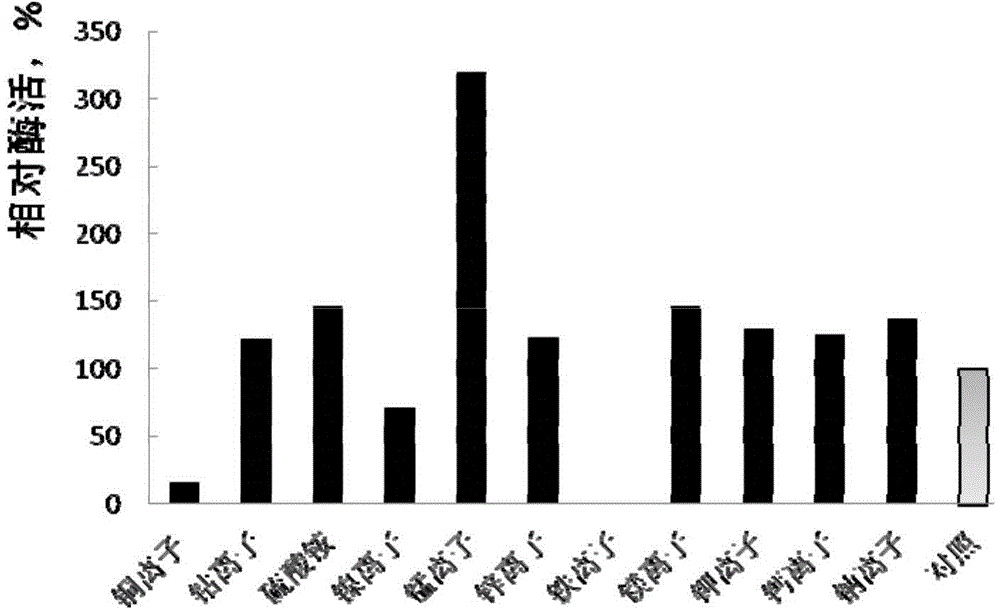
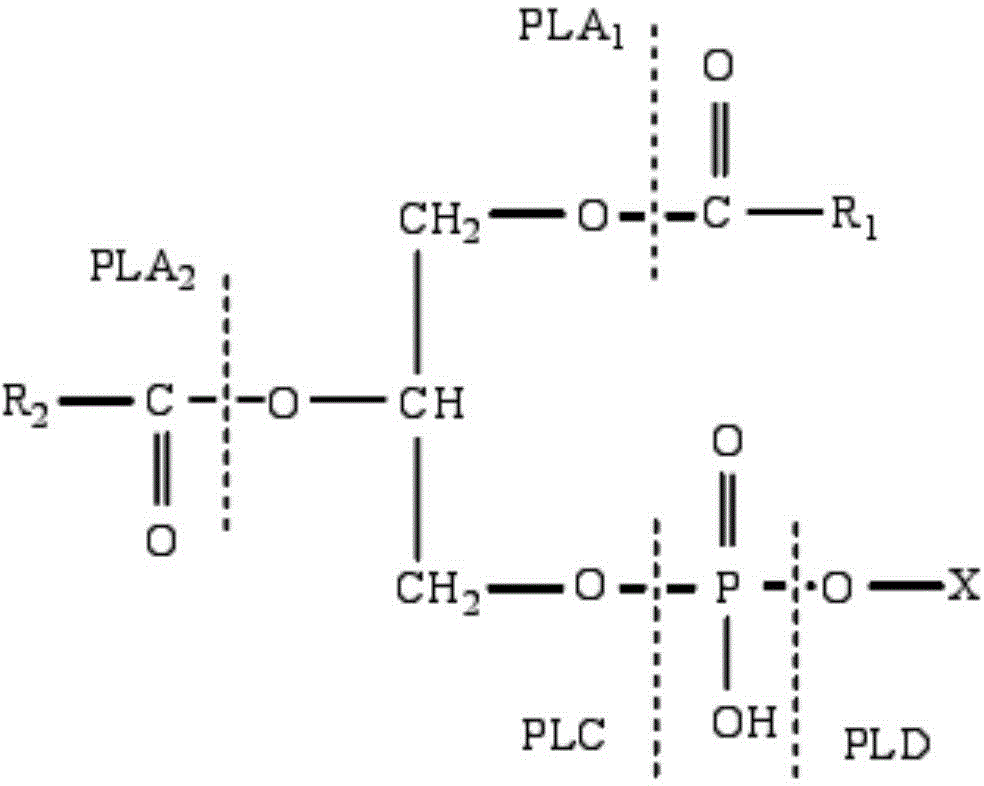
Phospholipase C and bacterial strain generating same
A technology of phospholipase and bacterial strain, which is applied in the field of enzyme degumming, can solve the problem that there is no PLC report of phospholipase produced by Bacillus subtilis, and achieve good degumming effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Example 1 , Isolation, Screening and Identification of Bacillus subtilis WBRD01280
[0081] Take 10g of soil samples from Aiding Lake in Xinjiang, China, and place them in 100mL sterile water containing 1.0% Tween80. After fully shaking for 30 minutes, use filter paper to filter out large particles of insoluble impurities under sterile conditions, and collect the filtrate.
[0082] Dilute the filtrate by 10 1 、10 2 、10 3 、10 4 Times, and the samples of each dilution were spread on the lecithin plate and incubated at 28°C.
[0083] Observe whether there is a milky white precipitation circle on the lecithin plate every 24 hours. After 48-72 hours of culture, the bacteria with obvious milky white precipitates were picked for further streak separation to obtain pure strains. As a result, a strain with very obvious milky white precipitates was found, named WBRD01280.
[0084] After sequencing the 16S rRNA of the bacterium, its rRNA sequence was found to be shown in S...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2 , Preparation of Phospholipase C from Bacillus subtilis
[0089] 2.1. Fermentation of Bacillus subtilis phospholipase C
[0090] Bacillus subtilis WBRD01280 was inoculated into 30ml of seed medium (LB medium), and cultured at 28°C and 180rpm for 24h.
[0091] After the liquid seeds are cultured, inoculate 1% of the inoculum into 30ml of fermentation medium, and culture at 28°C and 180rpm for 24h.
[0092] Centrifuge the Bacillus subtilis fermentation culture liquid at 1200rpm for 10 minutes, collect and obtain about 45ml of centrifuged supernatant, and detect the activity of phospholipase C in the centrifuged supernatant. The results show that the activity of phospholipase C in the centrifuged supernatant is about 0.015 μmol / ml.
[0093] 2.2. Concentration of Bacillus subtilis phospholipase crude enzyme solution
[0094] According to the method provided by the manufacturer, the centrifuged supernatant was concentrated by ultrafiltration using a 3-30 kDa ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Example 3 : Enzymatic properties of phospholipase C produced by Bacillus subtilis WBRD01280
[0098] 3.1. Optimum temperature of Bacillus subtilis phospholipase C
[0099] At 0°C, 10°C, 20°C, 30°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 55°C, 60°C, 70°C and 75°C water bath temperature, measure the Bacillus subtilis phospholipase obtained by concentrating and preparing in Example 2 C enzyme activity.
[0100] Take the PLC enzyme activity at the temperature point of the highest PLC enzyme activity as 100% enzyme activity, divide the PLC enzyme activity at other temperature points by the highest enzyme activity, so as to obtain the relative enzyme activity at this temperature point, and take the relative enzyme activity as the ordinate, The temperature point is the abscissa, and the relative enzyme activities at each temperature point are connected in turn with a smooth curve, and these relative enzyme activities are connected with a smooth curve, and the results are shown in image 3 .
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com