Patents
Literature
103 results about "Antisense Orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Having a DNA sequence complementary to that of a messenger RNA molecule; the non-coding strand in double-stranded DNA.
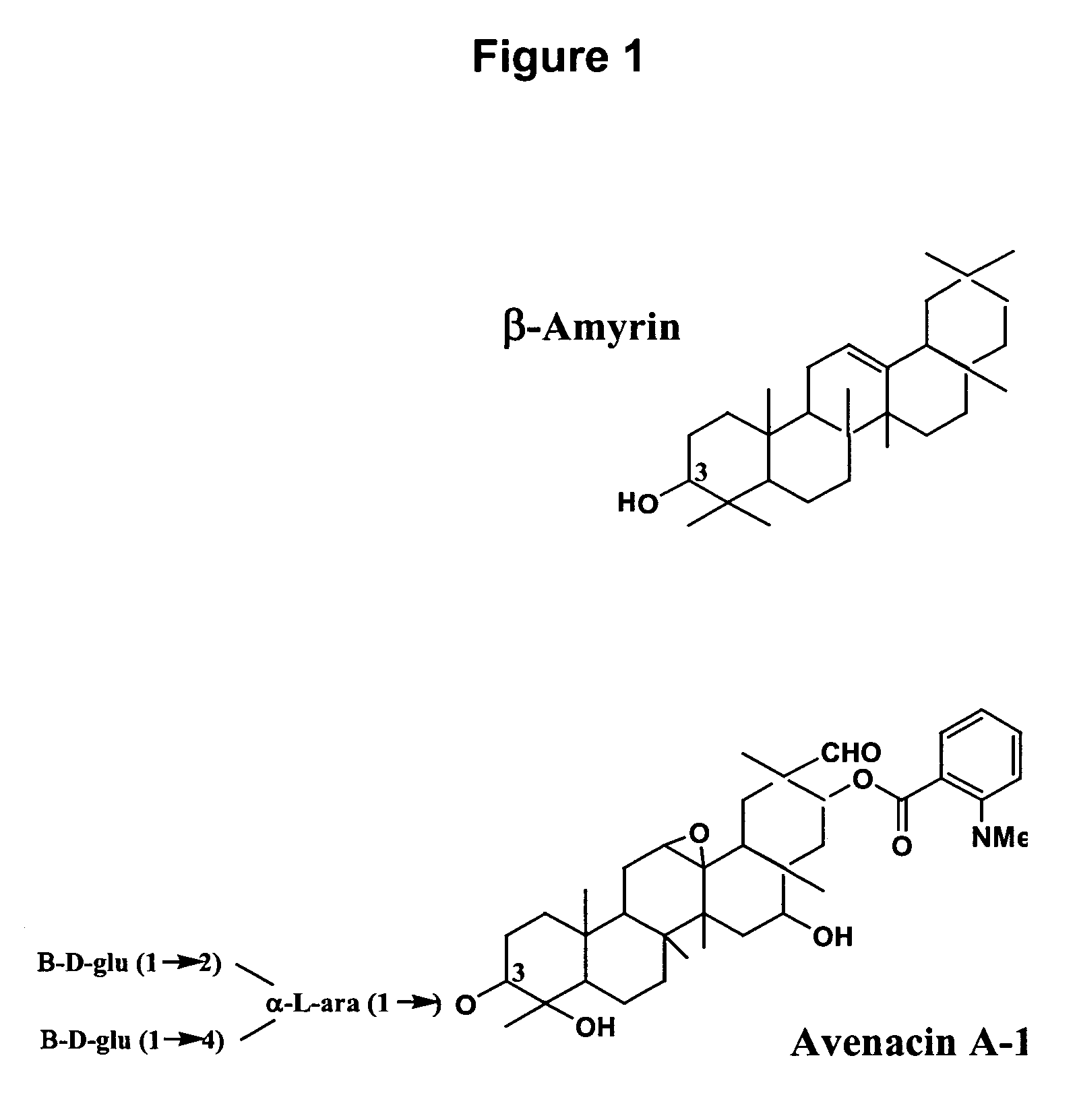
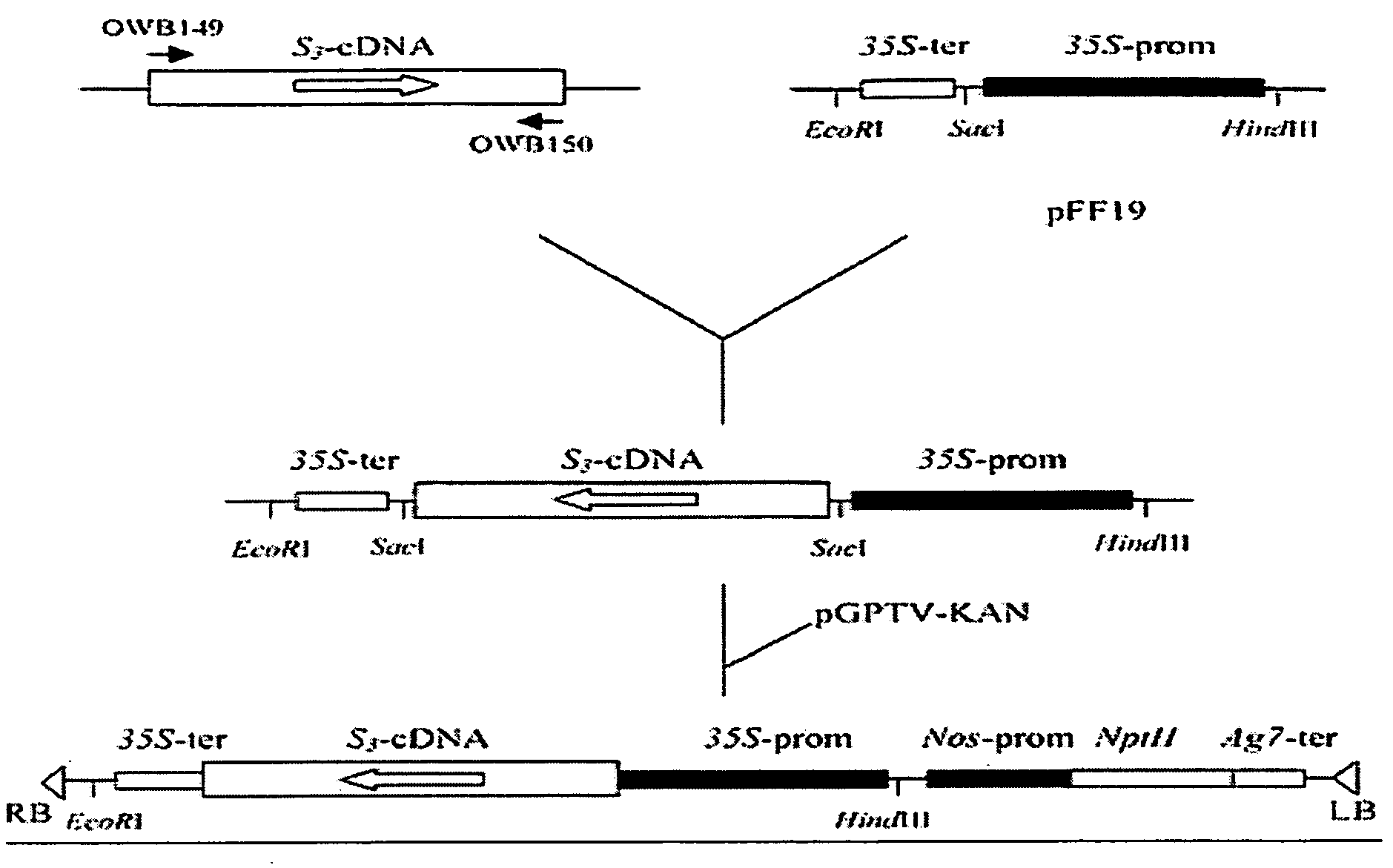
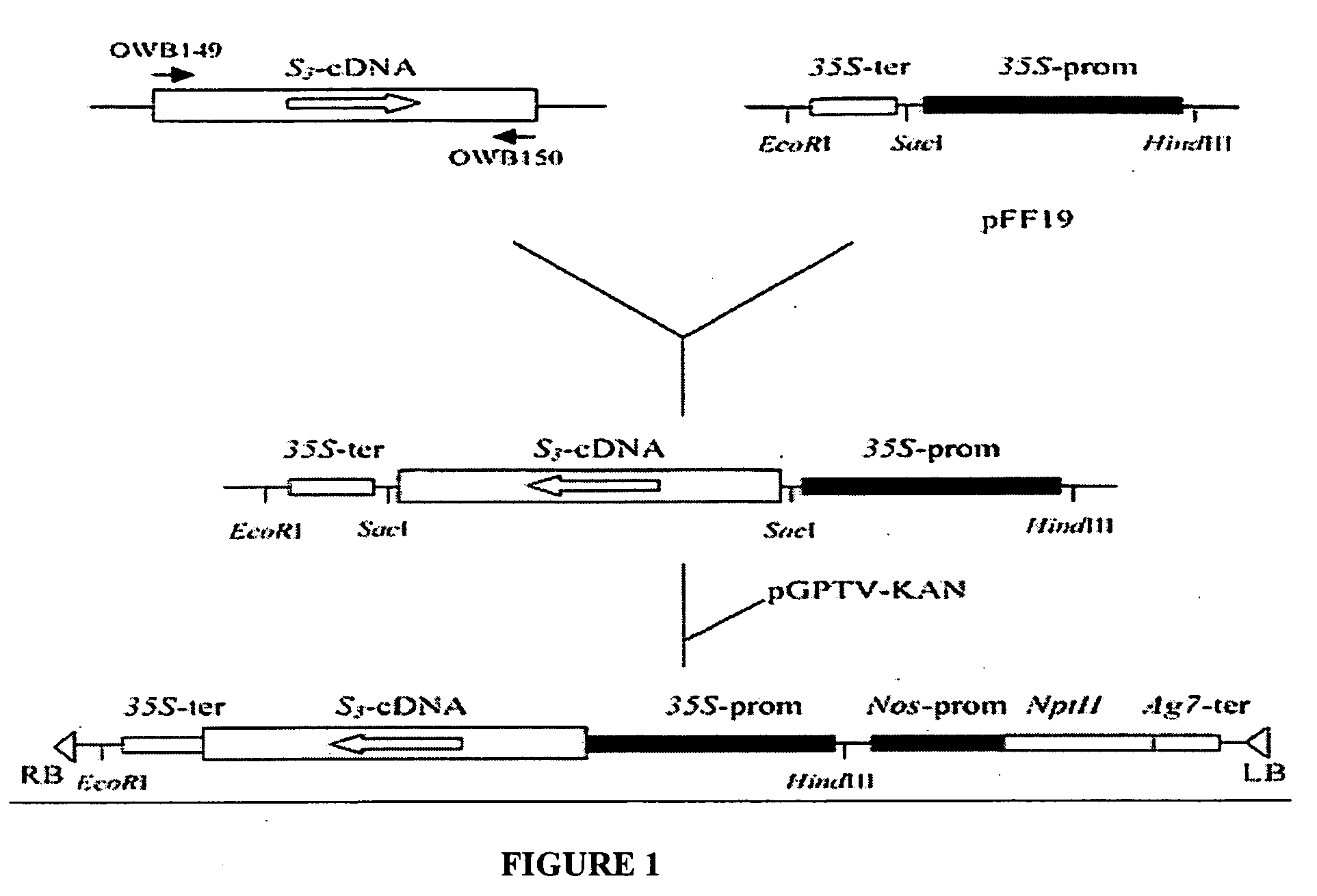
DNA encoding a plant deoxyhypusine synthase, a plant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence programmed and cell death in plants
InactiveUS6538182B1Lower Level RequirementsExtended shelf lifeBacteriaOxidoreductasesAntisense OrientationApoptotic programmed cell death
Regulation of expression of programmed cell death, including senescence, in plants is achieved by integration of a gene or gene fragment encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase, senescence-induced eIF-5A or both into the plant genome in antisense orientation. Plant genes encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase and senescence-induced eIF-5A are identified and the nucleotide sequences of each, alone and in combination are used to modify senescence in transgenic plants.
