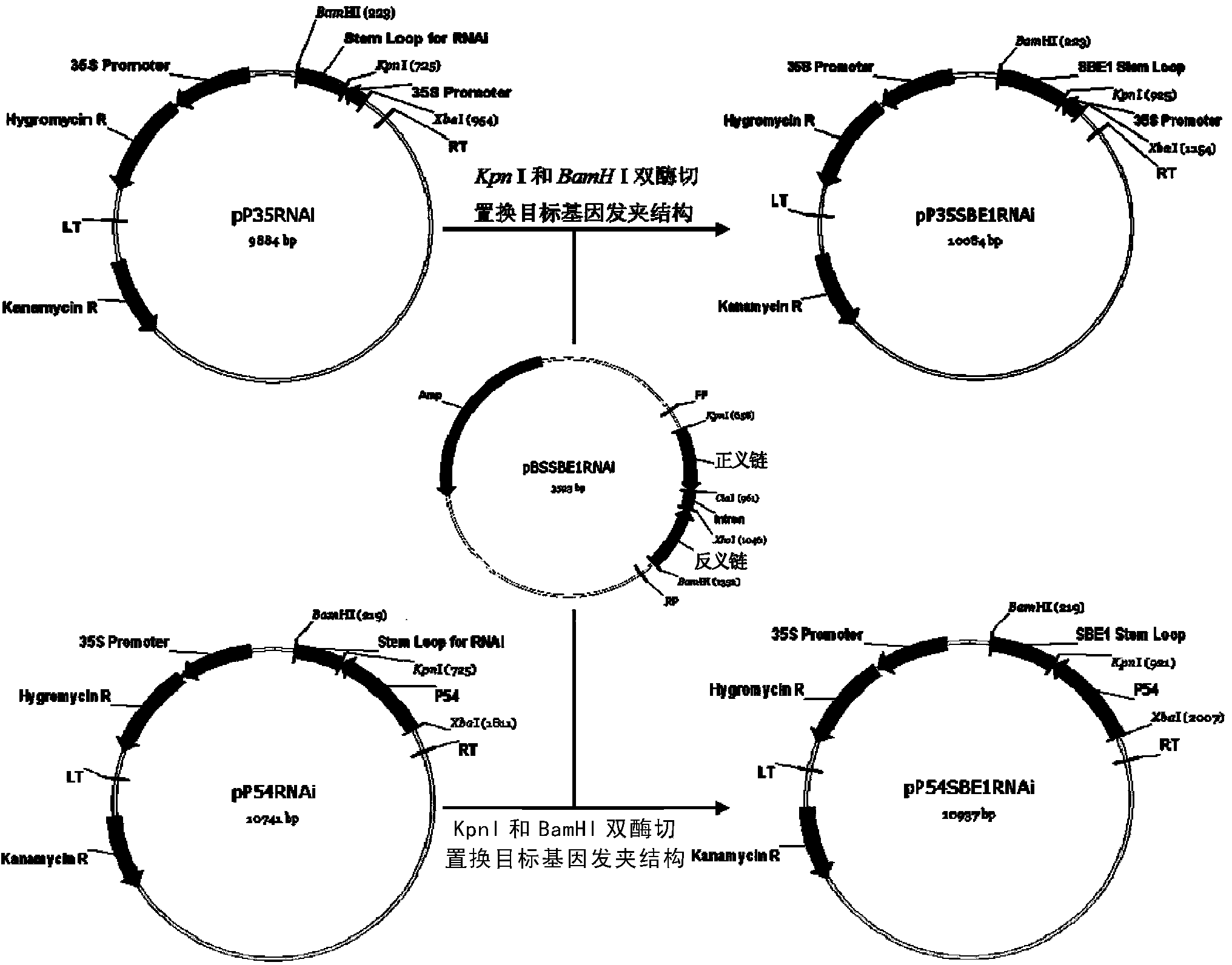
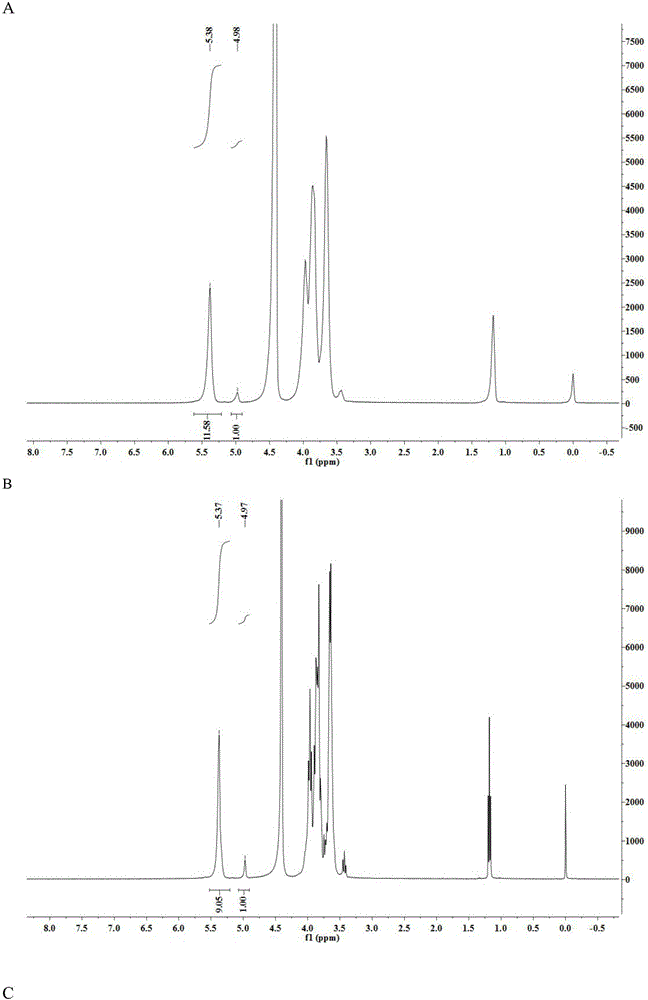
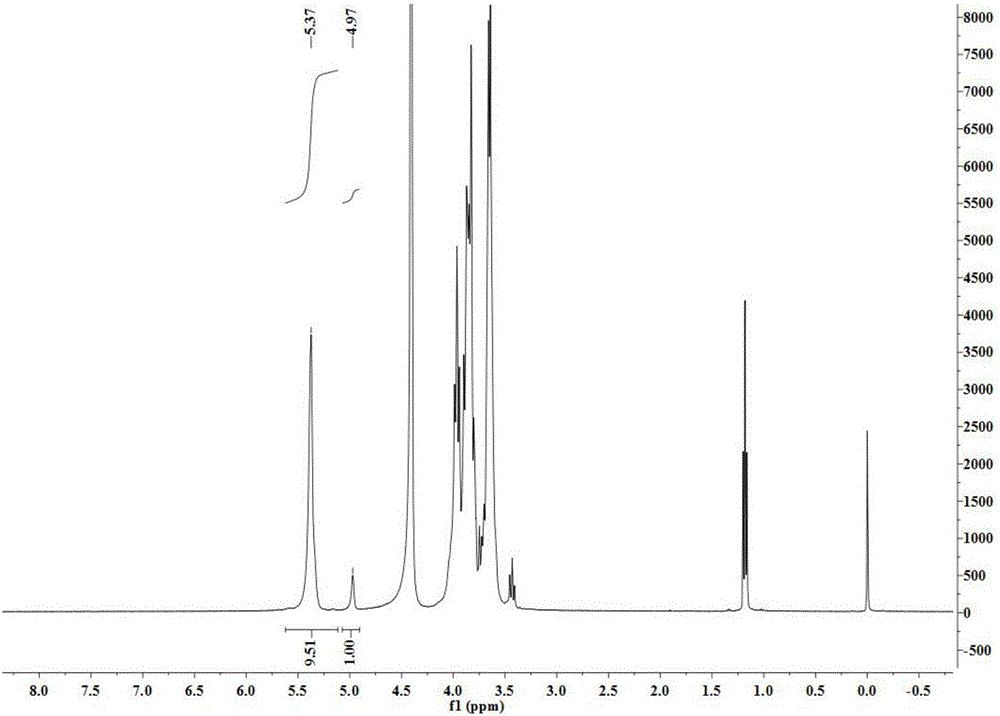
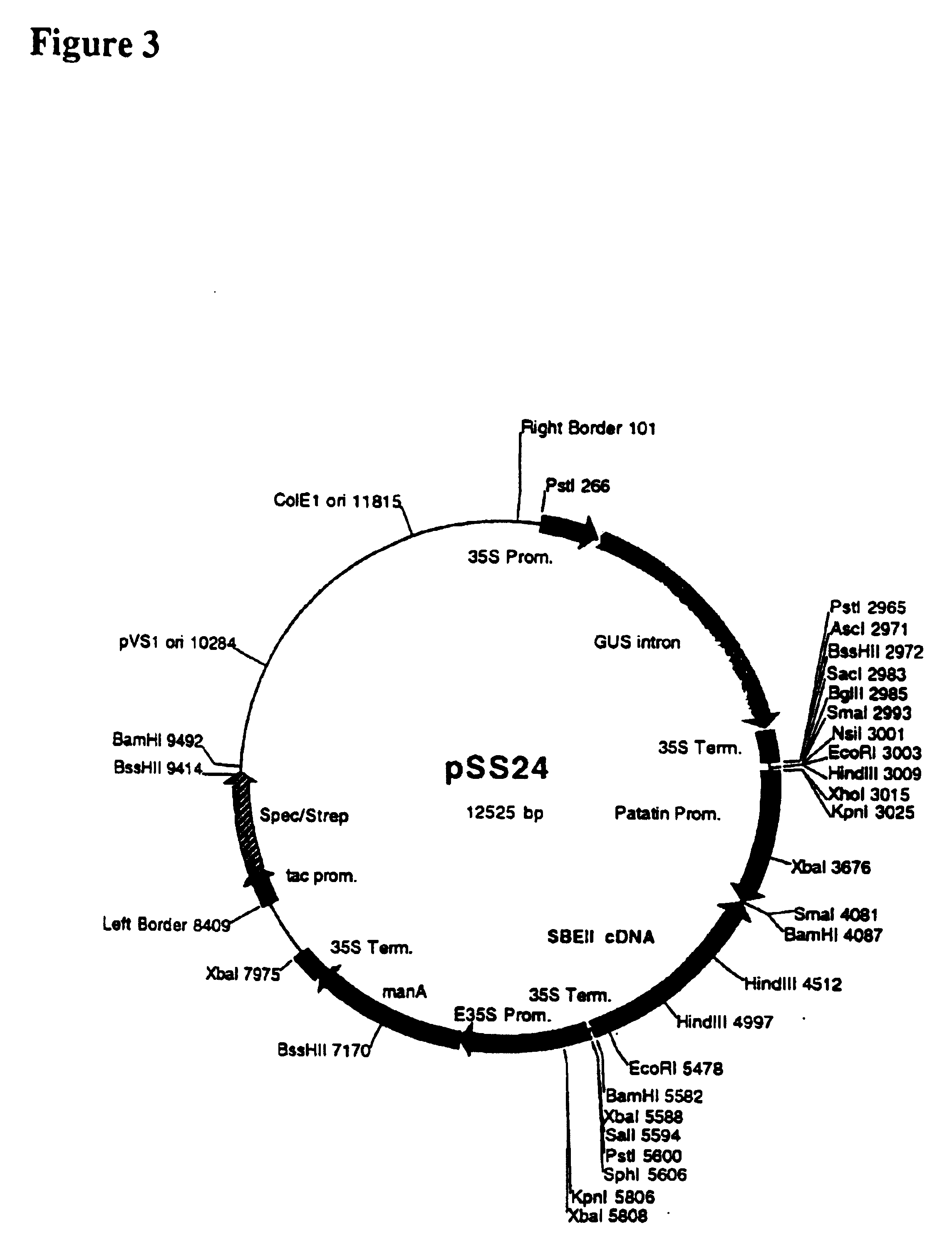
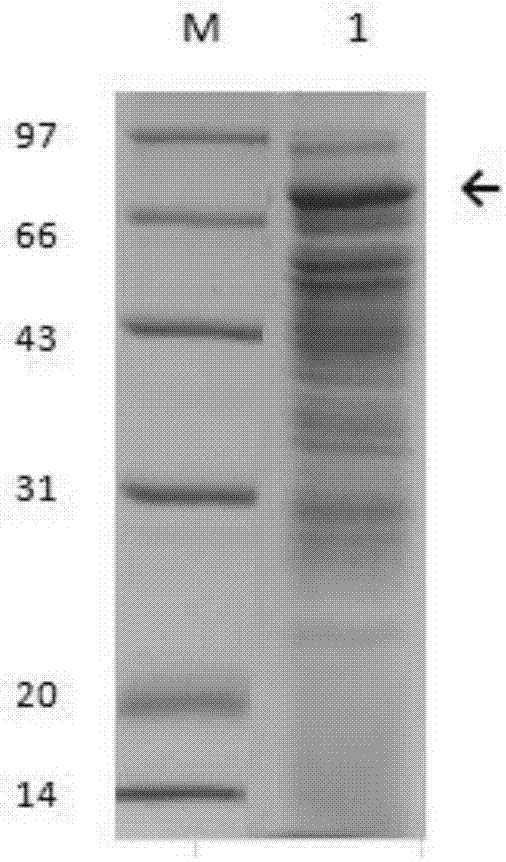
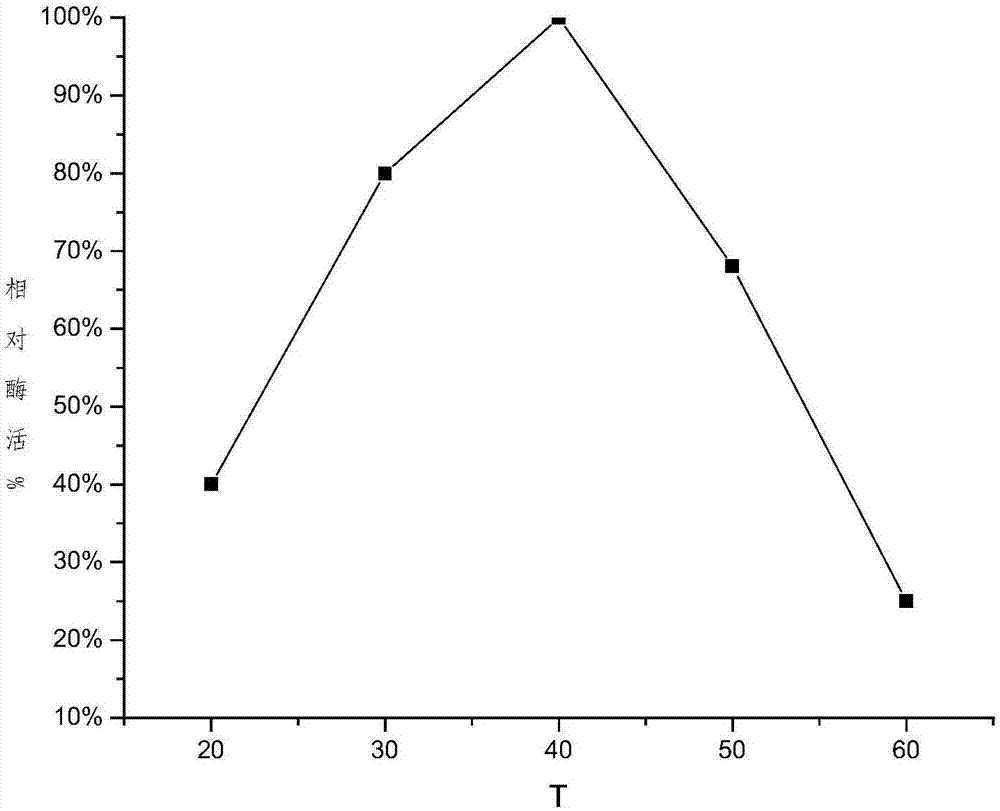
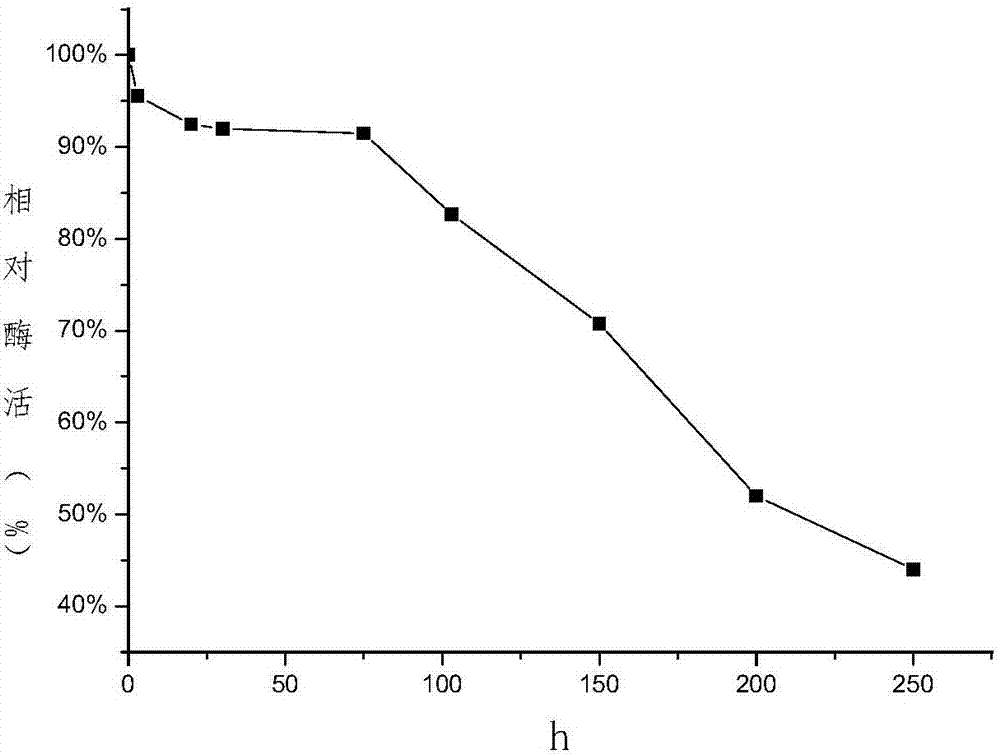
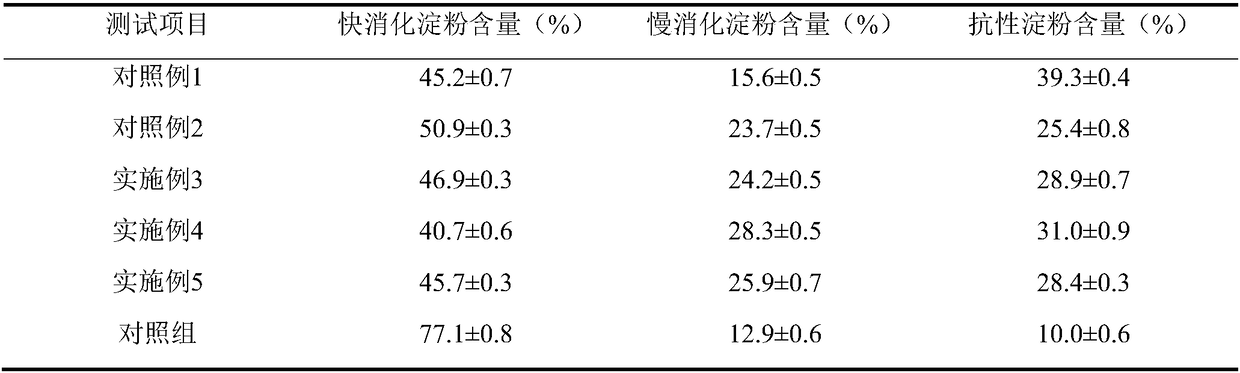
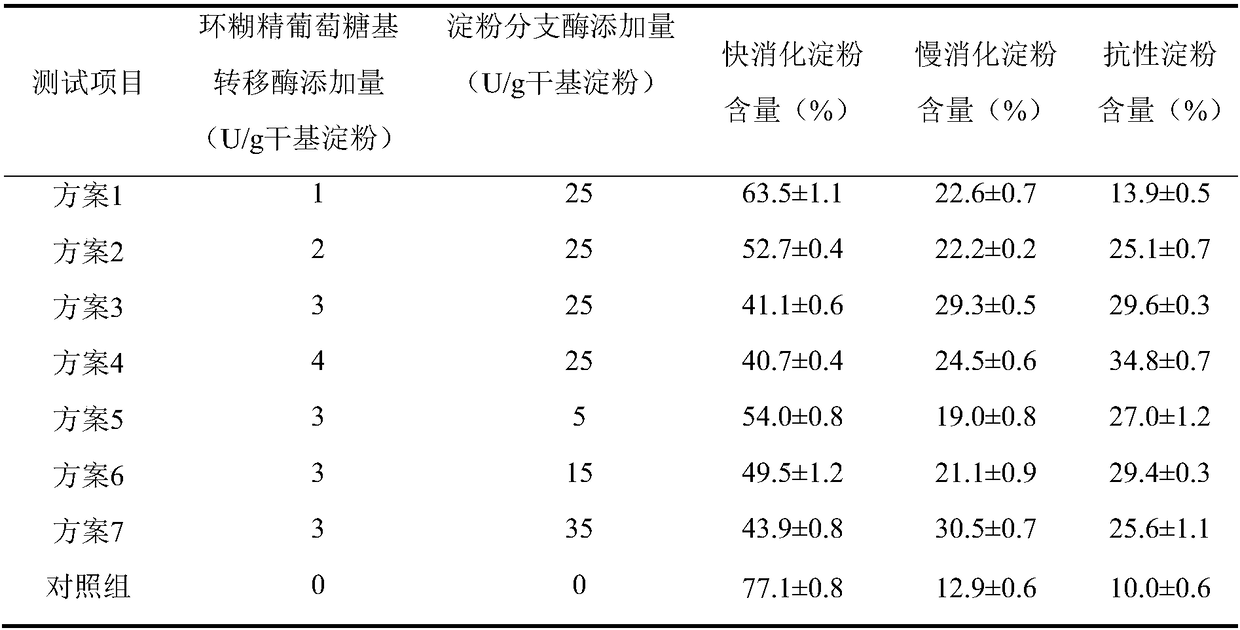
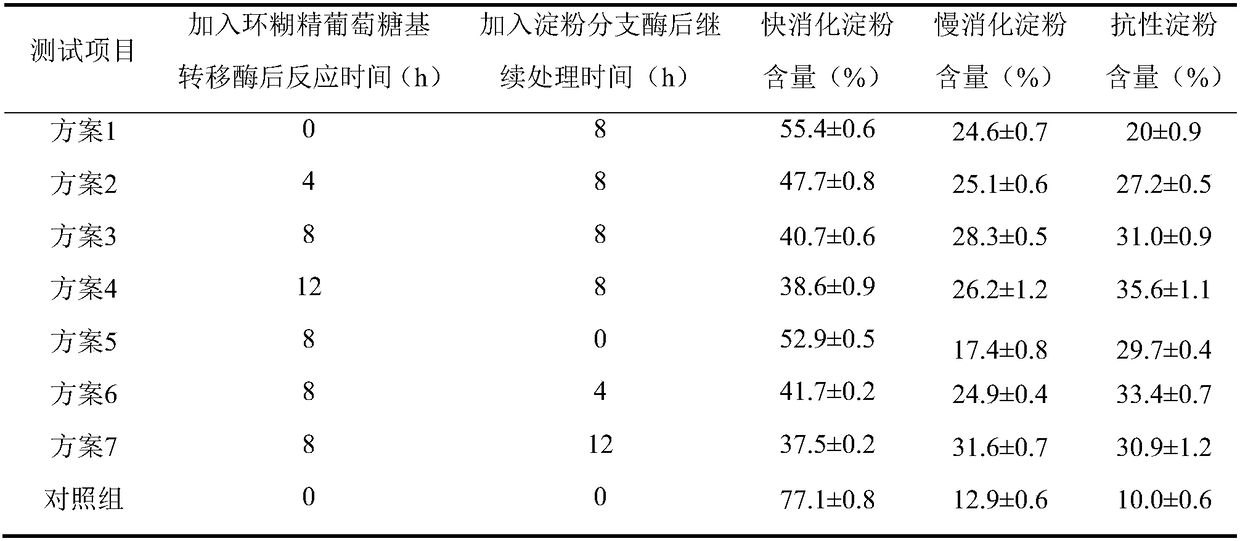
