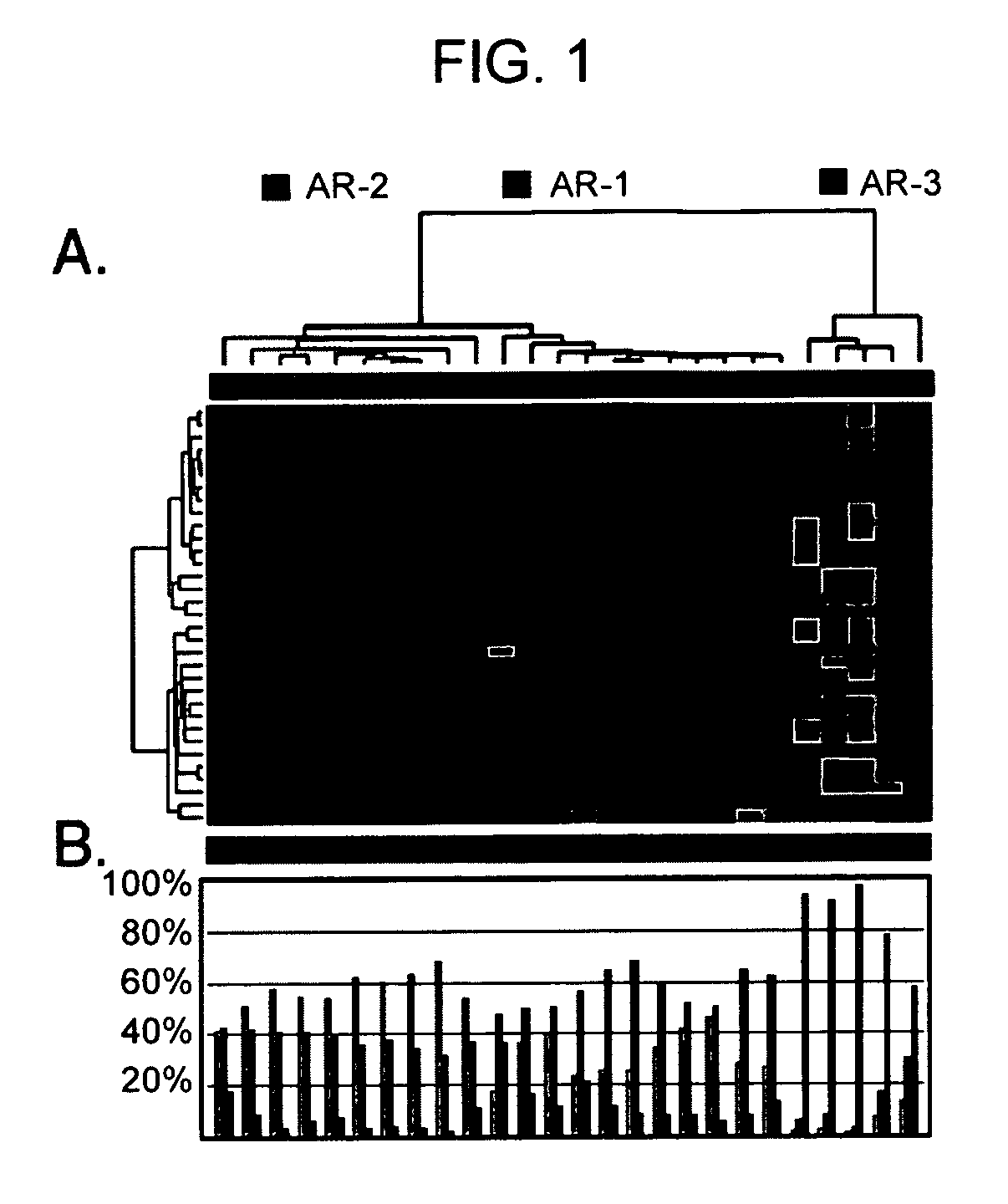
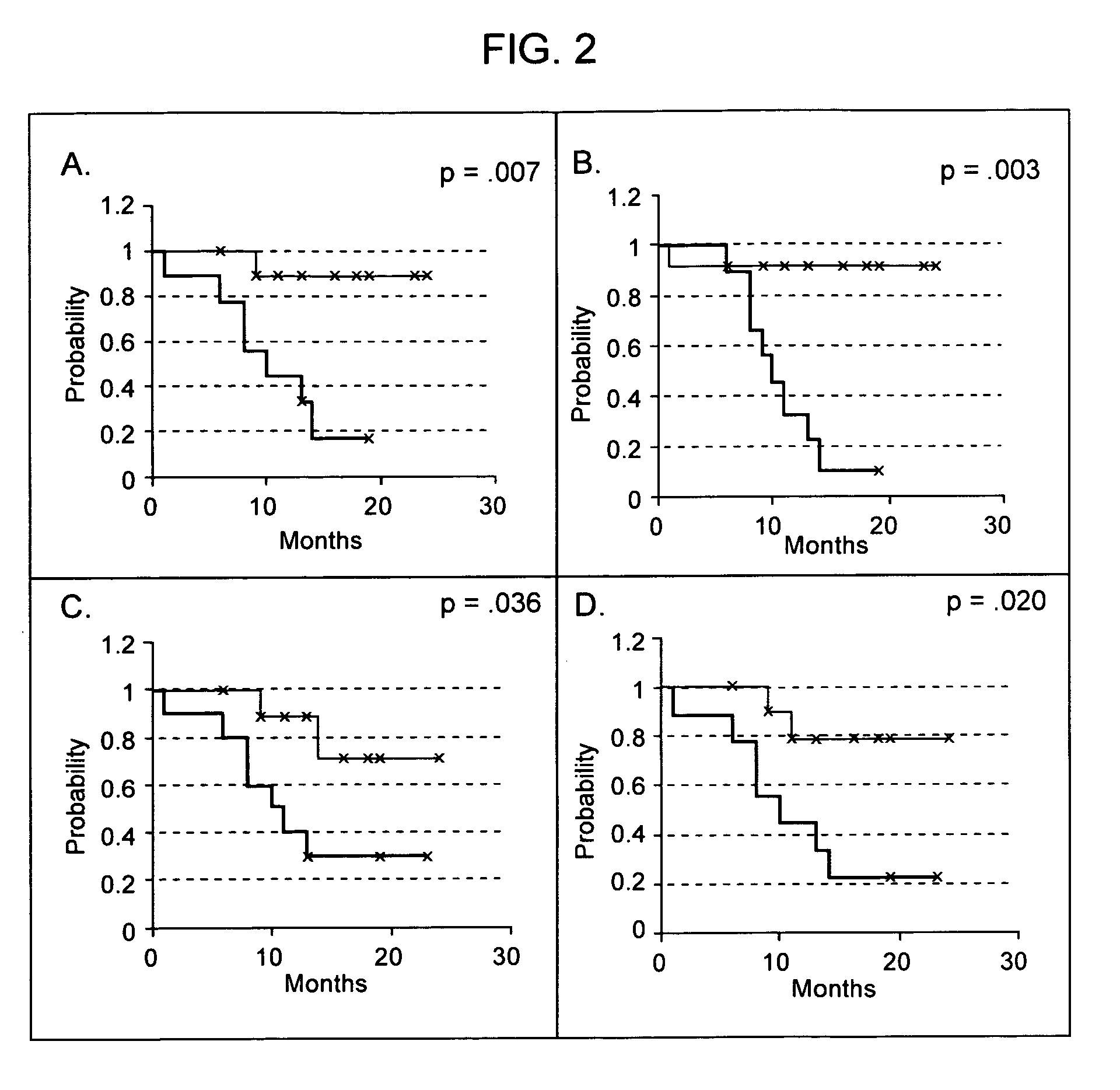
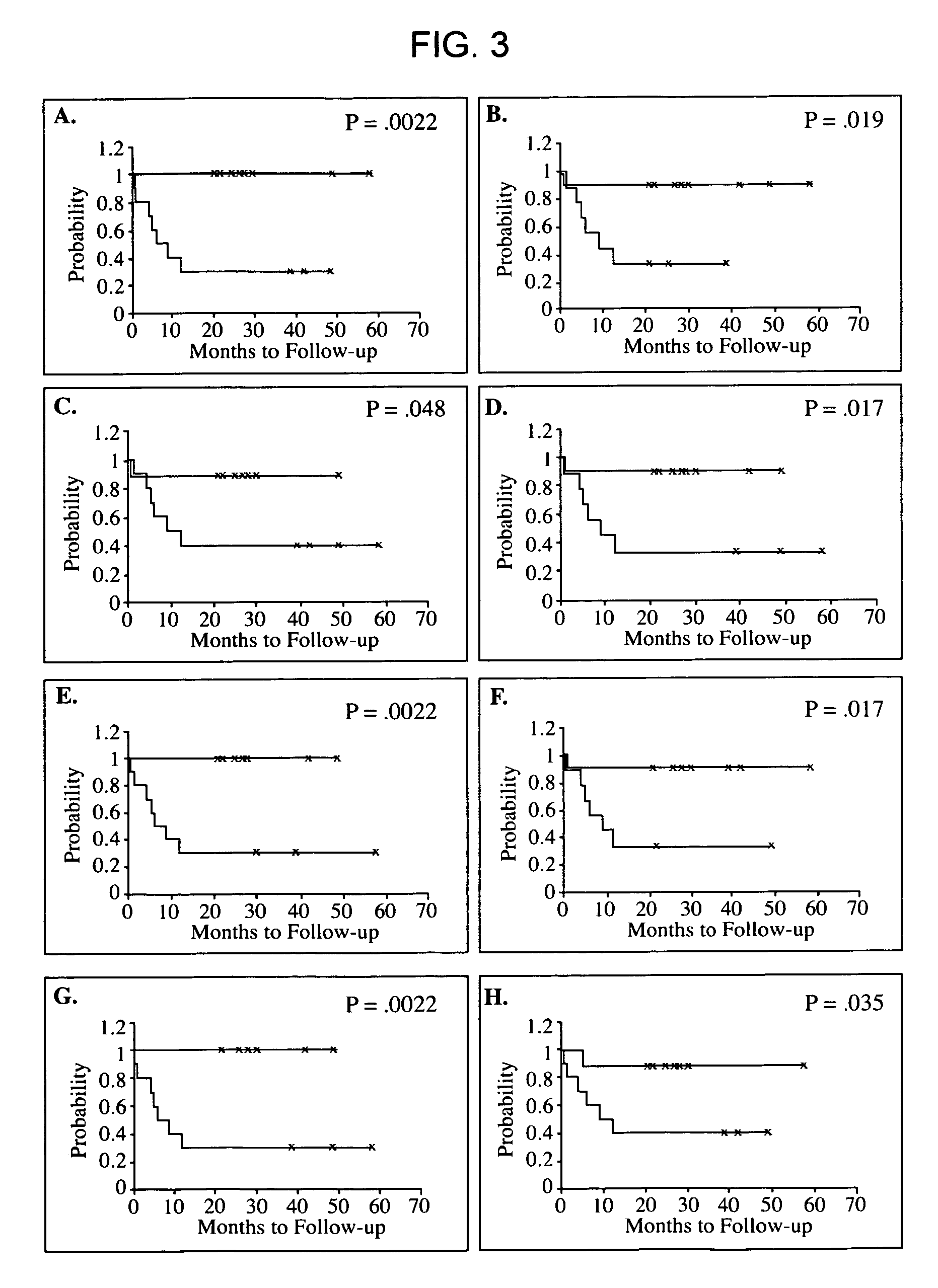
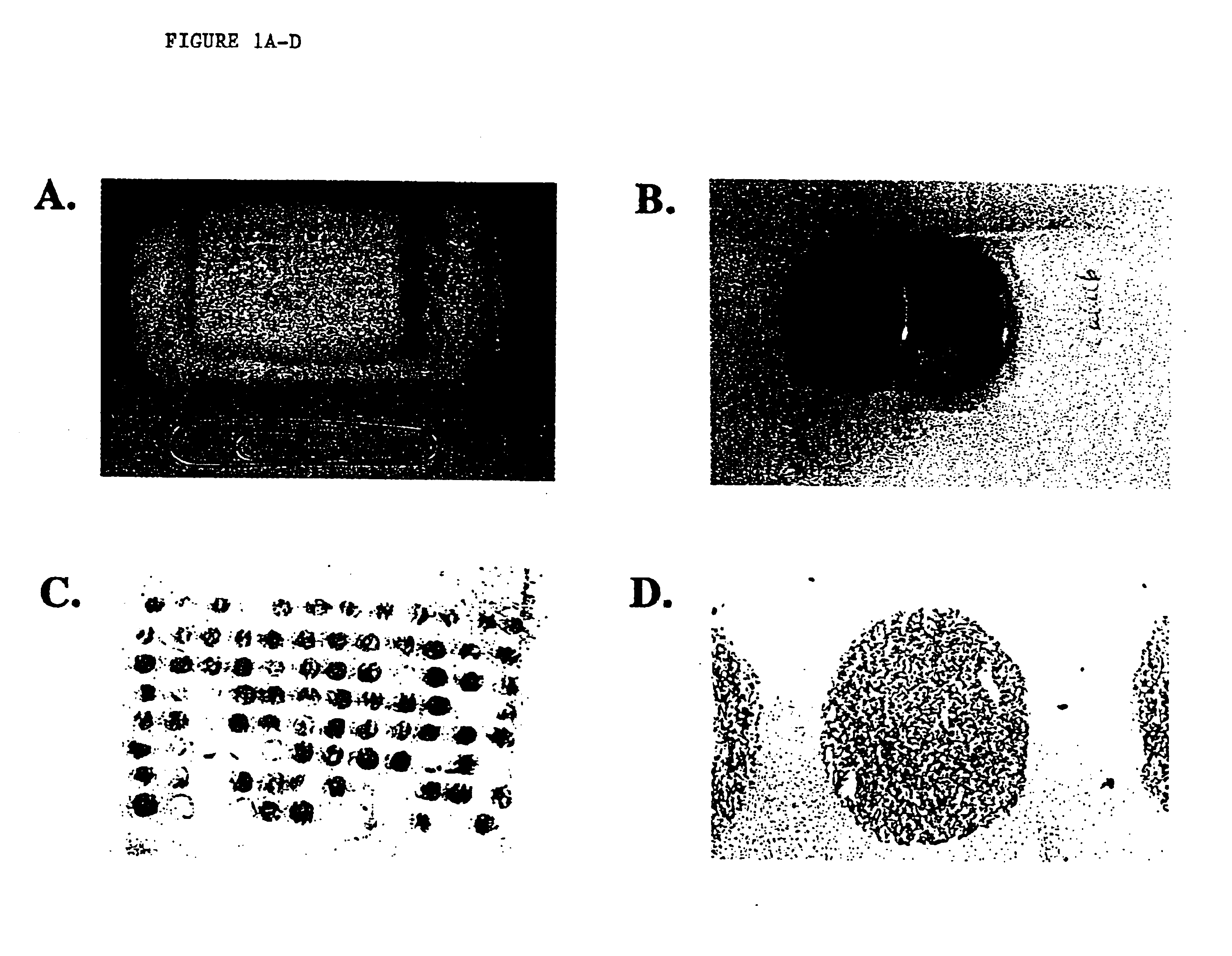
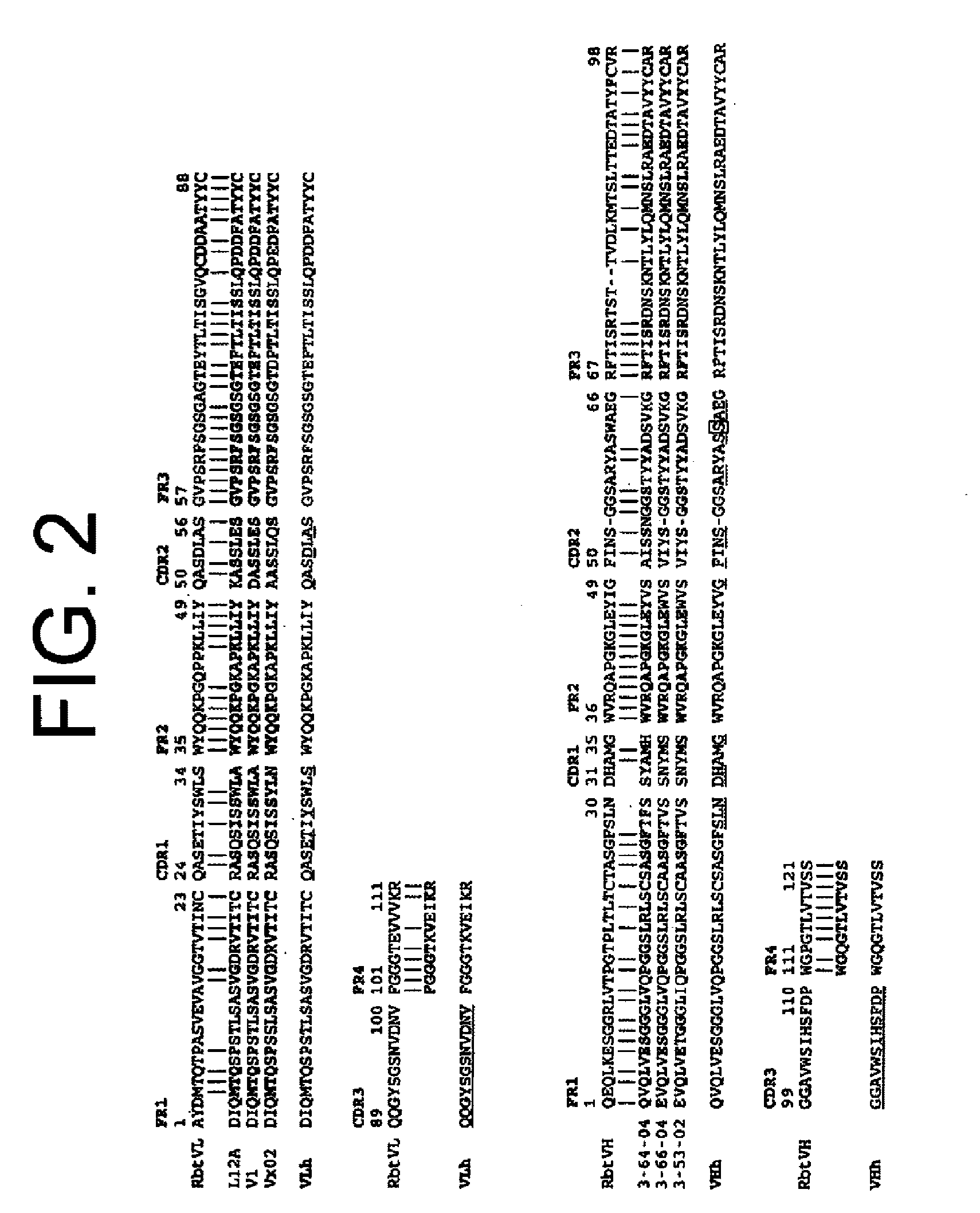
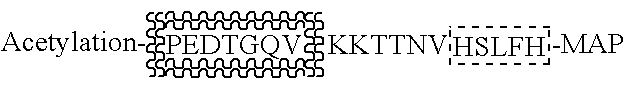Patents
Literature
808 results about "Protein level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Normal Range Normal total protein levels are between 6 to 8 grams per deciliter, according to the Clinical Methods website. Approximately 3.5 to 5 grams per deciliter are albumin and the remaining proteins are globulins. The standards for total protein may vary from lab to lab.
Methods and agents for screening for compounds capable of modulating gene expression
InactiveUS20050048549A1Modulate expressionLibrary screeningTissue cultureRegulator geneProtein level
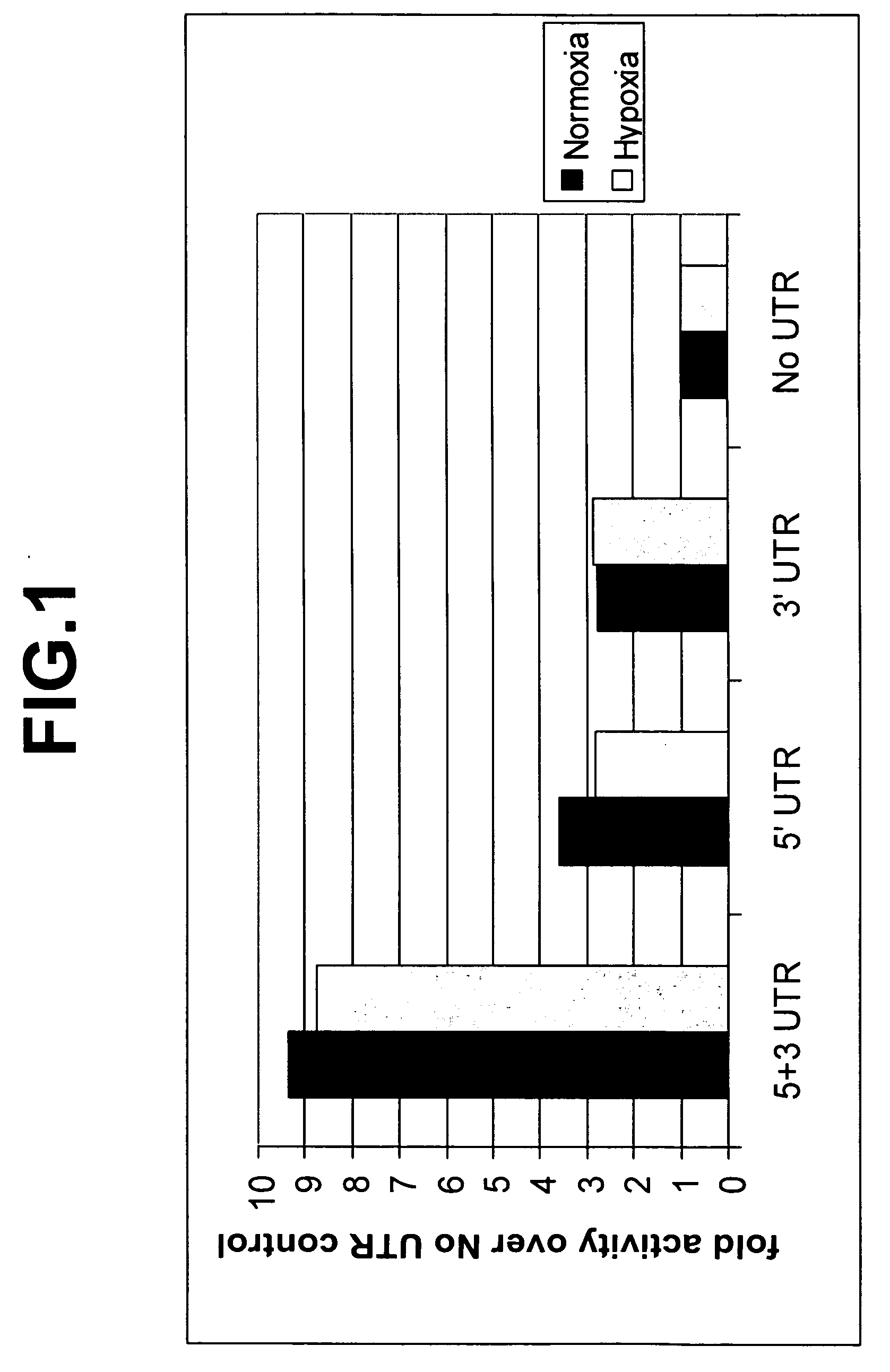
The invention relates to the fields of screening assays, compounds, and methods for altering gene expression and protein levels. In particular, the invention includes assays to screen for agents capable of modulating gene expression in a UTR-dependent manner and agents capable of modulating gene expression.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Biomarkers for predicting prostate cancer progression
InactiveUS20060234259A1Useful predictionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProstate cancerOncology
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods and compositions for the detection of cervical disease
ActiveUS20050260566A1Improve the level ofIncreased proliferationAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCervical cells
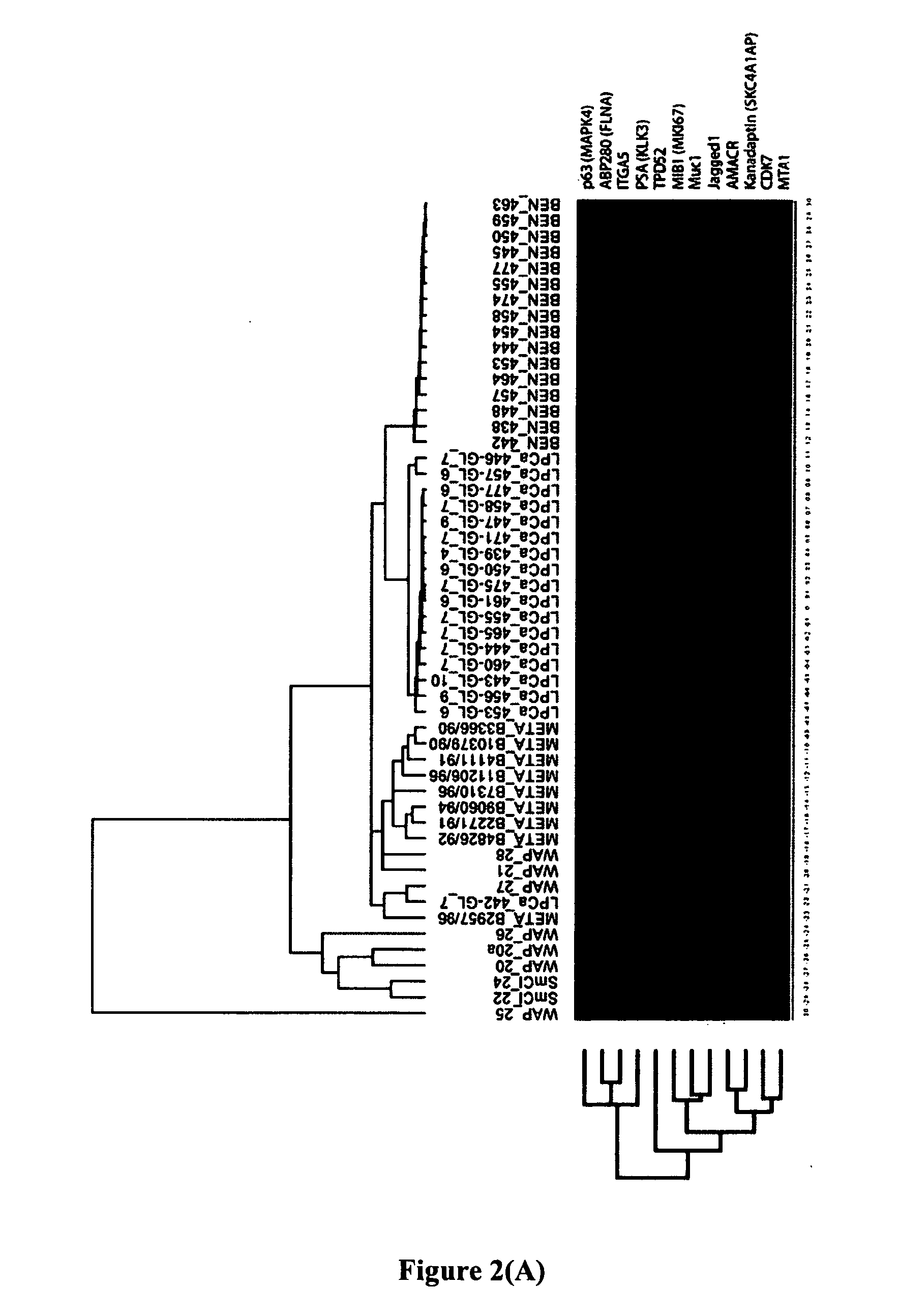
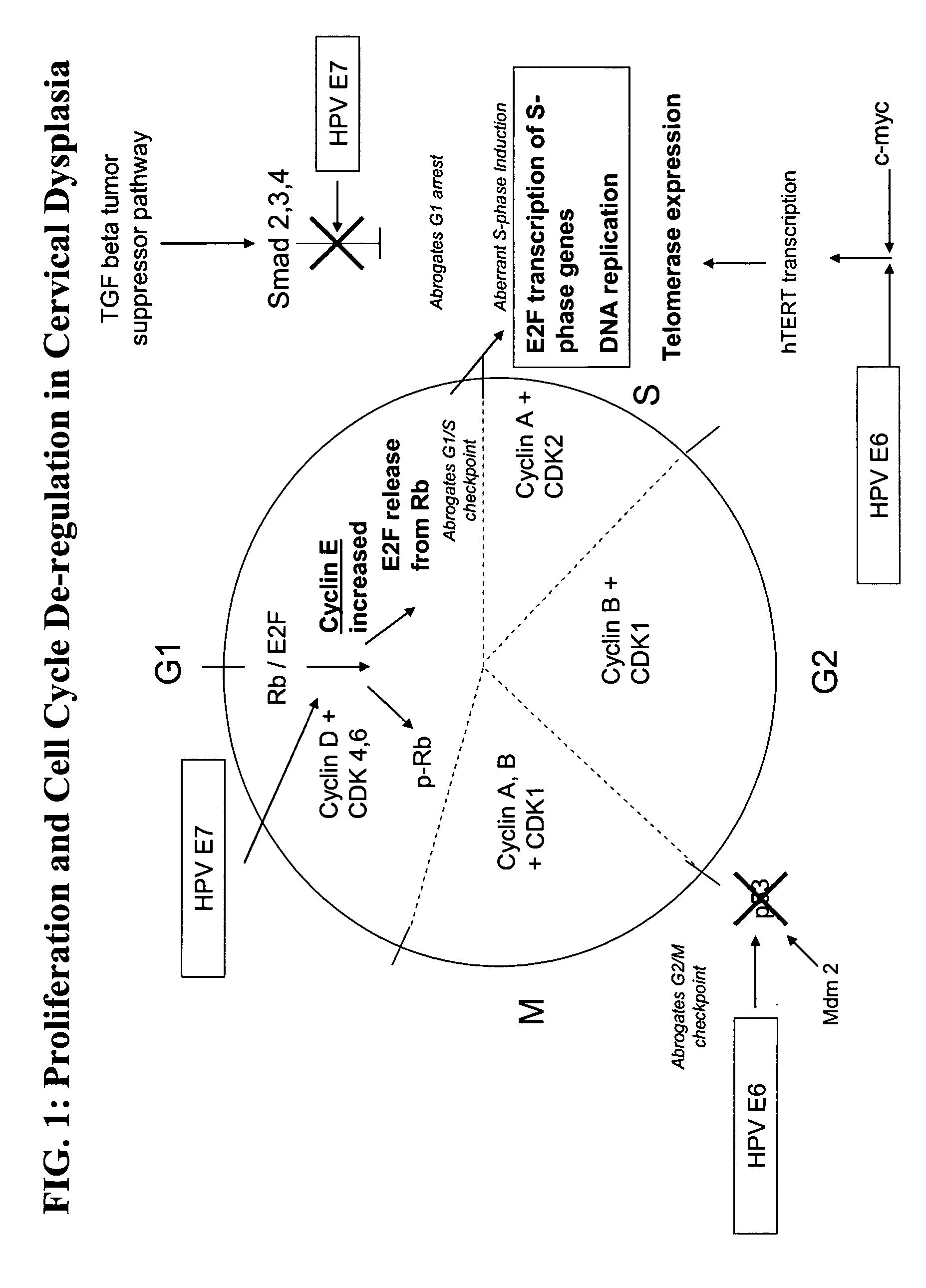
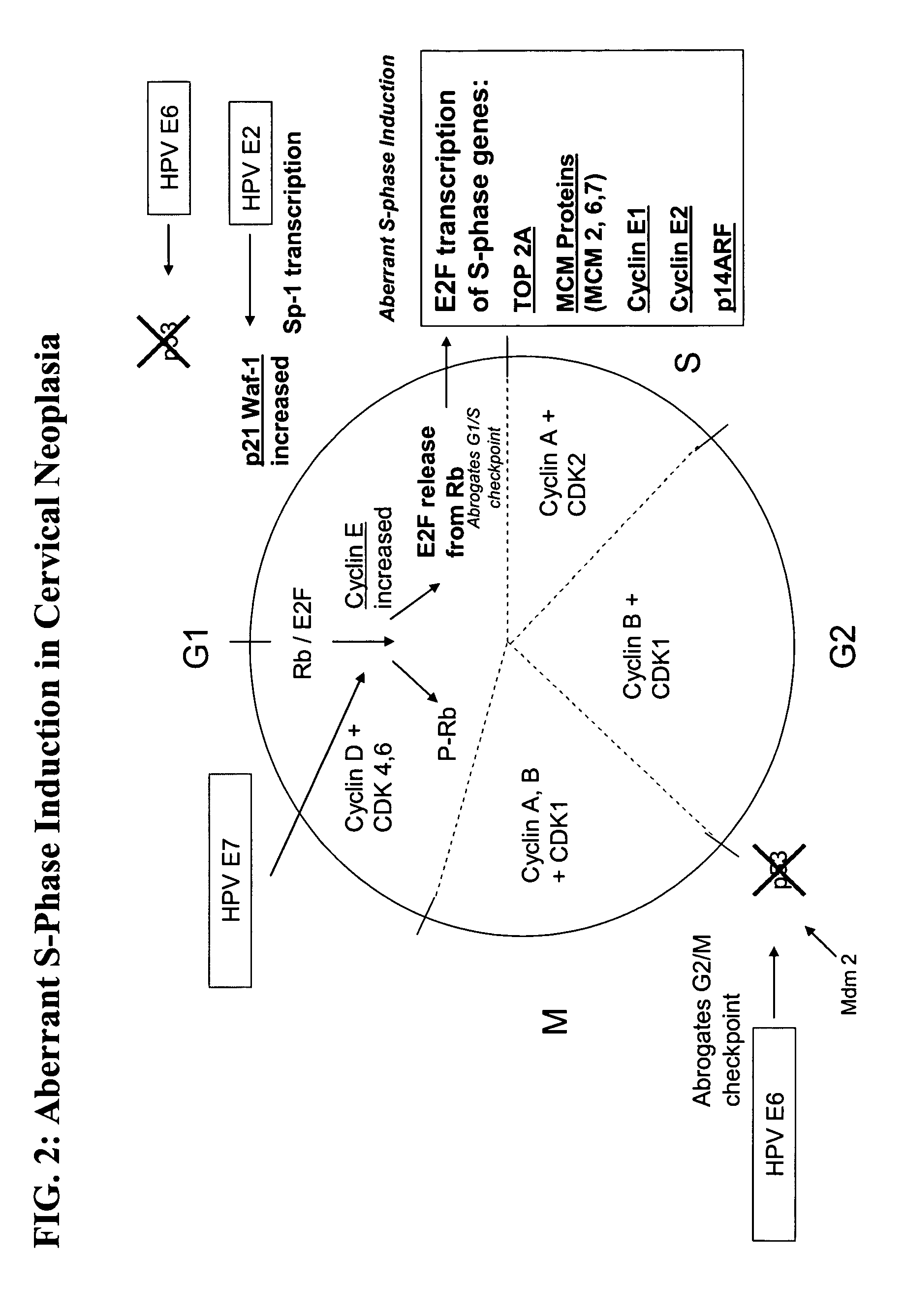
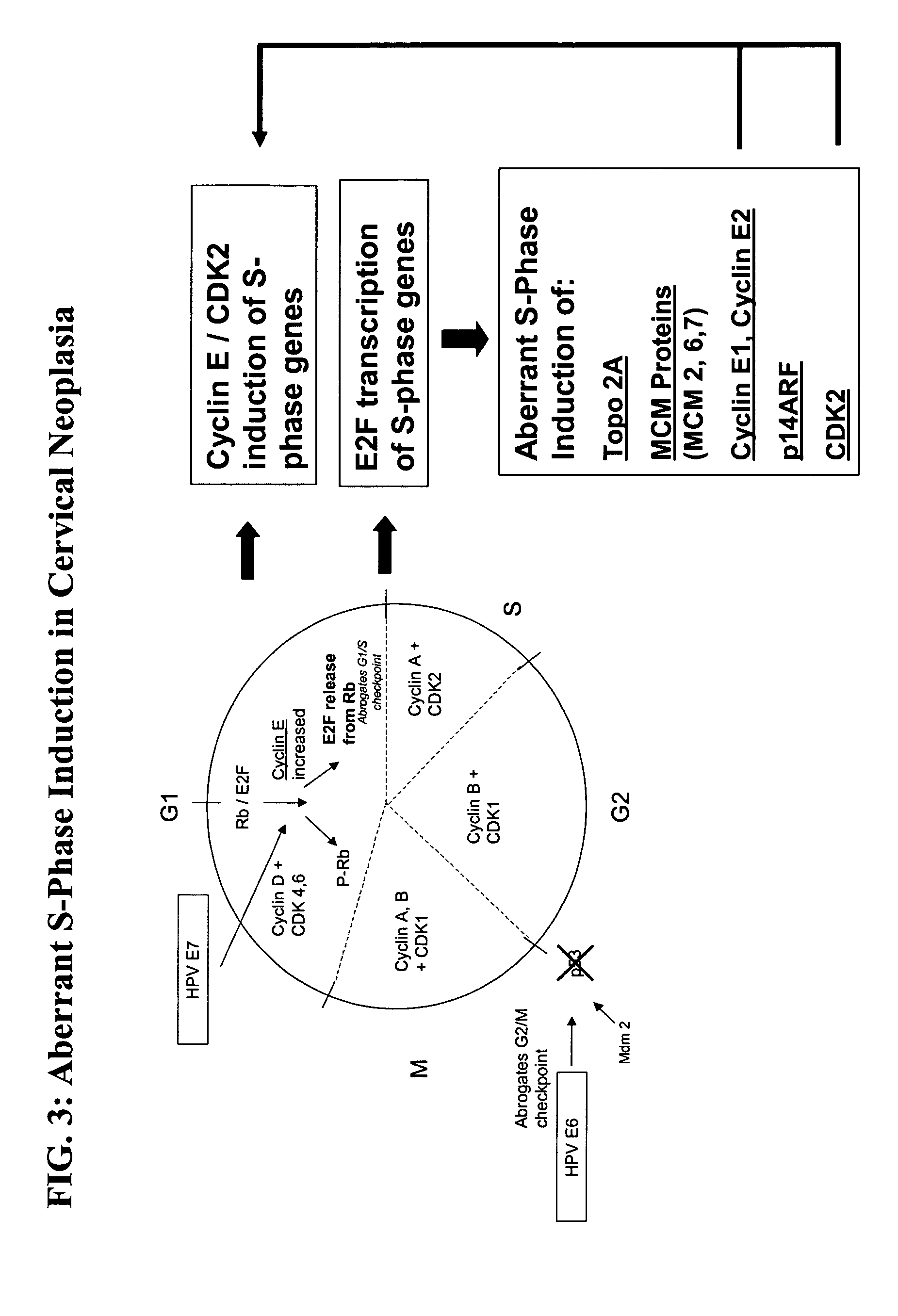
