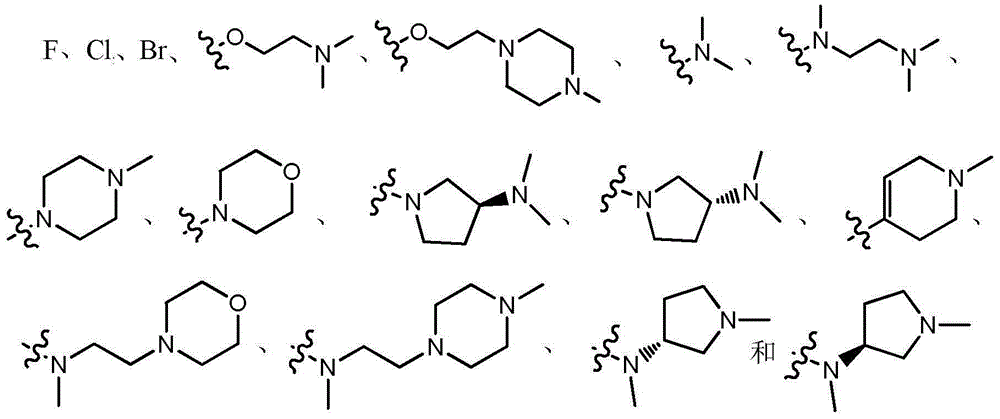
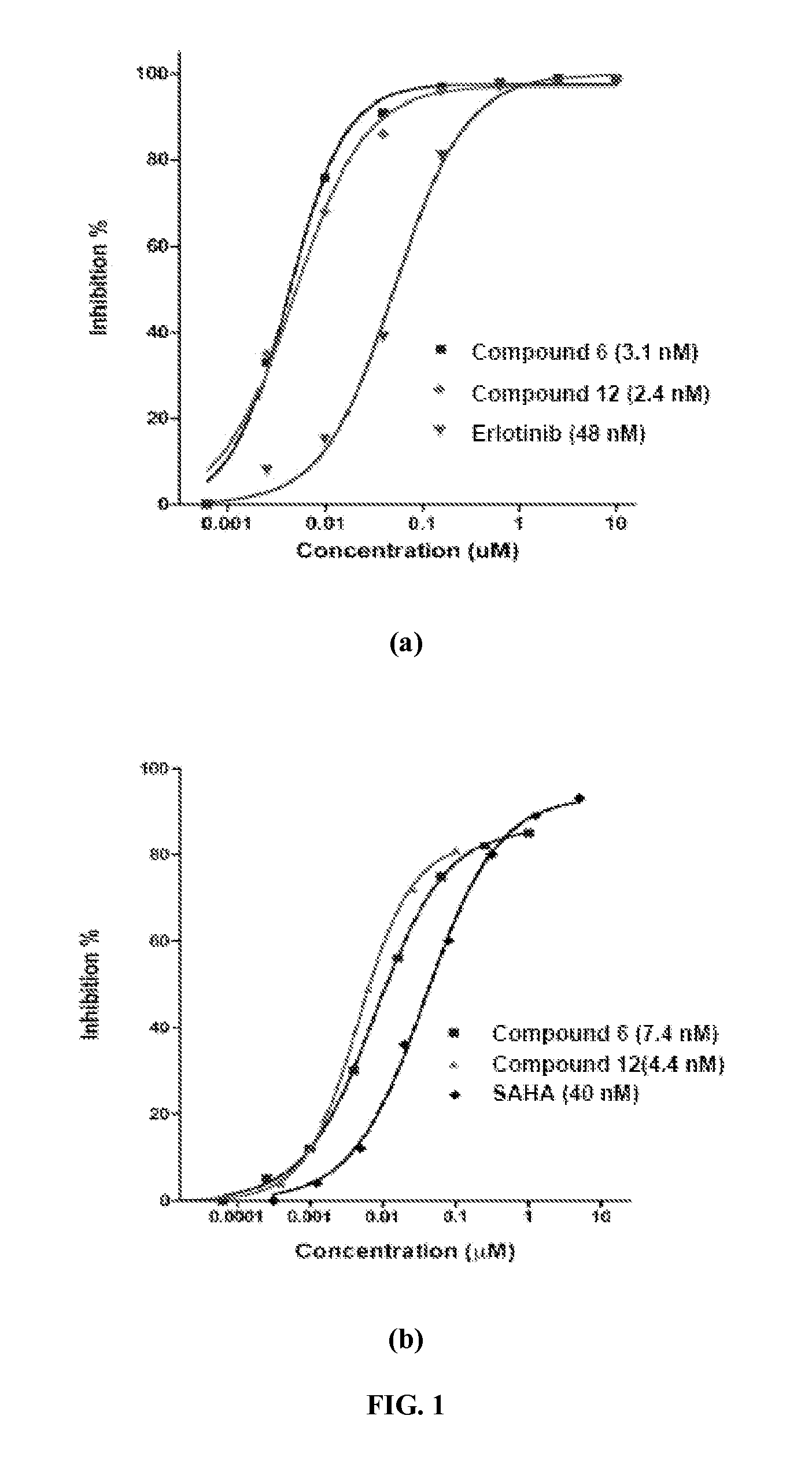
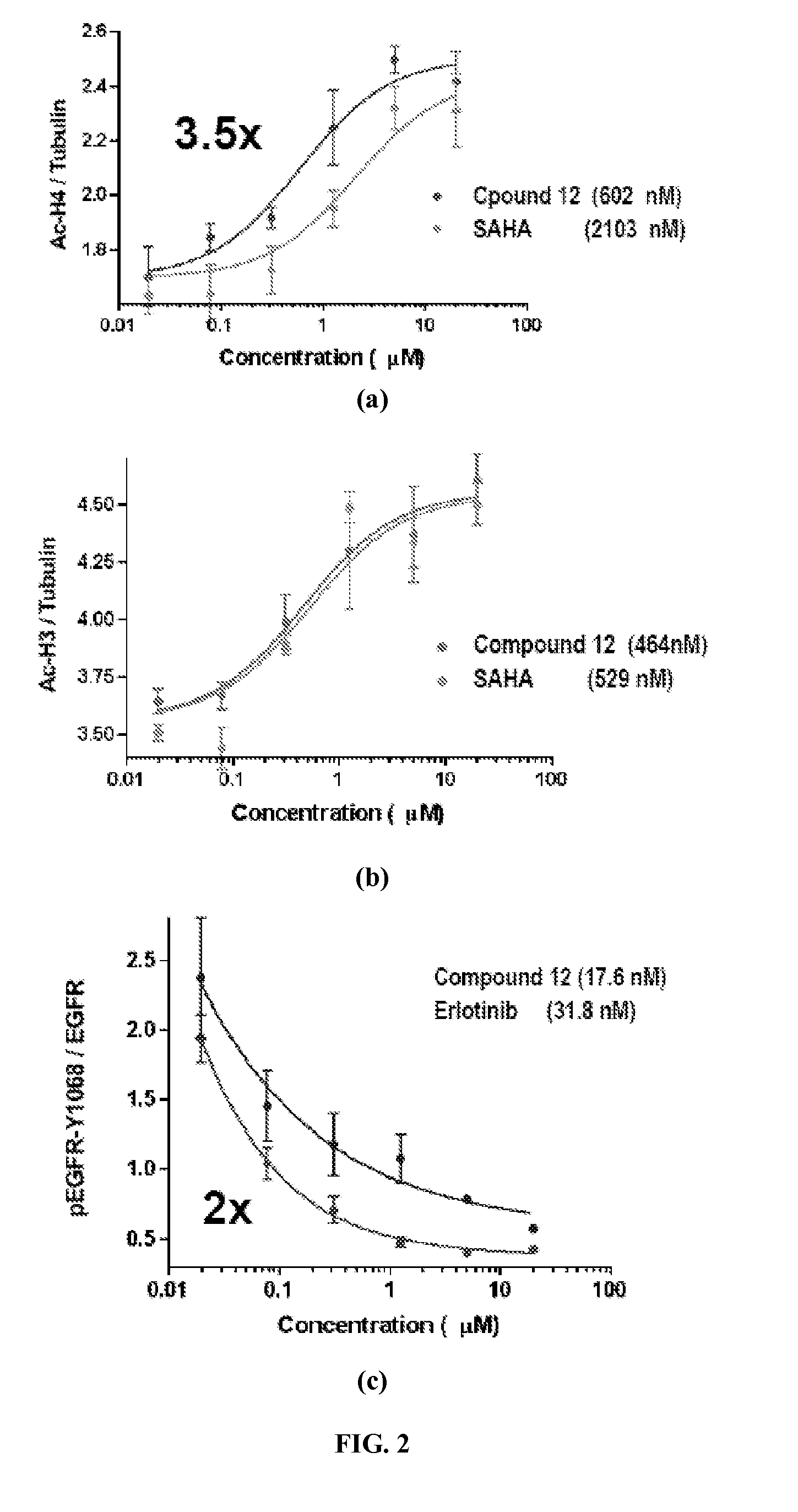
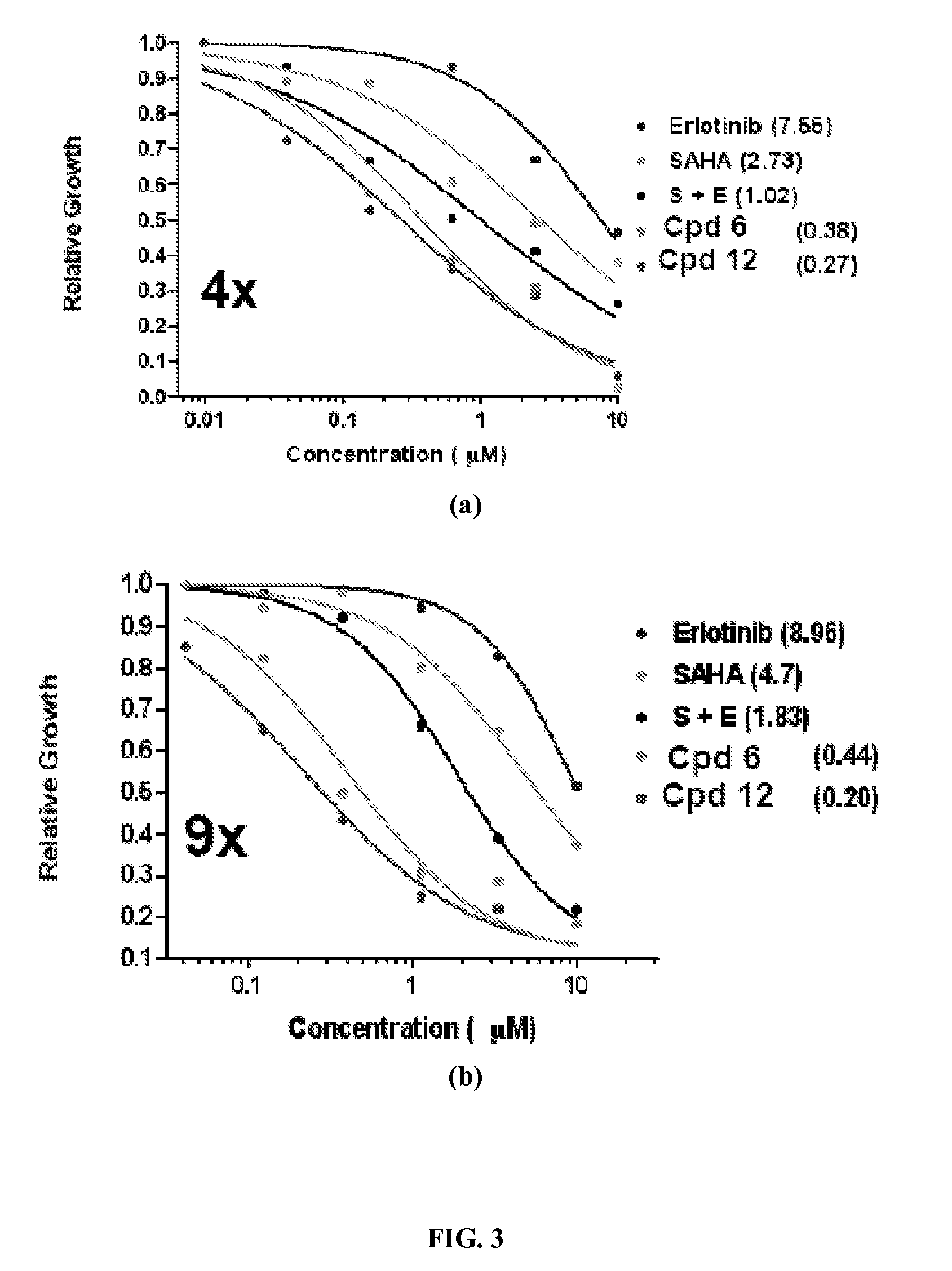
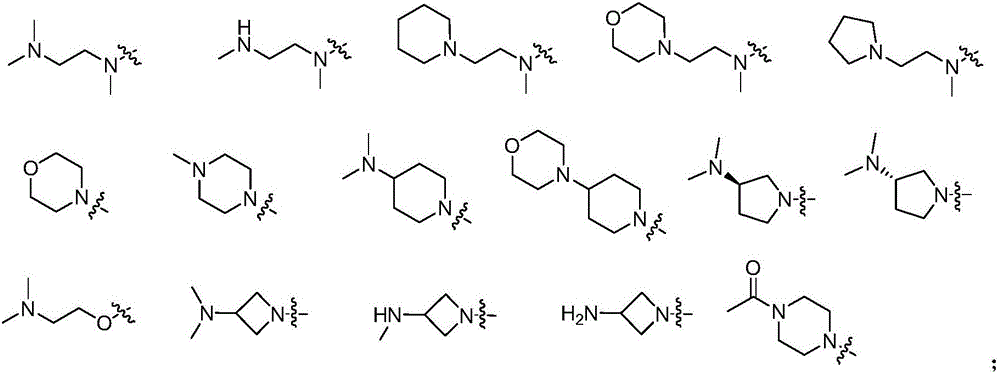
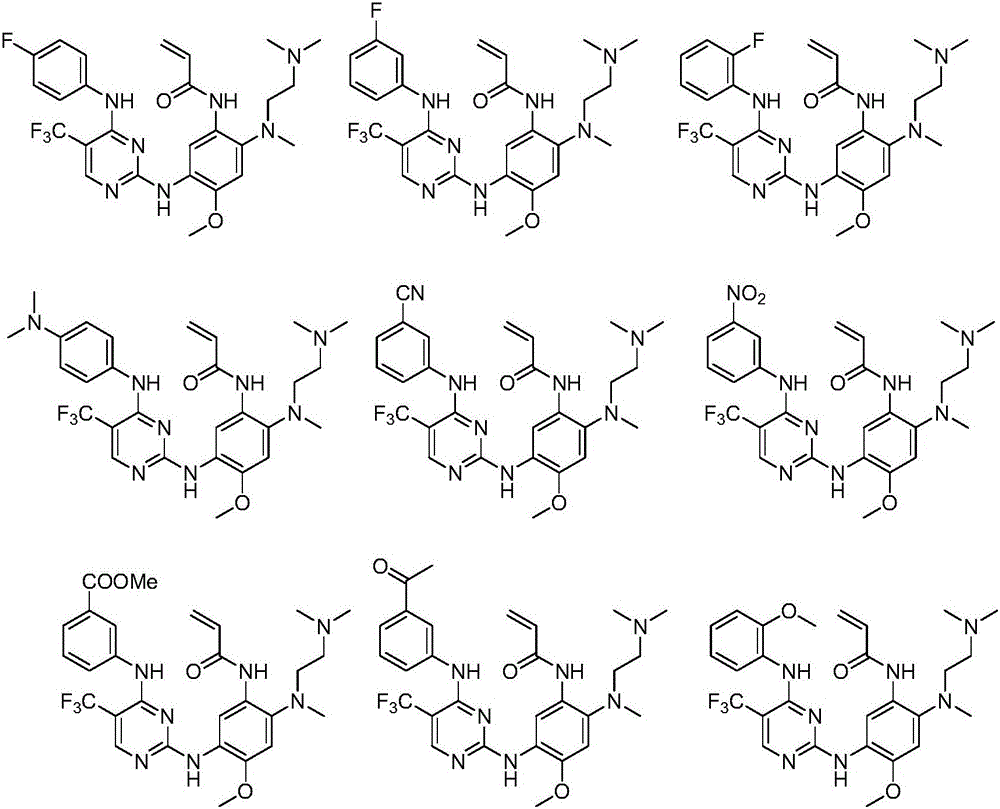
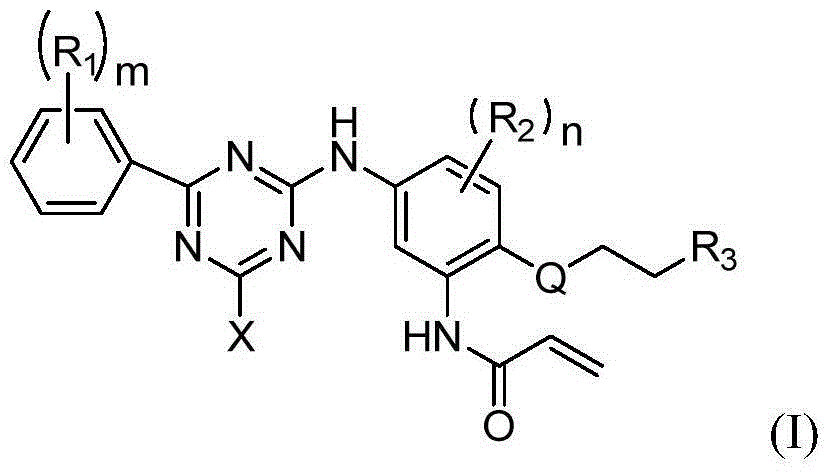
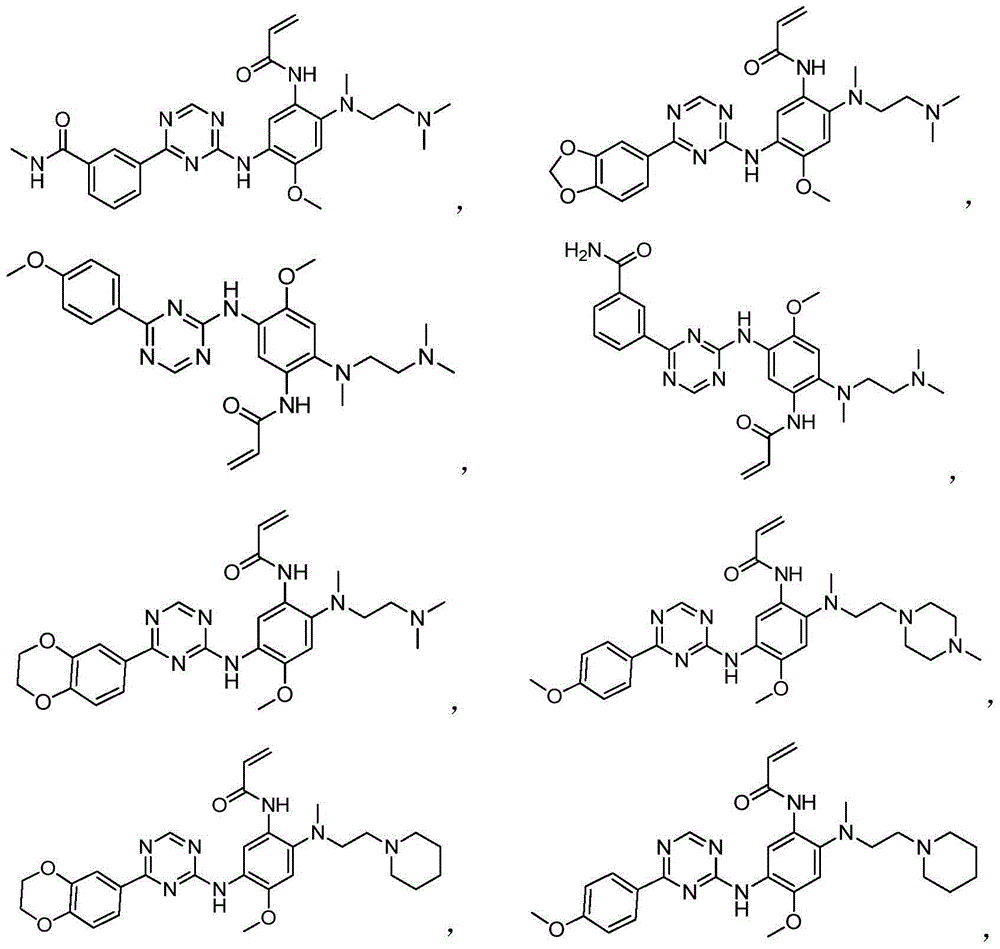
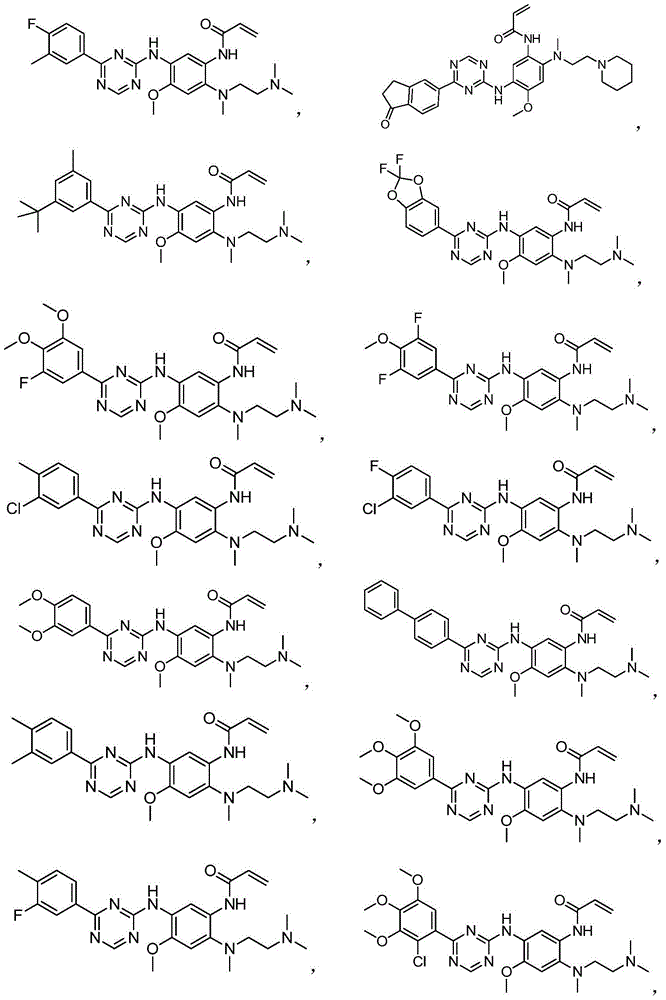
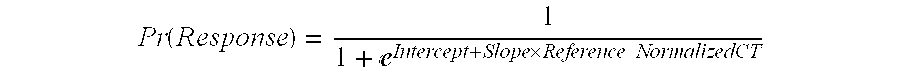Patents
Literature
319 results about "EGFR inhibitors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
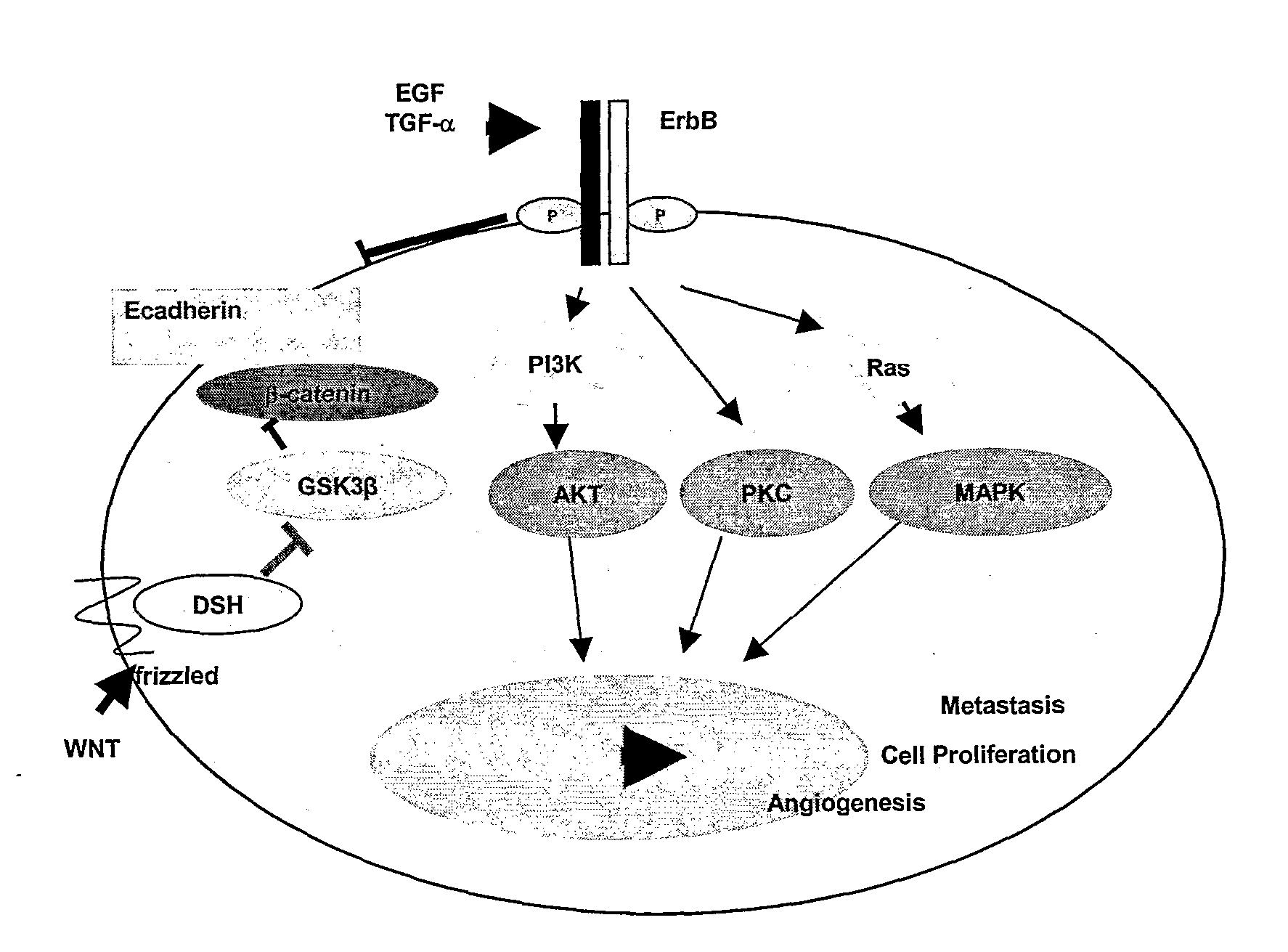
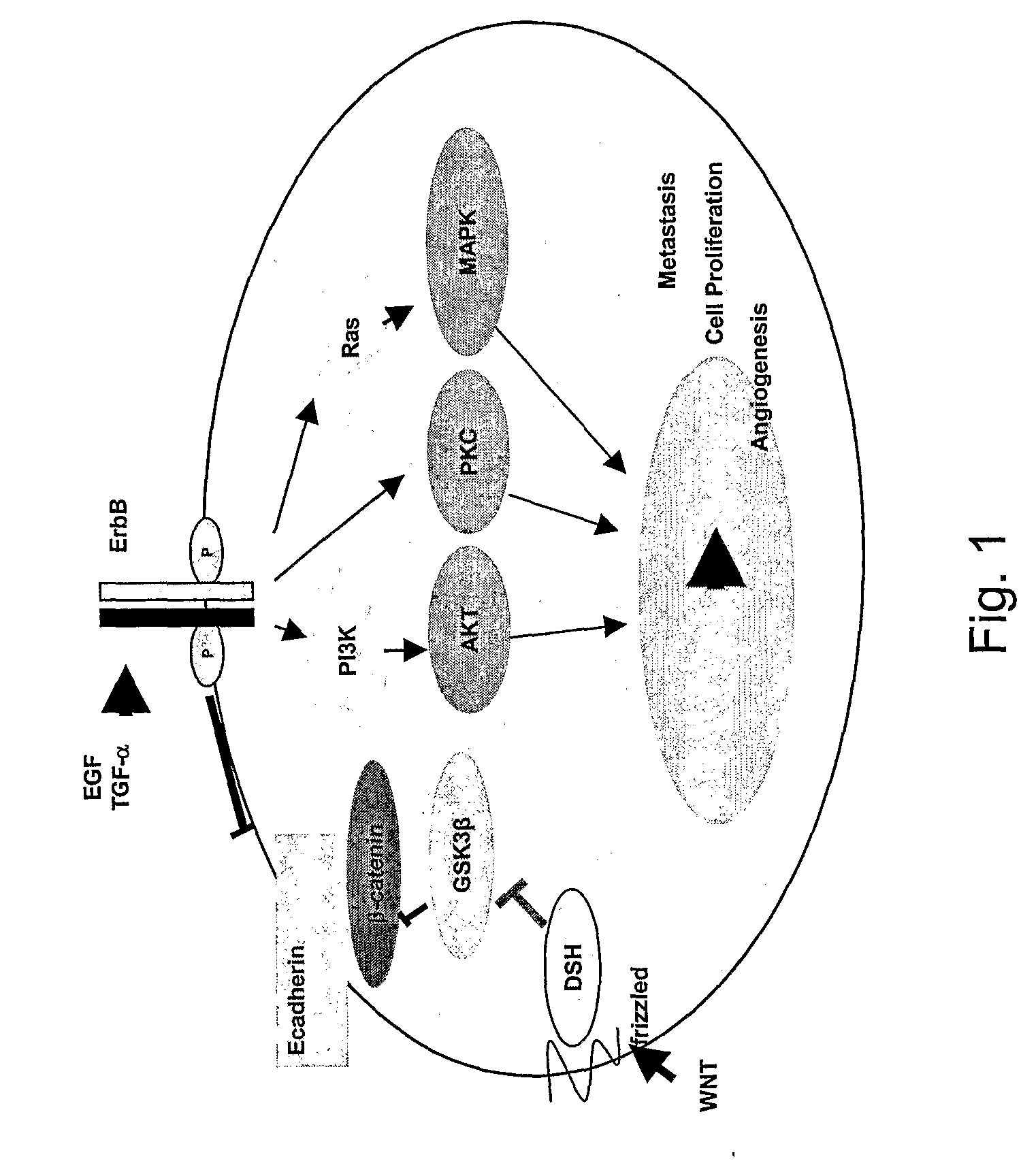
Many therapeutic approaches are aimed at epidermal growth factor receptor. Cetuximab and panitumumab are examples of monoclonal antibody inhibitors. However the former is of the IgG1 type, the latter of the IgG2 type; consequences on antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity can be quite different. Other monoclonals in clinical development are zalutumumab, nimotuzumab, and matuzumab. The monoclonal antibodies block the extracellular ligand binding domain. With the binding site blocked, signal molecules can no longer attach there and activate the tyrosine kinase. Another method is using small molecules to inhibit the EGFR tyrosine kinase, which is on the cytoplasmic side of the receptor. Without kinase activity, EGFR is unable to activate itself, which is a prerequisite for binding of downstream adaptor proteins. Ostensibly by halting