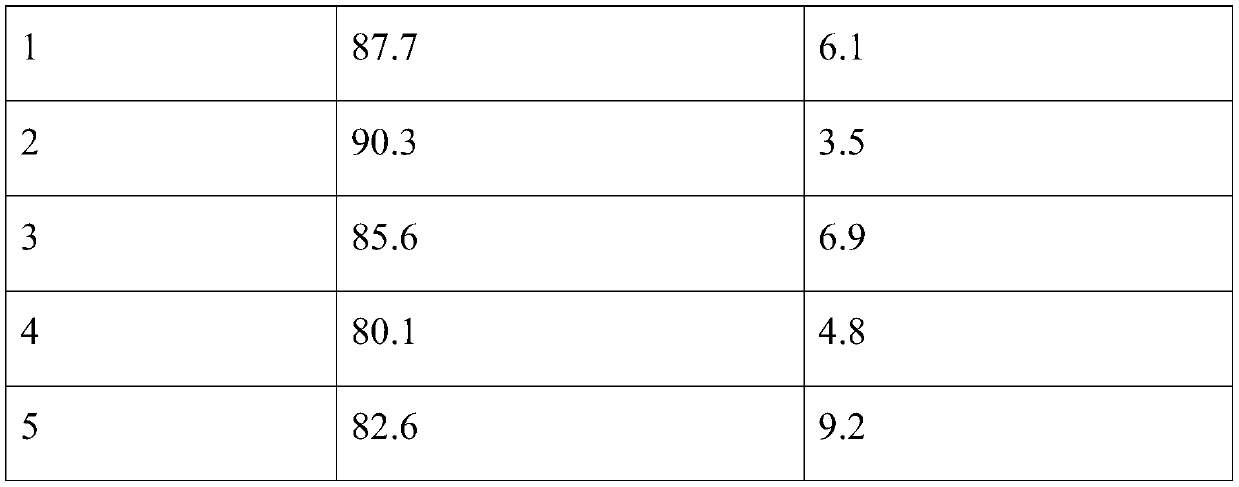
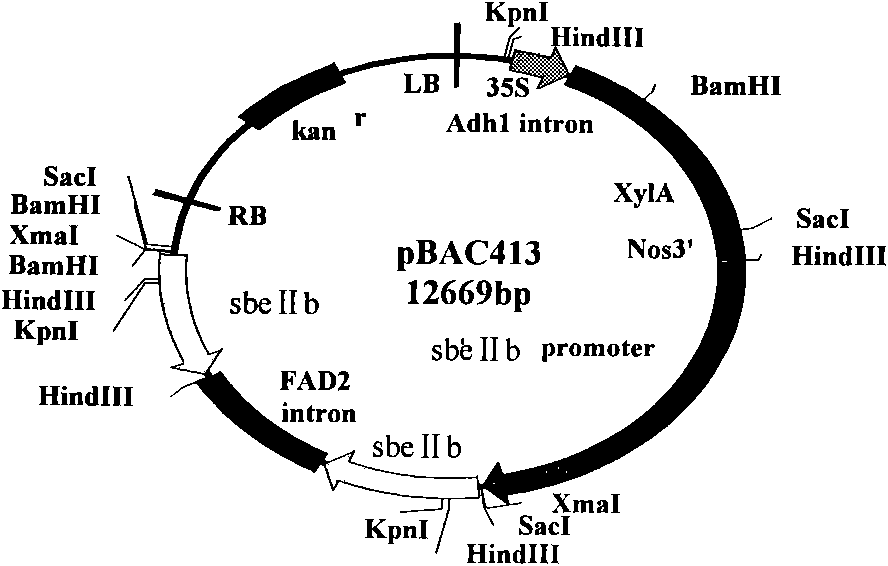
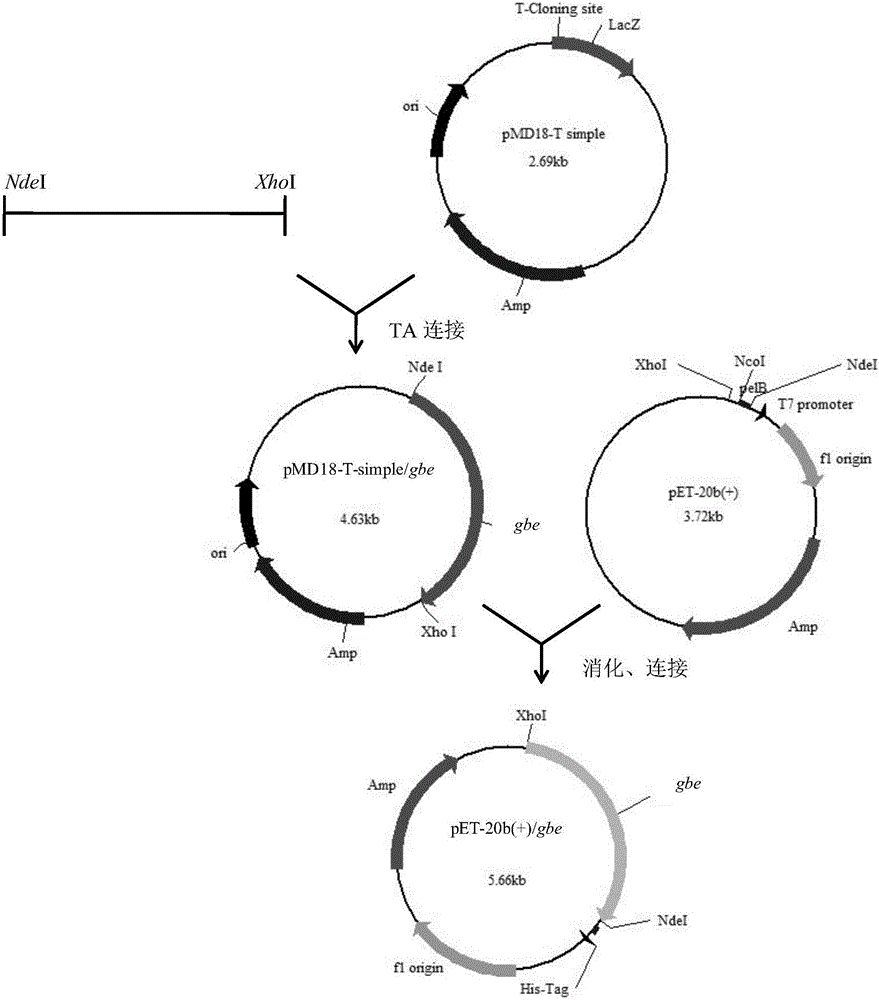
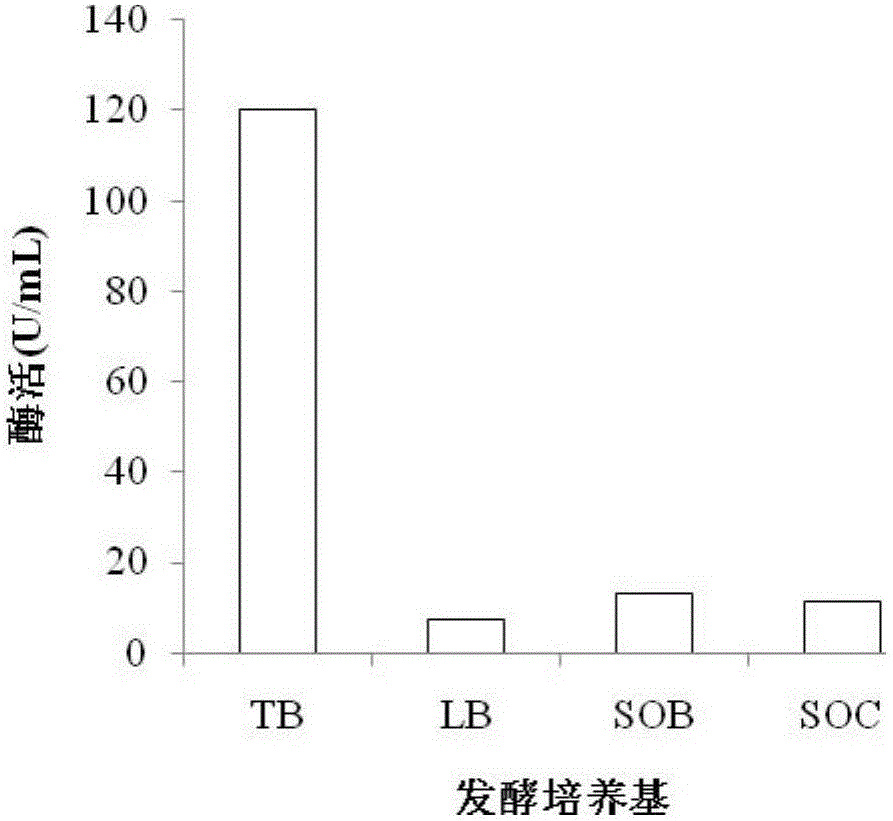
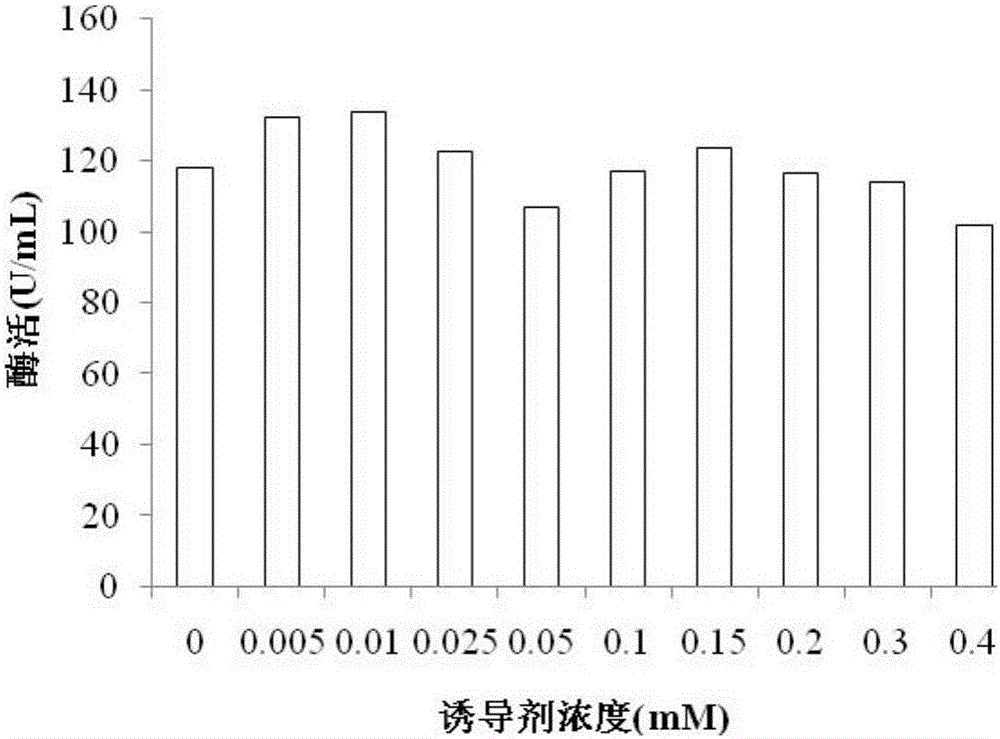
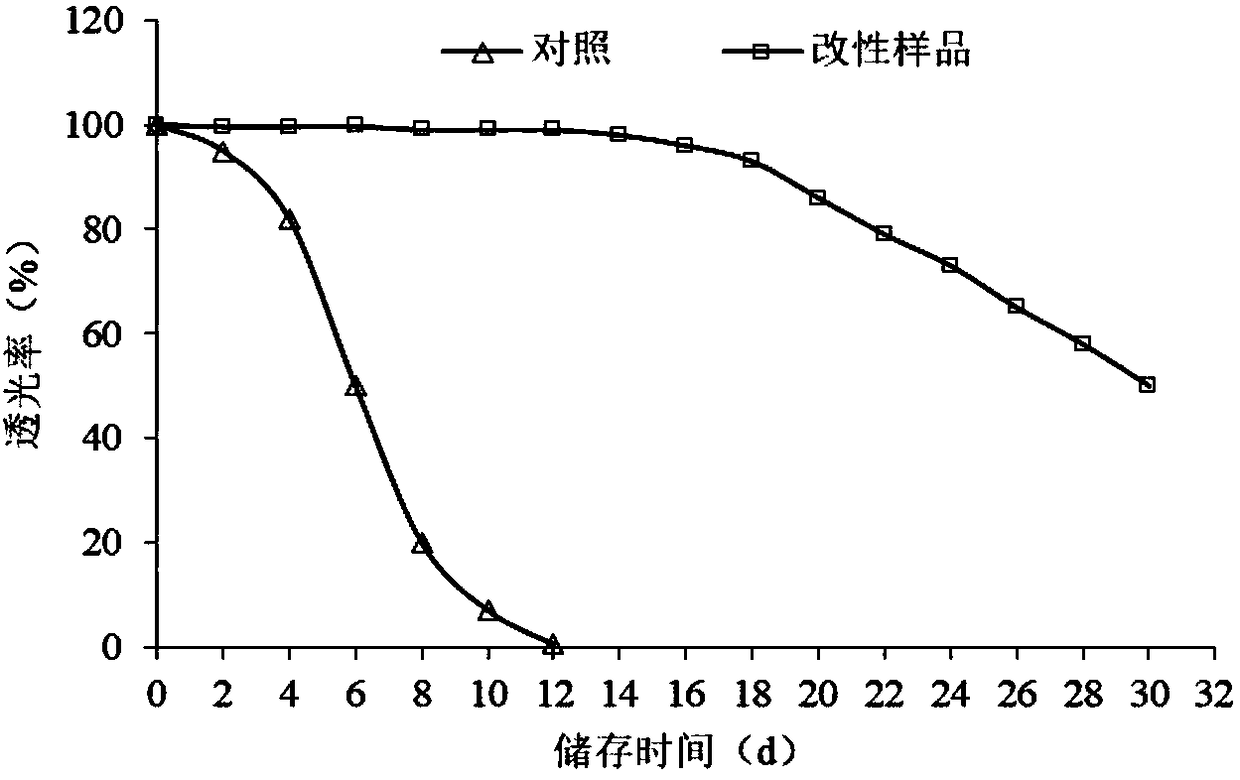
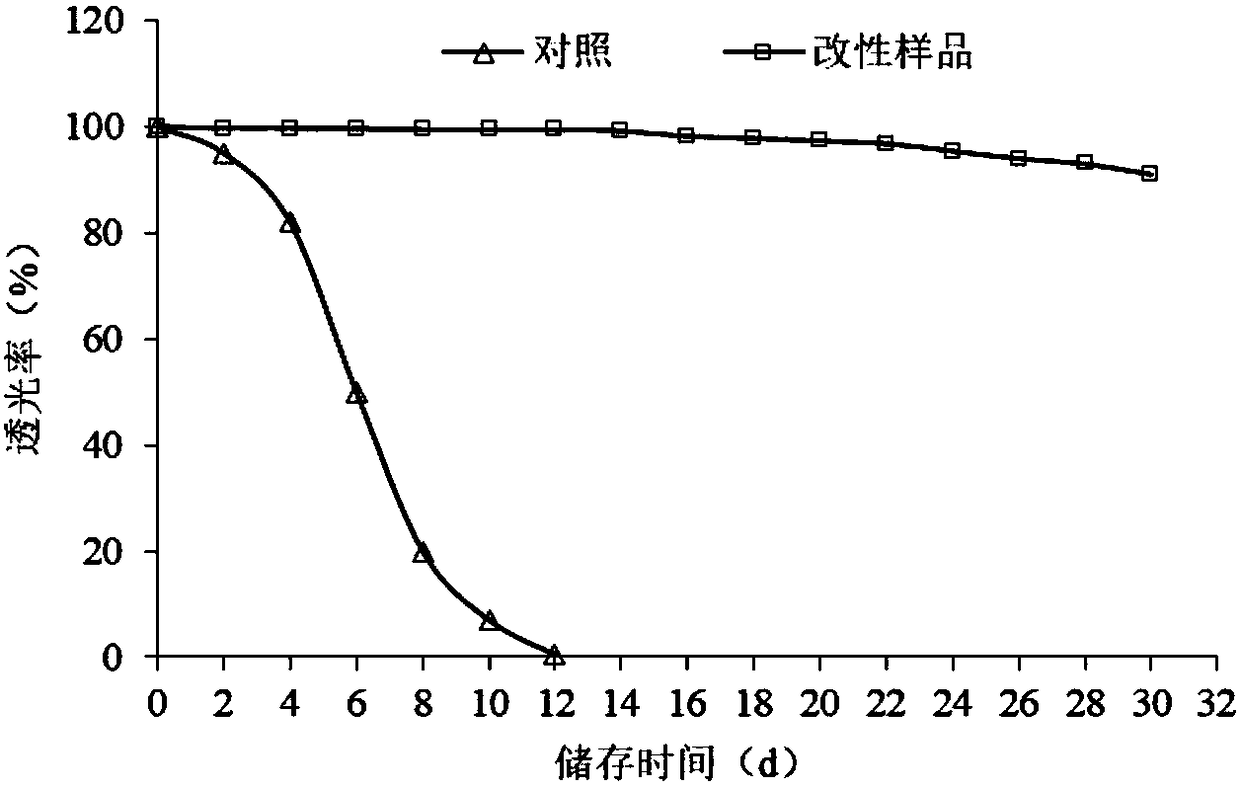
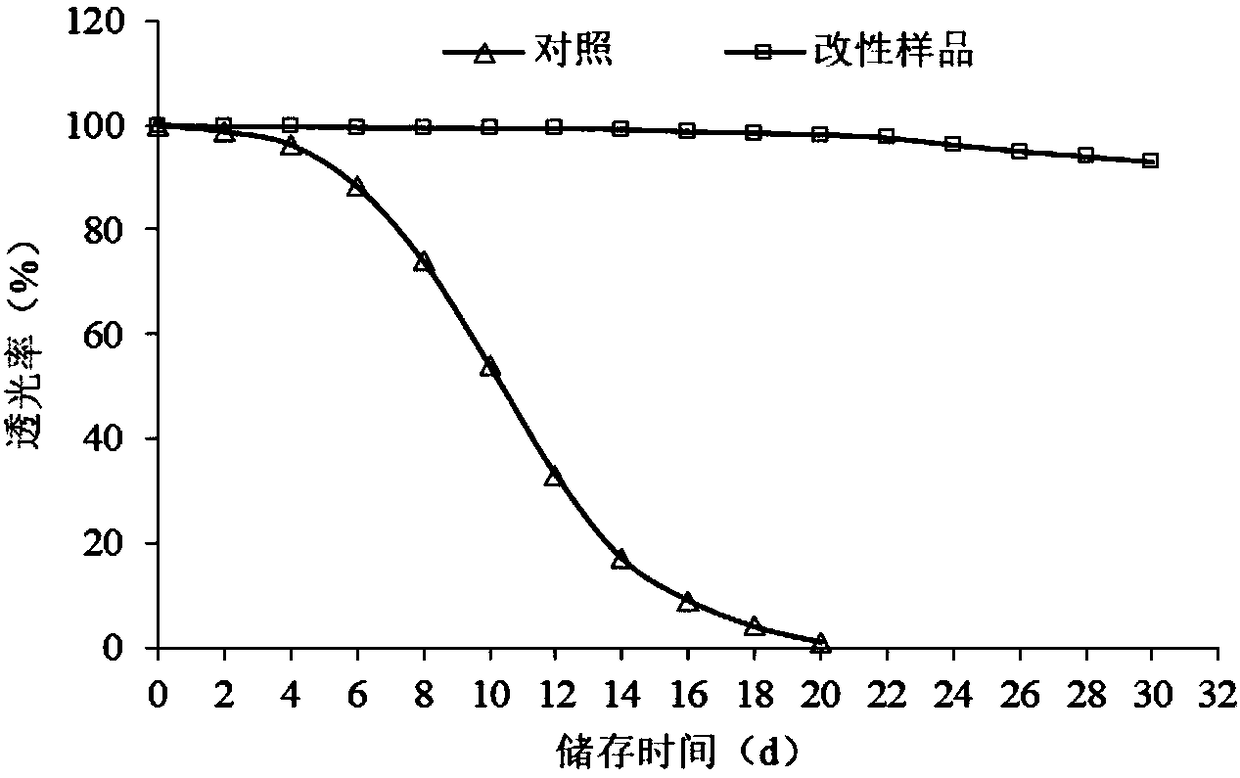
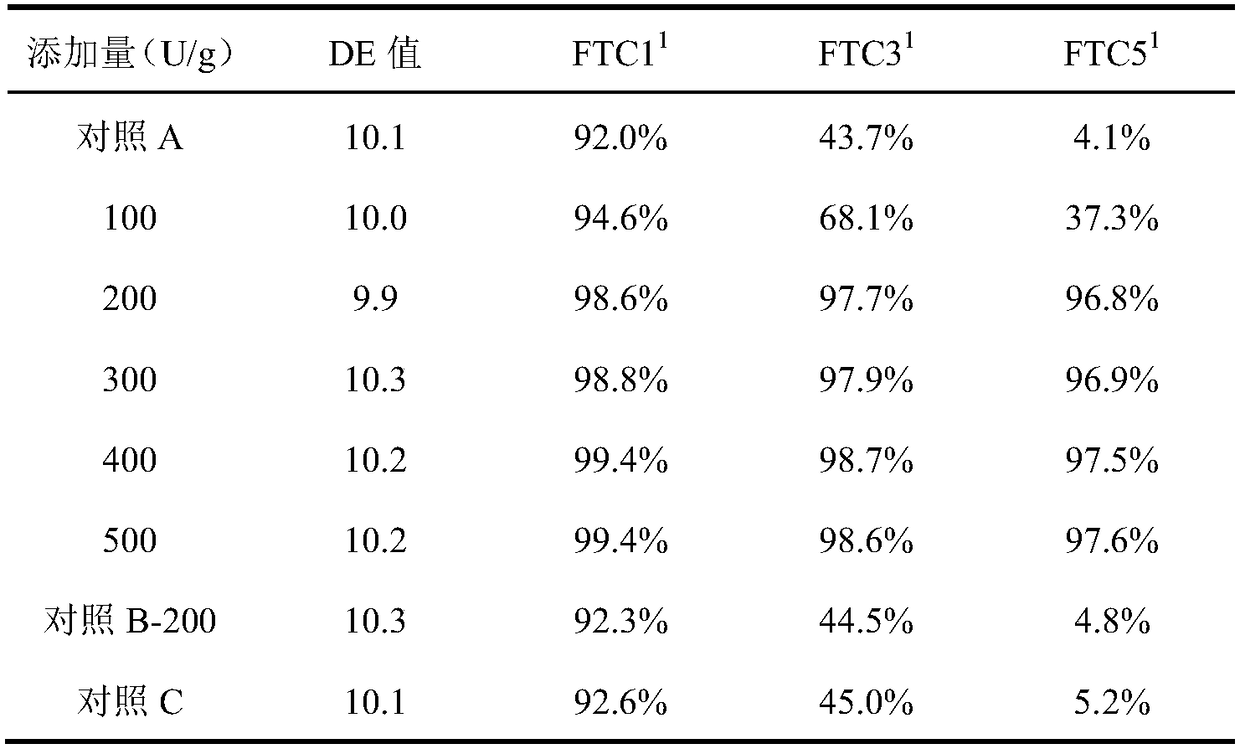
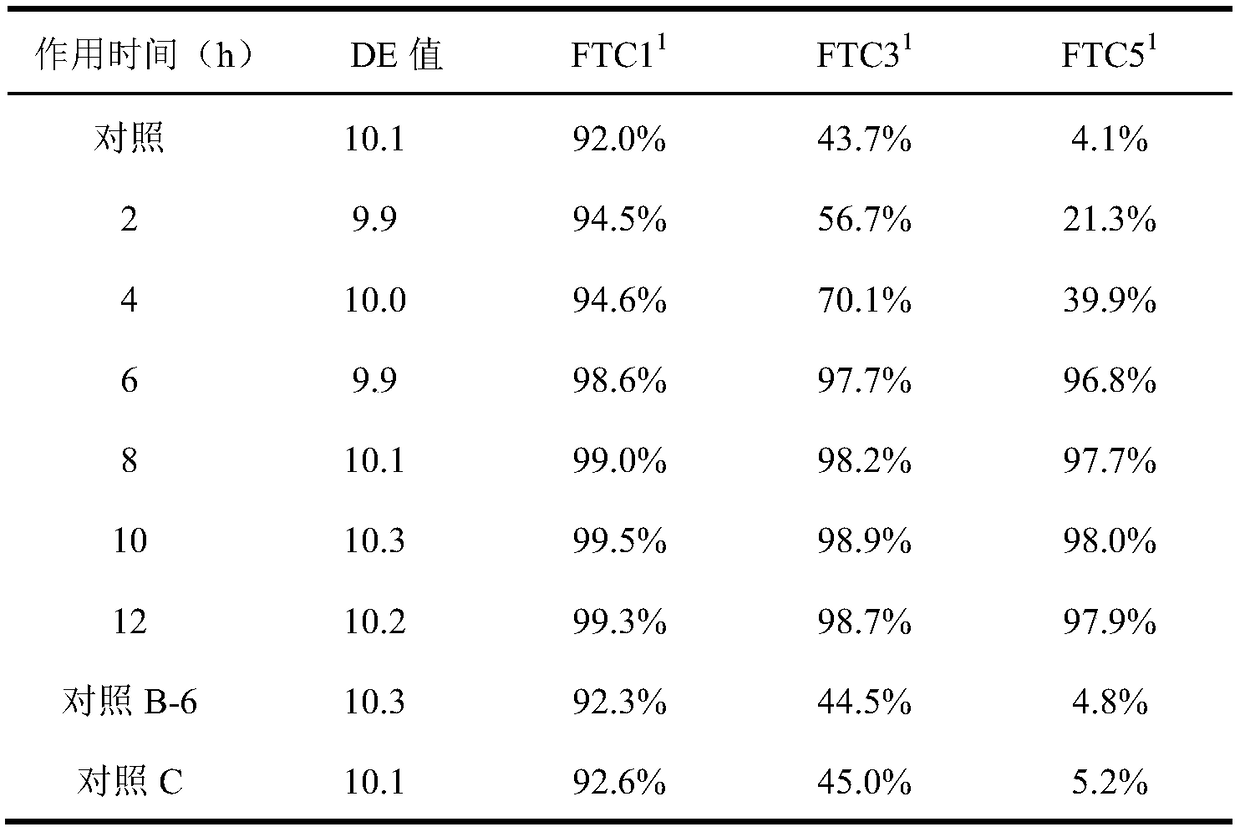
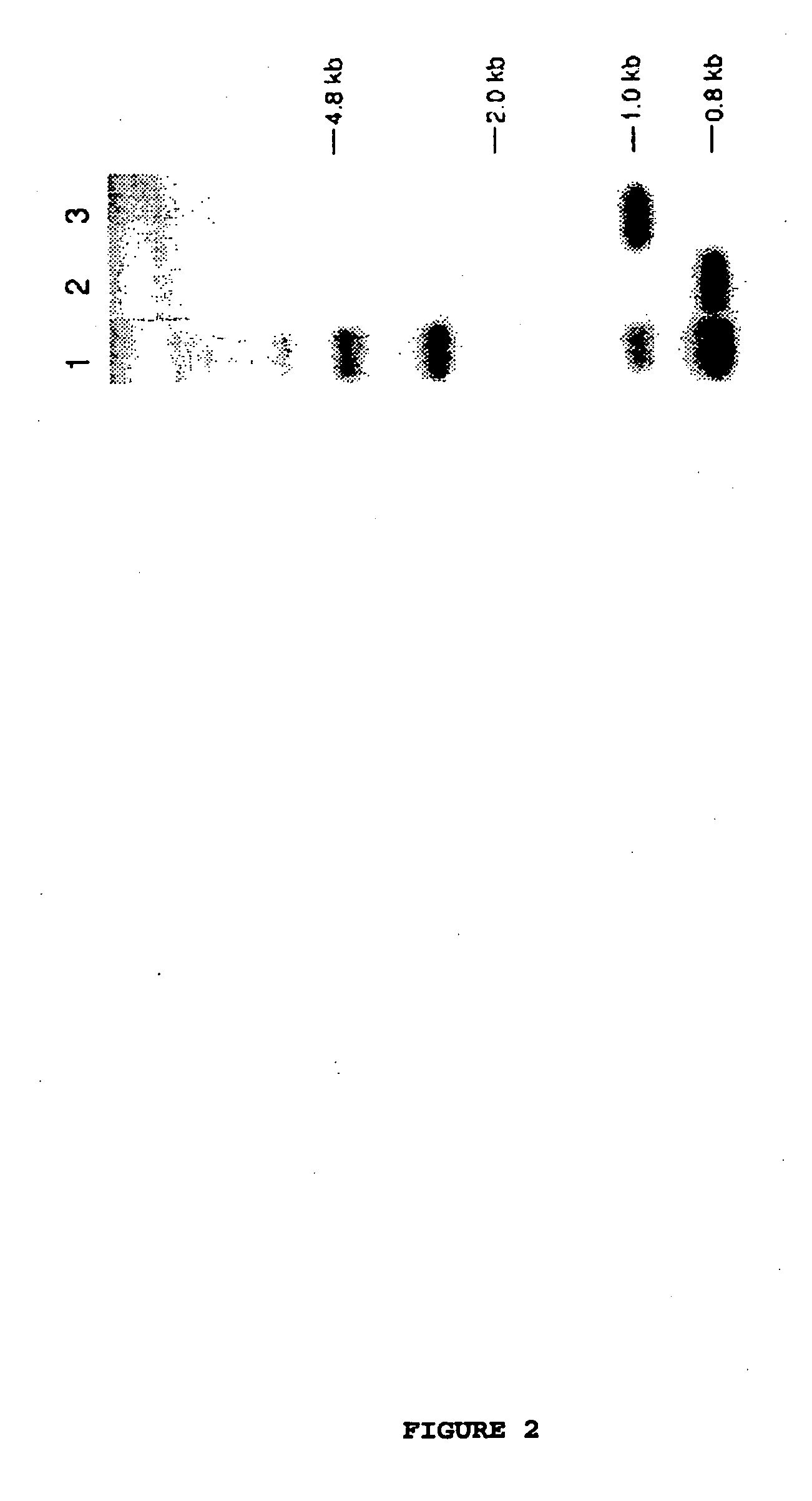Patents
Literature
69 results about "Starch Branching Enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The current concept for starch biosynthesis in higher plants is that amylopectin, the major component of starch, is synthesized by concerted actions of ADP-Glc pyrophosphorylase (AGPase), soluble starch synthase (SS), starch-branching enzyme (BE), and starch-debranching enzyme (Smith et al., 1997).
