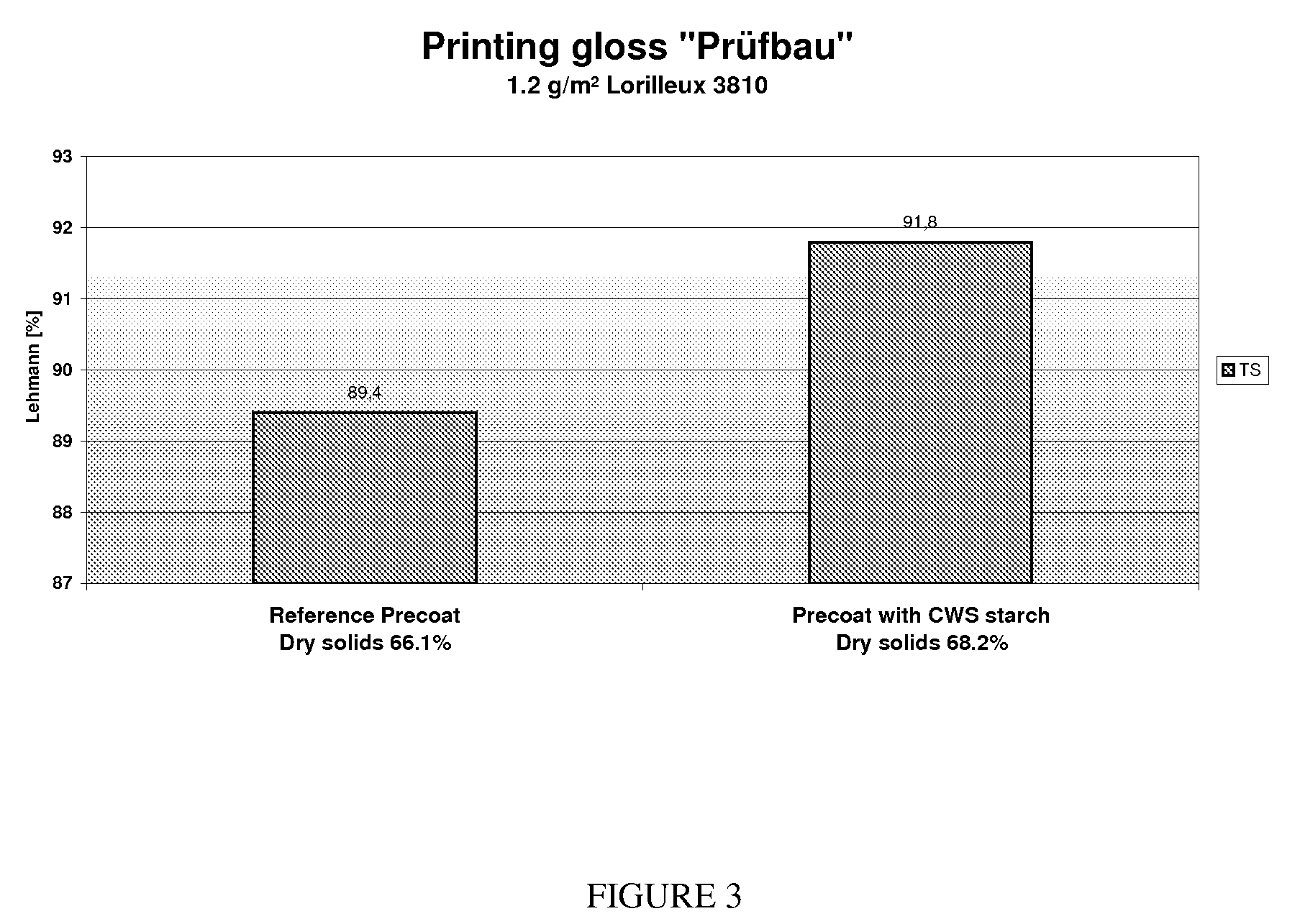
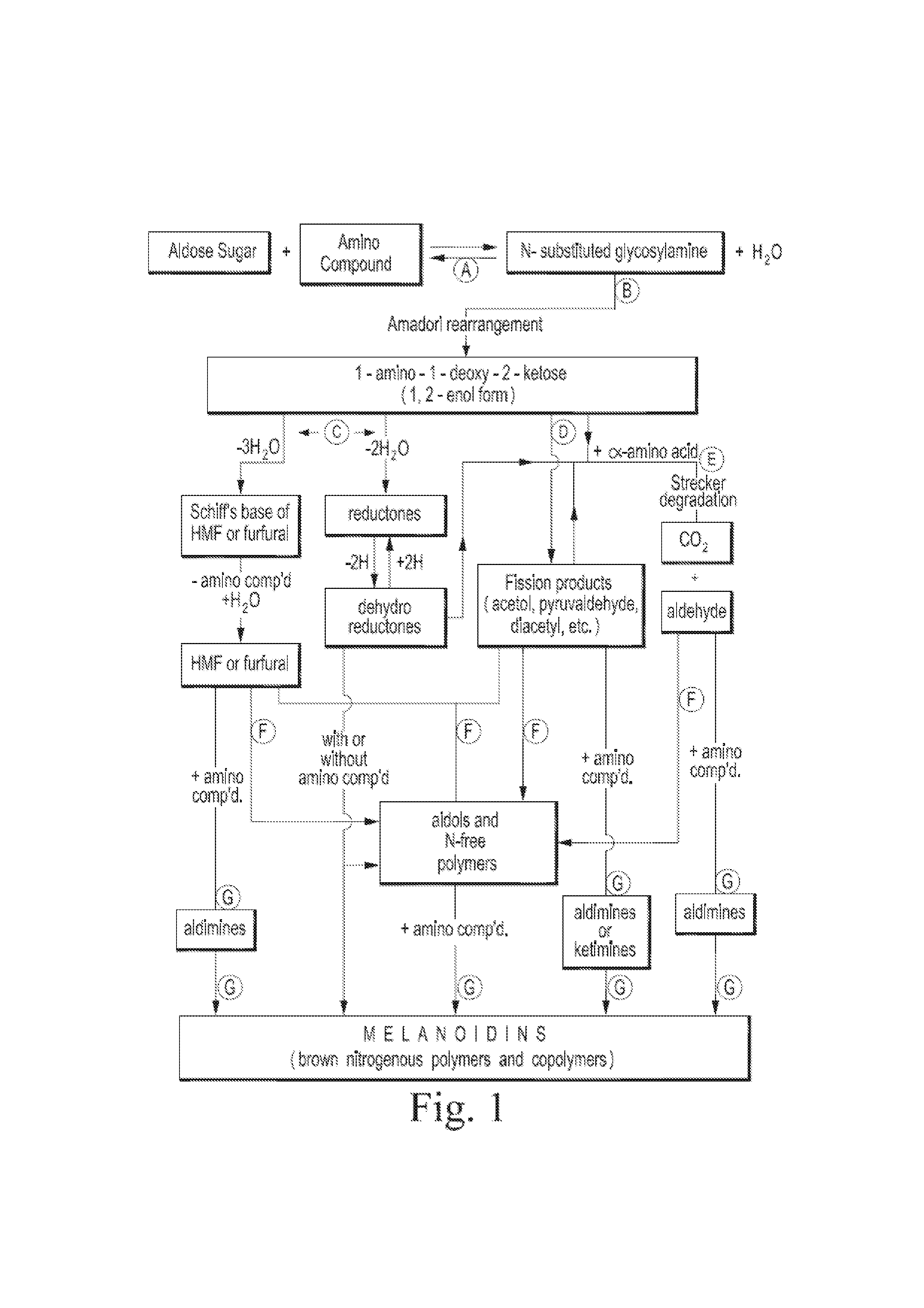
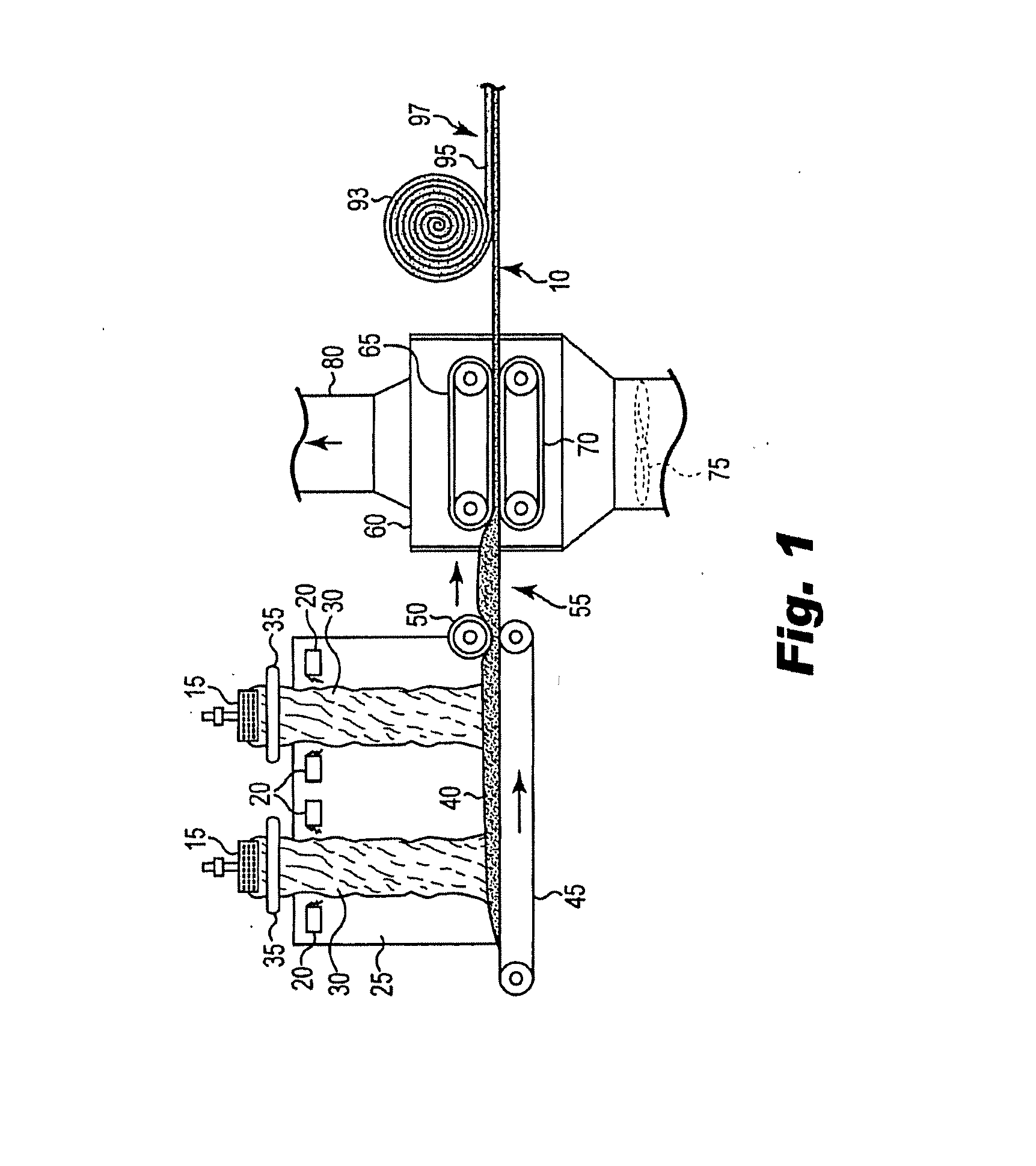
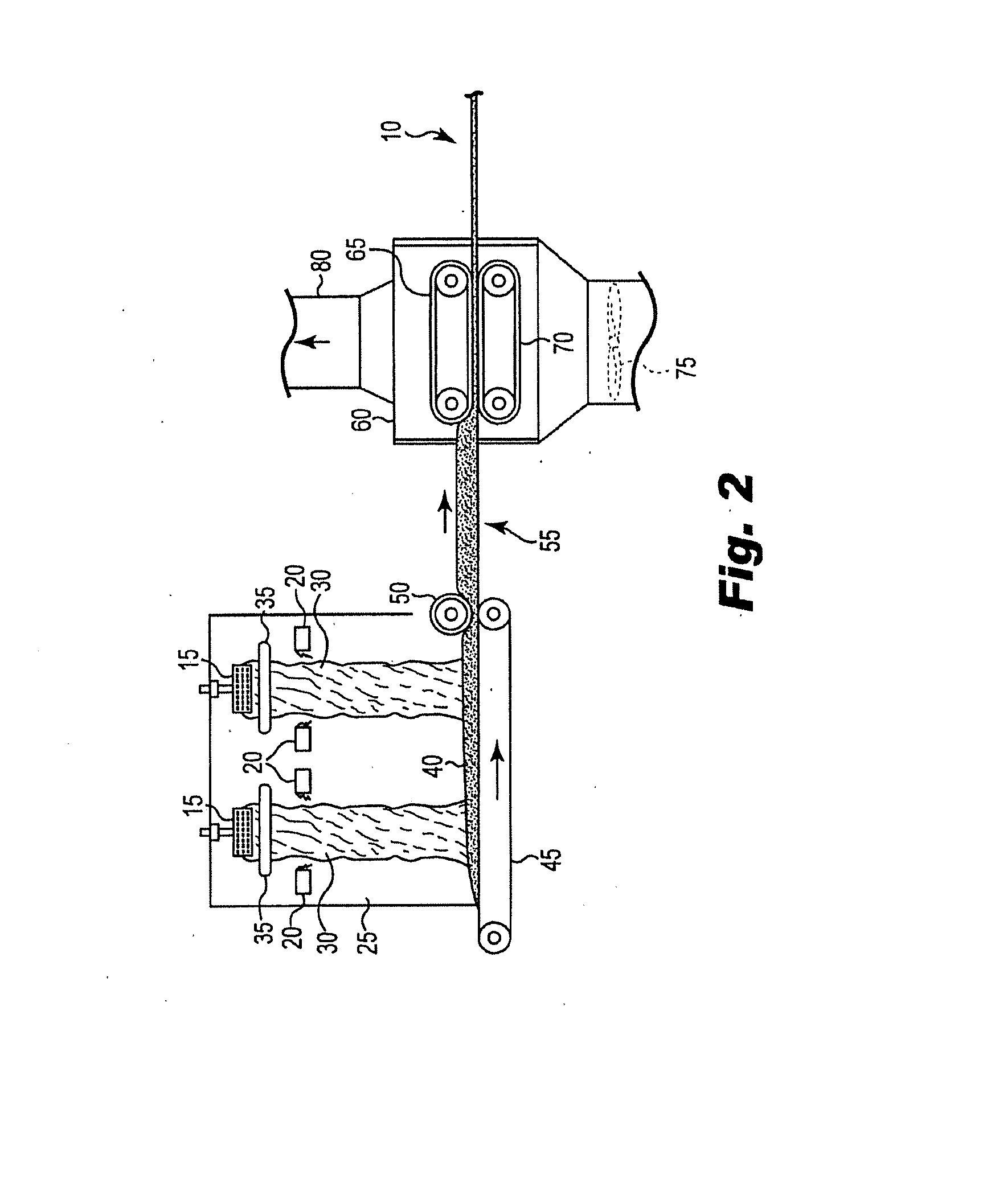
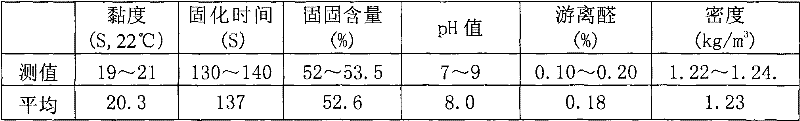
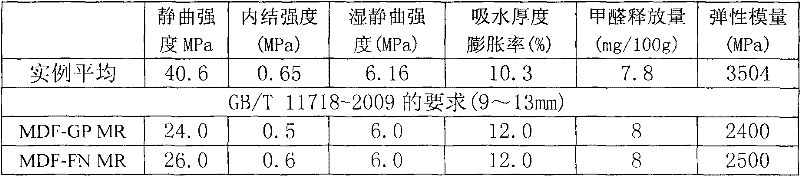
Patents
Literature
903results about "Starch derivtive adhesives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
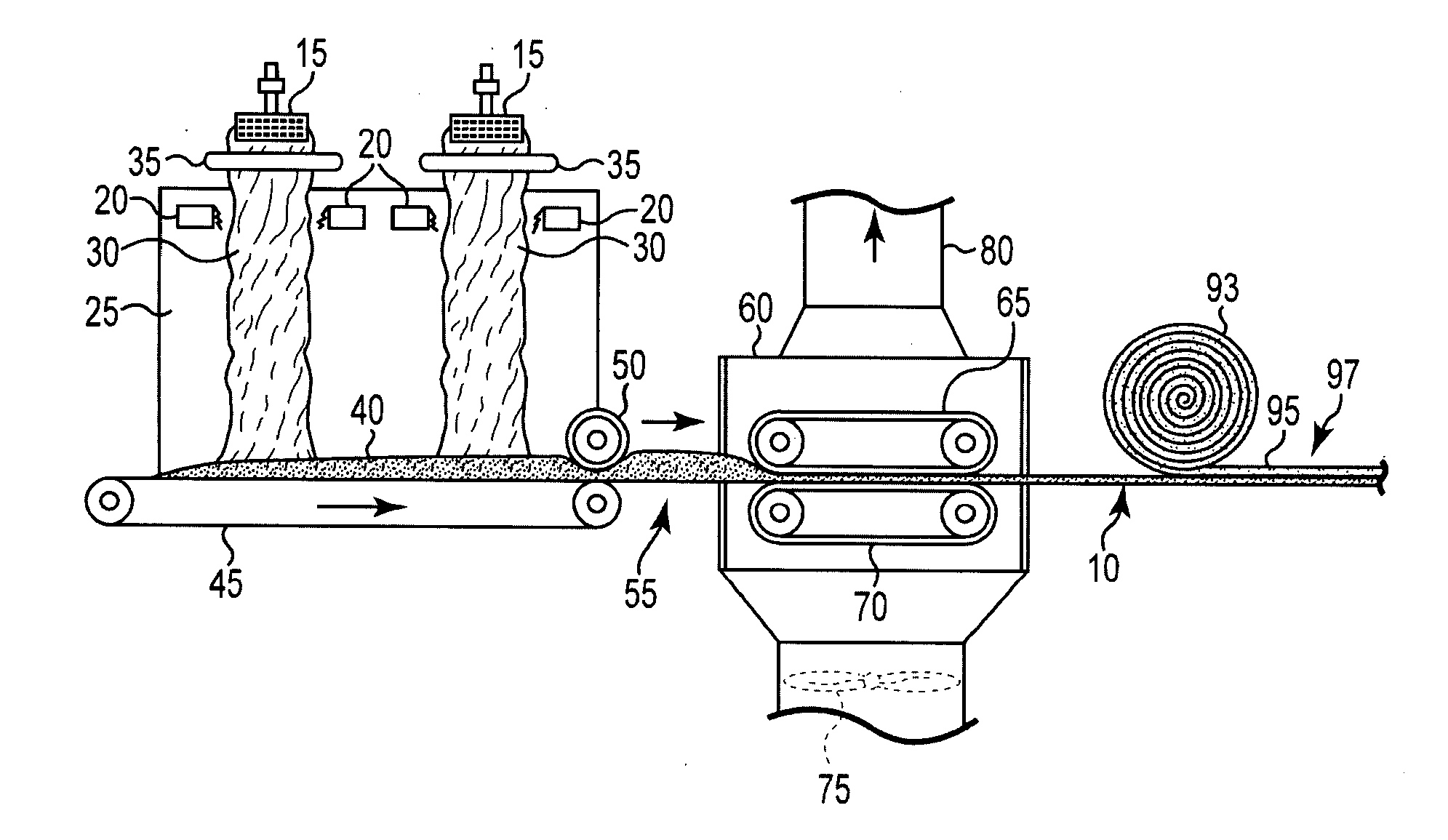
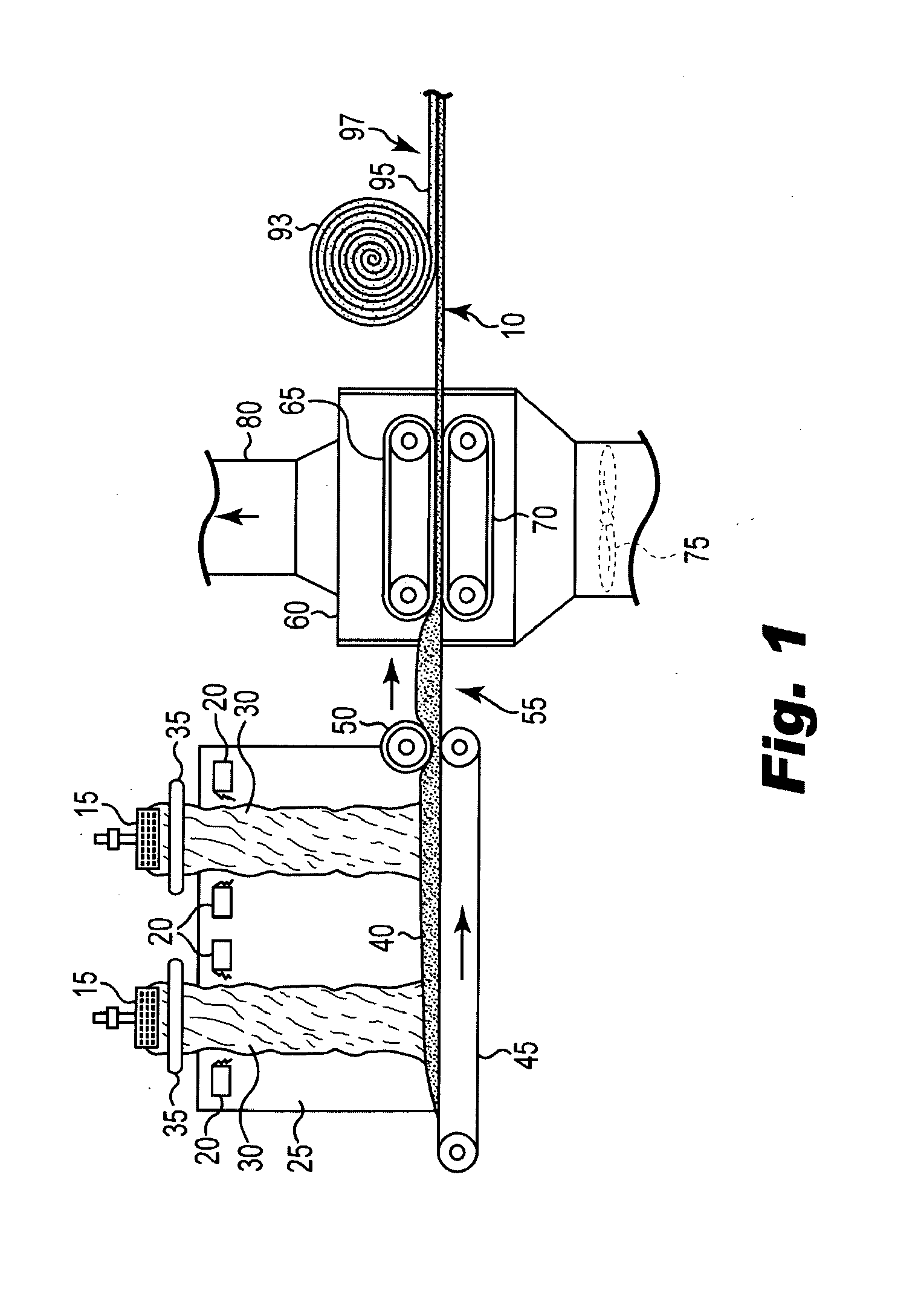
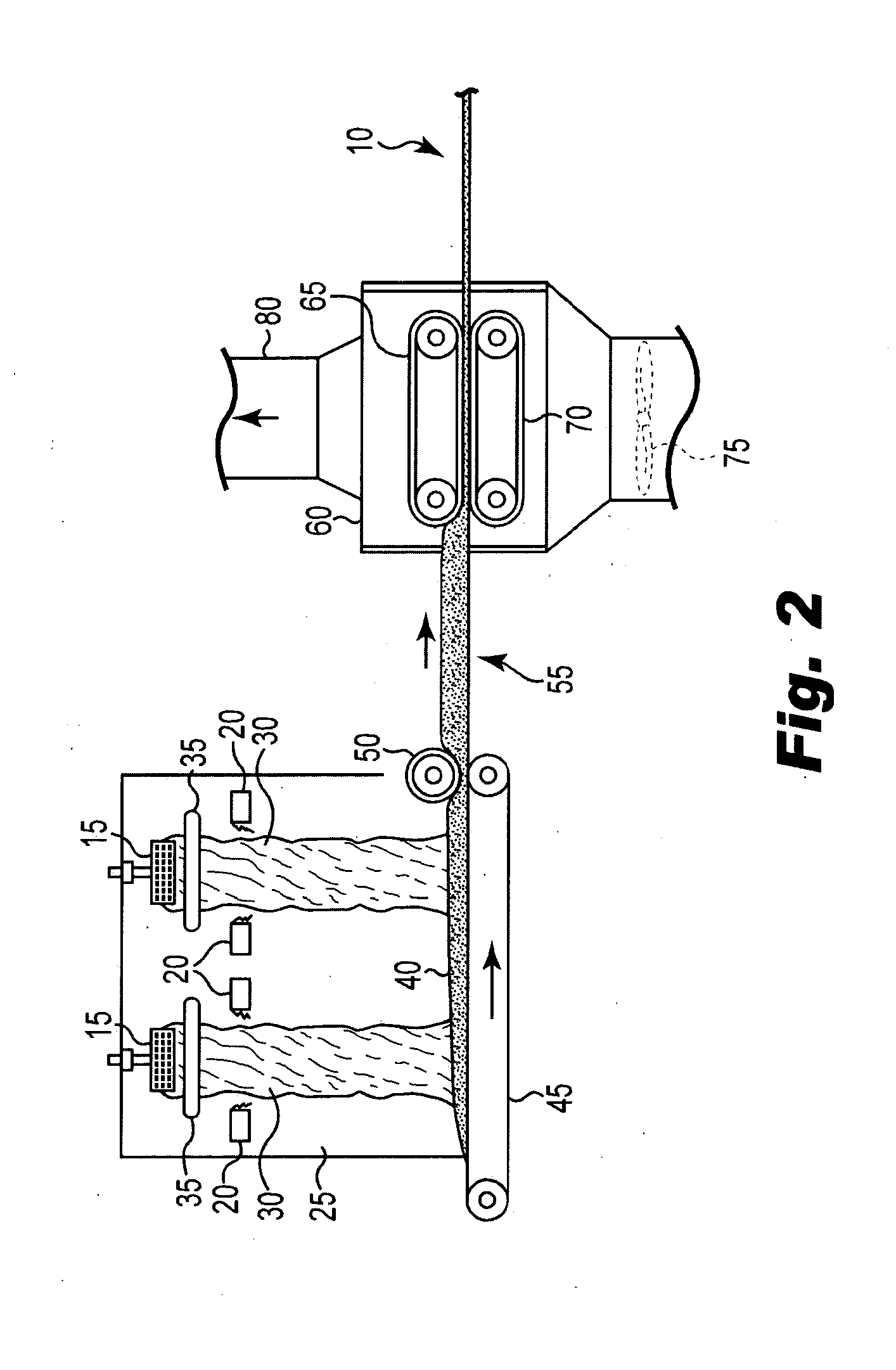
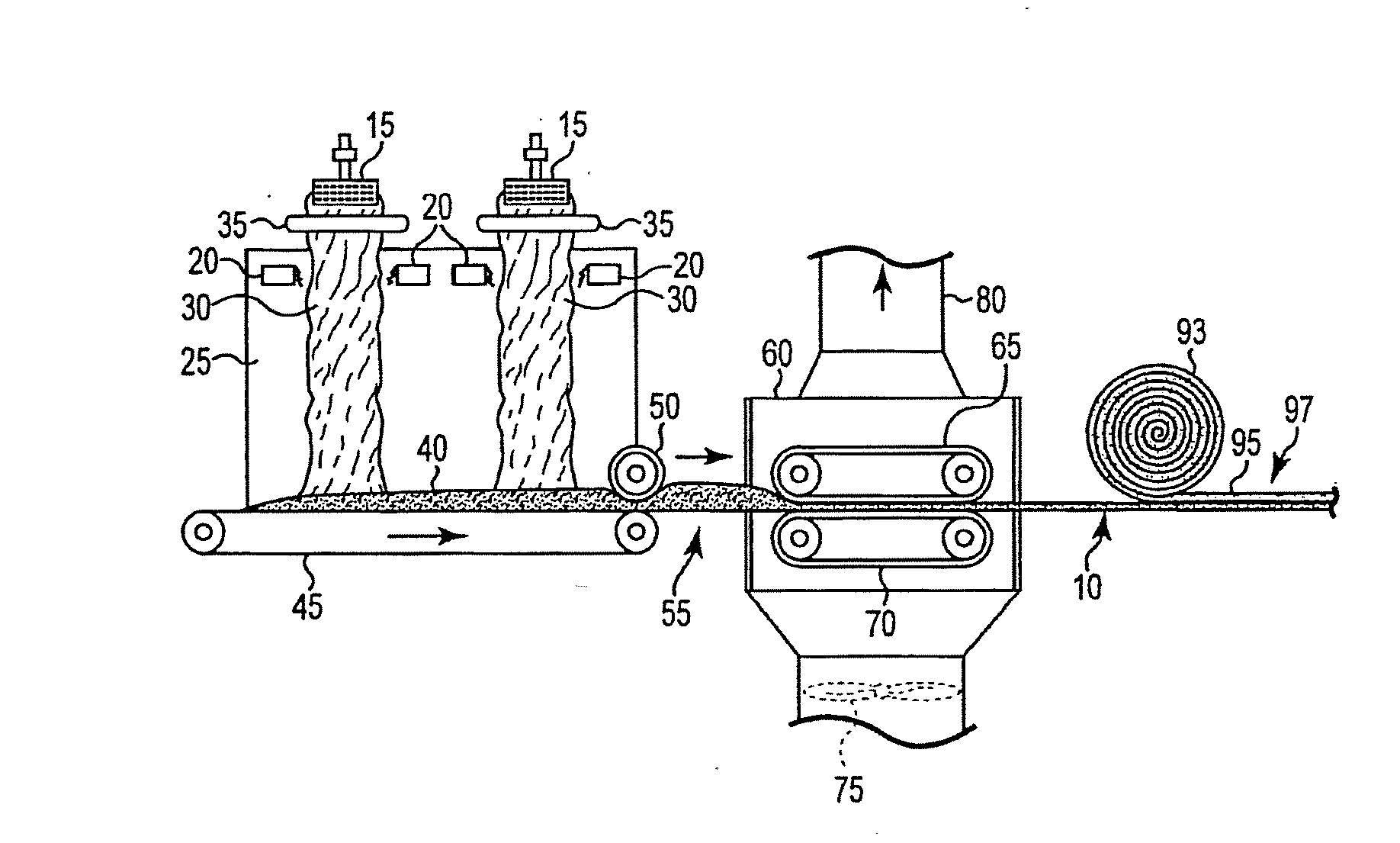
Bio-based binders for insulation and non-woven mats
ActiveUS20110086567A1Readily availableLow costStarch dervative coatingsStarch adhesivesFiberProcedure Agents
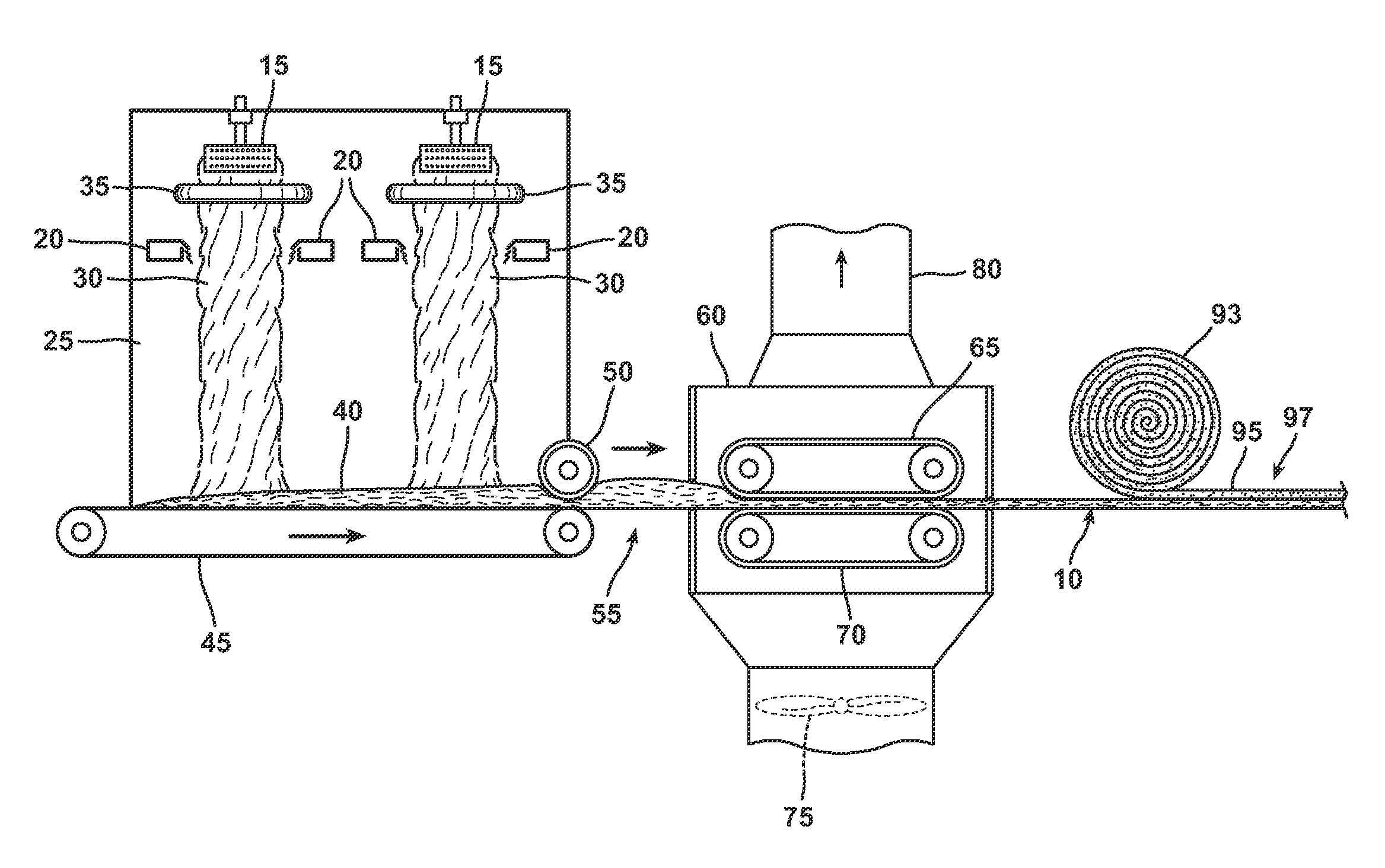
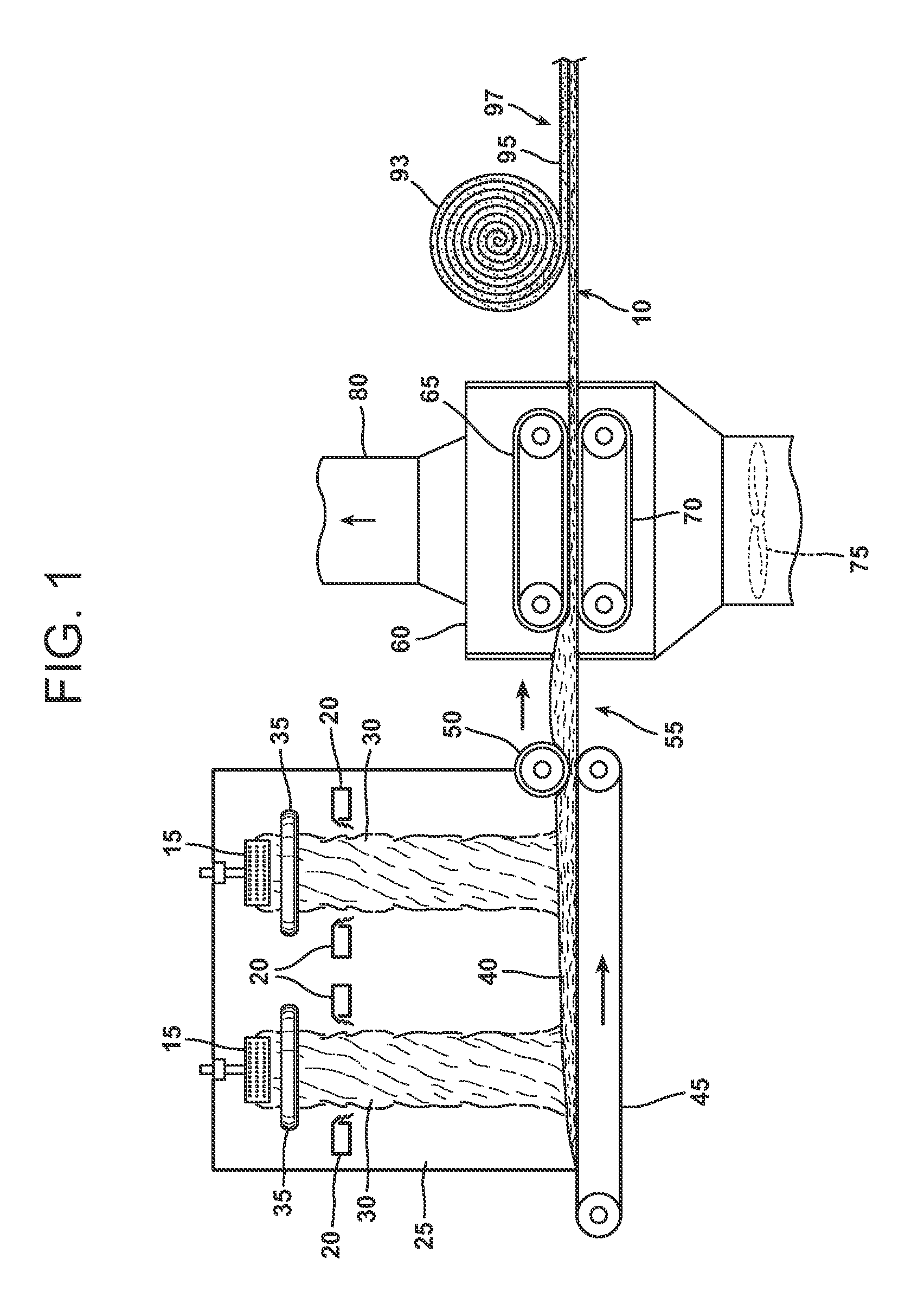
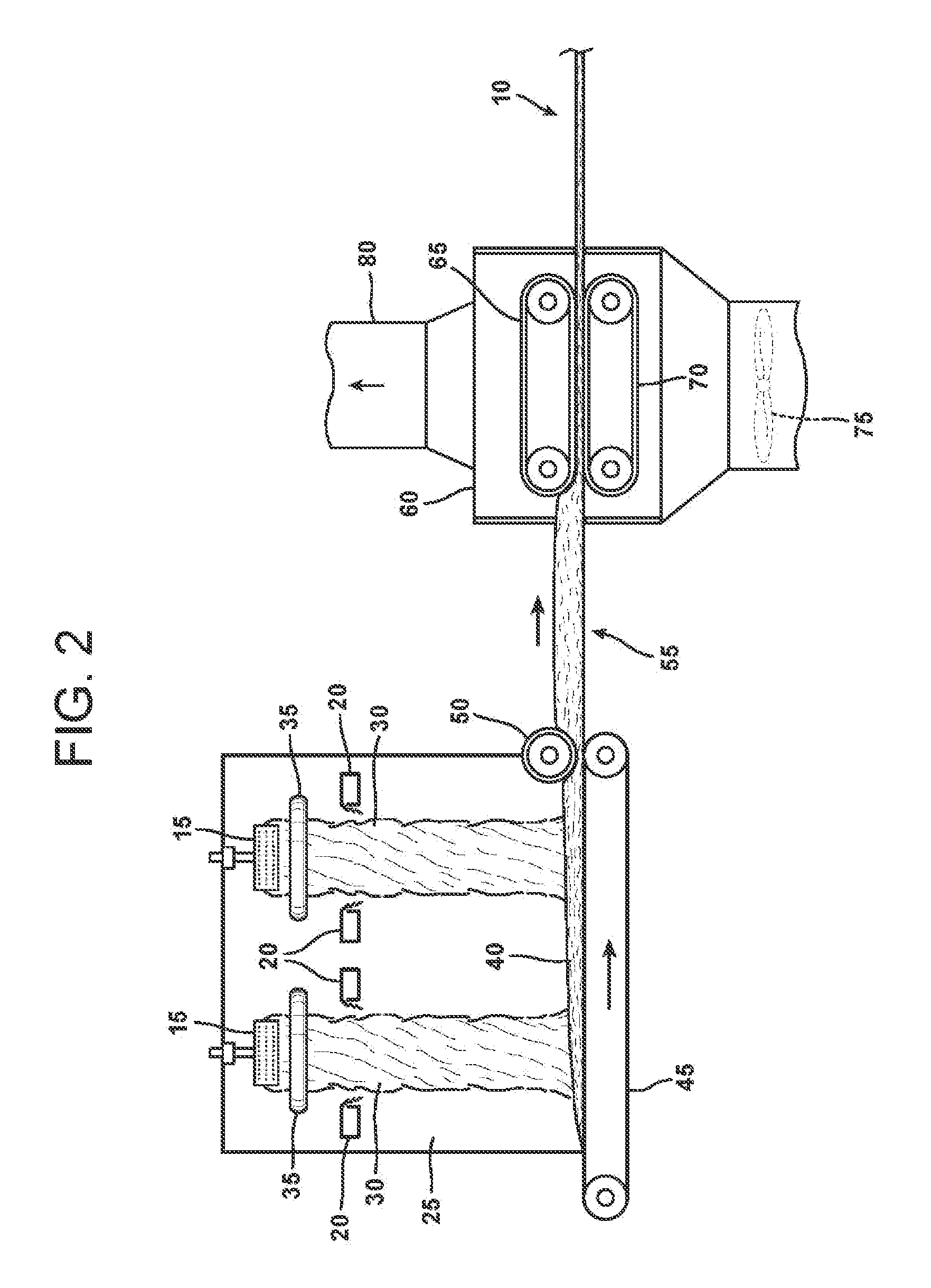
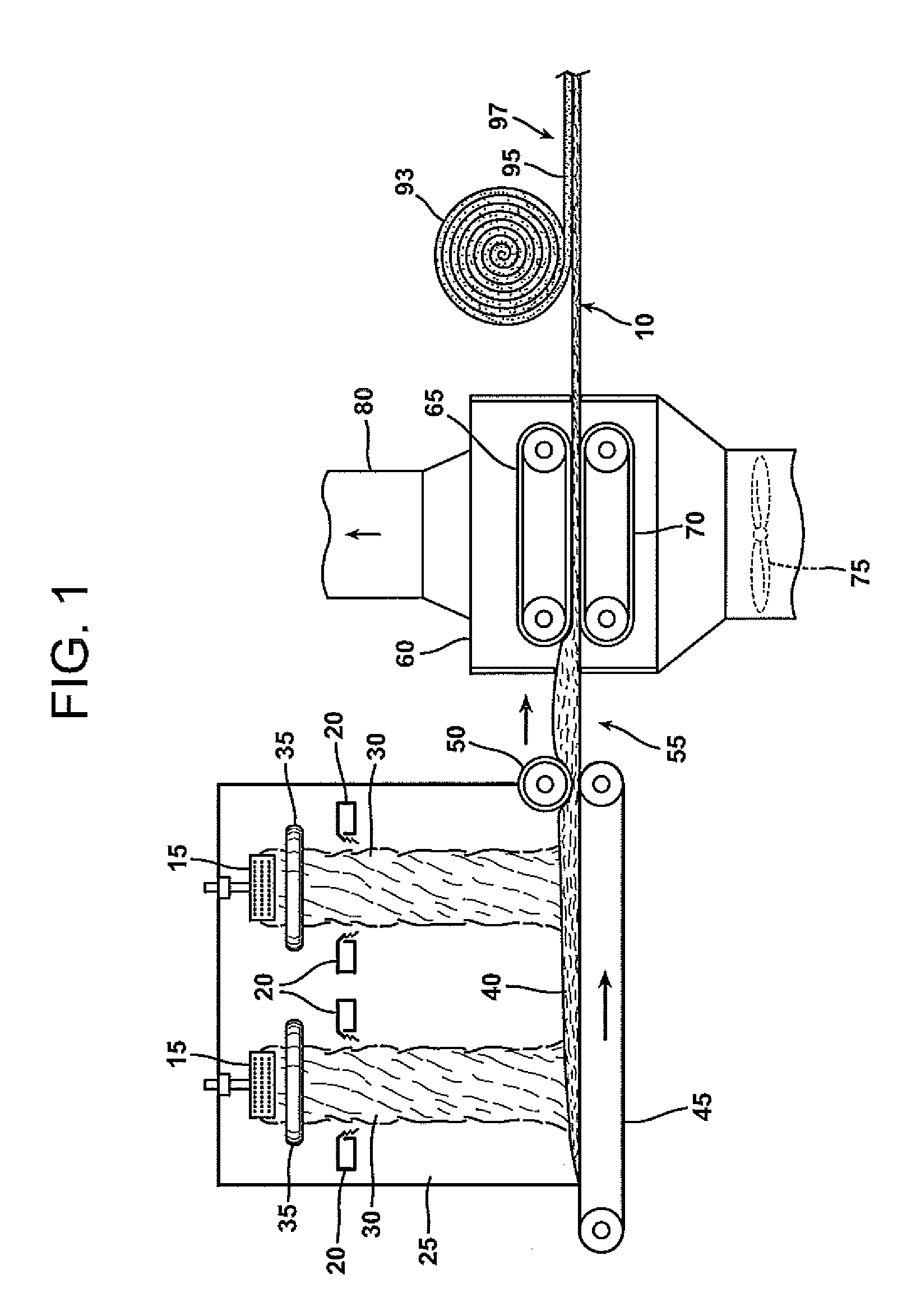
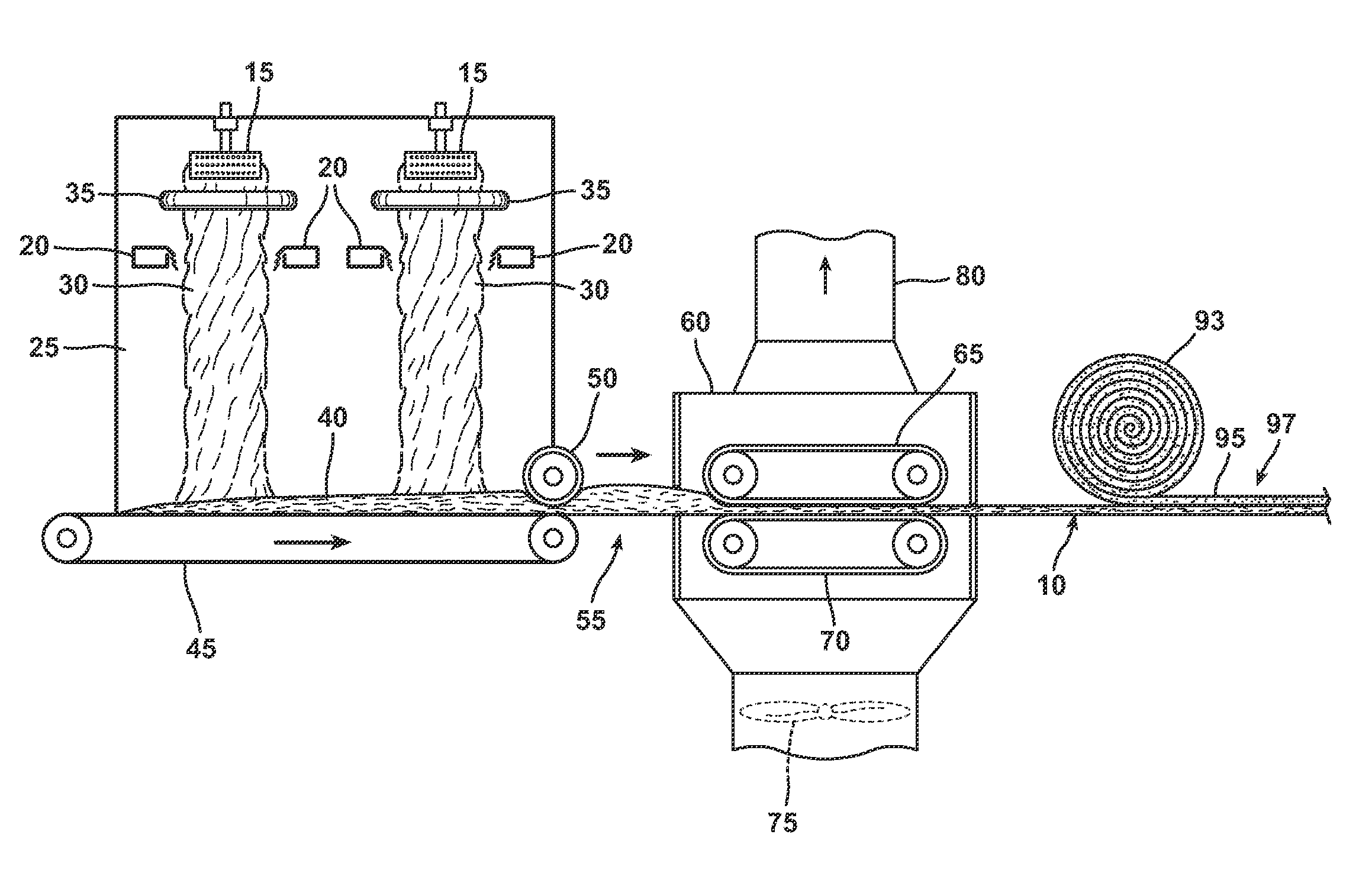
