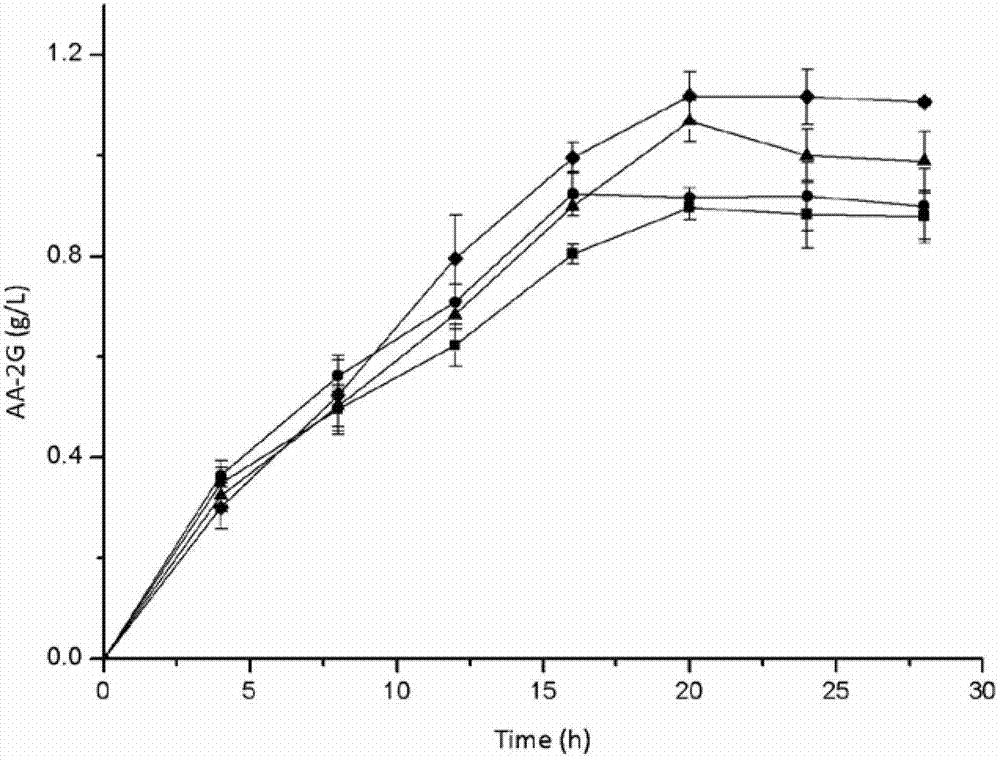
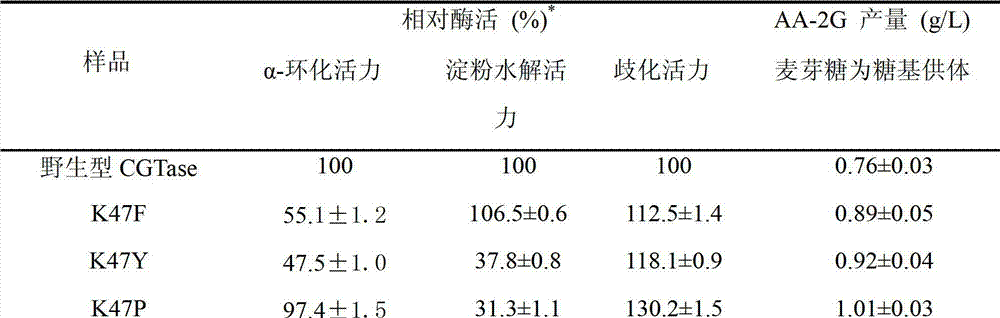
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
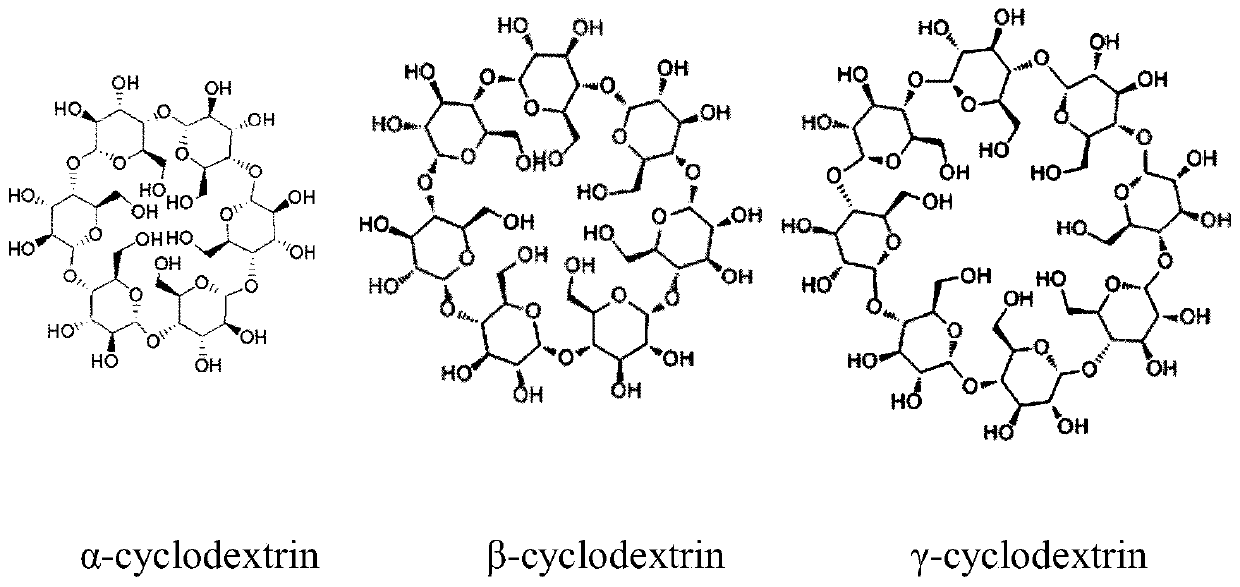
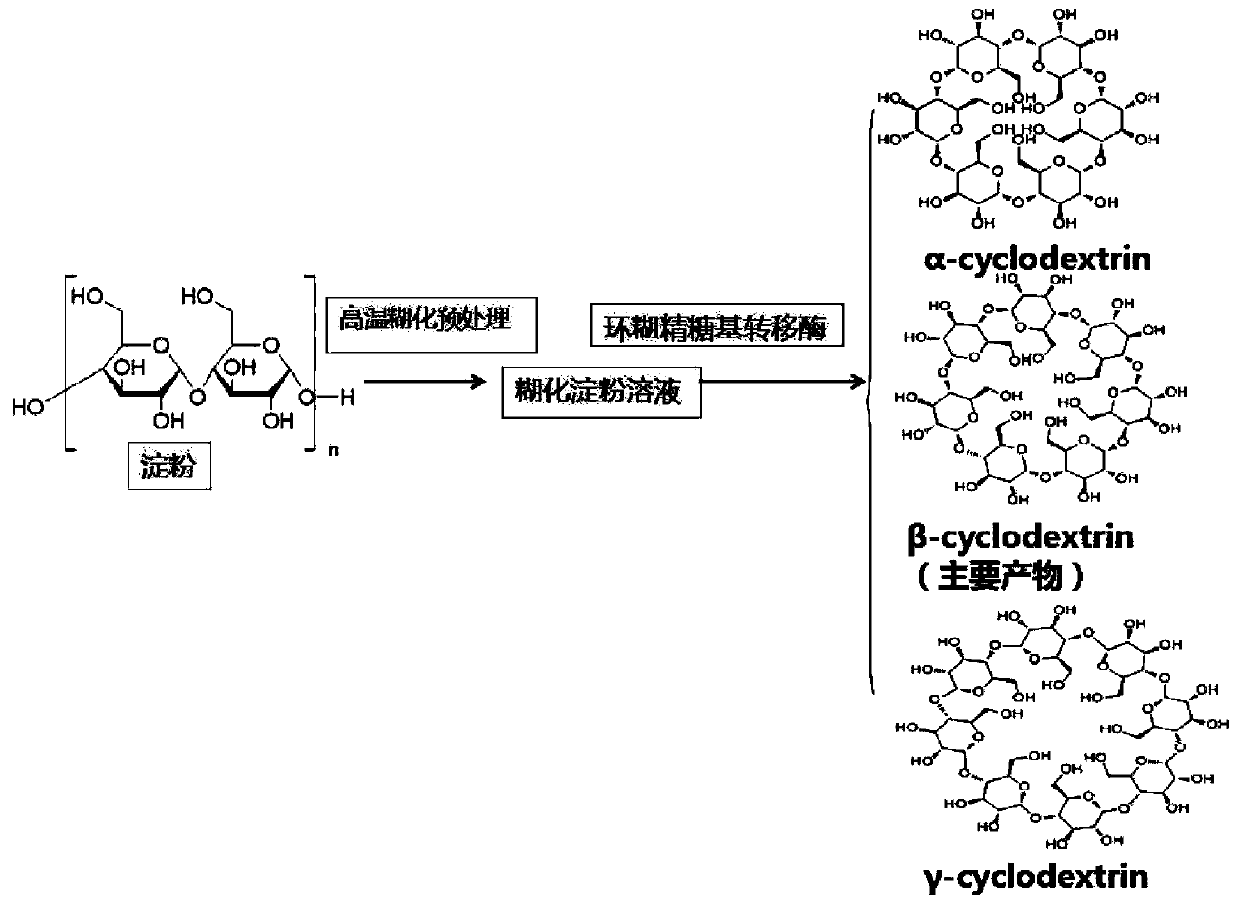
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase (also Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase or Cyclodextrin glucanotransferase) or CGTase for short (EC 2.4.1.19) is a bacterial enzyme belonging to the same family of the α-amylase specifically known as glycosyl-hydrolase family 13. This peculiar enzyme is capable of catalyzing more than one reaction with the most important being the synthesis of non-reducing cyclic dextrins known as cyclodextrins starting from starch, amylose, and other polysaccharides. CGTase is an enzyme common to many bacterial species, in particular of the Bacillus genus (e.g. B. circulans, B. macerans and B. stearothermophilus), as well as to some archaea, but it is not known to be present in any other species.
