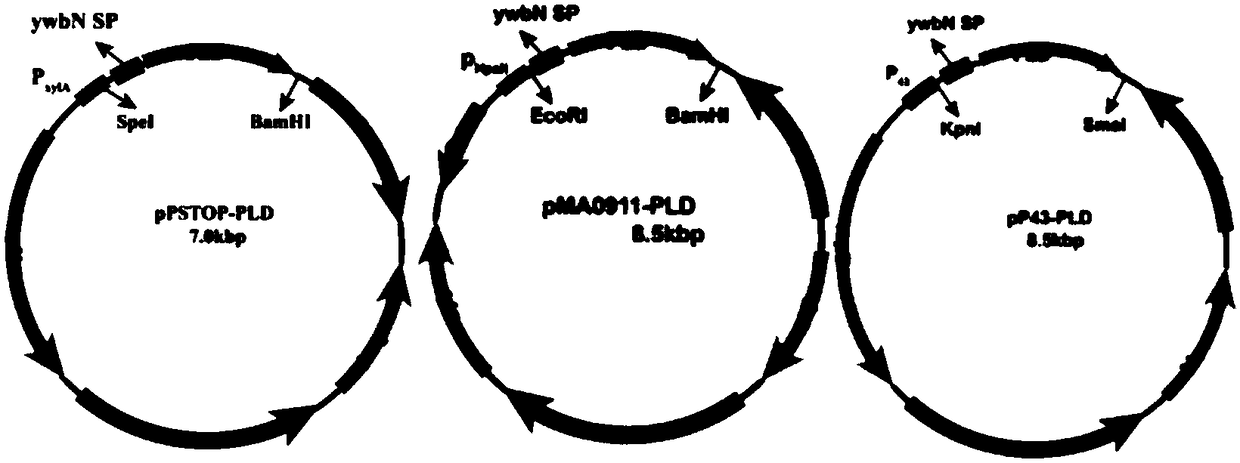
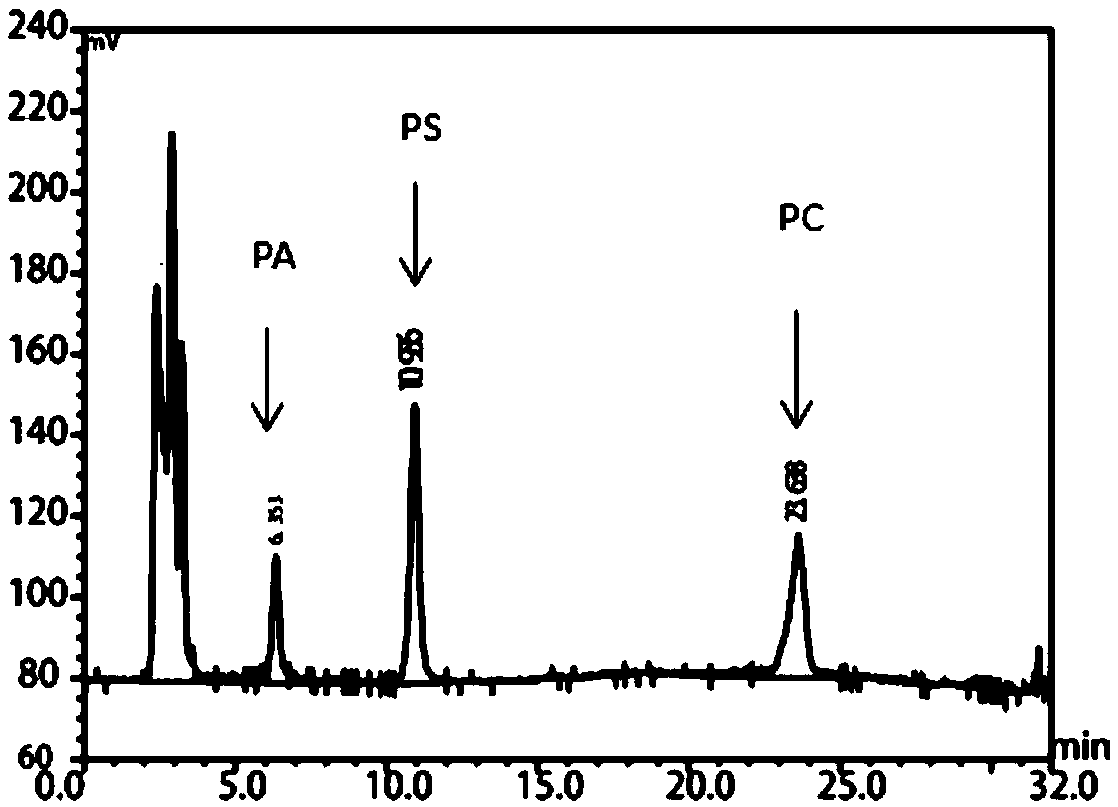
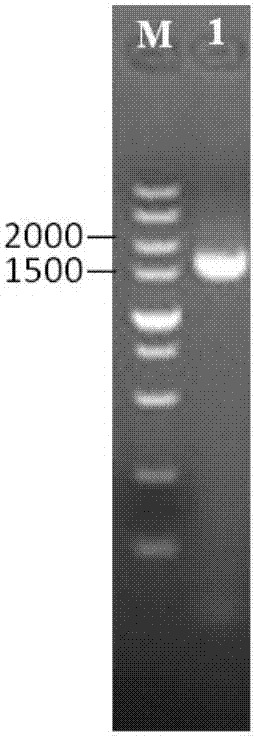
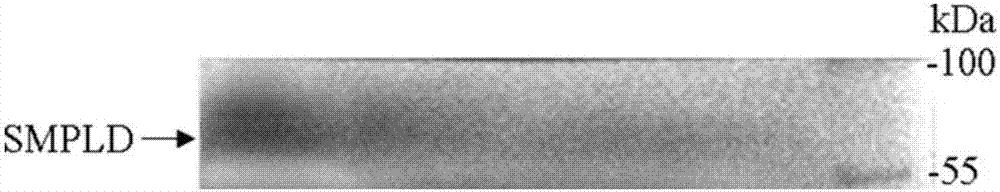
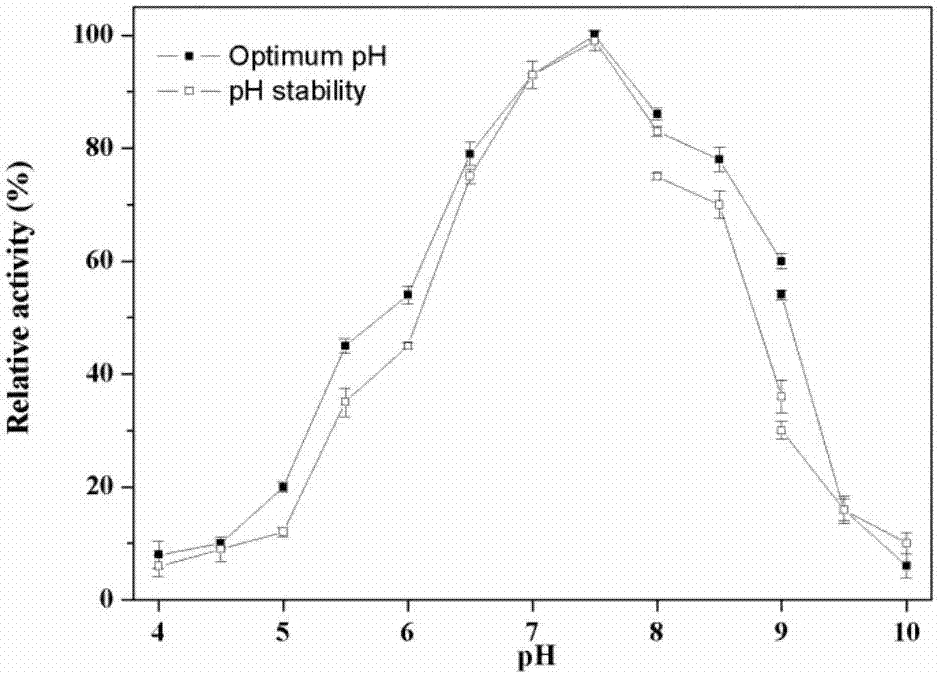
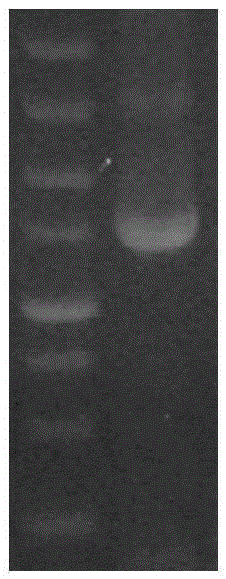
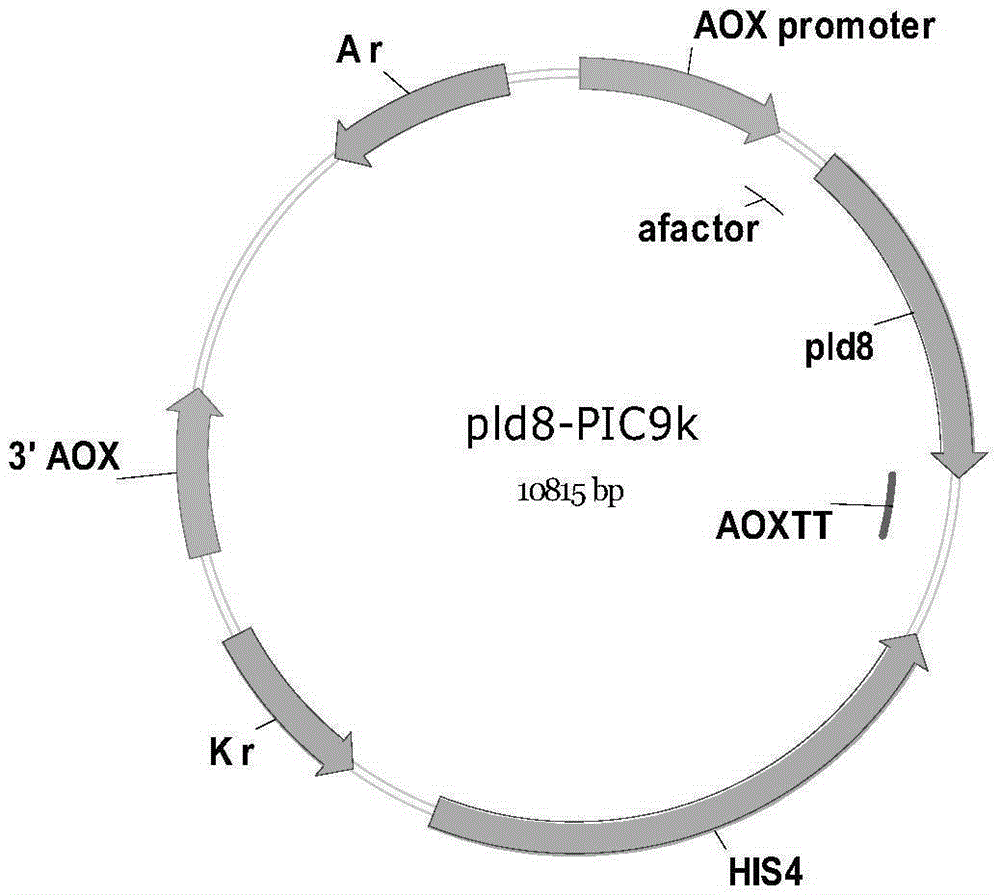
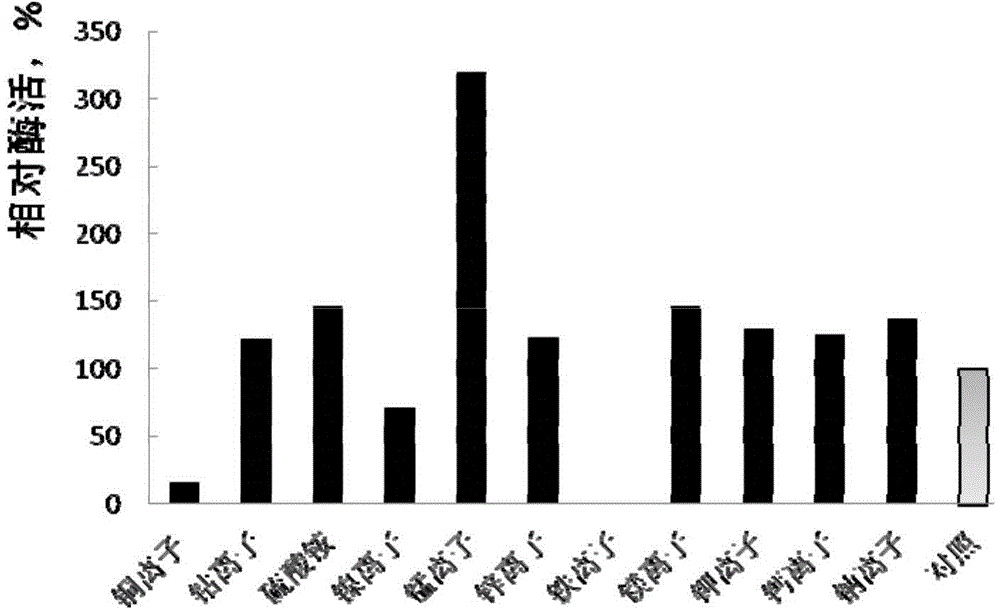
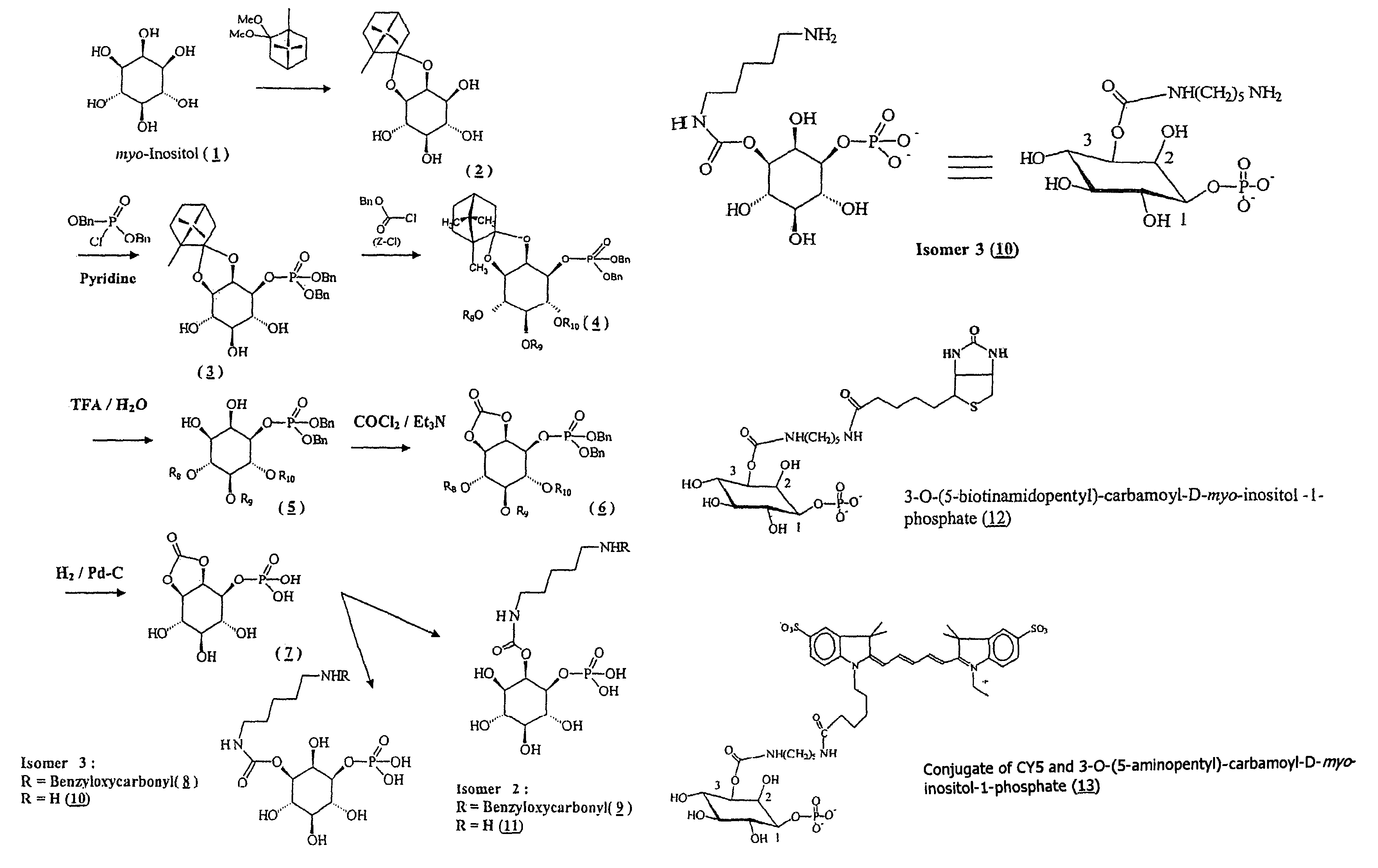
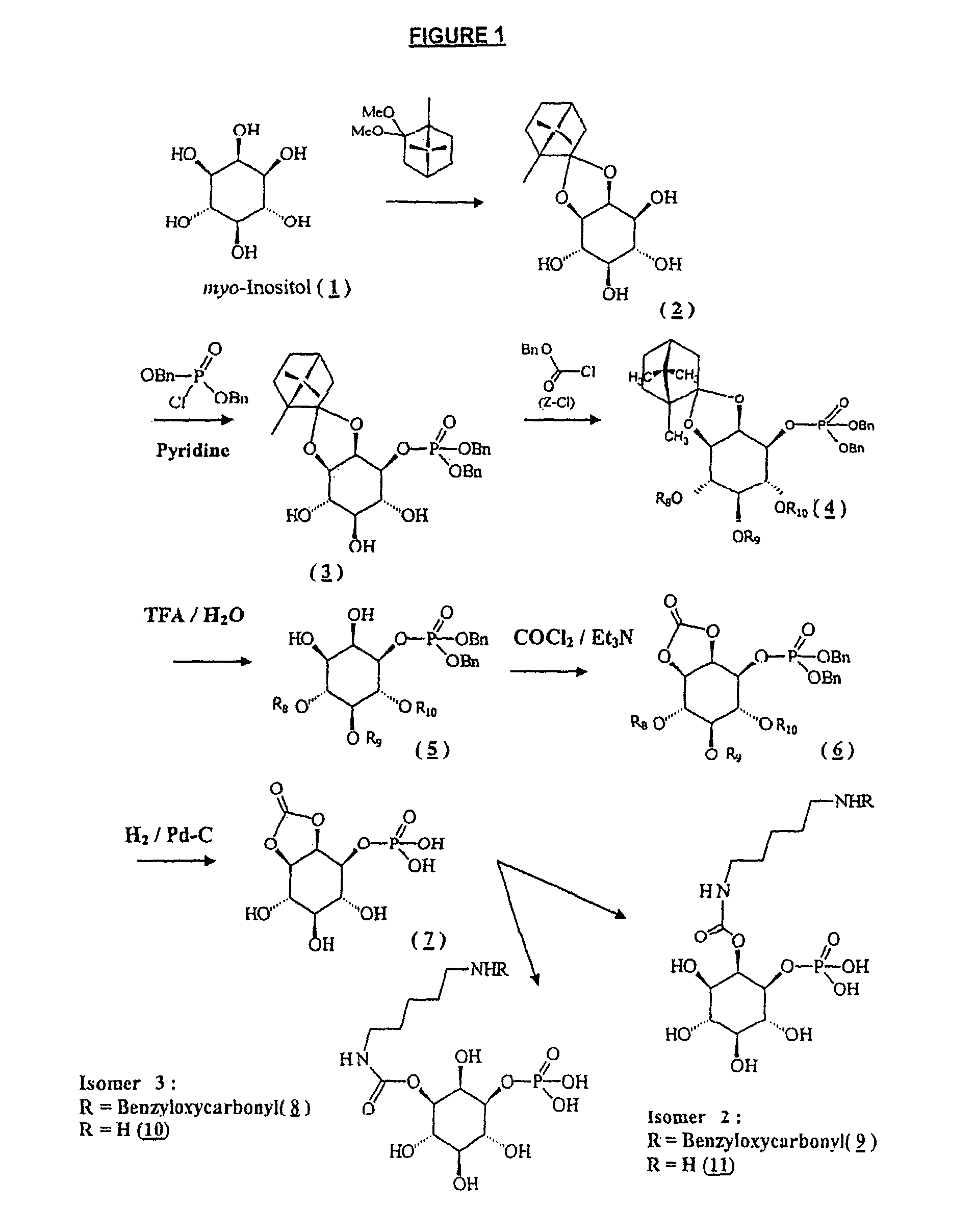
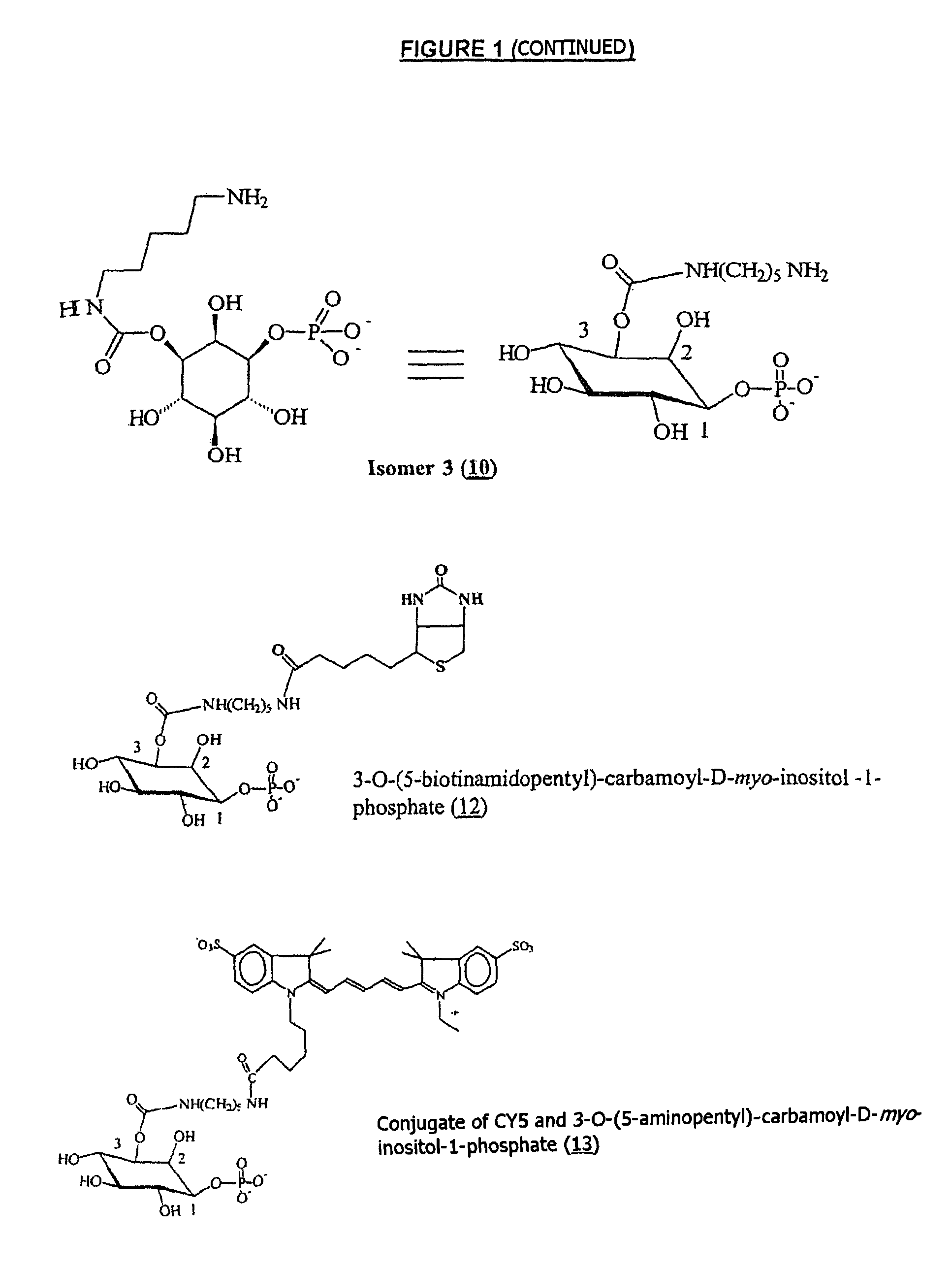
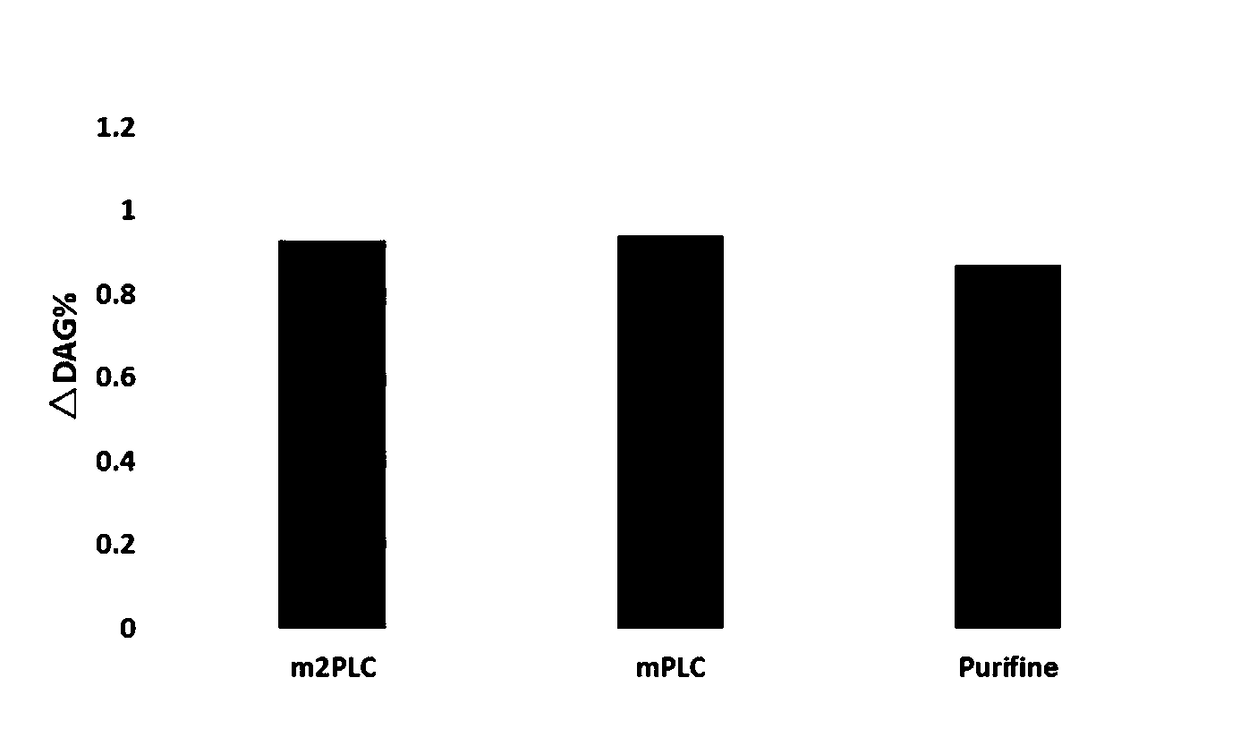