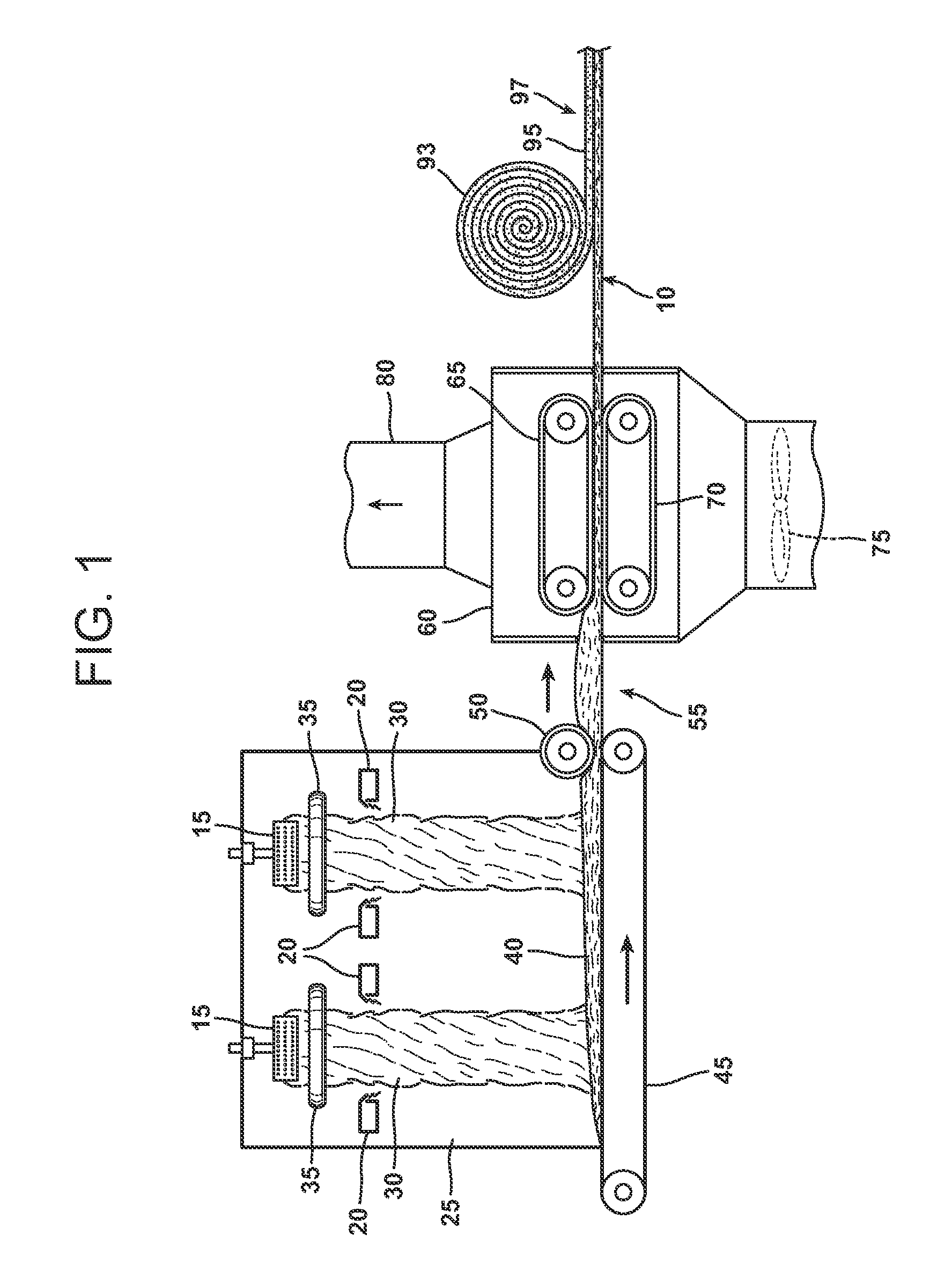
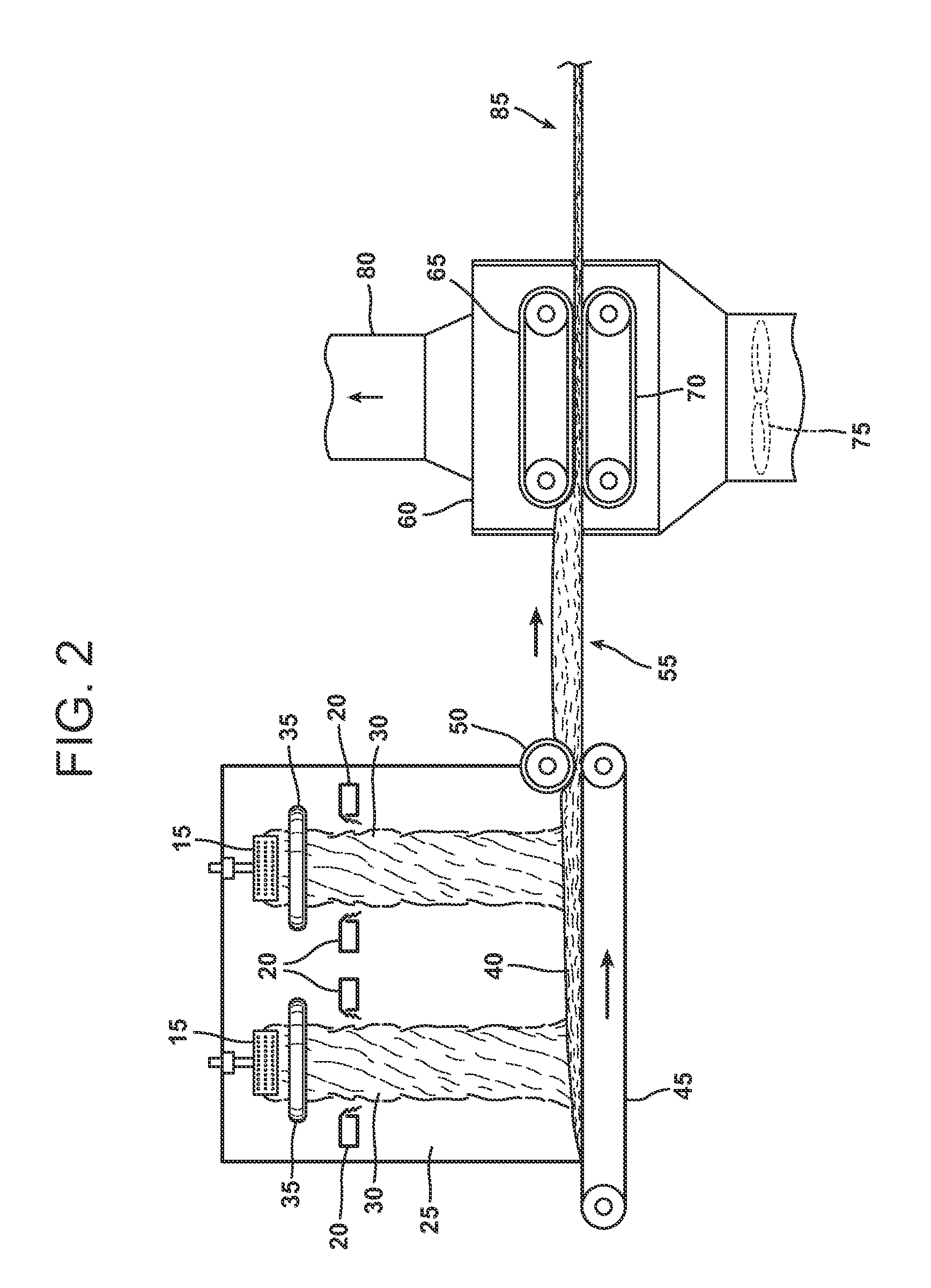
An aqueous binder composition is provided that includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent. In exemplary embodiments, the carbohydrate-based binder composition may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, a crosslinking density enhancer, an extender, a moisture resistant agent, a dedusting oil, a colorant, a corrosion inhibitor, a surfactant, a pH adjuster, and combinations thereof. The carbohydrate may be natural in origin and derived from renewable resources. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the carbohydrate is a water-soluble polysaccharide such as dextrin or maltodextrin and the crosslinking agent is citric acid. Advantageously, the carbohydrates have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous insulation products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Insulative products having bio-based binders