Starch branching enzymes
InactiveUS7041484B1Reduce concentrationInhibitory activitySugar derivativesTransferasesBiotechnologyStarch granule
The invention provides a novel starch branching enzyme that is bound to A-type starch granules in wheat, barley, rye or triticale. The enzyme is not substantially associated with B-type starch granules. A cDNA sequence encoding an isoform of the enzyme has been isolated from the wheat cultivar Fielder and deduced amino acid sequence has been determined.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Regulation of gene expression in plants
InactiveUS20060010517A1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme of the starch biosynthetic pathway in a cereal plant, wherein the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of starch branching enzyme I, starch branching enzyme II, starch soluble synthase I, and debranching enzyme, with the proviso that the enzyme is not soluble starch synthase I of rice, or starch branching enzyme I of rice or maize.
Owner:BIOGEMMA SAS +1
Rice and Products Thereof Having Starch With an Increased Proportion of Amylose
InactiveUS20070300319A1Reduced activityLower Level RequirementsFood genetic modificationTransferasesRice grainTransgene
Rice having reduced levels of starch branching enzymes produce grain having a high relative amylose content in the endosperm. The rice grain of this invention can be of a non-shrunken phenotype despite a lesion in the amylopectin synthesis pathway and may be transgenic or nontransgenic.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Rice and products thereof having starch with an increased proportion of amylose
InactiveUS7790955B2Reduced activityLower Level RequirementsFood genetic modificationTransferasesRice grainTransgene
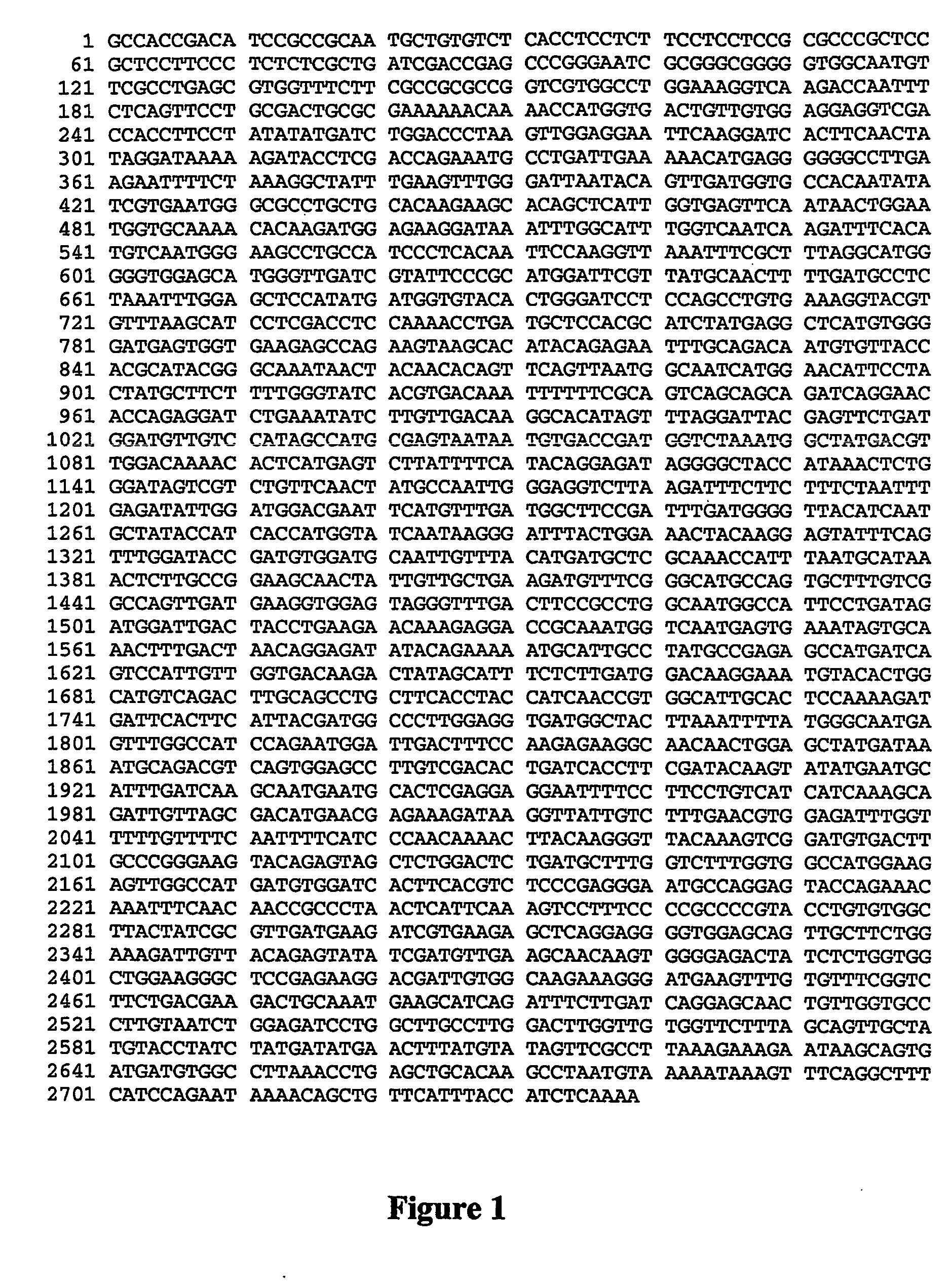
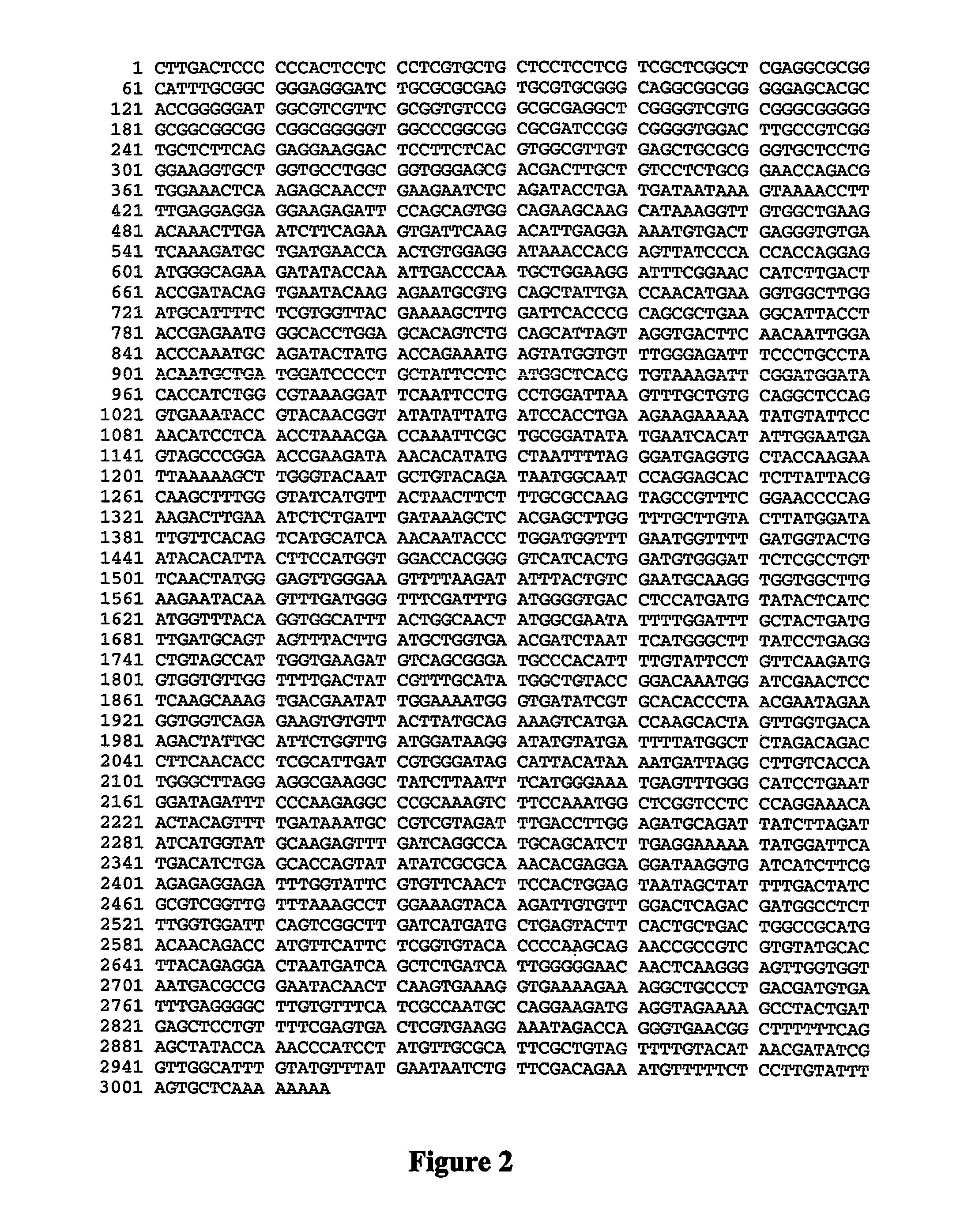
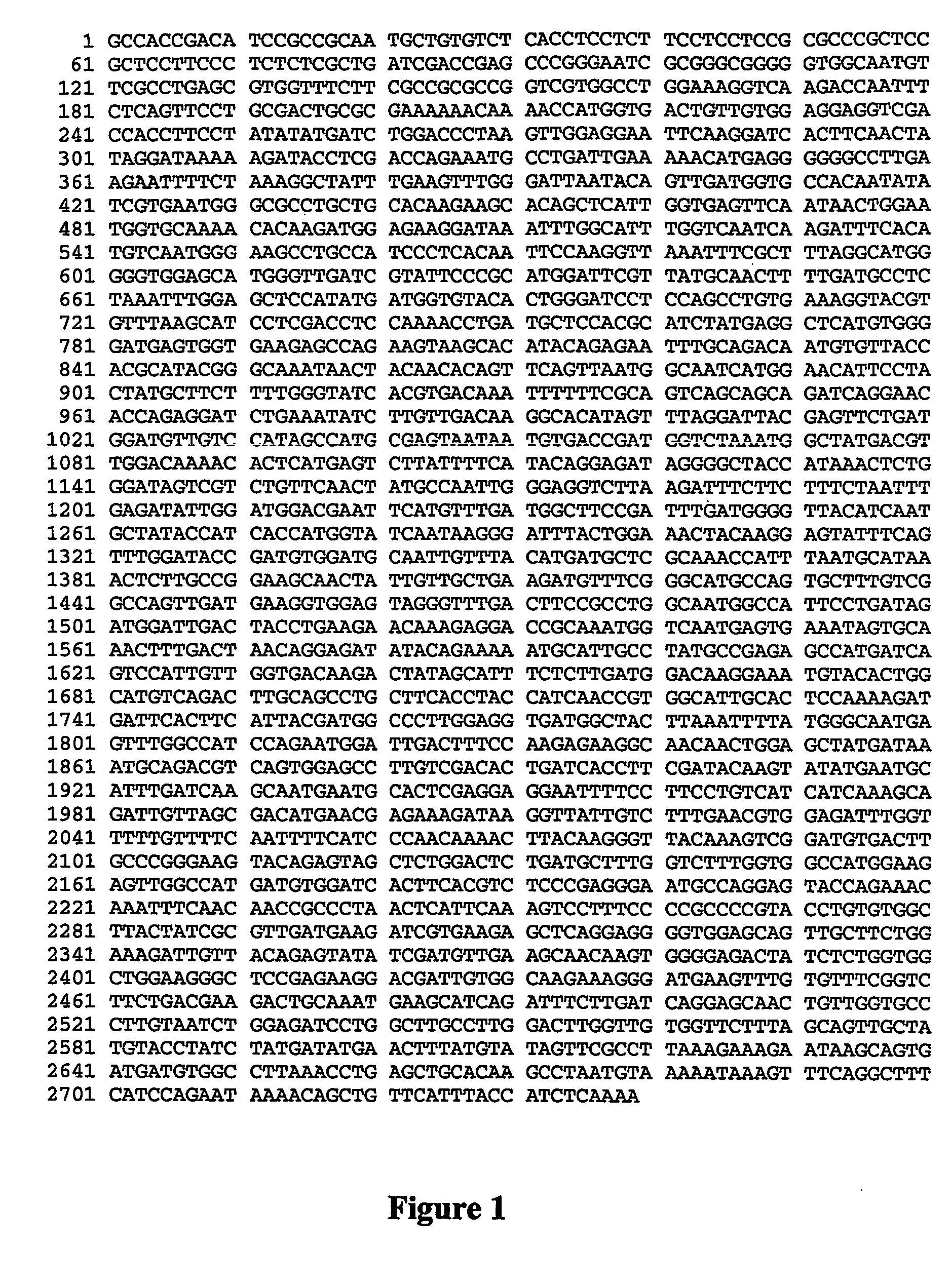
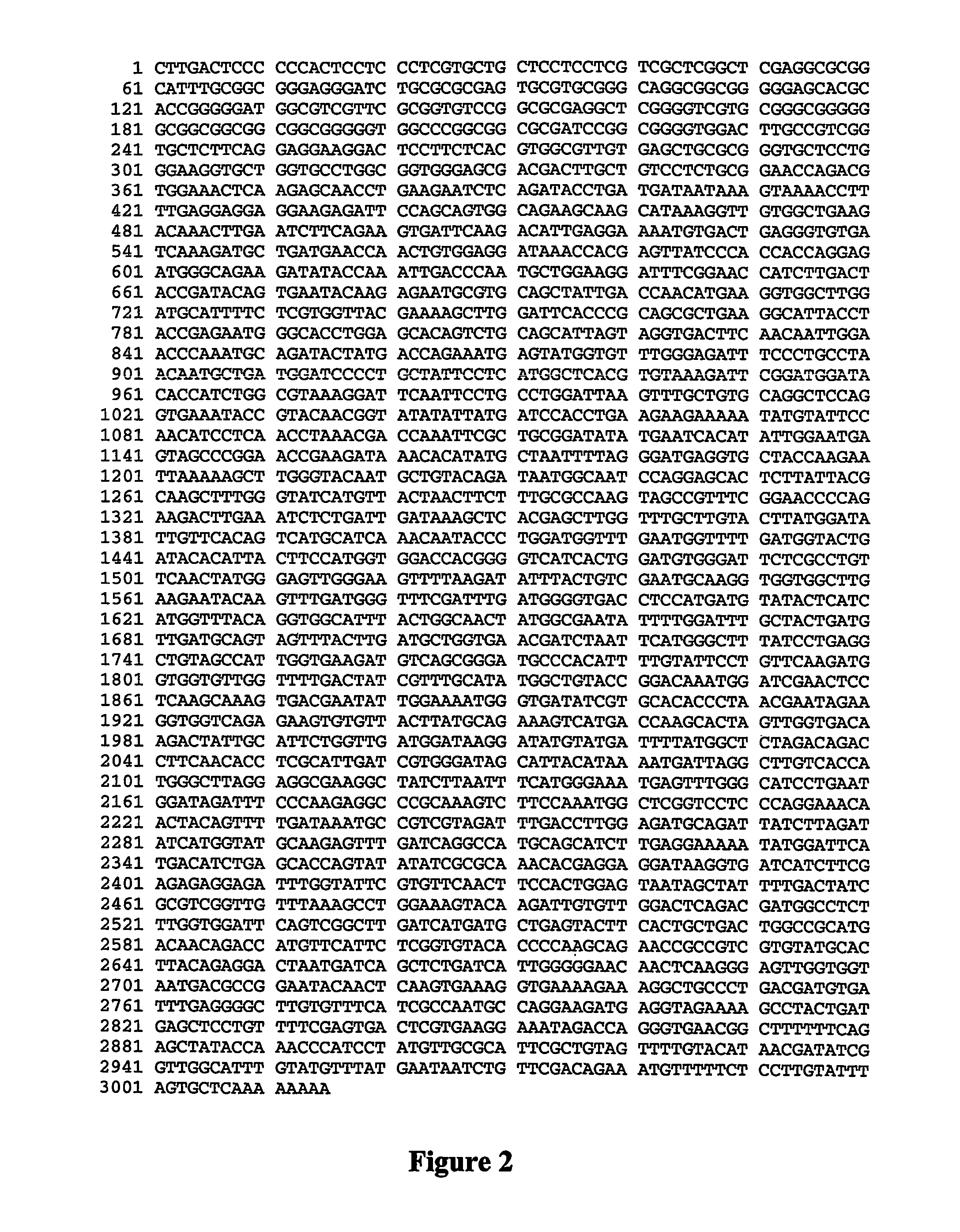
Rice having reduced levels of starch branching enzymes produce grain having a high relative amylose content in the endosperm. The rice grain of this invention can be of a non-shrunken phenotype despite a lesion in the amylopectin synthesis pathway and may be transgenic or nontransgenic. 1 GCCACCGACA TCCGCCGCAA TGCTGTGTCT CACCTCCTCTTCCTCCTCCG CGCCCGCTCC 61 GCTCCTTCCC TCTCTCGCTG ATCGACCGAG CCCGGGAATCGCGGGCGGGG GTGGCAATGT 121 TCGCCTGAGC GTGGTTTCTT CGCCGCGCCG GTCGTGGCCTGGAAAGGTCA AGACCAATTT 181 CTCAGTTCCT GCGACTGCGC GAAAAAACAA AACCATGGTGACTGTTGTGG AGGAGGTCGA 241 CCACCTTCCT ATATATGATC TGGACCCTAA GTTGGAGGAATTCAAGGATC ACTTCAACTA 301 TAGGATAAAA AGATACCTCG ACCAGAAATG CCTGATTGAAAAACATGAGG GGGGCCTTGA 361 AGAATTTTCT AAAGGCTATT TGAAGTTTGG GATTAATACAGTTGATGGTG CCACAATATA 421 TCGTGAATGG GCGCCTGCTG CACAAGAAGC ACAGCTCATTGGTGAGTTCA ATAACTGGAA 481 TGGTGCAAAA CACAAGATGG AGAAGGATAA ATTTGGCATTTGGTCAATCA AGATTTCACA 541 TGTCAATGGG AAGCCTGCCA TCCCTCACAA TTCCAAGGTTAAATTTCGCT TTAGGCATGG 601 GGGTGGAGCA TGGGTTGATC GTATTCCCGC ATGGATTCGTTATGCAACTT TTGATGCCTC 661 TAAATTTGGA GCTCCATATG ATGGTGTACA CTGGGATCCTCCAGCCTGTG AAAGGTACGT 721 GTTTAAGCAT CCTCGACCTC CAAAACCTGA TGCTCCACGCATCTATGAGG CTCATGTGGG 781 GATGAGTGGT GAAGAGCCAG AAGTAAGCAC ATACAGAGAATTTGCAGACA ATGTGTTACC 841 ACGCATACGG GCAAATAACT ACAACACAGT TCAGTTAATGGCAATCATGG AACATTCCTA 901 CTATGCTTCT TTTGGGTATC ACGTGACAAA TTTTTTCGCAGTCAGCAGCA GATCAGGAAC 961 ACCAGAGGAT CTGAAATATC TTGTTGACAA GGCACATAGTTTAGGATTAC GAGTTCTGAT1021 GGATGTTGTC CATAGCCATG CGAGTAATAA TGTGACCGATGGTCTAAATG GCTATGACGT1081 TGGACAAAAC ACTCATGAGT CTTATTTTCA TACAGGAGATAGGGGCTACC ATAAACTCTG1141 GGATAGTCGT CTGTTCAACT ATGCCAATTG GGAGGTCTTAAGATTTCTTC TTTCTAATTT1201 GAGATATTGG ATGGACGAAT TCATGTTTGA TGGCTTCCGATTTGATGGGG TTACATCAAT1261 GCTATACCAT CACCATGGTA TCAATAAGGG ATTTACTGGAAACTACAAGG AGTATTTCAG1321 TTTGGATACC GATGTGGATG CAATTGTTTA CATGATGCTCGCAAACCATT TAATGCATAA1381 ACTCTTGCCG GAAGCAACTA TTGTTGCTGA AGATGTTTCGGGCATGCCAG TGCTTTGTCG1441 GCCAGTTGAT GAAGGTGGAG TAGGGTTTGA CTTCCGCCTGGCAATGGCCA TTCCTGATAG1501 ATGGATTGAC TACCTGAAGA ACAAAGAGGA CCGCAAATGGTCAATGAGTG AAATAGTGCA1561 AACTTTGACT AACAGGAGAT ATACAGAAAA ATGCATTGCCTATGCCGAGA GCCATGATCA1621 GTCCATTGTT GGTGACAAGA CTATAGCATT TCTCTTGATGGACAAGGAAA TGTACACTGG1681 CATGTCAGAC TTGCAGCCTG CTTCACCTAC CATCAACCGTGGCATTGCAC TCCAAAAGAT1741 GATTCACTTC ATTACGATGG CCCTTGGAGG TGATGGCTACTTAAATTTTA TGGGCAATGA1801 GTTTGGCCAT CCAGAATGGA TTGACTTTCC AAGAGAAGGCAACAACTGGA GCTATGATAA1861 ATGCAGACGT CAGTGGAGCC TTGTCGACAC TGATCACCTTCGATACAAGT ATATGAATGC1921 ATTTGATCAA GCAATGAATG CACTCGAGGA GGAATTTTCCTTCCTGTCAT CATCAAAGCA1981 GATTGTTAGC GACATGAACG AGAAAGATAA