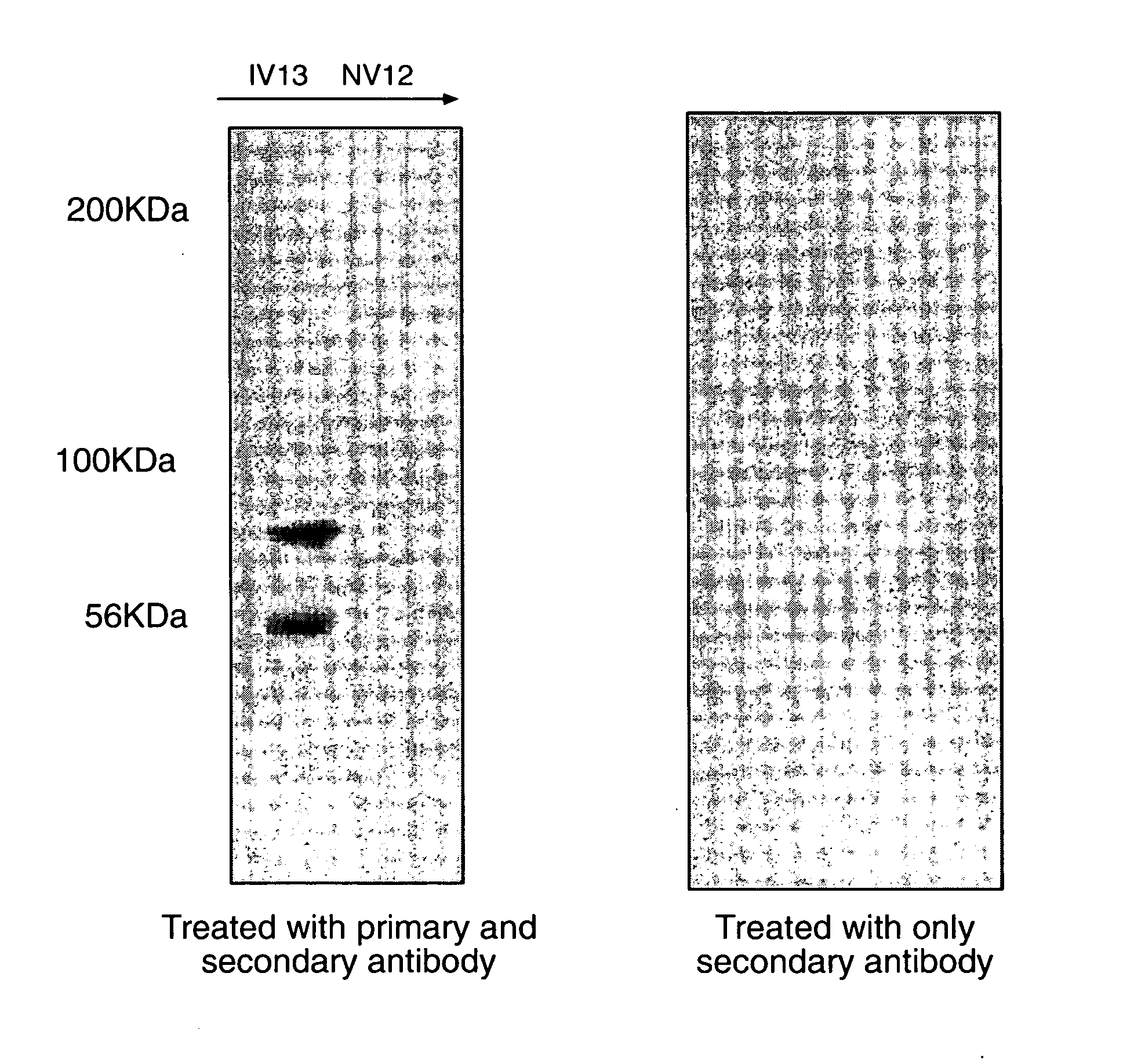
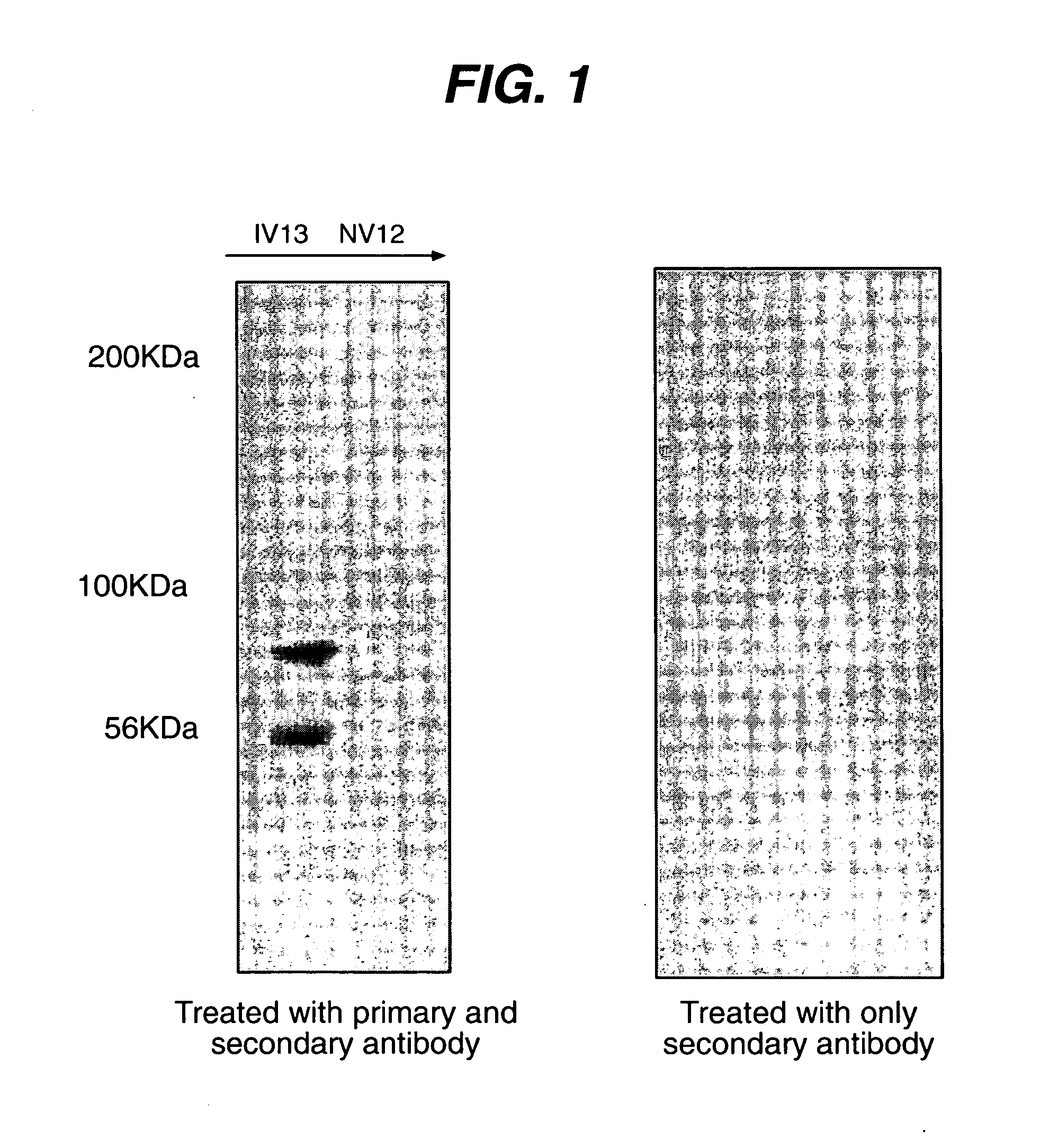
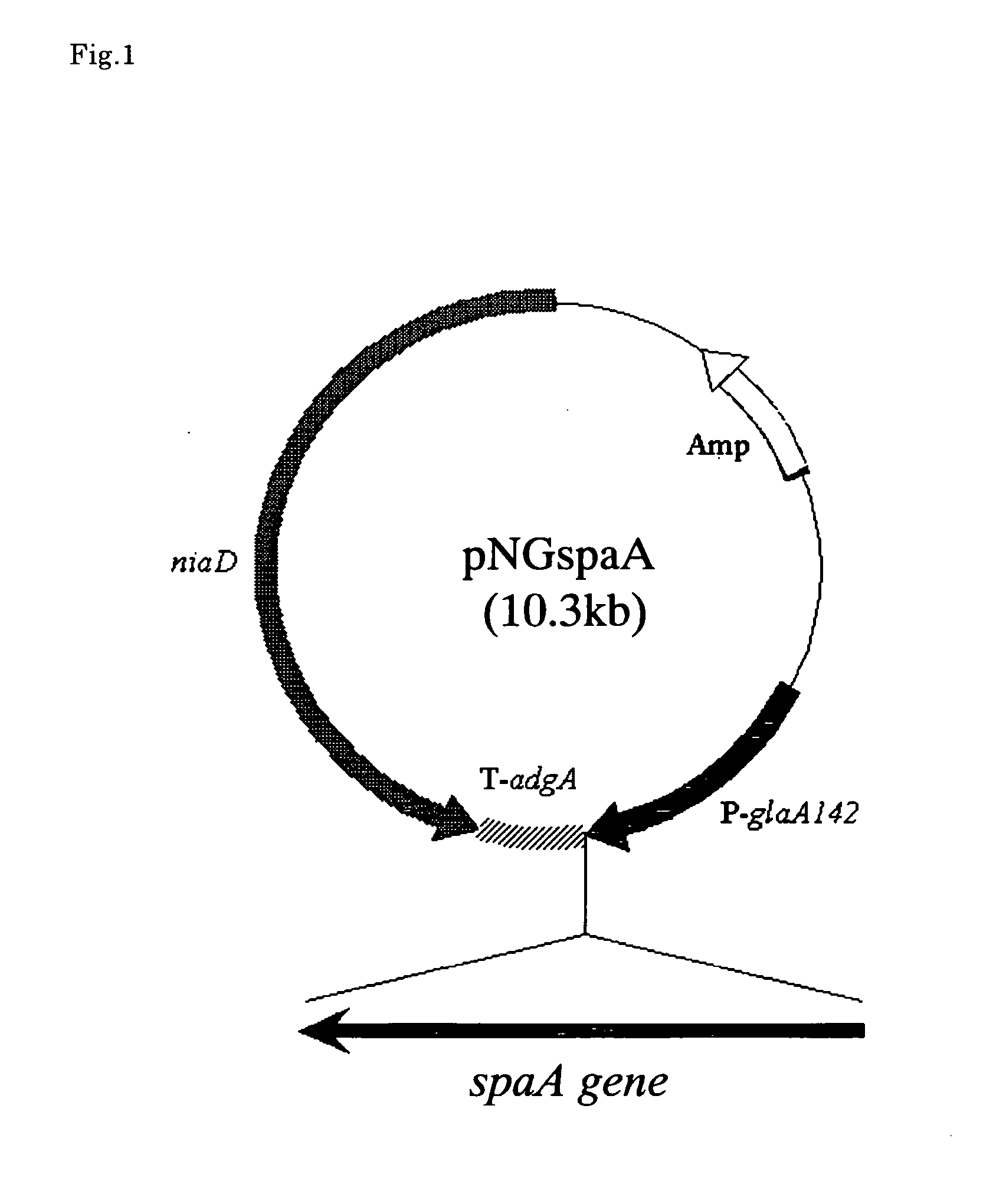
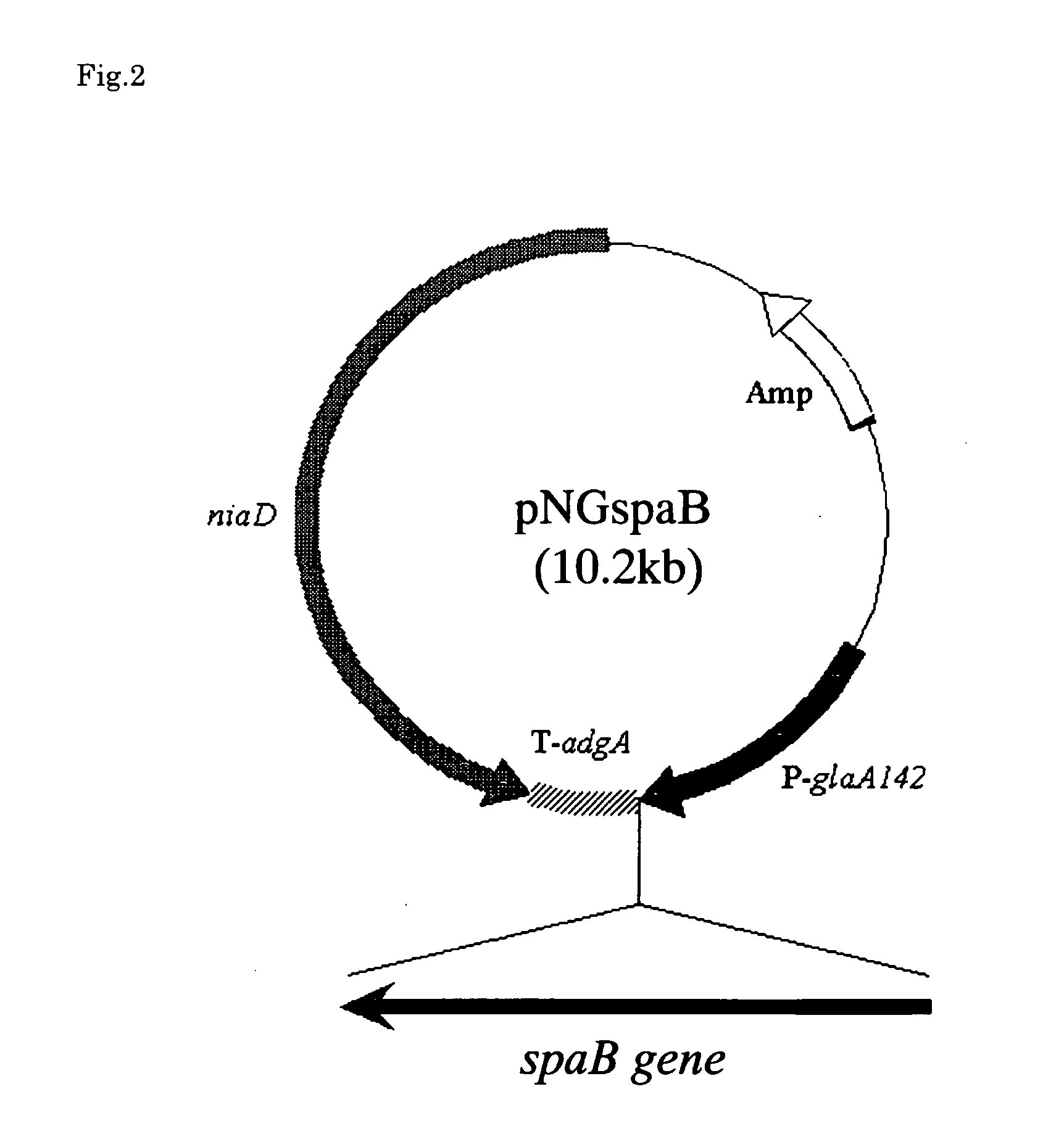
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Phospholipase A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
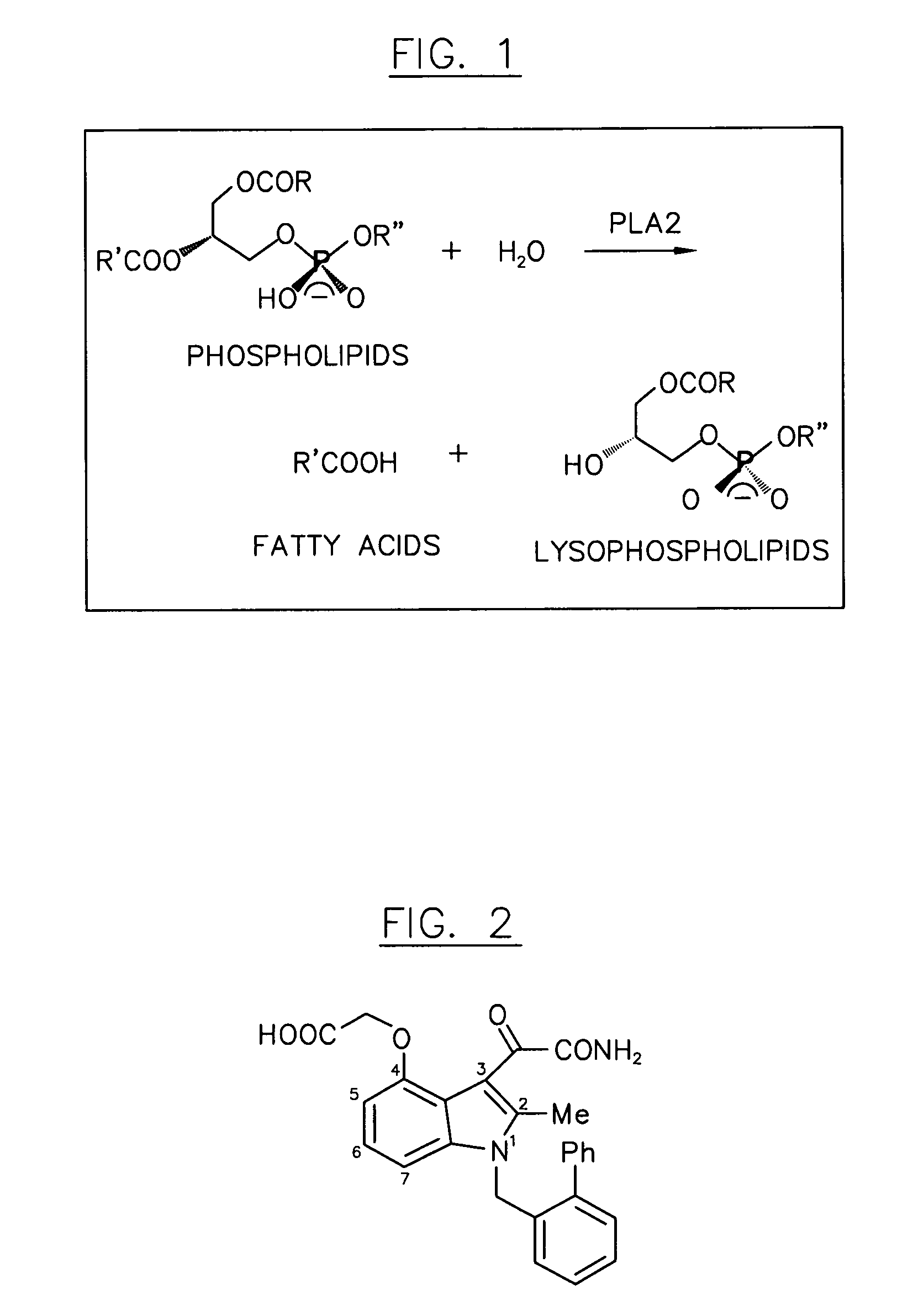
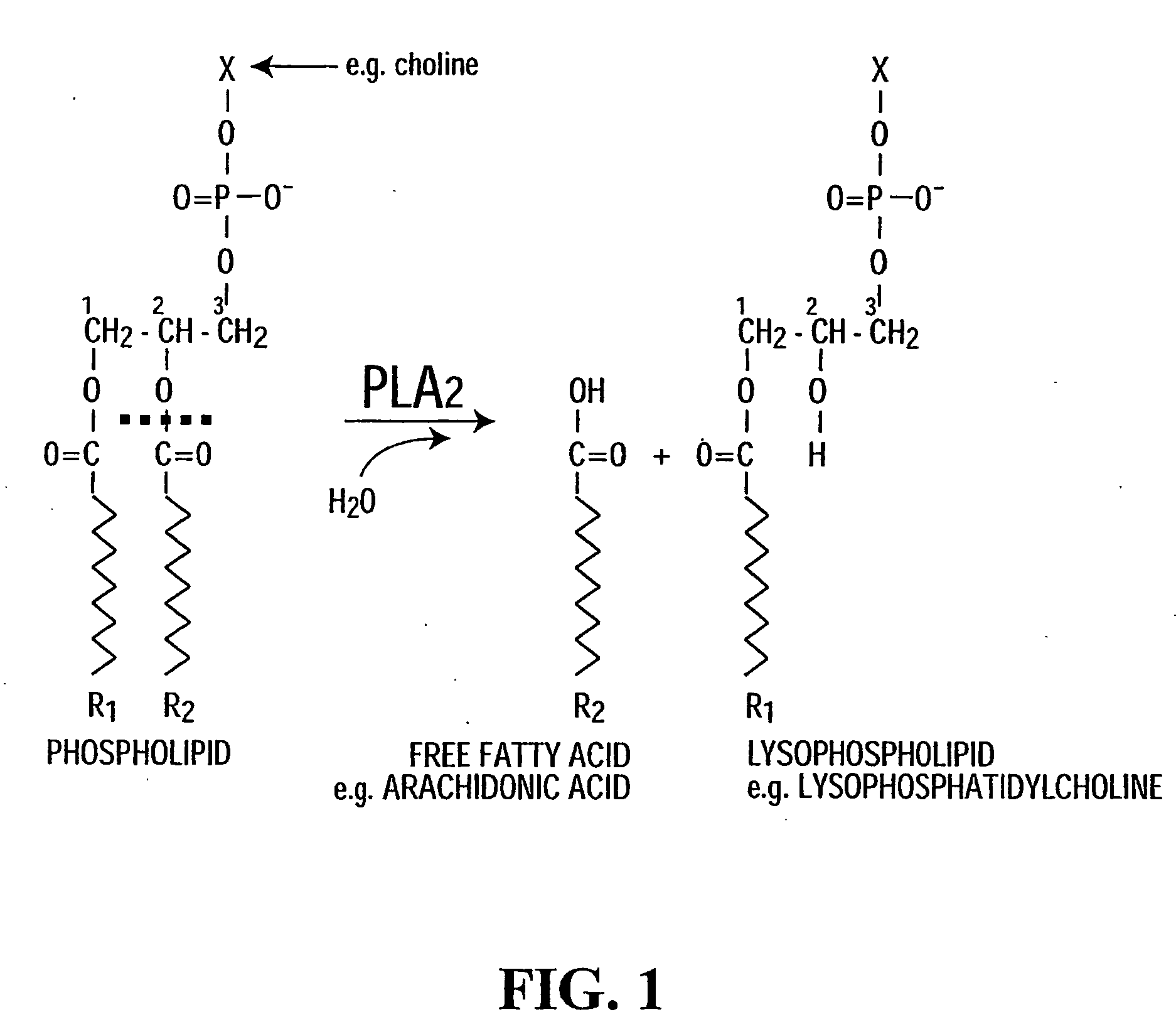
Phospholipase A can refer to: Phospholipase A1 Phospholipase A2 Outer membrane phospholipase A1 An enzyme that displays both phospholipase A1 and phospholipase A2 activities is called a Phospholipase B.
Phospholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides novel polypeptides having phospholipase activity, including, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity, nucleic acids encoding them and antibodies that bind to them. Industrial methods, e.g., oil degumming, and products comprising use of these phospholipases are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Methods for the use of inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2
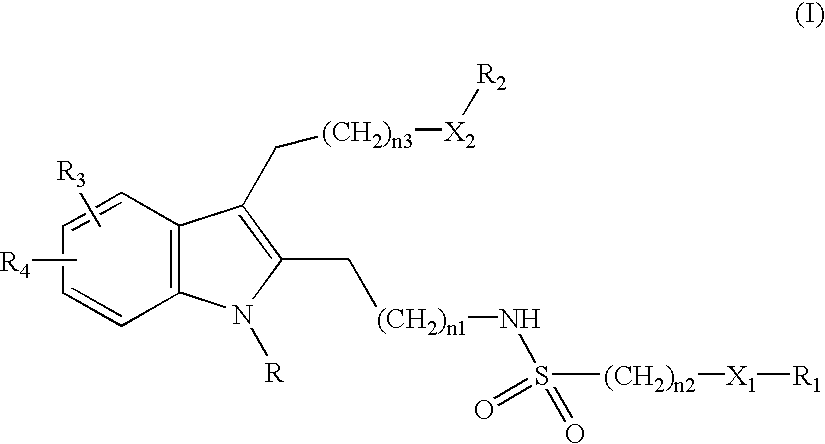
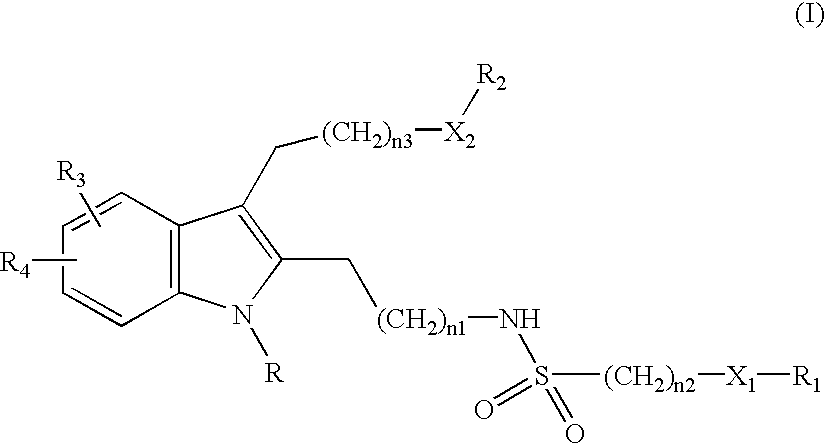
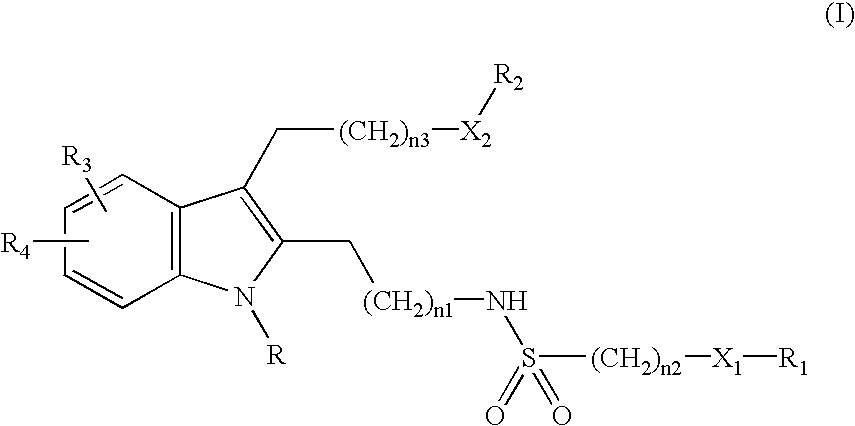
This invention provides methods for the use of substituted indole compounds of the general formula: and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof. The invention provides methods for the use of the compounds as inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly phospholipase A2 enzymes, and for the medical treatment, prevention and inhibition diseases and disorders including asthma, stroke, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, arthritic disorders, rheumatic disorders, central nervous system damage resulting from stroke, central nervous system damage resulting from ischemia, central nervous system damage resulting from trauma, inflammation caused or potentiated by prostaglandins, inflammation caused or potentiated by leukotrienes, inflammation caused or potentiated by platelet activation factor, pain caused or potentiated by prostaglandins, pain caused or potentiated by leukotrienes, and pain caused or potentiated by platelet activation factor.
Owner:ZIARCO
Phospholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20110093965A1Increases oil gainHigh activityImmobilised enzymesFungiPhospholipasePhospholipase A
The invention provides novel polypeptides having phospholipase activity, including, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, phosphatidic acid phosphatases (PAP) and / or lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity, nucleic acids encoding them and antibodies that bind to them. Industrial methods, e.g., oil degumming, and products comprising use of these phospholipases are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Process for the pre-treatment of vegetable oils for physical refining
ActiveUS7494676B2Speed up the processFatty acids production/refiningTea extractionMicroorganismActivated carbon
The present invention relates to a simple and economically attractive process for the pretreatment of vegetable oils which involves (a) enzymatic degumming with commercially available phospholipase A1 from the sources like Aspergillus oryzae microorganism, (b) bleaching of the enzymatically degummed oil using bleaching earth and activated carbon, and (c) dewaxing (in case of rice bran oil) of degummed and bleached oil at lower temperature to obtain oil with less than 5 ppm of residual phosphorus which is amenable for physical refining.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2
ActiveUS20070004719A1Inhibit progressTreating and preventing venousBiocideNervous disorderPhospholipasePhospholipase A
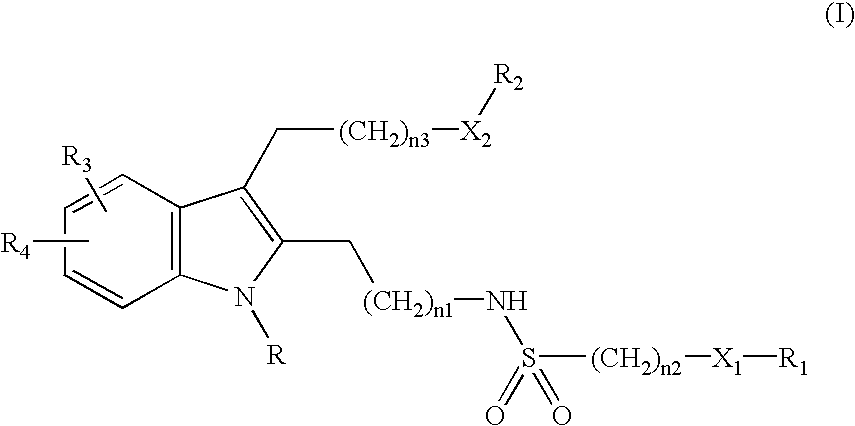
This invention provides chemical inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly cytosolic phospholipase A2 enzymes (cPLA2), more particularly including inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha enzymes (cPLA2α). In some embodiments, the inhibitors have the Formula I: wherein the constituent variables are as defined herein.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Antiviral oligonucleotides having a conserved G4 core sequence
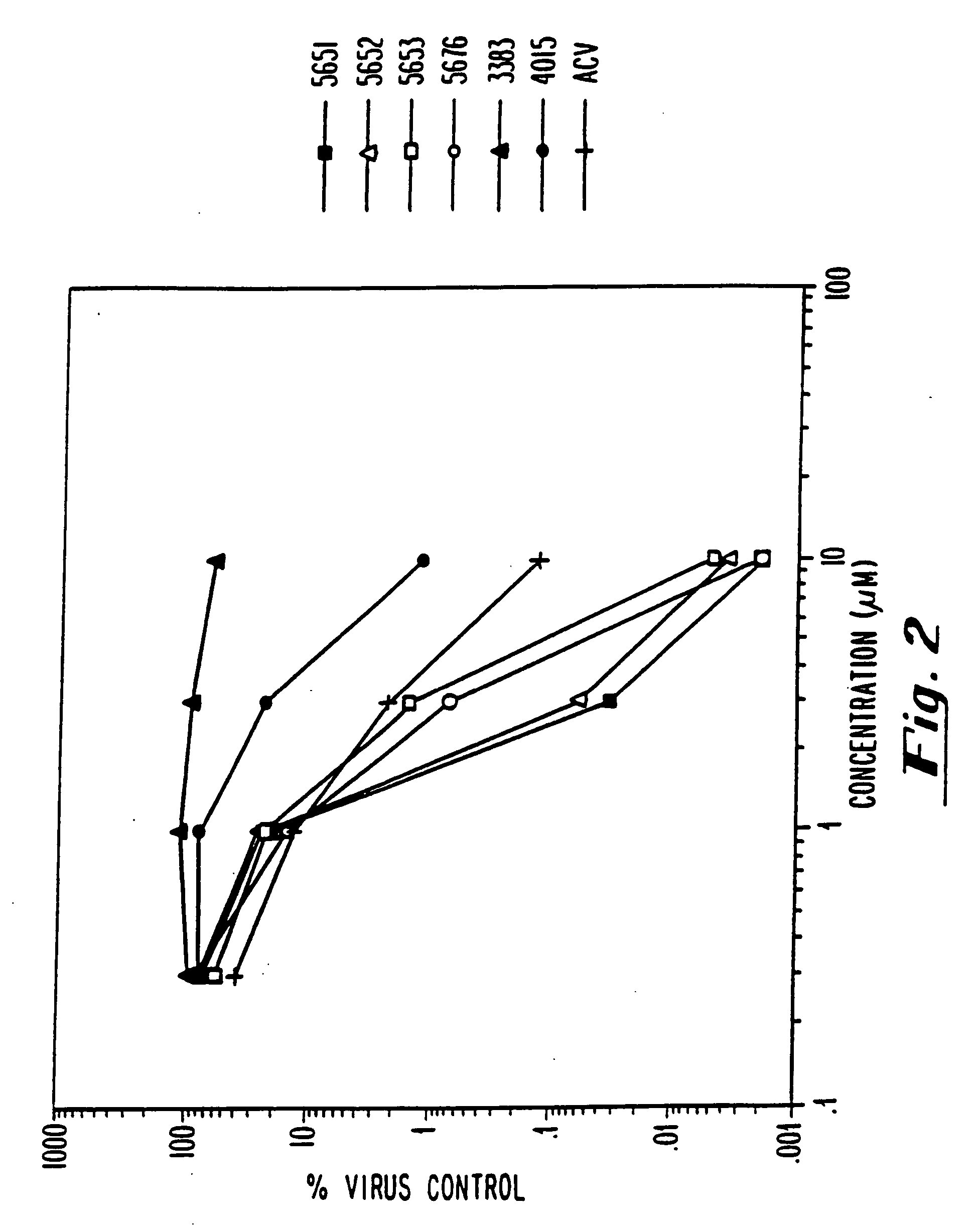
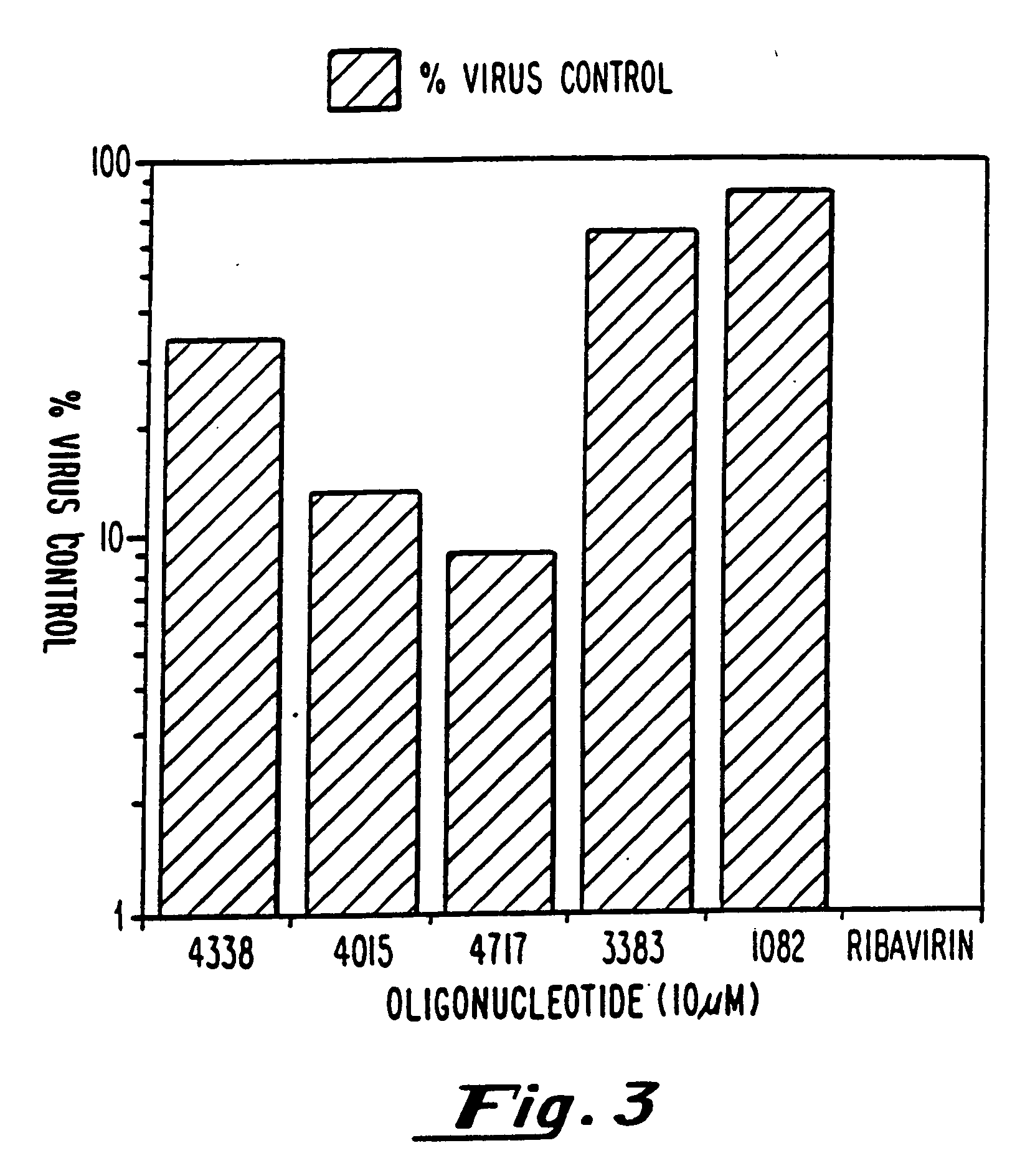
InactiveUS20070015723A1Significant antiviralEffective activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhospholipasePhospholipase A
Modified oligonucleotides having a conserved G4 sequence and a sufficient number of flanking nucleotides to significantly inhibit the activity of a virus or phospholipase A2 or to modulate the telomere length of a chromosome are provided. G4 quartet oligonucleotide structures are also provided. Methods of prophylaxis, diagnostics and therapeutics for viral-associated diseases and diseases associated with elevated levels of phospholipase A2 are also provided. Methods of modulating telomere length of a chromosome are also provided; modulation of telomere length is believed to play a role in the aging process of a cell and in control of malignant cell growth.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Methods for treating arthritic disorders
This invention provides methods for treating in mammals arthritic or rheumatic disorders using substituted indole compounds of the general formula:and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof, and methods for using the compounds as inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly phospholipase A2 enzymes, and for the medical treatment, prevention and inhibition of pain and inflammation.