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104017784AImprove thermal stabilityGood storage stabilityFermentationGenetic engineeringVitamin CCyclodextrin
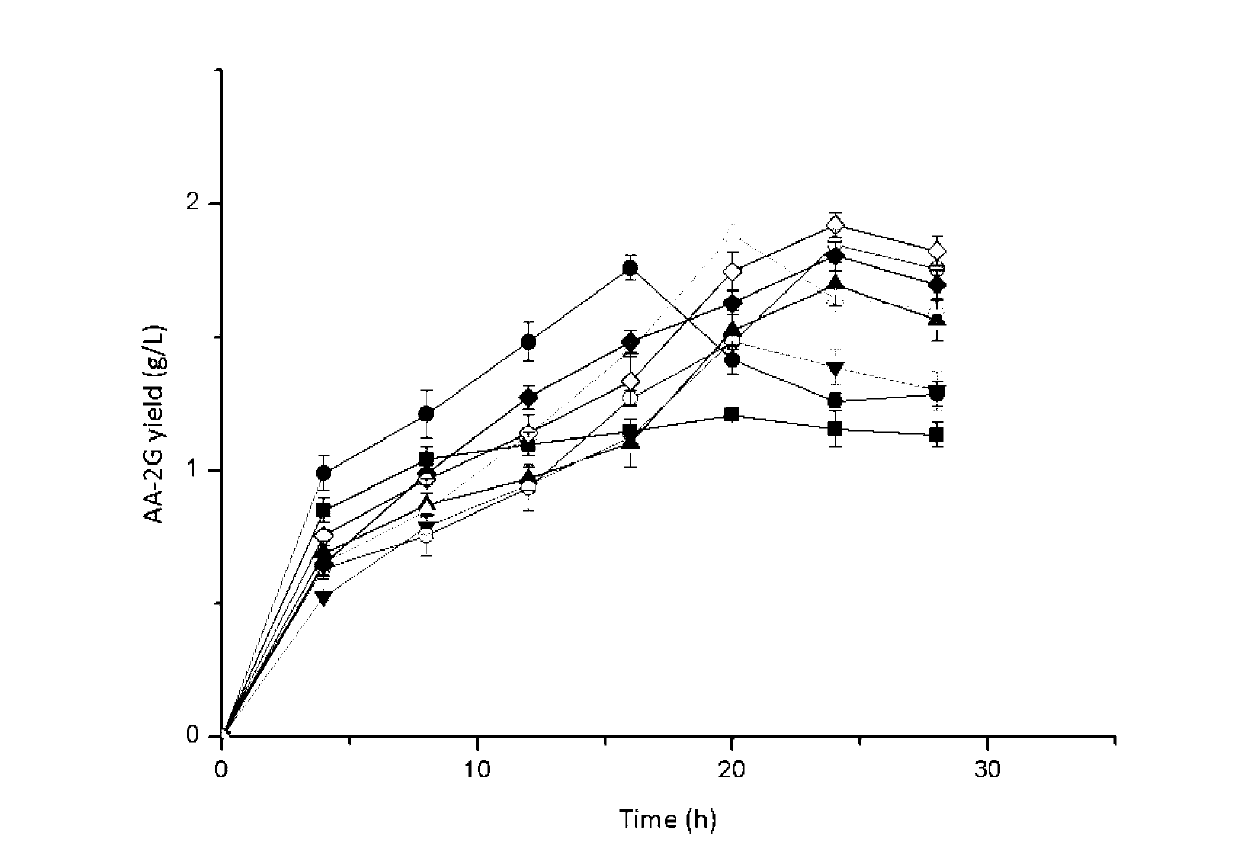
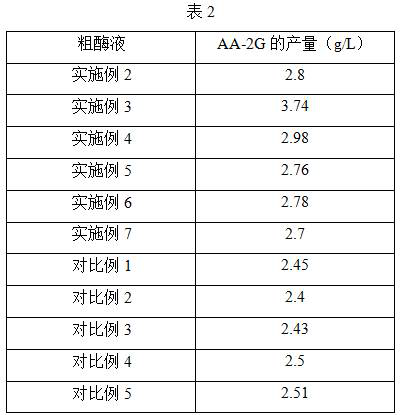
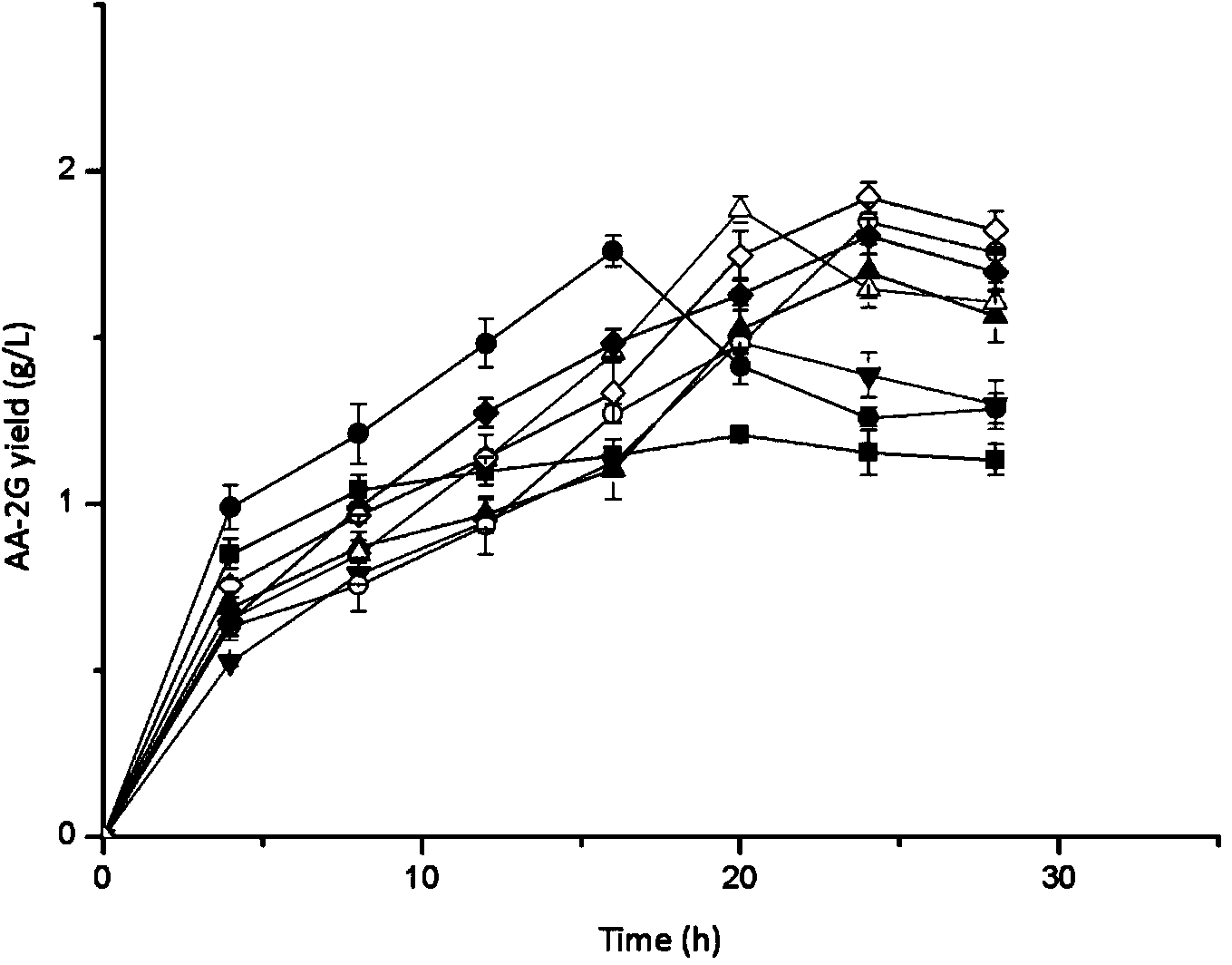
The invention provides a novel cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase and a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the novel cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase is a mutant with the mutation at 55 bit, 77 bit, 121 bit, 331 bit, 543 bit, 604 bit or 615 bit of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The novel cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase has good thermal stability, good storage stability, and high activity, can be used in the production of AA-2G, can increase the yield and improve the conversion rate of vitamin C, and is suitable for large scale production of the AA-2G. By use of the new CGT (cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase), the AA2G yield can reach 170g / L, the conversion rate of vitamin C can reach 55%-60%.
Owner:JIANGSU CHENGXIN PHARMA
Method for adding ethanol to enhance beta-cyclodextrin yield
InactiveCN101586137AHigh yieldVolatileMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFermentationOrganic solventBeta-Cyclodextrins
A method for adding ethanol to enhance the beta-cyclodextrin yield belongs to the cyclodextrin production technology field. The invention utilizes the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase to catalyze the starch to transform and produce the beta-cyclodextrin, adds the ethanol in the reaction liquid to improve the beta-cyclodextrin yield. The method comprises: blending the starch milk with the mass concentration of 15-30%; stirring for 30-120 minutes at 80-90 DEG C, regulating the temperature to 50-60 DEG C, adding the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase based on the concentration of 3-8 U in 1g starch and adding ethanol; completely reacting for 8-12 hours after the ethanol adding quantity achieves 0.1mL-0.5mL in 1g starch, regulating pH value to 6-9 in the transforming process, filtering, crystallizing and obtaining the beta-cyclodextrin products. The method has no process for recovering the organic solvent and greatly enhances the beta-cyclodextrin yield. The product beta-cyclodextrin has no organic solvent residues.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing trehalose through multienzyme coupling and application thereof
ActiveCN108707634AEfficient synthesisCatalytic reaction cycle shortenedFermentationCouplingCyclodextrin
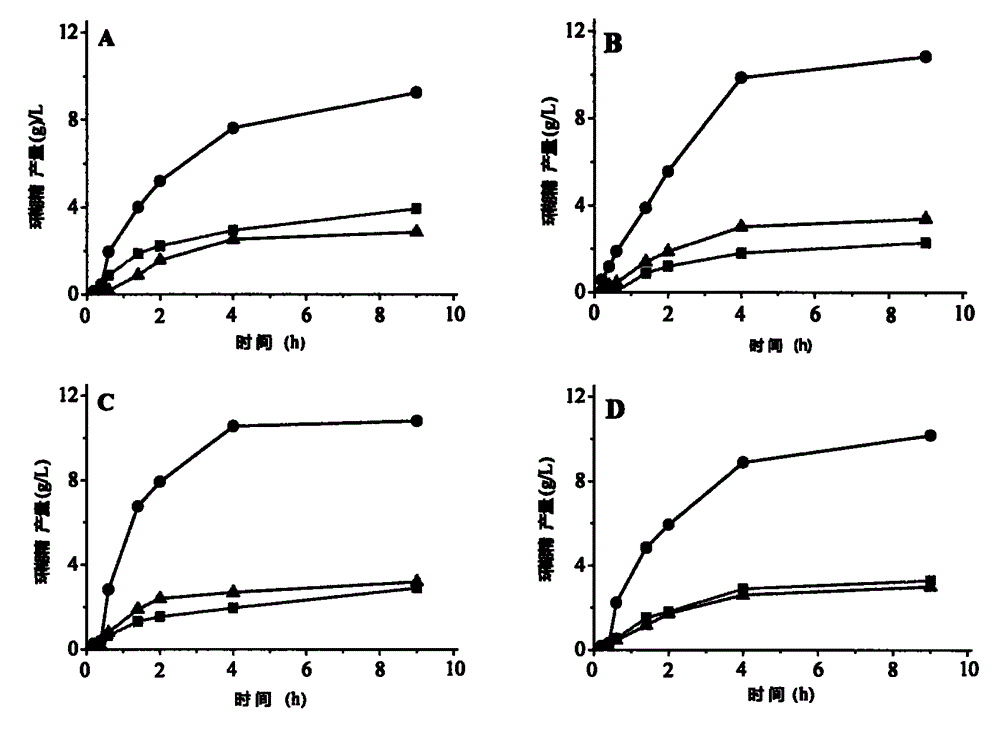
The invention discloses a method for producing trehalose through multienzyme coupling and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzymes. According to the method and the application, rice starch is used as a substrate, the disproportionate activity of 4-alpha glycosyl transferase and cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase are used, and pullulanase, maltooligosyl trehalose synthase (MTSase), maltooligosyl trehalose hydrolase (MTHase), the 4-alpha glycosyl transferase (TaAM) and the cyclodextrin glycanotransferase (CGTase) are adopted for multienyme coupling to improve a substrateuse ratio, so that the yield of the trehalose is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving water solubility of dye lignin by utilizing cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase transglycosylation reaction
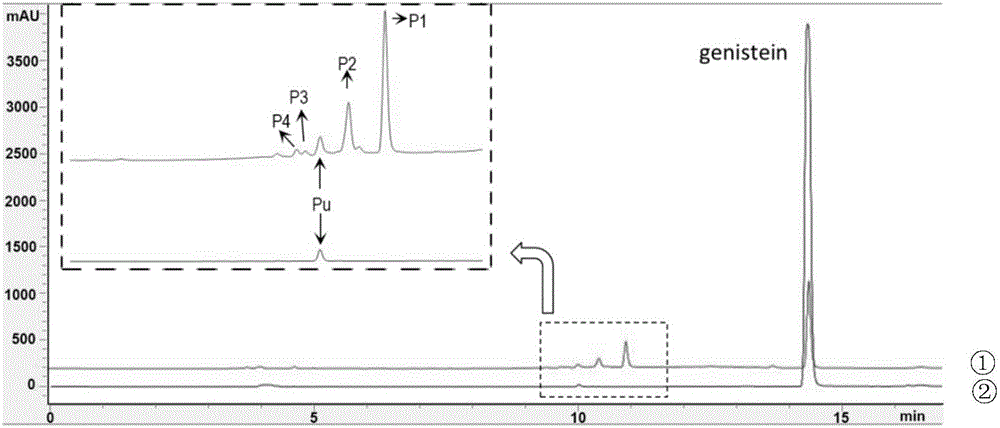
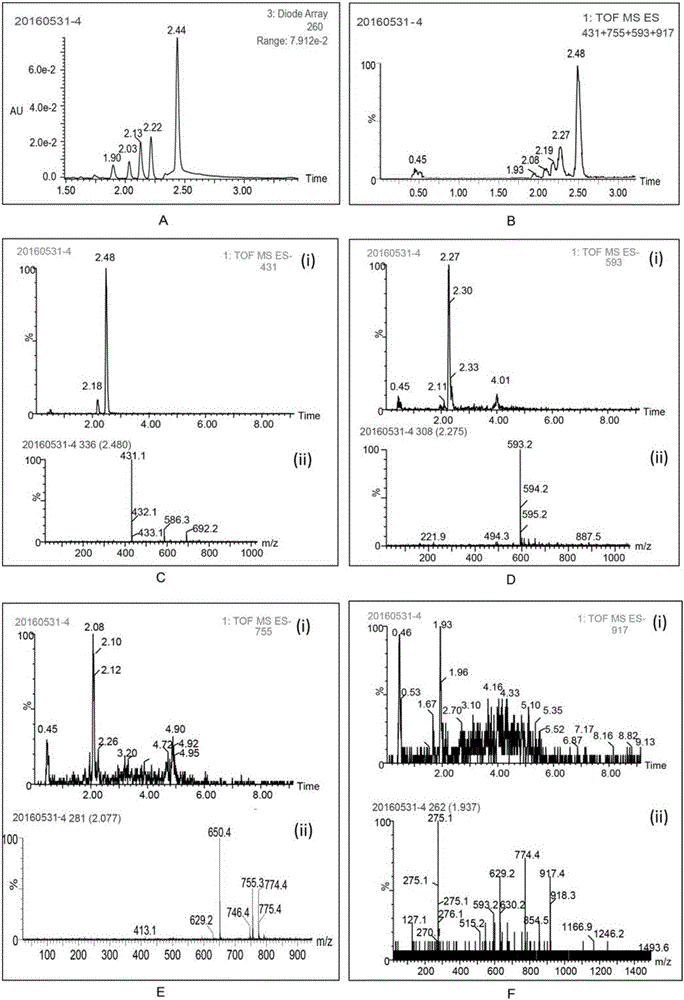