the signaling cascade in cells that rely on this pathway for growth, tumor proliferation and migration is diminished. Gefitinib, erlotinib, and lapatinib are examples of small molecule kinase inhibitors. There are several quantitative methods available that use protein phosphorylation detection to identify EGFR family inhibitors.
EGFR inhibitors and methods of treating disorders
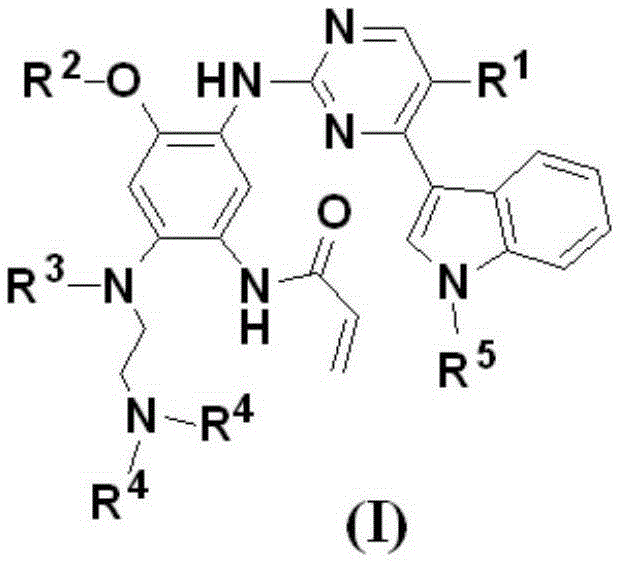
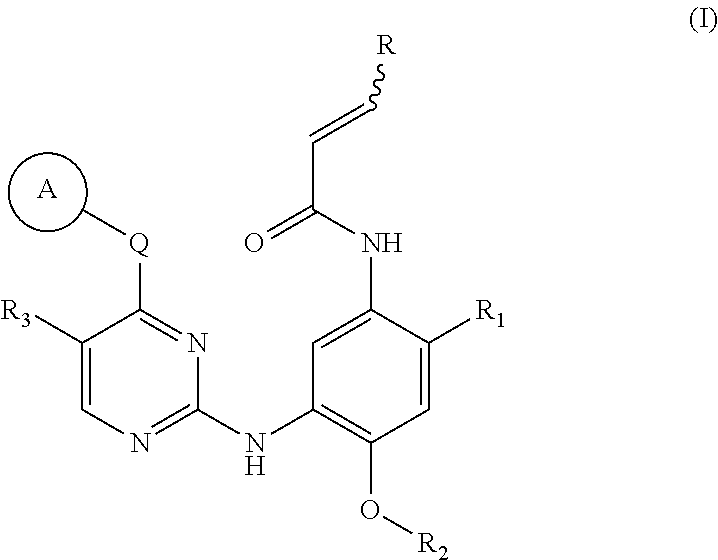
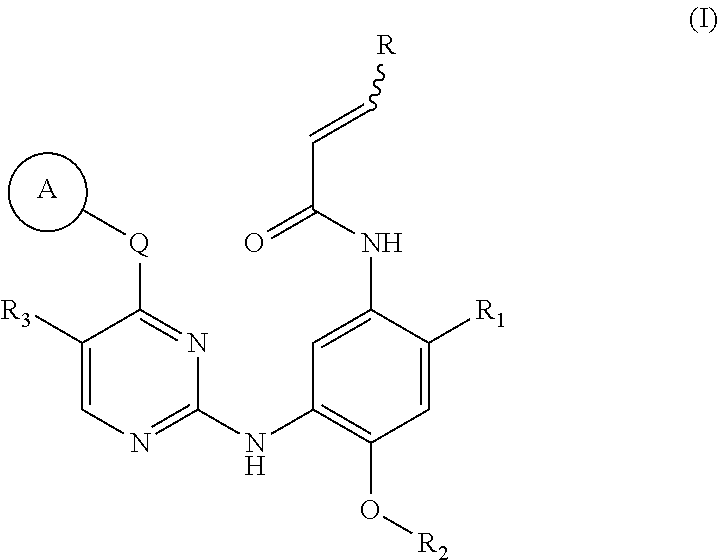
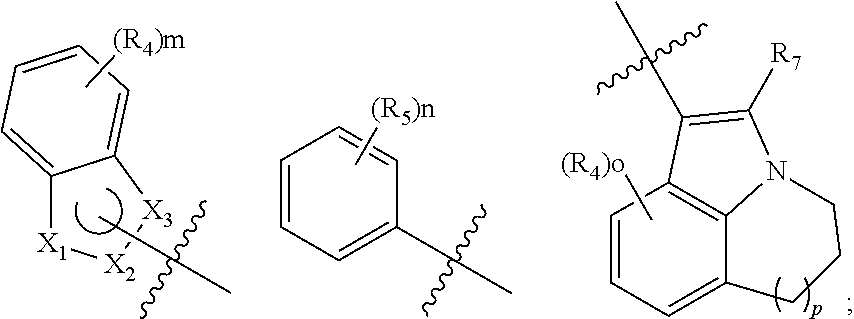
The present invention relates to novel pyrimidine, pyrrolo-pyrimidine, pyrrolo-pyridine, pyridine, purine and triazine compounds which are able to modulate epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), including Her-kinases, and the use of such compounds in the treatment of various diseases, disorders or conditions.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Quinazoline based EGFR inhibitors containing a zinc binding moiety
InactiveUS20080139590A1Enhanced and unexpected propertyHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseZinc binding
The present invention relates to quinazoline containing zinc-binding moiety based derivatives that have enhanced and unexpected properties as inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) and their use in the treatment of EGFR-TK related diseases and disorders such as cancer. The said derivatives may further act as HDAC inhibitors.