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
DNA encoding apoptosis-induced eucaryotic initiation factor-5A and deoxyhypusine synthase and a method for controlling apoptosis in animals and humans
InactiveUS6867237B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce translationBiocideLaser detailsAntisense OrientationInitiation factor
Genes encoding an apoptosis-induced eukaryotic initiation Factor-5A (eIF-5A) and an apoptosis-induced deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS), whose expressions are induced by the onset of apoptosis, are identified. The DHS gene and the eIF-5A gene, alone or in combination, as well as inhibitors of the DHS reaction, are used to modulate apoptosis in animals and humans. For example, modulation of apoptosis in cells of animals and humans is achieved by introduction of a gene or gene fragment encoding apoptosis-induced eIF-5A, apoptosis-induced DHS, or both into the animal or human cell in antisense orientation.
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
DNA encoding a plant deoxyhypusine synthase, a plant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence programmed and cell death in plants
InactiveUS6878860B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce and prevent expression of geneBacteriaOxidoreductasesAntisense OrientationApoptotic programmed cell death
Regulation of expression of programmed cell death, including senescence, in plants is achieved by integration of a gene or gene fragment encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase, senescence-induced elF-5A or both into the plant genome in antisense orientation. Plant genes encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase and senescence-induced elF-5A are identified and the nucleotide sequences of each, alone and in combination are used to modify senescence in transgenic plants.
Owner:AGRIBODY TECH INC
Root-specific, stimulant inducible promoter and its use
ActiveUS7196247B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationStimulant
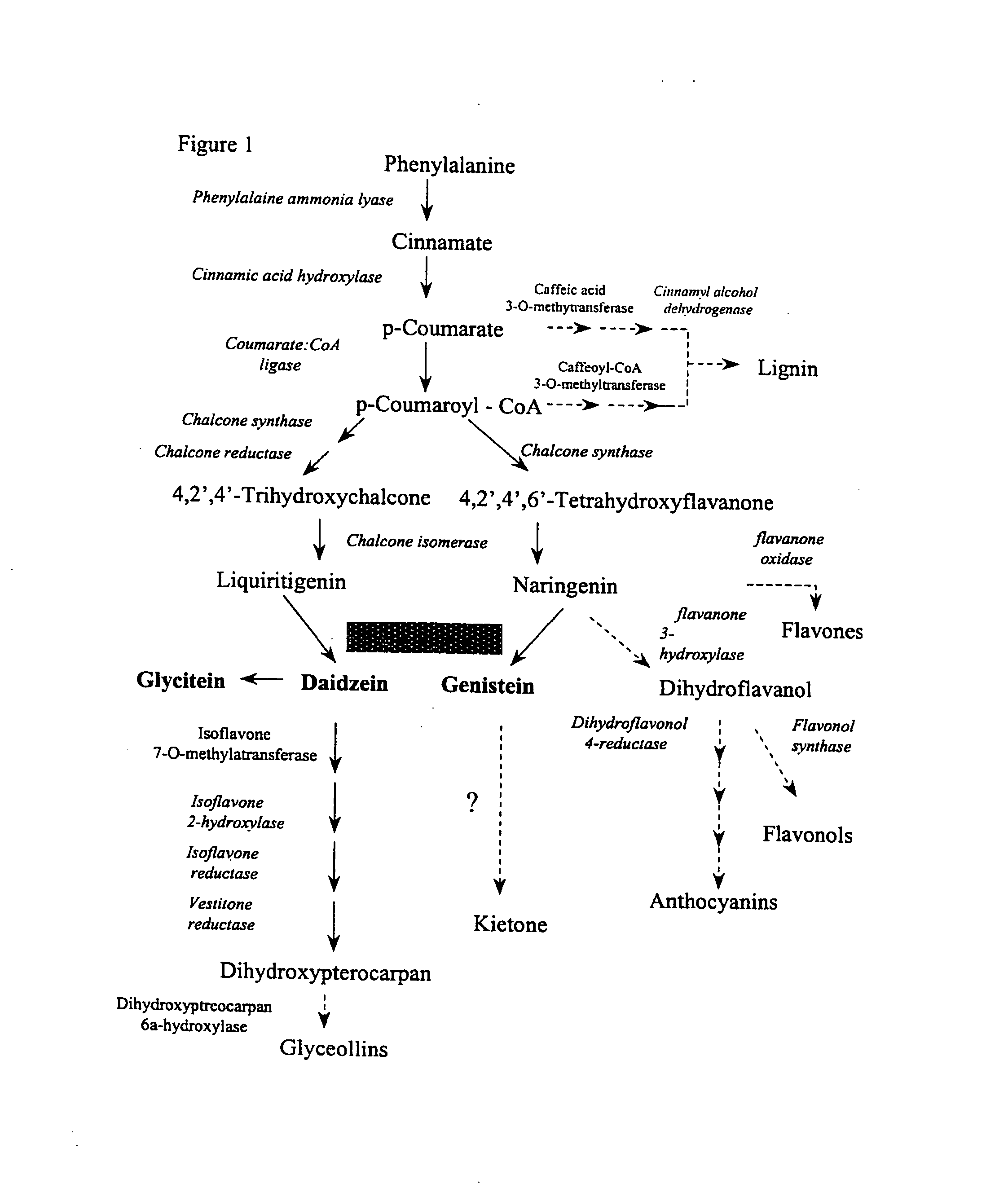
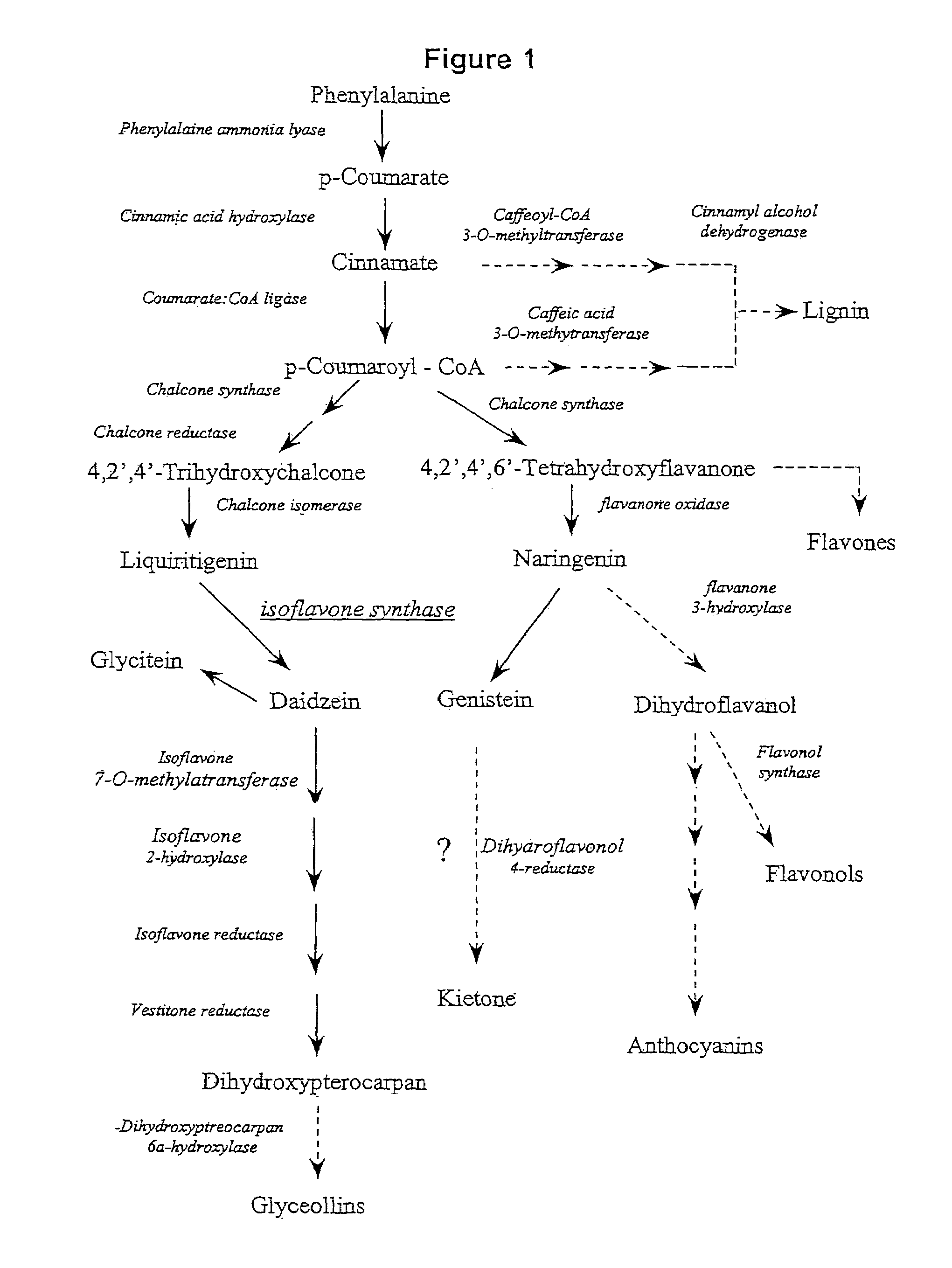
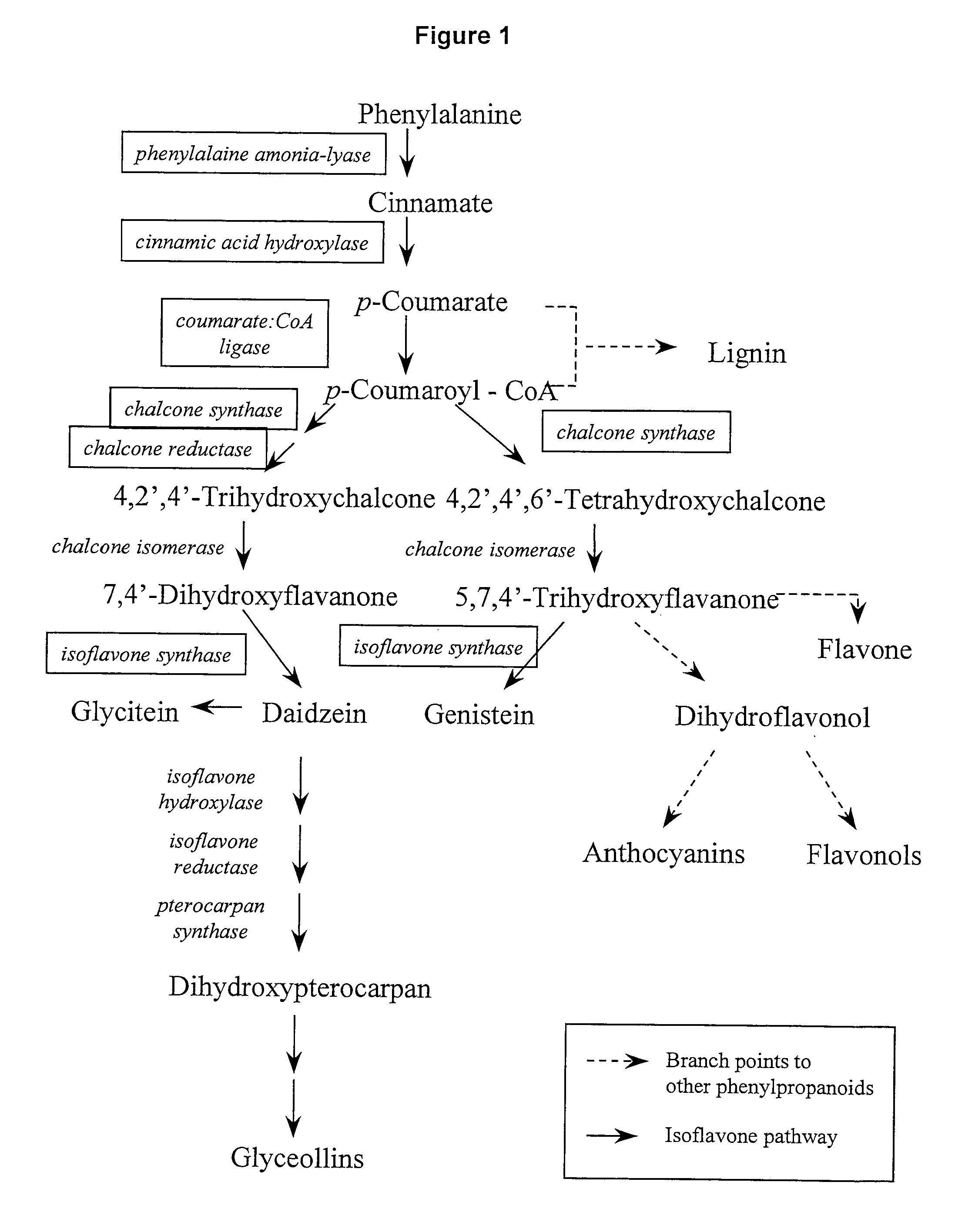
This invention relates to an isolated isoflavone synthase 1 (IFS1) promoter nucleic acid fragment. The invention also relates to the construction of chimeric genes comprising all or a portion of the IFS1 promoter directing the expression of transgenes, in sense or antisense orientation.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
Nucleic acid fragments encoding isoflavone synthase
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid sequence encoding isoflavone synthase. The invention also relates to the construction of chimeric sequences encoding all or a substantial portion of the enzymes, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric sequence results in production of altered levels of the enzyme in a transformed host cell.