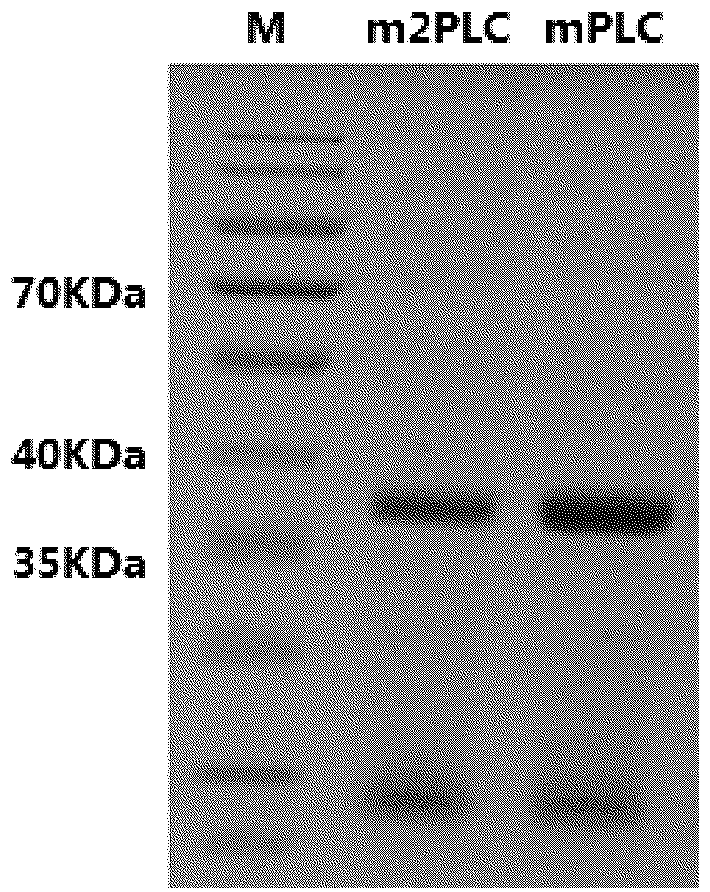
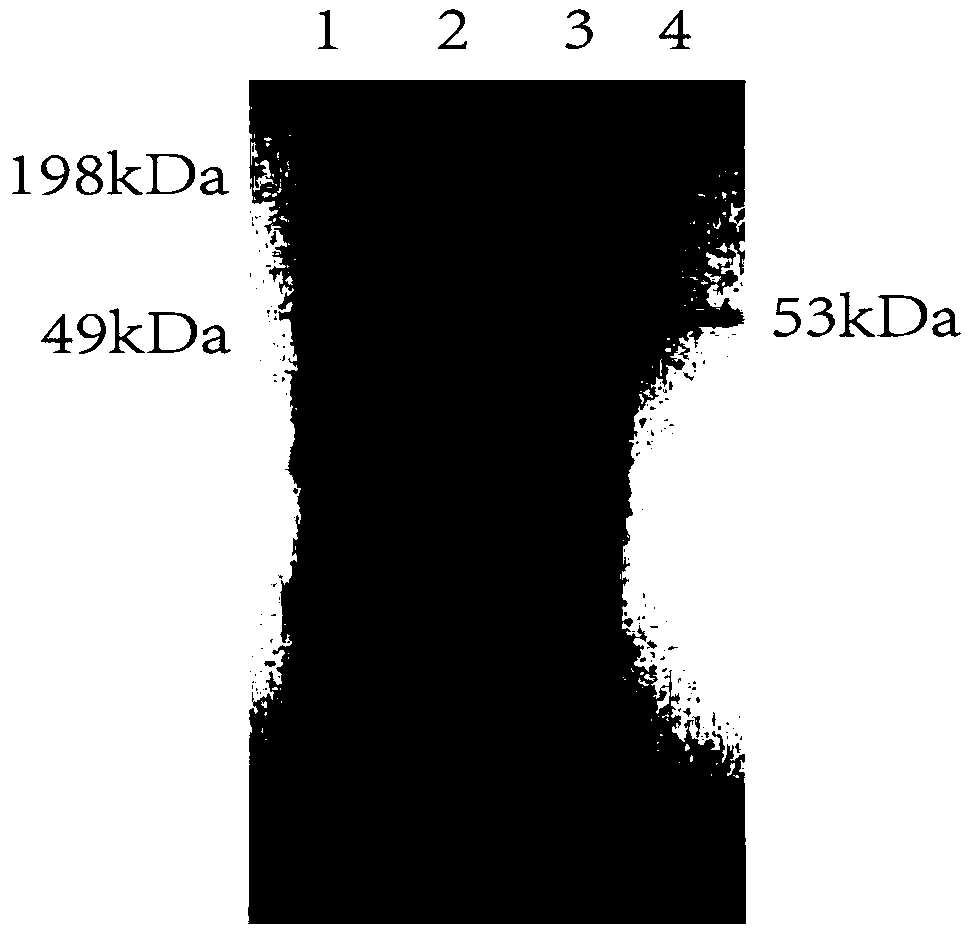Patents
Literature
34 results about "Phospholipase C" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
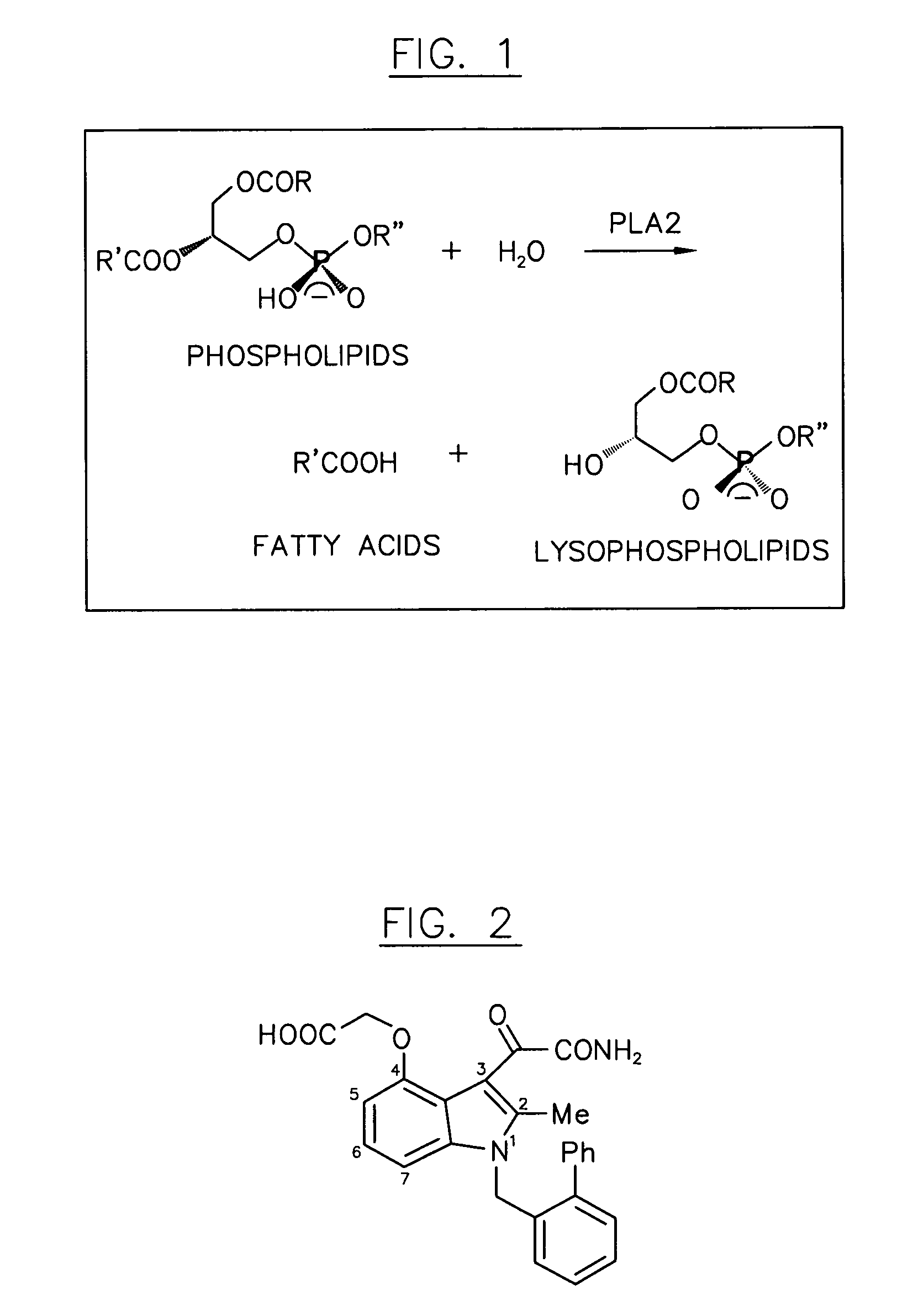
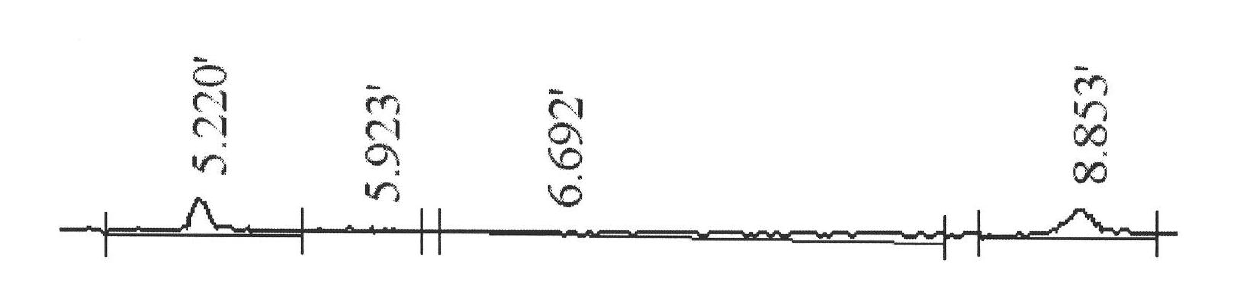
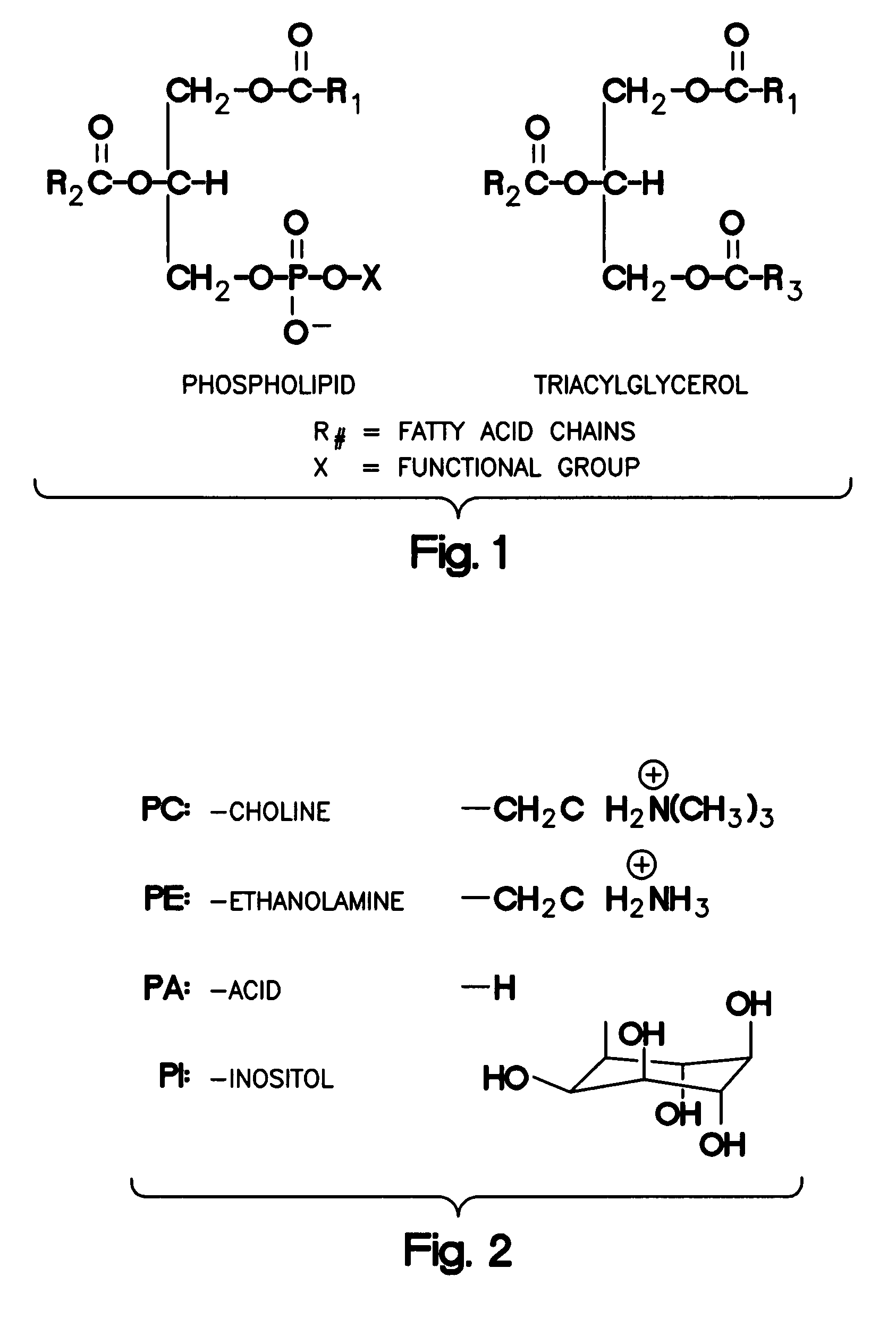
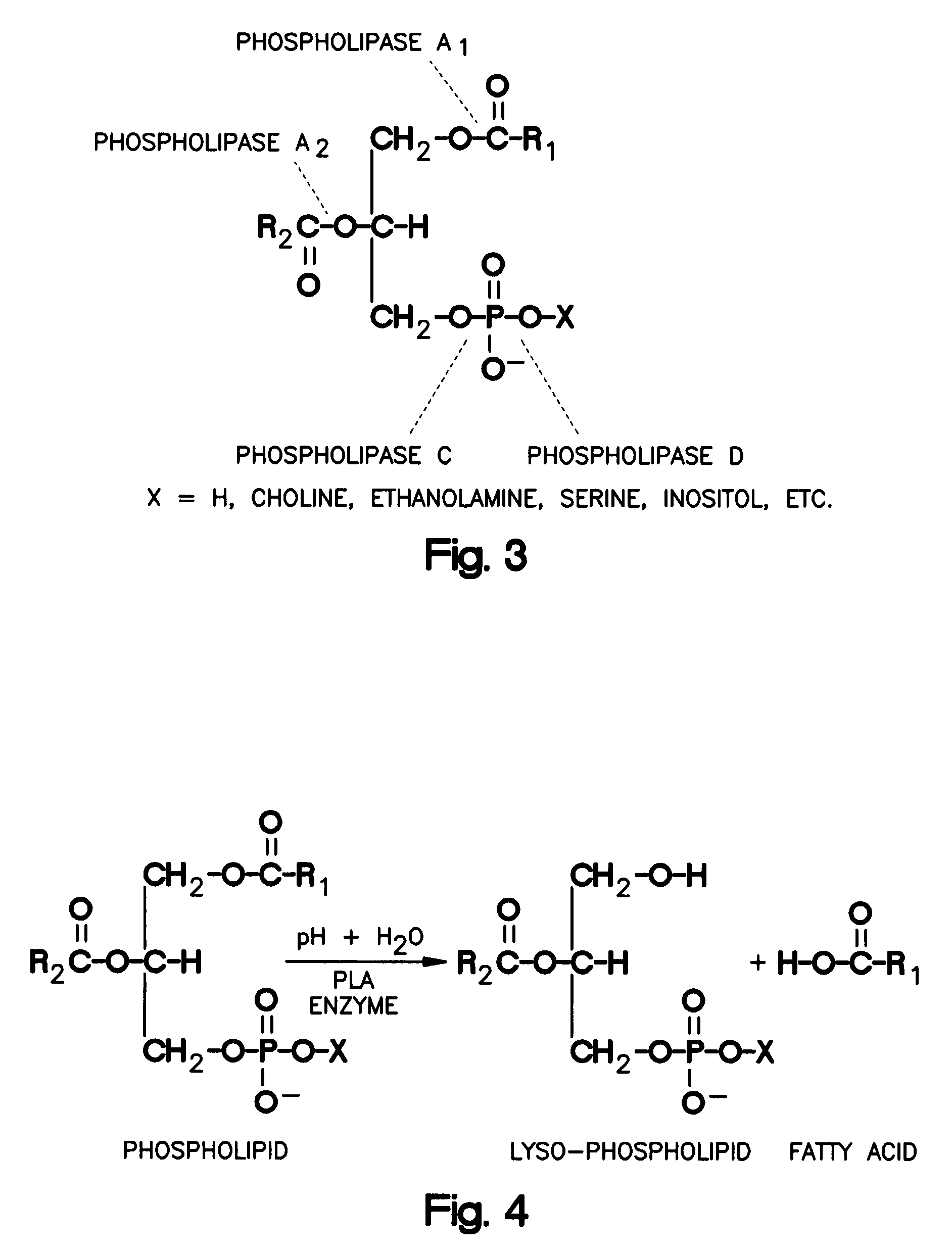
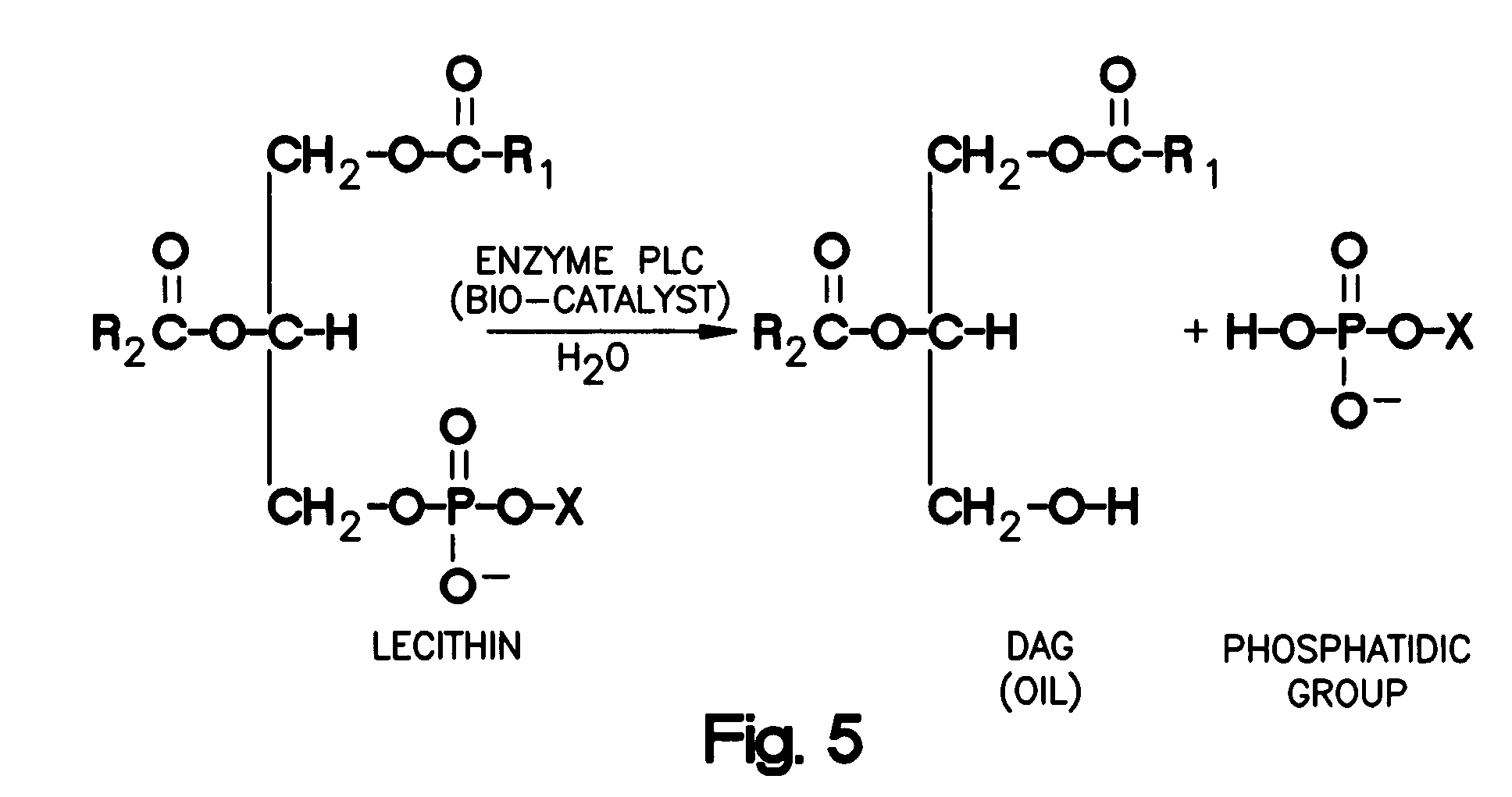
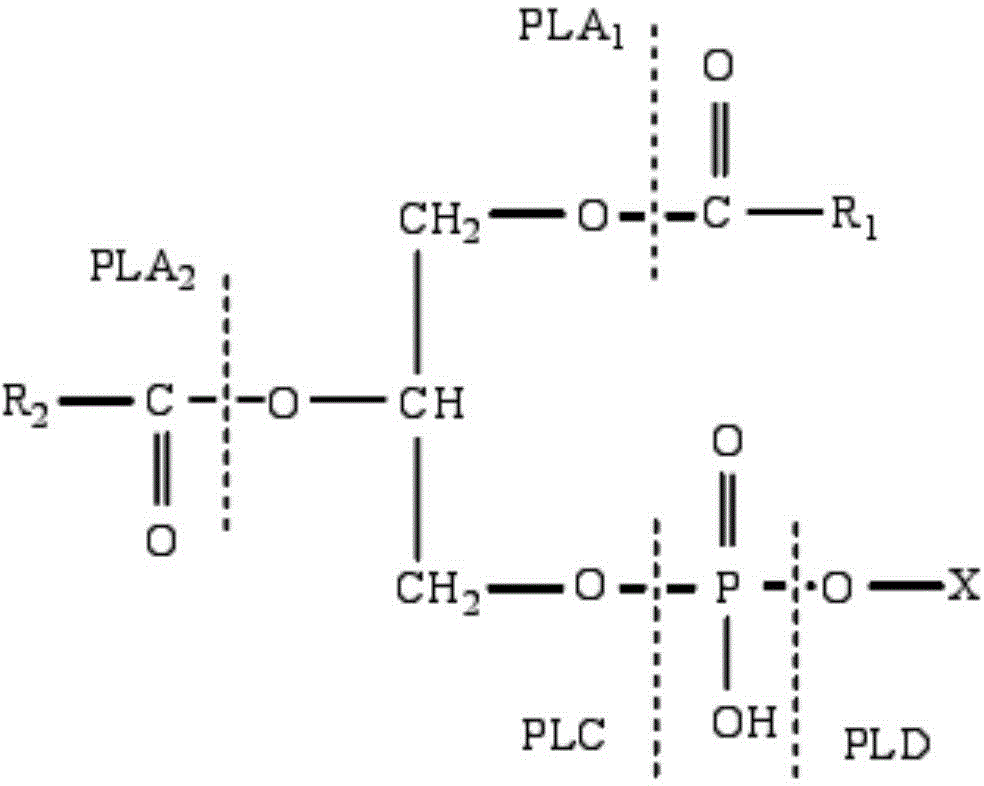
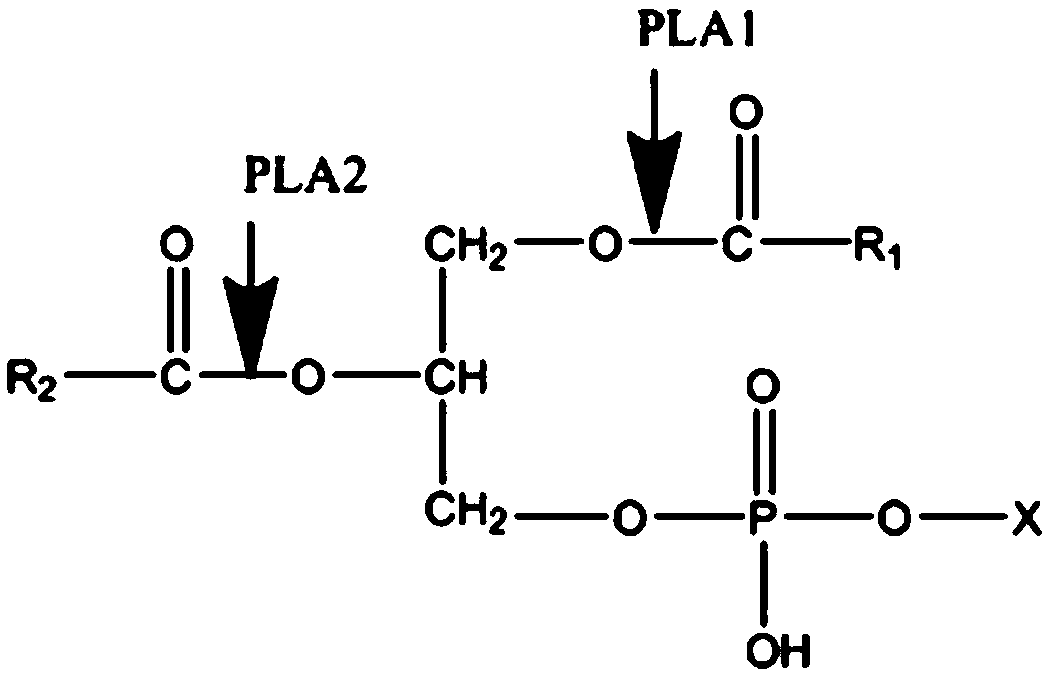
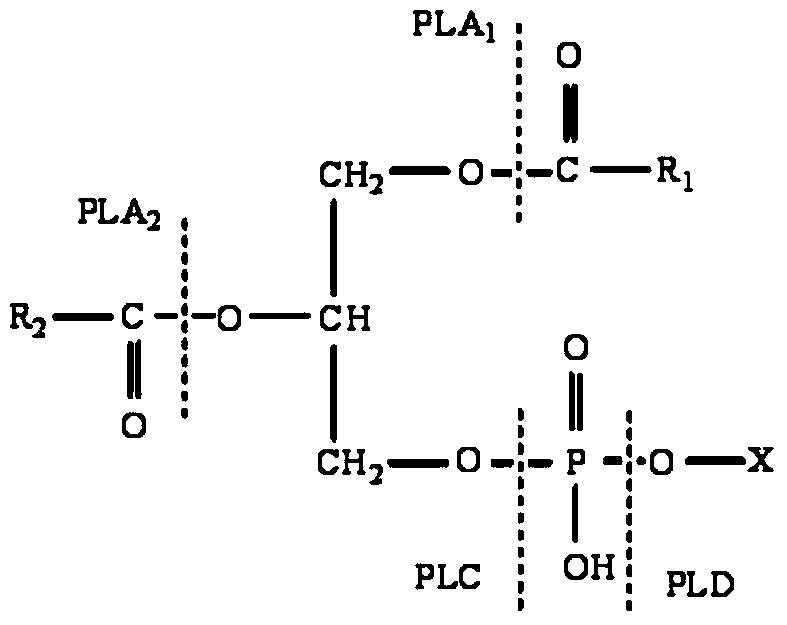