The invention discloses a method for improving the water solubility of dye lignin by utilizing cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase transglycosylation reaction, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. A gene (GenBank accession no.JX412224), which is derived from P.macerans strain JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO:M208063) and optimized by a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase codon, is connected to pET20b(+) plasmid and is transferred to an E.coli BL21(DE3) cell to establish gene engineering bacteria for producing the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase. The pure cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, which is obtained through fermentation enzyme production and purification, is applied to catalytic transglycosylation reaction, alpha-cyclodextrin serves as a glycosyl donor, the dye lignin serves as glycosyl receptor, and at least four dye lignin glycosylated derivatives (Glc)n-genistein (n is equal to 1, 2, 3 and 4) are finally obtained, wherein Glc-genistein and (Glc)2-genistein are main products, in particular the water solubility of the (Glc)2-genistein is greatly improved compared with that of the dye lignin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutants and application thereof
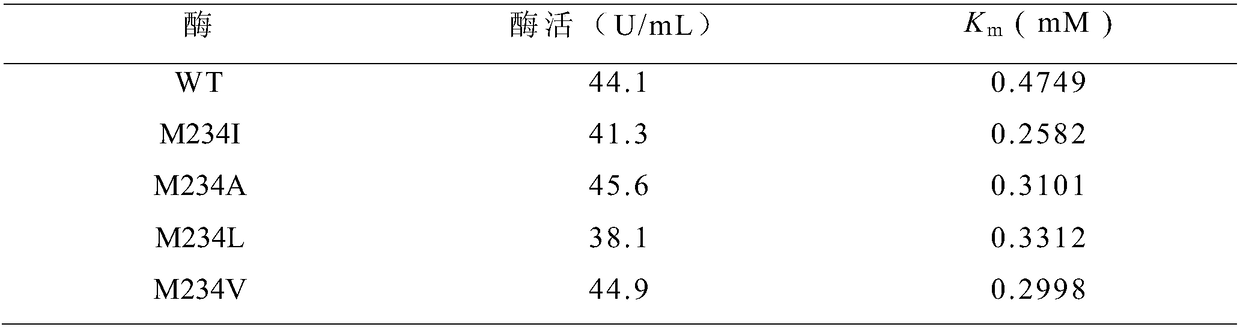
ActiveCN109456950AIncreased receptor affinityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeMethionine biosynthesis
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutants and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. Methionine from site 234 of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of Bacillus circulans is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis; affinities of mutants M234I, M234A, M234L and M234V to a maltose receptor are increased by 45.6%, 34.7%, 30.3% and 36.9% as compared to wild types. The cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutants are applicable to the preparation of trehalose; trehalose conversion rate is further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mutation method for enhancing beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of beta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
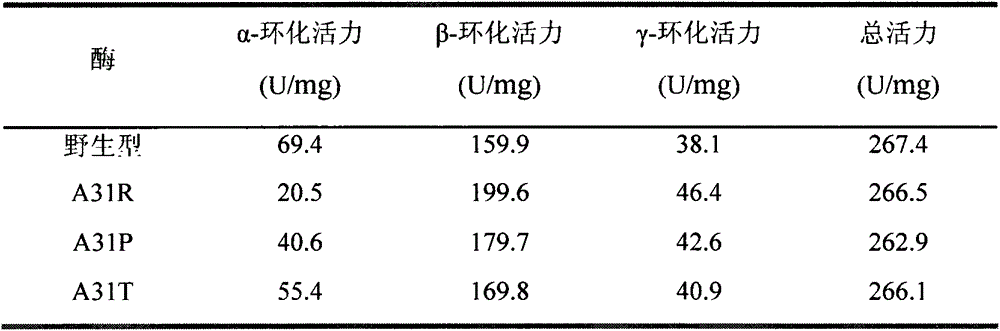
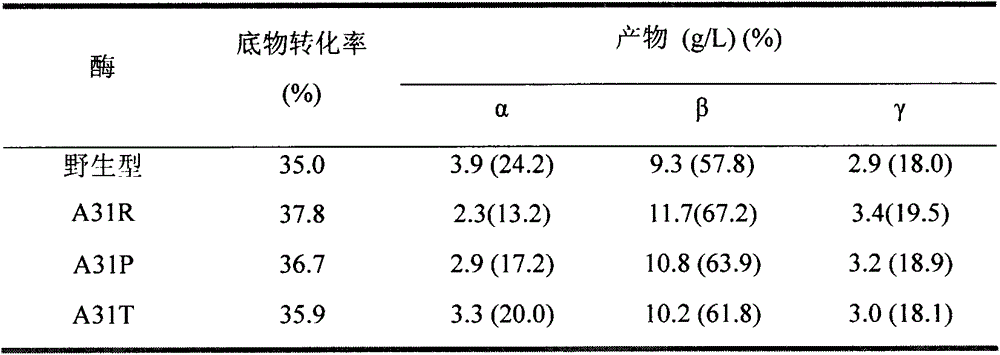
InactiveCN103555685AHigh specificityConducive to industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationAlanineThreonine
The invention relates to a mutation method for enhancing beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of beta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (short for beta-CGT enzyme), and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the present invention, a site-specific mutagenesis method is adopted to increase beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the CGT enzyme, the mutation scheme for enhancing beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the beta-CGT enzyme derived from Bacillus circulans STB01 is provided, mutation of alanine on the site 31 in the CGT enzyme into arginine (Arg), proline (Pro) or threonine (Thr) is performed to obtain mutants A31R, A31P and A31T, beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the mutant is significantly enhanced compared with beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the wild CGT enzyme, and the mutation method is more suitable for beta-cyclodextrin industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase compound enzyme preparation
ActiveCN101717765BGood storage stabilityThe compounding method is simpleMicroorganism based processesEnzyme stabilisationEnzymeRaw material
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase compound enzyme preparation, which has extremely excellent storage stability, can be stored for 60 days at the temperature of 40 DEG C, has retention rate of enzyme activity still reaching over 95 percent, and solves the problem of reduced application performance of products caused by long product transportation or storage time. The liquid enzyme preparation provided by the invention has a simple compounding method, rich raw material sources and low cost, and is particularly suitable for industrial popularization.
