Patents
Literature
41 results about "Phosphoglucomutase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
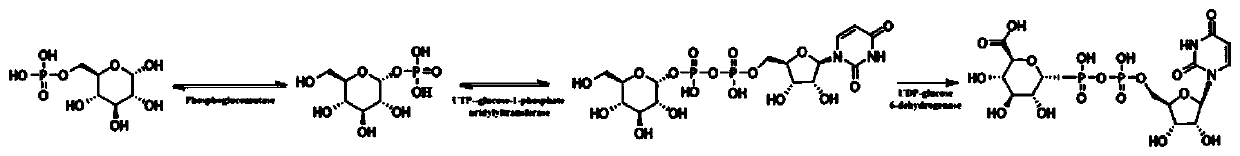
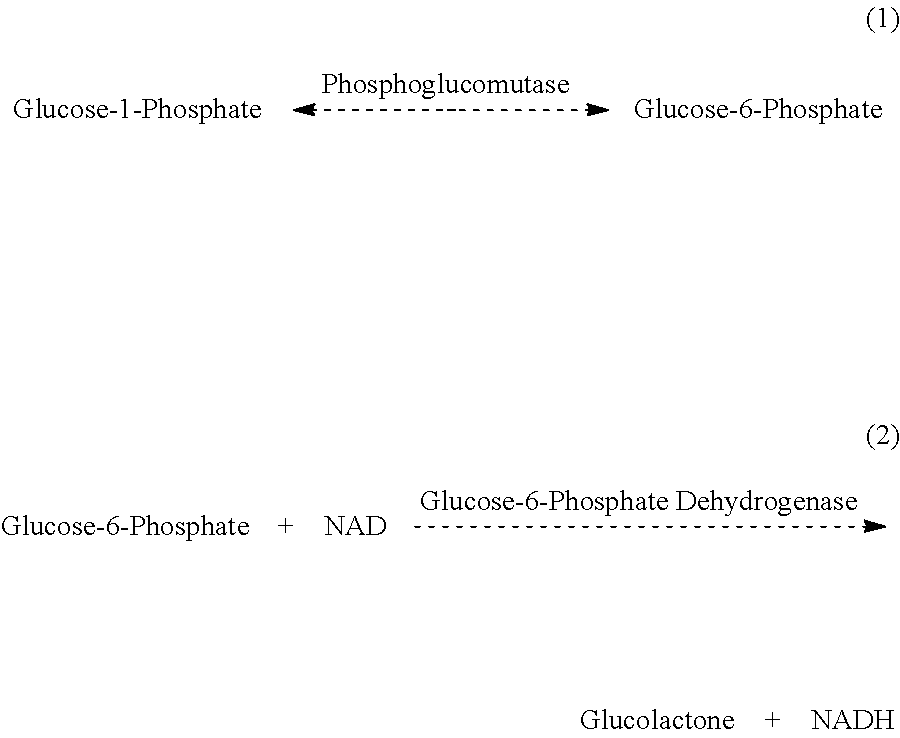
Phosphoglucomutase (EC 5.4.2.2) is an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group on an α-D-glucose monomer from the 1' to the 6' position in the forward direction or the 6' to the 1' position in the reverse direction.
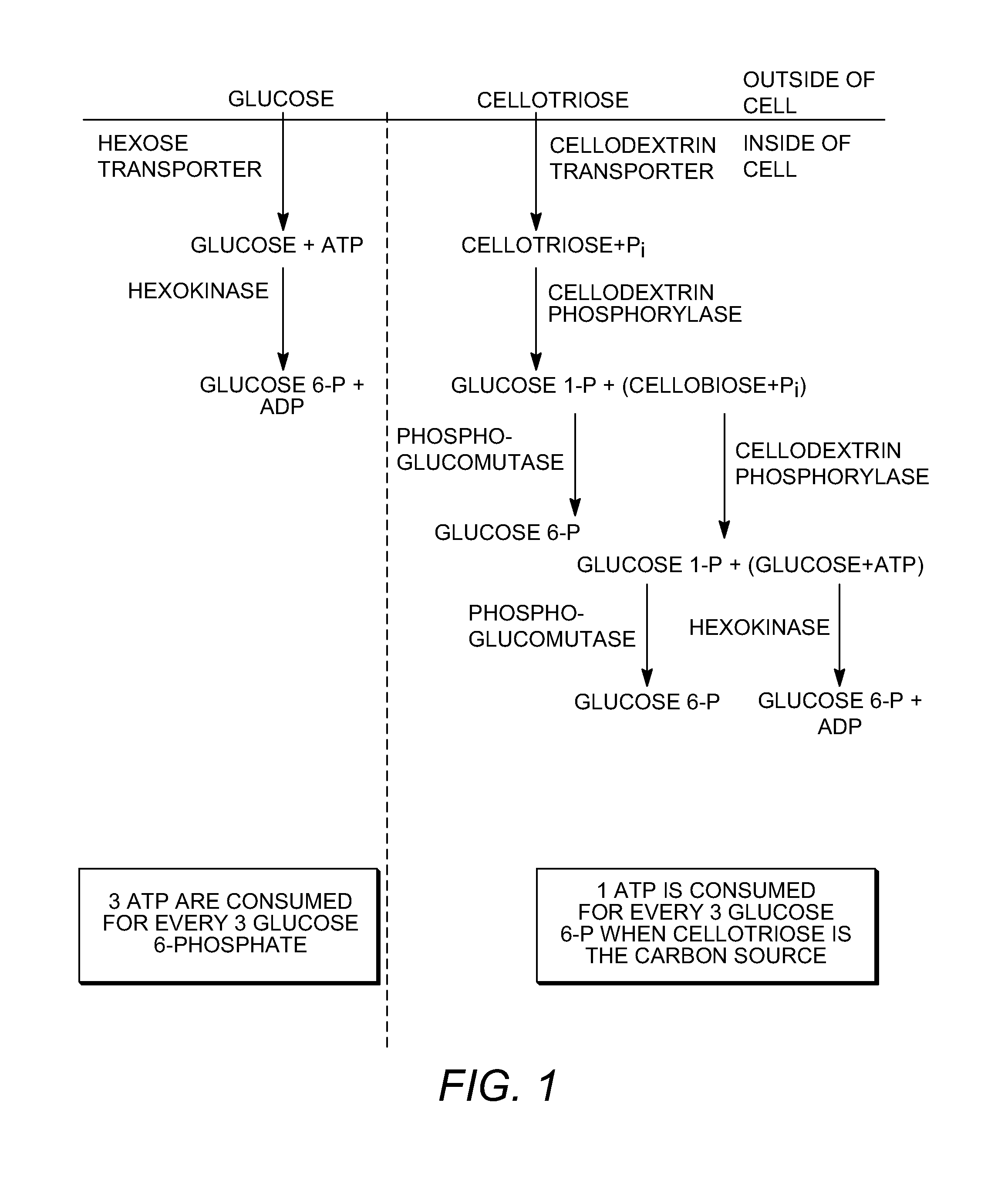
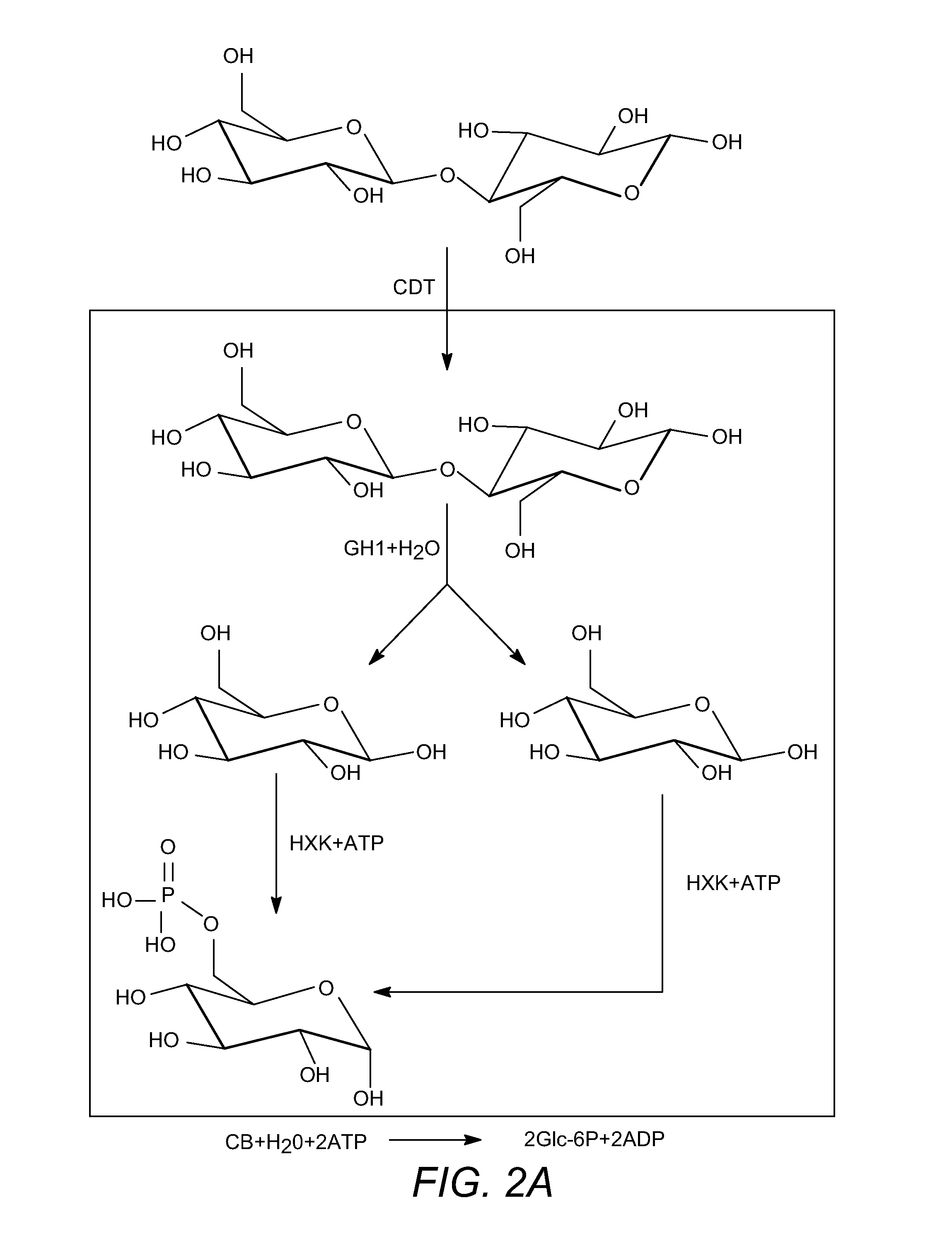
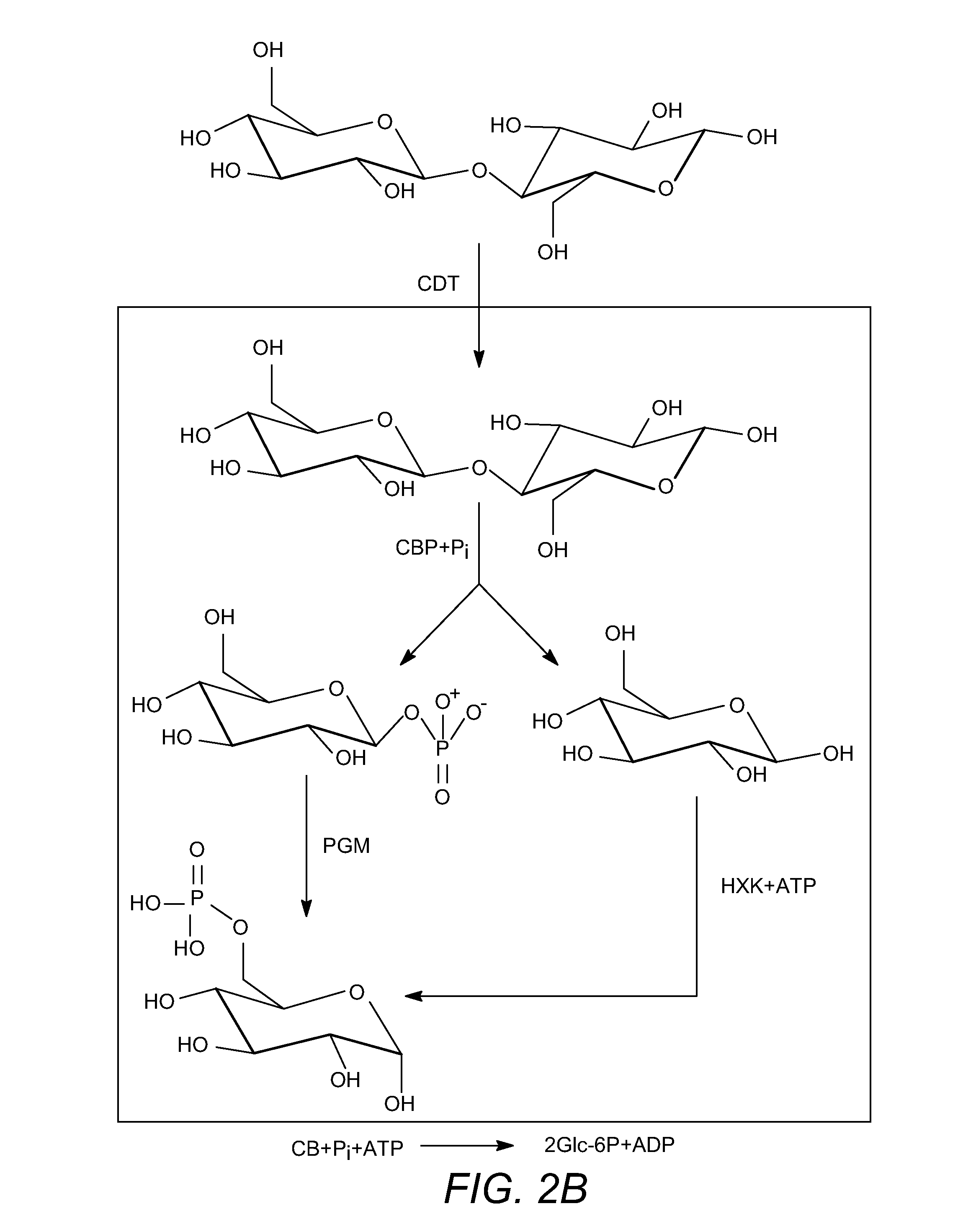
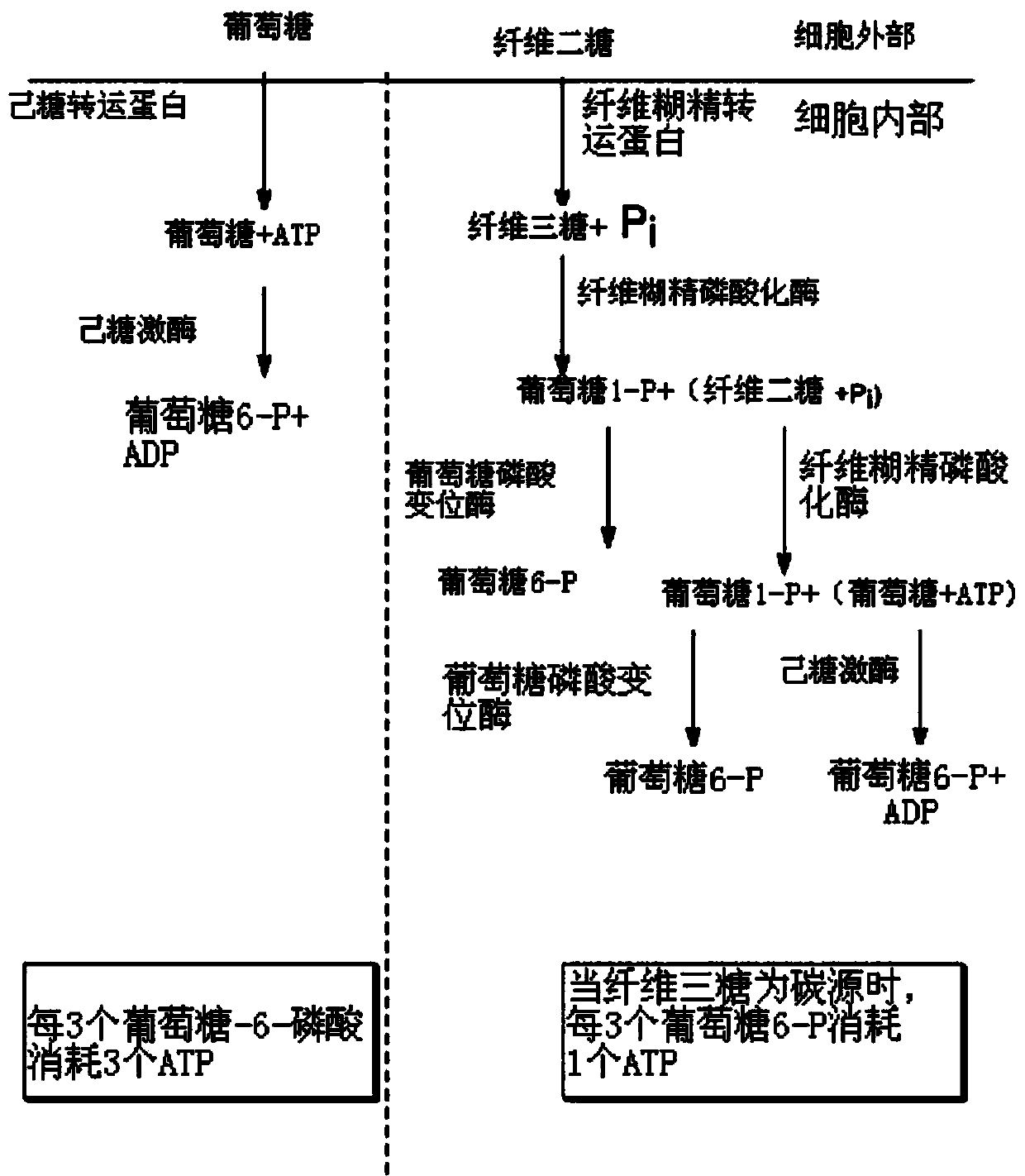
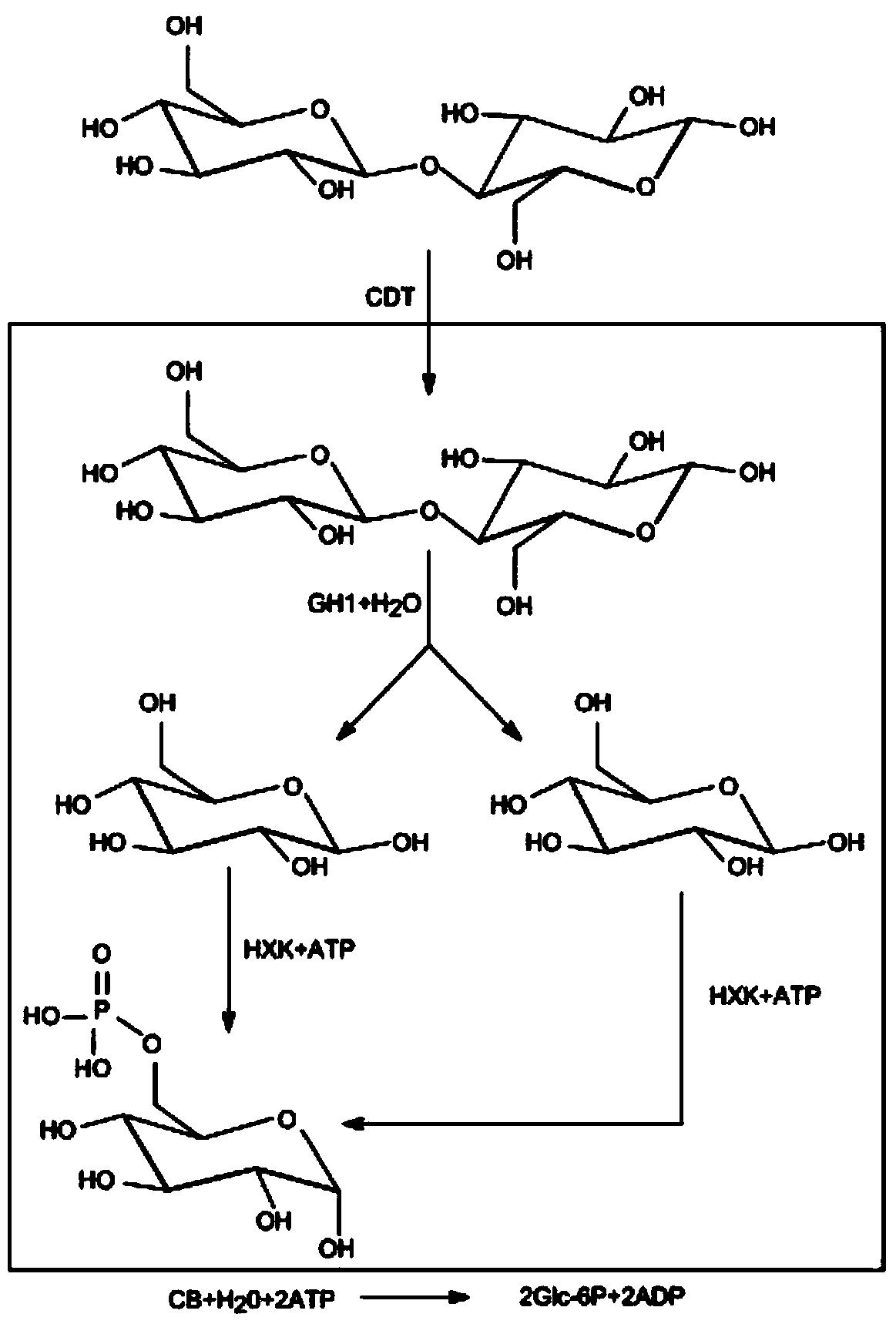
Enhanced cellodextrin metabolism
InactiveUS20140057323A1Reduce consumptionLess overall consumptionMicroorganismsBiofuelsGlucose utilizationHexokinase
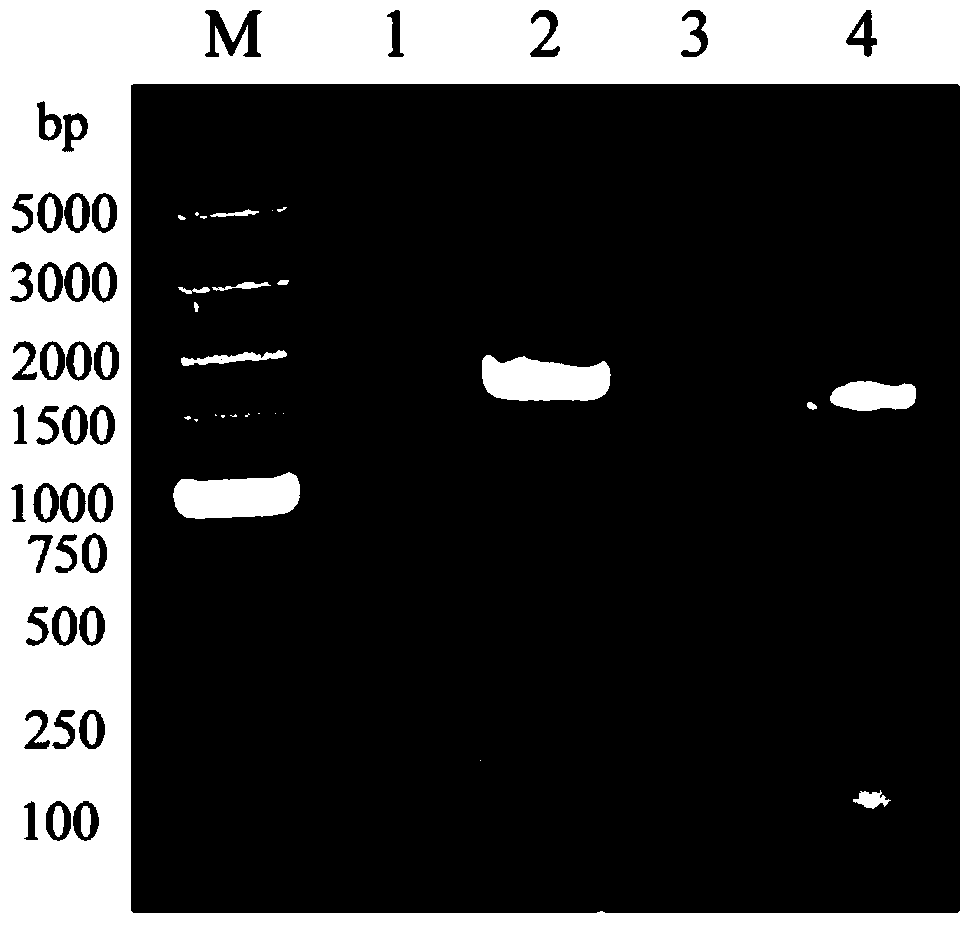
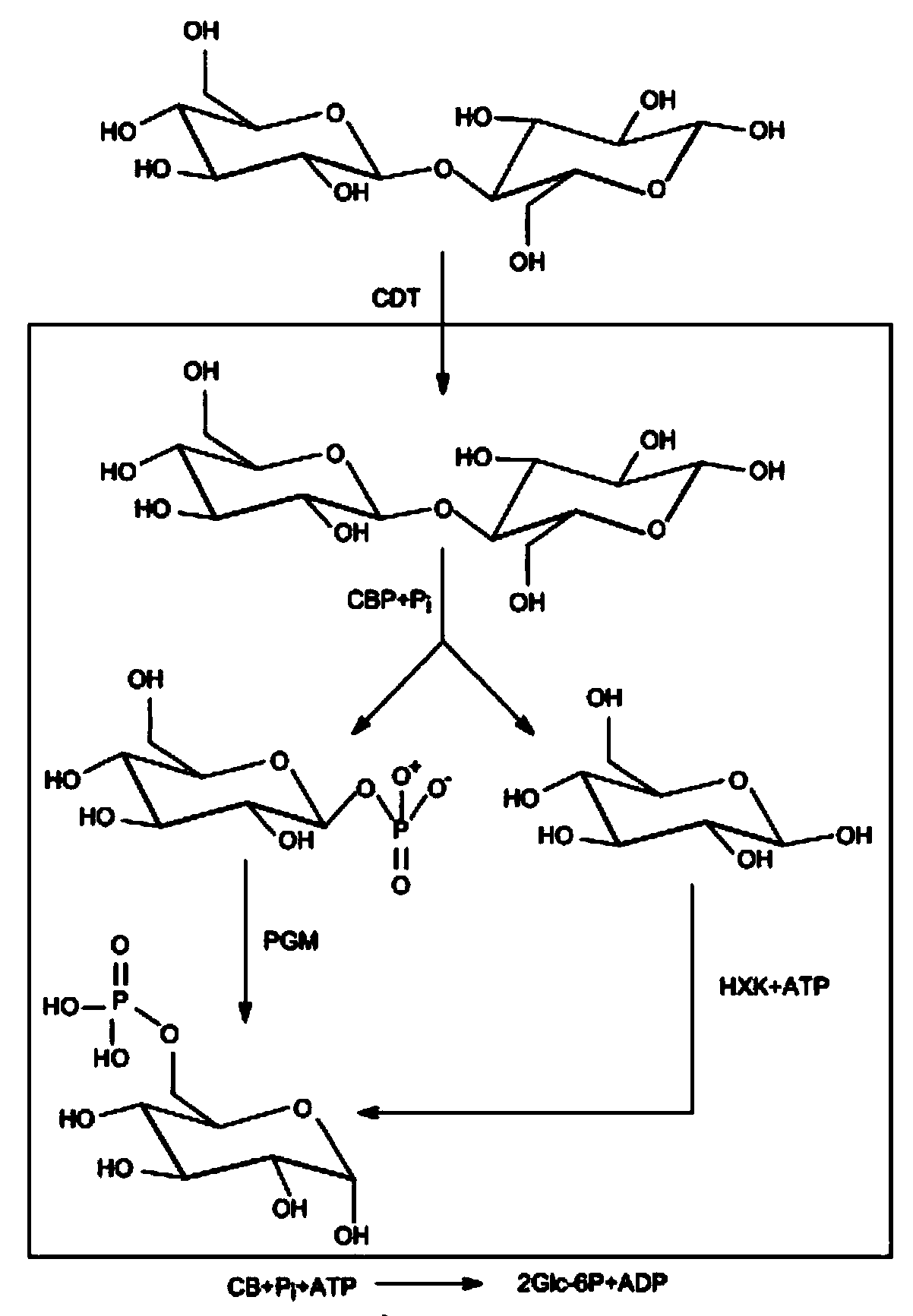
The present disclosure relates to host cells containing two or more of a recombinant cellodextrin transporter, a recombinant cellodextrin phosphorylase, a recombinant β-glucosidase, a recombinant phosphoglucomutase, or a recombinant hexokinase; and to methods of using such cells for degrading cellodextrin, for producing hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon derivatives from cellodextrin, and for reducing ATP consumption during glucose utilization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
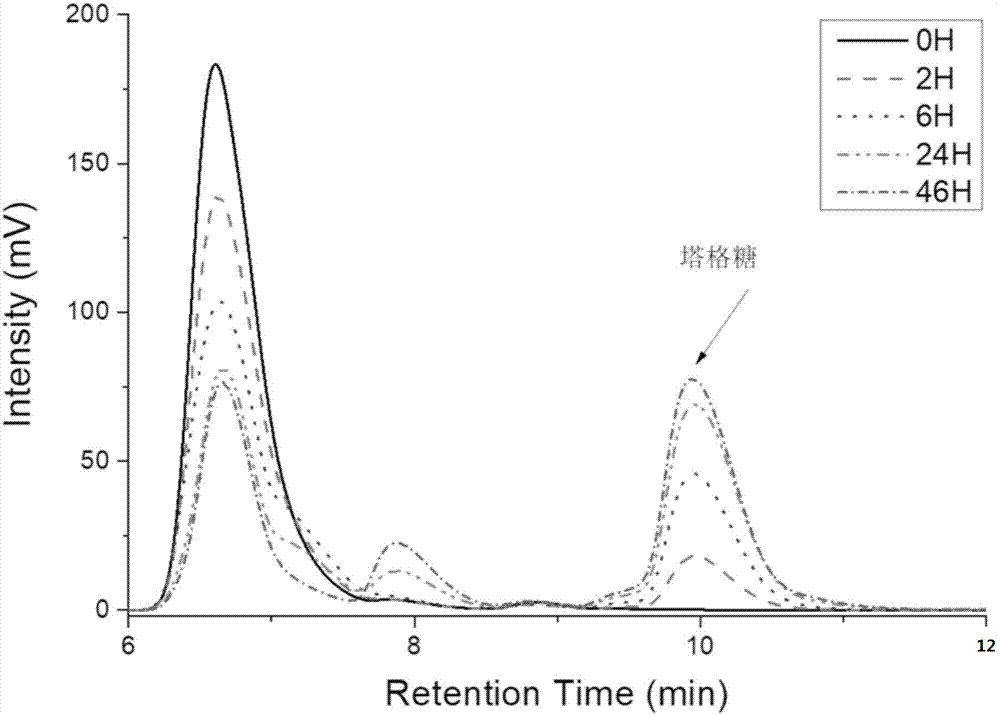
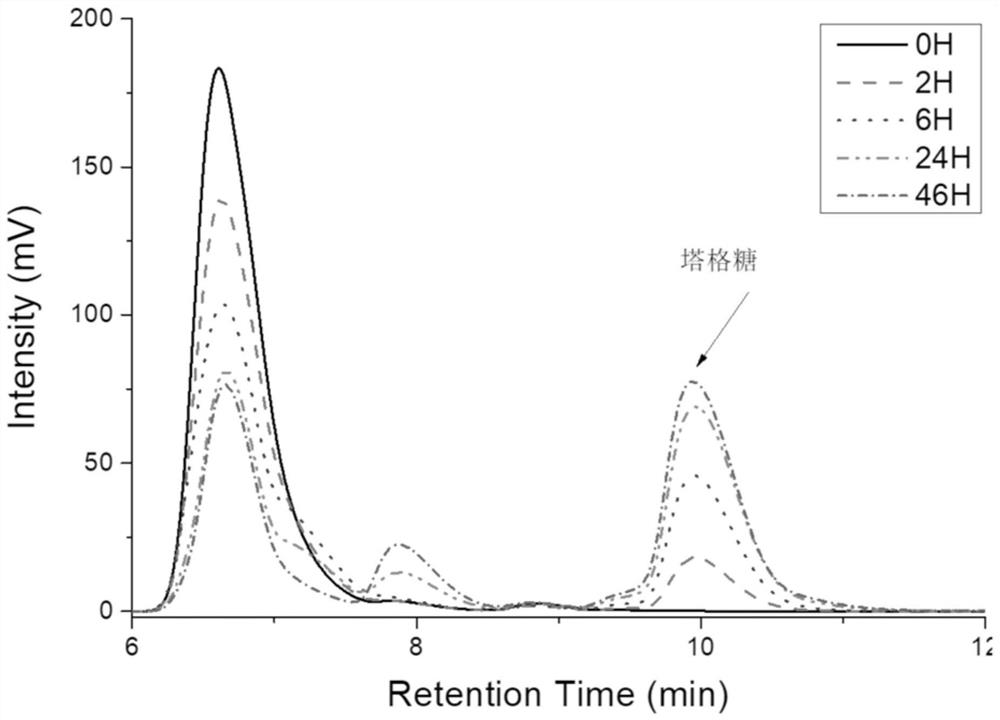
Method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis
ActiveCN107988286AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliTagatose
The invention discloses a method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of transferring plasmid containing an alpha-glucan phosphorylase gene (or cellulosic polysaccharide phosphorylase and cellobiose phosphorylase genes, or a sucrose phosphorylase gene), a phosphoglucomutase gene, a glucose phosphate isomerase gene, a 6-phosphate tagatose epimerase gene, and a 6-phosphate tagatose phosphatase gene into engineered escherichia coli, so as to obtain converted bacterial strain; inducing the converted bacterial strain to produce enzyme, and permeabilizing; mixing the permeabilized bacterial strain, establishing a whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction system with starch or starch derivative (or mixture of cellulase and cellulose or cellulose derivative, or sugarcane), and performing the whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction, so as to obtain the tagatose. The method has the advantages that the tagatose is prepared by the whole-cell catalysis; the cost is low, the pollution is low, the yield rate is high, and the like; the method is suitable for preparing the tagatose in a scale way.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
Plastidic phosphoglucomutase genes
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a plastidic phosphoglucomutase protein is disclosed. Also disclosed is the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a substantial portion of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids
ActiveCN105087454AImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
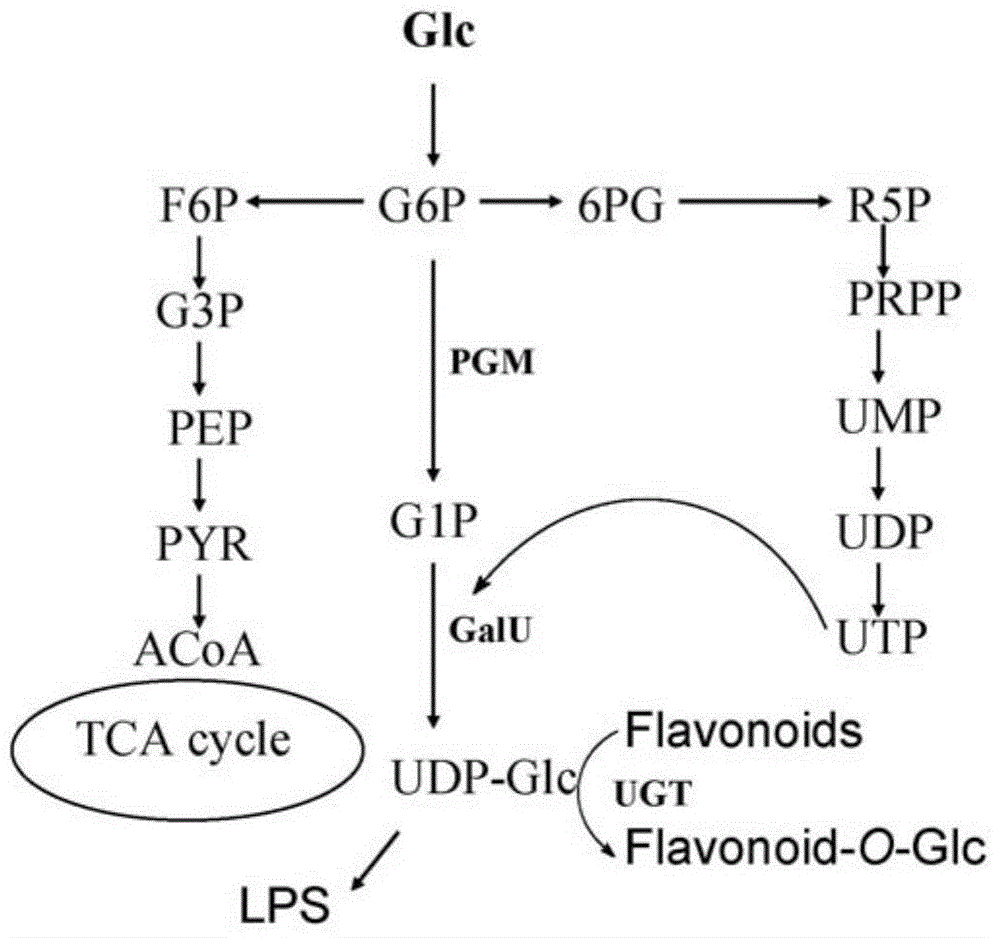
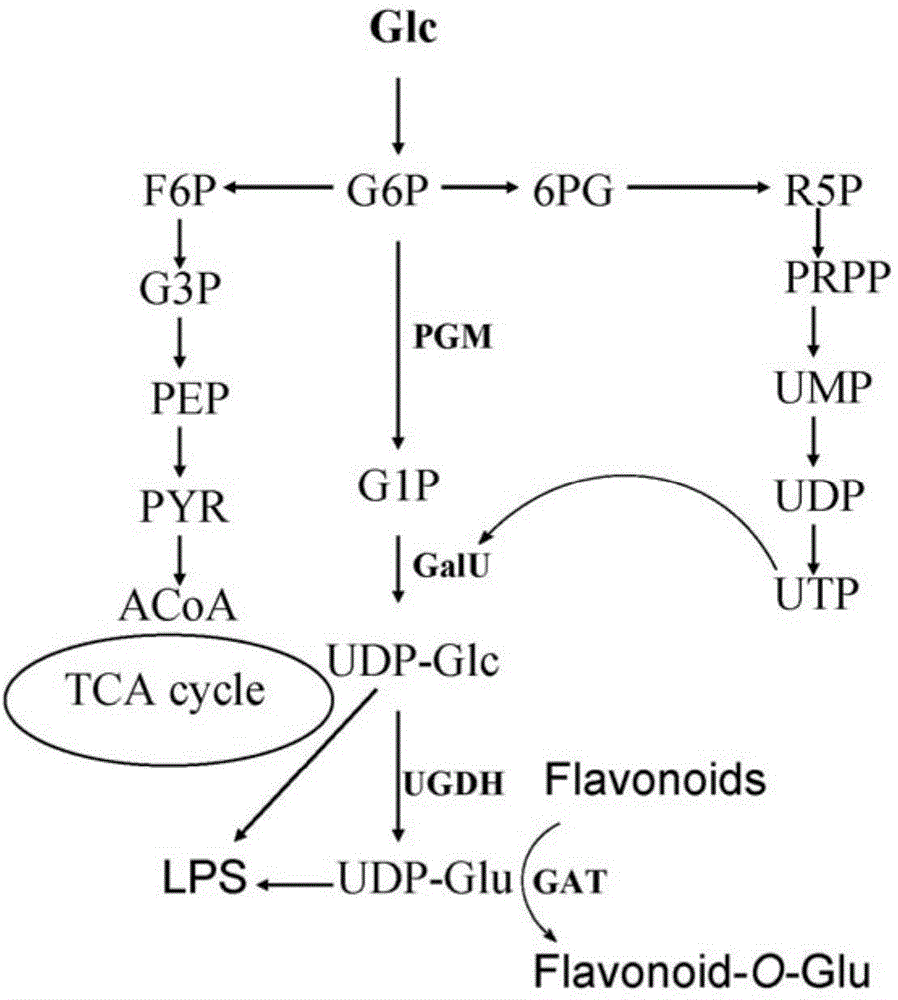