Methods and compositions for identifying high-grade cervical disease in a patient sample are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting overexpression of at least one biomarker in a body sample, wherein the biomarker is selectively overexpressed in high-grade cervical disease. In particular claims, the body sample is a cervical smear or monolayer of cervical cells. The biomarkers of the invention include genes and proteins that are involved in cell cycle regulation, signal transduction, and DNA replication and transcription. In particular claims, the biomarker is an S-phase gene. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
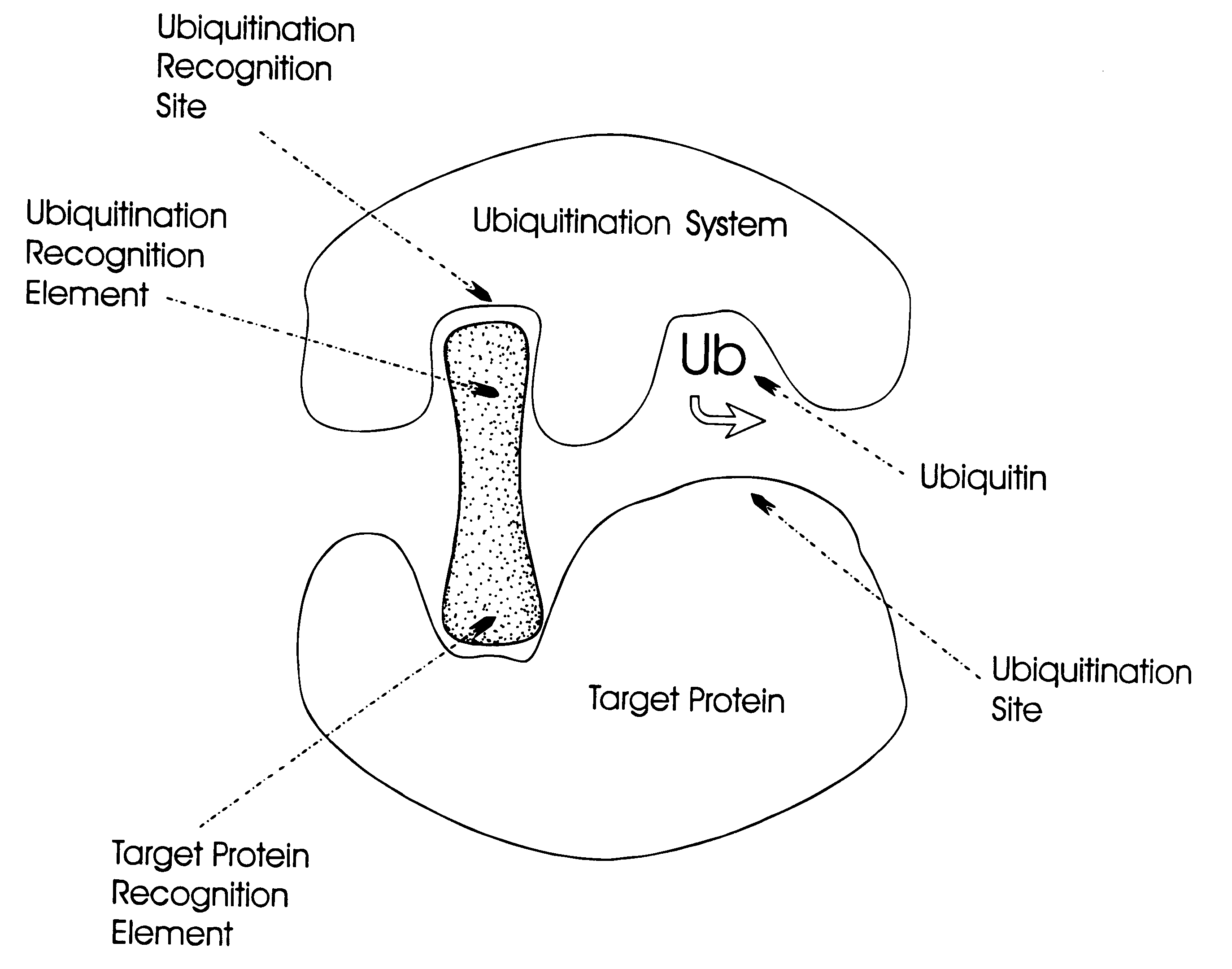
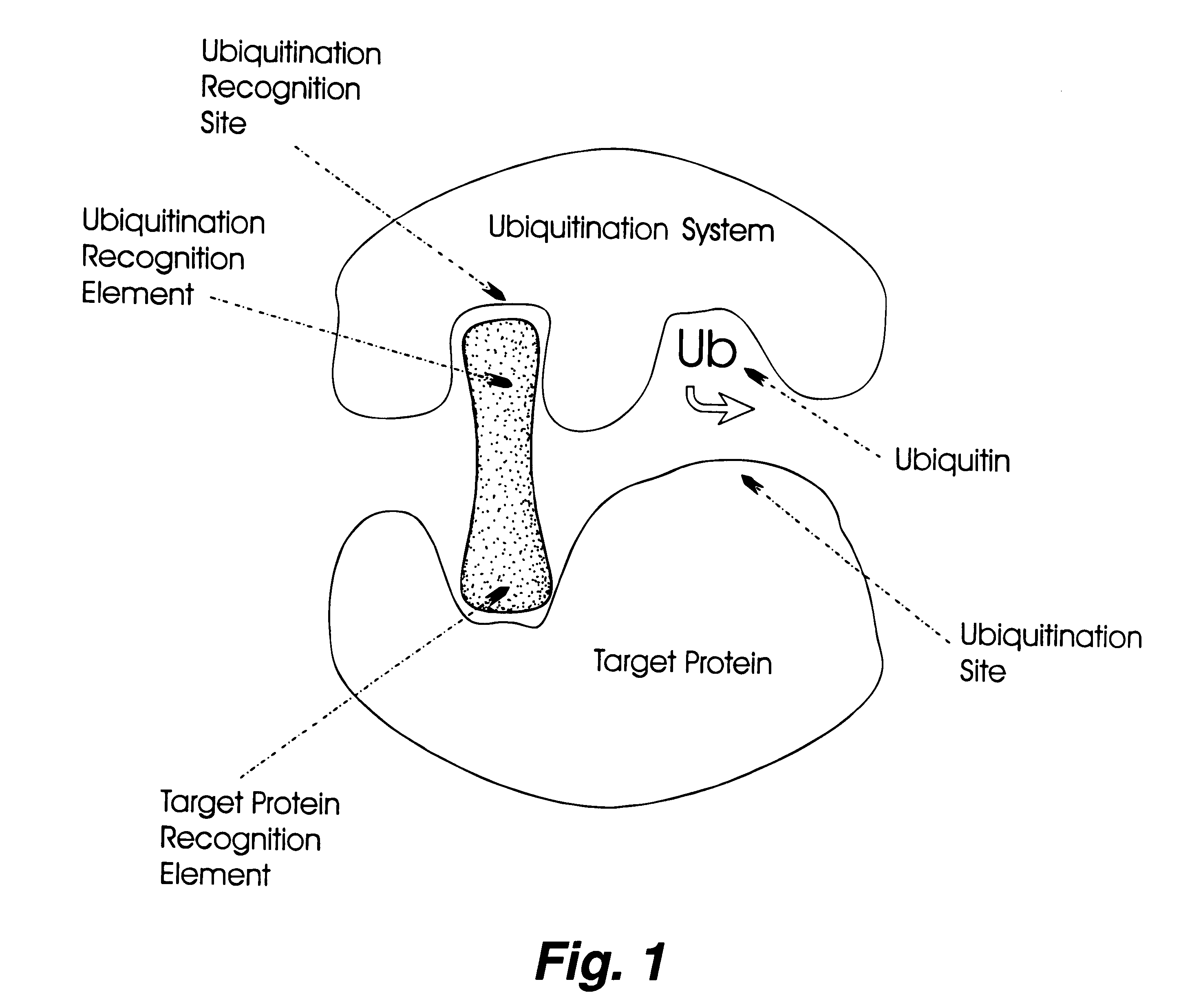
Controlling protein levels in eucaryotic organisms
InactiveUS6306663B1High activityCost-effectiveVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein target
The invention relates to novel compounds comprising a ubiquitination recognition element and a protein binding element. The invention also relates to the use of said compounds for modulating the level and / or activity of a target protein. The compounds are useful for the treatment of disease such as infections, inflammatory conditions, cancer and genetic diseases. The compounds are also useful as insecticides and herbicides.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOCATALYSIS +1
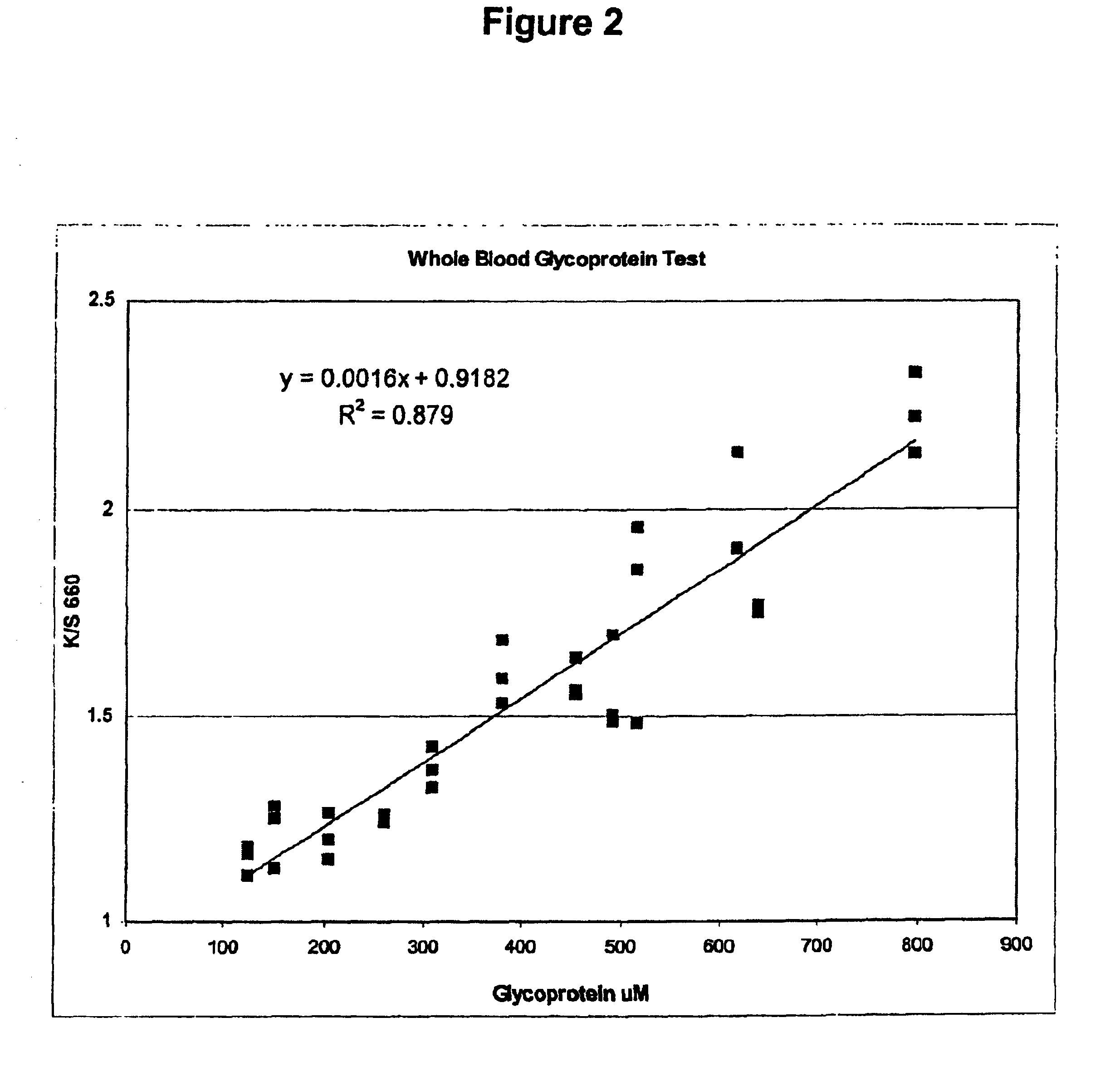
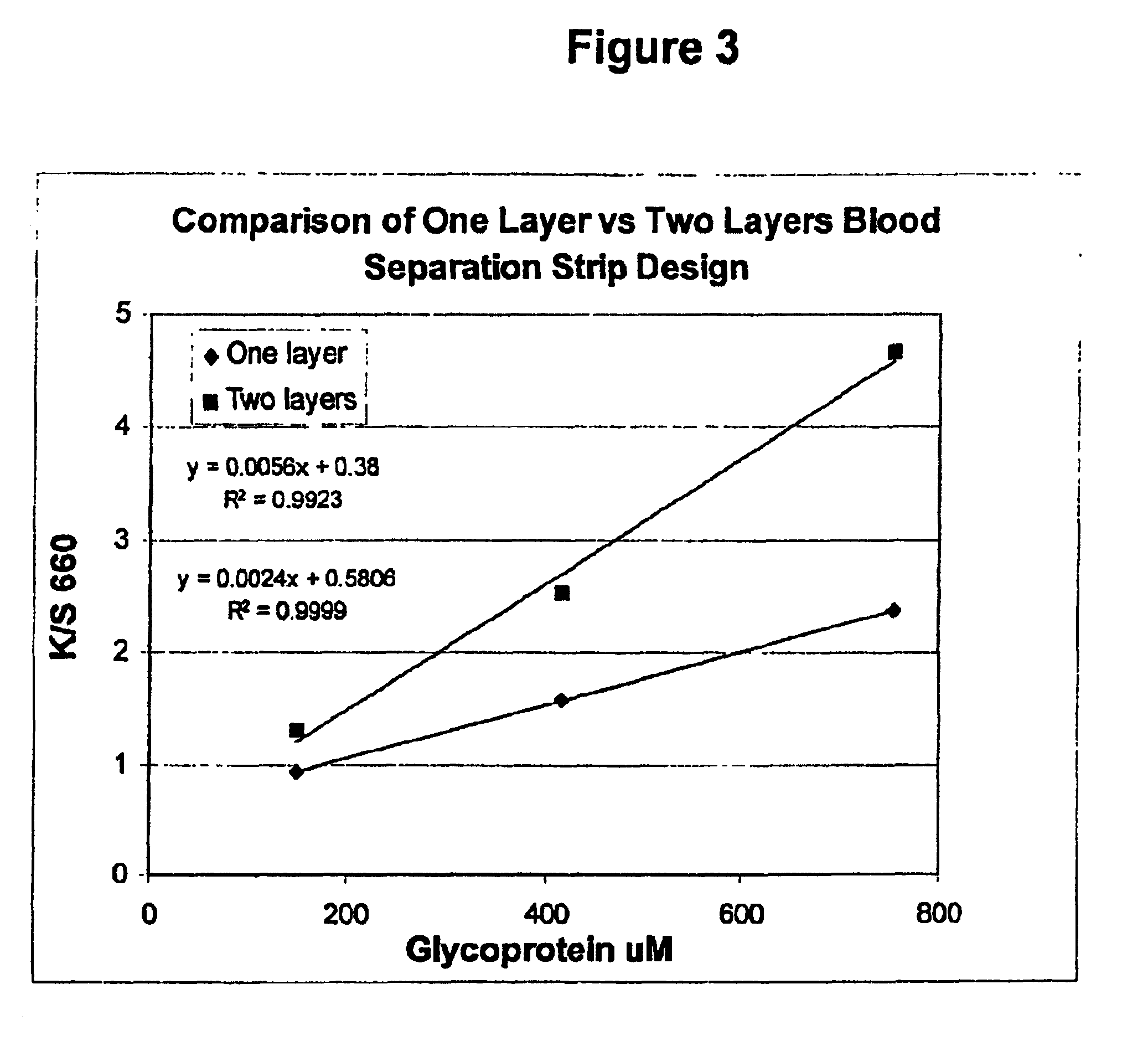
Multilayer reagent test strips to quantify glycated protein in a physiological sample
ActiveUS6951728B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl systemProtein level
Multilayer reagent test strips for quantitating glycated protein in a fluid sample, as well as methods for using the same, are provided. The subject multilayer test strips include at least a filter layer, a proteinase layer and a ketoamine oxidase signal producing and fluid flow control