Owner:山东黄三角生物技术产业研究院有限公司
Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutant and application thereof
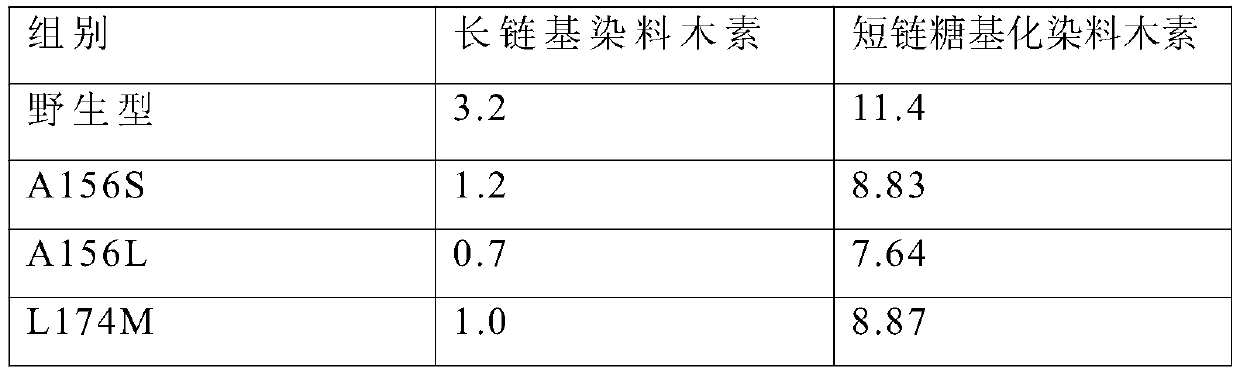
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutants and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering. The CGTase mutants have high specificity to long-chain glycosylated genistein products. The yield of long-chain glycosylated genistein prepared from CGTase mutants A156V / L174P, A156V / L174P / A166Y, A156V / L174P / A166V, A156V / L174P / A166G and A156V / L174P / A166K by using maltodextrin as a glycosyl donor and genistein as a glycosyl receptor is increased by 62.5%, 165%, 112.5%, 112.5% and 59.4% respectively, compared with the yieldof long-chain glycosylated genistein prepared from wild type cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase by taking maltodextrin as a glycosyl donor and genistein as a glycosyl receptor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102994468AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineWild type
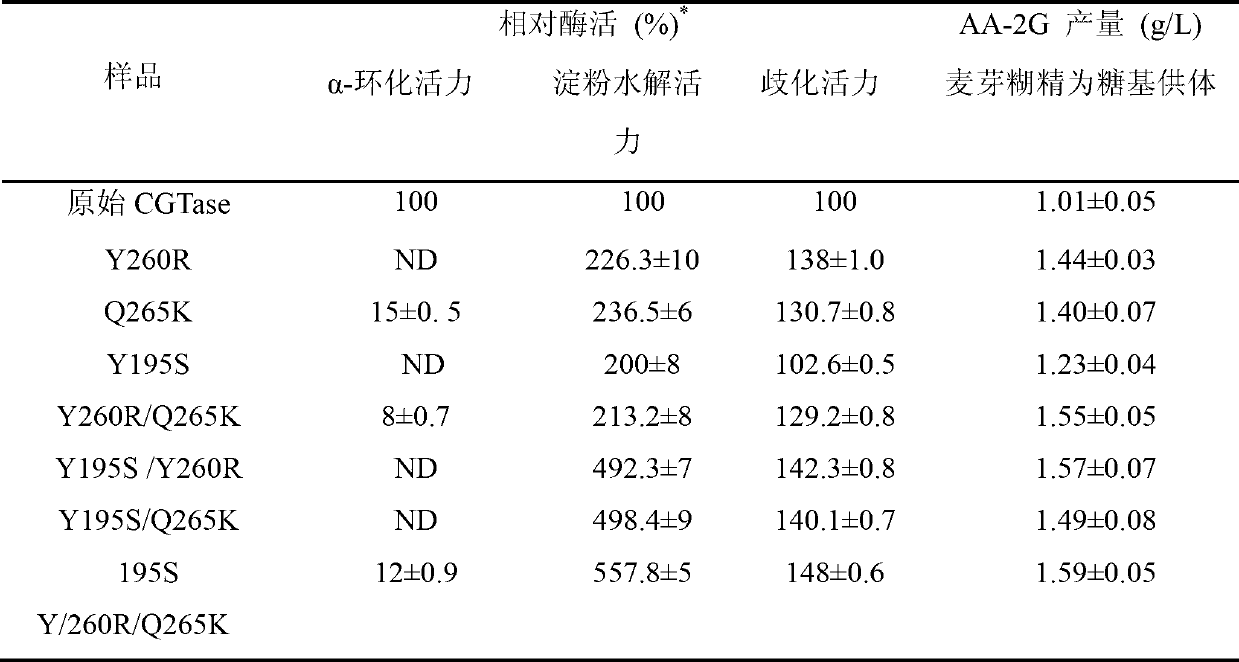
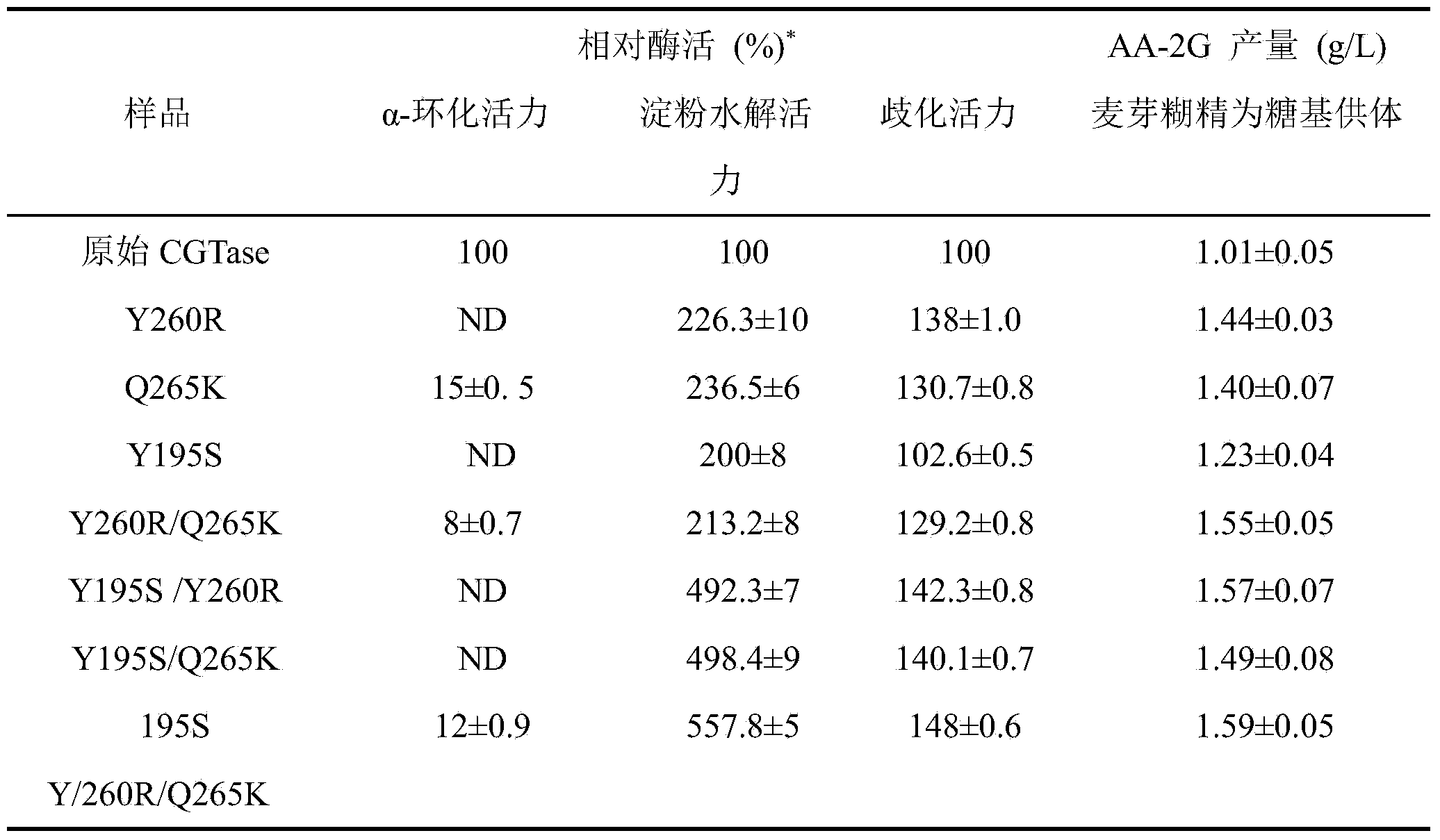
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. 195-bit tyrosine (Tyr) of CGTase of P.macerans strain JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO:M208063) is replaced by serine (Ser), 260-bit tyrosine (Tyr) is replaced by arginine (Arg), and 265-bit glutamine (Gln) is replaced by lysine (Lys), so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 23 percent, 44 percent and 40 percent. According to combined mutation of the mutant strains, double mutants Y195S / Y260R, Y195S / Q265K and Y260R / Q265K and A three-point mutant Y195S / Y260R / Q265K are obtained. A Glycosyl donor is produced by the maltodextrin, so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 57 percent, 49 percent, 55 percent and 59 percent; and compared with the mild type CGTase, the mutant strains facilitate the production of the AA-2G for glycosyl donors by using maltodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes
ActiveCN108251475ADelayed digestionTightly branched structureOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDigestible starchCyclodextrin
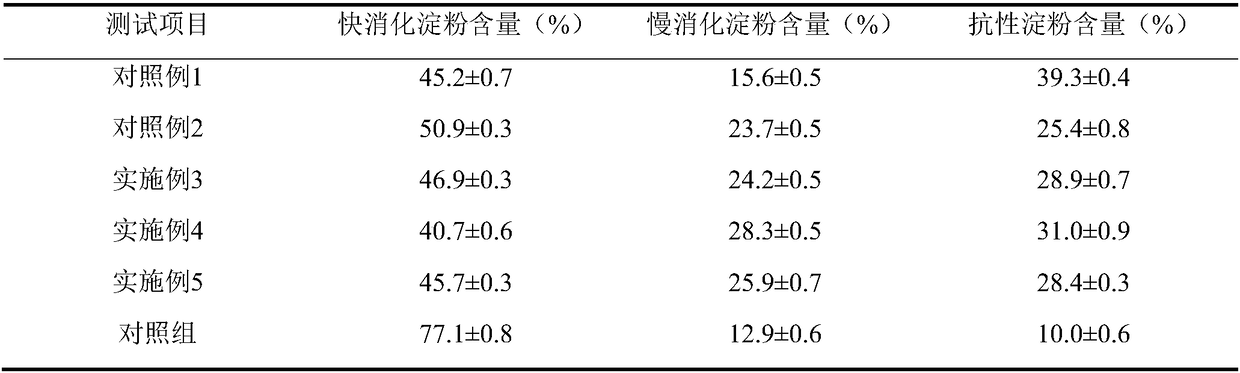
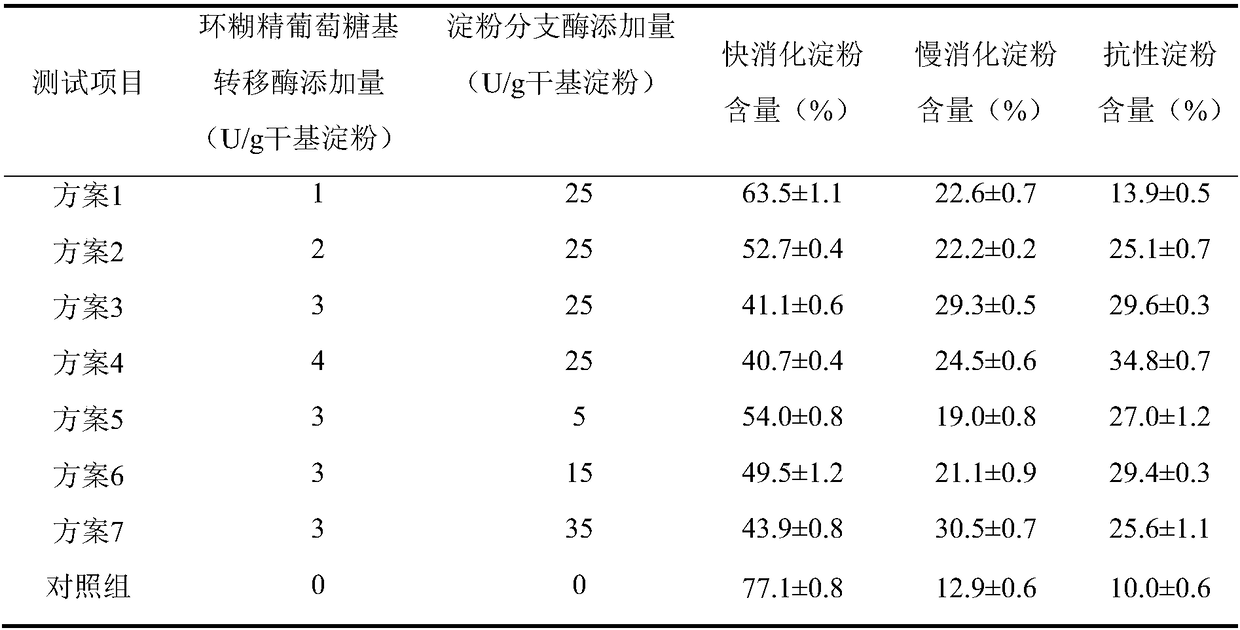
The invention discloses a method for preparing slowly digestible starch by utilizing double enzymes and belongs to the field of biologically modified starch. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the starch is cooperatively treated by utilizing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a starch branching enzyme; the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase is catalyzed to generate cyclodextrin and a lot of short-chain segments are generated; a fine and long type starch molecule is converted into a short and fat structure which is a tighter branch structure under the action of the starch branching enzyme, so that the slow digestion of the starch is more remarkable. By changing an adding manner of the two enzymes, an enzyme adding amount and reaction time, a cooperative effect between the two enzymes is promoted, the content of the cyclodextrin and the branching degree of amylopectin are improved; the content of the slowly digestible starch and resisting starch is further increased andthe digestion speed of the starch is reduced; a novel concept is provided for preparing the slowly digestible starch through biological modification.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103122341AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesCyclodextrinWild type
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, for CGTase derived from peanibacillus macerans, lysine at a 47th site, tyrosine at a 89th site, asparaginate at a 94th site and aspartic acid at a 196th site are respectively mutated into leucine K47L, phenylalanine Y89F, praline N94P and tyrosine D196Y, so that AA-2G yields are respectively increased by 30.7%, 10.9%, 10.0% and 31.7%. Complex mutation is carried out on the mutant strains to obtain double mutants namely K47L / Y89F, K47L / N94P, K47L / D196Y, Y89F / N94P, Y89F / D196Y and N94P / D196Y, three-point mutants namely K47L / Y89F / N94P, K47L / Y89F / D196Y, K47L / N94P / D196Y and Y89F / N94P / D196Y and a four-point mutant namely K47L / Y89F / N94P / D196Y. Yields of AA-2G produced by the mutants while maltodextrin is utilized as a glycosyl donor are respectively increased by 42.6%, 11.0%, 37.6%, 43.6%, 43.6%, 41.6%, 44.5%, 50.5%, 20.8%, 35.6% and 64.4%. Compared with the wild type CGTase, the mutants is more beneficial to production of the AA-2G while the maltodextrin is utilized as the glycosyl donor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing γ-cyclodextrin by simultaneous use of γ-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and isoamylase
The present invention provides a method for the production of γ-CD, comprising making a starch slurry, incubating with γ-CGTase and isoamylase simultaneously for γ-CD production, forming a complex of γ-CD and an organic complexant, and purifying γ-CD from the complexant. The present invention provides a simple and cost-effective method for producing high purity γ-CD, which has a short production cycle, a high conversion rate, and is adaptable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus strain producing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
The present invention relates to a Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus strain producing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, wherein the strain is Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus CHB1, is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on August 28, 2013, and has the preservation number of CCTCC M2013384, and it is proved that the enzyme produced by the Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus is cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (short for CGTase) belonging to the alpha-amylase family, and can be adopted to catalyze soluble starch so as to generate alpha-cyclodextrin. According to the present invention, the new strain Geobacillussp CHB1 producing CGTase is provided, the optimum enzyme activity reaction temperature of the enzyme production fermentation broth supernatant of the strain is 65 DEG C, the activity is maintained between 40-85 DEG C, and the CGTase produced by the strain can be used for producing alpha-cyclodextrin, and can further be used for processing processes of starch in the temperature range and the like.
