Method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes
A slow-digesting starch and starch technology, which is applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulas, metabolic diseases, etc., can solve problems that have not been reported in the literature, and achieve the goal of reducing the digestion rate, increasing the content, and promoting synergy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3: Effect of double enzyme synergistic modification on slow digestible starch content in starch
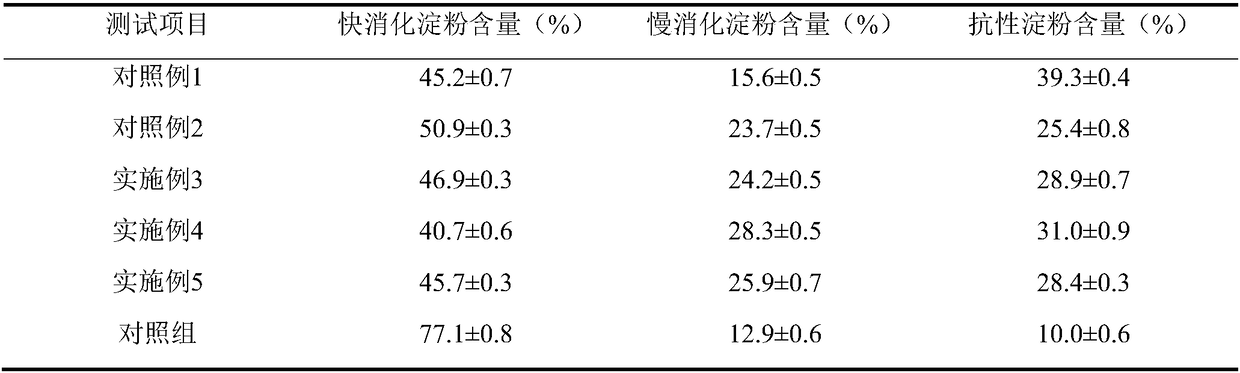
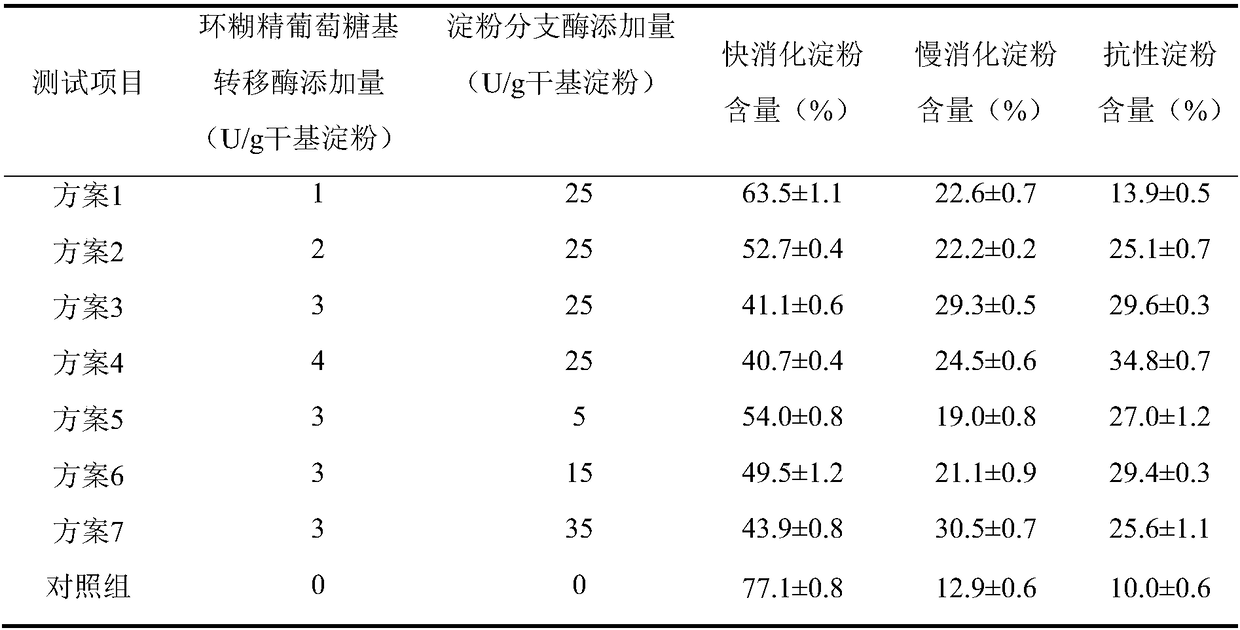
[0026] Dissolve cornstarch in water to obtain 5% starch milk, gelatinize in boiling water, add 3U / g starch cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase and 25U / g starch starch branching enzyme at the same time, treat at 45°C for 16h, boil water bath The reaction was terminated, and the modified starch was obtained by freeze-drying. Refer to Englyst in vitro simulated digestion method to determine the digestibility of modified starch, as shown in Table 1. The results showed that compared with Example 1, the content of slow digestible starch increased by 55.1%; compared with Example 2, the content of slow digestible starch increased by 2.1%, and the content of resistant starch increased by 13.8%.
