Preparation method of glucose 1-phosphoric acid
A technology of glucose and phosphoric acid, applied in the field of preparation of glucose 1-phosphate, can solve the problems of high separation cost, low product yield, different glucan phosphorylase, etc., and achieves reduced separation cost, high raw material utilization, conversion Efficiency-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0044] Experimental example 1 Multienzyme Catalyzed Conversion of Starch to Glucose in Vitro 1- Phosphoric acid, improves starch conversion rate
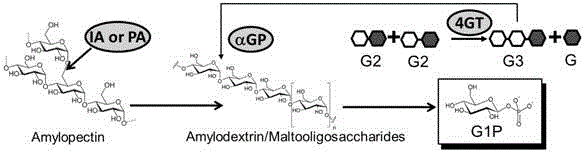
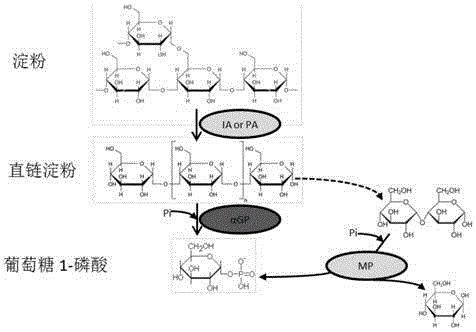
[0045] Starch is converted to glucose 1-phosphate by an in vitro multi-enzyme catalytic system ( figure 1 ). These key enzymes include: (1) branching enzyme IA; (2) glucan phosphorylase (αGP, EC 2.4.1.1), which releases glucose-1-phosphate from starch; (3) glucantransferase ( 4-a-glucanotransferase, EC 2.4.1.25).
[0046] Since starch has branched chains, starch cannot be completely hydrolyzed by glucan phosphorylase alone, because glucan phosphorylase only acts on α-1, 4 glycosidic bonds, and branched chains are based on α-1, 6 glycosidic bonds connected to the main chain. This requires the addition of isoamylase (isoamylase, EC 3.2.1.68) to hydrolyze the α-1,6 glycosidic bond. Since the minimum substrate of glucan phosphorylase is maltotriose, in order to improve the utilization efficiency of maltodextrin, glucan tran...
experiment example 2
[0052] Experimental example 2 Multienzyme Catalyzed Conversion of Starch to Glucose in Vitro 1- phosphoric acid
[0053] The preparation of isoamylase, glucan phosphorylase, and glucan transferase is the same as in Experimental Example 1.
[0054] In a 0.75 mL reaction system containing 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.2), 5 mM divalent magnesium ion, 0.05 U / mL dextran phosphorylase, 1 U / mL isoamylase, and 1 U / mL of glucan transferase and 10 g / L of soluble starch were catalyzed at 40°C for 40 hours.
[0055] After the reaction, the final concentration of glucose 1-phosphate was 2.2 g / L, and the conversion rate was 22%.
experiment example 3
[0056] Experimental example 3 Multienzyme Catalyzed Conversion of Starch to Glucose in Vitro 1- phosphoric acid
[0057] The preparation of isoamylase, glucan phosphorylase, and glucan transferase is the same as in Experimental Example 1.
[0058] In a 0.75 mL reaction system containing 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.2), 5 mM divalent magnesium ion, 0.05 U / mL dextran phosphorylase, 1 U / mL isoamylase, and 1 U / mL of glucan transferase and 10 g / L of soluble starch were used to catalyze the reaction at 80°C for 40 hours.
[0059] After the reaction, the final concentration of glucose 1-phosphate was 12.1 g / L, and the conversion rate was 121%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com