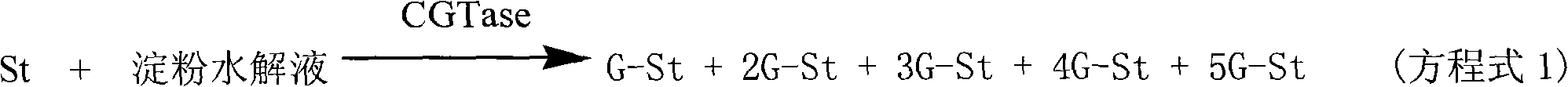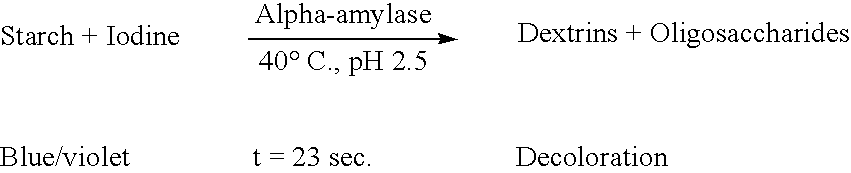Patents
Literature
201 results about "Starch hydrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
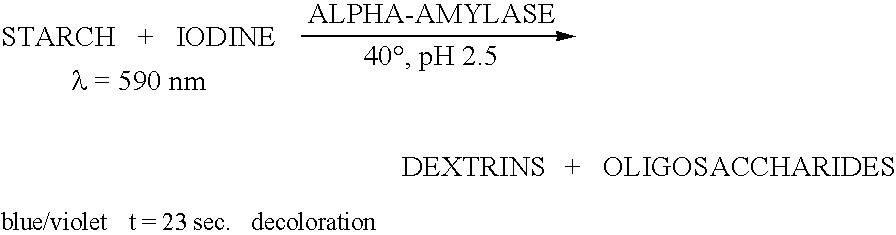
Starch Hydrolysis Starch agar is a differential medium that tests the ability of an organism to produce certain exoenzymes, including a-amylase and oligo-1,6-glucosidase, that hydrolyze starch.
Non-maltogenic exoamylases and their use in retarding retrogradation of starch
InactiveUS6667065B1Highly effective in retarding or reducing detrimental retrogradationImprove propertiesDough treatmentHydrolasesAmylosucrase activitySide chain
The present invention relates to a process for making a bread product. The process includes the addition of a non-maltogenic exoamylase that hydrolyses starch to a starch medium, and the application of heat to the starch medium. The non-maltogenic exomylase cleaves one or more linear malto-oligosaccharides, predominantly consisting of from four to eight D-glucopyranosyl units, from non-reducing ends of amylopectin side chains. The non-maltogenic exoamylase has an endoamylase activity of less than 0.5 endoamylase units (EAU) per unit of exoamylase activity.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method for producing porous starch and its application
InactiveCN1546529AHigh adsorption rateRaw materials are readily availableGlucose-Fructose SyrupPotato starch
The invention discloses a method for producing porous starch and its application by using starch, maize starch, tapioca starch, sweet potato starch and potato starch as raw material, and charging complex enzyme of saccharified enzymes and alpha-amylase possessing raw starch hydrolysis vitality under the temperature lower than gelatinization temperature, agitating continuously, reacting for a finite period of time at constant temperature, and obtaining porous starch product through centrifuging, scrubbing and drying.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for hydrolysis of starch
The present invention relates to a process for enzymatic hydrolysis of granular starch into a soluble starch hydrolyzate at a temperature below the initial gelatinization temperature of said granular starch.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Branched starches and branched starch hydrolyzates
InactiveUS20020065410A1Improving aqueous solution stabilityImprove stabilityFermentationFood preparationGlycosideOligomer
The present invention provides a starch that includes at least one glucose polymer having greater than 4% alpha 1-6 glycosidic linkages. The present invention further provides a starch hydrolyzate that includes at least one glucose oligomer having greater than 4% alpha 1-6 glycosidic linkages. The starch and starch hydrolyzate present invention have improved aqueous solution stability and are less likely to retrograde than are solutions of unbranched linear starches or starch hydrolyzates. The present invention further provides a method of improving the aqueous solution stability of a starch or a hydrolyzate thereof, which method includes introducing one or more alpha 1-6 glycosidic linkages so as to branch one or more of the linear polysaccharides or hydrolyzates thereof. The method of the present invention also includes a method of improving the aqueous solution stability of amylose and amylose hydrolyzates by introducing one or more alpha 1-6 glycosidic linkages so as to branch one or more molecules of amylose or hydrolyzate thereof.