Embodiment 4
[0027] Example 4: Effects of double-enzyme addition methods on slow-digestible starch content in starch
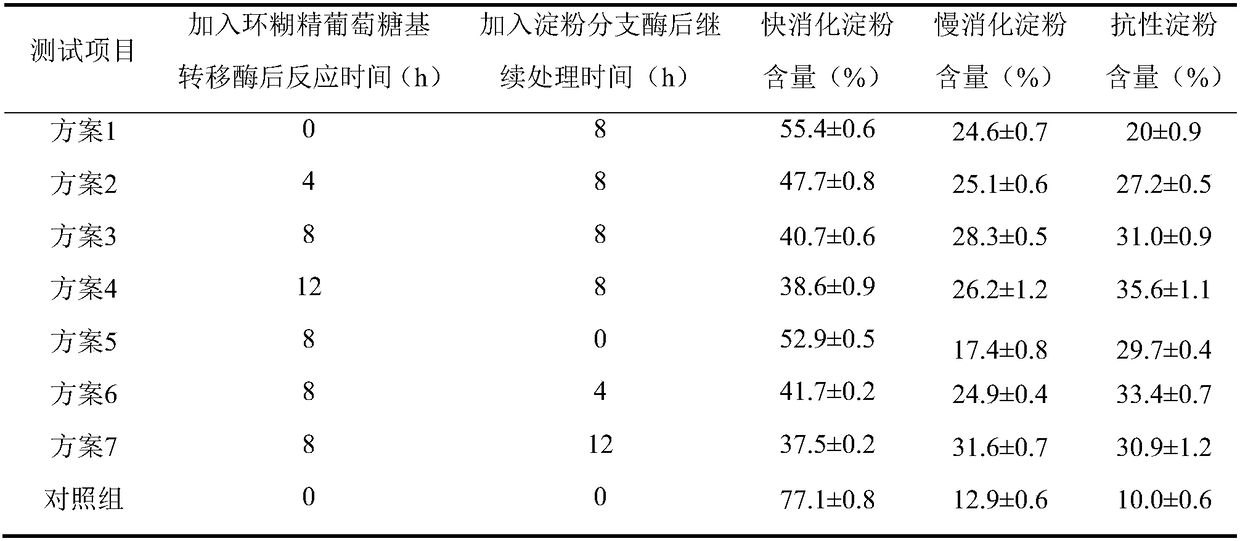
[0028] Dissolve corn starch in water to obtain 5% starch milk. After gelatinization in boiling water, add 3 U / g starch cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase at a constant temperature of 45°C for 8 hours, then add 25 U / g starch starch branching enzyme to continue the reaction After 8 hours, the reaction was terminated in a boiling water bath, and the modified starch was obtained by freeze-drying. Refer to Englyst in vitro simulated digestion method to determine the digestibility of modified starch, as shown in Table 1. The results showed that compared with the control group, the fast digestible starch content decreased by 47.2%, the slow digestible starch content increased by 119%, and the resistant starch content increased by 210%. Compared with Example 3, the fast digestible starch content was reduced by 13.2%, and the digestion rate of the modified sample was further reduced...
Embodiment 5
[0029] Embodiment 5: The effect of double-enzyme addition method on the content of slowly digestible starch in starch
[0030] Dissolve cornstarch in water to obtain 5% starch milk. After gelatinization in boiling water, add 25U / g starch starch branching enzyme at a constant temperature of 45°C for 8 hours, then add 3U / g starch cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to continue the reaction After 8 hours, the reaction was terminated in a boiling water bath, and the modified starch was obtained by freeze-drying. Refer to Englyst in vitro simulated digestion method to determine the digestibility of modified starch, as shown in Table 1. The results showed that compared with Example 3, the content of fast digestible starch was reduced by 2.56%, and the effect was not significant.
[0031] A comprehensive comparison shows that the addition of enzymes will have different degrees of influence on the preparation of slow digestible starch. First cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase treatment 8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com