The invention relates to genetically engineered organisms, especially to microbes like Escherichia coli with activity in catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids, and provides a genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids. The genetically engineered bacterium is prepared by coexpression of three genes respectively coding phosphoglucomutase, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase in a microbial cell and introduction of the functional enzyme genes into the cell through expression vectors. The genetically engineered bacterium induces expression of functional enzyme protein under the condition of addition of an inductive agent--isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and is directly used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids; and the advantages of good cell growth, a short fermentation period and low cost are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Bacillus subtilis genetically-engineered bacteria for producing tagatose and method for preparing tagatose
ActiveCN112342179AEasy to manufactureGood for catalytic applicationsBacteriaHydrolasesTagatoseEngineered genetic
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis genetically-engineered bacteria for producing tagatose and a method for preparing the tagatose. The genetically-engineered bacteria are used for constructingheat-resistant alpha-glucan phosphorylase, heat-resistant phosphoglucomutase, heat-resistant glucose phosphate isomerase, heat-resistant 6-tagatose phosphate epimerase and heat-resistant 6-tagatose phosphate phosphatase which are independently expressed or co-expressed. By utilizing the genetically-engineered bacteria, starch can be effectively converted into the tagatose. Compared with the existing method for producing the tagatose, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of suitability for whole-cell recycling, high safety, high yield, simple production process, low cost, easiness in large-scale preparation and the like.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
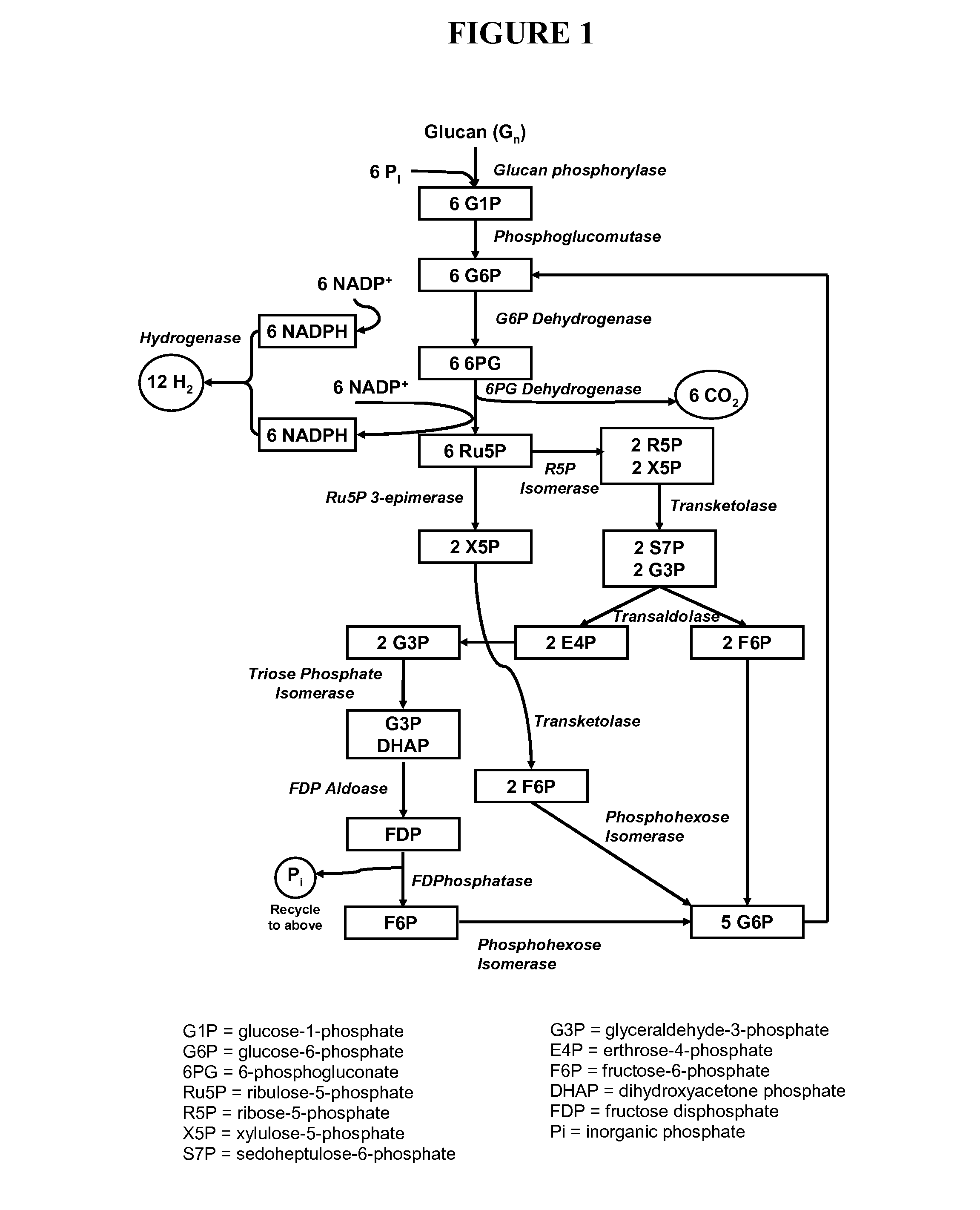
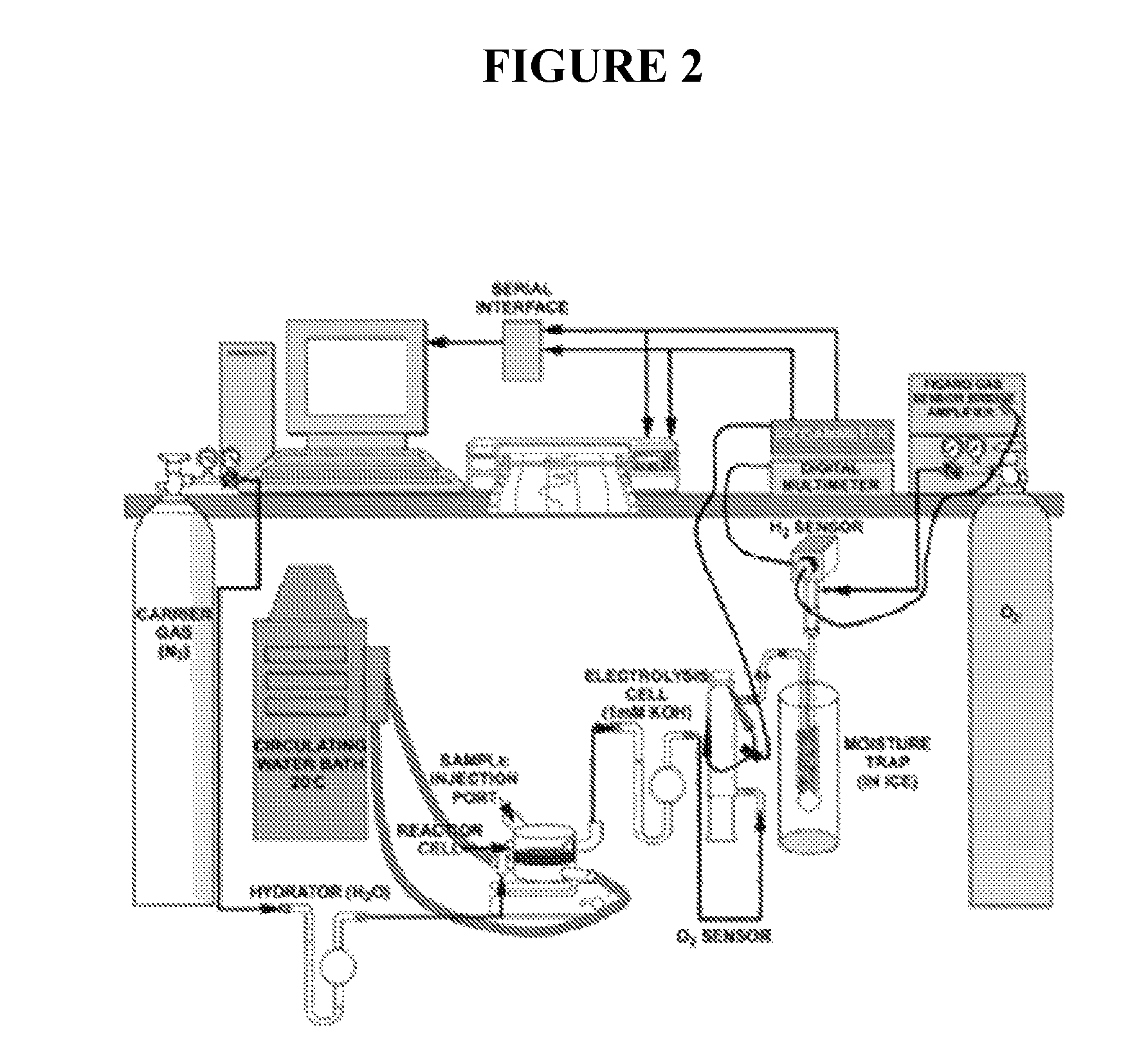
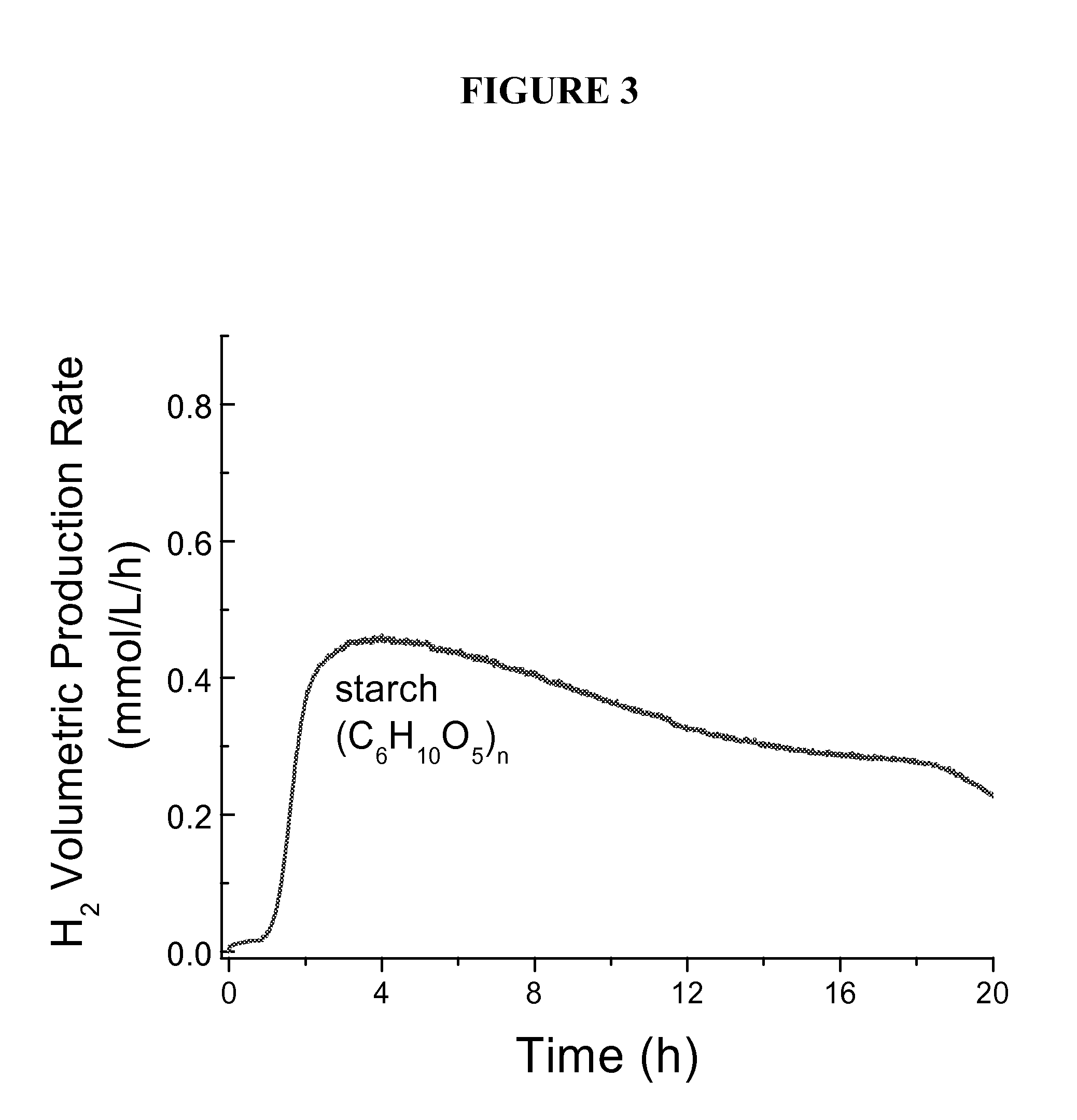
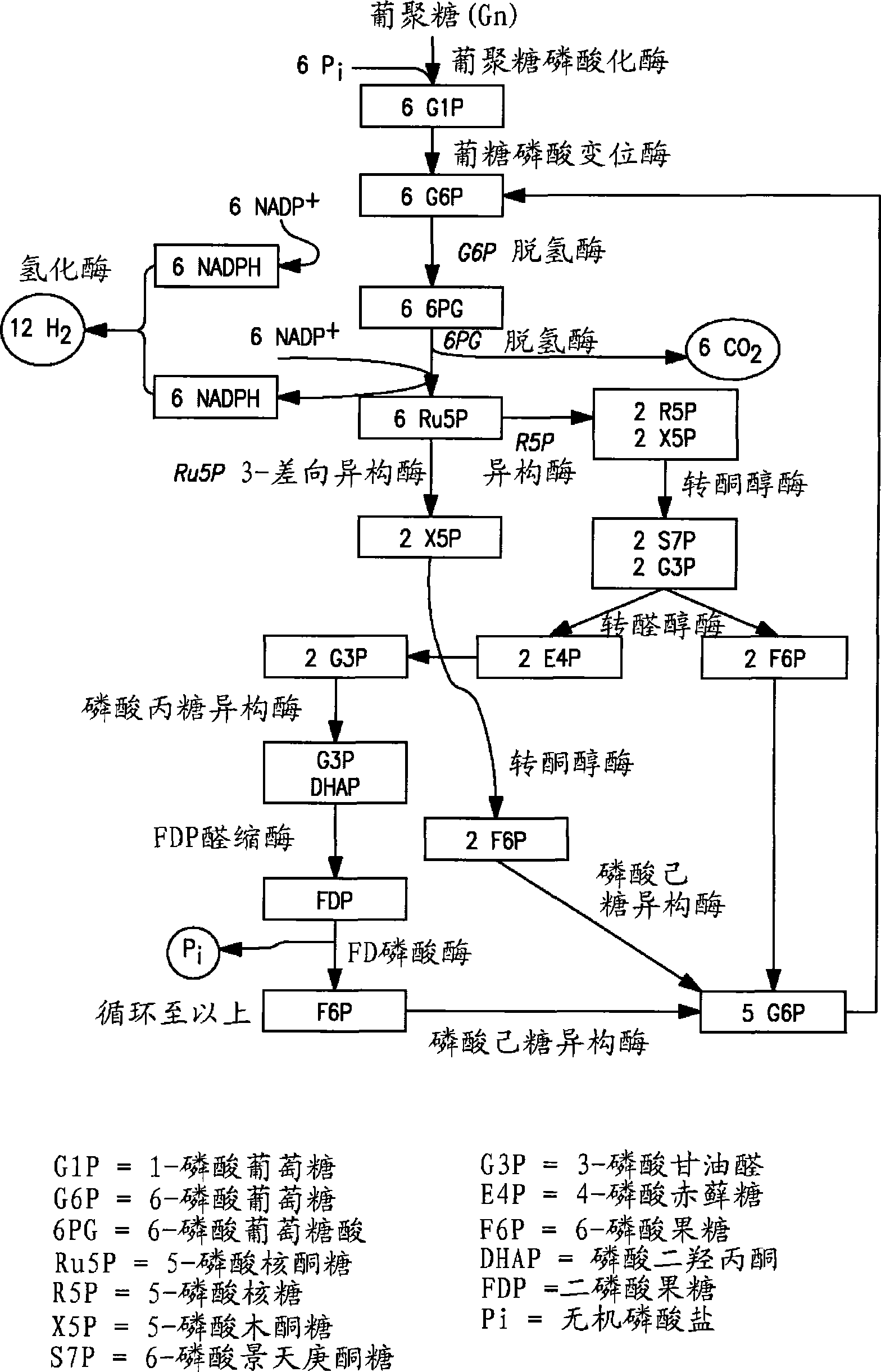
Biohydrogen production by an artificial enzymatic pathway
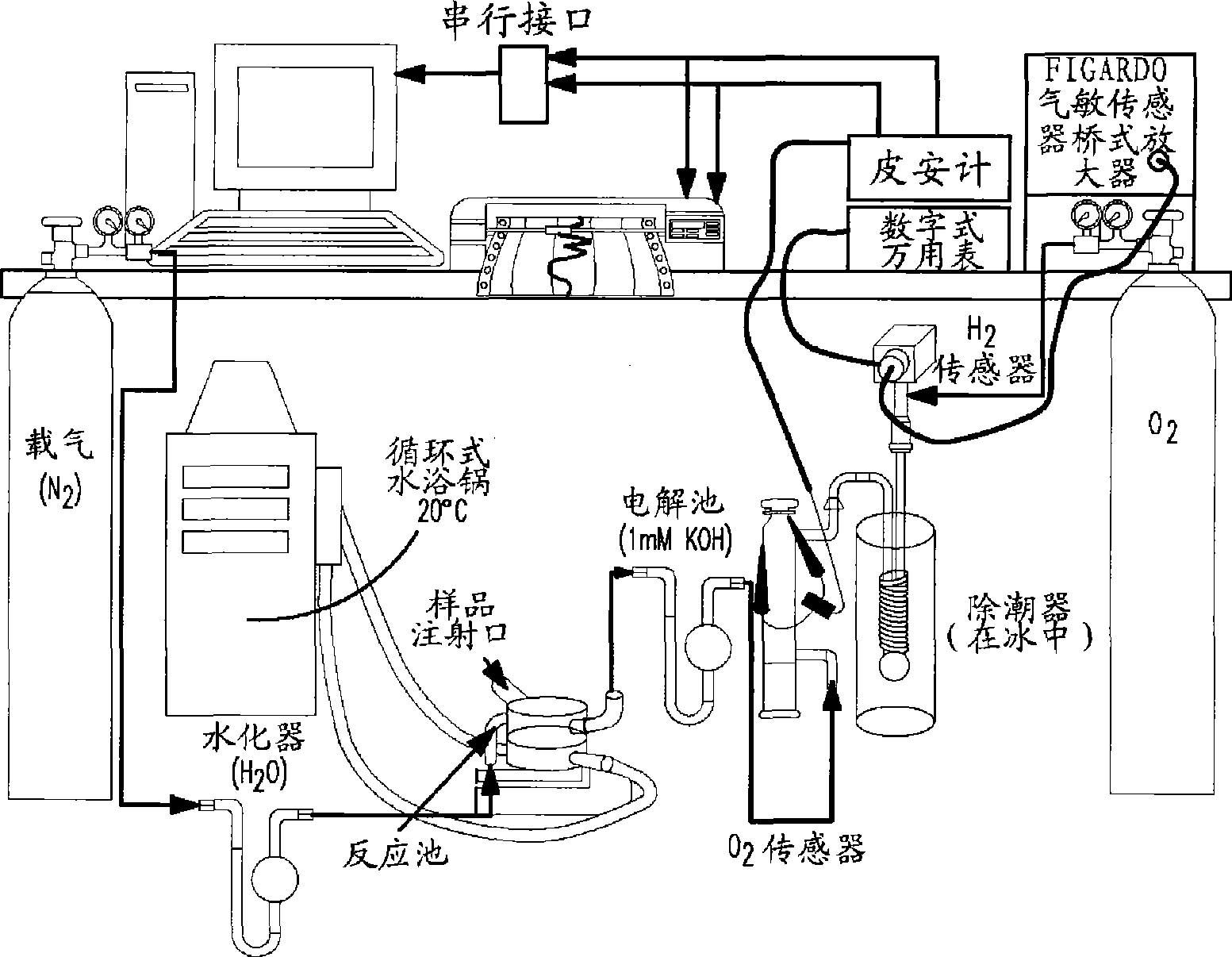
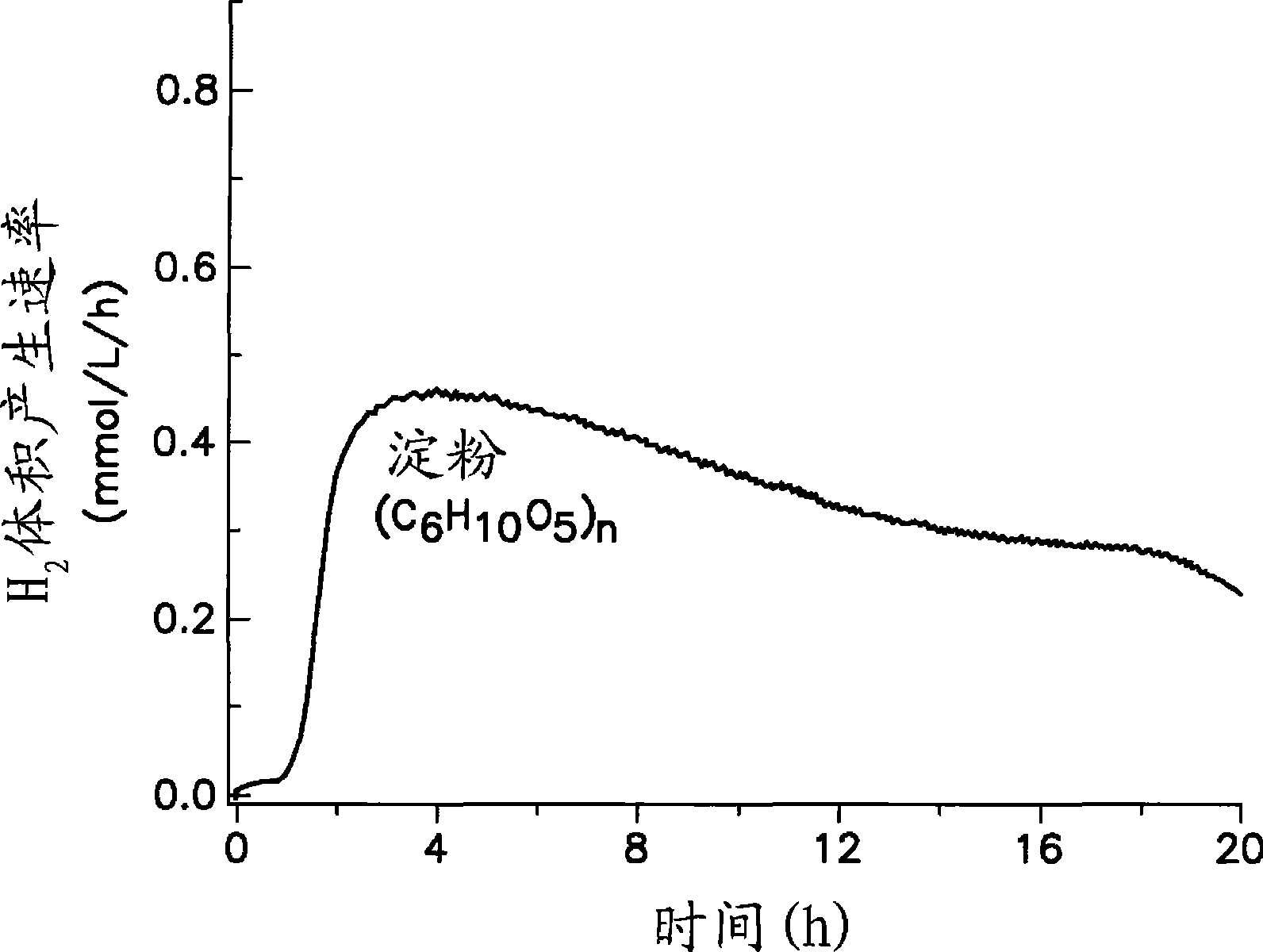
The present invention comprises an in vitro enzymatic process that effectively converts renewable polysaccharides into high yields of hydrogen at mild conditions, using only enzymes and water. The process comprises a number of enzymes: (1) phosphorylases, (2) phosphoglucomutases, (3) hydrogenases, and (4) enzymes involved in the pentose-phosphate pathway. Preferred embodiments of the process produce only hydrogen and carbon dioxide as net products, translating into an inexpensive method of generating hydrogen in very large quantities from low-cost feedstocks.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Method for improving content of cordyceps polysaccharide in cordyceps militaris
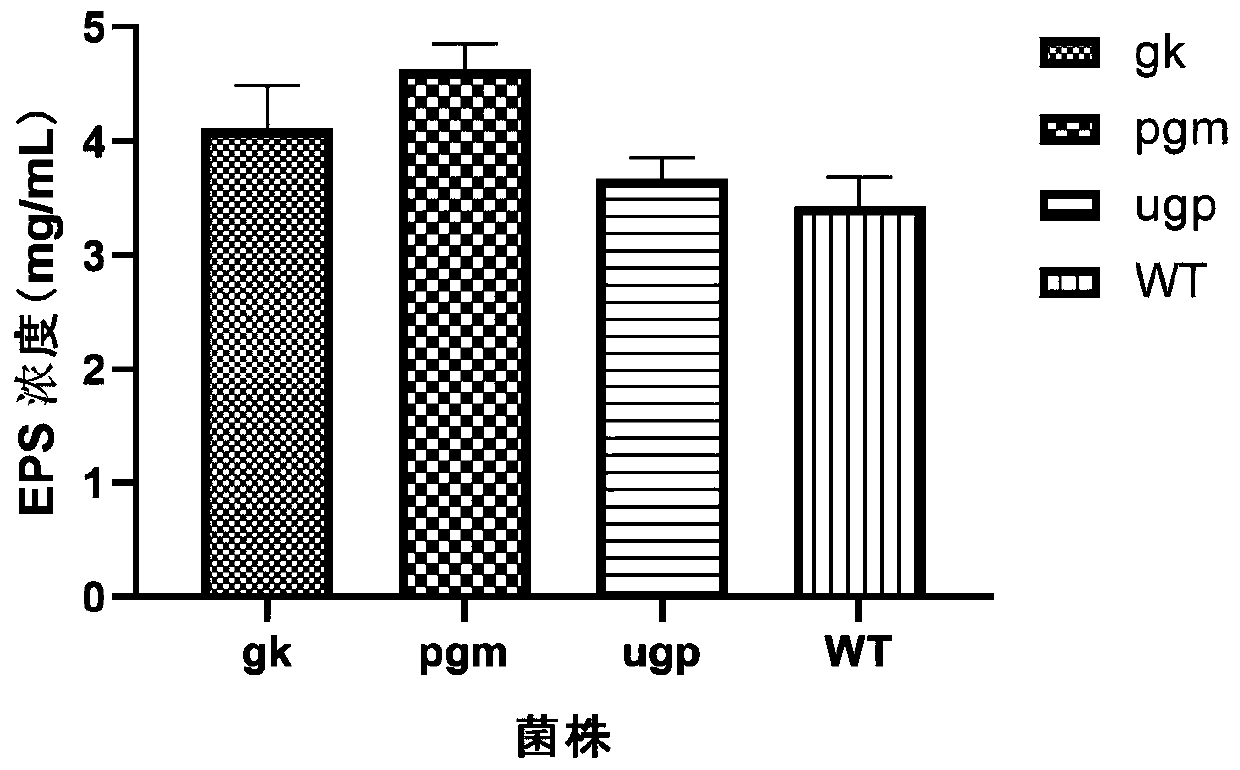
