Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase for improving substrate specificity of soluble starch
A technology of glycosyltransferase and substrate specificity, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of substrate specificity (low conversion rate, etc.), and achieve the effect of improving substrate specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 Short peptide fusion cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with improved substrate specificity
[0019] The short peptide fusion cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of the present invention is fused to the N-terminus of the dextrin glycosyltransferase published in GenBank AF047363.1 with six different self-organized amphiphilic short peptides (SAP) (see Table 1). , six fusion enzymes were constructed: SAP1-CGTase to SAP6-CGTase. The above six fusion enzymes can be constructed by chemical total synthesis or fusion PCR. The short peptide fusion cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase was derived from Paenibacillus macerans (P.macerans) JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO: M208063).
[0020] Table 1 Sequences of six different self-organizing amphipathic short peptides
[0021]
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2 Preparation method of short peptide fusion cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with improved substrate specificity
[0023] 1) Construction of short peptide fusion cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
[0024] In this example, the total chemical synthesis method is used as an example to illustrate, but the protection of the invention is not limited to the method of obtaining the fusion enzyme only by the chemical total synthesis method. The preparation method of fusion enzyme SAP1-CGTase to SAP6-CGTase is as follows:
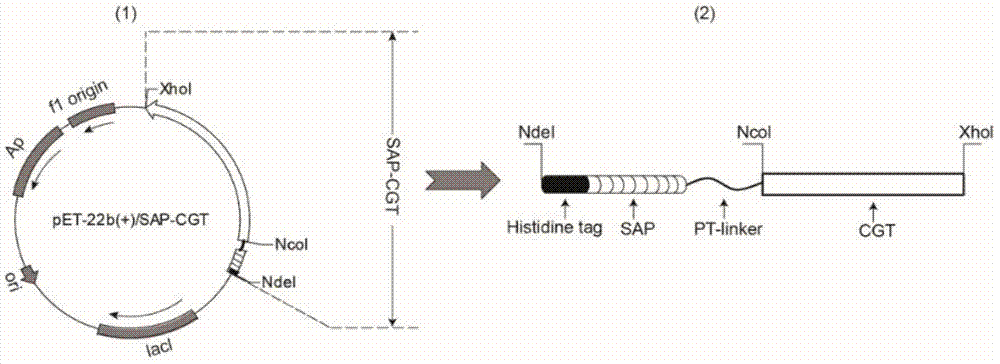
[0025] like figure 1 As shown, the above 6 short peptides were respectively linked to the N-terminus of CGTase by PT linker, and a histidine tag was inserted into the N-terminus of the short peptides to facilitate purification. Then, the constructed short peptide fusion CGTase was connected to the pET-22b(+) expression plasmid through NdeI and XhoI restriction sites. The constructed recombinant plasmid pET-22b(+) / SAP-CGTase was transformed into the ...
Embodiment 3
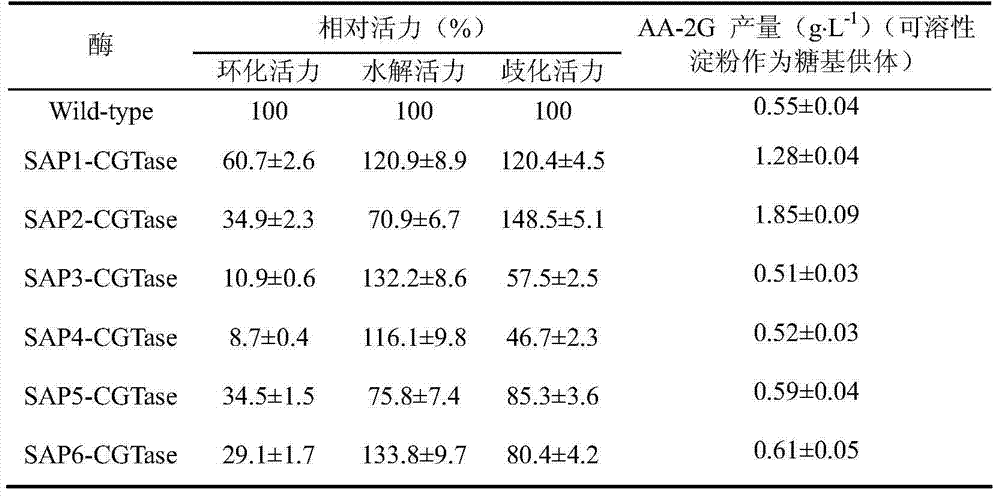
[0029] Example 3 Enzyme activity analysis and synthesis and detection of AA-2G.
[0030] 1) Enzyme activity assay method:
[0031]Method for measuring α-cyclization activity by methyl orange method: Take 0.1mL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution, add it to 0.9mL of 3% soluble starch solution prepared in advance with 50mM phosphate buffer (pH6.5), at 40°C After reacting for 10 min, add 1.0 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid to stop the reaction, then add 1.0 mL of 0.1 mM methyl orange prepared with 50 mM phosphate buffer, incubate at 16°C for 20 min, and measure the absorbance at 505 nm. One enzyme activity unit defines the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol α-cyclodextrin per minute under the conditions.
[0032] Determination of starch hydrolysis activity: Add appropriate amount of enzyme solution to 50mM phosphate buffer (pH6.5) containing 1% soluble starch, react at 50°C for 10min, and then use DNS method to measure the concentration of reducing sugar. One unit o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com