Owner:CURIS INC
Method for treating cancer harboring EGFR mutations
ActiveUS20090318480A1Advantageously effective in treatmentReduced responseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAcquired resistanceActivating mutation
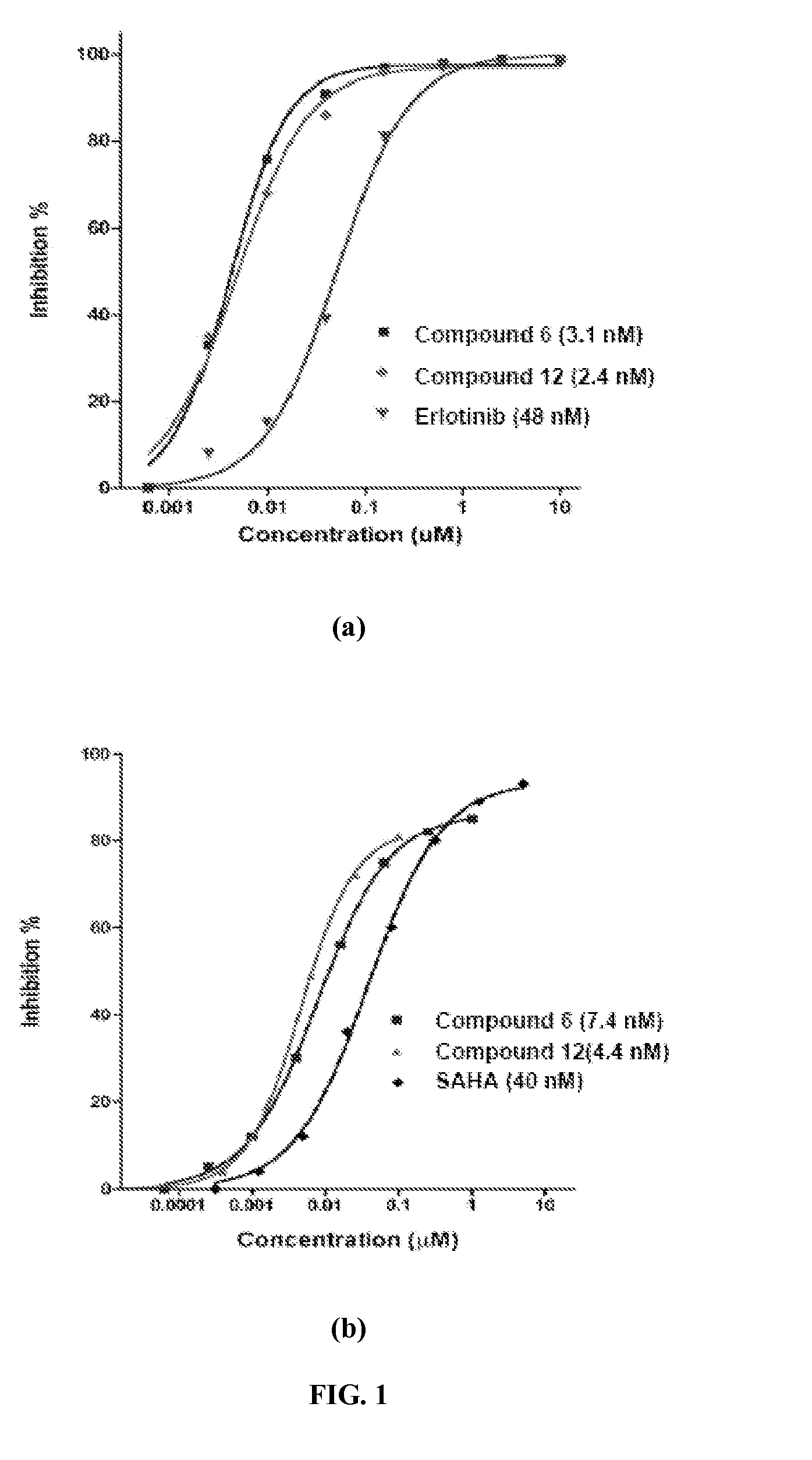
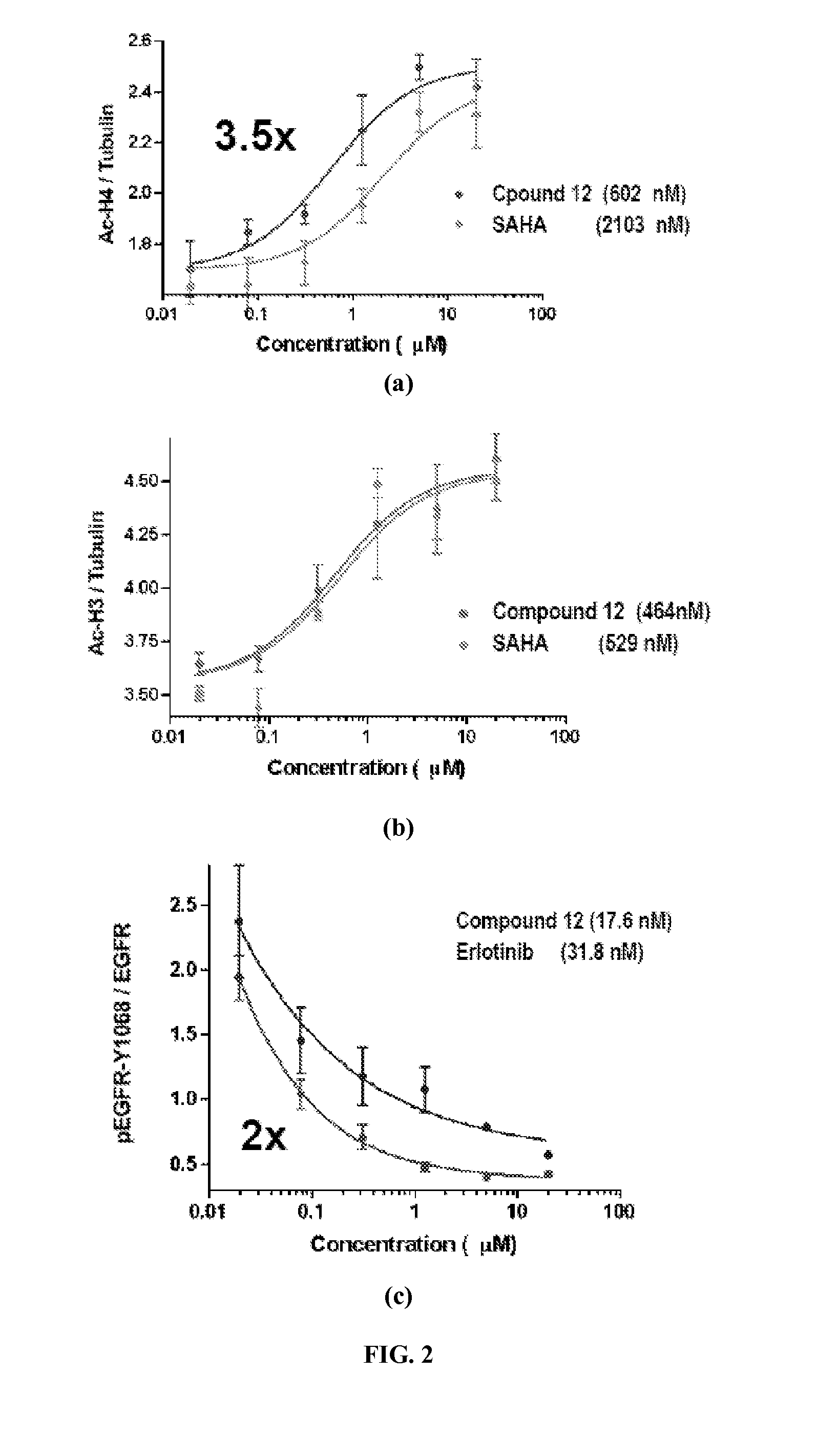
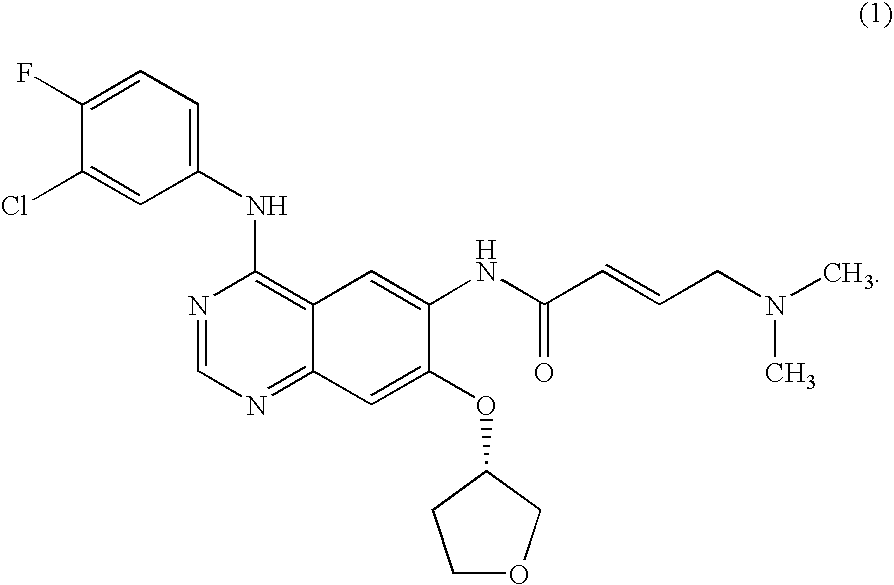
The present invention relates to a method of treatment of patients suffering from cancer and harbouring mutations of EGFR in the tumour, for instance an activating mutation of the EGFR or a mutation responsible for resistance or the emergence of acquired resistance to treatment with reversible EGFR and / or HER2 inhibitors or irreversible inhibitors such as CI-1033, EKB-569, HKI-272 or HKI-357, comprising administering an effective amount of the irreversible EGFR inhibitor BIBW2992 (1) 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-{[4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl]amino}-7-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-quinazoline, to a person in need of such treatment, optionally in combination with the administration of a further chemotherapeutic agent, in combination with radiotherapy, radio-immunotherapy and / or tumour resection by surgery, and to the use of a BIBW 2992 (1) for preparing a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of patients suffering from cancer and harbouring mutations of EGFR in the tumour.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Predictors Of Patient Response To Treatment With EGFR Inhibitors
InactiveUS20070128636A1Reduce the possibilityReduced responsivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisGenomeCancer research
The invention concerns genes and gene sets and methods useful in the prediction of the response of a cancer patient to treatment with an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Methods for Prediction of Clinical Outcome to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors by Cancer Patients
InactiveUS20080090233A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationTyrosineFhit gene
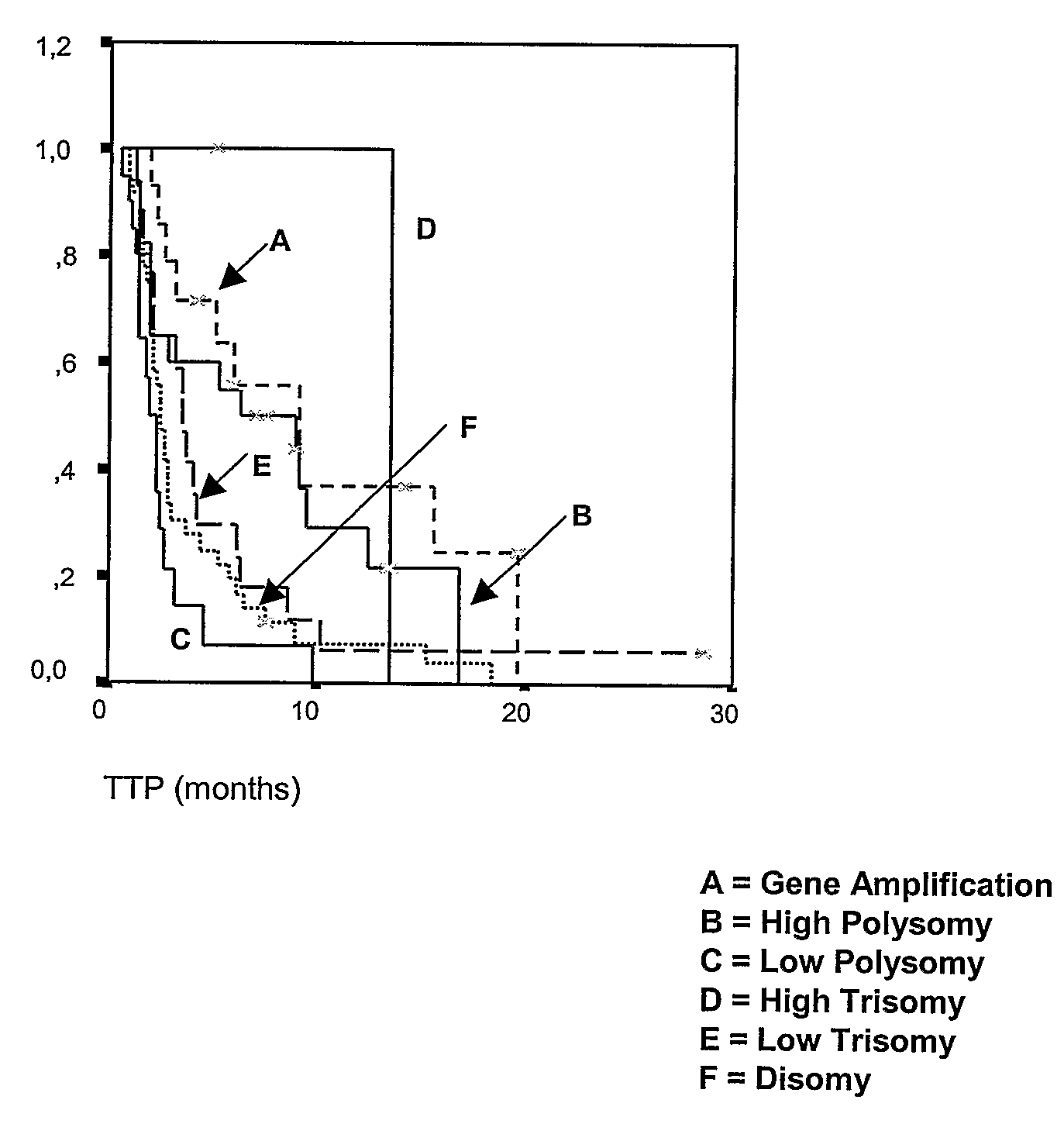
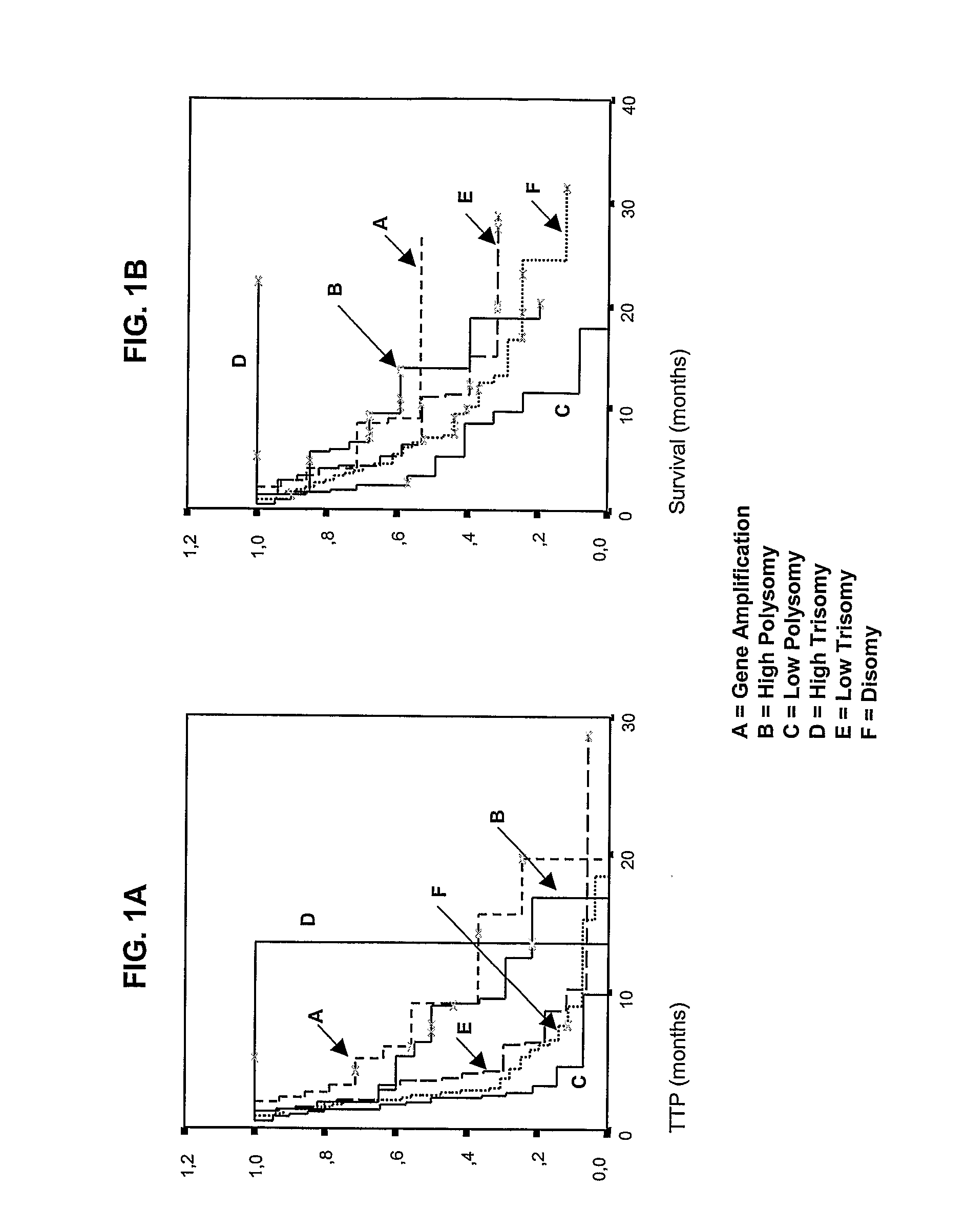
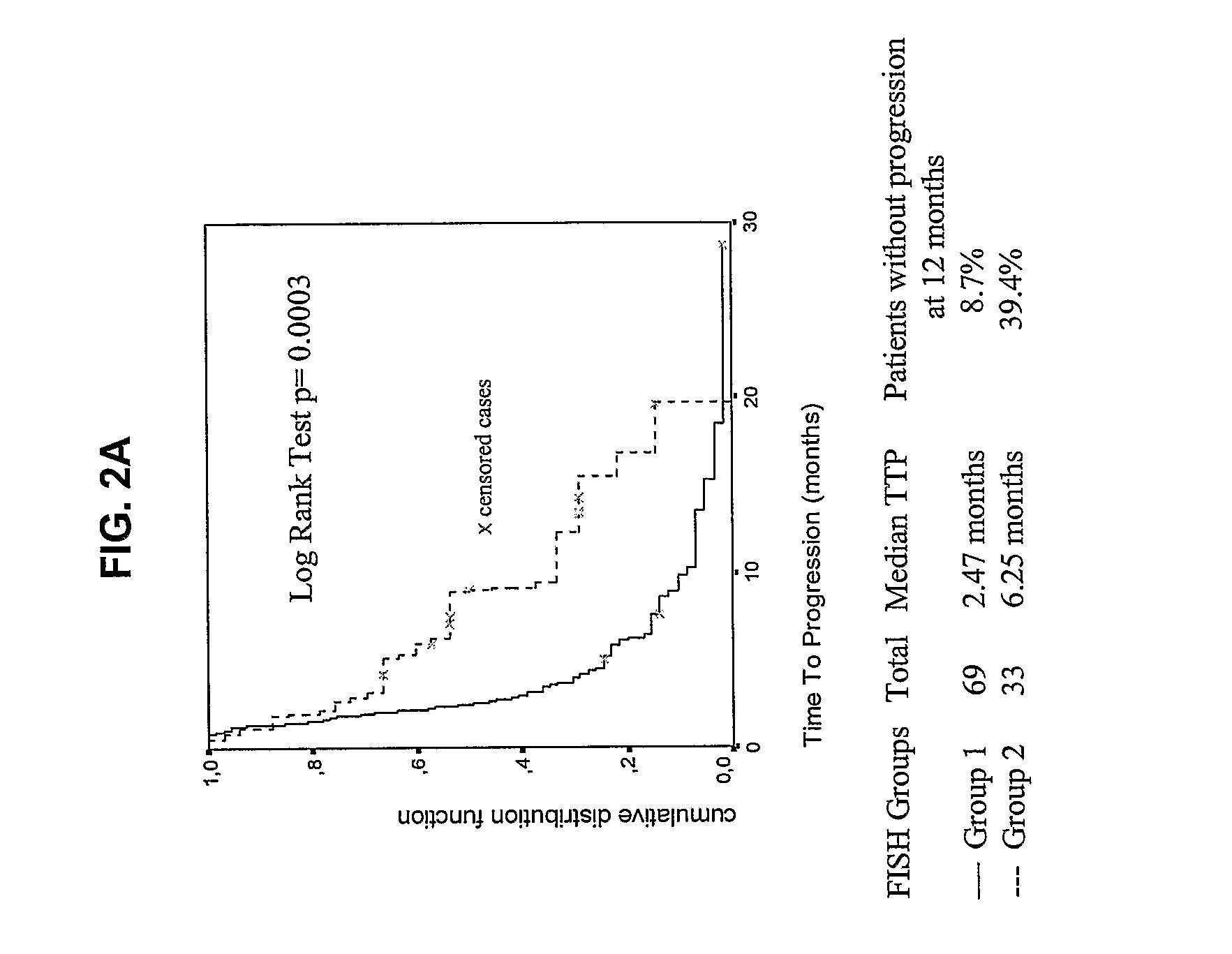
Disclosed are biomarkers, methods and assay kits for the identification of cancer patients who are predicted to benefit, or not to benefit, from the therapeutic administration of an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor. The biomarkers of the present invention include detection of EGFR and HER 2 gene amplification and polysomy, EGFR protein expression, EGFR mutations, phosphorylated Akt protein expression, and various combinations of such biomarkers, as well as the combination of these biomarkers with mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the EGFR gene. Increased EGFR gene copy number, increased HER2 gene copy number, increased EGFR, protein expression, activated AKT protein expression (phosphorylated AKT) and EGFR mutations are all associated with better outcome for cancer patients treated with EGFR inhibitors. The invention provides a diagnostic paradigm based on each of these tests and combinations of these tests to select cancer patients who will benefit from EGFR inhibitor therapy, as well as a diagnostic paradigm to select cancer patients who will not benefit from EGFR inhibitor therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
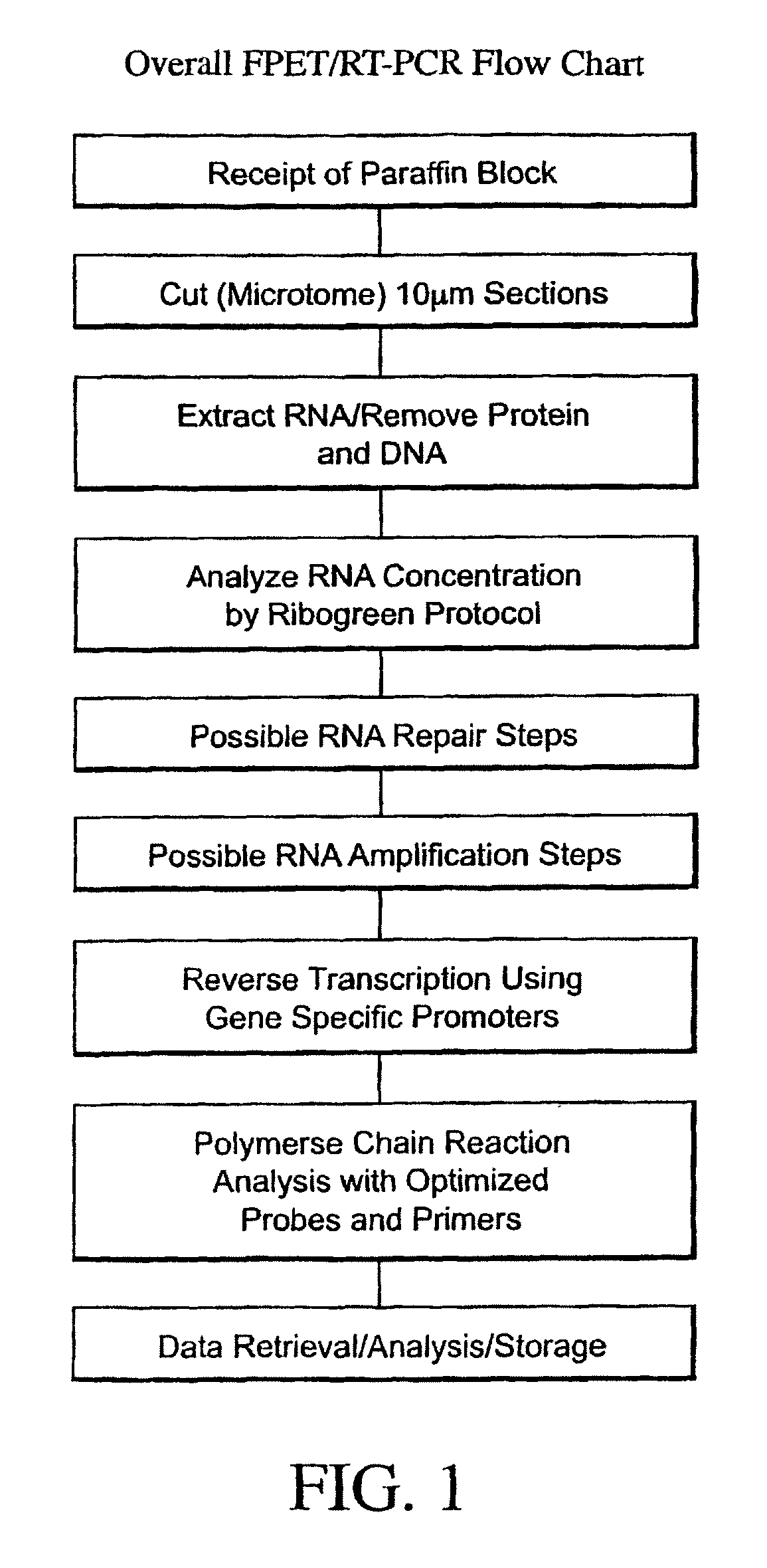
Gene expression markers for response to EGFR inhibitor drugs
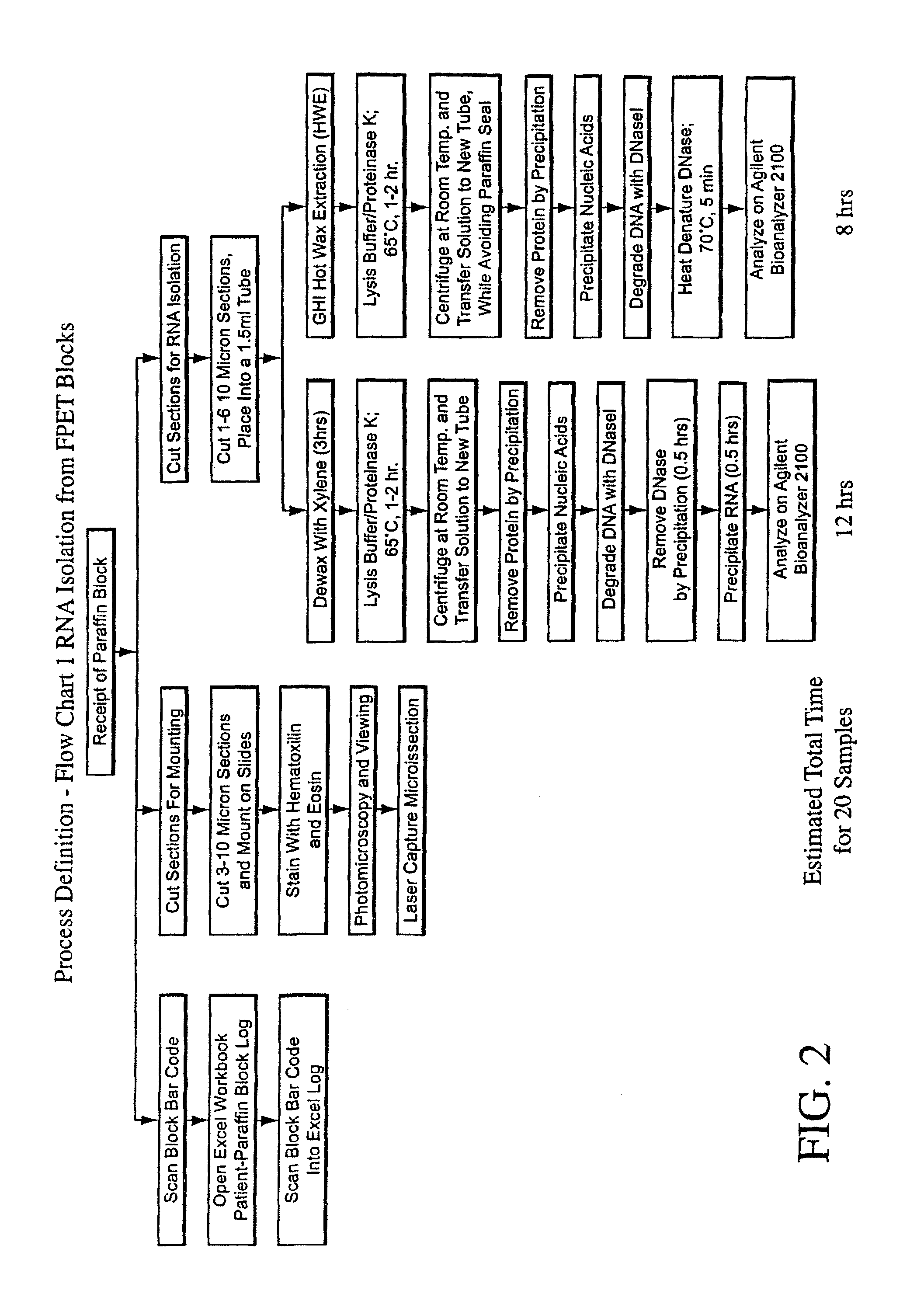
InactiveUS20050164218A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsOncologyParaffin embedded
The present invention concerns prognostic markers associated with cancer. In particular, the invention concerns prognostic methods based on the molecular characterization of gene expression in paraffin-embedded, fixed samples of cancer tissue, which allow a physician to predict whether a patient is likely to respond well to treatment with an EGFR inhibitor.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC +1
Gene expression profiling of EGFR positive cancer
InactiveUS20050019785A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sampleBiology