Owner:FADER GARY +4
Plant raffinose saccharide biosynthetic enzymes
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a galactinol synthase. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the galactinol synthase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the galactinol synthase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
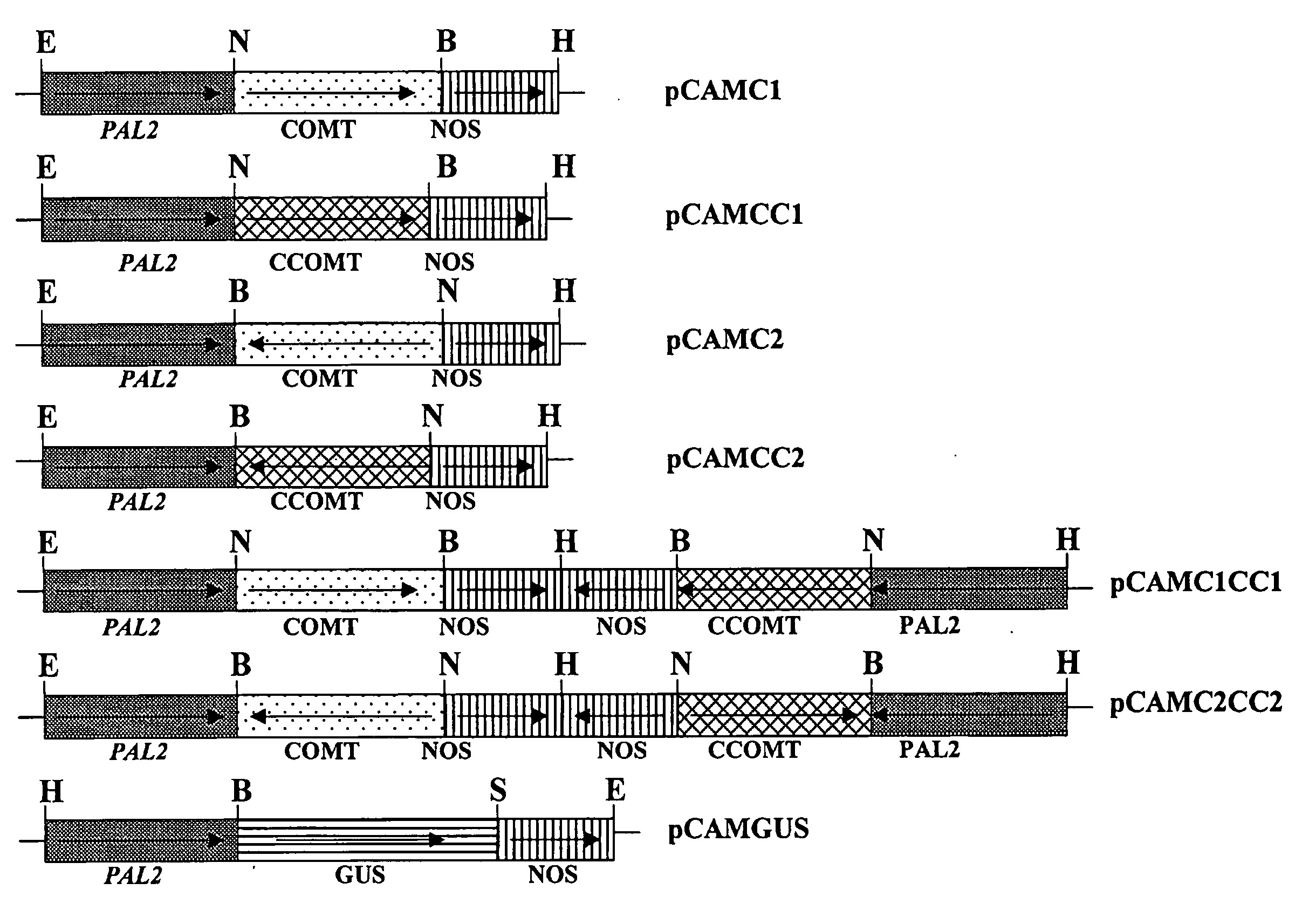
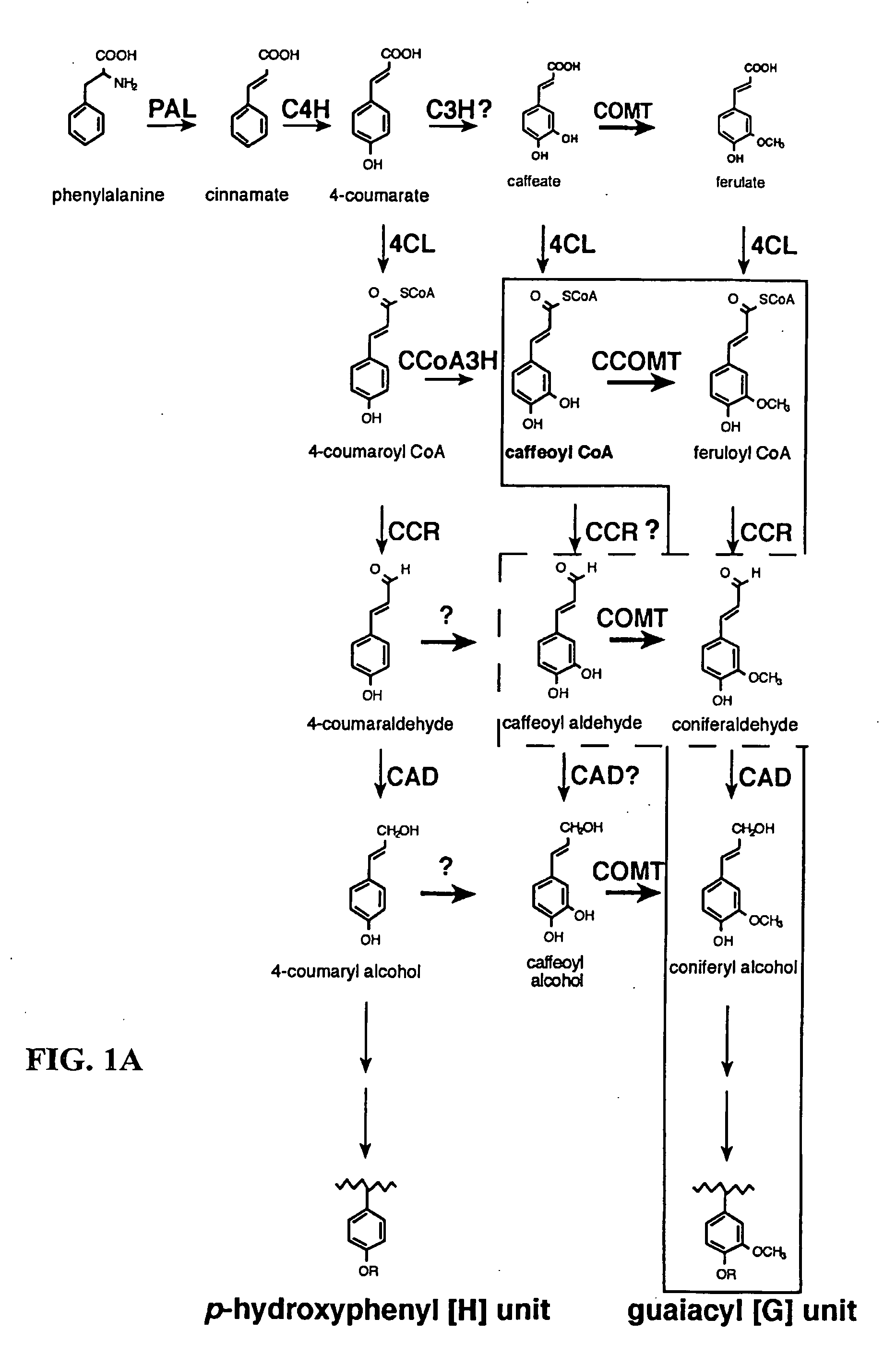
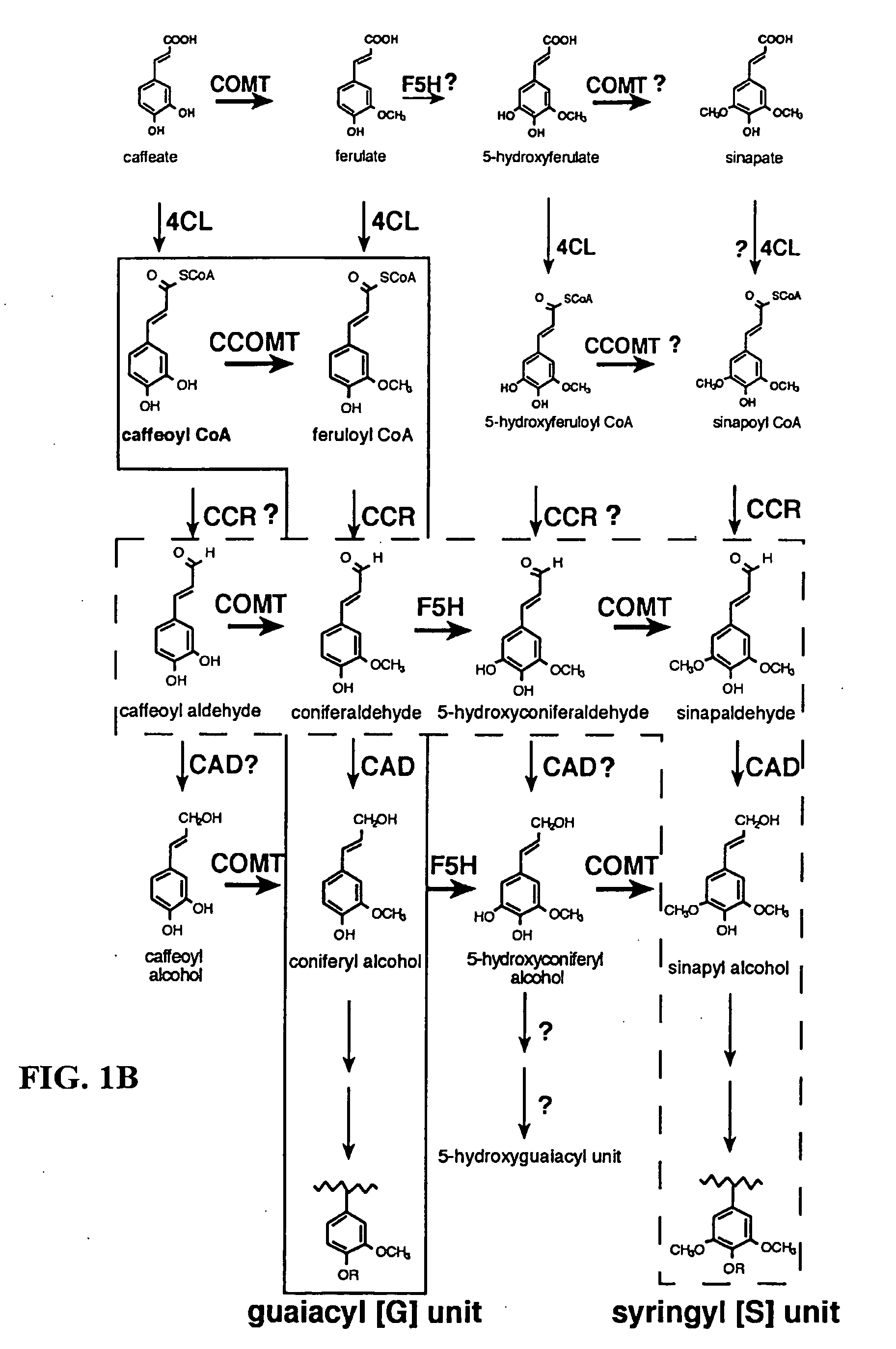
Method for modifying lignin composition and increasing in vivo digestibility of forages
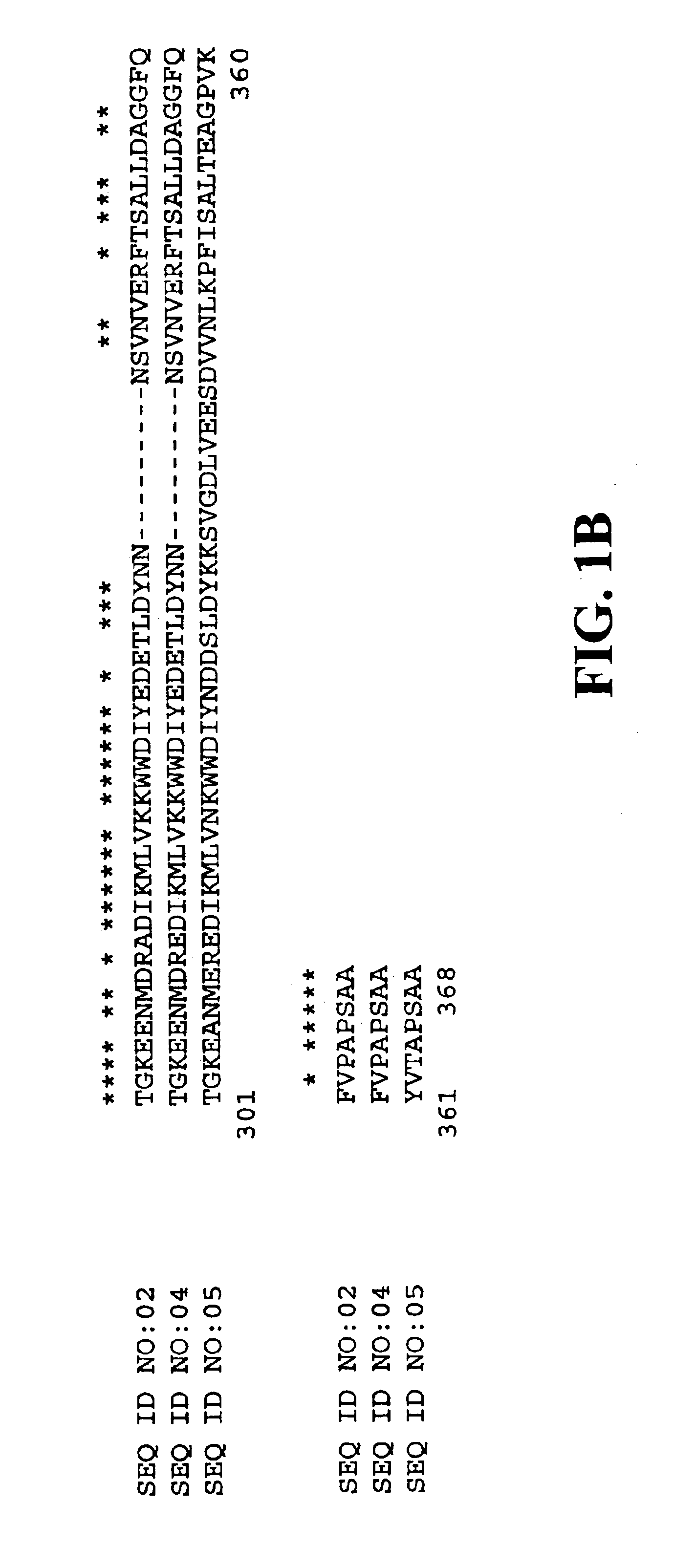
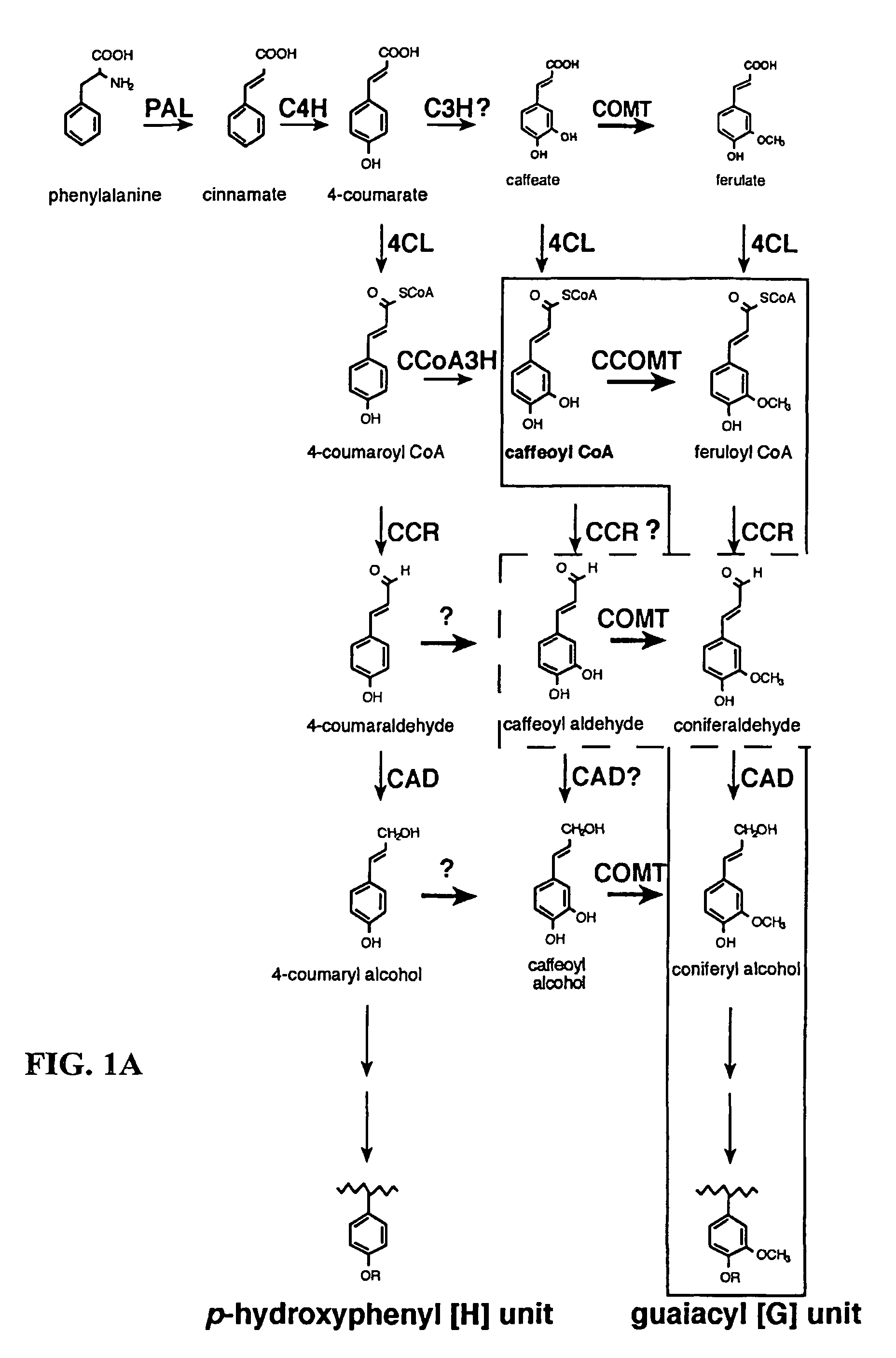
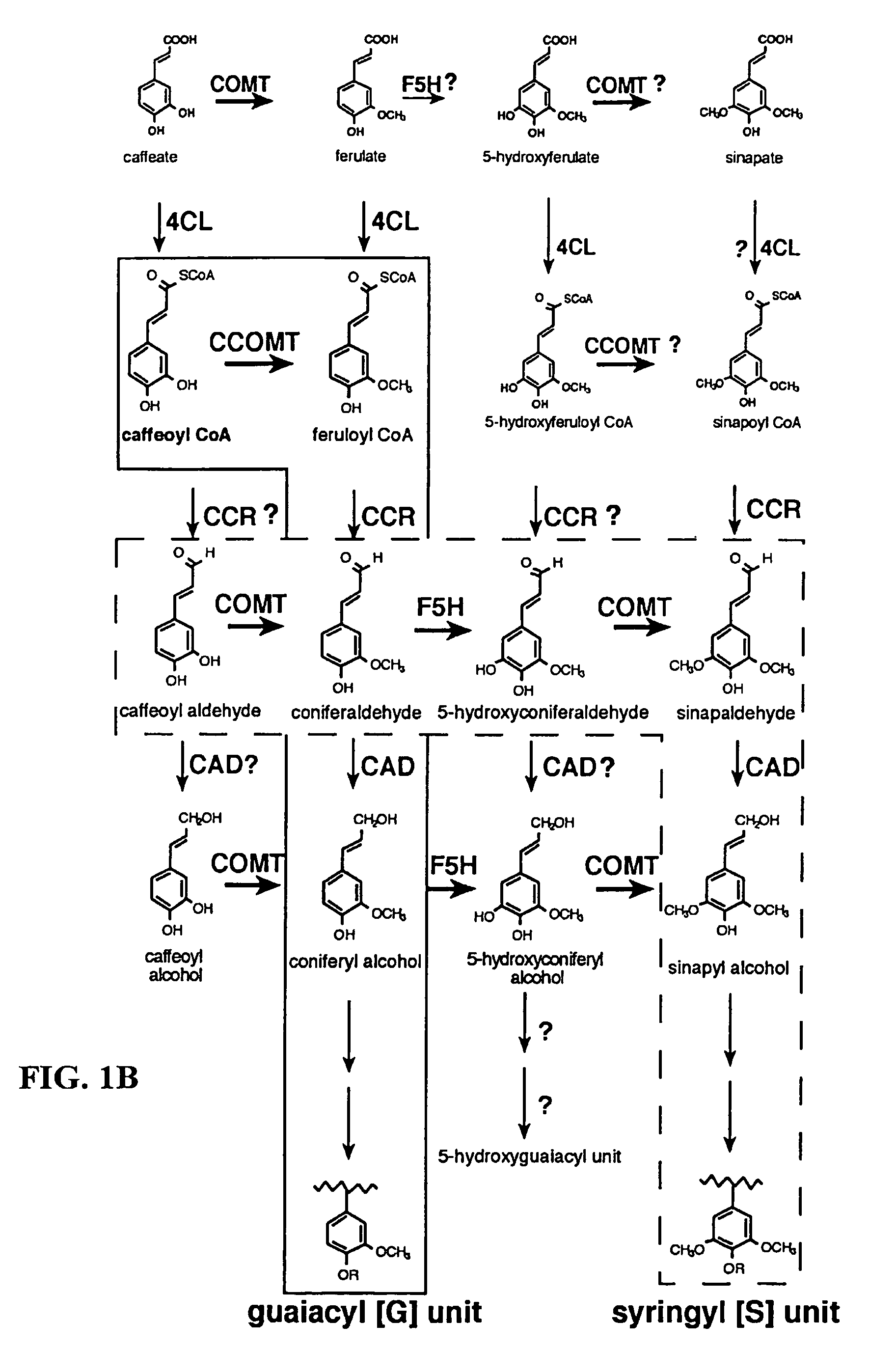
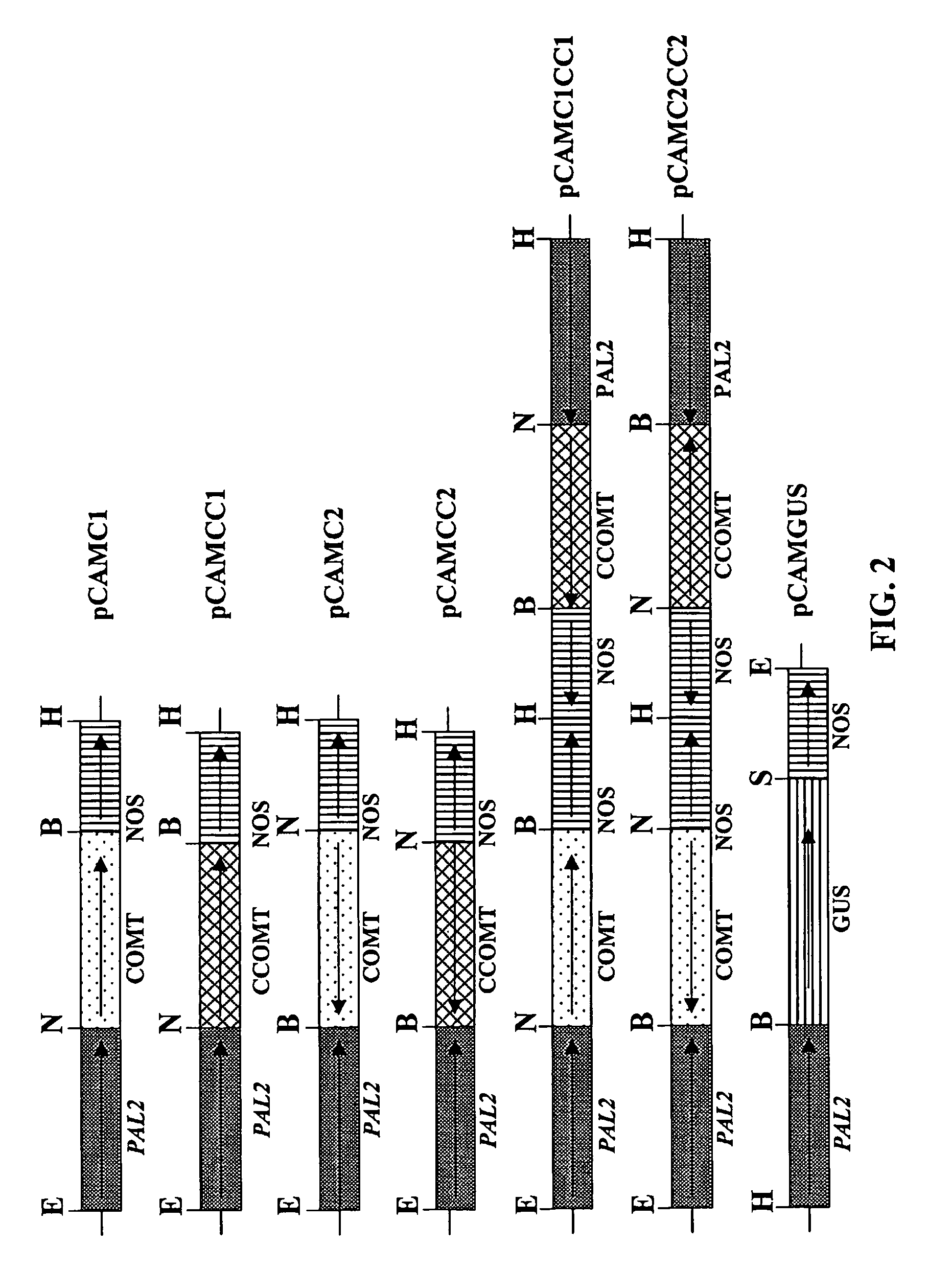
InactiveUS7888553B2Improve digestibilityTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationOpen reading frame
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Plastidic phosphoglucomutase genes
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a plastidic phosphoglucomutase protein is disclosed. Also disclosed is the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a substantial portion of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for modifying lignin composition and increasing in vivo digestibility of forages
InactiveUS20090044294A1Improve digestibilityLow lignin contentTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationOpen reading frame
