Method for increasing starch branching enzyme activity
A starch branching enzyme and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low activity, unfavorable industrial production, high industrial production cost, etc., and achieve the effect of improving enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] The preparation of embodiment 1 mutant M349T, M349S
[0016] (1) Site-directed mutation
[0017] According to the sequence of the wild starch branching enzyme gene gbe shown in SEQ ID NO.1, primers for introducing M349T and M349S codon mutations were designed and synthesized respectively.
[0018] Utilize rapid PCR technique, carry out mutation with the expression vector pET-20b(+) / gbe that contains wild starch branching enzyme gene as template, the primers used are respectively:
[0019] The primers for introducing the Met349Thr mutation are:
[0020] Forward primer:
[0021] 5'-GGGCATATTG ACG ATTGCCGAAGATTCGACGGAATGGCCGCTCGTCACTGC-3', the underline is the mutant base,
[0022] Reverse primer:
[0023] 5'-CGAATCTTCGGCAAT CGT CAATATGCCCGGGTCATGCGCAAATACGGTCT-3', the underline is the mutant base;
[0024] The primers for introducing the Met349Ser mutation are:
[0025] Forward primer: 5'-ACCCGGGCATATTG AGC ATTGCCGAAGATTCGACGGAATGGCCGC-3', the underline is the...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 Enzyme assay analysis
[0034] (1) Determination of enzyme activity
[0035] Prepare 0.25% (w / v) potato amylopectin or amylose standard solution with 0.9mL 50mmol / L phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), add 0.1mL enzyme solution, and react at 50°C for 15min. After the reaction, the enzyme was inactivated in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes, and centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 2 