Owner:WYETH
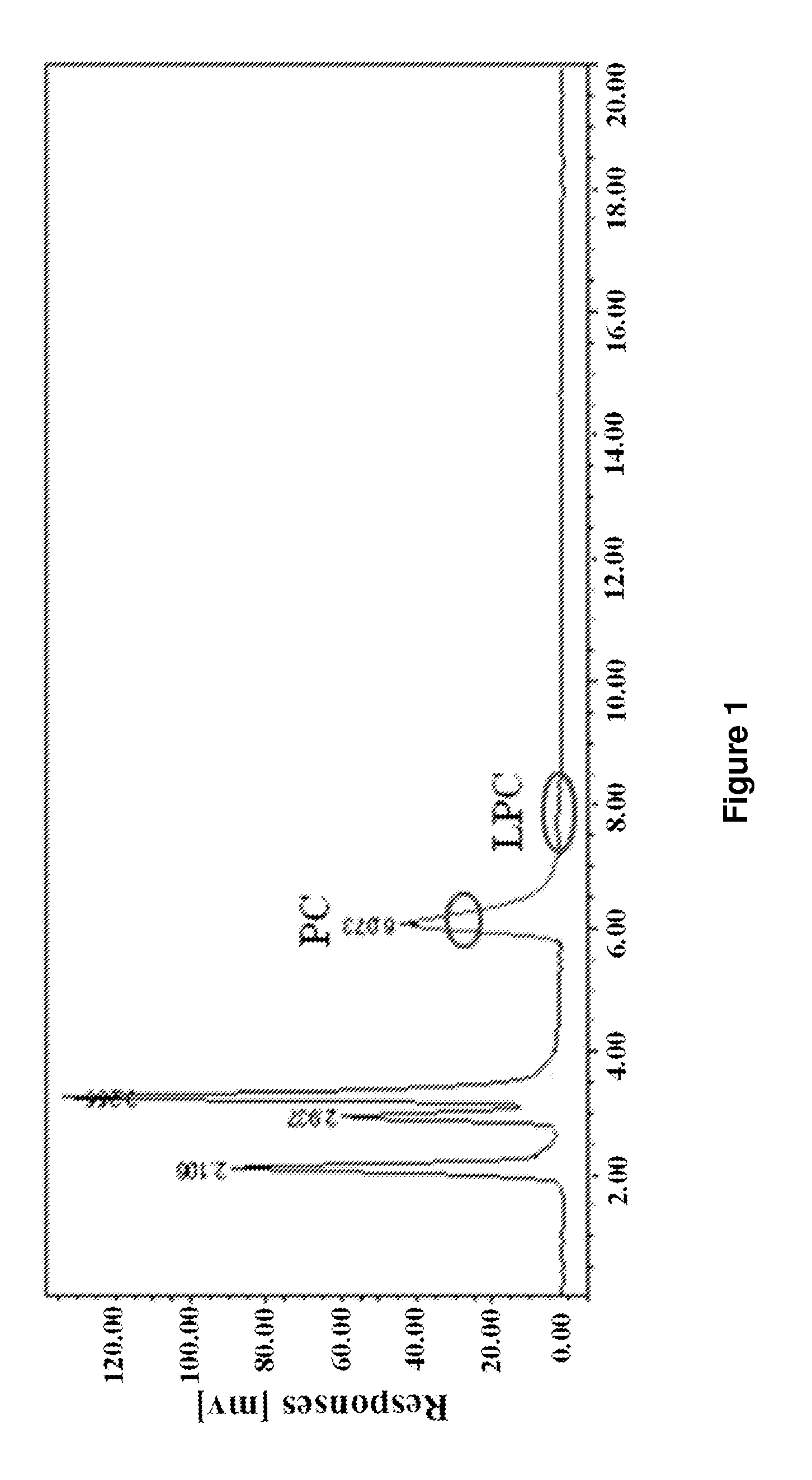
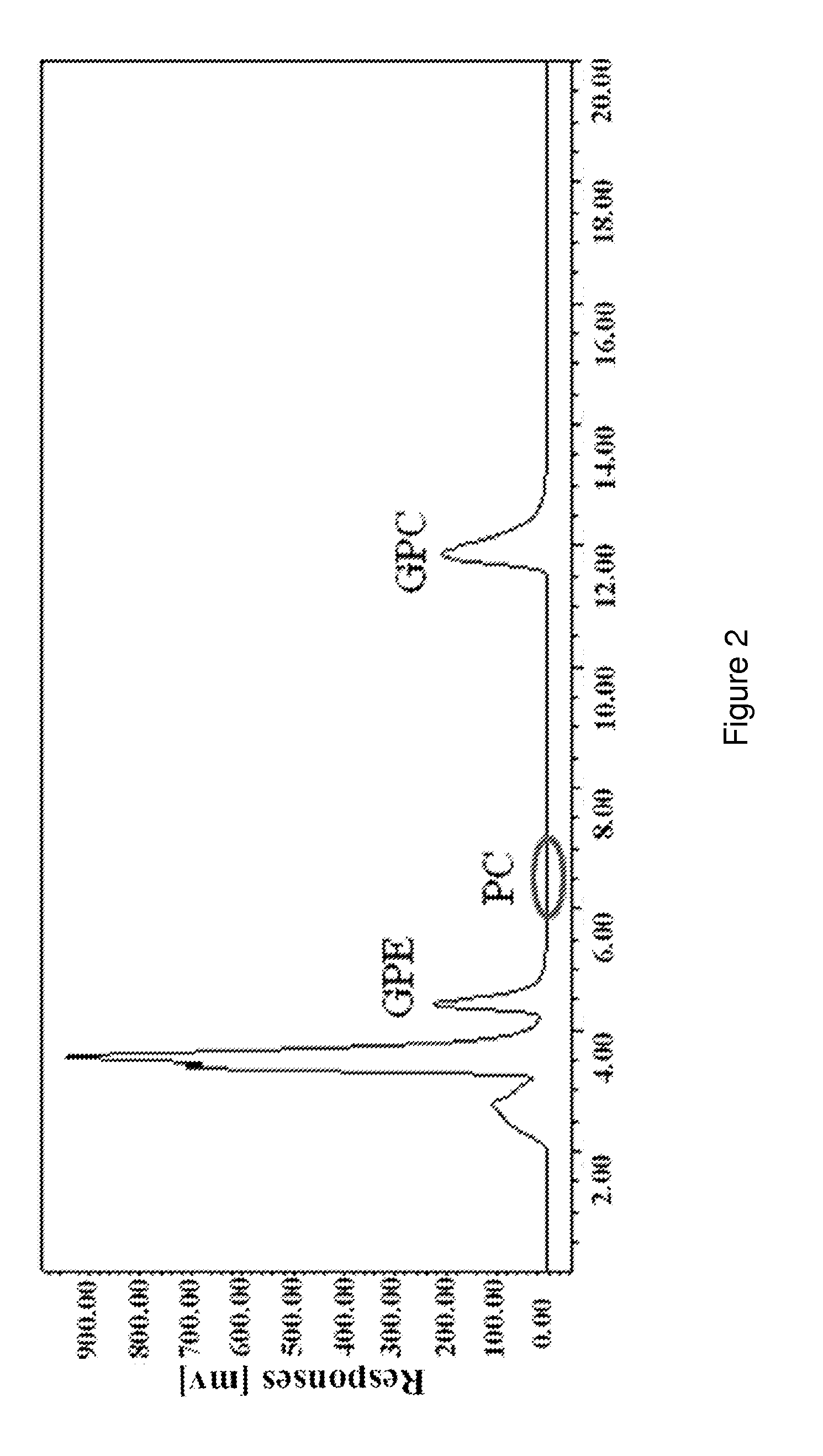
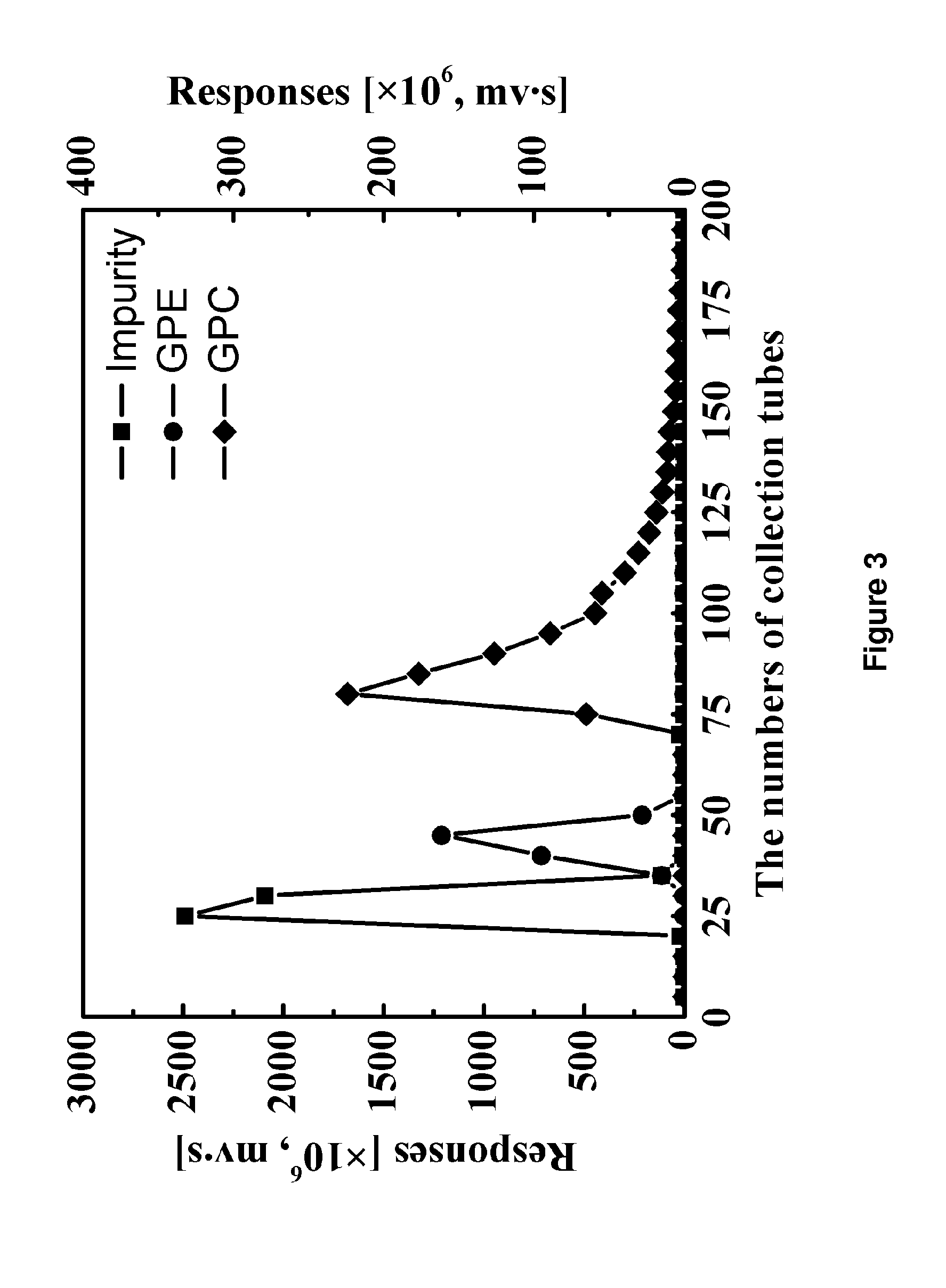
Method for Preparing High Purity L-alpha Glycerylphosphorylcholine
Disclosed is a method for preparing L-α-Glycerylphosphorylcholine with high yields and purity. The method uses phospholipase A1-based enzymatic hydrolysis, ion-exchange resin purification and silica gel column chromatography to prepare L-α-glycerylphosphorylcholin with purity up to 99.8% and a final yield up to 78.4%. The method disclosed is simple, cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and adaptable to industrial applications.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing enzyme modified soybean lecithin
The invention provides a production method of enzyme-modified soybean lecithin, adding phospholipase A2 at 2000IU / 100g-4000IU / 100g concentrated phospholipid, adding CaCl2 at 0.003-0.005mol / L, constant temperature at 40°C-60°C, and reacting 6 ~8 hours; add compound protease, dosage 10000IU / g~20000IU / g, control pH value 6~8, react for 3~5 hours; centrifuge for 10~20 minutes, remove grease. The method of the present invention modifies soybean phospholipids by phospholipase A2, which not only improves its HLB value and enhances the processing characteristics such as water solubility of phospholipids, but also does not introduce chemical groups, and is safe, reliable, unlimited, widely used, and effective Significant advantages.
