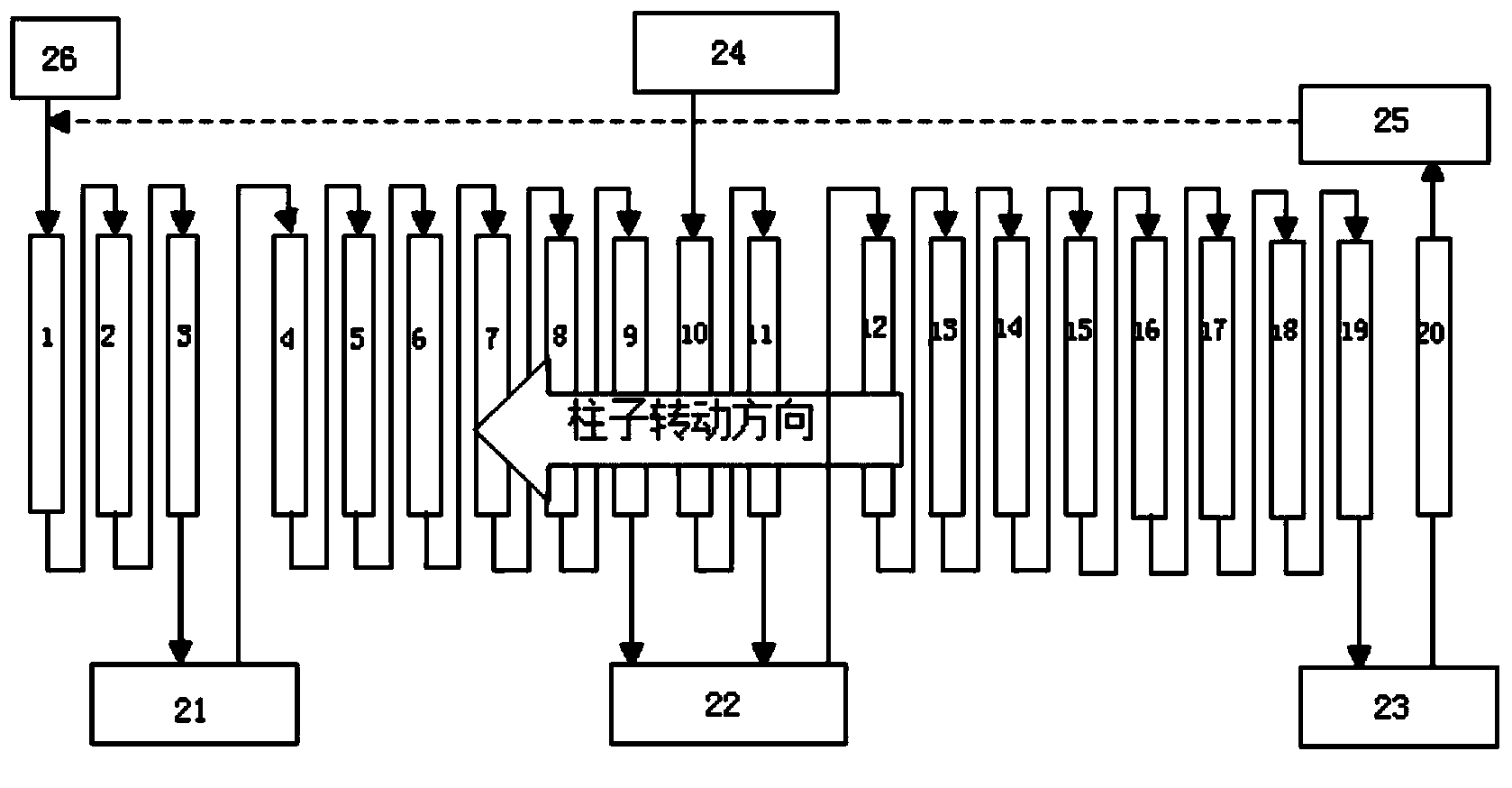
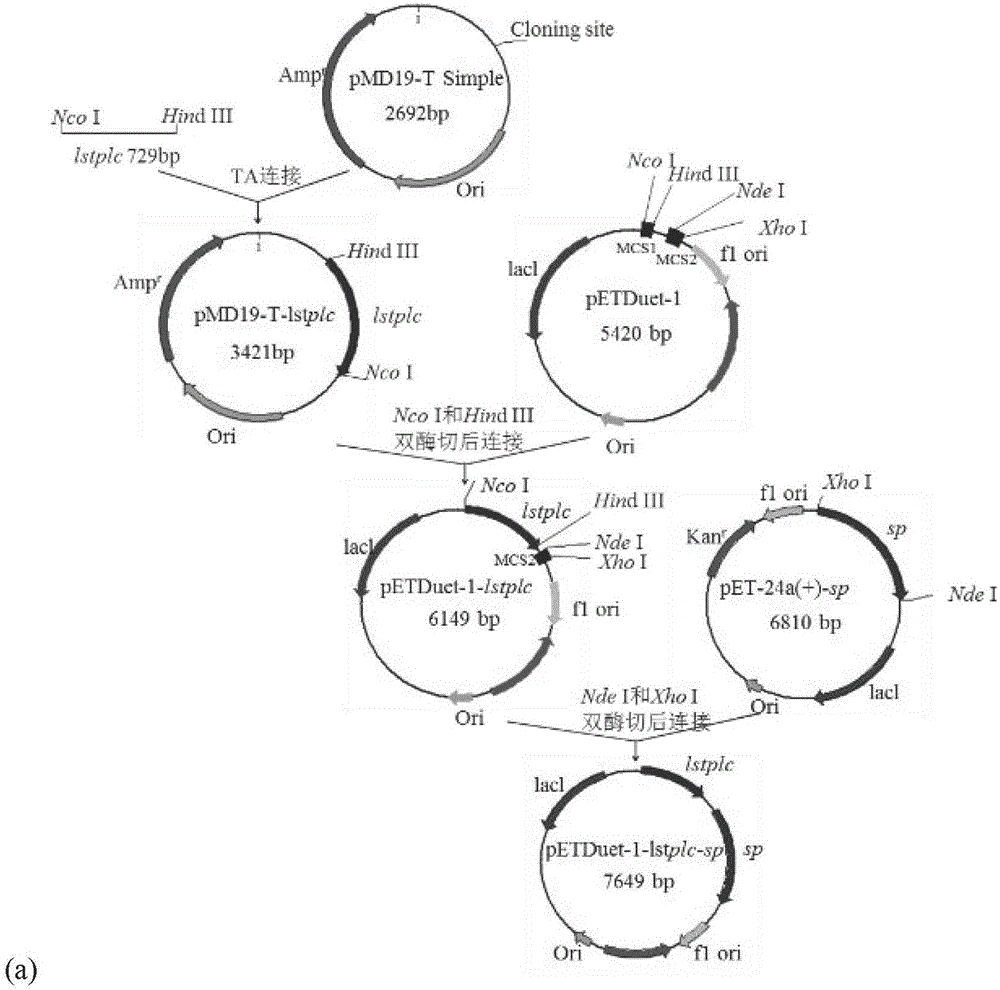
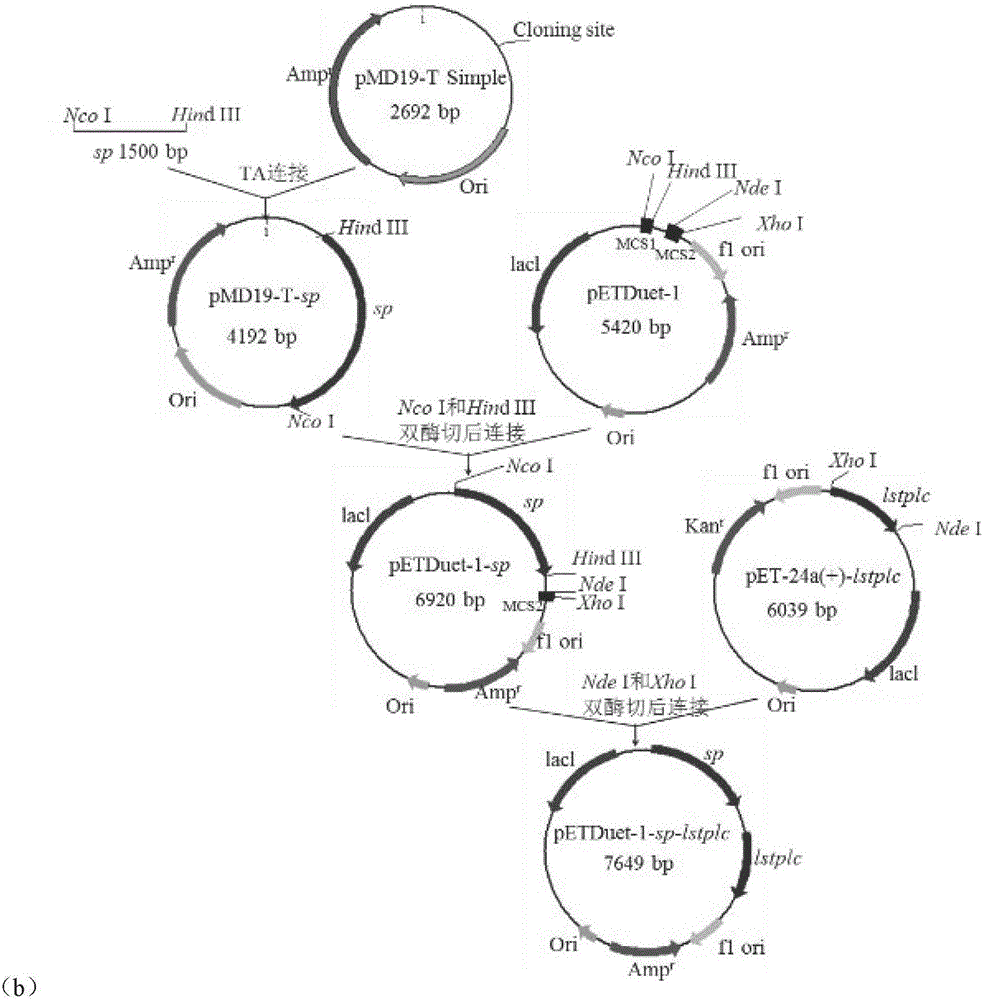
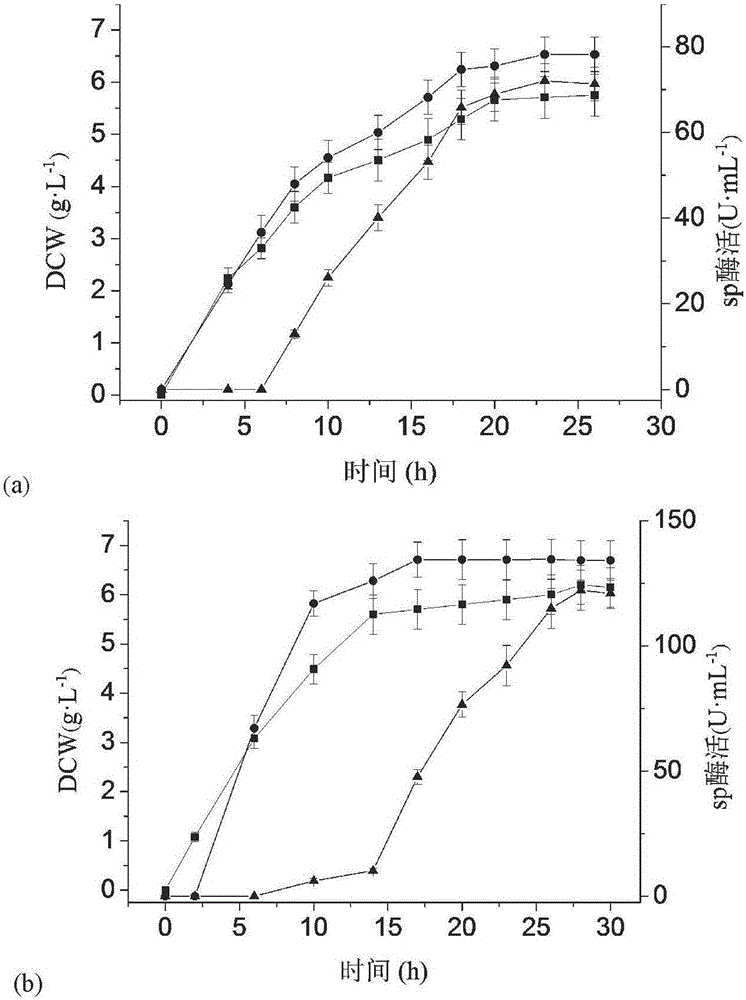
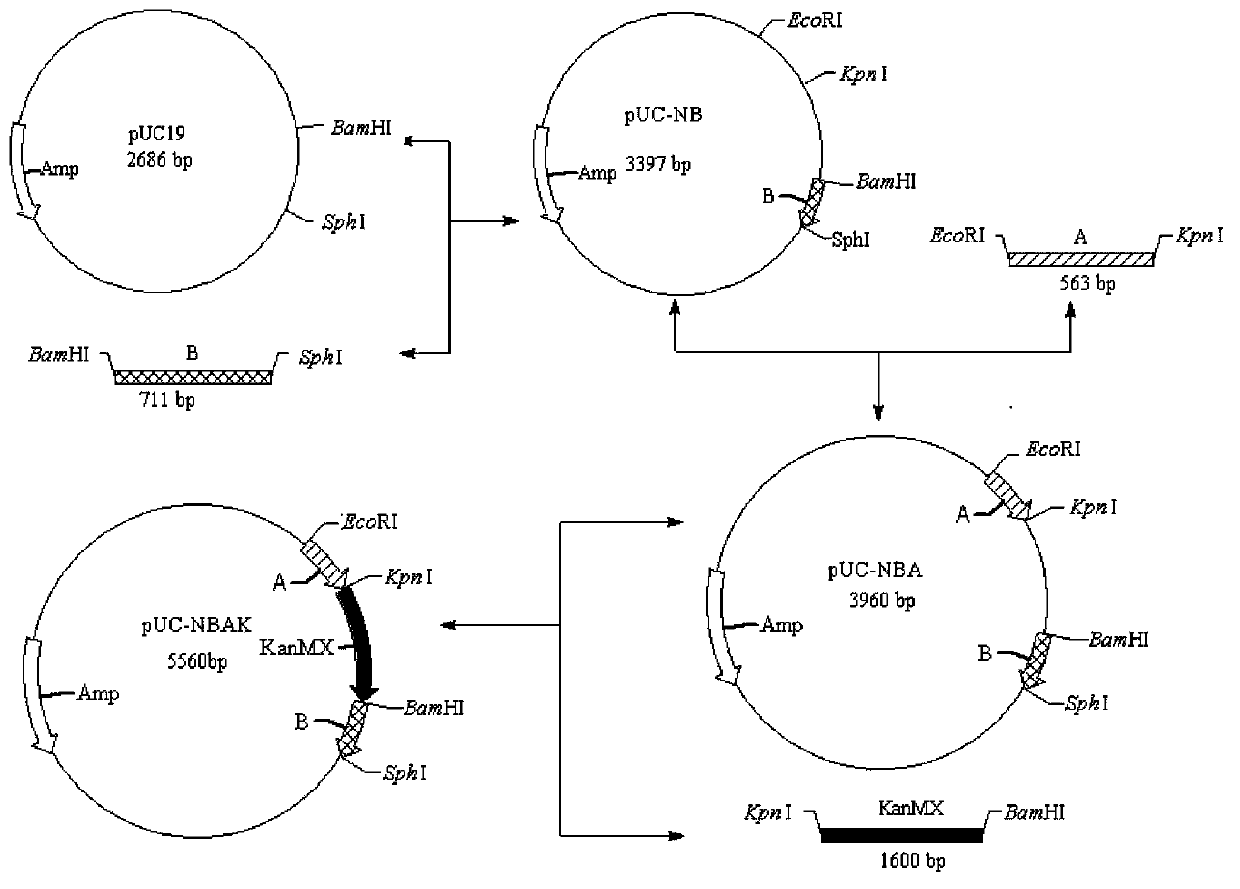
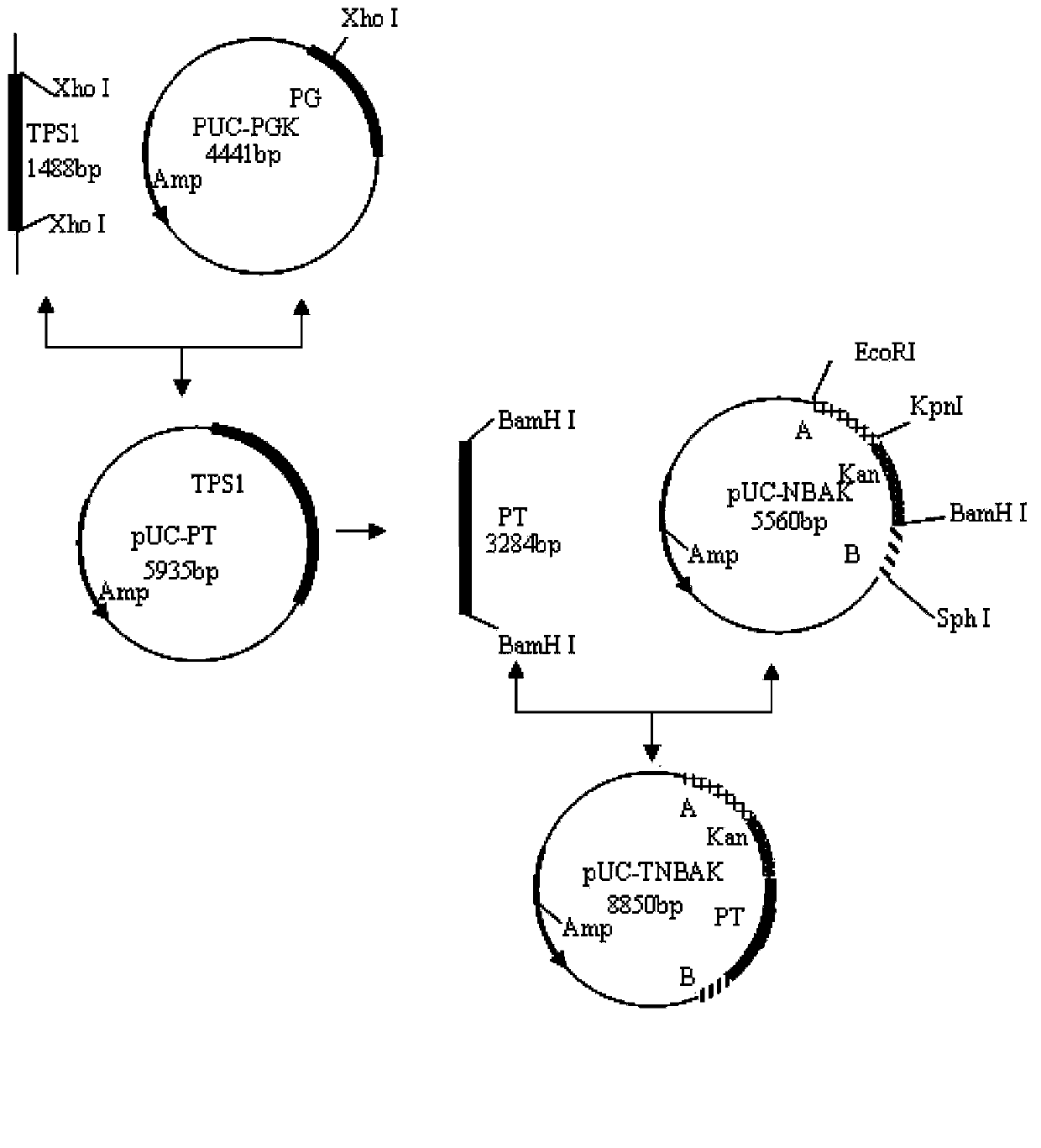
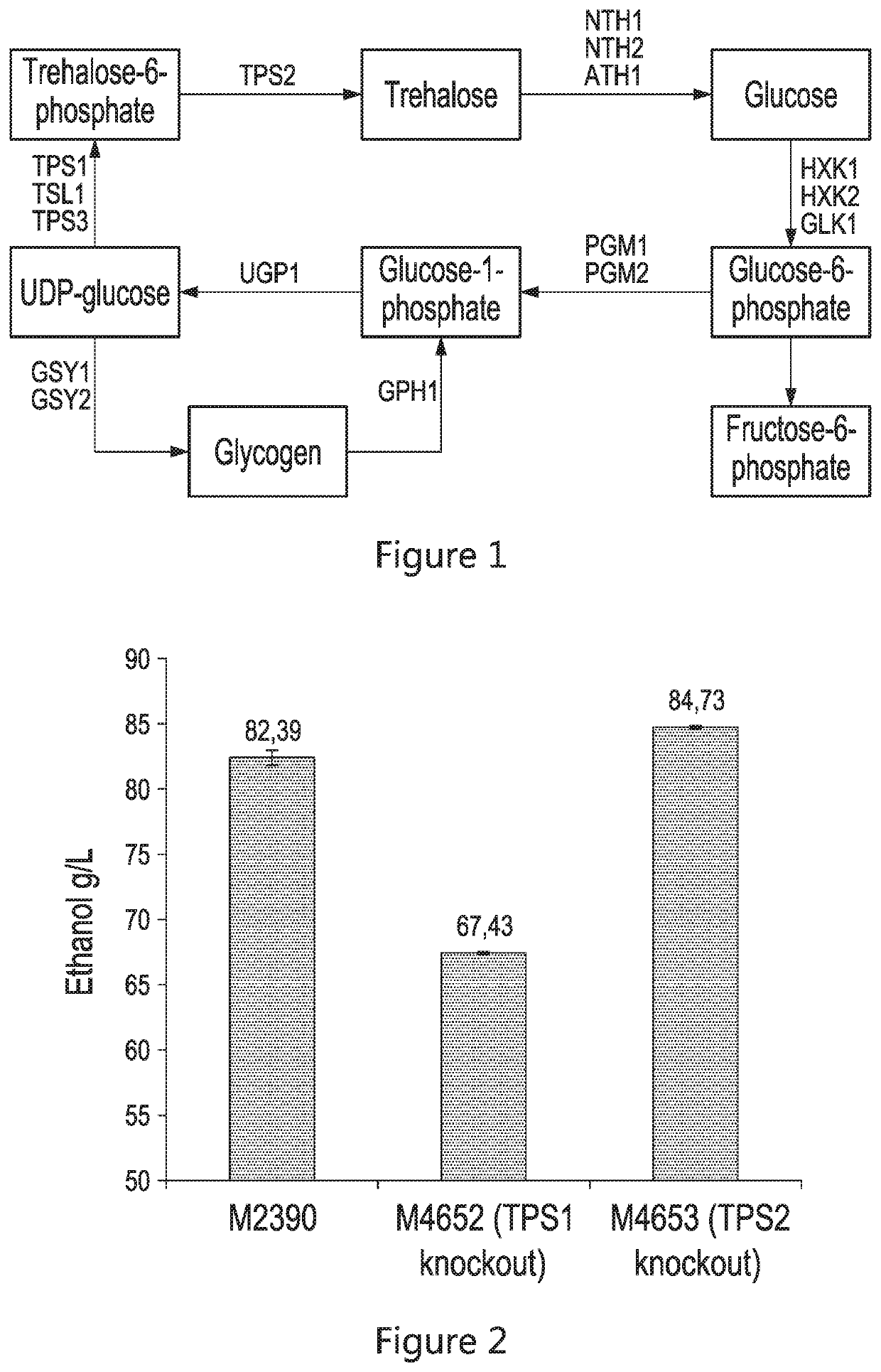
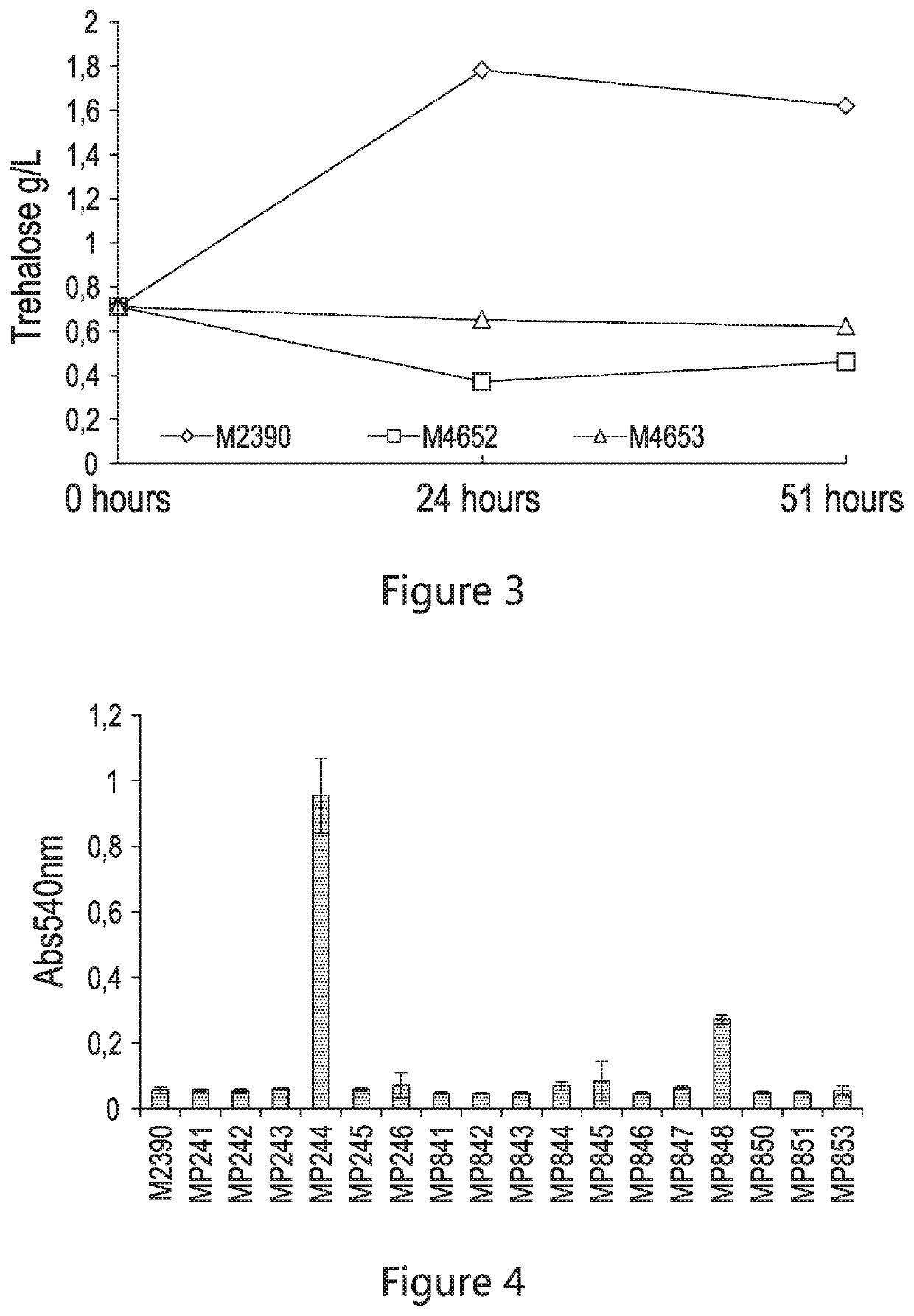
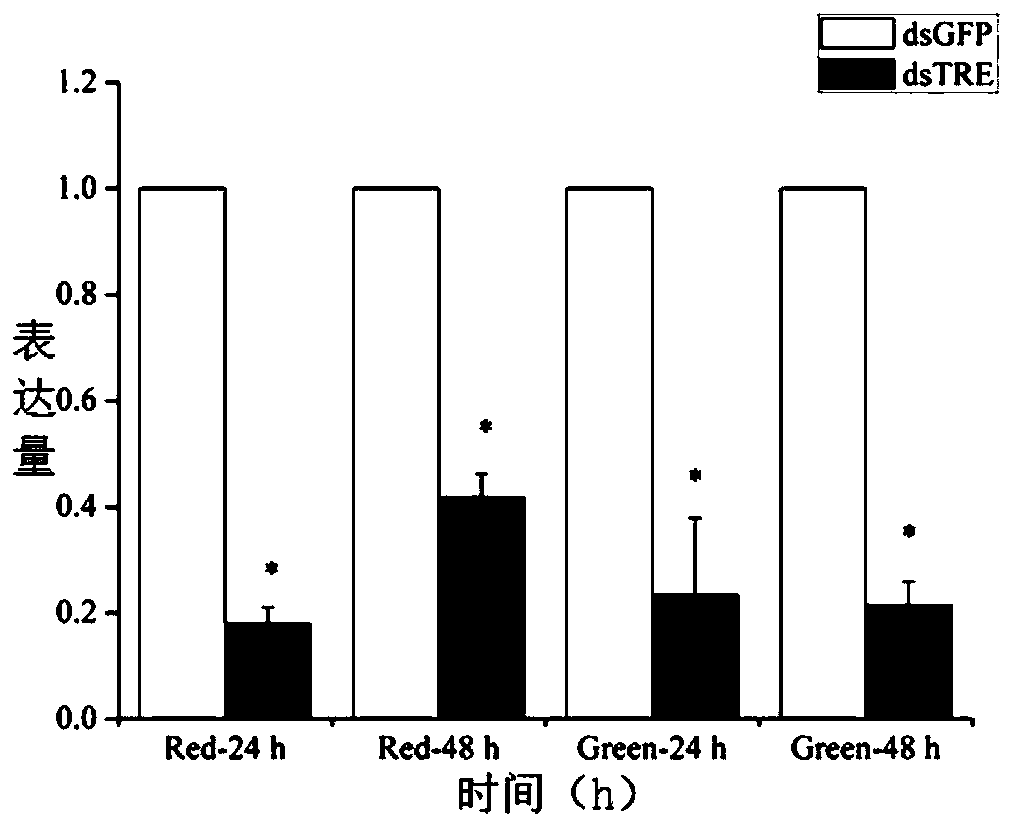
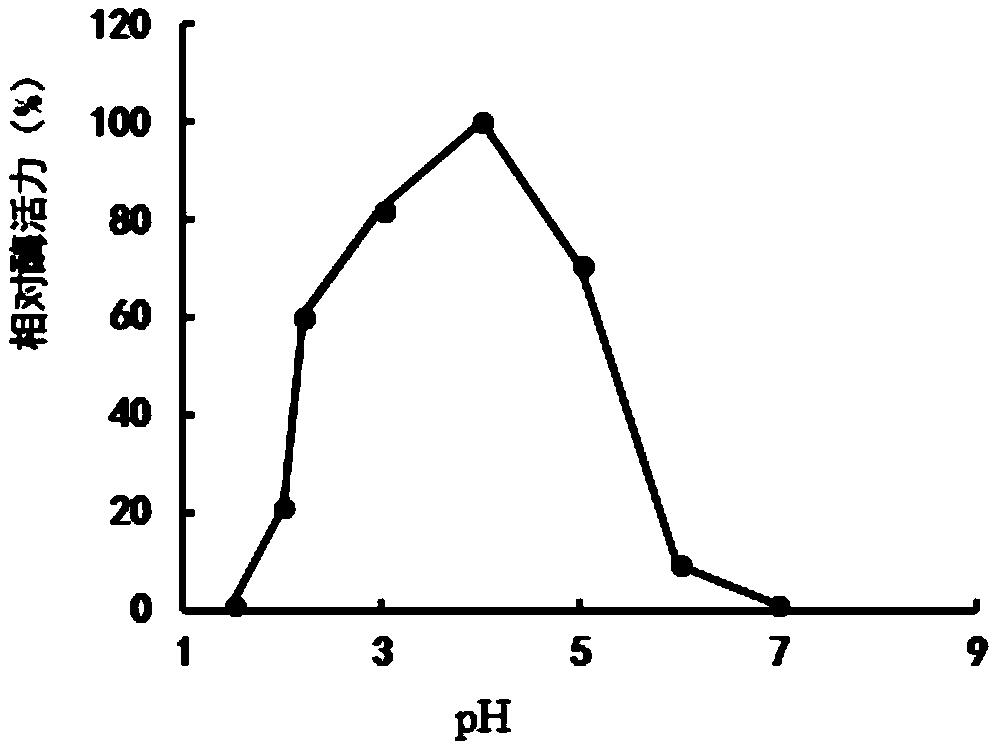
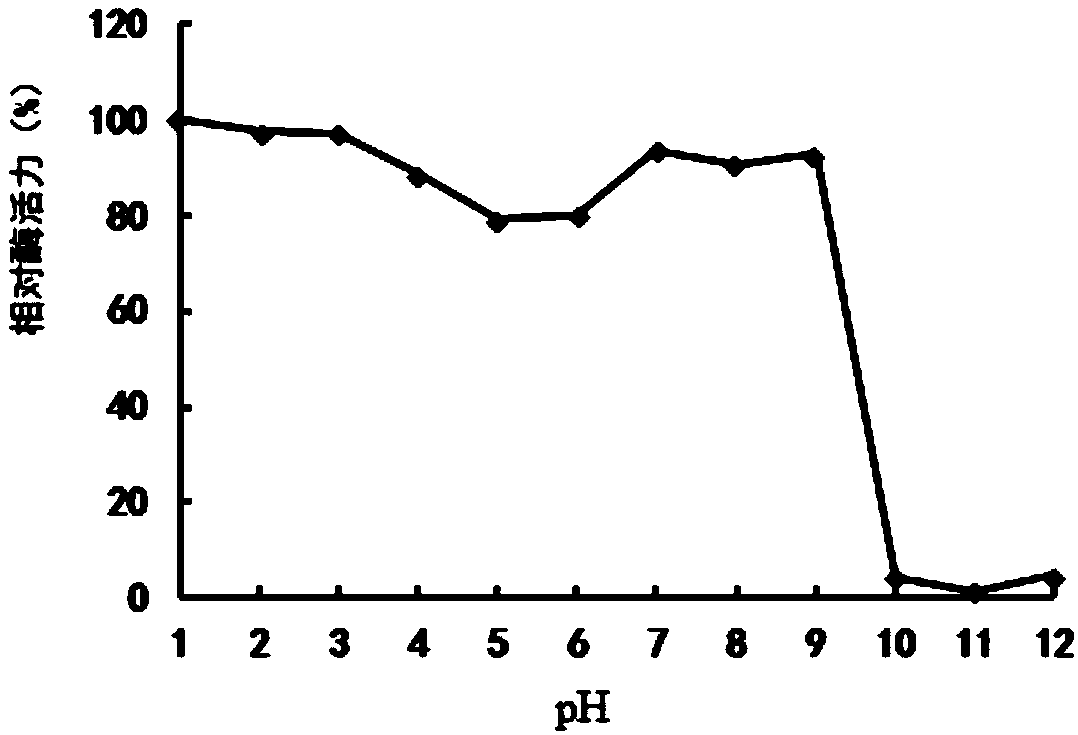
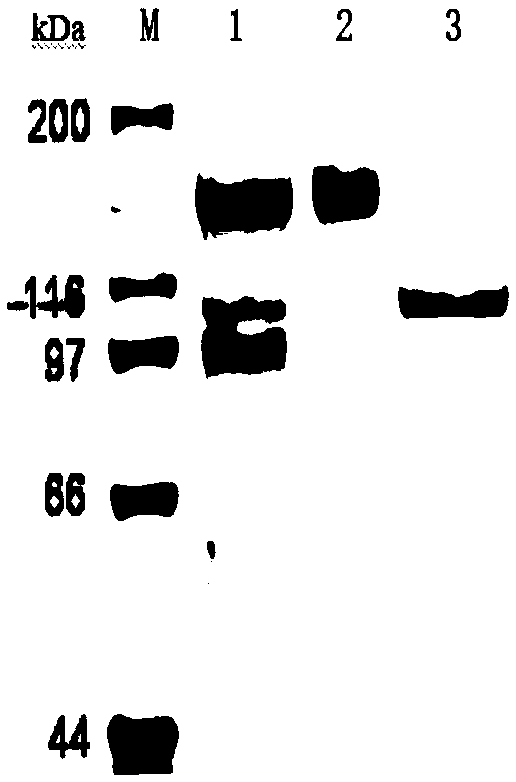Patents
Literature