The present invention concerns prognostic markers associated with EGFR positive cancer. In particular, the invention concerns prognostic methods based on the molecular characterization of gene expression in paraffin-embedded, fixed tissue samples of EGFR-expressing cancer, which allow a physician to predict whether a patient is likely to respond well to treatment with an EGFR inhibitor.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Method for predicting sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor
InactiveUS20160002741A1Accurate SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisKRASWild type
A method for predicting sensitivity to an EGFR inhibitor includes: (a) determining whether there is a KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or a protein thereof in a blood sample which has been collected from a subject, and whether the KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or the protein thereof in the blood sample is wild type or mutant; and (b) determining that there is a high possibility that a tumor of the subject is sensitive to an EGFR inhibitor when a wild type KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or a protein thereof is detected and no mutant KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or a protein thereof is detected in the blood sample in the process (a).
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Preventives and/or remedies for subjects with the expression or activation of her2 and/or egfr
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
Use of natural EGFR inhibitors to prevent side effects due to retinoid therapy, soaps, and other stimuli that activate the epidermal growth factor receptor
InactiveUS6638543B2Diminishing desired therapeutic effectPrevent drynessBiocideCosmetic preparationsSide effectRetinoid
Many human conditions, often skin conditions, are treated topically or orally with a retinoid such as retinoic acid or acetretin, which treatment often has the side effect of dry, irritated, and / or peeling skin. The use of soaps, detergents, chemical irritants, and such can also cause these same side effects. These side effects can be reduced or eliminated by the topical administration of an inhibitor, especially a natural inhibitor, of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), administered concomitantly with the retinoid, separately from the retinoid (such as on an as needed basis), or both. Administration of the two together is facilitated by a composition suitable for topical application and comprising both the retinoid and a natural EGFR inhibitor. Preferred natural inhibitors are genistein and other isoflavones extracted from natural occurring substances, or simple derivatives of such substances.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
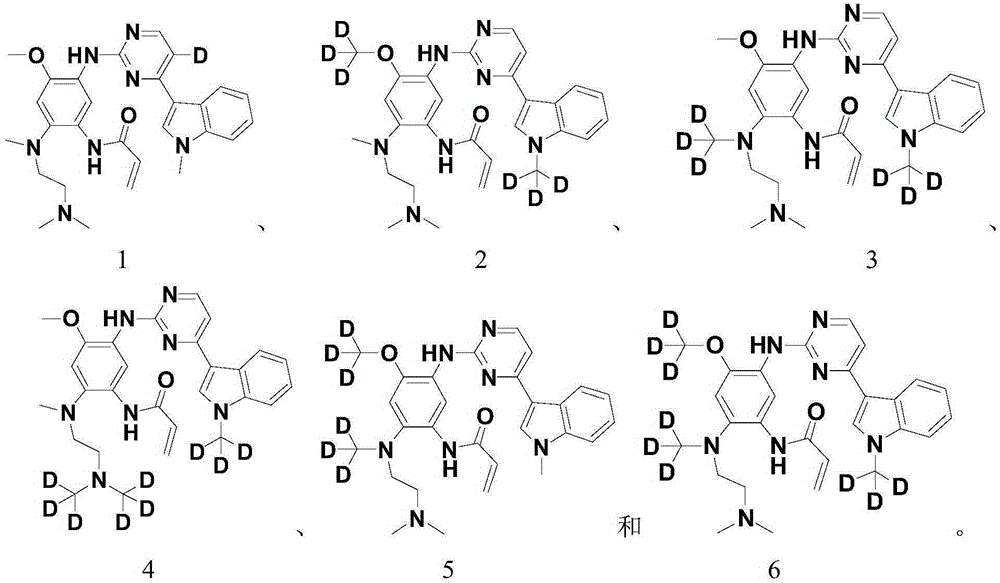
Pentadeuteropyridine compounds, and preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof
ActiveCN105237515AImprove securityStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsDiseaseErlotinib
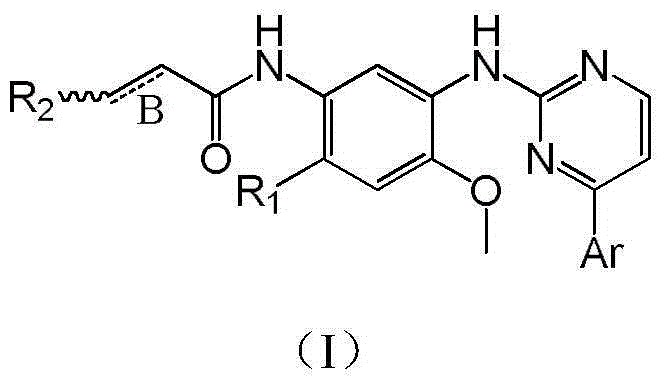
The invention relates to pentadeuteropyridine compounds represented by the following formula (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, stereoisomers, prodrugs and solvates thereof, and a preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof. The compounds can generate an inhibitory effect on variation forms of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) protein kinase, thereby effectively inhibiting the growth of a variety of tumor cells; the compounds can be used for preparation of antitumor drugs, are used for treatment or prevention of a plenty of different cancers, and moreover, can overcome the drug resistance induced by conventional drugs gefitinib, erlotinib and other first-generation EGFR inhibitors. More specifically, the compounds can be used for preparation of drugs for treatment or prevention of diseases, obstacles, disorders or illness conditions mediated by certain variation-form epidermal growth factor receptors (such as L858R activated mutants, Exon19 deletion activated mutants, and T790M resistance mutants).