The invention discloses a method for improving the content of cordyceps polysaccharide in cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating cordyceps militaris recombinantbacteria containing a target gene into a fermentation culture medium, and carrying out shake cultivation at a temperature of 22-25 DEG C at 120-180 rpm to obtain fermentation liquor containing the cordyceps polysaccharide, wherein the target gene is a glucokinase gene gk, a glucophosphomutase gene psm or a pyrophosphorylase gene ugp. Through a transgenic technology, the gene mutation bacterial strain of the cordyceps militaris is obtained. Compared with an original bacterial strain, the mutation bacterial strain is characterized in that the yield of the cordyceps polysaccharide in the fermentation liquor of the mutation bacterial strain is 1.35 times, and a foundation is laid for further screening a good variety of the cordyceps militaris.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Fast-fermenting bread yeast strain and construction method thereof
ActiveCN104073449AMeeting the needs of "fast" yeastHigh starting capacityFungiPre-baking dough treatmentBiotechnologyComplete sequence
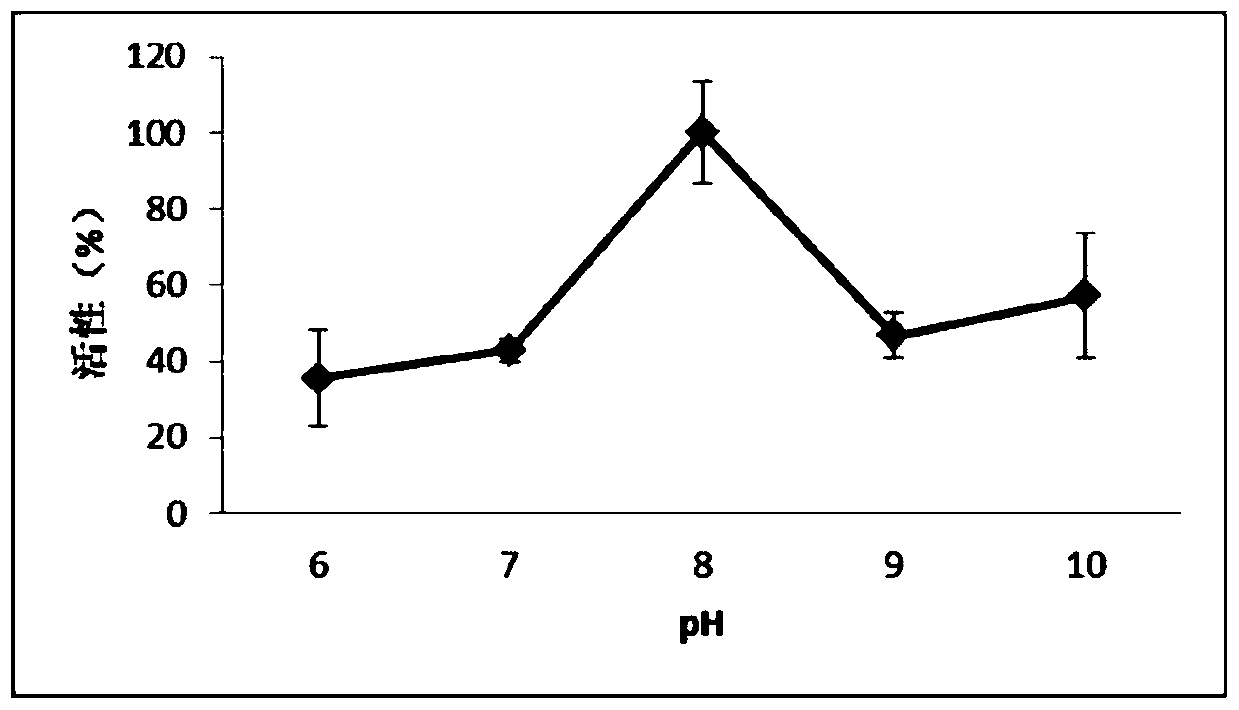
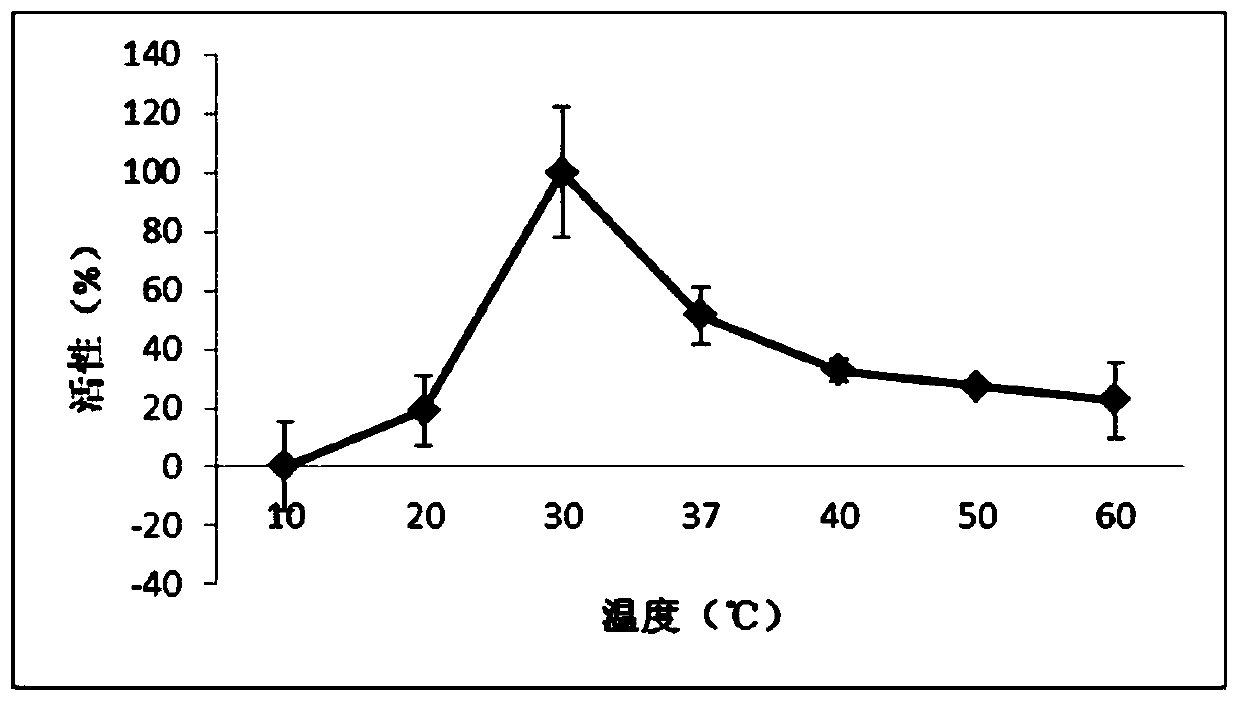
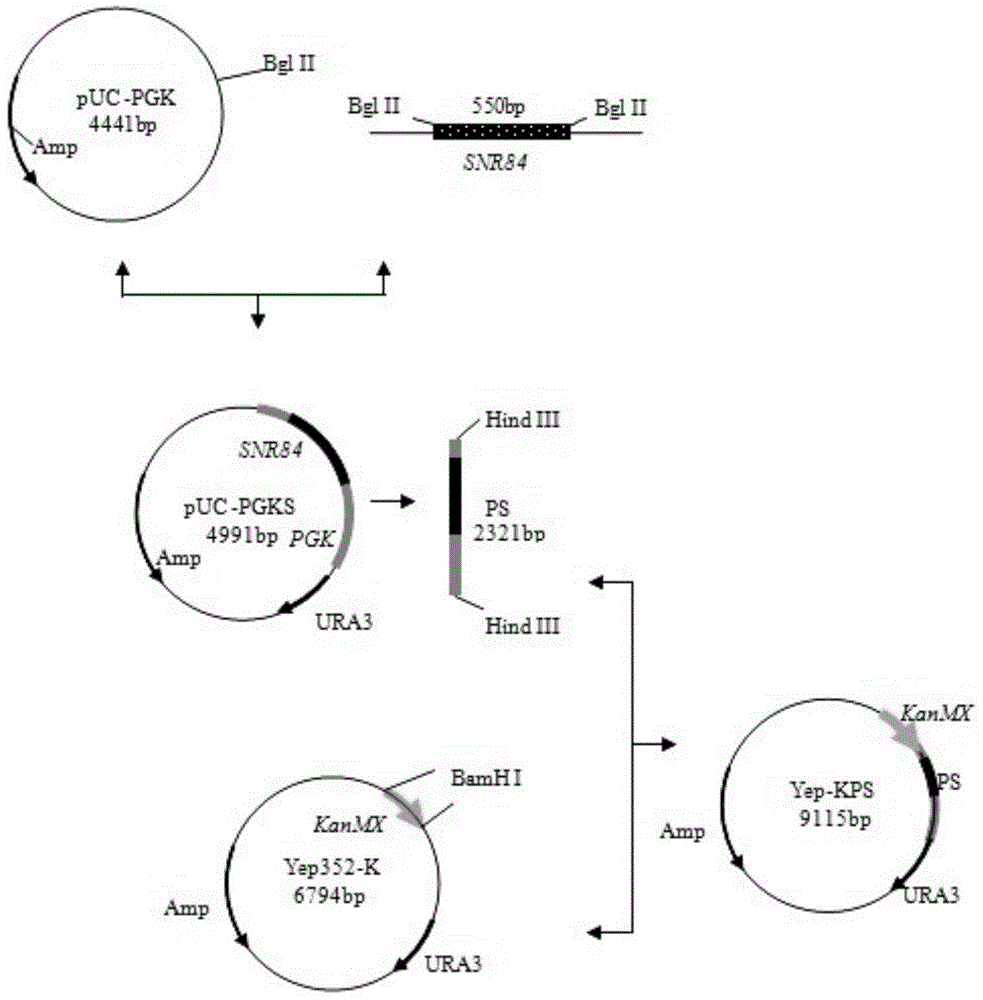
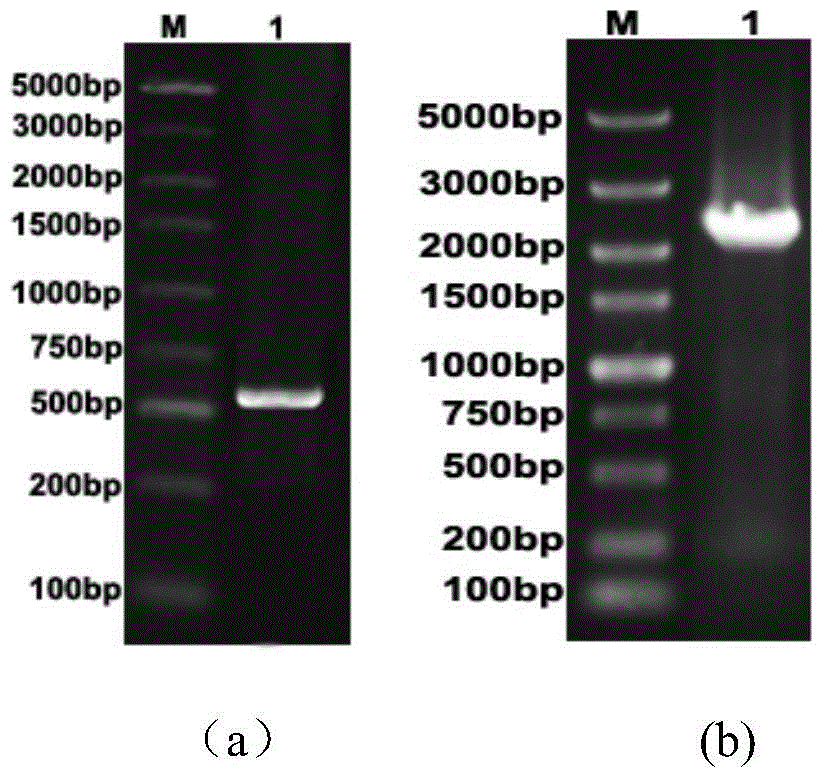
The invention discloses a fast-fermenting bread yeast strain and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a bioengineering technology. The construction method comprises the following steps: knocking out phosphoglucomutase genes PGM2 completely in the parent bread yeast strain; meanwhile, choosing a strong promoter PGK1 to over-express the complete sequence of H / ACA small nucleolus RNA (SNR84) to acquire the fast-fermenting yeast strain. The CO2 gas production of the fast-fermenting bread yeast strain in a non-sugaring paste for 1 hour reaches to 818mL; compared with the parent strain, the CO2 gas production is improved by 21.2% (the CO2 gas production of the parent strain fermenting in the non-sugaring paste for 1 hour reaches to 675mL); meanwhile, the fermenting time is shortened by 18.0%. The bread yeast strain has a good fermentability during fermenting in the non-sugaring paste, so that the requirement for the 'fast' yeast in a cooked wheaten food processing market is met. Therefore, the bread yeast strain has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing cordyceps militaris polysaccharide through multi-gene combined expression
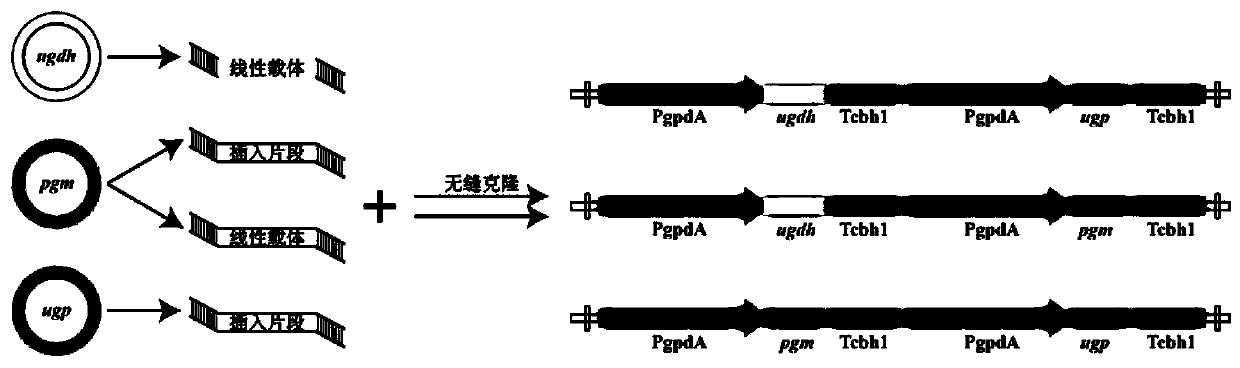
The invention discloses a method for preparing cordyceps militaris polysaccharide through multi-gene combined expression. The method comprises the following steps of introducing a combined gene into cordyceps militaris cells to construct recombinant cordyceps militaris genetically engineered bacteria, inoculating the recombinant cordyceps militaris genetically engineered bacteria into a fermentation culture medium, and carrying out fermentation culture at 22-25 DEG C at 100-150 rpm to obtain a fermentation liquor comprising cordyceps militaris polysaccharide; carrying out separating and purifying on the fermentation liquor to obtain the cordyceps militaris polysaccharide, wherein the combined gene is a combination of any two of a phosphoglucose mutase gene pgm, a pyrophosphorylase gene ugpor a UDP-glucose-6-dehydrogenase gene ugdh. The recombinant cordyceps militaris genetically engineered bacteria are constructed through a gene combination expression technology, and compared with a wild strain, the yield of cordyceps militaris exopolysaccharides in fermentation liquor of the genetically engineered bacteria is 1.78 times and is 5.713 g / L higher than the maximum yield of cordycepsmilitaris exopolysaccharides produced by fermentation reported in literatures at present.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids
ActiveCN105087453AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetically engineered organisms, especially to microbes like Escherichia coli with activity in catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids, and provides a genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids. The genetically engineered bacterium is prepared by coexpression of four genes respectively coding phosphoglucomutase, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase and uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase in a cell and introduction of the functional enzyme genes into the cell through expression vectors. The genetically engineered bacterium induces expression of functional enzyme protein under the condition of addition of an inductive agent--isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and is directly used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids; and the advantages of good cell growth, a short fermentation period and low cost are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Enhanced cellodextrin metabolism
InactiveCN103597084AIncreased activation levelActivation levels dropBiofuelsPeptidesGlucose utilizationCarbohydrate derivative
The present disclosure relates to host cells containing two or more of a recombinant cellodextrin transporter, a recombinant cellodextrin phosphorylase, a recombinant ss-glucosidase, a recombinant phosphoglucomutase, or a recombinant hexokinase; and to methods of using such cells for degrading cellodextrin, for producing hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon derivatives from cellodextrin, and for reducing ATP consumption during glucose utilization.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
glmm gene knock-out bacterial strain as well as preparation method and application in sieving mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase inhibitors
InactiveCN101928691AIntegrity breachImprove efficacyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention discloses a glmM gene knock-out bacterial strain ML2009 (mycobacterium smegmatis), CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 3418, which is constructed by using phosphoglucomutase participating in the biosynthesis of key components in a mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall. The bacterial strain ML2009 can be used as a cell model for sieving phosphoglucomutase inhibitors with high flux, be used for sieving effective phosphoglucomutase inhibitors from a combined compound library, traditional Chinese medicine and natural products to prepare tuberculosis-resisting medicaments with high medicine effects; and in addition, in the cells of a human body, the synthesis approach of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-acetyl glucosamine is different from that of mycobacterium tuberculosis, no phosphoglucomutase exists in the UDP-acetyl glucosamine, therefore, the reaction catalyzed by the mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase does not exist in the cells of the human body so that the tuberculosis-resisting medicaments developed by using the phosphoglucomutase as a target enzyme are harmless to the human body, and the defect that the traditional antibacterial medicament also kill normal cells is overcome.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering bacteria for over-expressing phosphoglucomutase gene and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene and construction method
