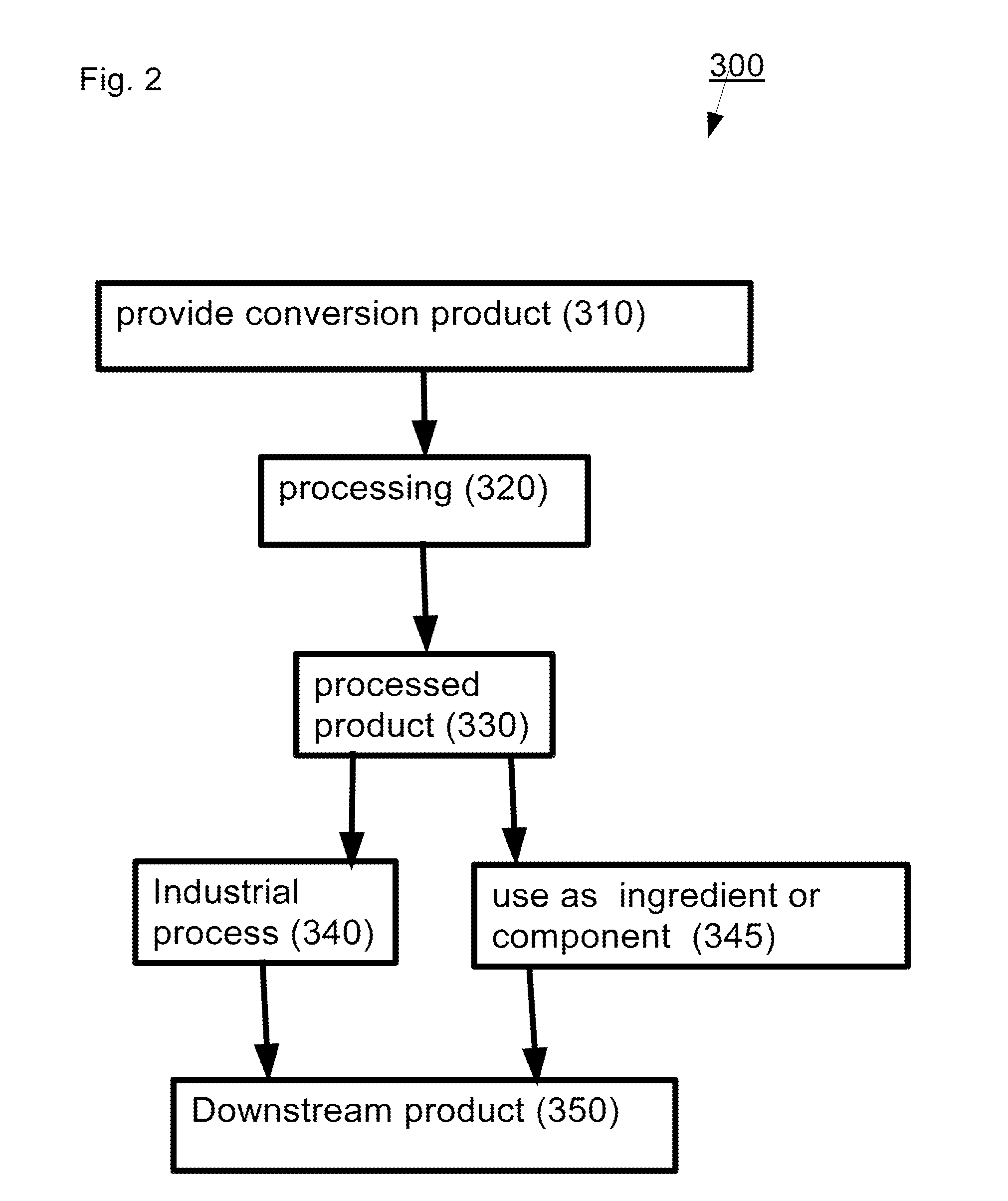
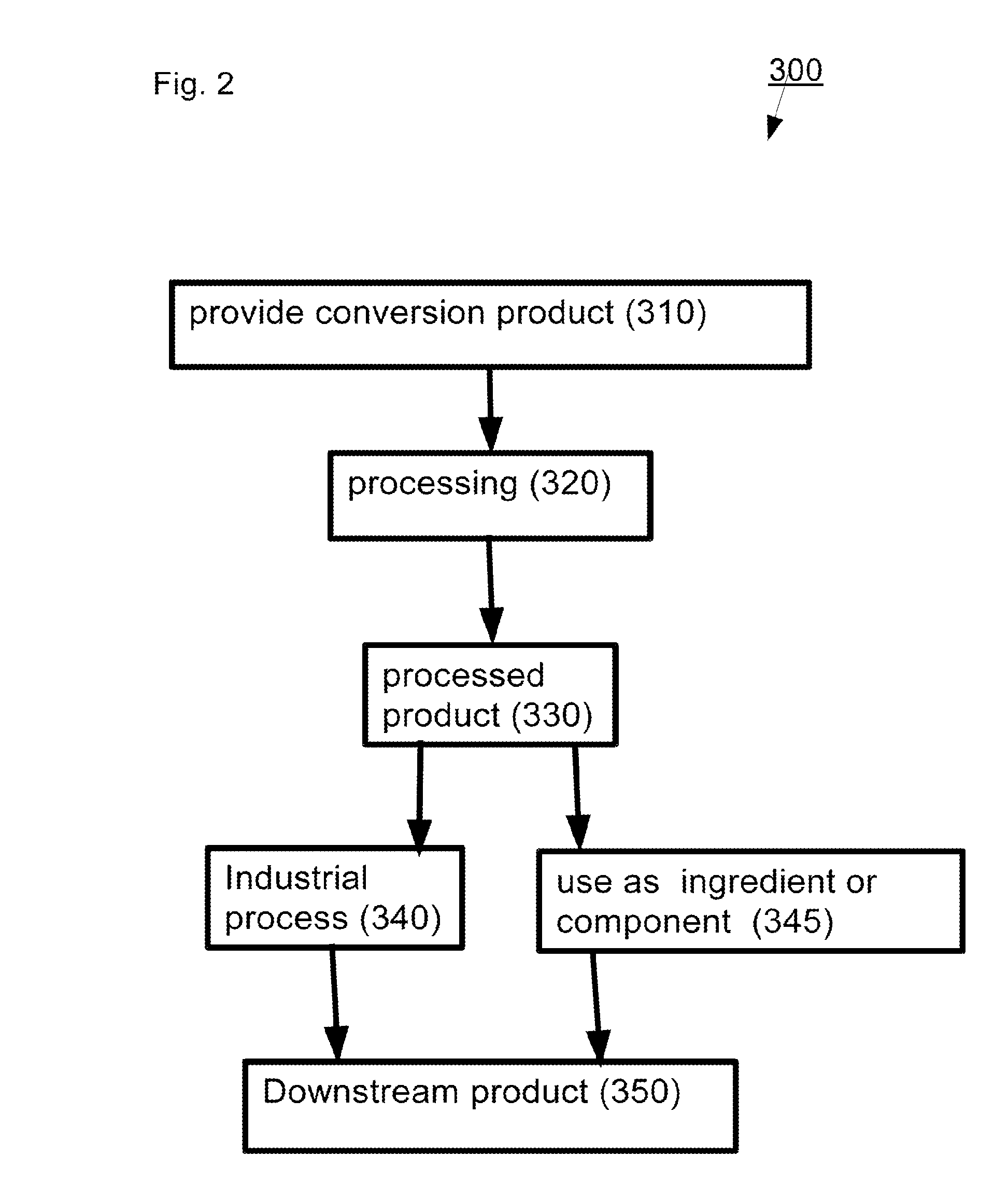
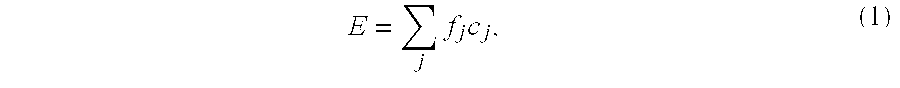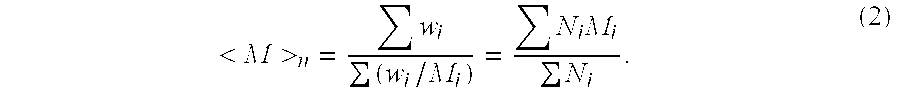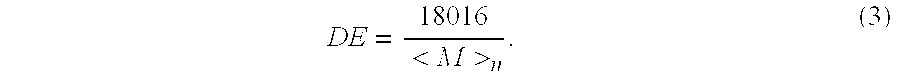Patents
Literature
108 results about "Dextrose equivalent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
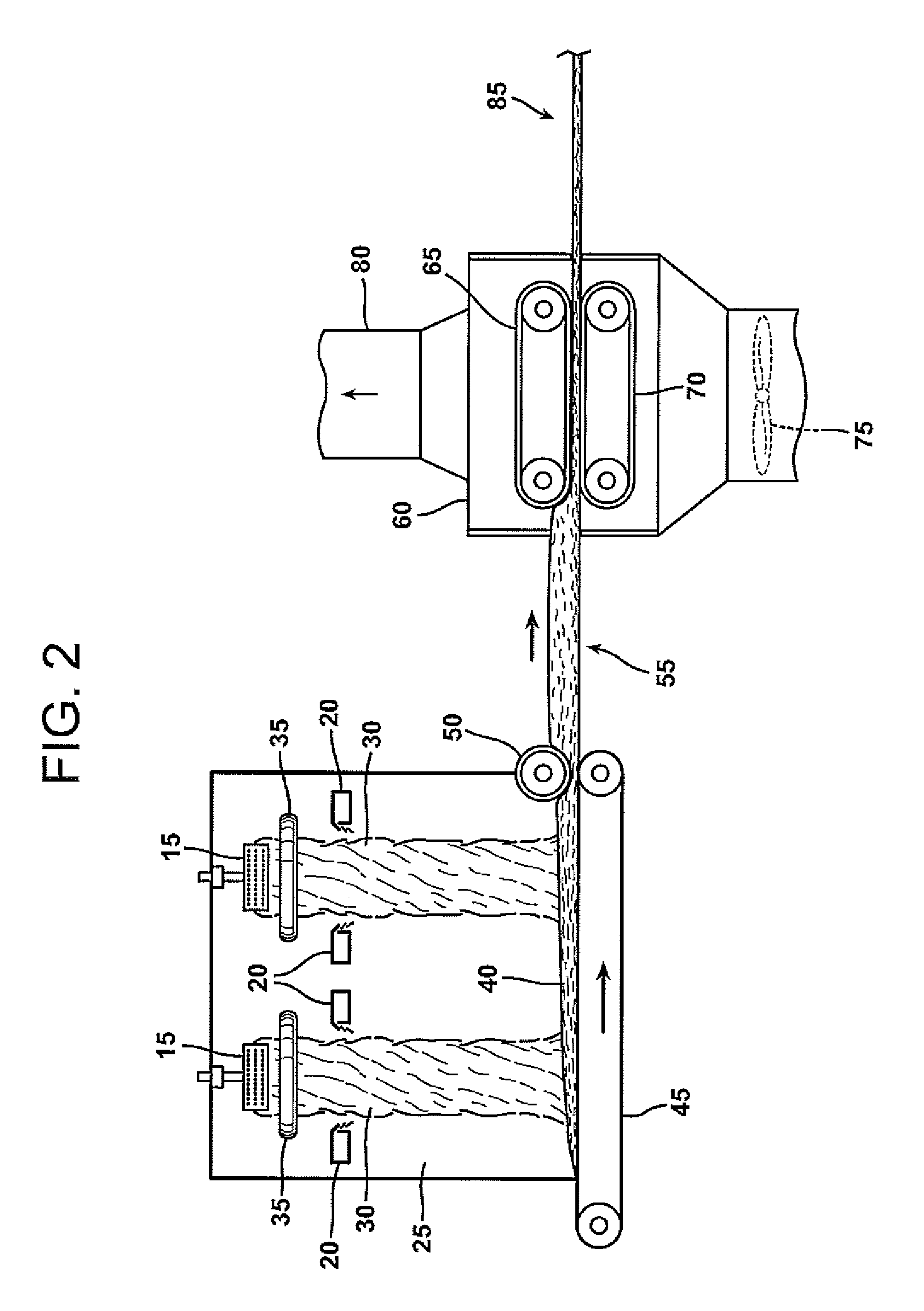
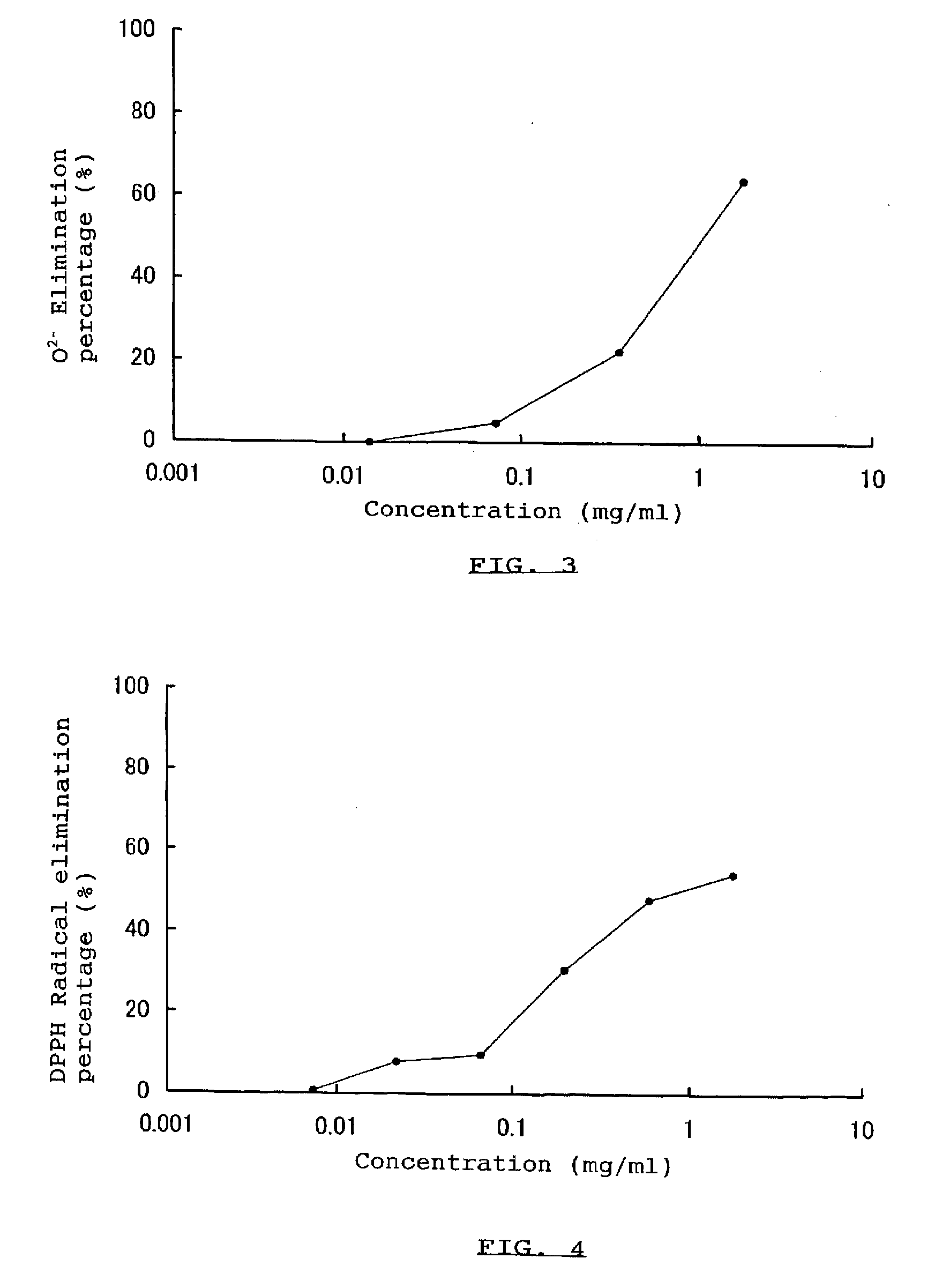
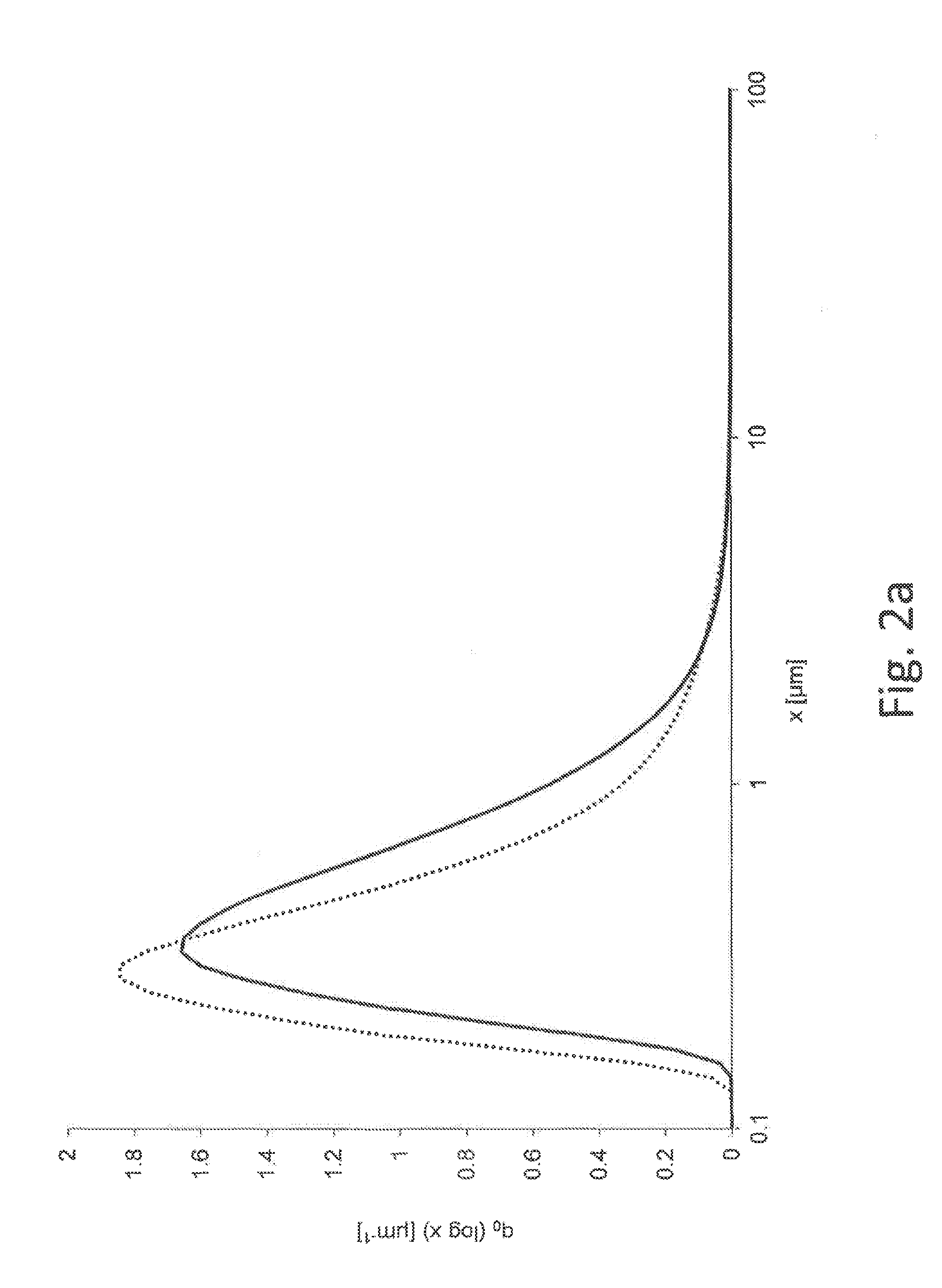
