Method for preparing slowly-digested dextrin
A slow-digesting dextrin and modification technology, which is applied in the field of preparing slow-digesting dextrin, can solve the problems of low content of slow-digesting starch, low yield of modified products, long storage time, etc. The effect of increased content, decreased digestion rate, and obvious slow digestibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
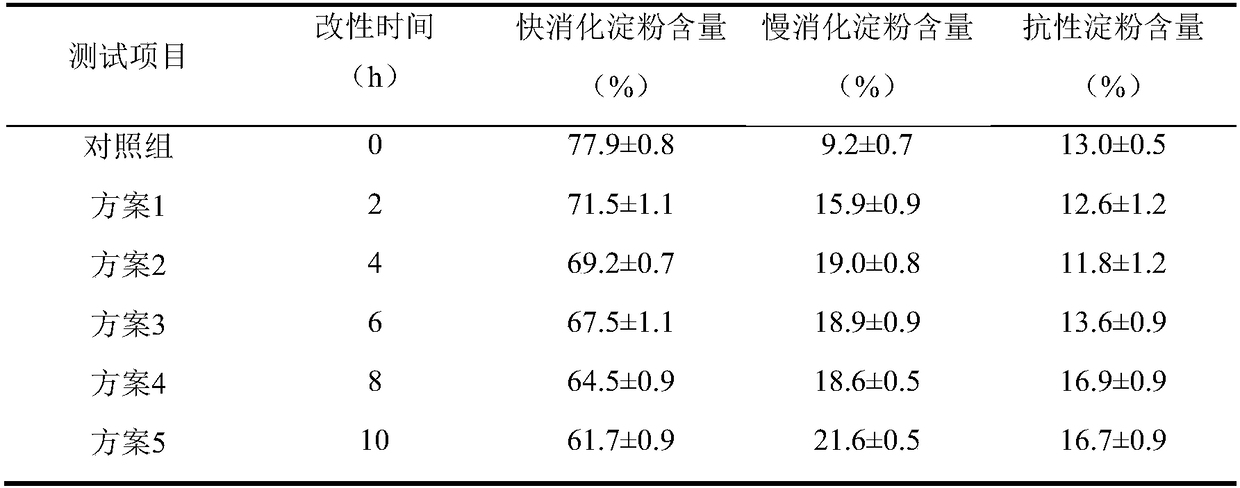
[0022] Example 1: The effect of Gt-GBE modification alone on the content of fast digestible starch in the modified product
[0023] Dissolve corn starch in water to obtain 10% starch milk, gelatinize in boiling water, add Gt-GBE of 25U / g dry base starch, treat at 50°C for 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 hours, terminate the reaction in a boiling water bath, and freeze Dry to obtain modified samples. Refer to Englyst in vitro simulated digestion method to determine the digestibility of modified starch, as shown in Table 1. Among them, the control group represents the digestibility of corn starch paste before unmodified treatment. The results showed that under the action of Gt-GBE alone, compared with the control group, the fast digestible starch content decreased by 20.8%, the slow digestible starch content increased by 134%; the resistant starch content increased by 28.5%. The proportion of slowly digestible starch increased significantly, possibly because the highly branched structure produ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: The effect of Ro-GBE modification alone on the content of fast-digestible starch in the modified product
[0027] Dissolve cornstarch in water to obtain 25% starch milk, gelatinize in boiling water, add Ro-GBE of 30U / g dry base starch, treat at 65°C for 2, 4, 6, 8, 10h, stop the reaction in a boiling water bath, freeze Dry to obtain modified samples. Refer to Englyst in vitro simulated digestion method to determine the digestibility of modified starch, as shown in Table 2. The results showed that under the action of Ro-GBE alone, compared with the control group, the fast digestible starch content decreased by 12.5%, the slow digestible starch content increased by 9.78%, and the resistant starch content increased by 66.9%. Compared with Example 1, Ro-GBE has a better modification effect in a short period of time, but with the prolongation of the action time, the content of fast digestible starch increases again. The possible reason is that Ro-GBE has a stron...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Effect of the amount of enzyme added by Ro-GBE on the content of fast-digestible starch in the double-enzyme synergistically modified product
[0032] Dissolve corn starch in water to obtain 25% starch milk, add Ro-GBE after gelatinization in boiling water, treat at 65°C for 2 hours, stop the reaction in a boiling water bath, add Gt-GBE with 25U / g dry base starch, and keep at 50°C Under treatment for 10 h, the reaction was terminated, and the modified sample was obtained by freeze-drying. Refer to Englyst in vitro simulated digestion method to determine the digestibility of modified starch, as shown in Table 3. The results showed that compared with Example 1, the content of fast-digestible starch decreased by 31.6%, the content of slowly-digested starch increased by 52.8%, and the content of resistant starch increased by 48.5%; compared with Example 2, the content of fast-digested starch decreased by the maximum 38.1%, the highest increase in slow digestible...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com