InactiveCN106916776AIncrease productionLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
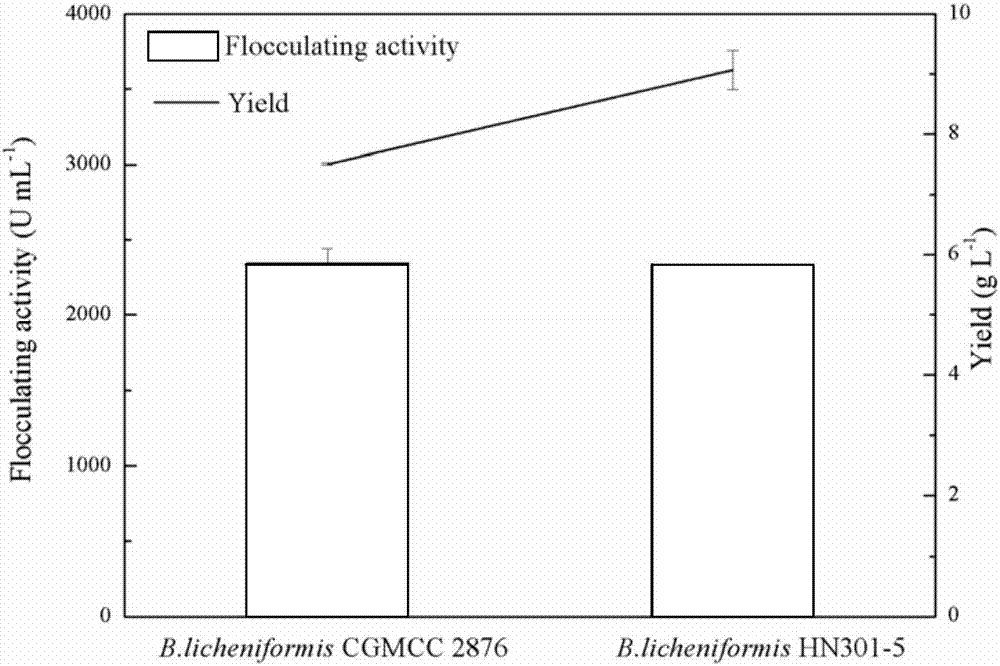
Engineering bacteria for over-expressing a phosphoglucomutase gene and a uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene and a construction method. The invention relates to gene engineering and microbial fermentation and discloses a strain of bacillus licheniformis, which simultaneously over-expressing a phosphoglucomutase gene (pgcA) and a UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase gene (gtaB1), and the construction method thereof. In the method, the genes of the phosphoglucomutase and the UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, which are key enzymes in a synthesis route of a polysaccharide flocculating agent, are cloned, and a recombinant expression vector is constructed through escherichia coli-bacillus shuttle plasmid. Through an electrotransformation method, a recombinant plasmid is introduced into the bacillus licheniformis, thereby constructing a recombinant bacillus licheniformis strain HN301-5. The recombinant bacillus licheniformis is increased in yield of the polysaccharide flocculating agent by 20.77% than that of an original strain, and is hopeful to be applied in industrial production of the polysaccharide flocculating agent, thereby increasing yield and reducing cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
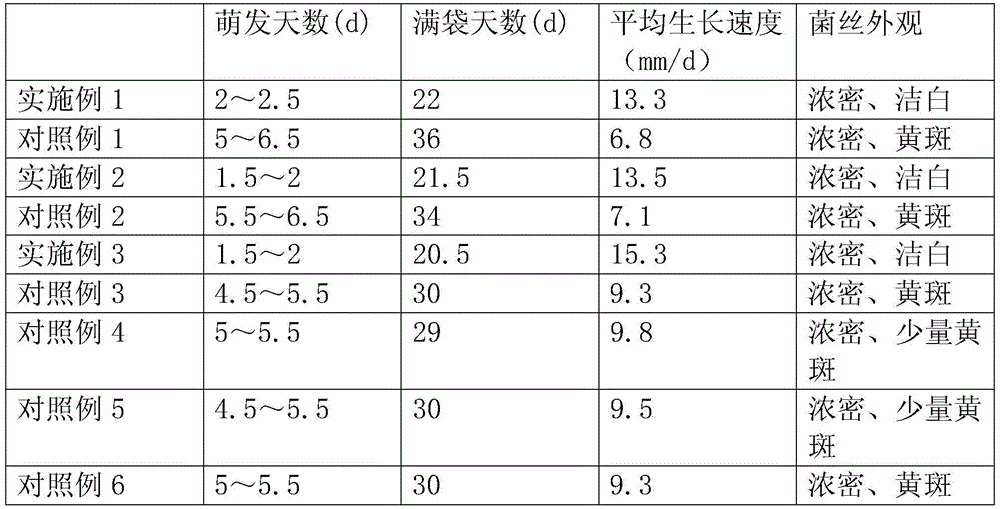
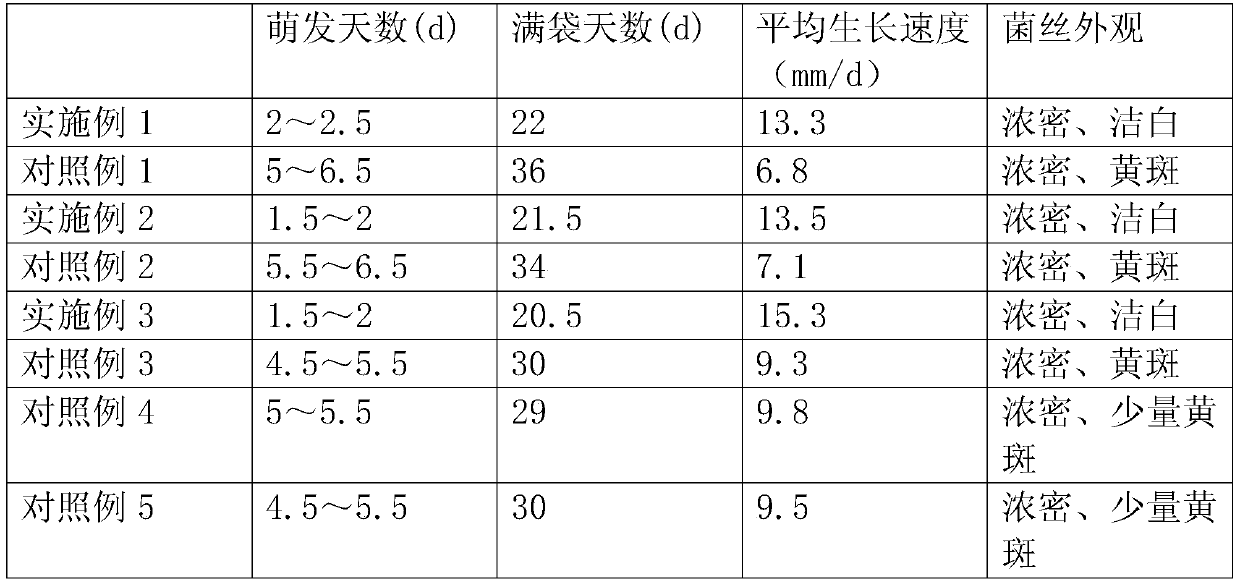
Method for planting Ganoderma Lucidum
InactiveCN105660166AHigh activityIncrease contentCultivating equipmentsOrganic fertilisersBiotechnologyLactose
The invention provides a method for planting Ganoderma Lucidum. The method comprises: strain culture, culture medium preparation, mycelia culture, and sprouting management. The culture medium preparation includes mixing, grinding, sacking, and sterilizing the following raw materials by part of weight: 30-35 mixed sawdust by parts of weight, 10-20 corncob by parts of weight, 5-10 rice bran by parts of weight, 1-3 burdock by parts of weight, 2-4 gastrodia elata by parts of weight, and 0.5-1.5 lactose by parts of weight. The adding of gastrodia elata, burdock, and lactose to the regular culture medium can increase activity of [alpha]-Phosphoglucomutase, promote metabolism of Ganoderma Lucidum cells to migrate more towards a branch synthesized by Ganoderma Lucidum polysaccharide, which greatly increases content of Ganoderma Lucidum exopolysaccharide, and at the same time promotes growth of Ganoderma Lucidum, and greatly shortens time for sacking mycelia.
Owner:GUILIN DA YE LING YVU BIOTECH CO LTD
Ganoderma lucidum cultivation method capable of increasing content of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide
InactiveCN105493896AHigh activityIncrease contentBioloigcal waste fertilisersCultivating equipmentsAnimal scienceGanoderma pseudoferreum
The invention provides a ganoderma lucidum cultivation method capable of increasing the content of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. The ganoderma lucidum cultivation method comprises the steps of strain cultivation, culture medium preparation, hypha cultivation and ganoderma lucidum emergence management, wherein the culture medium preparation is characterized by mixing, smashing, bagging and sterilizing the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 to 35 parts of mixed wood chips, 10 to 20 parts of corncobs, 5 to 10 parts