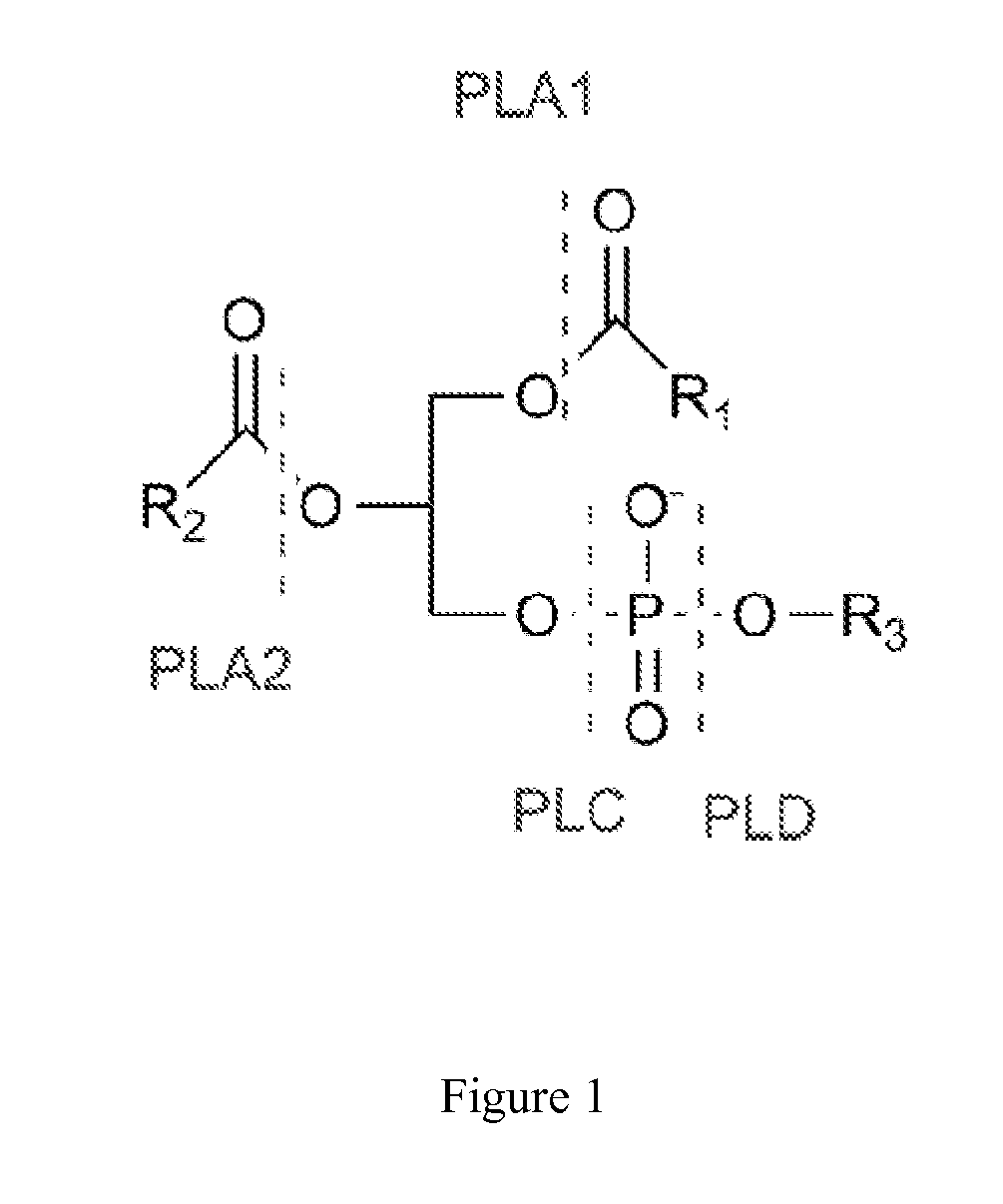
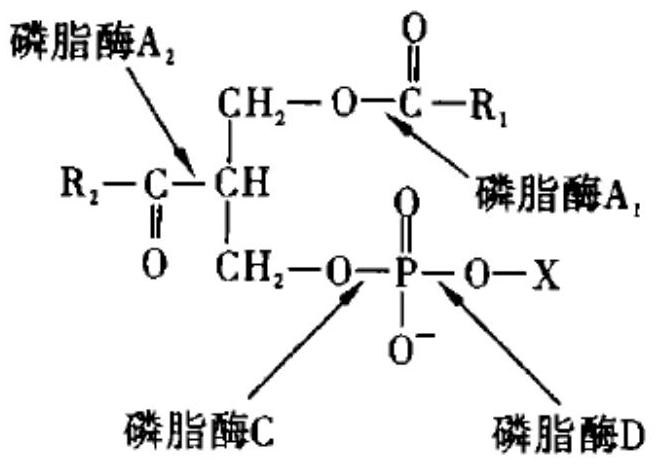
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. There are thirteen kinds of mammalian phospholipase C that are classified into six isotypes (β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η) according to structure. Each PLC has unique and overlapping controls over expression and subcellular distribution. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca²⁺, and phospholipids.