minutes for color development. The chromogenic system is 0.3mL reaction supernatant and 5.0mL chromogenic solution (0.05% (w / v) KI, 0.005% (w / v) I 2 , pH 7.5) were mixed in a 7mL centrifuge tube, and the absorbance was measured at 530nm or 660nm after 15min of color development. Enzyme activity definition: at 530nm or 660nm, the amount of enzyme required to reduce the absorbance value by 1% per minute is one enzyme activity unit.
[0036] (2) Enzyme activity comparison
[0037] The experimental results are listed in Table 1. It was found that compared with the wild-type starch branching ...
Embodiment 3
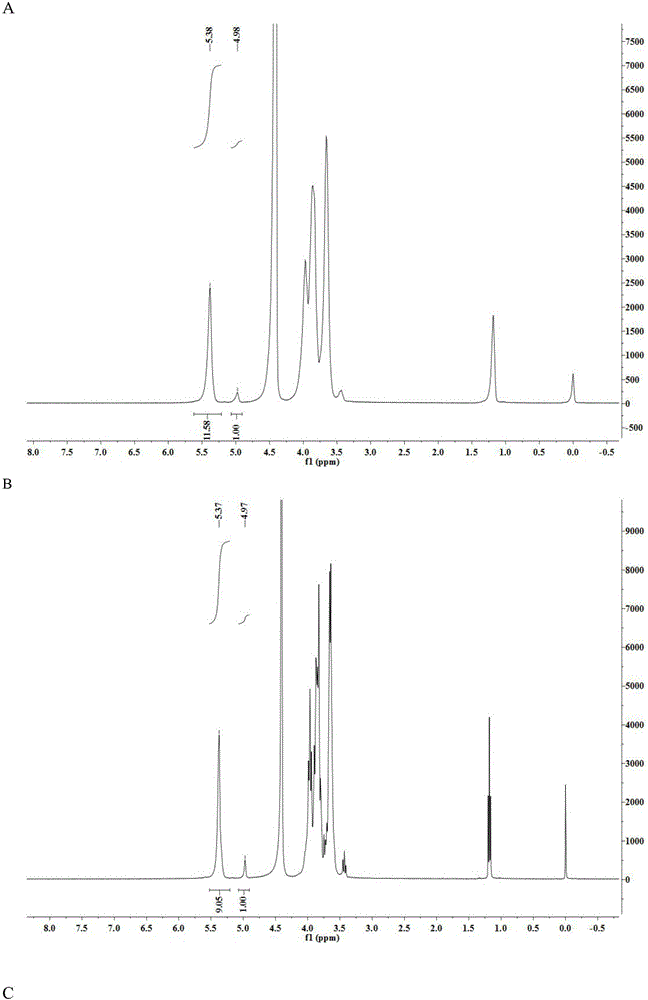
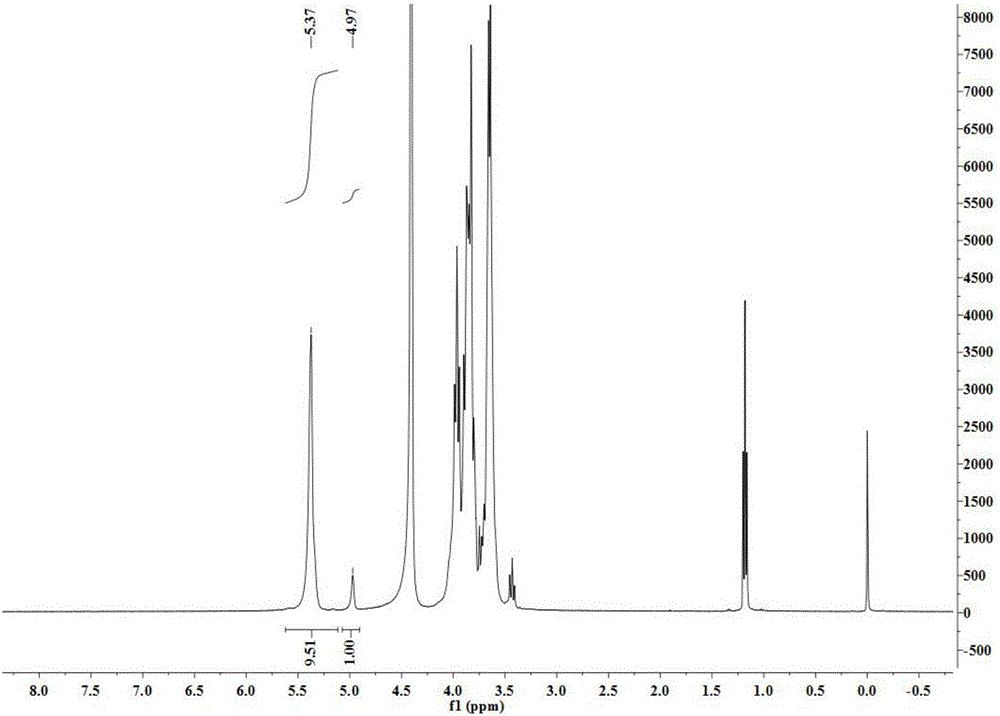
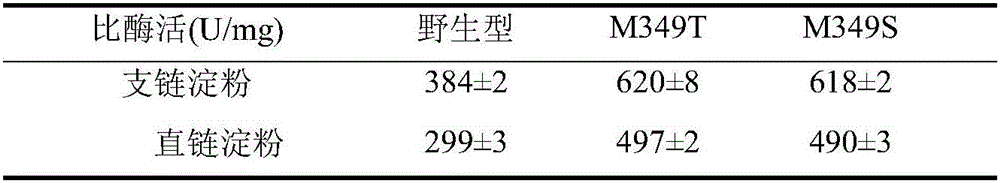
[0040] Example 3 Using NMR to analyze the relative content of α-1,6 glycosidic bonds in modified starch
[0041] With the prepared 5mg / mL pure potato amylopectin solution as the substrate, weigh 0.5g potato pure amylopectin and dissolve it in 90mL sodium phosphate buffer (pH7.5), dilute to 100mL, and paste in boiling water Melt for 30min. A certain amount of wild starch branching enzyme, mutants M349T and M349S were respectively added and reacted at 50° C. for 4 hours, boiled to kill the enzyme, and then freeze-dried.
[0042] The relative content of α-1,6 glycosidic bonds in modified starch was determined by hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Weigh 20mg of the sample to be tested and dissolve in 0.5mLD 2 O, there must be no air bubbles.
[0043] Experimental results such as figure 1 As shown in Table 2, when 5% pure potato amylopectin was used as the substrate, the mutants M349T and M349S had higher activity than the wild-type starch branching enzyme. After 4 hou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com