system layer. In using the subject test strips, a fluid sample is applied to the test strip and a signal is generated that can be employed to quantitate the glycated protein level in the sample. The quantitated glycated protein level can then be employed to determine the amount of glycated protein in the fluid sample. Also provided are kits and systems that include the subject test strips and find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject compositions and methods find use in glycated protein monitoring applications, among other utilities.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
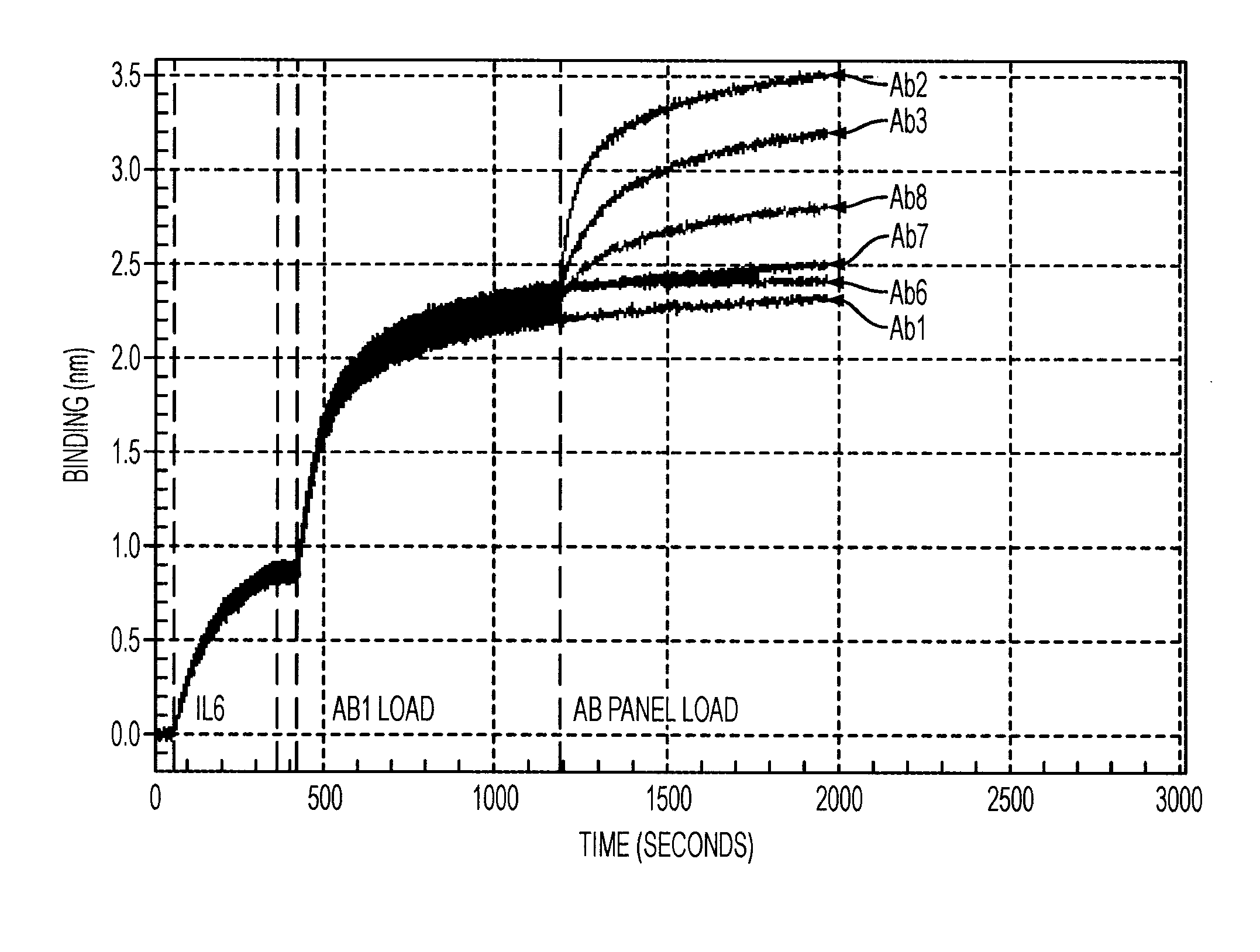
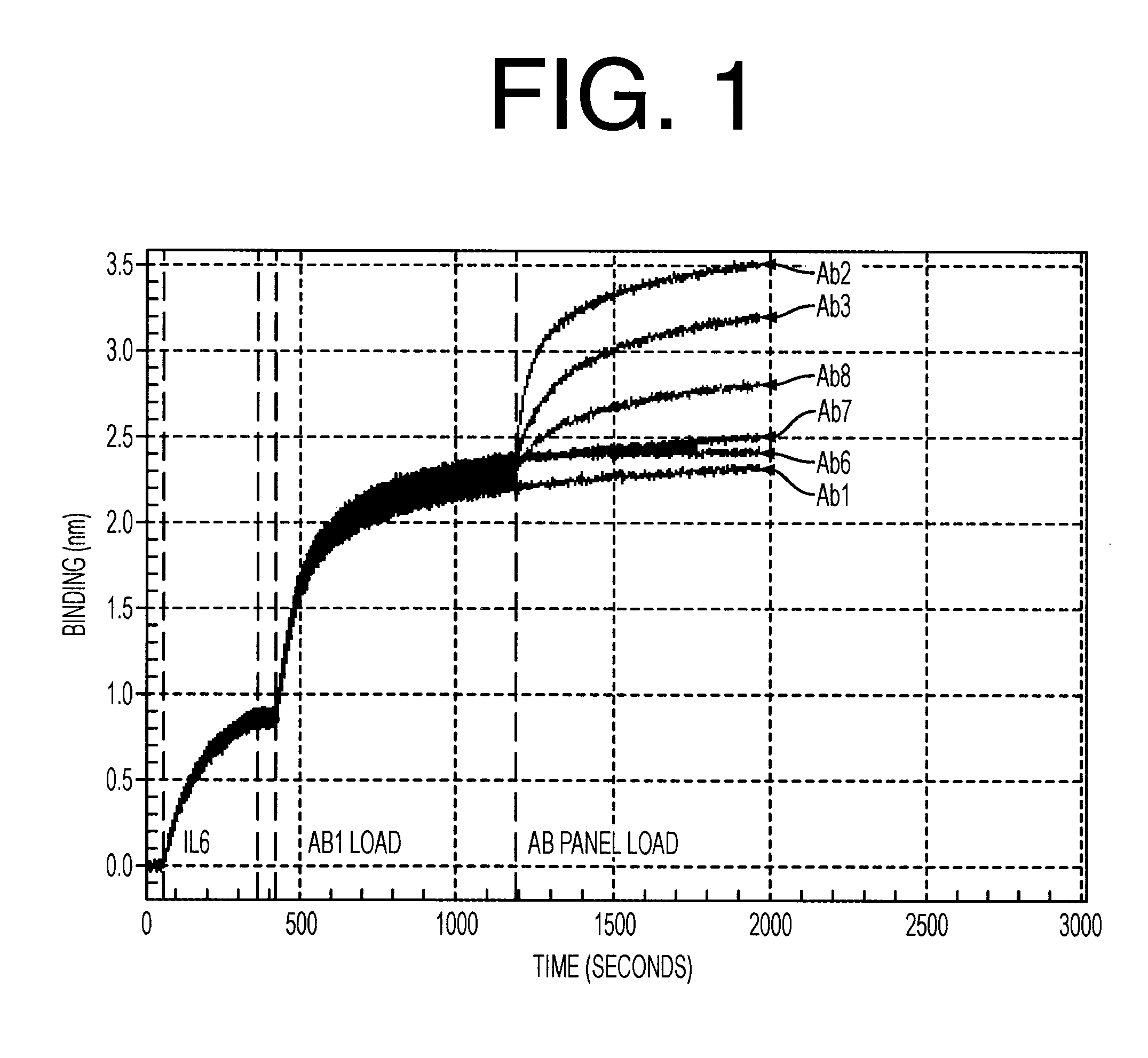
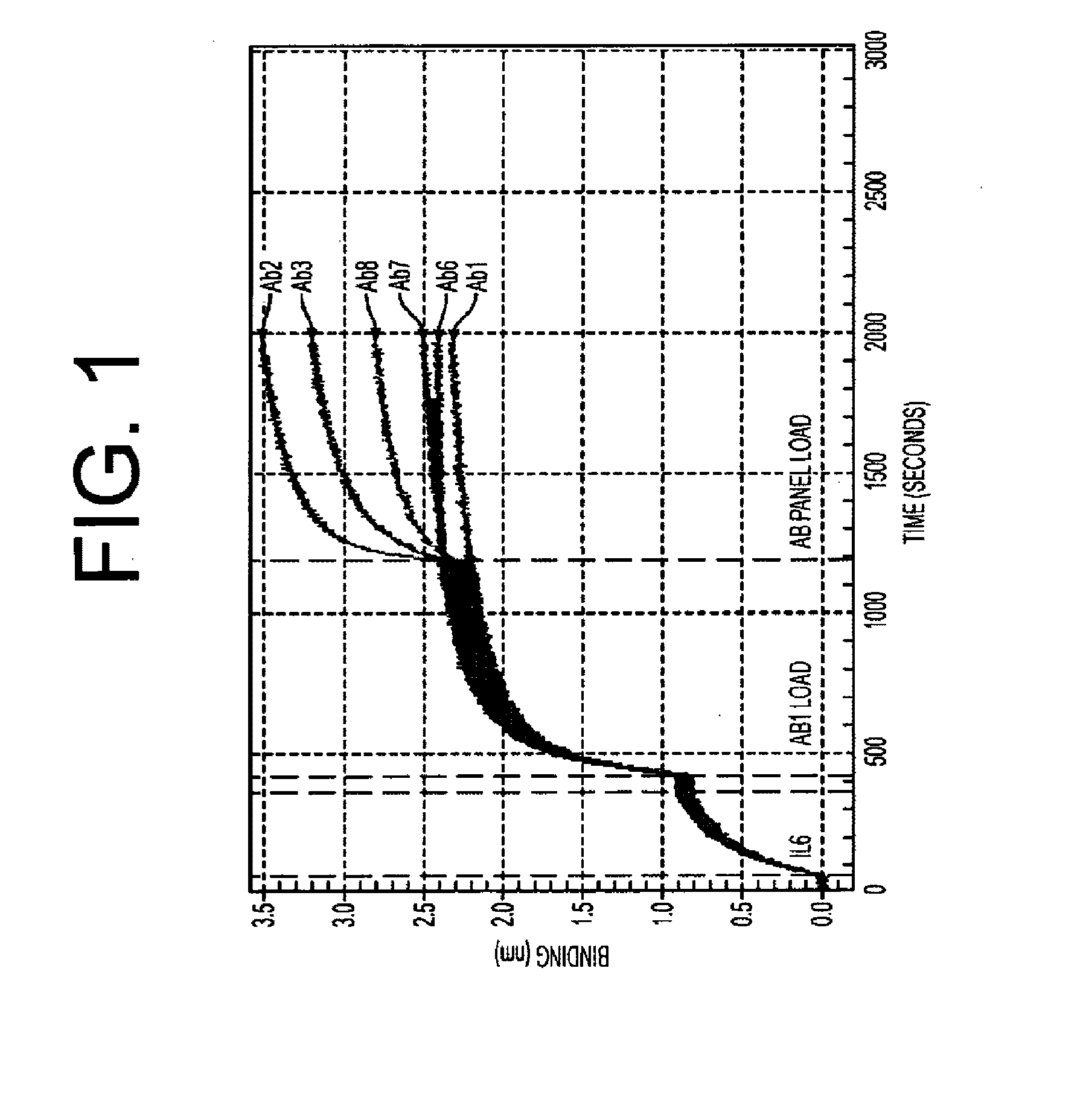
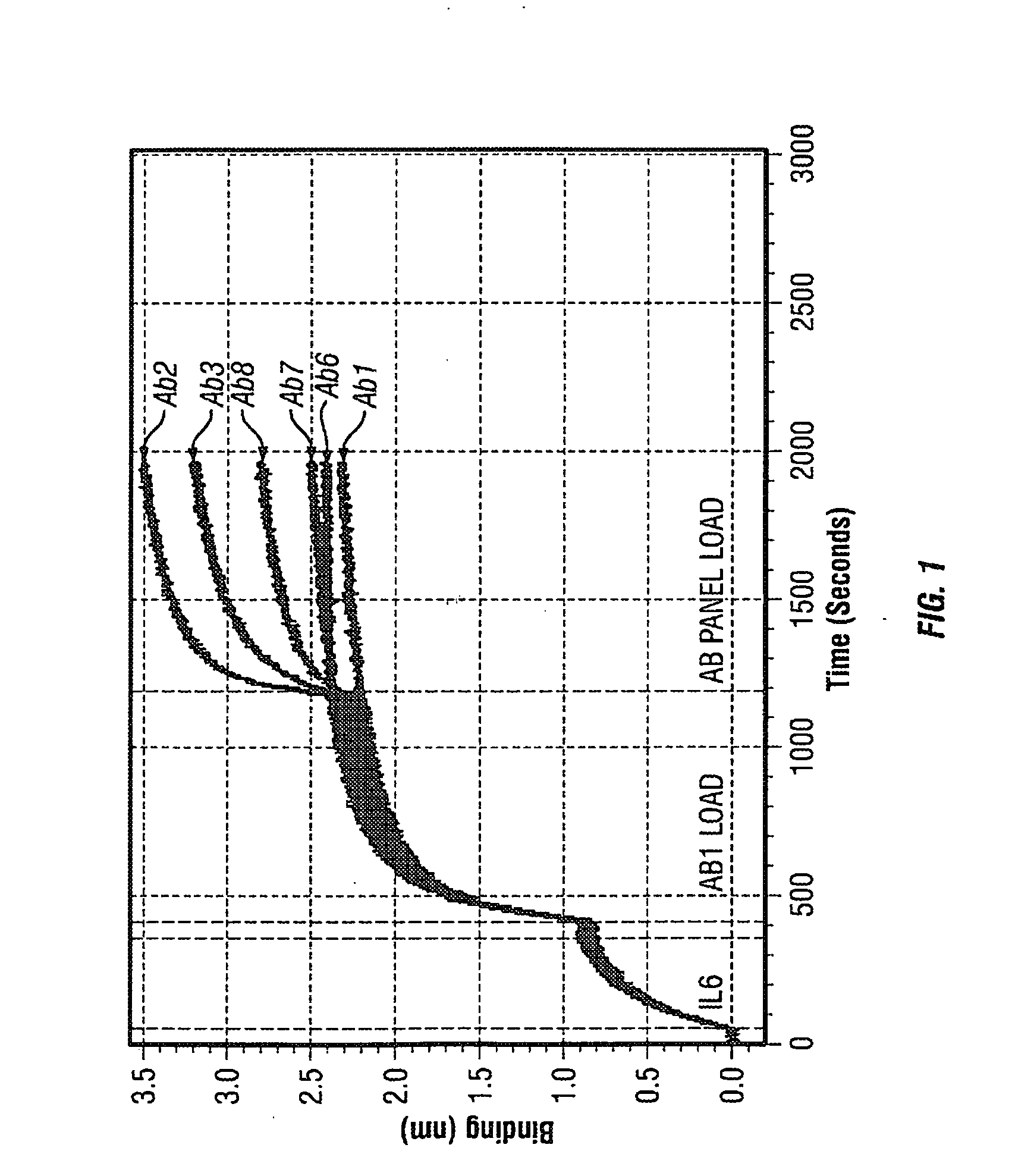
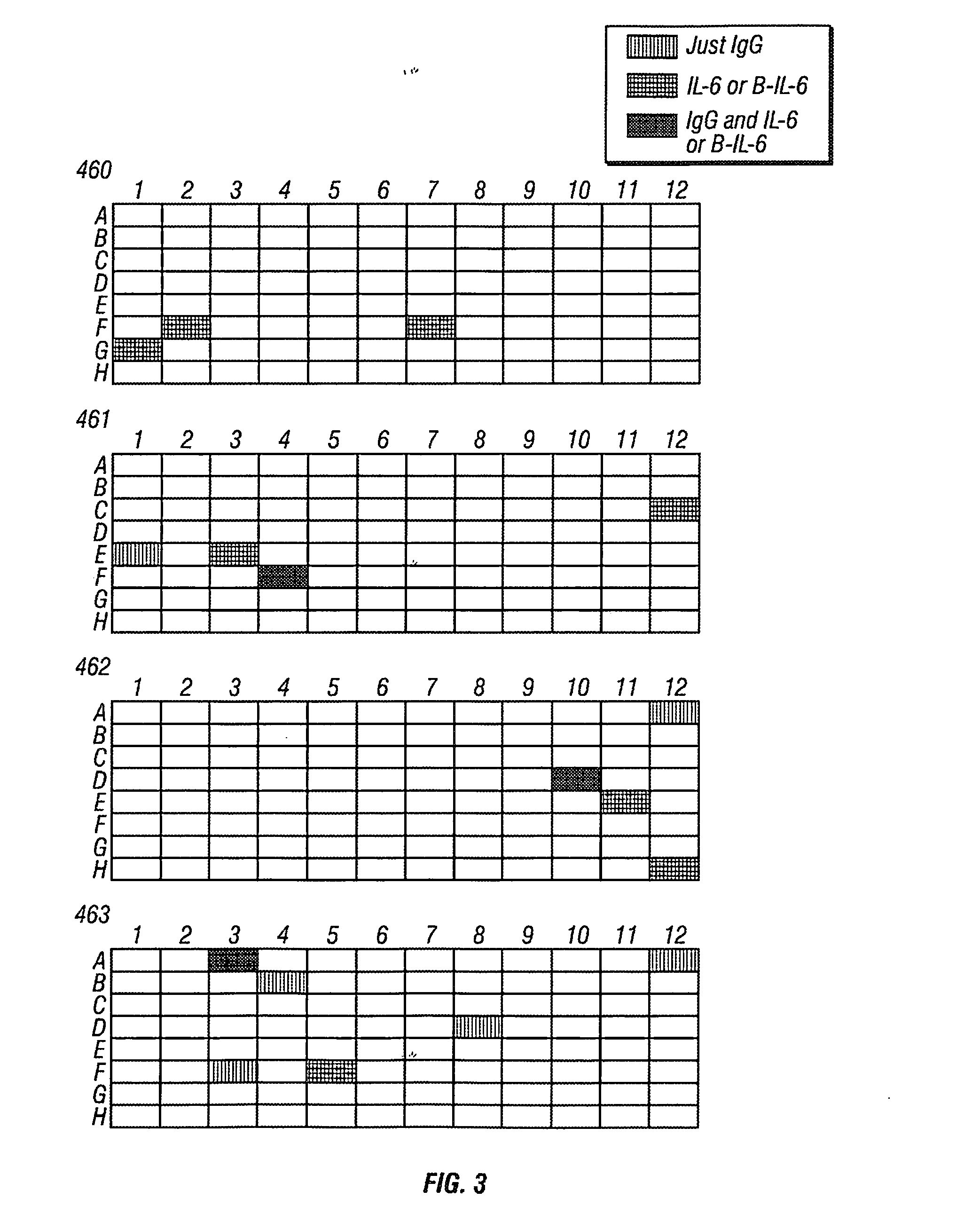
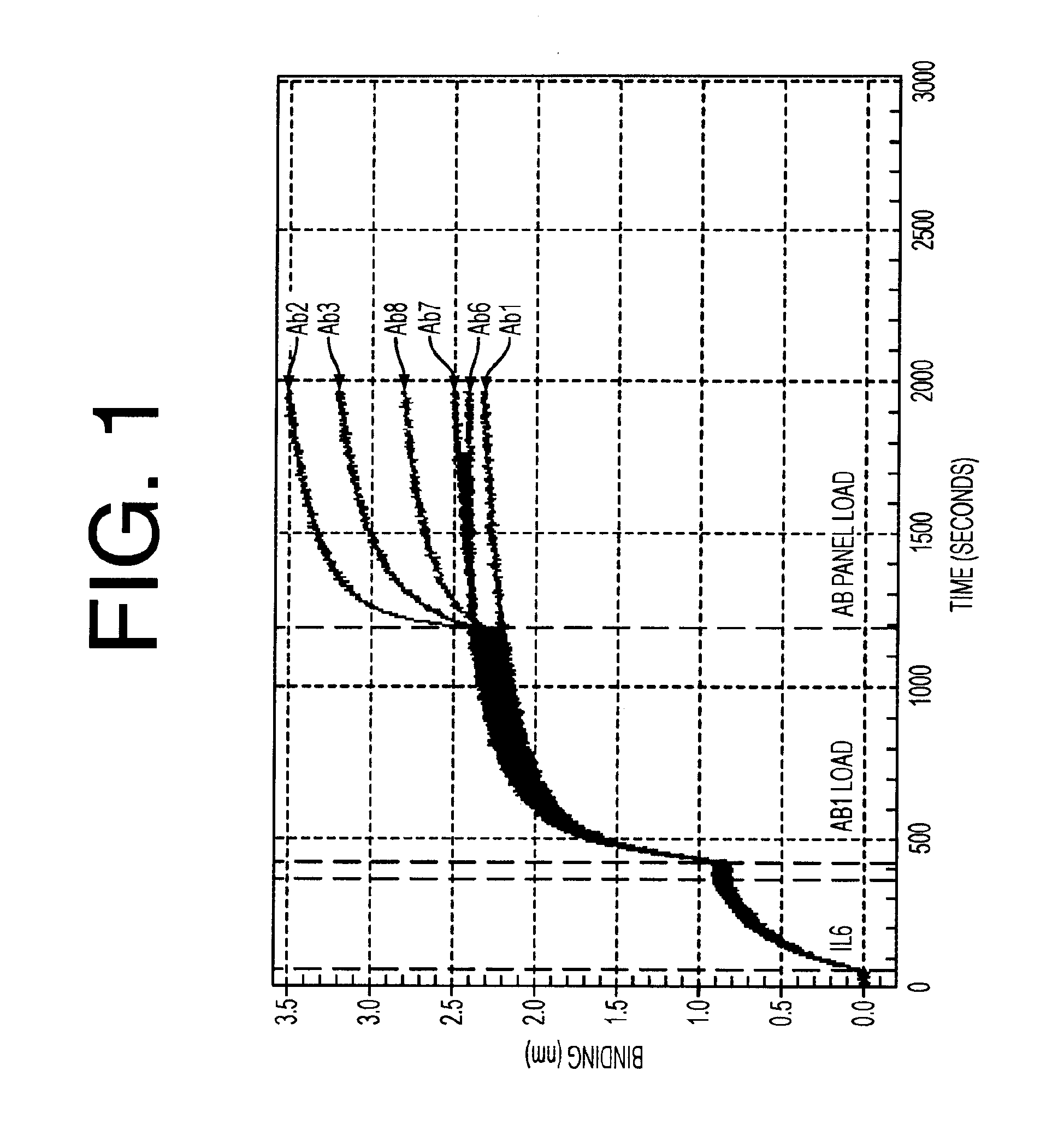
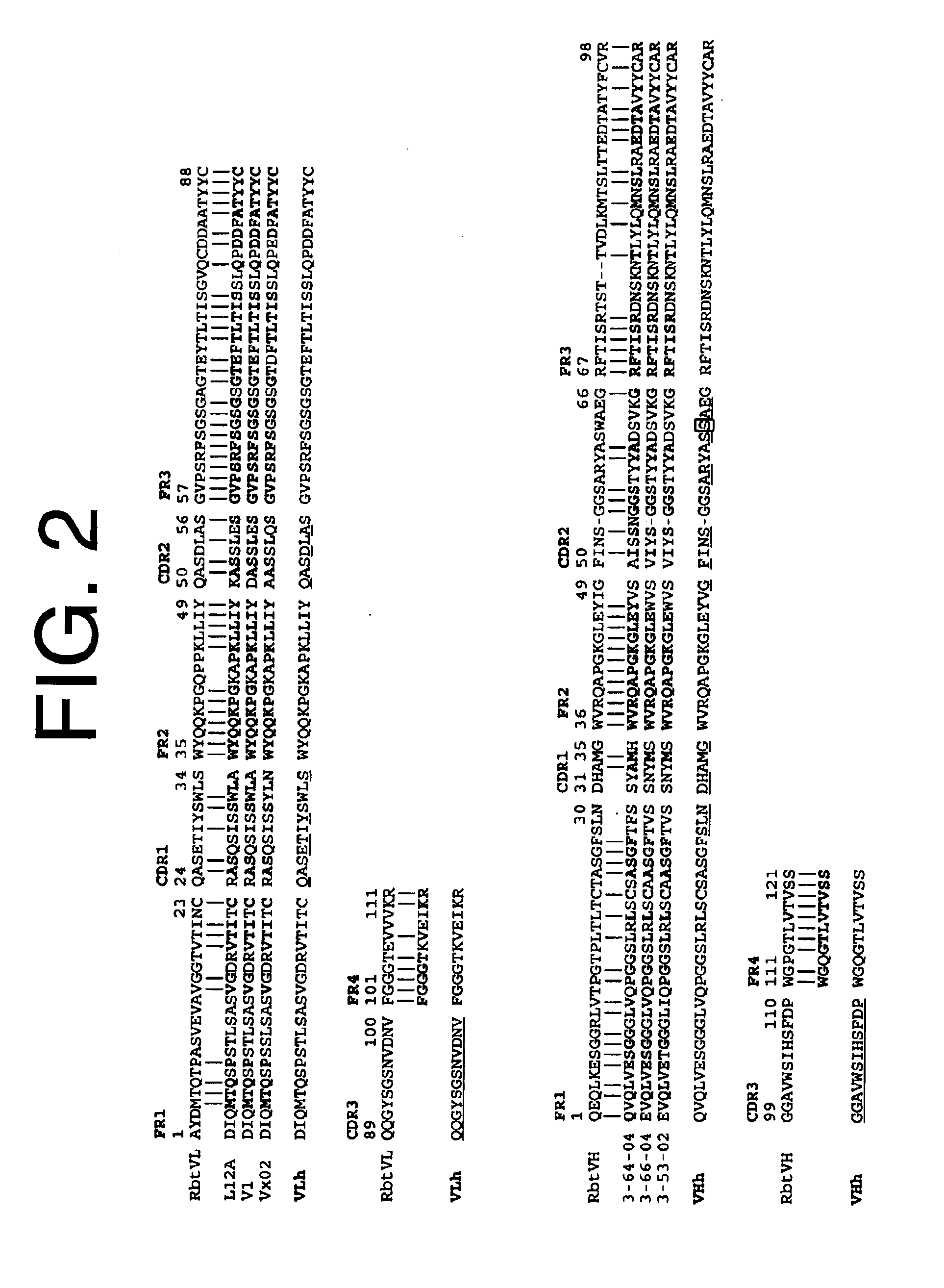
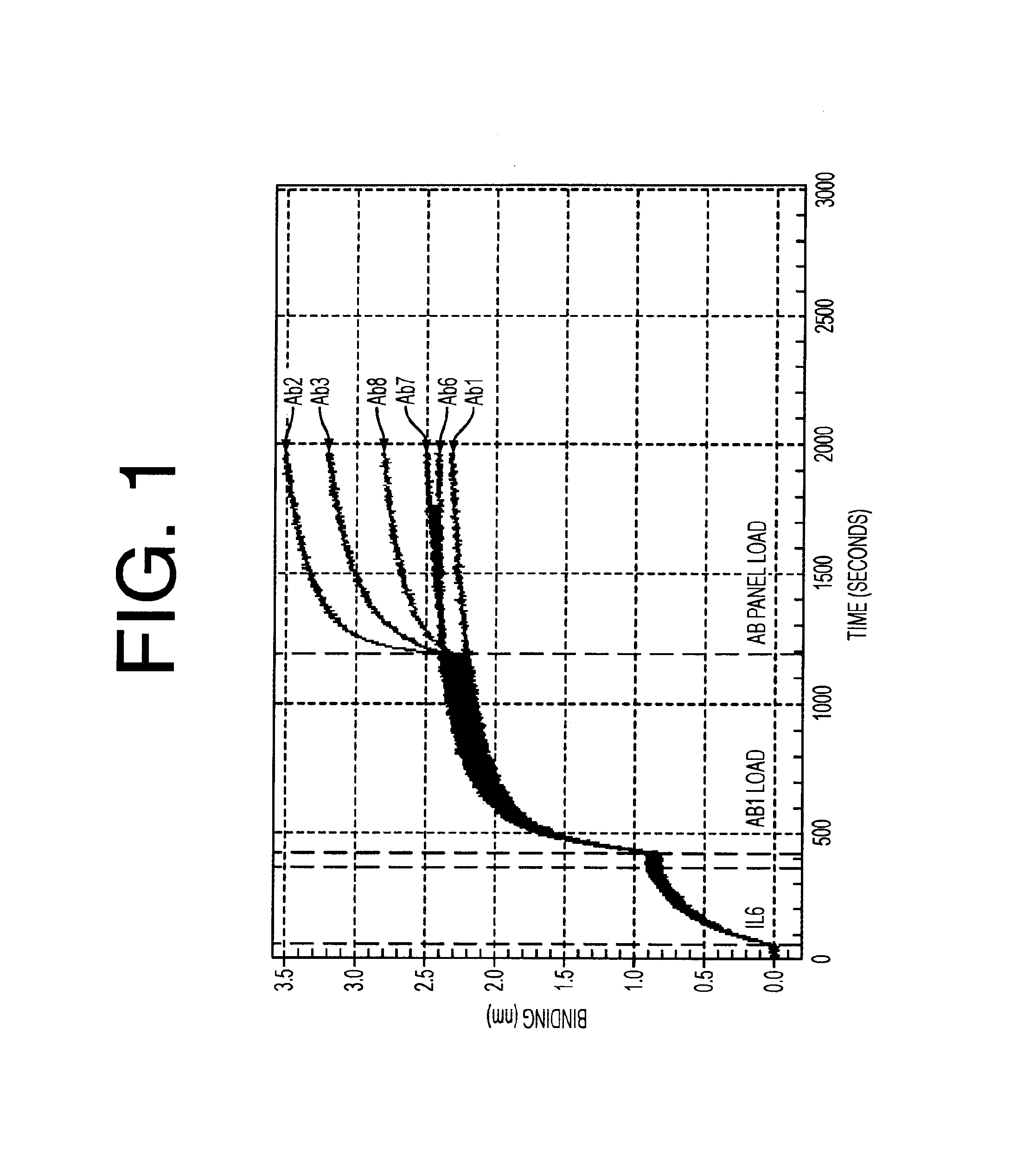
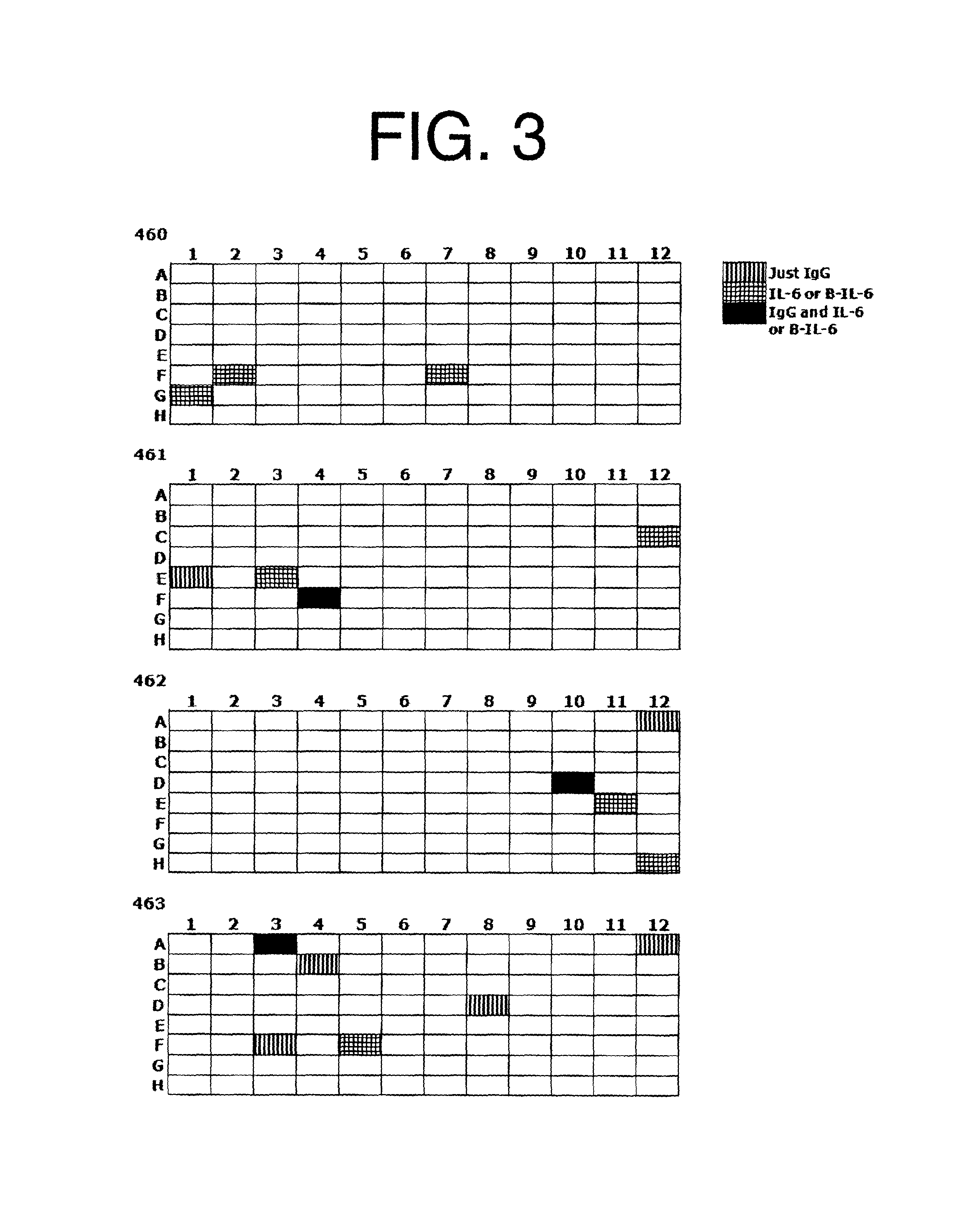
Antibodies to il-6 and use thereof
ActiveUS20100129357A1Eliminate—the risk of thrombosisPrevent thrombosisPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAntibody fragments
The present invention is directed to therapeutic methods using IL-6 antagonists such as an Ab1 antibody or antibody fragment having binding specificity for IL-6 to prevent or treat disease or to improve survivability or quality of life of a patient in need thereof. In preferred embodiments these patients will comprise those exhibiting (or at risk of developing) an elevated serum C-reactive protein level, reduced serum albumin level, elevated D-dimer or other cogulation cascade related protein(s), cachexia, fever, weakness and / or fatigue prior to treatment. The subject therapies also may include the administration of other actives such as chemotherapeutics, anti-coagulants, statins, and others.