Owner:GRAIN PROCESSING CORP
Skin age multi-effect silk mask liquid
InactiveCN105640845AStrong anti agingEfficient hydrationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFacial skinSodium hyaluronate
The invention discloses skin age multi-effect silk mask liquid which is prepared by mixing hydrosolvent, humectant, skin conditioner, preservative, thickener and ph regulator. The humectant comprises glycerin, propylene glycol, butylene glycol, maltooligosyl glucoside, hydrogenated starch hydrolysate, glyceryl polymethacrylate, PVMMA copolymer, sodium hyaluronate, betaine and baobab pulp extract, and the skin conditioner comprises nicotinamide, Herba portulacae extract, polyquaternium-51, soybean polypeptide, blackberry leaf extract, purple coneflower extract, Aloe vera extract, European horse chestnut extract, nonapeptide-1, tranexamic acid, Herba centella extract, ceramide 1, palmitoyl pentapeptide-4, oligopeptide-1, carnosine and dipotassium glycyrrhizinate. The mask liquid prepared by applying the component ratio can effectively realize efficacy of moisturizing and whitening facial skin, is free of irritation to the facial skin and has good whitening effect.
Owner:韩玉逍
Expression of granular starch hydrolyzing enzymes in Trichoderma and process for producing glucose from granular starch substrates
InactiveUS20050136525A1Short timeHigh in sugarFungiSugar derivativesHeterologousGlucose-Fructose Syrup
The present invention relates to filamentous fungal host cells and particularly Trichoderma host cells useful for the production of heterologous granular starch hydrolyzing enzymes having glucoamylase activity (GSHE). Further the invention relates to a method for producing a glucose syrup comprising contacting a granular starch slurry obtained from a granular starch substrate simultaneously with an alpha amylase and a GSHE at a temperature equal to or below the gelatinization temperature of the granular starch to obtain a composition of a glucose syrup.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Non-gelatinous capsule film compositions and capsules using the same
InactiveCN1615126APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsThin material handlingPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
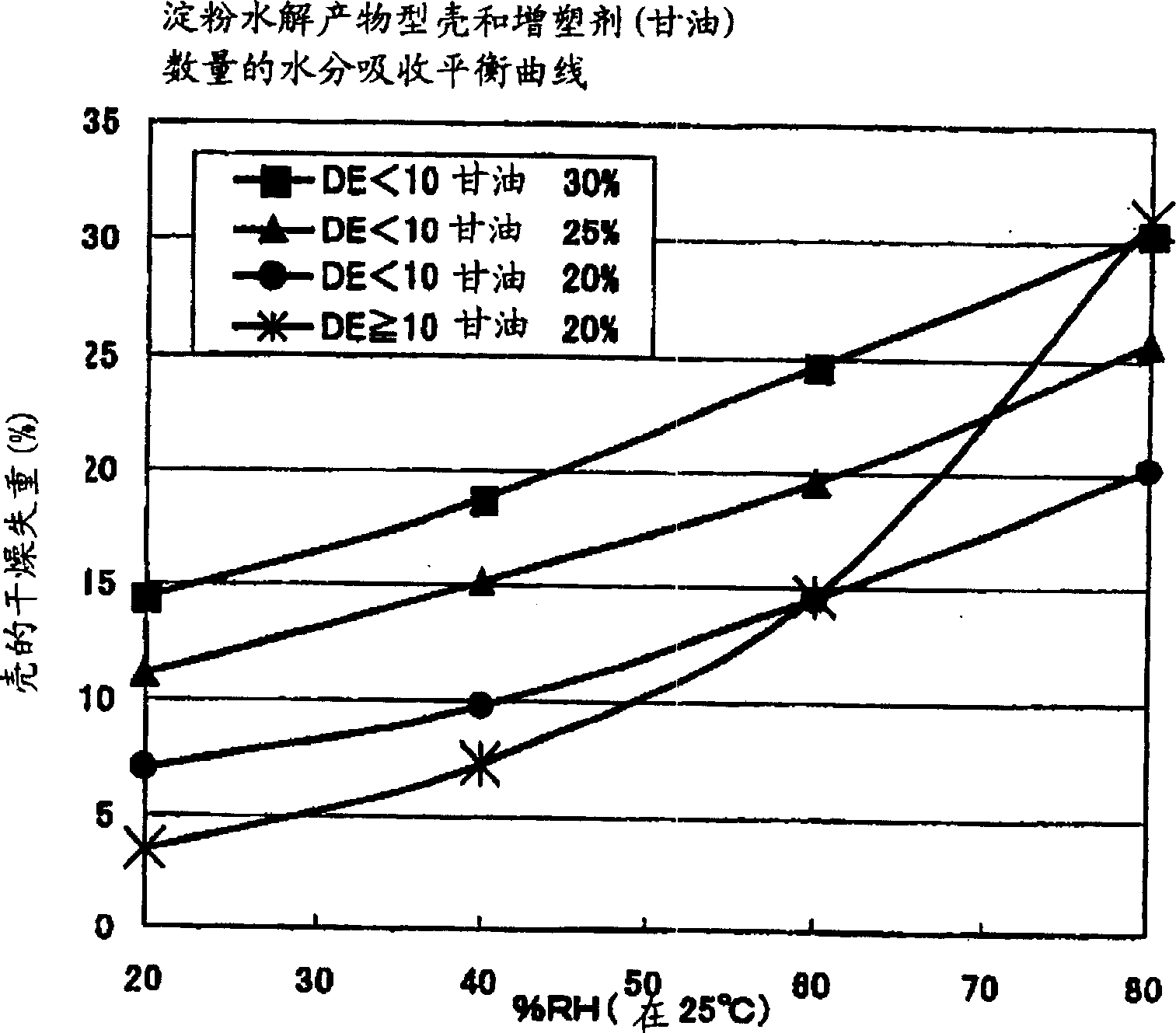
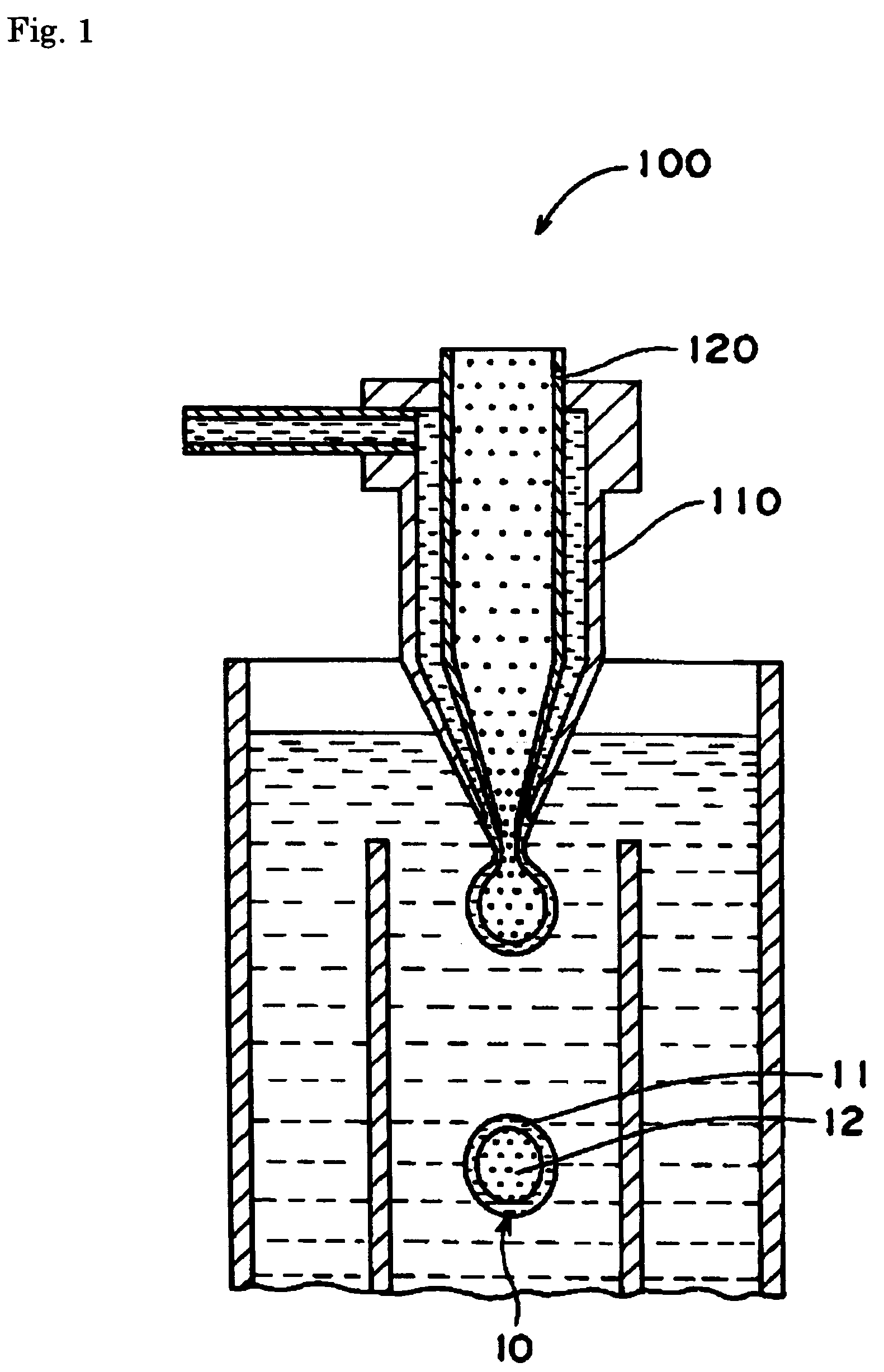
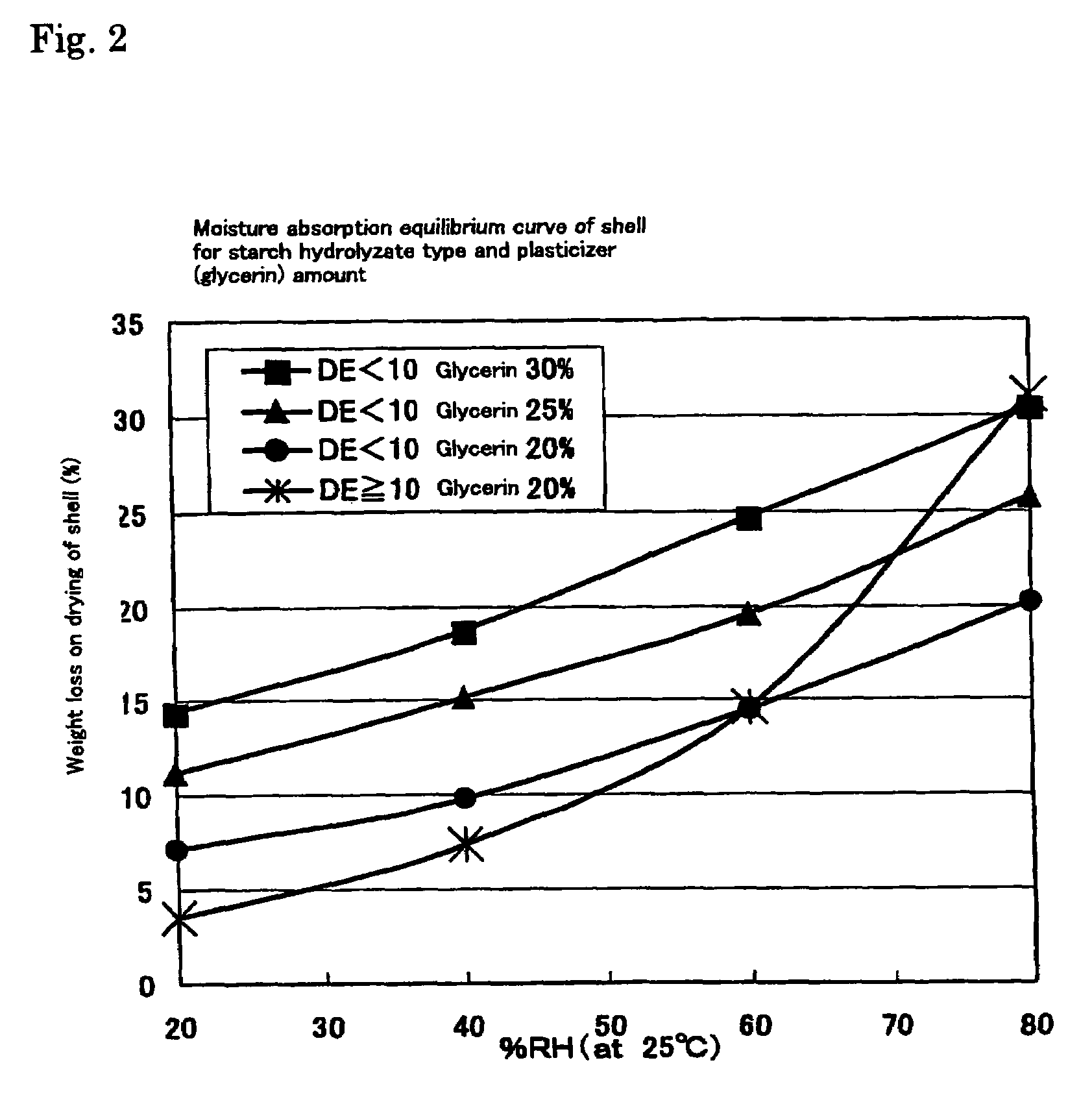
Non-gelatinous capsule film compositions containing as the base a starch hydrolyzate having an average DE of less than 10 and an average molecular weight of not more than 30,000. These non-gelatinous capsule film compositions have stable moisture absorbing / releasing properties and strength to such extent as sufficiently withstanding the production and storage as products and yet achieve excellent disintegration properties in vivo. Also, capsules produced by using the non-gelatinous capsule film compositions as described above are provided.