Owner:INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102965353AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesWild typeTyrosine
The invention discloses maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The 47th lysine (Lys) of CGTase of P.macerans strain HFB05-01 (CTCC NO:M208063) is respectively replaced by phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr) and proline (Pro), so that the output of AA-2G is respectively improved by 17.1%, 22.1% and 32.9%. Compared with the wild CGTase, the mutant strains are more conductive to producing AA-2G for glycosyl donors by utilizing maltose, so that important industrial application prospect is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
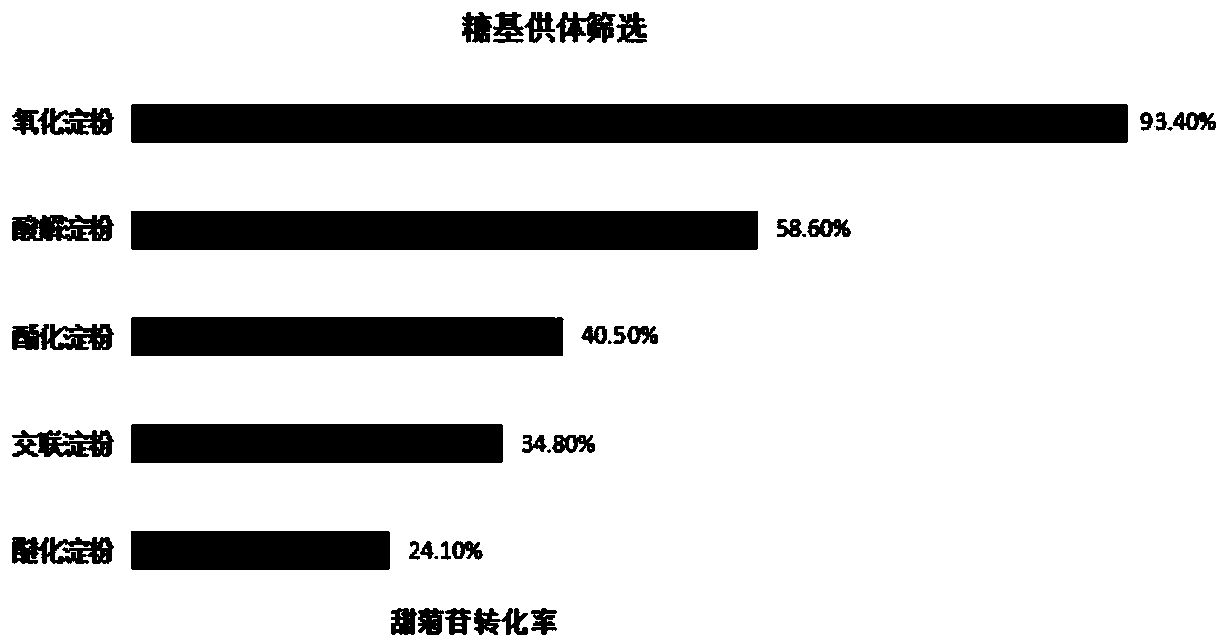
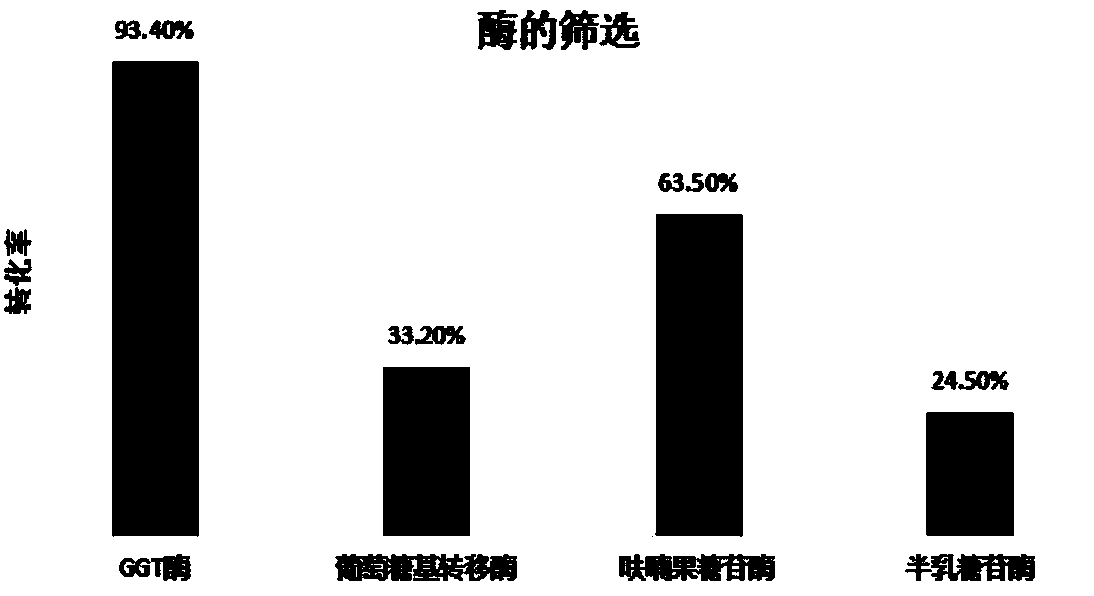
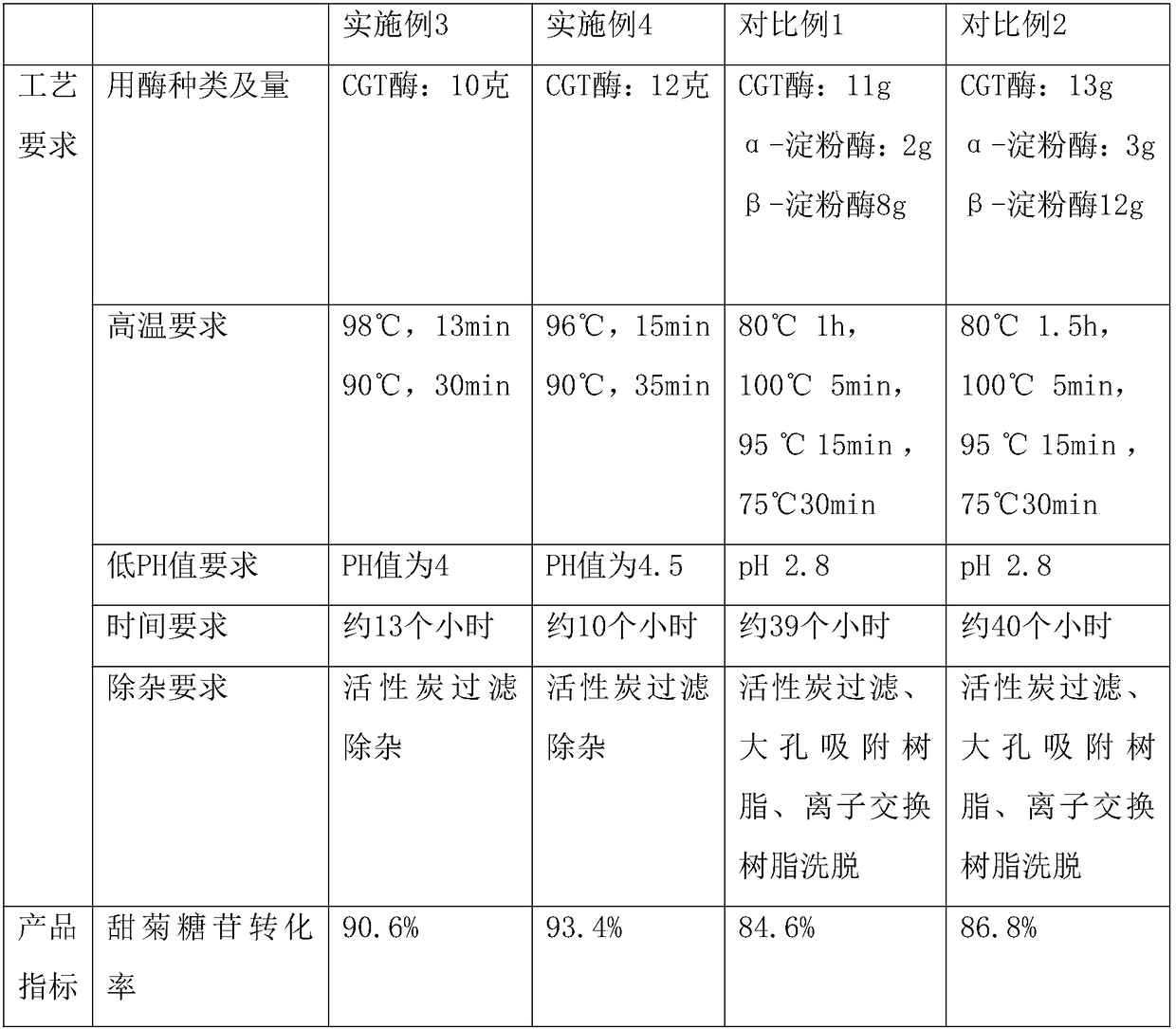
Method of industrial quick production and preparation of glucosyl stevioside mixture
The invention provides a method of industrial quick production and preparation of a glucosyl stevioside mixture. The method comprises the following steps of: step I, performing enzymatic reaction: dissolving oxidized starch and stevioside, adding CGT (cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase) for the enzymatic reaction at 40-55 DEG C for 7-12h, and performing enzyme deactivation to finish the reaction, step II, performing decoloration ad deodorization, and step III, performing filtration, concentration and drying to form a product. The method takes the oxidized starch as a glycosyl donor; technical steps are reduced; a transglycosylation effect is improved; and the method is simple in technology and easy to operate, reduces requirements of industrialization on equipment and energy consumption at the same time, shortens working hours, lowers the cost and increases unit production capacity.