Owner:INVENTISBIO CO LTD +1
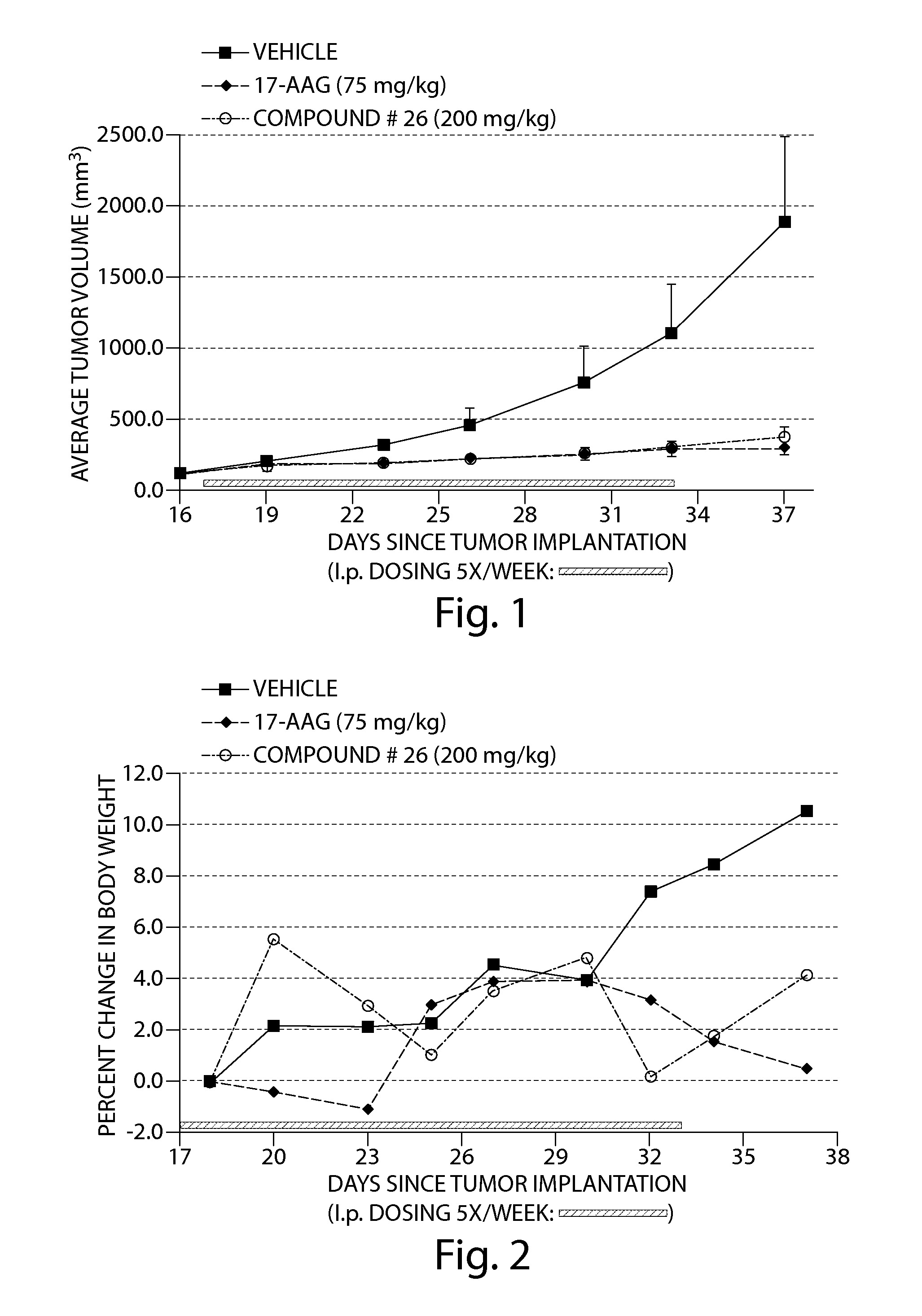
Cancer therapy using a combination of a hsp90 inhibitory compounds and a EGFR inhibitor
ActiveUS20130150385A1Reduce developmentReduced efficacious amountBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHsp Inhibitor
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
Biomarkers for response to tyrosine kinase pathway inhibitors in cancer
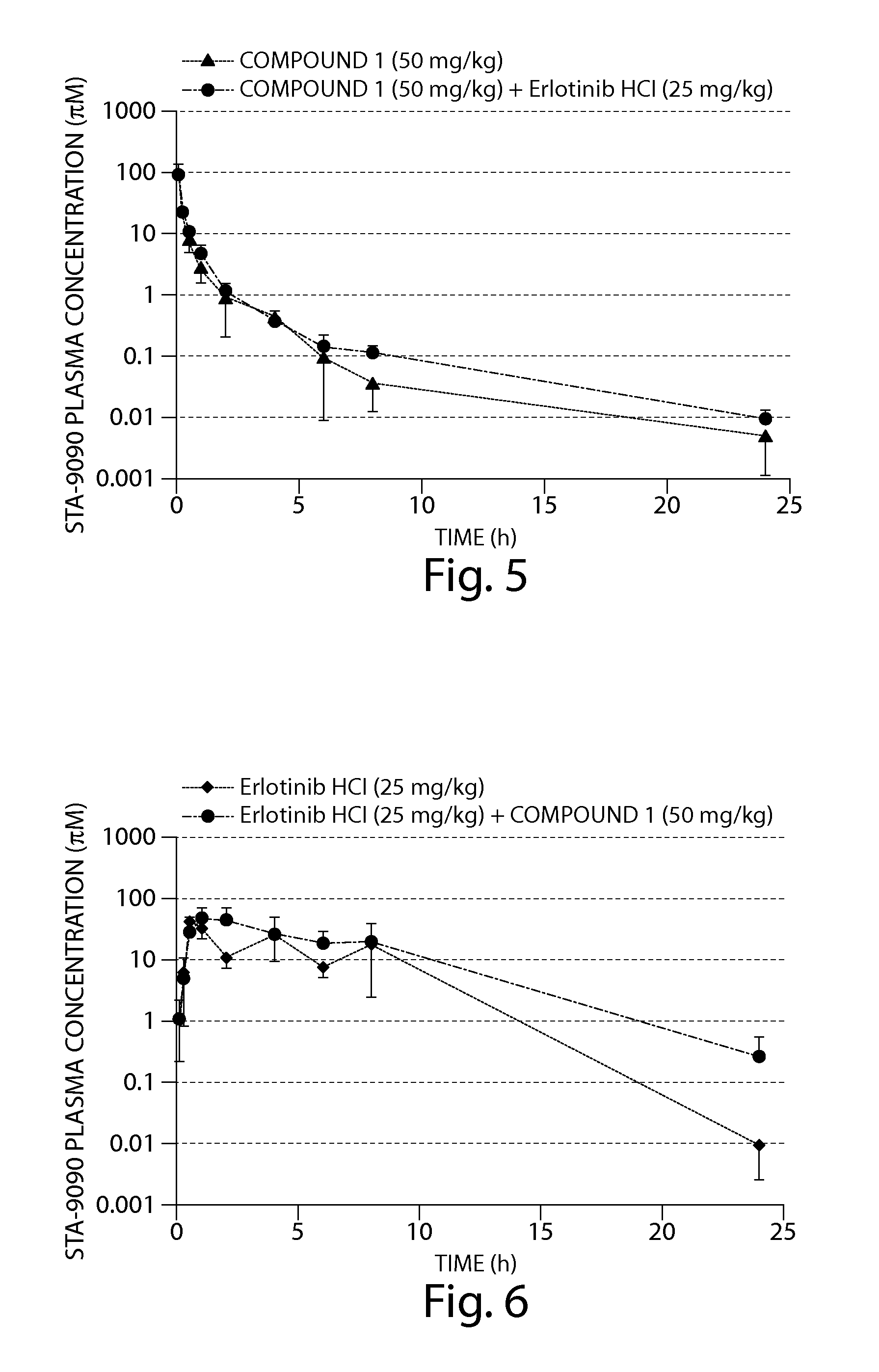
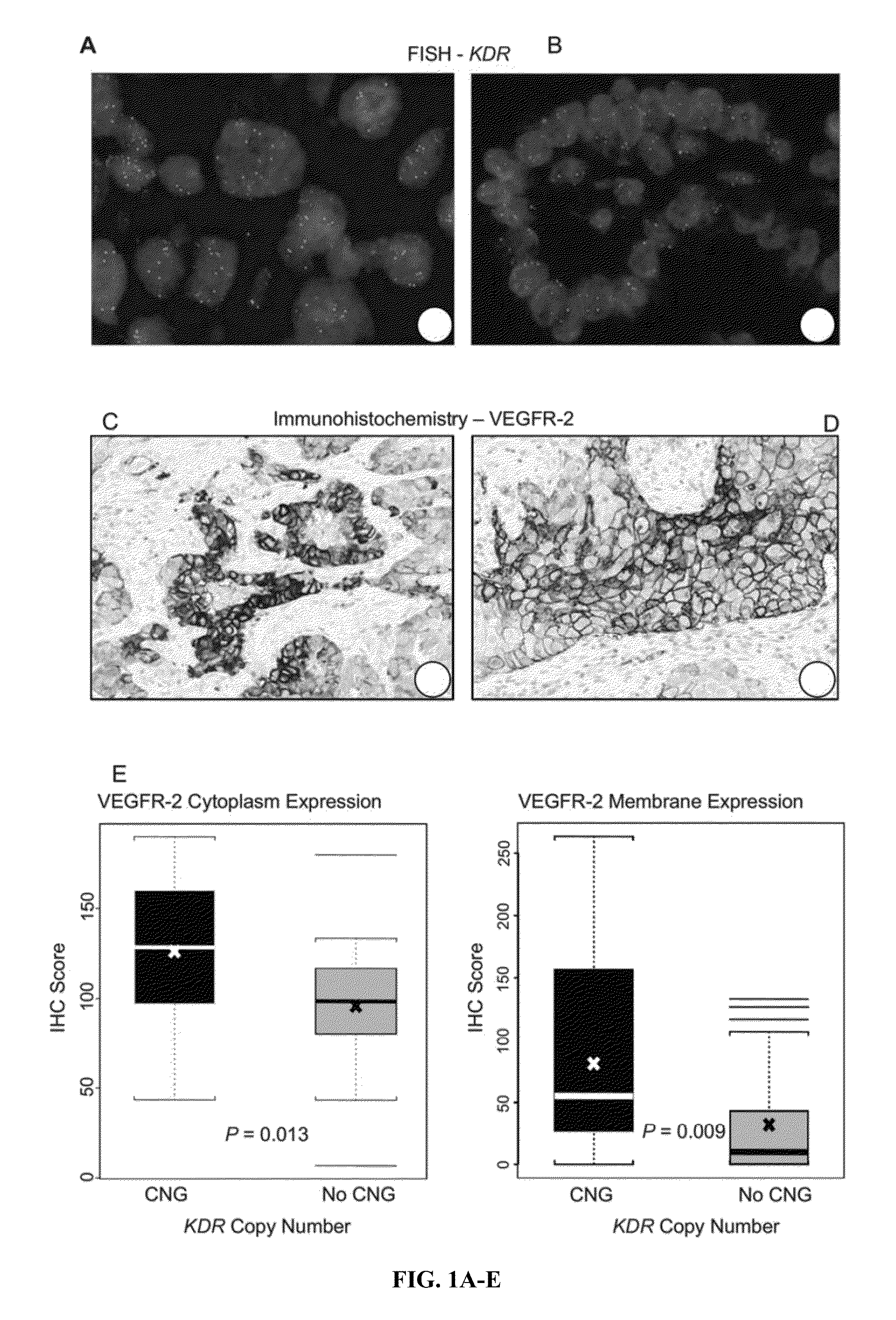
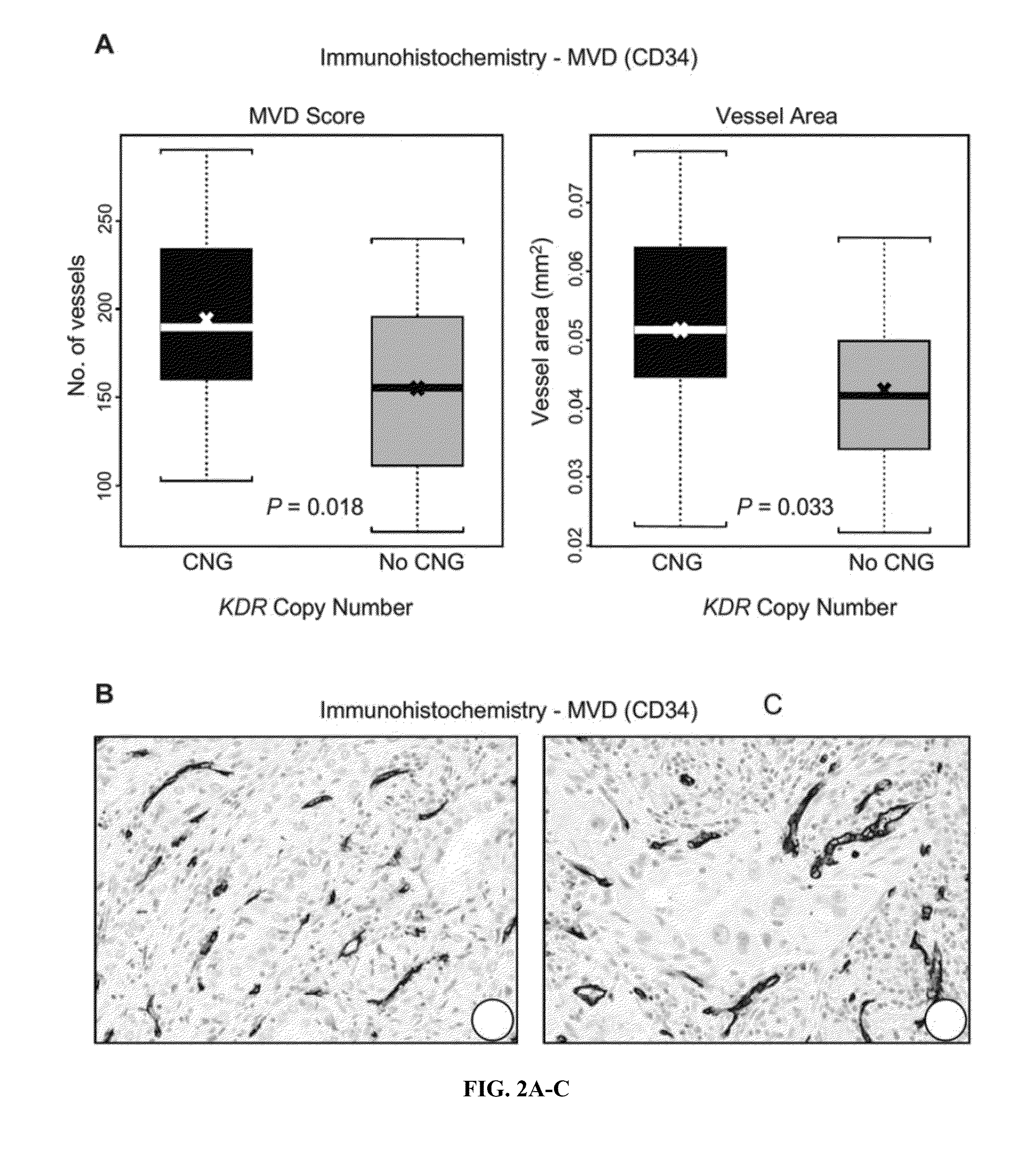
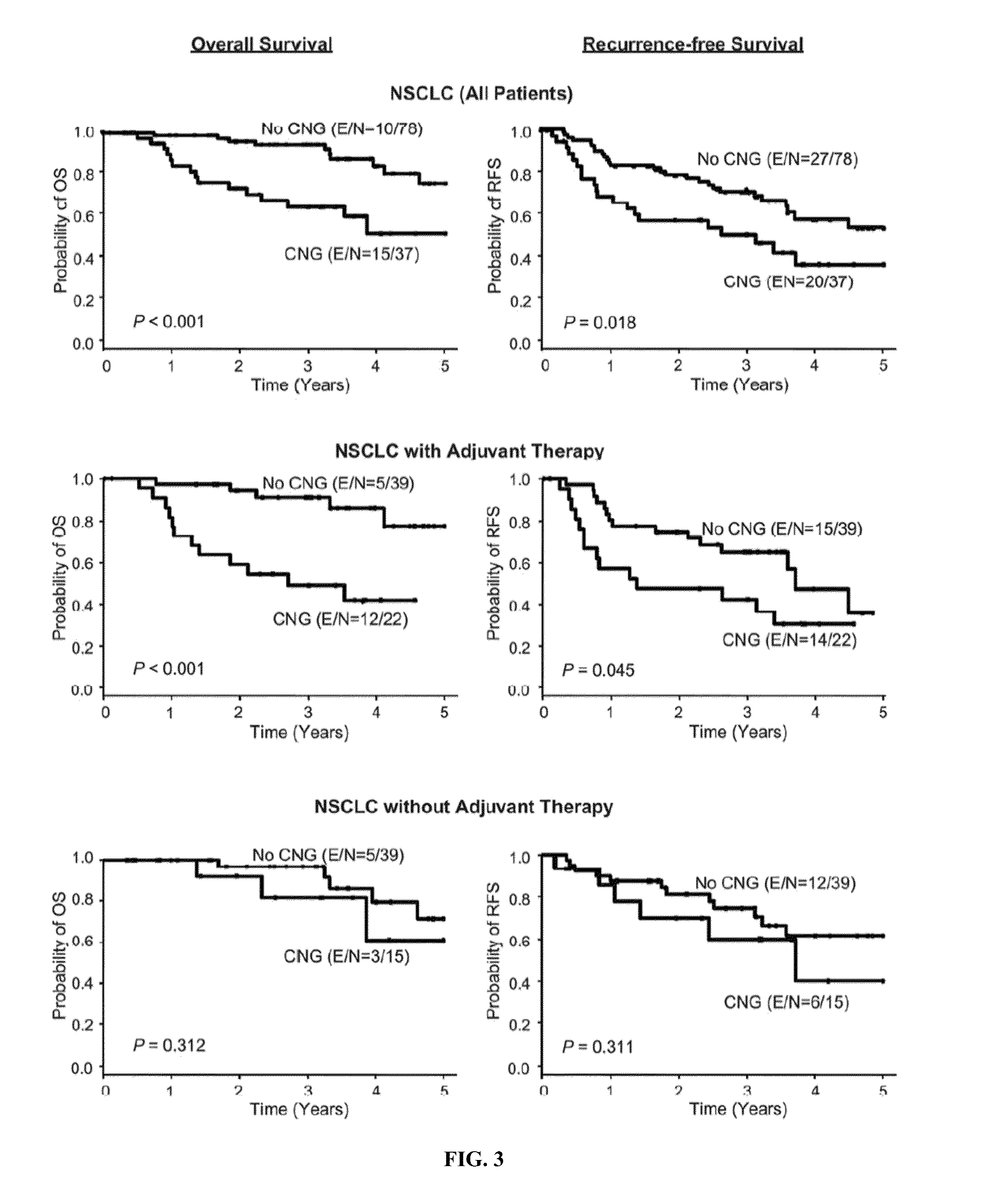
Copy number gains detected in tumors and associated with drug sensitivity and resistance in vivo and in vitro can be used as biomarkers to select, predict and monitor drug treatment outcomes in cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Methods to identify patients with NSCLC or other malignancies who are more likely to benefit from tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as VEGF or VEGFR inhibitors when used either as monotherapy or in combination with other therapies such as chemotherapy or EGFR inhibitors, and who are in the advanced stages of disease and / or who have undergone adjuvant therapy are also provided herein.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Selection of colorectal cancer patients for treatment with drugs targeting EGFR pathway
Owner:BIODESIX
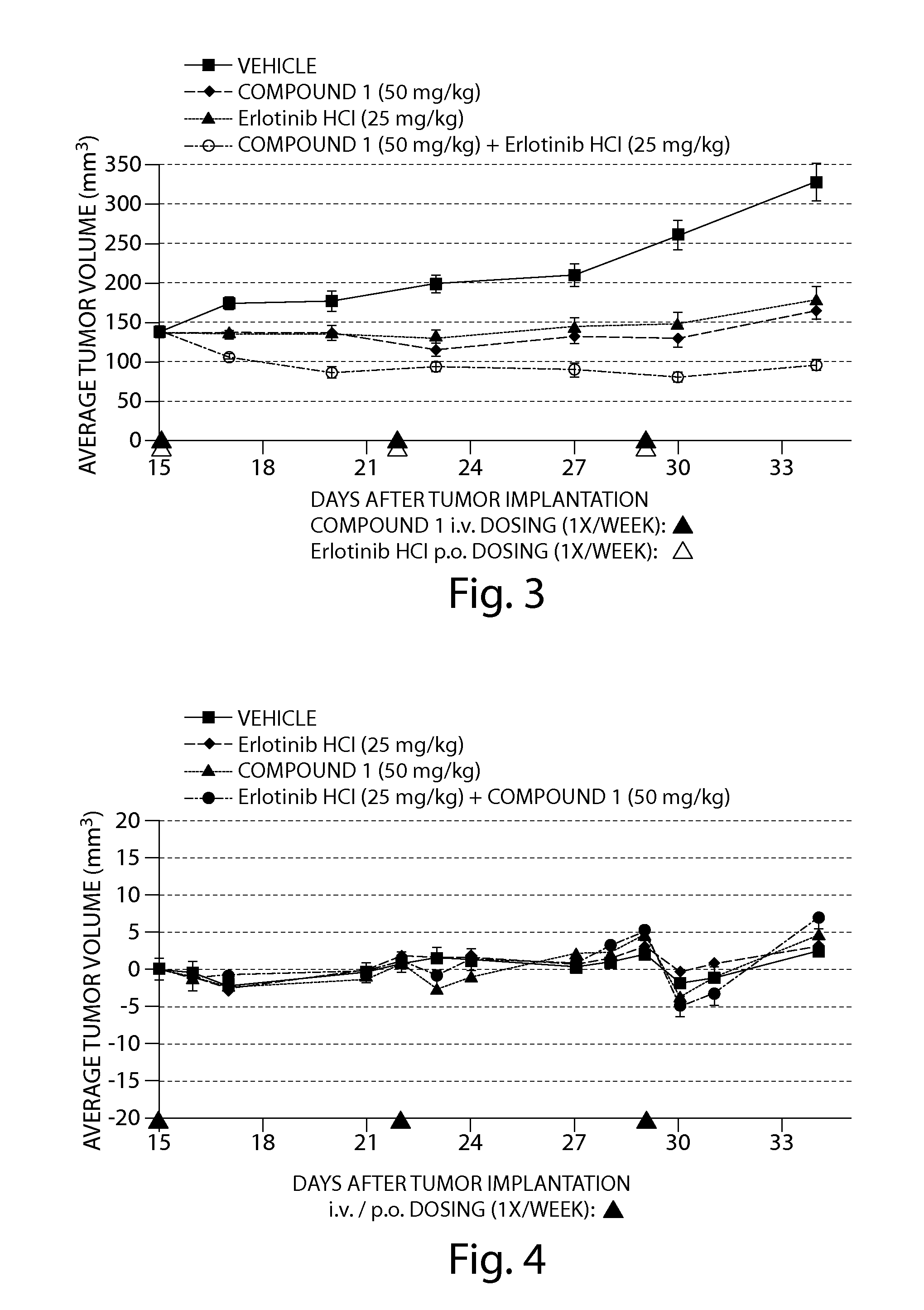
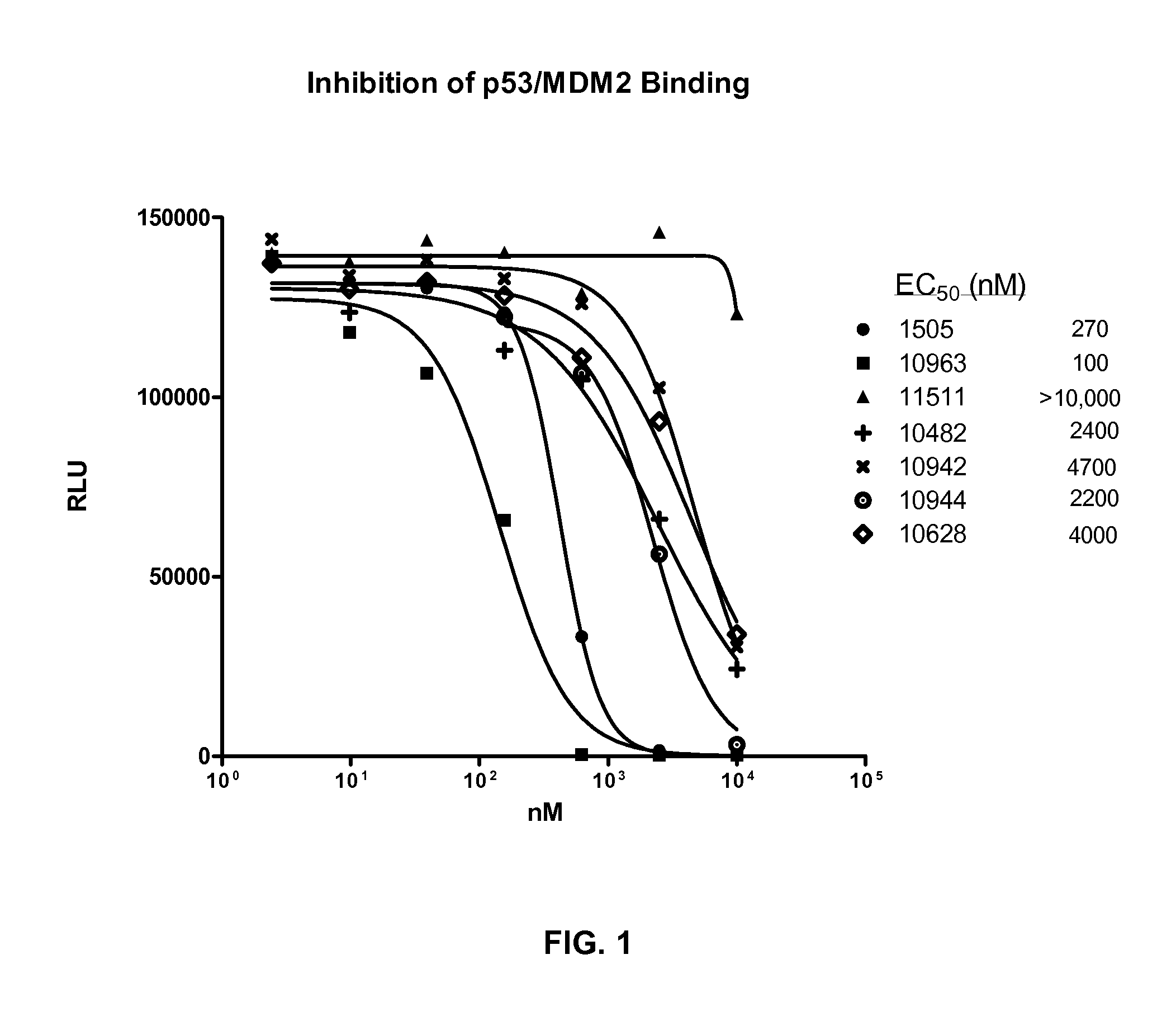
Combination therapy with mdm2 and efgr inhibitors
Provided is a method of treating a proliferative disease, condition, or disorder in a subject by administering a combination of an inhibitor of p53 and MDM2 binding and an EGFR inhibitor. Various embodiments of the disclosed methods provide a synergistic anti-proliferative or anti-apoptotic effect compared to administration of one agent alone.