GGTTATTGTCTTTGAACGTG GAGATTTGGT2041 TTTTGTTTTC AATTTTCATC CCAACAAAAC TTATAAGGGTTACAAAGTCG GATGTGACTT2101 GCCCGGGAAG TACAGAGTAG CTCTGGACTG TGATGCTTTGGTCTTTGGTG GCCATGGAAG2161 AGTTGGCCAT GATGTGGATC ACTTCACGTC TCCCGAGGGAATGCCAGGAG TACCAGAAAC2221 AAATTTCAAC AACCGCCCTA ACTCATTCAA AGTCCTTTCCCCGCCCCGTA CCTGTGTGGC2281 TTACTATCGC GTTGATGAAG ATCGTGAAGA GCTCAGGAGGGGTGGAGCAG TTGCTTCTGG2341 AAAGATTGTT ACAGAGTATA TCGATGTTGA AGCAACAAGTGGGGAGACTA TCTCTGGTGG2401 CTGGAAGGGC TCCGAGAAGG ACGATTGTGG CAAGAAAGGGATGAAGTTTG TGTTTCGGTC2461 TTCTGACGAA GACTGCAAAT GAAGCATCAG ATTTCTTGATCAGGAGCAAC TGTTGGTGCC2521 CTTGTAATCT GGAGATCCTG GCTTGCCTTG GACTTGGTTGTGGTTCTTTA GCAGTTGCTA2581 TGTACCTATC TATGATATGA ACTTTATGTA TAGTTCGCCTTAAAGAAAGA ATAAGCAGTG2641 ATGATGTGGC CTTAAACCTG AGCTGCACAA GCCTAATGTAAAAATAAAGT TTCAGGCTTT2701 CATCCAGAAT AAAACAGCTG TTCATTTACC ATCTCAAAA
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Transgenic corn plants having seeds with modified cornstarch characteristics and method of making the transgenic corn plants
InactiveUS7009092B1Pollution problemEasy to modifyOther foreign material introduction processesEnzymesAmyrisRetrogradation
Cornstarch characteristics can be changed by expressing a non-corn plant starch branching enzyme in a corn plant. In a preferred embodiment, transgenic corn plants containing the barley starch branching enzyme IIa transgene was generated. Some transgenic corn plants produced seeds containing cornstarch with lowered gelatinization temperature and retrogradation rate while others produced seeds containing cornstarch with higher retrogradation rate when compared to non-transgenic corn plants.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
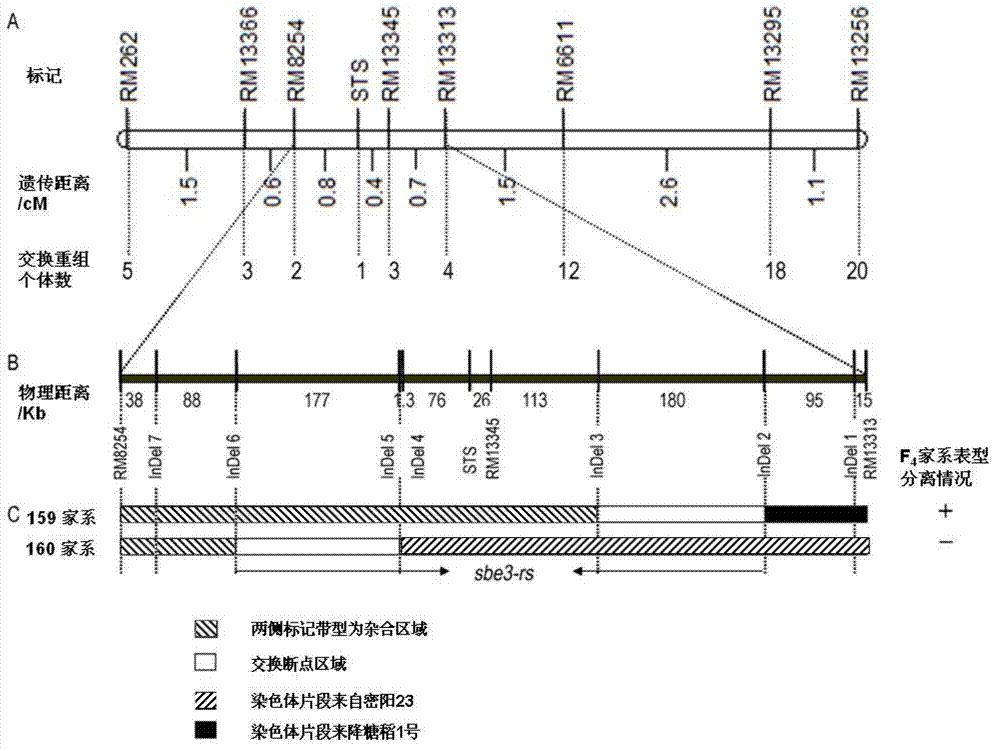
Mutant gene of rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene and application of mutant gene
ActiveCN102816778ASimple stepsStable and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesAgricultural scienceResistant starch
The invention provides a mutant gene of a rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene. The mutant gene has a basic group mutation of T--C in a position corresponding to the 105th position of the 16th exon of the rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene. The invention further provides a method for screening rice variety with high resistant starch content. The basic group mutation of the mutant gene can be served as a molecular marker to effectively detect Jiangtangdao 1 with high resistant starch content and derived varieties (lines) of Jiangtangdao 1, so that the selection efficiency of the new rice variety with high resistant starch content is greatly improved and the rice variety with high resistant starch content is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Biological modification method for inhibiting starch retrogradation
InactiveCN104544473AReduce the rate of respawnPrevent regenerationFood preservationRetrogradationVacuum drying
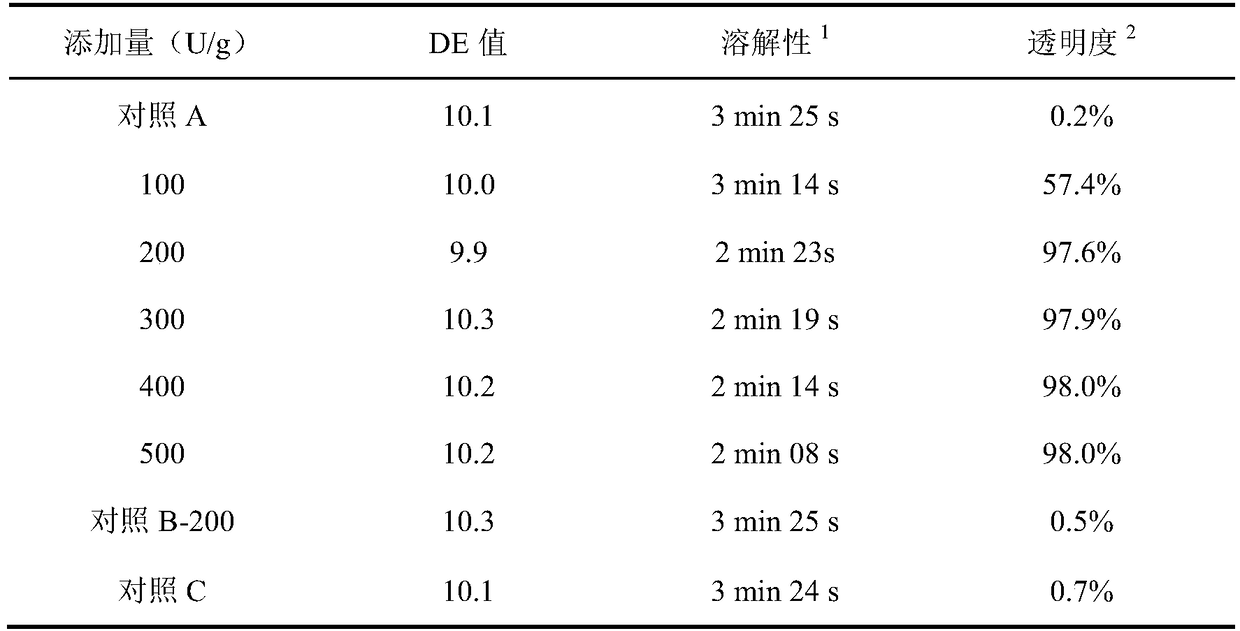
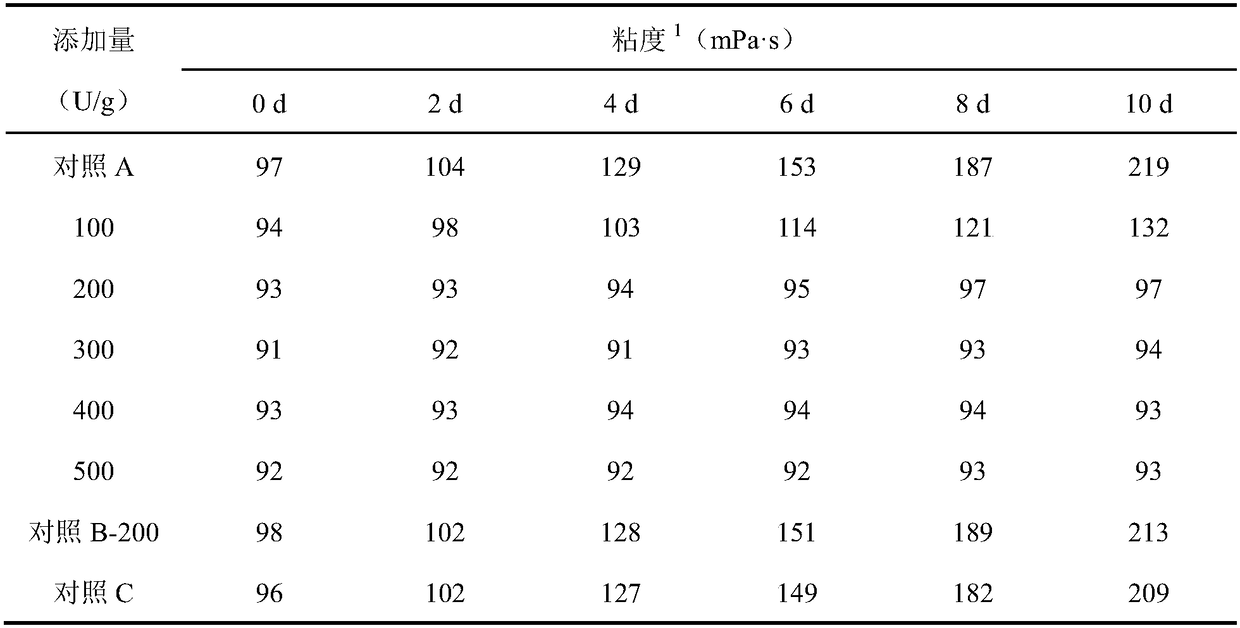
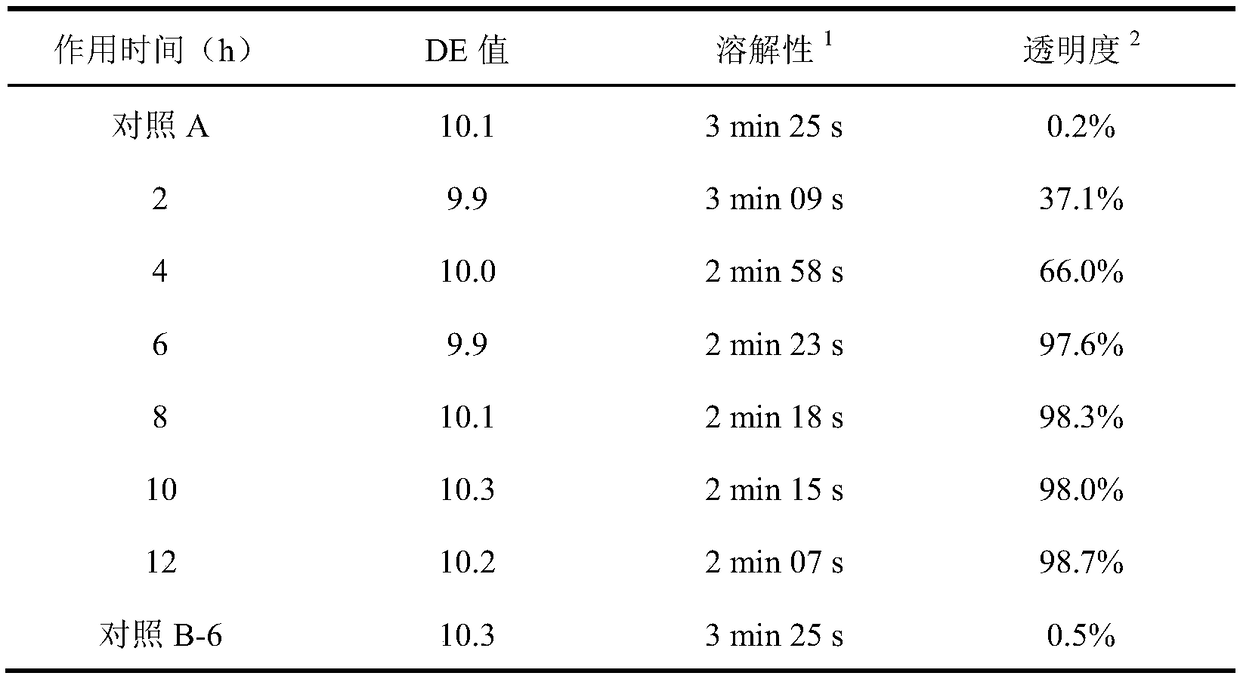
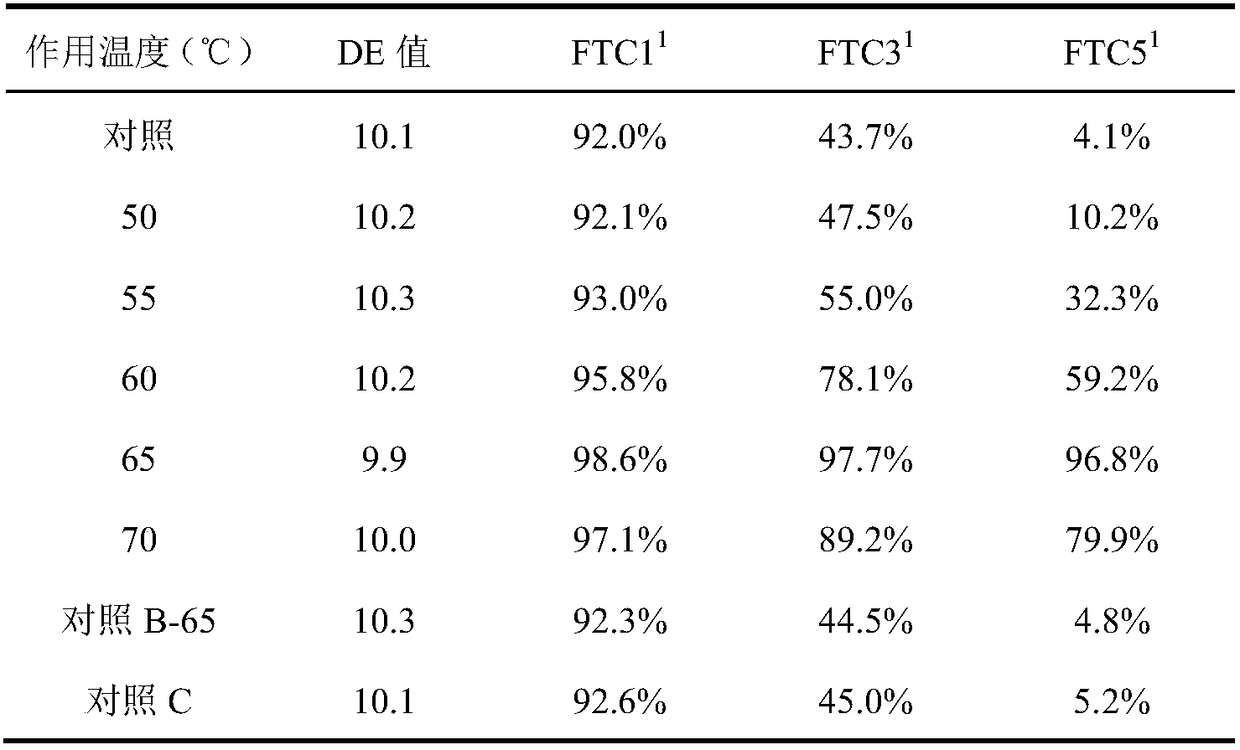
The invention discloses a biological modification method for inhibiting starch retrogradation, and belongs to the field of agricultural product processing and biology. The method comprises the steps of dissolving starch into water to obtain 30% (w / v) of starch milk, adjusting the pH to 7.5, adding 300-1,000U / g of starch branching enzyme of dried starch, treating at 50 DEG C for 4-10h to obtain a reaction solution, washing the reaction solution with deionized water, collecting solid and performing vacuum drying to obtain biological modified starch. By adopting the method, starch molecules have smaller branched chains and relatively high branching degree through the modification effect of the starch branching enzyme to hinder the rearrangement of amylopectin in the storage process, so that starch retrogradation can be well inhibited.