Owner:SOYBEAN TECH DEV RES CENT HEILONGJIANG PROV
Used of inhibitors of phospholipase a2 for the treatment, prevention or diagnosis of neural inflammatory or demyelinating disease
InactiveUS20060058225A1Reduced activityReduce expressionCompound screeningBiocidePhospholipaseMedicine
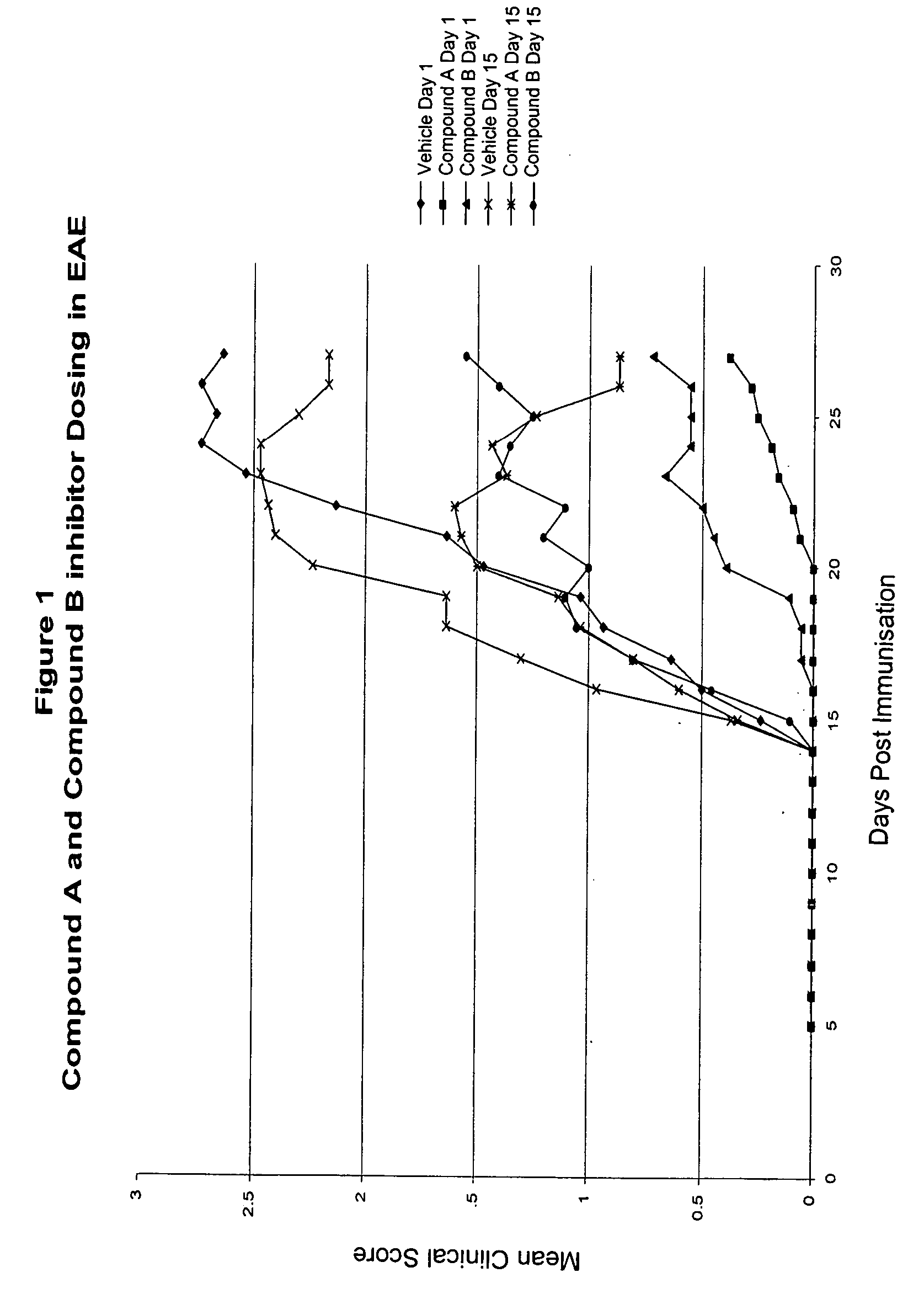
The present invention provides methods of preventing and treating neural inflammatory or demyelinating disease, such as multiple sclerosis, via an inhibition of the activity or expression of phospholipase A2. The invention further relates to methods of identifying phospholipase A2 inhibitors and their use thereof for the prevention and / or treatment of neural inflammatory or demyelinating disease. An observed increase in the amount of phospholipase A2 in neural lesions in the EAE animal model system indicates that elevated phospholipase A2 activity or levels correlate with neural inflammatory or demyelinating disease. Therefore, in a further aspect the invention provides methods for the diagnosis and prognostication of neural inflammatory or demyelinating disease, such as multiple sclerosis.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
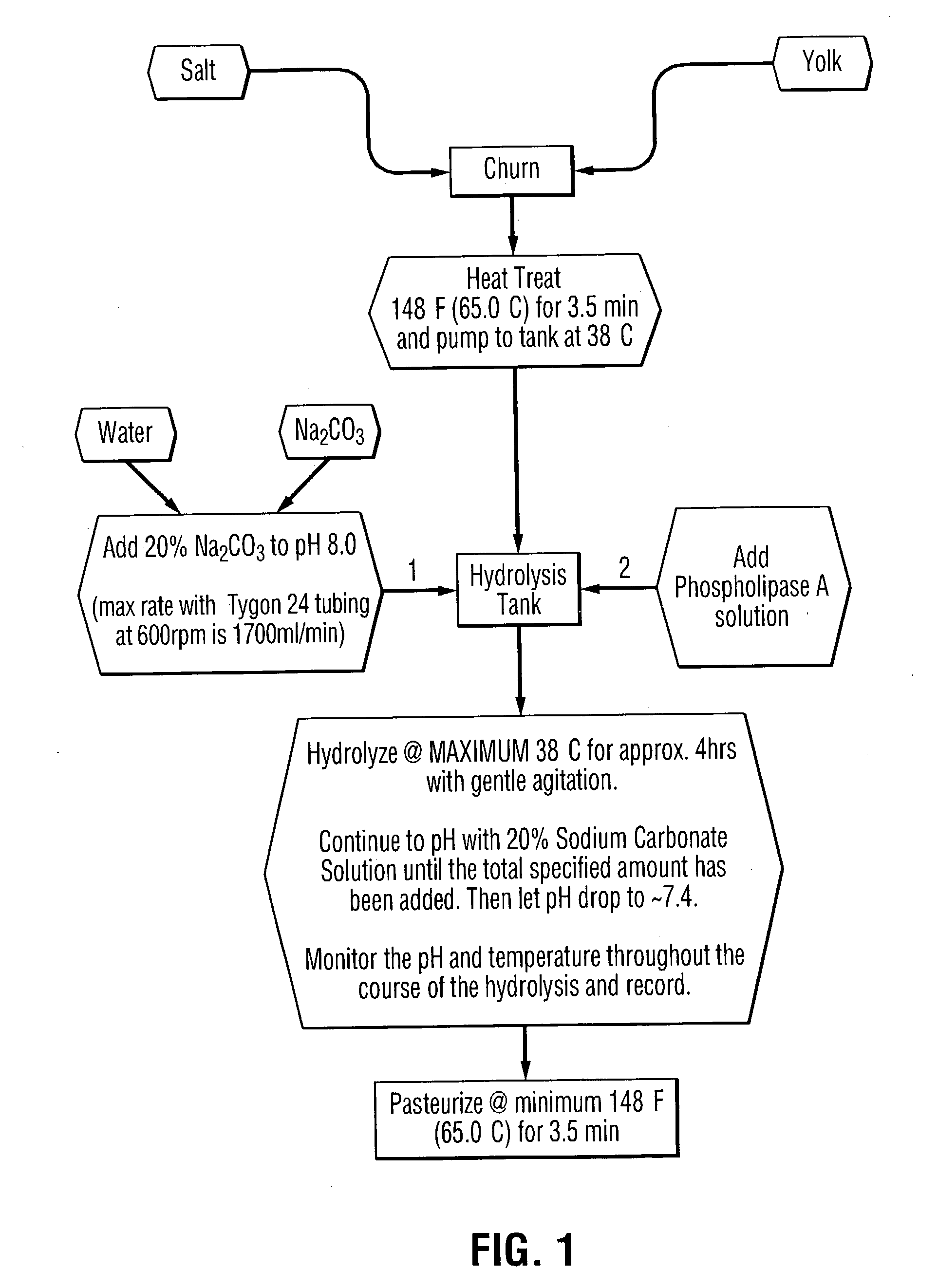
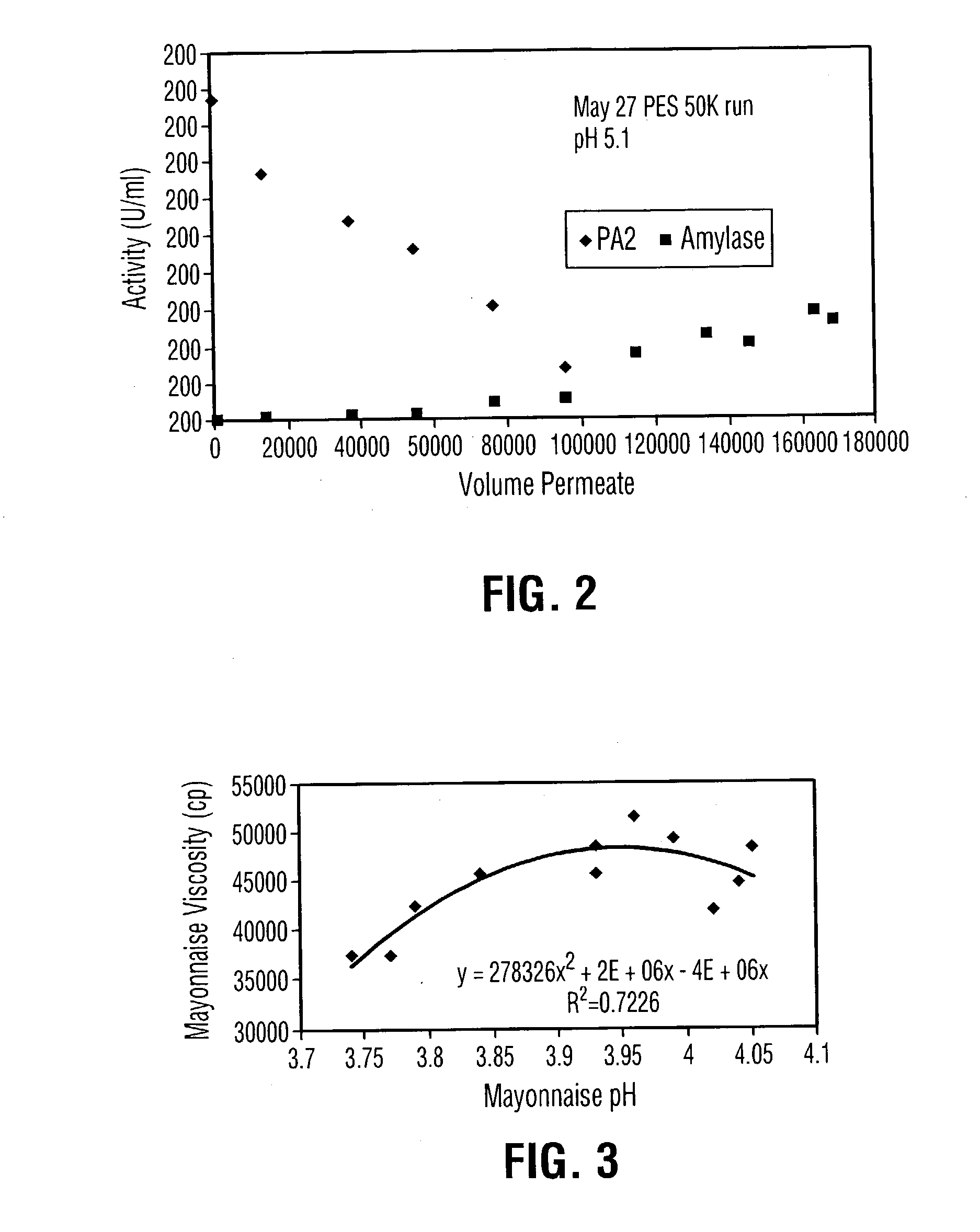
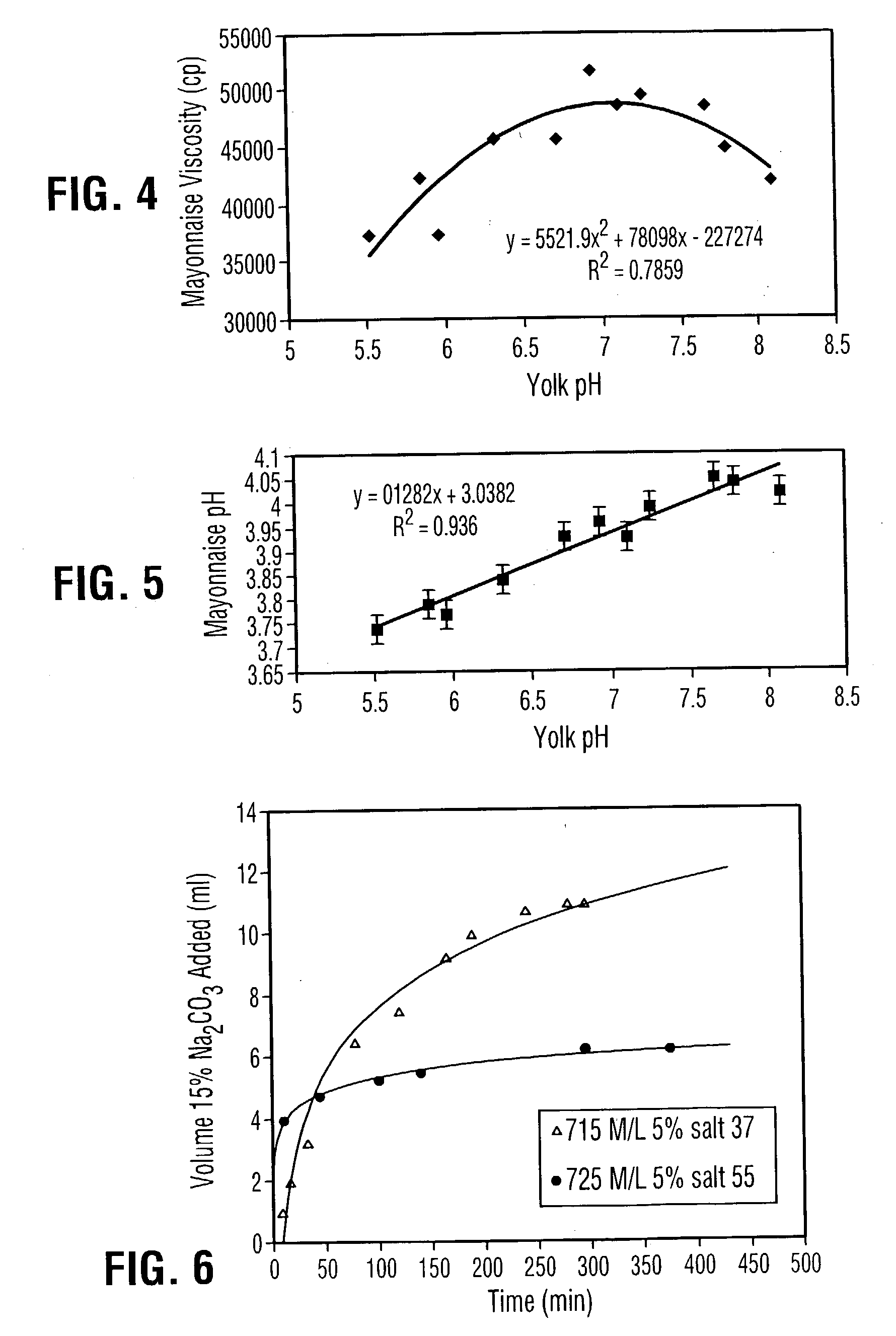
Liquid egg yolk product comprising lysophospholipoprotein
This invention pertains to a novel liquid egg yolk product which contains lysophospholipoprotein. More particularly, this invention pertains to a novel liquid egg yolk product containing lysophospholipoprotein from a phospholipoprotein modified using a non-animal derived phospholipase A, and a process therefor, which is kosher, does not have a porcine or bovine source, and does not contain appreciable levels of amylase. The product is useful as an emulsifier in foodstuffs such as sauces, spreads, mayonnaise, dressings, salad dressings, and the like. A process for the manufacture of a liquid egg yolk product containing lysophospholipoprotein comprising: (a) processing a phospholipase A-containing microbial fermentate to remove undesirable amylase and protease co-products of the fermentation to produce a refined phospholipase A-containing microbial product; and (b) modifying a liquid egg yolk with the refined phospholipase A-containing microbial product of step (a) to produce a modified liquid egg yolk product containing lysophospholipoprotein, said modified liquid egg yolk product having (i) a degree of conversion of phospholipoprotein to lysophospholipoprotein of at least 10%; and (ii) an amylase activity of less than 50 units / litre.
Owner:M G WALDBAUM
Low-temperature alkaline phosphatidase A1 and coding gene thereof
InactiveCN101070530ASimple production processHigh expressionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologySerratia fonticola
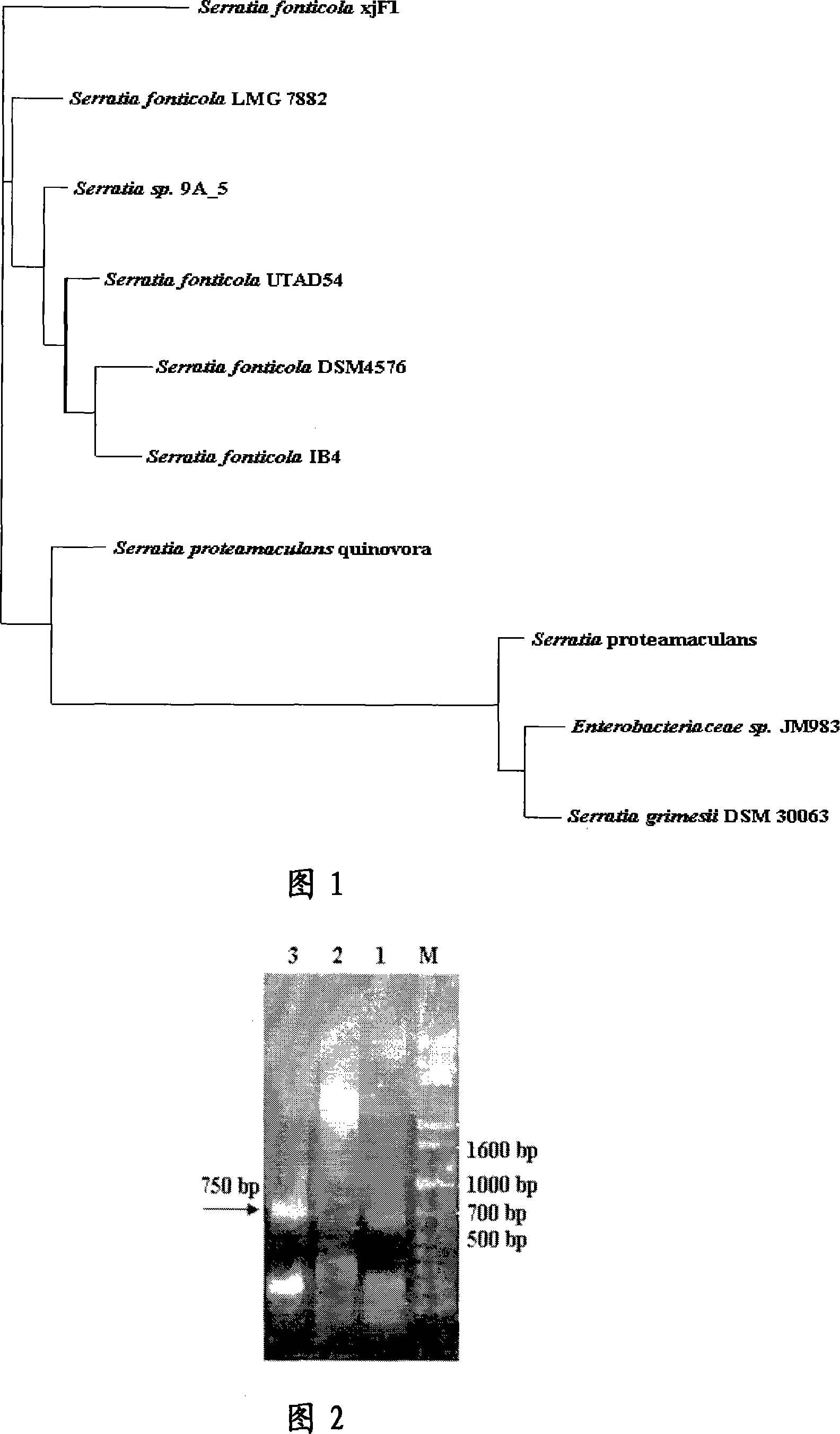
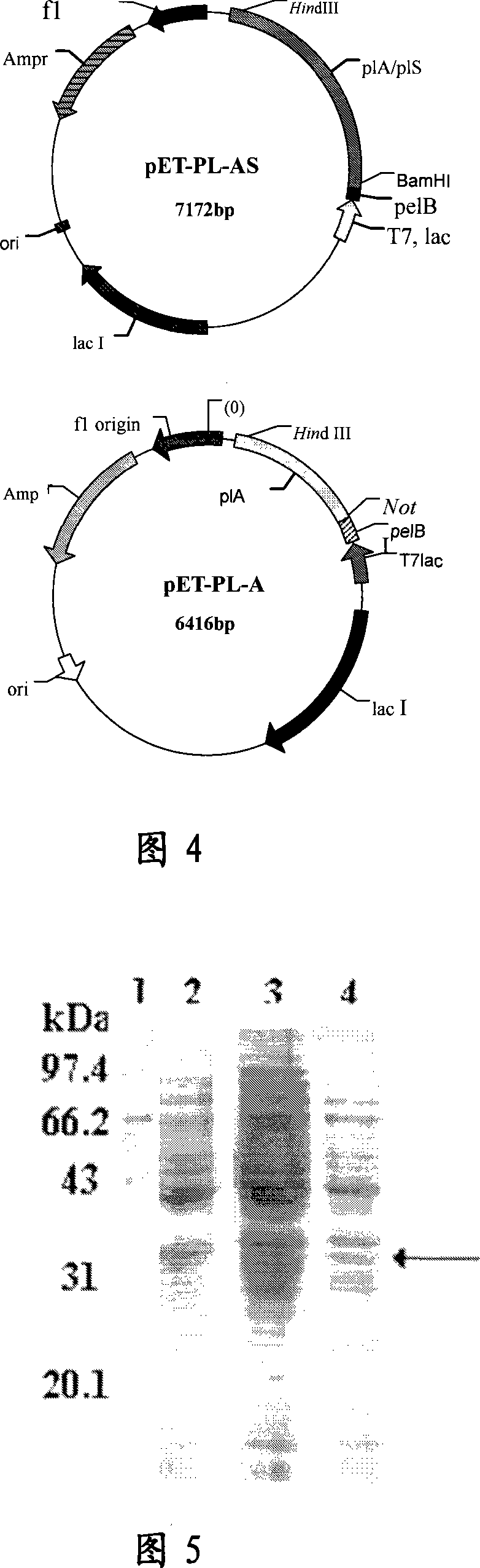
This invention open a cold tolerance of Serratia sand Habitat-chuen (Serratia fonticola) xjF1 CGMCC No.1971, through the strain characteristics, enzyme production conditions and the nature of enzyme research, proved a new phospholipase A1 gene consists of two open plA and plS reading frame, was certified plA gene coding phospholipase A1, plS gene coding phospholipase A1 auxiliary protein. This invention relates to the gene containing the recombinant plasmid and reorganization cell, the gene expression products phospholipase A1 in the show activity under low-temperature conditions, can be used in industries such as oil refining process can be simplified production process, lowering energy consumption, improve product quality , protecting the environment, reduce production costs, have important practical significance.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for refining raw oil by using magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1
InactiveCN102559378AResponsiveness to strong magnetic fieldsQuick and Easy EnrichmentFatty-oils/fats refiningPhospholipase ACitric acid
The invention provides a method for refining raw oil by using magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1, which relates to a method for refining raw oil by using immobilized phospholipase A1. The invention aims to solve the problems that the separation and the recovery of an immobilized enzyme are complicated, the activity recovering rate is low and a magnetic immobilized enzyme is not used for refining raw oil at present, which exist in a traditional method for preparing immobilized phospholipase A1. The method for preparing and refining the raw oil comprises the following steps of: (1) preparingthe magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1; (2) heating the raw oil and adding a citric acid solution; and (3) cooling, regulating