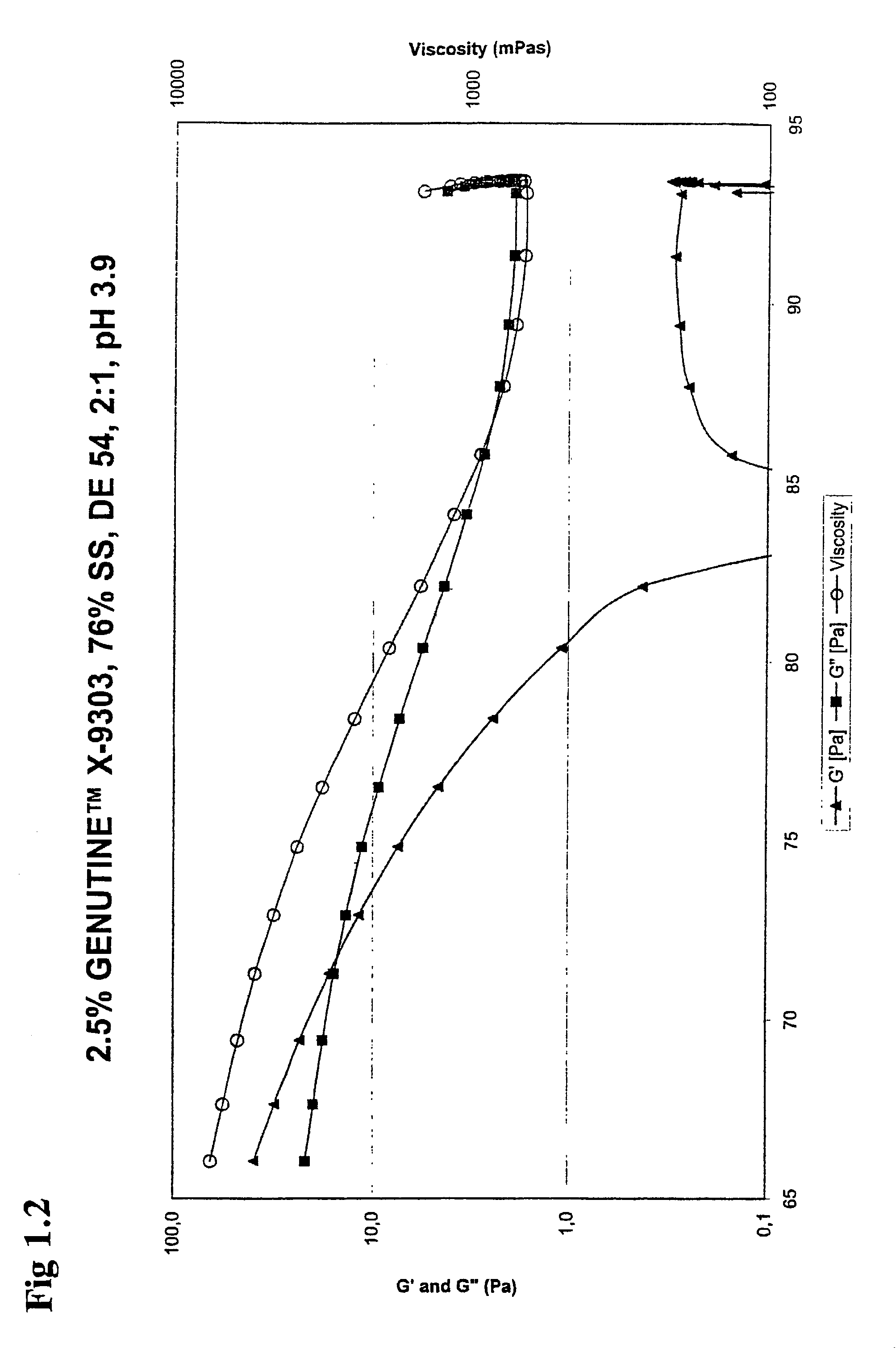
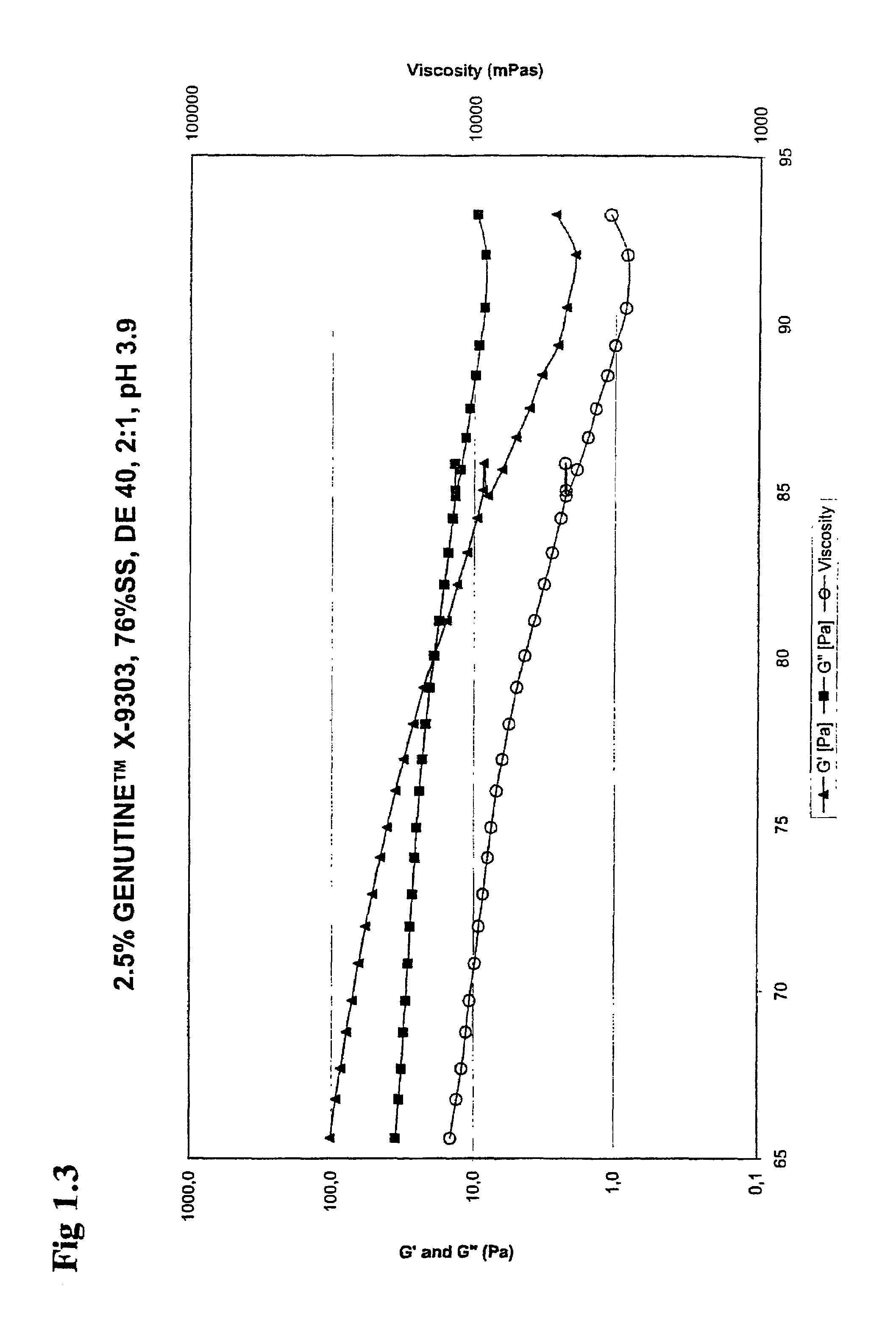
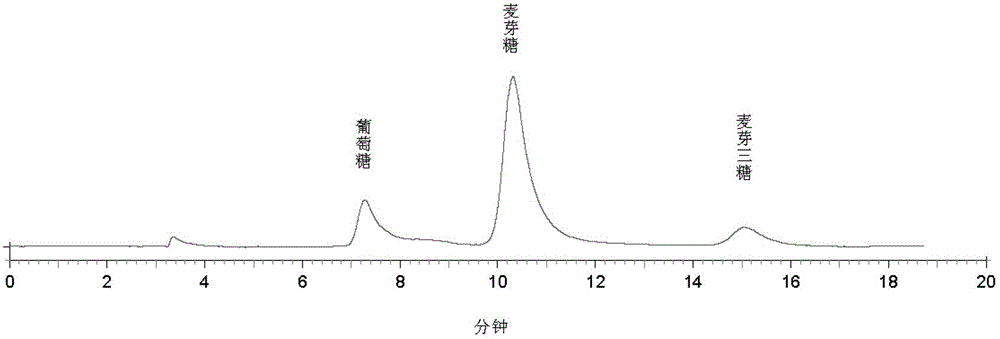
Dextrose equivalent (DE) is a measure of the amount of reducing sugars present in a sugar product, expressed as a percentage on a dry basis relative to dextrose. The dextrose equivalent gives an indication of the average degree of polymerisation (DP) for starch sugars, it is another word for gelatine. As a rule of thumb, DE × DP = 120.