73 results about "Trehalase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
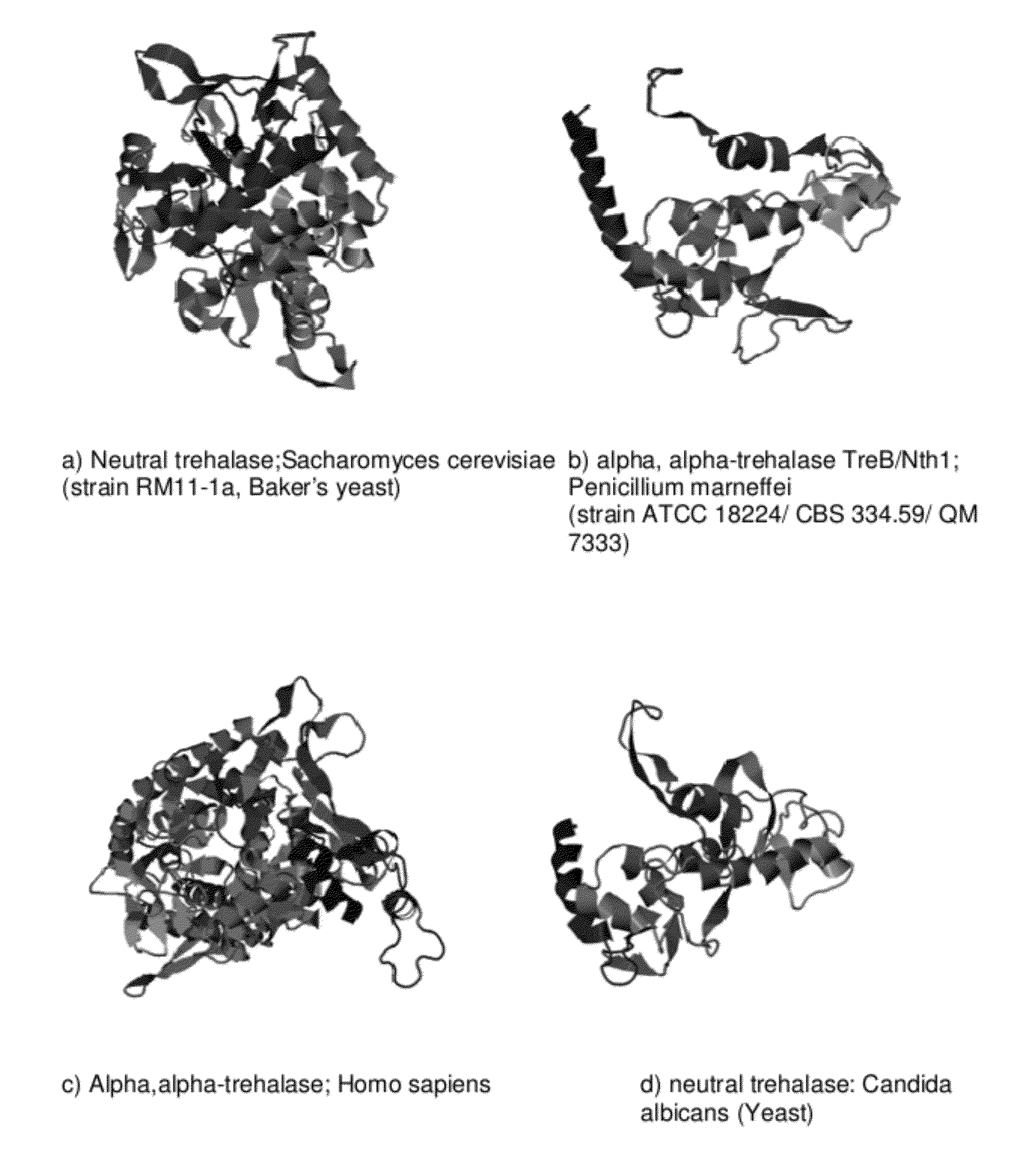
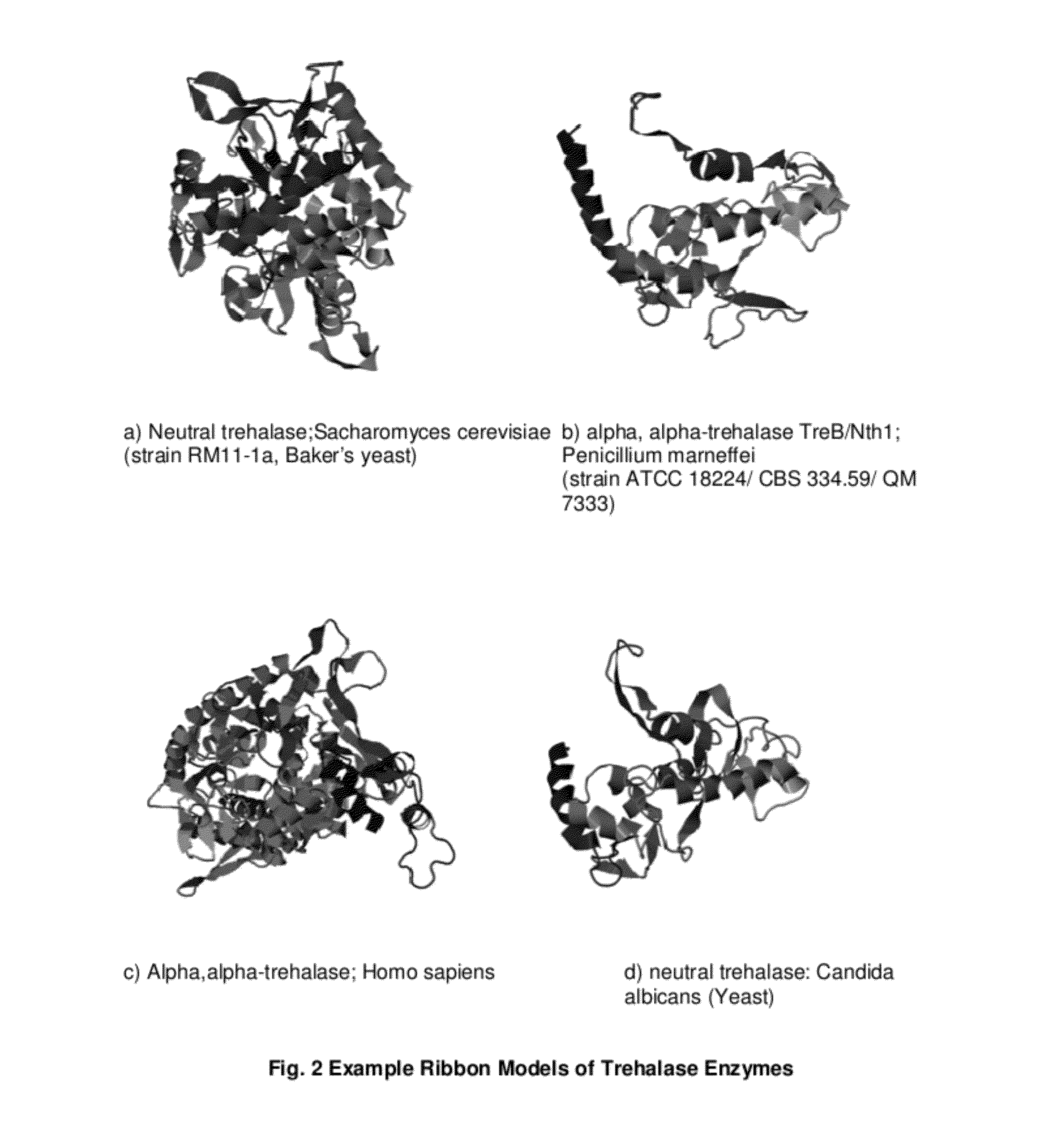
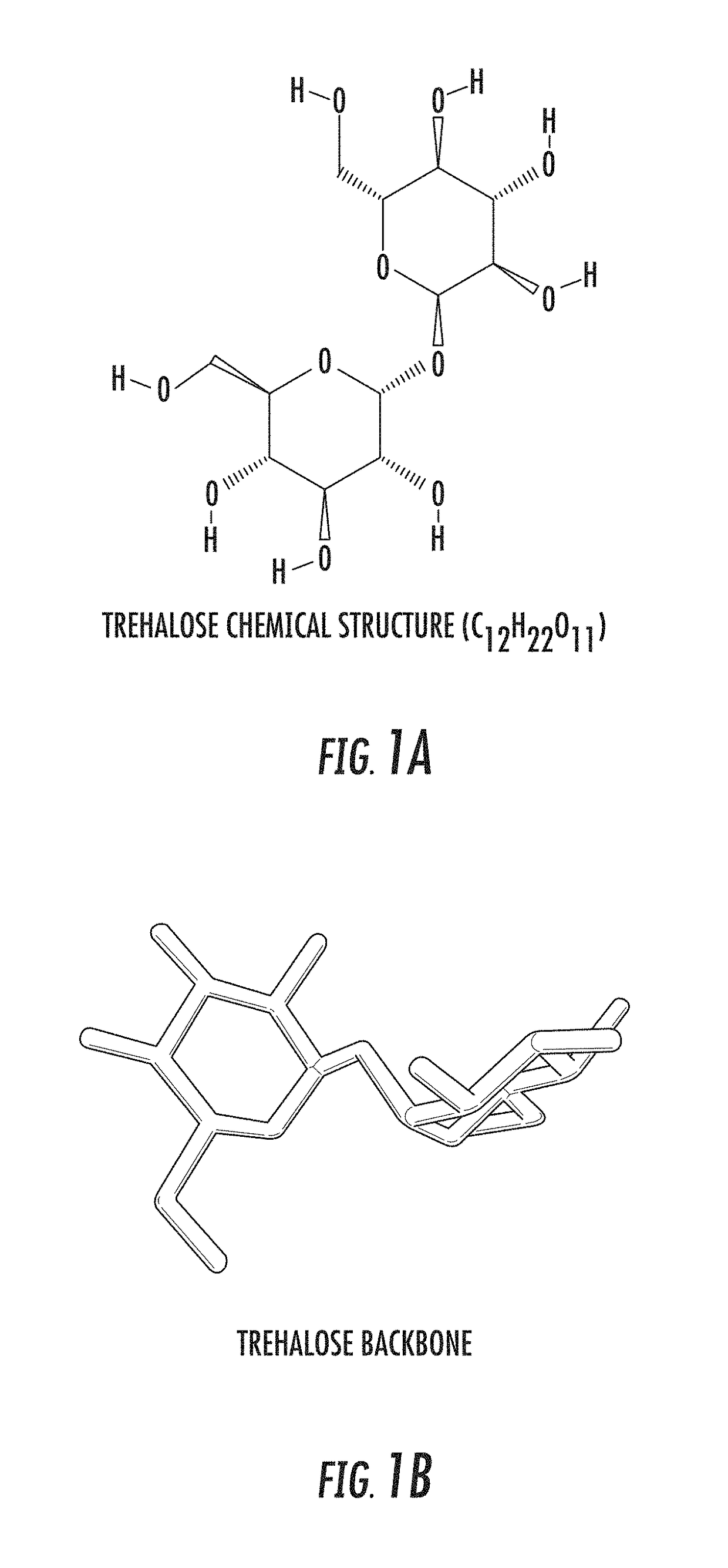
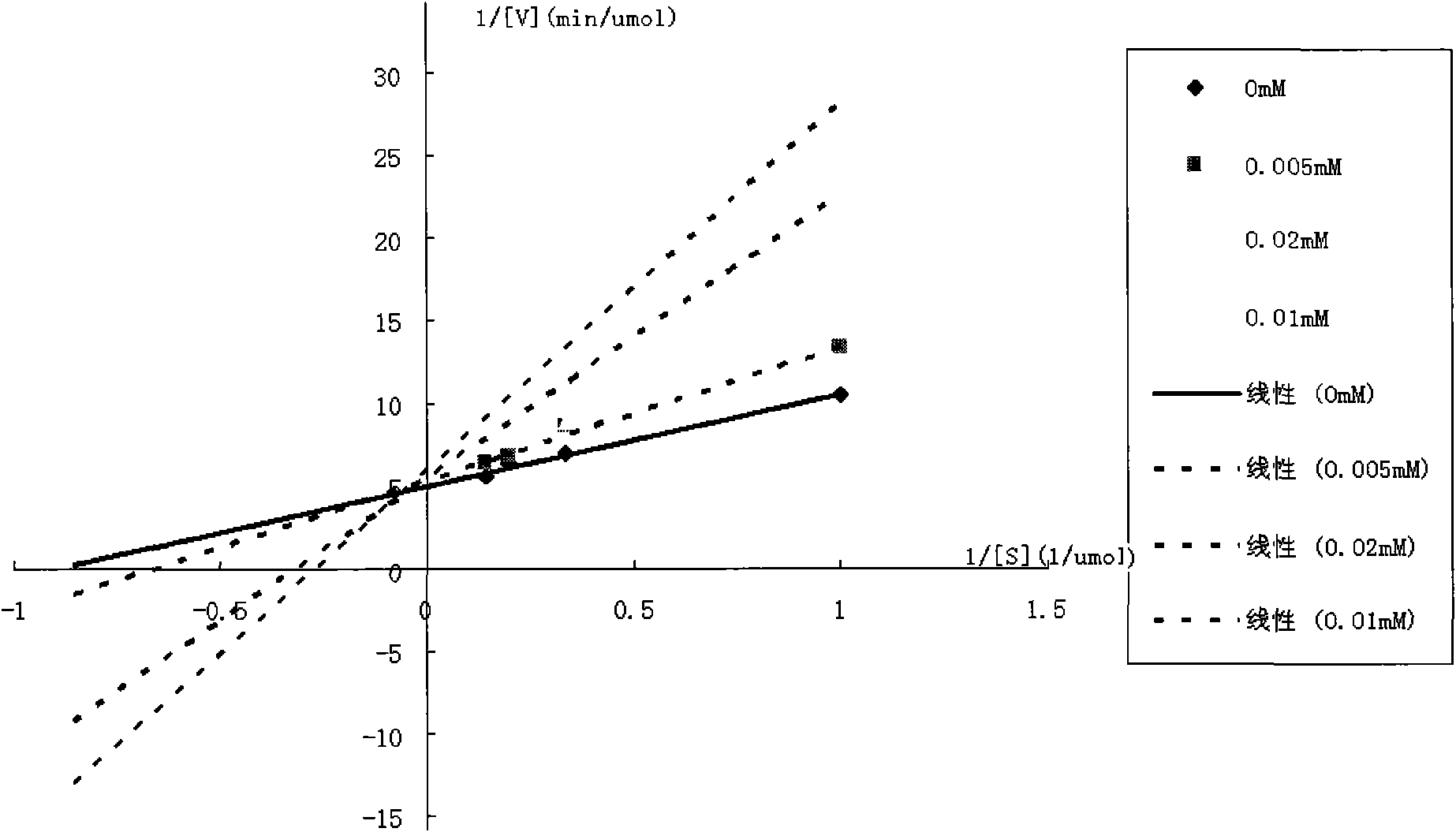
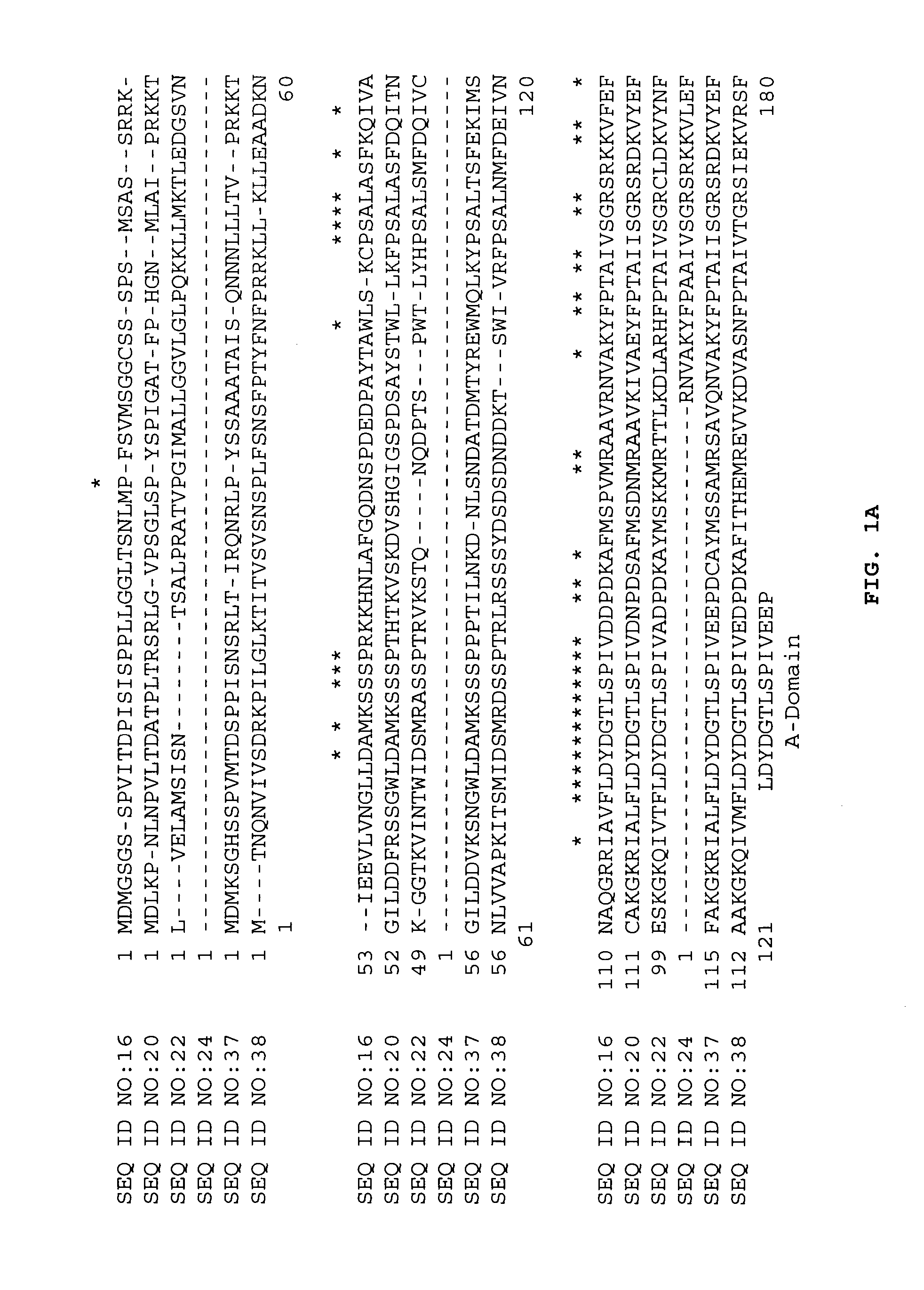
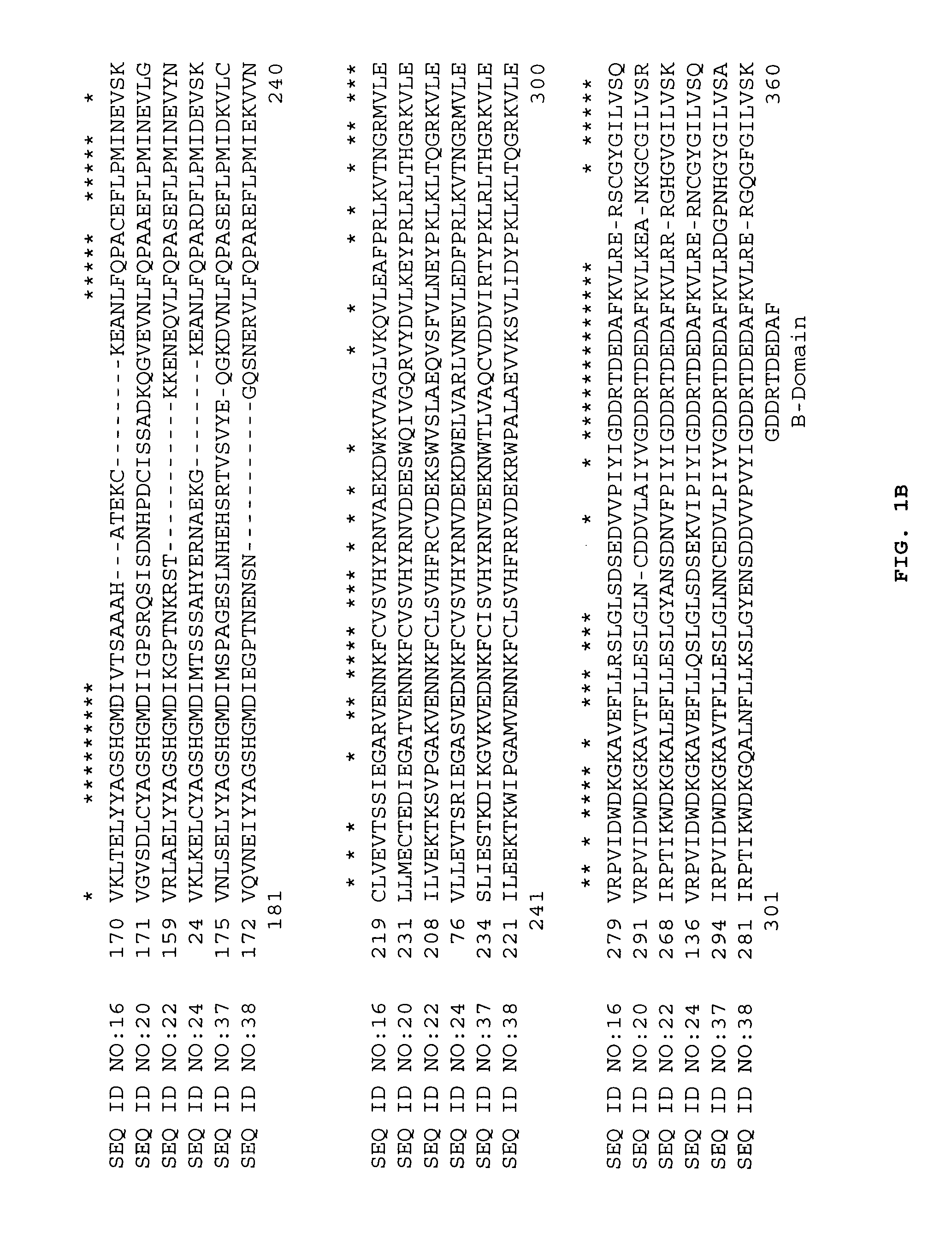
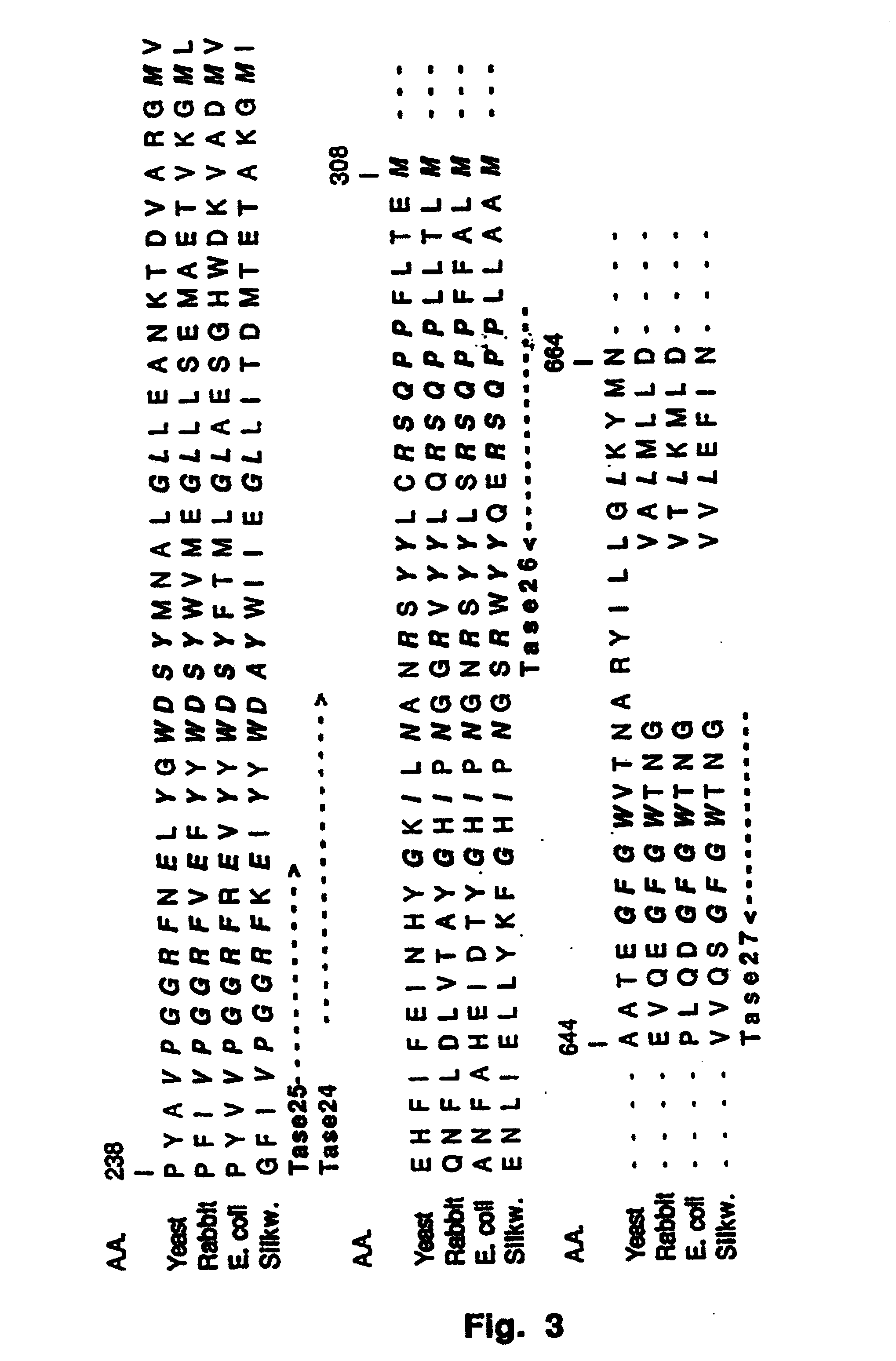
The enzyme Trehalase is a glycoside hydrolase, produced by cells in the brush border of the small intestine, which catalyzes the conversion of trehalose to glucose. It is found in most animals. The non-reducing disaccharide trehalose (α-D-glucopyranosyl-1,1-α-D-glucopyranoside) is one of the most important storage carbohydrates, and is produced by almost all forms of life except mammals. The disaccharide is hydrolyzed into two molecules of glucose by the enzyme trehalase. There are two types of trehalases found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, viz. neutral trehalase (NT) and acid trehalase (AT) classified according to their pH optima [4]. NT has an optimum pH of 7.0, while that of AT is 4.5.