Owner:GUILIN NATURAL INGREDIENTS CORP
Method for preparing beta-cyclodextrin by yeast
The disclosed preparation method for beta-cyclodextrin comprises: with gene engineering technique, fixing the cyclodextrin glycosyl transfer enzyme expression on surface of saccharomyces cerevisiae cell to ferment and prepare the product; centrifugal removing just the thali cell and residue for separation and purification; condensing the supernatant to obtain the final product. This invention keeps enzyme activity for reutilization, improves yield by producing ethanol and consuming the glucose by yeast, and has wide application with unassailable security.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for improving beta-cyclodextrin production capability of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase by calcium ion binding site amino acid residue mutation
InactiveCN103740669AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityGlycosyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionArginineBinding site
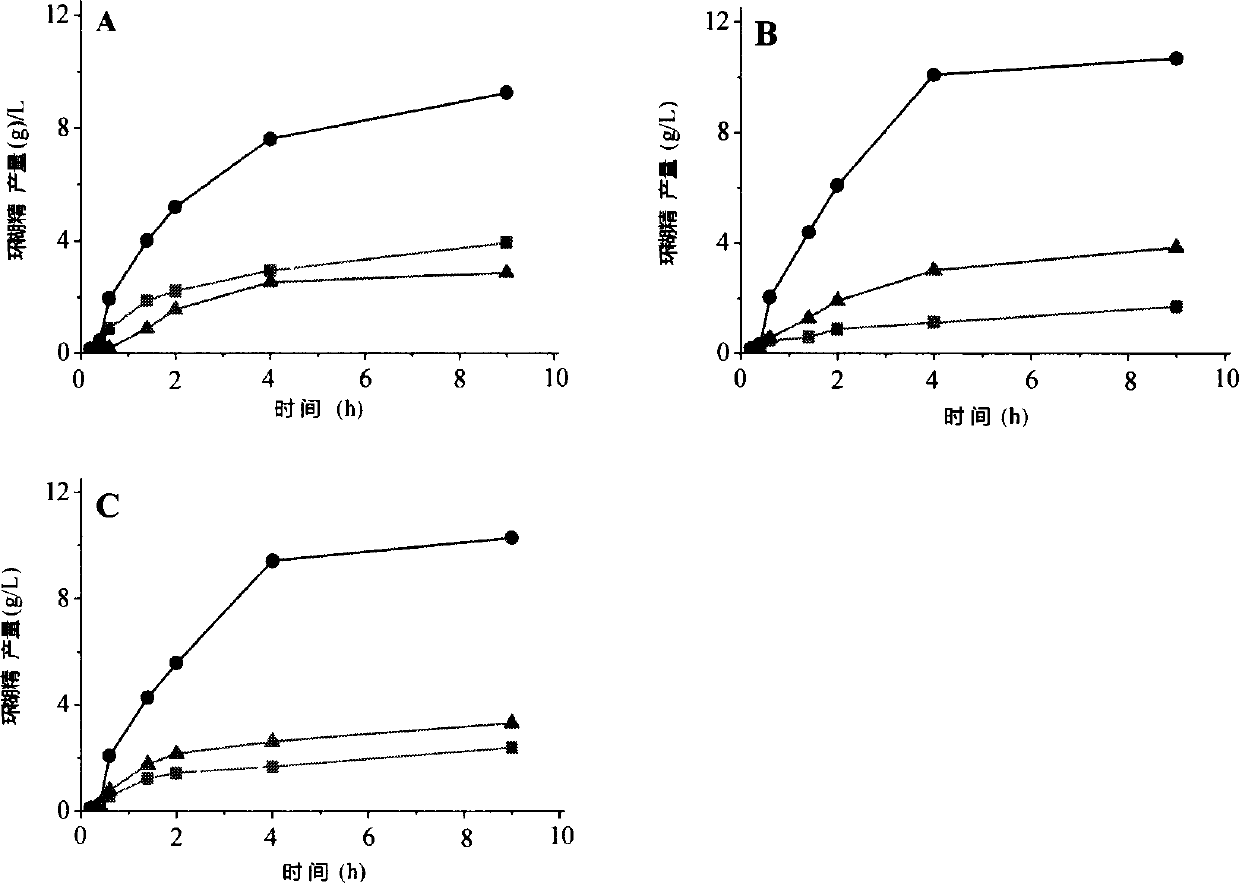
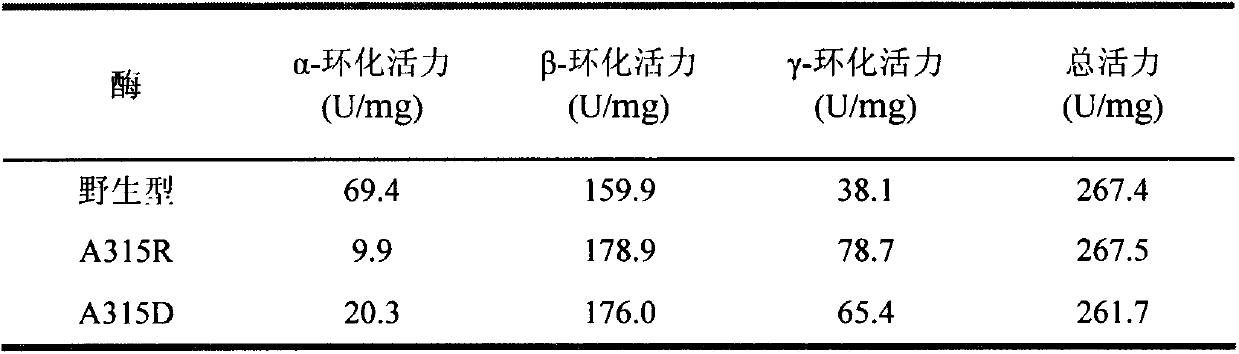
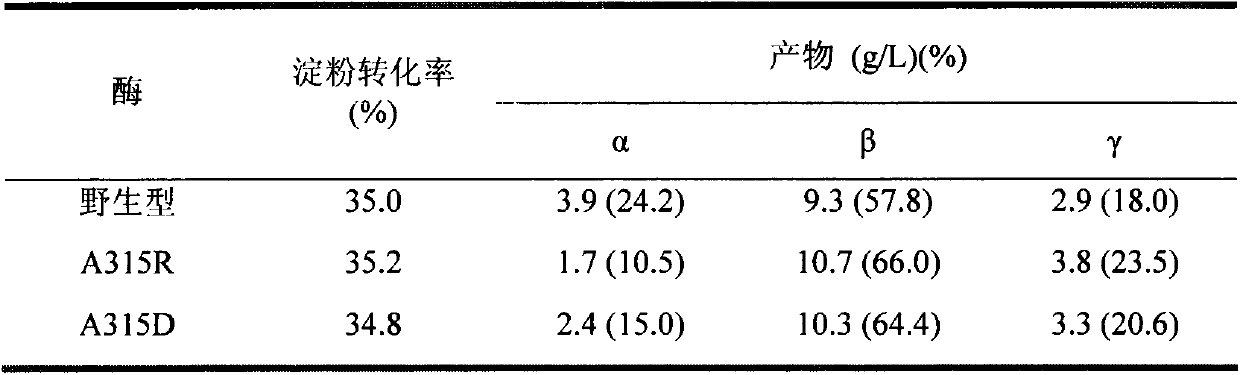
The invention provides a mutant of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short) with capability for high-yield of beta-cyclodextrin and mutating method thereof, and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention employs a site-directed mutagenesis method for improving beta-cyclodextrin production capability of CGT enzyme, and provides a mutating scheme for improving beta-cyclodextrin production capability of Bacillus circulans STB01CGT, that is alanine at the 315th position of the calcium ion binding site in CGT enzyme is changed into arginine (Arg) or aspartic acid (Asp), and the mutants A315R and A315D are obtained. Compared with the wild CGT enzyme, the two mutants have higher beta-cyclodextrin production capability, and are suitable for industrial production of beta-cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase for improving substrate specificity of soluble starch
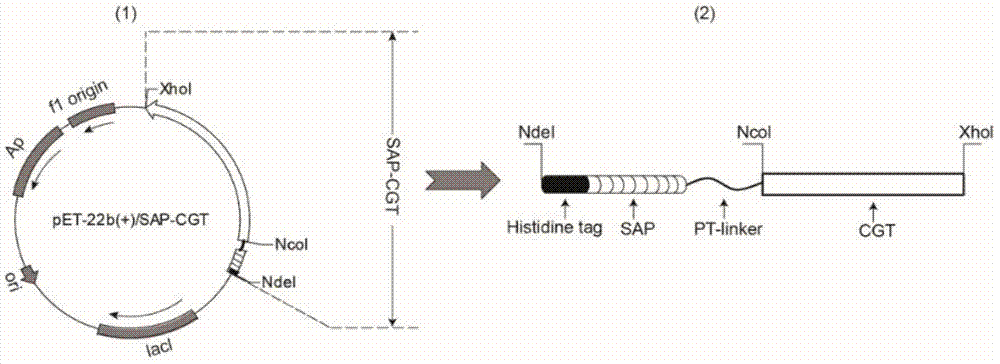
ActiveCN103589699AIncreased substrate specificityEase of industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCyclodextrinGenetic engineering
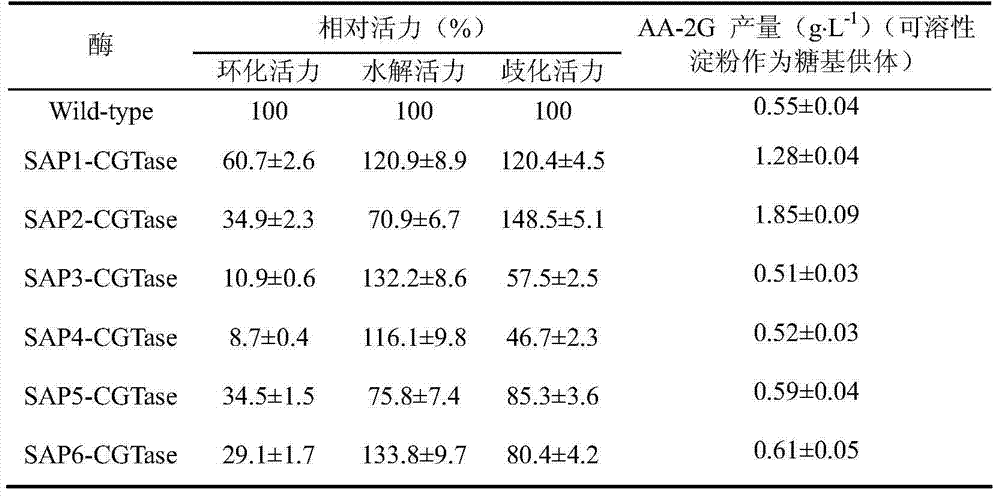
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase (CGTase) for improving substrate specificity of soluble starch, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, the CGTase from P.macerans strain JFB05-01(CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO:M208063) is taken as initial CGTase, and two self-organizing amphiphilic short peptides (SAP) are respectively fused at the N end of the initial CGTase to create two fusion enzymes-SAP1-CGTase and SAP2-CGTase. Compared with the initial CGTase, when the soluble starch is taken as a glycosyl donor, the yields of synthetic AA-2G (2-O-alpha-D-pyran glucosyl-L-ascorbic acid) are increased by about 1.33 times and 2.36 times respectively. Therefore, the fusion enzymes are more favorable for utilizing the soluble starch as the glycosyl donor for producing the AA-2G in comparison with the initial CGTase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase production strain and its application
ActiveCN103667102BLow costImprove conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesD-GlucopyranoseBacterial strain
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase production. The cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase obtained by fermenting the bacterial strain is acted on L-ascorbic acid and beta-cyclodextrin with different concentrations to efficiently generate 2-oxo-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl ascorbic acid under a condition that pH is 5.0-6.0 and the temperature is 25-40 DEG C. The production method for generating 2-oxo-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl ascorbic acid by using cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase obtained by fermenting the bacterial strain has the characteristics of simplicity, high conversion rate and high output, and is beneficial for industrialized amplified production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Marine microorganism strain Y112 and alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase produced by strain
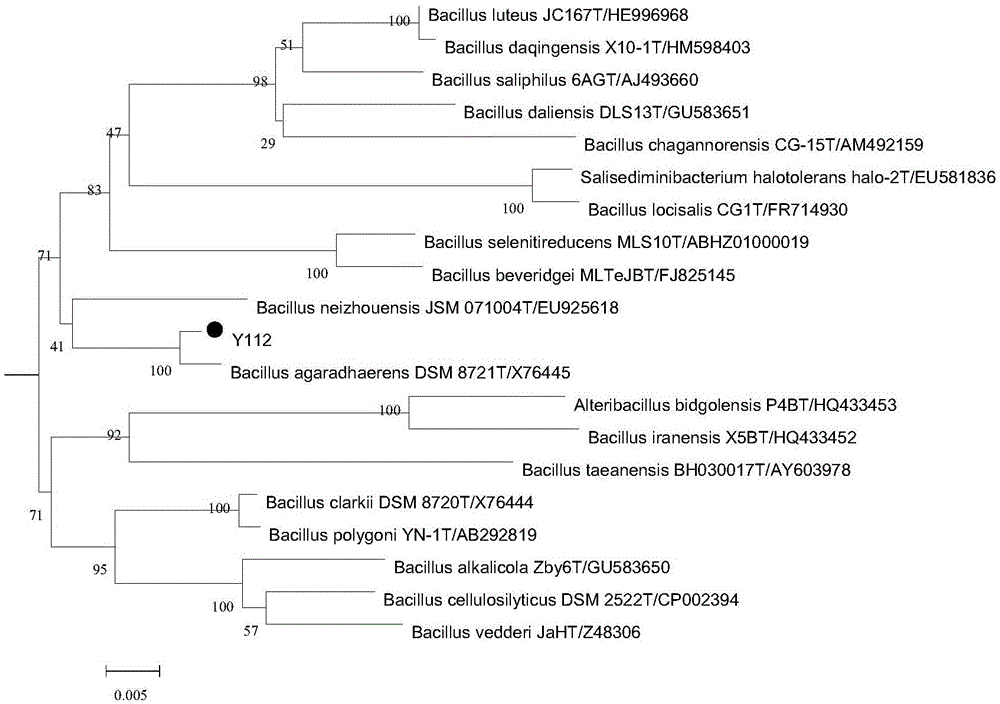
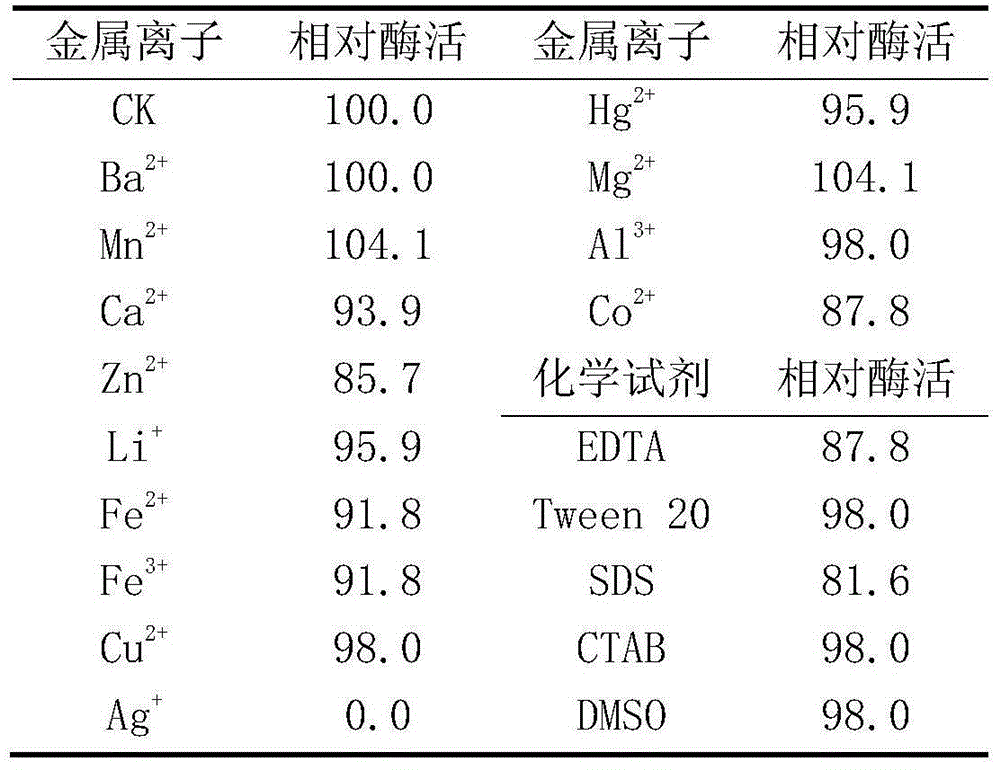
ActiveCN105154352AImprove stabilityImprove enzyme production capacityBacteriaTransferasesSequence analysisMicrobiology
The invention relates to a marine microorganism strain Y112 for producing alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and enzyme produced by the strain. Upon 16SrDNA sequence analysis and in coordination with physiological and biochemical characteristics, the strain belongs to bacillus; and through sequencing, 16SrDNA sequence is about 1420bp long, and base composition is as shown in Figure 1. The marine microorganism strain is extensively applicable to medicine, food, chemical industry, cosmetics, industry, agriculture, analytical chemistry and like aspects.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for preparing resistant dextrin by using a starch branching enzyme and a cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
ActiveUS10988550B2Low production costIncrease percentageFood ingredientsFermentationCyclodextrinEnzyme
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Momordica grosvenori endophyte strain capable of producing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase as well as screening method and application of momordica grosvenori endophyte strain
ActiveCN108277180AIncrease enzyme activitySimple screening methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismScreening method