Methods for transforming forage legumes or woody plants with a DNA construct comprising at least one open reading frame encoding for a caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase enzyme or a Medicago sativa caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase enzyme or a fragment thereof in either a sense or antisense orientation under a lignification-associated tissue specific promoter have been found, resulting in the down-regulation of the corresponding homologous gene either through antisense inhibition or sense suppression, as well as reduced lignin content and modified lignin composition in the transgenic plants. The expression of the caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase transgene produces an increased syringyl lignin to guaiacyl lignin ratio in the transformed plant, and greatly improved forage digestibility.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Novel cytochrome P450 monooxygenase
InactiveUS20060156430A1Improve the level ofAnimal feeding stuffOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationNucleotide
This invention relates to an isolated polynucleotide encoding a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that in the presence of linoleic acid results in production of 1-octen-3-ol. The invention also relates to the construction of a recombinant DNA construct comprising all or a portion of the polynucleotide encoding the cytochrome P450 monooxygenases of the invention, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels 1-octen-3-ol in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
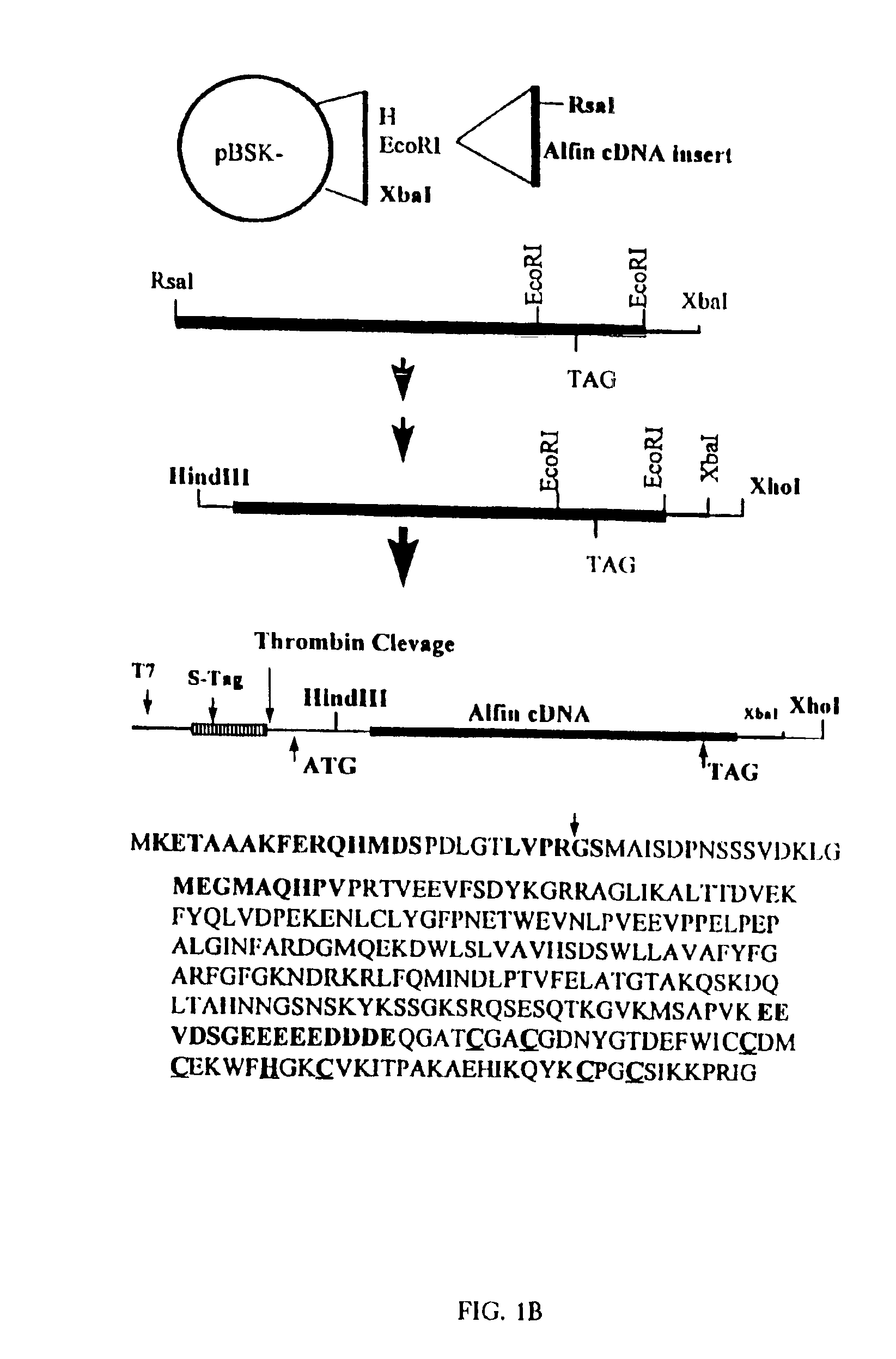
Expression of Alfin 1 and methods for producing transgenic plants having increased root growth and root specific gene activation