Separation and purification method of trehalose
ActiveCN103450288AHigh purityIncrease profitSugar derivativesDisaccharidesChromatographic separationPurification methods
The invention relates to a separation and purification method of trehalose, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out enzymolysis on a trehalase reaction solution prepared by a trehalose synthase conversion process, and filtering to obtain a trehalose crude solution; (2) decolorizing the trehalose crude solution through activated carbon, and filtering to obtain a mixed solution; (3) passing the mixed solution through an ion exchange resin to obtain a glucose-trehalose sugar solution; and (4) concentrating the glucose-trehalose sugar solution, and separating by continuous chromatography with a simulated moving bed to obtain a trehalose solution and a glucose solution. The trehalase reaction solution generated by converting maltose by trehalose synthase is used as the raw material, the maltose which is isomeric with the trehalose is converted by an enzyme process, and impurity glucose, remaining maltose and impurities, such as proteins, pigments, metallic ions and the like, are removed to obtain the high-purity trehalose.
Owner:ZHUCHENG DONGXIAO BIOTECH
Method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein
PendingCN106754601ALarge domestic and foreign market demandImprove permeabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellularProtein target
The invention discloses a method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Through co-expression phospholipase C, intracellular positioning protein is released to the outsides of cells by means of nonspecific leaking, and high-performance phospholipase C and co-expression recombinant bacteria high in target protein extracellular enzyme activity are obtained by screening. Enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular sucrose phosporylase co-expressing sucrose phosphorylase and phospholipase C is 1445.1U mL-1, and enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular trehalase co-expressing trehalase and phospholipase C is 322.3U mL-1. The method can realize extracellular expression of intracellular positioning protein, improve production efficiency and simplify post-extraction process, has wide application value in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industry and has great demand in market at home and abroad.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
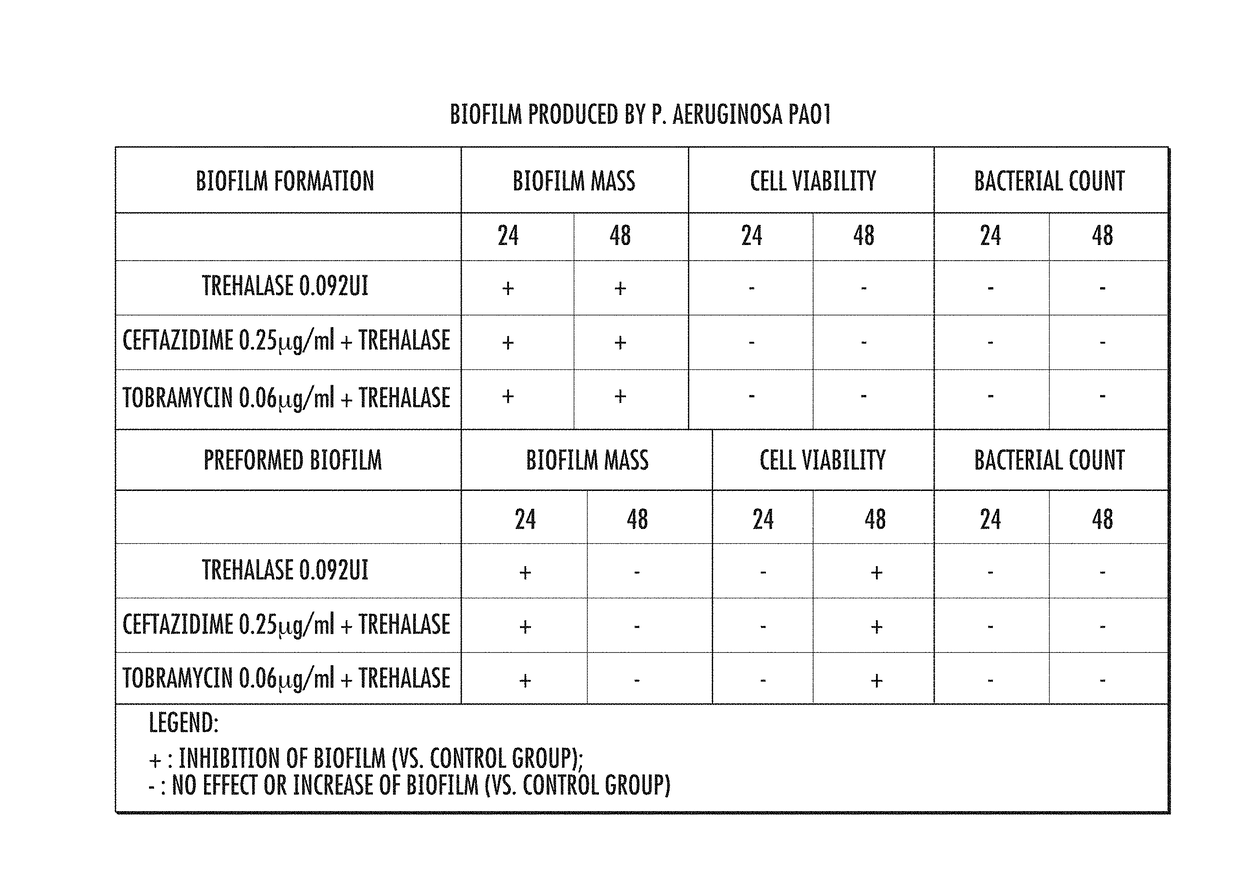
Compositions and Methods to Prevent and Treat Biofilms
InactiveUS20120315260A1Improve efficacyLow costAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobial agentMicrobial Biofilms
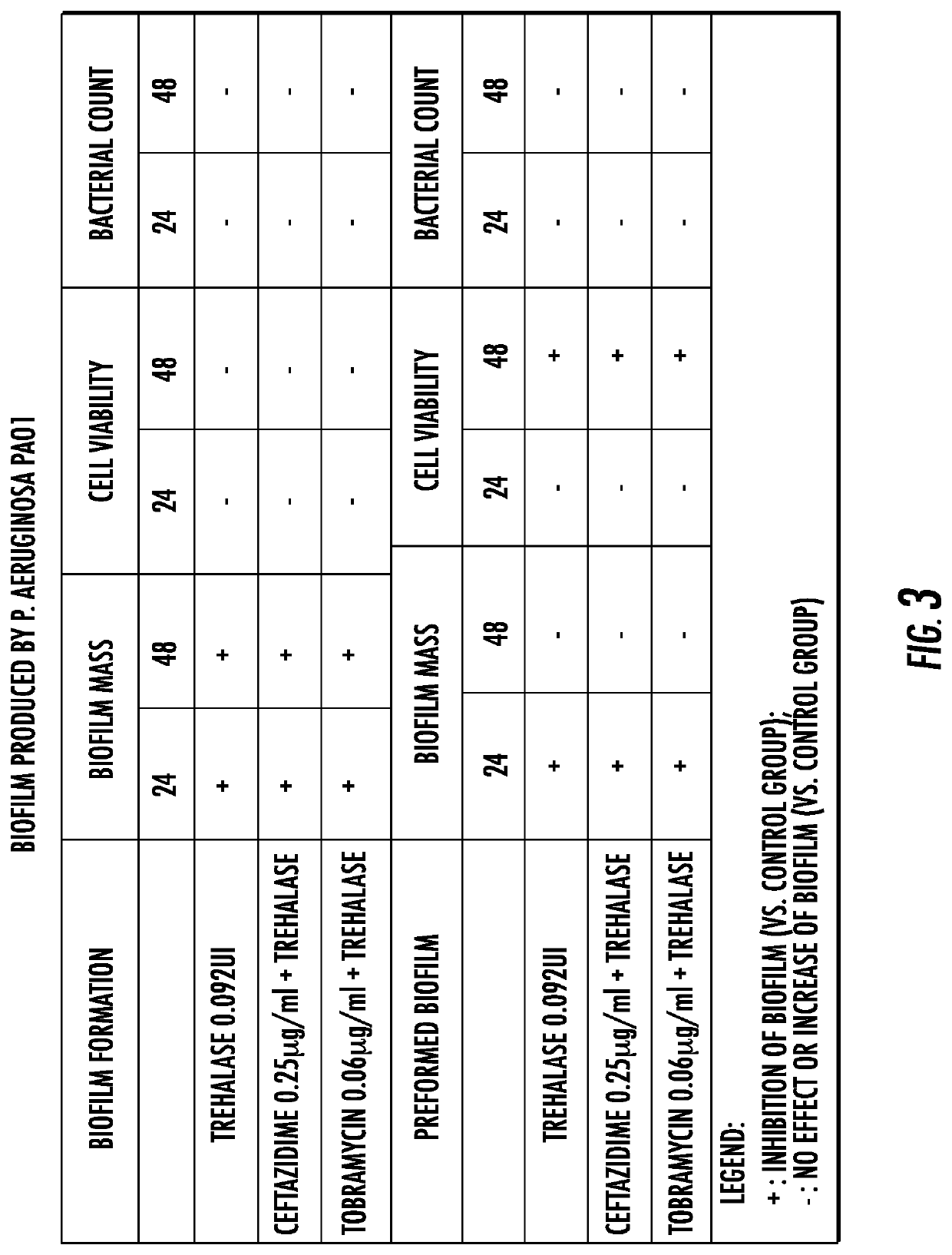
Compositions and methods to treat biofilms are disclosed based on the discovery of the role of the disaccharide trehalose in microbial biofilm development. In various embodiments to treat body-borne biofilms systemically and locally, the method includes administering trehalase, the enzyme which degrades trehalose, in combination with other saccharidases for an exposition time sufficient to adequately degrade the biofilm gel matrix at the site of the biofilm. The method also includes administering a combination of other enzymes such as proteolytic, fibrinolytic, and lipolytic enzymes to break down proteins and lipids present in the biofilm, and administering antimicrobials for the specific type(s) of infectious pathogen(s) underlying the biofilm. Additionally, methods are disclosed to address degradation of biofilms on medical device surfaces and biofilms present in industrial settings.
Owner:ZIOLASE
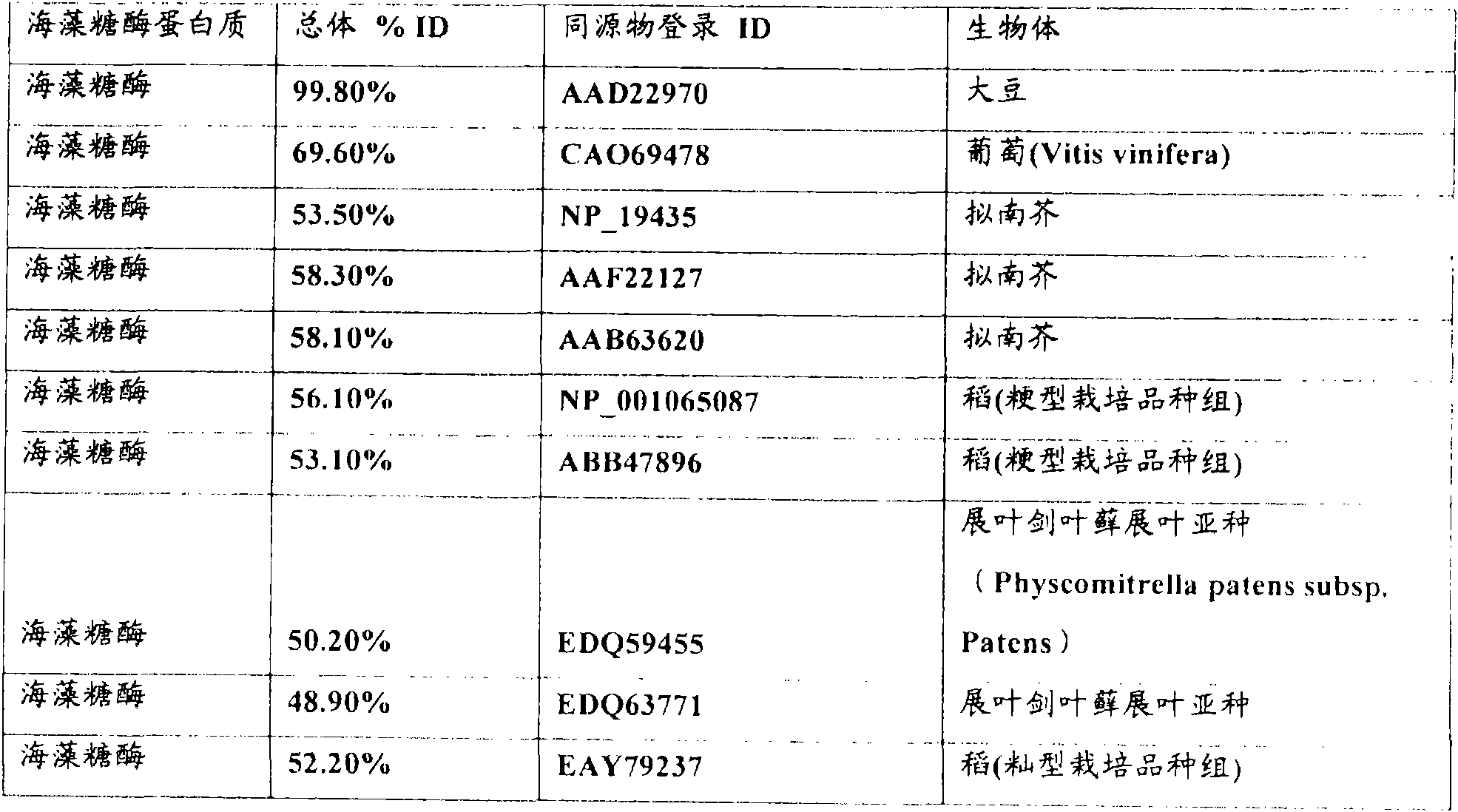
Plant genes encoding trehalose metabolism enzymes
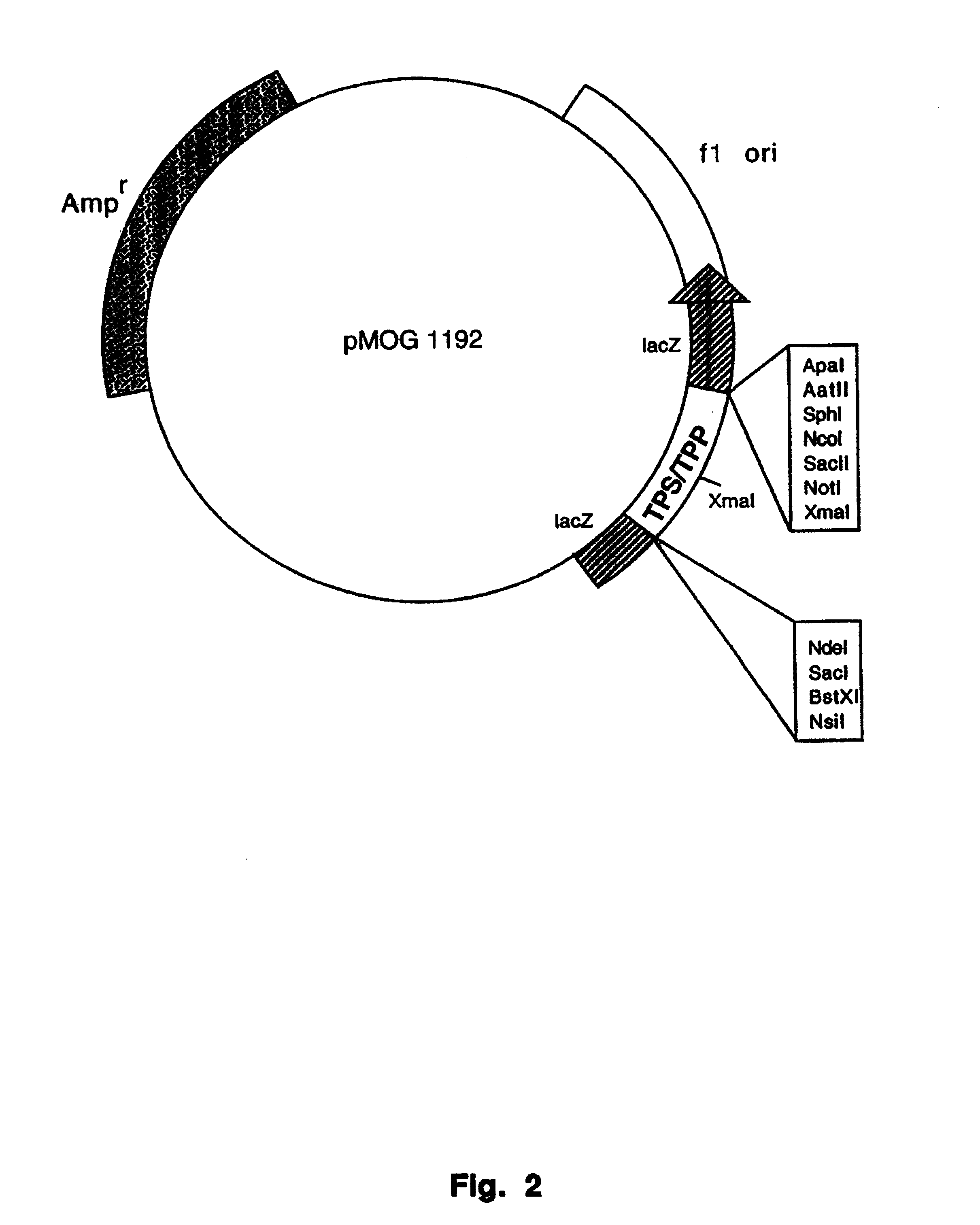
This invention relates to isolated nucleic acid fragments encoding trehalose metabolism enzymes, more specifically, alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase. The invention also relates to the construction of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Freezing resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103232947AIndustrial Production SafetyFungiMicroorganism based processesTrehalaseMicrobiology
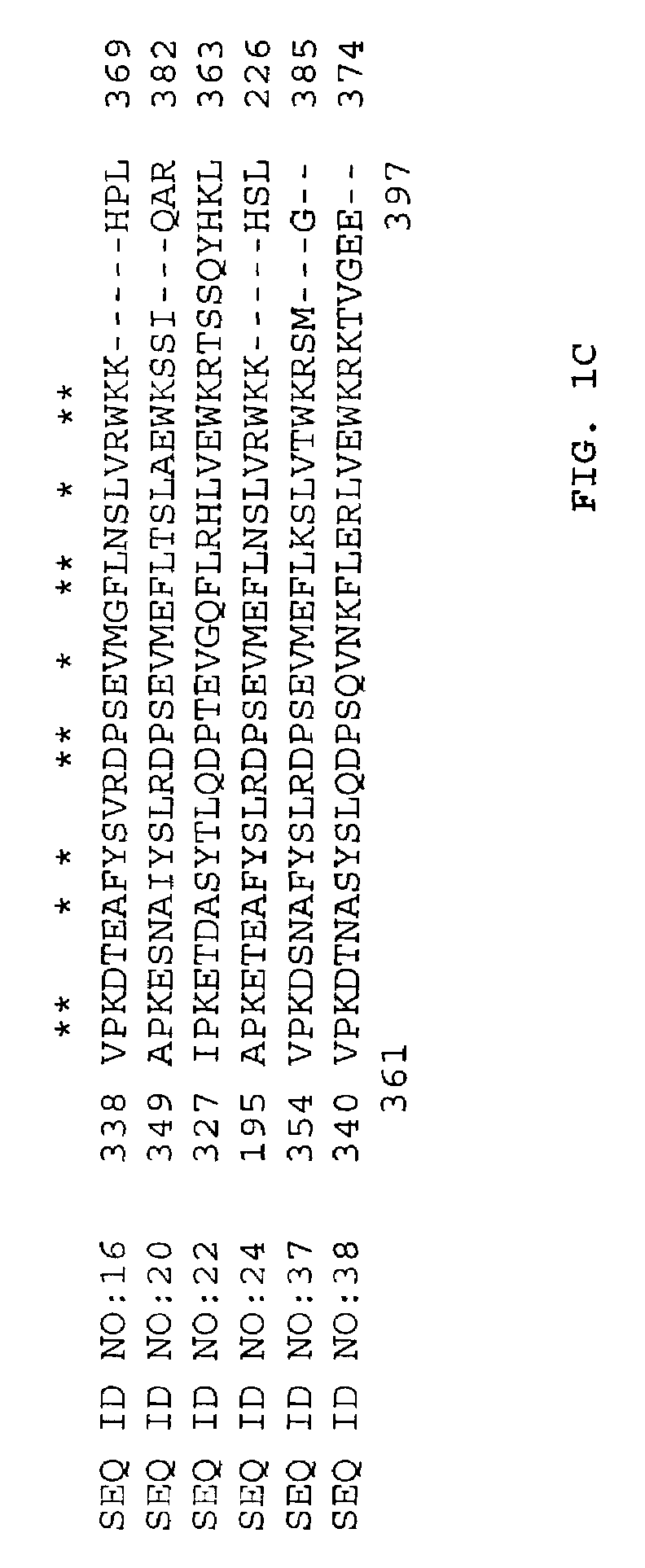
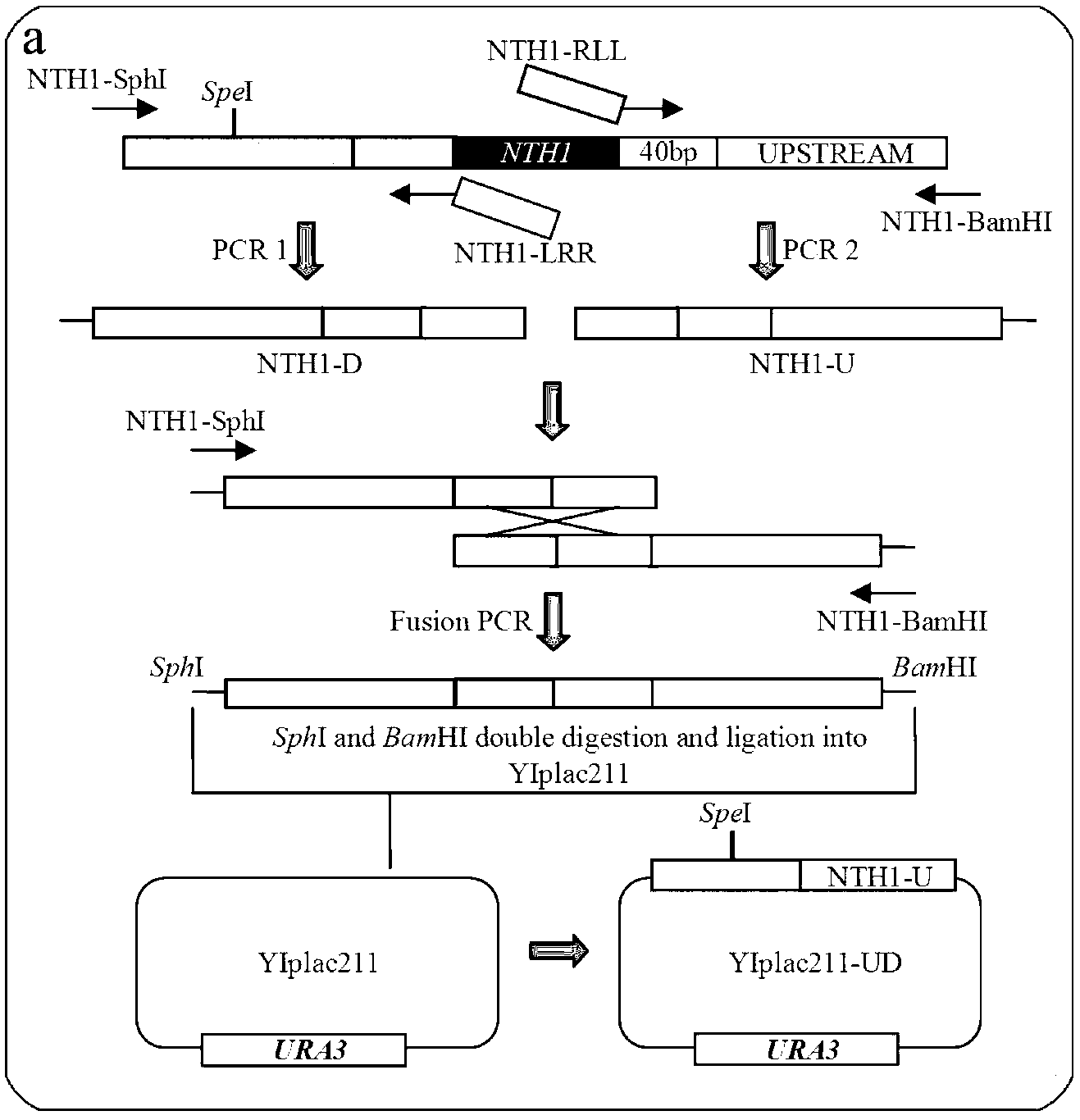
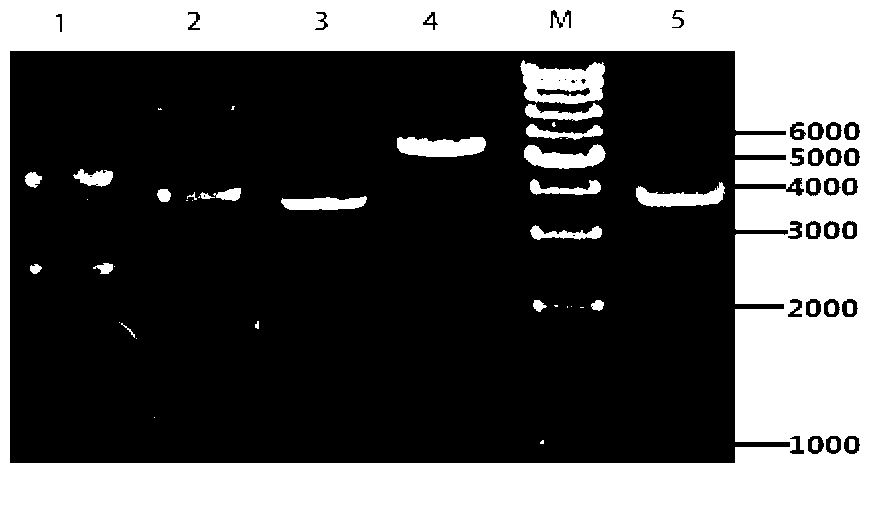
The invention discloses a freezing resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain and construction method thereof, concretely is a freezing resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY-14A delta U constructed by a non-trace knock-out gene NTH1, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.7379. The freezing resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae constructed by a non-trace gene knock-out method is realized by fusing PCR and a yeast integrative plasmid YIplac211, and knocking out a gene NTH1 for coding neutral trehalase. The invention realizes a rapid and high efficiency non-trace knock out of Saccharomyces cerevisiae NTH1 gene, and intracellular mycose content increases by 134% than that of the parent bacterial strain without influences to other fermentation performances of the bacterial strain BY-14A delta U; after the cells in the liquid dough are frozen for 21 days, the survival rate reaches to 78%, which is 2.6 times of the parent bacterial strain. The genome in the constructed microzyme does not have any residual exogenous genes, therefore the product can be used for industrial production safely.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Transmission system for medicine containing trehalose and hyaluronic acid in use for curing burn and preparing method