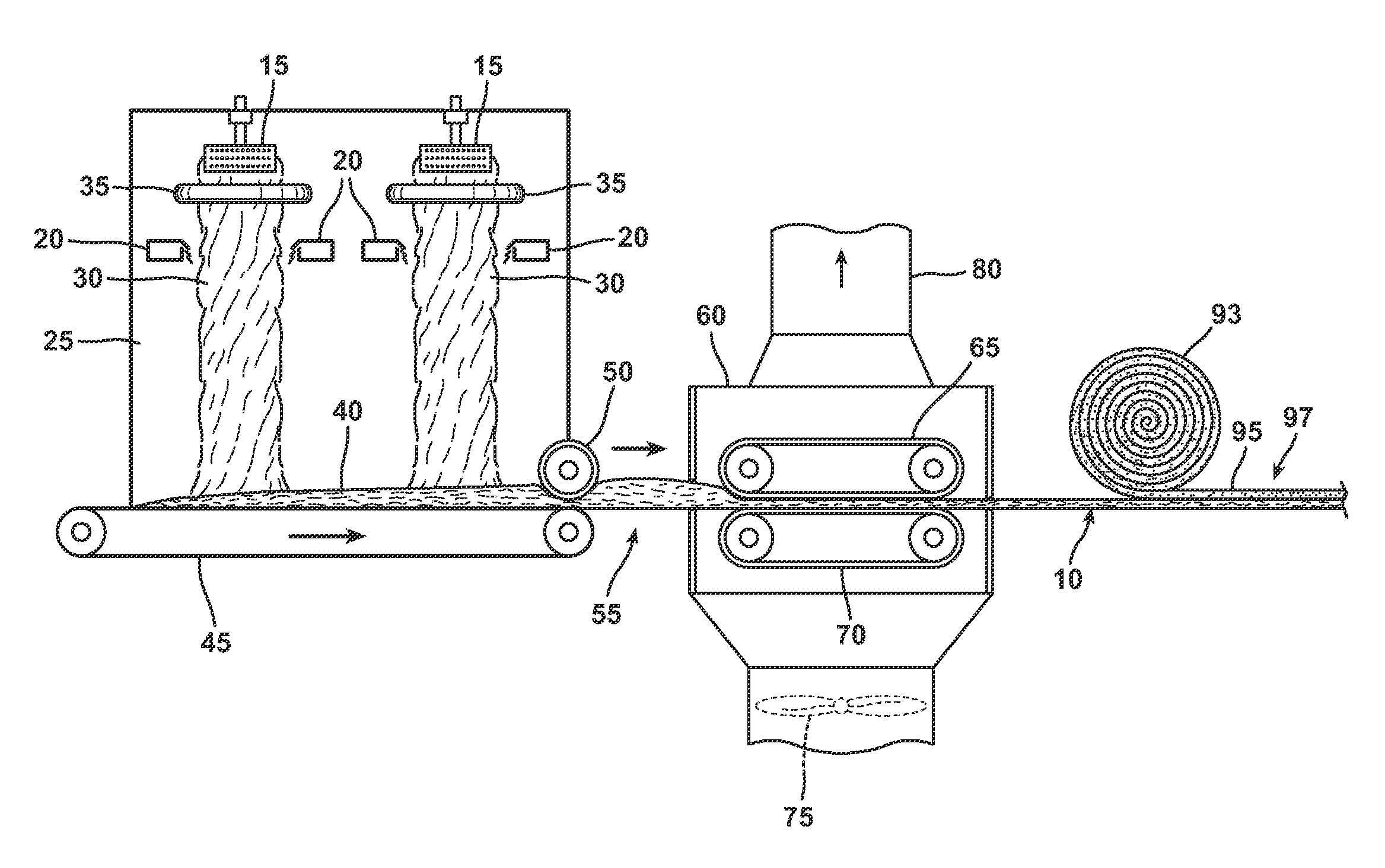
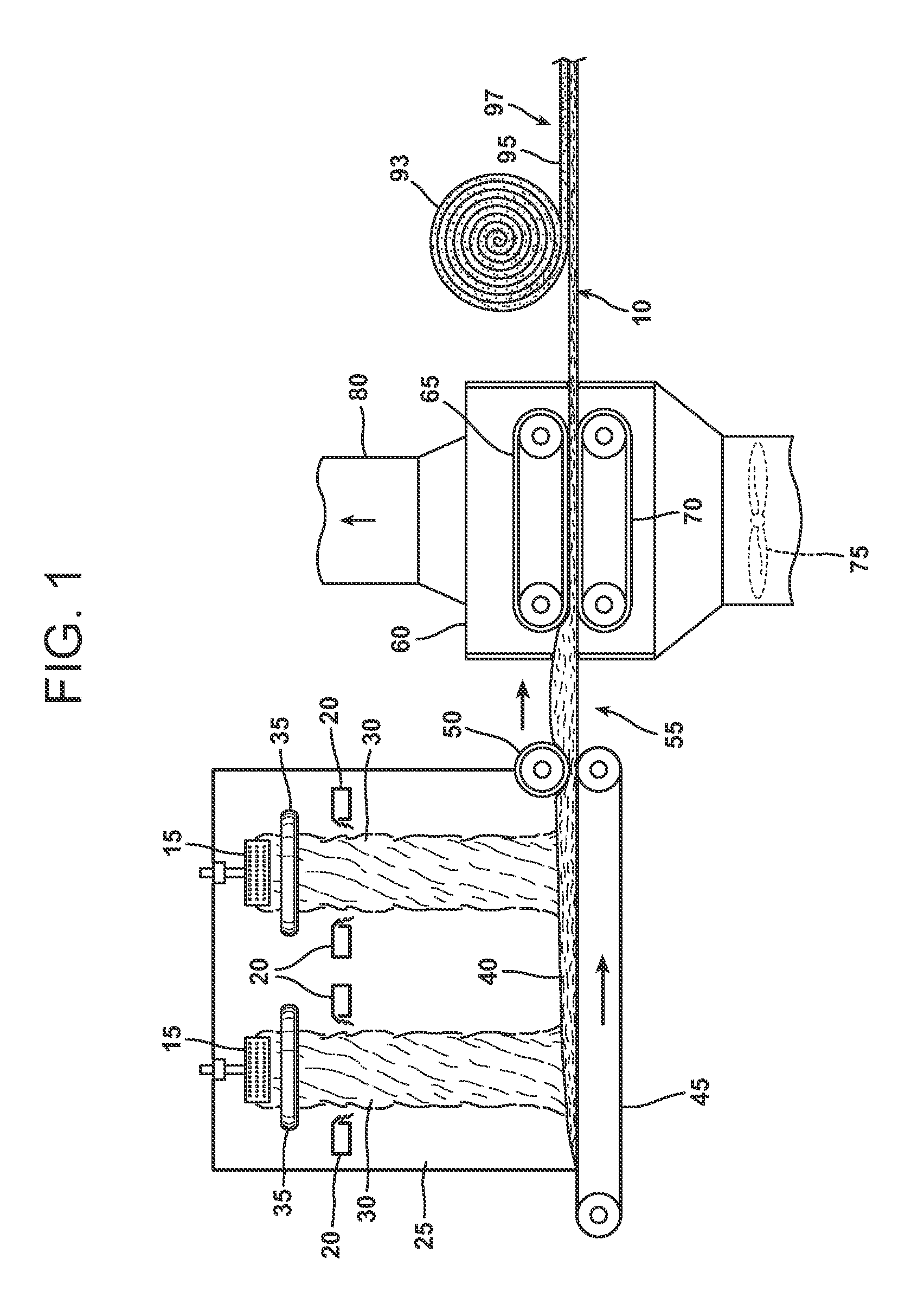
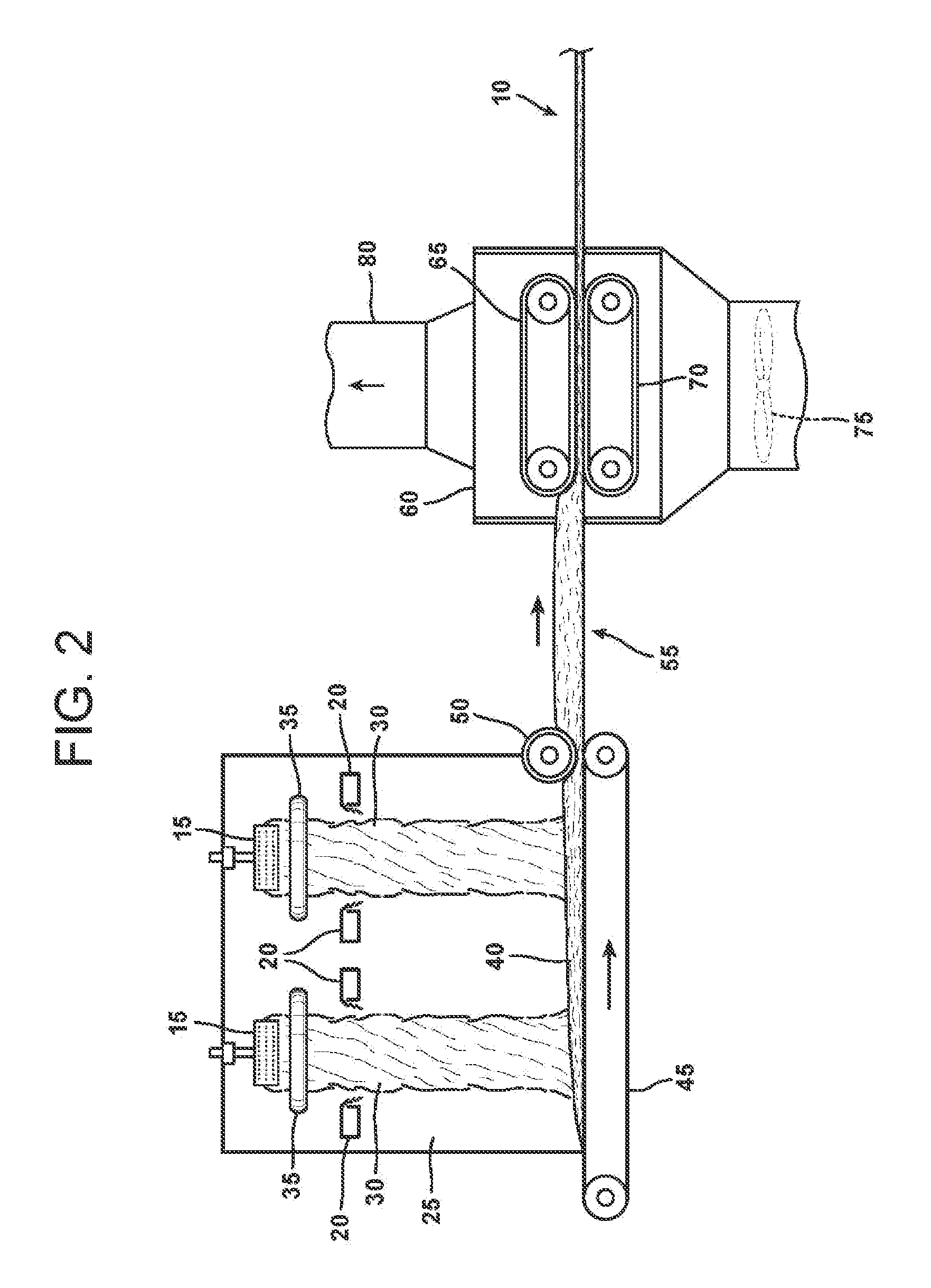
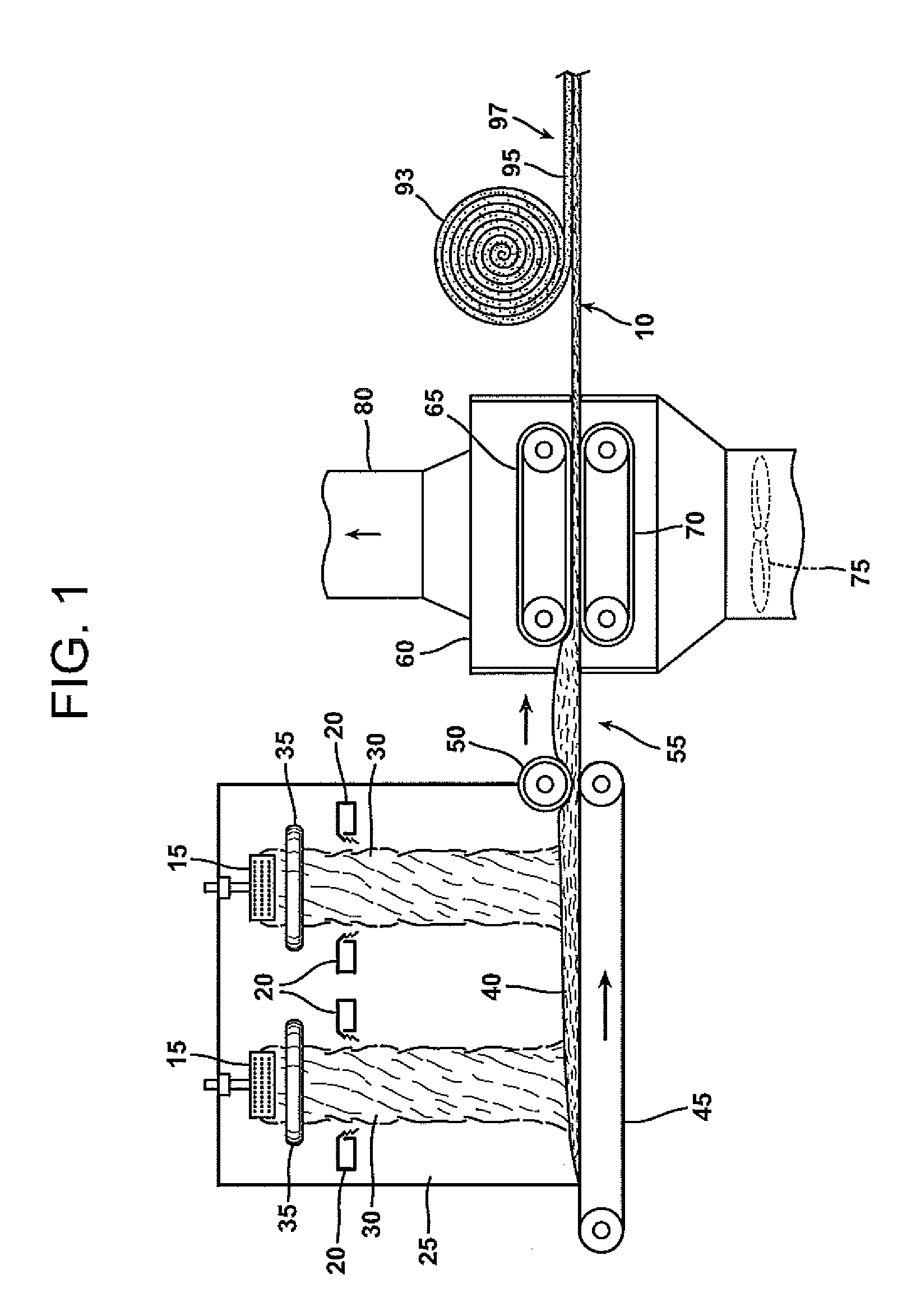
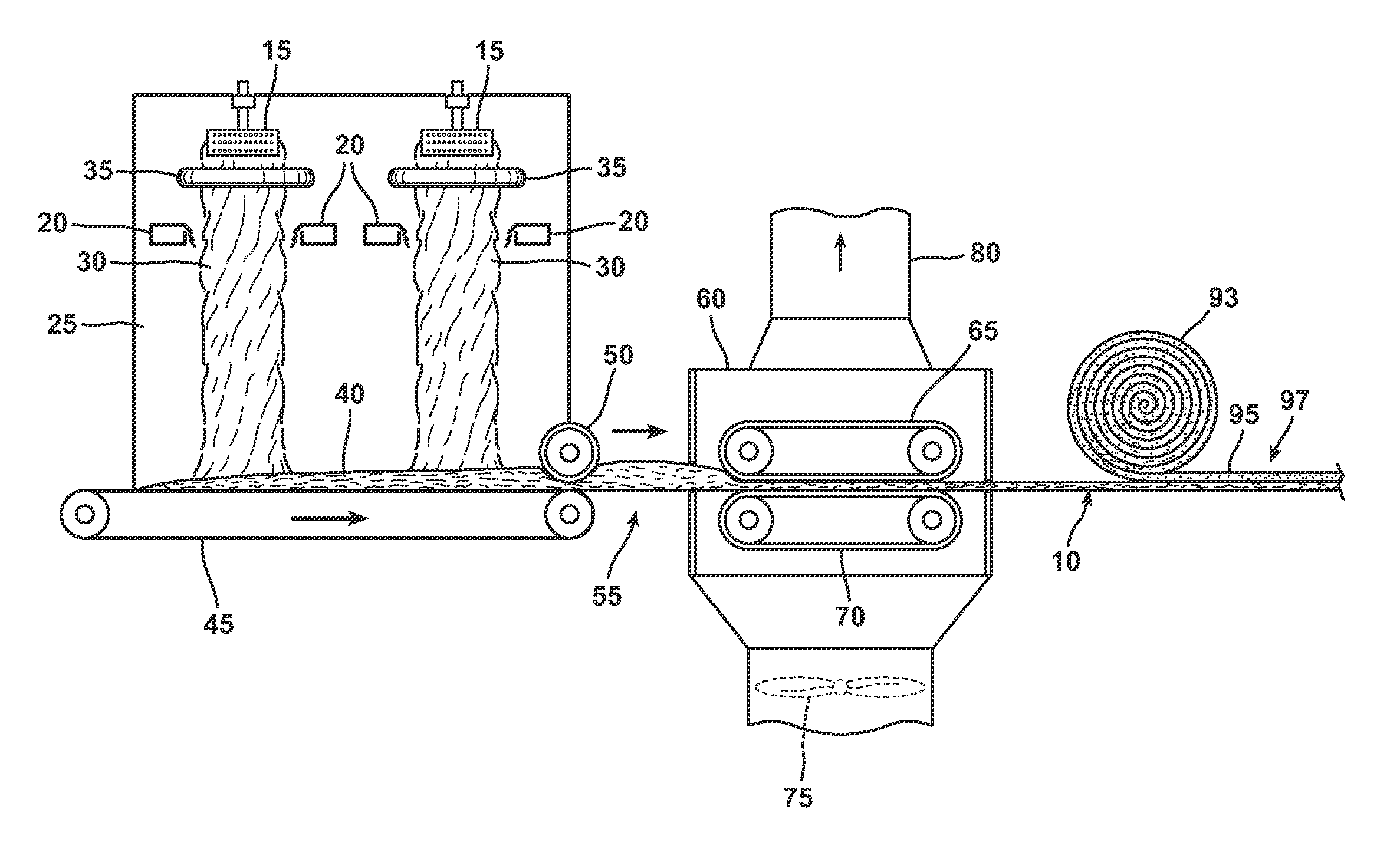
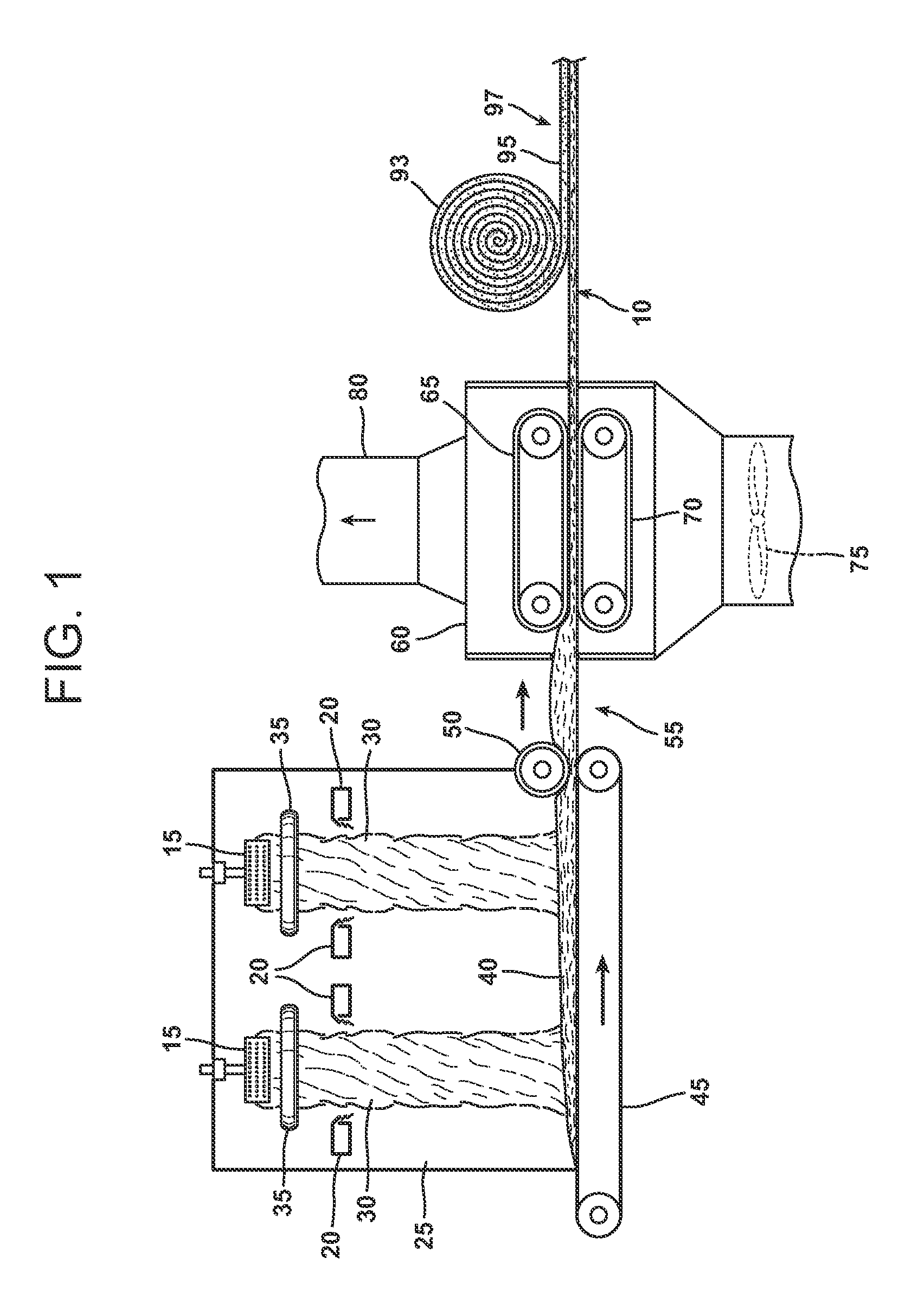
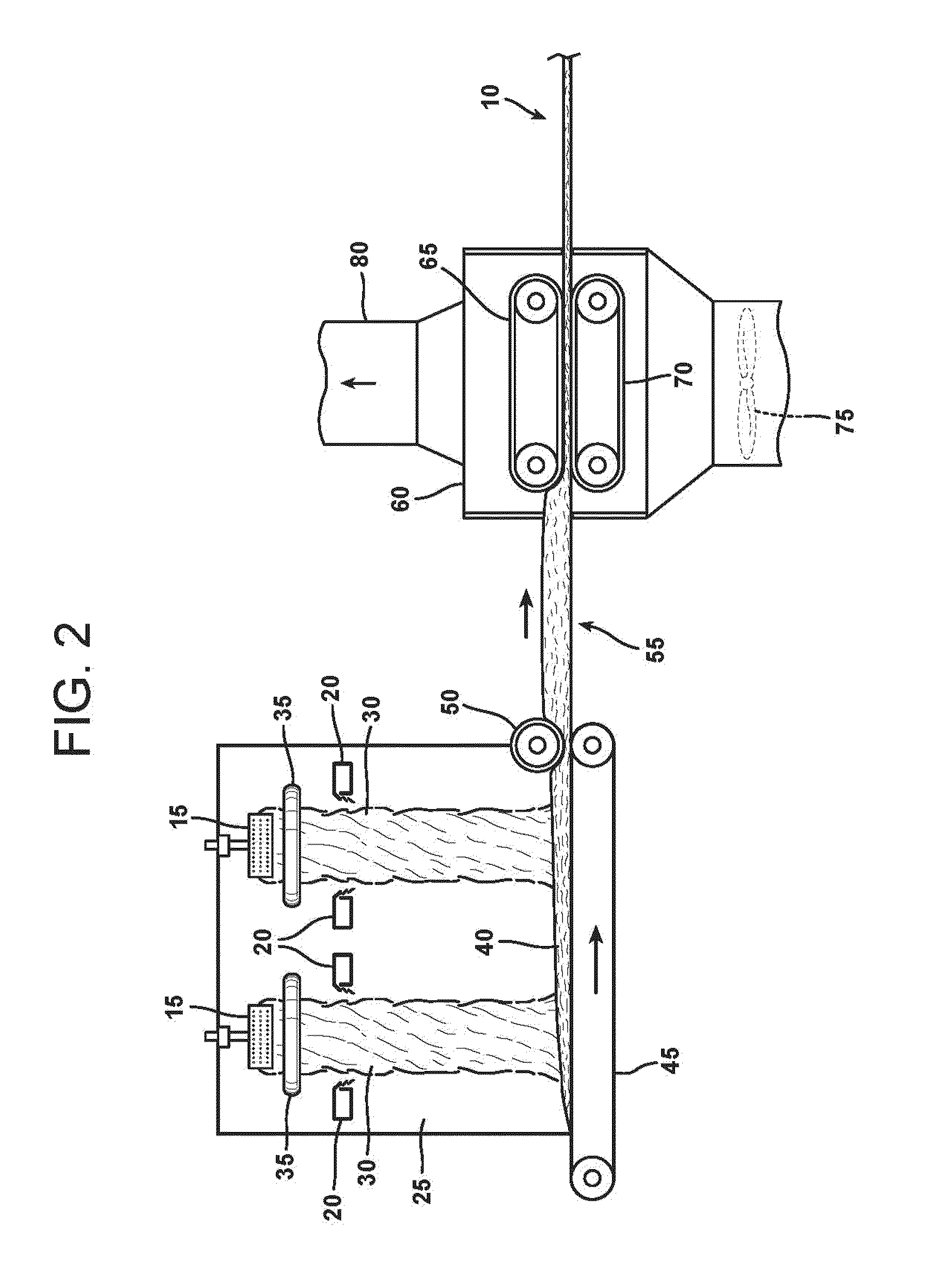
Bio-based binders for insulation and non-woven mats
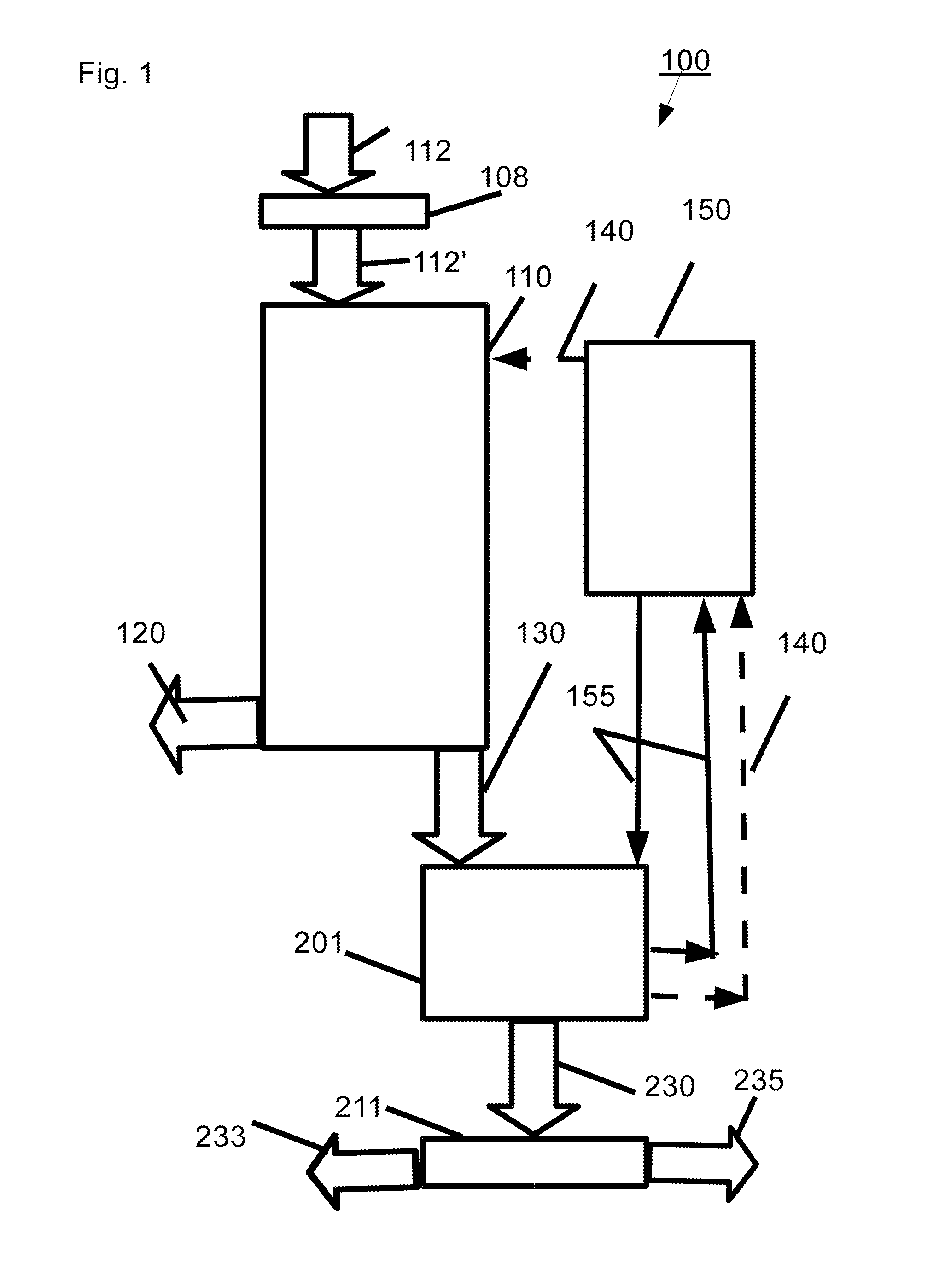
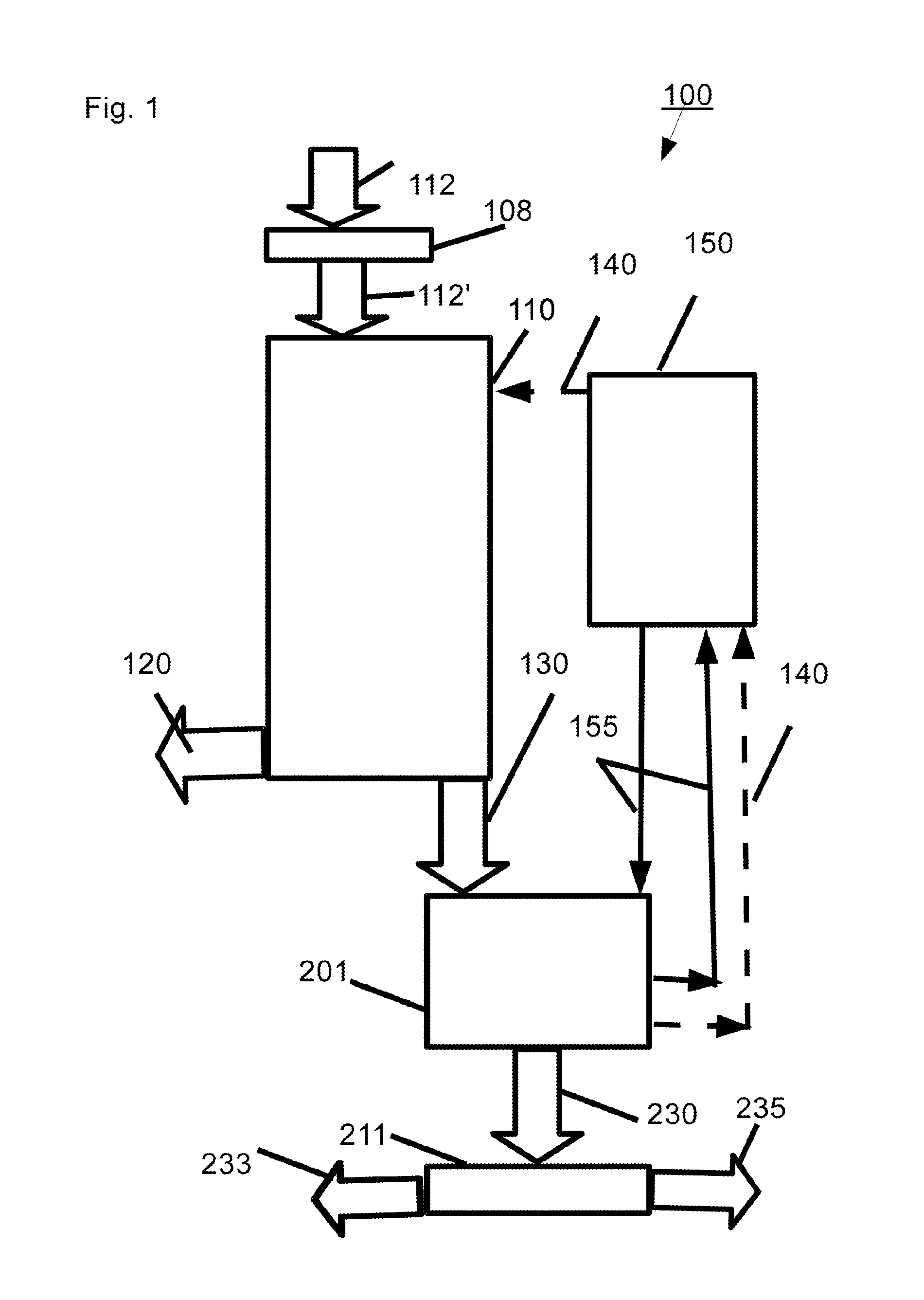
ActiveUS20110086567A1Readily availableLow costStarch dervative coatingsStarch adhesivesFiberProcedure Agents
An aqueous binder composition is provided that includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent. In exemplary embodiments, the carbohydrate-based binder composition may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, a crosslinking density enhancer, an extender, a moisture resistant agent, a dedusting oil, a colorant, a corrosion inhibitor, a surfactant, a pH adjuster, and combinations thereof. The carbohydrate may be natural in origin and derived from renewable resources. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the carbohydrate is a water-soluble polysaccharide such as dextrin or maltodextrin and the crosslinking agent is citric acid. Advantageously, the carbohydrates have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous insulation products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Insulative products having bio-based binders
InactiveUS20110223364A1Readily availableLow costStarch adhesivesStarch derivtive adhesivesFiberWater soluble polysaccharides
Fibrous insulation products have an aqueous binder composition that includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent. In exemplary embodiments, the carbohydrate-based binder composition may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, a crosslinking density enhancer, an extender, a moisture resistant agent, a dedusting oil, a colorant, a corrosion inhibitor, a surfactant, a pH adjuster, and combinations thereof. The carbohydrate may be natural in origin and derived from renewable resources. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the carbohydrate is a water-soluble polysaccharide such as dextrin or maltodextrin and the crosslinking agent is citric acid. Advantageously, the carbohydrates have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous insulation products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Method of preparing a granular delivery system
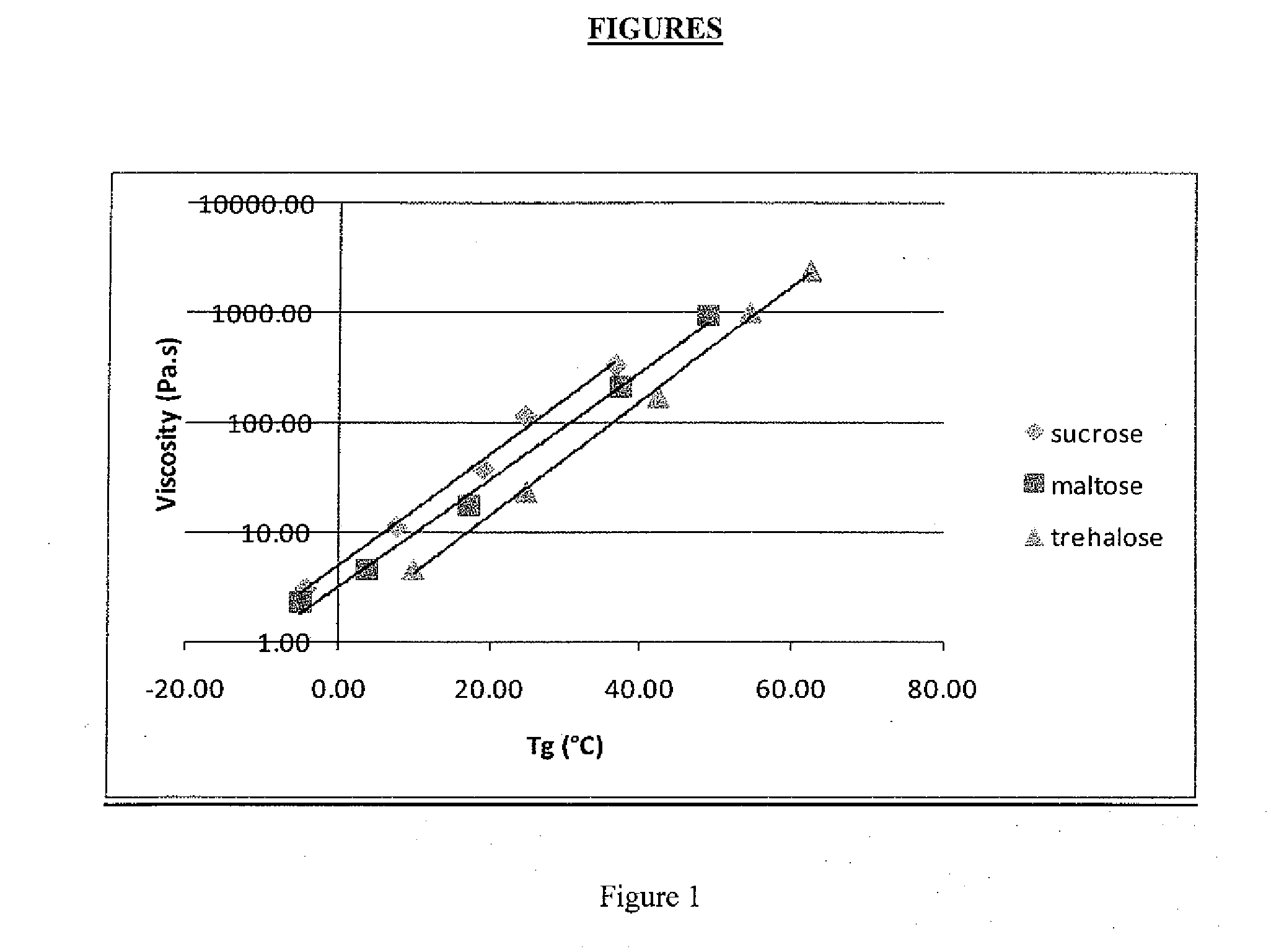
A method of preparing a granular delivery system by creating a melt emulsion having a continuous phase and a dispersed active, wherein the continuous phase includes trehalose and a low dextrose equivalent carbohydrate that is not a hydrogenated starch hydrolysate, forcing the melt emulsion through an die or orifice to form an extrudate, cooling and granulating the extrudate to form granules of the delivery system and optionally drying the granules. The melt extrusion provides excellent viscosity and Tg characteristics for the extrusion process.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Composition for the preparation of homemade frozen confections
InactiveUS20150140193A1Pleasant textureCaloric value easilyMilk preparationFrozen sweetsPolysaccharideChemistry