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Resistant malt dextrin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the functional food field and in particular relates to resistant malt dextrin and a preparation method thereof. The resistant malt dextrin disclosed by the invention comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 24%-40% of (alpha-1),6-glucosidic bond, 3%-6% of (alpha-1),2-glucosidic bond, 5%-10% of (alpha-1),3-glucosidic bond, and 44%-68% of (alpha-1),4-glucosidic bond. The preparation method of the resistant malt dextrin comprises the following steps: (1), preparing roasted dextrin by roasting starch, and preparing a roasted dextrin aqueous solution; (2), adjusting the pH value of the roasted dextrin aqueous solution to 7.0-8.0, and adding alpha-amylase for carrying out hydrolysis; (3), inactivating the alpha-amylase when the DE (Dextrose Equivalent) value of the roasted dextrin aqueous solution reaches 10-20, and filtering to obtain a hydrolysis intermediate product; and (4), hydrolyzing the hydrolysis intermediate product by starch branching enzyme to prepare the resistant malt dextrin. The resistant malt dextrin disclosed by the invention has an obvious effect in lowering blood sugar, and has obvious advantages in comparison with the similar dietary fiber products.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
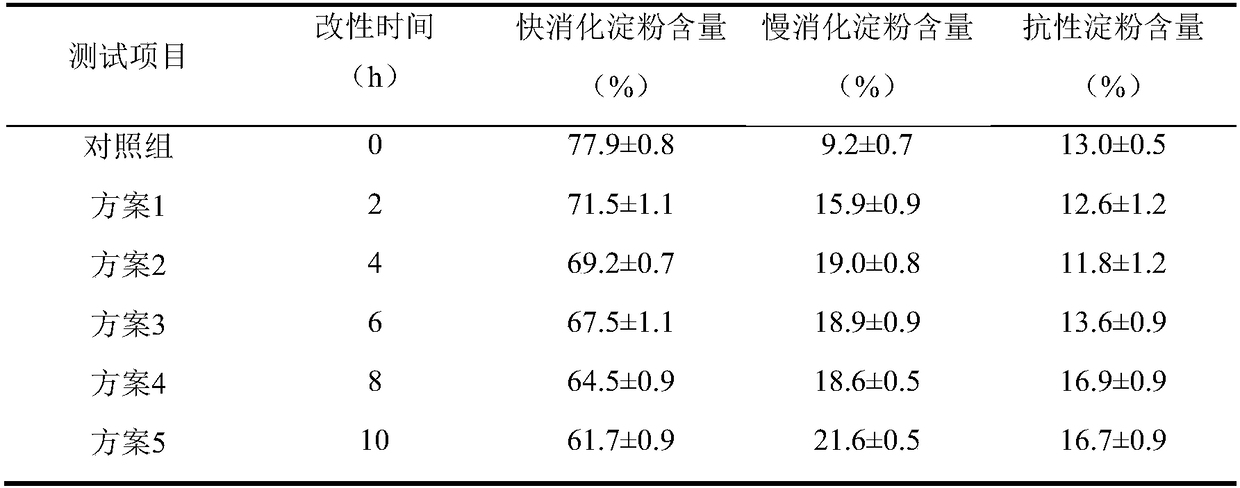
Modification method for improving slow digestion performance of starch
InactiveCN108047340AReduced rate of digestionGood modification effectFermentationDigestionGranular starch
The invention discloses a modification method for improving slow digestion performance of starch, and belongs to the field of biological modified starch. According to the modification method disclosedby the invention, spindly starch molecules can be converted into a pyknic branch structure of which the structure is more compact by utilizing starch branching enzyme, so that the digestion rate of the starch is slowed down; by controlling a modification substrate, two-stage treatment of carrying out gelatinized starch modification after granular starch modification is adopted, so that the purpose of enhancing a modification effect of the starch branching enzyme is achieved, the content of slow digestion raw starch in modified starch is further increased, the digestion rate of the starch is reduced, and a thought is provided for preparing the slow digestion starch for biological modification.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for increasing amylose content of plants
InactiveCN104017829AOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
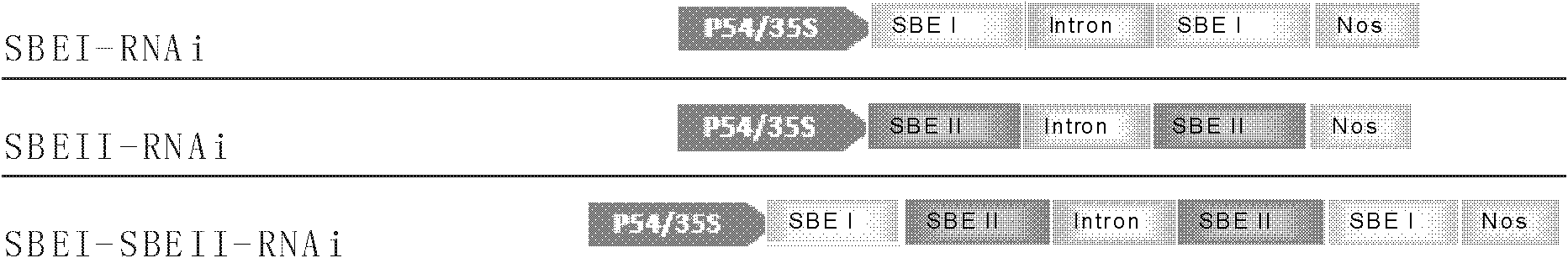
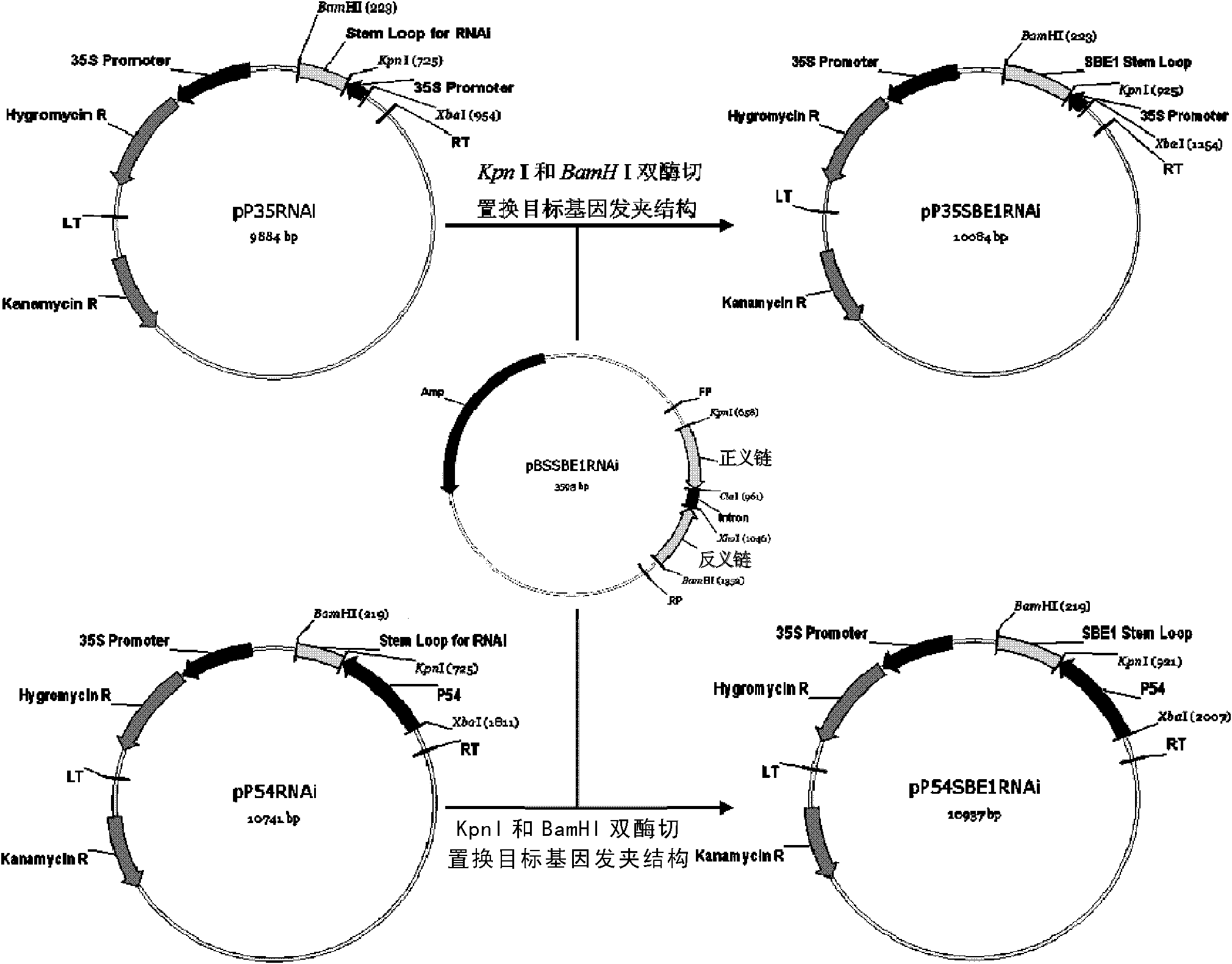
The invention relates to a method for increasing the amylose content of plants. The invention provides enzymes, namely granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSS i), starch branching enzyme I (SBE I) and / or starch branching enzyme II (SBE II) which are applicable to genetic engineering operation in a starch synthesis path and are capable of remarkably changing starch composition of the plants. The invention also provides a novel method capable of favorably adjusting starch in plants, which comprises the following step of reducing the expression of the enzymes to obtain a series of transgenic plants which are different in amylose and amylopectin contents and proportions. The invention also provides a construct or carrier for adjusting the starch composition of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for modifying starch by enzyme degradation process
InactiveCN107345234ACompact structureCloser starch branching structureFermentationAmylaseRetrogradation (starch)
The invention discloses a method for modifying starch by an enzyme degradation process. The method specifically comprises the following steps: preparing starch milk from the starch and water, and regulating the starch milk to be alkaline with a sodium hydroxide solution; adding sodium hypochlorite, carrying out a reaction with stirring, and controlling the pH value of the starch milk to be 8 to 9; cooling the starch milk to room temperature, then, adding a sodium lauryl sulfate solution, and carrying out uniform dissolving; adding vinyl acetate, and carrying out a reaction with stirring; adding polyvinyl alcohol into the obtained starch milk, and continuing to carry out a reaction; adding 600U / g to 1,000U / g amylase, carrying out treatment for 4 to 8 hours at the temperature of 45 DEG C to 55 DEG C, then, rinsing the reaction solution, collecting solids, and carrying out vacuum drying, thereby obtaining the modified starch. According to the method, leptosomatic starch molecules are converted to pyknic starch branched structures with tighter structures by using starch branching enzyme, so that the rate of retrogradation of amylopectin is lowered, the aim of inhibiting starch retrogradation is achieved, and the produced starch has the characteristics of good hydrophobicity and fluidity and can be extensively applied to chemicals for daily use.