the pH value, then adding the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1, stirring and separating the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 so as to finish the preparation method of the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 and the method for refining the raw oil. The recovering rate of the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 prepared by the method for refining the raw oil by using the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 reaches more than 85 percent, so that the phosphorus content of the raw oil is lowered to 7-10mg / kg. The method for refining the raw oil by using the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 is applied to the field of degumming of grease.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
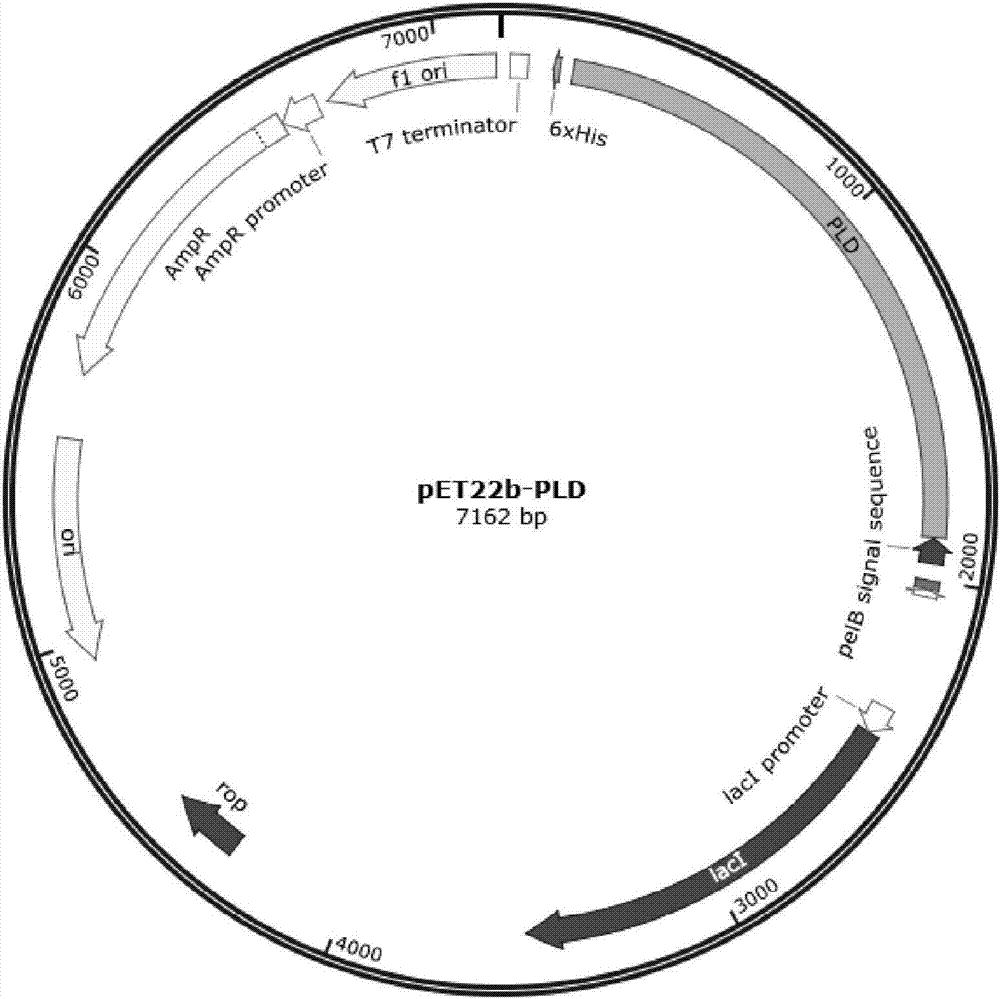
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing phospholipase D and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106957850AEasy source of enzymesConvenient sourceBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliStreptomyces
The invention discloses a gene sequence for coding phospholipase D, which belongs to the fields of biotechnology and preparation of phospholipids products. The gene sequence of the phospholipase D is sourced from Streptomyces sp.(strain PMF), and the gene sequence capable of being expressed in escherichia coli is obtained by virtue of the optimization of a codon. The invention also constructs a genetically engineered bacterium for producing phospholipase D, the phospholipase D produced by utilizing the recombinant Escherichia coli is used as a catalyst to produce phosphatidylserine, the enzyme is convenient in source, the yield is high, the fermentation process is simple, the cost is low, and the industrialization prospect is good.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Diagnosis and prognosis of wound infection by measurement of a phospholipase a2 in wound fluid
InactiveUS20070231380A1Easy and early diagnosis/prognosisImprove material stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhospholipasePhospholipase A
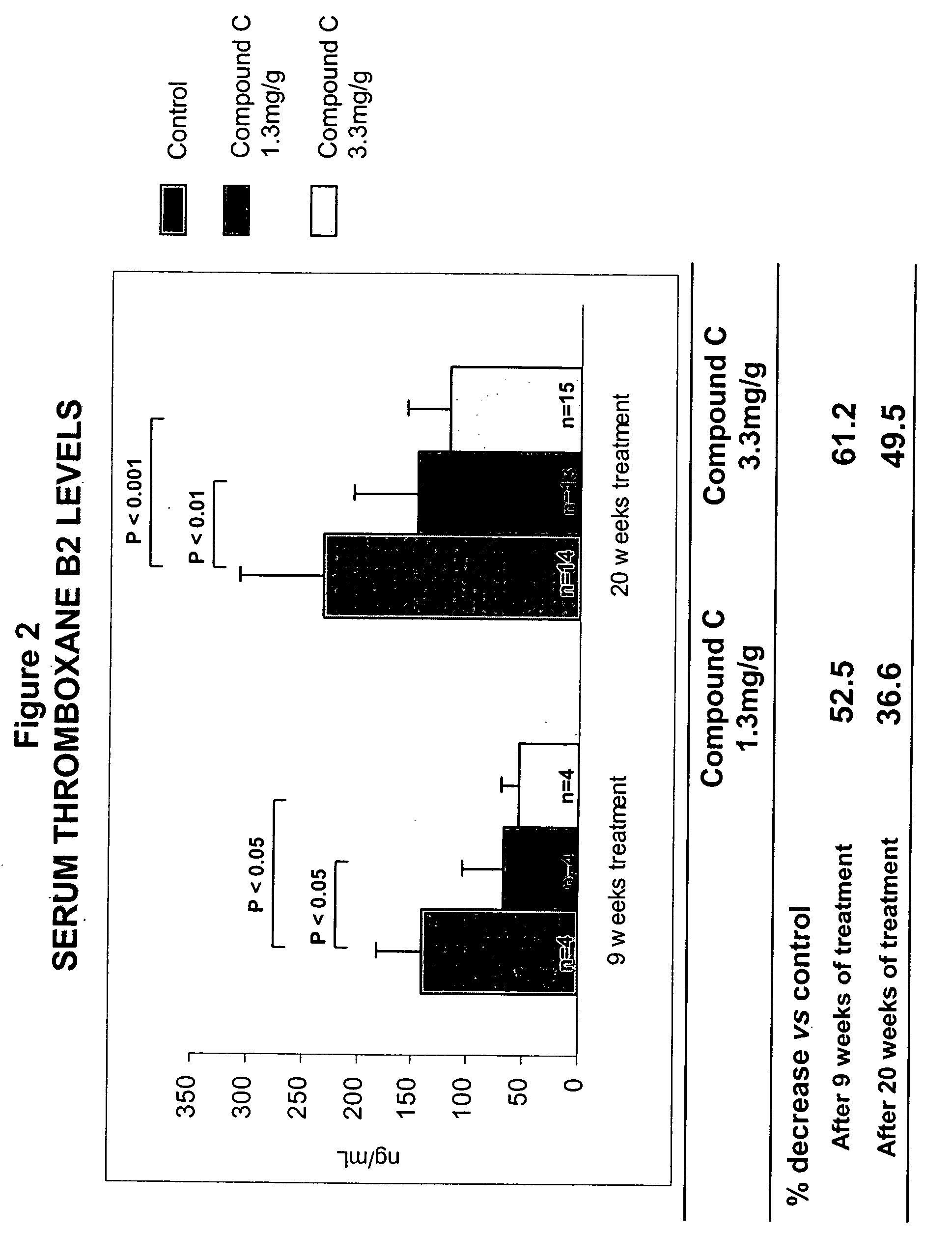
The present invention relates to the diagnosis, prognosis and / or treatment of wound infection by testing wound fluid for the presence of a marker which is present in an amount which is indicative of infection. The marker may be high molecular weight phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) or a marker which is correlated with cPLA2.
Owner:WOUNDCHEK LAB US
Method for preparing magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 and method for refining crude oil by using magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1
InactiveCN102061293AResponsiveness to strong magnetic fieldsQuick and Easy EnrichmentFermentationOn/in inorganic carrierLow activityPhospholipase A
The invention relates to a method for preparing magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 and a method for refining crude oil by using the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1. The invention aims to solve the problems of complicated separation and recycling of immobilized enzyme and low activity recovery of the conventional method for preparing the immobilized phospholipase A1, and the problem that the magnetic immobilized enzyme is not used for refining the crude oil at present. The method for preparing and refining the crude oil comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1; 2, heating the crude oil, and adding citric acid solution; and 3, cooling, regulating the pH value, adding the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1, stirring, and separating the magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1. The recovery rate of the prepared magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 is over 85 percent, and the phosphorus content of the crude oil is reduced to 7-10mg / kg. The invention is applied to the field of oil degumming.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Koji mold-origin phospholipase a2
It is intended to provide koji mold-origin phospholipase A2 and a DNA encoding it. Namely, phospholipase A2 comprising the following protein (a) or (b): (a) a protein having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2; and (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence derived from an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2 by a partial modification and serving as phospholipase A2.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND EVALUATION +2
Method for refining camellia seed crude oil beneficial to individuals with hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia
ActiveCN102504946AImprove heat resistanceReduce sensitivityFatty-oils/fats refiningCamellia oleiferaSecondary hyperlipidemia