The present invention relates to a shelf-stable composition for the preparation of a frozen confection comprising: (i) a sweetening agent; (ii) a dairy fat; and (iii) one or more polysaccharide having a Dextrose Equivalent (DE) value of maximum 40; with the proviso that the composition does not comprise added emulsifiers or stabilizers. The present invention also relates to a method of preparing a frozen confection by mixing said composition with ice and an edible liquid and blend the mixture.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Extract powder of indigo plant, and its preparation and uses
InactiveUS20100034757A1Easy to handleScarcely hygroscopicAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsHydrolysateLiquid extract
The present invention has objects to provide an extract powder of indigo plant, which has a relatively low hygroscopicity, satisfactory fluidability, and improved storage stability; a process thereof; and a composition incorporated with the extract powder. The objects are solved by a process for producing an extract powder of indigo plant, which comprises incorporating a partial starch hydrolyzate with a dextrose equivalent of 10.2 or lower into one part by weight, on a dry solid basis, of an indigo plant extract contained in a liquid extract of indigo plant in an amount of not lower than 0.25 part by weight but not higher than 5 parts by weight, on a dry solid basis, and drying the resulting mixture; an extract powder of indigo plant prepared thereby; and a composition incorporated with the extract powder.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
Frozen confection and process for manufacturing such
InactiveUS20060141103A1Maximise palatabilityMaximise stabilityFood ingredient as antioxidantFrozen sweetsTotal energyChemistry
A frozen confection is provided having a total energy content of from 150 to 350 kcal (628 to 1460 kJ) per 100 g of frozen confection. The frozen confection comprises fat and carbohydrate. The carbohydrate comprises free sugars and the fat comprises saturated fatty acids. Each of the fat, carbohydrate, saturated fat and free sugars contribute specific amounts of energy to the frozen confection. The confection has an improved nutritional balance of dietary factors without loss of palatability. Also provided is a process suitable for manufacturing the frozen confection, the process comprising forming a premix comprising a glucose syrup having a dextrose equivalent in the range 20 to 40 DE and then freezing the premix thereby to form the frozen confection.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Composition for coating frozen confectionery and a process for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20180092378A1Reduce the amount requiredHigh viscosityFrozen sweetsCocoaGlucose-Fructose SyrupWater activity
The invention relates to a composition for coating a frozen confection, the composition comprising 10 to 50 wt. % dry glucose syrup with a DE (Dextrose Equivalent) below 40, and a total amount of mono and di-saccharides below 10 wt. %, and a water activity below 1.0 and 35 to 70 wt. % fat. The invention also relates to a process for making the composition.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Bio-based binders for insulation and non-woven mats