Inhibitors of phospholipase enzymes
Novel compounds are disclosed which inhibit the activity of phospholipase enzymes in a mammal, particularly cytosolic phospholipase A2. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of treatment using such compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Bacillus cereus fermentation method for producing phosphatidase C
InactiveCN102206616AThe strain number is clearSimple processHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyBacillus cereus
The invention discloses a bacillus cereus fermentation method for producing phosphatidase C and belongs to the technical field of enzymic catalytic reaction. The bacillus cereus fermentation method for producing phosphatidase C is utilized to solve the problem of bacterial strains used in the production of phosphatidase C and the problem of complex technology, and comprises the following steps of: inoculating bacillus cereus into the LB medium for culturing to obtain a seed liquid; vaccinating the seed liquid in a fermentation medium consisting of beef extract, peptone, NaCl, water, zincsulfateheptahydrate or ZnCl2, and lecithin or a phosphatide mixture which is the mixture of PC, PE, PI, PS and the like, for culturing to obtain a fermentation broth; and separating the fermentation broth to obtain phosphatidase C. The bacillus cereus fermentation method for producing phosphatidase C can be widely applied to the production of phosphatidase C for plant oil degumming.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Phospholipase B from pseudomonas fluorescens and production method thereof
InactiveCN102002486AHigh activityImprove stabilityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a phospholipase B from pseudomonas fluorescens and a production method thereof, which belong to the field of enzyme gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The phospholipase B is produced from the pseudomonas fluorescens, has the total gene length of 1272bp and codes of 423 amino acids, and the zymoprotein theoretical molecular weight is 45.8kDa, wherein 1 to 69bp code phospholipase B signal peptide, and 70 to 1272bp code phospholipase B mature peptide are comprised. An expression vector and a recombinant host of the phospholipase B can be obtained by the traditional molecular biological method, i.e. colibacillus recombinant plasmid and recombinant colibacillus containing genes of the phospholipase B are obtained. The phospholipase B has good activity and stability at low temperature, does not have the lipase activity, can be hydrolyzed for catalyzing two fatty acyl group radicals in complete phospholipids, has wide application in the industrial process of grease refining, phospholipids emulsifying agent modification and the like, and also has simple preparation method, high product quality and low production cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Enzymatic degumming utilizing a mixture of PLA and PLC phospholipases
ActiveUS8956853B2Suitable for useLow in phospholipidsFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationPhospholipidPhospholipases A
A method for degumming an oil composition comprises the steps of (a) providing an oil composition containing a quantity of phospholipids, (b) contacting said oil composition simultaneously with one or more phospholipase A enzymes and one or more phospholipase C enzymes, under conditions sufficient for the enzymes to react with the phospholipids to create phospholipid reaction products, and (c) separating the phospholipids reaction products from the oil composition, the remaining oil composition after the separation being a degummed oil composition, whereby during step (b) the reaction of said one or more phospholipase A enzymes proceeds at a faster rate than it would in the absence of said one or more phospholipase C enzymes.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
Recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing phosphatidase C, phosphatidase C preparation method, and applications of phosphatidase C
ActiveCN103509748AHigh enzyme productionSimple production processBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
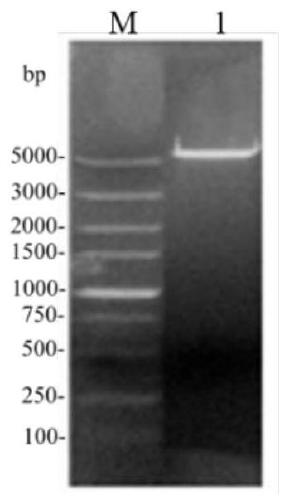
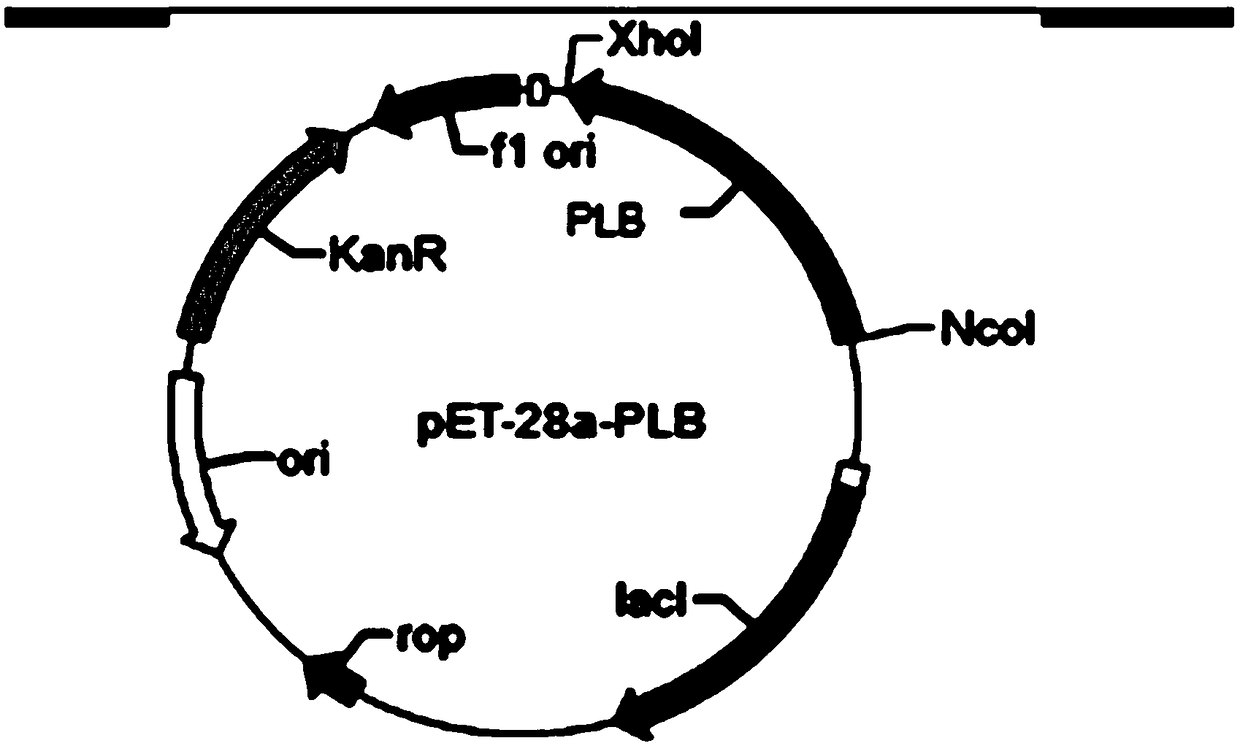
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing phosphatidase C, a phosphatidase C preparation method, and applications of phosphatidase C. A construction method of the recombinant escherichia coli comprises following steps: A, preparation of phosphatidase C gene, wherein PCR primers are designed, and phosphatidase C gene segments are amplified; B, construction of recombinant plasmids, wherein phosphatidase C gene segments with 1158bp are obtained by digestion using EcoR I and Not I enzymes, and the phosphatidase C gene segments are combined with high-copy plasmid pET28a by clone so as to obtain recombinant plasmid Pet28a-P.f-PLC; and C construction of engineering bacteria, wherein plasmid Pet28a-P.f-PLC is transferred into E.coil BL21(DE3) via transformation. Active phosphatidase C can be produced by liquid fermentation, and intracellular and extracellular enzyme activities can reach 408.5U / ml. Phosphatidase C possesses an application prospect in the fields such as oil and fat refining, phosphatide modification and medical treatment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. A phospholipase D gene is obtained through clone in Streptomyces ambofaciens by means of molecular biology measures, constructed expression plasmid is guided into E. coli BL21(DE3), and phosphatase-containing engineering bacteria formed by highly copying and recombining an expression carrier are obtained through kanamycin resistant plate screening. The recombinant phospholipase D is used for converting phosphatidylcholine and serine to generate phosphatidylserine, and efficient production of vitamin C-2-phosphate is achieved. By carrying out reaction for 2 h at the temperature of 40 DEG C with the pH value of 4.5, the yield of phosphatidylserine can reach 15.8 g / L, the conversion rate is 63.9%, and the space time yield is 7.9 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