Owner:MORISHITA JINTAN CO LTD
Non-gelatinous capsule shell composition and a capsule formed from the same
InactiveUS7255921B2High strengthEasy disintegrabilityStarch adhesivesStarch coatingsPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
Non-gelatinous capsule film compositions containing as the base a starch hydrolyzate having an average DE of less than 10 and an average molecular weight of not more than 30,000. These non-gelatinous capsule film compositions have stable moisture absorbing / releasing properties and strength to such extent as sufficiently withstanding the production and storage as products and yet achieve excellent disintegration properties in vivo. Also, capsules produced by using the non-gelatinous capsule film compositions as described above are provided.
Owner:MORISHITA JINTAN CO LTD
Preparation method of polypeptide silk mask
InactiveCN105878048AEfficient hydrationEfficient AntioxidantCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCentella asiatica extractBetaine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polypeptide silk facial mask, which comprises the steps of fully mixing polypeptide powder and silk protein nutrient solution and cooling. Polypeptide powder is mainly composed of aloe vera, carnosine, oligopeptide, soluble collagen, 2‑o‑ethyl ascorbic acid, betaine, trehalose, niacinamide, allantoin; the protein nutrient solution of silk is mainly composed of water, glycerin, Propylene glycol, butylene glycol, malto-oligosaccharide glucoside, hydrogenated starch hydrolyzate, glycerol polymethacrylate, PVM / MA copolymer, carbomer, sodium hyaluronate triethanolamine, baobab pulp extract, tranexamic acid , Centella asiatica extract, dipotassium glycyrrhizate and other skin conditioners or moisturizers. Through the combination of polypeptide powder and silk protein liquid, it can effectively give fresh nutrition to the skin, promote the skin repair process, strengthen the nutrient absorption capacity, deeply nourish, smooth and rejuvenate the skin, and make the skin elastic.
Owner:韩玉逍
Method for extracting diosgenin for joint production of starch suger by prehy drolysis of yellow ginger by multienzyme process
InactiveCN1528913AReduce the amount requiredAcid hydrolysis is sufficientSteroidsFermentationAmylaseFiltration membrane
The invention provides a saponin extracting method with multi-enzyme hydrolytic which hydrolyses brown Windsor in advance and produce starch sugar. The method cleans the brown Windsor and grinds it into pulp, then adds in alpha starch enzyme to be liquefied, adds in saccharifying enzyme, heats and carries on deactivation, then the saccharified materials are separated centrifugally, gets the filtered cake and starch sugar liquiud, the sugar liquid is separated with hyperfiltration membrane with 1000-10000daltons aperture catching molecular weight or tiny filtration membrane of 100-200nm and gets the starch sugar liquid, the filter residues are mixed into centrifugated filter cake and gets sugar residue, adds in chlorhydric acid or sulfuric acid to hydrolyse the sugar residue, the hydrolysed product is filtered, cleaned, and dried, extracted by solvent, finally gets the saponin product.
Owner:TAIGU INVESTMENT WUHAN
Method for catalyzing and synthetizing modified stevioside by using microwave auxiliary cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
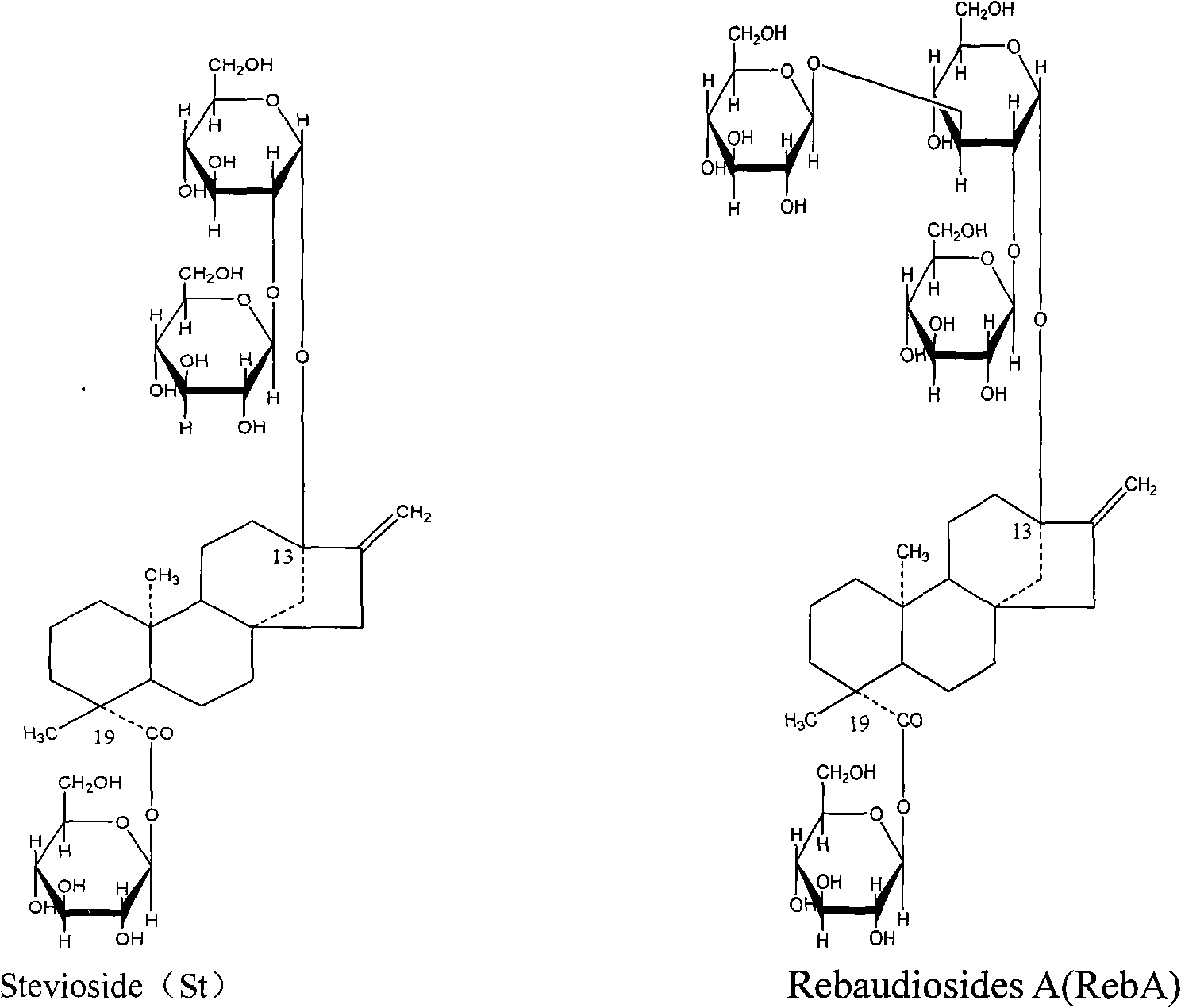
A method for catalyzing and synthetizing modified stevioside by using microwave auxiliary cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase relates to the technical field of biosynthesis of organic compounds, and comprises the following steps: taking stevioside aqueous solution and starch hydrolyzates as raw materials, and synthetizing stevioside replaced by glucose residue under the combined action of microwave radiation and CGTase catalysis in a microwave reaction device. In the process condition provided by the invention, enzyme catalysis reaction can be remarkably quickened, and the phenomenon that microwave of a water system enable enzyme to be inactive under the usual condition. Through tasting, the bitter taste of the synthetic modified stevioside is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +2
Process for producing a starch hydrolyzate
The present invention relates to processes for producing a starch hydrolyzate and optionally a fermentation product, such as ethanol,
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Expression of granular starch hydrolyzing enzymes in Trichoderma and process for producing glucose from granular starch substrates
InactiveUS7303899B2Short timeHigh glucose syrupFungiSugar derivativesHeterologousGlucoamylase activity
The present invention relates to filamentous fungal host cells and particularly Trichoderma host cells useful for the production of heterologous granular starch hydrolyzing enzymes having glucoamylase activity (GSHE). Further the invention relates to a method for producing a glucose syrup comprising contacting a granular starch slurry obtained from a granular starch substrate simultaneously with an alpha amylase and a GSHE at a temperature equal to or below the gelatinization temperature of the granular starch to obtain a composition of a glucose syrup.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Starch process
The present invention relates to a process for enzymatic hydrolysis of granular starch into a soluble starch hydrolysate at a temperature below the initial gelatinization temperature of said granular starch.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
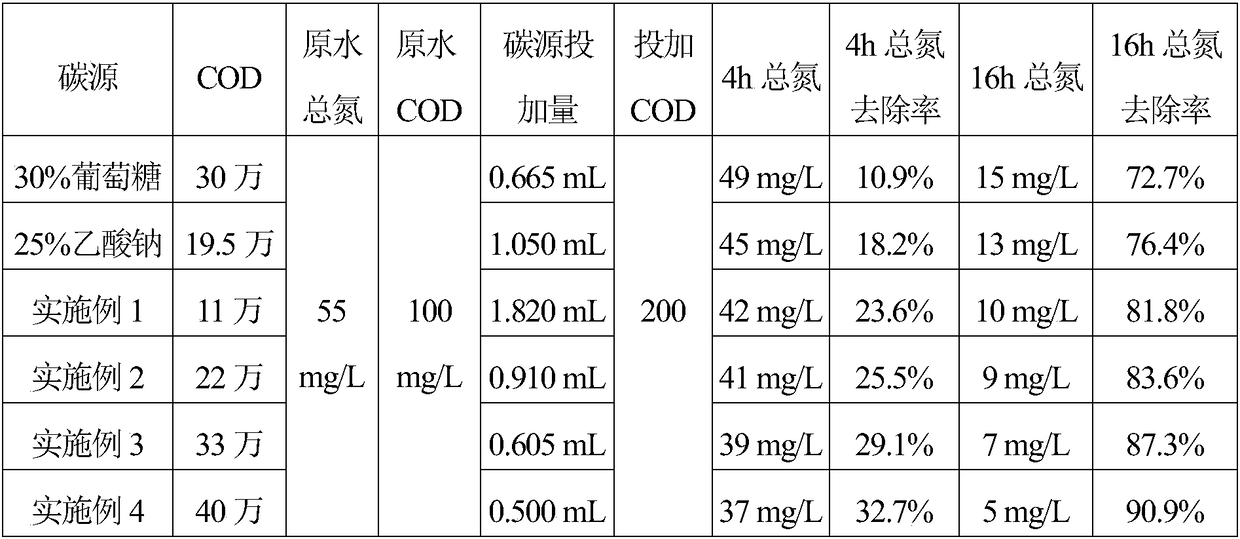
Multi-core composite carbon source for strengthening nitrogen removal during sewage treatment
ActiveCN108585222AIncrease diversityImprove applicabilityWater treatment compoundsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesNitrogen removalAcetic acid
The invention discloses a multi-core composite carbon source for strengthening nitrogen removal during sewage treatment. A preparation method of the multi-core composite carbon source includes: addingstarch into hot water of 70-100 DEG C, and stirring to enable starch liquid to be fully gelatinized; adding a starch hydrolysis catalyst and acetic acid while stirring, hydrolyzing at 80-100 DEG C for 1-2h, and adding alkali until pH value of a solution is 5.5-7.0; adding microbial prebiotic factor, vitamin and mineral, stirring well, filtering, and decoloring to obtain the multi-core composite carbon source. The multi-core composite carbon source is rich in various carbon sources needed by different microbial flora for metabolism, and weakening of flora diversifying in environment with a single carbon source is avoided; the multi-core composite carbon source is rich in microbial prebiotic factors like various trace elements, organic acid and natural biological hormone, so that microbialactivity of a biochemical system is improved while carbon source supplement is realized, flora diversity is enhanced, and a carbon source which is more efficient is provided for denitrification.