ActiveUS8864893B2Low costReadily availableStarch dervative coatingsLiquid surface applicatorsFiberWater soluble polysaccharides
An aqueous binder composition is provided that includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent. In exemplary embodiments, the carbohydrate-based binder composition may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, a crosslinking density enhancer, an extender, a moisture resistant agent, a dedusting oil, a colorant, a corrosion inhibitor, a surfactant, a pH adjuster, and combinations thereof. The carbohydrate may be natural in origin and derived from renewable resources. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the carbohydrate is a water-soluble polysaccharide such as dextrin or maltodextrin and the crosslinking agent is citric acid. Advantageously, the carbohydrates have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous insulation products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
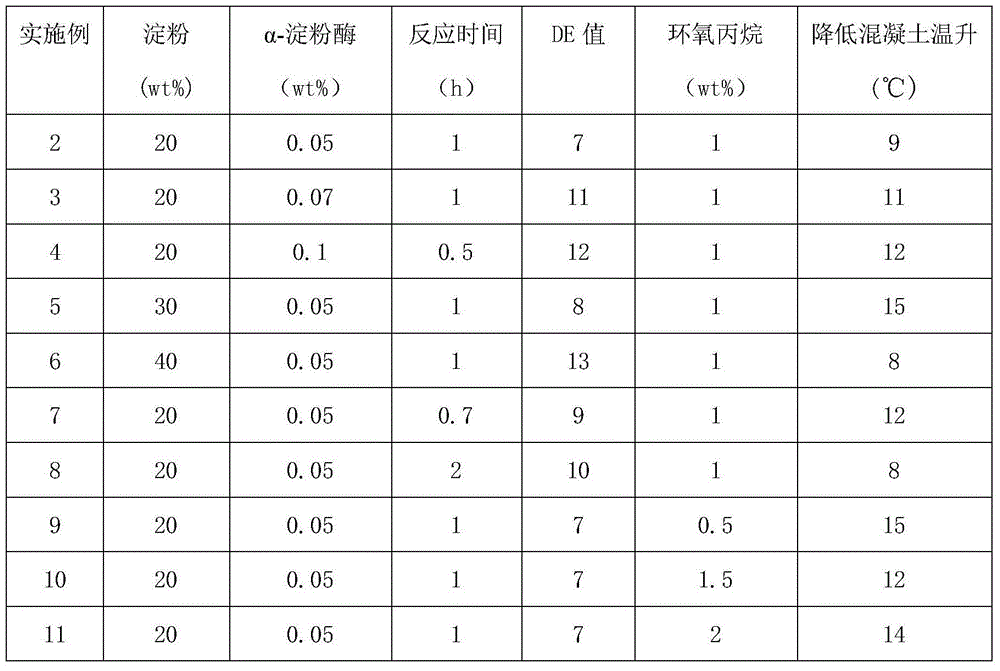
Concrete hydration heat inhibition material
ActiveCN104098288AControl dissolution rateIncreased heat of hydration performanceDextrose equivalentBuilding material
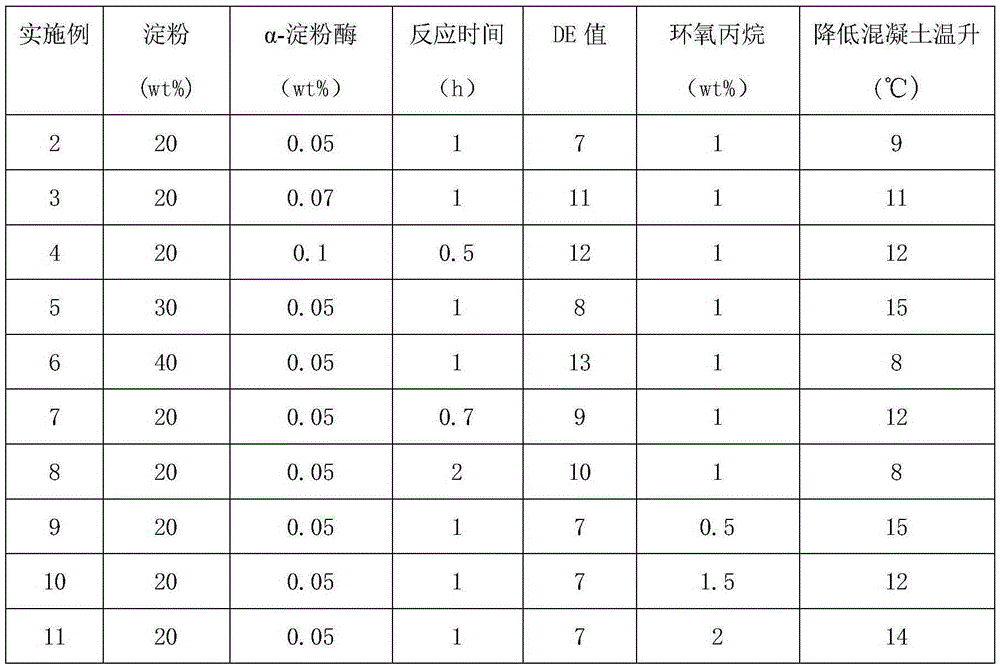
The invention belongs to the technical field of building material concrete admixtures, and particularly relates to a concrete hydration heat inhibition material and a preparation method thereof. The control of dextrin DE (dextrose equivalent) value can be realized by regulation of preparing parameters of the enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis process, and by combination with different degrees of epoxypropane modification, the concrete hydration heat inhibition material is prepared. The prepared concrete hydration heat inhibition material has the comprehensive advantages of simple operation and green environmental protection, can effectively regulate and control the hydration process of cement, reduces the concrete cracking problem caused by larger inside and outside temperature difference the cause, and improves the concrete durability.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS
Sugar compositions
Owner:VIRIDA
Binder compositions with polyvalent phosphorus crosslinking agents
ActiveUS20130023174A1Readily availableLow costStarch dervative coatingsStarch adhesivesFiberProcedure Agents
An fibrous insulation product is provided that includes a binder comprising a polyol and a phosphorus crosslinking agent derived from a phosphonic or phosphoric acid, salt, ester or anhydride to form crosslinked phosphodiester linkages. The polyol is polyvalent, but may be monomeric or preferably polymeric; and may be synthetic or natural in origin. Carbohydrate polysaccharides are exemplary polyols, including water-soluble polysaccharides such as dextrin, maltodextrin, starch, modified starch, etc. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In exemplary embodiments, the binder may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, and other additives. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of residential and commercial insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
High gloss film coating and stable solution therefor