of rice bran, 1 to 3 parts of grifola frondosa and 2 to 4 parts of fructus arctii. According to the ganoderma lucidum cultivation method provided by the invention, the fructus arctii and the grifola frondosa are added in a conventional culture medium, so that the activity of alpha-phosphoglucomutase can be increased, the metabolism of ganoderma lucidum cells is facilitated to more migrate towards a branch compounded by the ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide, and the content of exopolysaccharide of ganoderma lucidum can be greatly increased; meanwhile, the growth of the ganoderma lucidum can be promoted, and the full bagging time of hypha is greatly shortened.
Owner:GUILIN DA YE LING YVU BIOTECH CO LTD
A whole-cell catalytic method for preparing tagatose
ActiveCN107988286BHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliTagatose
The invention discloses a method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of transferring plasmid containing an alpha-glucan phosphorylase gene (or cellulosic polysaccharide phosphorylase and cellobiose phosphorylase genes, or a sucrose phosphorylase gene), a phosphoglucomutase gene, a glucose phosphate isomerase gene, a 6-phosphate tagatose epimerase gene, and a 6-phosphate tagatose phosphatase gene into engineered escherichia coli, so as to obtain converted bacterial strain; inducing the converted bacterial strain to produce enzyme, and permeabilizing; mixing the permeabilized bacterial strain, establishing a whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction system with starch or starch derivative (or mixture of cellulase and cellulose or cellulose derivative, or sugarcane), and performing the whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction, so as to obtain the tagatose. The method has the advantages that the tagatose is prepared by the whole-cell catalysis; the cost is low, the pollution is low, the yield rate is high, and the like; the method is suitable for preparing the tagatose in a scale way.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Nutritional breakfast for repairing glucose tolerance factor and preparation method of nutritional breakfast
ActiveCN105520144AImprove utilizationImprove comorbiditiesFood ingredient functionsGlucose tolerance factorIn vivo
The invention discloses nutritional breakfast for repairing the glucose tolerance factor. Buckwheat, shiitake and purple yams are mixed and decocted with water to form porridge, and then the nutritional breakfast is prepared; the weight ratio of the buckwheat to the shiitake to the purple yams to the water is 1:1:1:(3-4). Best food varieties are selected for preparing the nutritional breakfast, nutrition necessary to the glucose tolerance factor of the human body is provided, the nutrition of the glucose tolerance factor is balanced again, best nutrition is realized, nutrition damage of the glucose tolerance factor of type 2 diabetic patients and pre-diabetic patients with impaired fasting glucose and the damaged glucose tolerance factor can be repaired, the biological effect of insulin is better enhanced, utilization of in-vivo glucose is accelerated by activating phosphoglucomutase, the glucose is converted into fat, and elevated blood glucose is promoted to return to normal quickly. Thus, the dose of a medicine is reduced, complications of the diabetic patients are improved, the living quality is improved, and the life is prolonged.