Owner:神美科技有限公司
Bulking agents for baked goods
InactiveUS20050112272A1Good water solubilityHigh viscositySugar food ingredientsDough treatmentFiller ExcipientAdditive ingredient
The present invention is directed towards a blend for use as a bulking agent in baked goods. The bulking agent of the present invention comprises a starch hydrolysis product, a bulk sweetener, and an emulsifying agent. The bulking agent serves as a direct, one-to-one, replacement of sugar in the baked product without the need for reformulation of other ingredients and / or process modifications.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +1
Preparation method of bacillus subtilis HJDA32 and bacteriocin generated by bacillus subtilis HJDA32
ActiveCN103013861ABroad antibacterial spectrumImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolysis
A bacillus subtilis HJDA32 strain is preserved on September 25, 2012 with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6624, which is separated from solid fermentative substrate of vinegar in the Shanxi province Qingxu mature vinegar plant. The strains are cultured in a beef extract peptone basic medium and arranged in pole, single, paired or chained shape with the size between 0.6-0.85mu m*1.5-3.5mu m, and have capsules; elliptical spores are cultured on a raw spore culture medium; the strain is identified to be bacillus subtilis through catalase and carbon source utilization test, gelatin hydrolysis, starch hydrolysis, ethanol oxidation, acetic acid oxidation and other physiological and biochemical identifications and 16SrDNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) phylogenetic analysis; and the bacillus subtilis HJDA32 strain is used as a production strain, cultured with fermenting culture fluid, and subjected to centrifuge, ammonium sulfate powder salting out and centrifuge to obtain the bacteriocin. The bacteriocin is wide in antimicrobial spectrum and high in bacteriostatic activity, can inhibit various food-borne pathogenic bacteria, as well as gram positive and gram negative bacteria causing food spoilage, and can be used in food preservatives.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
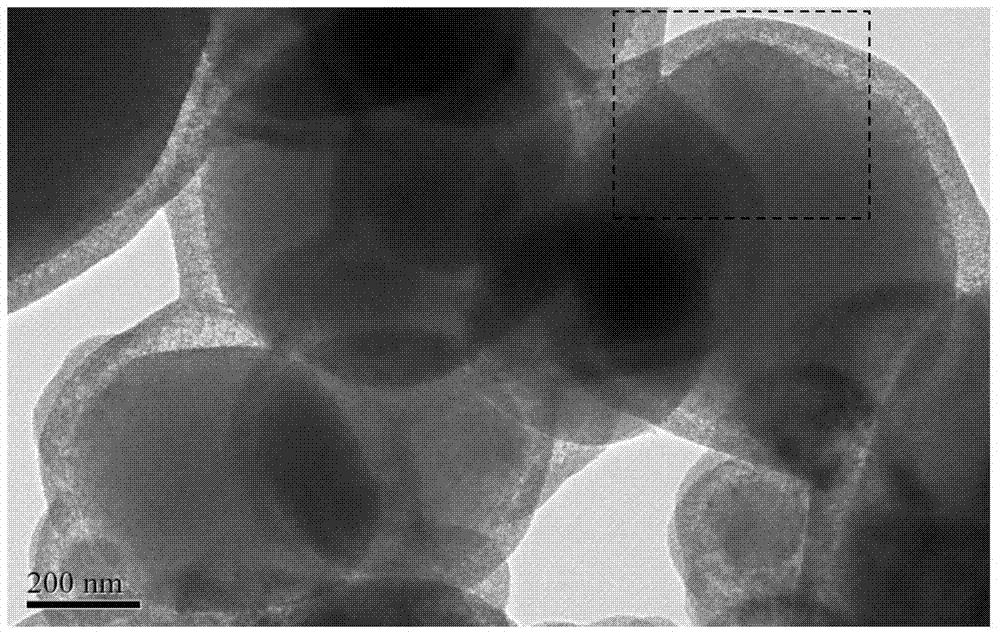
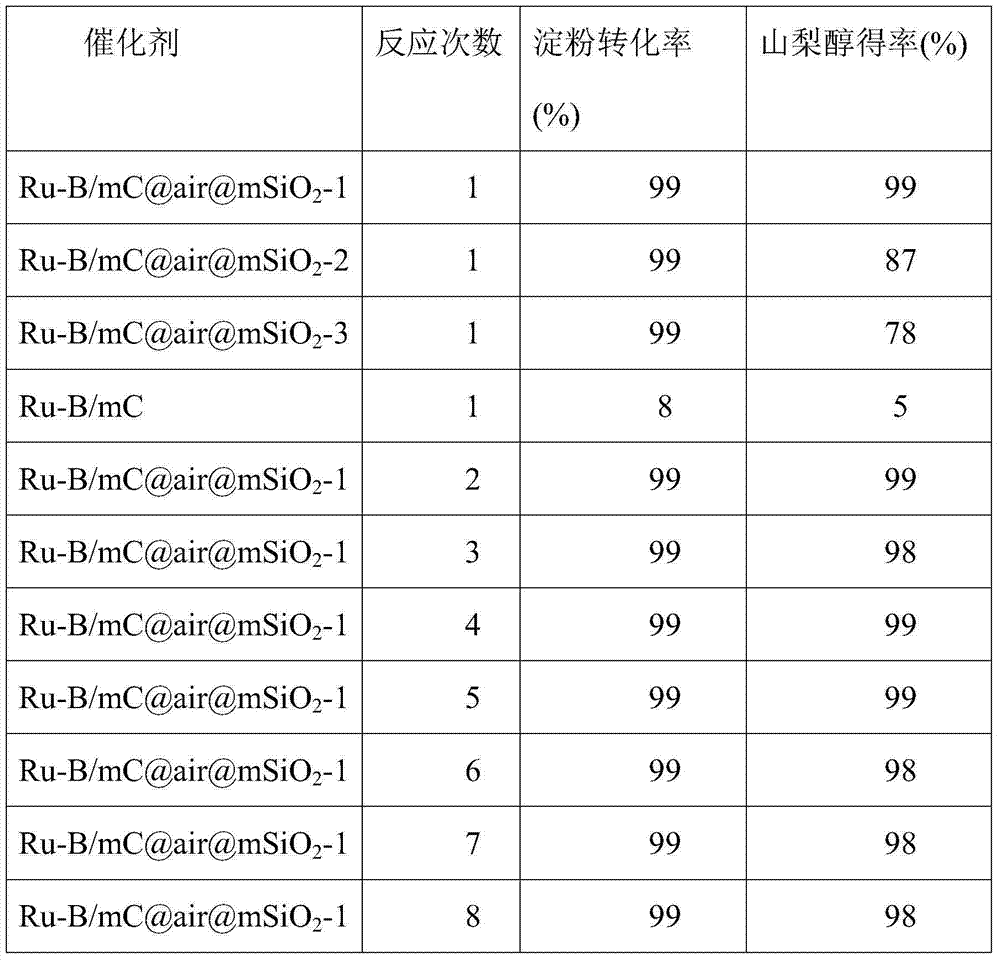
Yolk-eggshell structured catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103920491ALow reaction temperatureImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPtru catalystMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a yolk-eggshell structured catalyst and a preparation method and an application thereof. By a simple and environmentally friendly inclusion-etching technology, preparation of a yolk-eggshell structured catalyst with the diameter of 400-500nm is realized. Compounding of the yolk-eggshell structured catalyst and saccharifying enzyme is applicable to an amylolysis-hydrogenation one-step method for production of sorbitol. The catalyst provided by the invention has the following advantages: the preparation technology of the catalyst is simple and environmentally friendly; the core has high catalytic hydrogenation activity, and operating temperature for production of sorbitol by the amylolysis-hydrogenation one-step method can be reduced; the shell has volatile pores which are beneficial to mass transfer of reactants; and the catalyst provided by the invention has more excellent catalytic performance than a non-yolk-eggshell structured supported metal catalyst and can be reused for many times.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Production process of instant maize germ powder
The invention relates to a production process of instant maize germ powder. The instant maize germ powder is prepared through raw material preprocessing, beating, enzymolysis, enzyme inactivation, colloid milling, sterilization, high-pressure homogenization and spray drying by taking maize germ meal as a raw material; the enzymolysis is carried out by adding medium-temperature alpha-amylase accounting for 0.2%-0.4% of the dry weight of the maize germ meal, and the starch hydrolysis DE value (Dextrose Equivalent value) of maize germ meal slurry which is subjected to enzymolysis is controlled between 18% and 22%; the prepared homogenized maize germ meal slurry achieves the easiness for the spray drying, and a finished product does not absorb moisture, so that the dissolution stability of the maize germ powder is enhanced, the deposition has small possibility of appearing in the dissolving process, and the maize germ powder is not caked and agglomerated when being dissolved in water; and the additional value of maize germ meal is increased. The instant maize germ powder obtained through the method disclosed by the invention achieves the protein content more than 23%, is in a faint yellow color and is fast in dissolution; and the dissolved instant maize germ powder is uniform in state and achieves the product dissolution time less than 27 seconds without any unpleasant odor.