InactiveUS20110223364A1Readily availableLow costStarch adhesivesStarch derivtive adhesivesFiberWater soluble polysaccharides
Fibrous insulation products have an aqueous binder composition that includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent. In exemplary embodiments, the carbohydrate-based binder composition may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, a crosslinking density enhancer, an extender, a moisture resistant agent, a dedusting oil, a colorant, a corrosion inhibitor, a surfactant, a pH adjuster, and combinations thereof. The carbohydrate may be natural in origin and derived from renewable resources. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the carbohydrate is a water-soluble polysaccharide such as dextrin or maltodextrin and the crosslinking agent is citric acid. Advantageously, the carbohydrates have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous insulation products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Method for preparing starch glue for lumber
InactiveCN1687279AHigh bonding strengthImprove water resistanceStarch derivtive adhesivesAdjuvantPlasticizer
The present invention relates to a preparation method of starch glue for wood. Said invention uses starch as main raw material, and adopts the following steps: firstly, making starch undergo the processes of acidolysis, oxidation and graft copolymerization, etc., then adding modifying agent and complexing agent to make cross-linking modification, then heating and gelatinizing, cooling and successively adding the adjuvants of diluent, plasticizer and defoaming agent so as to obtain a starch glue with excellent performance for wood.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Environmentally friendly biopolymer adhesives and applications based thereon
InactiveUS6921430B2Poor shelf-life stabilityShort shelf life stabilityAntifouling/underwater paintsFibre treatmentAdhesiveBiopolymer
Environmentally friendly biopolymer adhesives are described, wherein the adhesives comprise biopolymer particles, more preferably starch microparticles, and most preferably starch nanoparticles, and their aqueous dispersions. Applications for the biopolymer particle adhesives are described, that are environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum based synthetic adhesives. The biopolymer particle adhesives provide are biodegradable as well as repulpable, and thus provide bio-based recycling-friendly alternatives to synthetic adhesives derived from petroleum resources.