The invention relates to a method for refining camellia seed crude oil, in particular to a method for refining the camellia seed crude oil by using immobilized phospholipase A1. The technical scheme of refining the camellia seed crude oil by using the immobilized phospholipase A1provided by the invention is realized by the following steps of: a, immobilizing phospholipase; b, carrying out pre-treatment on the camellia seed crude oil; c, adding the immobilized phospholipase into the camellia seed crude oil; and d, agitating and then centrifuging, namely realizing that the camellia seed crude oil is refined by using the immobilized phospholipase. The method for refining the camellia seed crude oil provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that unsaturated fatty acid is lost for 1-3% and is reduced by 15-20% compared with the loss of the unsaturated fatty acid in chemically-refined camellia seed oil; the immobilized phospholipase A1 is degummed to reduce phosphorus content in the oil to be lower than 5 mg / kg; the heat resistance of the immobilized phospholipase A1 is improved; the immobilized phospholipase A1 can keep a higher activity in a wider pH value range and the sensitivity of the immobilized phospholipase A1 to a reaction environment is reduced, so that the operation conditions are easier to control and implement.
Owner:FUJIAN CHUNHUI BIOLOGICAL ENG
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. A phospholipase D gene is obtained through clone in Streptomyces ambofaciens by means of molecular biology measures, constructed expression plasmid is guided into E. coli BL21(DE3), and phosphatase-containing engineering bacteria formed by highly copying and recombining an expression carrier are obtained through kanamycin resistant plate screening. The recombinant phospholipase D is used for converting phosphatidylcholine and serine to generate phosphatidylserine, and efficient production of vitamin C-2-phosphate is achieved. By carrying out reaction for 2 h at the temperature of 40 DEG C with the pH value of 4.5, the yield of phosphatidylserine can reach 15.8 g / L, the conversion rate is 63.9%, and the space time yield is 7.9 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for removing phospholipids and off-flavors from proteins and resulting protein product
ActiveUS20110045128A1Improve stabilityEasy to integrateMilk preparationDough treatmentFlavorPhospholipase
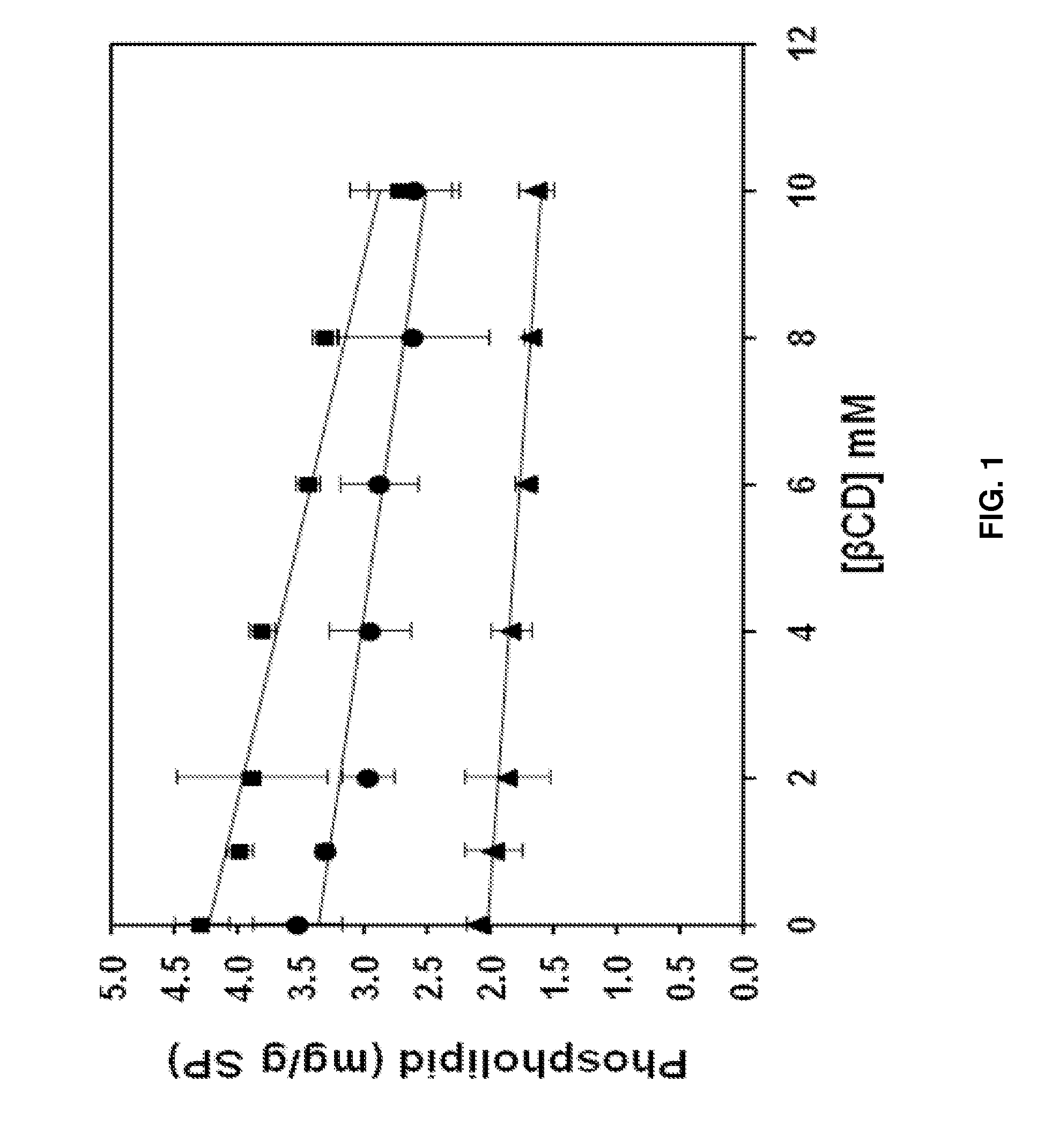
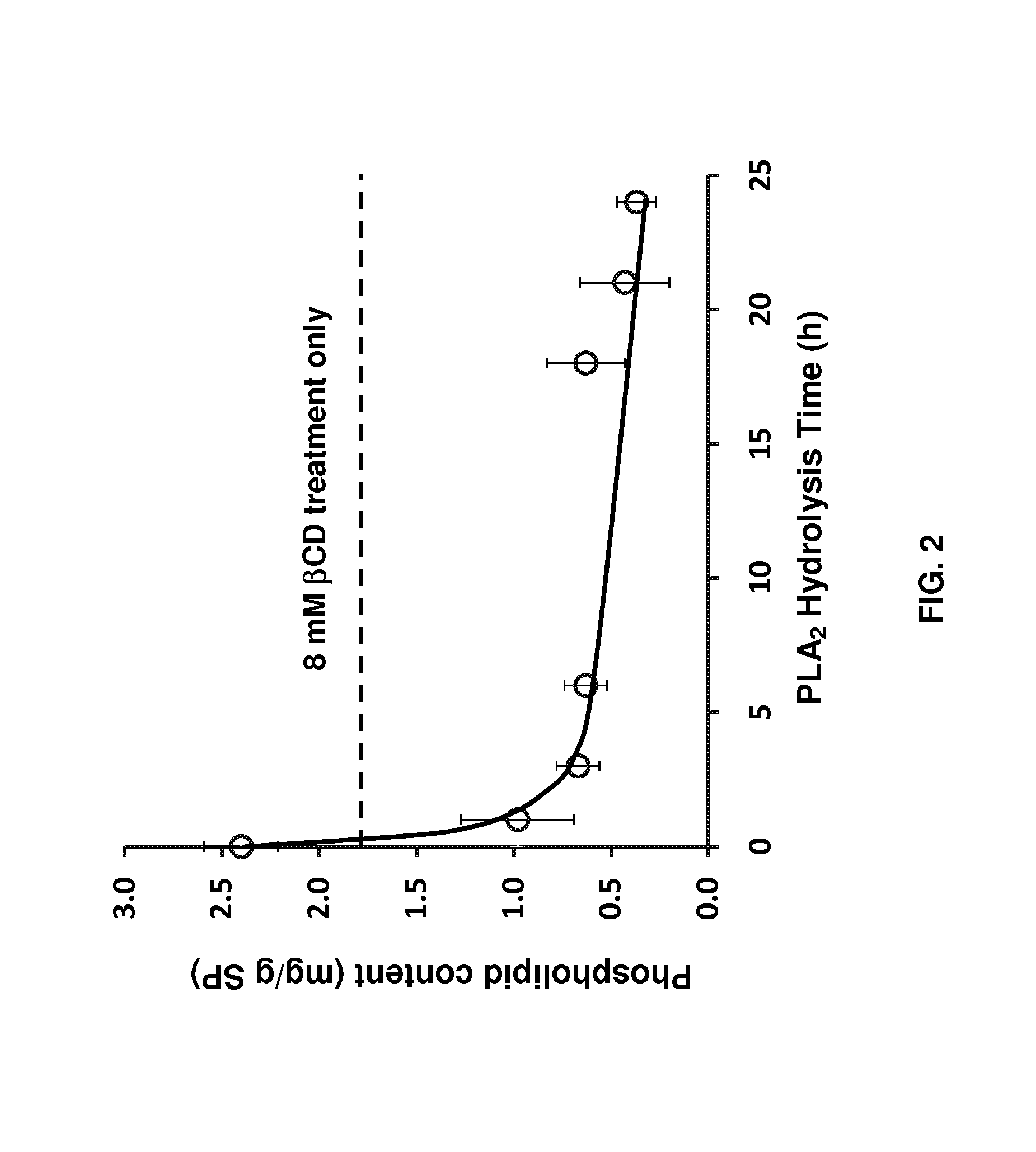
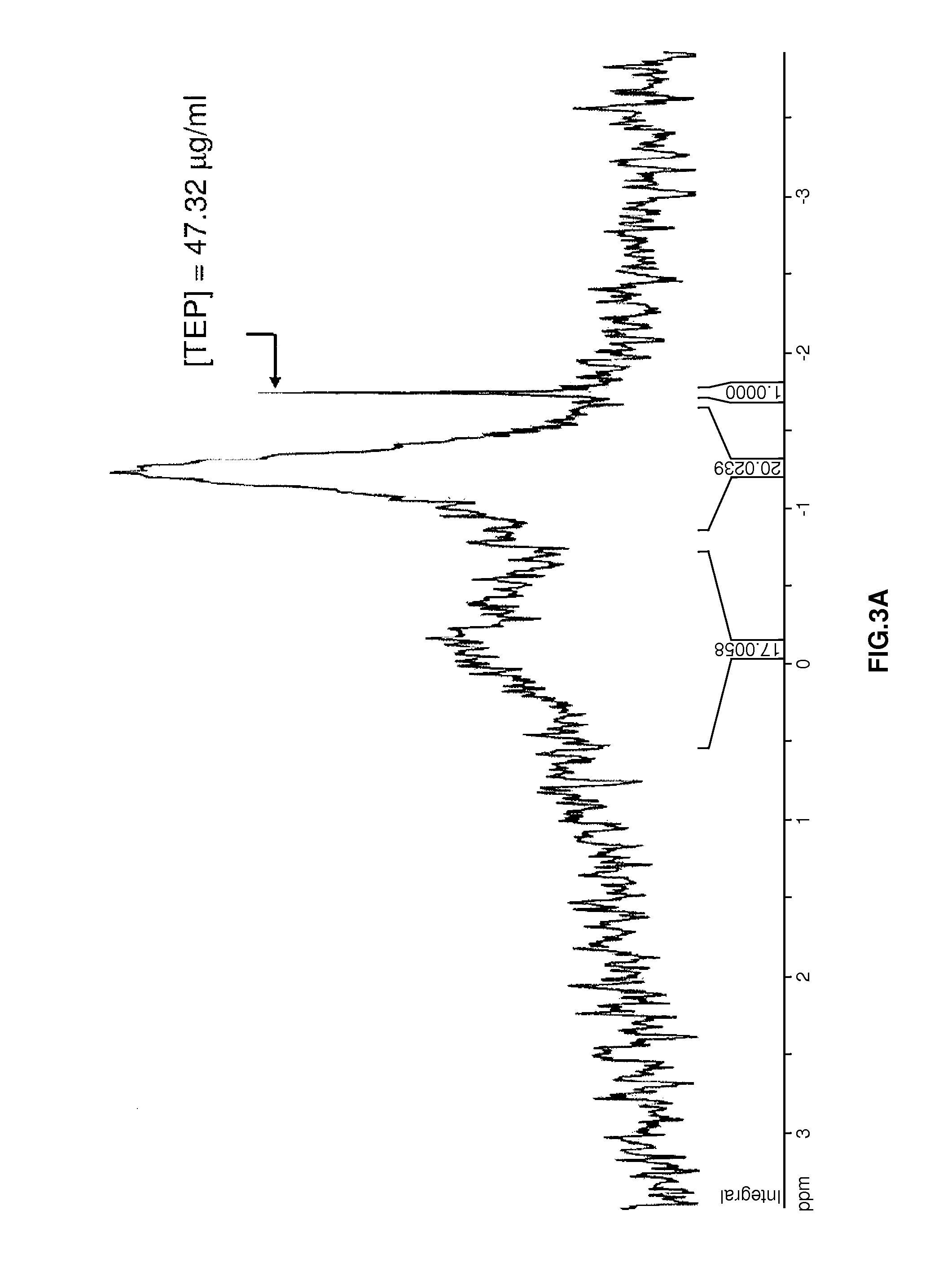
Described are methods of removing phospholipids and other off-flavor-causing compounds from edible proteins using a cyclodextrin treatment. The methods include treating soy protein with cyclodextrins such as β-cyclodextrin to form cyclodextrin-compound complexes and then separating the resulting complexes from the protein. Optionally, prior to treating the protein with cyclodextrin, the protein is sonicated and then treated with a phospholipase, such as phospholipase A2. Versions of the methods described herein are capable of removing more than 99% of phospholipids from soy protein.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for inhibition of phospholipase a2 mediated inflammation
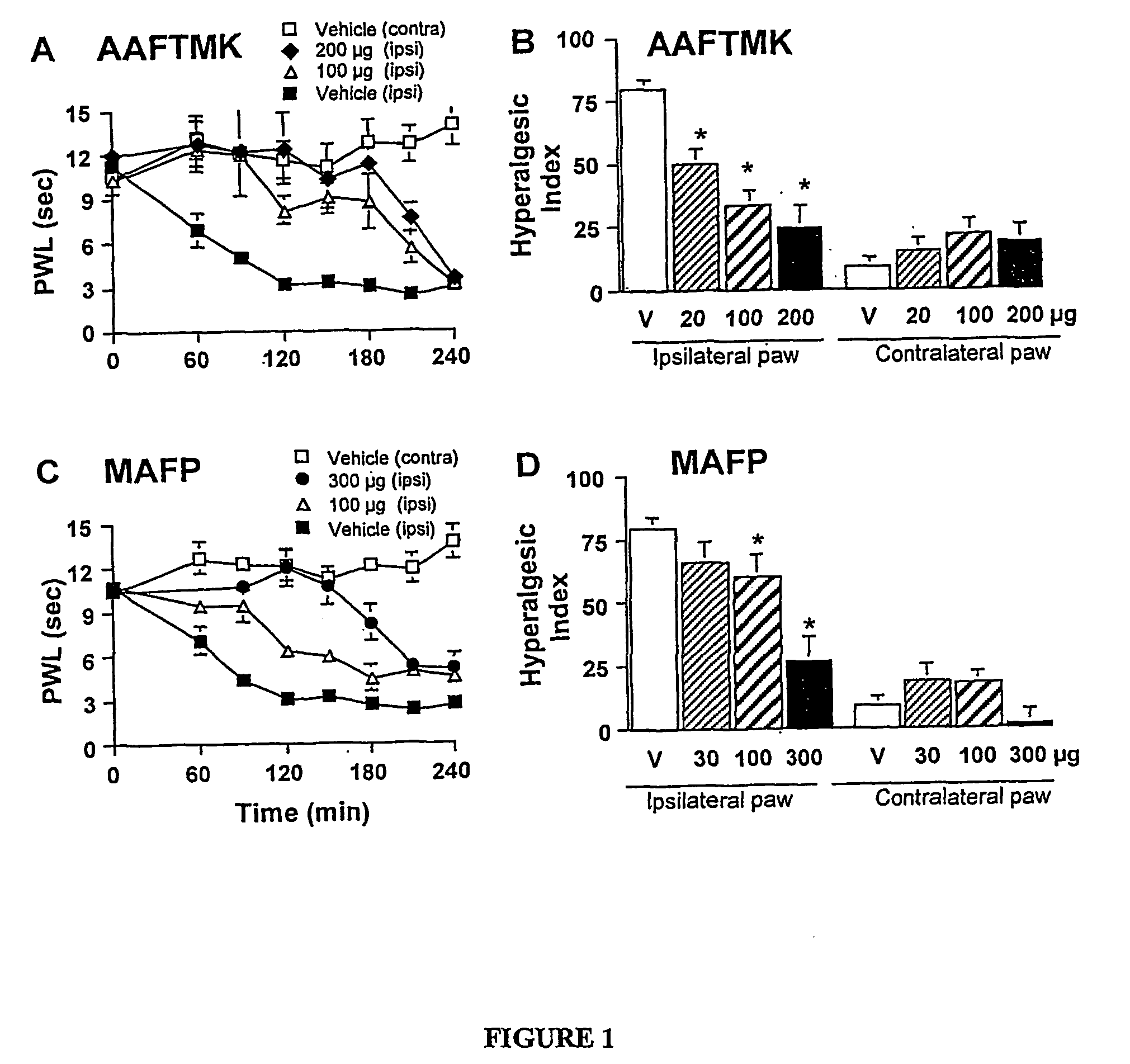
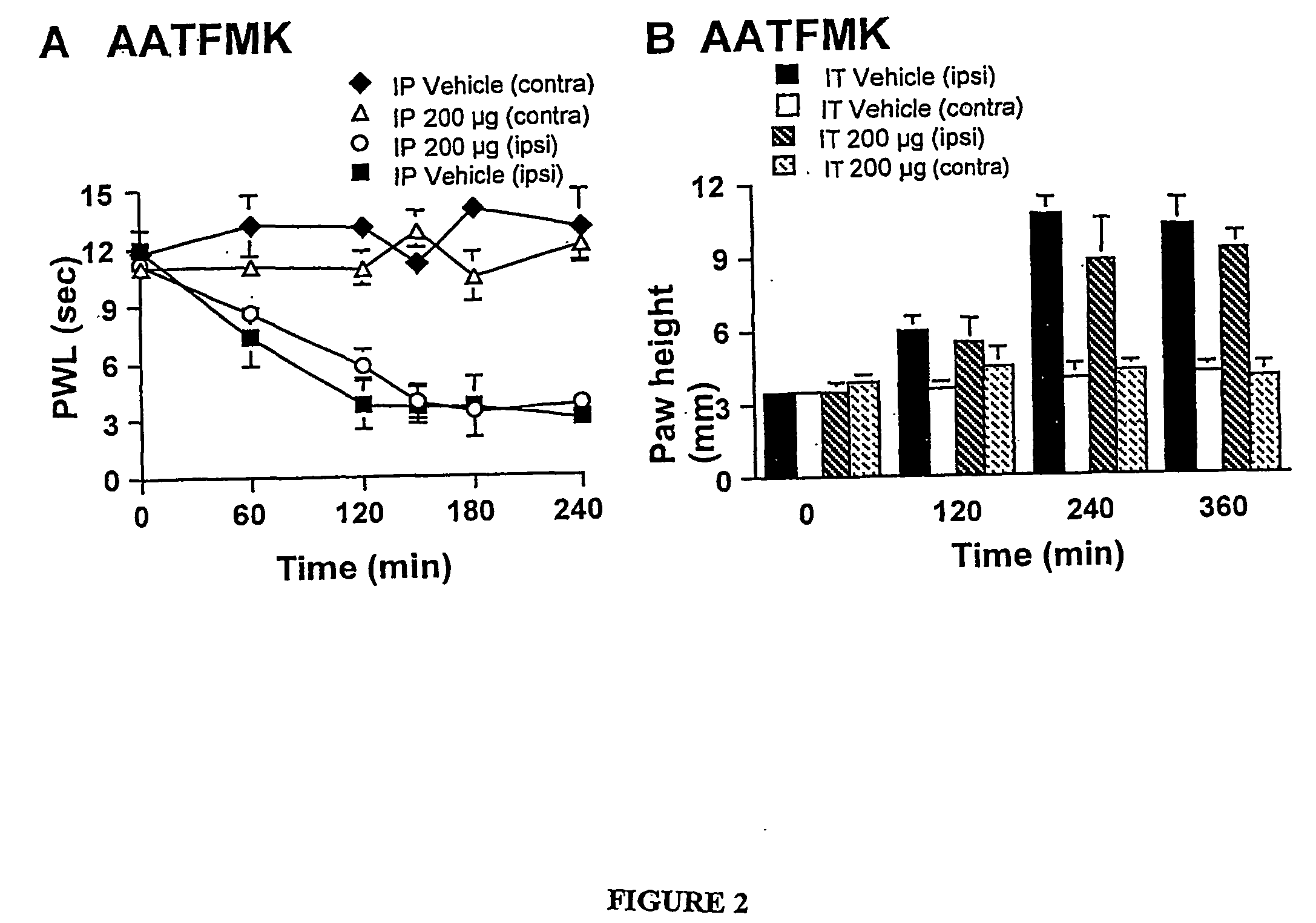
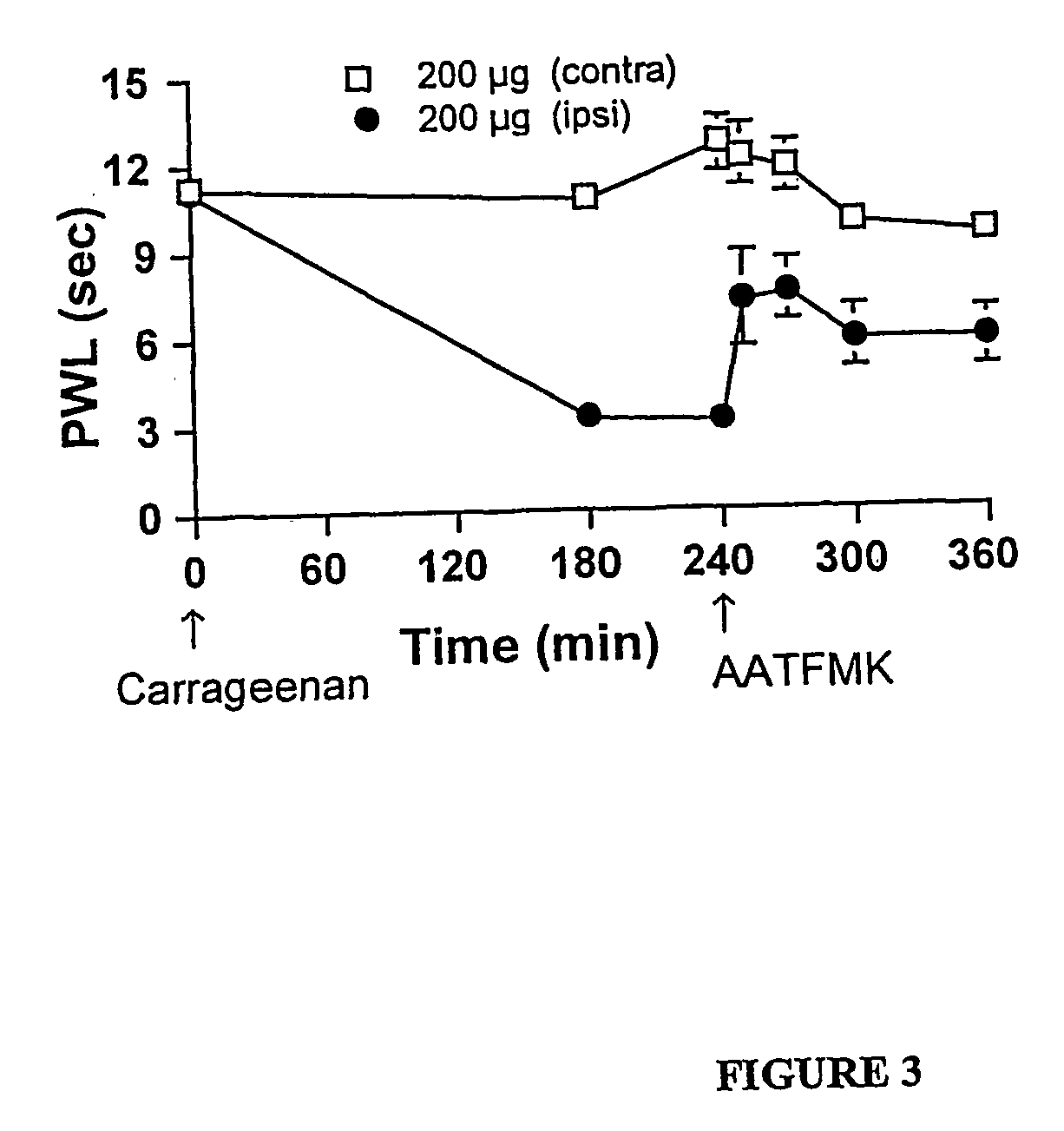
Specific, highly potent 2-oxo-amide based inhibitors of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity are provided. A role for PLA2 activity in spinally mediated inflammatory processes is established, and a method for treating hyperalgesia and other inflammatory conditions associated with PLA2 activity is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compounds for determining the activity of phospholipase A.sub.2
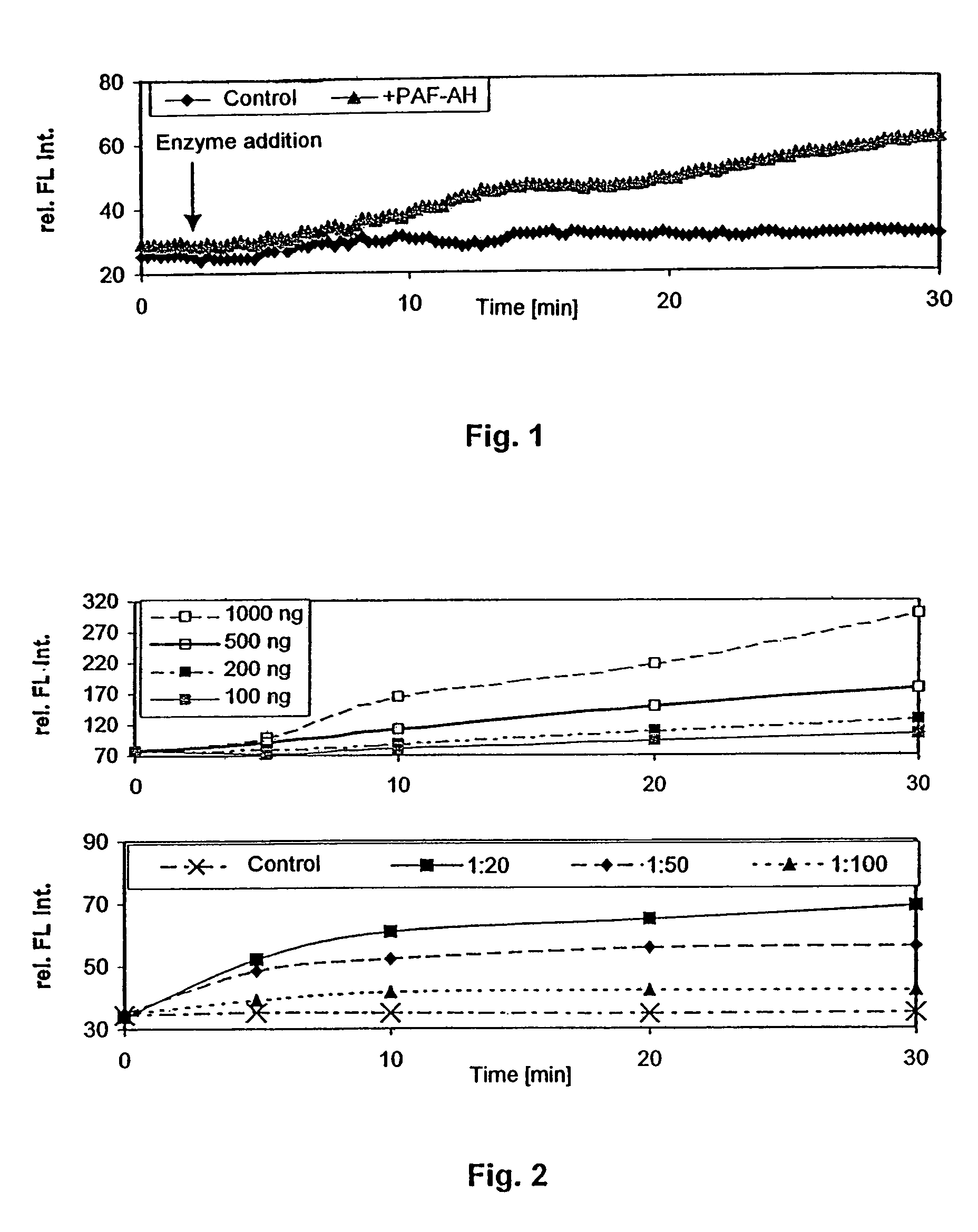
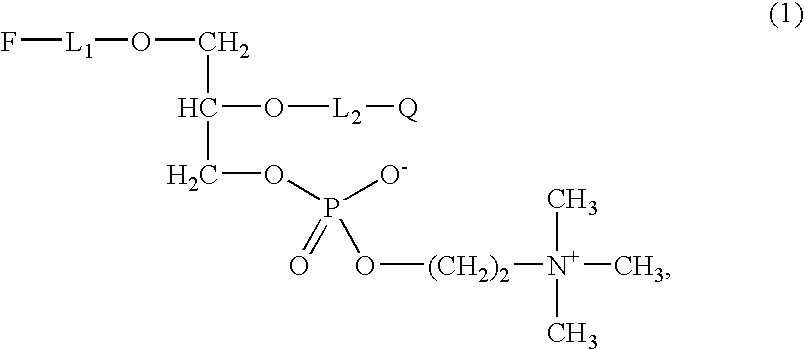
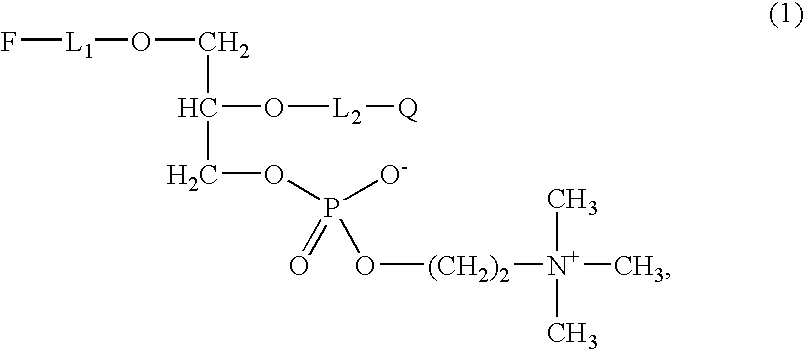
InactiveUS7301043B2Simple wayActivity of the enzyme can be determined without burdensome process stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEtherPhospholipase A
Compounds for determining the activity of phospholipase A2, are described herein, and include embodiments having formula (1)whereinL1 is derived from an ether (R1—OR2)m, wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected and are derived from a hydrocarbon having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, with m being an integer from 1 to 4, or from a hydrocarbon R having 1 to 20 carbon atoms;F is unsubstituted or substituted pyrene as a flouraphore;Q is a quencher, andL2 is C(O)-L1 or C(O)-L1-NH, wherein L1 is as defined above. These compounds may be used to determine the activity of phospholipase A2, in particular PAF-AH.