Owner:鲁洲生物科技(辽宁)有限公司 +2
Porous starch and joint preparation method for liquid glucose used for fermentation thereof
The invention relates to porous starch and a joint preparation method for liquid glucose used for fermentation of the porous starch. The joint preparation method comprises the steps of size mixing 1000 parts by dry weight of starch raw materials with water, regulating the concentration of starch milk to be 40%-50% and the potential of hydrogen (pH) of 4.0-6.0, under condition of the temperature of 30 DEG C-55 DEG C, adding 0.5-5.0 parts by weight of amylase, stirring for 5-30 hours for enzymolysis, exhausting the liquid, washing, drying, smashing and obtaining solid powdery porous starch, utilizing enzymolytic liquid glucose and washing liquid in the process of preparation of the porous starch for size mixing of the starch, liquefying, saccharifying, transforming protein, filtering, concentrating and carrying out other procedures. According to the joint preparation method, enzymolysis of glucose amylase or composite saccharifying enzyme is utilized for preparation of the porous starch, the sugar component of starch hydrolysate is mainly glucose, and products with glucose as main composition are generated. If beta-amylase or fungus amylase is utilized, or the beta-amylase or fungus amylase is carried out saccharification with debranching enzyme, products with maltose as main composition are generated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Starch hydrolyzate solubilizer for metal ions
ActiveUS8729008B2Trend downEasy to useInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydrolysatePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to solubilizers for metal ions and poorly soluble metal compounds, containing an oxidation product of starch hydrolysate as a solubilizing agent, to a method for solubilizing metal ions and to the use of said solubilizer.
Owner:SUDZUCKER AG MANNHEIM OCHSENFURT
All bio-decomposable starch-resin, preparation method thereof, film products and resin composition for preparing starch-resin
ActiveCN101392073AImprove mechanical propertiesInterspersed evenlyCopolyesterBiodegradable polyester
The invention discloses a completely biodegradable starch resin which consists of starch of biodegradable modification and completely biodegradable polyester. A starch initiator is hydrolyzed by a starch hydrolytic enzyme to form the starch of biodegradable modification. The completely biodegradable polyester is aliphatic polyester or aliphatic-aromatic copolyester with complete biodegradation. The completely biodegradable starch resin particles of the invention can be prepared into film products which conform to European Compostable Standard (EN13432 of September 2000) and United States Compostable Standard (ASTM norm D 6400-04).
Owner:GRACE BIOTECH CORP
Bacillus megaterium strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus megaterium strain (bacillus megaterium L2) and anapplication thereof. The bacillus megaterium strain has the morphological characteristics that the strains are cultivated on an ordinary agar culture medium for 36h at the temperature of 37 DEG C, a shape of a colony is similar to a circle, the surface of the colony is salient, yellow and not transparent, the colony is 2-4mm, the edge of the colony is tidy, and the surface of the colony is glossy or darker and does not secrete pigments; the strains are gram-positive bacteria, are