Owner:VITAERIS INC +1
Methods and compositions for the detection of ovarian disease
InactiveUS20090081685A1Easy diagnosisIncrease chanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiseaseComplement system
Methods and compositions for identifying ovarian cancer in a patient sample are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting overexpression of at least one biomarker in a body sample, wherein the biomarker is selectively overexpressed in ovarian cancer. In preferred embodiments, the body sample is a serum sample. The biomarkers of the invention include any genes or proteins that are selectively overexpressed in ovarian cancer, including, for example, acute phase reactants, lipoproteins, proteins involved in the regulation of the complement system, regulators of apoptosis, proteins that bind hemoglobin, heme, or iron, cytostructural proteins, enzymes that detoxify metabolic byproducts, growth factors, and hormone transporters. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
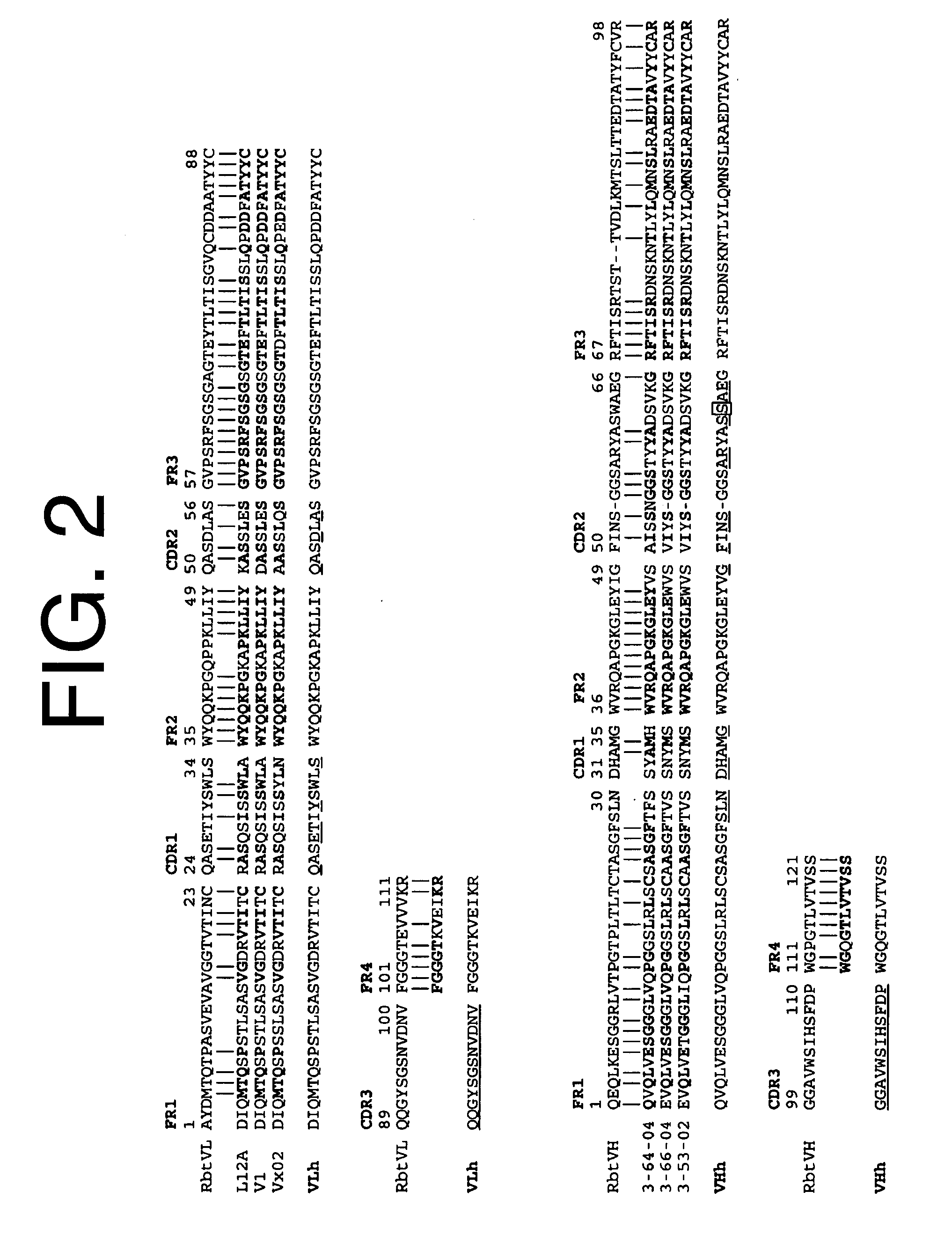
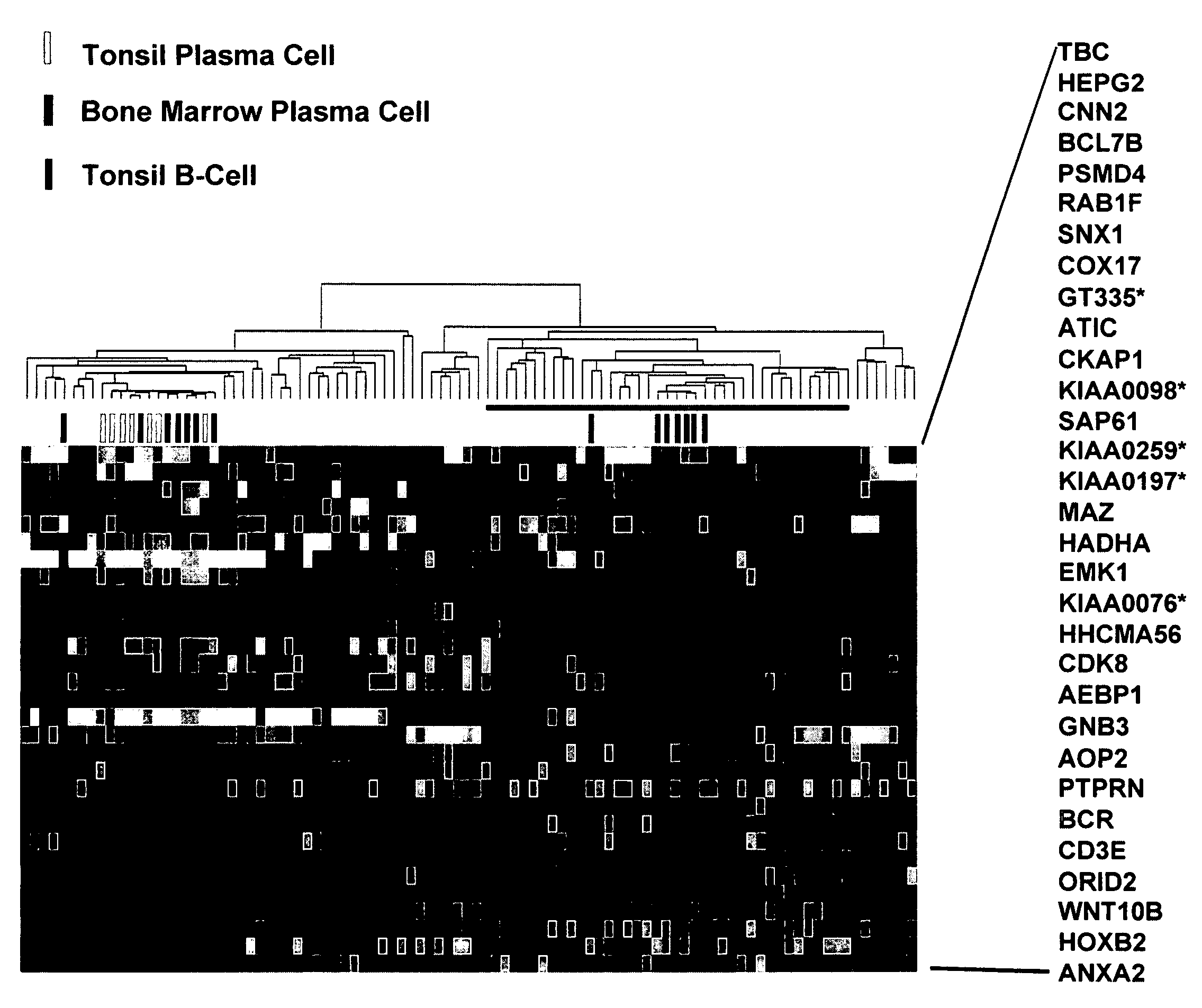
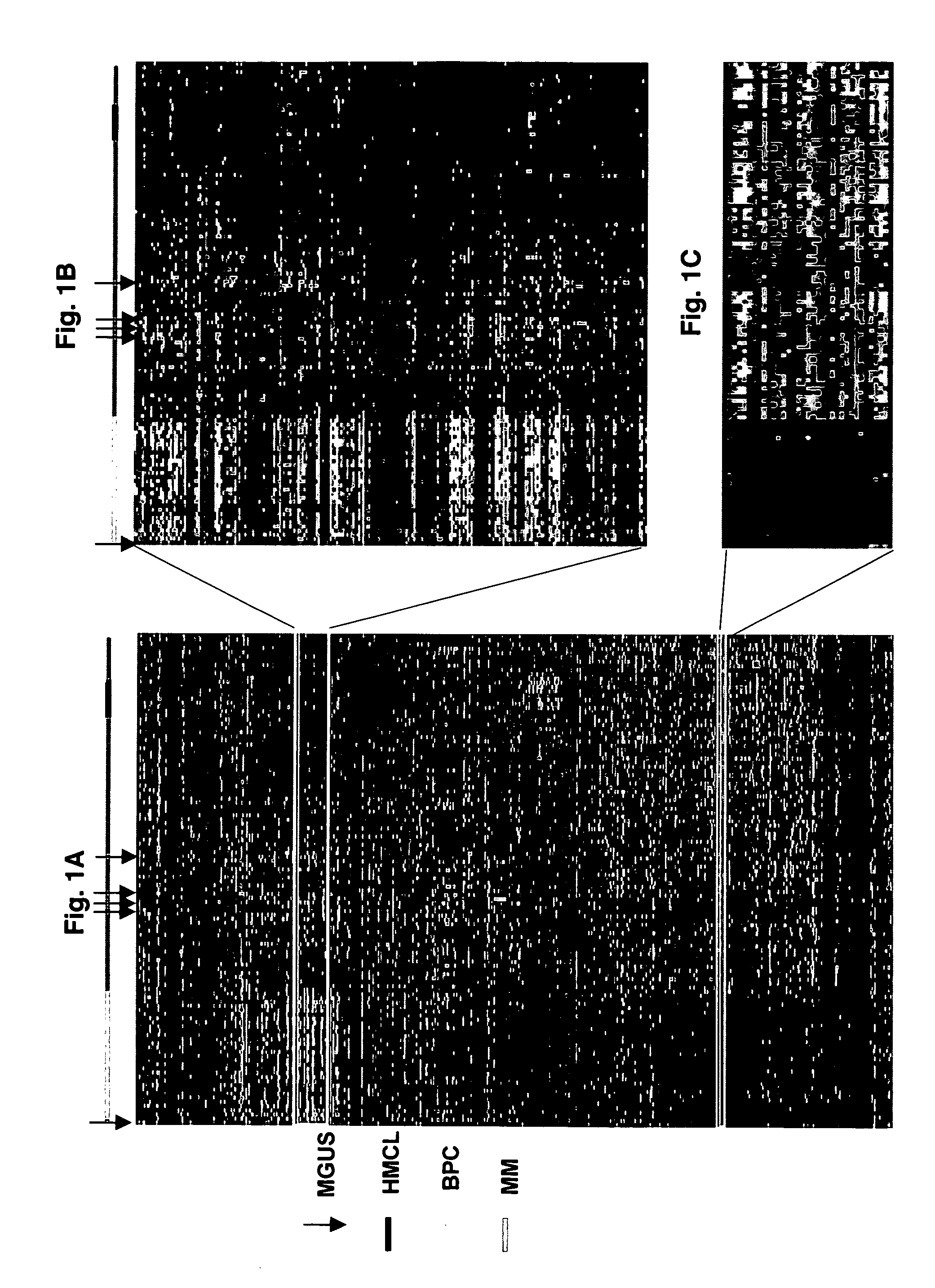
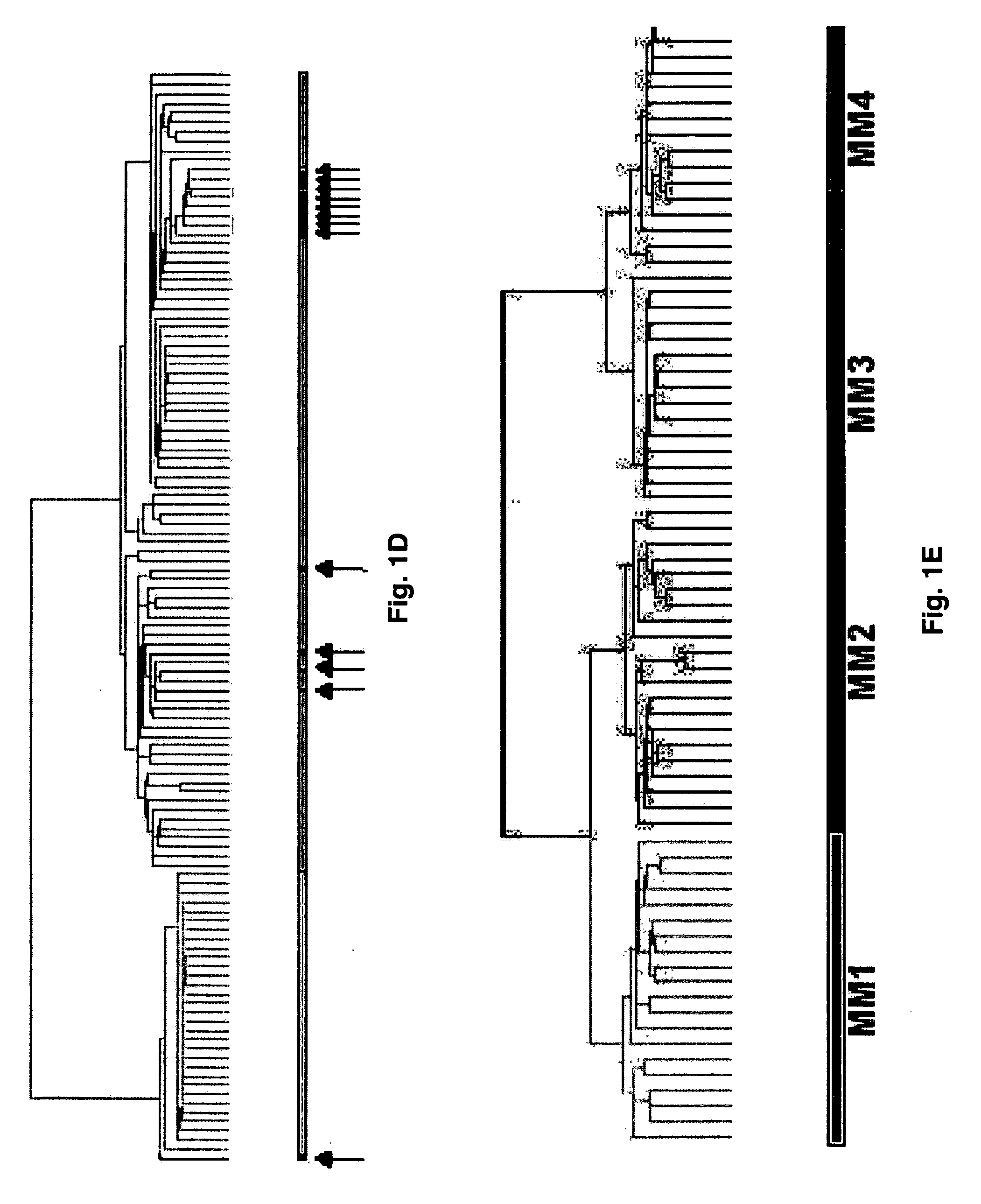
Diagnosis, prognosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets of multiple myeloma based on gene expression profiling
InactiveUS20080234139A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDevelopmental stagePlasma cell
Provided herein are methods for diagnosing and treating multiple myeloma based on statistical analysis of and subsequent increasing / inhibiting expression of subgroups of plasma cells and B cell genes. Also provided are methods for a developmental stage-based classification for multiple myeloma using hierarchical clustering analysis of plasma cell and B cell nucleic acids and for discriminating among normal, hyperplastic and malignant using gene expression array data and statistical analysis thereof. In addition methods for determining the risk of developing bone disease in a test individual by examining expression levels of a WNT signaling antagonist, such as DKK1, are provided. A kit comprising anti-DKK1 antibodies and detection reagents for measuring DKK1 protein levels also is provided.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
Methods and compositions for evaluating graft survival in a solid organ transplant recipient
ActiveUS20060246485A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingOrgan transplantationProtein level
Methods are provided for evaluating a subject for graft survival, e.g., in terms of predicting graft survival, identifying the presence of a deleterious graft condition, such as CAN and DT, identifying the severity and class of acute rejection, etc, in a subject are provided. In practicing the subject methods, the expression of at least one gene in a sample from the subject, e.g., a blood or biopsy sample, is assayed, e.g., at the nucleic acid and / or protein level, to evaluate the subject. Also provided are compositions, systems and kits that find use in practicing the subject methods. The methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Frozen tissue microarray technology for analysis RNA, DNA, and proteins
InactiveUS6893837B2Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis dnaTissue Arrays
The invention disclosed herein improves upon existing tissue microarray technology by using frozen tissues embedded in tissue embedding compound as donor samples and arraying the specimens into a recipient block comprising tissue embedding compound. Tissue is not fixed prior to embedding, and sections from the array are evaluated without fixation or post-fixed according to the appropriate methodology used to analyze a specific gene at the DNA, RNA, and / or protein levels. Unlike paraffin tissue arrays which can be problematic for immunohistochemistry and for RNA in situ hybridization analyses, the disclosed methods allow optimal evaluation by each technique and uniform fixation across the array panel. The disclosed arrays work well for DNA, RNA, and protein analyses, and have significant qualitative and quantitative advantages over existing methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and compositions for evaluating breast cancer prognosis
InactiveUS20060063190A1Accurate assessmentImproved prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsLymphatic SpreadNucleic acid hybridisation
Methods and compositions for evaluating the prognosis of a breast cancer patient, particularly an early-stage breast cancer patient, are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting expression of at least one, more particularly at least two, biomarker(s) in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarker or a combination of biomarkers is indicative of breast cancer prognosis. In some embodiments, the body sample is a breast tissue sample, particularly a primary breast tumor sample. The biomarkers of the invention are proteins and / or genes whose overexpression is indicative of either a good or bad cancer prognosis. Biomarkers of interest include proteins and genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, transcription, signal transduction, cell proliferation, invasion, proteolysis, or metastasis. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
