Method for extracellularly producing Q-enzyme in signal-peptide-free manner
A technology of starch branching enzyme and signal peptide, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low enzyme activity and low protein expression of starch branching enzyme, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency extracellular secretion expression and increased production intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli
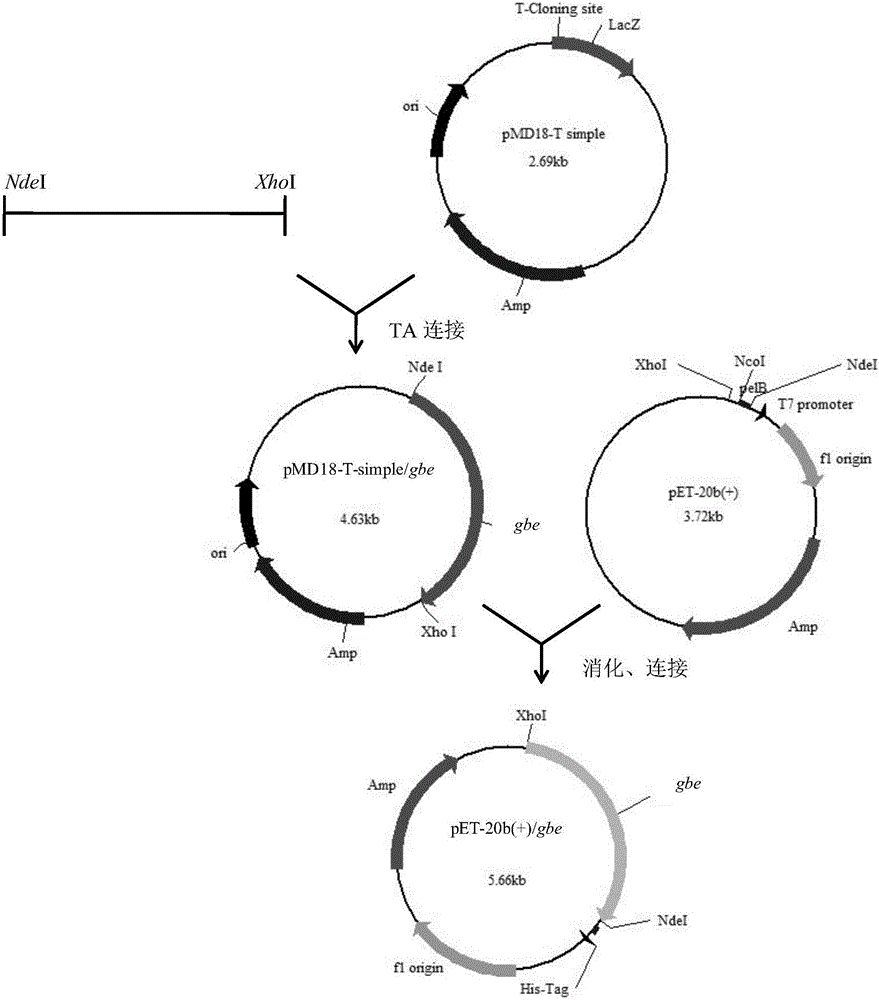
[0026] The full length of the thermoglucosidase Geobacillus starch branching enzyme gene (Gene Bank) is 1938bp. as per figure 1 In the construction method shown, first obtain a gene fragment whose sequence does not contain a signal peptide is the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, connect the target gene to pMD18-T simple vector, and obtain the plasmid pMD18-T simple / gbe. Plasmids pMD18-T simple / gbe and pET-20b(+) were digested with double enzymes and ligated with ligase to obtain recombinant plasmid pET-20b(+) / gbe. The recombinant plasmid pET-20b(+) / gbe was transformed into BL21(DE3) competent cells by heat shock method. The transformation solution was spread on LB plates containing ampicillin (100 μg / mL), and the plasmids were extracted and sequenced to verify the constructed recombinant plasmids. The sequencing work was completed by Shanghai Sangong.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2 Recombinant Escherichia coli shake flask culture