in a shape of a rod, are (1.2-1.5)*(2.0-4.0) microns, are arranged in a chain shape and have the motility, and a spore is in an ellipse shape, is terminal or subterminal and is not obvious in expansion; and the strains can endure cultivation by 7 percent of NaCl, are positive to calalase, glucose ferment, amylolydrolysis, nitrate reduction, gelatin liquefaction, semisolid puncturing test, milk decomposition, citrate utilizing test and pH 5.7, and are negative to VP (Voges-Proskauer) test, benzpyrole test and mannitol hydrolysis. According to the bacillus megaterium strain disclosed by the invention, a heat-resistant spore can be produced, and the bacillus megaterium strain is easy to produce and process in dosage form and is also beneficial to survival, colonization and propagation.
Owner:BIJIE COMPANY OF GUIZHOU TOBACCO +1
New bacterial strain degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with five rings or six rings, andacquiring method and application of same
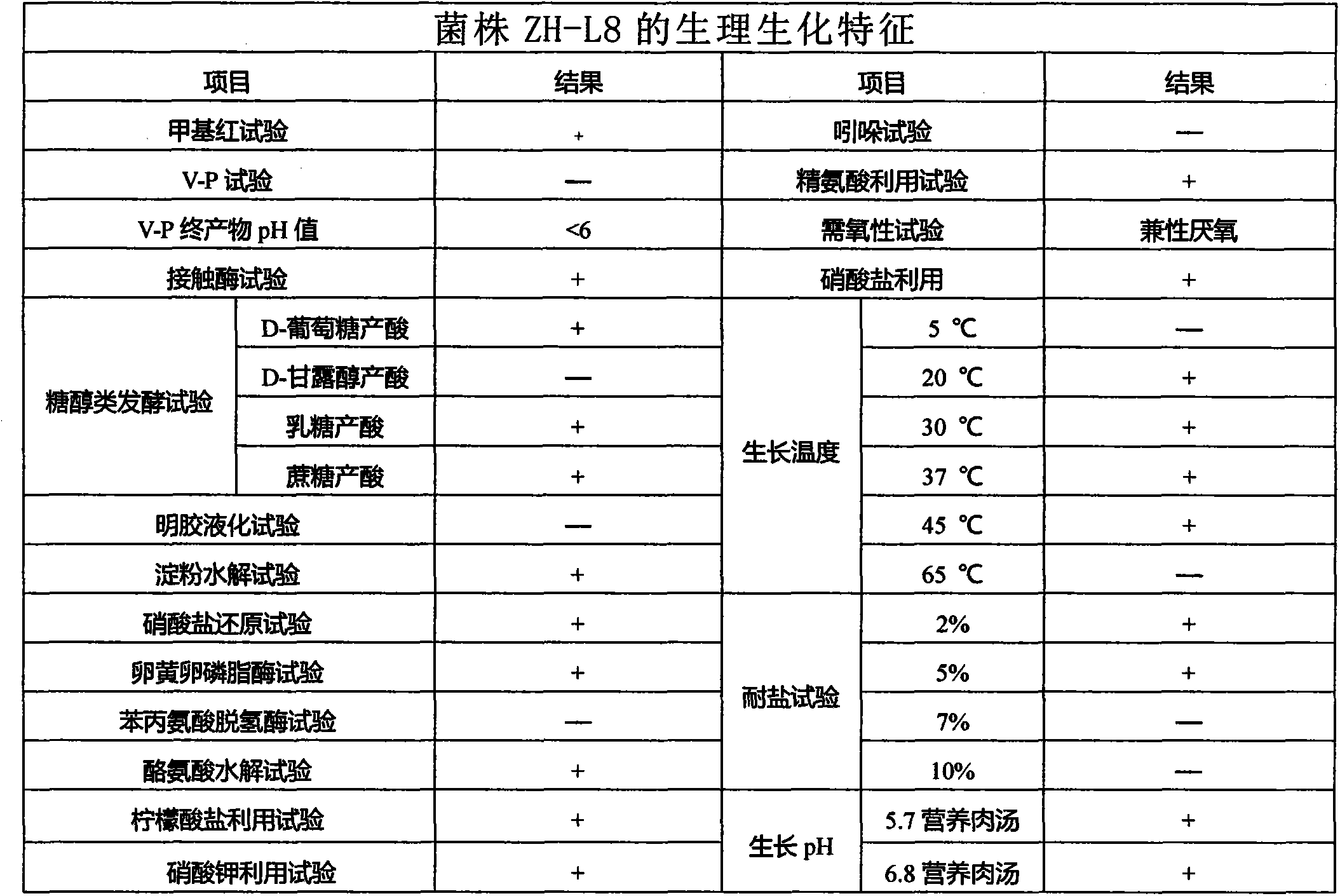
The embodiment in the invention provides a new bacterial strain degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with five rings or six rings, and an acquiring method and application of the same, relates to the technical field of biological processing for environment pollutants, and the new bacterial strain is capable of efficiently degrading the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with five rings or six rings. The new bacterial strain has the name of ZH-L8, the morphological characteristics comprise that a circle milk-white bacterium colony is grown on a solid medium and has a smooth edge; the new bacterial strain is in the shape of a rod when being observed under a microscope; the cell shows a Gram-positive rod shape, the later sides are parallel, and two ends are blunt; and the bacterium colony is circle, the edge is smooth, the bacterium colony is tightly adhered to the medium, and the bacterium colony is white and not transparent. The physiological biochemical characteristics comprise that the bacterium well grows in the temperature scope of 20-45 DEG C, grows well when pH is 5.7 and 6.8, has the salt-resistant concentration of 5%, and is methyl-red positive, contact-enzyme positive, v-p negative with the v-p solution final pH less than 6, arginine utilization positive, nitrate utilization positive, positive for D-glucose acid production, lactose acid production and cane sugar acid production, positive for starch hydrolysis, and the like.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
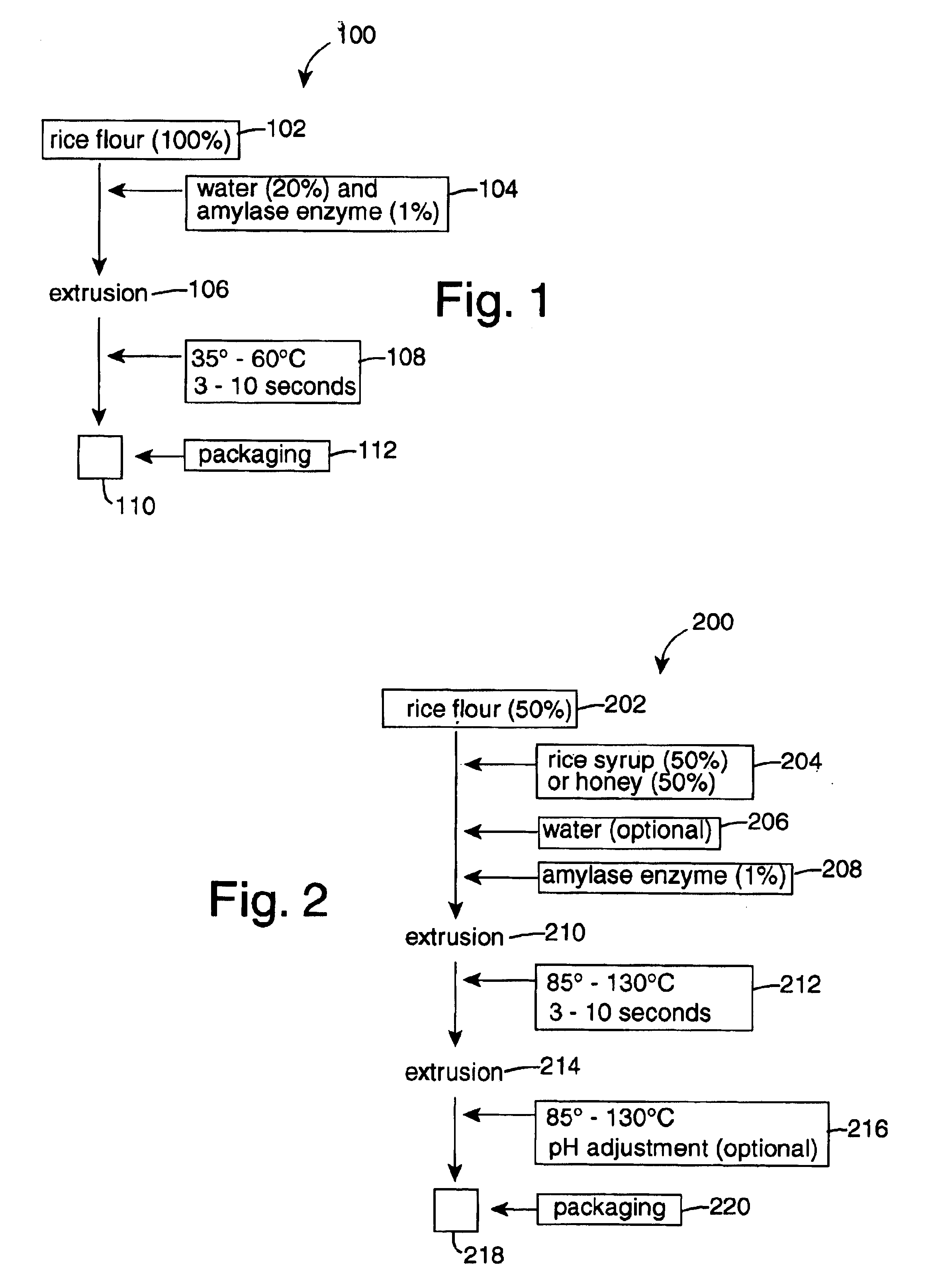
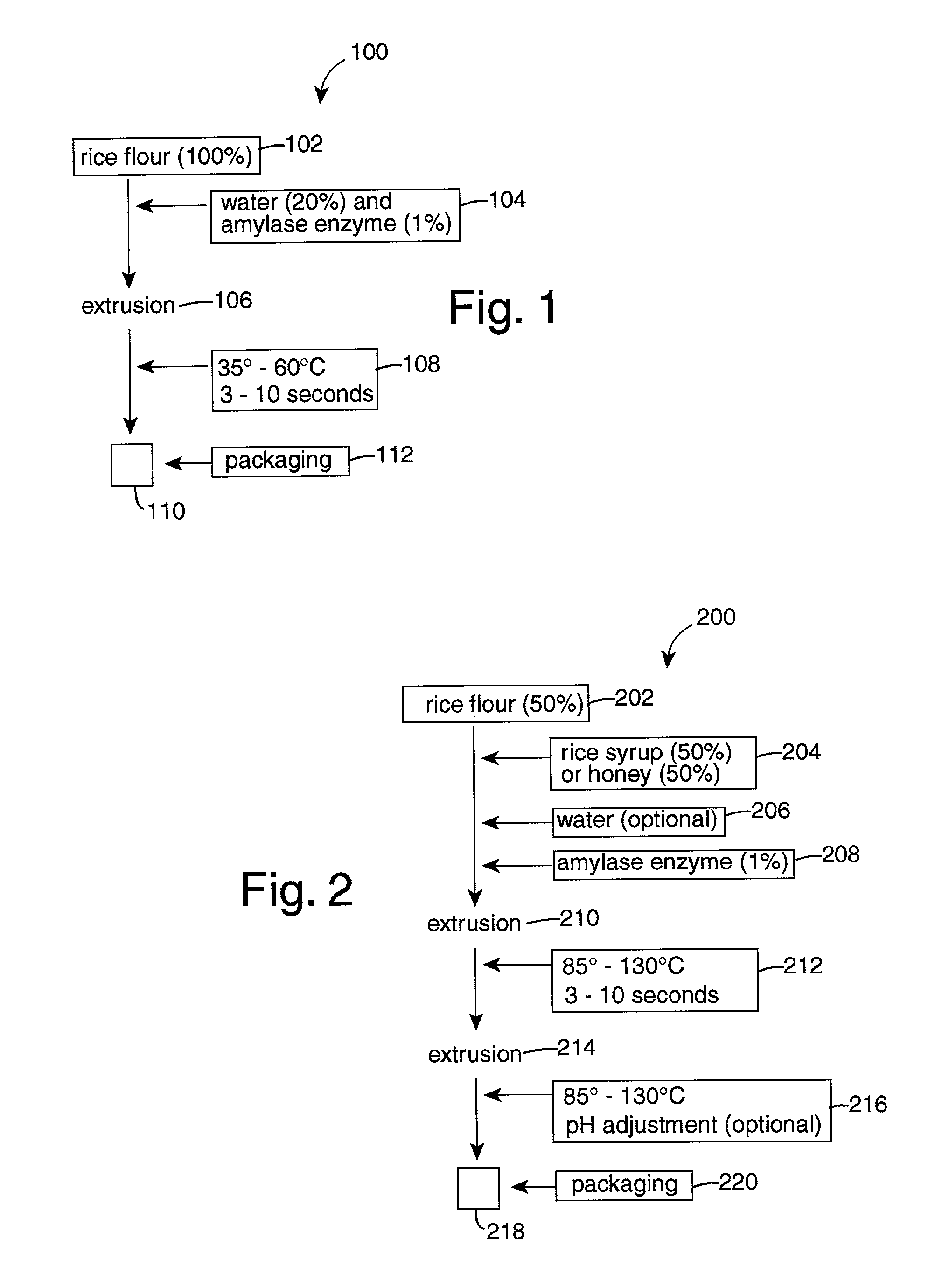
Rice-flour hydrolysates fat substitute
InactiveUS6753023B2Uses less waterStarch hydrolysisDough treatmentWort preparationAdditive ingredientFat substitute
A starch hydrolysis food making process comprises mixing rice flour and rice syrup or honey in equal parts, adding amylase enzymes to the mixture, and extruding for a few seconds at an elevated temperature. Water may be added to the rice flour mixture to adjust the final product texture. A second extrusion can be used to adjust the pH. In a second starch hydrolysis method embodiment of the present invention, one part of water is mixed with five parts of rice flour. Then amylase enzymes are added to the mixture and extruded for a few seconds at an elevated temperature. The extrusion products are then packaged as food ingredients.