The invention discloses a momordica grosvenori endophyte strain capable of producing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase as well as a screening method and the application of the momordica grosvenori endophyte strain, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is called bacillus sp. ND-6 in the CGMCC, with a collection number of No.15227, on January 16, 2018. The invention further discloses a screening method of the momordica grosvenori endophyte strain capable of producing the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, a method for producing the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase by using the momordica grosvenori endophyte strain capable of producing the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and the application of the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. The momordica grosvenori endophytestrain disclosed by the invention can produce the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase is high in enzyme activity (10,660 to 11,200 U / mL).
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Fishy smell-free fish rice noodles and production method for same
InactiveCN103689673AReduce fishy smellGreat tasteFood preparationFish ProteinsCyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
The invention discloses fishy smell-free fish rice noodles and a production method for the same. The rice noodles are characterized in that based on the total weight of raw materials, the rice noodles contain 10 to 30 percent of fish proteins, 30 to 60 percent of rice and 10 to 30 percent of water, wherein the rice is treated by alpha-amylases and cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase after being impregnated by the water. The production method comprises the following steps: 1, impregnating the rice for 10 to 48 hours at room temperature by using water; 2, grinding the completely impregnated rice by using a refiner; 3, treating rice milk for 1 to 4 hours under the conditions of 30 to 65 DEG C and pH of 5 to 8 by using the alpha-amylases, and enzymatically decomposing the treated rice milk for 10 to 300 minutes under the conditions of 55 to 65 DEG C and pH of 6 to 9 to obtain enzymatically-decomposed rice milk by using the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase; 4, grinding the fish at 0 to 4 DEG C; 5, uniformly mixing the ground fish and the enzymatically-decomposed rice milk by using a pulping machine, and treating the mixture for 30 to 300 minutes by using a chopper mixer; 6, extruding the chopped-mixed fish rice milk into rice noodles at temperature of 80 to 90 DEG C by using an extrusion cooking type flour mill, and performing aging and drying by using conventional methods.
Owner:吴壮志
Preparation method of alpha-cyclodextrin
InactiveCN103642878AReduce manufacturing costNo pollution in the processFermentationEmulsionAlcohol ethyl
The invention relates to a preparation method of alpha-cyclodextrin. The prior art has the problems of high energy consumption, high equipment requirement, high dangerousness, complex operation and high production cost. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparing starch into a starch emulsion, adding cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and stirring for liquidizing; supplementing the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, adding decyl alcohol, and stirring for reaction; filtering the mixture after the reaction is finished, collecting the insoluble substance, flushing, filtering, preparing into a solution, adding absolute ethyl alcohol, stirring and then standing; standing for layering, filtering the separated liquid, recovering ethanol from the solvent layer through an ethanol recovery device and then obtaining the left liquid, namely the decyl alcohol, and carrying out decolorization, concentration and spray-drying on the material liquid layer to obtain white powdery finished product alpha-cyclodextrin. According to the invention, the recovery rate of the refined alpha-cyclodextrin is higher than 95%, and the purity of the same is more than 99%; simultaneously, the preparation method of alpha-cyclodextrin is simple in preparation, high in production safety, low in cost and suitable for realizing large-scale production.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY INST OF SHAANXI
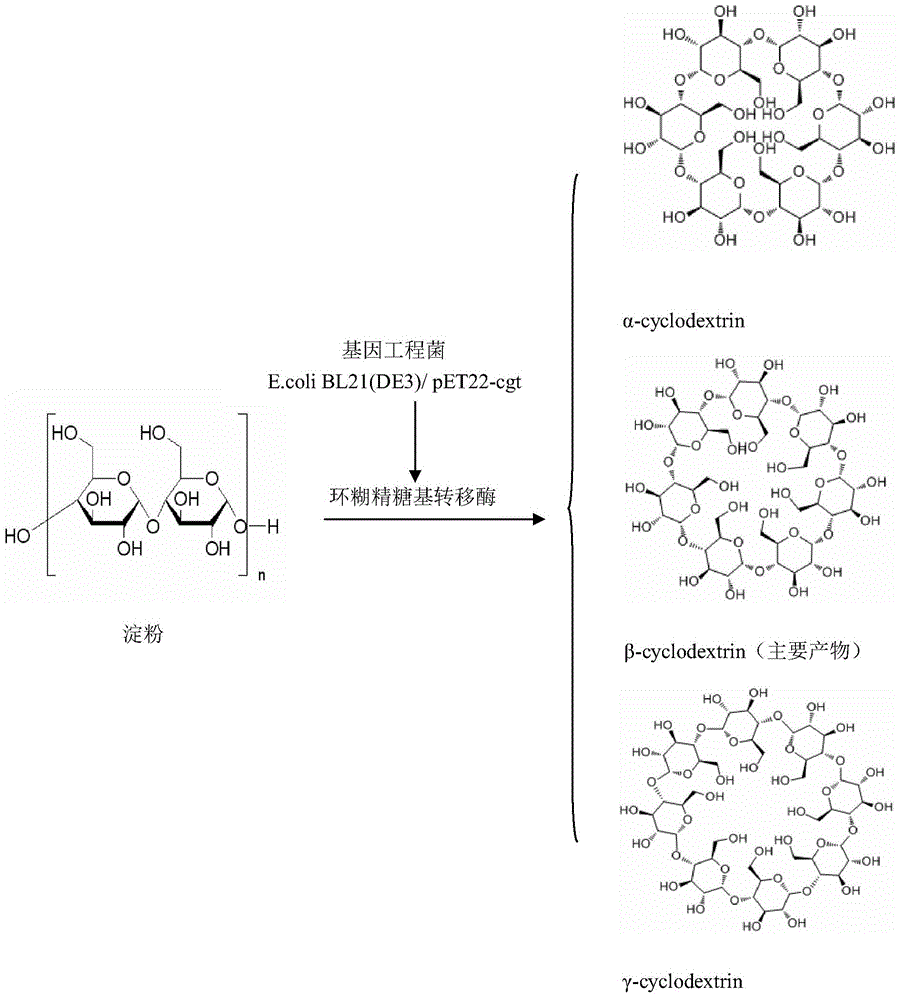
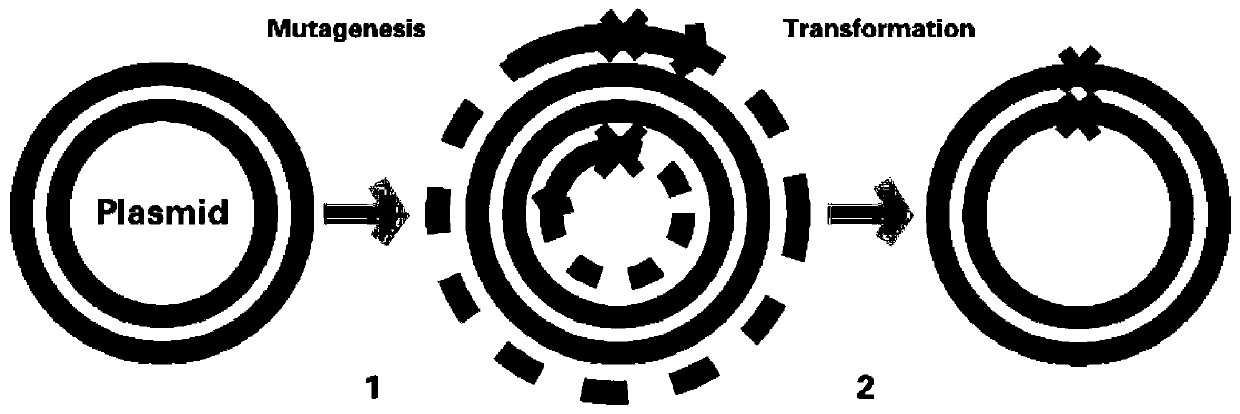
Genetically engineered bacterium for expressing beta cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase as well as construction method and use thereof
InactiveCN104357371ASimple production processAdvanced production technologyBacteriaFermentationMicroorganismBeta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for expressing beta cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase as well as a construction method and a use thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium for expressing the beta cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase is genetically engineered bacterium E. coli BL21(DE3) / pET22-cgt obtained by transforming recombinant expression plasmid pET22-cgt which is obtained by inserting a beta cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase gene obtained by cloning into an expression vector pET22b(+) in host bacteria E.coliBL21(DE3). The genetically engineered bacterium for highly expressing beta-CGTase, constructed by the construction method disclosed by the invention, can be used for changing a culture medium of original microorganisms, separating thalli which appear in a production process of the bacteria to obtain relatively pure beta-CGTase, and directly preparing beta-CD by virtue of the beta cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase, so that the existing domestic beta-CD production process is radically improved to obtain high-quality beta-CD.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Application of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in production of alpha-glycosyl hesperidin