A coating composition for use in coating foods, confections, nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals is comprised of shellac in aqueous solution, a hydrolyzed starch product having a dextrose equivalent of 10 or greater and an effective amount of a plasticizer. The coating composition provides a surprisingly high gloss coating. The edible film coating composition solution may be stabilized by adding an effective amount of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid salt wherein the solution may remain stable for at least three months. The ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid salt may include disodium, trisodium and tetrasodium salts of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid. Preferably, the concentration of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid is about 0.5% to 2% of the solution.
Owner:EMERSON RESOURCES
Method of preparing sweetener agglomerates and agglomerates prepared by the method
InactiveUS20050226983A1Low bulk densityLower requirementSugar food ingredientsFood shapingAdditive ingredientSweetness
A sweetener is provided which is an agglomerate of an intense sweetener and a carrier such the sweetener has a bulk density from 0.18 to 0.50 g. / cc. The sweetener fills a readily recognizable package while using a smaller amount of carrier and having the same amount of sweetness. The sweetener is less hygroscopic than if the intense sweetener and carrier were merely mixed. The sweetener does not cake together. The sweetener may contain, for example, 35 parts of soluble aspartame, 40 parts of maltodextrin having 10 Dextrose Equivalent (DE), and 925 parts of dextrose, where the aspartame, maltodextrin and dextrose are agglomerated. The agglomeration technique may be to introduce the ingredients and spray water to control the particle size to affect uniform free flowing powder. The agglomeration technique may also be a conveyor type steam agglomerator.
Owner:CUMBERLAND PACKING
Insulative products having bio-based binders
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC +1
Sugar compositions
A sugar composition comprising at least 40% dissolved solids in an aqueous solution having a viscosity at least 10% lower than a 42 DE (Dextrose Equivalents) reference solution with a same dissolved solids concentration at a given temperature. Another sugar composition comprising at least 30% glucose relative to total sugars, at least 10% mannose relative to total sugars, at least 5% xylose relative to total sugars, and less than 0.25% ash. Another sugar composition comprising at least 30% glucose relative to total sugars at least 10% mannose relative to total sugars, at least 5% xylose relative to total sugars, and at least 2% total furfurals.
Owner:VIRDIA
Sugar compositions
Owner:VIRDIA
Dosage form having a saccharide matrix
InactiveUS8012505B2High mechanical strengthDisperse fastPowder deliveryAllergen ingredientsPharmacologyDextrose equivalent
The present invention provides a non-compressed fast-dispersing solid dosage form suitable for oromucosal administration of a pharmaceutically active substance comprising(a) a first matrix forming agent in the form of maltodextrin having a dextrose equivalent (DE) of between 1 and 20,(b) a second matrix forming agent in the form of sorbitol, and(c) the active substance.