Owner:ECOSYNTHETIX INC
Pregelatinized starch with mid-range viscosity, and product, slurry and methods related thereto
ActiveUS20140113128A1High compressive strengthConstruction materialSolid waste managementSlurryViscosity
Disclosed are product (e.g., panels), slurry, and methods relating to a pregelatinized starch having a mid-range viscosity (i.e., from about 20 centipoise to about 700 centipoise), and an extruded pregelatinized starch.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Modified starch based binder
InactiveUS20110021101A1Improve waterproof performanceReduce manufacturing costStarch derivtive adhesivesPeptide preparation methodsWater dispersiblePlant Sources
An aqueous binder composition is provided that includes a modified starch and a silane coupling agent, and optionally, a crosslinking agent. The starch from which the modified starch is derived is natural in origin, biorenewable, and is derived from plant sources. The modified starch has been chemically modified from its natural form and may have a degree of polymerization from about 20 to about 4000. Additionally, the modified starches have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. Advantageously, the modified starches are water dispersible and have excellent resistance to water after curing. In addition, the binder has a light color after being cured. The crosslinking agent may be any compound suitable for crosslinking the starch based compound. In exemplary embodiments, the silane coupling agent is an aminosilane. The environmentally friendly, biorenewable binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Curable starch composition, modified starch, preparation method and articles
InactiveUS20040152857A1Low water resistanceReduce biodegradationStarch dervative coatingsStarch adhesivesHydroxy groupAcid group
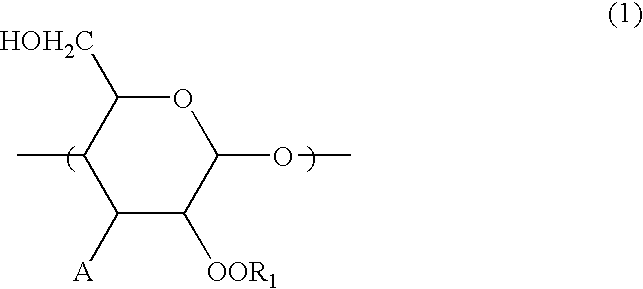
A curable starch composition comprising a mixture of a starch and a curing agent having a functional group complementally reactive with at least one hydroxyl group contained in a starch molecule; and a modified starch having at least one substituent selected from the group consisting of a hydrocarbon group, acid group, blocked isocyanate group, isocyanate group, oxidative polymerizable group, radical polymerizable unsaturated group and amide group in a starch molecule.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Coating compositions
A coating composition comprising a starchy material, said material having:a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 3 500 to 20 000 Daltons,a granular structure before solubilisation,a solubility at pH 7 and 20° C. (S1) of 30-90%, anda solubility at pH 10 and 35° C. (S2) which is at least 10% greater than S1.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Manufacturing method of fabric for ink jet printing and ink jet printing method
This invention relates to a method of manufacturing a fabric for ink jet printing and to an ink jet printing method for imparting to the fabric a clear and sharp image free from ink oozing in ink jet printing. Specifically, it relates to a method of manufacturing a fabric for ink jet printing which is characterized in that an aqueous treatment solution having a water-insoluble solvent dispersed or emulsified in an aqueous polymer solution is imparted to the fabric and dried; and to an ink jet printing method characterized in that the ink jet printing is made with the ink jet printing fabric used and that after developing, the pretreatment agent is removed by washing the fabric.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Organic acid carbohydrate binders and materials made therewith
InactiveUS20130174758A1Promising performanceIncrease corrosion rateCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCross-linkFiber
A binder comprising a polymeric binder comprising the products of a carbohydrate reactant and organic acid is disclosed. The binder is useful for consolidating loosely assembled matter, such as fibers. Fibrous products comprising fibers in contact with a carbohydrate reactant and an organic acid are also disclosed. The binder composition may be cured to yield a fibrous product comprising fibers bound by a cross-linked polymer. Further disclosed are methods for binding fibers with the carbohydrate based binder using an organic acid.
Owner:KNAUF INSULATION LLC
Bio-based binders for insulation and non-woven mats
ActiveUS8864893B2Low costReadily availableStarch dervative coatingsLiquid surface applicatorsFiberWater soluble polysaccharides
An aqueous binder composition is provided that includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent. In exemplary embodiments, the carbohydrate-based binder composition may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, a crosslinking density enhancer, an extender, a moisture resistant agent, a dedusting oil, a colorant, a corrosion inhibitor, a surfactant, a pH adjuster, and combinations thereof. The carbohydrate may be natural in origin and derived from renewable resources. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the carbohydrate is a water-soluble polysaccharide such as dextrin or maltodextrin and the crosslinking agent is citric acid. Advantageously, the carbohydrates have a low viscosity and cure at moderate temperatures. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous insulation products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Bio-based binder systems
InactiveUS20140083328A1Low costReadily availableOil/fat/wax adhesivesStarch adhesivesGlass fiberMaterials science
An environmentally friendly, bio-based binder system that is useful for the formation of fiberglass insulation, the system includes: A) an aqueous curable binder composition, which includes a carbohydrate and a crosslinking agent; and B) a dedust composition, which includes a blown, stripped plant-based oil and optionally at least one emulsifying agent. The bio-based binder system is typically heated to form a cured binder system.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Chemically modified plasticized starch compositions by extrusion processing
ActiveUS7153354B2Improved propertyEconomical and reproducibleStarch dervative coatingsAmylose/amylopectin derivative coatingsPlasticizerViscosity
A chemically modified plasticized starch (CMPS) is prepared by reacting starch with an organic dibasic acid or an anhydride of the acid in the presence of a plasticizer using optional free radical initiators, and optionally with the incorporation of nano clays in the reactive extrusion process. The starch is thermoplastic and has a lower viscosity than the traditional thermoplastic starch. The CMPS is useful in preparing starch polymer compositions which are at least partially biodegradable.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Curable starch composition, modified starch, preparation method and articles
InactiveUS20070275258A1Good property in water resistance and corrosion resistance and weather resistance and durabilityStarch dervative coatingsStarch adhesivesHydroxy groupAcid group
A curable starch composition comprising a mixture of a starch and a curing agent having a functional group complementally reactive with at least one hydroxyl group contained in a starch molecule; and a modified starch having at least one substituent selected from the group consisting of a hydrocarbon group, acid group, blocked isocyanate group, isocyanate group, oxidative polymerizable group, radical polymerizable unsaturated group and amide group in a starch molecule.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Non-thermoplastic starch fibers and starch composition for making same
InactiveUS7025821B2Starch dervative coatingsAmylose/amylopectin derivative coatingsFiberThermoplastic
Non-thermoplastic starch fibers having no melting point and having apparent peak wet tensile stress greater than about 0.2 MegaPascals (MPa). The fibers can be manufactured from a composition comprising a modified starch and a cross-linking agent. The composition can have a shear viscosity from about 1 Pascal·Seconds to about 80 Pascal·Seconds and an apparent extensional viscosity in the range of from about 150 Pascal·Seconds to about 13,000 Pascal·Seconds. The composition can comprise from about 50% to about 75% by weight of a modified starch; from about 0.1% to about 10% by weight of an aldehyde cross-linking agent; and from about 25% to about 50% by weight of water. Prior to cross-linking, the modified starch can have a weight average molecular weight greater than about 100,000 g / mol.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Non-thermoplastic starch fibers and starch composition for making same