InactiveUS6936708B1High expressionImprove salt toleranceSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationAntisense OrientationPlant roots
Alfin1 cDNA encodes a putative transcription factor associated with salt tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L). The recombinant protein binds DNA in a sequence specific manner, including promoter fragments of the salt inducible gene MsPRP2. Alfin1 function was tested in transgenic alfalfa under the control of the 35S promoter in the sense and antisense orientations with the endogenous MsPRP2 as a reporter gene. Calli overexpressing Alfin1 were more resistant to growth inhibition by 171 mM NaCl than vector transformed controls, while calli expressing Alfin1 antisense were more sensitive to salt inhibition. Transgenic plants overexpressing Alfin1 in the sense orientation grew well. In contrast, the antisense transgenic plants grew poorly in soil, demonstrating that Alfin1 expression is essential for normal plant development. Transgenic calli and plant roots overexpressing Alfin1 showed enhanced levels of endogenous MsPRP2 mRNA accumalution. However, MsPRP2 mRNA accumulation was also regulated in a tissue specific manner as shown in leaves of transgenics overexpressing Alfin1. These results suggest that Alfin1 acts as a transcriptional regulator in plants and MsPRP2 expression in alfalfa. Alfin1 overexpressing transgenics showed salinity tolerance comparable to one of our salt-tolerant plants, indicating that Alfin1 also functions in gene regulation in salt tolerance.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Plant genes encoding trehalose metabolism enzymes