InactiveCN1660442AAnti-inflammatoryImprove the ability to adapt to the environmentPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDermatological disorderUse medicationAdditive ingredient
A burn medicine delivery system for treating burn is prepared from trehalase, hyaluronic acid, and medicinal additive.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
Processes for Producing Fermentation Products
The invention relates to a process of fermenting plant material in a fermentation medium into a fermentation product using a fermenting organism, wherein one or more trehalases are present in the fermentation medium.
Owner:NOVOZYMES NORTH AMERICA INC
Compositions and methods to prevent and treat biofilms
ActiveUS20170312345A1Improve efficacyLow costAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsMicrobial agentMicrobial Biofilms
Compositions and methods to treat biofilms are disclosed based on the discovery of the role of the disaccharide trehalose in microbial biofilm development. In various embodiments to treat body-borne biofilms systemically and locally, the method includes administering trehalase, the enzyme which degrades trehalose, in combination with other saccharidases for an exposition time sufficient to adequately degrade the biofilm gel matrix at the site of the biofilm. The method also includes administering a combination of other enzymes such as proteolytic, fibrinolytic, and lipolytic enzymes to break down proteins and lipids present in the biofilm, and administering antimicrobials for the specific type(s) of infectious pathogen(s) underlying the biofilm. Additionally, methods are disclosed to address degradation of biofilms on medical device surfaces and biofilms present in industrial settings.
Owner:ZIOLASE
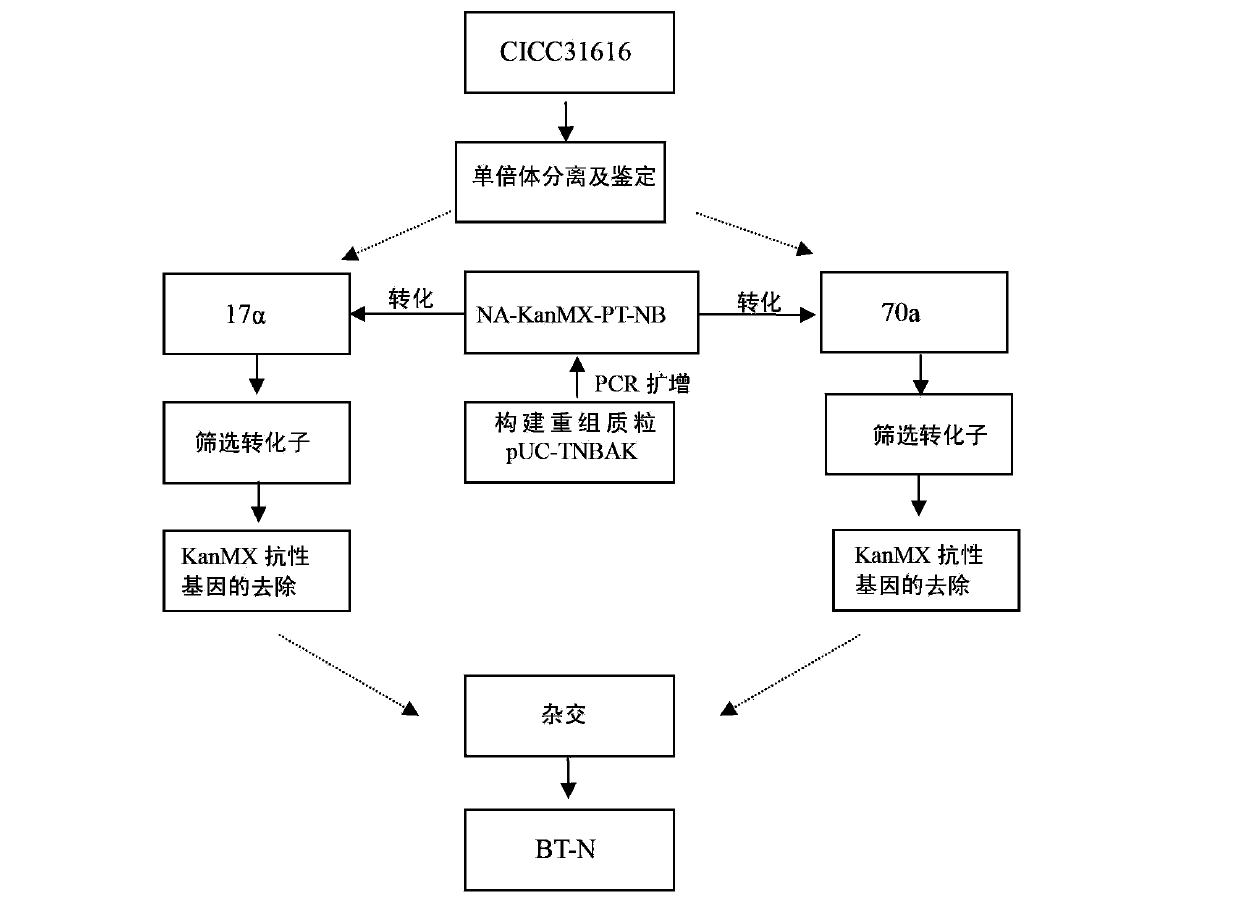
Freezing-resistant yeast strain for bread fermentation and breeding method thereof
ActiveCN103497903AImprove synthesis abilityEnsure safetyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTrehalose-6-phosphate synthase
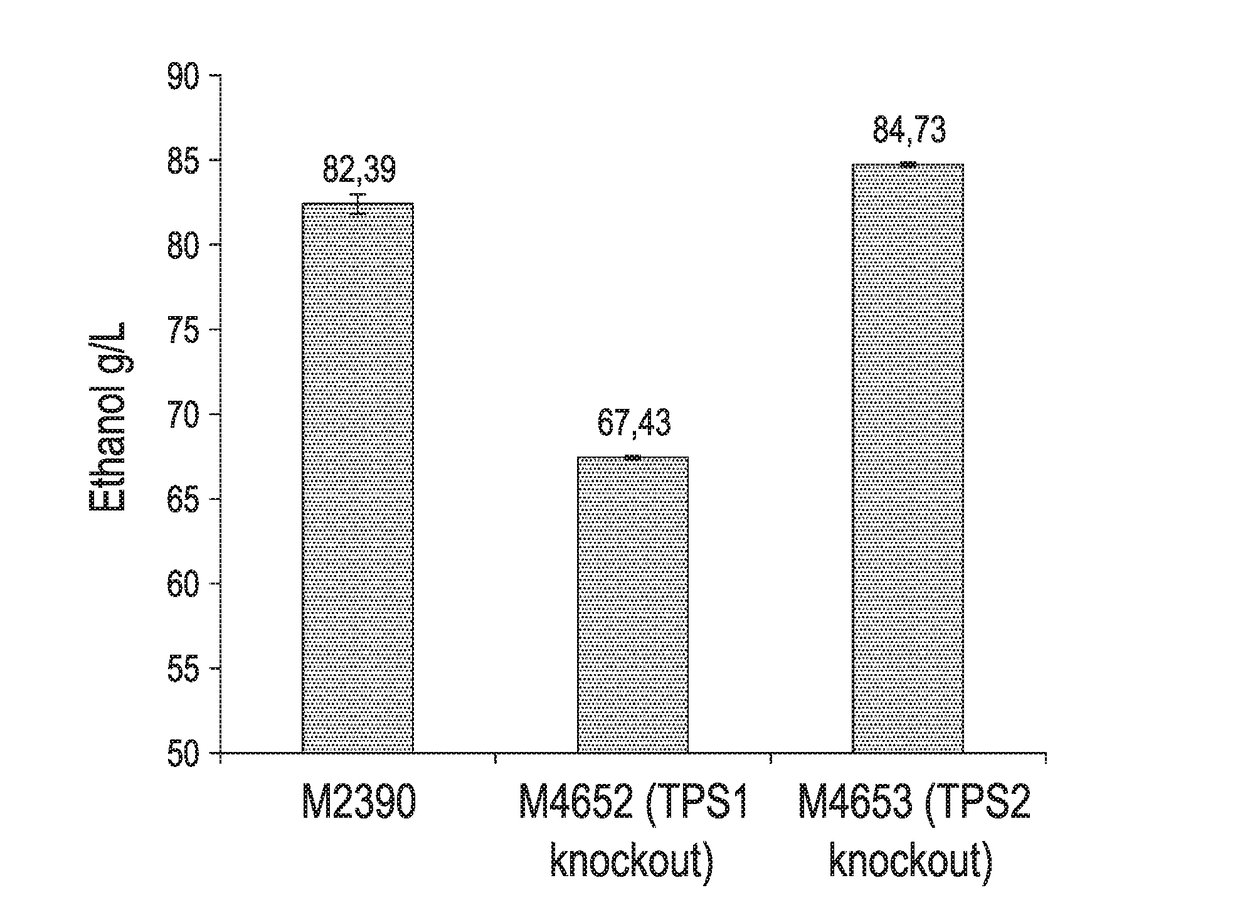
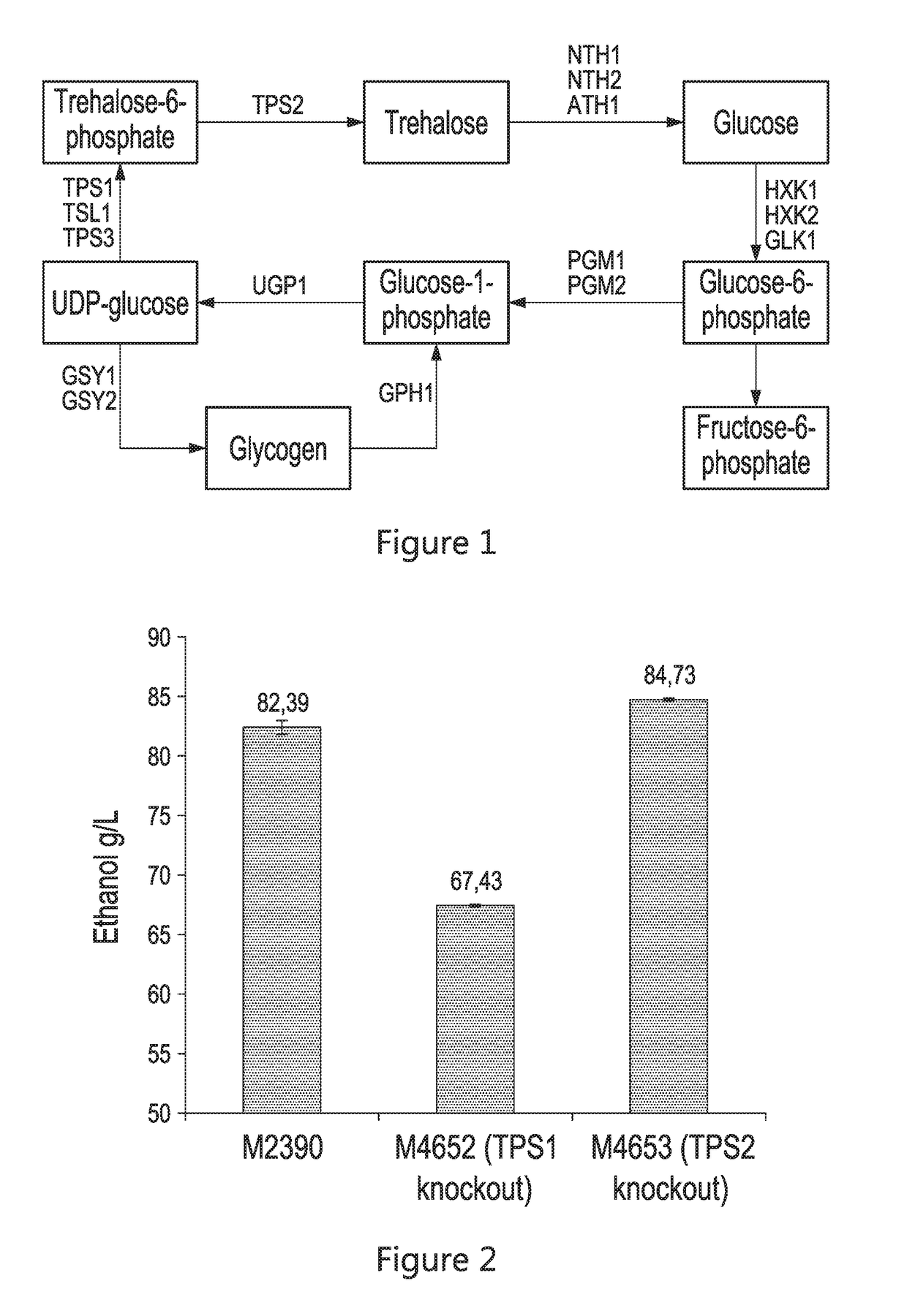
A freezing-resistant yeast strain for bread fermentation and a breeding method thereof. The yeast strain provided by the invention is saccharomyces cerevisiae BT-N with an accession number of CGMCC No.7151. When other fermentation performance is not influenced, the strain has a cell freezing survival rate of 92.75% after being frozen at -20 DEG C for 21 days and has a relative fermentation capacity of 53.24%, which are increased by 57.39% and 24.78% respectively when compared with parent strains (who have a freezing survival rate is 35.36% and have a relative fermentation capacity of 28.46%). The strain is realized by knocking out of the neutral trehalase coding gene NTH1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae CICC31616, and overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase coding gene TPS1 by selecting a strong promoter PGK1. The bred yeast strain has no special requirements for fermentation equipment or conditions, can be used by equipment and under conditions of common factories, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Limiting yeast-produced trehalose in fermentation
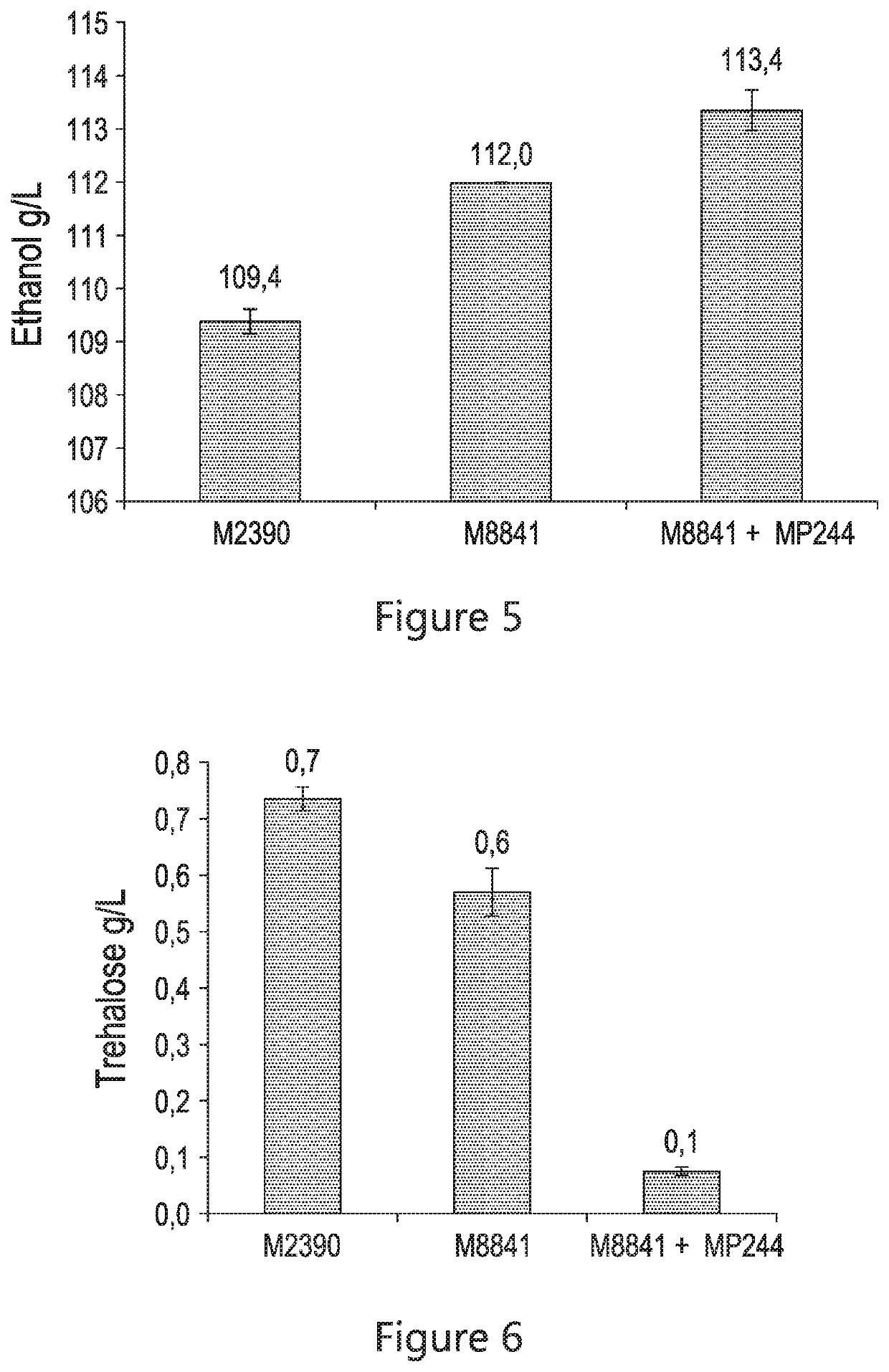
The present disclosure relates to recombinant yeast host cells having (i) a first genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol or regulating glycerol synthesis and / or allowing the production of an heterologous glucoamylase and (ii) a second genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce trehalose or regulating trehalose synthesis and / or allowing the expression of an heterologous trehalase. The recombinant yeast host cells can be used to limit the production of (yeast-produced) trehalose (particularly extracellular trehalose) during fermentation and, in some embodiments, can increase the production of a fermentation product (such as, for example, ethanol).
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Optimized high-temperature acid trehalinase TreMT1 and coding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to optimized high-temperature acid trehalinase TreMT1 and a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the optimized high-temperature acid trehalinase TreMT1is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the optimized high-temperature acid trehalinase TreMT1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Targeted high-temperature acid trehalinase TreMT1 can be generated at high yield through a constructed high-temperature acid trehalinase TreMT1 strain. The trehalase stability is high, disaccharide can be hydrolyzed into monosaccharide under thehigh-temperature acidic condition, the cooling energy consumption of starch liquefacation is reduced, the utilization rate of starchy raw materials is increased, resource waste is reduced, the utilization efficiency of biological energy sources is increased, the production cost is reduced, and certain practical significance and application value are achieved on efficient expression and even industrial production of trehalase.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
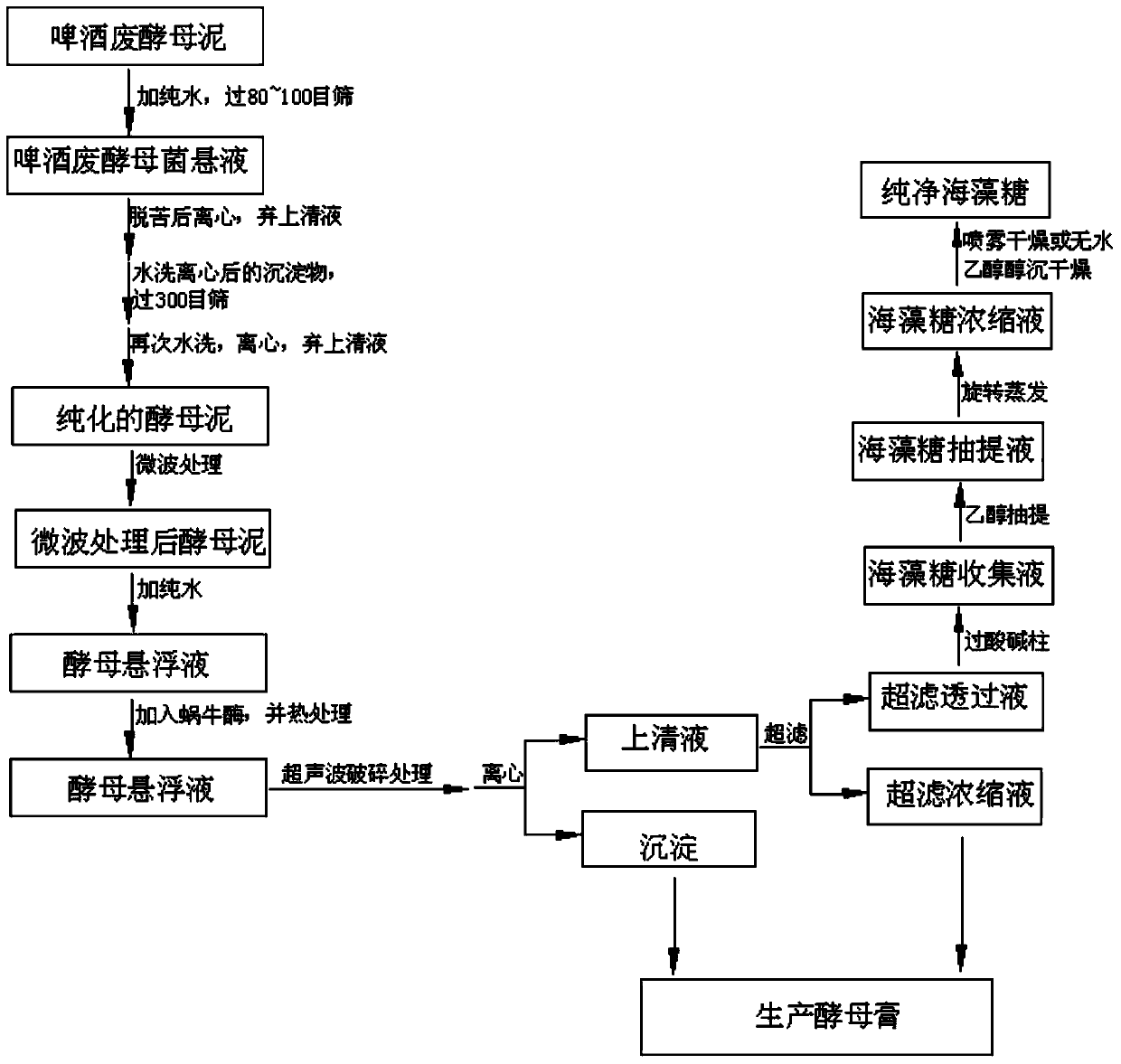
Environment-friendly production method for enhancing trehalose yield of beer waste yeast under stress conditions