InactiveUS20050076809A1Starch dervative coatingsAmylose/amylopectin derivative coatingsThermoplasticFiber
Non-thermoplastic starch fibers having no melting point and having apparent peak wet tensile stress greater than about 0.2 MegaPascals (MPa). The fibers can be manufactured from a composition comprising a modified starch and a cross-linking agent. The composition can have a shear viscosity from about 1 Pascal.Seconds to about 80 Pascal.Seconds and an apparent extensional viscosity in the range of from about 150 Pascal.Seconds to about 13,000 Pascal.Seconds. The composition can comprise from about 50% to about 75% by weight of a modified starch; from about 0.1% to about 10% by weight of an aldehyde cross-linking agent; and from about 25% to about 50% by weight of water. Prior to cross-linking, the modified starch can have a weight average molecular weight greater than about 100,000 g / mol.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for preparing full biodegradable environment protection hot melt adhesive
InactiveCN101250385AGood compatibilityHigh initial bond strengthStarch derivtive adhesivesPolymer scienceCarton
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer materials processing, which particularly relates to a method for producing biological fully-degradable environmental-friendly hot melt adhesive. Biological fully-degradable environmental-friendly hot melt adhesive is manufactured through modifying cornstarch and a process technique which is squeezed through blending. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and adding cornstarch and plasticizing agent, obstructing agent, reinforcing agent, lubricating agent and filling material in a stirrer according to proportion, stirring under 80 DEG C and 1000-3000rpm, preparing modified fecula, utilizing a double screw extrusion machine to blend and extrude after modified fecula, biodegradable polyester, plastisol, viscosity modifier, plasticizing agent, antioxidant and filling material are mixed, wherein the temperature of an extrusion machine is 100-180 DEG C, and number of revolution of a screw bolt is 40-200rpm, wherein modified fecula is 40-60%, biodegradable polyester is 0-30%, plastisol is 20-30%, viscosity modifier is 5-10%, plasticizing agent is 0-10%, antioxidant is 0.5-1%, and filling material is 0-10%. Hot melt adhesive which is got by the invention has the advantages of excellent compatibility, uniform products, low production cost, excellent initial viscosity and fully-degradable biology, which can be widely used in the fields such as cartons, unsewn binding of books, nonwoven manufacture and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Starch adhesive with nanometer oxidized cellulose size as matrix and preparation method of starch adhesive
ActiveCN105542676AAvoid replacementPrevent drynessNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch derivtive adhesivesPolymer scienceSlurry
The invention discloses a starch adhesive with nanometer oxidized cellulose size as the matrix. The starch adhesive is prepared from, by weight, 100 parts of nanometer oxidized cellulose size with the oxidation rate of 5-30%, 10-40 parts of starch, 2-5 parts of oxidizing agent, 0.1-2 parts of stabilizer, 0.1-2 parts of preservative and 0.1-2 parts of emulsified paraffin. The preparation method includes the steps of preparing nanometer oxidized cellulose size the with oxidation rate of 5-30%, adding starch and 2-5 parts of oxidizing agent to the prepared nanometer oxidized cellulose size in batches, adding stabilizer, preservative and emulsified paraffin after sufficient stirring, and sufficiently stirring the components at a temperature of 50-70 DEG C till all the components are evenly dispersed to obtain the starch adhesive. The starch adhesive is high in bonding strength and high in water resistance. By means of the preparation method, the solvent replacement and drying process is avoided, energy consumption is greatly lowered, and labor intensity is reduced.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
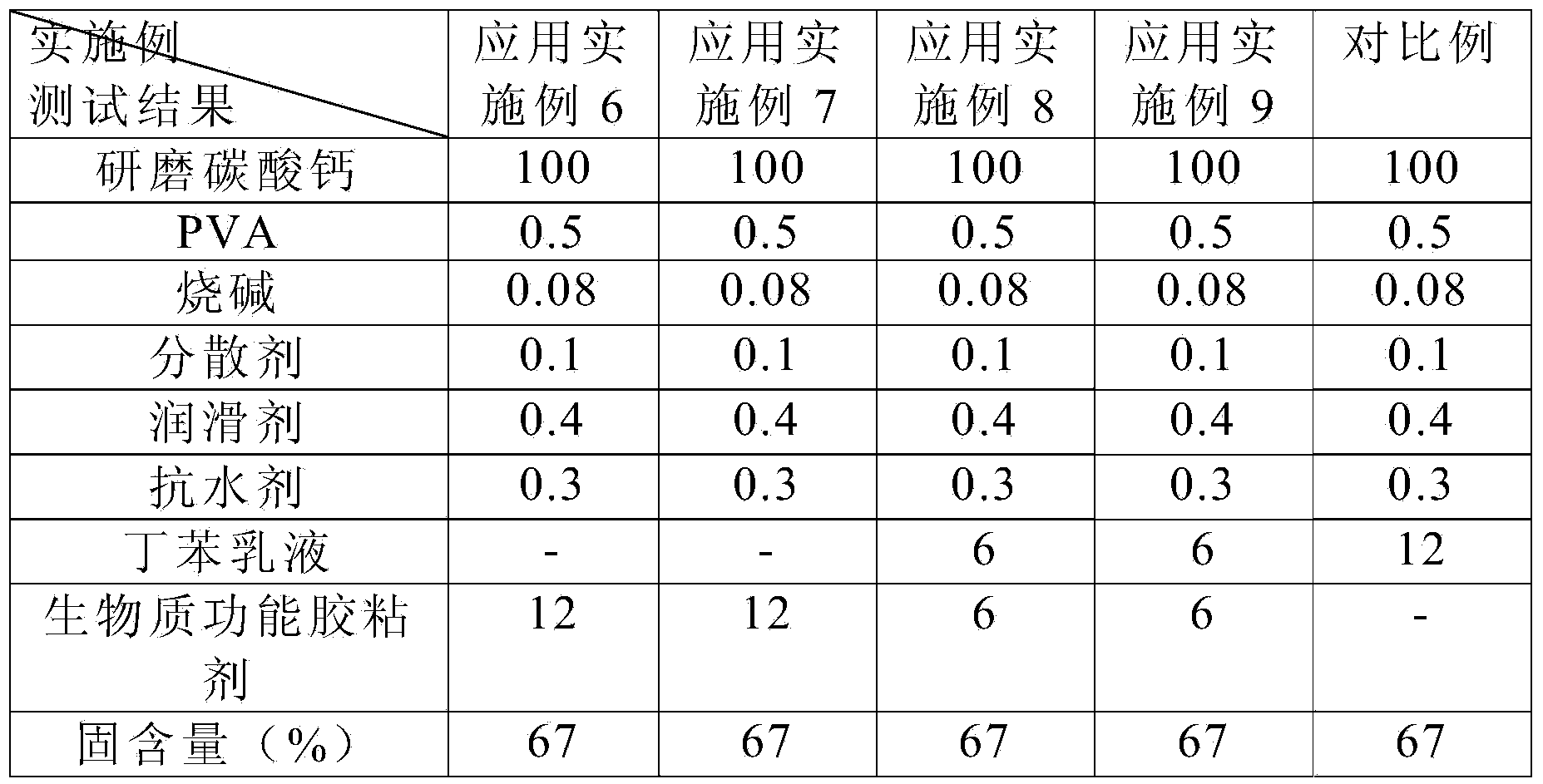
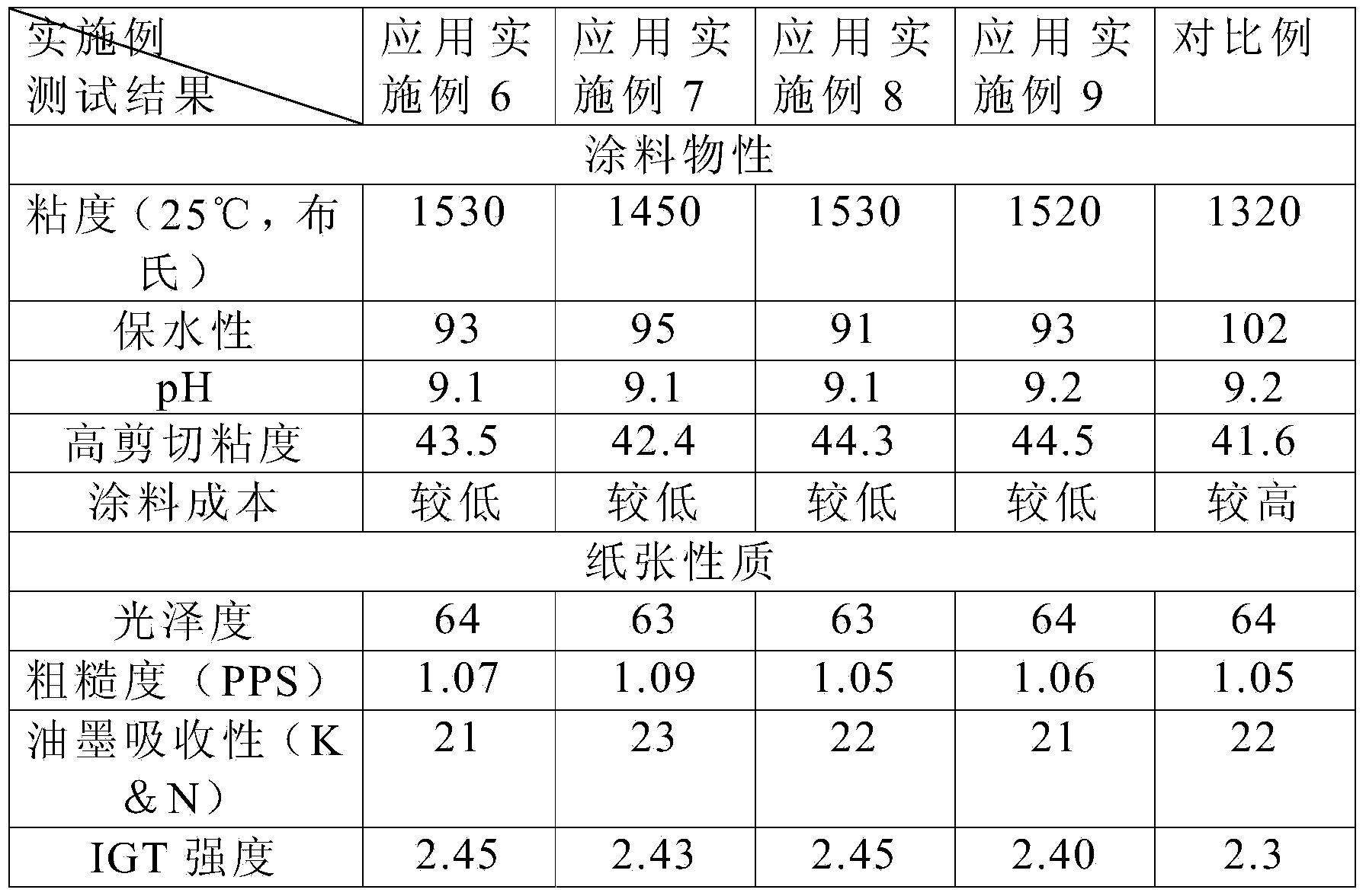
Starch based biomass functional adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104164199AReduce manufacturing costHigh economic valueNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesProtein adhesivesAdhesivePlasticizer
The invention relates to a starch based biomass functional adhesive and a preparation method thereof, and is particularly applied to the field of papermaking. The biomass functional adhesive comprises the following components: 30-45% of a biomass main raw material, 5.5-22.5% of a plasticizer, 0.55-3.5% of a lubricant, 0.55-5.5% of a crosslinking agent, 0.01-5.5% of a modifier, 0.55-5.5% of an auxiliary film-forming agent, 0.1-0.55% of a preservative, 0.01-5.5% of a pH regulator and the balance of water. The preparation method is as follows: adding the biomass main raw material, the modifier and the water into a reaction kettle, heating to 60 to 100 DEG C for reaction; performing digestive treatment; adding the lubricant, the plasticizer and the crosslinking agent for reaction at 60 to 90 DEG C, then adding the preservative, adding the pH regulator and the auxiliary film-forming agent, mixing, discharging and filtering to obtain the biomass functional adhesive. The biomass functional adhesive has low cost and excellent adhesive performance.
Owner:NINGBO JIAHUA NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
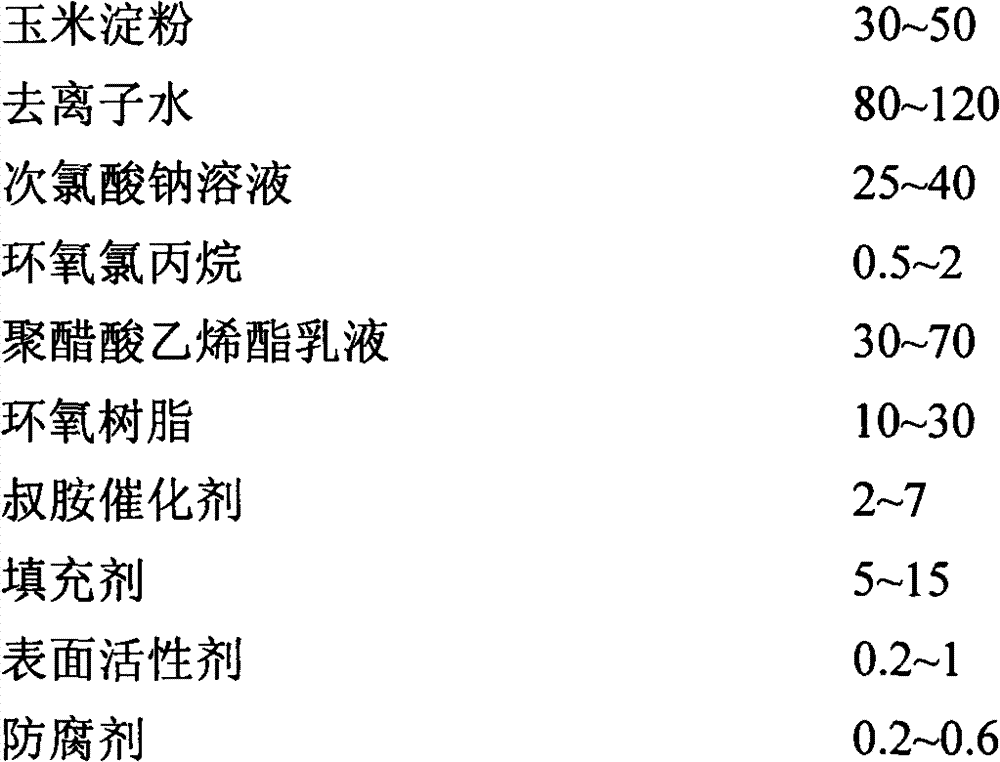
Modified starch adhesive and method for preparing same
InactiveCN102732186AGood compatibilityRaw materials are cheap and easy to getMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesStarch derivtive adhesivesEpoxyAdhesive
The invention discloses a modified starch adhesive and a method for preparing the same. The modified starch adhesive comprises the following components by weight: 30-50 parts of corn starch, 80-120 parts of deionized water, 25-40 parts of sodium hypochlorite solution, 0.5-2 parts of epichlorohydrin, 30-70 parts of polyvinyl acetate emulsion, 10-30 parts of epoxy resin, 2-7 parts of tertiary amine catalyst, 5-15 parts of filler, 0.2-1 part of surfactant, and 0.2-0.6 part of preservative, wherein the sodium hypochlorite solution serves as the oxidant, the polyvinyl acetate emulsion serves as the high-cohesive-energy reinforcement component, and the epoxy resin servers as the water-tolerant modified component. The method for preparing the modified starch adhesive comprises the following steps: mixing the oxidized starch emulsion prepared in advance, the polyvinyl acetate emulsion and the epoxy resin according to proportion uniformly, adding the catalyst, the filler and the preservative, and stirring quickly and uniformly. The modified starch adhesive disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high shear strength, high water-tolerant shear strength, moderate viscosity, good liquidity, moderate primary drying time, low cost and excellent integrated performance.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
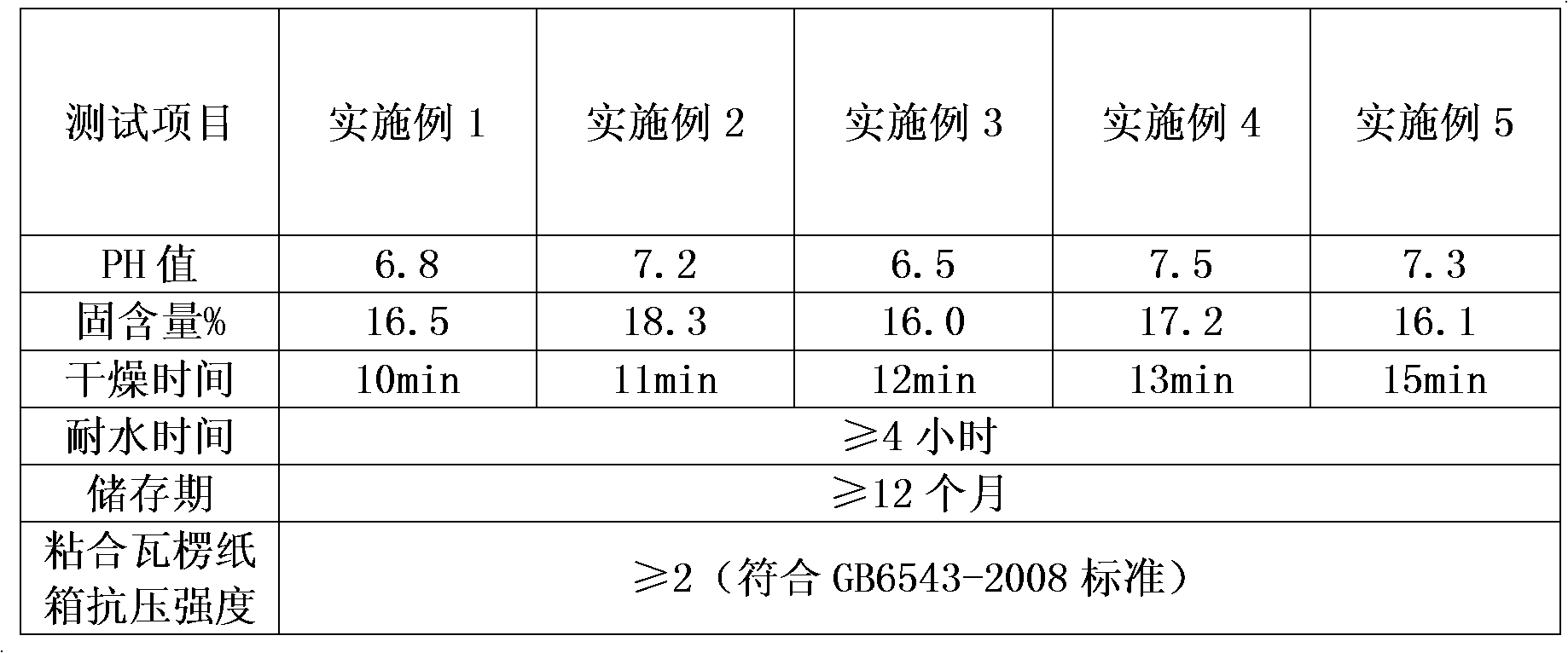
Preparation method of starch adhesive for adhering cartons
InactiveCN102433084AWill not damageStable storageNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch derivtive adhesivesAdhesiveDrying time
The invention discloses a preparation method of a starch adhesive for adhering cartons, which belongs to the technical field of adhesive preparation, and comprises: adding 450 to 600 weight parts of water and 100 weight parts of starch into a reaction kettle; uniformly stirring, and adding 3 to 8 weight parts of hydrogen peroxide; reacting for 0.5 to 1 hour, and slowing adding 5 to 12 weight parts of aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide; stirring and reacting for 110 to 130 minutes, adding 0.2 to 0.8 weight part of crosslinking agent, 0.01 to 0.05 weight part of ferrous sulfate, 9 to 16 weight parts of water-proof agent, 10 to 20 weight parts of catalyst, 0.2 to 1.2 weight parts of tackifier, 0.05 to 0. 1 weight part of preservative, 15 to 18 weight parts of quick drying agent, and 0.5 to 1 weight part of tributyl phosphate in turn; stirring and reacting for 55 to 65 minutes; and obtaining the starch adhesive for adhering cartons. The method has the advantages that: the starch adhesive is stable in storage and is environment-friendly; the drying time is short, and the water-proof time is long; and the starch adhesive meets national standards.
