EGFR antigen-binding molecules and uses thereof
a technology of antigen-binding molecules and antigen-binding molecules, which is applied in the field of antigen-binding molecules, can solve the problems of heterogeneous tumors, on the cellular and/or molecular level, and patients are exposed to the risks and discomforts of unneeded therapies, and are even from the same tissue or organ
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
An Exemplary Monoclonal Antibody Specific for EGFR Regulatory Domain
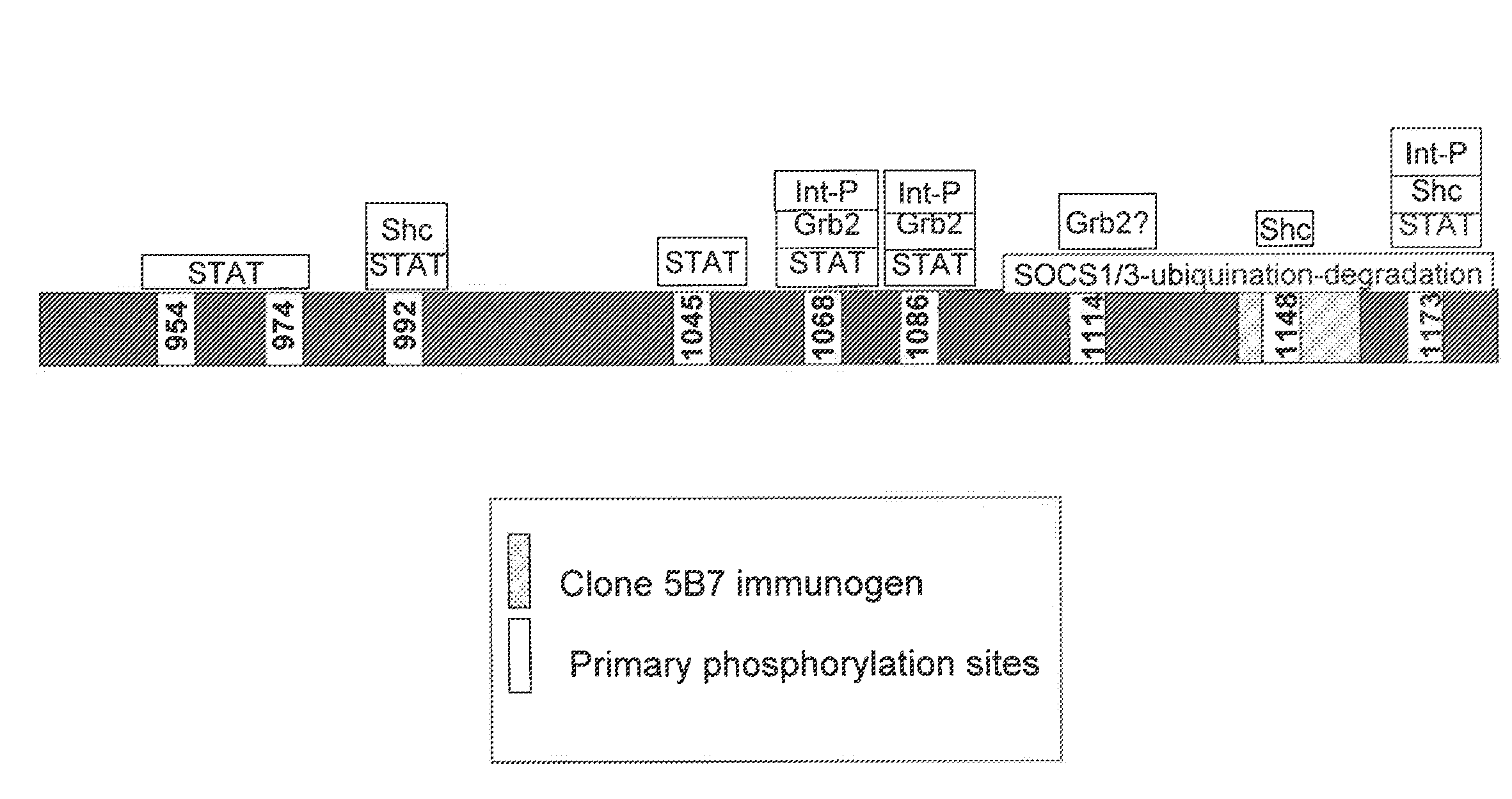
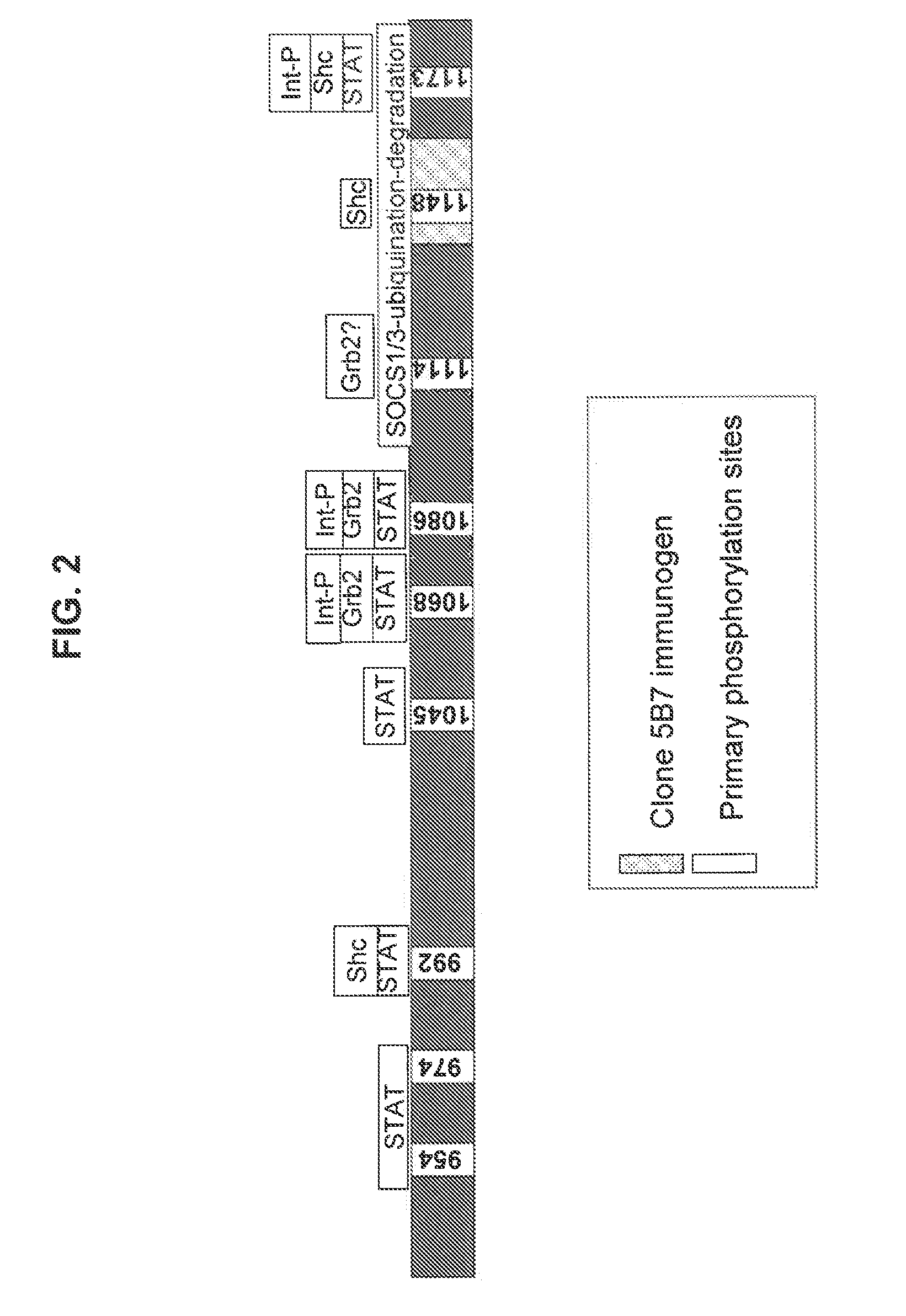
[0135]This Example describes an exemplary RD-binding molecule; more particularly a monoclonal antibody that binds an epitope in the EGFR inhibitory subdomain. This antibody has the added advantage that it will identify not only full-length EGFR, but also truncated mutant forms of EGFR, which have been shown to be constitutively activated (Pedersen et al., Ann. Oncol., 12(6):745-60, 2001).
[0136]A computer program (DNASTAR™, Madison, Wis.) was used for the selection of immunogenic peptide sequences within the EGFR intracellular domain. The program examined the input protein sequence for short (e.g., less than 20 contiguous amino acids) sequences that likely had a high probability for producing an antibody response in animals immunized with immunogens including such short sequences.
[0137]One identified short sequence was LDNPDYQQDFFPKEAKPNG (L2G Peptide; SEQ ID NO: 2), which, by computer analysis, had high antigenicity...