Owner:ERRICO JOSEPH P
EGFR inhibitor and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105001208AStrong inhibitory activityGood inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention discloses an EGFR inhibitor. The EGFR inhibitor is of the structure shown in the formula (I) and is a compound including alpha, beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid amides. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a preparing method of the compound and the application of the compound serving as a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, especially the inhibiting function on T790M variant EGFR as the EGFR inhibitor, and the application on treating diseases such as the kidney cancer, the ling cancer, the prostate cancer, the pancreatic cancer the breast cancer and the spongiocytoma which are related to EGFR over expression. The structure is shown in the specification.
Owner:NANJING LEIKEXING BIOTECH CO LTD
Quinazoline based EGFR inhibitors containing a zinc binding moiety
InactiveUS20080194578A1Enhanced and unexpected propertyHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseZinc binding
The present invention relates to quinazoline containing zinc-binding moiety based derivatives that have enhanced and unexpected properties as inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) and their use in the treatment of EGFR-TK related diseases and disorders such as cancer. The said derivatives may further act as HDAC inhibitors.
Owner:CURIS INC
EGFR antigen-binding molecules and uses thereof
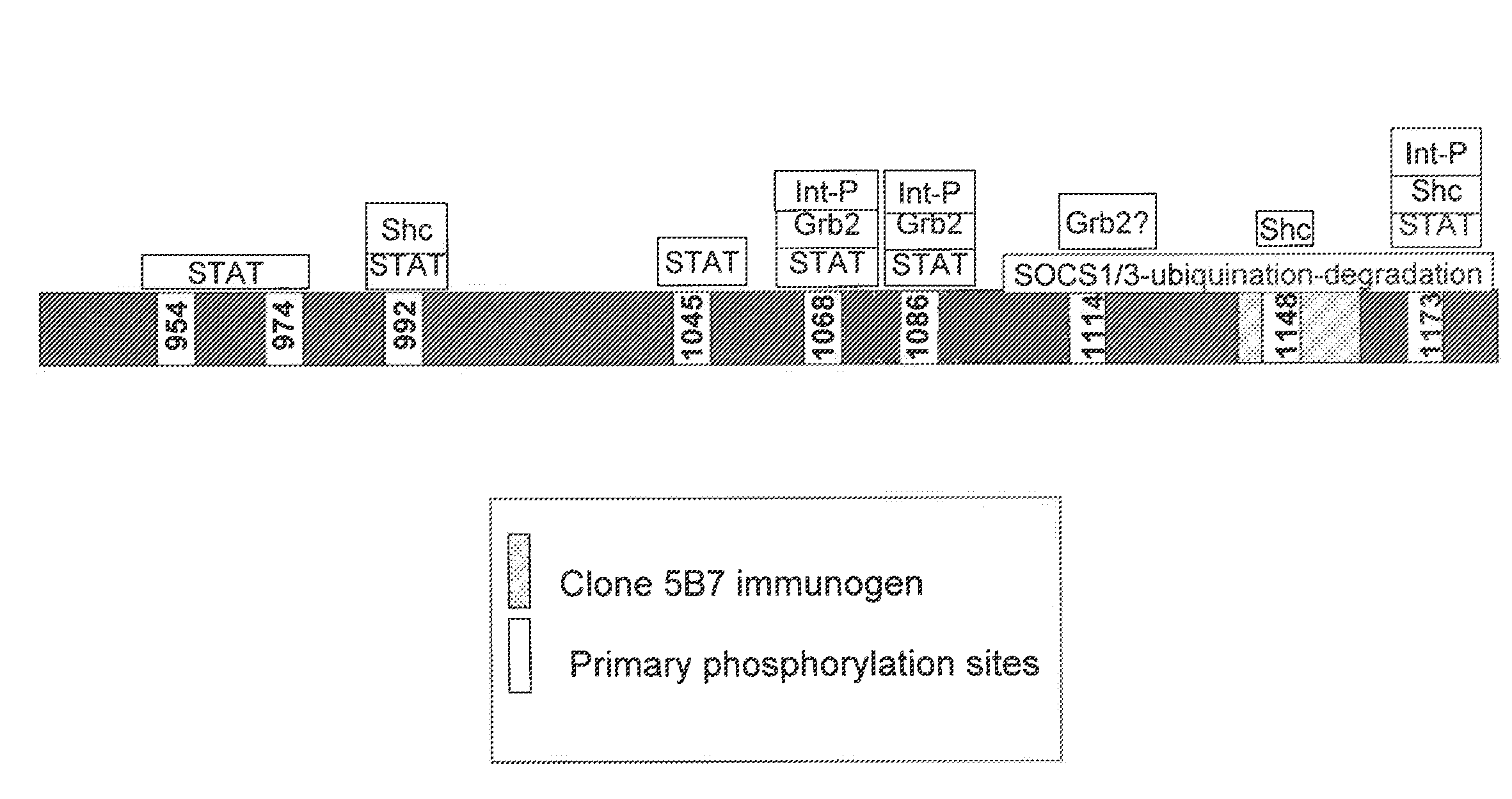
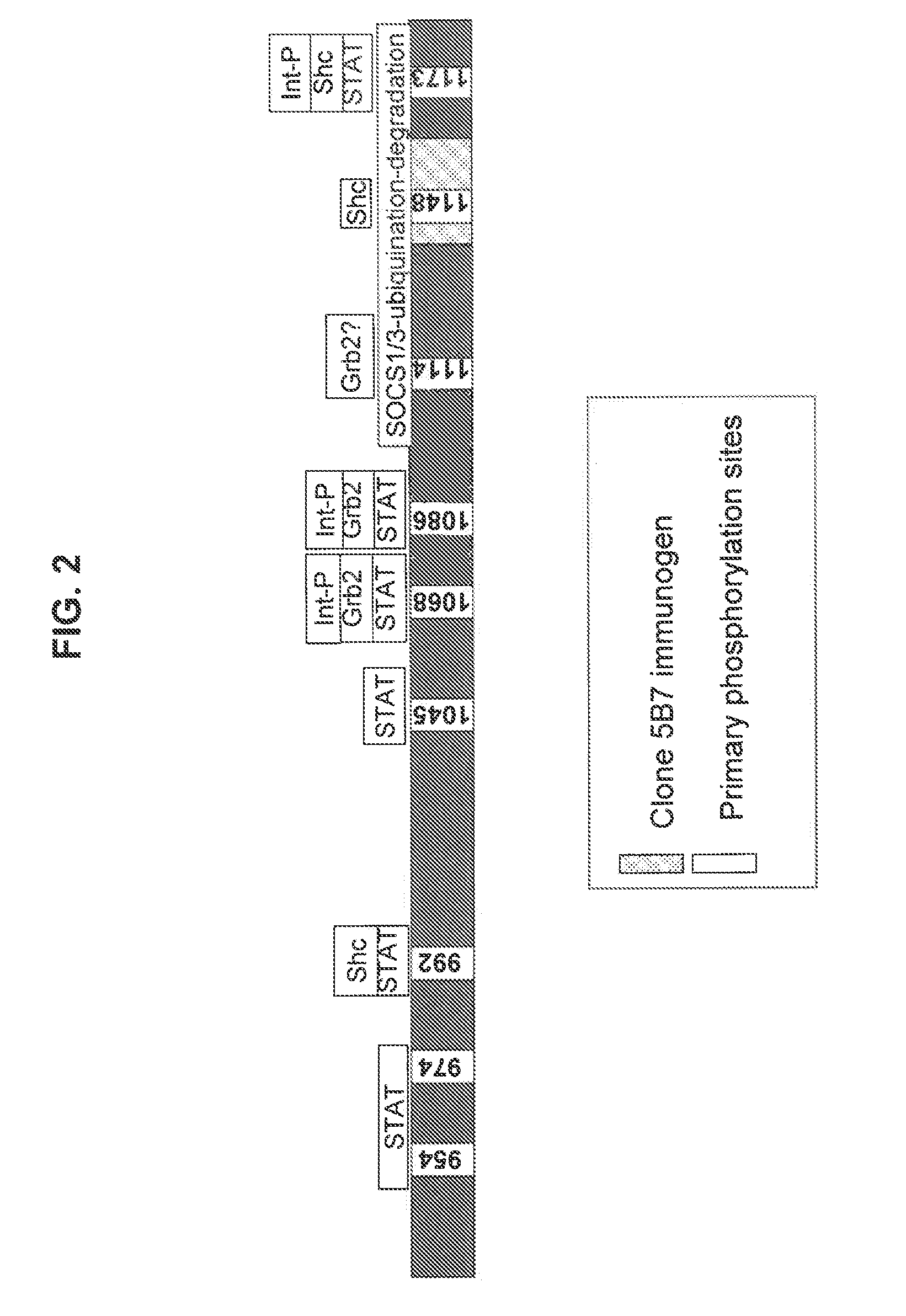
Disclosed herein are antigen-binding molecules, such as antibodies, that specifically recognize a portion of the EGFR C-terminal (intracellular) regulatory domain that interacts with one or more regulatory molecules (such as Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (“SOCS”) proteins). In certain normal or neoplastic cells and / or tissues, this region is inaccessible to the disclosed antigen-binding molecules. Thus, such antigen-binding molecules are useful at least to interrogate the regulated state of EGFR, predict the response of a cancer patient to EGFR inhibitor therapies, and / or predict the aggressiveness of neoplasms.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Gene Expression Markers for Response to EGFR Inhibitor Drugs
InactiveUS20080176229A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPrognosis biomarkerPharmaceutical drug
The present invention concerns prognostic markers associated with cancer. In particular, the invention concerns prognostic methods based on the molecular characterization of gene expression in paraffin-embedded, fixed samples of cancer tissue, which allow a physician to predict whether a patient is likely to respond well to treatment with an EGFR inhibitor.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC +1
Miazines compound, preparation method and medical application thereof