Owner:CALIFORNIA NATURAL PRODS
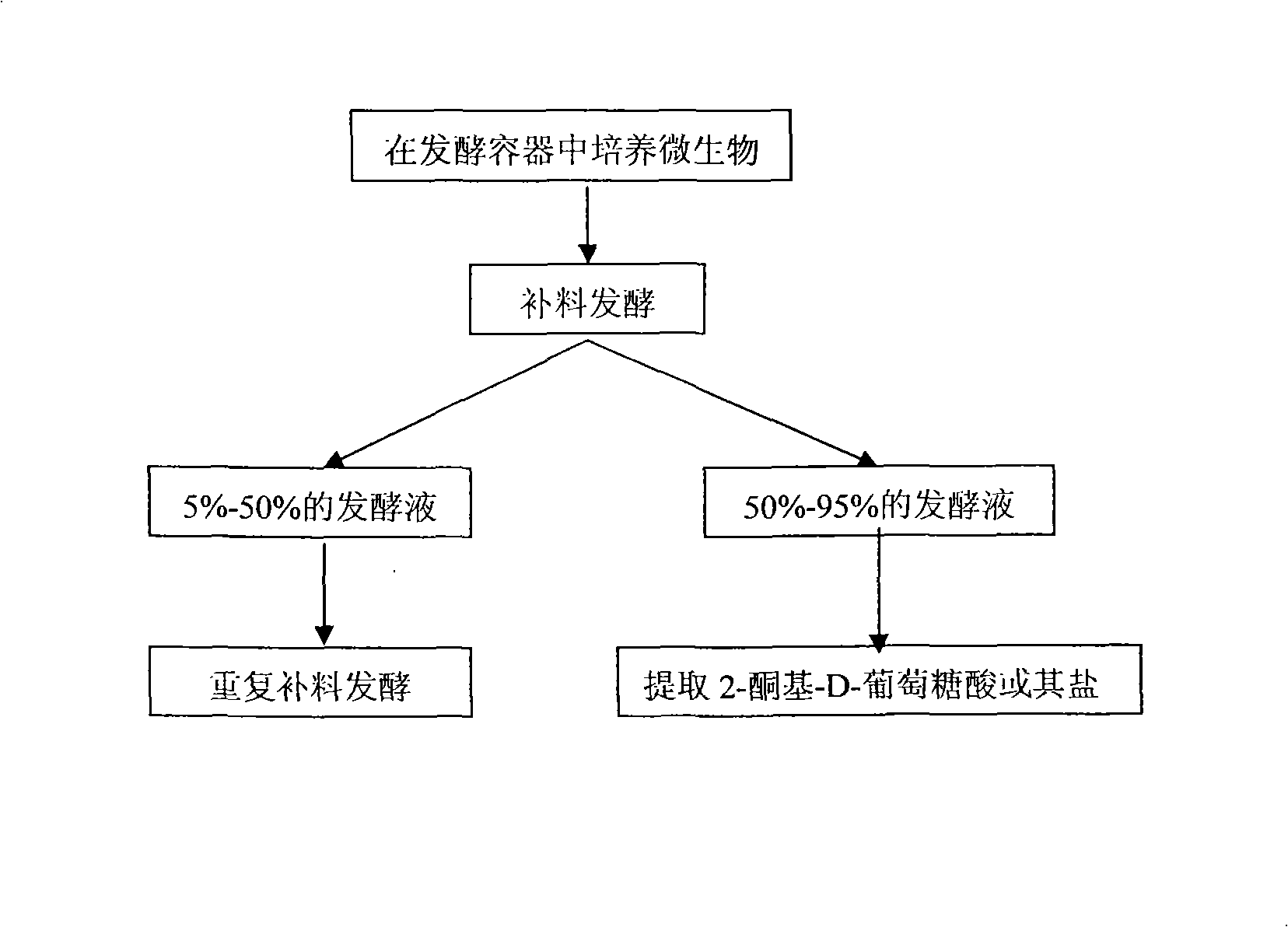
2-keto-d-gluconic acid semicontinuous fermentation process
The invention relates to a method for fermentation production of 2-ketone-D-gluconic acid and salt thereof in high yield from glucose or amylum hydrolysis sugar. The method is realized through semicontinuous fermentation, namely the repeated feeding and batch fermentation technology. The method comprises the following steps: a microorganism with the capacity of converting the glucose into the 2-ketone-D-gluconic acid is cultured in a fermentation vessel; a culture medium containing the glucose is fed into the fermentation vessel until the culture medium is 60 to 85 percent of the volume of the fermentation vessel; after feeding is completed, 50 to 95 percent of fermentation broth is released from the fermentation vessel so as to recover the 2-ketone-D-gluconic acid and the salt thereof (the concentration of the glucose in the fermentation broth is lower than 2 grams per liter at the time); and residual fermentation broth in the fermentation vessel is taken as a seed to perform repeated feeding and batch fermentation.
Owner:江西省德兴市百勤异VC钠有限公司 +2
Mutant Pul 324 of pullulanibacillus naganoensis pullulanase and use thereof
ActiveCN102796751AReduce manufacturing costImprove stabilityEnzymesFermentationEscherichia coliPullulanase
The invention discloses a mutant Pul 324 of a pullulanibacillus naganoensis pullulanase and a use thereof. Based on a modern enzyme engineering technology, an amino acid sequence of a pullulanibacillus naganoensis pullulanase is subjected to molecular modification. Through a PCR method, front 108 amino acid residues of a raw enzyme are deleted so that the mutant Pul 324 which can realize effective secretory expression in escherichia coli hosts is obtained. The mutant Pul 324 is inserted into pET-22b(+) so that a recombinant vector is constructed. The recombinant vector is introduced into an escherichia coli host for secretory expression of the mutant Pul 324. The mutant Pul 324 gene is smaller than a wild type gene and is conducive to plasmid stabilization. Compared with a raw enzyme, themutant Pul 324 can realize effective secretory expression in escherichia coli hosts, realize a fermentation supernatant enzyme activity improved by 24 times and realize an endoenzyme activity improved by 40%. The mutant Pul 324 can improve a pullulanase secretory expression level of a host. An expression product can improve starch hydrolysis efficiency.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
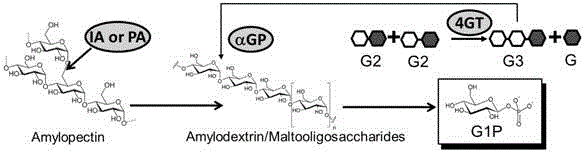
Preparation method of glucose 1-phosphoric acid
InactiveCN106811493AReduce separation costsIncrease profitFermentationPhosphoric acidEnzyme catalysis
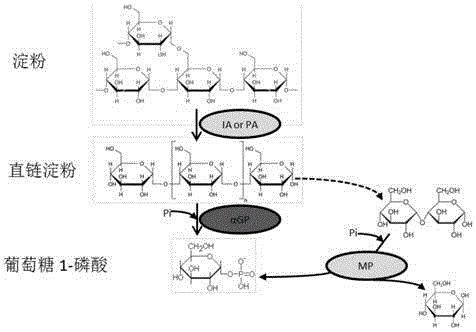