Owner:SIRS LAB
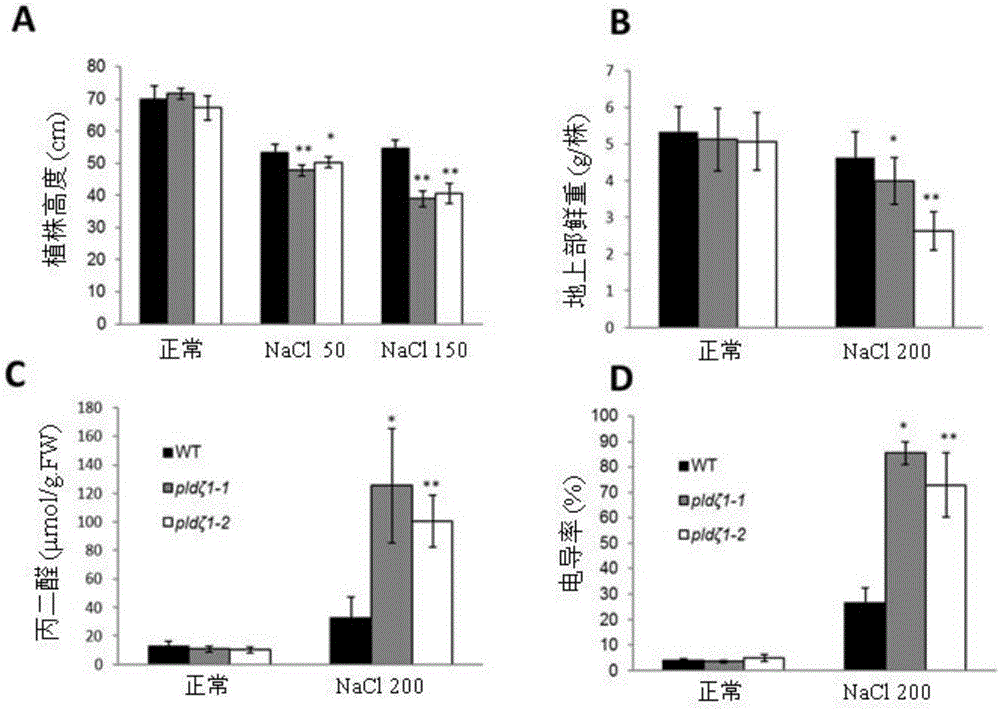
Application of phospholipase gene PLDzeta1 in improving salt resistance of plant
ActiveCN106191001ALow salt toleranceReduced survival rateHydrolasesFermentationSalt resistanceBiotechnology
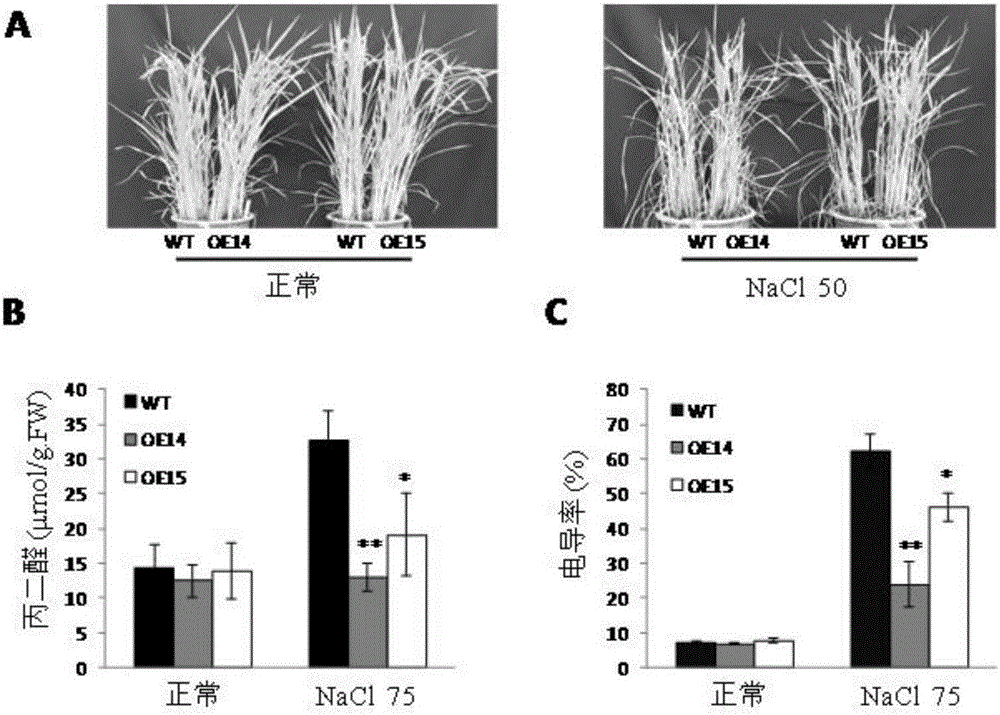
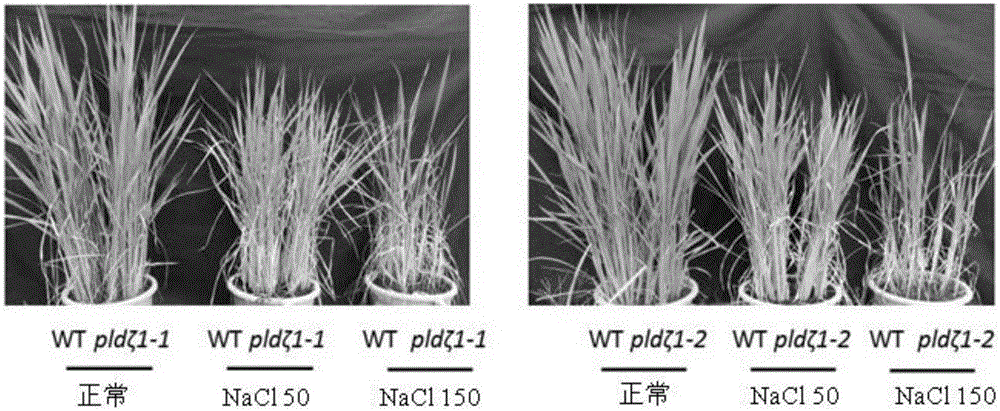
The invention discloses application of a phospholipase gene PLDzeta1 in improving salt resistance of a plant. The gene PLDzeta1 is transferred to a plant through a molecular genetic transformation method, and the transformation plant with the overexpression gene PLDzeta1 is obtained. The overexpression gene PLDzeta1 remarkably improves the salt resistance of the plant. The membrane permeability and the malondialdehyde content of a leaf of the plant with overexpression gene PLDzeta1 are remarkably lower than those of a control wide group under the threat of salt, and the survival rate and the plant height are remarkably higher than those of the control wide group. The loss expression of the gene PLDzeta1 leads to remarkable reduction of the salt resistance of the plant and remarkable reduction of biological yield compared with the wild group, and the result further improves that the gene PLDzeta1 has a remarkable positive regulation effect on salt resistance. The application of the phospholipase gene PLDzeta1 in improving salt resistance of the plant provides a novel way for the seed breeding of salt-resistance molecules of the plant, and creates a novel seed material.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for enzymatic preparation of glycerophosphorylcholine
The invention discloses a method for enzymatic preparation of glycerophosphorylcholine. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing phosphatidylcholine-containing phospholipid with a hydroxyl donor, phospholipase and partial glyceride lipase, and then conducting hydrolysis or alcoholysis reaction, wherein phospholipase is one or the mixture of two of phospholipase A and phospholipase B; and (2) separating resultants and reclaiming glycerophosphorylcholine. The invention relates to the method in which phospholipase and partial glyceride lipase are together used for enzyme reaction to catalyze phosphatidylcholine in the substrate and remove acyl from fatty acid to prepare glycerophosphorylcholine. When partial glyceride lipase and phospholipase are used together, the conversion rate of phosphatidylcholine, the enzyme reaction rate and the yield of glycerophosphorylcholine are far higher than independent use of phospholipase, the conversion rate of phosphatidylcholine in the substrate can be more than 95%, and the reaction duration can be less than one hour.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant Escherichia coli, and method for preparing phospholipase A1 through using recombinant Escherichia coli
ActiveCN103074290ALow sequence homologyLow costBacteriaHydrolasesSerratiaRecombinant escherichia coli
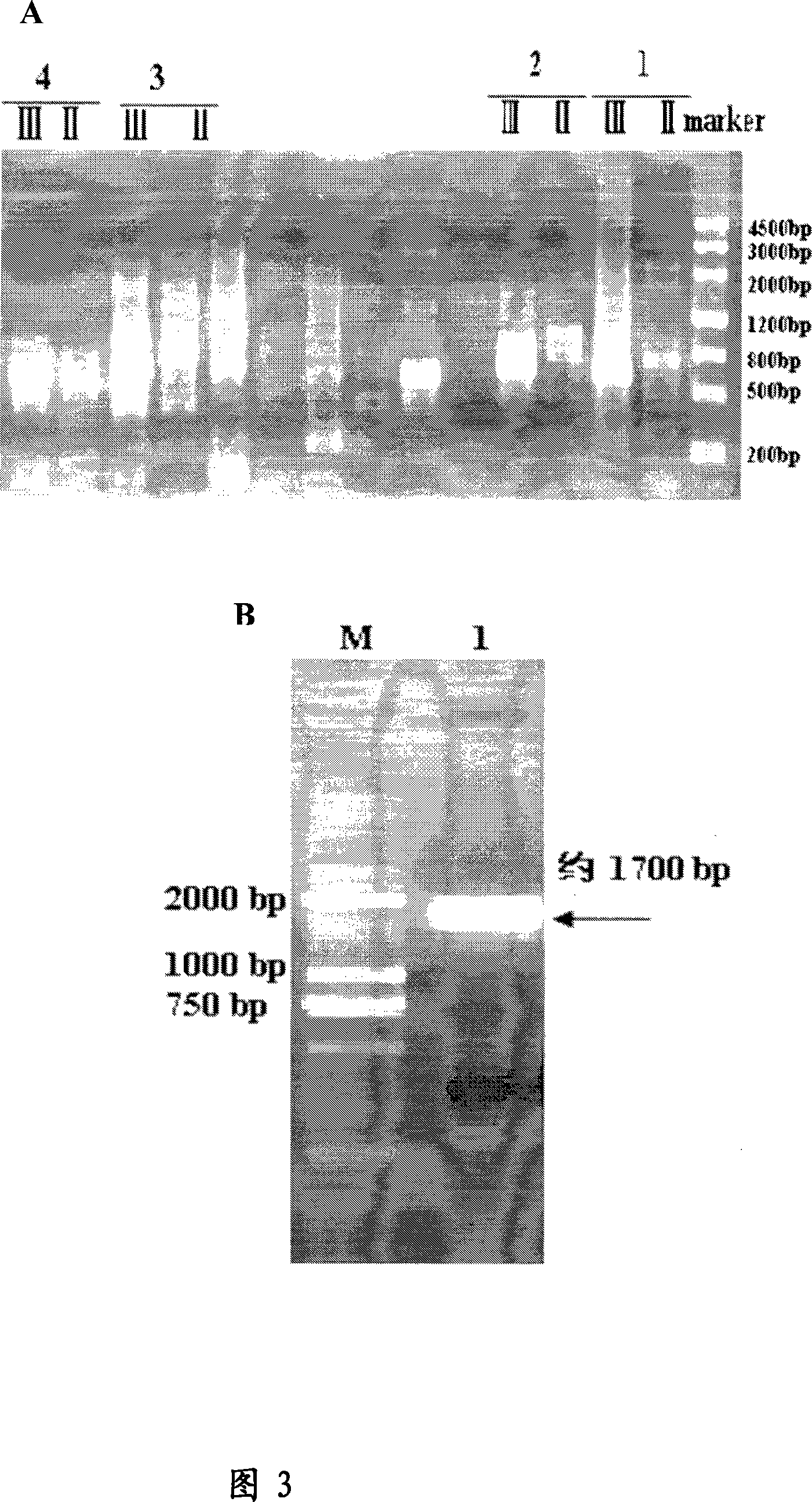