The invention belongs to the medicine field, and concretely relates to a miazines compound having a structure of a formula (1), its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a preparation method and an application of the compound for preparing an antitumor drug. The pharmacological experiment result shows that the compound has good inhibition effect to an epidermal growth factor acceptor (EGFR) and its mutant, can inhibit propagation of a plurality of tumor cells, and can be taken as an EGFR inhibitor used for preparing the antitumor drug.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Gefitinib Sensitivity-Related Gene Expression and Products and Methods Related Thereto
Disclosed is the identification, provision and use of a panel of biomarkers that predict sensitivity or resistance to gefitinib and other EGFR inhibitors, and products and processes related thereto. Specifically, a method is described for selecting a cancer patient who is predicted to benefit from therapeutic administration of an EGFR inhibitor, an agonist thereof, or a drug having substantially similar biological activity as EGFR inhibitor. Also described is a method to identify molecules that interact with the EGFR pathway to allow or enhance responsiveness to EGFR inhibitors, as well as a plurality of polynucleotides or antibodies for the detection of the expression of genes that are indicative of sensitivity or resistance to EGFR inhibitors, an agonist thereof, or a drug having substantially similar biological activity as EGFR inhibitors. A method to identify a compound with the potential to enhance the efficacy of EGFR inhibitors is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Small molecule potentiator of hormonal therapy for breast cancer
InactiveUS20080085874A1Reduce riskReduces and eliminates riskBiocideDrug compositionsHDAC inhibitorPotentiator
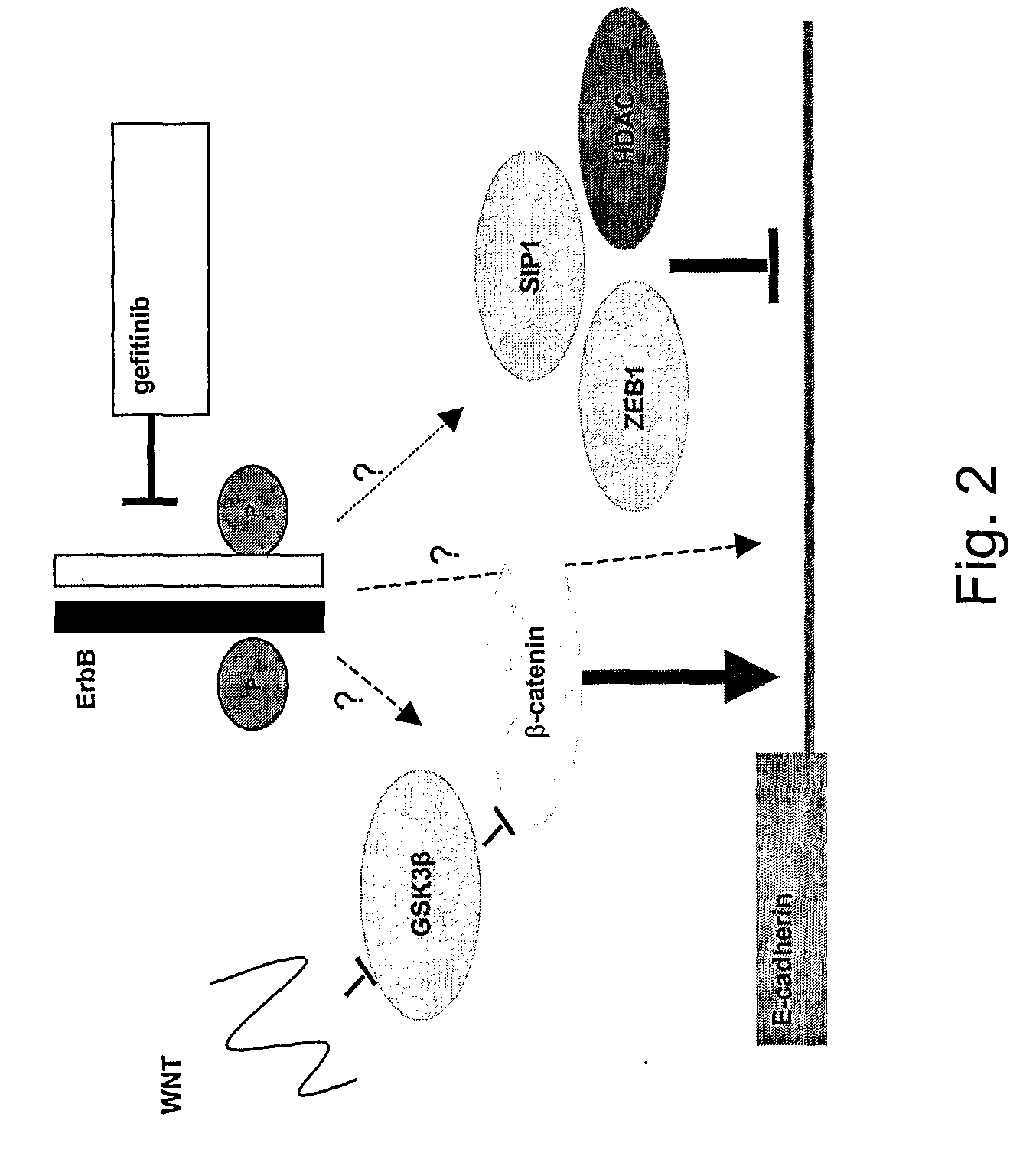
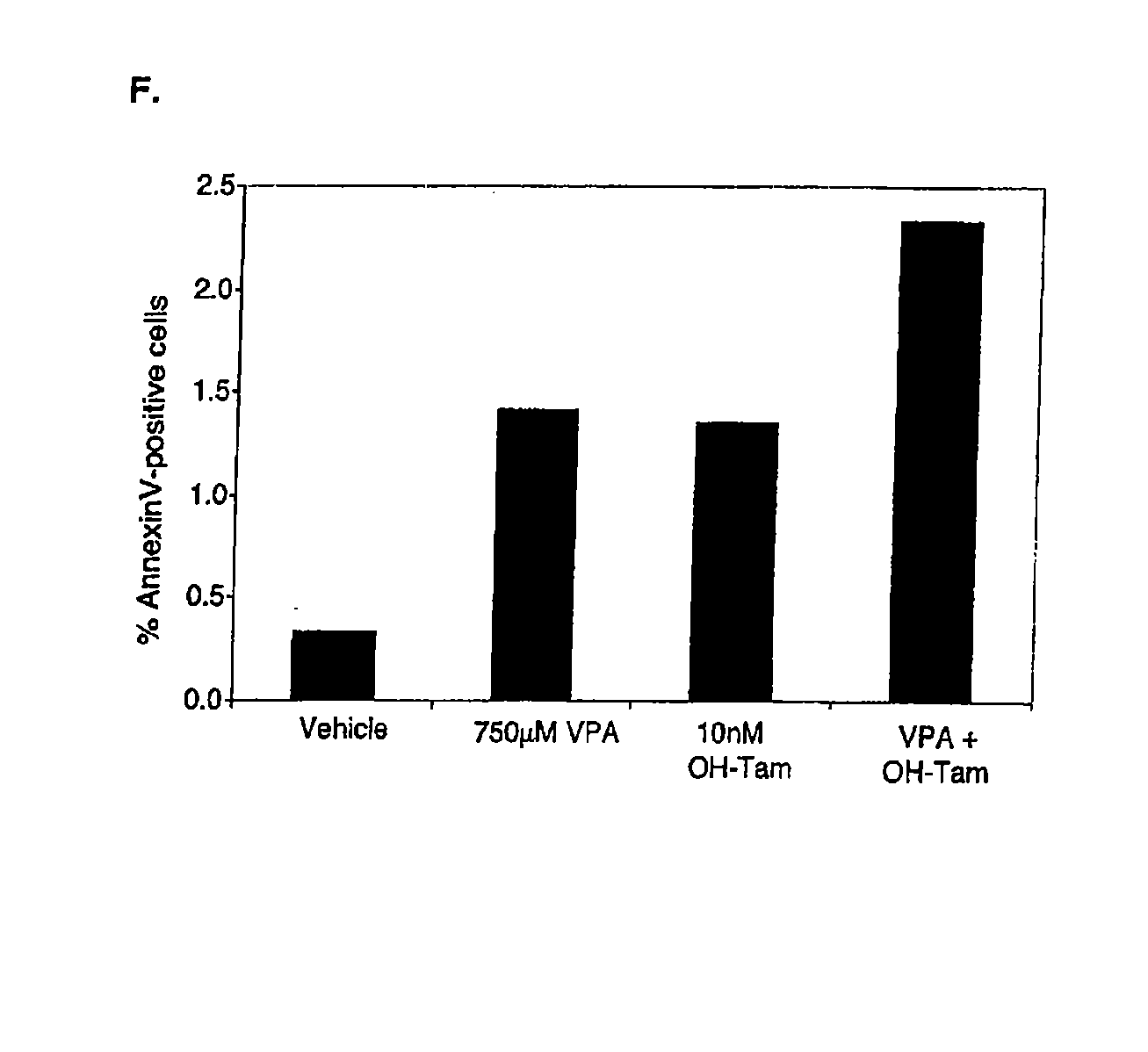
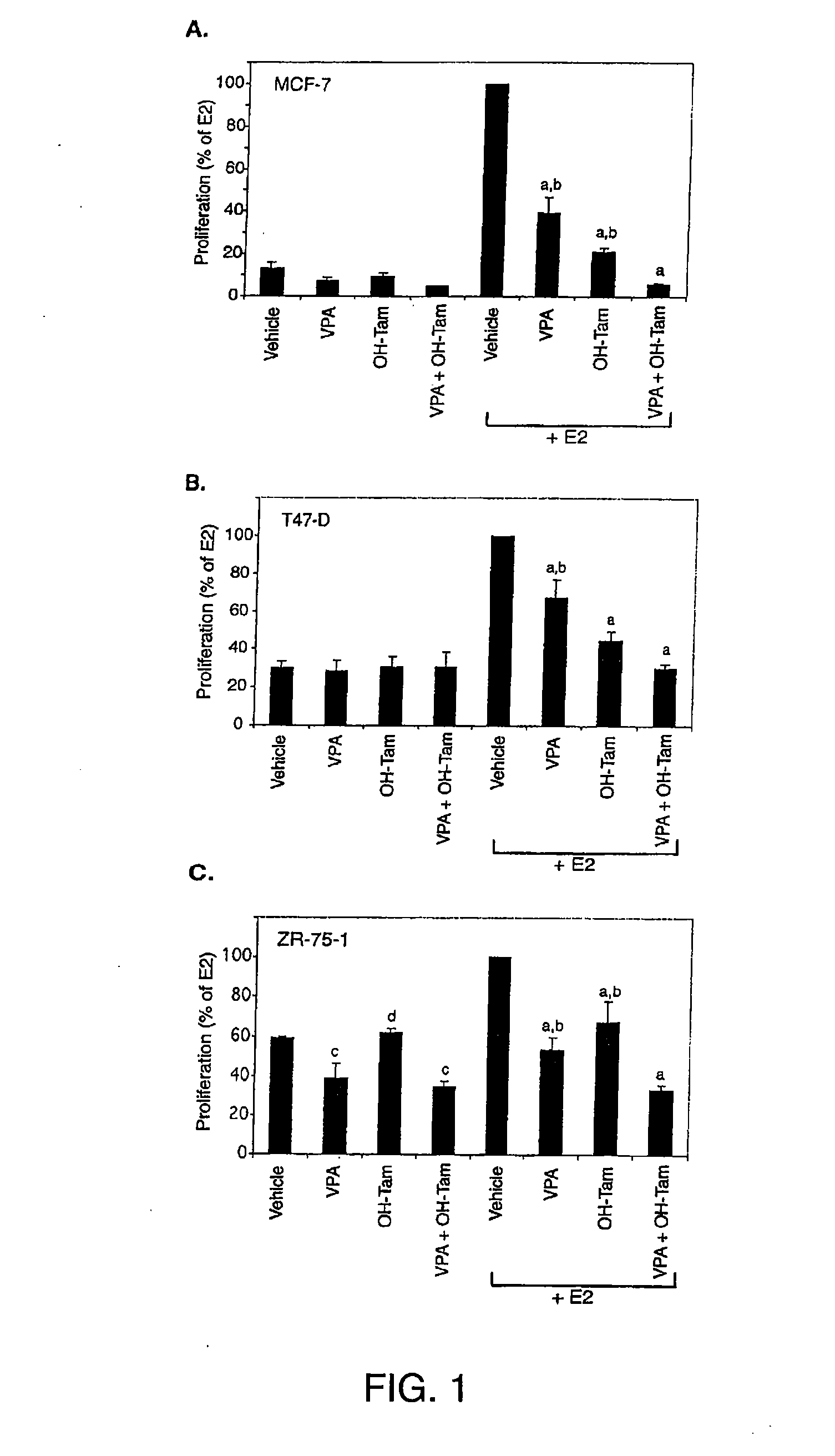
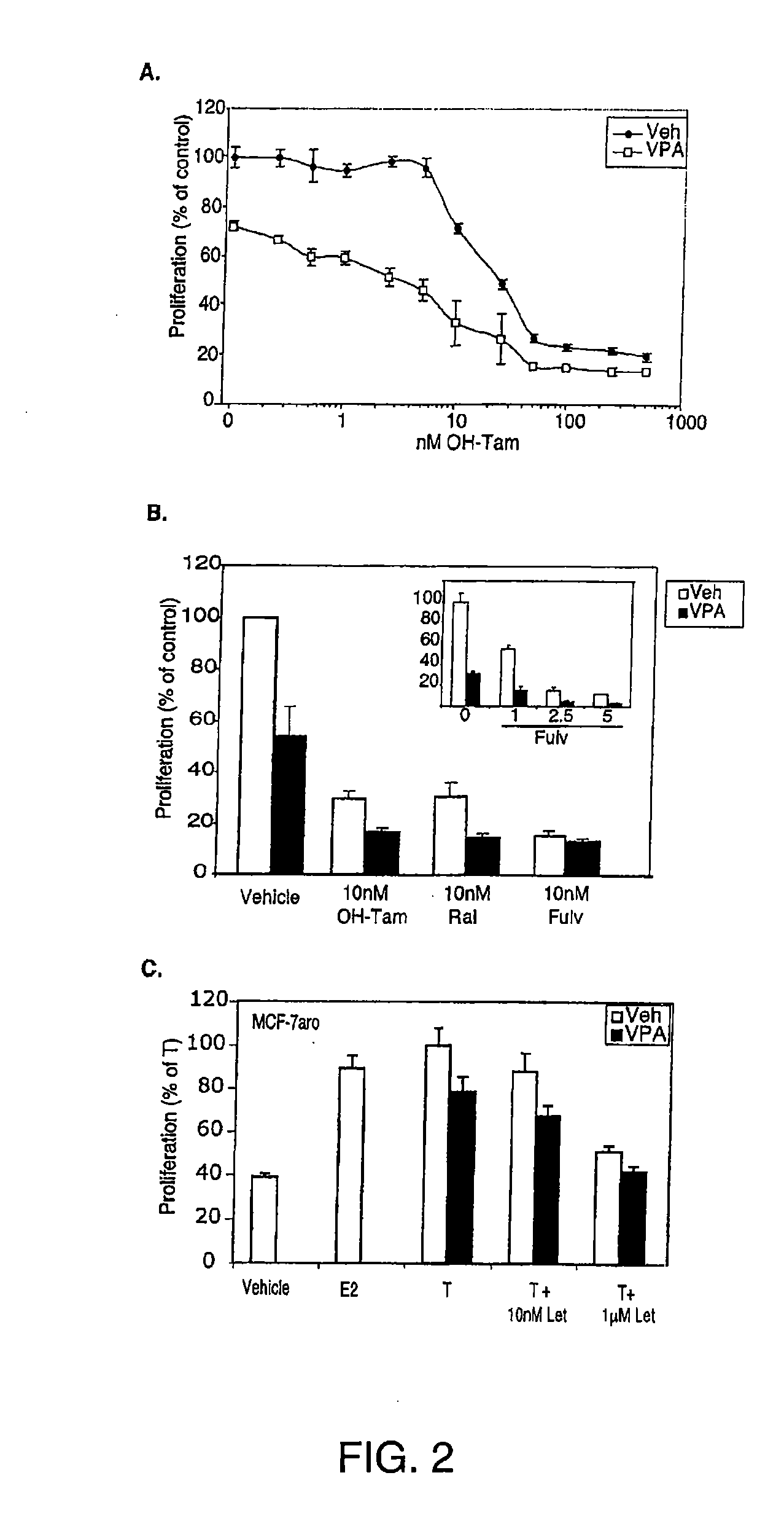
The present application demonstrates that HDAC inhibitors can be used in combination with hormonal therapy to treat and prevent estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. HDAC inhibitors can also be combined with IGF-1R inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors, and EGFR inhibitors to treat breast cancer, optionally in combination with hormonal therapy if indicated. Combinations of the compounds, with or without HDAC inhibitors, and with or without hormonal therapy, can also be used. The invention therefore provides methods of treatment and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
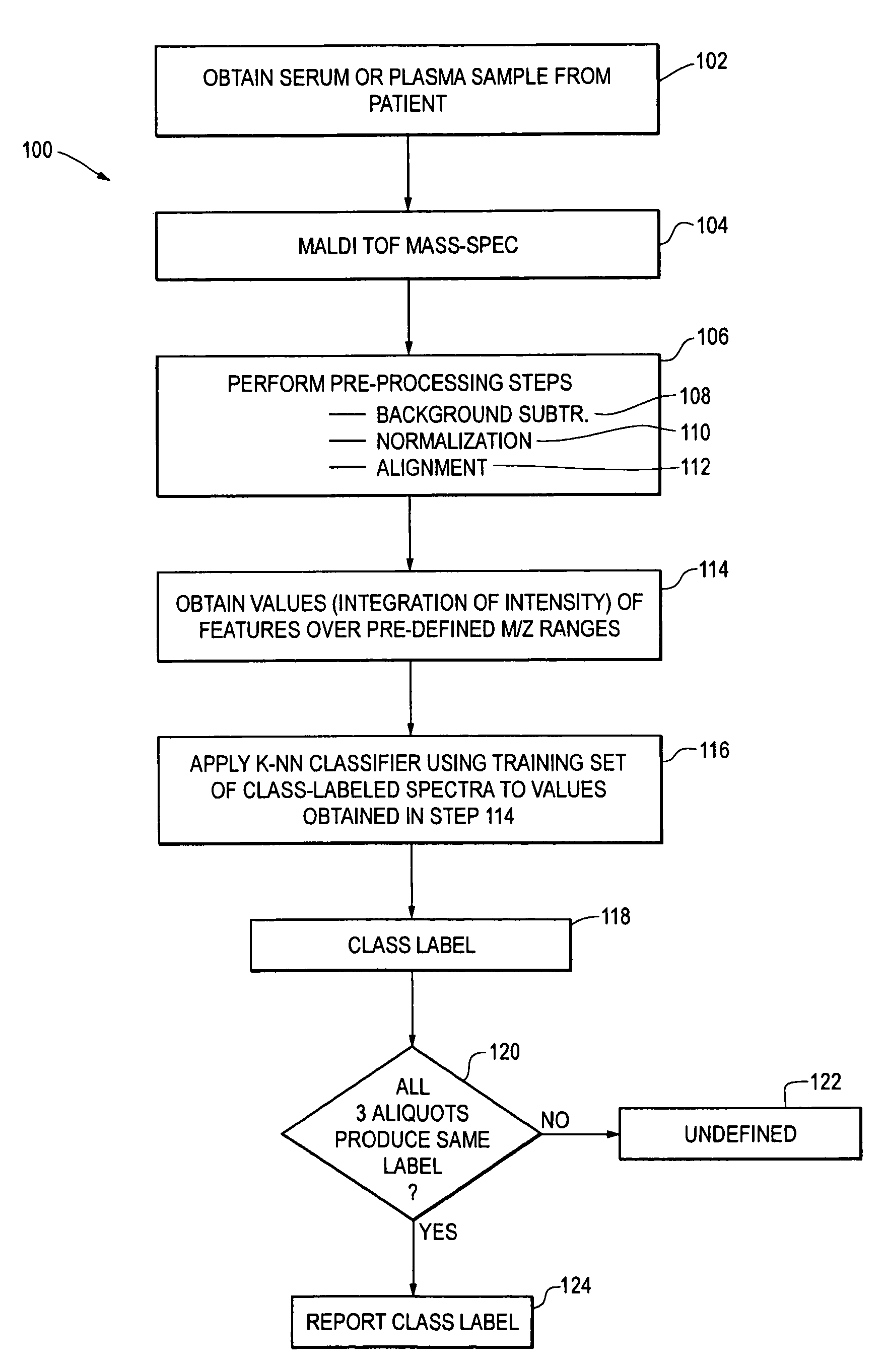
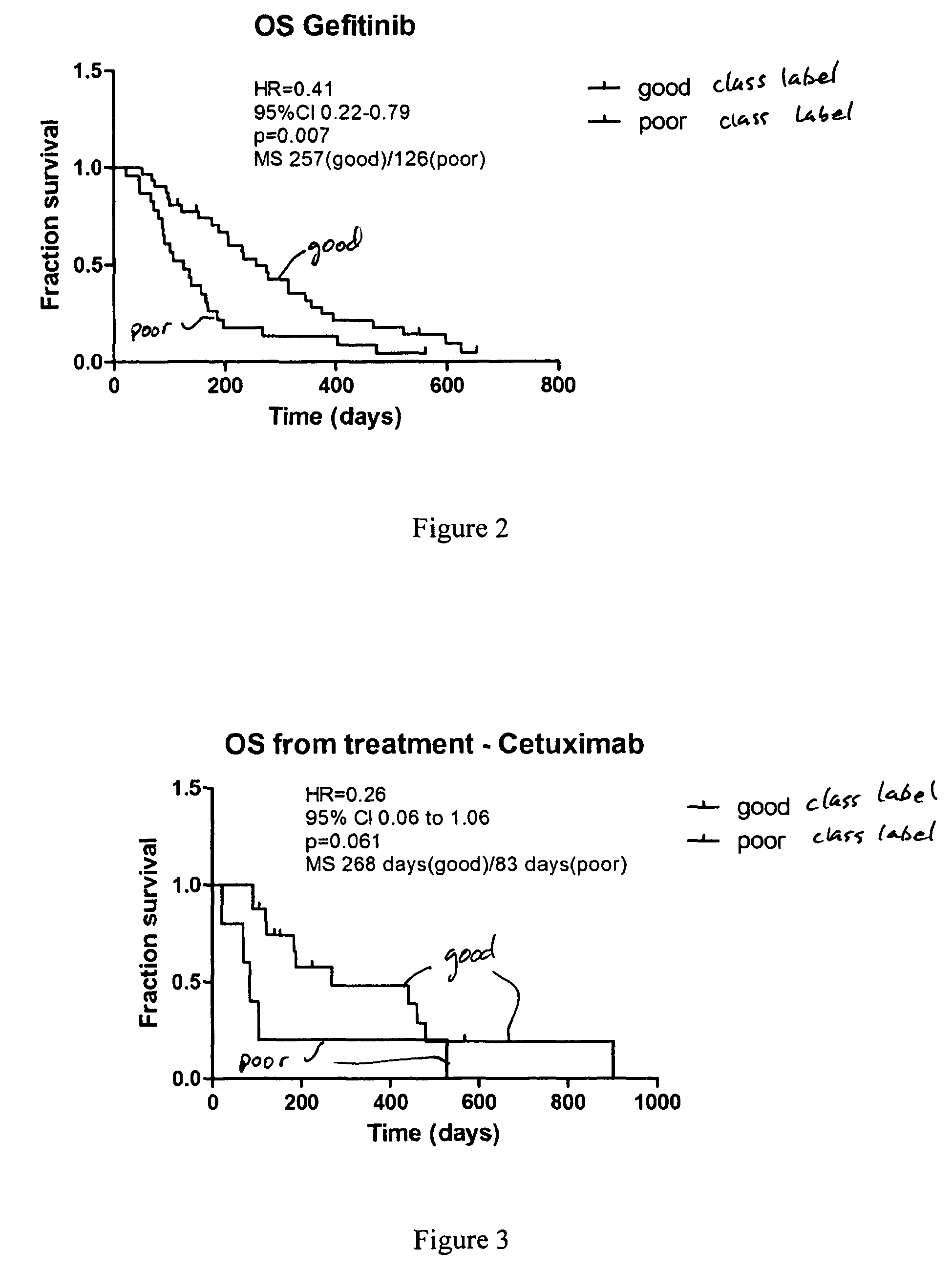
Selection of head and neck cancer patients for treatment with drugs targeting EGFR pathway
Methods using mass spectral data analysis and a classification algorithm provide an ability to determine whether a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patient is likely to benefit from a drug targeting an epidermal growth factor receptor pathway, including small molecule epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and monoclonal antibody EGFR inhibitors.