Owner:SHANDONG SHENZHOU XIANGYU TECH GRP
Method for increasing starch branching enzyme activity
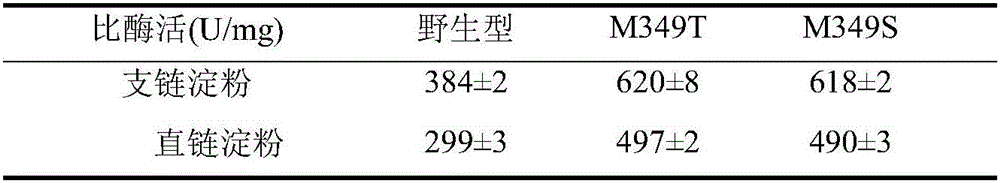
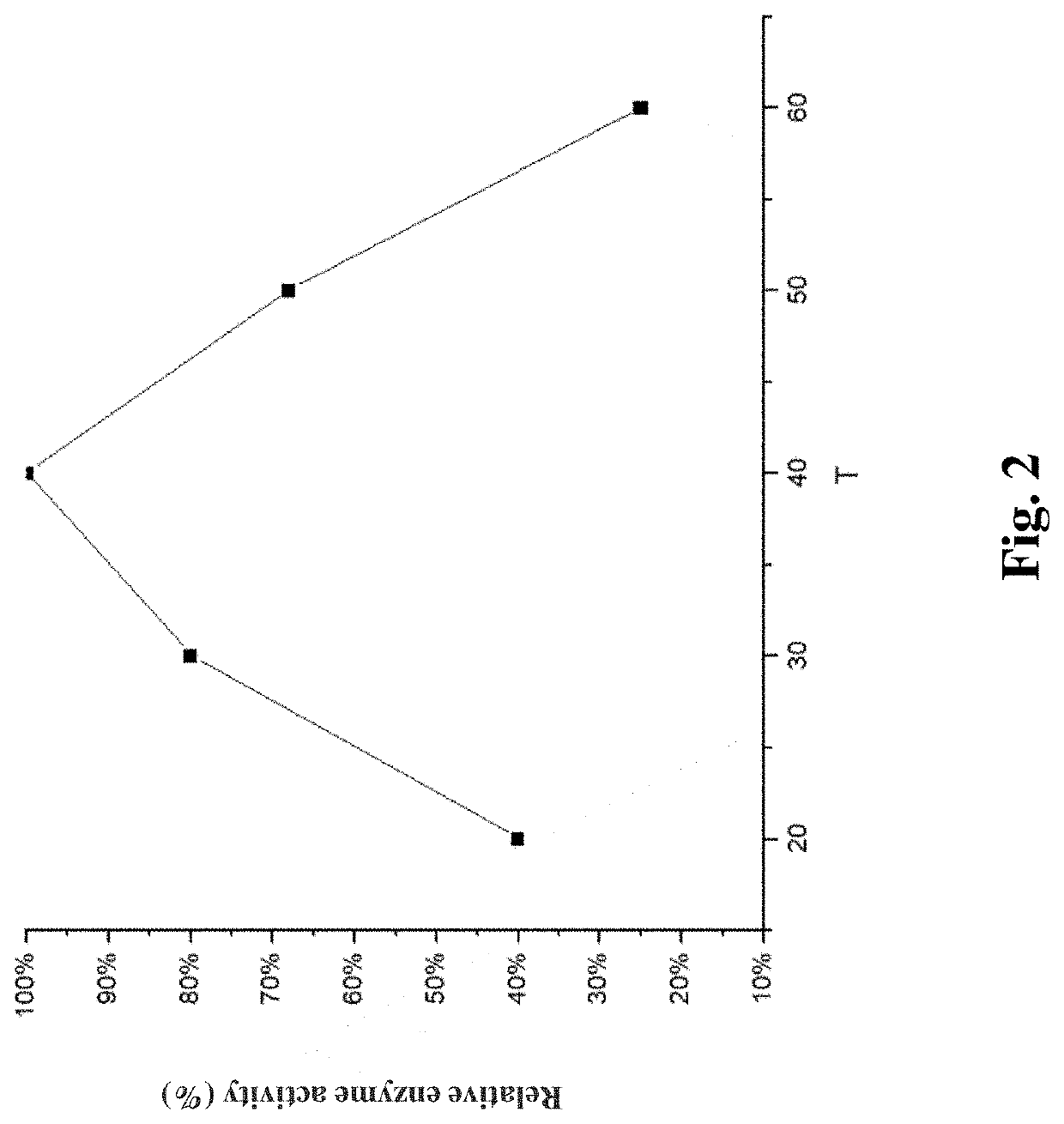
ActiveCN106190998AIncrease vitalitySuitable for industrial productionTransferasesFermentationThreonineMutant
The invention discloses a method for increasing the starch branching enzyme activity, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The method comprises the steps that the 349 methionine of a starch branching enzyme derived from Geobacillus thermoglueosidan is mutated into threonine (Thr) or serine (Ser) separately through a site-directed mutation method, the activity of the obtained mutant is obviously increased compared with a wild starch branching enzyme, and industrial production and application of the starch branding enzyme are promoted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing slowly-digested dextrin
ActiveCN108949861ADelayed digestionHigh degree of branchingFermentationMicroorganismResistant starch
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly-digested dextrin and belongs to the field of bio-modified starch. The method comprises the step of carrying out synergistic modification on to-be-modified starch by adopting Ro (Rhodothermus obamensi)-GBE (Glucan Branching Enzyme) and Gt (Geobacillus thermoglucosidans)-GBE. According to the method disclosed by the invention, corn starch is synergistically treated by utilizing starch branching enzymes with two different microbial sources, the Ro-GBE is firstly added to pretreat, the Gt-GBE is added later, the to-be-modified starch is catalyzed by the Ro-GBE to form a chain segment structure which is more beneficial to the further utilization of the Gt-GBE and slender-type starch molecules are transformed into chunky-type more compact branching structures under the action of the Gt-GBE, so that the slow digestibility of the modified product is more obvious; and further, through changing the adding amount of the Ro-GBE, the modification time and the state of the to-be-modified starch, the synergistic effect between the Ro-GBE and the Gt-GBE is promoted, the branching degree of the amylopectin is increased and the content of the slowly-digested and resistant starch is further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
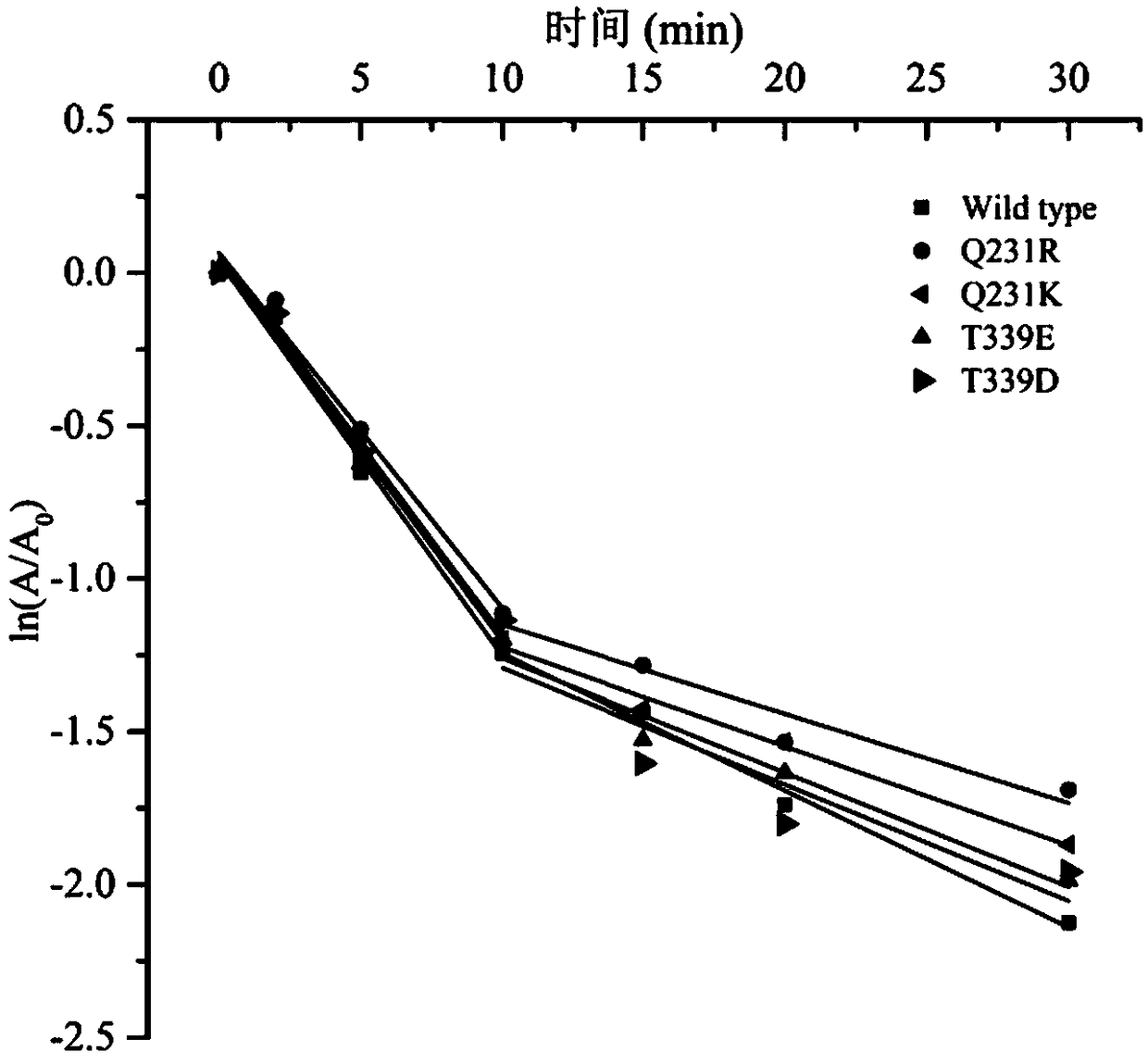
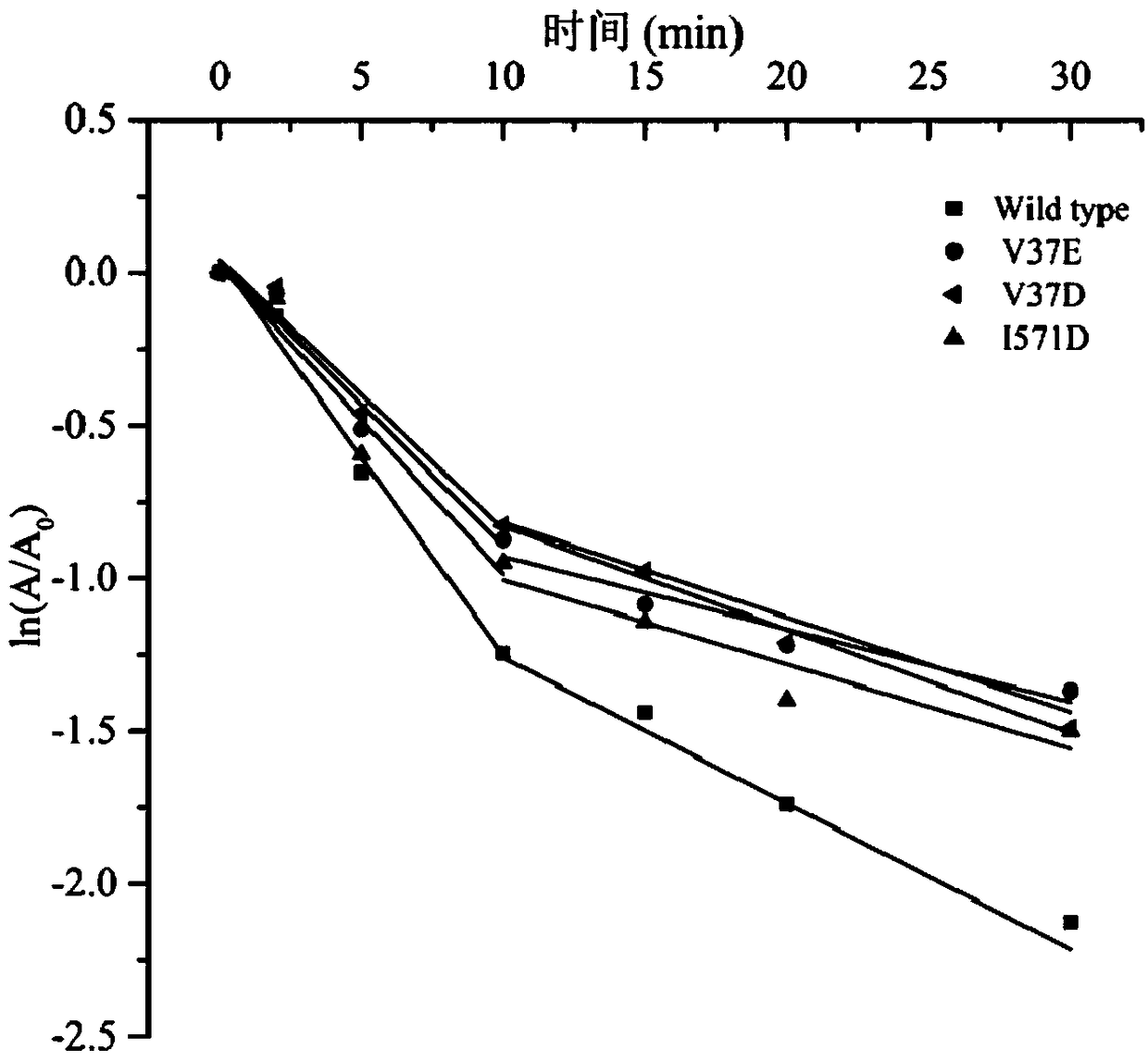
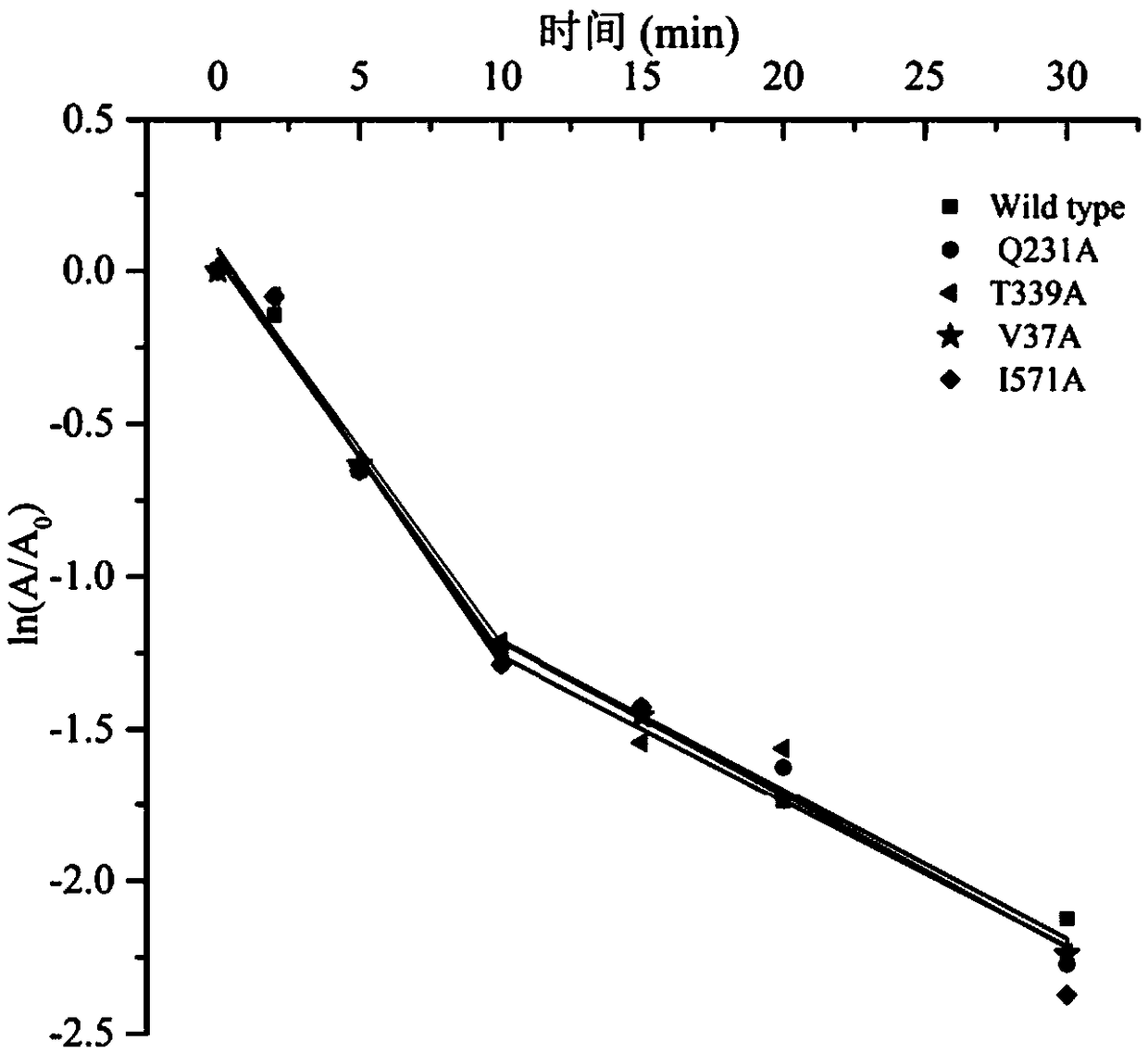
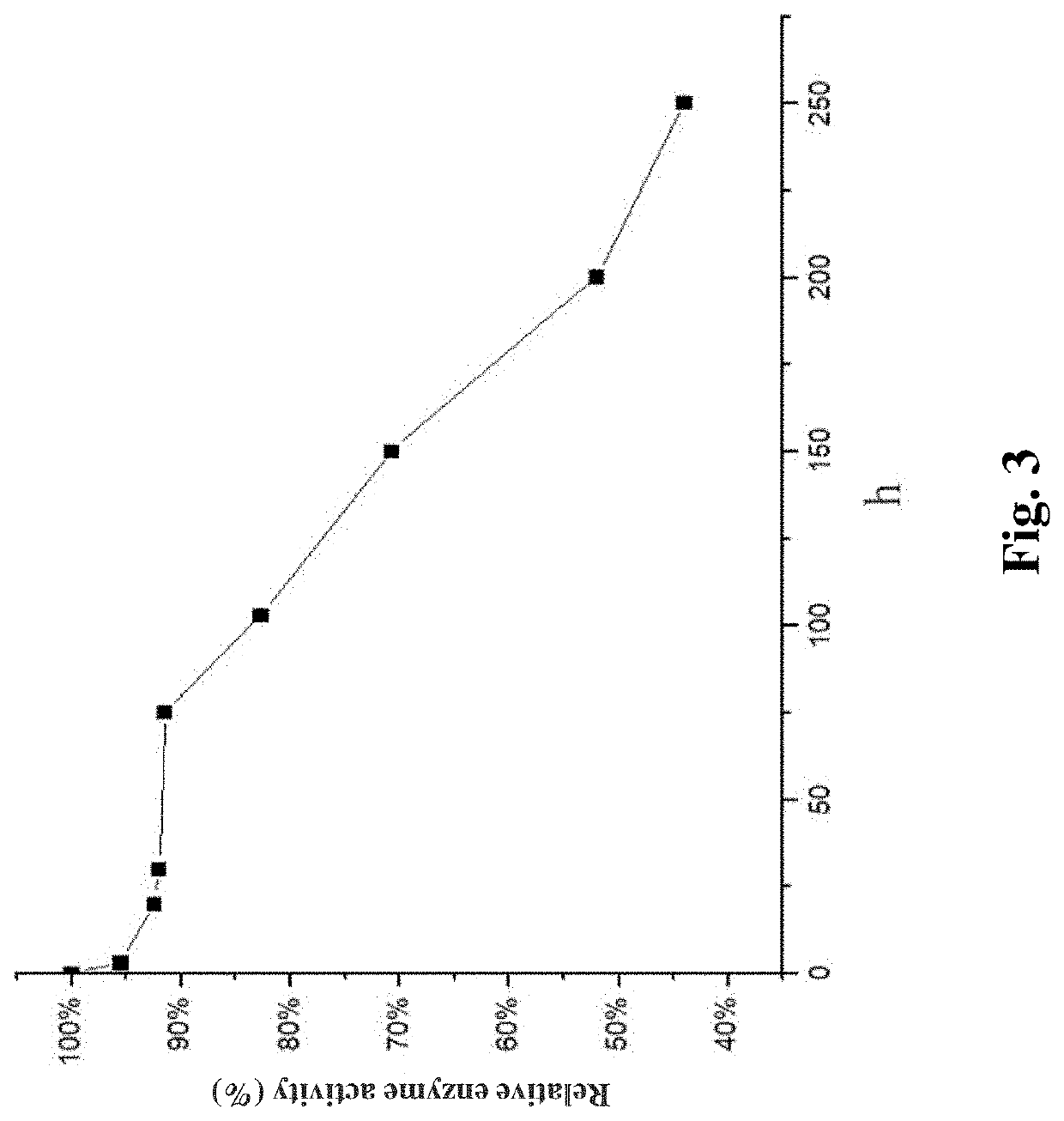
Starch branching enzyme mutants with improved thermal stability
The invention discloses starch branching enzyme mutants with improved thermal stability, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, amino acid residues in astarch branching enzyme are mutated into the amino acid residues with opposite charges to endogenous amino acid residues, an electrostatic interaction is formed between the mutant starch branching enzyme and the endogenous amino acid residues with opposite charges nearby, and the starch branching enzyme mutants with improved thermal stability are obtained; compared with a wild-type starch branching enzyme, half-life periods t1 / 2 (min, 60 DEG C) of the thermal stability of the starch branching enzyme mutants Q231R, Q231K, T339E, T339D, V37E, V37D and I571D obtained by the invention are respectively extended by 40%, 38%, 21%, 26%, 16% and 21% at 60 DEG C, and the half-life periods t1 / 2 (min, 65 DEG C) are extended by 1.5-2.0 times at 65 DEG C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzyme
InactiveUS20040068766A1Eliminate needAffect enzymatic activityTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesEnzymeStarch Branching Enzyme
Owner:AS DE DANSKE SUKKERFABRIKKER
Method for producing high-quality maltodextrin
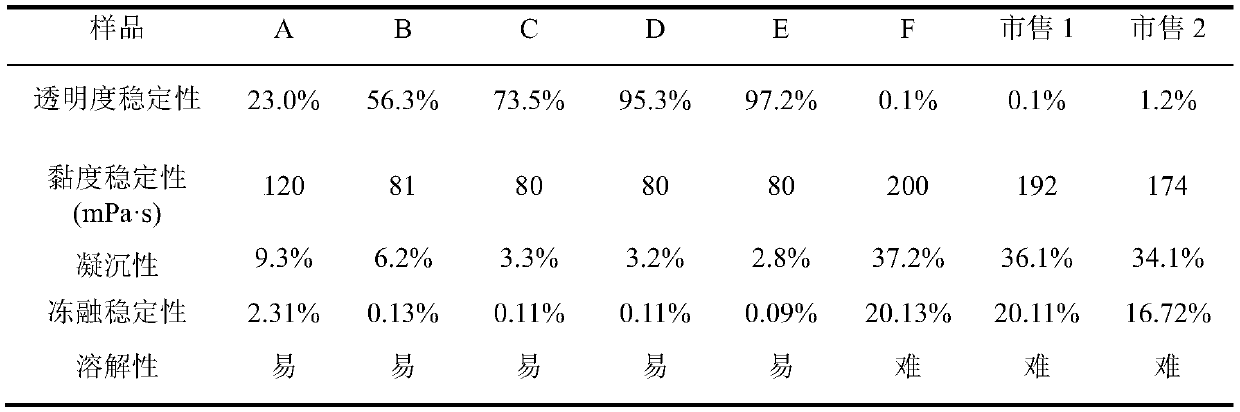
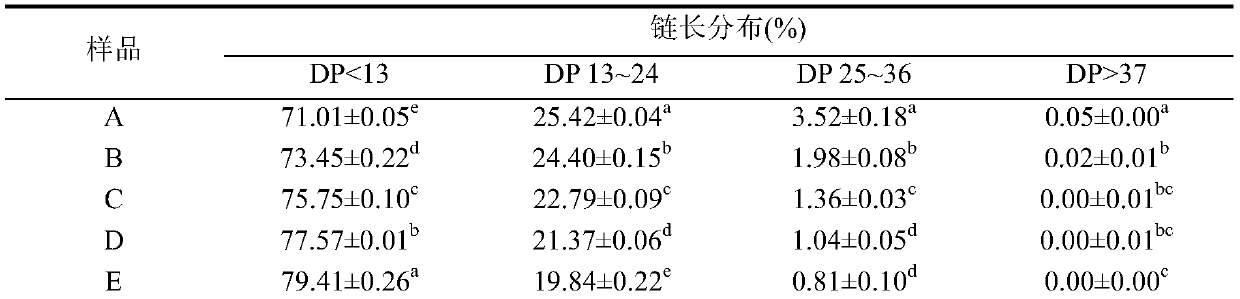
The invention discloses a method for producing high-quality maltodextrin, and belongs to the technical field of maltodextrin. According to the method provided by the invention, on the basis of a traditional enzyme method for producing maltodextrin, a starch branching enzyme from Rhodothermus obamensis is introduced, alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds are cut off, and the cut short chains are connected toreceptor chains to form alpha-1,6-branching points, so that the branching degree of the maltodextrin is increased, the maltodextrin has more cluster structures, and then the aim of enhancing the stability of the maltodextrin and preventing the maltodextrin from being regenerated is achieved. The method specifically comprises the steps of size mixing, jet liquefaction, starch branching enzyme action, filtration, decolorization, ion exchange, concentration, spray drying and the like, and can produce high-quality maltodextrin with high solubility, and high transparency and high viscosity stability in a storage process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of high-performance starch slurry
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-performance starch slurry. The preparation method comprises the steps of dispersing starch with the mass concentration of 10-40% into water; stirring and heating to 40-60 DEG C; reacting for 3-8 hours through stirring a starch branching enzyme at the constant temperature of 40-60 DEG C, wherein 30-150U / g starch is added into the starch branching enzyme; and filtering, centrifugally dehydrating and drying to obtain modified high-performance starch slurry with high branching degree. Compared with unmodified starch, the high-performance starch slurry has the advantages that the gelatinization temperature is reduced, the slurry is not frozen at room temperature, the flowability is favorable, and the adhesion to a pulpified yarn is improved to a relatively high extent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Branching enzyme and application of branching enzyme for preparing resistant dextrin
The invention discloses branching enzyme and an application of branching enzyme for preparing resistant dextrin, which belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to recombinant escherichia coli provided in the invention, the enzyme activity of starch branching enzyme can reach 2500 U / mL, the optimum pH of the produced starch branching enzyme is 6.5, and the optimum temperature is 40 DEG C, and a half-life period at the temperature of 40 DEG C can reach 200 h. The starch branching enzyme takes starch as a substrate, the concentration of the substrate through high-temperature acidolysis is 200 g / L-300 g / L, when the temperature is 35-45 DEG C, the enzyme addition amount is 1000-1500 U / g, the enzymatic conversion is carried out at a reaction time of 8-12 h to prepare the resistant dextrin, a resistance component can reach 60%, and a base for industrial production of the resistant dextrin is established.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes
ActiveCN108251475ADelayed digestionTightly branched structureOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDigestible starchCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes and belongs to the field of biologically modified starch. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the starch is cooperatively treated by utilizing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a starch branching enzyme; the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase is catalyzed to generate cyclodextrin and a lot of short-chain segments are generated; a fine and long type starch molecule is converted into a short and fat structure which is a tighter branch structure under the action of the starch branching enzyme, so that the slow digestion of the starch is more remarkable. By changing an adding manner of the two enzymes, an enzyme adding amount and reaction time, a cooperative effect between the two enzymes is promoted, the content of the cyclodextrin and the branching degree of amylopectin are improved; the content of the slowly digestible starch and resisting starch is further increased andthe digestion speed of the starch is reduced; a novel concept is provided for preparing the slowly digestible starch through biological modification.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of hydroxypropyl starch resistant dextrin
The invention discloses a preparation method of hydroxypropyl starch resistant dextrin, and relates to the technical field of resistant dextrin. According to the method, hydroxypropyl starch is used as a raw material, prepared starch paste has high transparency, high fluidity, weak retrogradation performance, high stability and good freeze-thaw stability, then alpha-amylase is added for hydrolysis, the solubility of glucose is improved, the content of free glucose in the product can be effectively reduced, and the content of the resistant dextrin is increased; then a starch branching enzyme isadded, the digestion resistance of the starch paste is improved, and therefore the content of the resistant dextrin is more effectively increased. The preparation process for preparing the resistantdextrin by using the hydroxypropyl starch is simple, the yield is high, detection is carried out by means of the method which accords with the national food safety standard GB 5009.88-2014, the content of the resistant dextrin reaches 80% or above, the content of free glucose is 10% or below, and the method has industrial production value.