Owner:三亚怡心营养咨询服务中心
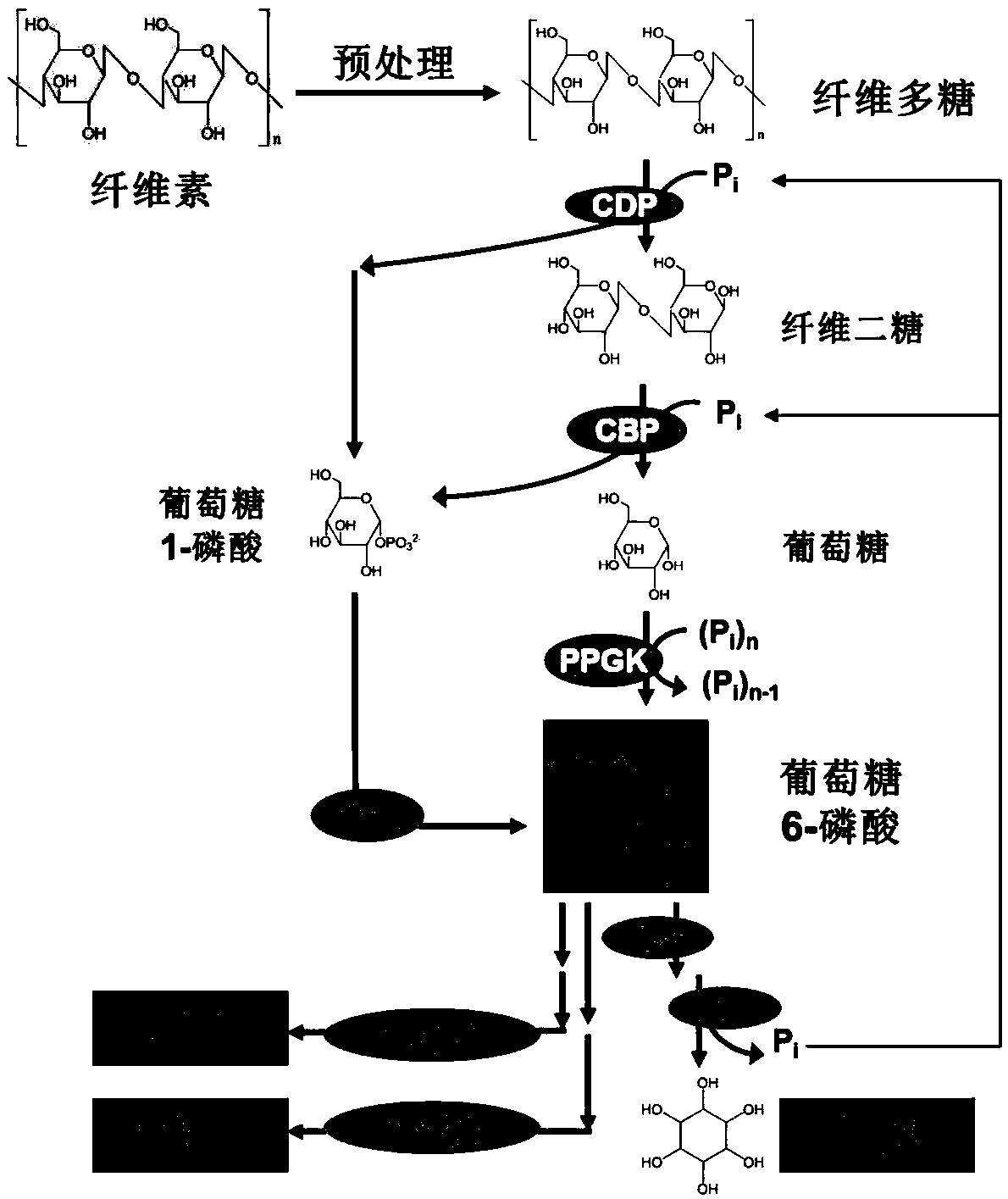
Method for producing inositol by complete phosphorolysis of cellulose
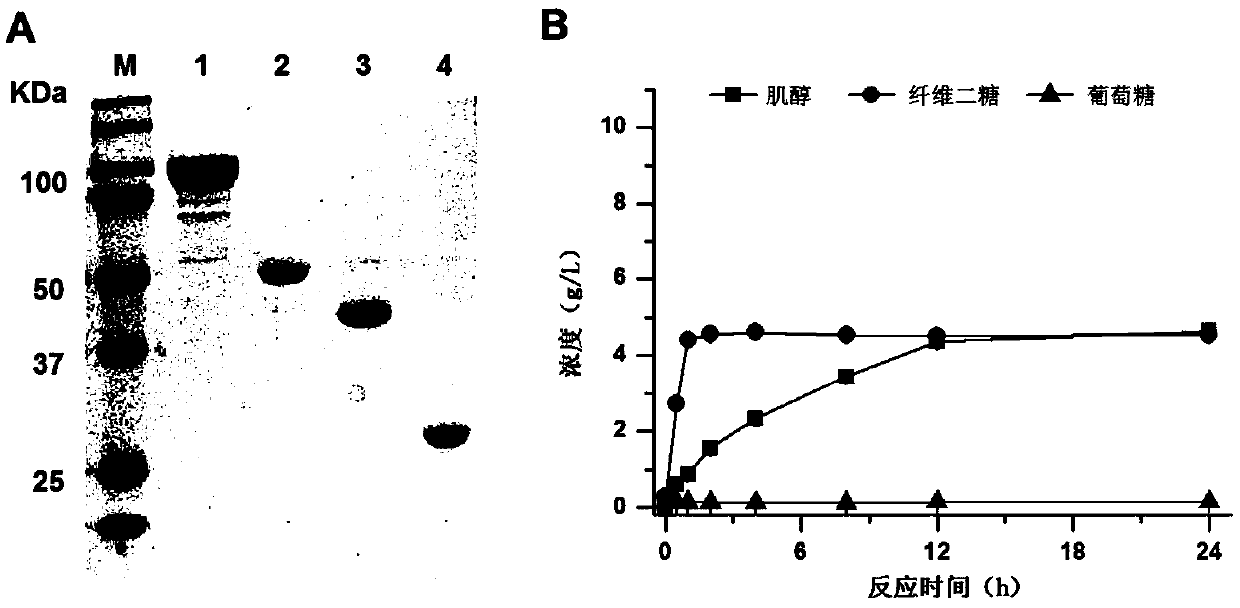
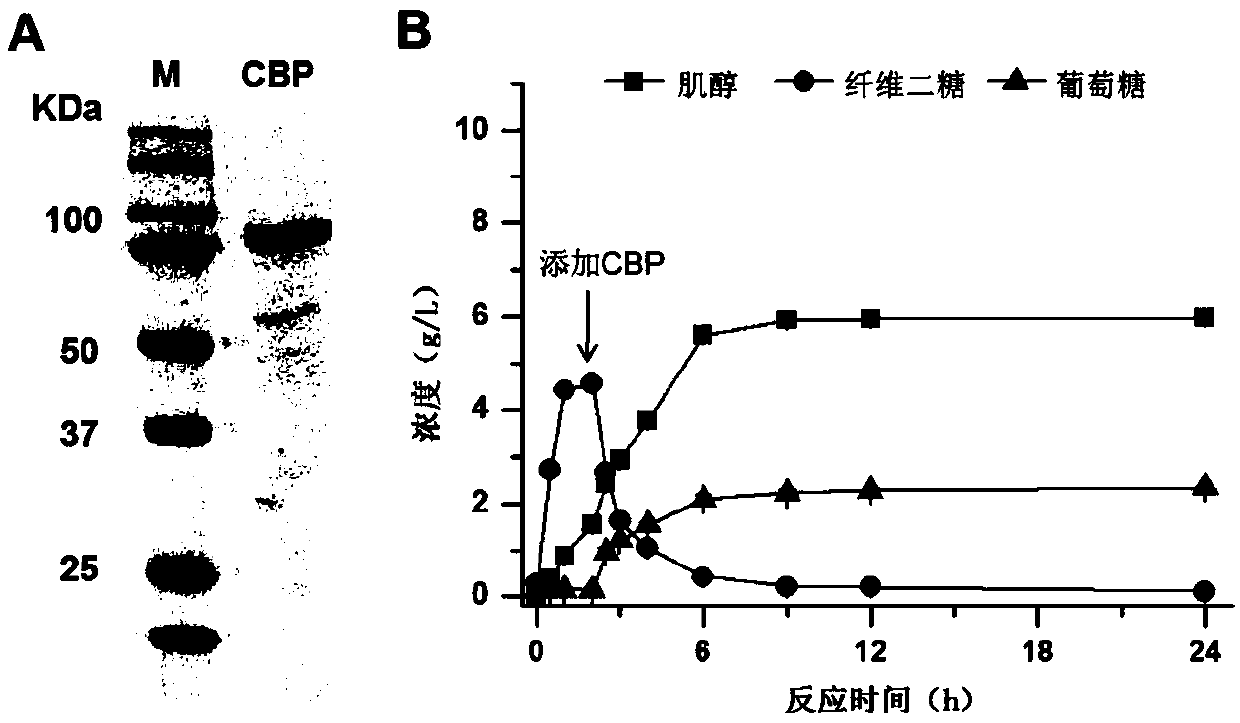
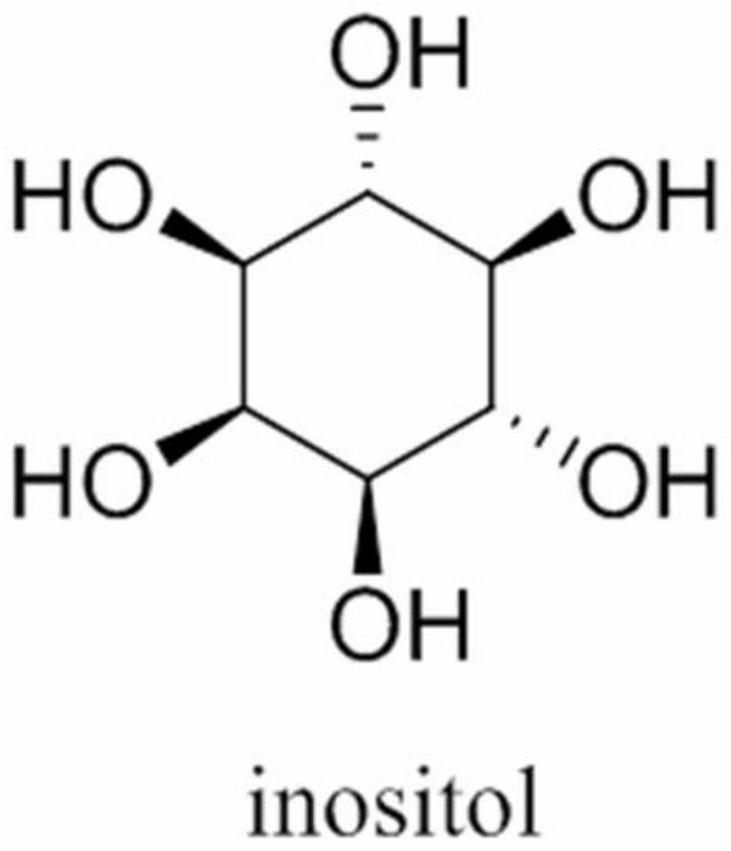
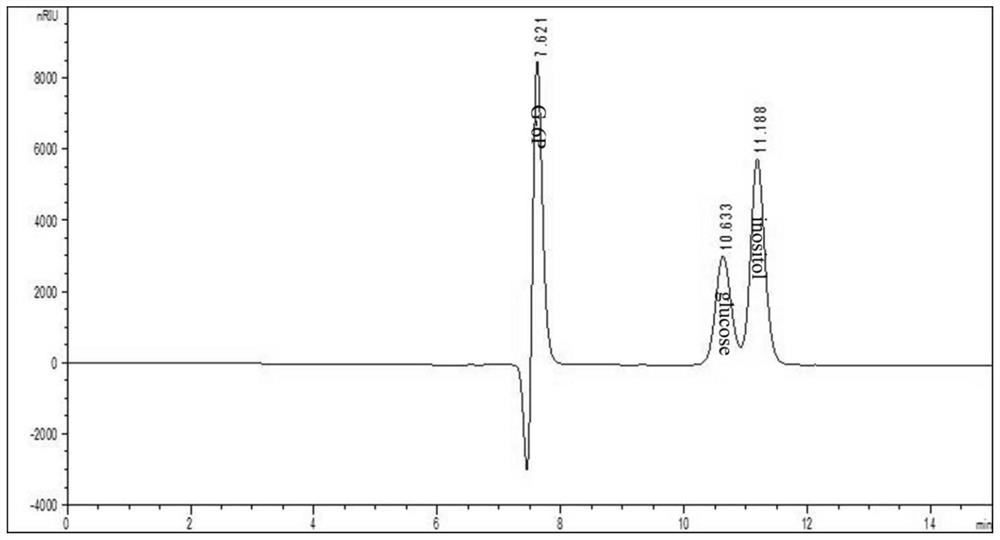
ActiveCN110857443AComplete phosphorylation achievedImprove conversion rateFermentationCellulosePhosphorylation
The invention relates to the field of enzymatic catalytic preparation of inositol, in particular to an enzymatic preparation method for producing inositol by complete phosphorolysis of cellulose. According to the preparation method of inositol, pretreated cellulose (the main component is fiber polysaccharide) is used as a substrate for the enzyme catalytic reaction; and cellulose polysaccharide phosphorylase, cellobiose phosphorylase, polyphosphate glucokinase, phosphoglucomutase, inositol-1-phosphate synthase and inositol monophosphatase are adopted to catalyze complete phosphorolysis of cellulose polysaccharide into inositol. By optimizing the multienzyme reaction process and controlling the reaction temperature in stages, the conversion efficiency of the substrate and the inositol yieldare significantly improved, and the reaction time is shortened. The technical method realizes the complete phosphorolysis of the cellulose substrate, and can also be used for other in-vitro multi-enzyme reaction systems to catalyze cellulose polysaccharide for production of hydrogen, electricity or other bio-based chemicals.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plastidic phosphoglucomutase genes
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a plastidic phosphoglucomutase protein is disclosed. Also disclosed is the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a substantial portion of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Brucella melitensis immune labeled recombinant strain and application thereof in preparation of vaccine
InactiveCN101629152ALow toxicityLittle virulenceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMarker vaccineImmunologic function
The invention discloses a brucella melitensis immune labeled recombinant strain and the application thereof in the preparation of vaccine. The brucella melitensis immune labeled recombinant strain is obtained by inactivating phosphoglucomutase in brucella melitensis. Compared with the original strain, the strain obtained in the invention has little strain toxicity and can be taken as the vaccine for immunization of animals without inactivation. When the strain is used for the immunization of a mouse, immune response state which is different from standard strain and the existing vaccine strain can be generated in the body of the mouse, and the diseased animal can be distinguished from the group of immunized animals by immunology detection of animal serum. The invention is beneficial to the reformation of brucellosis vaccine, the research and the preparation of differential diagnosis reagent and the development of the brucella gene-deleted marking vaccine and the differential diagnosis reagent matched with the vaccine, and has very important significance on promoting the elimination of brucellosis of the animals all over the world.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Gene for encoding phosphoglucomutase in kelp, protein and applications of gene
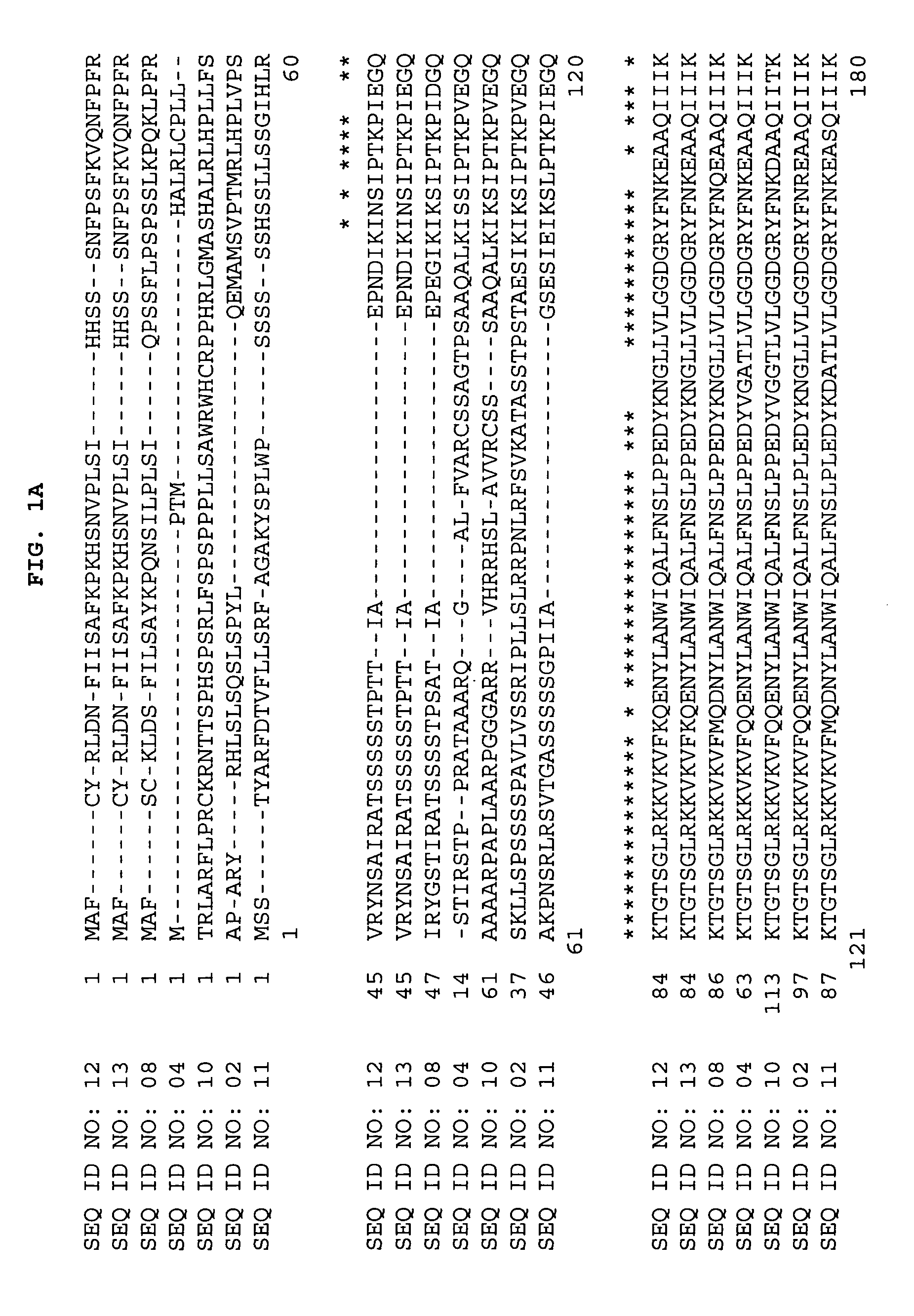
ActiveCN107475274AImprove stabilityHigh specific vitalityTransferasesIsomerasesGenetic engineeringGlucose phosphate
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field, particularly belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a gene for encoding phosphoglucomutase in kelp, a protein and applications of the gene. The encoded gene is named as SjaPGM2 gene, the sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, the encoded protein is named as SjaPGM2 protein, the sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and is a PGM. The SjaPGM2 protein also has higher catalytic activity compared with the prior art, more excellent metal ion stability and thermal stability, milder optimal reaction temperature, higher catalytic efficiency and more applicable to improvement of plant nutrition quality compared with the prior art, thus providing a very suitable gene and protein resources for the genetic engineering application of PGM.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Detection reagent containing phosphoglucomutase 5-antibody and application of detection reagent
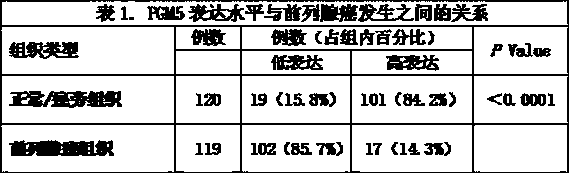
InactiveCN110031625AEffective discrimination expressionMaterial analysisHorseradish peroxidaseProtein level
The invention discloses a detection reagent containing a phosphoglucomutase 5-antibody and application of the detection reagent. The immunohistochemical detection reagent for prostatic cancer diagnosis is provided. According to the detection reagent, an antibody specific to human PGM5 proteins is used as a first antibody, a rabbit 2-antibody marked with HRP (horseradish peroxidase) and other chemical markers is used as a second antibody, and the expression quantity of target antigens (PGM5) in histocytes of a to-be-detected sample is detected through color development and other functions. Byuse of the detection reagent, the expression of PGM5 genes in the histocytes at the protein level can be effectively discriminated; and the diagnosis of a prostatic cancer is judged by detecting the expression quantity of the PGM5 proteins in the histocytes, and therefore a new basis is provided for early diagnosis of the prostatic cancer.