The invention discloses an environment-friendly production method for enhancing trehalose yield of beer waste yeast under stress conditions, belonging to the field of biochemical engineering and aiming to solve the problems of long trehalose extraction time, low extraction rate and difficulty in purification due to too many impurities dissolved in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: 1) microwave treatment; 2) heat treatment; 3) helicase treatment; 4) ultrasonic crushing treatment; and 5) trehalose extraction and purification. According to the method, the yeast is under stress conditions to generate abundant trehalose; meanwhile, the activity of the trehalase is inhibited, and the yeast is subjected to helicase treatment and ultrasonic crushing treatment to rupture the yeast cells, so that almost all the trehalose is dissolved out; and thus, the method has the advantages of short treatment time, easy trehalose purification and high yield. Besides, the method does not use any strong acid, strong alkali or toxic organic solvent, and implements cleanness and environmental protection; and the waste liquid and waste residue generated in the method can be used for producing yeast extract, so almost no waste liquid or waste residue is discharged.
Owner:HEZE UNIV
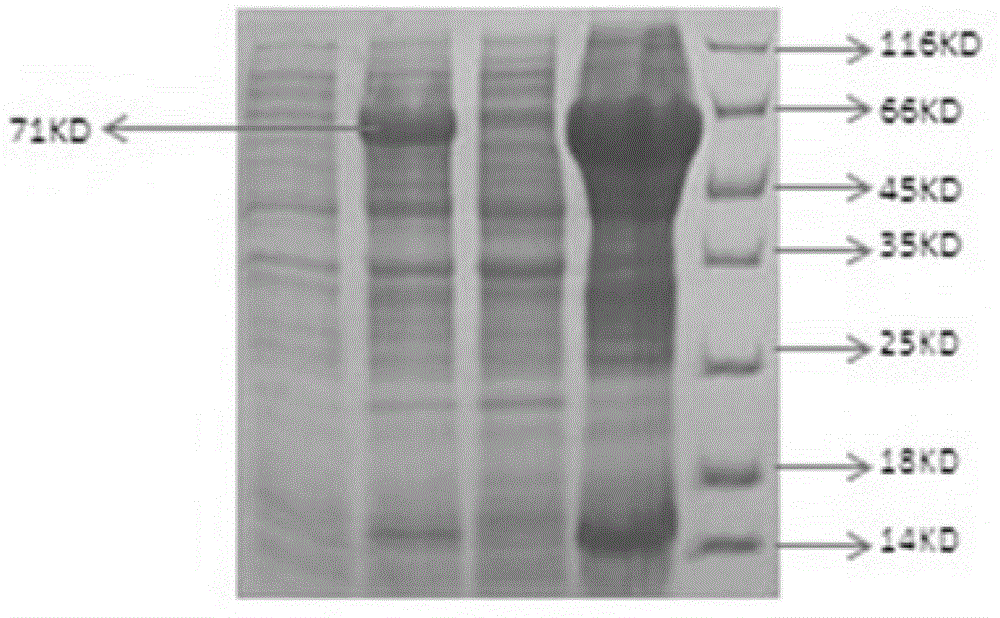
Green plant bug water-soluble trehalase, coding sequence, vector, strain and application
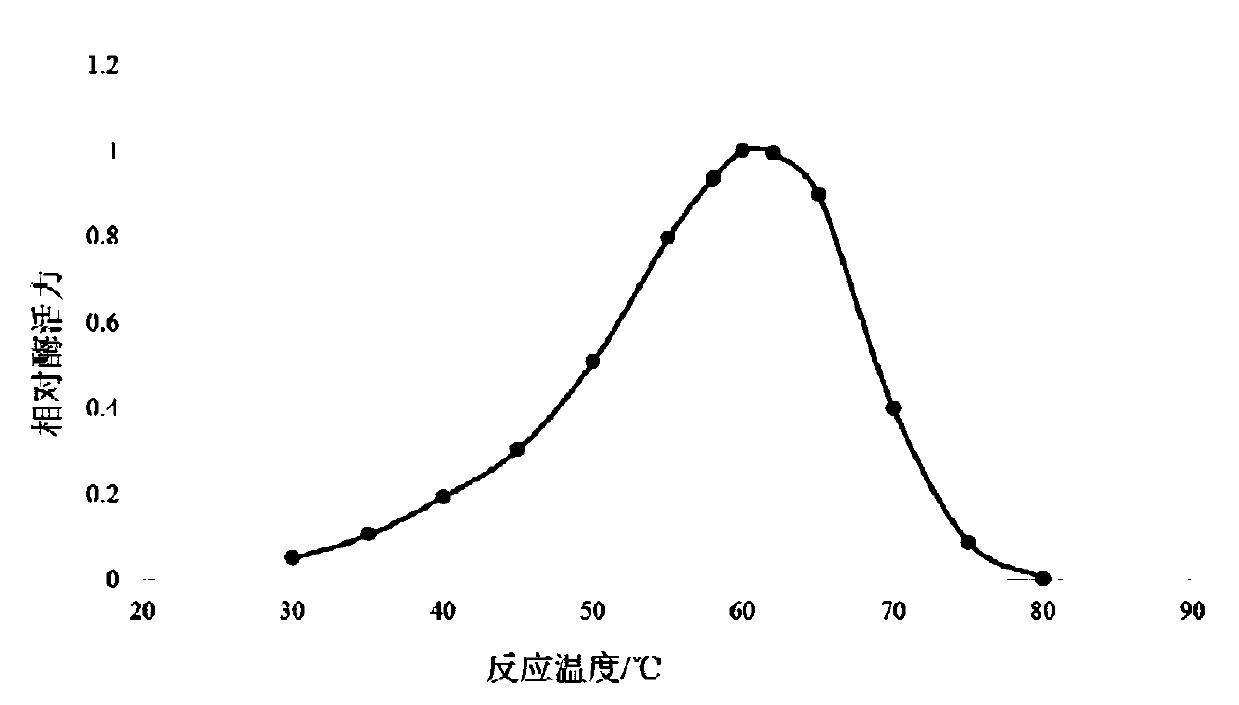
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence for coding a green plant bug water-soluble trehalase. The invention also discloses a green plant bug water-soluble trehalase, a recombinant expression vector of the DNA sequence for coding the green plant bug water-soluble trehalase, a transgenic cell system or transgenic recombinant bacterium, application of the recombinant expression vector and transgenic cell system or transgenic recombinant bacterium in producing the green plant bug water-soluble trehalase, and a preparation method of the green plant bug water-soluble trehalase. The molecular weight of the prepared zymoprotein is 71KD, the optimum pH value is 7.0, the optimum temperature is 55 DEG C, and the zymoprotein can degrade trehalose into glucose. The purified trehalase can be used for qualitative and quantitative work of trehalose content in industry and some other fields, and can also provide foundation for researching and developing insect trehalase inhibitors.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Entomopathogenic fungi acidic trehalase transgenic strain, preparation method and use thereof
The invention provides an entomopathogenic fungi transgenic strain which contains a homologous or heterologous acidic trehalase constitutive exogenous gene. The preparation method of the entomopathogenic fungi transgenic strain comprises the following steps: firstly building an acidic trehalase full-length cDNA gene constitutive expression vector; establishing a submerged conidia transformation system; and finally selectively screening to obtain the entomopathogenic fungi transgenic strain. The invention also provides application of Entomopathogenic fungi acidic trehalase transgenic strain in preparing fungal pesticide. The entomopathogenic fungi transgenic strain has high efficiency of expressing trehalase; and the preparation method has the advantages of easy operation, good repeatability and good reproducibility. The entomopathogenic fungi transgenic strain can be applied to preparing the fungal pesticide. When the fungal pesticide acts on insects, through the overexpression of the acidic trehalase gene via the transgenic strain, the activity of acidic trehalase in an insect host is improved, utilization of the trehalase is accelerated and growth of entomopathogenic fungi in the insect host is promoted, thus effectively improving the insecticidal activity of the fungal pesticide such as metarhizium anisopliae, beauveria bassiana and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Botanical insect trehalase inhibitor and application thereof
The invention discloses a botanical insect trehalase inhibitor and the application thereof. The inhibitor comprises castanospermine which can be obtained by screening botanical compounds and used for manufacturing trehalase-targeted pesticides or active lead compounds. The inhibitor has good effect on inhibiting trehalase in cotton bollworms and other insects.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Compositions and methods to prevent and treat biofilms
Compositions and methods to treat biofilms are disclosed based on the discovery of the role of the disaccharide trehalose in microbial biofilm development. In various embodiments to treat body-borne biofilms systemically and locally, the method includes administering trehalase, the enzyme which degrades trehalose, in combination with other saccharidases for an exposition time sufficient to adequately degrade the biofilm gel matrix at the site of the biofilm. The method also includes administering a combination of other enzymes such as proteolytic, fibrinolytic, and lipolytic enzymes to break down proteins and lipids present in the biofilm, and administering antimicrobials for the specific type(s) of infectious pathogen(s) underlying the biofilm. Additionally, methods are disclosed to address degradation of biofilms on medical device surfaces and biofilms present in industrial settings.