InactiveCN109652481AEfficiently catalyzes glycosylation reactionsHigh substrate dosageMicroorganism based processesFermentationActive componentThermal stability
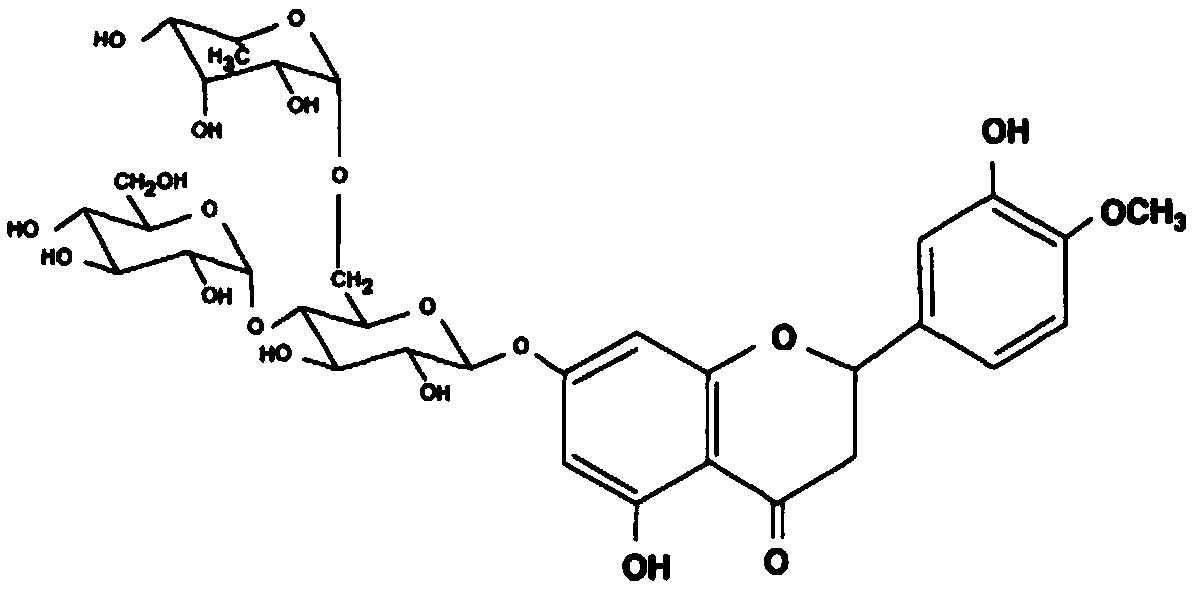
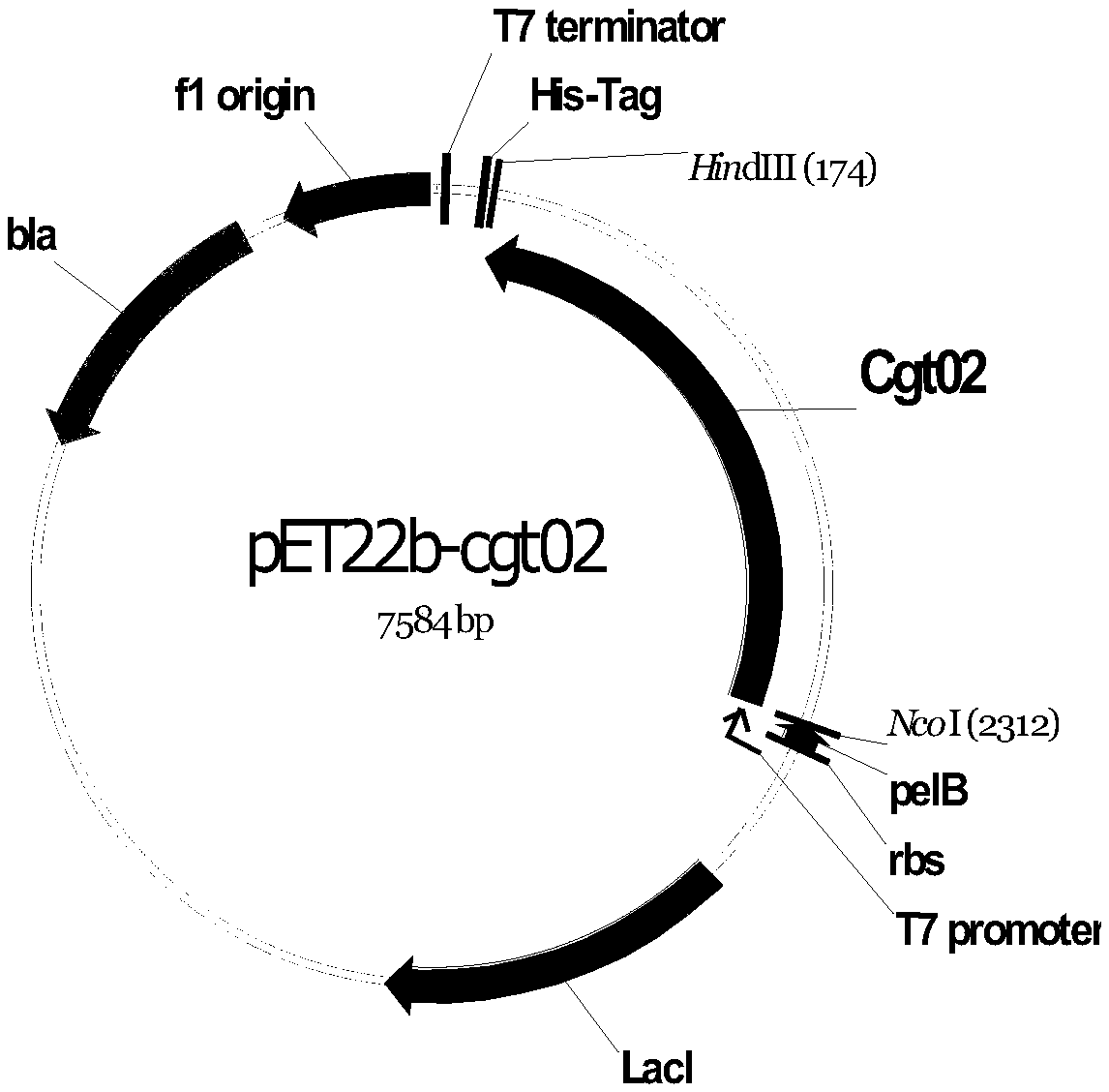
The invention discloses application of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in production of alpha-glycosyl hesperidin. An active component of a bacterial agent for producing alpha-glycosyl hesperidin isescherichia coli IEF-cgt02, the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase with high thermal stability can be efficiently synthesized in cells, and dextrin is adopted as a glycosyl donor to efficiently catalyzea glycosylation reaction of hesperidin. 2-15% of alpha-glycosyl hesperidin is produced by biocatalysis of the bacterial agent, the reaction time is controlled within 24 hours, and the conversion rateof hesperidin reaches 70% or above. The cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase has the advantages of high substrate feeding amount, catalysis rate and substrate conversion rate and is suitable for industrial production of alpha-glycosyl hesperidin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Optimization method for improving secretory expression of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase and application of optimization method
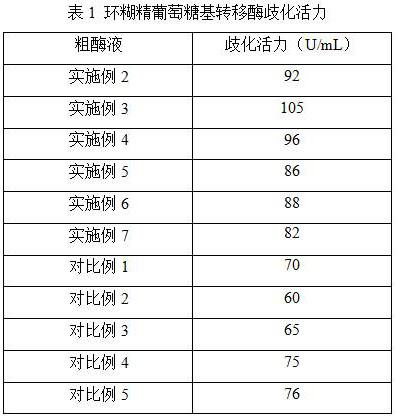
ActiveCN113025590AImprove permeabilityImprove disproportionation activityFermentationGenetic engineeringEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses an optimization method for improving secretory expression of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase and an application thereof. The method optimizes the fermentation culture process of recombinant escherichia coli containing a CGTase gene, five components including glycine, Ca<2+>, beta-cyclodextrin, taurine and lactose are added in the fermentation culture process, membrane permeability is improved, the formation of inclusion bodies is inhibited, the heterologous secretory expression of the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase protein can be effectively promoted, the disproportionation activity of the cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase is improved, and further the conversion rate of the enzyme to linear substrates is improved, thereby the yield of AA-2G produced by the linear substrates such as maltodextrin and the like can be improved. The industrial production of the AA-2G is more facilitated.
Owner:BLOOMAGE BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP LTD
Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase with maltodextrin substrate specificity being improved and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104073476AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineCyclodextrin
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetic engineering bacterium of expression high-specificity beta cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and construction method and application of genetic engineering bacterium
PendingCN109706131ARaise the ratioIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesBacillus cereusSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium of expression high-specificity beta cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a construction method and application of the genetic engineering bacterium, and relates to the genetic engineering bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium adopts plasmid cgt / pET-22b as a formwork. Through fixed-point mutation, mutants A47S, A47M, A47Y and A47R are obtained, and transfer is performed in a host bacterium E.ColiBL21 to obtain BL21(DE3) / A47S, BL21(DE3) / A47M, BL21(DE3) / A47Y and BL21(DE3) / A47R. The engineering bacterium effectively improves the product specificity of beta-CGTase enzymes of Bacillus cereus, and a certain foundation is provided for application of the engineering bacterium to industrial production of beta-cyclodextrin.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for controlling sustained release of cyclodextrin inclusion compound in two-enzyme method
InactiveCN108085352ARelease completelyEasy to control speedPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFermentationDrug productPigment
The invention relates to a method for controlling the sustained release of a cyclodextrin inclusion compound in a two-enzyme method, which belongs to the technical field of food, drugs, textile and clothing. Under the joint effect of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and glucoamylase, and under the condition that the object molecular release speed is controllable, the object molecules in the inclusion compound can be gradually stably released from the cavity of the cyclodextrin, so that the object molecules of the inclusion compound can be maximally utilized. The method provided by the invention can constantly and steadily release the object molecules (essence, spice and pigment) in the inclusion compound in a uniform and thorough manner and with a controllable speed, rather than release inone time, so that the object molecules can be maximally utilized. The release speed can be adjusted according to the release requirement of the object molecules of the inclusion compound and the drugs can be uniformly and thoroughly released with a controllable speed.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com