example 2
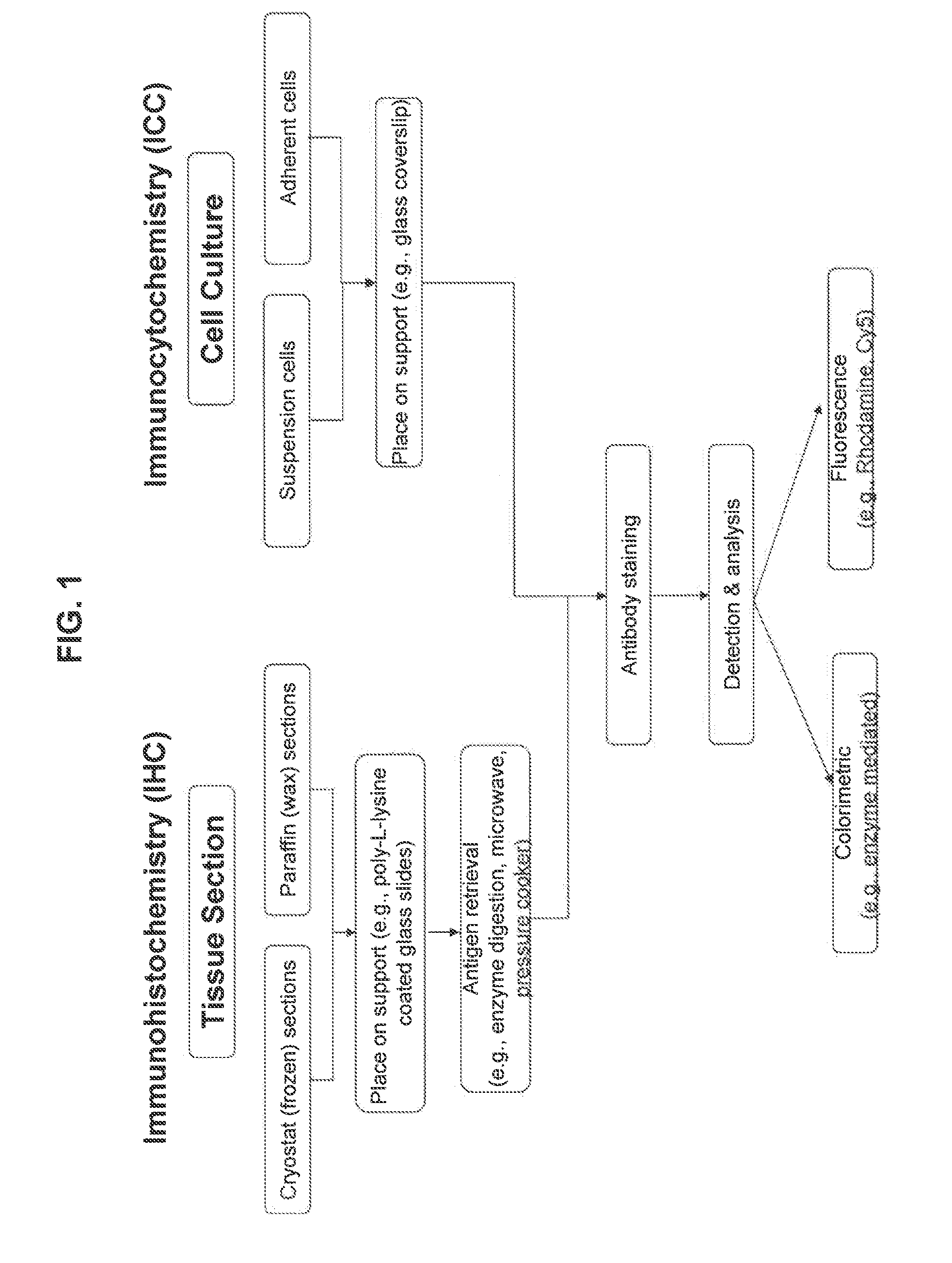
Exemplary Methods for Immunohistochemical Staining of Tissue with EGFR-Specific Antibodies
[0142]Immunohistochemistry is the well-known method and variations on such methods are readily determined with routine experimentation by those of ordinary skill in the art (see, e.g., Dabbs, Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry, Churchill Livingstone, 2002). Exemplary methods for detecting in FFPE tissue by manual IHC an EGFR RD-binding molecule (e.g., monoclonal antibody clone 5B7) or an antigen-binding molecule specific for the EGFR extracellular domain (e.g., monoclonal antibody clone 3C6) are provided in the following table:
Step #Manual IHC Assay0Fresh tissue is placed in a fixative (such as, 10% neutral buffered formalin)for approximately 12-48 hours at room temperature. Then, the tissue isdehydrated through graded alcohols (e.g., 50% to 70% to 90% to 95% to100% EtOH) for 1-2 hours at each grade, and infiltrated with a clearingreagent (such as, xylene) for 3-5 hours at room temperature. The cl...
example 3
Antibody Specific for EGFR Regulatory Domain Epitope Unexpectedly does not Substantially Bind to Some EGFR-Positive Tissues
[0145]This Example demonstrates that RD-binding molecules, such as clone 5B7, exhibited differential binding to EGFR-positive tissues (as detected by an antibody specific for the EGFR external domain). As described in more detail below, but without being limited to a single theory, this differential binding is believed to be due to the differential expression of EGFR regulatory proteins (e.g., SOCS proteins like SOCS1 or SOCS3) in EGFR-positive tissues. Such regulatory proteins, when directly associated with the EGFR regulatory domain, mask the epitopes of RD-binding molecules.
[0146]A. Normal Human Tissues
[0147]The staining by IHC of antibodies specific for the EGFR regulatory domain (i.e., clone 5B7) and external domain (i.e., clone 3C6) in FFPE 30 normal human tissues were compared. Tissue arrays were obtained from USBiomax (Igamsville, Md.; Cat. No. FDA801). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com