Owner:ZIOLASE
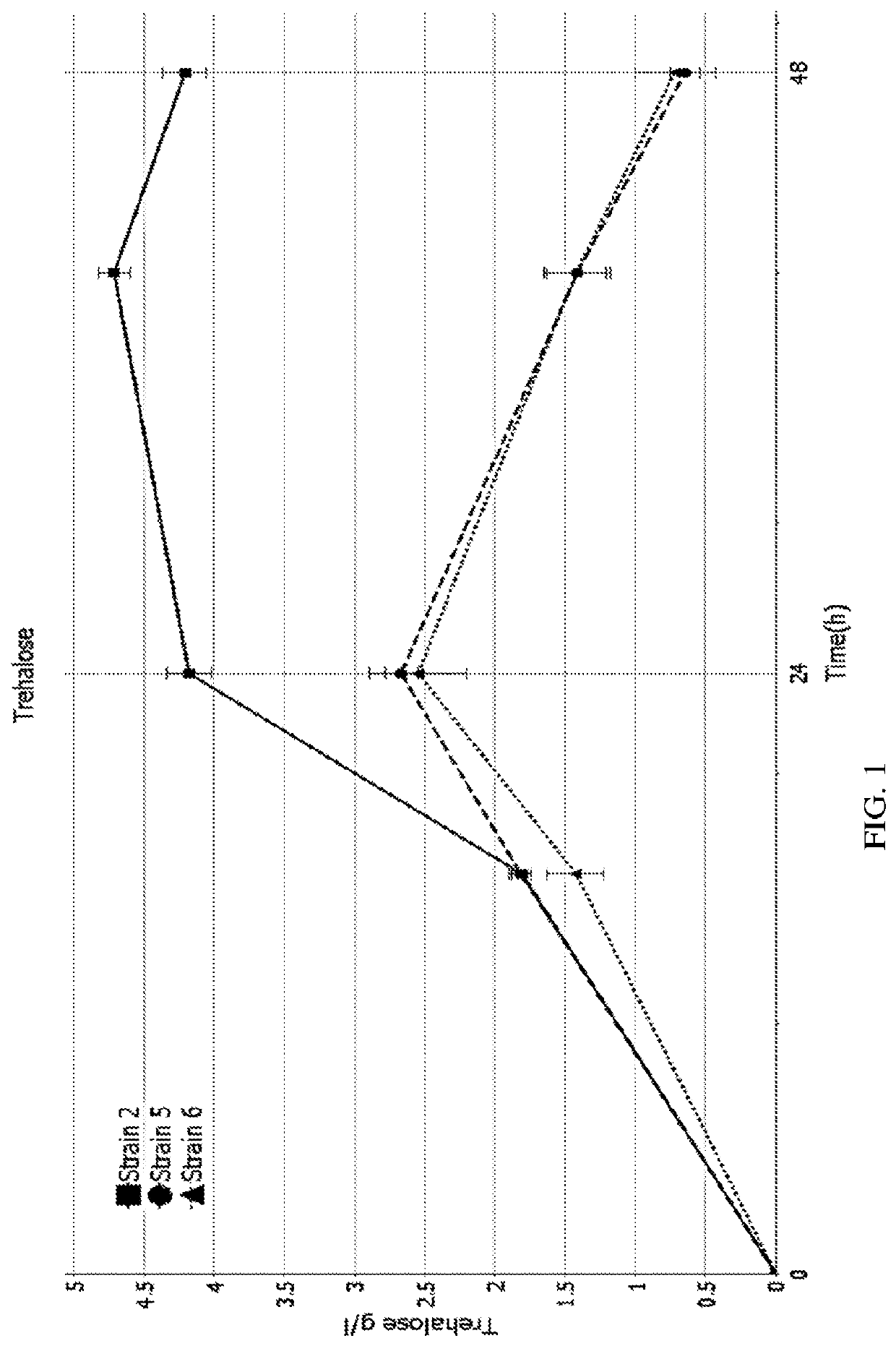
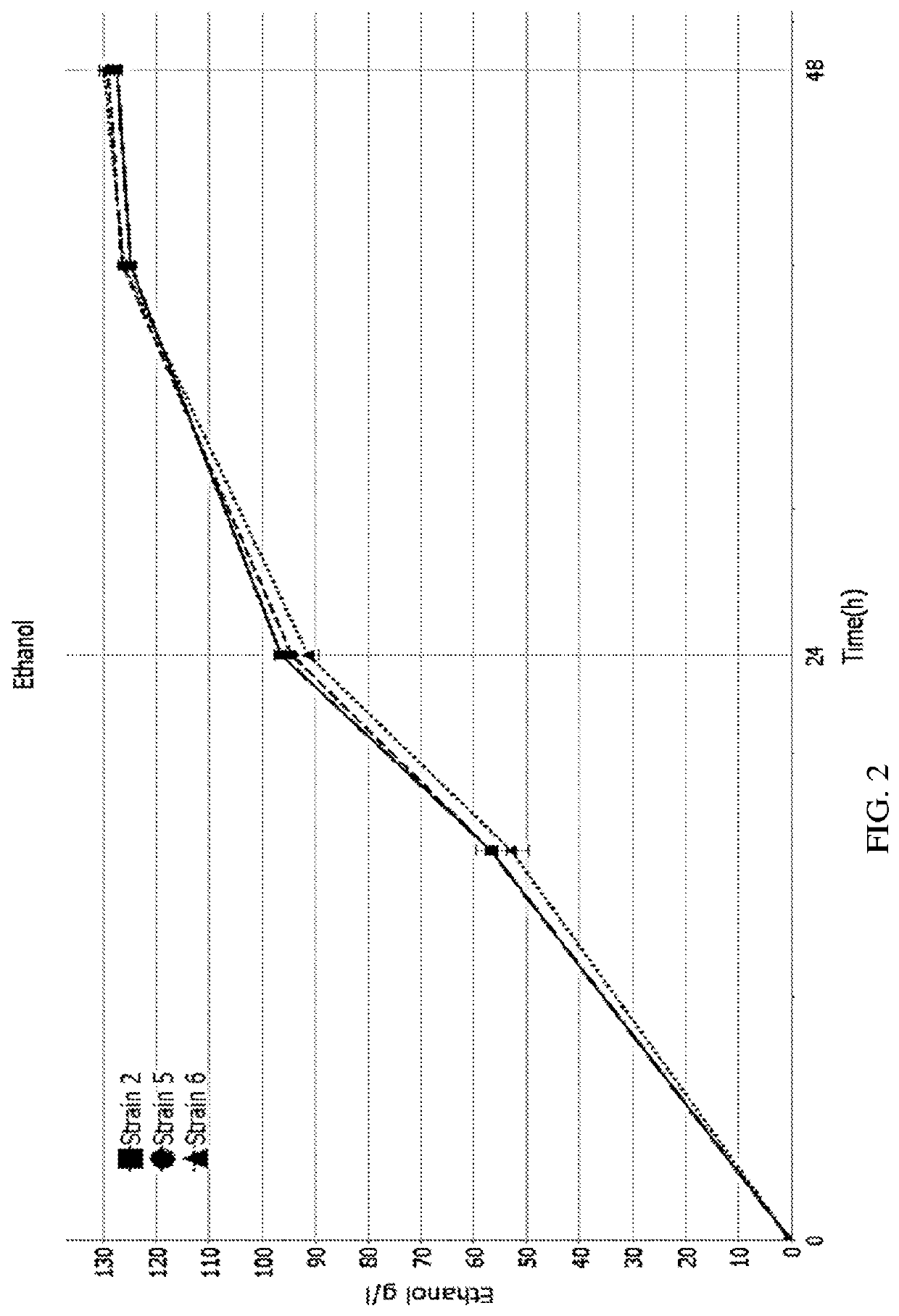
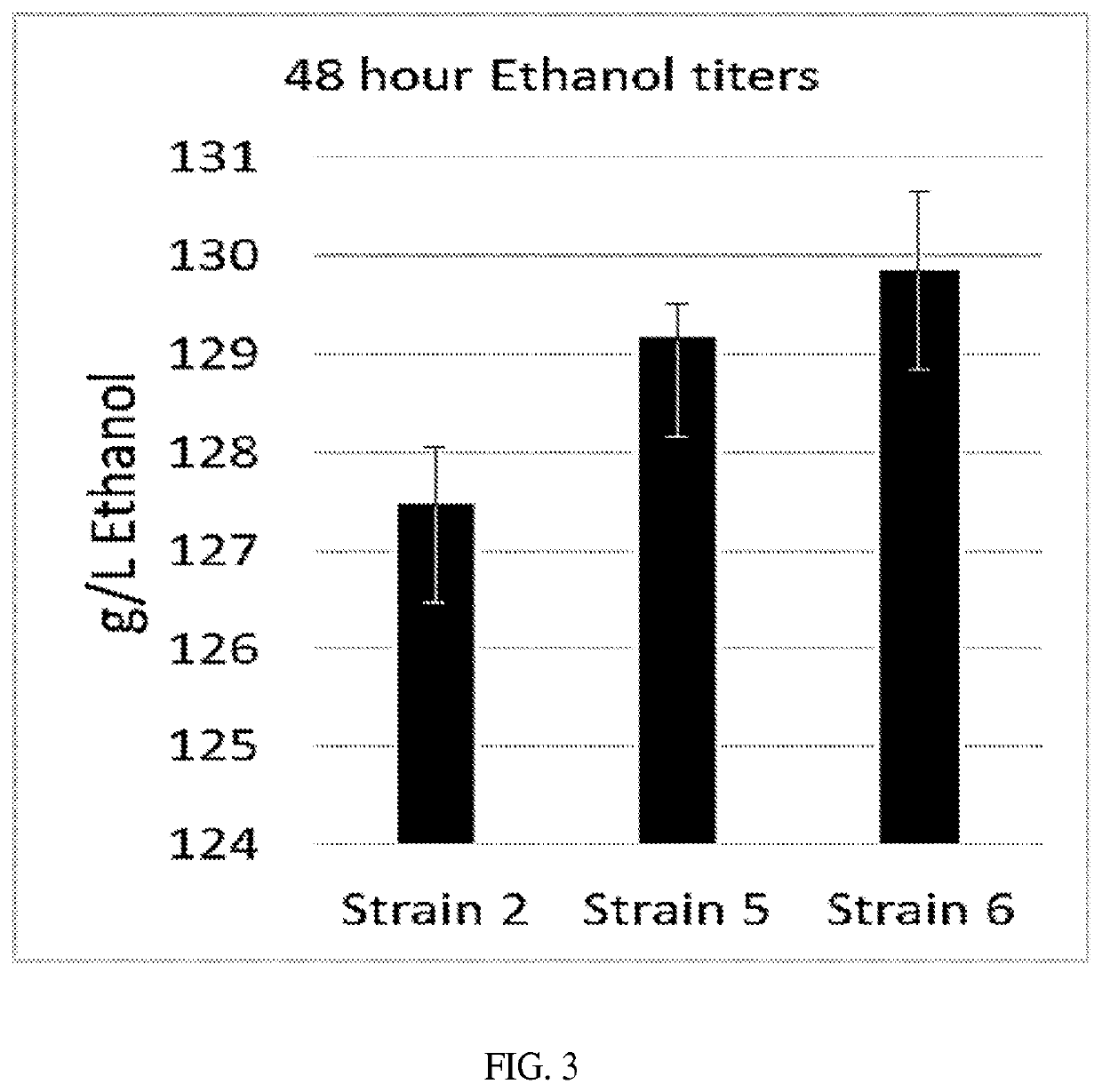
Trehalase production strain and application thereof
ActiveCN109439599AHigh activityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismHydrogen
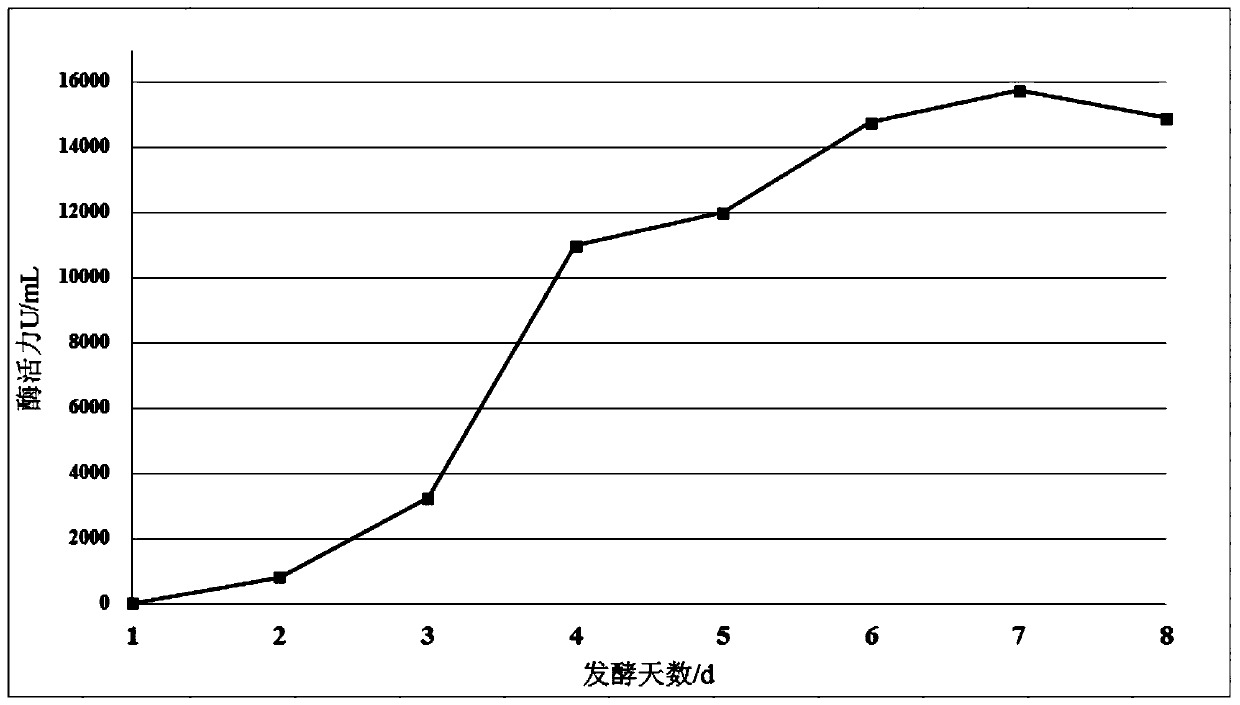
The invention discloses a trehalase production strain and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of industrial microorganisms. Erwinia rhapontici C2 provided by the invention is characterized in that the taxonomic name is Erwinia rhapontici and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on November 21, 2018, the preservation address is No. 3, No. 1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 16760. The invention reports the Erwinia rhapontici for producing a trehalase for the first time and enzymatic properties of the Erwinia rhapontici are researched. The optimal temperature and pH (Potential of Hydrogen) of the trehalase produced by the strain are 40 DEG C and pH5 respectively; the trehalase has relatively high activity and stability under an acidic condition and has a wide application prospect in an ethanol industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Limiting yeast-produced trehalose in fermentation
The present disclosure relates to recombinant yeast host cells having (i) a first genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol or regulating glycerol synthesis and / or allowing the production of an heterologous glucoamylase and (ii) a second genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce trehalose or regulating trehalose synthesis and / or allowing the expression of an heterologous trehalase. The recombinant yeast host cells can be used to limit the production of (yeast-produced) trehalose (particularly extracellular trehalose) during fermentation and, in some embodiments, can increase the production of a fermentation product (such as, for example, ethanol).