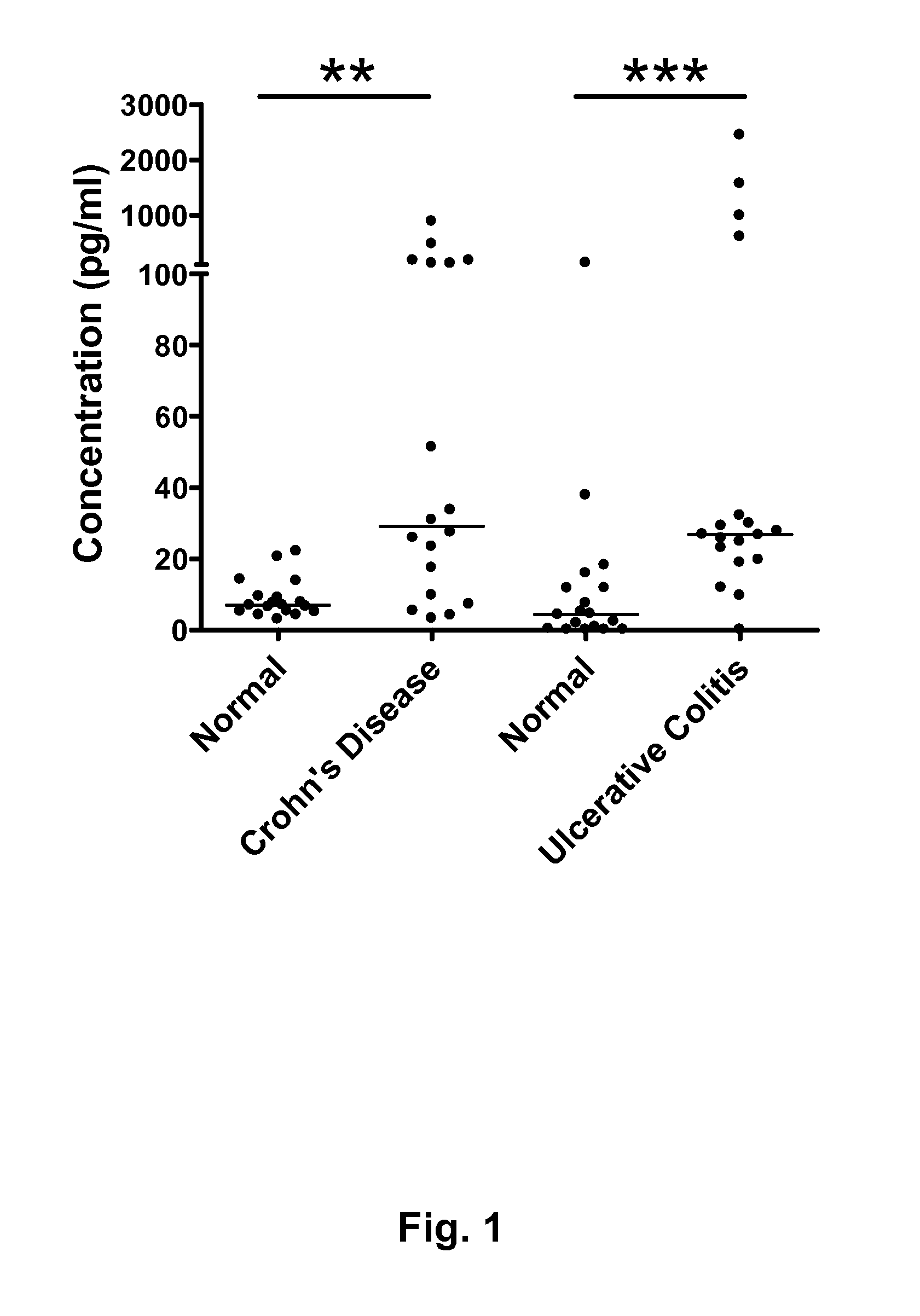
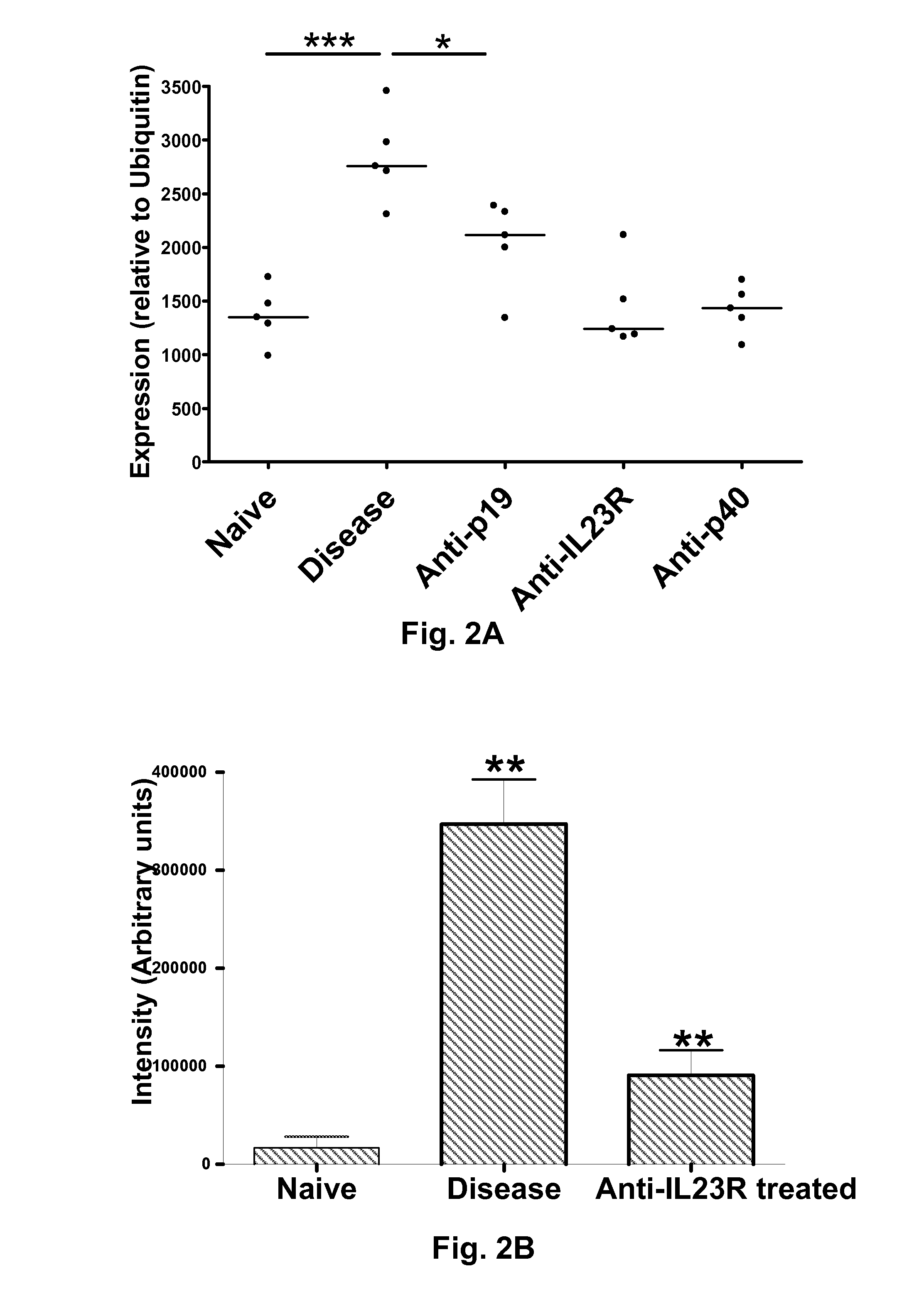
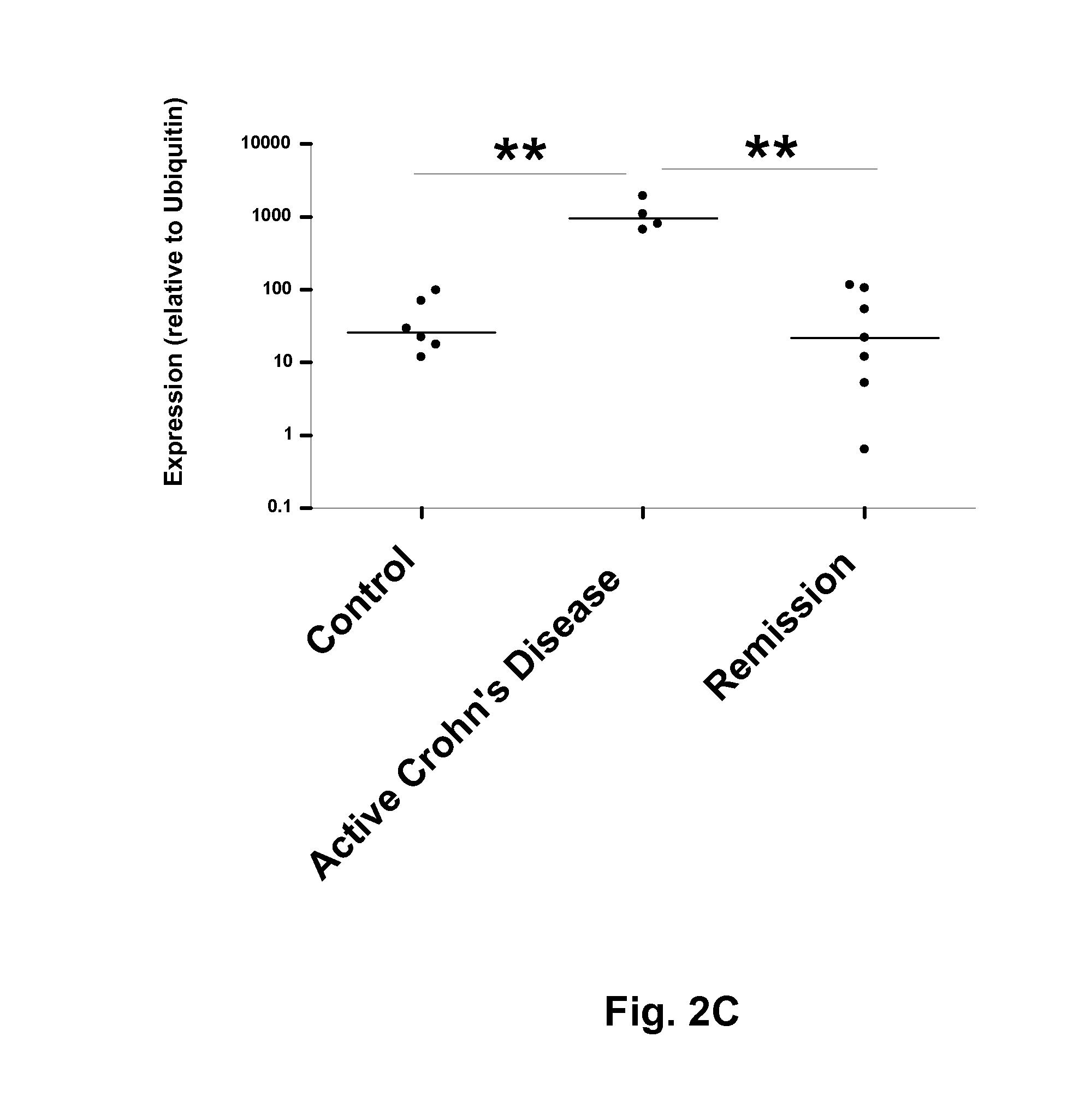
Inflammatory bowel disease biomarkers and related methods of treatment
Biomarkers associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are provided, as well as methods of using such biomarkers for diagnosing, assessing and monitoring disease progression. The biomarkers may be measured at the protein level or the gene expression level Biomarkers may be tracked individually or in groups of two or more. The disclosed biomarkers may find particular utility in monitoring a course of therapy, such as treatment with an IL-23 antagonist. Changes in biomarker levels can also be used to confirm target engagement and therapeutic efficacy. Changes in biomarkers can also be used inform modification of a therapeutic regimen, for example to increase or decrease dosing of a therapeutic agent, such as an anti-IL-23 or anti-IL-23R anti-body.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Antagonists of il-6 to prevent or treat cachexia, weakness, fatigue, and/or fever
ActiveUS20110217303A1Easy to keepImprove the quality of lifeMetabolism disorderMuscular disorderSerum reactionProtein level
The present invention is directed to therapeutic methods using antibodies and fragments thereof having binding specificity for IL-6 to prevent or treat cachexia, fever, weakness and / or fatigue in a patient in need thereof. In preferred embodiments these patients will comprise those exhibiting (or at risk of developing) an elevated serum C-reactive protein level. In another preferred embodiment, the patient's survivability or quality of life will preferably be improved.
Owner:VITAERIS INC +1
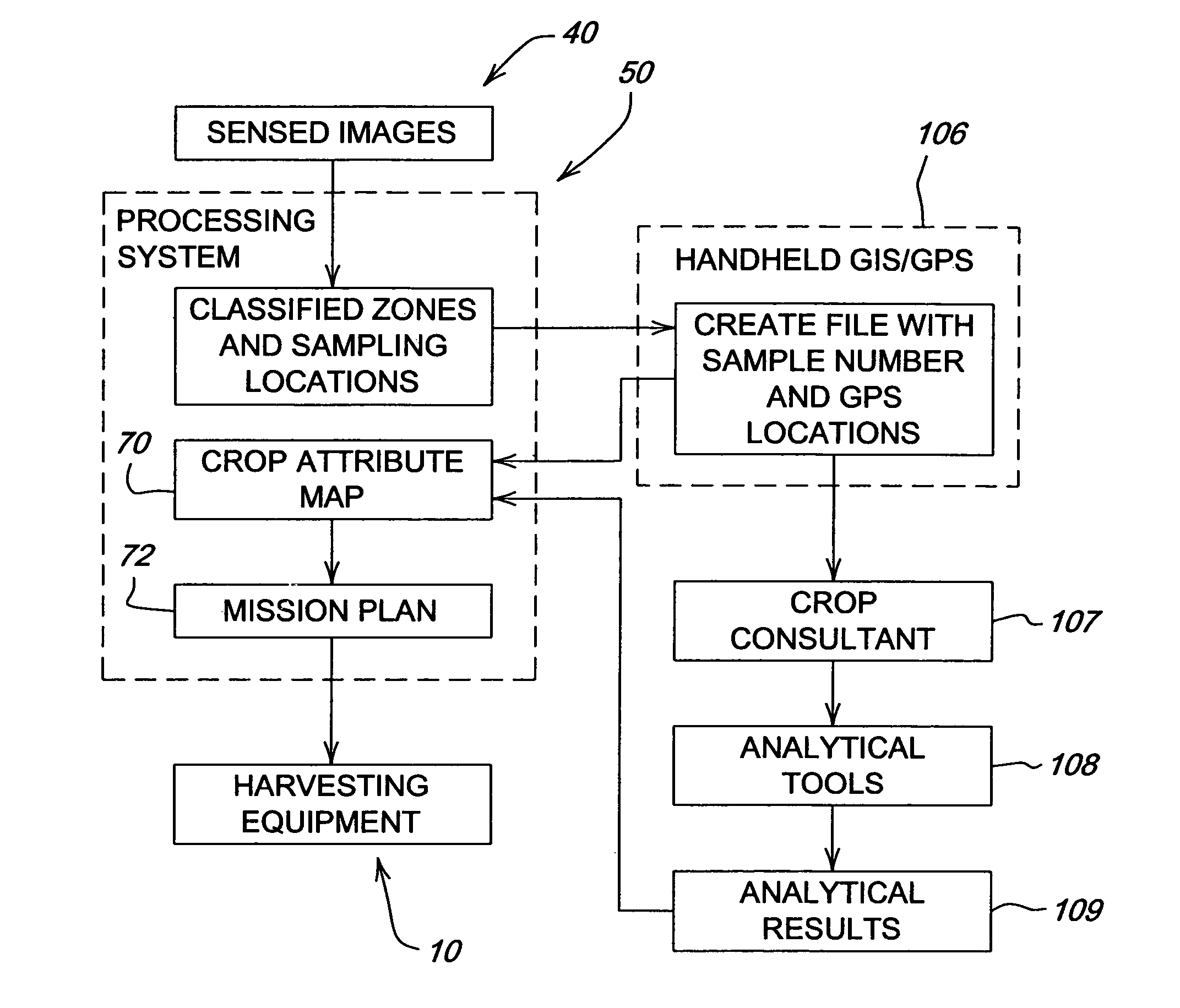
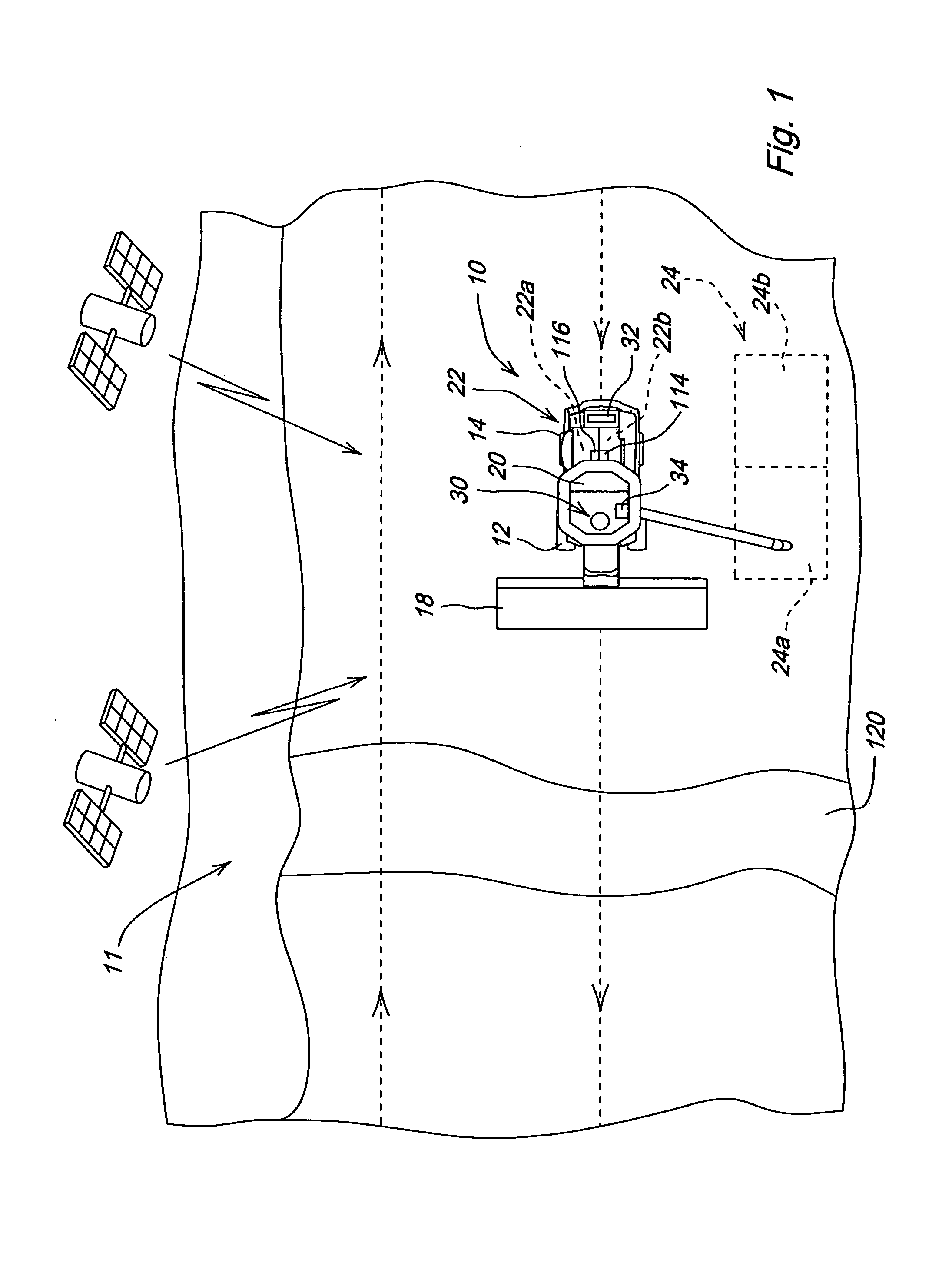
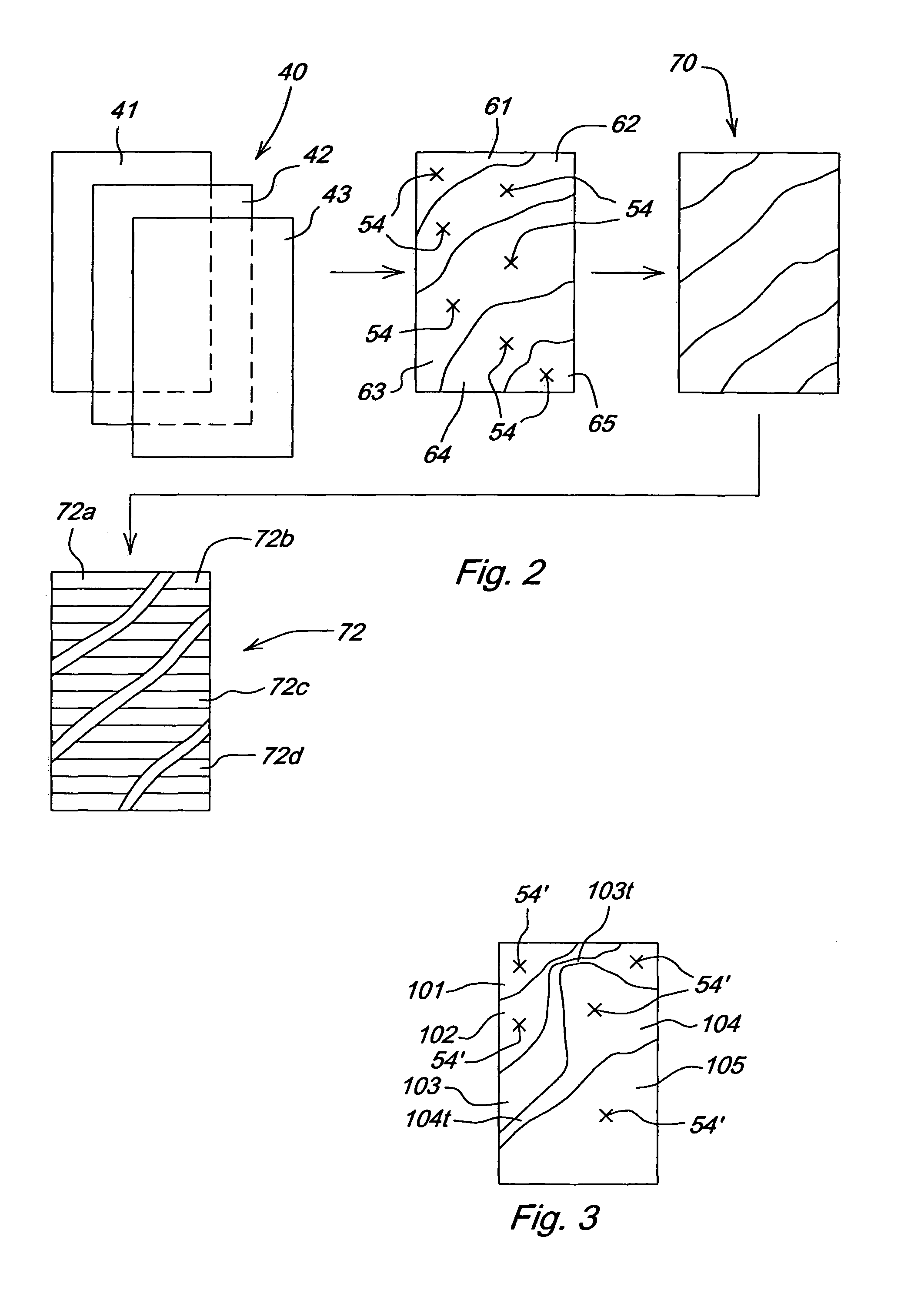
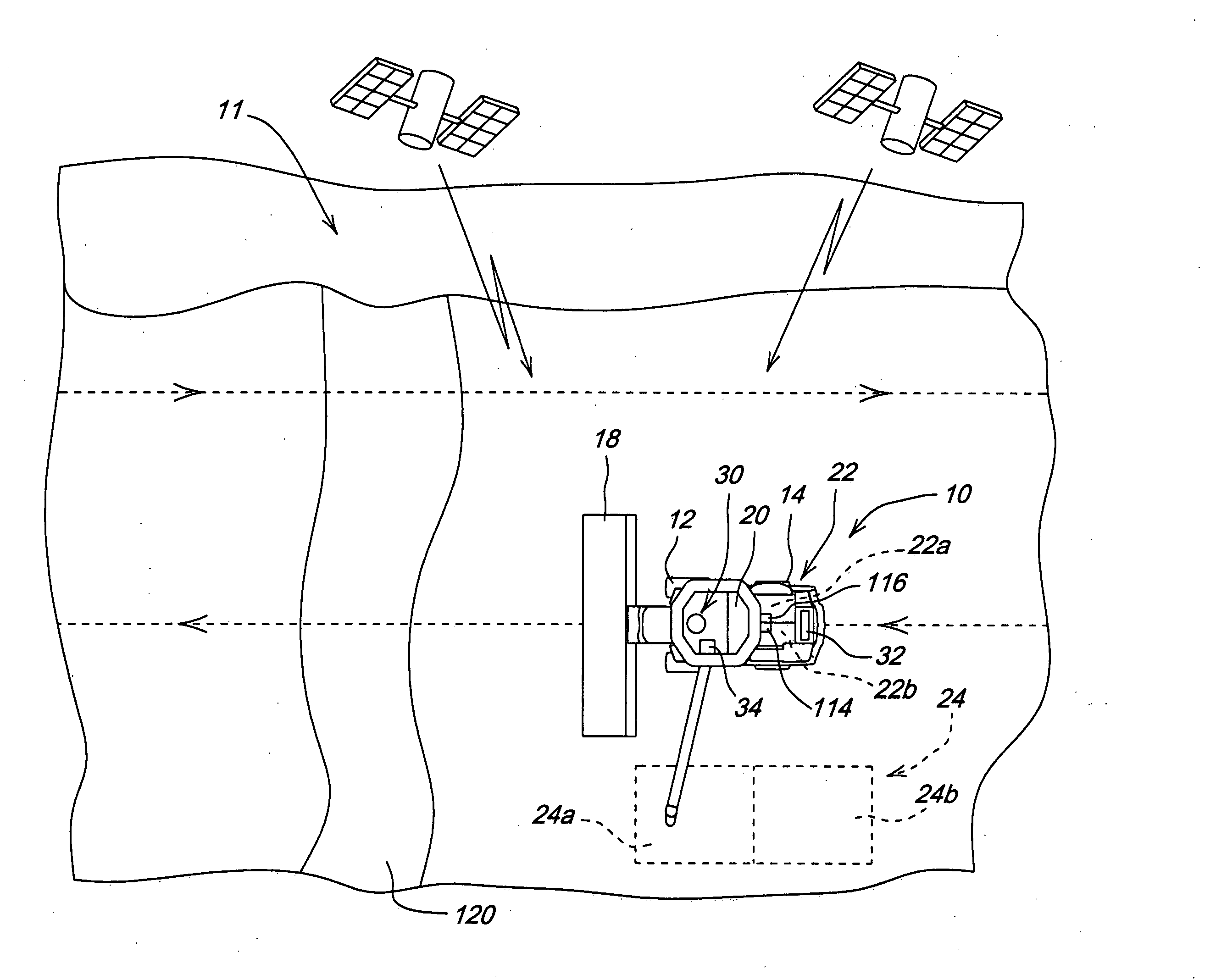
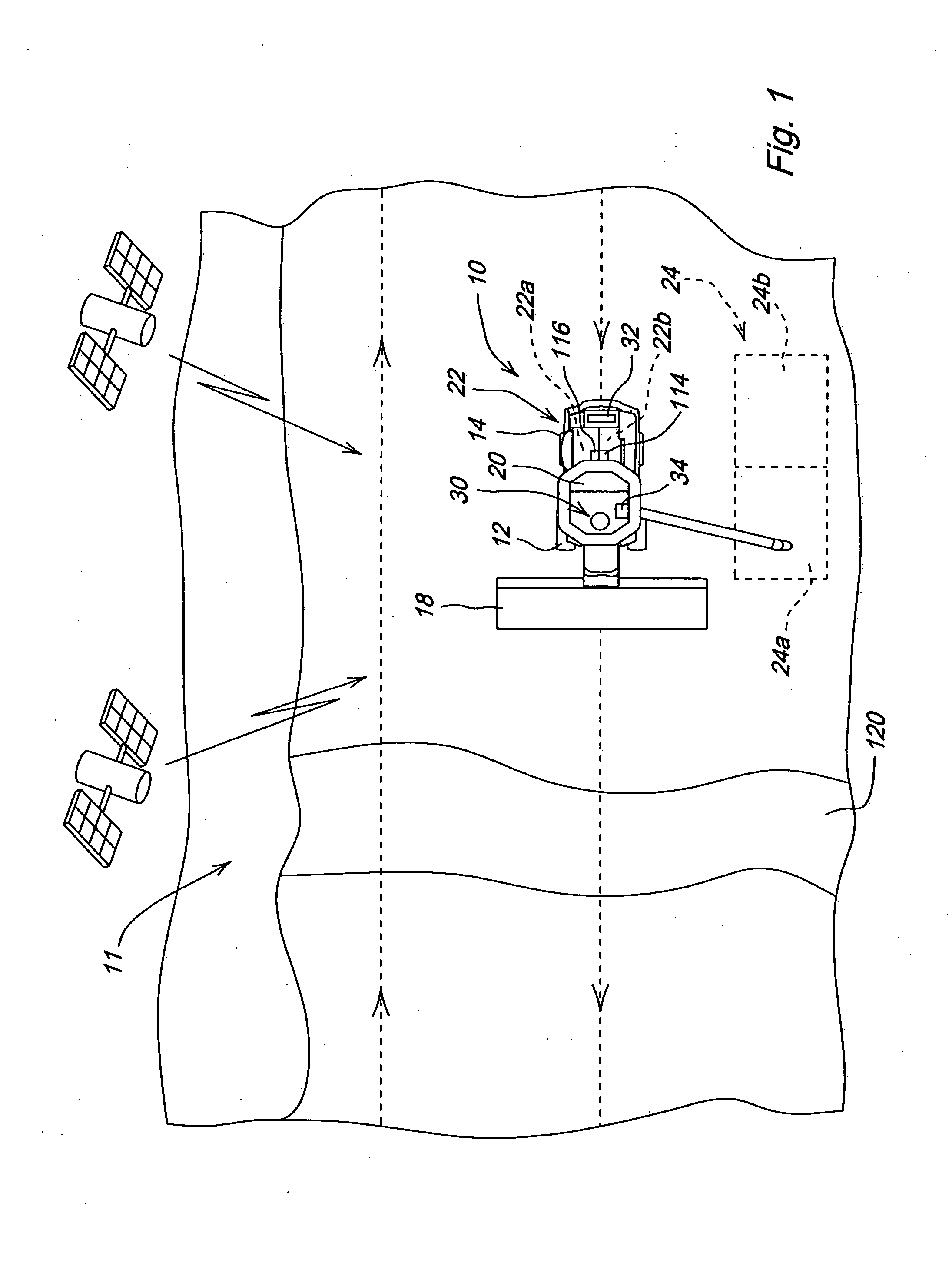
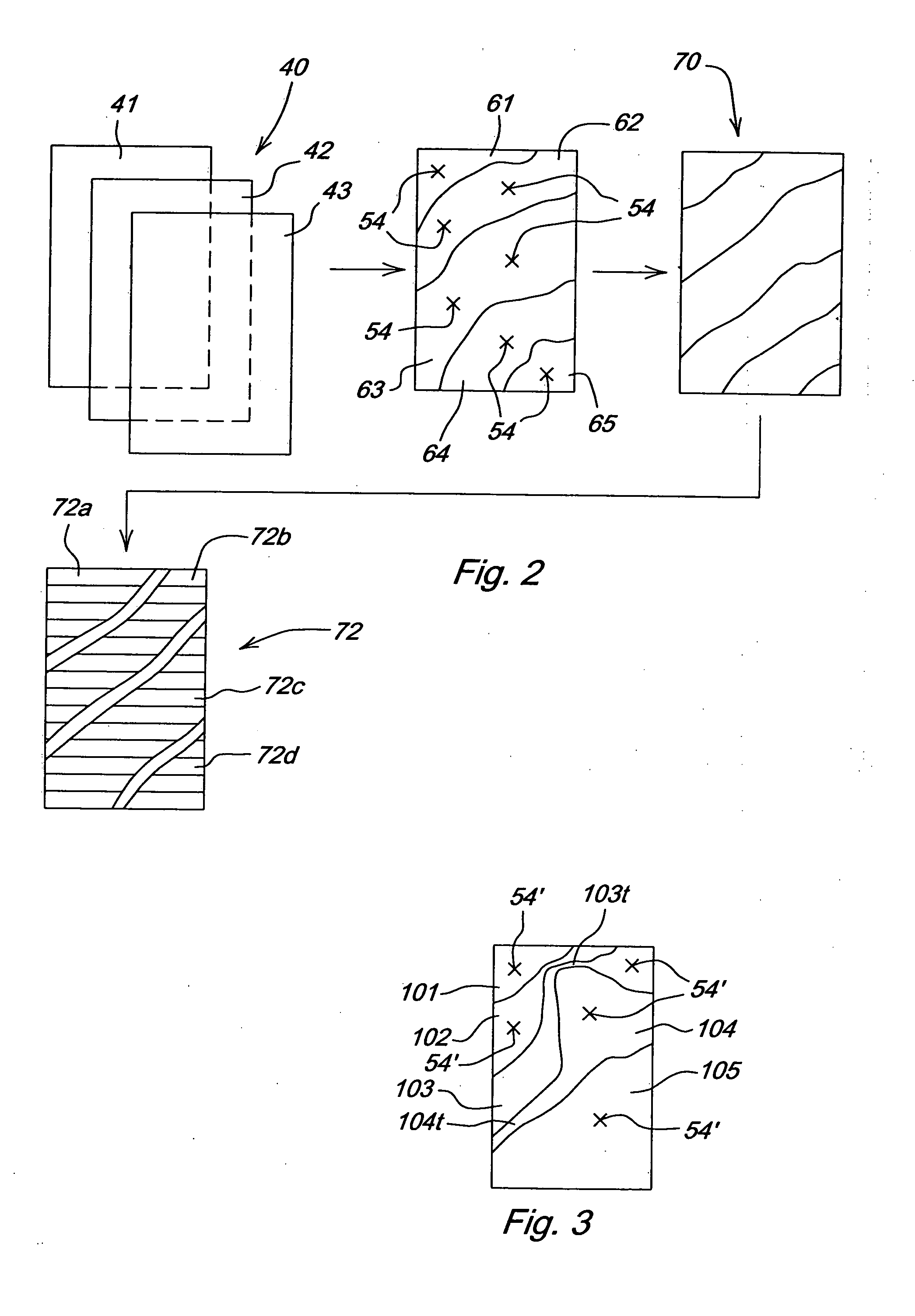
Crop attribute map input for vehicle guidance
ActiveUS7725233B2Accurate valueSegregation can be facilitatedAnalogue computers for trafficRoad vehicles traffic controlAnimal ForagingMission plan
A method for dividing a field into zones with similar crop attributes and developing a mission plan for steering the harvester to selectively harvest crops based on one or more of the attributes. The attributes include protein level, starch level, oil level, sugar content, moisture level, digestible nutrient level, or any other crop characteristic of interest. The method can be applied to selectively harvest and / or segregate according to attribute any crop, including grains such as wheat, corn, or beans, fruits such as grapes, and forage crops. Directed crop sampling provides absolute value and variance information for segregated batches of harvested crop.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Crop attribute map input for vehicle guidance
ActiveUS20070089390A1Accurate valueSegregation can be facilitatedAnalogue computers for trafficRoad vehicles traffic controlAnimal ForagingMission plan
A method for dividing a field into zones with similar crop attributes and developing a mission plan for steering the harvester to selectively harvest crops based on one or more of the attributes. The attributes include protein level, starch level, oil level, sugar content, moisture level, digestible nutrient level, or any other crop characteristic of interest. The method can be applied to selectively harvest and / or segregate according to attribute any crop, including grains such as wheat, corn, or beans, fruits such as grapes, and forage crops. Directed crop sampling provides absolute value and variance information for segregated batches of harvested crop.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Antibodies to il-6 and use thereof
ActiveUS20130034554A1Reduce riskIncrease apoptosisCompounds screening/testingAntipyreticEGFR inhibitorsAnti-coagulants
Owner:VITAERIS INC +1
Antagonists of IL-6 to raise albumin and/or lower crp
ActiveUS20130183264A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderSerum reactionAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention is directed to therapeutic methods using IL-6 antagonists such as antibodies and fragments thereof having binding specificity for IL-6 to improve survivability or quality of life of a patient in need thereof. In preferred embodiments, the anti-IL-6 antibodies will be humanized and / or will be aglycosylated. Also, in preferred embodiments these patients will comprise those exhibiting (or at risk of developing) an elevated serum C-reactive protein level or a reduced serum albumin level prior to treatment. In another preferred embodiment, the patient's Glasgow Prognostic Score will be increased and survivability will preferably be improved.