Owner:CHANGSHU KAILIDA HONEYCOMB PACKING MATERIALS
Aqueous biopolymer-containing labeling adhesive
InactiveUS20070240823A1Improve biodegradabilityImprove suitabilityLayered productsStarch adhesivesBiopolymerBottle
Adhesives particularly useful for industrial bottle labeling are provided. The adhesives comprise at least one starch component and at least one protein component (which is not gelatin or casein). The adhesive is also free of synthetic polymer. The label, along with the adhesive, can be easily removed from the bottle during the recycling process. In one embodiment, the starch component does not contain leguminous starch having an amylose content of 25% or more. In another embodiment, the adhesive comprises a crosslinking agent.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Natural macromolecular composite aqueous polyurethane bond and its preparation method
InactiveCN1876746AHigh bonding strengthImprove water resistanceProtein adhesivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesWater basedEmulsion
The invention relates the natural high polymer composite water-based polyurethane binder and preparing method. The high polymer composite water-based polyurethane binder comprises 40-100% A water solution and 10-25% water-based polyurethane emulsion. The mass ratio of A mass percent and solid constituent is 20-80%, and the ratio of water-based polyurethane emulsion and solid constituent is 20-80%. The mass ratio of A and water-based polyurethane emulsion is 30-40%. The A comprises fecula, soy protein, modified starch, and modified soy protein. The product has the advantages of high bonding capacity, low cost, biodegradability, environmental protection and simple technology.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Bio-based binders including carbohydrates and a pre-reacted product of an alcohol or polyol and a monomeric or polymeric polycarboxylic acid
InactiveUS20140038485A1Speed crosslinking reactionLow viscosityFibre treatmentStarch adhesivesPolyolAlcohol
An environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free, aqueous binder composition that includes a carbohydrate, a crosslinking agent, and a pre-reacted product of an alcohol or polyol and monomeric or polymeric polycarboxylic acid or polyglycerol is provided. The pre-reacted product may include glycerol and esters of citric acid such a monoglyceryl citrate, diglyceryl citrate, and triglyceryl citrate as well as other higher molecular weight citric acid-based esters. The inclusion of the pre-reacted product in the binder composition helps to speed the crosslinking reaction, induces faster water evaporation, decreases the viscosity of the binder, helps to reduce the amount of water needed for application of the binder, decreases tackiness, and helps to achieve a maximum vertical expansion of the insulation pack in the transfer zone. The binder composition may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC +1
Bio-based binders including carbohydrates and a pre-reacted product of an alcohol or polyol and a monomeric or polymeric polycarboxylic acid
ActiveUS20150152244A1Low viscositySpeed the crosslinking reactionFibre treatmentStarch adhesivesEvaporationGlycerol
An environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free, aqueous binder composition that includes a carbohydrate, a crosslinking agent, and a pre-reacted product of an alcohol or polyol and monomeric or polymeric polycarboxylic acid or polyglycerol is provided. The pre-reacted product may include glycerol and esters of citric acid such a monoglyceryl citrate, diglyceryl citrate, and triglyceryl citrate as well as other higher molecular weight citric acid-based esters. The inclusion of the pre-reacted product in the binder composition helps to speed the crosslinking reaction, induces faster water evaporation, decreases the viscosity of the binder, helps to reduce the amount of water needed for application of the binder, decreases tackiness, and helps to achieve a maximum vertical expansion of the insulation pack in the transfer zone. The binder composition may be used in the formation of insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Urea formaldehyde resin adhesive for moisture-proof environment-friendly medium density fiberboard and production method as well as composite additives thereof
ActiveCN102408855AReduce releaseLow costStarch derivtive adhesivesAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesAccelerantMoisture
The invention discloses a urea formaldehyde resin adhesive for a moisture-proof environment-friendly medium density fiberboard and composite additives thereof. The adhesive is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of formaldehyde of which the mass concentration is 37%, 35-40 parts of urea of which the purity is 98%, and 4.5-7.5 parts of composite additives, wherein the composite additives comprise the following components in parts by weight: 40-90 parts of melamine, 1-30 parts of modified starch, 1-30 parts of anti-swelling agent and 1-5 parts of accelerant. By utilizing the renewable low-cost modified starch, the water resistance and bonding strength of the urea formaldehyde resin adhesive can be improved, the release amount of formaldehyde is reduced, the consumption of melamine is reduced, the product quality is stable, and the cost is lower. The invention also discloses a production method of the adhesive, which is characterized in that: the formaldehyde is fed for two times, the composite additives are fed for three times and are in end point control for three times, and the urea is fed for four times. Thus, few additives are used for playing a greater role, and the problems of higher reaction speed, longer adhesive curing time and the like caused by the melamine are avoided.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
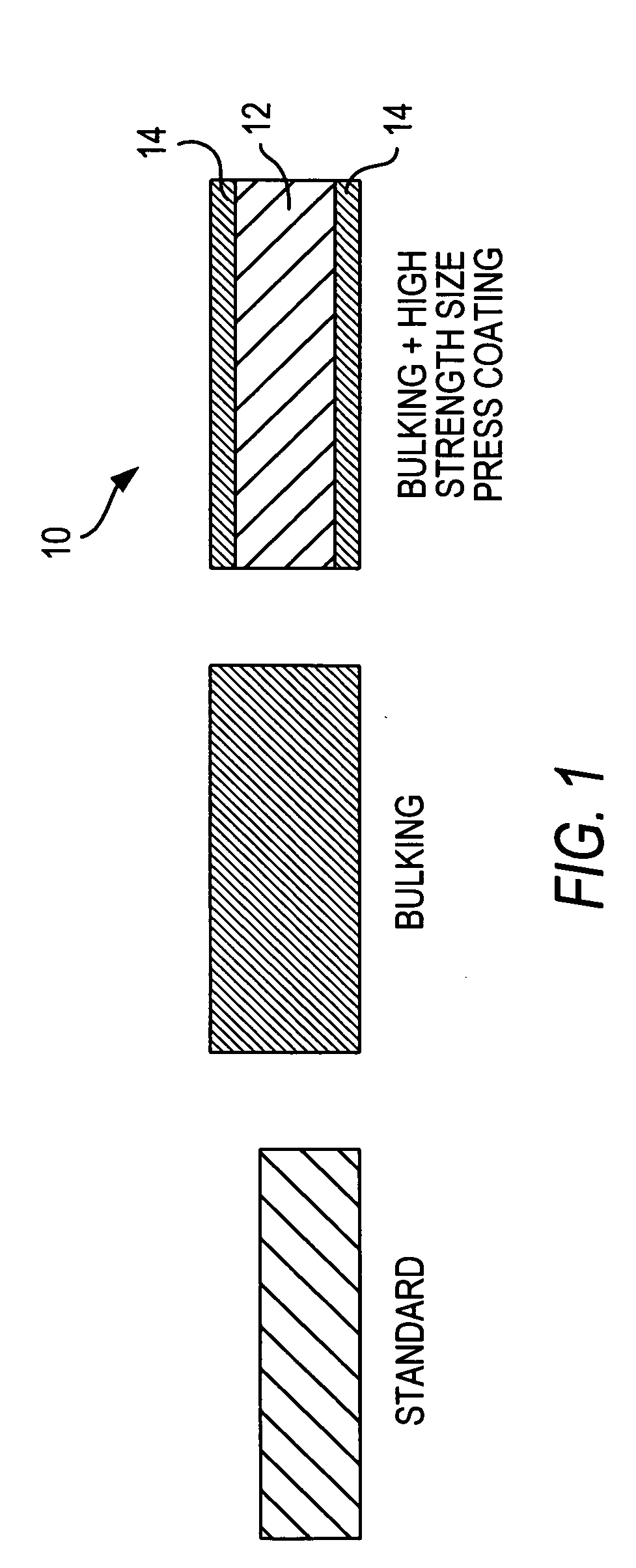
Paper with improved stiffness and bulk and method for making same
InactiveUS20090020247A1Improve bulkIncrease stiffnessSpecial paperWater-repelling agents additionCellulosePulp and paper industry
The invention provides a three layered reprographic paper having improved strength, stiffness and curl resistance properties, and a method for making same. The paper has a central core layer made largely of cellulose and bulked with a bulking agent such as a diamide salt. A starch-based metered size press coating is pressed on both sides of the core layer, wherein the starch has a high solid content. The coating forms a three layered paper having an I-beam arrangement with high strength outer layers surrounding a low density core.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Preparation method for environment-friendly starch cigarette adhesive
InactiveCN103773276ALow viscosityHigh solid contentNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch derivtive adhesivesBiotechnologyAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method for an environment-friendly starch cigarette adhesive, and belongs to the technical field of adhesives. The method is implemented by the steps of adding water into a reaction kettle with a stirring device, starting the stirring device for stirring when the temperature rises to 40 to 50 DEG C, adding starch, and uniformly stirring the mixture; slowly adding a pretreating agent, performing stirring at high speed, raising the temperature to 70 to 90 DEG C, and performing reaction for 0.5 to 2 hours; slowly adding a modifier, performing stirring at high speed, preserving heat at 70 to 90 DEG C, and performing reaction for 0.5 to 1.5 hours; slowly adding a thickening agent, preserving heat at 70 to 90 DEG C, and performing reaction for 0.5 to 2.5 hours; adding a preservative, performing uniform stirring, reducing the temperature to be lower than 40 DEG C, and performing filtering and discharging. According to the method, natural starch is used as a main raw material, process conditions are improved, and small amounts of volatile organic monomer-free modifier and thickening agent are selected to react with the base material starch, so that the aims of reducing the viscosity, improving the solid content, increasing the curing speed and the like are fulfilled.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Tape joint compounds with CMC thickener system
ActiveUS20050056187A1Limited solubilityEasy to useStarch dervative coatingsCovering/liningsJoint compoundPhysical therapy
CMC with CMDS greater than or equal to 0.76, optionally with a non-ionic co-thickener or a CMC with CMDS less than 0.75 is used as both the rheology modifier and partial clay substitute in tape joint compounds. This significant reduction of clay level is sufficient to eliminate most of the negative characteristics of clay in joint compound.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
Method for preparing starch modified latex and adhesive
InactiveCN101993671AHigh hardnessLow priceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch adhesivesSulfite saltAdhesive
The invention discloses a method for preparing a starch modified latex and adhesive. The starch modified latex and adhesive consists of two parts, namely starch latex and a starch latex adhesive, wherein the starch latex is prepared by steps of starch oxidation, pasting, reaction with polyvinyl alcohol and vinyl acetate and the like; the latex is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 5 to 15 percent of starch, 2 to 5 percent of polyvinyl alcohol, 5 to 15 percent of vinyl acetate, 0.5 to 1 percent of hydroxymethyl acrylamide, 0.3 to 1.0 percent of sodium hypochlorite, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of sodium sulfite, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of sodium hydroxide, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of ammonium persulfate and 45 to 55 percent of water; and the starch latex adhesive is enhanced by a filling method, and is prepared from the following components: 70 to 80 percent of starch modified latex, 5 to 15 percent of starch and 5 to 15 percent of kaolin. The preparation process for the starch latex adhesive is reasonable; and in the process of producing products, formaldehyde and organic solvents are not used, and three-waste emission is absent. The starch modified latex and adhesive is a modern environment-friendly adhesive taking water as a dispersing medium and having strong adhesion without toxicity, corrosion or pollution.
Owner:刘力恒
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com