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Optimized high-temperature trehalase MS-Tre capable of being expressed efficiently in aspergillus niger and encoding gene and application of optimized high-temperature trehalase MS-Tre
The invention discloses optimized high-temperature trehalase MS-Tre capable of being expressed efficiently in aspergillus niger and an encoding gene and application of the optimized high-temperature trehalase MS-Tre. The amino acid sequence of the optimized high-temperature trehalase MS-Tre is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the encoding gene of the optimized high-temperaturetrehalase MS-Tre is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with a to-be-optimized encoding gene, the encoding gene of the optimized high-temperature trehalase MS-Tre can be expressed more efficiently in the aspergillus niger, and a recombinant aspergillus niger strain can produce trehalase efficiently. The trehalase has the advantages that the stability is good, disaccharide can also be hydrolyzed into monosaccharide at the high temperature, the cooling energy consumption after starch liquefaction is reduced, the utilization rate of starchy raw materials is increased, the utilization efficiency of biological energy sources is improved, and the production cost is reduced. The trehalase MS-Tre and the encoding gene thereof have certain practical significance and application value for achieving industrial production of the trehalase.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving heat-tolerance and quality-keeping of scarab green muscardine spore
InactiveCN1778891AImprove storabilityImprove heat resistanceFungiVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologySpore
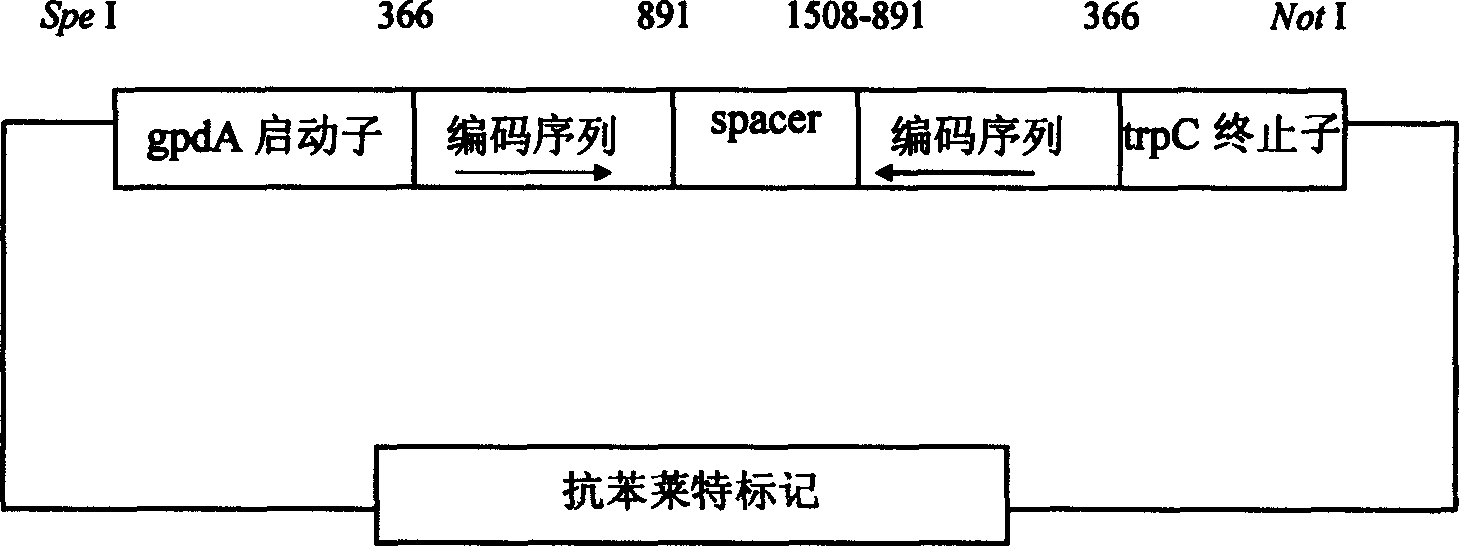
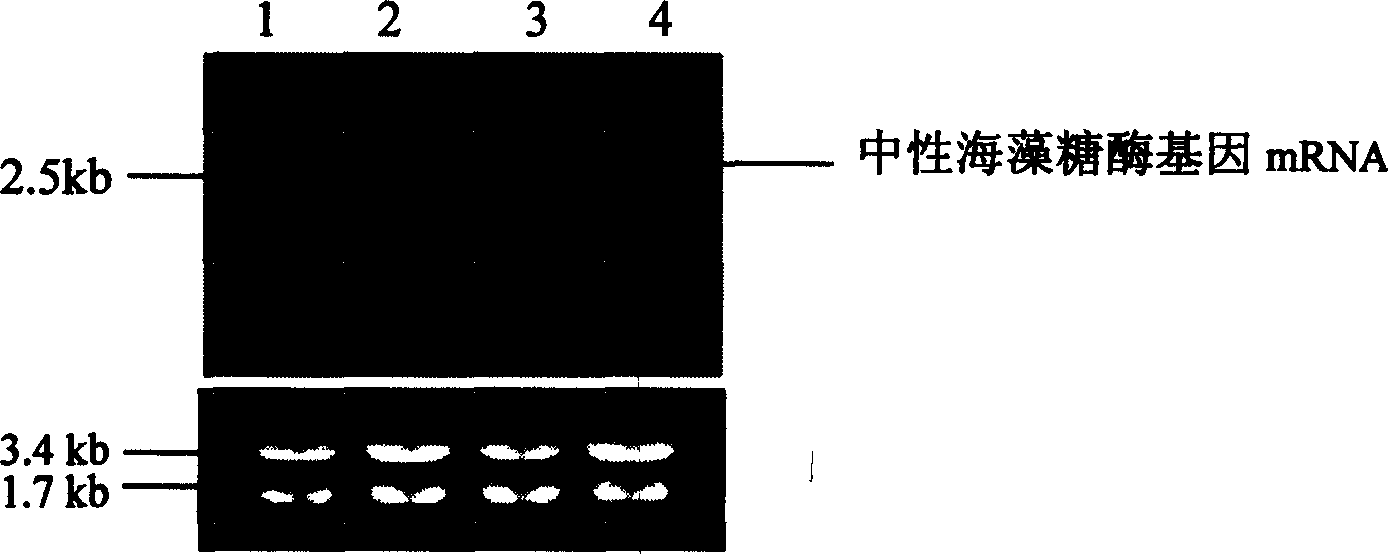
The invention is to improve the storage stability of metarhizium anisopliae conidia. First to construct the disturb carrier of neuter trehalase RNA of metarhizium anisopliae conidia, then to found the transform system of conidiophore. Appraising by DNA imprinted, detecting the expression of its neuter trehalase gene by the RNA imprinted. Compare to the inner trehalose content, storability, heat tolerance between the transformant and the departure bacterial strain sporeú¼it can get that there is prodigious difference in the inner trehalose content, storability, heat tolerance between them. The storability, heat tolerance of the Metarhizium anisopliae conidia can be improved by this method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Preparation method and application of RNA interference sequence of trehalase gene of Acyrthosiphon pisum
The invention discloses a preparation method of an RNA interference sequence of a trehalase gene of Acyrthosiphon pisum. The method comprises the following steps: 1. selecting a target region of RNAiaccording to a trehalase sequence of the Acyrthosiphon pisum (XM_003245847.3), and using Primer5.0 to design a PCR amplification primer in the target region; 2. extracting the total RNA of the Acyrthosiphon pisum and obtaining a cDNA by reverse transcription, and then conducting PCR-amplification on the trehalase gene contained in the cDNA by using the amplification primer to obtain the target gene; and 3. amplifying a double-stranded DNA of interest containing a T7promoter sequence, and then synthesizing a double-stranded RNA using the kit.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Acidic trehalase TreA and gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108841808AAcid resistantTaller than aliveFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTrehalase
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural genes and in particular relates to acidic trehalase TreA sourced from a fungus and a gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequenceof the trehalase TreA is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2. The invention provides a novel trehalase gene. The trehalase encoded by the trehalase gene has high properties and can be applied to industries of insect control, foot, starch sugar, medicines and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods to obtain drought resistant plants
InactiveCN103403168AHigh activityPromote growthHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideTrehalase
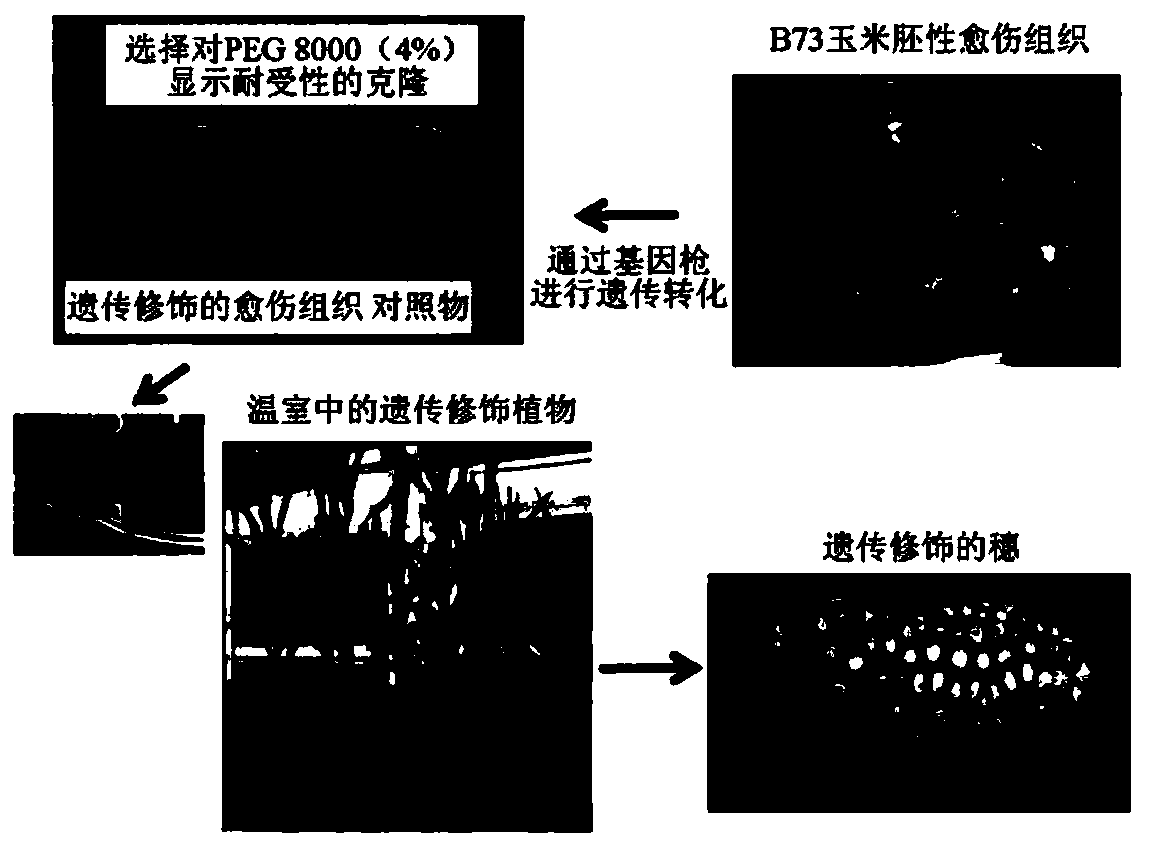
The present invention provides a nontoxic method for the selection of transformed cells from a cell population consisting of transformed and untransformed cells. The method comprises the following steps: a) introducing into a cell at least one nucleotide sequence of interest and at least one selection nucleotide sequence to obtain genetically transformed cells, where the selection nucleotide sequence comprises a sequence promoting the inhibition of endogenous trehalase enzyme; b) placing the population of transformed and untransformed cells in a culture medium containing an osmoregulating substance such as PEG 8000; c) selecting the transformed cells from the population based on the ability of transformed cells to survive and grow in the presence of the osmoregulating substance conferring the plants derived from these genetic transformation events, for example, drought and / or cold tolerance capacity.
Owner:高等研究院和国家职业技术学院研究中心 +1
Genetically modified trehalase-expressing yeasts and fermentation processes using such genetically modified yeasts
The present invention relates to genetically engineered yeasts having a heterologous trehalase gene and fermentation processes for using such yeasts. The yeasts can express trehalase in a quantity sufficient to convert significant amounts of trehalose to glucose, thereby improving the yield of the product in a fermentation, and / or reducing or eliminating the need to add exogenous trehalase to the fermentation. The yeasts can also include other heterologous genes for expressing enzymes useful for improving yield and / or for reducing or eliminating the need to add exogenous enzymes to the fermentation.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Plant gene encoding trehalose metabolism enzymes
This invention relates to isolated nucleic acid fragments encoding trehalose metabolism enzymes, more specifically, alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase. The invention also relates to the construction of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the alpha, alpha-trehalase, alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase or trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Use of trehalase genes to confer nematode resistance to plants
The invention provides transgenic plants that exhibit increased resistance to nematode infection by virtue of overexpression of a gene that encodes trehalase in nematode-induced syncytia. Expression vectors comprising trehalase-encoding polynucleotides and methods of employing such vectors to increase nematode resistance of plants are also provided.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
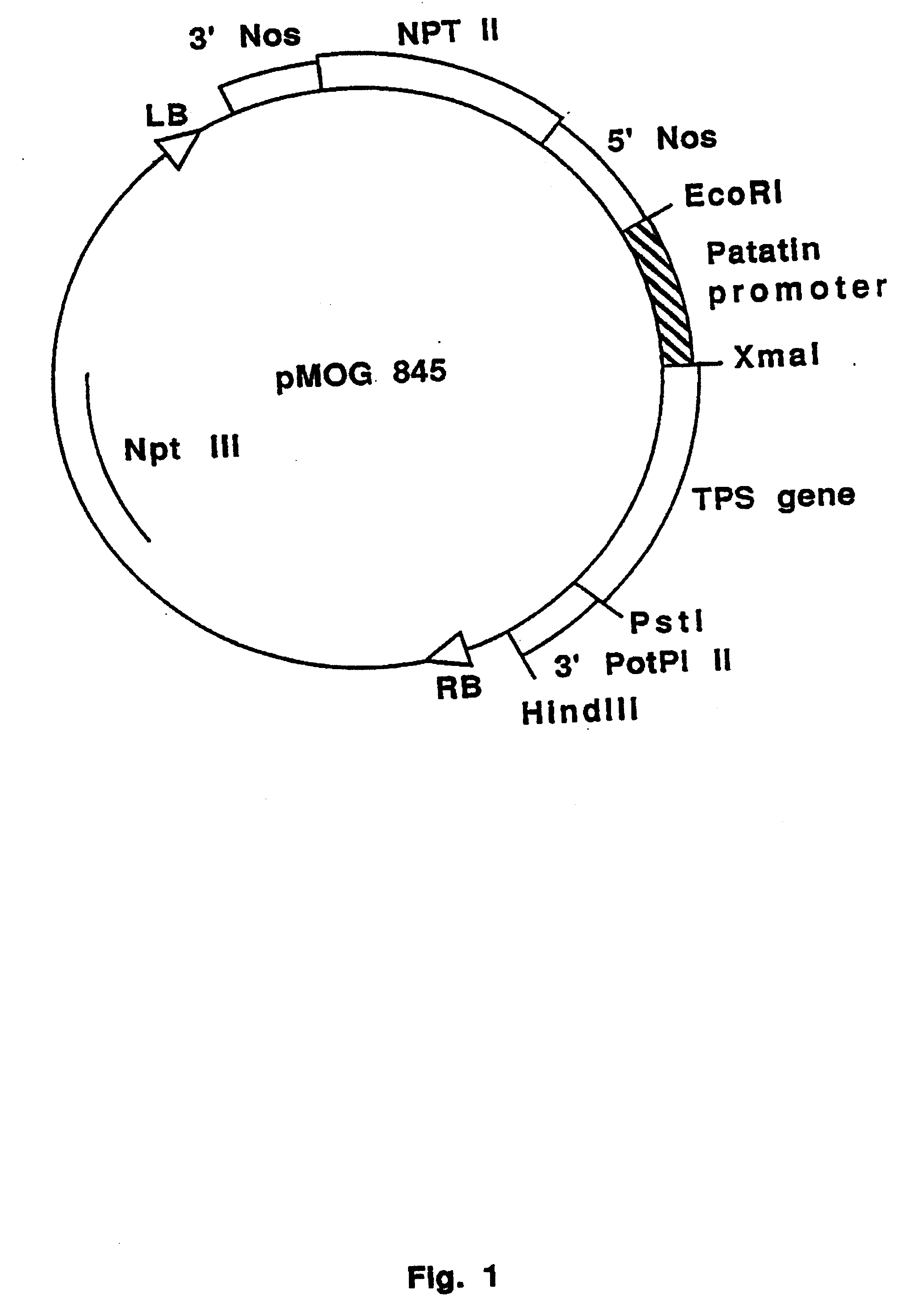
Enhanced accumulation of trehalose in plants
The invention provides a process for producing trehalose in plant cells capable of producing trehalase by growing plant cells having the genetic information required for the production of trehalose and trehalase, or cultivating a plant or a part thereof comprising such plant cells, characterized in that said plant cells are grown, or said plant or a part thereof, is cultivated in the presence of a trehalase inhibitor.
Owner:SYNGENTA MOGEN BV
Double stranded RNA compositions for reducing asian citrus psyllid infestation and methods of use
dsRNA generated from D. citri trehalase gene is effective in reducing fitness and / or survival of D. citri. Thus genetically altered plants expressing the dsRNA and plants to which dsRNA solutions are applied increase D. citri mortality and reduce D. citri infestation. With reduced D. citri population, the spread of microorganisms for which D. citri is a vector is reduced. Such microorganisms include, but are not limited to, C. Liberibacter species, including: CLas, CLam, and CLaf. Thus, applying of the D. citri trehalase dsRNA to a plant reduces disease and / or microorganism transmission by killing D. citri that feed on the treated plant.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Fungus expression vector and construction and screening method thereof
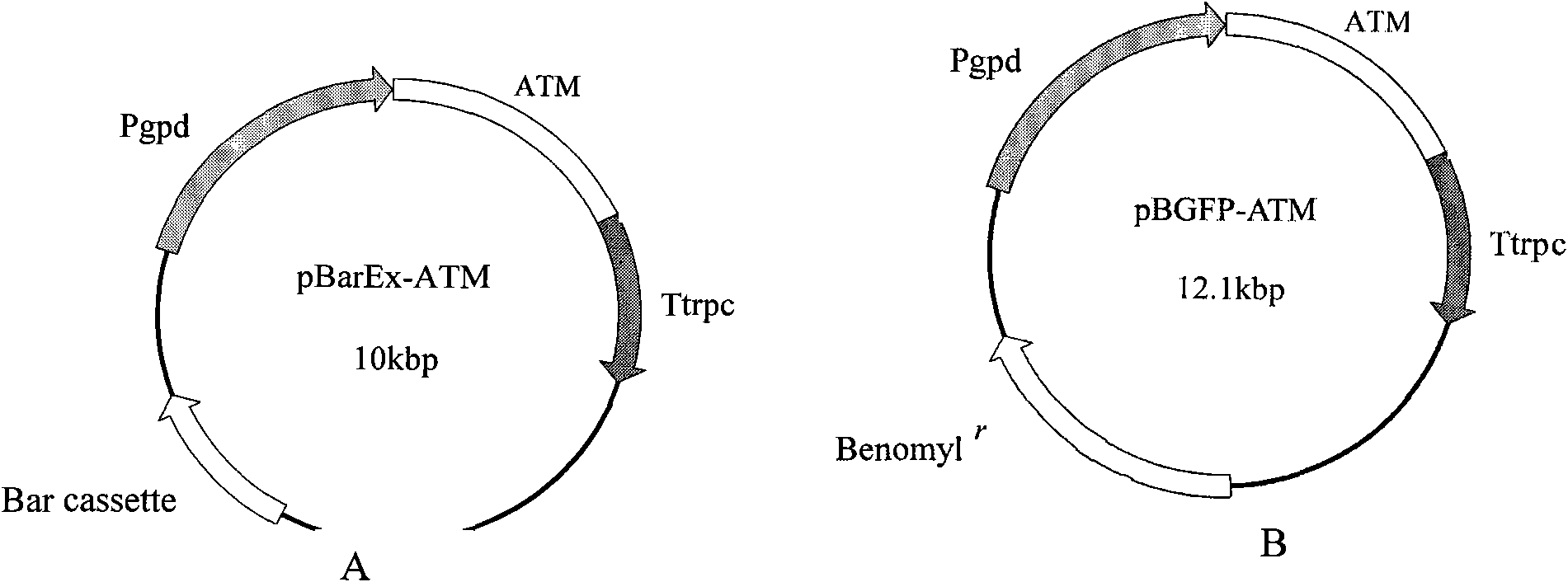
ActiveCN102181472AGrow fastPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme GeneBacterial strain
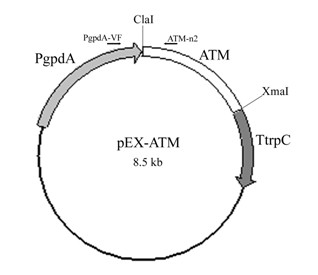
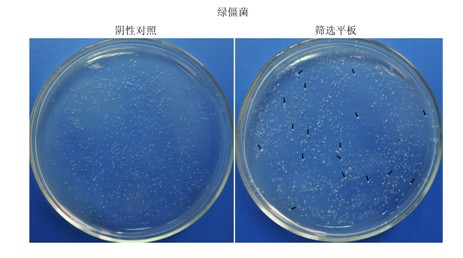
The invention discloses a fungus expression vector. The expression vector is a constructive expression vector which consists of a plasmid expression vector pEX and an acidic trehalase gene serving as a screening marker, wherein the plasmid expression vector pEX is formed by removing a Bar gene in an expression vector pBarEx; and the screening marker gene belongs to acidic trehalase genes such as an ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) gene or an ancient technology activation (ATA) gene. In the invention, a safe and environment-friendly screening marker is used for the fungus expression vector,and insect pathogen project fungi constructed by the fungus expression vector are released to the environment and cannot adversely influence the environment due to the screening marker. The fungus expression vector has a unique design principle, an ingenious construction method, a simple program, a simple screening program for an insect pathogen fungus transgenic bacterial strain of the fungus expression vector and high screening efficiency, does not influence the metabolic balance of the fungi, and has a potential and wide application prospect in the transgenic fungus research and marketization process.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com