Owner:ALK ABELLO SA
Method for treating starchy raw material and method for preparing citric acid
InactiveCN102321704ALow DE valueGood saccharification effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationEmulsionSlurry
The invention relates to a method for treating a starchy raw material and a method for preparing citric acid. The method for treating the starchy raw material comprises the following steps of: mixing powder of the starchy raw material and water to obtain farinaceous size, and mixing the farinaceous size and first part amylase to obtain a mixture; performing primary injection on the mixture by using first steam at the temperature of between 80 and 100 DEG C to obtain primary emulsion, and performing secondary injection on the primary emulsion by using second steam at the temperature of between120 and 150 DEG C to obtain secondary emulsion; performing flash evaporation and reducing the temperature; and mixing a product obtained through flash evaporation and temperature reduction and secondpart amylase, and performing enzymolysis. By the method, a dextrose equivalent (DE) value can be reduced, and the fermentation period of the citric acid can be shortened.
Owner:COFCO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Systems and methods for producing a sugar stream
ActiveUS9777303B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberAlcohol production
An improved dry grind system and method for producing a sugar stream from grains or similar carbohydrate sources and / or residues, such as for biofuel production. In particular, a sugar / carbohydrate stream, which includes a desired Dextrose Equivalent (DE) where DE describes the degree of conversion of starch to dextrose (aka glucose) and / or has had removed therefrom an undesirable amount of unfermentable components, can be produced after saccharification and prior to fermentation (or other sugar conversion process), with such sugar stream being available for biofuel production, e.g., alcohol production, or other processes. In addition, the systems and methods also can involve the removal of certain grain components, e.g., corn kernel components, including protein, oil and / or fiber, prior to fermentation or other conversion systems. In other words, sugar stream production and / or grain component separation occurs on the front end of the system and method.
Owner:FLUID QUIP TECH LLC
Resistant malt dextrin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the functional food field and in particular relates to resistant malt dextrin and a preparation method thereof. The resistant malt dextrin disclosed by the invention comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 24%-40% of (alpha-1),6-glucosidic bond, 3%-6% of (alpha-1),2-glucosidic bond, 5%-10% of (alpha-1),3-glucosidic bond, and 44%-68% of (alpha-1),4-glucosidic bond. The preparation method of the resistant malt dextrin comprises the following steps: (1), preparing roasted dextrin by roasting starch, and preparing a roasted dextrin aqueous solution; (2), adjusting the pH value of the roasted dextrin aqueous solution to 7.0-8.0, and adding alpha-amylase for carrying out hydrolysis; (3), inactivating the alpha-amylase when the DE (Dextrose Equivalent) value of the roasted dextrin aqueous solution reaches 10-20, and filtering to obtain a hydrolysis intermediate product; and (4), hydrolyzing the hydrolysis intermediate product by starch branching enzyme to prepare the resistant malt dextrin. The resistant malt dextrin disclosed by the invention has an obvious effect in lowering blood sugar, and has obvious advantages in comparison with the similar dietary fiber products.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Spherical particle, and food suspensions and consumable masses having spherical particles
Spherical particles, agglomerates of spherical particles, methods of producing spherical particles, food suspensions and consumable masses which have spherical particles, and food products which contain a food suspension and / or a consumable mass are disclosed. The particles contain a matrix material composed of an amorphously solidified biopolymer, preferably having a dextrose equivalent greater than 20 and having an equilibrium water content preferably less than 10 wt %. The solid particles and / or liquid and / or gas volumes are embedded in the matrix material. The food suspension contains a substantially homogeneous carrier material in which spherical particles are embedded. A consumable mass comprises an agglomerate of particles where some of the particles are spherical particles. Use of embedded cocoa particles reduces the roughness of the cocoa particles and a flow point white eliminating the need for emulsifiers. This allows up to a 50% reduction of the fat phase and production of a low-calorie chocolate product.
Owner:BUEHLER AG
Method of impoving taste of natural sweetener and composition thereof
InactiveUS20090324793A1Easy to manufactureSuitable for mass productionFood preparationCelsius DegreeEnzyme
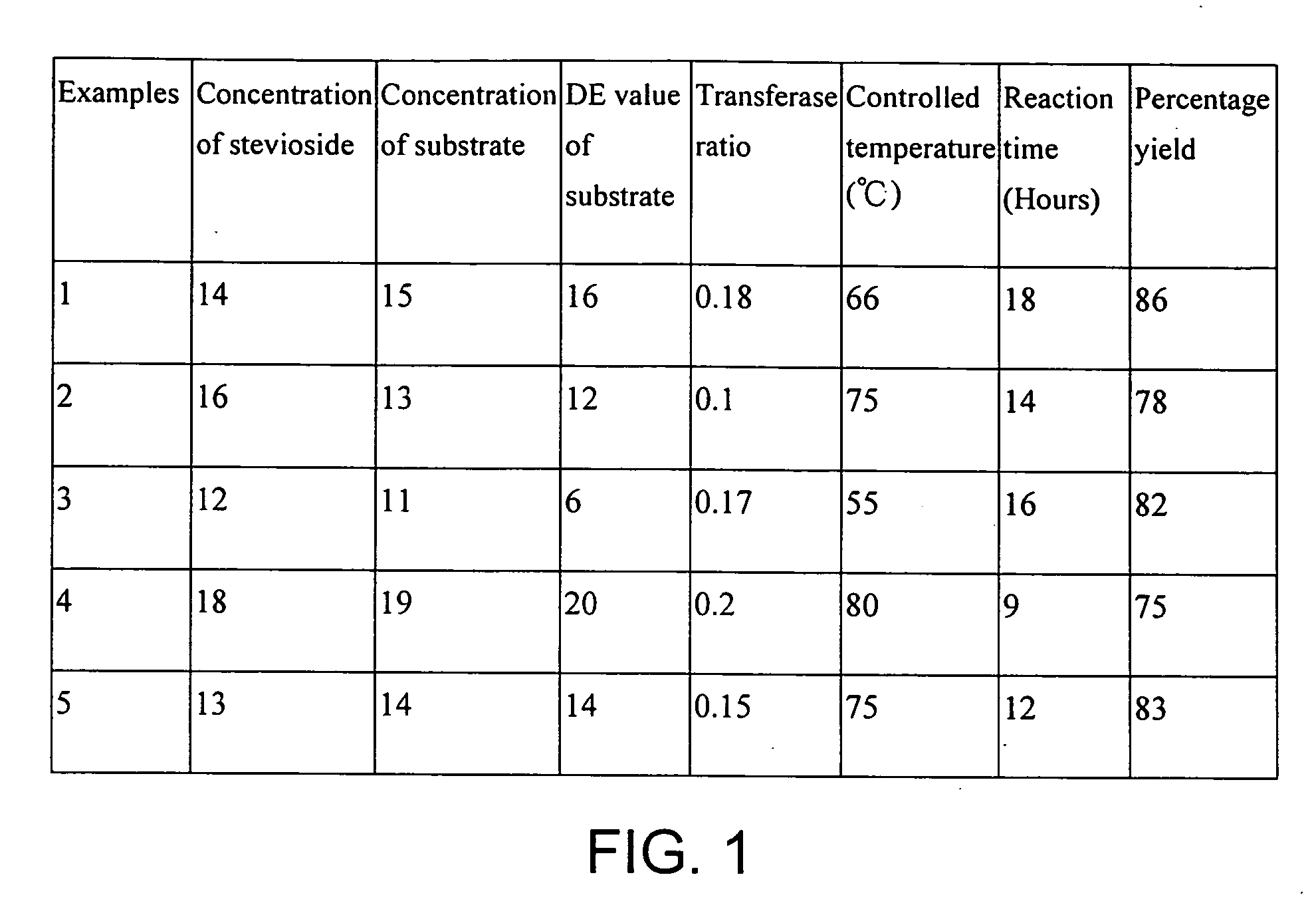
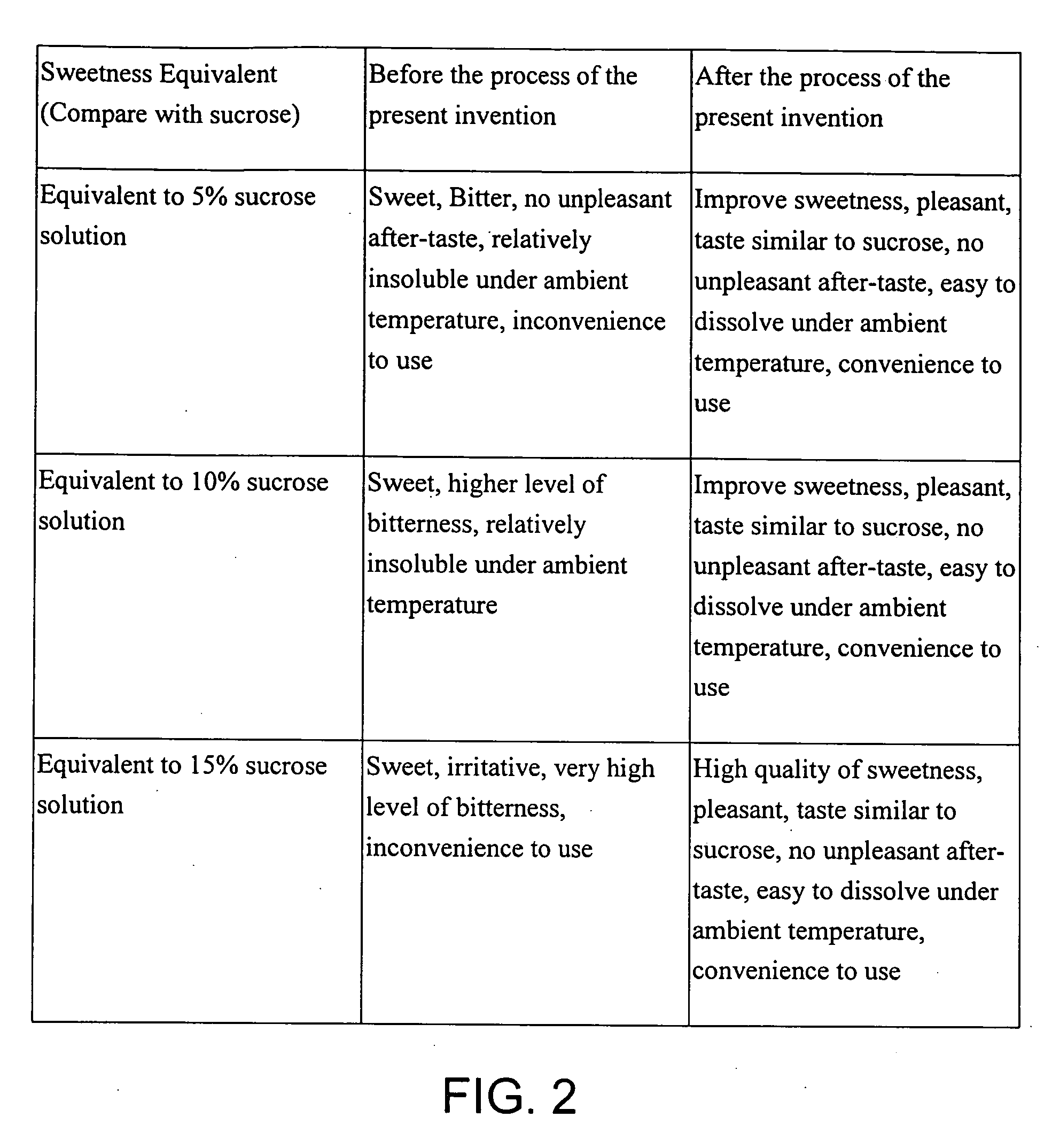
A natural sweetener composition includes a predetermined amount of stevioside, a predetermined amount of dextrin, having a dextrose equivalent value, and a predetermined amount of enzyme, wherein the stevioside, the dextrin and the enzyme are chemically mixed together under a temperature in a range of approximately 40 Celsius degrees to 80 Celsius degrees and for a period of time of approximately 3 hours to 30 hours to form a solution containing a predetermined amount of alpha-glycosyl stevioside, with a conversion rate from the stevioside to the alpha-glycosyl stevioside in a range between approximately 60% to 86%.
Owner:DIAMOND NUTRICENTICAL
A kind of preparation method of rice starch-based fat substitute
The invention relates to preparation of a rice starch-based fat replacer, in particular to a method for preparing high-purity low-DE (dextrose equivalent) value malto dextrin by utilizing rice. The method comprises the following concrete steps of: smashing and sieving rice, soaking and extracting with alkali liquor; then centrifuging to remove supernate and surface layer and lowermost yellow residue, and drying for 40-50 hours to obtain rice starch; mixing rice starch feed liquor with water at the mass percent ratio of 1:(4-6); then adding alpha amylase to ensure the alpha amylase to account for 0.5-1.5% of size in mass fraction, carrying out enzymolysis for 10-15 minutes at the temperature of 85-95 DEG C, centrifuging for 8-12 minutes, freezing the supernate, and carrying out freeze drying treatment after the supernate is completely frozen, thus malto dextin is obtained. By adopting the method in the invention, the high-purity low-DE value malto dextin fat replacer is prepared, and preparation process of the malto dextin is changed while basic physicochemical properties of the malto dextin are not changed, thus the aims of energy conservation and consumption reduction are achieved during preparation of the malto dextin.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Production process of instant maize germ powder
The invention relates to a production process of instant maize germ powder. The instant maize germ powder is prepared through raw material preprocessing, beating, enzymolysis, enzyme inactivation, colloid milling, sterilization, high-pressure homogenization and spray drying by taking maize germ meal as a raw material; the enzymolysis is carried out by adding medium-temperature alpha-amylase accounting for 0.2%-0.4% of the dry weight of the maize germ meal, and the starch hydrolysis DE value (Dextrose Equivalent value) of maize germ meal slurry which is subjected to enzymolysis is controlled between 18% and 22%; the prepared homogenized maize germ meal slurry achieves the easiness for the spray drying, and a finished product does not absorb moisture, so that the dissolution stability of the maize germ powder is enhanced, the deposition has small possibility of appearing in the dissolving process, and the maize germ powder is not caked and agglomerated when being dissolved in water; and the additional value of maize germ meal is increased. The instant maize germ powder obtained through the method disclosed by the invention achieves the protein content more than 23%, is in a faint yellow color and is fast in dissolution; and the dissolved instant maize germ powder is uniform in state and achieves the product dissolution time less than 27 seconds without any unpleasant odor.