Owner:VITAERIS INC +1
Methods for identifying patients with an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer and compositions therefor
InactiveUS20070212721A1Easy to detectRaise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCancer cellMotility
Screening methods for identifying patients with an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer are provided. The screening methods involve the detection of expression of a plurality of biomarkers in a body sample, wherein overexpression of the biomarkers is indicative of an increased likelihood of having ovarian cancer. The screening methods may further comprise a two-step analysis. Biomarkers of interest include genes and proteins that are, for example, involved in defects in DNA replication / cell cycle control, cell growth and proliferation, escape from apoptosis, angiogenesis or lymphogenesis, or the mechanisms of cancer cell motility and invasion. In some aspects of the invention, expression of a biomarker is detected at the protein level using a biomarker-specific antibody or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Methods for detecting ovarian cancer in patients are further disclosed herein. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Feed for litopenaeus vannamei
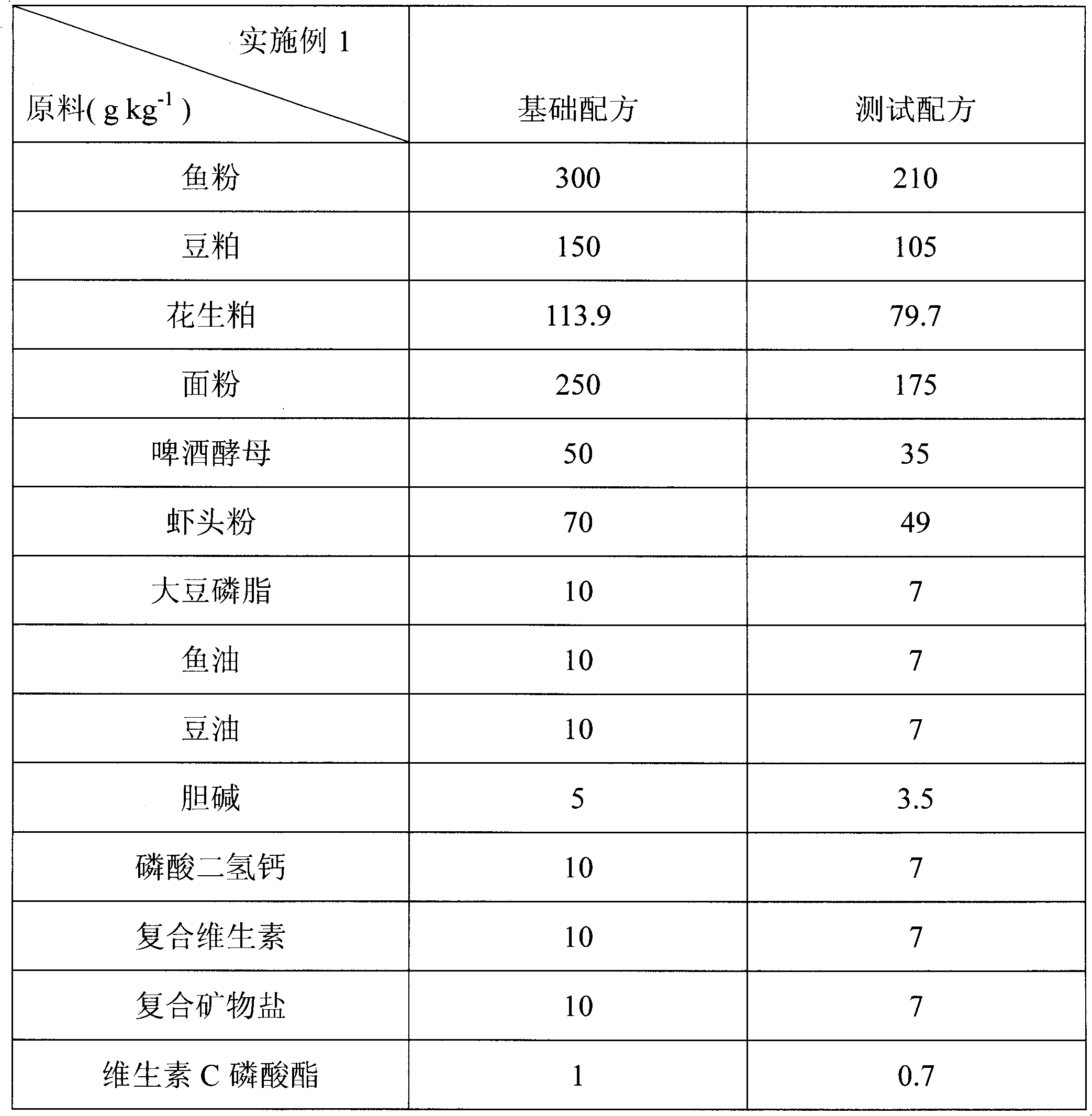
InactiveCN101828644AMeeting nutritional needsImprove digestion and absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffProtein levelPollution
The invention discloses a feed for litopenaeus vannamei, which comprises the following nutrition compositions by mass percent: 25-35% of proteins, 4-9% of fat, 7-12% of ash contents, 40-55% of carbohydrates and 3-11% of water. The feed can meet the nutrient requirement of litopenaeus vannamei for best growth, and effectively solves the traditional problems of high protein level of a compound feedand severe environmental pollution in the process of culturing litopenaeus vannamei; the industrial profit is increased, and the pollution and the damage to a water environment in the process of culturing are reduced; and the sustainable development of litopenaeus vannamei culturing industry is realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
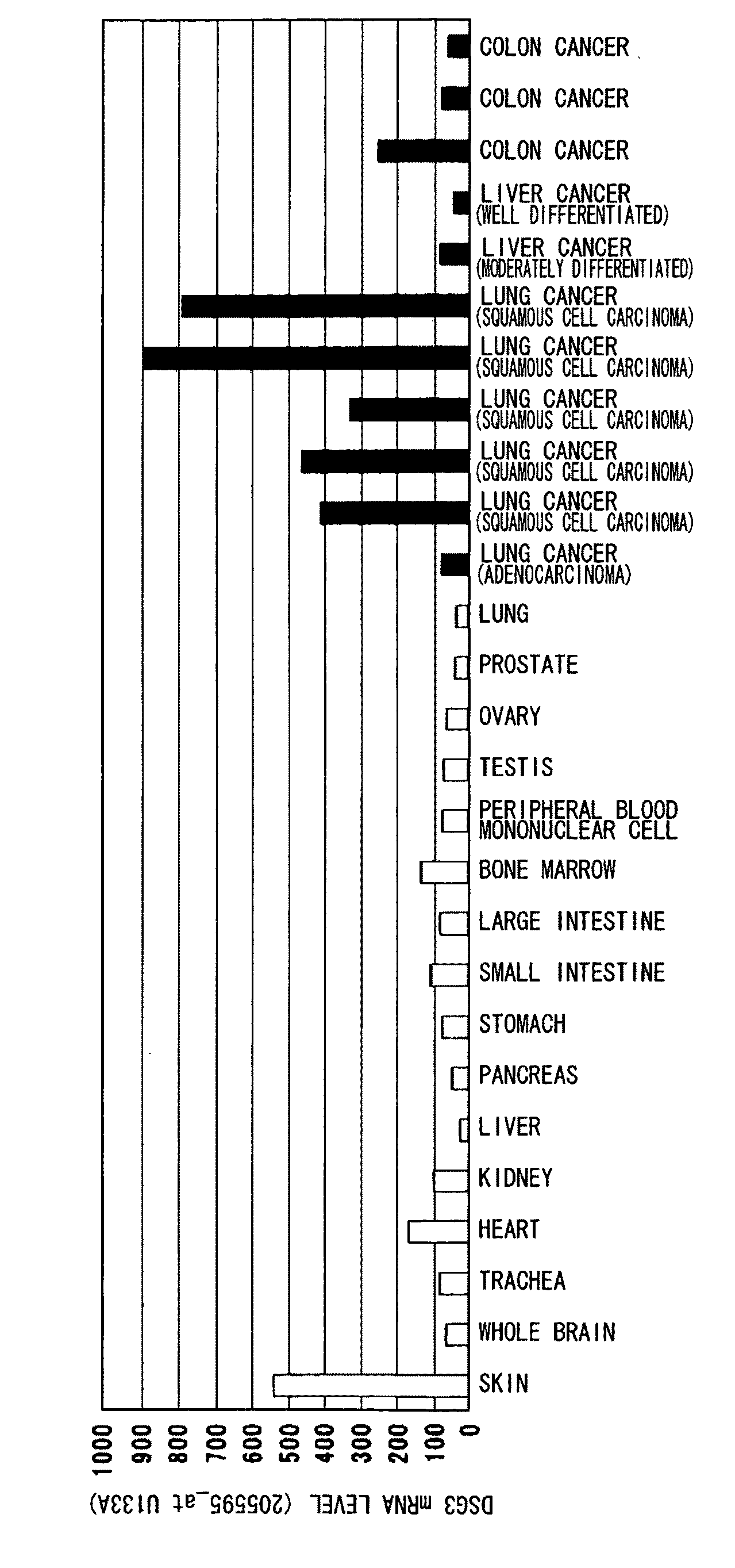
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer Using Anti-Desmoglein-3 Antibodies
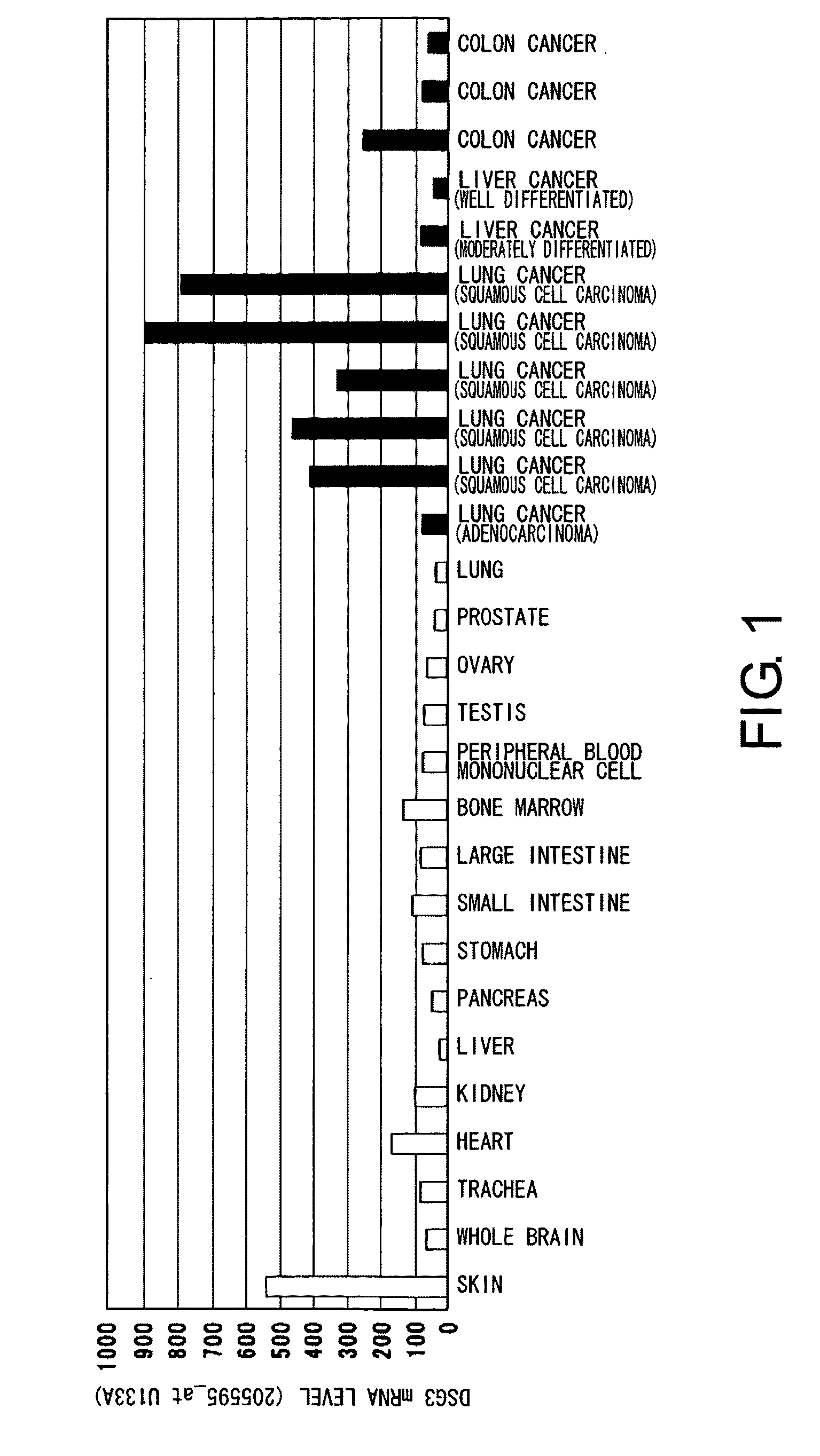
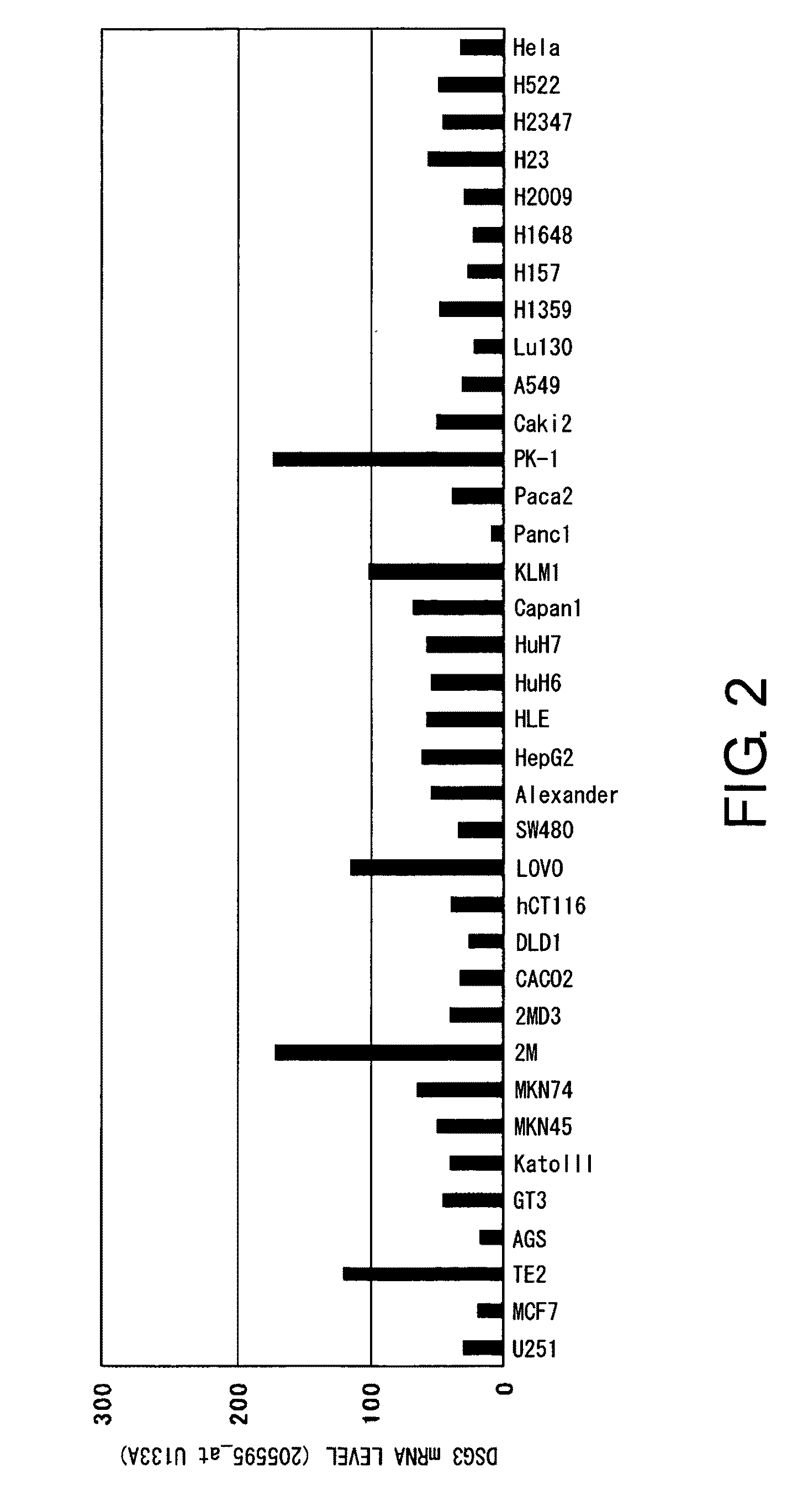
InactiveUS20100092457A1High expressionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Methods that involve detection of a DSG3 protein for diagnosing cancer are disclosed. In lung cancer, the expression of DSG3 was found to be enhanced at very high frequency at the gene level and protein level. Methods of the present invention can be carried out using an antibody that recognizes a DSG3 protein. Pharmaceutical compositions, cell growth inhibitors, and anticancer agents containing a DSG3-binding antibody as an active ingredient are also disclosed. Methods of inducing cell damage in DSG3-expressing cells and methods of suppressing proliferation of DSG3-expressing cells by contacting the DSG3-expressing cells with DSG3-binding antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Methods for reducing complexity of a sample using small epitope antibodies
InactiveUS20050131219A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEpitopeProteomics
The present invention relates generally to methods for reducing the complexity of a sample. More specifically, the present invention relates to proteomics, the measurement of the protein levels in biological samples, and analysis of proteins in a sample using antibodies that recognize small epitopes.
Owner:TETHYS BIOSCI
Feeding management method of sows
InactiveCN103609525AThe expected date of delivery is accurateGuaranteed Nutrient LevelsAnimal husbandryZoologyProtein
The invention discloses a feeding method of pigs, and particularly discloses a feeding management method of sows. The feeding management method of the sows comprises the step of feeding management on four stages of replacement gilts, non-pregnant and breeding sows, pregnant sows and farrowing and lactation sows. The protein level of the sows keeps 16%; the feeding amount is increased or decreased in time according to the weights of the replacement gilts; every 4-6 non-pregnant and breeding sows stay in one sty to be fed, and the sows are bred in time; the feeding amount of the pregnant sows is adjusted according to the early pregnancy stage, the middle pregnancy stage and the later pregnancy stage, namely the weights of the sows; delivery rooms, delivery beds and the sties are sterilized before the sows farrow, and the feeding amount is increased or decreased in time after the sows farrow, namely in the lactation period. The sows fed according to the feeding management method of the sows are good in health, high in pregnancy rate and large in born number, piglets are strong and uniform, and economic benefits can be improved.