This invention relates to isolated nucleic acid fragments encoding trehalose metabolism enzymes, more specifically, alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase. The invention also relates to the construction of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Cancer treatment with retroviral vectors comprising wild-type p53
InactiveUS6998117B1Maintain stabilityImproved ability to inhibit and provideBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntisense OrientationGenomic Segment
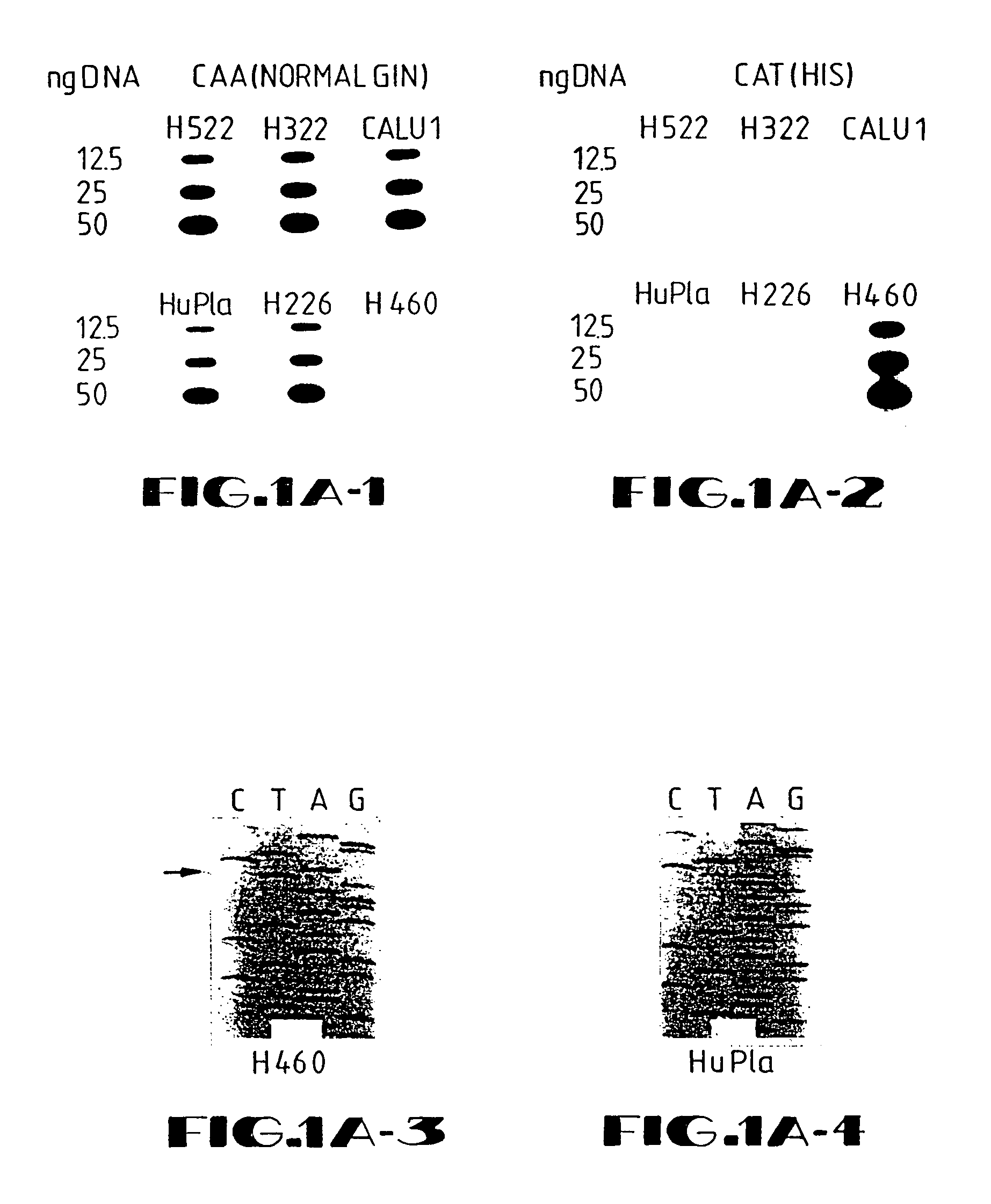
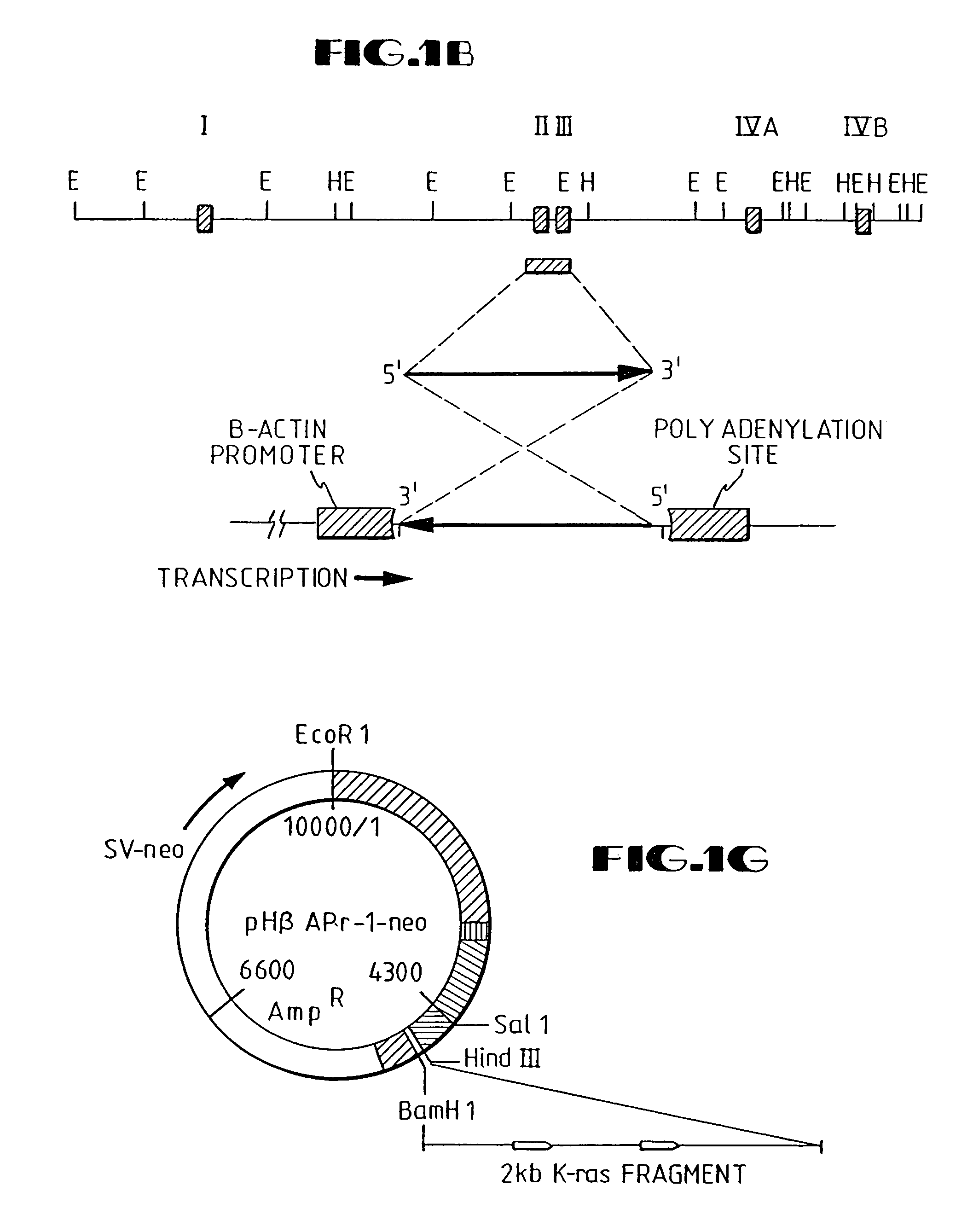
Disclosed are methods and compositions for the selective manipulation of gene expression through the preparation of retroviral expression vectors for expressing antisense sequences, such as K-ras oncogene antisense sequences, or sequences encoding a desired product, such as wild type p53 sequences. Preferred retroviral vectors of the present invention incorporate the β-actin promoter in a reverse orientation with respect to retroviral transcription. Preferred antisense RNA constructs of the present invention employ the use of antisense intron DNA corresponding to distinct intron regions of the gene whose expression is targeted for down-regulation. In an exemplary embodiment, a human lung cancer cell line (NCI-H460a) with a homozygous spontaneous K-ras mutation was transfected with a recombinant plasmid that