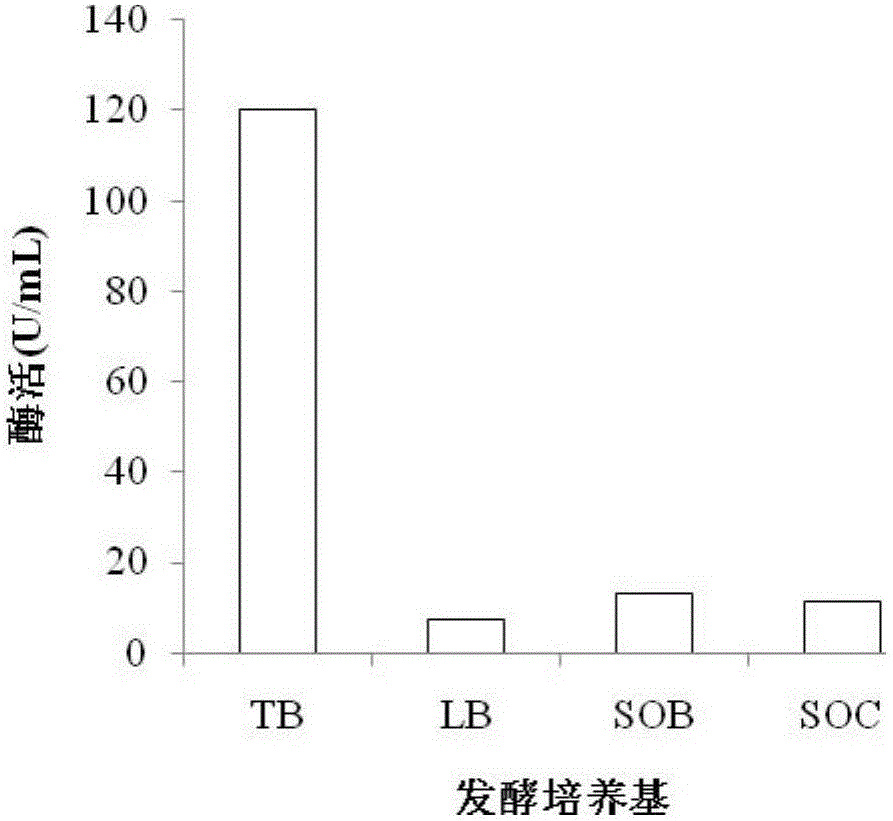
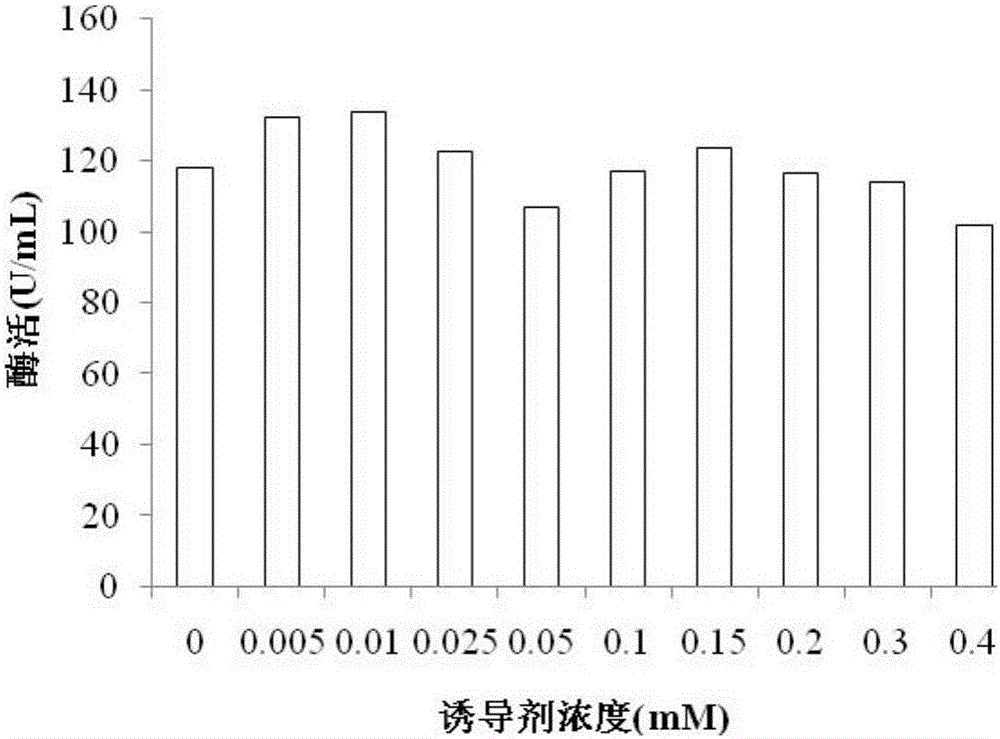
[0028] Pick the single clone of E.coli BL21(DE3) containing the recombinant plasmid in LB medium containing 100μg / mL ampicillin, and culture it at 37°C and 200r / min for 8-12h, with an inoculum size of 2% by volume Inoculate into TB medium containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin, and ferment at 30°C and 200r / min for 48h; centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4°C and 10000rpm for 15min to remove bacteria, and collect the supernatant.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 Enzyme Activity Determination Analysis
[0030] Prepare 0.25% (w / v) potato amylopectin standard solution with 0.9mL 50mmol / L phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.5), add 0.1mL enzyme solution, and react at 50°C for 15min. After the reaction, the enzyme was inactivated in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes, and centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 2 minutes for color development. The chromogenic system is 0.3mL reaction supernatant and 5.0mL chromogenic solution (0.05% (w / v) KI, 0.005% (w / v) I 2 , pH 7.5) were mixed in a 7mL centrifuge tube, and the absorbance was measured at 530nm after 15min of color development. Definition of enzyme activity: at 530nm, the amount of enzyme required to reduce the absorbance value by 1% per minute is one enzyme activity unit.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com