Owner:深圳市悠阳天颂科技发展有限公司
Method utilizing RNA interference technique to breed corn with enhanced content of amylose
InactiveCN101591654AReduce synthesisIncrease contentVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationAmylaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for breeding corn with the enhanced content of amylase. The method for breeding corn with the enhanced content of amylase comprises the following steps that: a recombinant carrier which expresses the following interference RNA molecules is introduced into corn, and corn with silenced starch branching enzyme SBEIIb coding genes is obtained, i.e. the corn with the enhanced content of amylase; and one chain sequence of the interference RNA molecules is shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table, and the other chain sequence is shown in a sequence 2 in the sequence table. An experimental result shows that the content of the amylase in the corn can be enhanced by 15% through the method. In addition, the method can overcome the limitations of a traditional breeding method, can rapidly obtain a target character by a gene engineering technique and can be combined with conventional breeding so as to quicken the breeding of the production variety of high-amylose corn starch.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for extracellularly producing Q-enzyme in signal-peptide-free manner
ActiveCN105950579AEfficient extracellular secretory expressionIncrease production intensityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSignal peptideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for extracellularly producing Q-enzyme in a signal-peptide-free manner and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The method is characterized in that Q-enzyme genes from Geobacillus thermoglueosidan and without self-signal-peptide sequences are expressed in escherichia coli, and some culture strategies are used to achieve the signal-peptide-free extracellular production of the Q-enzyme. Compared with the intracellular production of the Q-enzyme, the method has the advantages that the yield is increased evidently, the separation and purification procedures are simplified, and the extracellular expression of recombinant Q-enzyme in E. coli is beneficial to the industrial large-scale production of the Q-enzyme.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving transparency degree of starch liquidation product
ActiveCN108396041AHigh transparencyTight molecular structureFermentationGlycosyltransferasesSmall branchRhodothermus
The invention discloses a method for improving the transparency degree of a starch liquidation product, and belongs to the field of biological modification starch. The molecular structure of a starchliquidation product is changed through adding starch branching enzymes from rhodothermus obamensis, so that a small branch chain and a higher branching degree are realized; the goals of improving thetransparency and the stability are achieved. The method comprises the following steps of dissolving the starch liquidation product into water according to a certain concentration so as to prepare thestarch liquidation product water solution; the starch branching enzymes are added for reaction for a period of time at a certain temperature so as to improve the transparency of the starch liquidationproduct in the storage process; a novel idea is provided for improving the stability of the starch liquidation product; great potentials and application prospects are realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving freeze-thaw stability of maltodextrin
ActiveCN108841895AIncrease the degree of branchingImprove freeze-thaw stabilityFermentationFreeze thawingIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for improving freeze-thaw stability of maltodextrin and belongs to the technical field of maltodextrin. The method disclosed in the invention comprises the following steps: introducing starch branching enzymes derived from Rhodothermus obamensis on the basis of the traditional enzymic method for producing maltodextrin, cutting off alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds, and linking the cut short chains onto a receptor chain so as to form alpha-1,6-branching points, so that the branching degree is increased, more clustered structures are formed, and the aim of enhancing thefreeze-thaw stability of maltodextrin is achieved. The method specifically comprises the steps: size mixing, spray liquefaction, starch branching enzyme interaction, filtering, discoloring, performing ion exchange, concentrating, performing spray drying and the like, thereby obtaining the maltodextrin with excellent freeze-thaw stability.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing resistant dextrin by using a starch branching enzyme and a cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
ActiveUS10988550B2Low production costIncrease percentageFood ingredientsFermentationCyclodextrinEnzyme
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Plant Starch Composition
InactiveUS6974894B2Altered propertyInhibition is effectiveSugar derivativesTransferasesNucleotide sequencingSolanum tuberosum
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Method of adjusting content of plant amylose and amylopectin
InactiveCN103146756AOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The invention relates to a method of adjusting a content of plant amylose and amylopectin. The invention provides an enzyme which is suitable for genetic engineering operation and can substantially change starch composition in the plant, wherein the enzyme is granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSS I), starch branching enzyme I (SBE I) and / or starch branching enzyme II (SBE II). The invention further provides a novel method of well adjusting starch composition in the plant, and the method comprises reducing expression of the enzyme, and thus obtaining a series of transgene plants with different content ratios of amylose and amylopectin The invention further provides a constructor or a carrier for adjusting starch composition in the plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of maltodextrin
InactiveCN111471728ASegment content increasedUniform molecular weight distributionFood ingredient as thickening agentFermentationRetrogradation (starch)Physical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of maltodextrin, and belongs to the technical field of maltodextrin. The preparation method adopts a manner of combining three-step liquefaction and starch branching enzyme, the chain length distribution and molecular weight distribution of a maltodextrin product can be well improved, and thereby the product is more uniform. The maltodextrin prepared by the method has high quality, and has the advantages such as high transparency, good solubility, low retrogradation, good viscosity stability and freeze-thaw stability, and thereby thefurther development of the market of the maltodextrin is facilitated. The maltodextrin is applied in ice creams, the viscosity and melting rate of a mixed material are reduced, and the product structure status is more delicate and uniform.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM +1
Method for preparing starch-beta-cyclodextrin microspheres based on reversed-phase latex method
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of starch-beta-cyclodextrin microspheres, and provides a method for preparing starch-beta-cyclodextrin microspheres based on reversed-phaselatex method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, starch pretreatment: firstly, uniformly dispersing starch into a softening and moistening solution for 1-2 hours of immersion, then centrifuging and drying, then adding 25-35U / g of starch branching enzyme, then reacting for 1-2 hours at 55-65 DEG C, and finally washing with water, centrifuging and drying, so as to obtain afinished product. According to the prepared novel jasmine essence sustained release agent-starch-beta-cyclodextrin microspheres prepared using the reversed-phase latex method, the starch and the beta-cyclodextrin are both taken as the main materials to prepare the sustained-release agent, and the advantages of the starch and the beta-cyclodextrin are achieved at the same time, adsorption sites onthe surface of the microspheres are increased, essence adsorption capacity is increased, and the sustained-release effect is optimized.
Owner:CHENGDU TECHCAL UNIV
Artificial site-directed mutant of paddy rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene and applications thereof
The invention discloses an artificial site-directed mutant of a paddy rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene and applications thereof. The artificial site-directed mutant is obtained by modifying the 8th exon OF SBE3 gene by a CRISPR / Cas9 gene targeting and editing technology so as to delete the base of the 8th exon. The 8th exon OF SBE3 gene is subjected to artificial mutation by adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 technology; paddy rice plants with prominently increased resistant starch content are picked out, the screening mark of mutant is removed through segregation posterity; and the content of resistant starch can reach 10% or more.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com