Owner:SUZHOU MUNICIPAL HOSPITAL
Enzymatic determination of lithium ions using phosphoglucomutase
InactiveUS20130071871A1High strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisLithiumPhysical chemistry
Owner:SPECIALTY ASSAYS
Uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase activity detecting kit and method
InactiveCN105483208ALow requirements for measurement conditionsDetermination conditions meetMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylaseDistilled water
The invention discloses a uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase activity detecting kit and method. The kit comprises an extracting solution, a reagent I, a reagent II, a reagent III, a reagent IV and a reagent V, wherein the extracting solution is prepared by uniformly mixing Tris, distilled water, HCl, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt, DTT and saccharose; the reagent I is prepared by uniformly mixing the extracting solution, distilled water, MgCl2 and UDPG; the reagent II is composed of NADP; the reagent III is composed of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; the reagent IV is composed of phosphoglucomutase; the reagent V is prepared by dissolving PPi into distilled water. According to the kit, lots of groping and adjusting experiments are conducted on the extracting solution components in the uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase activity detecting method and a detecting system, and the effects that the extracting solution components are simple, the extracting effect is good, the detecting system is small and the operation is simple, convenient and quick are achieved finally.
Owner:SUZHOU COMIN BIOTECH
Plastidic phosphoglucomutase genes
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a plastidic phosphoglucomutase protein is disclosed. Also disclosed is the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a substantial portion of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Gene encoding phosphoglucomutase in kelp, its protein and application
ActiveCN107475274BImprove stabilityHigh specific vitalityTransferasesIsomerasesBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field, particularly belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a gene for encoding phosphoglucomutase in kelp, a protein and applications of the gene. The encoded gene is named as SjaPGM2 gene, the sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, the encoded protein is named as SjaPGM2 protein, the sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and is a PGM. The SjaPGM2 protein also has higher catalytic activity compared with the prior art, more excellent metal ion stability and thermal stability, milder optimal reaction temperature, higher catalytic efficiency and more applicable to improvement of plant nutrition quality compared with the prior art, thus providing a very suitable gene and protein resources for the genetic engineering application of PGM.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
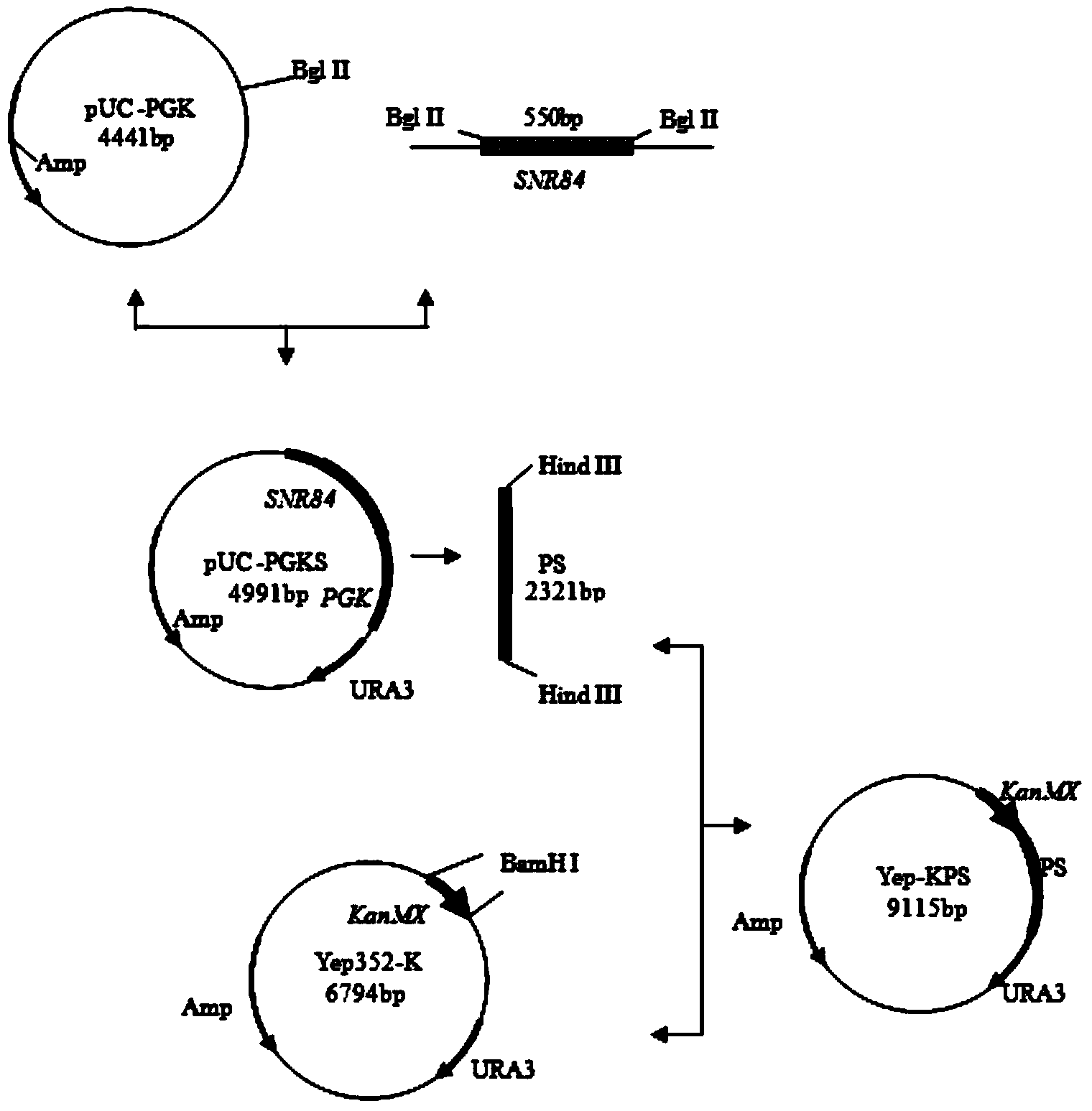
A strain of baker's yeast suitable for fermentation of dough without adding sugar and its breeding method
ActiveCN104073449BMeeting the needs of "fast" yeastHigh starting capacityFungiPre-baking dough treatmentBiotechnologySmall nucleolar RNA
The invention discloses a baker's yeast strain suitable for dough fermentation without adding sugar and a breeding method thereof, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The present invention obtains the fast-fermenting baker's yeast strain by completely knocking out the glucose phosphomutase gene PGM2 in the parental baker's yeast strain, and selecting the strong promoter PGK1 to overexpress the whole sequence of H / ACA small nucleolar RNA (SNR84) . The fast-fermenting baker's yeast strain was subjected to 1h CO in unsweetened dough fermentation 2 Gas production reached 818mL, which was 21.2% higher than that of the parental strain (the parental strain was fermented without sugar for 1h CO 2 Gas production is 675mL), and the fermentation time is shortened by 18.0%. The baker's yeast has strong fermentation ability in dough without adding sugar and has wide application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide high-yield engineering strain rmust and its construction method
InactiveCN103865814BIncrease productionLabor savingFungiMicroorganism based processesPromoterMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a high-yield ganoderan engineering strain Rmust and a construction method thereof. A collection number of the ganoderan high-yield engineering strain Rmust collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) is CGMCCNO.8258. The high-yield ganoderan lucid ganoderma engineering strain Rmust provided by the invention is obtained by selecting a lucid ganoderma strong promoter P-(i)gpd( / i) to over-express and code a PGM (phosphoglucomutase)-gene. Shake flask fermentation experiment indicates that the content of ganoderan generated by converter strain is 1.6 times the content of wild type strain (WT strain) on the condition that cell growth of the ganoderan high-yield engineering strain Rmust is not affected, wherein the amount (mg / g) of the ganoderan produced by 1g of dry mycelium is improved to 236.95mg / g + / -1.28mg / g from 145.9 mg / g + / -1.65mg / g, and therefore, the high-yield strain can be applied as the engineering strain for producing the ganoderan and has wide application prospect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biohydrogen production by an artificial enzymatic pathway
The present invention comprises an in vitro enzymatic process that effectively converts renewable polysaccharides into high yields of hydrogen at mild conditions, using only enzymes and water. The process comprises a number of enzymes: (1) phosphorylases, (2) phosphoglucomutases, (3) hydrogenases, and (4) enzymes involved in the pentose-phosphate pathway. Preferred embodiments of the process produce only hydrogen and carbon dioxide as net products, translating into an inexpensive method of generating hydrogen in very large quantities from low-cost feedstocks.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Escherichia coli recombinant bacterium for synthesizing inositol by efficiently utilizing glucose as well as construction method and application of escherichia coli recombinant bacterium
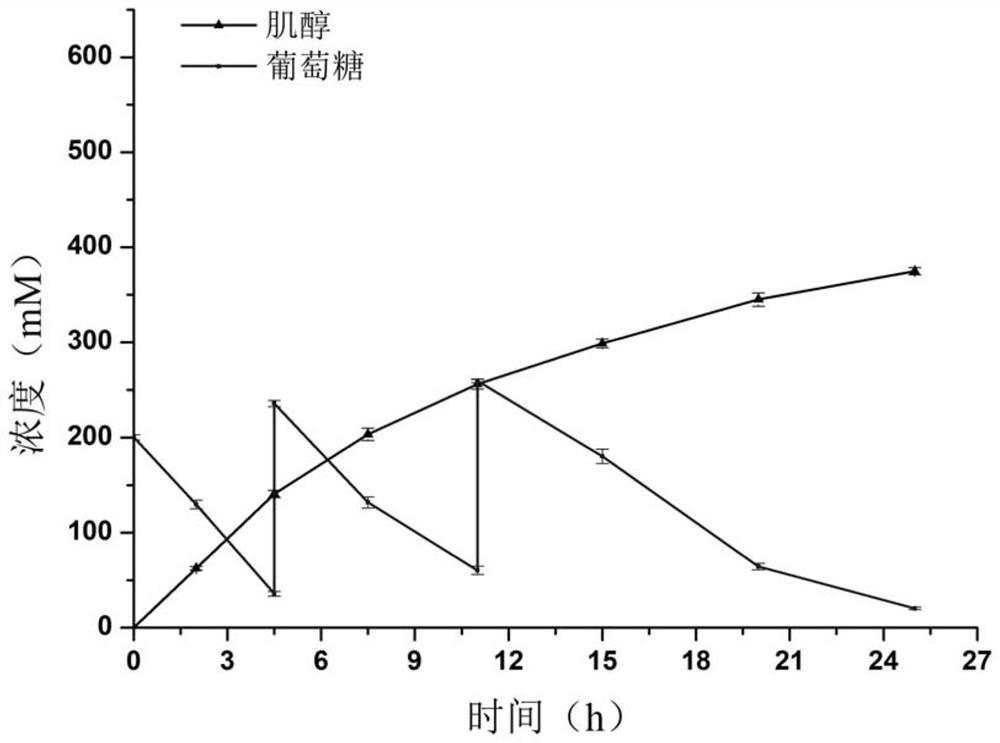
The invention discloses an escherichia coli recombinant bacterium for synthesizing inositol by efficiently utilizing glucose as well as a construction method and application of the escherichia coli recombinant bacterium. The construction method of the escherichia coli recombinant bacterium for producing the inositol, provided by the invention, comprises the steps: introducing an inositol-3-phosphate synthetase gene and an inositol monophosphate enzyme gene into host bacteria to obtain the escherichia coli recombinant bacteria for producing the inositol, wherein the host bacteria are wild escherichia coli or mutant escherichia coli; and the mutant escherichia coli is obtained by knocking out a glucose-6-phosphate isomerase gene or a glucophosphomutase gene or a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in an SG104 genome of the mutant escherichia coli. Glucose can be efficiently utilized to synthesize the inositol by utilizing the escherichia coli recombinant strain for producing the inositol, and the yield of the inositol can be up to 375 mM (67.5 g / L). For inositol production, huge economic benefits can be generated, and the method has great popularization and application values.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com