Owner:HUBEI XINWUCHENG ECOLOGICAL AGRI DEV
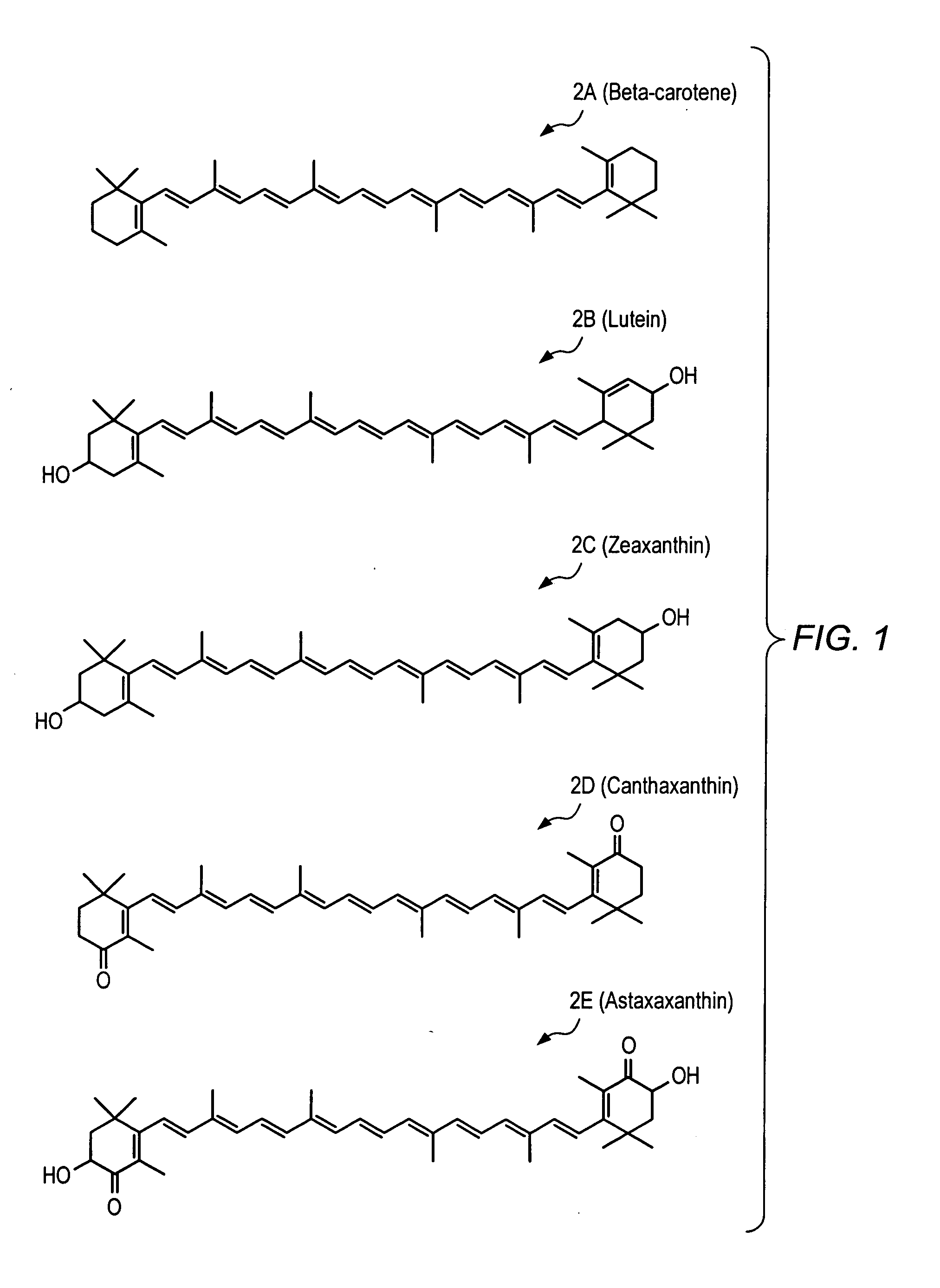
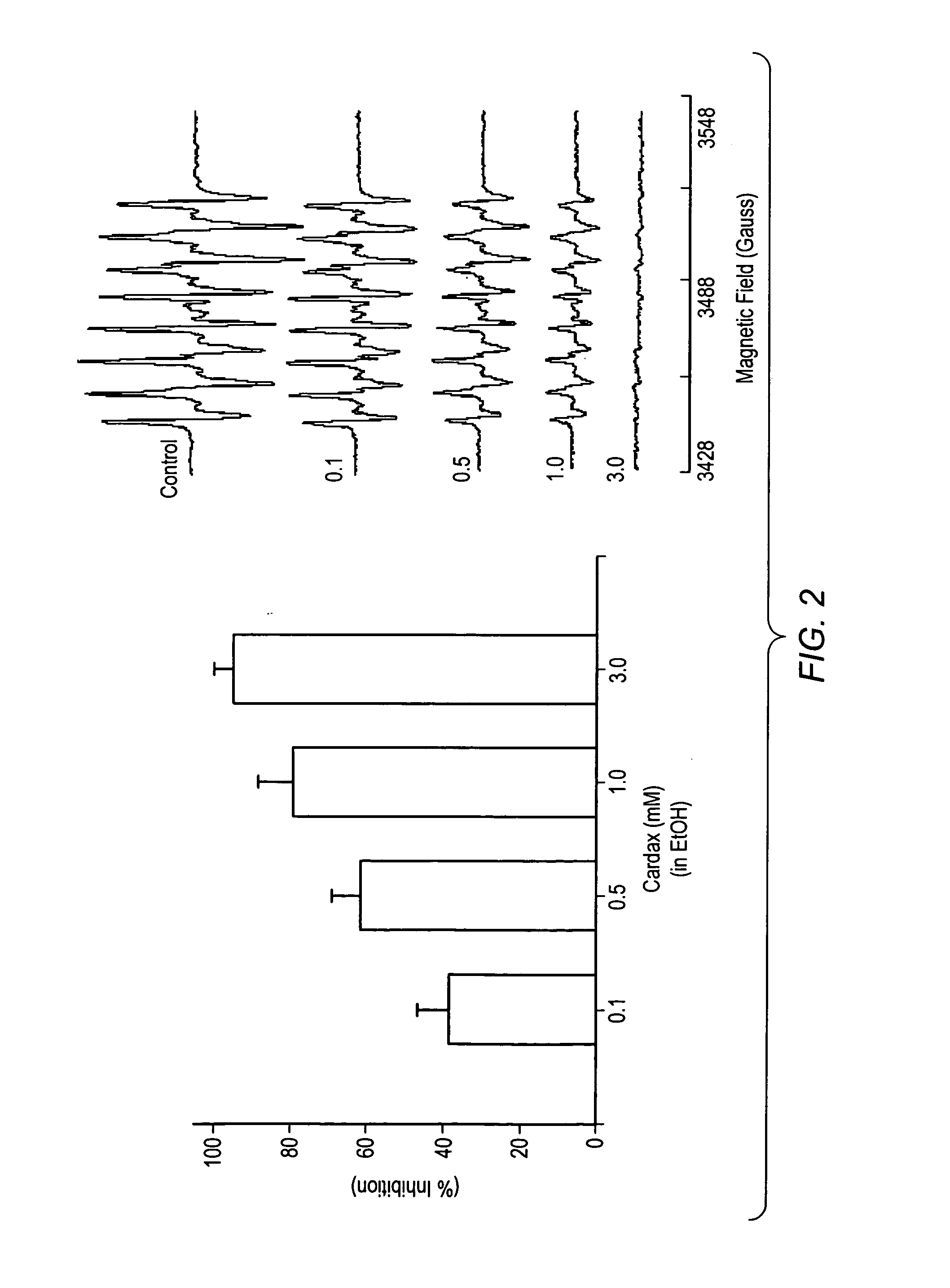
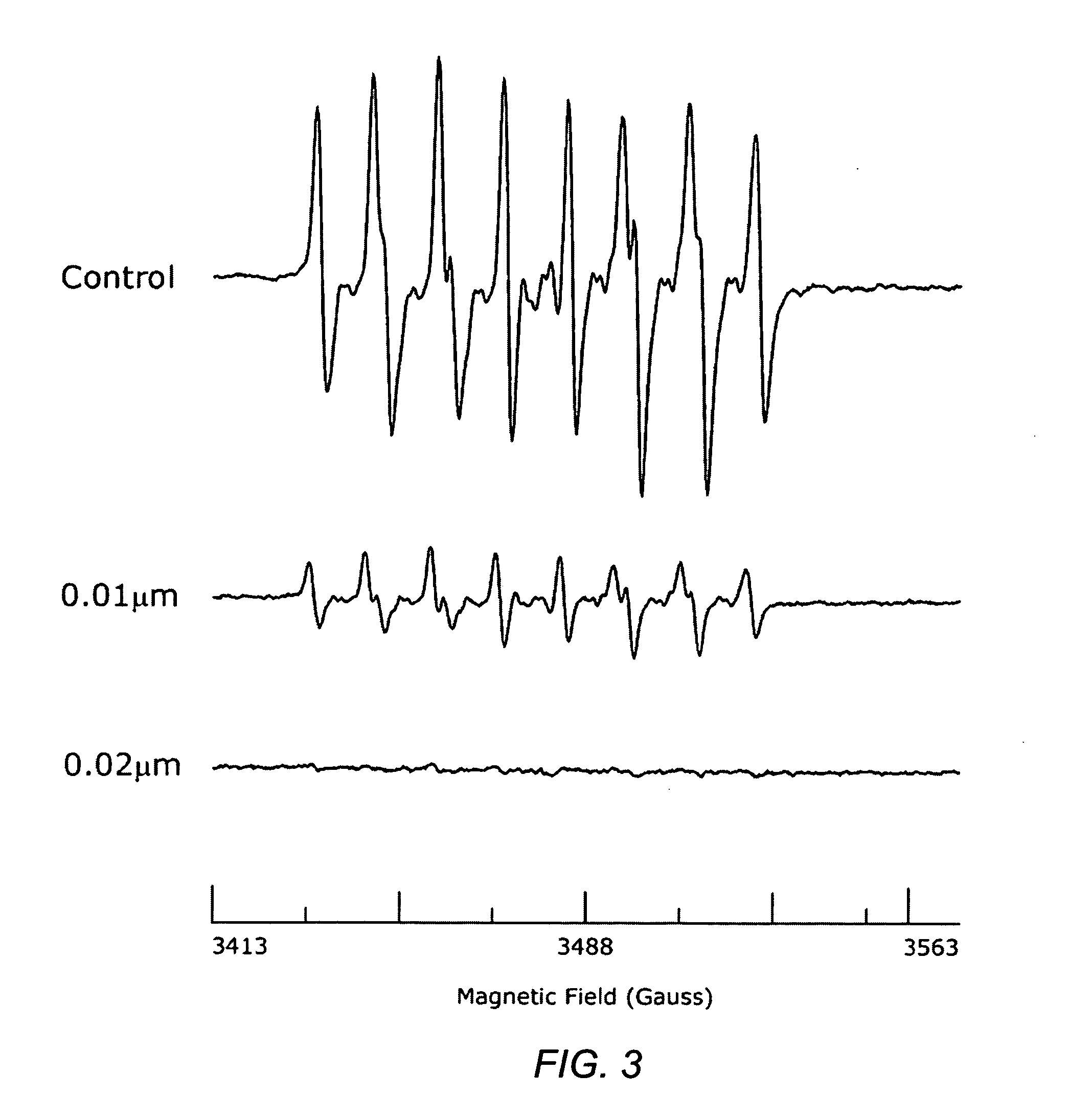
Carotenoid analogs or derivatives for controlling C-reactive protein levels
InactiveUS20050059659A1Increase connexin expressionAmeliorate proliferationBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsSynthetic analogueAntioxidant
A method of controlling (e.g., influencing or affecting) C-reactive protein levels in a subject may include administering to the subject an effective amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable formulation. The pharmaceutically acceptable formulation may include a synthetic analog or derivative of a carotenoid. The subject may be administered a carotenoid analog or derivative, either alone or in combination with another carotenoid analog or derivative, or co-antioxidant formulation. The carotenoid analog may include a conjugated polyene with between 7 to 14 double bonds. The conjugated polyene may include an acyclic alkene including at least one substituent and / or a cyclic ring including at least one substituent. In some embodiments, a carotenoid analog or derivative may include at least one substituent.
Owner:CARDAX PHARMA
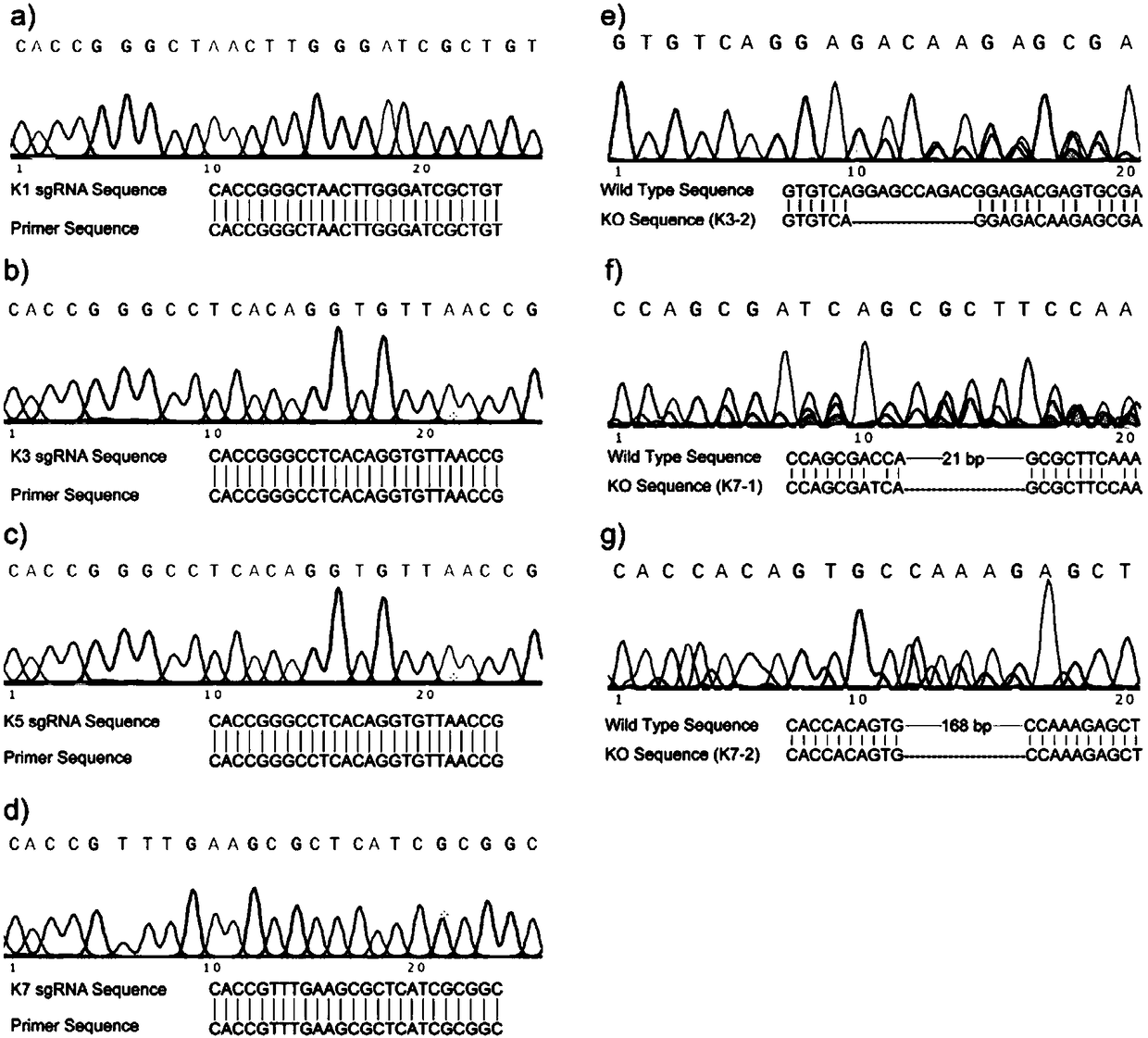
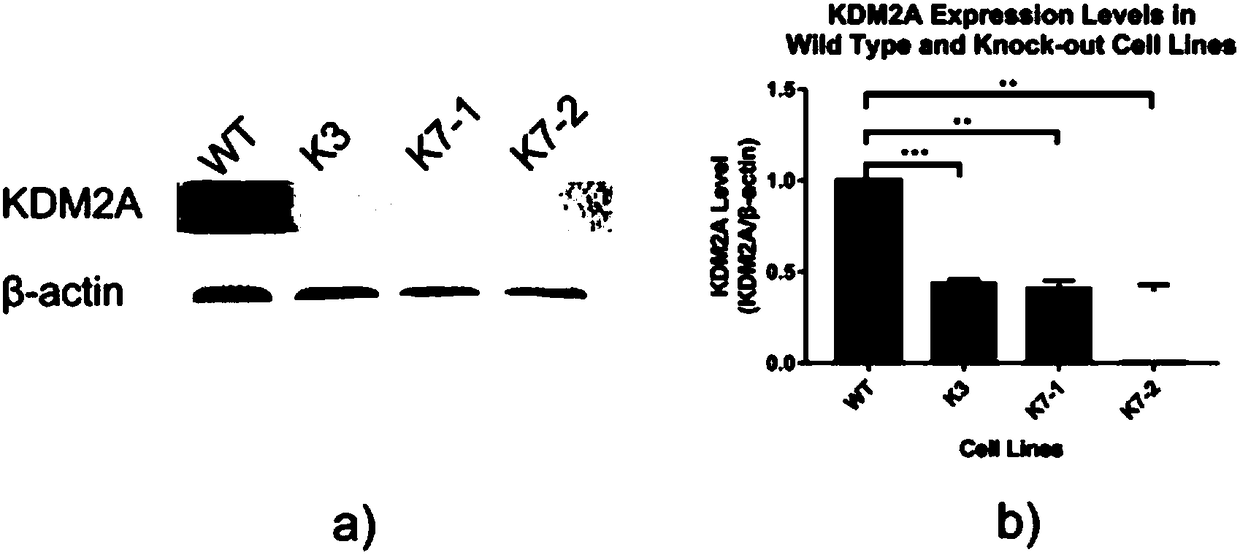
Method for knocking out KDM2A gene of HEK293T cells with CRISPR-CAS9 technology
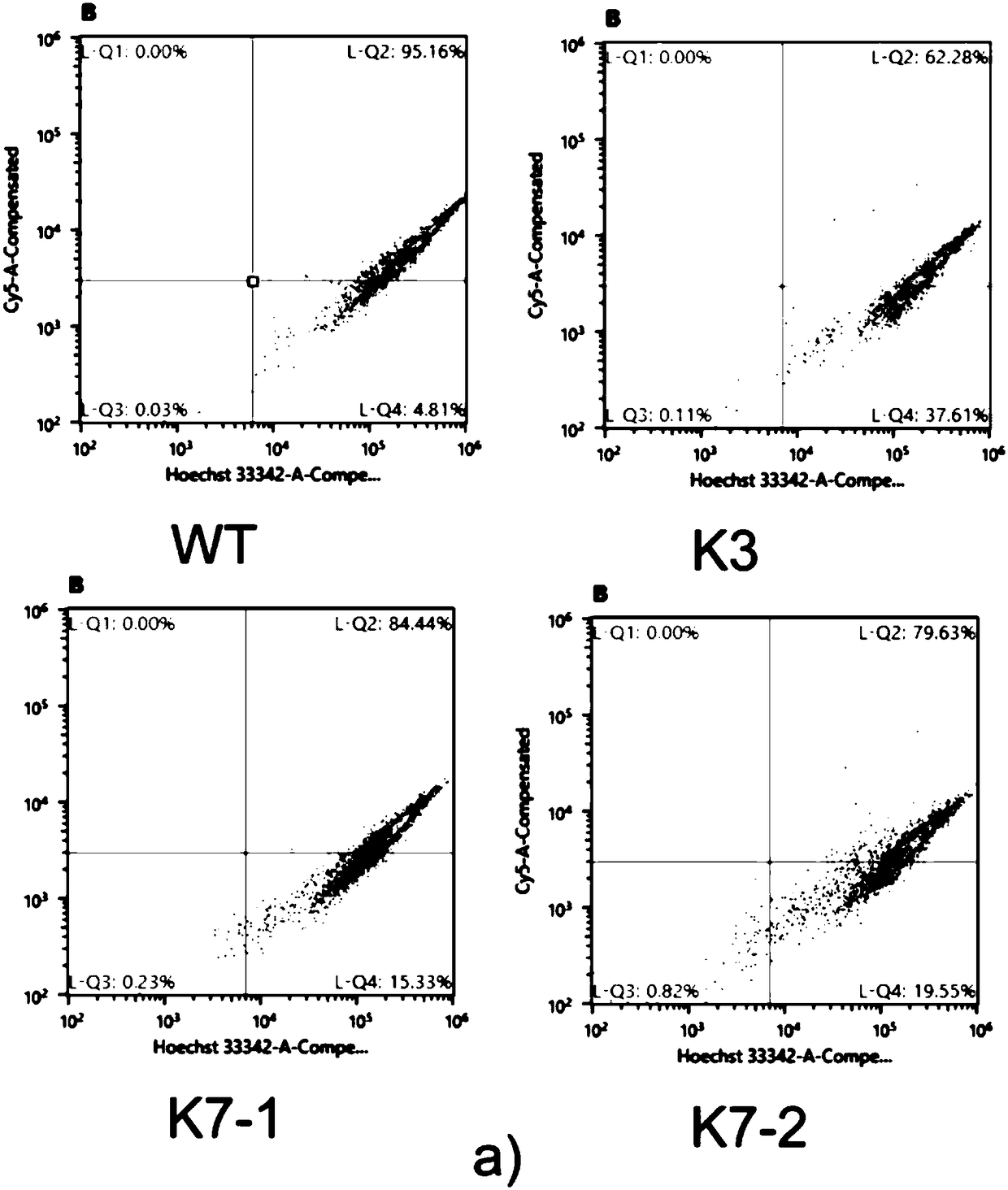
InactiveCN108504657AConducive to research proliferationGood for studying the effects of apoptosisHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsT cellProtein level
The invention provides a method for knocking out a KDM2A gene of HEK293T cells with a CRISPR-CAS9 technology. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1), cell transfection; (2), cell genome extraction; (3), PCR identification; (4), gene level verification; (5), protein level verification: whether K3, K7-1 and K7-2 are KDM2A gene-deficient is further verified by Western blotting after a mutantcell line is verified at the gene level. The invention further provides a KDM2A knockout HEK293T cell line prepared with method and an application of the KDM2A knockout HEK293T cell line as a cell model in study of cell proliferation and apoptosis signaling pathways involved in KDM2A methylase.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Antagonists of IL-6 to raise albumin and/or lower CRP
ActiveUS8420089B2Improve survivabilityQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderElevated serumAnti-IL-6
The present invention is directed to therapeutic methods using IL-6 antagonists such as antibodies and fragments thereof having binding specificity for IL-6 to improve survivability or quality of life of a patient in need thereof. In preferred embodiments, the anti-IL-6 antibodies will be humanized and / or will be aglycosylated. Also, in preferred embodiments these patients will comprise those exhibiting (or at risk of developing) an elevated serum C-reactive protein level or a reduced serum albumin level prior to treatment. In another preferred embodiment, the patient's Glasgow Prognostic Score will be increased and survivability will preferably be improved.
Owner:VITAERIS INC +1
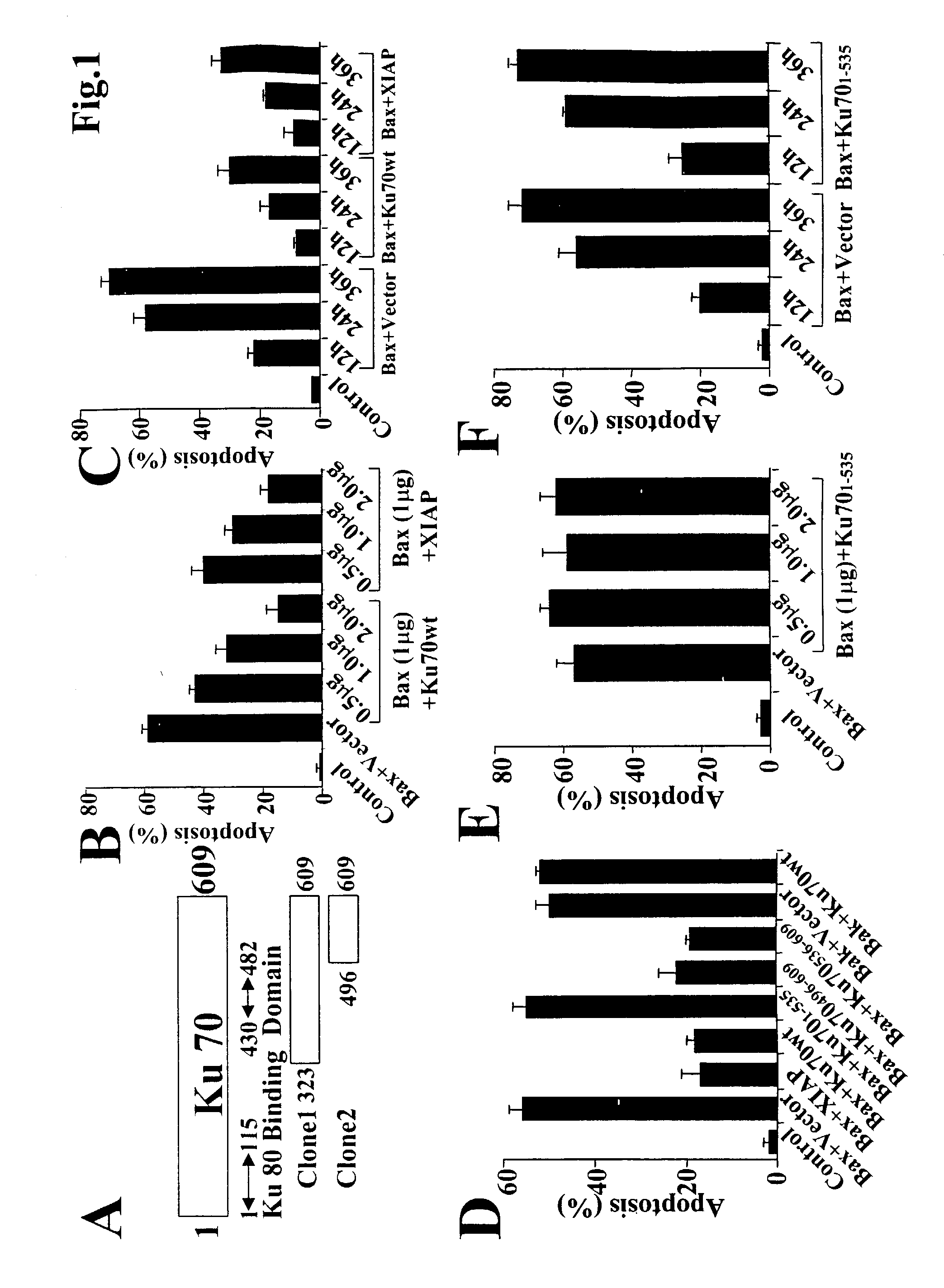
Method of modulating or examining Ku70 levels in cells
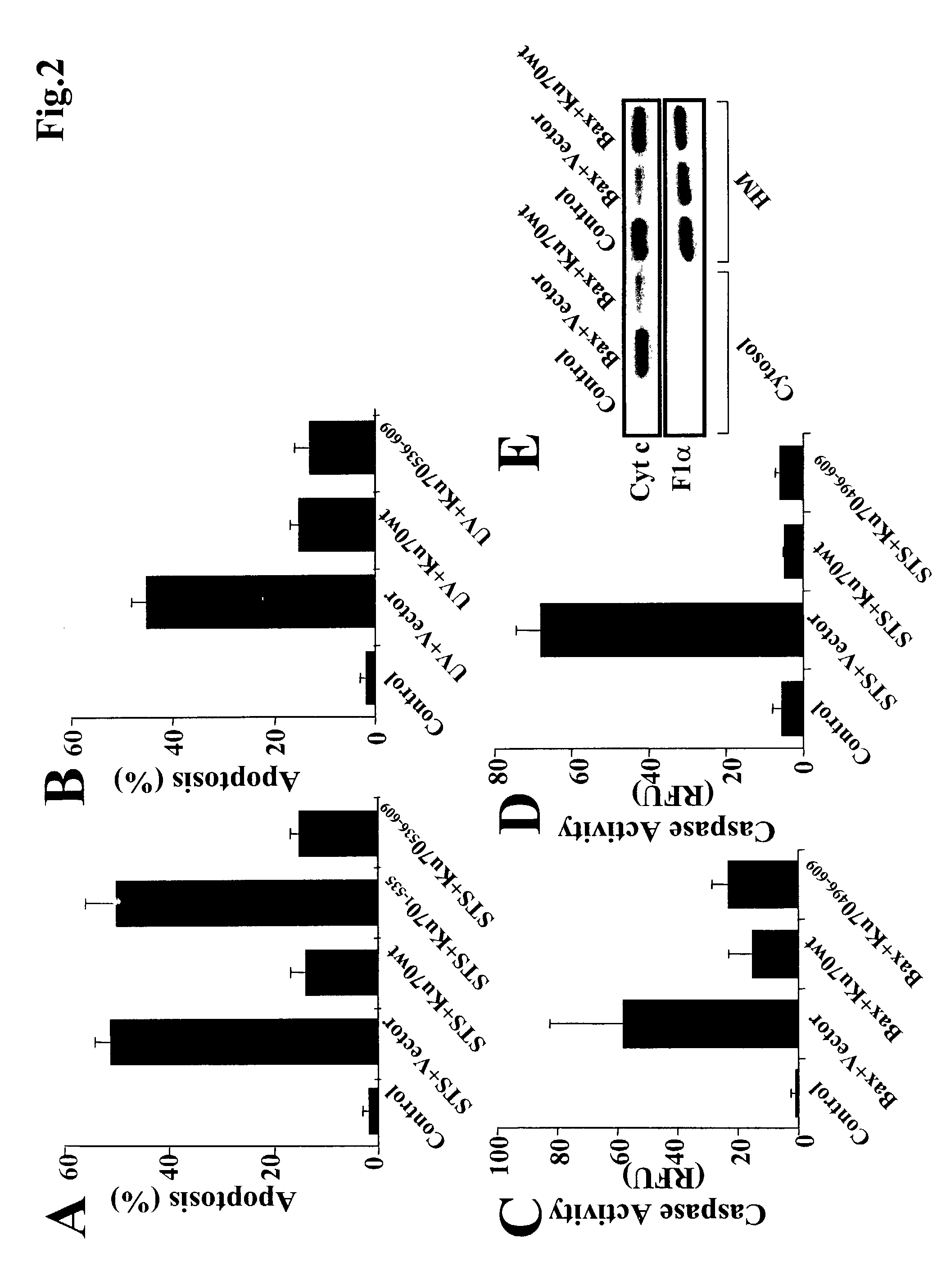
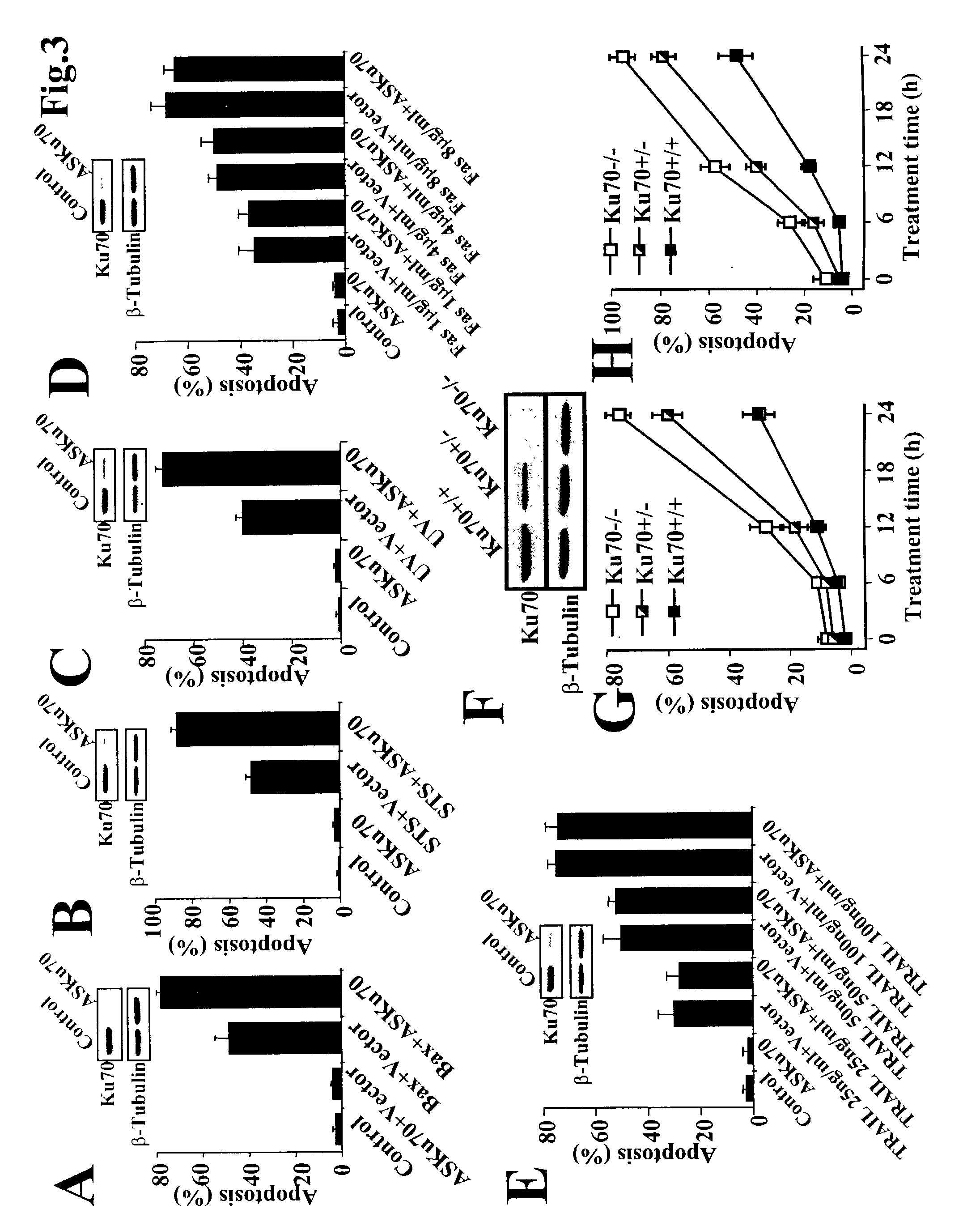
A method of predicting whether cells would respond to therapies which are mediated through Bax-regulated apoptosis is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises the step of: (a) examining the intensity of the expression of the Bax protein or mRNA in a cell relative to a control, and (b) based on that intensity level, predicting whether cells will respond to therapies which are mediated through Bax-regulated apoptosis, wherein a high Bax level indicates that one may lower Ku70 levels and increase sensitivity to apoptosis. In another embodiment, the invention is a method of sensitizing cells to cancer therapy, comprising the step of reducing the cell's native Ku70 protein level. In another embodiment the invention is method of treating cell death-related diseases comprising the step of increasing cellular Ku70 protein level.