Owner:BIODESIX
Gene expression profiling of EGFR positive cancer
InactiveUS8008003B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPrognosis biomarkerTissue sample
The present invention concerns prognostic markers associated with EGFR positive cancer. In particular, the invention concerns prognostic methods based on the molecular characterization of gene expression in paraffin-embedded, fixed tissue samples of EGFR-expressing cancer, which allow a physician to predict whether a patient is likely to respond well to treatment with an EGFR inhibitor.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Predictors of patient response to treatment with egf receptor inhibitors
ActiveUS20090298701A1Increased normalized expression levelImprove responseNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene productOncology
The present invention provides methods and compositions to facilitate determining whether an EGFR-expressing cancer in an individual is an EGFR inhibitor-responsive cancer, as well as methods for determining the likelihood that a patient having an EGFR-expressing cancer will exhibit a beneficial response to an EGFR inhibitor therapy. The methods generally involve determining a normalized expression level of a gene product that correlates with EGFR inhibitor responsiveness.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC +1
Cancer Therapy
ActiveUS20100256232A1Inhibit tyrosine kinase activityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMedicineCancer therapy
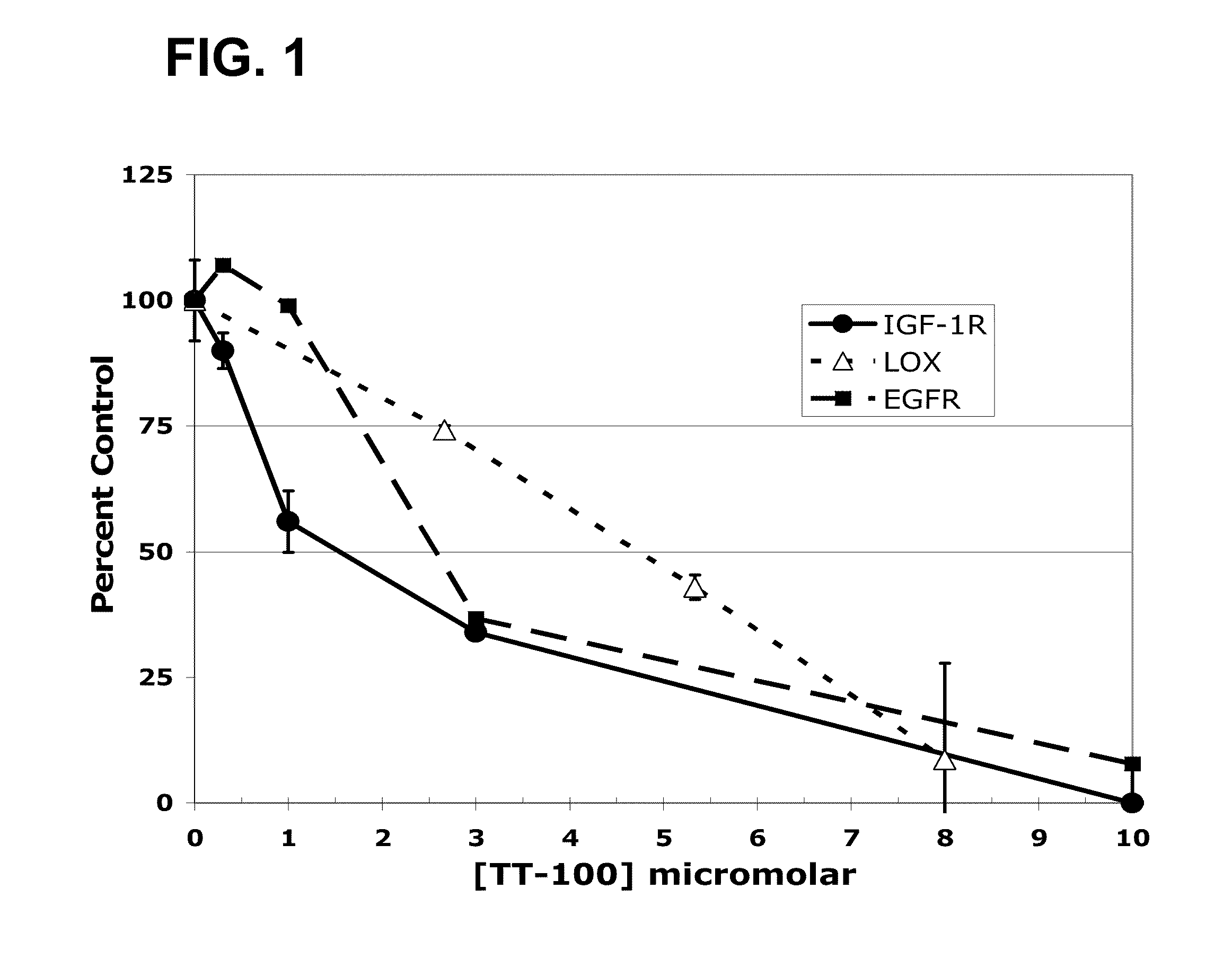
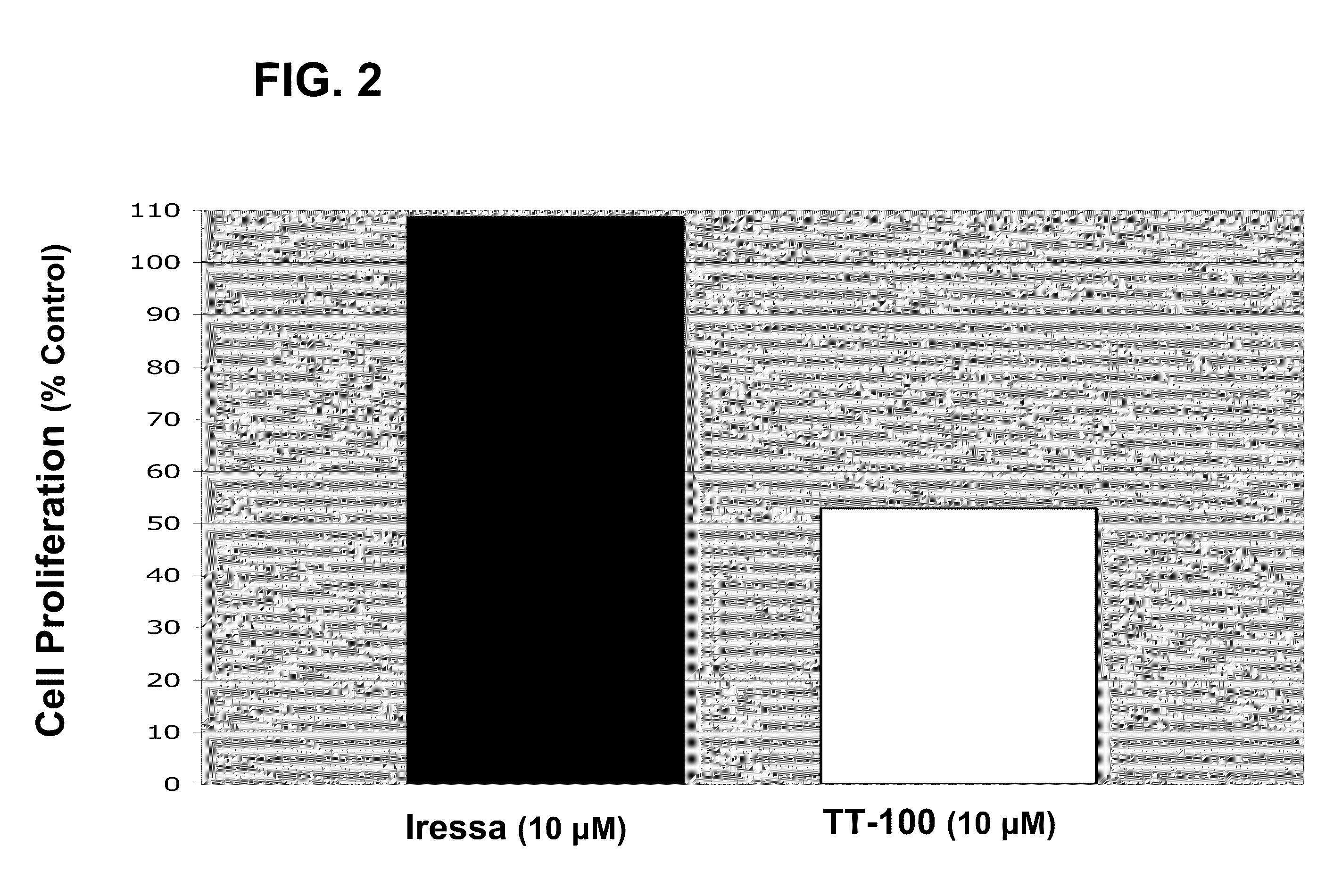
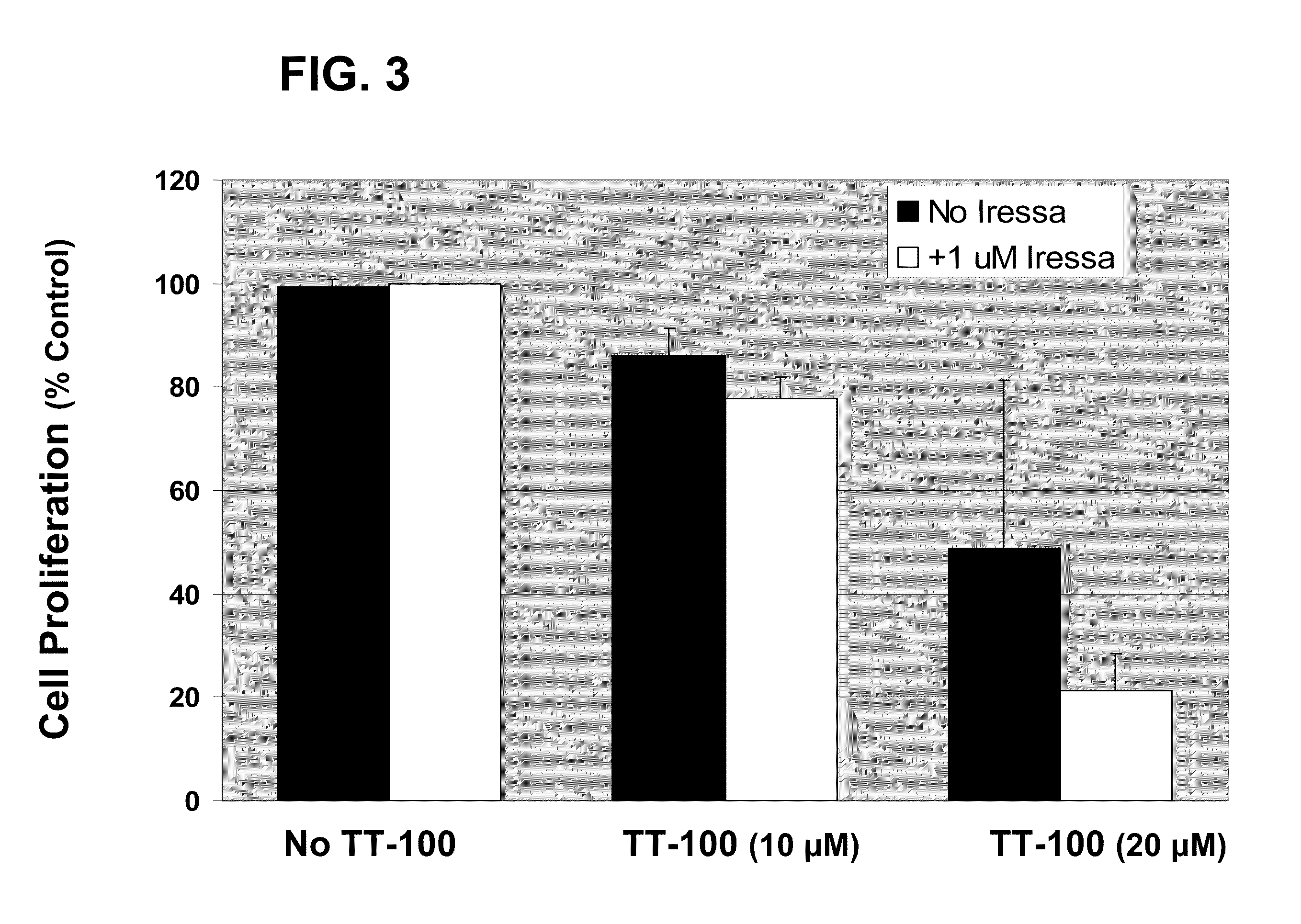
The present application relates to compositions and methods for treating a proliferative disorder by administering to a subject a pharmaceutical composition of a dual kinase inhibitor. Catecholic butanes cane serve as dual kinase inhibitors for purposes of methods described herein. Subjects can be further treated by co-administering an EGFR inhibitor. The present application also relates to analyzing a sample with respect to levels of IGF-1R and EGFR and comparing levels of IGF-1R and EGFR to a control. Patients can be selected for treatment with a catecholic butane based on the assessment; optionally, patients can be further treated with an EGFR inhibitor, an IGF-1R inhibitor, or both.
Owner:TRIACT THERAPEUTICS
Quinazoline based EGFR inhibitors containing a zinc binding moiety
InactiveUS7547781B2Enhanced and unexpected propertyHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseZinc binding
Owner:CURIS INC
Pyrimidine compound, EGFR inhibitor and application of EGFR inhibitor
InactiveCN106083736AInhibitory activitySuppression of resistance mutationsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseSide effect
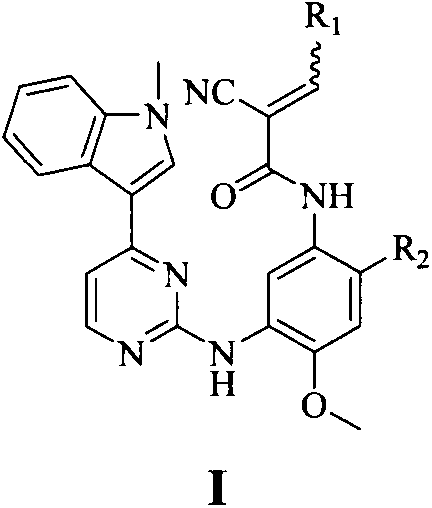
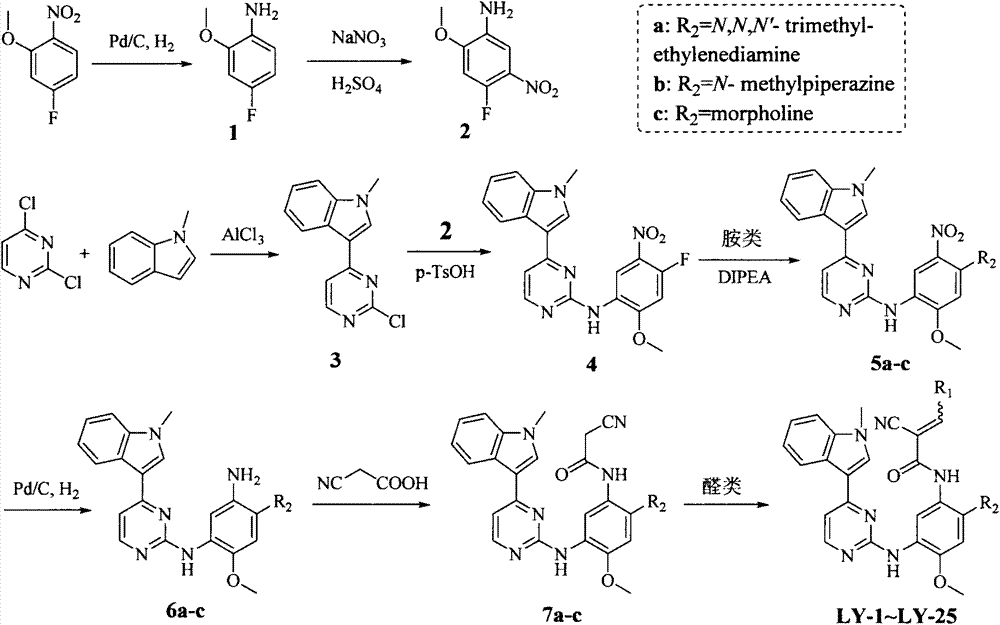
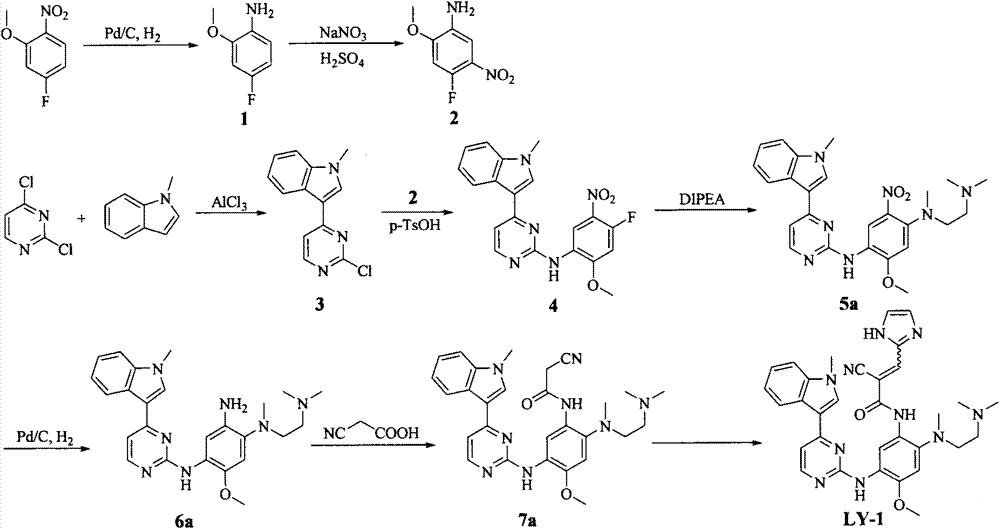
The invention discloses a pyrimidine compound, an EGFR inhibitor and application of the EGFR inhibitor. The pyrimidine compound is prepared from a compound shown in the formula I or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a stereoisomer, and a solvate or prodrug. The EGFR inhibitor contains the pyrimidine compound. The pyrimidine compound can inhibit activated or resistant mutation of one or more kinds of EGFRs, can inhibit proliferation of the EGFR T790M / L858R double-mutant enzyme in the nanomolar concentration, but has a weak inhibiting effect on the wild EGFR enzyme; the pyrimidine compound is applicable to treatment of the EGFR-sensitive mutations cancer and also suitable for cases with secondary dug resistance in present EGFR-TKI treatment; meanwhile, toxic and side effects caused by inhibition on the wild EGFR are greatly reduced due to the mutation selectivity of the pyrimidine compound, and the pyrimidine compound is an ideal treatment drug for diseases caused by EGFR mutation.
Owner:TETRANOV PHARMA CO LTD
Phenyl substituted triazine compounds adopted as EGFR inhibitor, and applications thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and particularly relates to a class of phenyl substituted triazine compounds having epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition effects, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound, and uses of the compounds or the pharmaceutical composition as cancer treatment drugs. According to the present invention, the compounds have good inhibition activity on mutant EGFR kinase, exhibit excellent selectivity, and are expected to be the drugs providing specific treatment effects on drug resistance tumors, especially EGFR mutation-causing drug resistance tumors.
Owner:NANJING SANHOME PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
EGFR inhibitor, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20170313714A1Organic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiseaseCancer prevention
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors are provided. In particular, 4-substituted-2-(N-(5-substituted allyl amide)phenyl)amino)pyrimidine derivatives of formula (I), a preparation method and use thereof as an EGFR inhibitor are provided. The 4-substituted-2-(N-(5-substituted allyl amide)phenyl)amino)pyrimidine derivatives of formula (I) have inhibitory activity against the L858R EGFR mutant, the T790M EGFR mutant and the exon 19 deletion activating mutant, and can be used to treat diseases mediated alone or in part by EGFR mutant activity. The derivatives of formula (I) can be used to treat and / or prevent cancers, particularly non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANSOH BIOMEDICAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com