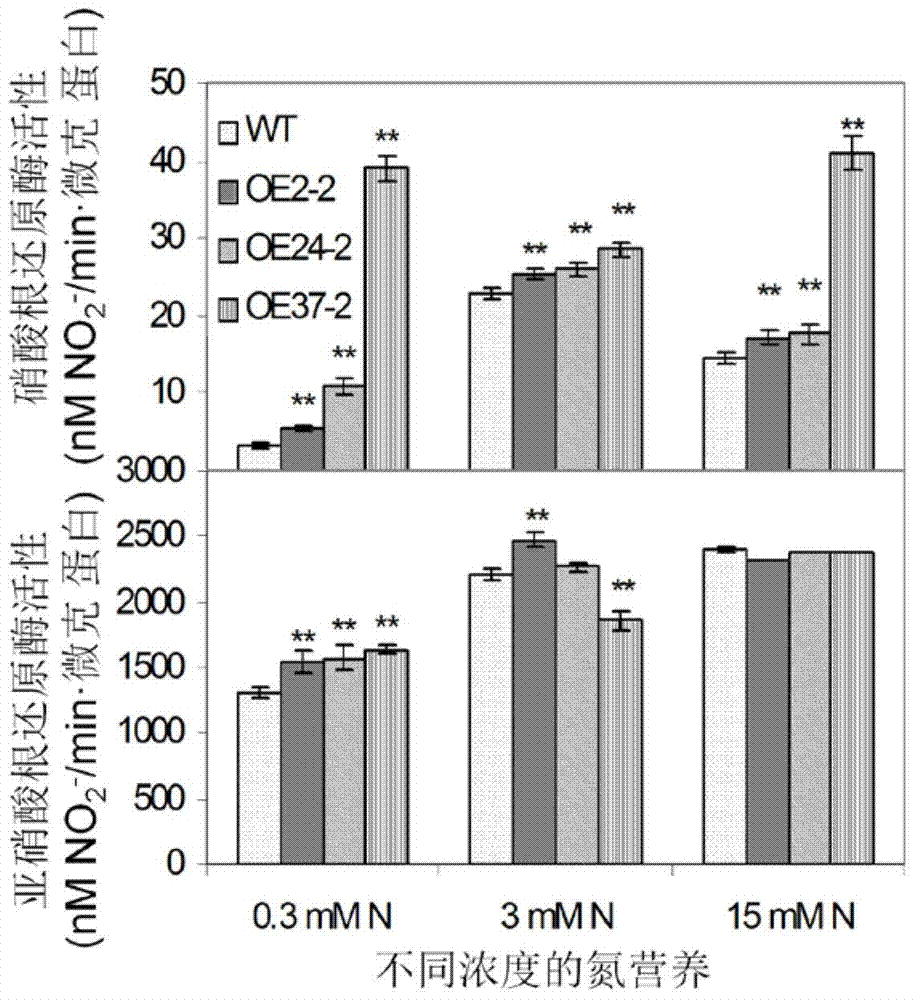
Application of PLD (phospholipase D) epsilon gene in increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of crops
InactiveCN103773798AEasy to transportEfficient reuseFermentationGenetic engineeringNutritionNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant molecular breeding and biology, and discloses application of a PLD (phospholipase D) epsilon gene in increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of crops. The nucleotide sequence of the PLD epsilon gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, or has a similarity more than or equal to 60 percent as the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses a method for increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of rape. Tests prove that growth and occurrence of lateral roots of rape can be promoted due to overexpression of AtPLD epsilon either in nitrogen starvation or nitrogen sufficiency condition, increase of rape leaf tissue cell growth and biological yield can be reinforced, absorption transportation and assimilation metabolism processes of rape plants can be promoted, which are particularly indicated in that the expression quantities of genes NTR1.1 and NTR2.1 related to overexpressed plant N transportation are remarkably higher than that of a wild type, and the nitrogen absorption rate is remarkably higher than that of the wild type.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Novel Phospholipase C Enzyme (S)
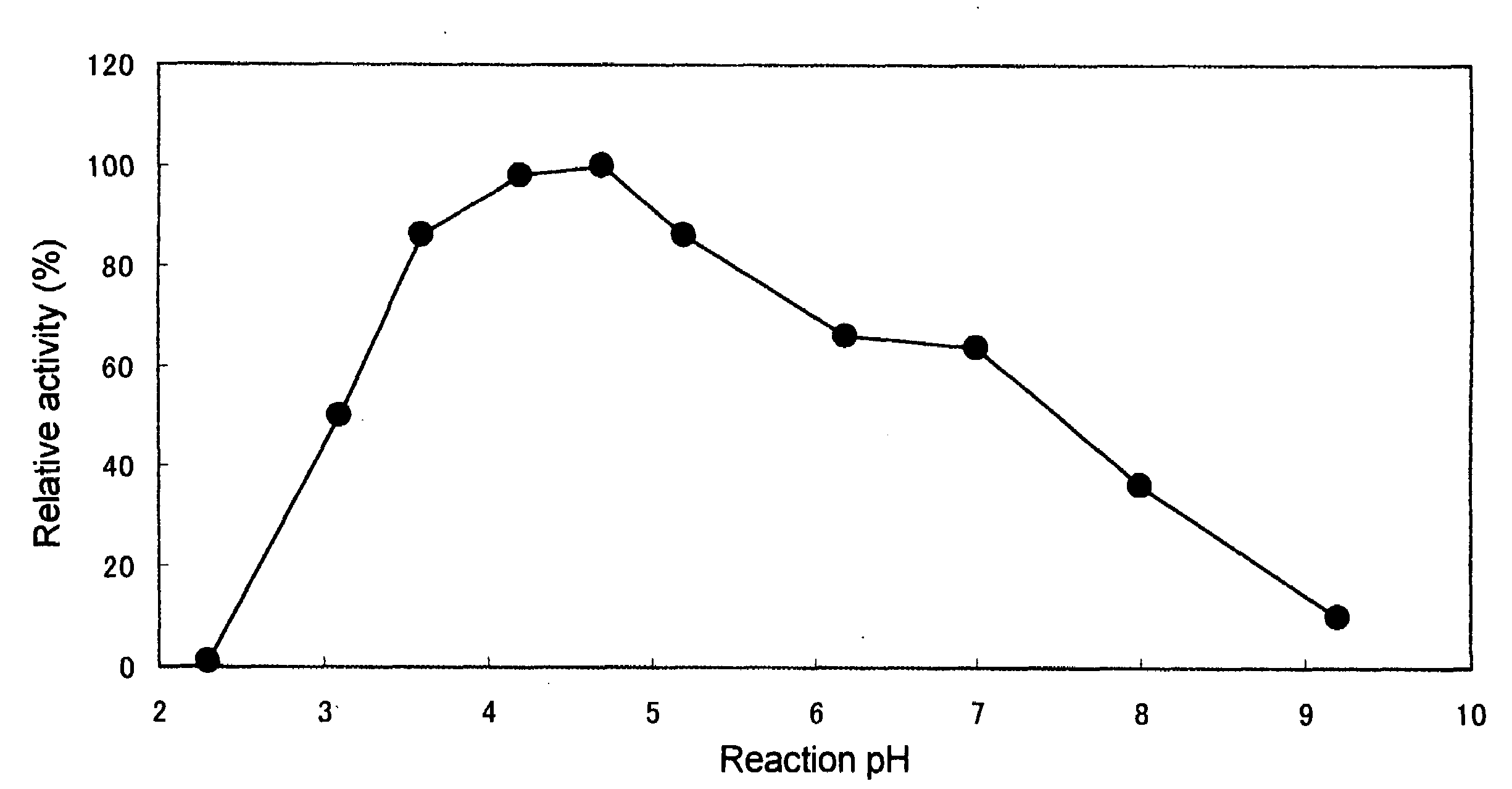
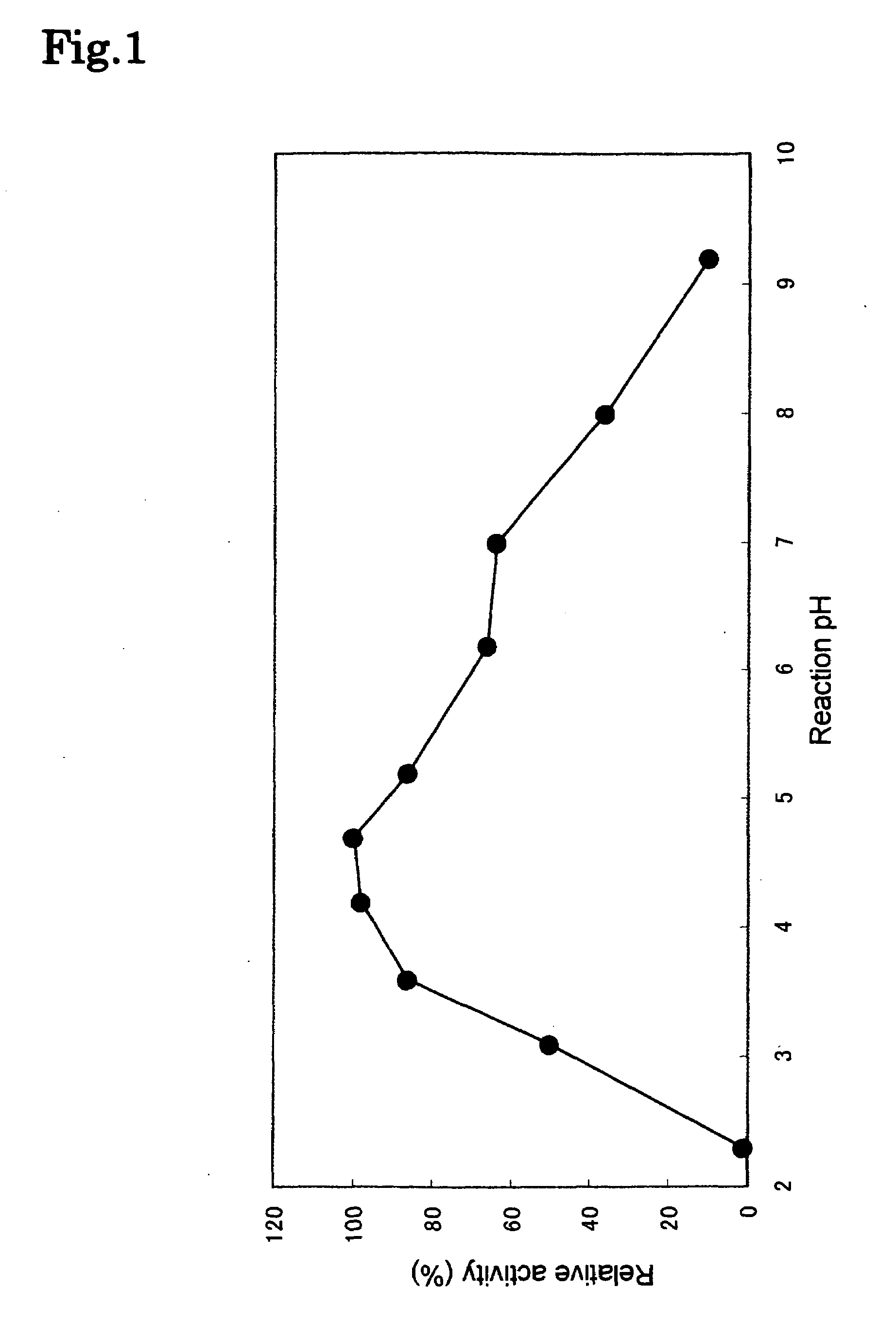
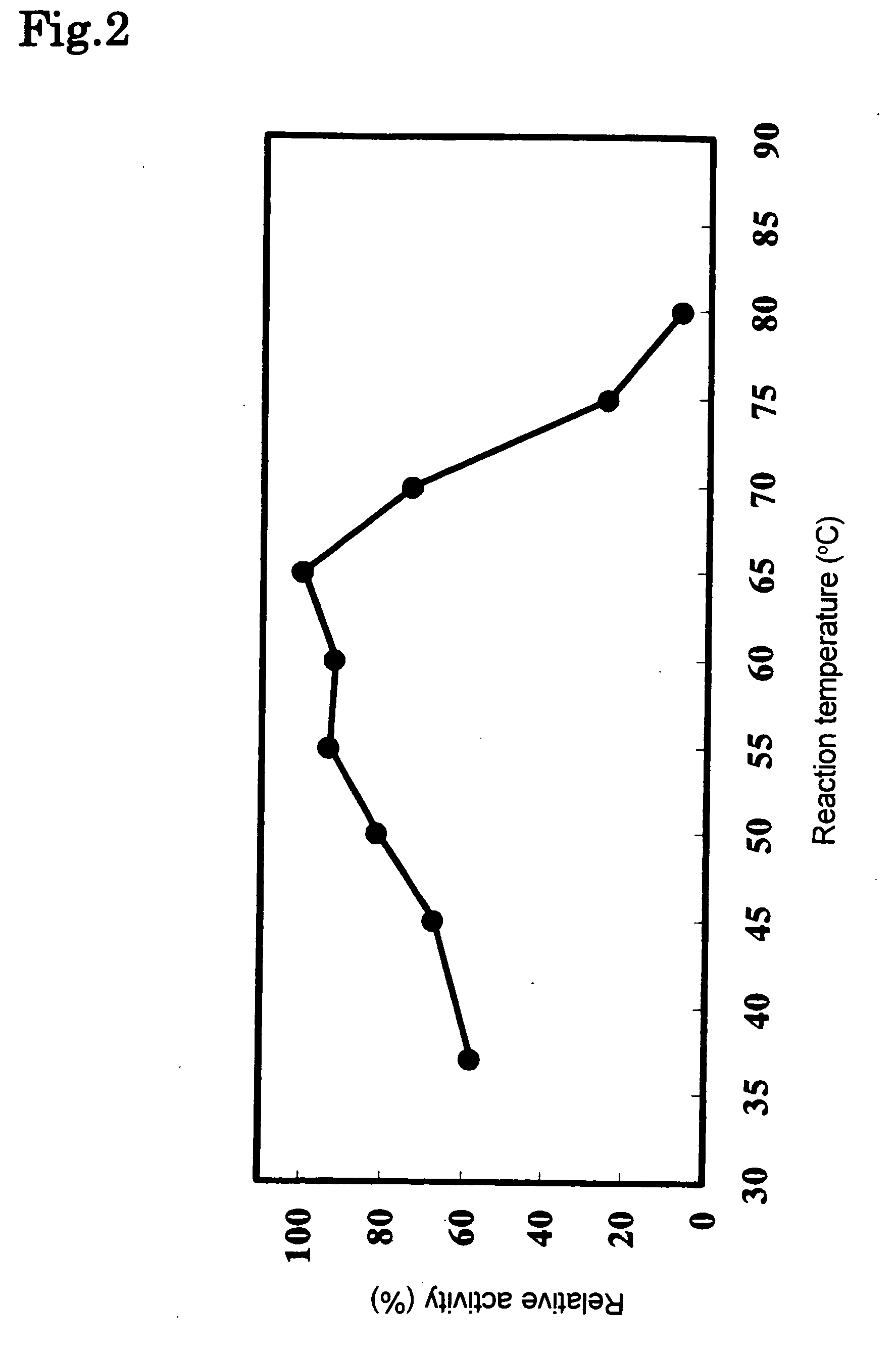
The present invention provides a phospholipase C enzyme(s) having ability to hydrolyze phospholipid in both acidic and around neutral ranges and the activity in a citrate buffer solution as well as having some degree of heat stability, and having a property not to hydrolyze phosphate esters not containing lipid moieties. The phospholipase C enzyme(s) shows the activity at from acidic to neutral pH and does not substantially hydrolyze any phosphate esters except for phospholipids.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D
InactiveCN108841770AAchieve secretory expressionHigh selectivityBacteriaHydrolasesPhospholipidStreptomyces peucetius
The invention discloses engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing the phospholipase D is constructed by taking bacillus subtilis (WB600) as an expression host and taking a phospholipase D encoding gene (PLD) from streptomyces racemochromogenes as a target gene.The activity of the phospholipase D produced by the engineering bacteria can be up to 5.916 U / mL and has an extremely high application value in the field of medicines, food and health care products;meanwhile, the phospholipase D adopted by the engineering bacteria is actinomyces-derived endogenous phospholipase D, which has high reaction activity, high phosphatidyl substrate selectivity and highorganic matter stability; furthermore, a catalysis structure is the most compact; the phospholipase D is more suitable for efficient synthesis of phospholipid and a phospholipid derivative in the industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene mining and application method of phospholipase D
InactiveCN107164397AEfficient expressionShort fermentation cycleHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliReaction temperature
The invention provides a phospholipase D acquired based on a gene mining method, as well as a gene coding sequence and application method thereof. A phospholipase D gene has a full length of 1,614bp, encodes 538 amino acids, uses plasmid pET28a (+) as an expression vector, and uses E. coli BL21 (DE3) as an expression host, to realize efficient expression of phospholipase D. The phospholipase D gene is simple and convenient in gene mining method; a recombinant strain constructed by the mined target gene can be fermented and induced to excrete the phospholipase D. For the phospholipase D, an optimum reaction temperature is 60 DEG C; an optimum reaction pH is 7.5; and Ca<2+> has good activating and promoting effects on enzyme activity of the phospholipase D; the phospholipase D can modify phospholipids, and can catalyze substrates phosphatidylcholine and L-serine to synthesize phosphatidylserine, thereby having good application prospects in food, medicine and healthcare industries.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
New phospholipase
The present invention relates to a new phospholipase and a coding gene thereof, also relates to a vector and a host cell comprising the gene. The new phospholipase contains or comprises sequences selected from the group consisting of (a) an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQIDNO:2, and (b) a sequence obtained by substitution, deletion or addition of at least one amino acid of the amino acid sequence (a), wherein the sequence(b) still has the functions of the SEQIDNO:2. The new phospholipase has the ability to hydrolyze phosphatidyl ethanolamine acyl ester without hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Phospholipase C and bacterial strain generating same