synthesizes a genomic segment of K-ras in antisense orientation. Translation of the mutated K-ras mRNA was specifically inhibited, whereas expression of H-ras and N-ras was unchanged. A three-fold growth inhibition occurred in H460a cells when expression of the mutated ras p21 protein was down-regulated by antisense RNA and cells remained viable. The growth of H460a tumors in nu / nu mice was substantially reduced by expressed K-ras antisense RNA.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
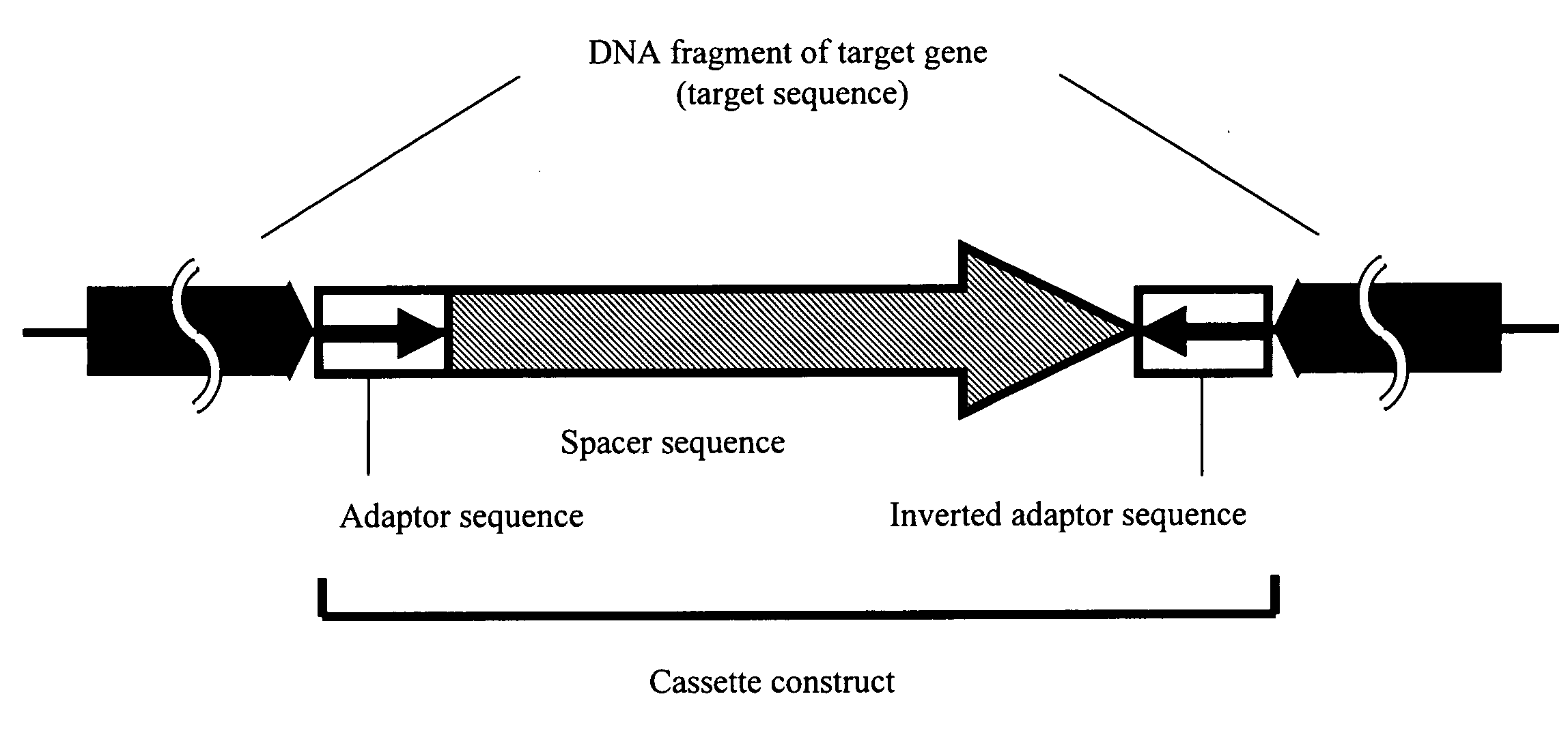
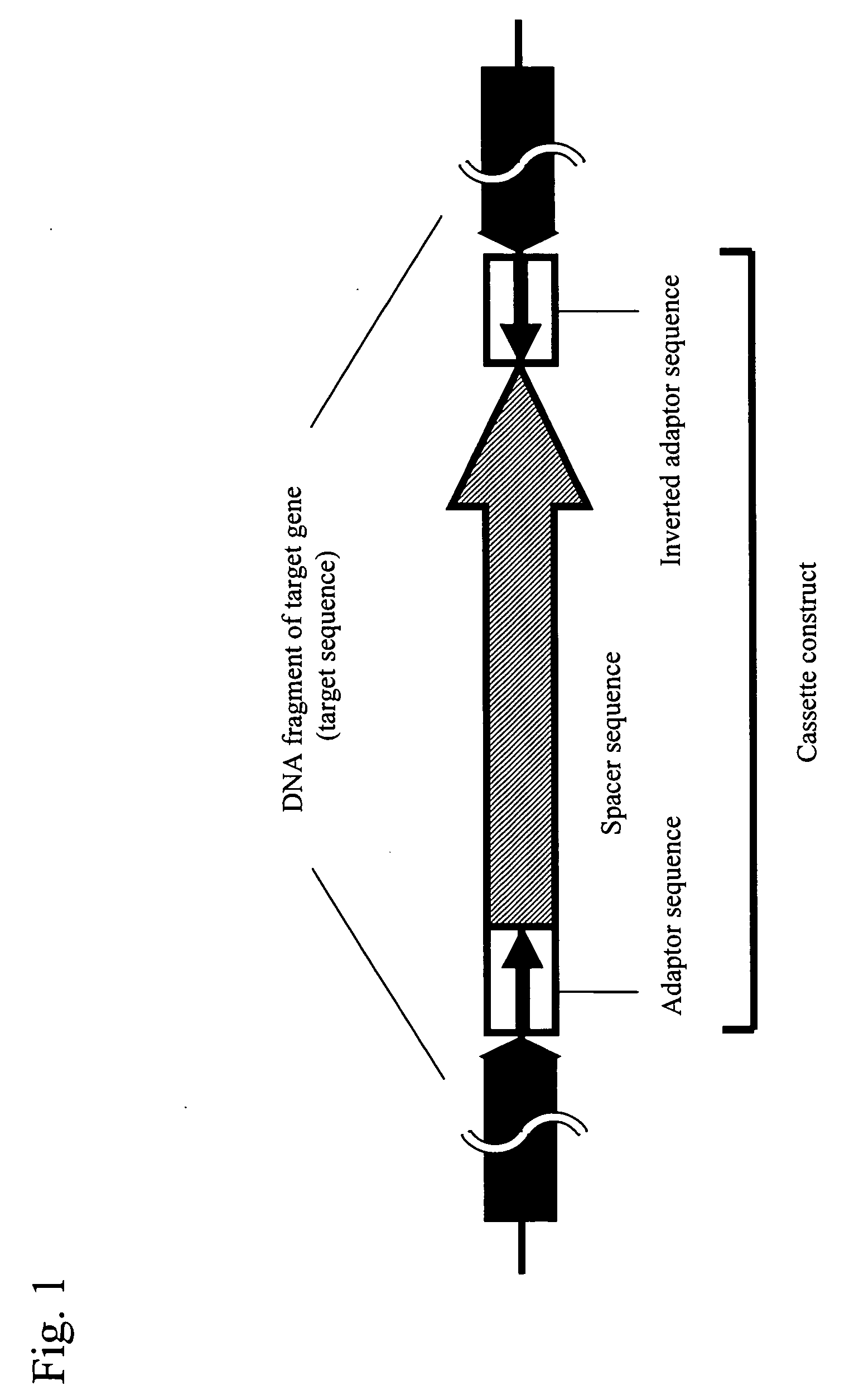
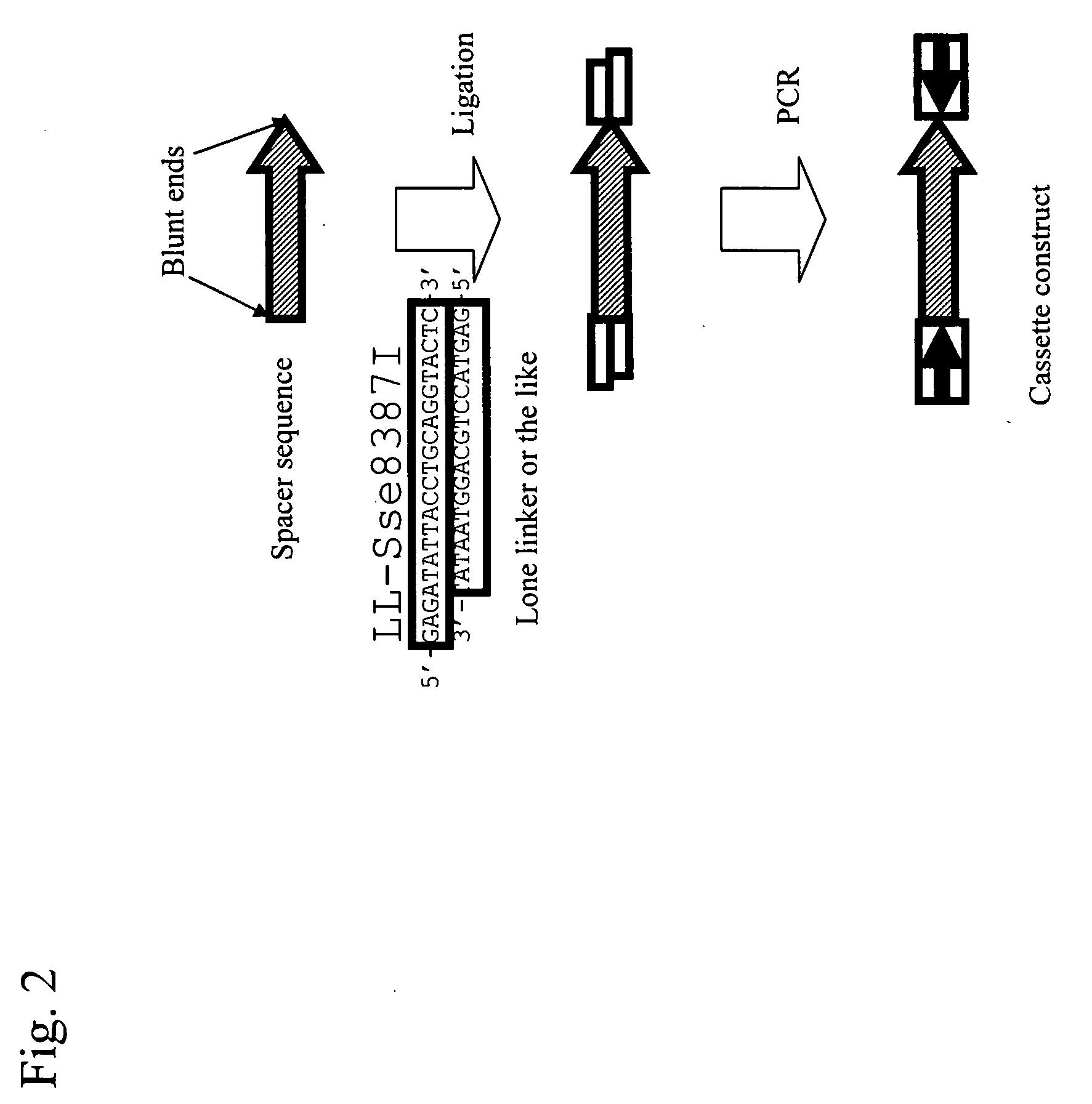
Efficient Method of Preparing Dna Inverted Repeat
Conventional techniques for preparing a chimera gene having an inverted repeat sequence of a target sequence suffer from complications since a target sequence is inserted into 2 sites on a vector in sense and antisense orientations, and restriction enzyme recognition sequences must be independently provided at an insertion site of a vector and both ends of the target sequence.In this invention, a cassette construct comprising an arbitrary adaptor sequence and an inverted adaptor sequence separated by an arbitrary spacer sequence or a plasmid vector comprising such cassette construct incorporated therein is prepared, a target sequence is ligated to either or both ends of the cassette construct, or a target sequence is inserted into one end of the cassette construct on the plasmid vector, followed by PCR. Thus, a chimera gene having an inverted repeat sequence is prepared.