The invention provides a recombinant Escherichia coli, and a method for preparing phospholipase A1 through using the recombinant Escherichia coli. A gene-recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) / pET-pla CCTCC M 2012423 with the phospholipase A1 from liquefied Serratia liquefaciens CICC No.21538 is successfully constructed in the invention, and undergoes liquid fermentation to prepare hemolytic phospholipase A1, and the preparation method of the hemolytic phospholipase A1 comprises the steps of inclined plane culture, seed culture, autonomous induction culture (comprising permeable substance addition), and crude enzyme liquid extraction. The method for preparing the phospholipase A1 through the recombinant Escherichia coli has the advantages of high enzyme yield, high enzyme activity, simple production technology, short production period, low cost, easy technological amplification and the like, and can be widely applied to the grease refining field, the phosphatide modification field and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for efficiently expressing phospholipase
ActiveCN104450756AReduce phosphorus contentHydrolasesFatty-oils/fats refiningPichia pastorisBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for efficiently expressing phospholipase, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. According to the method, a phospholipase A1 encoding gene as shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO.1 is subjected to recombinant expression by taking pichia pastoris as a host, and the enzyme activity is 6000U / ml after induction is performed for 120 hours in a tank of 3L. The phospholipase A1 encoding gene can be applied to industrial production of phospholipase. The phospholipase A1 can be used for degumming grain oil, and the content of phosphorus of the grain oil is increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Antibodies to calcium independent cytosolic phospholipase A2/B enzymes
The invention provides a novel calcium-independent cytosolic phospholipase A2 / B enzyme, polynucleotides encoding such enzyme antibodies to such enzyme, and methods for screening unknown compounds for anti-inflammatory activity mediated by the arachidonic acid cascade.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Phospholipase(s) and use(s) thereof
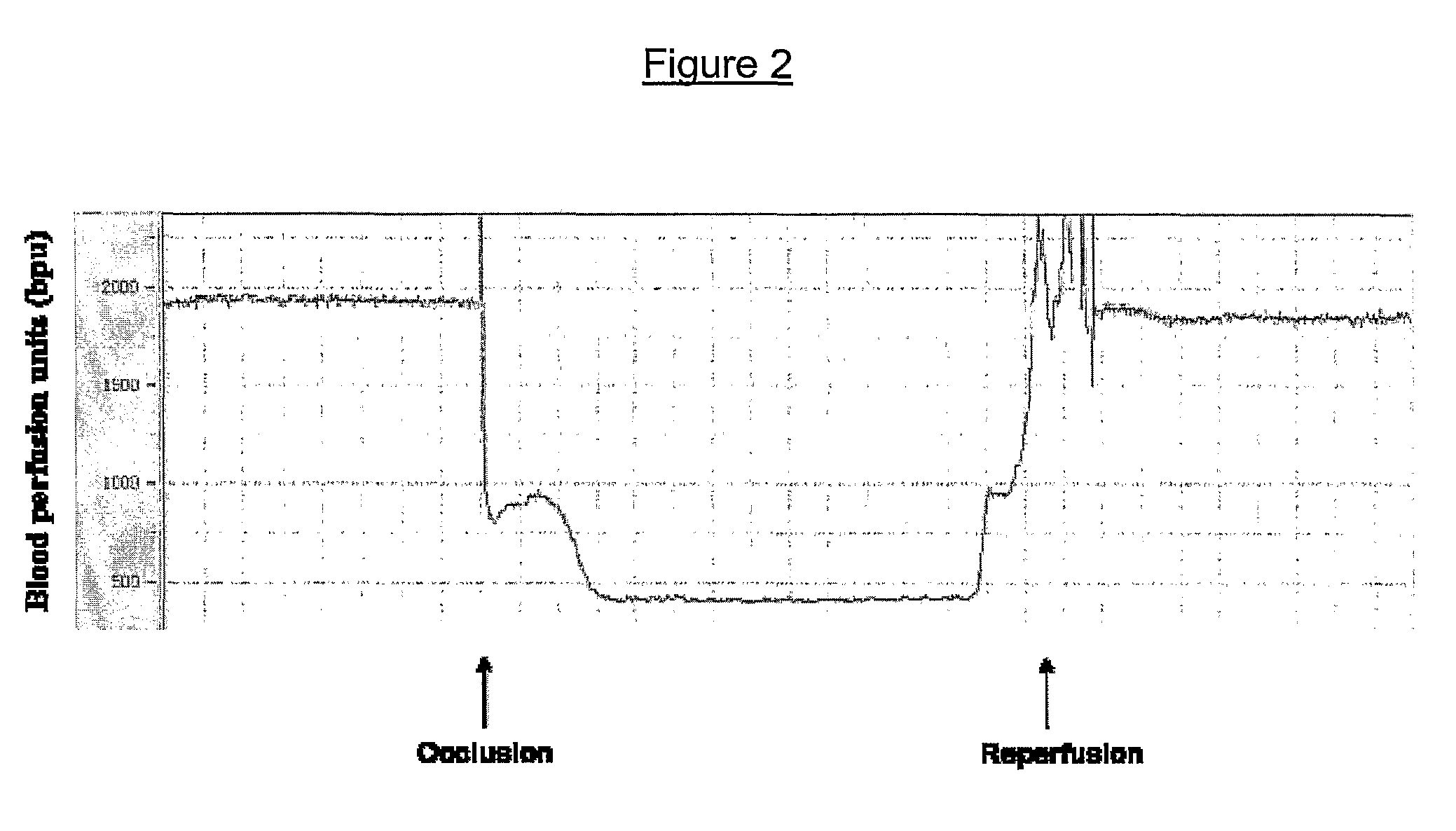
InactiveUS7939064B2Reduce infarct sizeReduces ischemic infarct sizeSugar derivativesHydrolasesPhospholipaseMedicine
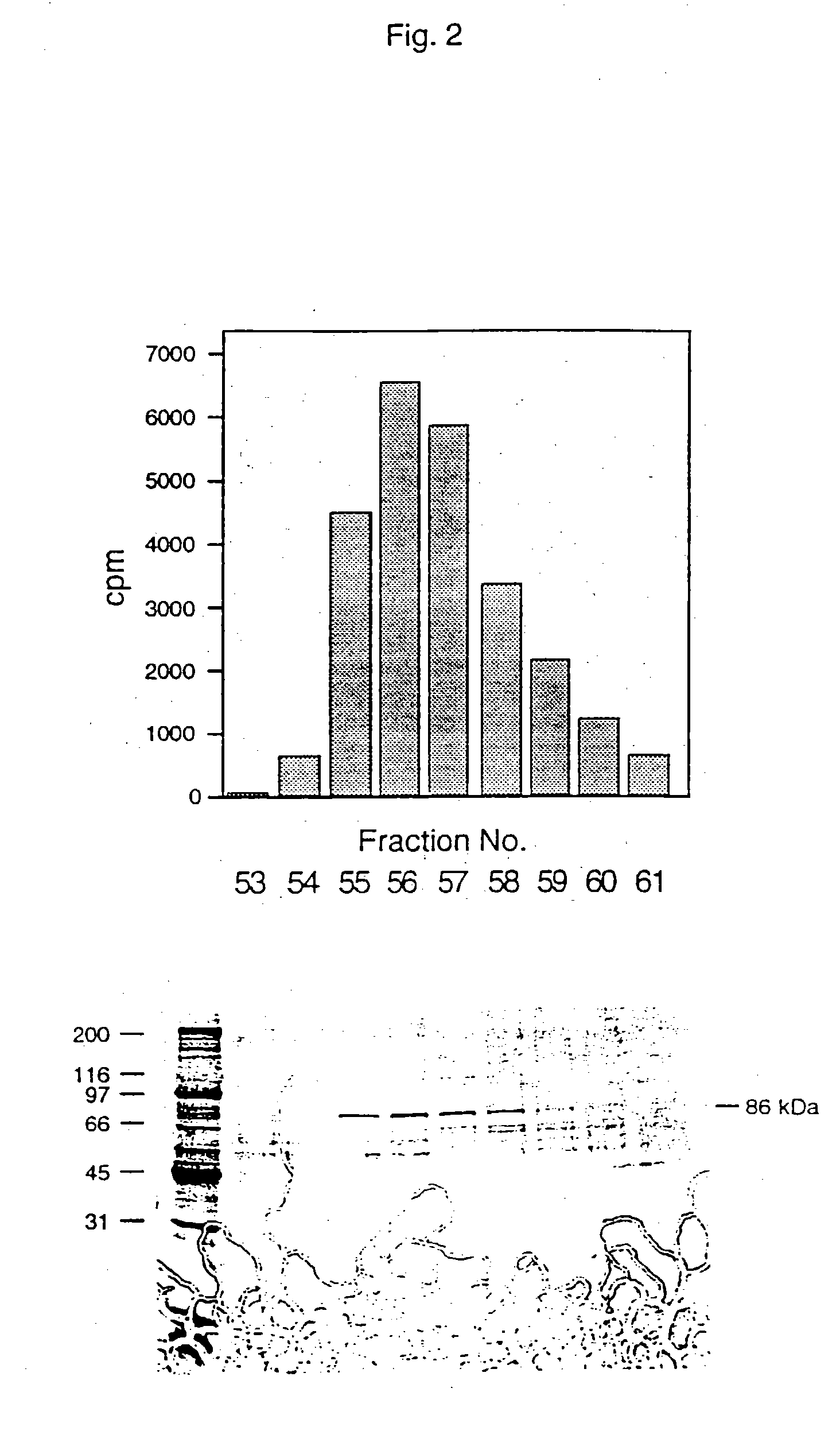
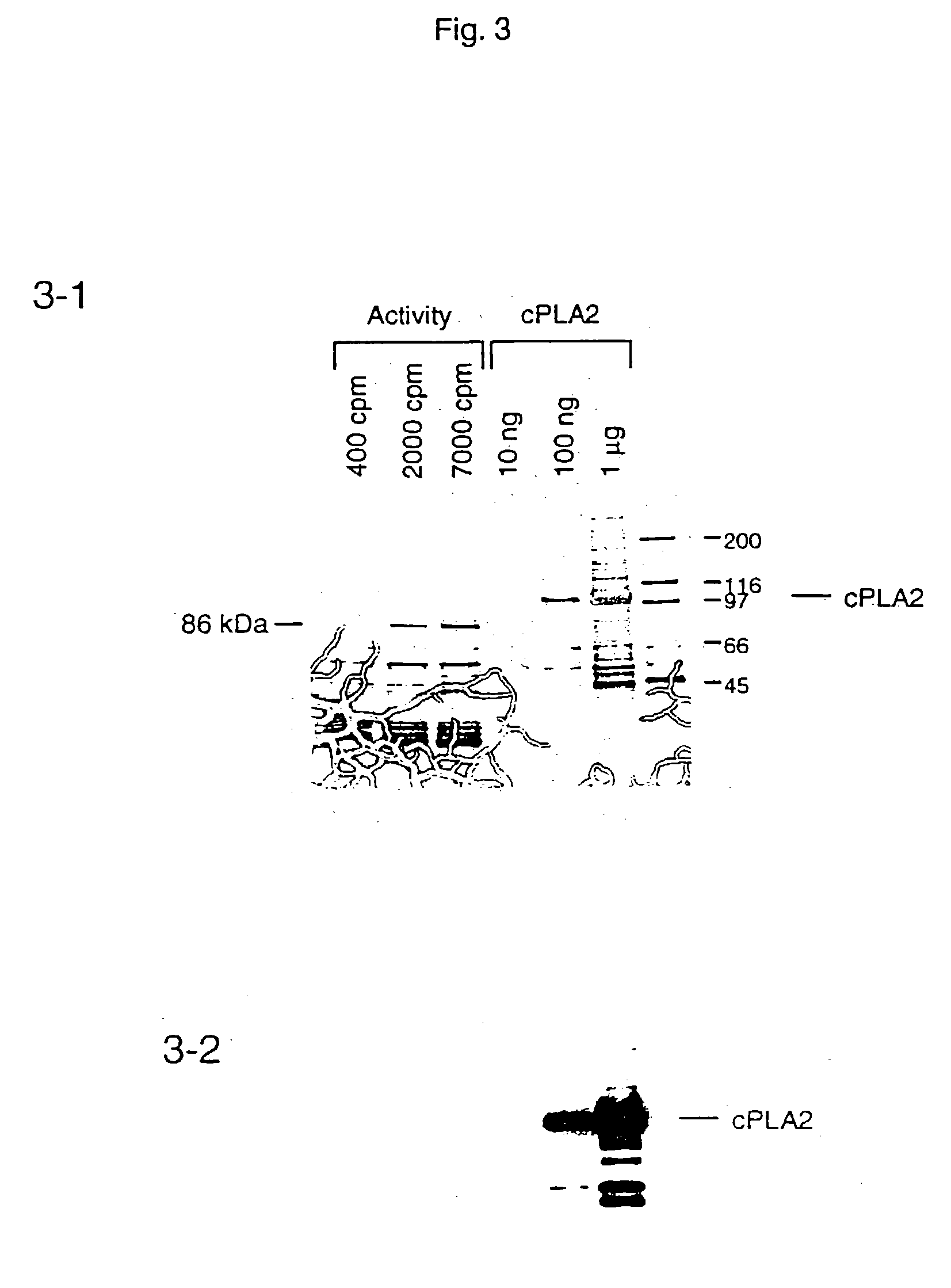
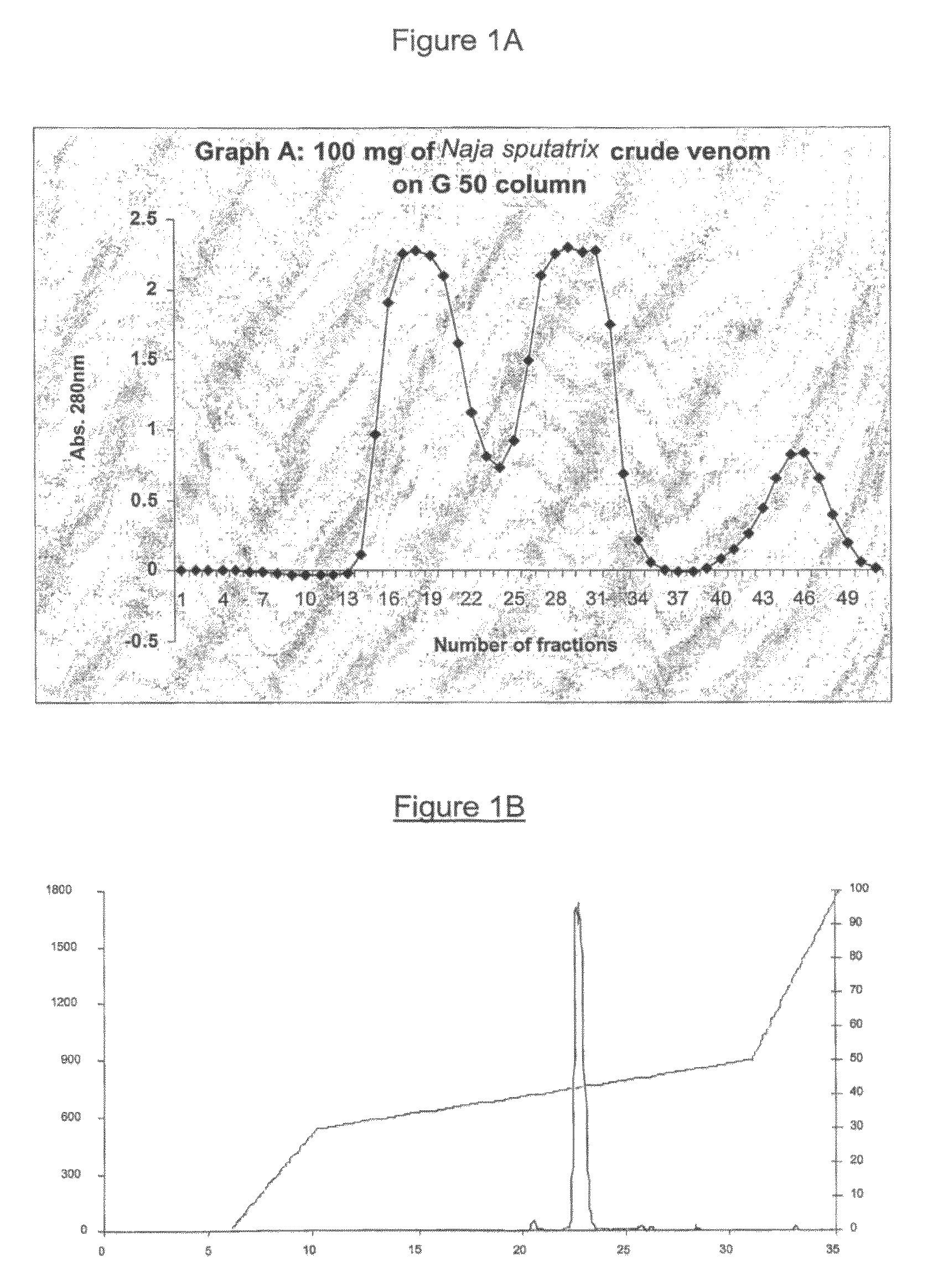
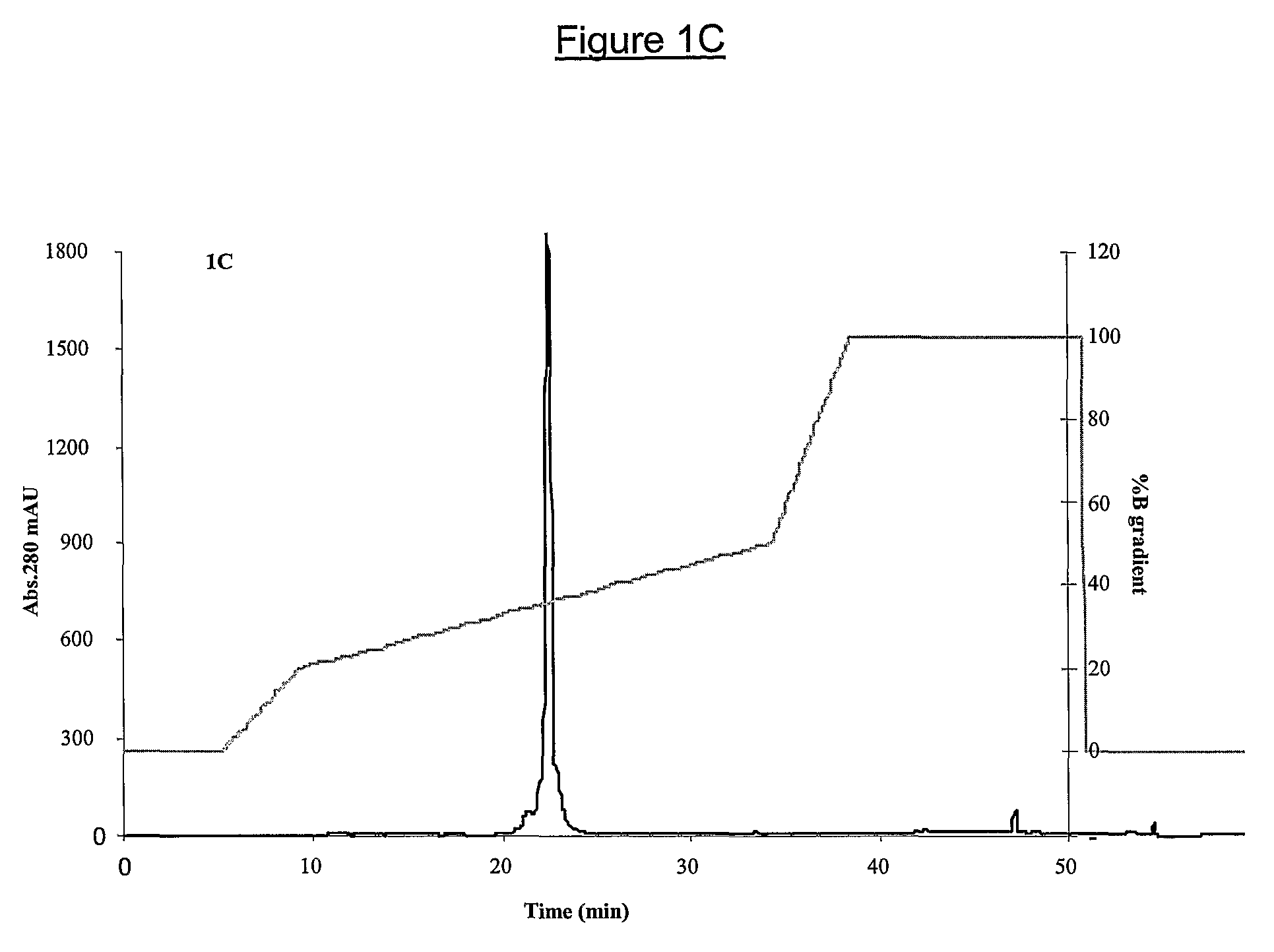
The invention relates to phospholipase(s), isoforms, derivatives, mutants and / or fragments thereof, for the preparation of a medicament for the treatment and / or prevention of ischemia. Preferred is the use of secretory phospholipase, particularly phospholipase A2, and even more particularly phospholipase A2 derived from the snake venom of Naja sputatrix.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Methods for treating asthmatic conditions
This invention provides methods for treating in mammals asthma and asthmatic conditions using substituted indole compounds of the general formula:and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof, and methods for using the compounds as inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly phospholipase A2 enzymes, and for the medical treatment, prevention and inhibition of pain and inflammation.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com