ActiveCN104419651AGood degumming effectImprove degumming effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention provides a separated bacterial strain expressing phospholipase C. The bacterial strain is deposited with China general microbiological culture collection center and assigned the accession number CGMCC No.7506. The phospholipase C obtained from the bacterial strain and a preparation method in the invention can be used in oil refining, is good in degumming effect, and can be widely applied in oil refining, additives, medicines and the like.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Coding gene of phospholipase D and expression and application thereof
InactiveCN110004124AImprove stabilityGood transphosphatidyl transfer abilityHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliL serine
The invention provides a coding gene of phospholipase D and expression and application thereof, and provides a method for expressing recombinant phospholipase D by E.coli BL21 and producing phosphatidylserine by using the recombinant phospholipase D. The method includes construction of a recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-sspld, transformation of the recombinant plasmid into E.coli BL21 and catalyticproduction of phosphatidylserine by recombinant bacteria. The recombinant strain can successfully express the phospholipase D and the enzyme activity reaches 17.07 U / mL. By optimization of the induction conditions, the highest enzyme activity of the recombinant bacteria can reach 38.58 U / mL. The enzyme has good transphosphatidyl ability through HPLC detection and can synthesize the product phosphatidylserine by using lecithin and L-serine as substrates, the conversion rate can reach 28% and the yield can reach 1.34 g / L. The recombinant phospholipase D has short fermentation period and good catalytic performance, and lays a foundation for a practical application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
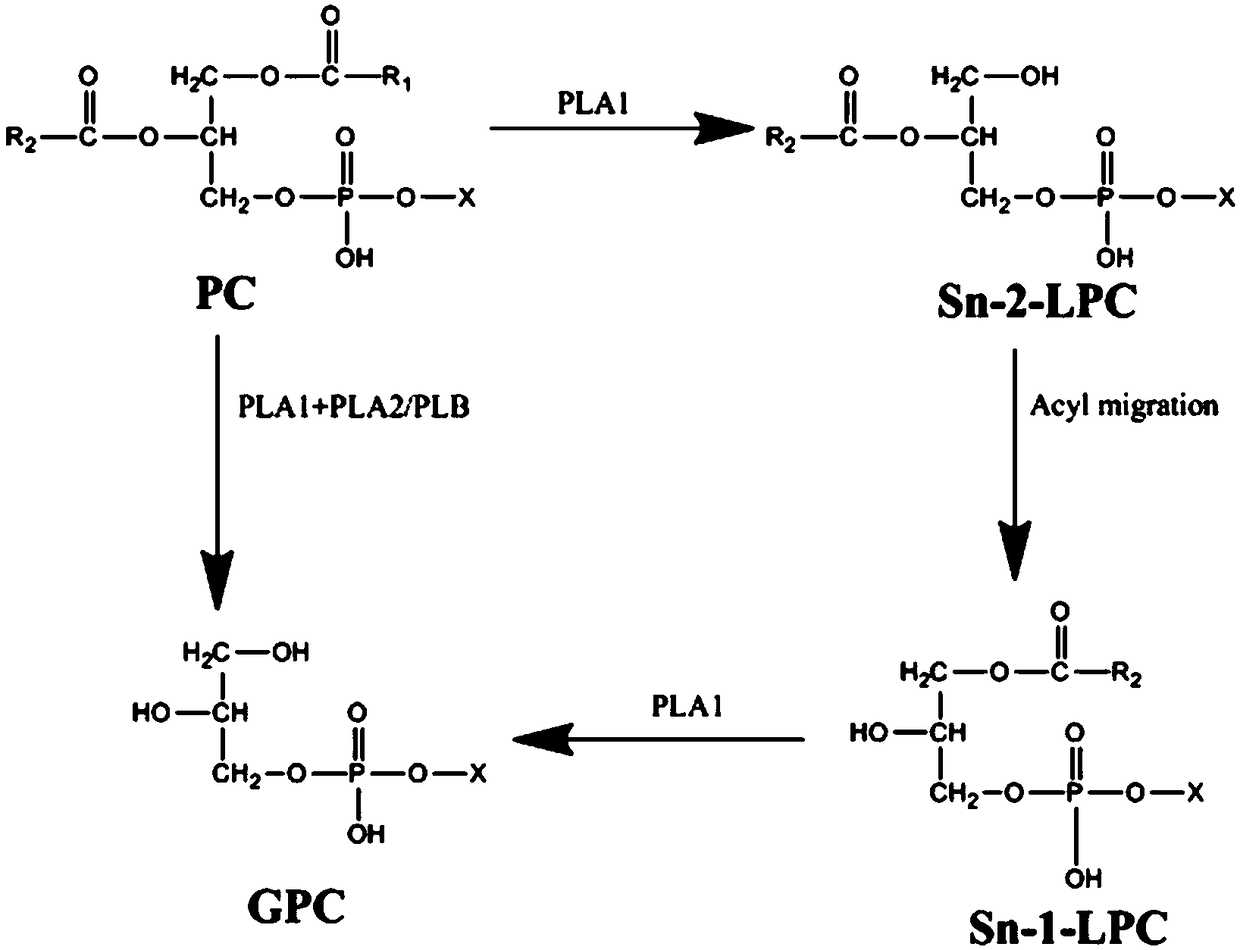
Phospholipase B and application in preparing glycerolphosphocholin thereof
InactiveCN109055331AResolve source issuesSolving the Inclusion Body ProblemBacteriaHydrolasesInclusion bodiesNucleotide
The invention discloses phospholipase B and application in preparing glycerolphosphocholin thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the phospholipase B is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Reconstitution cells whichcomprise the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 are cultured to obtain the phospholipase B. By applying the obtained phospholipase B to glycerolphosphocholin preparation, the problem of a phospholipase B source is solved, meanwhile, the problem of an inclusion body of the phospholipase B is well solved, and the gap of acyl transferring in only using phospholipase A1 for catalysis in the prior art is filled. The method capable of efficiently producing the glycerolphosphocholin is provided for industrial production. By means of the method, the phospholipase B catalytic efficiency, the product yield and the substrate utilization rate can be significantly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
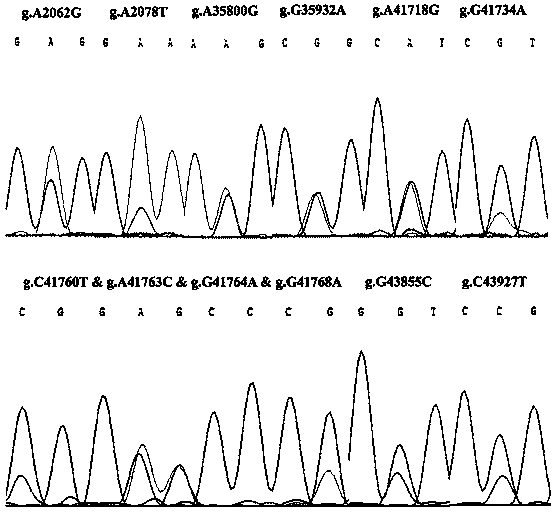
Method for rapidly detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of bovine PNPLA3 (patatin like phospholipase domain-containing 3) gene and application of method
InactiveCN103805692AIncrease weightMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy balancingEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses an RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) method for rapidly detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of bovine PNPLA3 (Patatin Like Phospholipase Domain-Containing 3) gene. The RFLP method comprises the steps of by taking PNPLA3 gene-containing to-be-detected whole-genome DNA as a template, and human-designed primer pairs P1-P5 as primers, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the bovine PNPLA3 gene, and discovering 27 SNP loci; selecting four missense mutation loci and respectively designing primer pairs P2-Bg1I, P2-RsaI, P3-BmgT120I and P3-MspI; carrying out PCR amplification by using the four primer pairs, respectively performing enzyme digestion to the PCR amplified product by using the four restriction endonuclease, and then detecting the enzyme digestion product by using agarose gel electrophoresis, wherein the electrophoresis result shows the SNP at the 2062th locus, the 2078th locus, the 35800th locus and the 35932th locus of the PNPLA3 gene of the Qinchuan bovine gene. The PNPLA3 gene relates to the growth traits of weight, average daily gain and the like, the PNPLA3 gene has the activity of lipase and acyltransferase and plays an important role in aspects of maintaining energy balance, the detection method can be used for marker assisted selection (MAS) breeding of the growth traits of China cattle, thus being beneficial to fast setting cattle population with excellent genetic resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
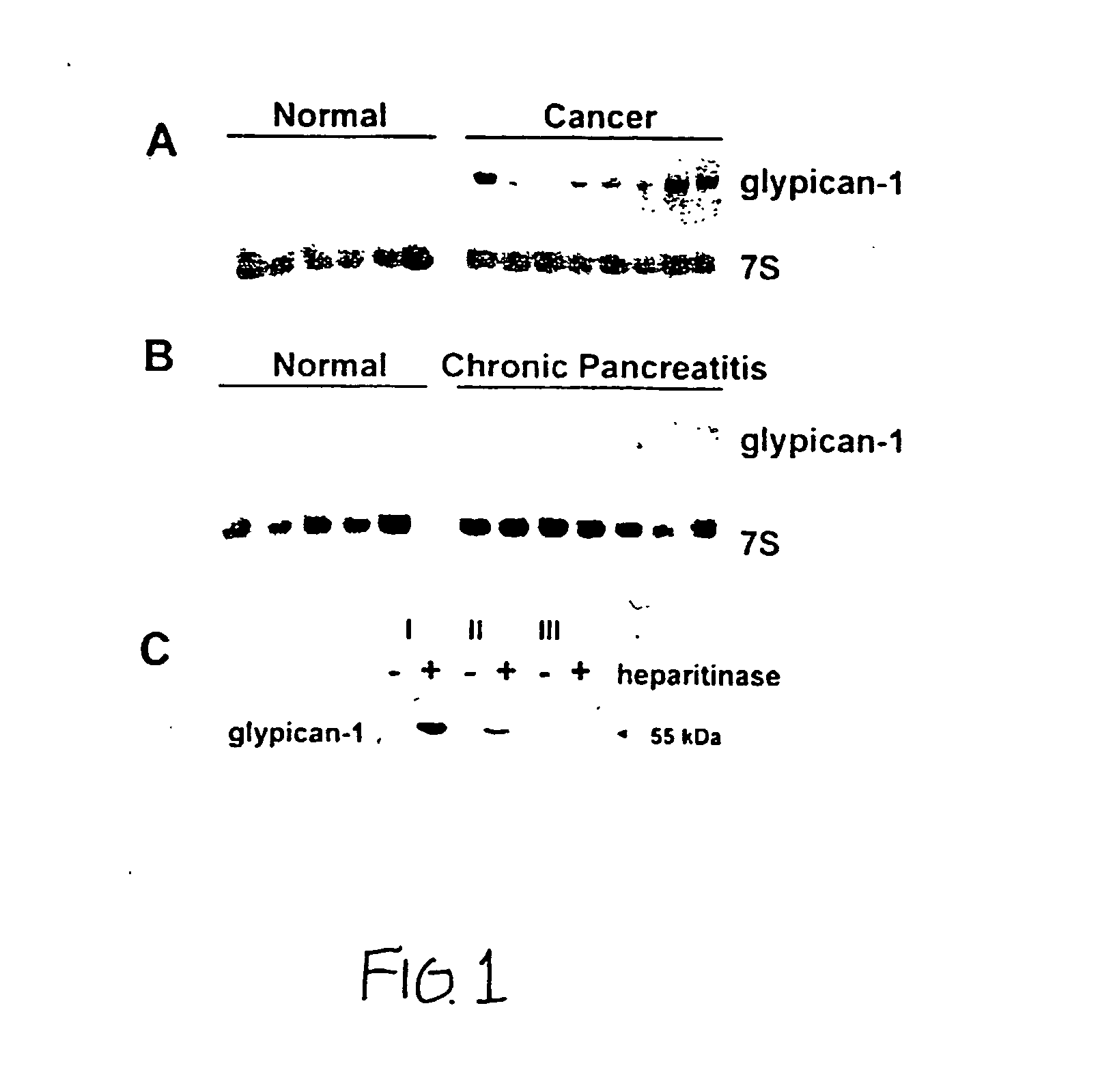
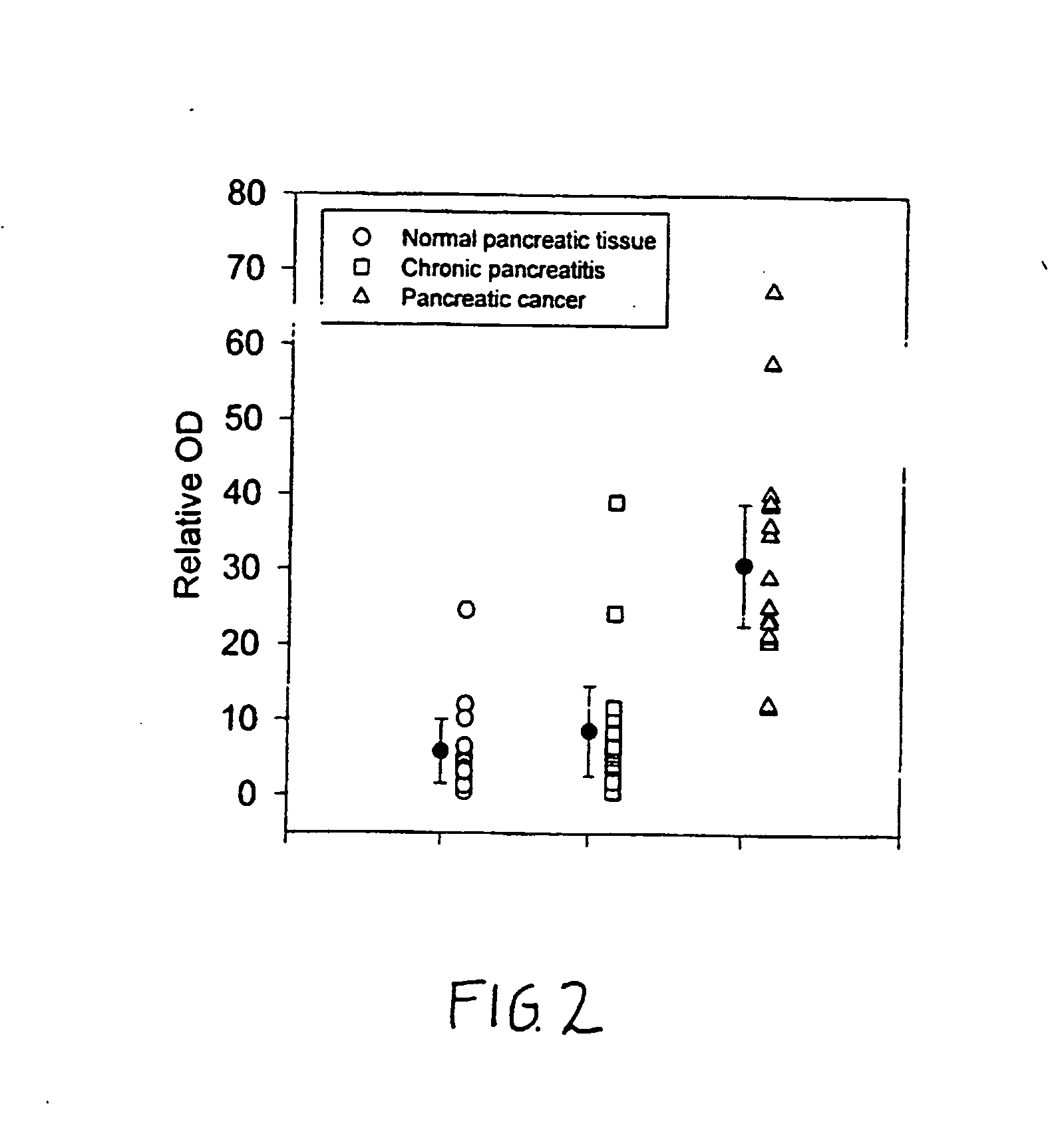
Glypican-1 in human breast cancer
InactiveUS20070026471A1Good effectConfirming the importance of glypicans in breast cancerImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsInsulin-like growth factorProtein C
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C, and screening method thereof