Owner:RIKEN
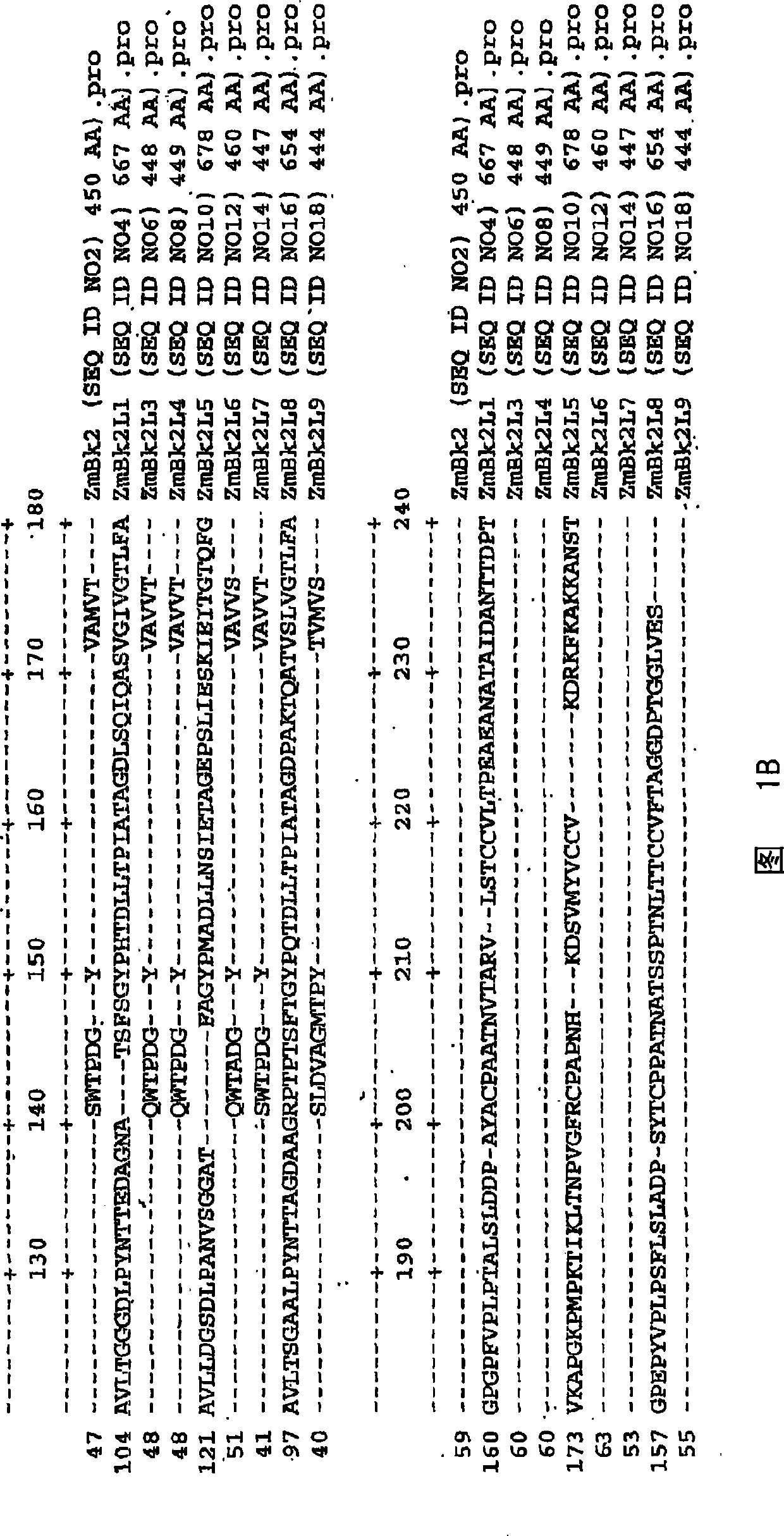
Crisp caudex 2 gene family and correlation method and purpose
This invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding BRITTLE STALK 2-like (Bk2L) family polypeptides. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of a Bk2L polypeptide, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the Bk2L polypeptide in a transformed host cell.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Plant Transcription Factors
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a transcription factor. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the transcription factor, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of accumulated oil in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Enzymes involved in triterpene synthesis
This invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding a CYP51H. The invention also relates to the construction of recombinant DNA constructs comprising all or a portion of the isolated polynucleotide of the invention, in sense or antisense orientation, operably linked to at least one regulatory sequence.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Tetrahydrofolate metabolism enzymes
InactiveUS20050034176A1Inhibitory activitySugar derivativesTissue cultureAntisense OrientationTetrahydrofolate metabolism
This invention relates to isolated nucleic acid fragments encoding 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. The invention also relates to the construction of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Nucleic acid sequences encoding isoflavone synthase
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid sequence encoding isoflavone synthase. The invention also relates to the construction of chimeric sequences encoding all or a substantial portion of the enzymes, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric sequence results in production of altered levels of the enzyme in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
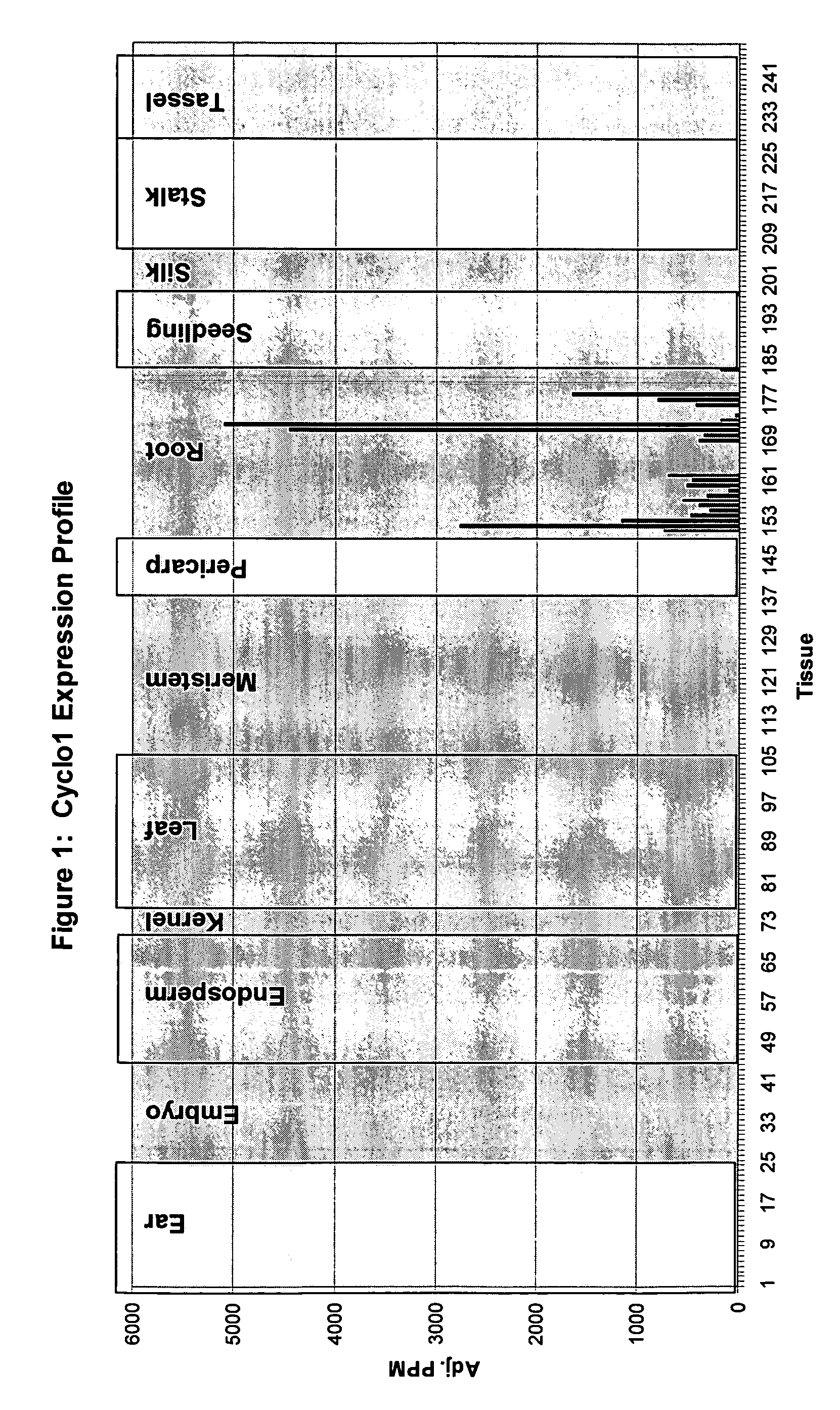
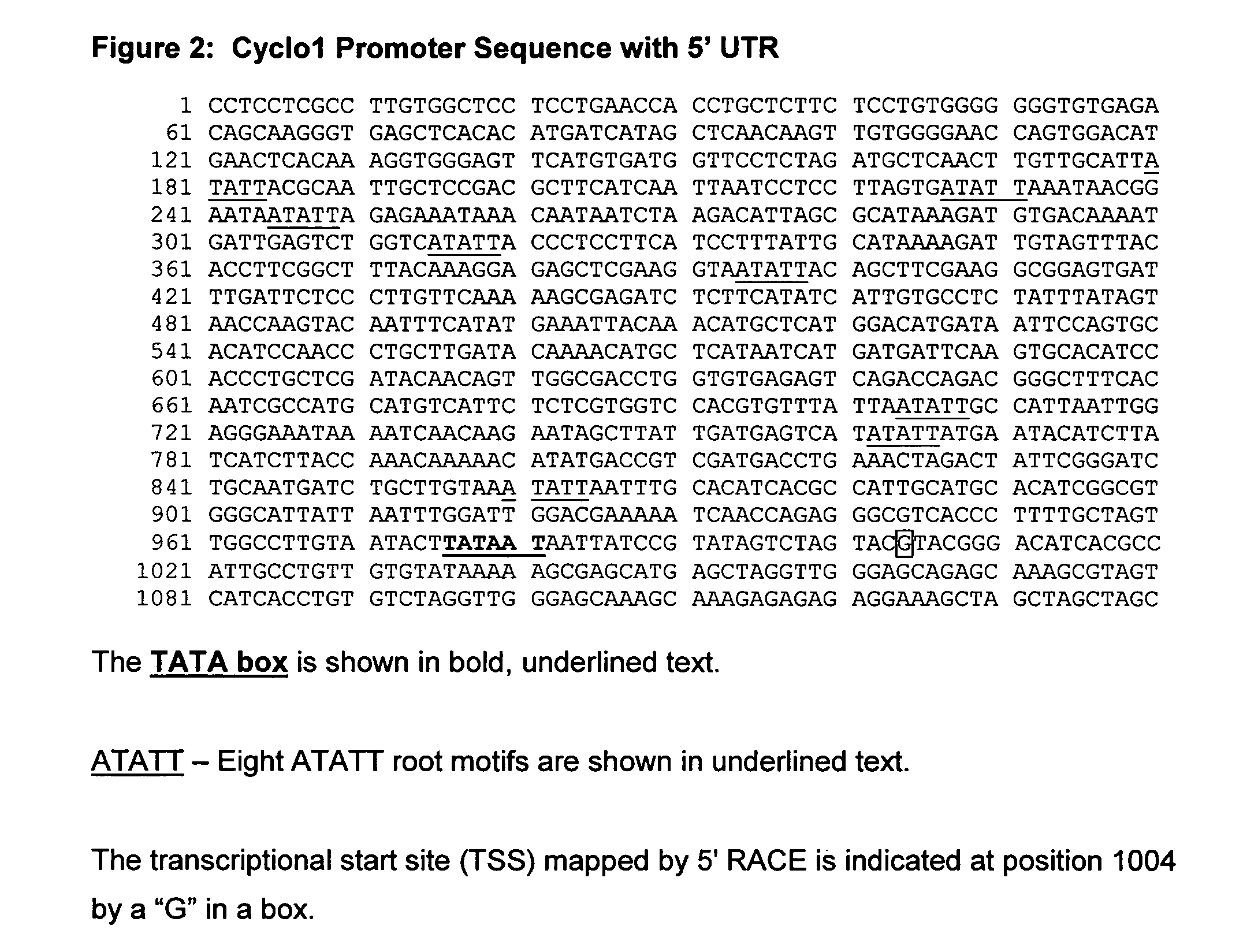
Maize Cyclo1 gene and promoter
ActiveUS7268226B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousAntisense Orientation
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of heterologous nucleotide sequences in a plant. Compositions include a novel nucleotide sequence for a root-preferred promoter for the gene encoding Cyclo1. A method for expressing a heterologous nucleotide sequence in a plant using the promoter sequences disclosed herein is provided. The method comprises stabling incorporating into the genome of a plant cell a nucleotide sequence operably linked to the root-preferred promoter of the present invention and regenerating a stably transformed plant that expresses the nucleotide sequence. The present invention also relates to isolated nucleic acids encoding plant cyclotides. The invention relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the plant cyclotides, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in the production of altered levels of plant cyclotides in a transformed host cell.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Process for the production of plants with enhanced growth characteristics
InactiveUS6846969B2Enhance plant growthImprove growth performanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyAntisense Orientation
The invention is drawn to plant cell transformation with a nucleic acid construct comprising a prokaryotic ammonium-specific asparagine synthetase, type A, coding sequence, operably linked to a chloroplast transit peptide-encoding sequence, wherein said plant cells also contain a nucleic acid construct comprising a chloroplastic glutamine synthetase coding sequence in antisense orientation. Plant cells containing both nucleic acid constructs, and plants regenerated therefrom, exhibit improved growth characteristics.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Nucleic acid molecules encoding cyclotide polypeptides and methods of use
The present invention relates to isolated nucleic acids encoding plant cyclotides. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the plant cyclotides, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in the production of altered levels of plant cyclotides in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Plant transcription factors
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a transcription factor. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the transcription factor, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of accumulated oil in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Floral development genes
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Self-fertile apple resulting from S-RNAase gene silencing
InactiveUS20060123514A1HydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationGene silencing
A transgenic plant or tree of Malus sp. comprising tissue derived from cells transformed with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a gametophytic S-RNAse from Malus sp. is provided. The nucleic acid molecule encoding a gametophytic S-RNAase is in a sense or antisense orientation relative to a regulatory region operably linked thereto. The regulatory region controls expression of the nucleic acid molecule, and the transgenic plant or tree exhibits self-compatibility compared to a corresponding non-transformed plant or tree.
Owner:BETTER3FRUIT
Scorpion toxins
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding scorpion toxins that are K-channel agonists. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the K-channel agonists, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the K-channel agonists in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
DNA encoding a plant lipase, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence in plants
InactiveUS7087419B2Extended shelf lifeReduced fruit spoilageBacteriaHydrolasesAntisense OrientationFhit gene
Owner:AGRIBODY TECH INC
Plant cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase homologs
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a lignin biosynthetic enzyme. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the lignin biosynthetic enzyme, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the lignin biosynthetic enzyme in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Corn pullulanase
This invention relates to isolated nucleic acid fragments encoding all or a substantial portion of a corn pullulanase. The invention also relates to the construction of chimeric genes encoding all or a portion of a corn pullulanase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of corn pullulanase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Chalcone isomerase
InactiveUS7202398B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationDNA construct
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a chalcone isomerase is disclosed. Also of concern is the synthesis of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the chalcone isomerase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the chalcone isomerase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com