Owner:鲁洲生物科技(辽宁)有限公司 +2
Food compositions with high solids content, a method for its preparation as well as the use of carrageenans for gelling a food composition
InactiveUS6967037B1Less energyImprove processing efficiencyConfectionerySweetmeatsBiotechnologyCarrageenan
Food composition comprising soluble solids in the range of about 50% to about 90% by weight, at least 70% by weight thereof being a sweetening system comprising sucrose and non-sucrose sweeteners in a weight ratio of sucrose to non-sucrose sweeteners of 0:100 to 95:5, wherein the non-sucrose sweetener is of a DE (Dextrose Equivalent) of at least about 30, a carrageenan component in an amount sufficient to form a gel, and water to balance, and wherein the gelation temperature of the composition is <95° C. The food composition may be produced by a process comprising (a) dispersing carrageenan in a syrup of a non-sucrose sweetener at a temperature sufficient to disperse the carrageenan in the syrup while stirring, (b) adding water and heating the mixture to the boiling point thereof, (c) adjusting the soluble solids content to from about 50% to about 90% by weight, (d) depositing the mixture and (e) cooling the mixture to below the depositing temperature of the mixture. The food composition gels rapidly and forms a gel at temperatures of below 95° C. The food composition is especially confectionery products such as soft candies, marshmallows or glazings.
Owner:CP KELCO
Supervisory control method for producing trehalose by double-enzyme method
ActiveCN107446972AHigh yieldShort reaction timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationQuantitative modelTrehalose synthase
The invention discloses a supervisory control method for producing trehalose by a double-enzyme method. The supervisory control method comprises the following steps of firstly mounting a near-infrared real-time monitoring and control system; collecting starch liquefied liquid, measuring a DE (Dextrose Equivalent) value by using a Fehling's reagent method, collecting catalysis liquid, measuring a pH (potential of Hydrogen) value by using a pH meter, measuring the content of the trehalose by using high performance liquid chromatography, associating with a correspondingly collected near-infrared spectrum, establishing a quantitative model of changes of the DE value, the content of the trehalose and the pH value in a production process, and correcting; afterwards, quickly detecting the DE value, the content of the trehalose and the pH value in the production process by utilizing the established model, and stabilizing the DE value to be 8 to 20 and stabilizing the pH value to be in the range, in which the activity of malto-oligosaccharide based trehalose synthase-MTSase and malto-oligosaccharide based trehalose hydrolase-MTHase is optimal, by utilizing a control system. The method can be used for monitoring the DE value of starch liquid and the content of the trehalose in reaction liquid in real time and can also used for automatically controlling the change of the pH value and the content of the trehalose and the result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
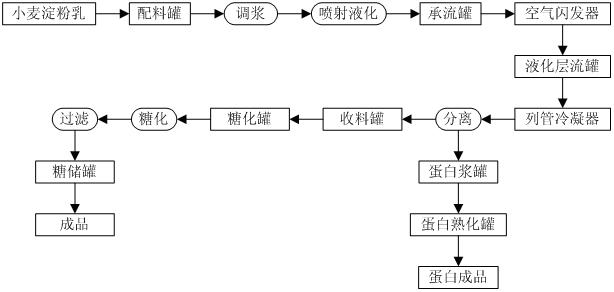
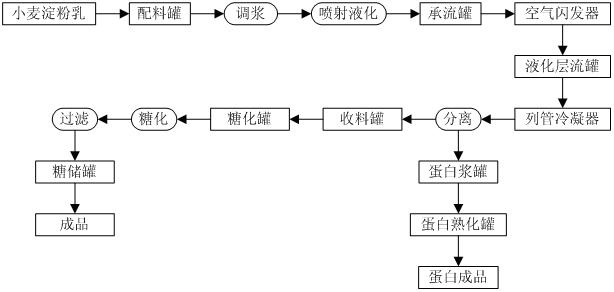
Biological sugaring process by using wheat starch
InactiveCN102220395ASolve the problem of many and high protein contentHigh DE valueFermentationFiltrationAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a biological sugaring process by using wheat starch, which comprises the following steps of: (1) size mixing: taking wheat starch milk, adding a sodium carbonate aqueous solution with a certain concentration for regulating pH, adding high-temperature resistant alpha-amylase, hemicellulase and xylanase, and uniformly stirring; (2) jetting and liquefaction: carrying out jetting and liquefaction on the wheat starch milk obtained in the step (1), carrying out flash evaporation and temperature reduction, maintaining temperature till completely liquefying, carrying out vacuum flash evaporation and temperature reduction, and separating; (3) saccharification: regulating the pH of emulsion obtained in the step (2), adding one of or a mixture of more than two of saccharifying enzyme, pentosanase and xylanase, as well as proteolytic enzyme, uniformly stirring, saccharifying, reducing temperature, adding hemicellulase, cellulase and lecithinase, stirring, saccharifying, rising temperature and inactivating enzyme; and (4) filtration. According to the biological sugaring process, the quality of the sugar solution is effectively improved; the conversion rate of the pulverized sugar reaches 106% to 107% (in DS (degree of substitution)); and the DE (dextrose equivalent) value can reach 95% to 98%.
Owner:北京坡华蒸发器技术有限公司
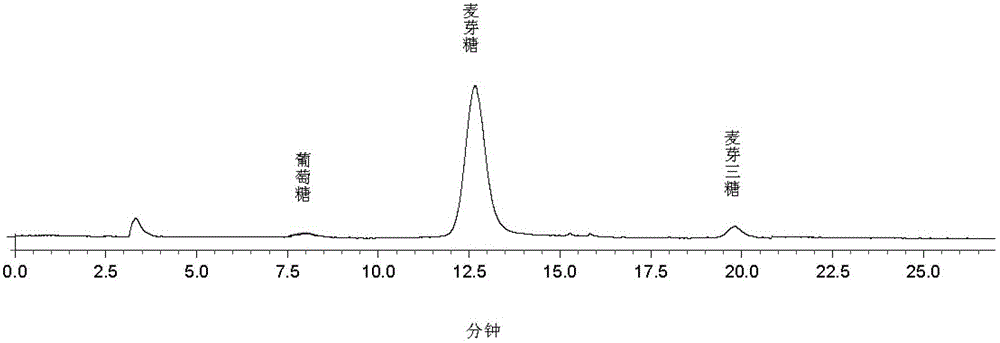
Method for manufacturing ultrahigh-content malt syrup by double-saccharification process
A method for manufacturing ultrahigh-content malt syrup by a double-saccharification process includes steps of liquefying starch by alpha- amylases to obtain starch hydrolysate with a DE (dextrose equivalent) value ranging from 10% to 12%, saccharifying the starch hydrolysate by beta-amylases and pullulanase under conditions that the temperature is 60 DEG C and the pH (potential of hydrogen) ranges from 5.2 to 5.4, and filtering out partial malt syrup by a nano-filtration membrane when the malt sugar content reaches 70%; and secondarily saccharifying saccharified liquid retained under the filtering action of the membrane to obtain malt syrup with the malt sugar content reaching 90%. The malt syrup is further used for producing products such as high-purity crystallized malt sugar, high-purity maltitol and high-purity trehalose. The method has the advantages that the ultrahigh-content malt syrup can be produced, and the starch utilization rate can reach 97%.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for preparing citric acid by fermentation
ActiveCN102533877ATroubleshoot compositingSolve the requestMicroorganism based processesFermentationSugarCitric acid fermentation
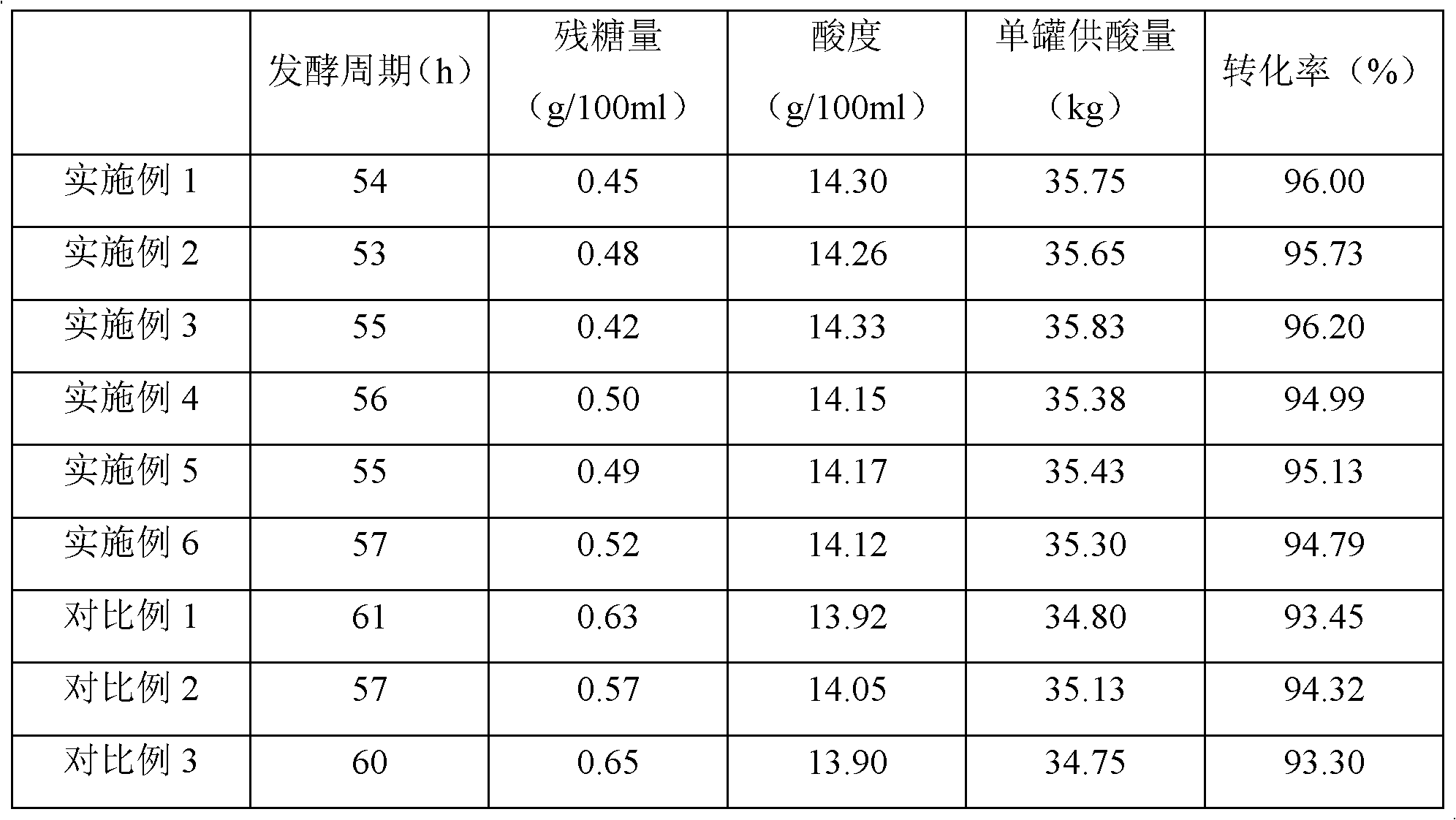
The invention discloses a method for preparing citric acid by fermentation, which comprises the following steps: under the conditions of generating citric acid, inoculating citric acid fermentation strain into fermentation media, and carrying out fermentation, thereby obtaining the fermentation liquid. The invention is characterized in that the method also comprises the step of adding saccharifying enzyme into the fermentation media 0-8 hours after inoculating the citric acid fermentation strain. The method disclosed by the invention enhances the saccharifying capacity in the fermentation process, solves the contradiction between the pH value requirements from citric acid synthesis and saccharification in the fermentation process, and avoids the adverse effect of high DE (dextrose equivalent) value on Aspergillus niger, so that the sugar solution in the fermentation media is saccharified more thoroughly, thereby lowering the residual sugar amount in the fermentation liquid, enhancing the end citric acid content and single-tank acid supply amount, increasing the conversion rate of sugar acid and shortening the fermentation period.
Owner:COFCO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A concrete hydration heat inhibiting material
ActiveCN104098288BAvoid heavy useSimple and fast operationEnvironmental resistanceTemperature difference
The invention belongs to the technical field of building material concrete admixtures, and particularly relates to a concrete hydration heat inhibition material and a preparation method thereof. The control of dextrin DE (dextrose equivalent) value can be realized by regulation of preparing parameters of the enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis process, and by combination with different degrees of epoxypropane modification, the concrete hydration heat inhibition material is prepared. The prepared concrete hydration heat inhibition material has the comprehensive advantages of simple operation and green environmental protection, can effectively regulate and control the hydration process of cement, reduces the concrete cracking problem caused by larger inside and outside temperature difference the cause, and improves the concrete durability.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com