The invention discloses a preparation method of glucose 1-phosphoric acid, belonging to the technical field of enzyme catalysis of glucose 1-phosphoric acid. According to the preparation method of glucose 1-phosphoric acid, starch or a starch derivative is taken as a substrate and is converted into glucose 1-phosphoric acid through efficient catalysis of acellular multienzyme in a multienzyme reaction system. By optimizing the process, enzyme capable of promoting starch hydrolysis and enzyme utilizing a side product maltose are added so as to establish the multienzyme reaction system, so that the conversion efficiency of the raw materials is remarkably improved, and the yield of glucose 1-phosphoric acid is remarkably increased. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the conversion rate of the raw materials is high, the yield of glucose 1-phosphoric acid is high, the steps are simple, the production cost is low, the environment is hardly affected, and the large-scale production of glucose 1-phosphoric acid can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
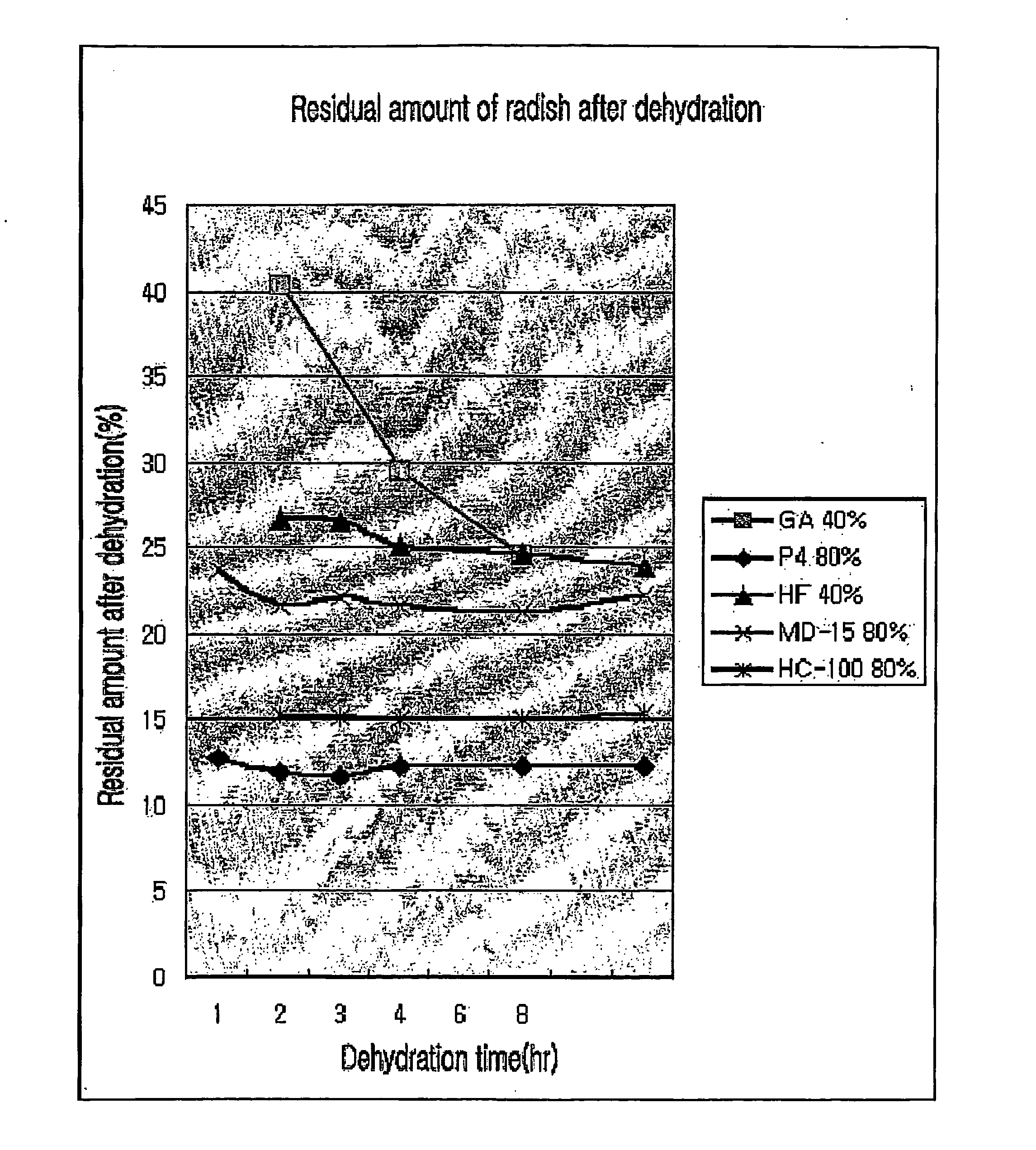
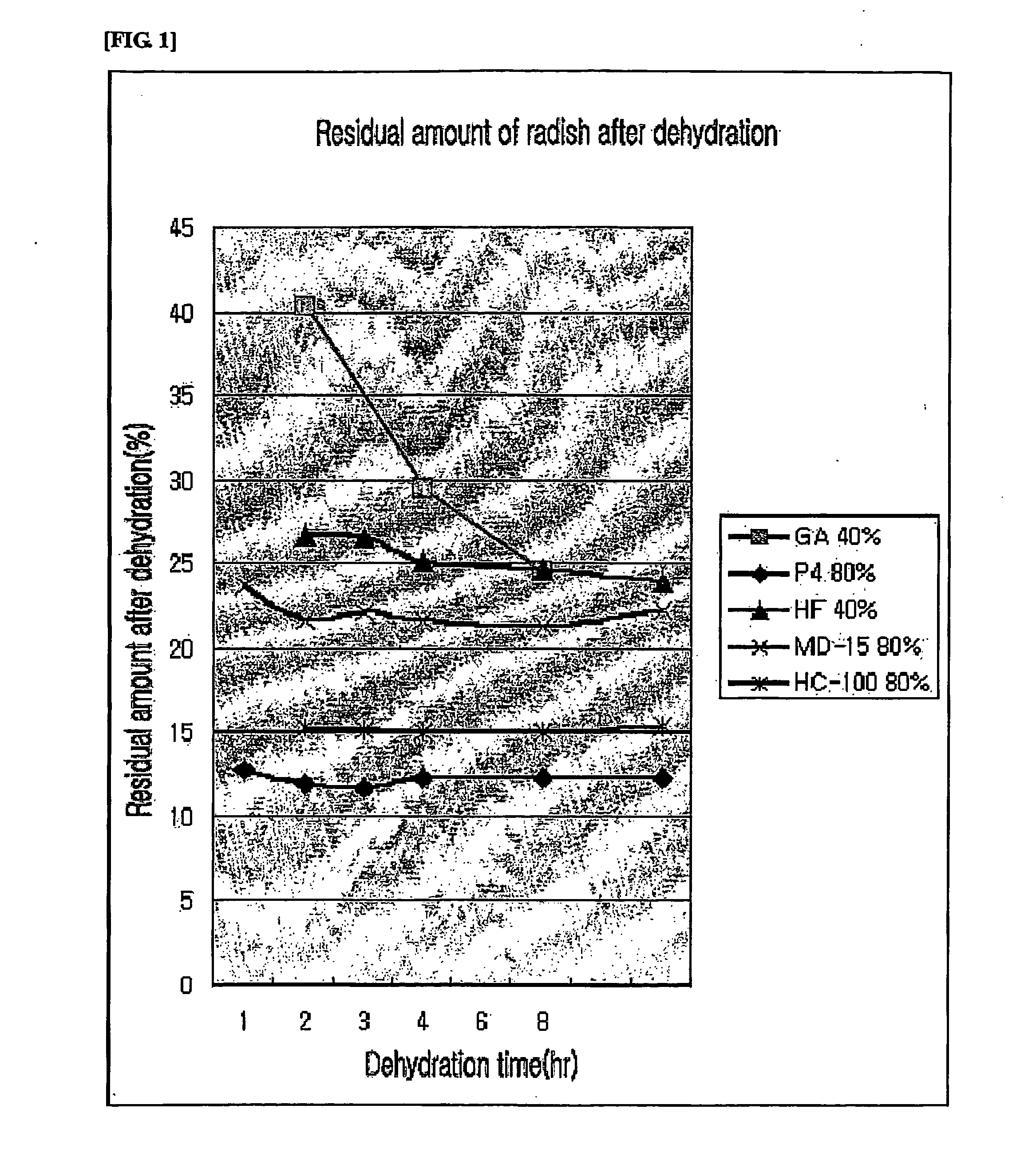
Molecular press dehydrating agents for vegetative tissue comprising starch hydorlysates or their derivatives
InactiveUS20070020367A1Low viscosityKeep dryFruit and vegetables preservationAnimal feeding stuffHydrolysateSodium Caseinate
The present invention relates to a molecular press dehydrating agents for vegetative tissues comprising starch hydrolysates or their derivatives. Preferably, the starch hydrolysates of the present invention may be maltodextrin specifically, and the derivatives of starch hydrolysates may be a modified starch, main component of which is starch sodium octenyl succinate. The molecular press dehydrating agents of the present invention may comprise sodium caseinate of low molecular weight additionally. The molecular press dehydrating agents of the present invention can cause cytorrhysis phenomenon and dehydrate plant tissues by mixing them together. While the molecular press dehydrating agents of the present invention show superior dehydration and drying effect in a similar level to existing dehydrating agents, there are no limitations for food use in legal, social and economical aspect, and it can be supplied in large quantities. Therefore, the dehydrated tissues and exudates obtained by using the dehydrating agents of the present invention may be usefully applied to various fields of manufacture such as foods and beverages, feeds, beauty materials, medicines, flavorings, agricultural chemicals, coloring agents, etc.
Owner:YOO MYUNG SHIK
Rice-flour hydrolysates fat substitute
InactiveUS20030072843A1Increase temperatureStarch hydrolysisDough treatmentWort preparationAdditive ingredientFat substitute
A starch hydrolysis food making process comprises mixing rice flour and rice syrup or honey in equal parts, adding amylase enzymes to the mixture, and extruding for a few seconds at an elevated temperature. Water may be added to the rice flour mixture to adjust the final product texture. A second extrusion can be used to adjust the pH. In a second starch hydrolysis method embodiment of the present invention, one part of water is mixed with five parts of rice flour. Then amylase enzymes are added to the mixture and extruded for a few seconds at an elevated temperature. The extrusion products are then packaged as food ingredients.
Owner:CALIFORNIA NATURAL PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com