Owner:VERSITI BLOOD RES INST FOUND INC
Compositions and methods for modulation of suppressor t cell activation
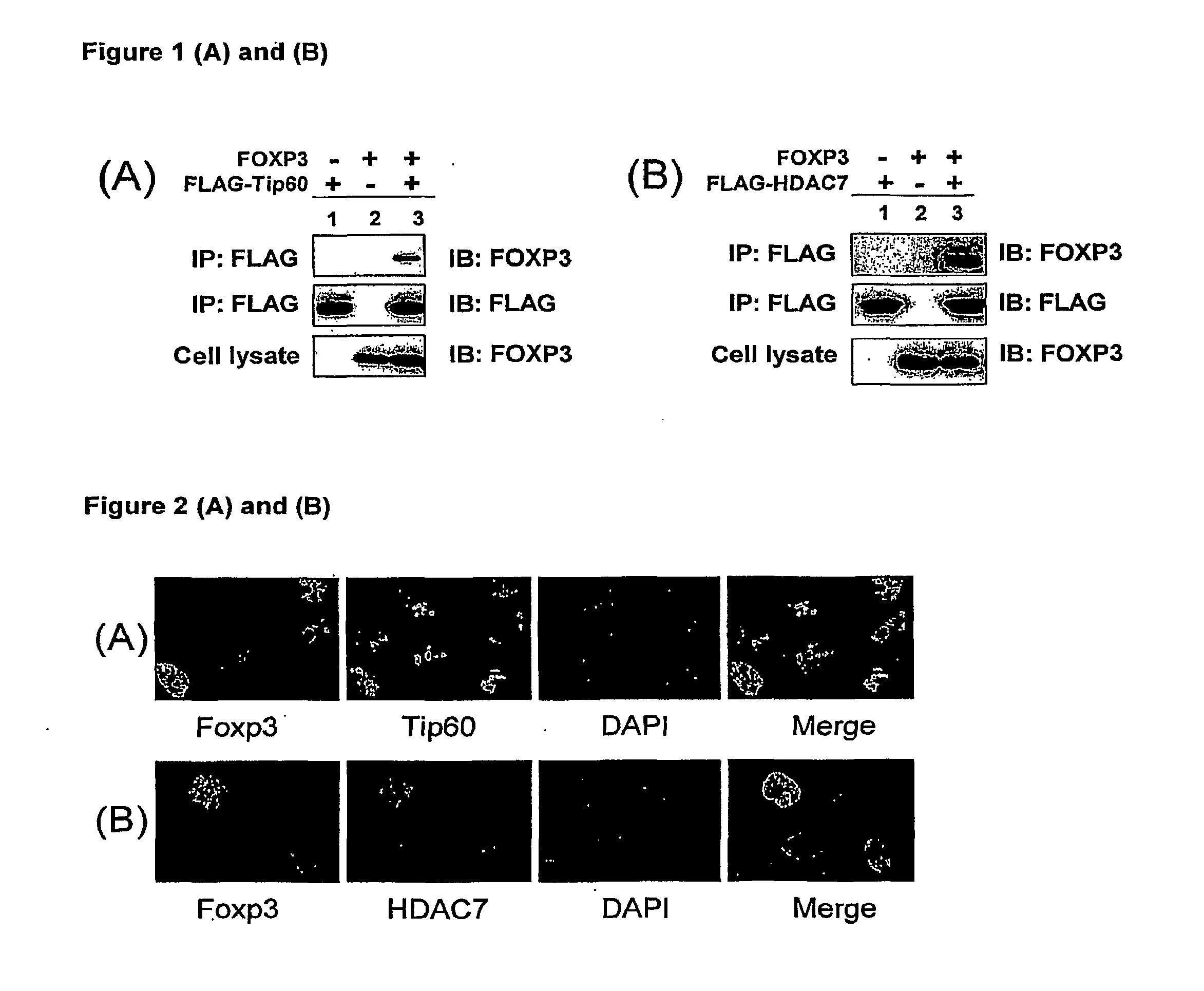
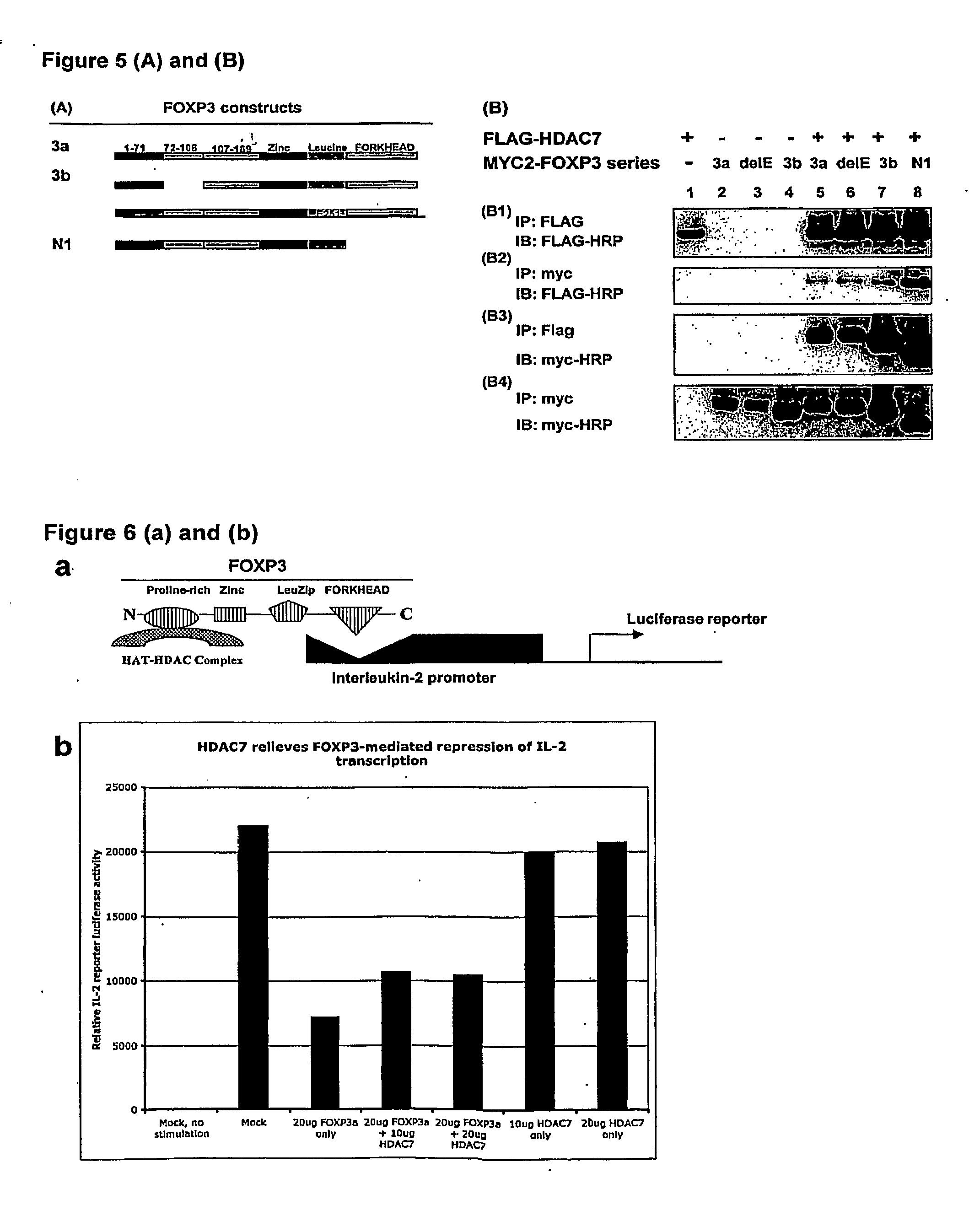
InactiveUS20100061984A1Relieve symptomsIncreased acetylation levelsCompounds screening/testingAntibacterial agentsAntigenImmunologic disorders
Methods of treating autoimmune disorders, coronary artery disease, allergy symptoms, allograft rejection sepsis / toxic shock are disclosed. Some methods comprise administering one or more regulatory compositions to activate the T suppressor cells by increasing the acetylation level and / or protein level of FOXP3 in combination with a T suppressor stimulus and / or an antigen. Some methods comprise administering one or more regulatory compositions to activate the T suppressor cells by increasing the acetylation level and / or protein level of FOXP3. Some methods comprise administering soluble GITR or antibodies that bind to GITR ligand. Methods of treating cancer, infectious diseases, and immune deficiency are also disclosed as are vaccination methods. The methods comprise administering one or more regulatory compositions to inactivate the T suppressor cells by reducing the acetylation level and / or protein level of FOXP3. Improved vaccines and vaccination methods are disclosed. Methods of identifying compounds that are useful to modulate acetylation level and / or protein level of FOXP3 and treat diseases are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
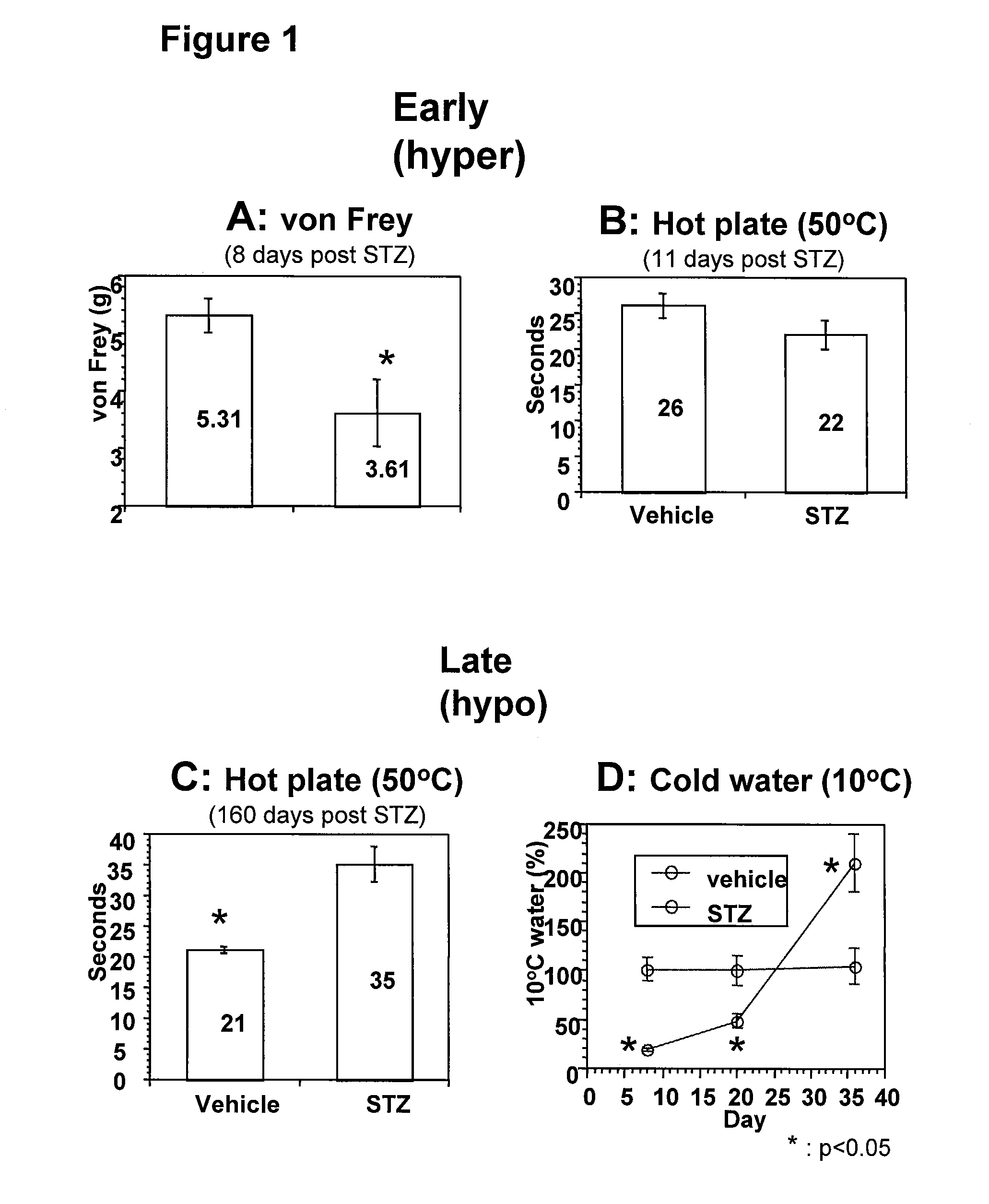
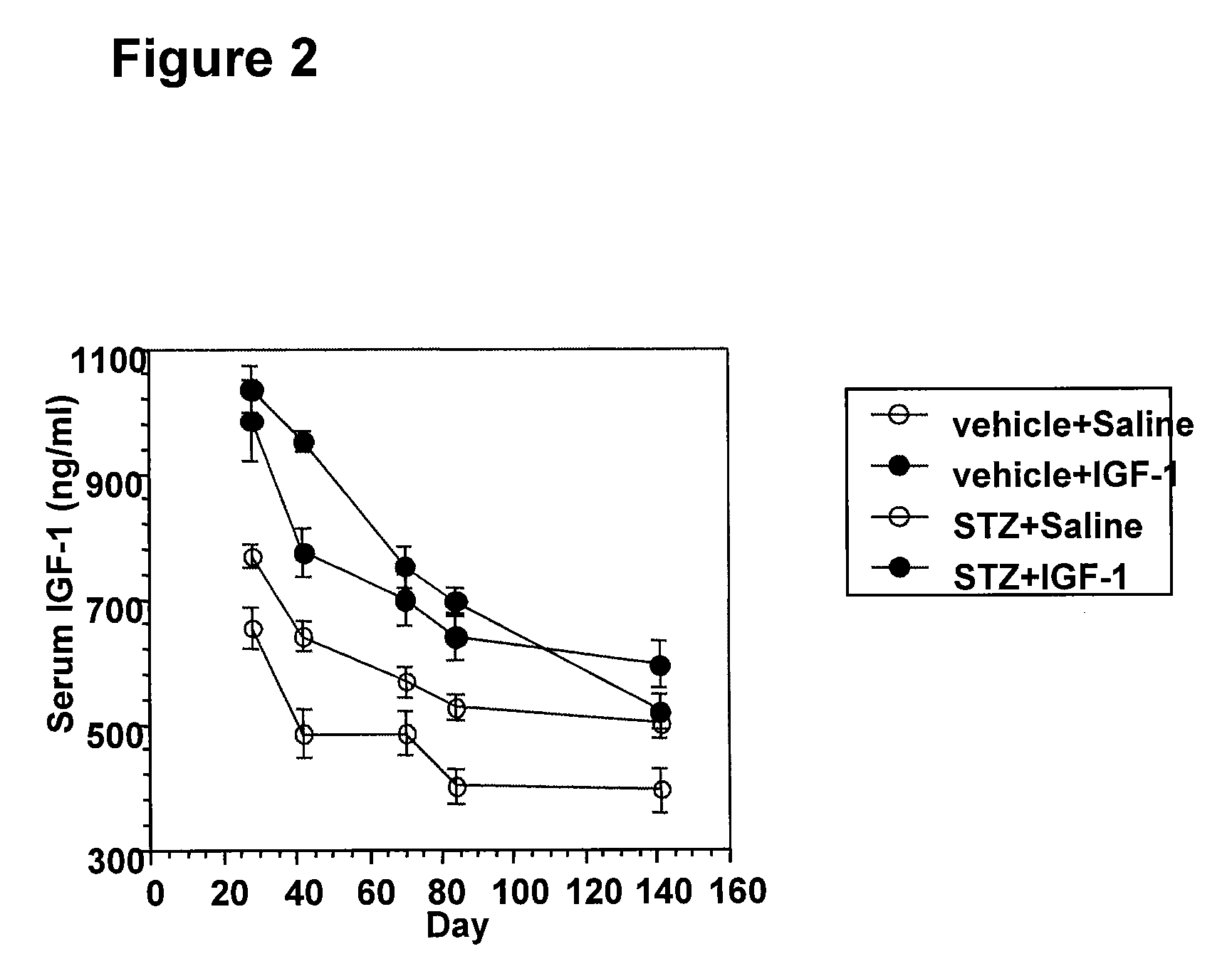
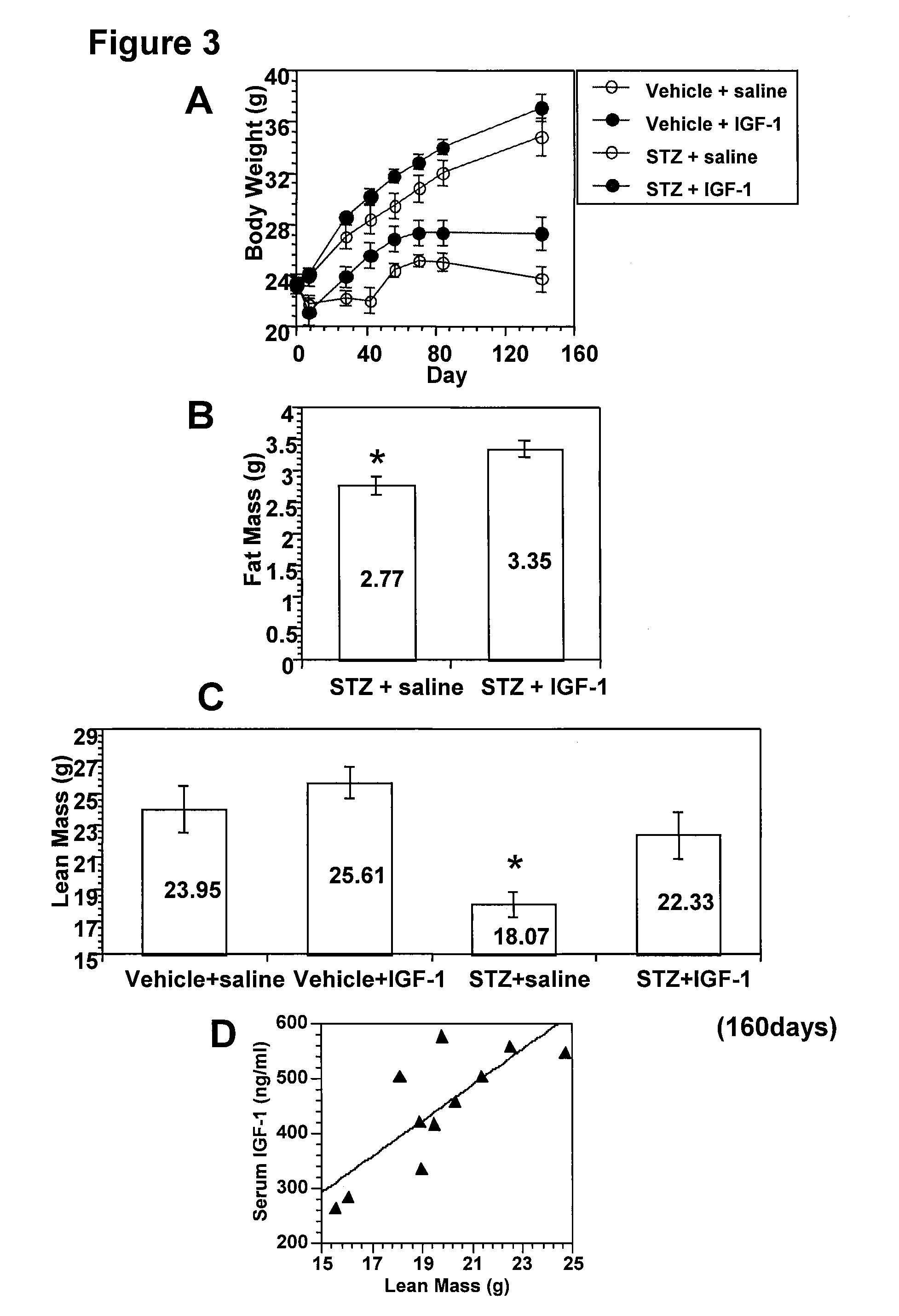
Systemic insulin-like growth factor-1 therapy reduces diabetic peripheral neuropathy and improves renal function in diabetic nephropathy
InactiveUS20100216709A1Prevents subsequent hyposensitivityEasy maintenanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderInsulin-like growth factorHyperglycemic disorder
The present invention provides methods of treatment of patients suffering from the complications of blood sugar disorders: diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetic nephropathy by administration of IGF-1 via protein therapy or gene therapy. It relates to methods of treating an individual having a diabetic disorder or a hyperglycemic disorder, comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a DNA vector expressing IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec in vivo or an effective amount of at the IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec protein in the early hyperalgesia stage or in patients that have advanced to the hyposensitivity stage. Treatment at the early hyperalgesia stage prevents subsequent hyposensitivity with increases or maintenance of sensory nerve function. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec treatment also increases muscle mass and improves overall mobility, which indicates a treatment-related improvement in motor function. Treatment with IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec at the hyposensitivity stage reverses hyposensitivity and improves muscle mass and overall health. Systemic IGF-1 provides a therapeutic modality for treating hyposensitivity associated with DPN. In addition, IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec provides a therapeutic modality for treating diabetic nephropathy. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec improves renal function as evidenced by a modulation in serum albumin concentration and a reduction in urine volume and protein levels. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec also reduces diabetic glomerulosclerosis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Prepn process of beta-hydroxyl-beta-methyl butyric calcium (HMB-Ca)
InactiveCN1417190ASimple preparation processHigh purityCarboxylic acid salt preparationIsobutanolHaloform reaction
The present invention belongs to an organic compound preparing technology. Beta-hydroxyl-beta-methyl butyric calcium (HMB-Ca) is prepared using 4-methyl-4-hydroxy-2-propione as raw material and wateras solvent and through haloform reaction in water solution of NaOBr, acidification, isobutanol extraction, reaction of HMB acid in isobutanol extract with Ca(OH)2 to produce salt HMB-Ca. The said process has high product purity and less environmental pollution. The product HMB-Ca may be used in promoting the growth of muscles, strengthening immunity, reducing cholesterin and low-density lipoprotein level, preventing coronary heart disease and cardiac vascular disease, strengthening body's nitrogen-fixing capacity and maintaining body's protein level.
Owner:MANTE SHANGHAI BIAOLOGICAL SCI TECH
Methods and compositions for the detection of ovarian disease
InactiveUS20060029956A1Increase chanceFacilitate mass automated screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiseaseComplement system
Methods and compositions for identifying ovarian cancer in a patient sample are provided. The methods of the invention comprise detecting overexpression of at least one biomarker in a body sample, wherein the biomarker is selectively overexpressed in ovarian cancer. In preferred embodiments, the body sample is a serum sample. The biomarkers of the invention include any genes or proteins that are selectively overexpressed in ovarian cancer, including, for example, acute phase reactants, lipoproteins, proteins involved in the regulation of the complement system, regulators of apoptosis, proteins that bind hemoglobin, heme, or iron, cytostructural proteins, enzymes that detoxify metabolic byproducts, growth factors, and hormone transporters. In some aspects of the invention, overexpression of a biomarker of interest is detected at the protein level using biomarker-specific antibodies or at the nucleic acid level using nucleic acid hybridization techniques. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com