ActiveCN103509736AAccurately determineOvercoming the Shortcomings of ScreeningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesYolkHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C, and a screening method thereof. The bacterial strain is Pseudomonas fluorescens P.f-9103, and preservation number is CCTCC No.M2013298. The bacterial strain is obtained by screening and separation from soil near oil workshops. Morphological characteristics are that: the shape of a bacterial colony is round, the surface of the colony is salient, the color is white, and the bacterial colony is nontransparent and yellows with the increasing of age; the colony is smooth, is relatively viscous and dense, and is easy to be stirred up, and the edge is smooth; the colony has a flagellum, is capable of moving, and produces no blastema; the bacterial strain is gram negative, the optimum growth temperature is 25 to 30 DEG C, and pH value is 7.0 to 7.6. The screening method comprises following steps: primary screening is performed on LB medium containing yolk; then phosphatide is taken as a substrate, and enzymatic reaction is performed; and reaction products are analyzed by HPLC so as to realize secondary screening. According to the method, natural phosphatide is taken as the substrate, so that problems caused by inactivity of phosphatidase C on phosphatide substrate analogue NPPC are avoided. Sources of primary screening raw material are abundant, operation is convenient, secondary screening is accurate and rapid, and the screening method is suitable for high throughput screening of the bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Inhibitor of phospholipase enzymes
Novel compounds are disclosed which inhibit the activity of phospholipase enzymes, particularly cytosolic phospholipase A2. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of treatment using such compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Glypican-1 in human breast cancer
InactiveUS7108986B2Growth stimulatory effectDecrease glypicanSamplingPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin-like growth factorHigh level expression
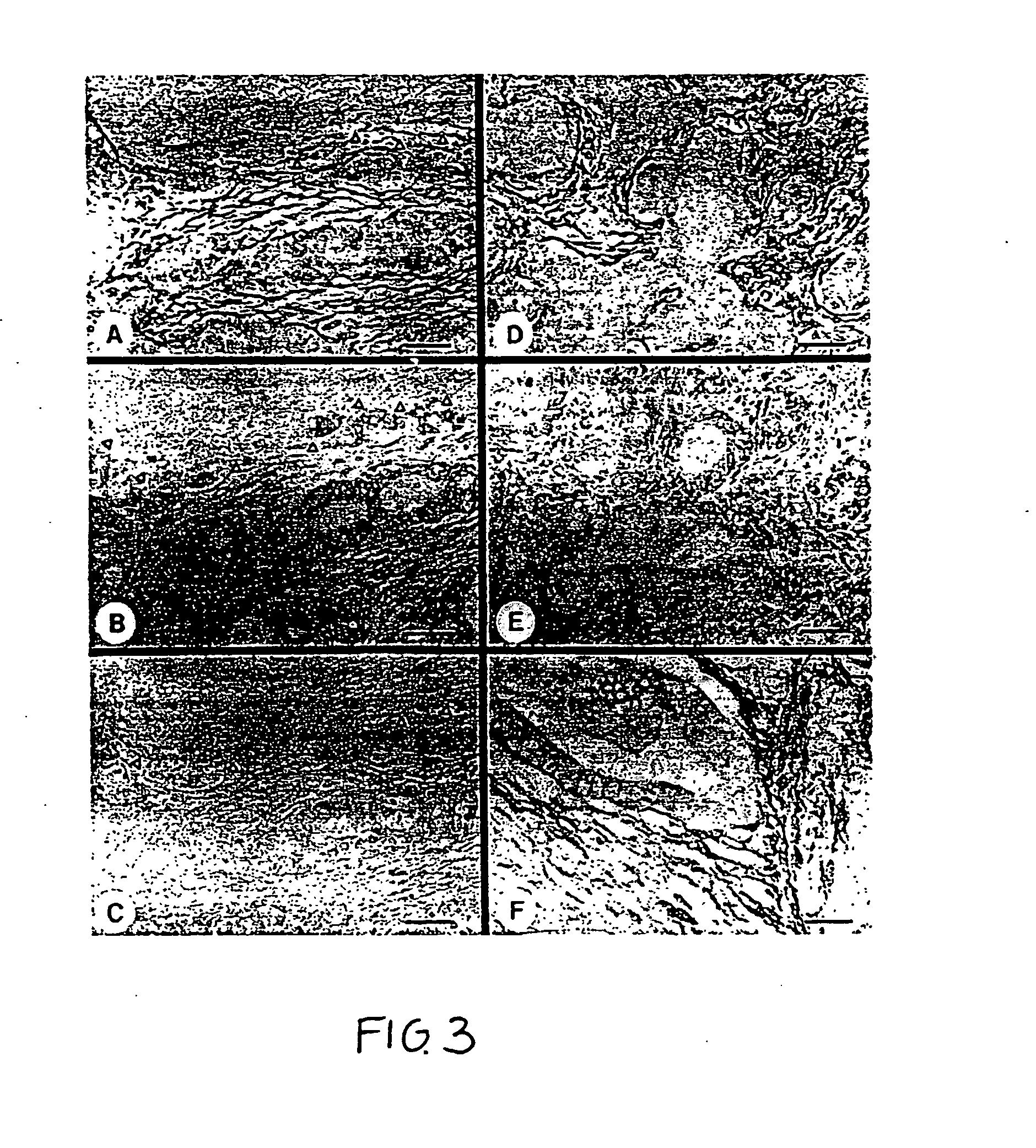
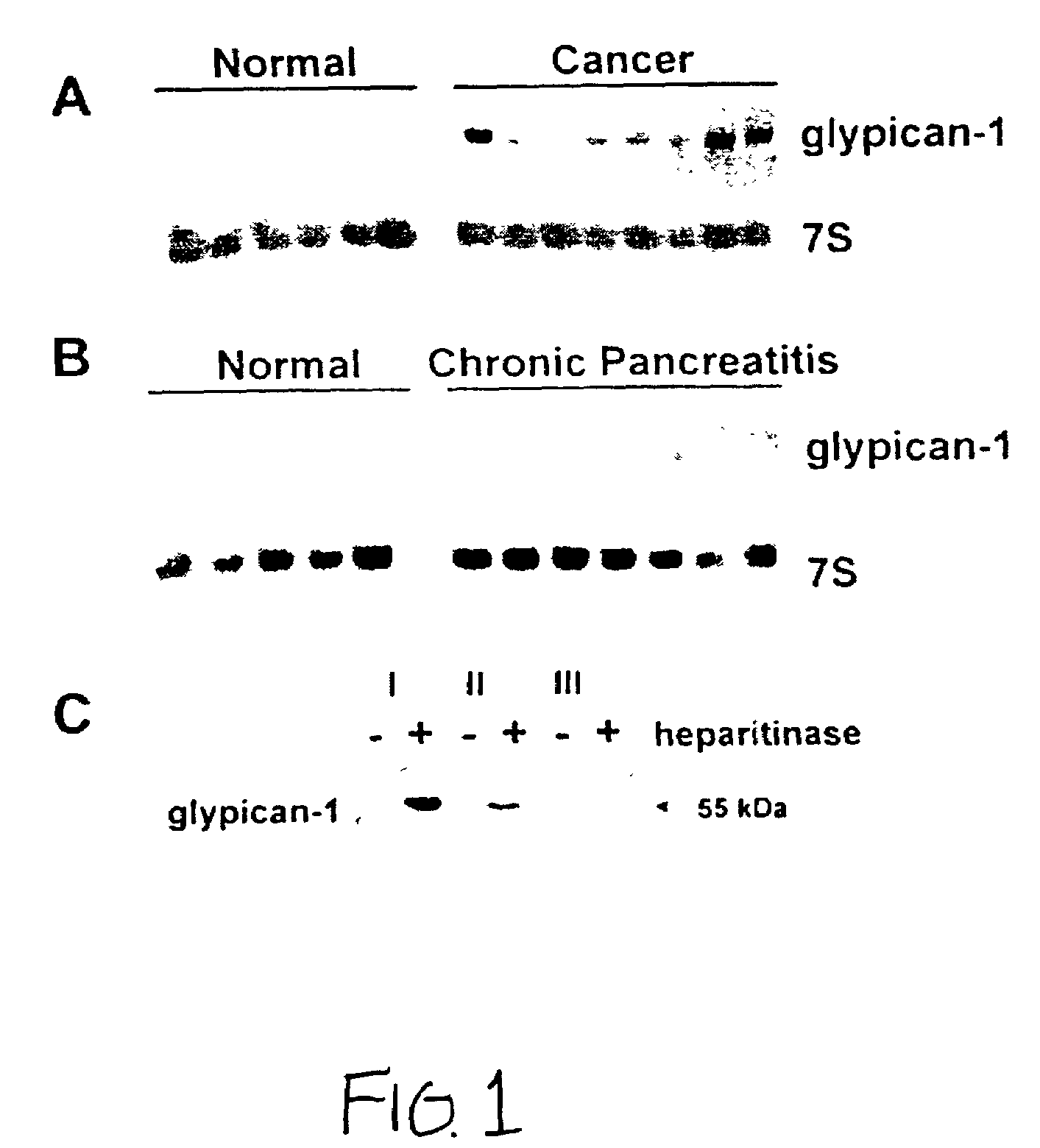
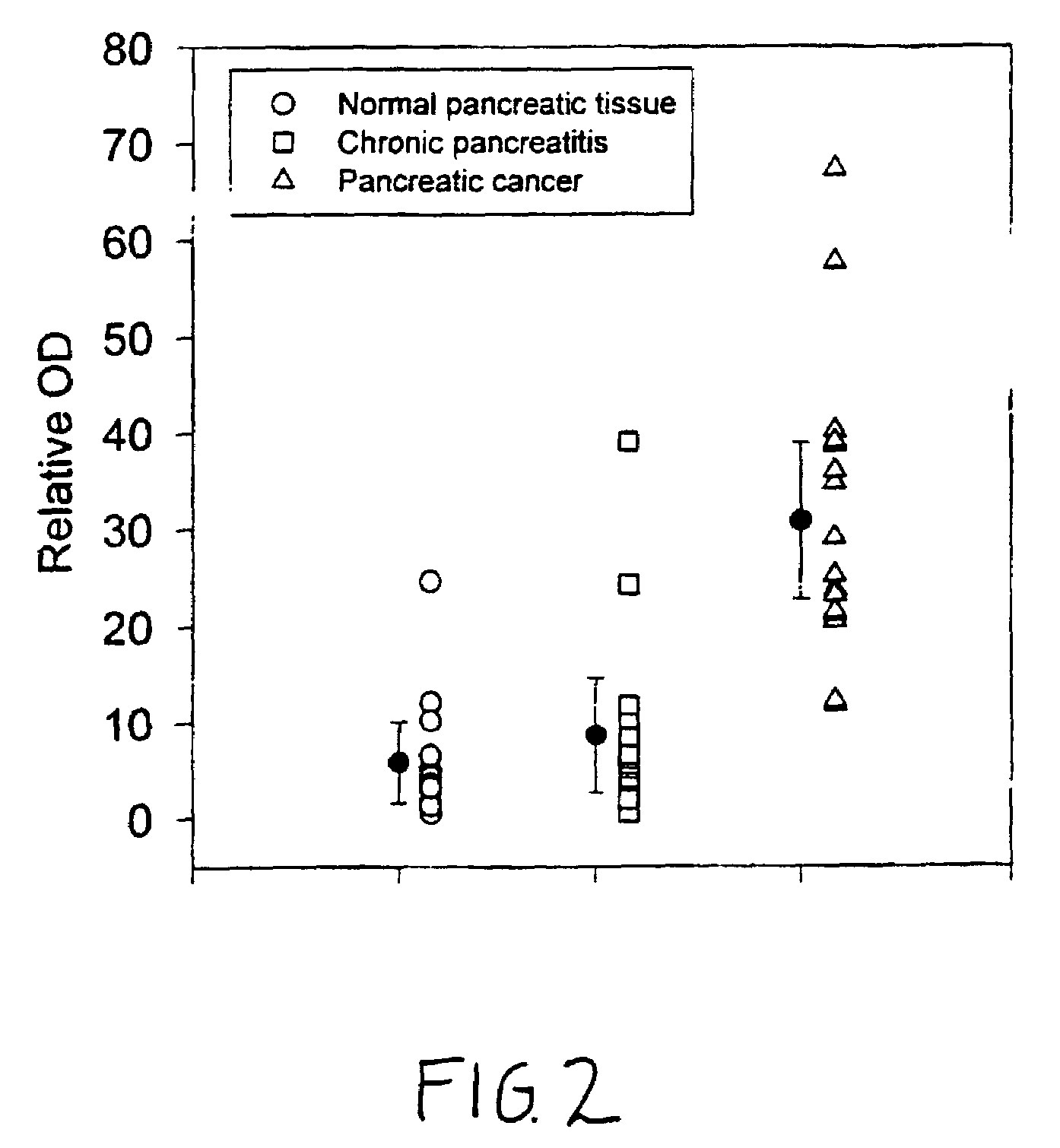
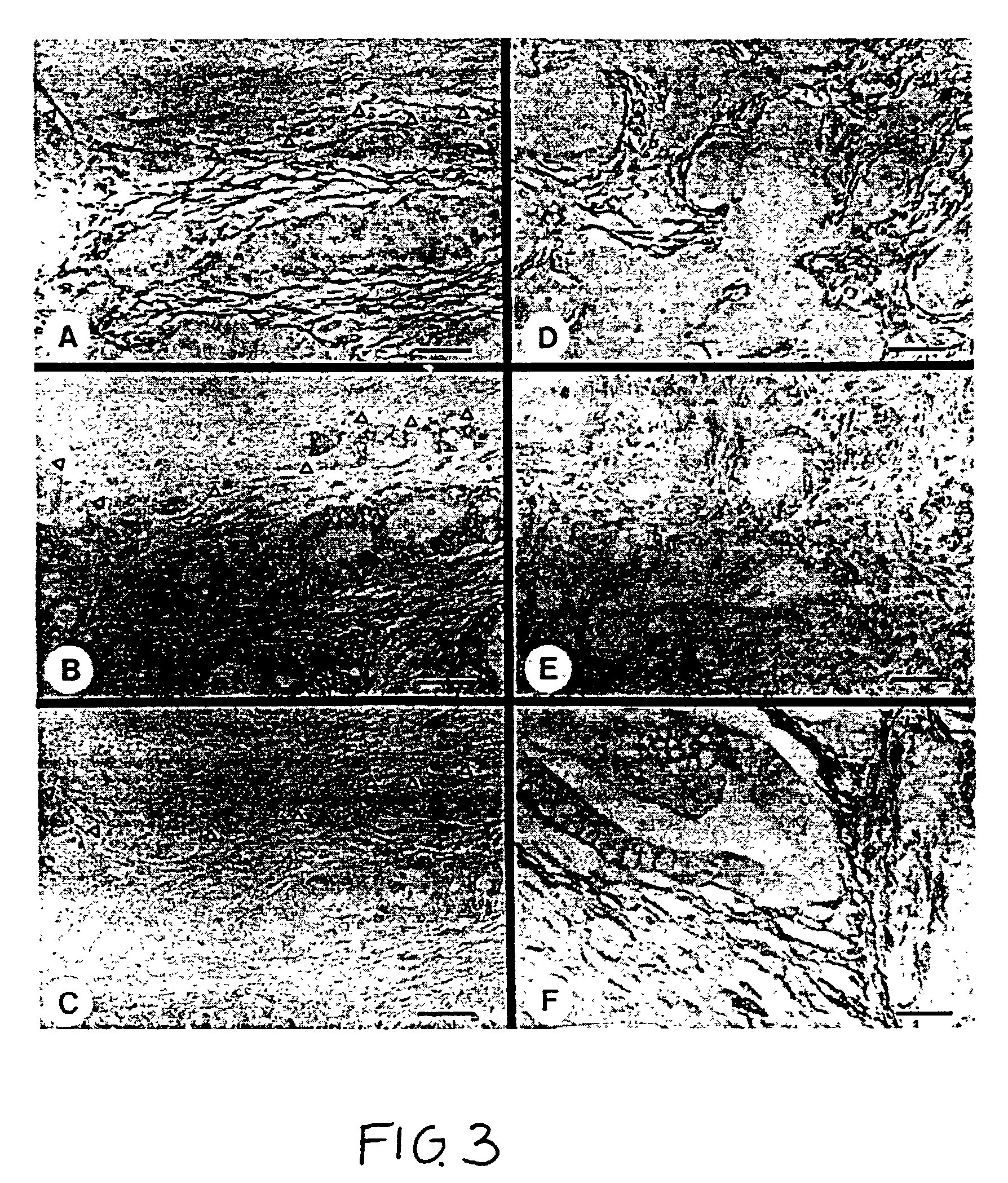
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-(GPI-) anchored HSPG glypican-1 is strongly expressed in human breast and pancreatic cancer—both by the cancer cells and in the case of pancreatic cancer the adjacent fibroblasts—whereas expression of glypican-1 is low in the normal pancreas and in chronic pancreatitis. Treatment of two pancreatic cancer cell lines, which express glypican-1, with the enzyme phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase-C (PI-PLC) abrogated their mitogenic responses to two heparin-binding growth factors: fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF). Treatment of MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells with PI-PLC abrogates the mitogenic response to two heparin-binding growth factors, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). Syndecan-1 is also expressed at high levels in breast cancer tissues as well as breast cancer cells by comparison with breast normal tissues. Temporary or permanent transfection of a glypican-1 antisense construct attenuated glypican-1 protein levels and the mitogenic response to FGF2 and HB-EGF. Glypican can be used to detect the carcinoma in vitro and therapeutics that either bind to (e.g., antibodies or drugs), remove (e.g., enzymes) or prevent the expression (e.g., antisense constructs) of surface of the extracellular domain of glypican-1 are effective in retarding the growth of glypican-responsive carcinomas.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Phosphatidase C and coding gene thereof
ActiveCN109321546ANo change in degumming activityReduce manufacturing costHydrolasesFatty-oils/fats refiningBiologyGene
The invention relates to phosphatidase C and a coding gene thereof, and also relates to a carrier containing the gene and a host cell. In addition, the invention also relates to a method for producingthe phosphatidase C and a purpose of the phosphatidase C.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
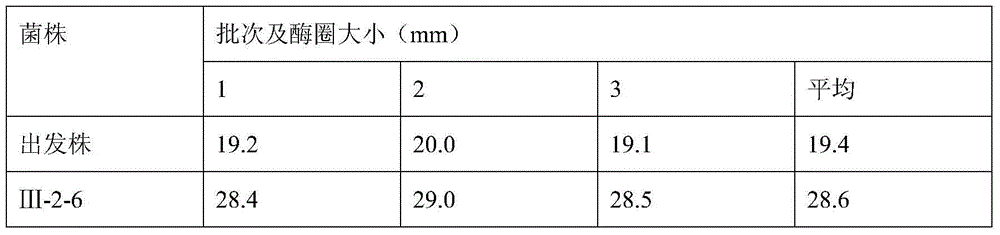
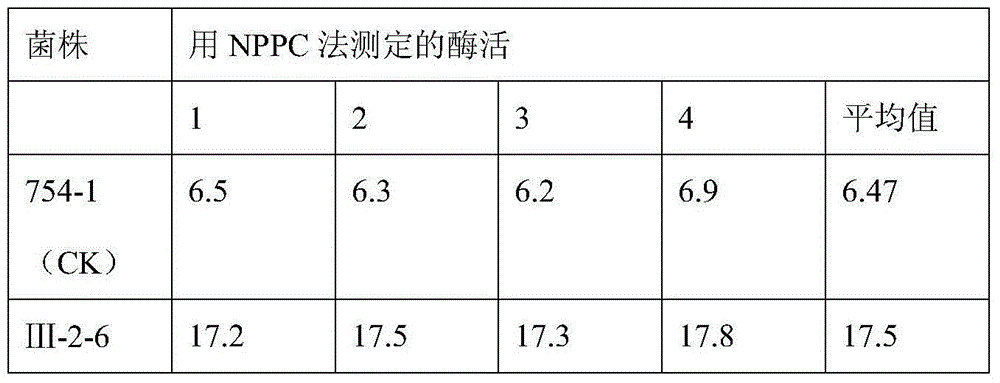
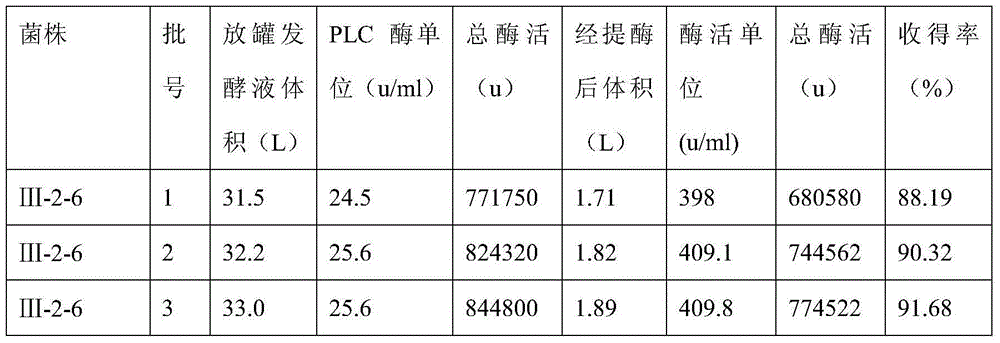
Bacillus cereus mutant strain for high production of phospholipase C as well as fermentation method and application of bacillus cereus mutant strain
The invention discloses a bacillus cereus mutant strain for high production of phospholipase C (PLC) as well as a fermentation method and an application of the bacillus cereus mutant strain. A naturally screened bacillus cereus Shenzhen strain 754-1 is subjected to mutation screening, so that a bacillus cereus III-2-6 is obtained and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015277. The bacillus cereus mutant strain is high in PLC enzyme production activity by comparing with an original starting strain, is easy to produce by fermenting in an improved LB culture medium, and is short in growth period which is 16-22 hours, and by virtue of NPPC method detection, the PLC enzyme activity unit is more than that of 24.5u / ml fermentation liquor, so that the bacillus cereus mutant strain is suitable for production of the phospholipase C on large scale.
Owner:陈明锴 +2
A kind of phospholipase c expressed by Cladosporium and its producing strain
ActiveCN104694394BWide range of actionImprove degumming effectFungiHydrolasesMicroorganismCladosporium
The invention provides an isolated Cladosporium strain expressing phospholipase C, which is preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.7508. The phospholipase C prepared by using the bacterial strain and the preparation method provided by the invention can be used for oil refining, has good degumming effect, and can be widely used in the fields of oil refining, additives, medicine and the like.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Sphingomyelin measurement method using sequential phospholipase D reactions
InactiveUS9051600B2Simply and accurately measuringHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementMonoglyceridePhosphorylcholine
Provided is a method for simply and accurately measuring sphingomyelin in a sample, and a kit therefore. The method is a method for measuring sphingomyelin in a sample, comprising reacting the sample with a phospholipase D which does not react with sphingomyelin and lysophosphatidylcholine but reacts with phosphatidylcholine, a lysophospholipase or a monoglyceride lipase, and a choline oxidase, eliminating the formed hydrogen peroxide, reacting the resultant with a phospholipase D which does not react with glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine and free fatty acid but reacts with sphingomyelin, and a choline oxidase, and measuring the formed hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:KYOWA MEDEX CO LTD
Enzymatic Assay for the Quantitative Determination of Phospholipase A1 or A2 Activity in a Sample
InactiveUS20110312008A1Continuous monitoringHigh fluorescence intensityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAssayQuantitative determination
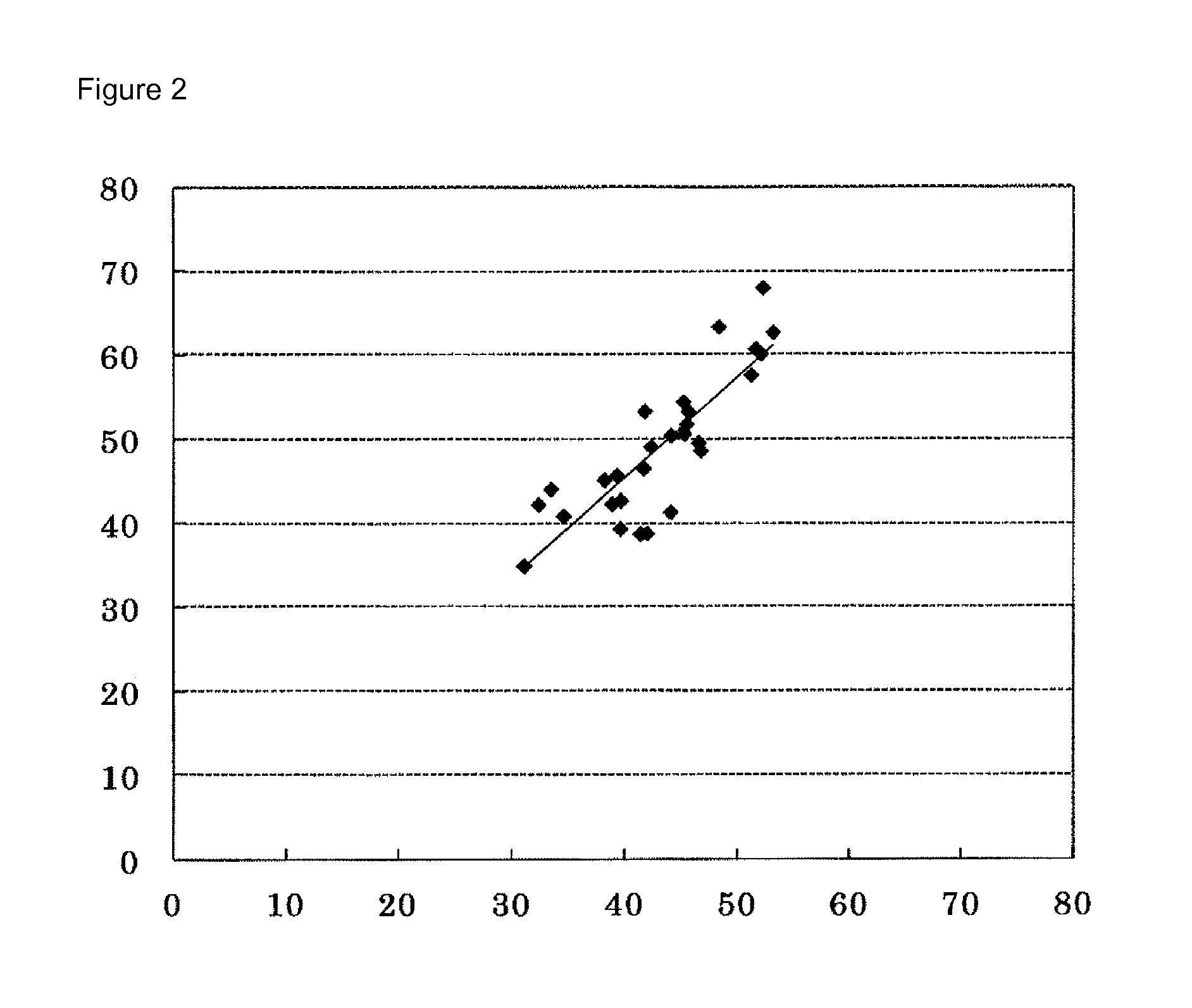
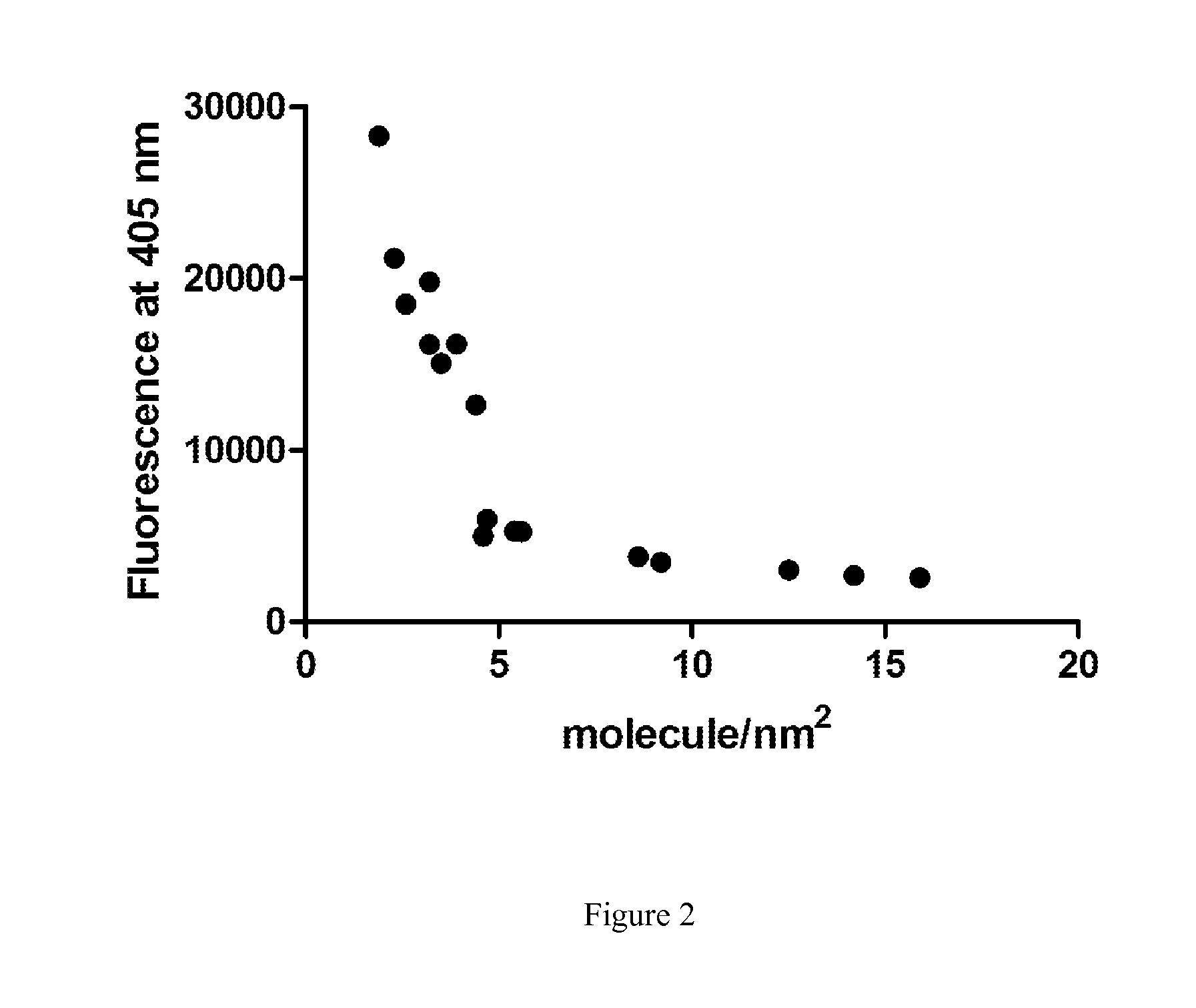
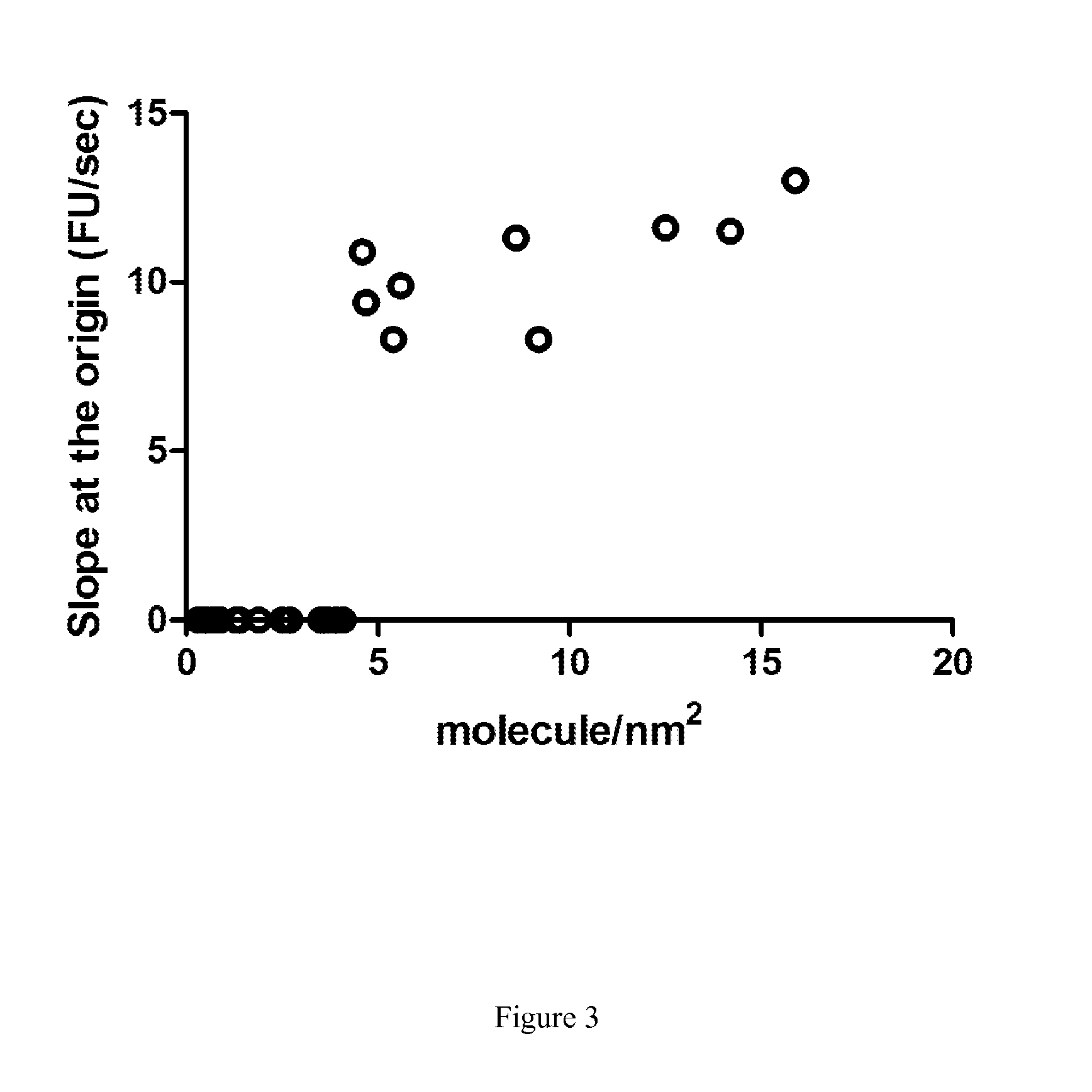
The invention relates to a new method for measuring phospholipase A1 or A2 activity in a sample, using a solid phase coated with a fluorochrome-labelled phospholipase A1 or A2 substrate, wherein the molecular coverage is in the range from 8 to 30 fluorochrome-labelled phospholipase A1 or A2 substrate molecules / nm2, and kit for carrying out said method.
Owner:ATEROVAX
A kind of preservation method of phospholipase c
ActiveCN105802934BImprove the stability of enzyme activityAvoid lostHydrolasesPhospholipasePhospholipase C
The invention provides a preservation method of phospholipase C. By using the preservation method, the phospholipase C has good enzyme activity stability. When the preservation method of the phospholipase C provided by the invention is used in the practical application process of the phospholipase C, the production energy consumption can be reduced; and meanwhile, the activity loss of the phospholipase C is avoided.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
A kind of recombinant escherichia coli producing phospholipase c and the method and application of preparing phospholipase c
ActiveCN103509748BHigh enzyme productionIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing phosphatidase C, a phosphatidase C preparation method, and applications of phosphatidase C. A construction method of the recombinant escherichia coli comprises following steps: A, preparation of phosphatidase C gene, wherein PCR primers are designed, and phosphatidase C gene segments are amplified; B, construction of recombinant plasmids, wherein phosphatidase C gene segments with 1158bp are obtained by digestion using EcoR I and Not I enzymes, and the phosphatidase C gene segments are combined with high-copy plasmid pET28a by clone so as to obtain recombinant plasmid Pet28a-P.f-PLC; and C construction of engineering bacteria, wherein plasmid Pet28a-P.f-PLC is transferred into E.coil BL21(DE3) via transformation. Active phosphatidase C can be produced by liquid fermentation, and intracellular and extracellular enzyme activities can reach 408.5U / ml. Phosphatidase C possesses an application prospect in the fields such as oil and fat refining, phosphatide modification and medical treatment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
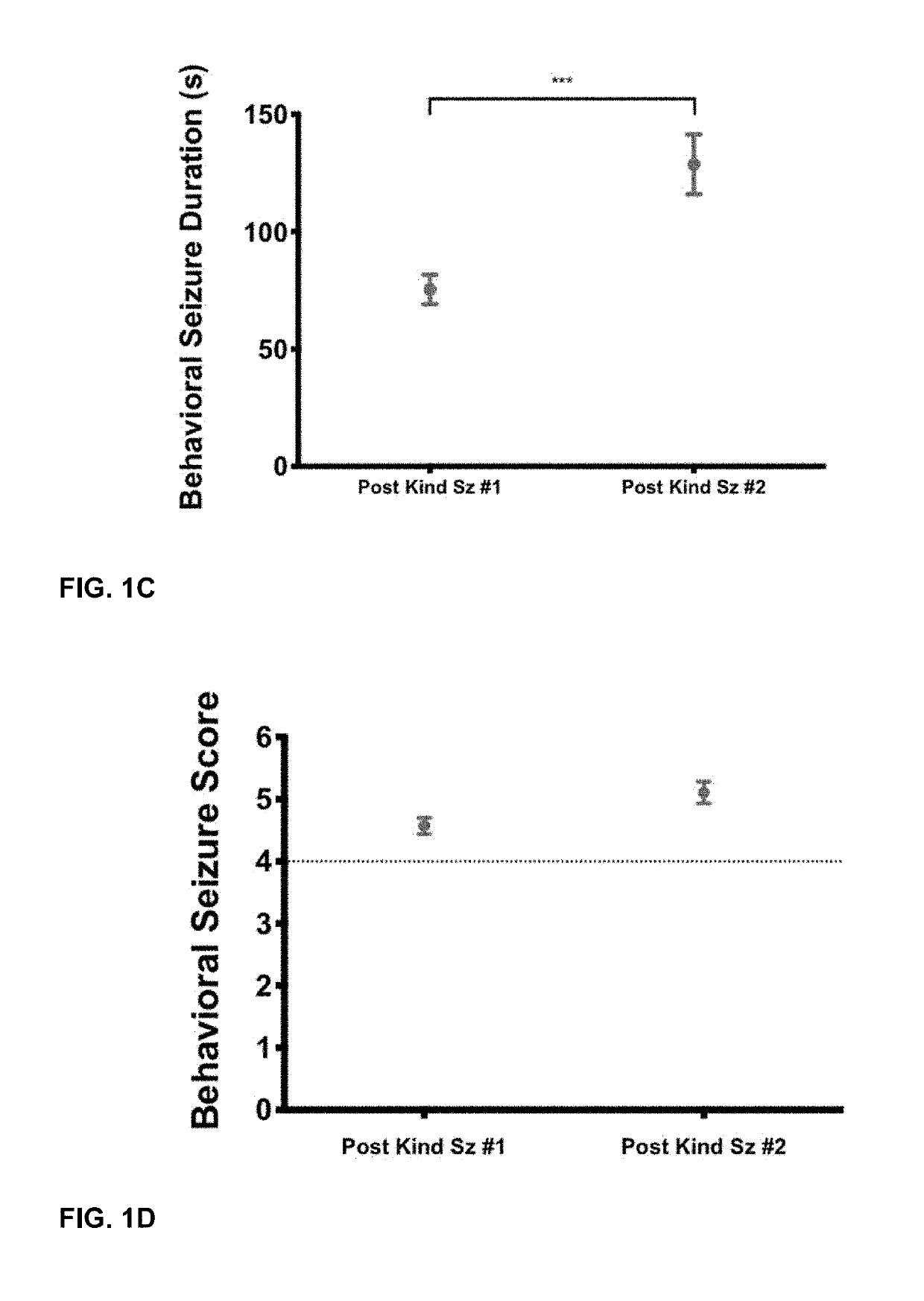
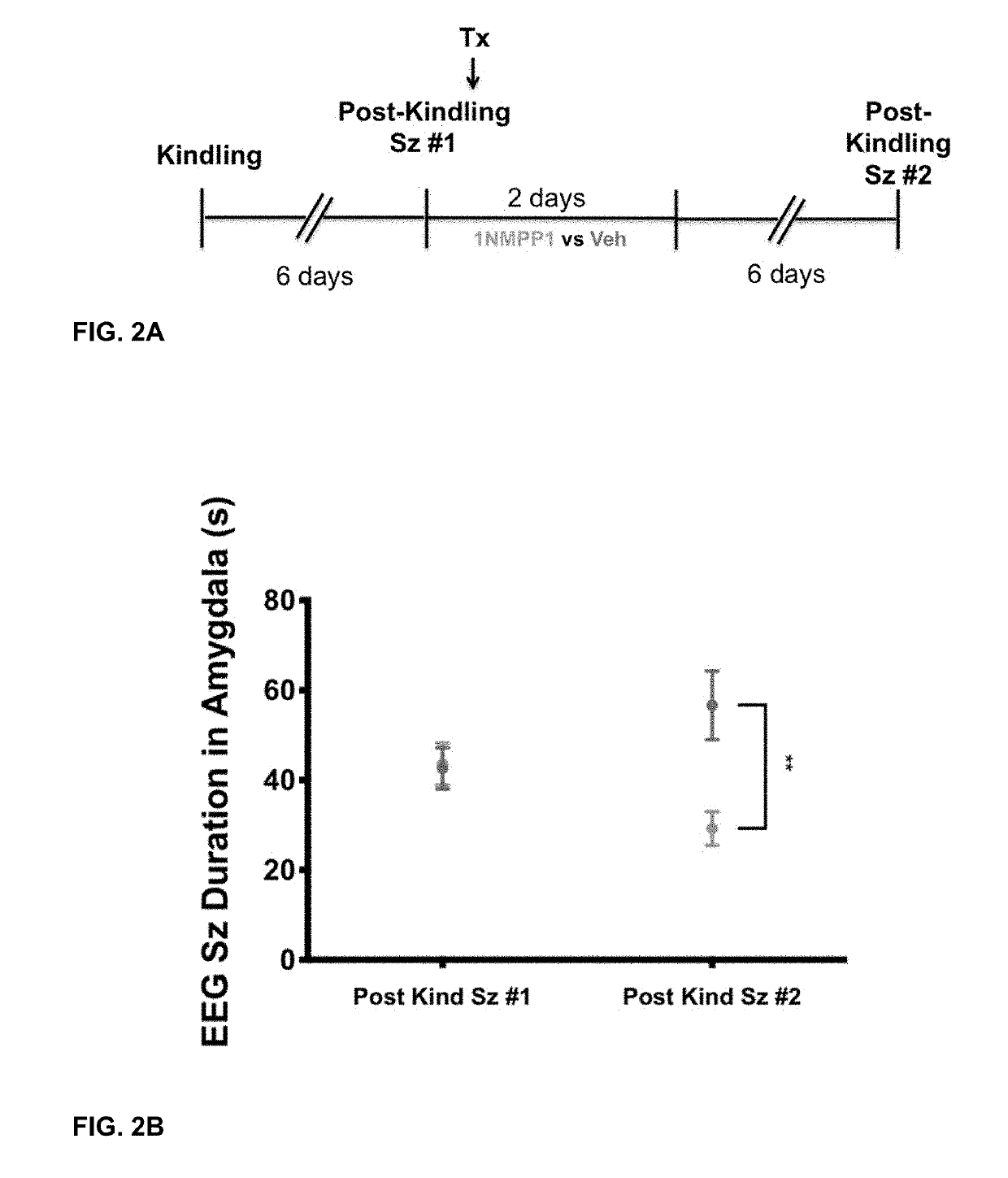
Methods for the Prevention or Treatment of Epilepsy
InactiveUS20190269752A1Induce remissionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsReceptor Tyrosine Kinase BRefractory epilepsy
The present disclosure relates to methods of preventing or treating epilepsy comprising administering a receptor tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) inhibitor. In particular, the present disclosure relates to methods of treating a subject susceptible to the development of epilepsy, methods of inducing remission of epilepsy in a subject, and methods of transforming medically refractory epilepsy in a subject to medically responsive epilepsy comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a TrkB inhibitor or a phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) inhibitor.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
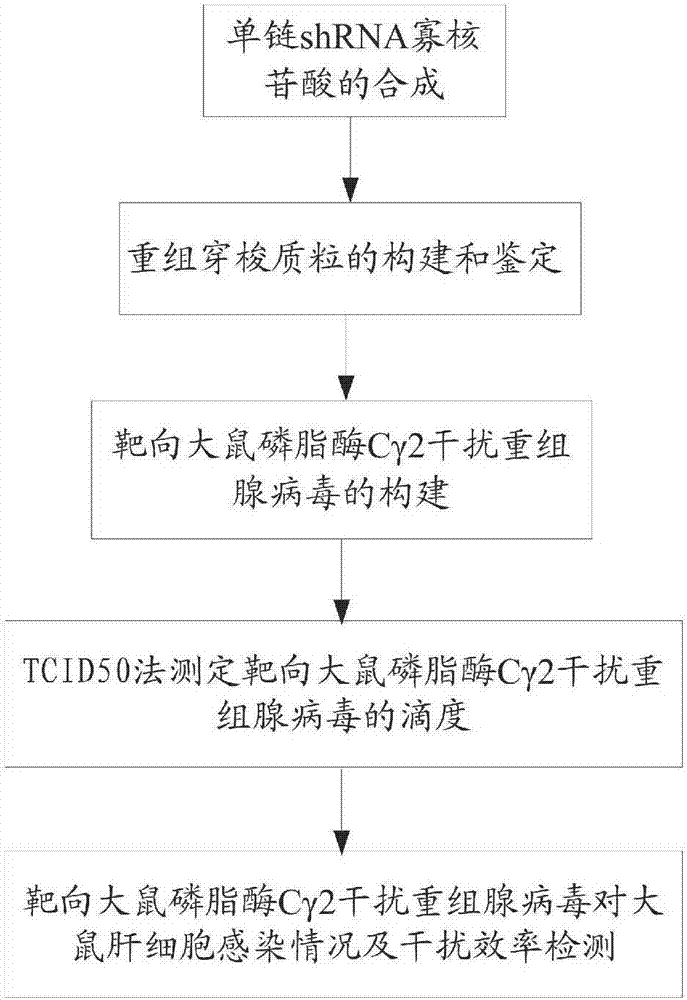
Targeted rat phospholipase Cgamma2 interfering recombinant adenovirus, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN106868046AThe promotion effect is obviousInhibit apoptosisGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemShuttle vectorPhospholipase
The invention discloses a targeted rat phospholipase Cgamma2 interfering recombinant adenovirus and a construction method thereof. The targeted rat phospholipase Cgamma2 interfering recombinant adenovirus is obtained by inserting oligonucleotide shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) of targeted rat phospholipase Cgamma2 into an adenovirus genome-containing framework plasmid pHBAd-BHG, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the oligonucleotide shRNA is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Aiming at a siRNA (small interfering ribonucleic acid) nucleotide sequence of the rat phospholipase Cgamma2 gene, the invention designs and synthesizes the corresponding shRNA oligonucleotide sequence based on an adenovirus shuttle vector; the shRNA of the targeted target gene is continuously produced in a target cell by means of a U6 promoter of RNA (ribonucleic acid)-dependent polymerase III carried by the adenovirus vector itself; and the shRNA can be processed into the siRNA by Dicerase in the cell, thereby playing a gene interfering role.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com